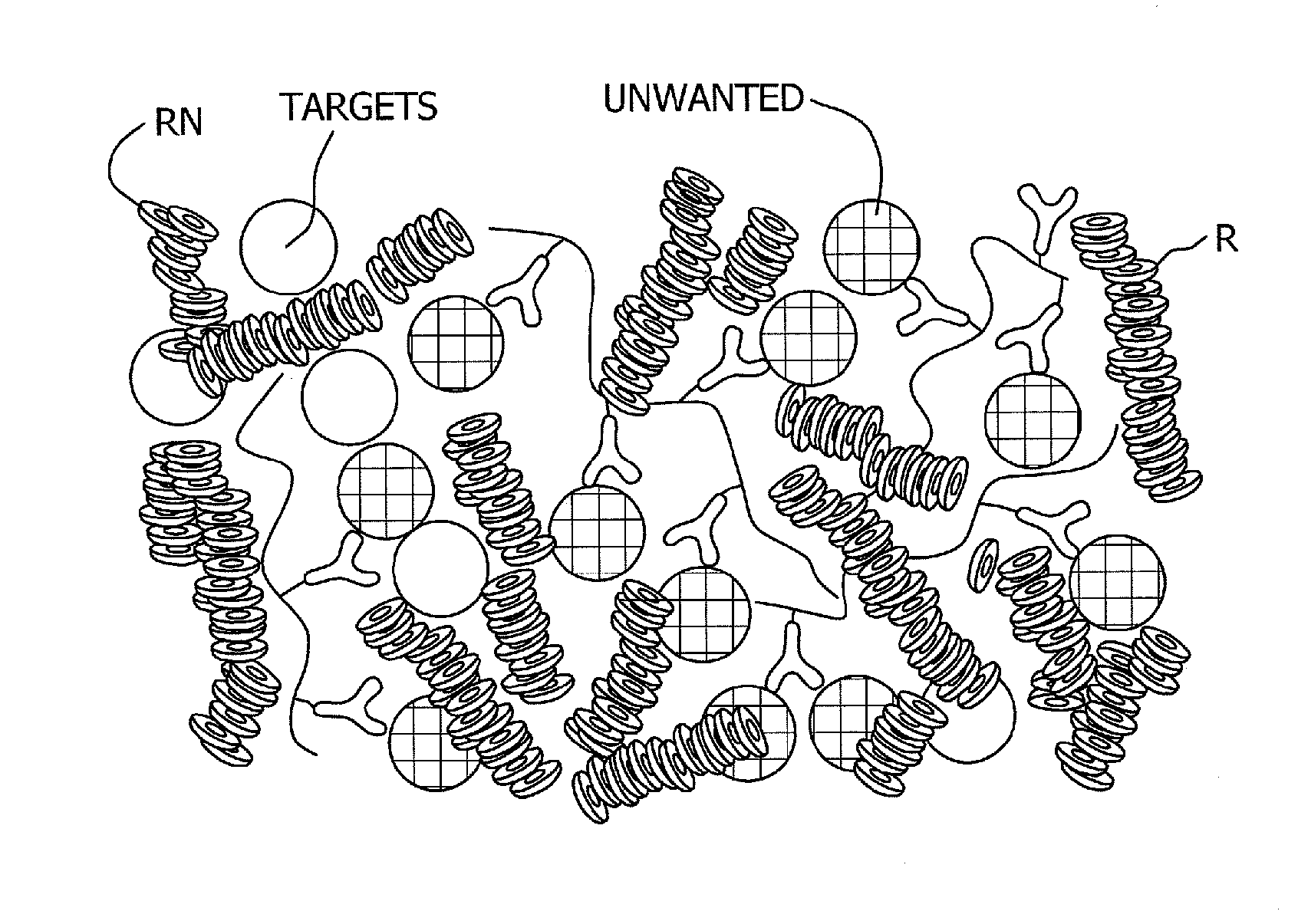
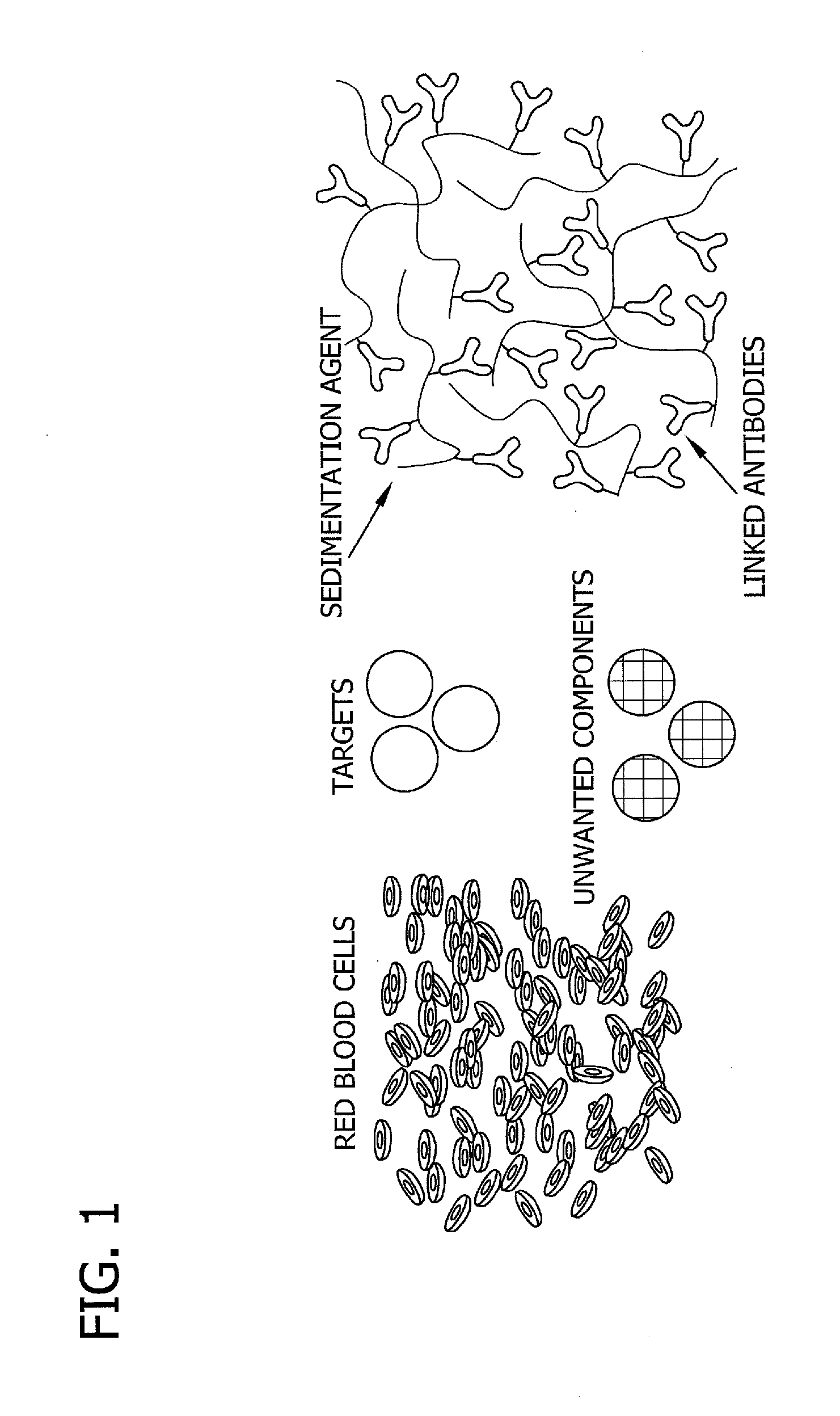
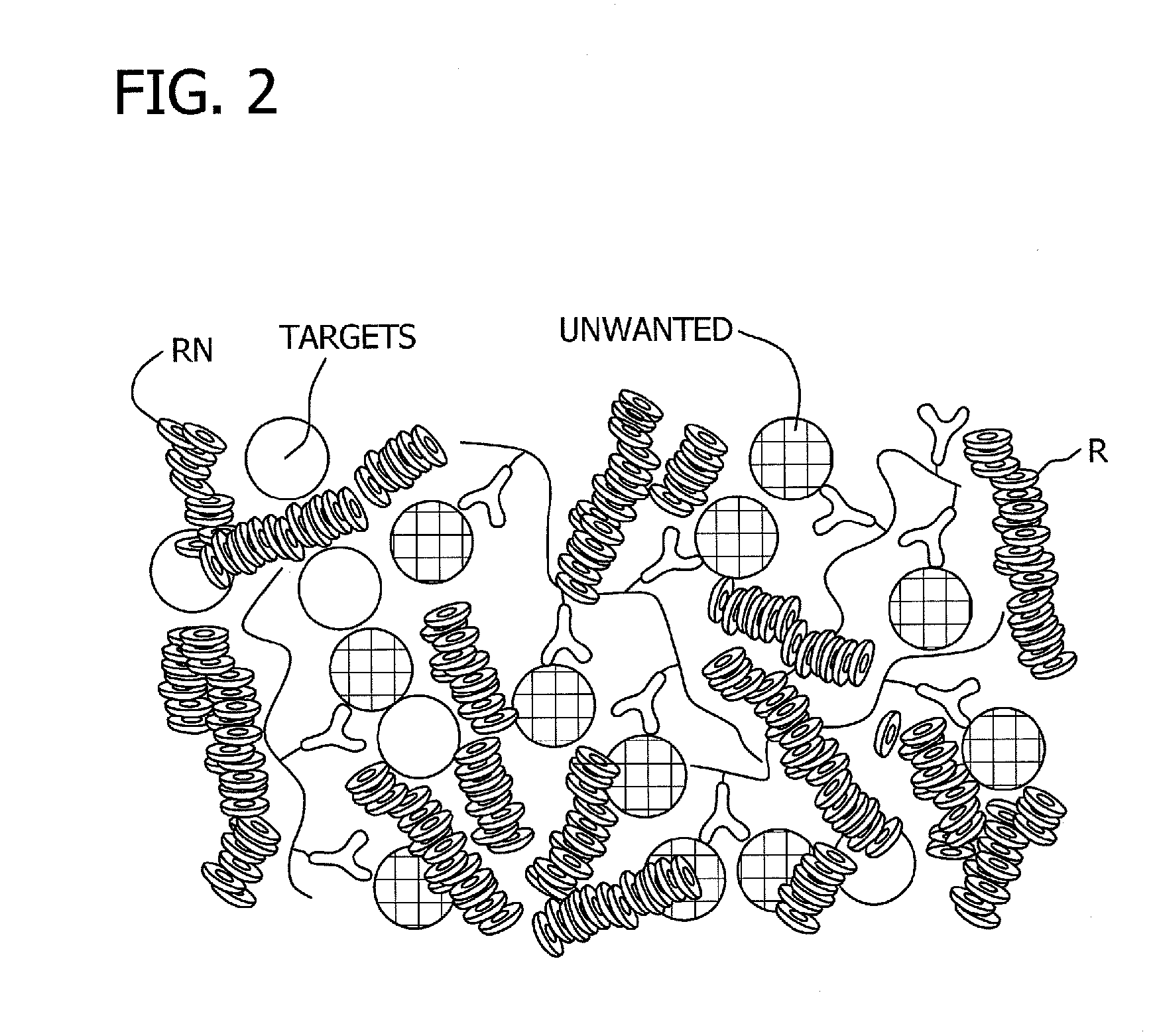
Antibody-linked immuno-sedimentation agent and method of isolating a target from a sample using same
a target and antibody-linked technology, applied in the field of target isolation, can solve the problems of complex and equipment-intensive cell separation, affinity agents that are not frequently used in cell separation techniques, and require multiple complex steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
ALISA Preparation Using Tricholor-s-triazine
[0107]In this Example, ALISA is prepared using Tricholor-s-triazine. Anhydrous sodium carbonate (1 g) is added to 200 ml of anhydrous organic solvent (e.g., acetone, methylene chloride, dimethylsulfoxide, benzene, or 1,4-dioxane). Then, 0.55 g of Trichloro-s-triazine (TsT) is dissolved in the sodium carbonate solution. The sedimentation agent (1 mmol) (approximately 20 g of polyethylene glycol-PEG-20,000, 70 g of dextran-Dextran-70, or 180 g of hydroxyethyl starch-Hetastarch) is added to the sodium carbonate solution. The solution is then stirred overnight at room temperature. The solution is then filtered. The filtrate is then added to a sufficient amount of a non-polar organic solvent (e.g., of petroleum ether or diethyl ether) (500 ml) to produce an activated sedimentation agent precipitate that is collected by filtration. This activated sedimentation agent precipitate is further cleaned by re-dissolving in the organic solvent, filterin...
example 2
ALISA Preparation Using N-Succinimidyl Chloroformate
[0108]In this Example, ALISA is prepared using N-Succinimidyl Chloroformate. The sedimentation agent (1 mmol) (approximately 20 g of polyethylene glycol-PEG-20,000, 70 g of dextran-Dextran-70, or 180 g of hydroxyethyl starch-Hetastarch) is added to 200 ml of an anhydrous organic solvent (e.g., acetone, methylene chloride, dimethylsulfoxide, benzene, or 1,4-dioxane) at room temperature. Separately, N-succinimidyl chloroformate (6 mmol) is dissolved in 10 ml of dry acetone. Separately, 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine is dissolved in 10 ml of dry acetone. The succinimidyl chloroformate solution is added to the sedimentation agent solution with stirring. Next, the 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine solution is added to the combined succinimidyl chloroformate / sedimentation agent reaction solution. The solution is stirred for 2 hours at room temperature. The solution is filtered to remove precipitated 4-(dimethylamino)pyridine hydrochloride byproduct. ...
example 3
ALISA Preparation Using N,N′-Carbonyldiimidazole
[0109]In this Example, ALISA is prepared using N,N′-carbonyldiimidazole (CDI). The sedimentation agent (1 mmol) (approximately 20 g of polyethylene glycol-PEG-20,000, 70 g of dextran-Dextran-70, or 180 g of hydroxyethyl starch-Hetastarch) is added to 200 ml of an anhydrous organic solvent (e.g., acetone, methylene chloride, dimethylsulfoxide, benzene, or 1,4-dioxane) at room temperature. Separately, CDI (6 mmol) is dissolved in 10 ml of the organic solvent. The CDI solution is added to the sedimentation agent solution with stirring. The combined reaction solution is stirred for 2 hours at 37° C. The reaction solution is then added to a non-polar organic solvent (e.g., petroleum ether or diethyl ether) (500 ml) to precipitate the CDI activated sedimentation agent. The activated sedimentation agent is collected by filtration. The activated sedimentation agent precipitate is further cleaned by re-dissolving in the organic solvent, filteri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentration | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com