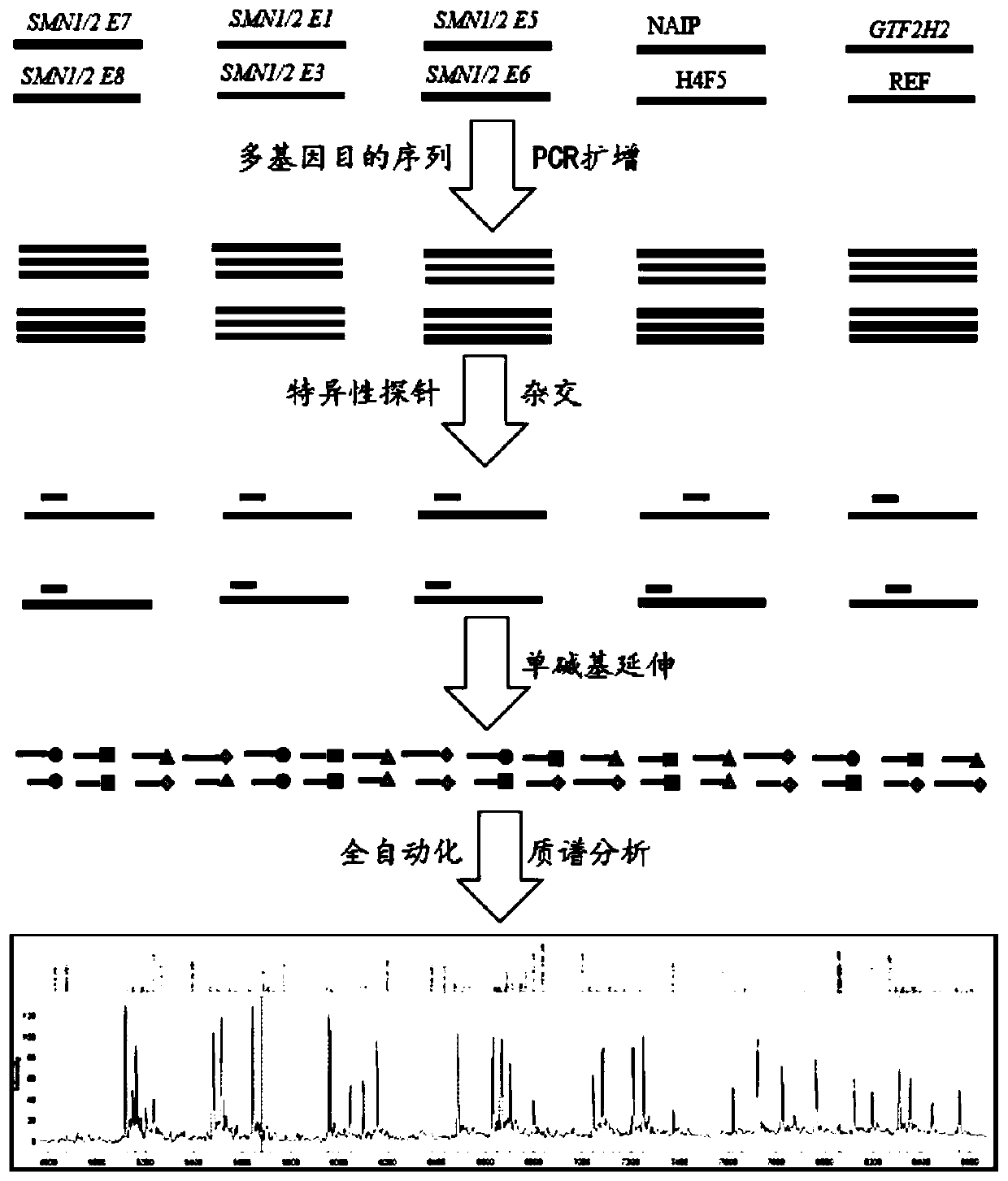
Time-of-flight mass spectrometry nucleic acid analysis method for detecting human spinal muscular atrophy gene mutation
A spinal muscular atrophy and human technology, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, microbial measurement/testing, DNA/RNA fragments, etc., can solve the problems of high cost, time-consuming detection, difficult large-scale population screening and technology promotion And other issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0105] Embodiment 1 A kind of human spinal muscular atrophy gene detection kit
[0106] 1. Composition
[0107] Nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1-22 amplification primer, nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 23-35 mass spectrum extension probe primer, multiplex PCR reaction reagent, single base extension reaction reagent Reagents with de-dNTP mix.
[0108] Wherein, all the amplification primers are premixed as a PCR amplification primer mixture; all the mass spectrum extension probes are premixed as a primer extension primer mixture.
[0109] Wherein, the multiplex PCR reaction reagents include: PCR amplification primer mixture, multiplex PCR enzyme, extension reaction multiplex PCR buffer, magnesium chloride buffer, and dNTP mixture.
[0110] More preferably, the single base extension reaction reagent includes: extension buffer, extension termination mixture, reaction catalyzing enzyme, and extension primer mixture.
[0111] More preferably, the dNTP remov...
Embodiment 2
[0156] Example 2 Calculation of relative copy number of target gene
[0157] Taking two samples as an example, the method of using the formula for calculating the copy number given by the present invention is illustrated.
[0158]
[0159] The following table shows the peak areas obtained after each sample is tested according to the kit of Example 1, and further calculates the peak area ratio (peak area ratio=target gene peak area / reference gene peak area)
[0160] Table 12:
[0161]
[0162]The relative copy number of the reference gene of all specimens is maintained at 2, and the relative copy number of the target gene of the normal reference sample is 2. The relative copy number of the target gene of the tested sample can be calculated based on the peak area ratio of the reference sample.
[0163] *: The target gene copy number of the tested sample 1 = (0.43 / 0.44) × 2 = 1.955, that is, 2 copies;
[0164] The target gene copy number of the tested sample 2=(0.20 / 0.44)...
Embodiment 3
[0165] Example 3 Detection of known genotype samples
[0166] 1. Experimental method
[0167] 1. Sample source and type
[0168] SMA gDNA specimens with confirmed genotypes selected from the laboratory specimen bank and collected by cooperative medical institutions, the genotypes are SMN1 / SMN2=2 / 0, SMN1 / SMN2=0 / 2 and there are no NAIP, GTF2H2 and H4F5 genes 5 samples for each deletion (10 samples in total), 10 samples of SMN1 / SMN2=2 / 2 and no deletion of NAIP, GTF2H2 and H4F5 genes, dilute gDNA samples to 10-50ng / μL with sterile double distilled water spare. Three cases of plasmid DNA with c.5C>T, c.22dupA, c.275G>C, c.683T>A, c.819_820insT and c.830A>G mutations in SMN1 gene were diluted to 0.001 with sterile double distilled water -0.002pg / μL spare.
[0169] 2. Sample detection
[0170] Sample detection was performed using the kit of Example 1.
[0171] 2. Experimental results
[0172] The results are shown in Table 13. The results obtained by using the kit of Example ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com