Method for controlling virtual reactance of photovoltaic grid-connected inverter
A control method and virtual reactance technology, applied in photovoltaic power generation, single-network parallel feeding arrangement, etc., can solve problems such as poor stability of photovoltaic grid-connected inverters, achieve enhanced system stability, increase output impedance, and improve output The effect of impedance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
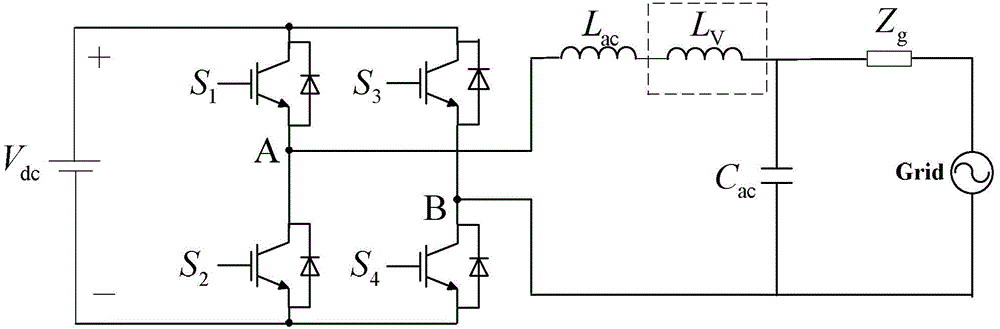
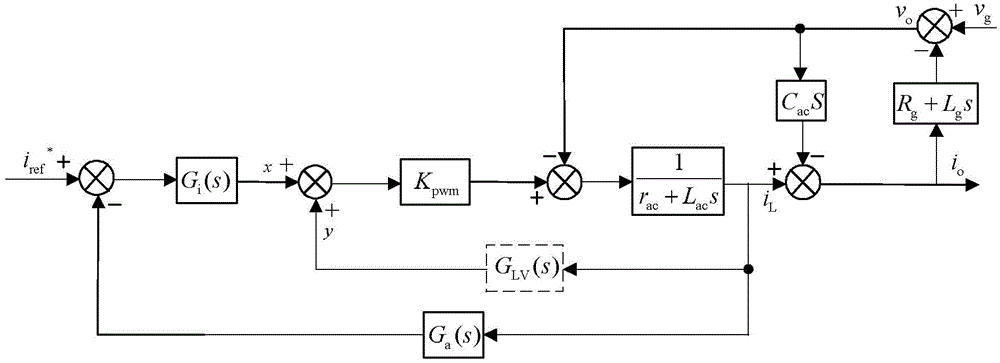
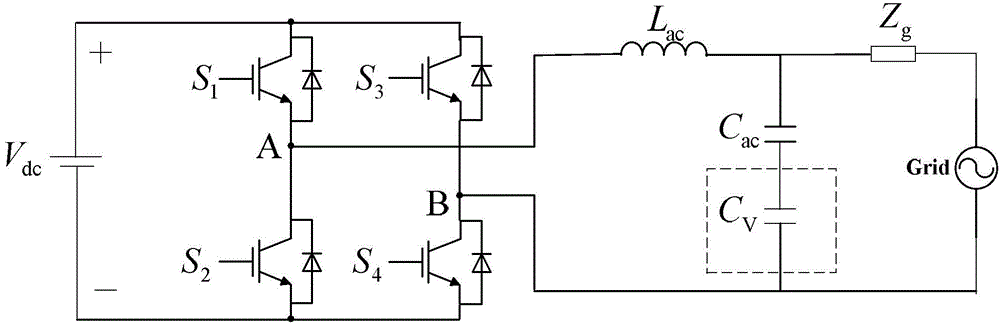
[0026] Specific implementation mode 1. Combination Figure 1-Figure 6 To illustrate this specific embodiment, the virtual reactance control method of a photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in this specific embodiment includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1. According to the actual grid impedance Z g , Photovoltaic grid-connected inverter output impedance Z o (s) and the amplitude-frequency characteristic and phase-frequency characteristic of the output impedance stability criterion of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter to obtain the virtual inductance L V , The equivalent internal resistance r of the virtual inductance V and virtual capacitance C V ;
[0028] Step 2. According to the virtual inductance L V and the equivalent internal resistance r of the virtual inductance V , and combined with the full-bridge gain K PWM , to obtain the equivalent feedforward path transfer function G of the virtual inductor LV (s);
[0029] Step 3. According to th...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0038] Embodiment 2. The difference between this embodiment and the virtual reactance control method of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in Embodiment 1 is that the actual grid impedance Z described in step 1 g It is obtained through impedance testing equipment or grid impedance online detection method.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0039] Specific embodiment 3. The difference between this specific embodiment and the virtual reactance control method of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in the second specific embodiment is that the output impedance Z of the photovoltaic grid-connected inverter described in step 1 o The expression of (s) is:
[0040] Z o ( s ) = - v o i o | i L * = 0 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com