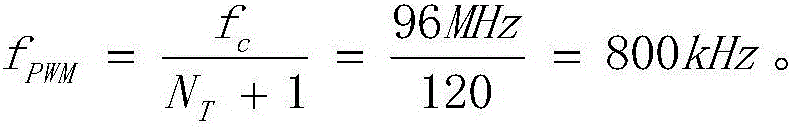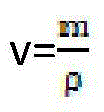Patents
Literature
160 results about "Linear variable differential transformer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
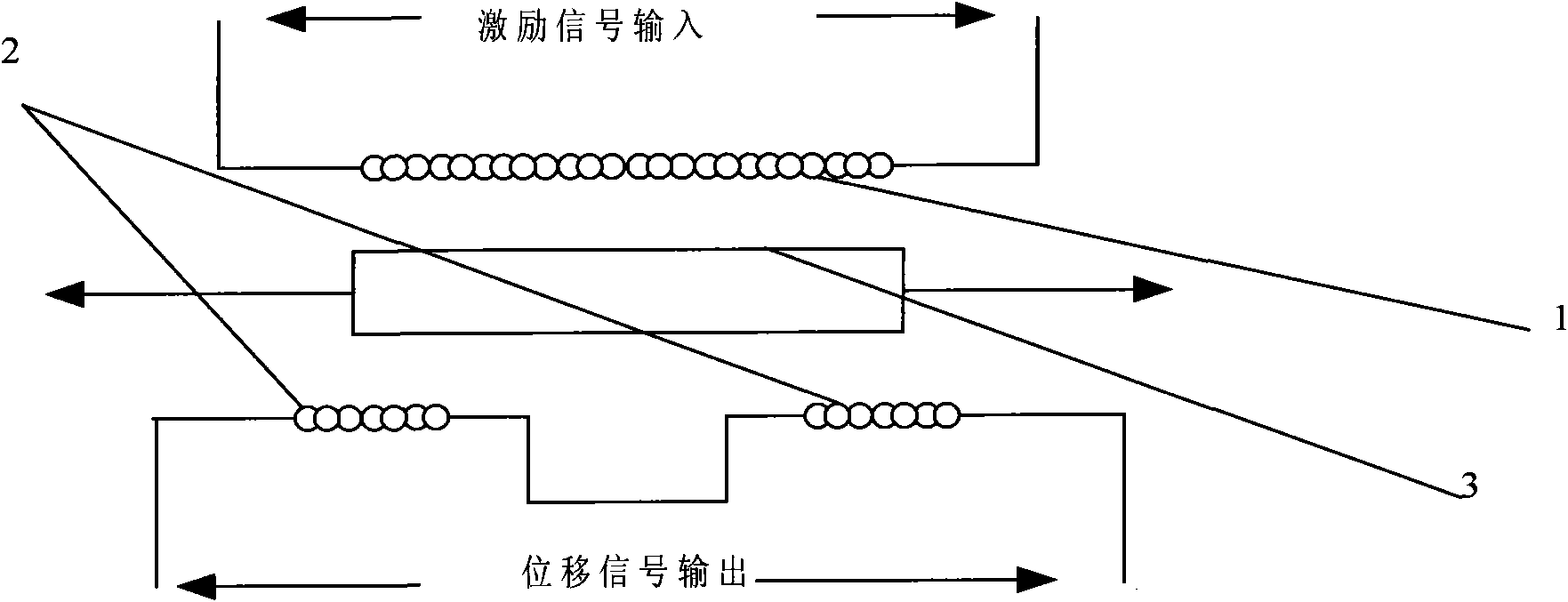
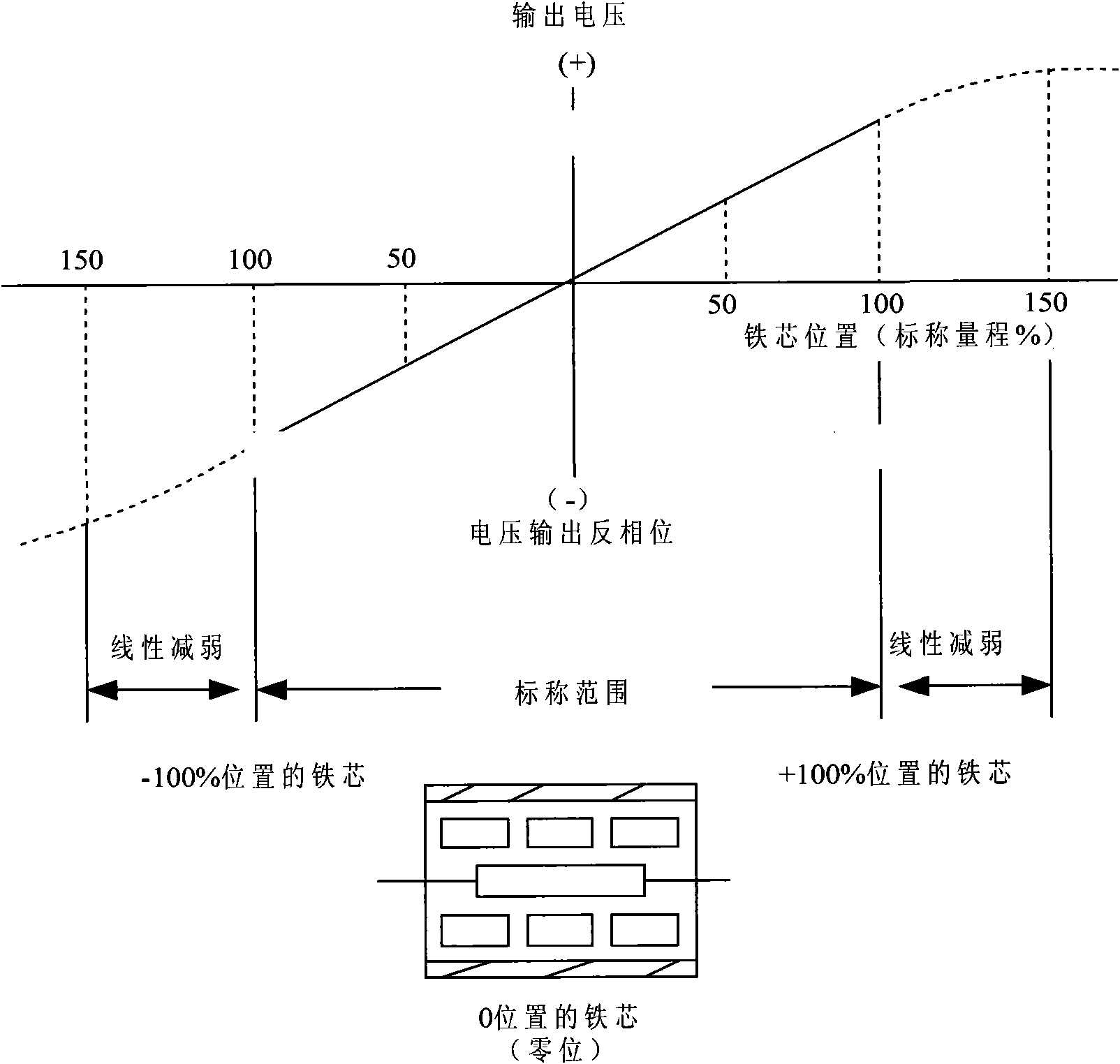
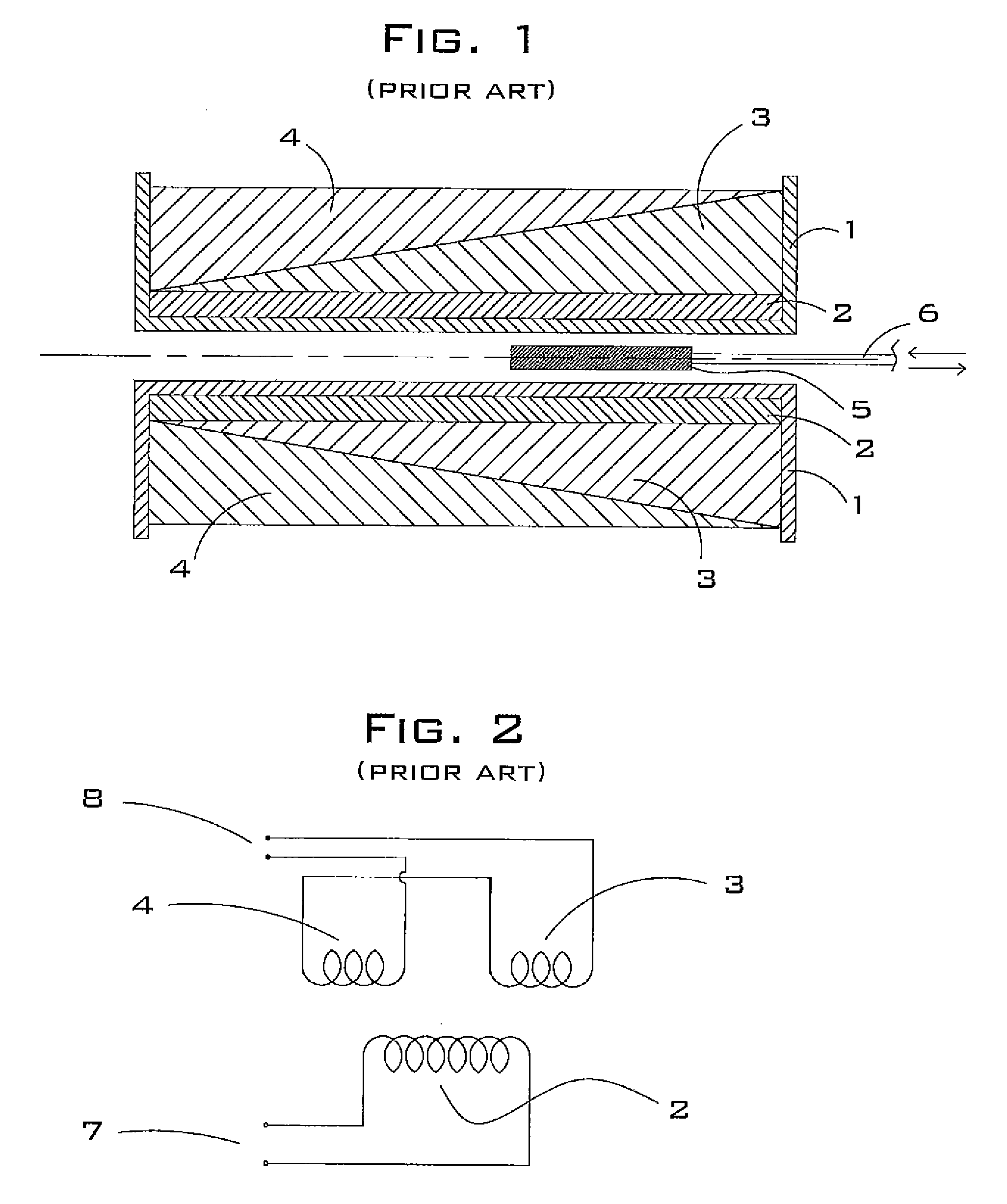
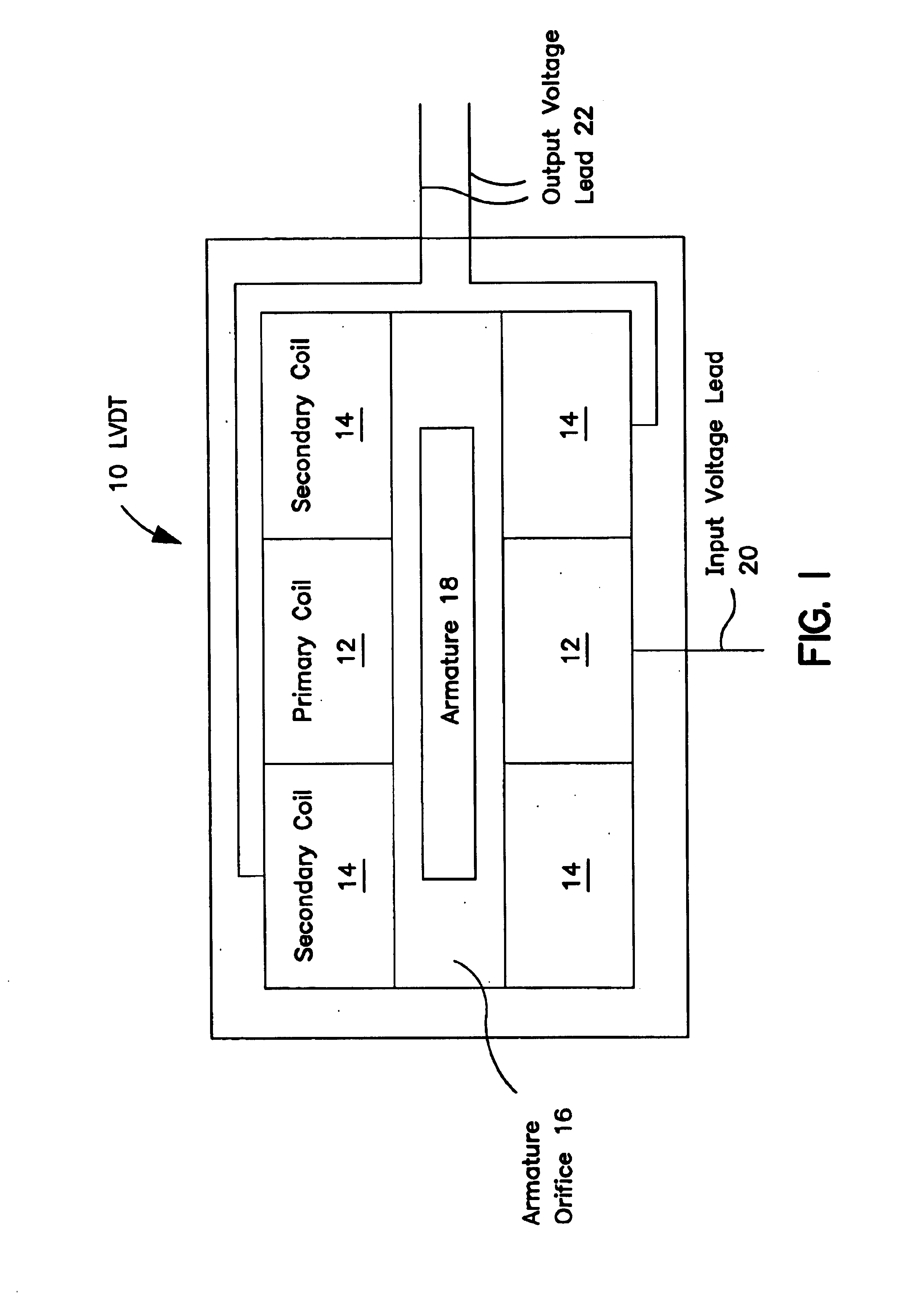
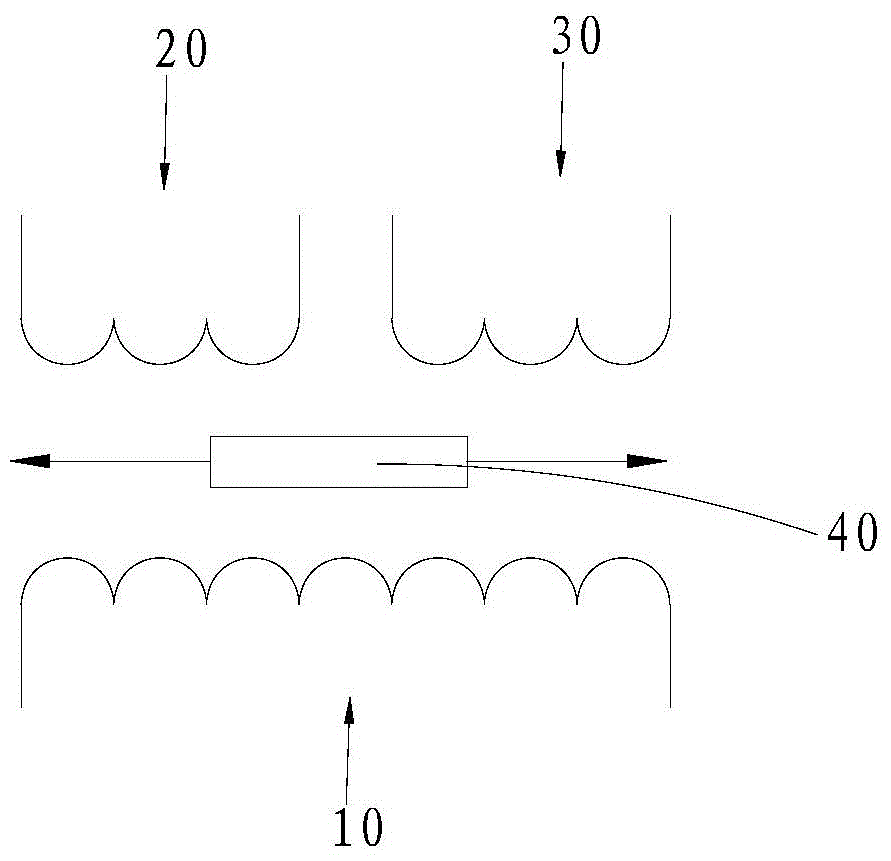
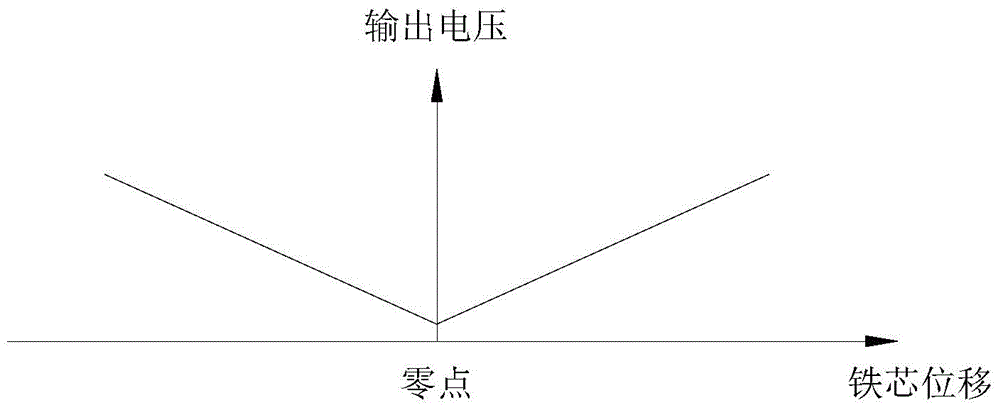
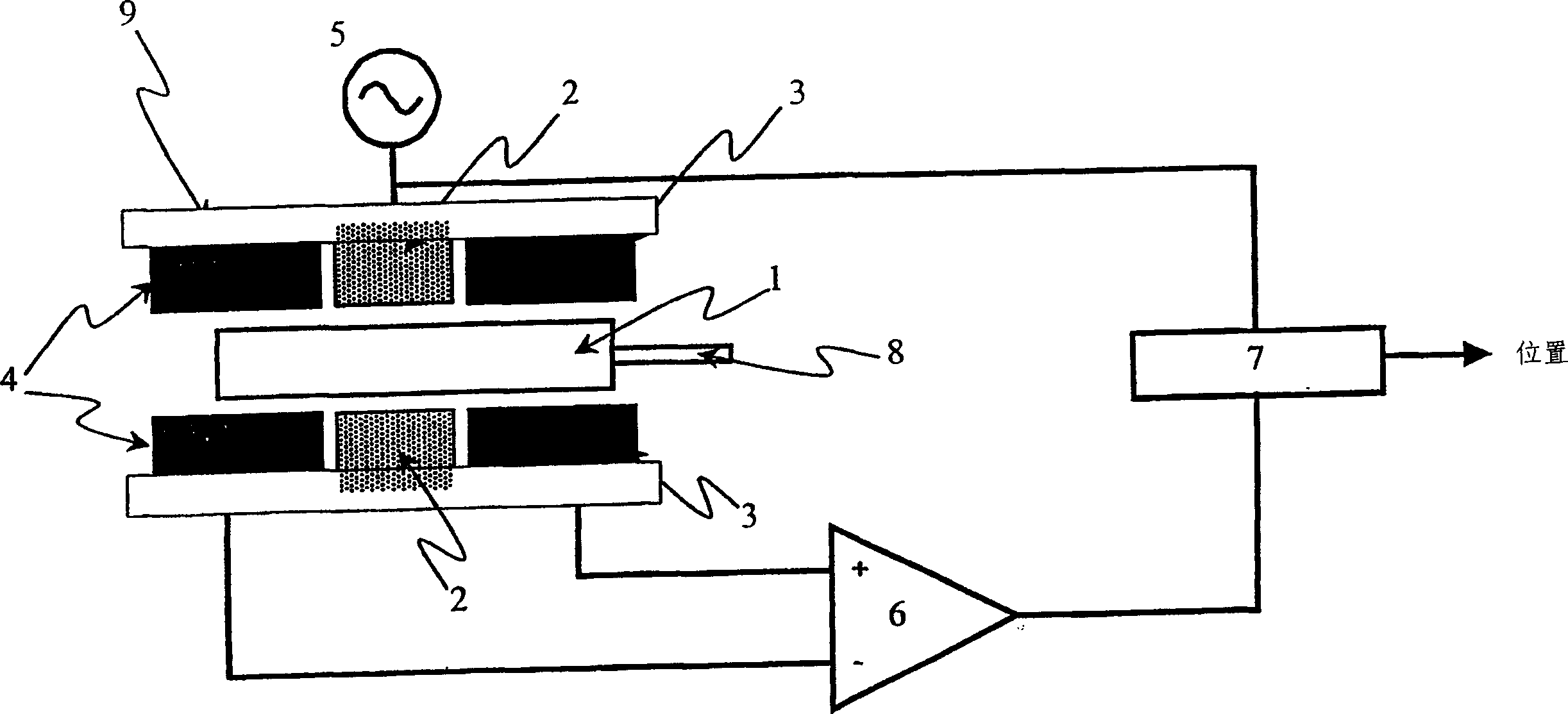
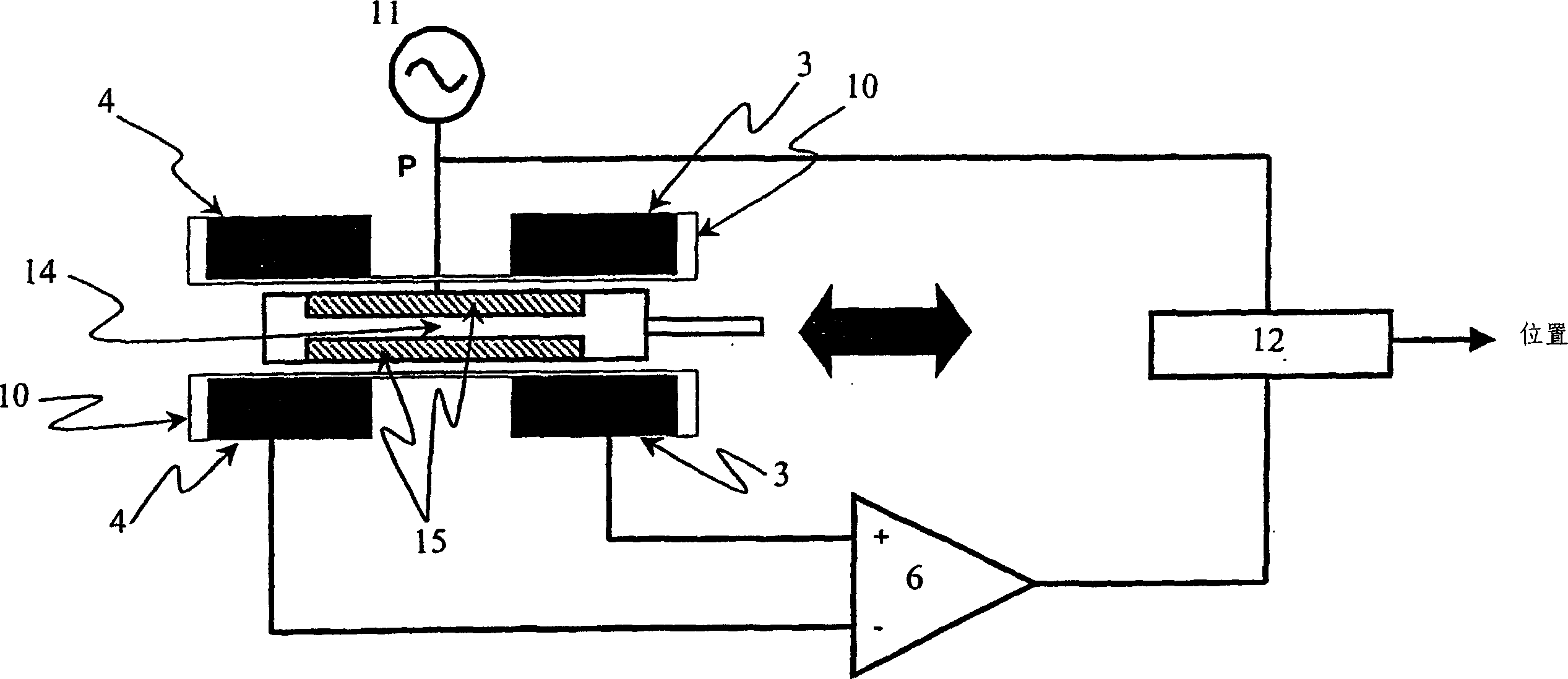
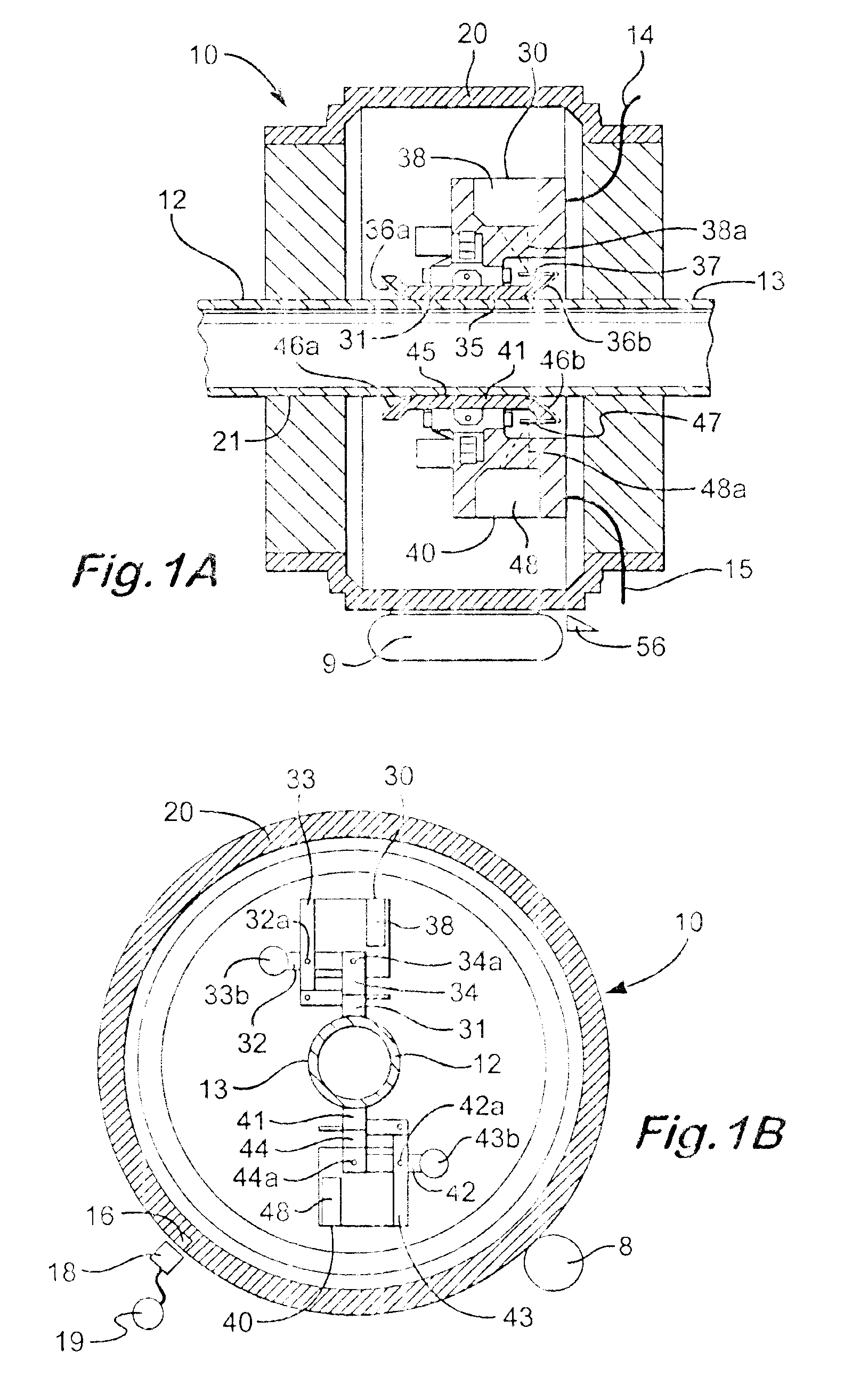
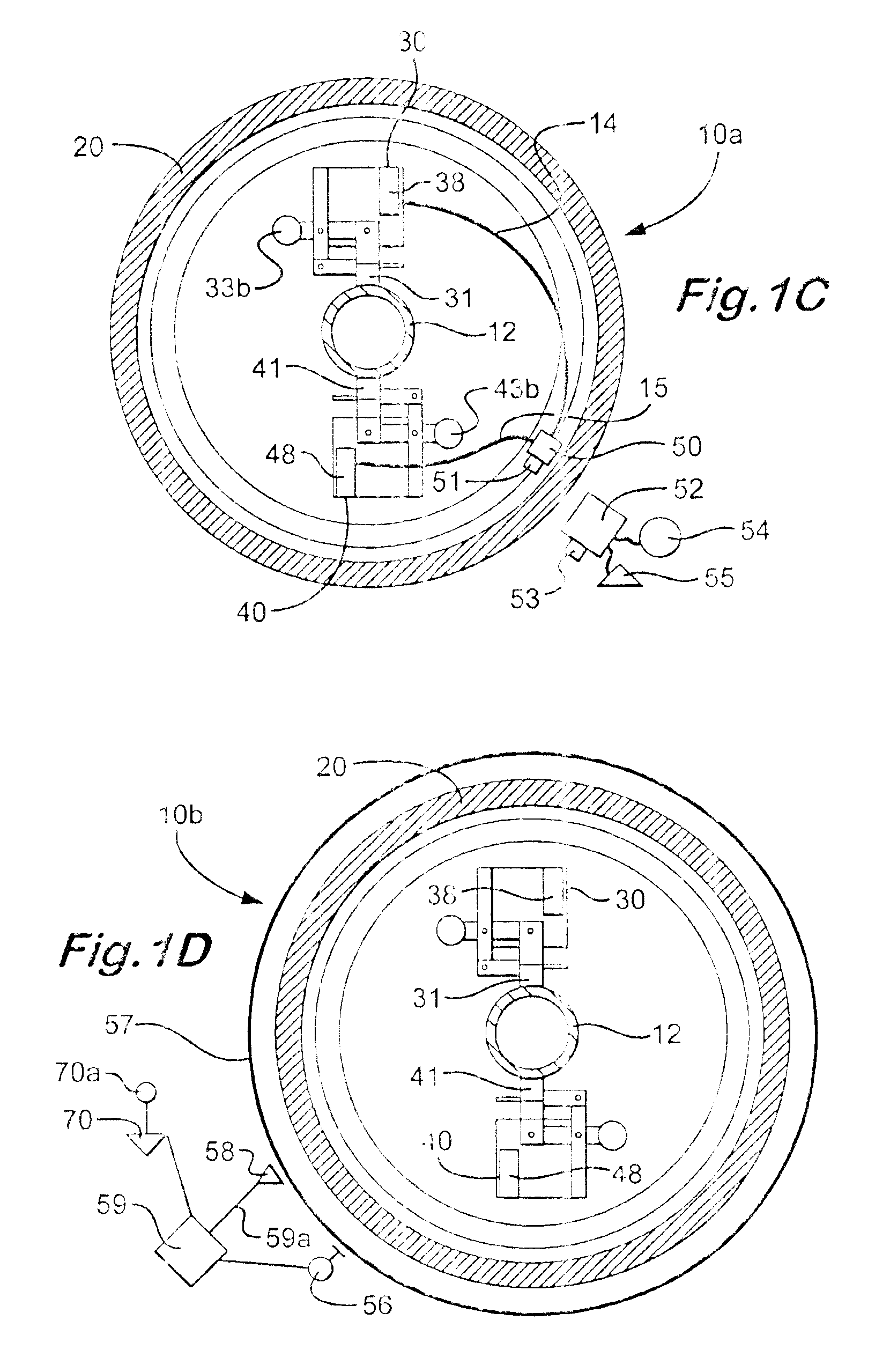
The linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) (also called linear variable displacement transformer, linear variable displacement transducer, or simply differential transformer) is a type of electrical transformer used for measuring linear displacement (position). A counterpart to this device that is used for measuring rotary displacement is called a rotary variable differential transformer (RVDT).
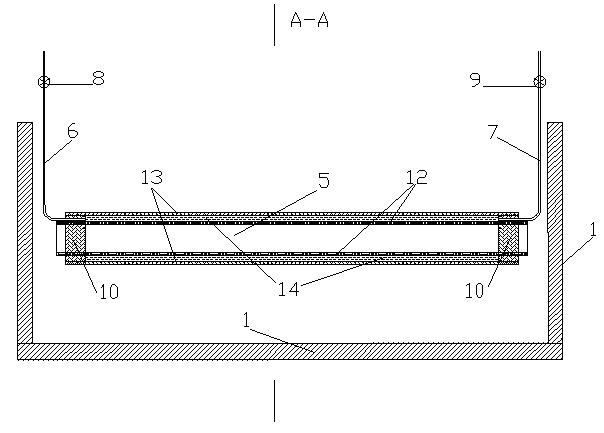
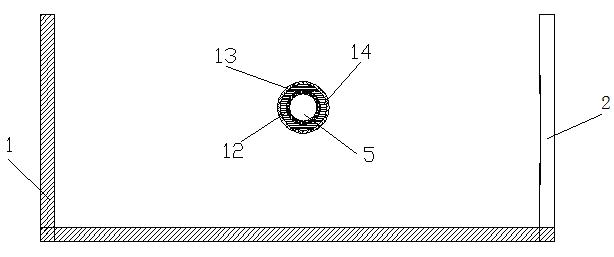
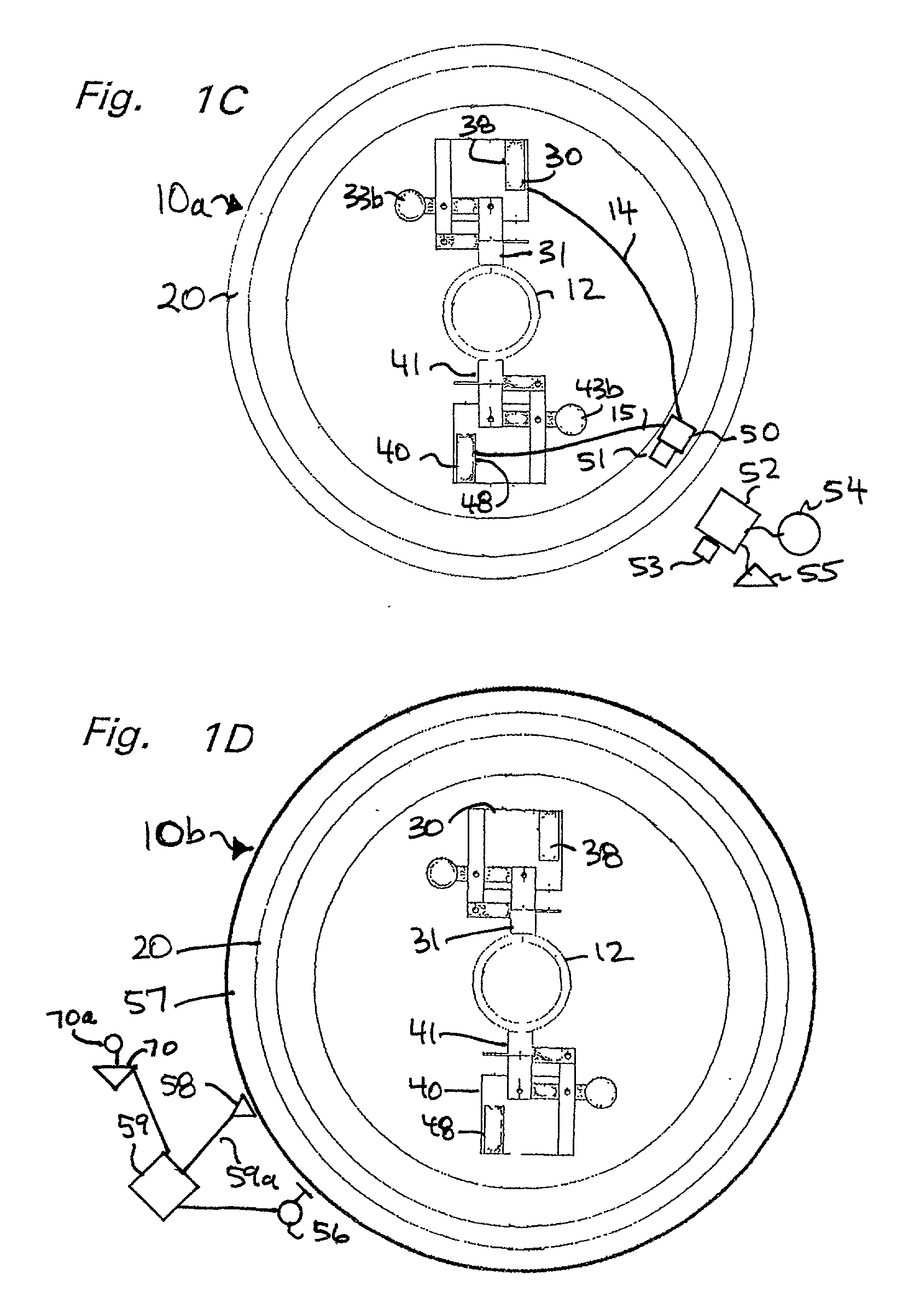
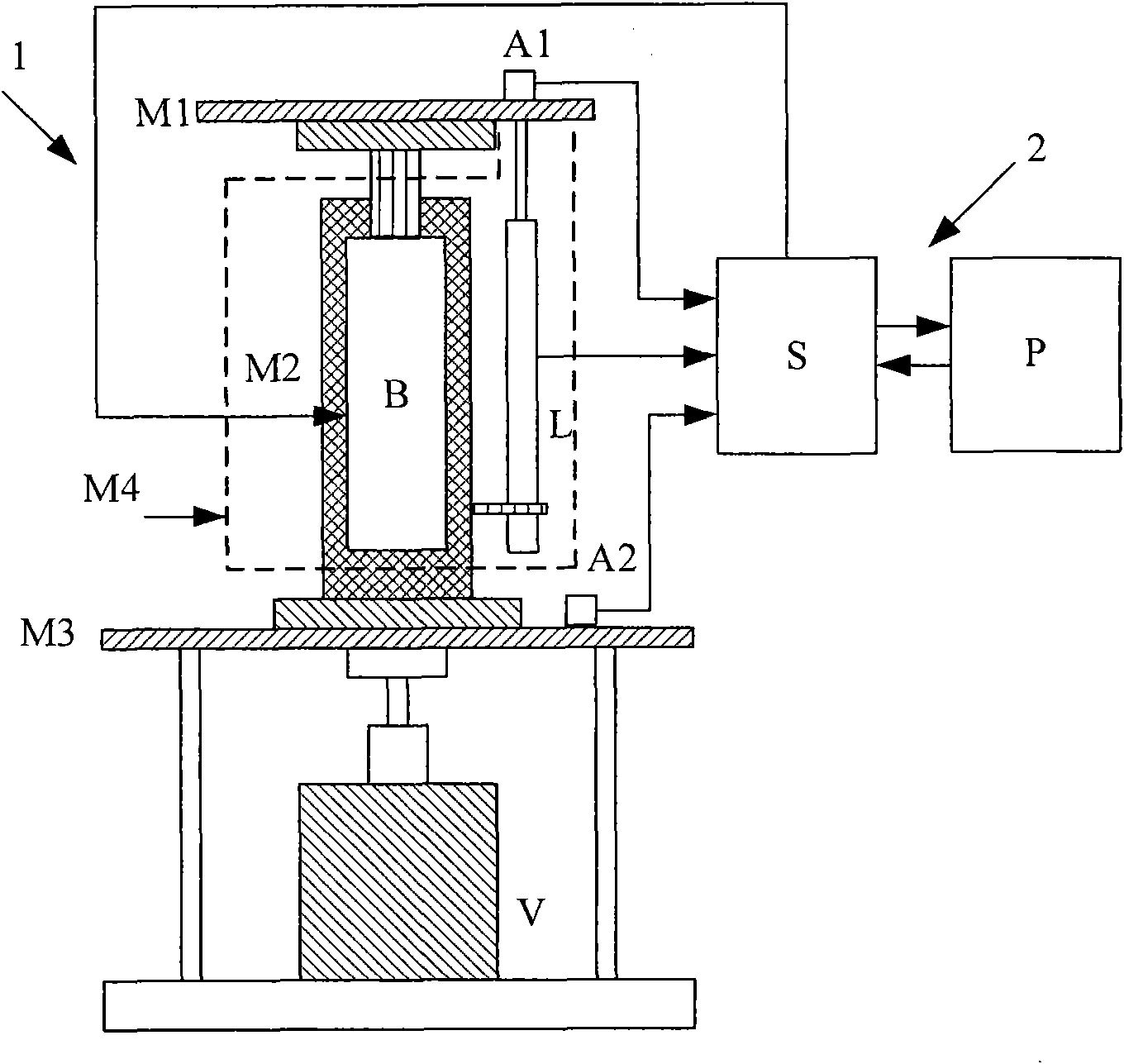
Centrifugal experimental simulation testing device for surface subsidence induced by city shield tunnel construction
InactiveCN102071943AAccurate measurementPlay a shockproof roleHeight/levelling measurementTunnelsLinear variable differential transformerEngineering
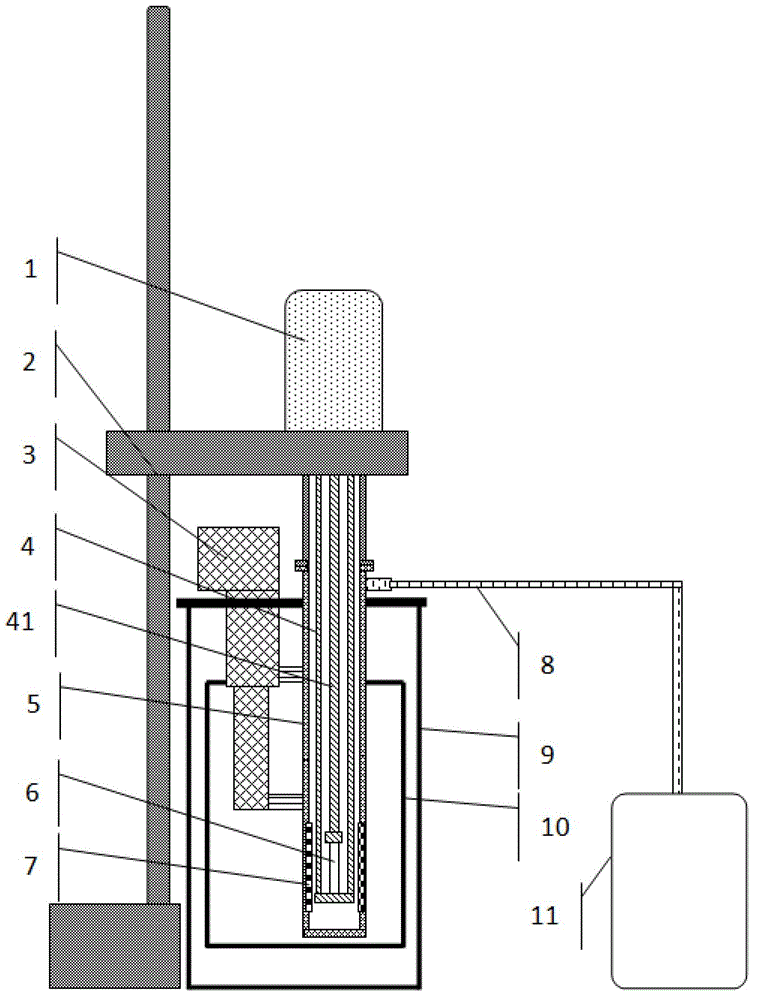
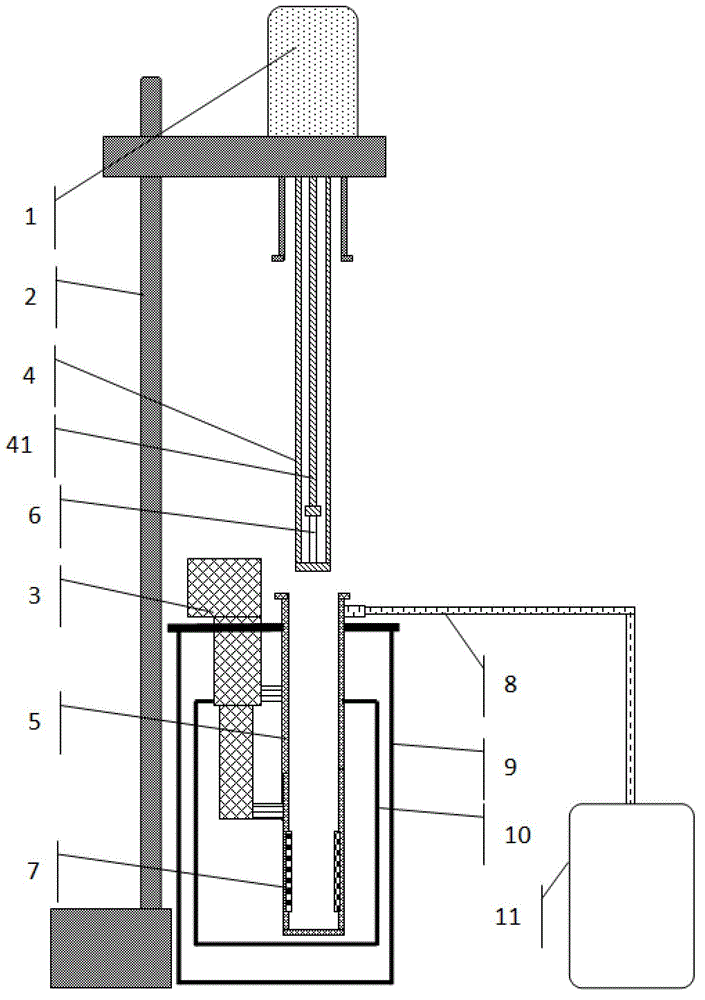
The invention belongs to the field of tunneling in geotechnical engineering and underground engineering, and particularly relates to a centrifugal experimental simulation testing device for surface subsidence induced by city shield tunnel construction. The testing device mainly comprises a model box, a small displacement meter bracket, a big displacement meter bracket, a tunnel excavation device, a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) displacement meter and the like, wherein the model box is a hollow cuboid; the small displacement meter bracket and the big displacement meter bracket adjust the LVDT displacement meter along the horizontal direction and the vertical direction, so that the surface subsidence and the soil layer deformation can be measured; and the tunnel excavation device can simulate the soil body deformation caused by stratum loss by discharging a certain volume of water. Through the device, the deformation influence of the city shield tunnel construction on surrounding soil layer can be more conveniently, really and effectively simulated, so more real and accurate experimental data can be provided for tunnel design and construction, and high efficiency and safety of the city shield tunnel construction are guaranteed.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
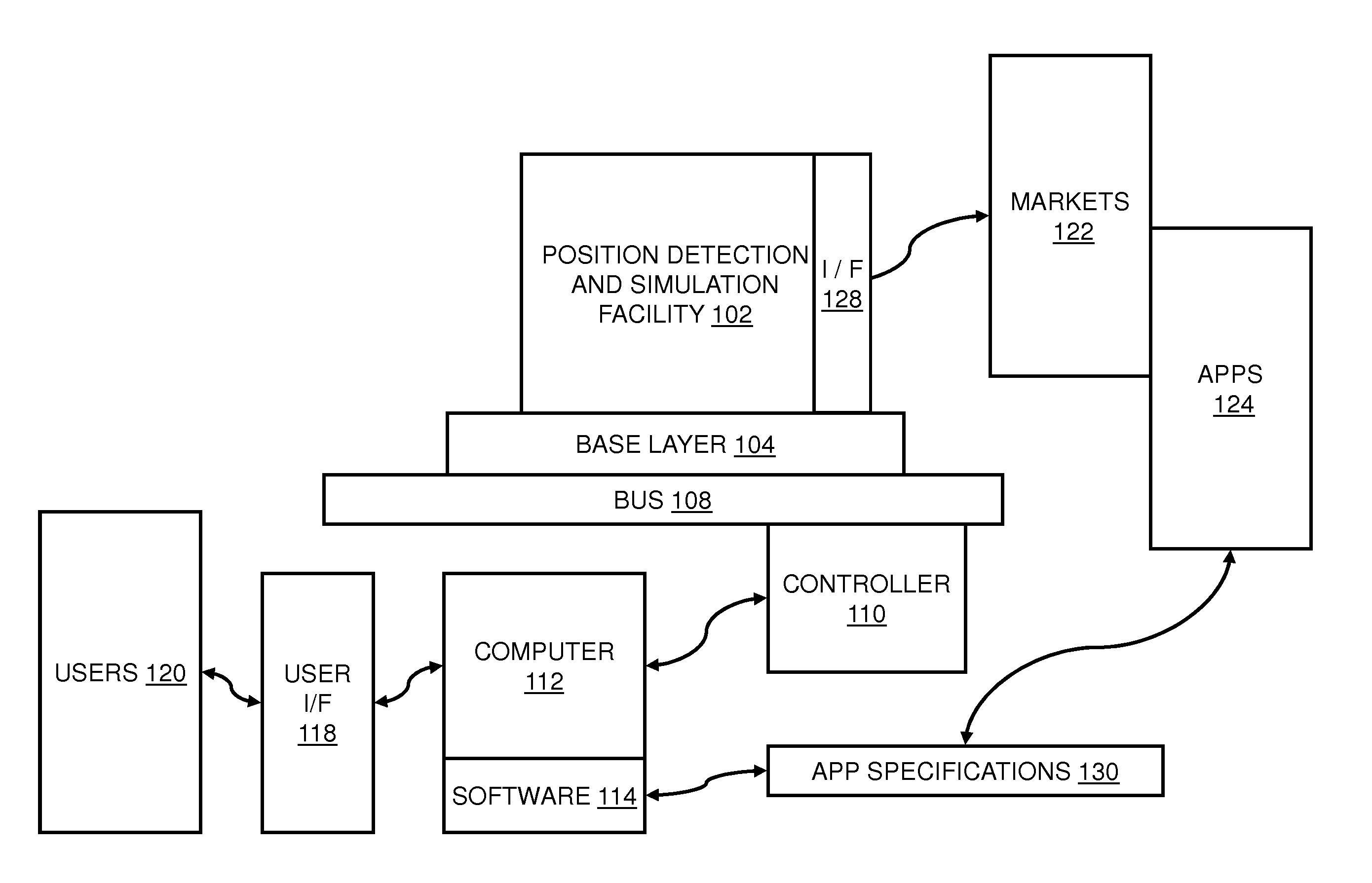
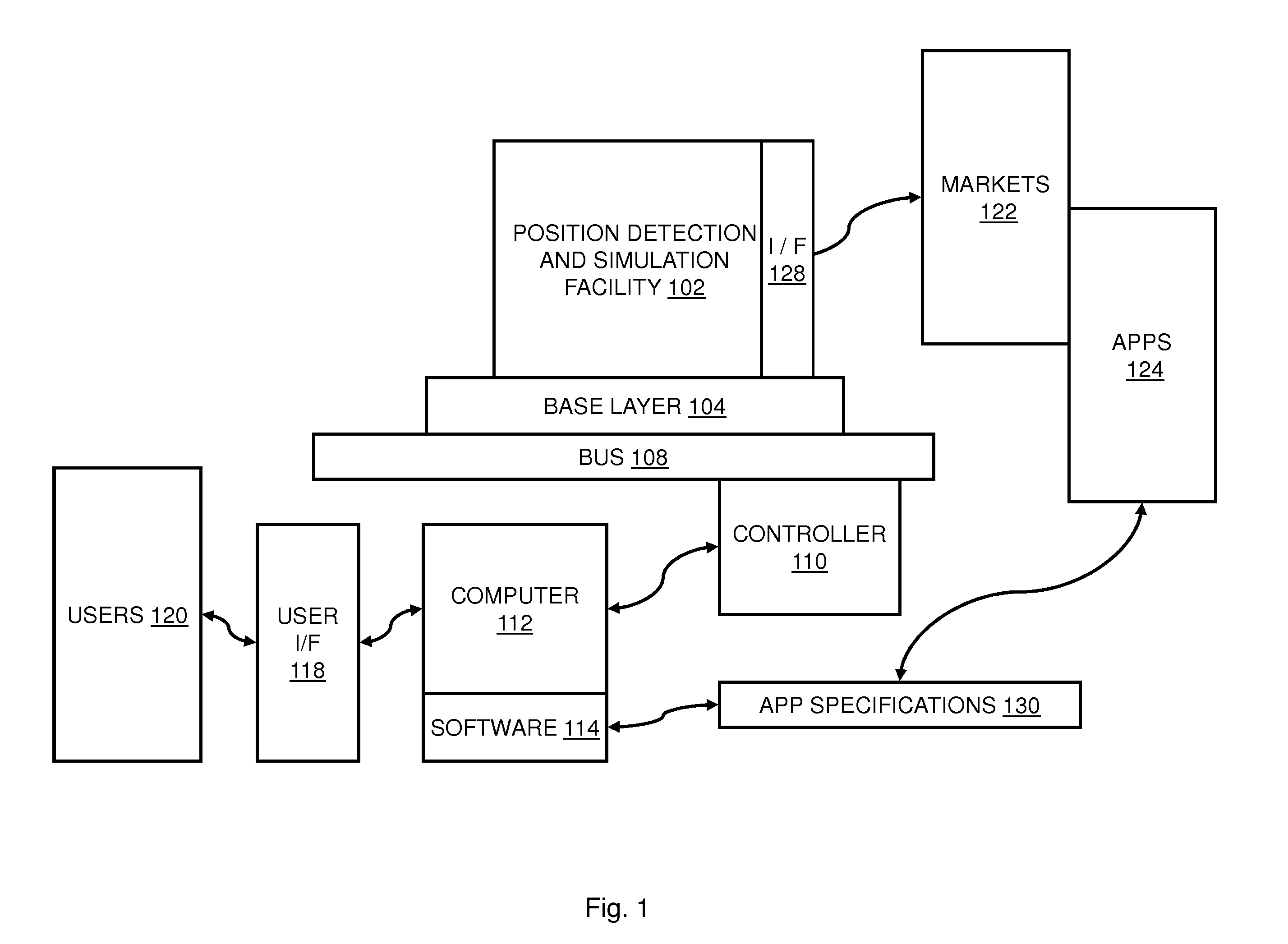
Dynamically powering a position and angle digital detection and simulation output
ActiveUS20110227556A1Reduce power consumptionImprove product reliabilityDigital data processing detailsAc-dc network circuit arrangementsLocation detectionLinear variable differential transformer
A position detection and simulation platform includes software configurable logic and programmable inputs and outputs to support software configuration only changes for use with a variety of position feedback devices including synchros, resolvers, linear variable differential transformers, and rotary variable differential transformers. Power to the software configurable outputs is dynamically controlled so that the power supply voltage presented to the outputs satisfies a minimum threshold above the amplitude of the output signal. Dynamic control is based on at least one of a digital representation of a signal to be output, an analog version of the signal to be output, or the signal being output.
Owner:UNITED ELECTRONICS IND
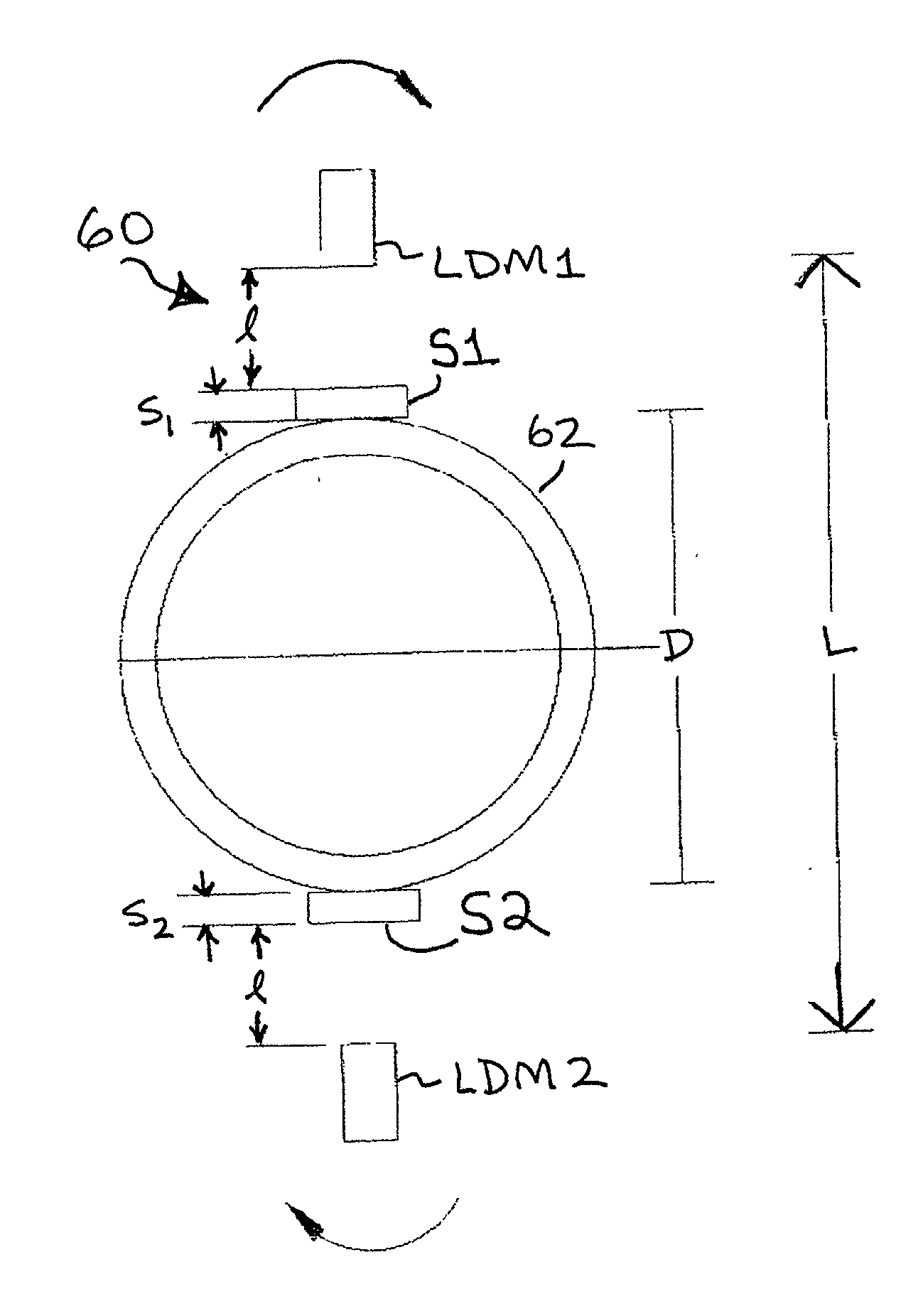
Tubular ovality testing
InactiveUS20030189713A1Eliminate the effects ofAccurate centerInvestigating moving sheetsUsing mechanical meansLinear variable differential transformerProcess equipment
A system for measuring diameter (inner and / or outer) of a tubular, the system in at least certain aspects including at least one linear distance measuring device with respect to which a tubular to be measured is movable, the at least one linear distance measuring device including a detector for detecting a surface of the tubular, the detector movably mounted to mount apparatus, the detector movable longitudinally along the surface of the tubular and movable axially in response to variation in diameter of the tubular, a rotatable head rotatable with respect to the tubular either outside of it or within it, the mount apparatus secured to the rotatable head, at least one signal production apparatus secured to the mount apparatus or head, and in communication with the linear distance measuring device, the at least one signal production apparatus for producing a signal indicative of distance between said detector and a known point, and transmitting apparatus for transmitting said signals to processing equipment for determining diameter of the tubular; and in certain aspects the linear distance measuring device is a laser device, electronic measurement device, acoustic measurement device, infrared measurement device, or linear variable differential transformer device.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
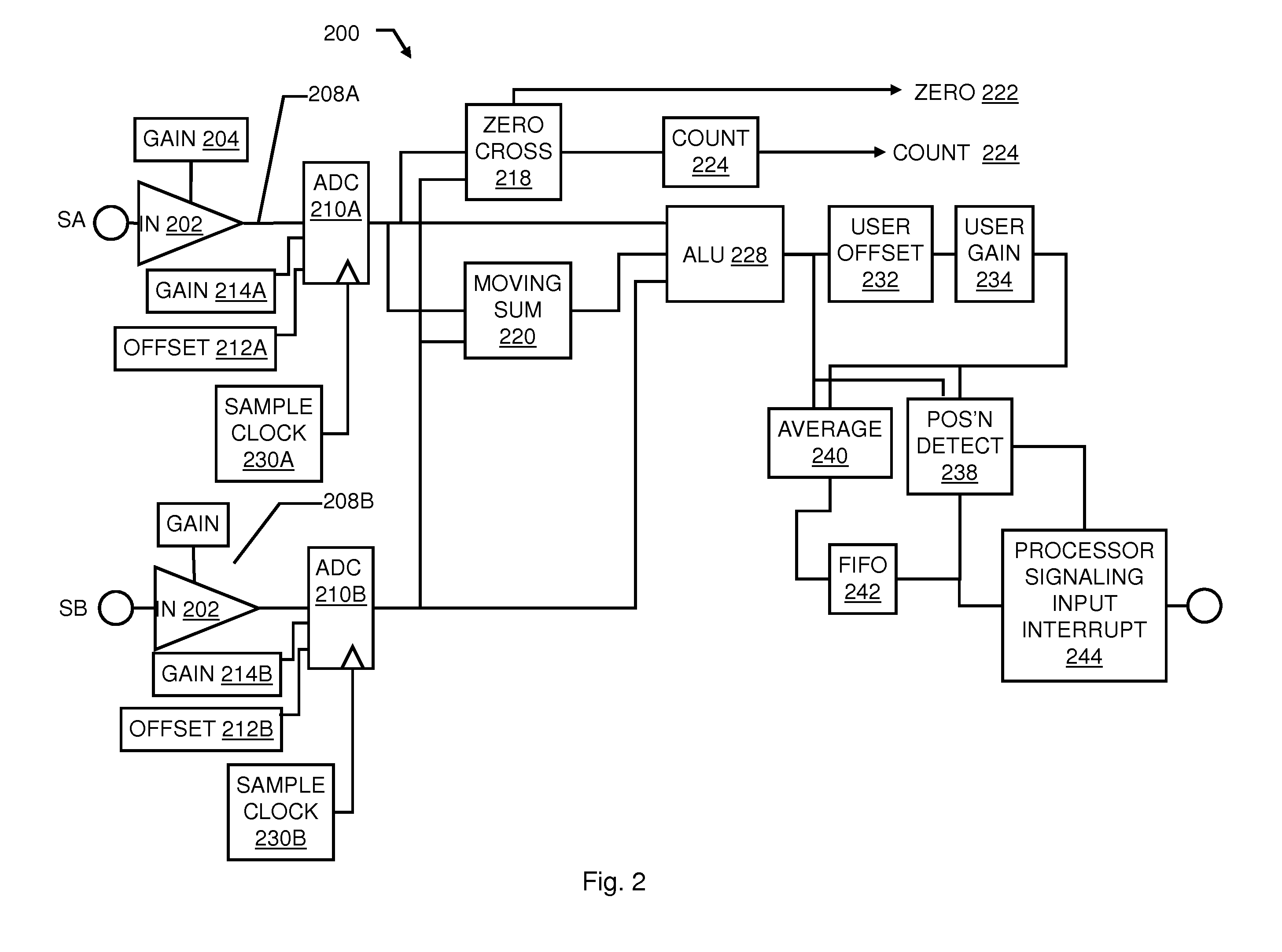
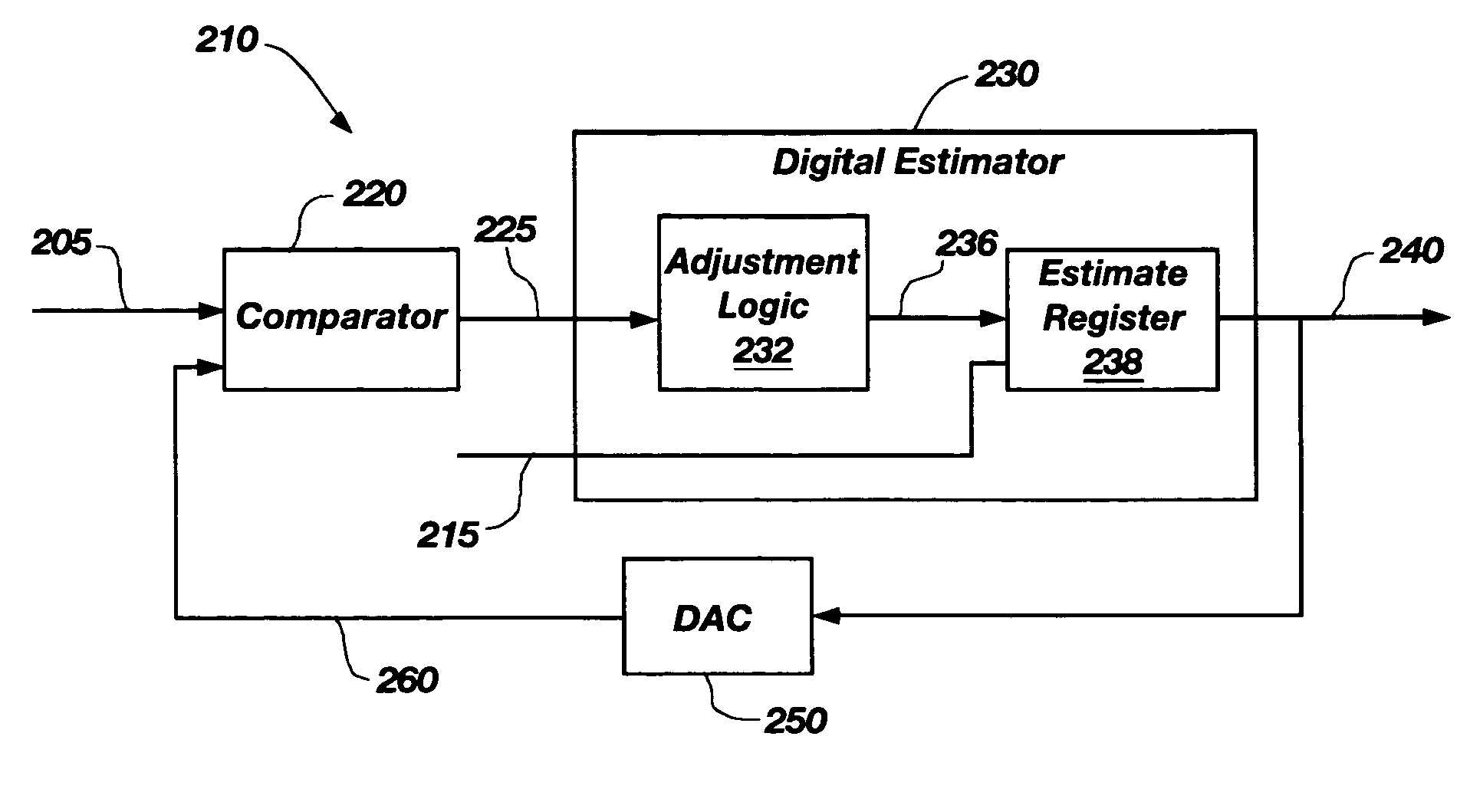
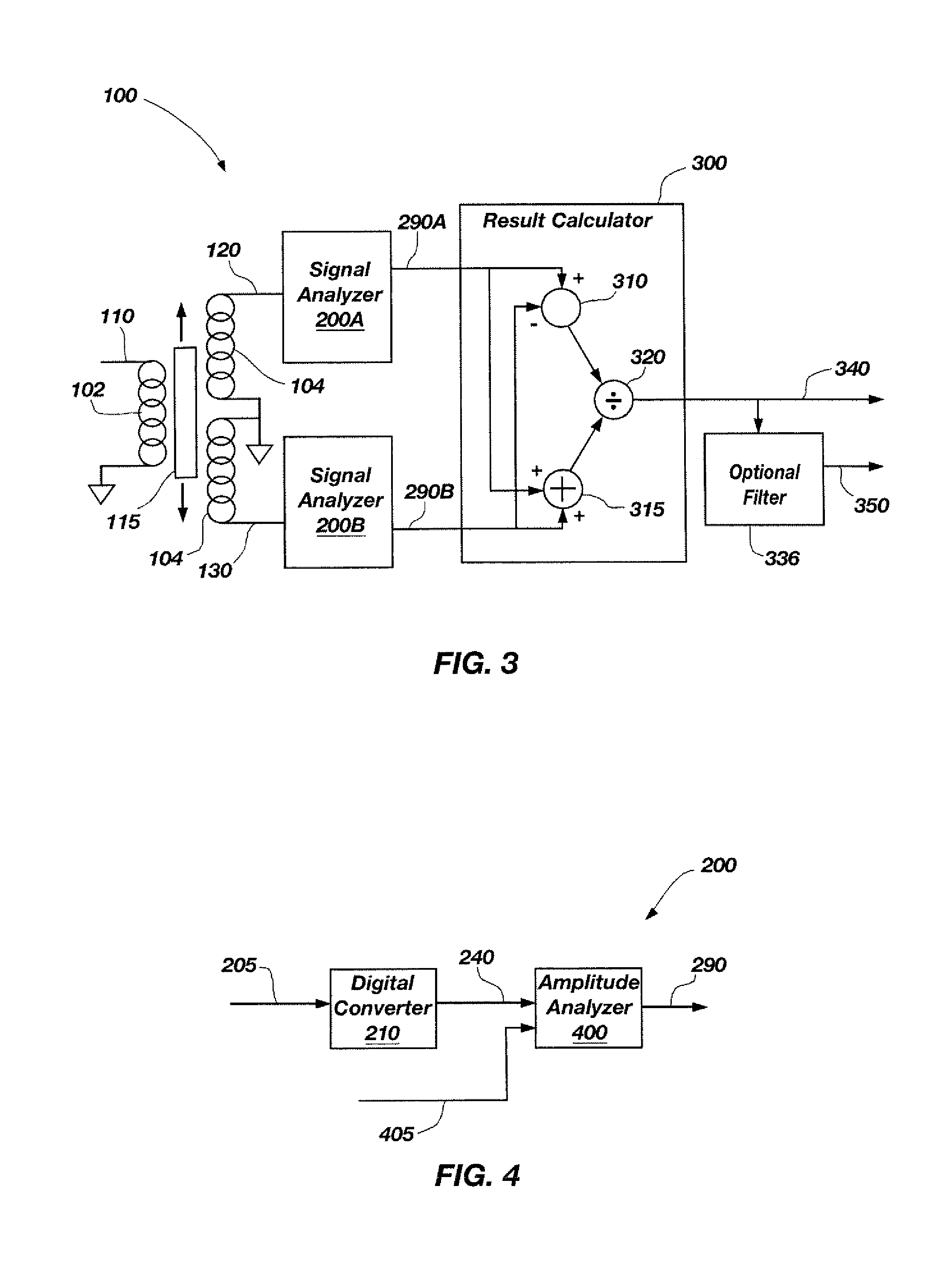
Digital method and apparatus for sensing position with a linear variable differential transformer
ActiveUS7248994B1Reduce complexityReduce the numberMagnetic measurementsIncline measurementLinear variable differential transformerAnalog feedback
An apparatus and method for determining a linear position from a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) including a primary coil driven by an excitation signal, and two secondary coils coupled to two correlated signals. The method includes converting the correlated signals to a digital estimate, for each of the correlated signals, and evaluating an amplitude of the correlated signals to determine the linear position. The process of converting the correlated signals comprises comparing the correlated signal to an analog feedback signal to generate a comparison result and incrementally adjusting the digital estimate in response to sampling the comparison result at an estimation frequency. The converting process also includes converting the digital estimate to the analog feedback signal, collecting a digital estimate history at a sample frequency that is a binary multiple of the excitation frequency, and analyzing the digital estimate history to determine the amplitude substantially near the excitation frequency.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
Digital transmission demodulating method of differential transformer displacement transducer
InactiveCN102012209AHigh measurement accuracyOvercome the disadvantage of excessive noise interferenceUsing electrical meansObservational errorMoving average
The invention relates to a digital transmission demodulating method of a differential transformer displacement transducer, belonging to a method for processing signals for accurately measuring the small displacement of an object by using an LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer). The method comprises the following steps of: driving a primary coil of the LVDT by a transformer manufactured by a field programmable gate array (FPGA), collecting the output signals Va and Vb of two secondary coils of the LVDT, carrying out digital demodulation on the collected output signals Va and Vb of the two secondary coils of the LVDT in the formula of S=(Va-Vb) / (Va+Vb), and detecting signals of the LVDT by the mapping relationship between the actual displacement of the LVDT iron core and the S. The addition and subtraction as well as the demodulation method of the division are used on the secondary coil signals in the LVDT, and the actual displacement of the LVDT iron core is obtained by a moving average algorithm and the mapping relationship. The invention reduces the noise interference to the measuring result and greatly reduces the measuring error.
Owner:BEIJING JINGHAIQUAN SENSING TECH
Linear variable differential transformer with complimentary step-winding secondary coils
InactiveUS7317371B1Variable inductancesVariable transformersLinear variable differential transformerTransformer
A linear variable differential transformer comprising a coil form; a first primary coil; an optional second primary coil; a first secondary coil; and a second secondary coil; wherein the windings of the secondary coils create complimentary and preferably uniform steps. Each step is preferably wound in at least two layers. In the embodiment comprising two primary coils, the inductive couplings between the primary and secondary coils cause null position to be physically centered within the transformer.
Owner:RHINESMITH R BRET
Active vibration isolation control platform
ActiveCN101609341ASimple structureReduce noiseMechanical oscillations controlEnergy industryLinear variable differential transformerExecution control
The invention discloses an active vibration isolation control platform. The active vibration isolation control platform comprises an active vibration isolation device and an active vibration isolation controller; the active vibration isolation device comprises a lower platform, a midbody and an upper platform; a voice coil motor actuator is arranged between the midbody and the lower platform; a linear variable differential transformer type displacement sensor is arranged between the upper platform and the midbody; and two three-freedom-degree acceleration sensors are arranged on the upper platform and the lower platform respectively. The vibration isolation controller is designed according to a master-slave open type control structure and consists of an upper control computer and a lower execution controller, wherein the upper control computer is a mainframe of an embedded type industrial control computer PC / 104; and the lower execution controller is an open-type controller. The active vibration isolation control platform is quite effective on low-frequency vibration isolation and is applicable to precise manufacture, precise measurement, aerospace application and other vibration isolation fields with special requirement on vibration environment.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Sub sea hybrid valve actuator system and method
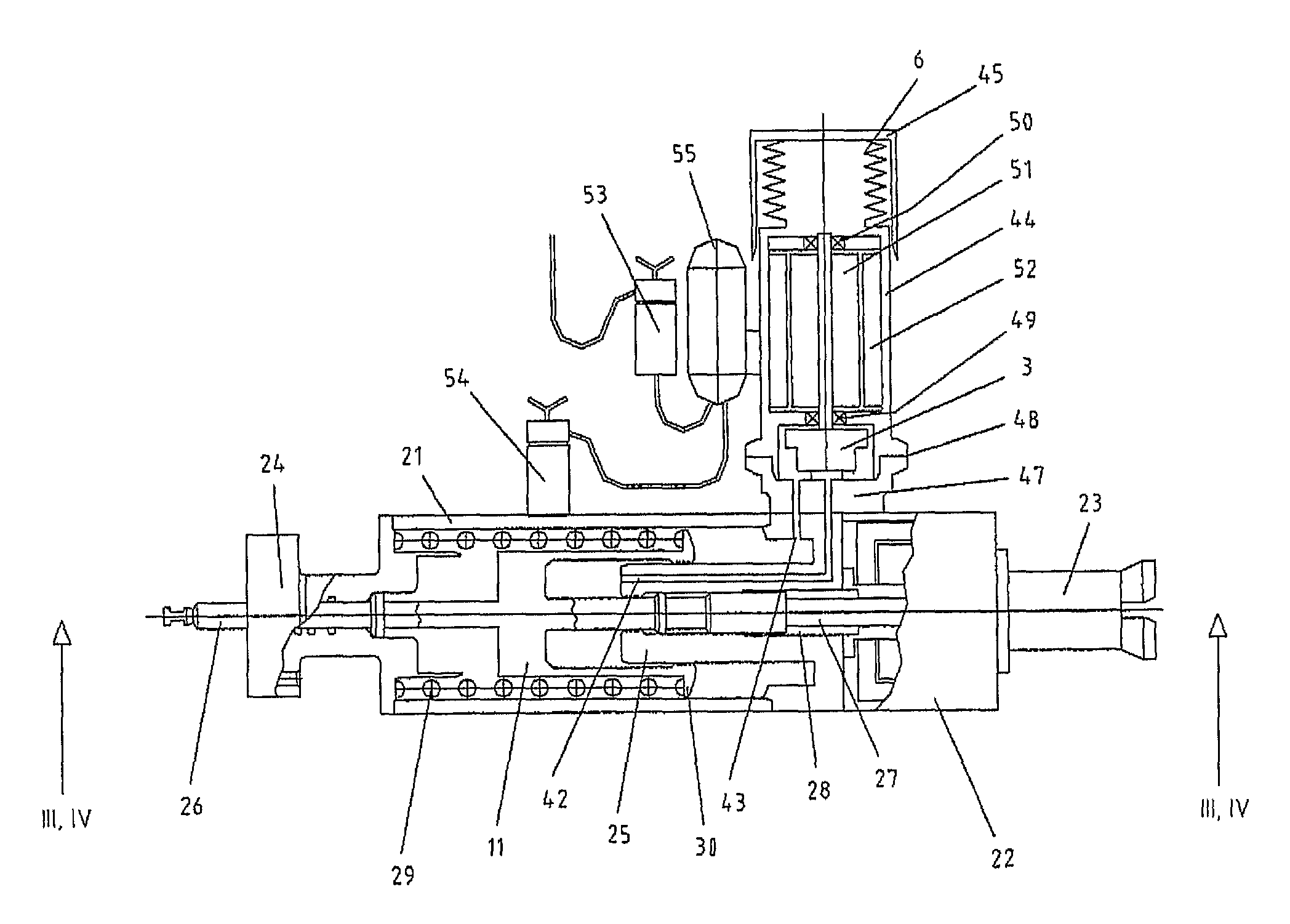
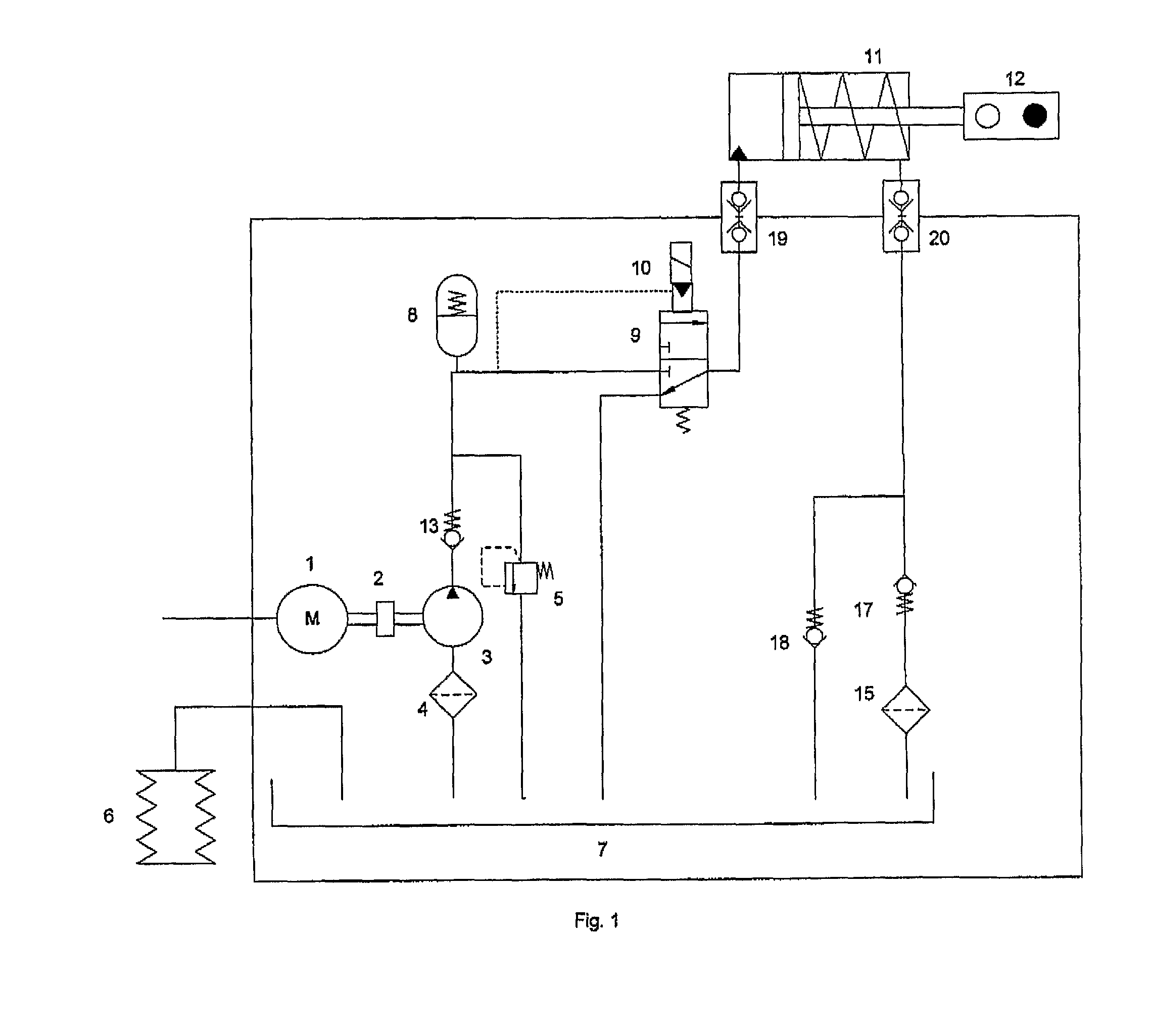
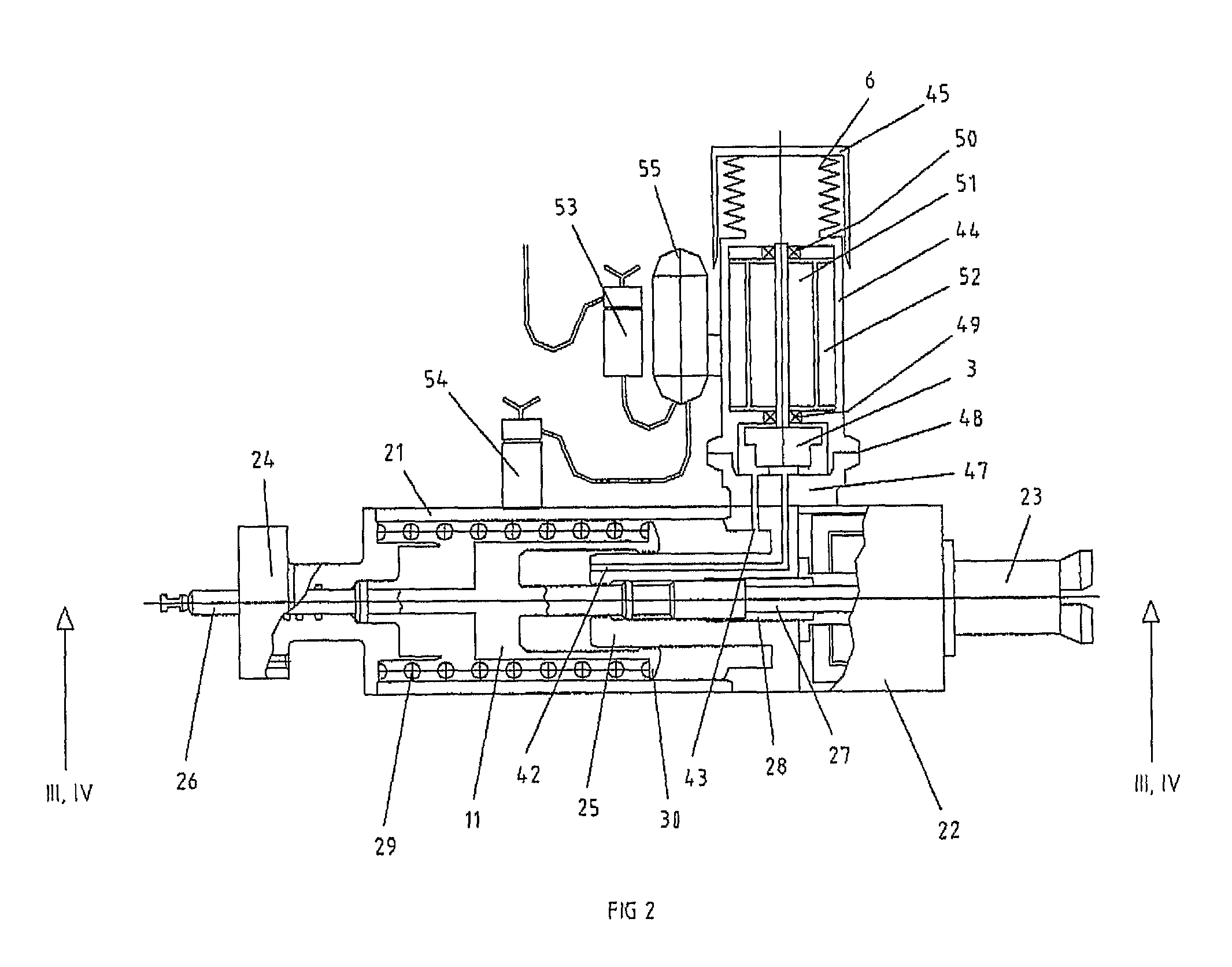
ActiveUS20110126912A1Improve robustnessImprove reliabilityValve arrangementsPipeline systemsLinear variable differential transformerRelative displacement
A sub sea valve actuator system including a piston and cylinder assembly and a return spring arranged in an actuator housing, a hydraulic pump and electric motor assembly associated with the piston and cylinder assembly, and hydraulic flow lines for hydraulic medium driving the piston and cylinder in relative displacement against a force of the return spring. The valve actuator system includes a detector configured to detect an end-of-stroke position of the piston and cylinder assembly. The detector includes at least one of: a motor current monitoring circuit unit, a hydraulic medium pressure sensor unit, a position sensor unit, and a linear variable differential transformer unit. An electromechanical arresting mechanism is arranged to be energized for releasably arresting the return spring in a compressed state in result of the detected end-of-stroke position. A method for operation of a sub sea valve actuator system by which an end-of-stroke position for a piston and cylinder assembly in a sub sea valve actuator system can be determined.
Owner:VETCO GRAY SCANDINAVIA
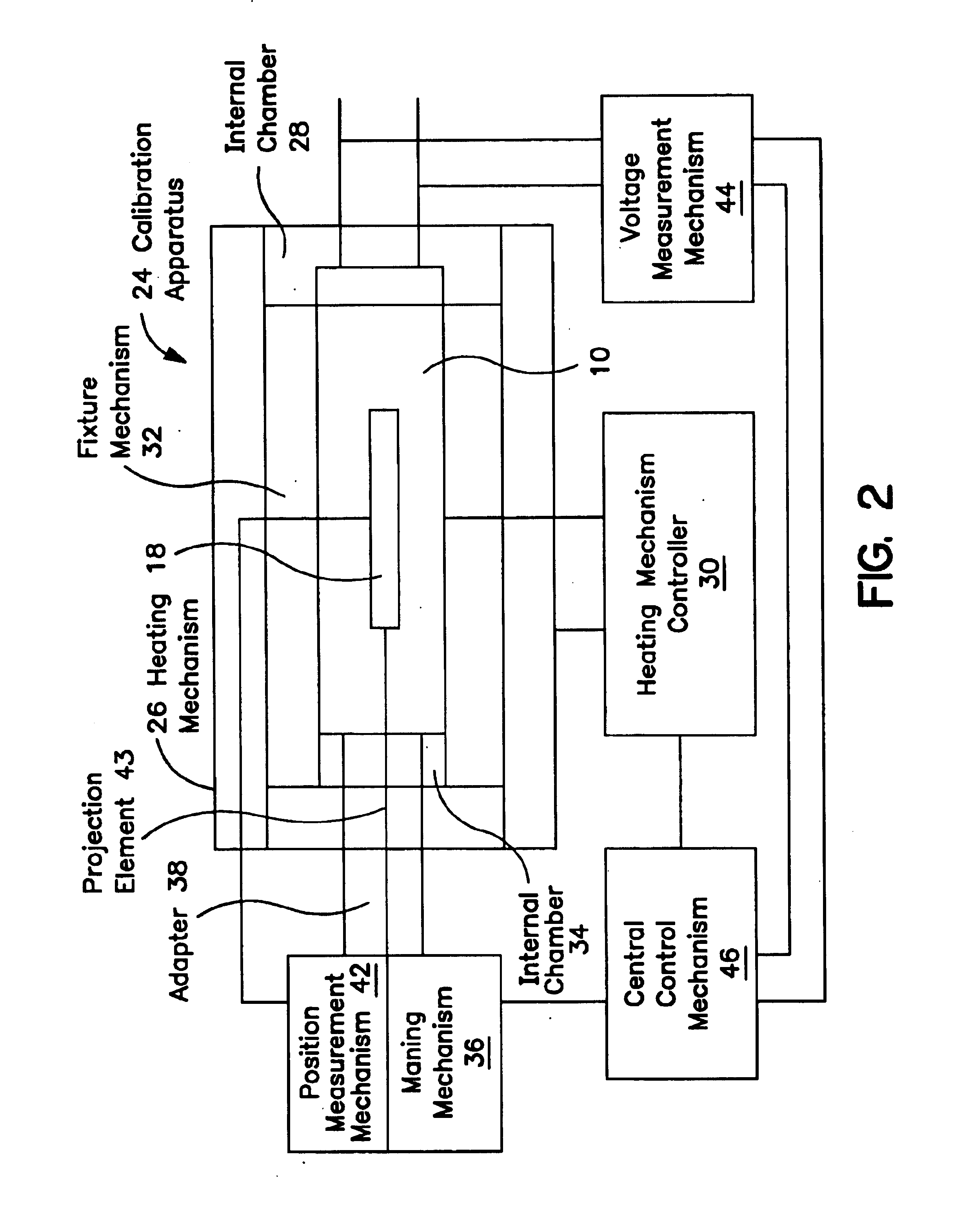
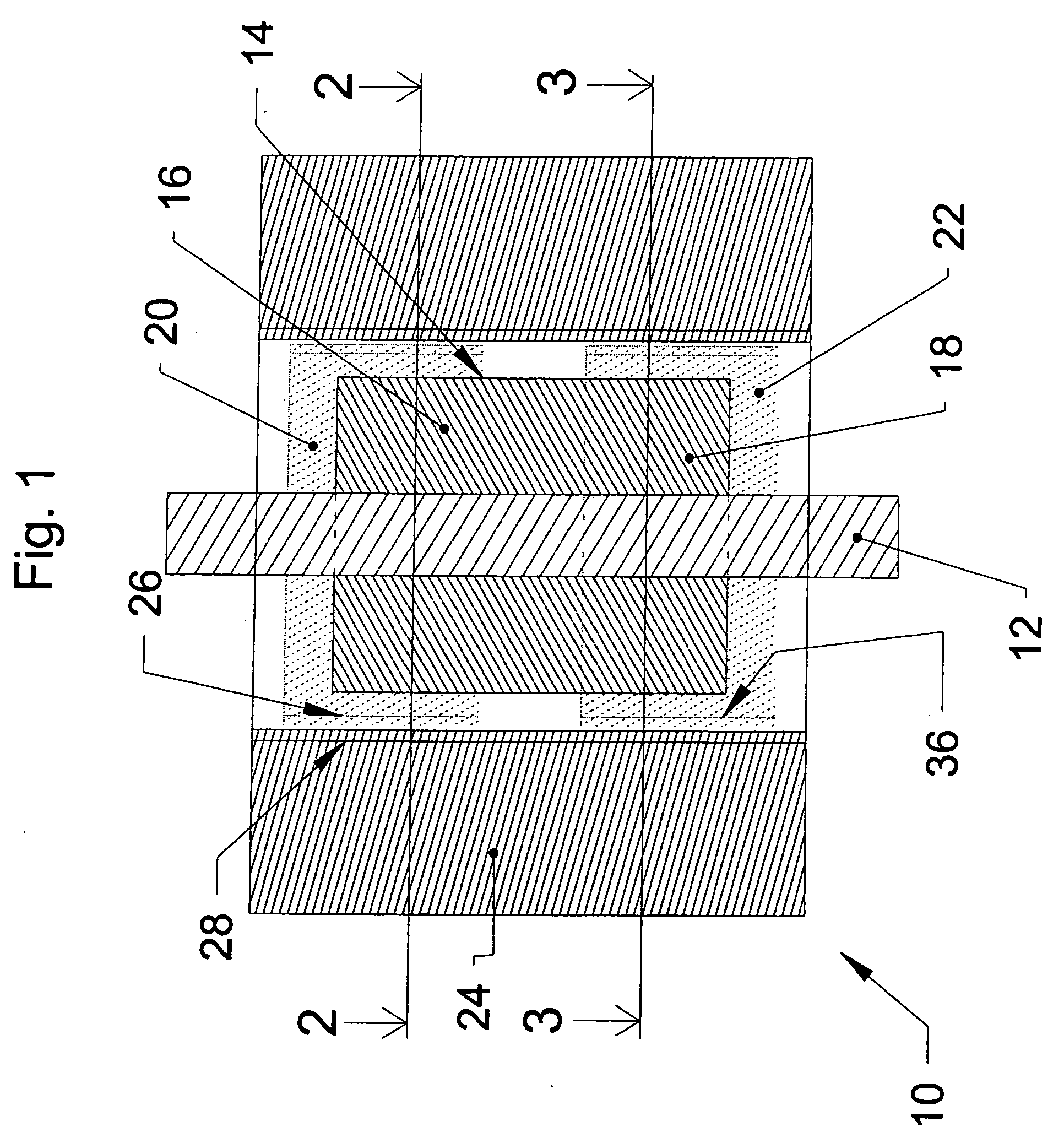
Method and apparatus for calibrating a linear variable differential transformer
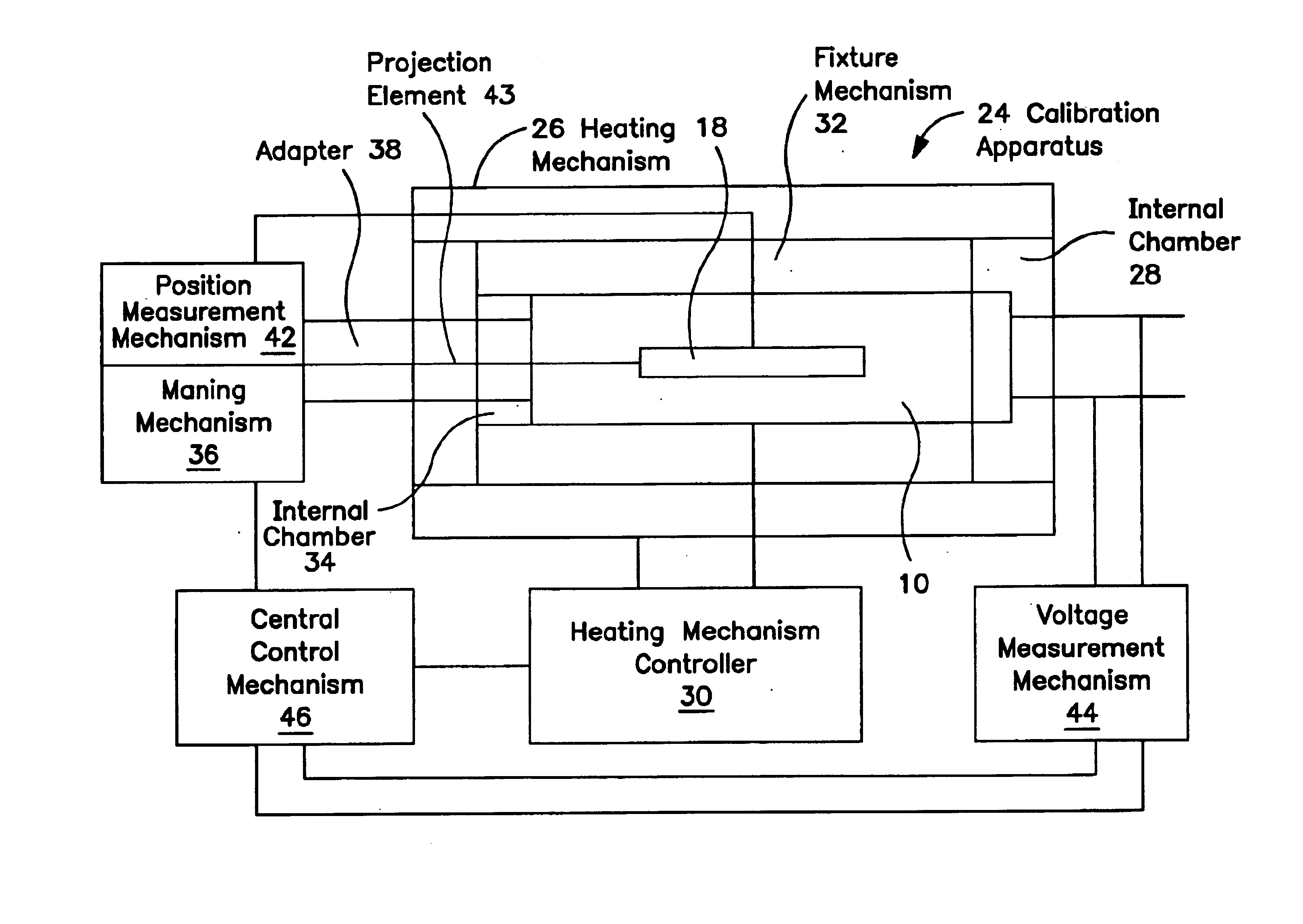
InactiveUS6844720B1Overcome deficienciesValid calibrationThermometer detailsWalking sticksLinear variable differential transformerEngineering
A calibration apparatus for calibrating a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) having an armature positioned in au LVDT armature orifice, and the armature able to move along an axis of movement. The calibration apparatus includes a heating mechanism with an internal chamber, a temperature measuring mechanism for measuring the temperature of the LVDT, a fixture mechanism with an internal chamber for at least partially accepting the LVDT and for securing the LVDT within the heating mechanism internal chamber, a moving mechanism for moving the armature, a position measurement mechanism for measuring the position of the armature, and an output voltage measurement mechanism. A method for calibrating an LVDT, including the steps of: powering the LVDT; heating the LVDT to a desired temperature; measuring the position of the armature with respect to the armature orifice; and measuring the output voltage of the LVDT.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES AS REPRESENTED BY THE DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY
Integrated resolver for high pole count motors
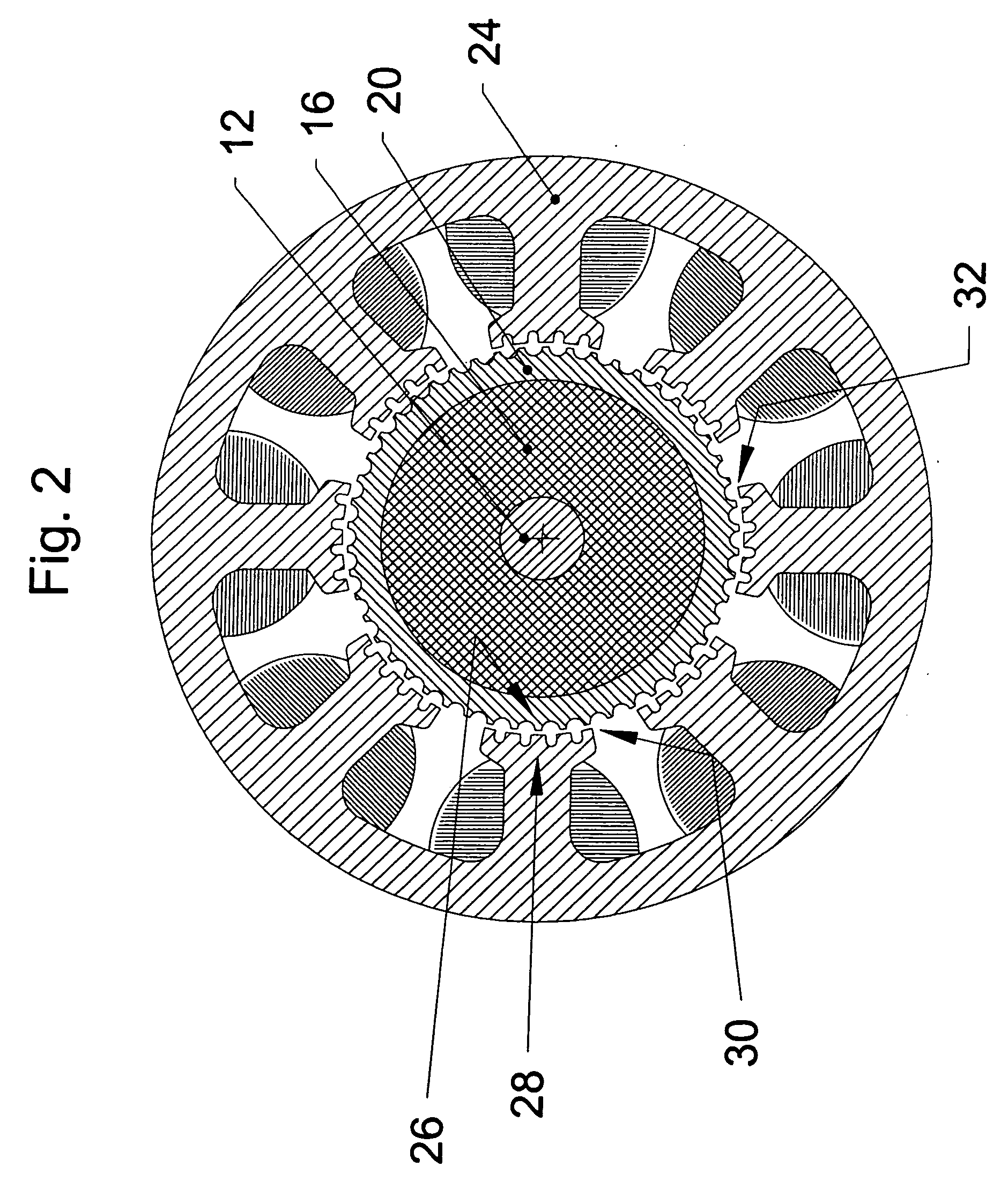
InactiveUS20060197393A1Synchronous generatorsWindingsLinear variable differential transformerSynchronous motor
Owner:QUICKSILVER CONTROLS
Intelligent electrohydraulic flow servo valve
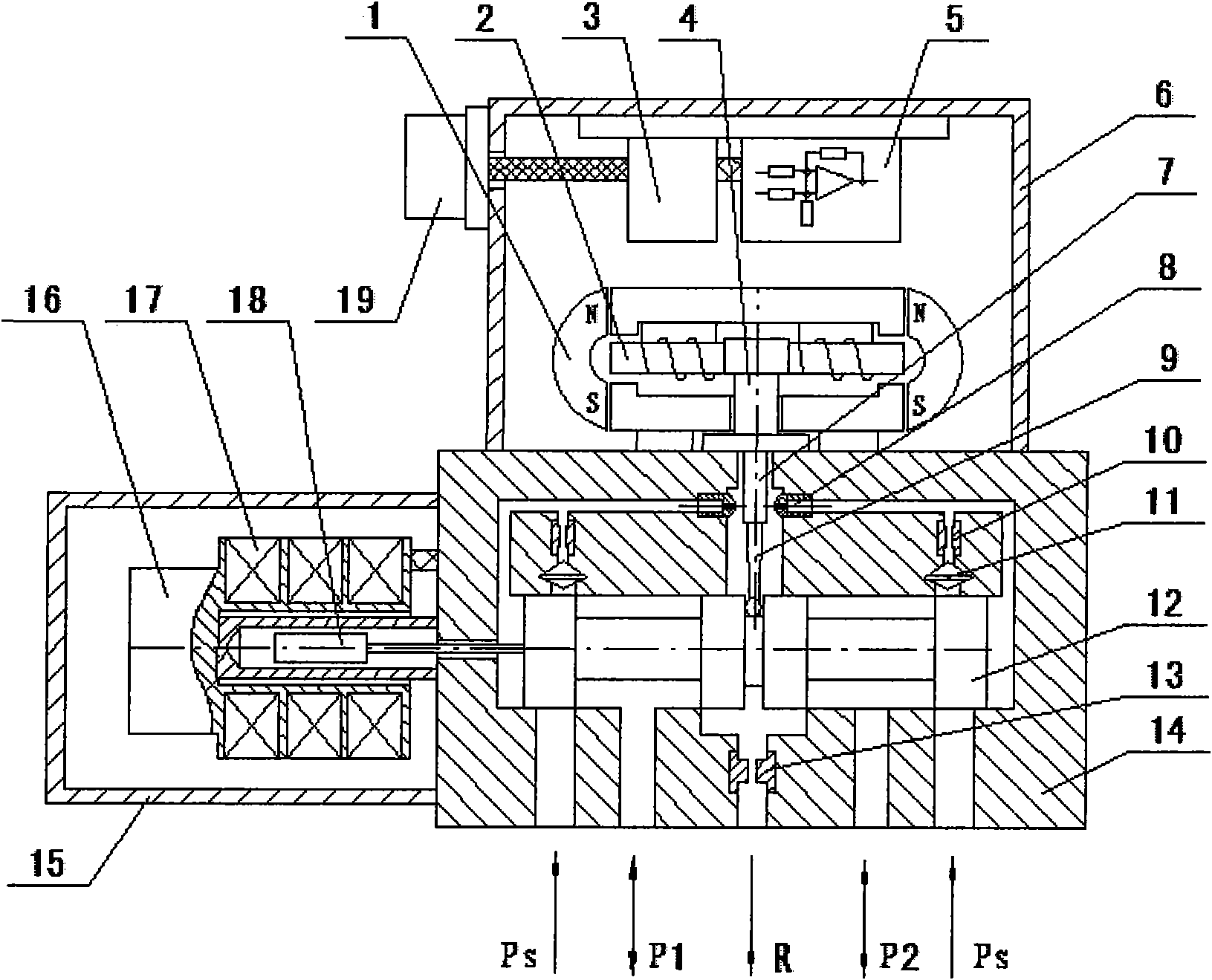
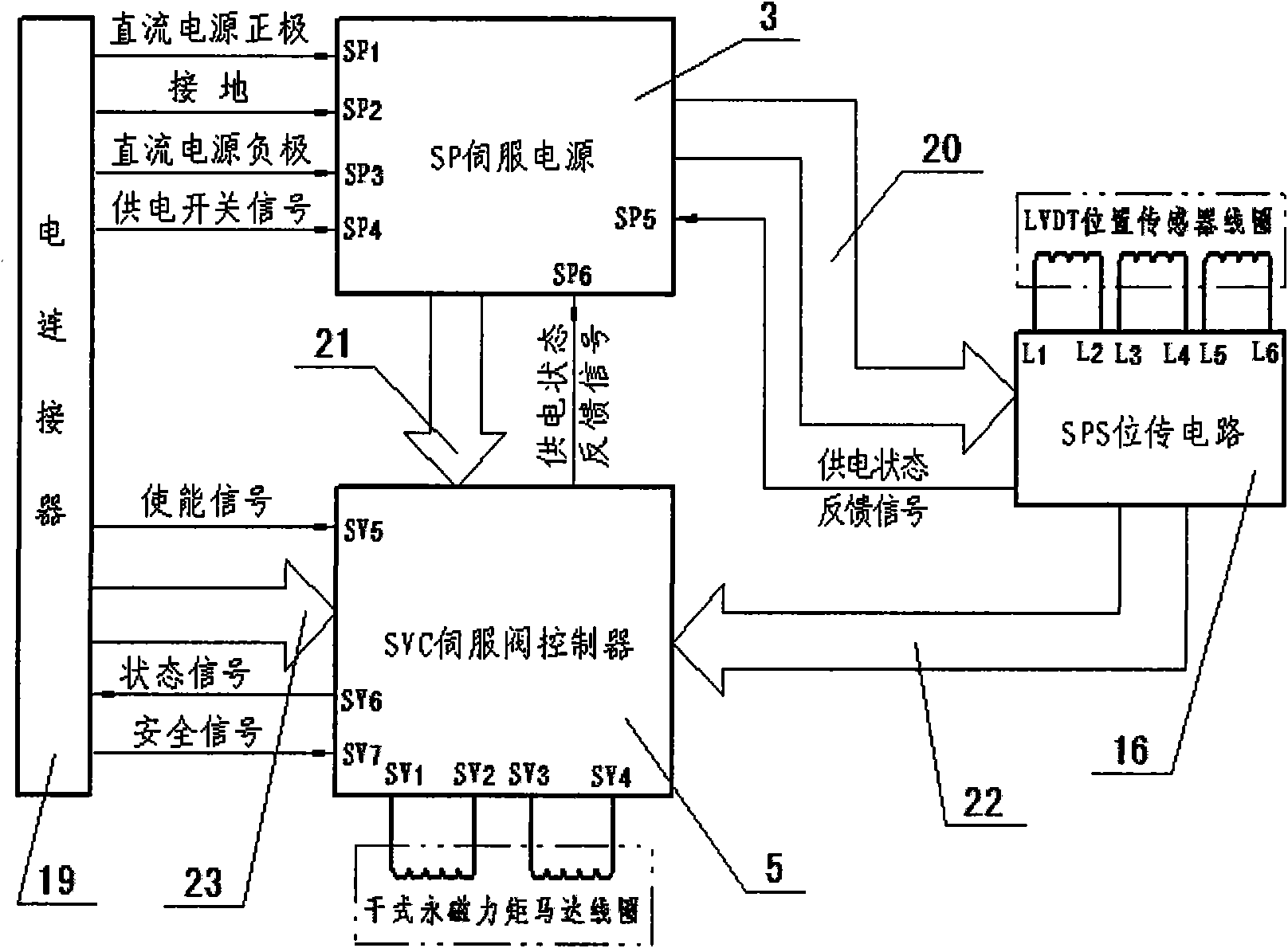
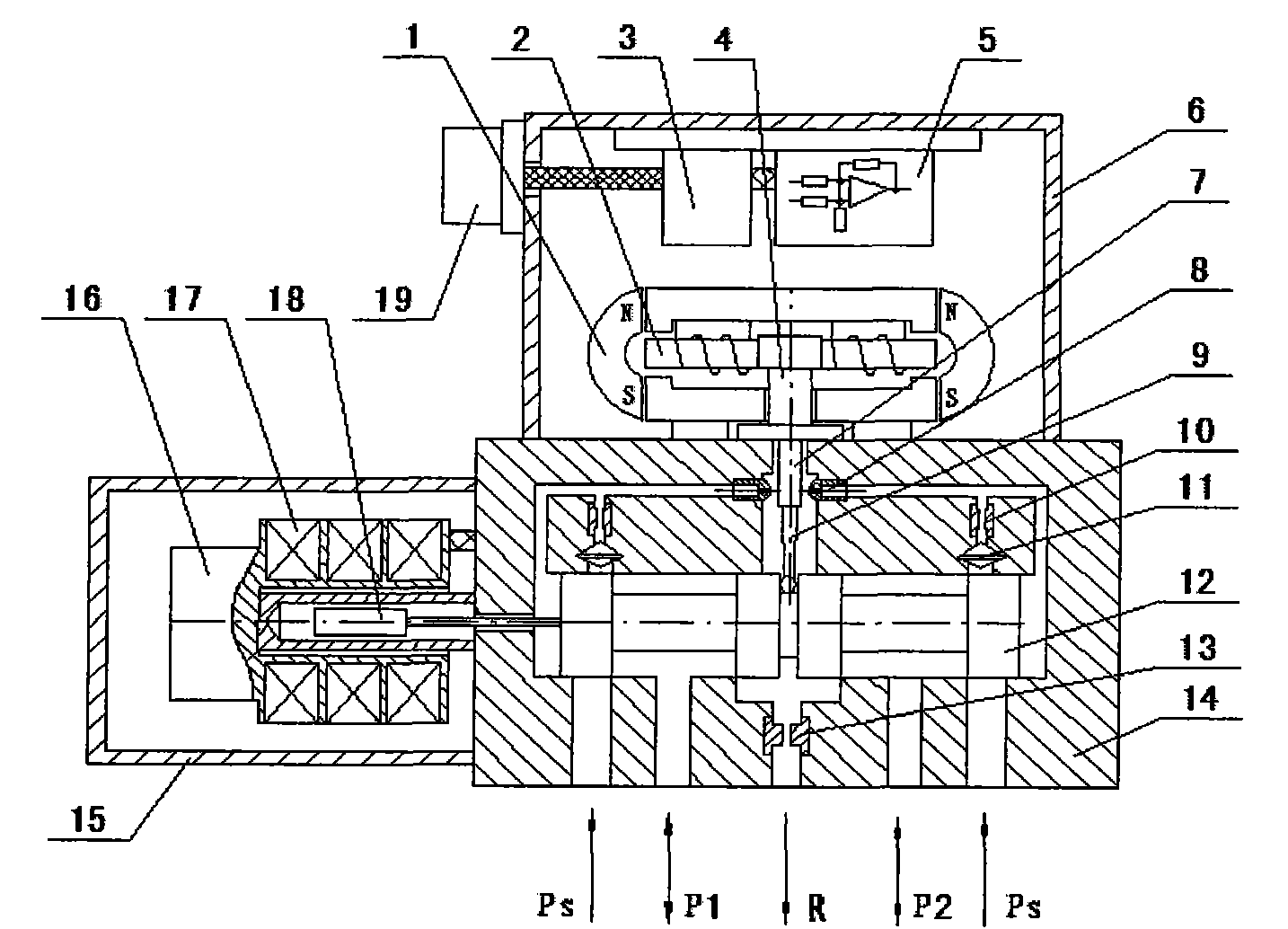
ActiveCN102094865AExtended service lifeImprove use reliabilityServomotor componentsLinear variable differential transformerSpool valve
The invention discloses an intelligent electrohydraulic flow servo valve. The intelligent electrohydraulic flow servo valve is characterized in that: a servo power (SP) and a servo valve controller (SVC) are arranged in a top cover of the electrohydraulic flow servo valve; a dry permanent magnet torque motor, and a baffle assembly is arranged on a valve body; a double nozzle flapper is connected with a high-pressure oil cavity, an overflow cavity, and control cavities at two ends of a force feedback centering slide valve through an oil path respectively; the force feedback centering slide valve is connected with the high-pressure oil cavity, a load cavity and an oil return cavity through the oil path respectively; the baffle assembly of the dry permanent magnet torque motor is connected with a feedback rod and the force feedback centering slide valve; an iron core of a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) is connected with the force feedback centering slide valve; an SPS position transmission circuit is directly fixed on the side of a coil framework of the LVDT; and the high-precision LVDT, and the SPS position transmission circuit are arranged in an outer cover on one side of the valve body.
Owner:陈镇汉 +2
Sub sea hybrid valve actuator system and method
ActiveUS8596608B2Improve protectionImprove scalabilityOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEqualizing valvesLinear variable differential transformerRelative displacement
A sub sea valve actuator system including a piston and cylinder assembly and a return spring arranged in an actuator housing, a hydraulic pump and electric motor assembly associated with the piston and cylinder assembly, and hydraulic flow lines for hydraulic medium driving the piston and cylinder in relative displacement against a force of the return spring. The valve actuator system includes a detector configured to detect an end-of-stroke position of the piston and cylinder assembly. The detector includes at least one of: a motor current monitoring circuit unit, a hydraulic medium pressure sensor unit, a position sensor unit, and a linear variable differential transformer unit. An electromechanical arresting mechanism is arranged to be energized for releasably arresting the return spring in a compressed state in result of the detected end-of-stroke position. A method for operation of a sub sea valve actuator system by which an end-of-stroke position for a piston and cylinder assembly in a sub sea valve actuator system can be determined.
Owner:VETCO GRAY SCANDINAVIA
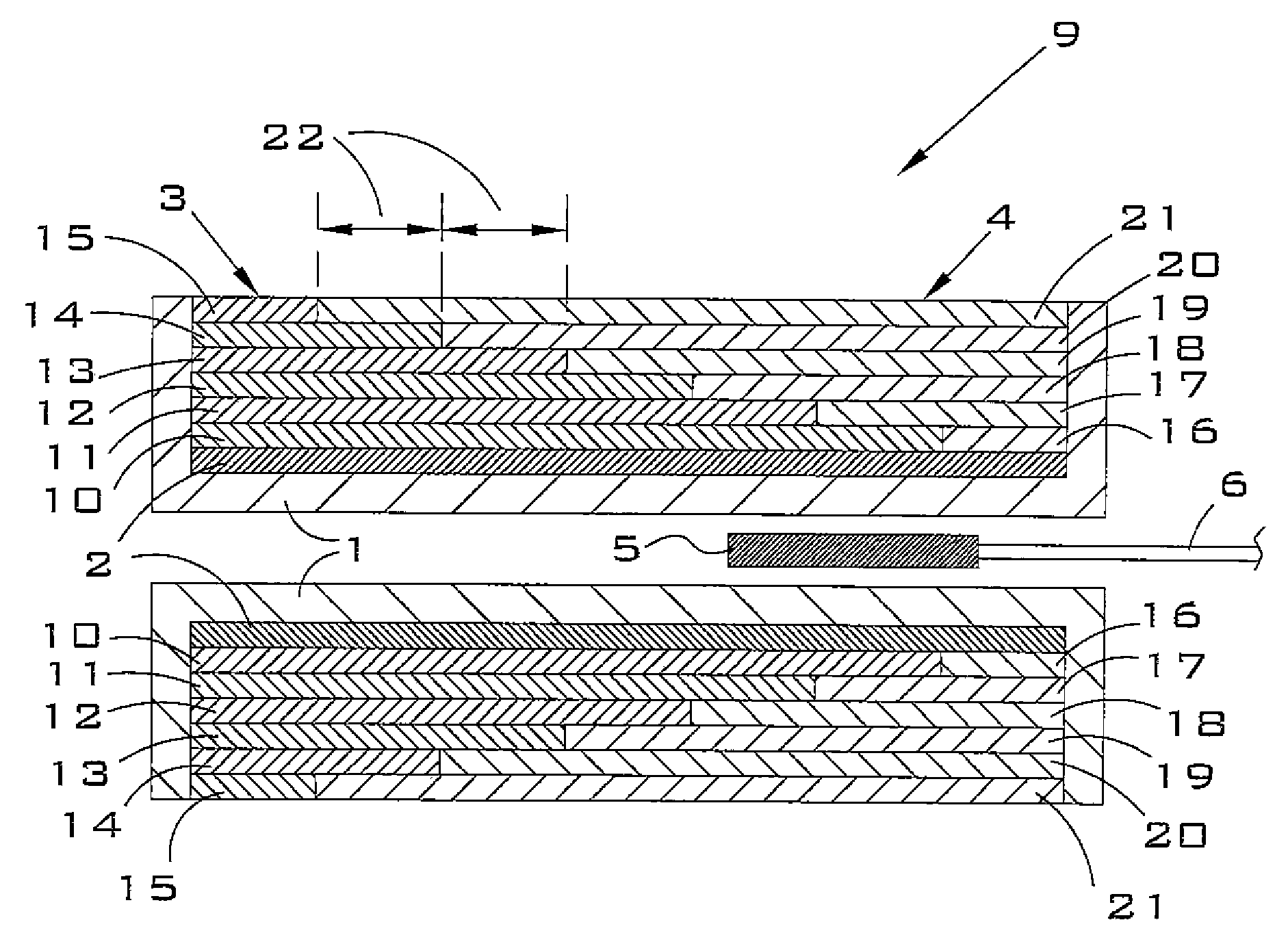
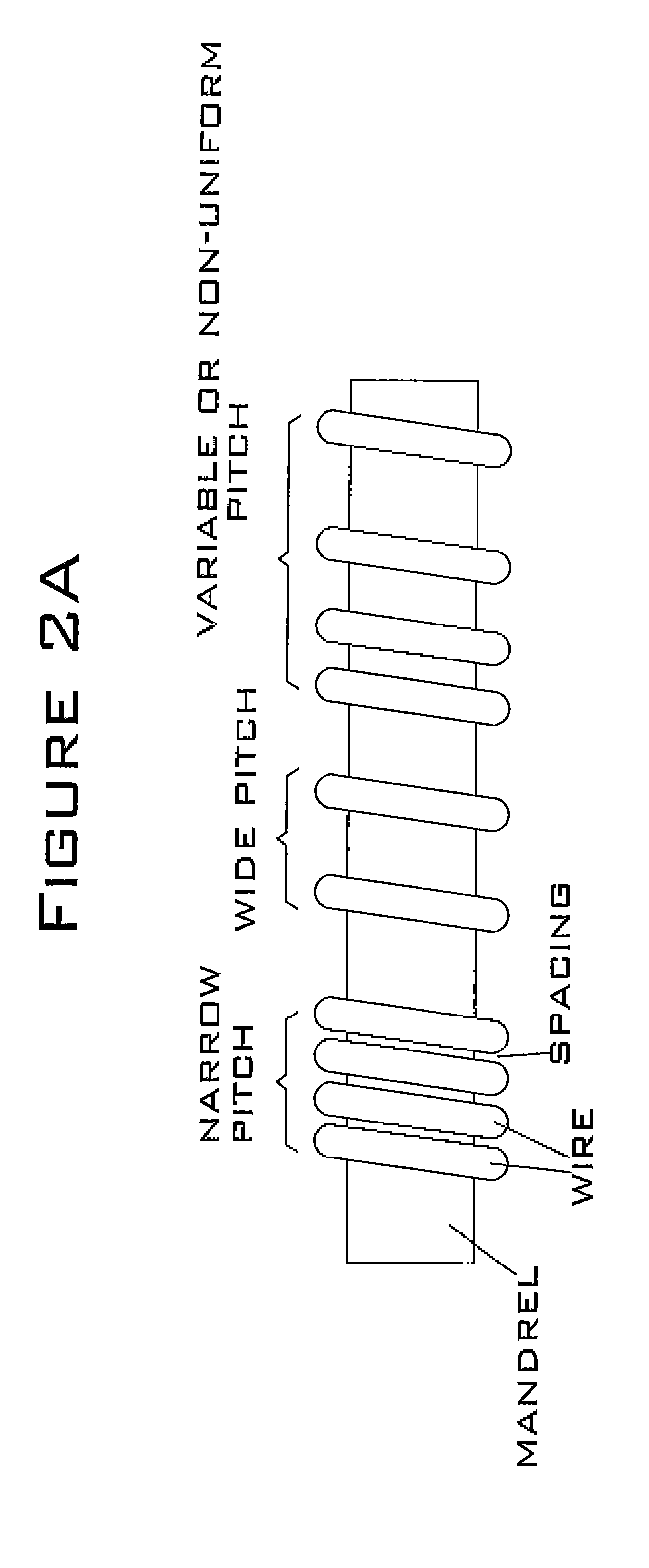
Linear variable differential transformer and winding method thereof
ActiveCN104465044AGood symmetryAccuracy meetsTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsUsing electrical meansLinear variable differential transformerElectrical performance
The invention belongs to the technical field of displacement sensors and provides a linear variable differential transformer. Magnetic flux generated by coupling of a first secondary winding and a primary winding and magnetic flux generated by coupling of a second secondary winding and the primary winding are symmetric, so that symmetry of the linear variable differential transformer is improved. Coils are compact in structures, improving anti-vibration, anti-mechanical shock and anti-heat shock capabilities of the linear variable differential transformer, and the user requirements for high precision, good temperature characteristic and high reliability and stability in the linear variable differential transformer in the aviation field are met. The invention further provides a winding method of the linear variable differential transformer. The winding method is simple to operate, turn numbers per unit length of the coils in the first secondary winding and the second secondary winding linearly progressively increase or decrease, the secondary windings output induced electromotive force linearly progressively increases or decreases with core displacement, zero residual voltage is reduced, and electrical performance and temperature stability of the linear variable differential transformer are enhanced.
Owner:MEASUREMENT SPECIALTIES CHINA
Material low-temperature thermal expansion coefficient testing device using refrigerator as cold source
InactiveCN103063699AAccurate temperature controlSimple structureMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionPreparing sample for investigationLinear variable differential transformerTemperature control
The invention discloses a material low-temperature thermal expansion coefficient testing device using a refrigerator as a cold source. The device comprises a high-resolution linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) displacement sensor, a cylindrical quartz holder, an ejection rod, a vacuum heat insulation barrel, a test sample cavity, a thermal radiation-proof screen and an external gas storage bag, wherein the high-resolution LVDT displacement sensor is arranged on a horizontal supporting plate; one end of the cylindrical quartz holder is arranged on the lower end face of the displacement sensor, the cylindrical quartz holder is provided with a bottom plate, the lower side wall of the cylindrical quartz holder is provided with a side wall hole, and the ejection rod is positioned in the axial center of the quartz holder; the vacuum heat insulation barrel is arranged below the displacement sensor and the horizontal supporting plate; the lower middle part of the test sample cavity is arranged in the vacuum heat insulation barrel, and a temperature controller is arranged in the test sample cavity; the test sample cavity covers the quartz holder; the thermal radiation-proof screen is positioned in the vacuum heat insulation barrel; helium is filled in the external gas storage bag; the external gas storage bag is connected with the test sample cavity; and a cold head of the refrigerator is arranged in the vacuum heat insulation barrel and is in contact with the test sample cavity through soft connection. By adopting the testing device, liquid helium and liquid nitrogen are not required, and the thermal expansion coefficient of a material can be tested at any temperature of between 4.2K and 300K; and the device is accurate in temperature control, simple in structure, easy to operate and high in efficiency.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
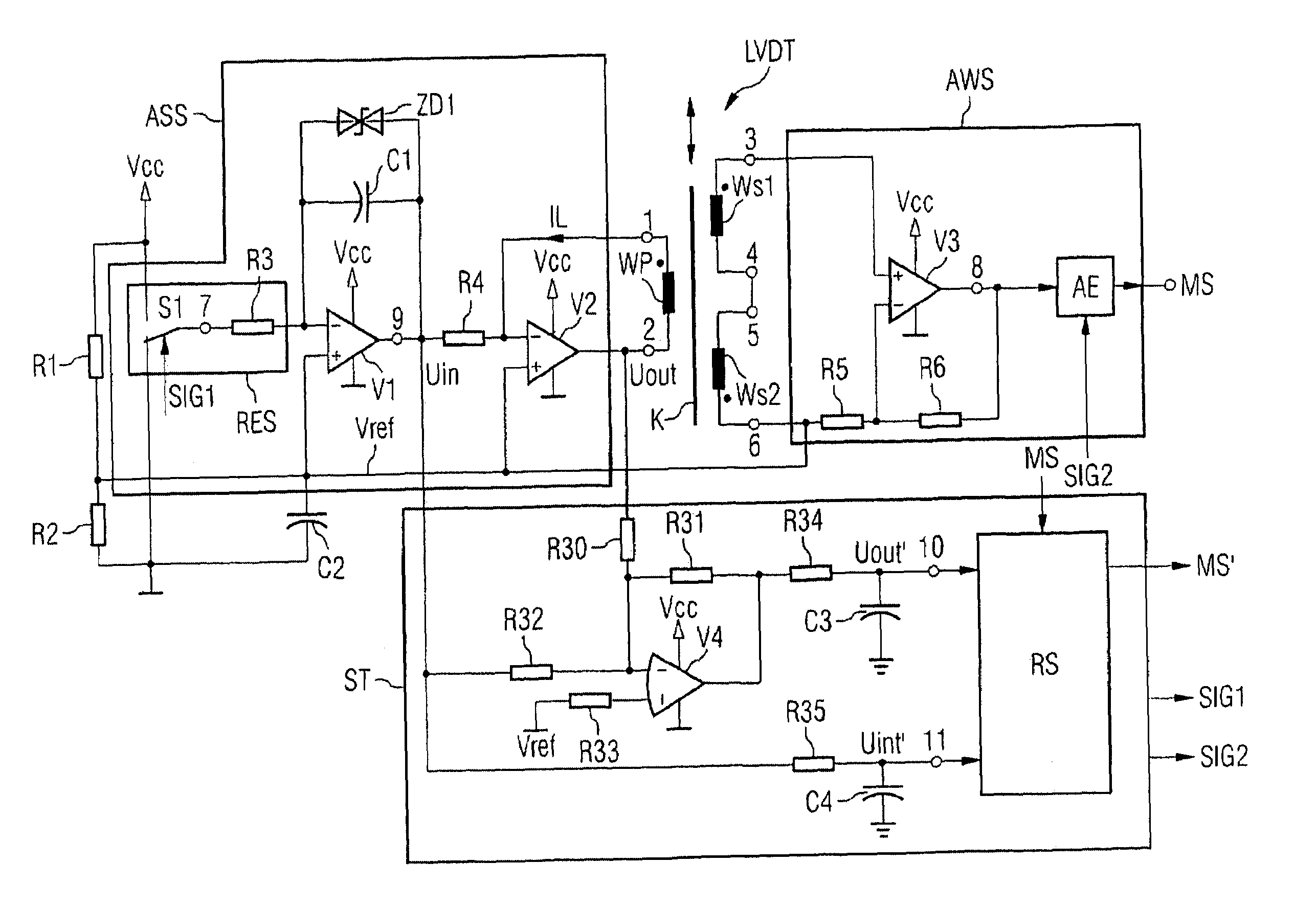
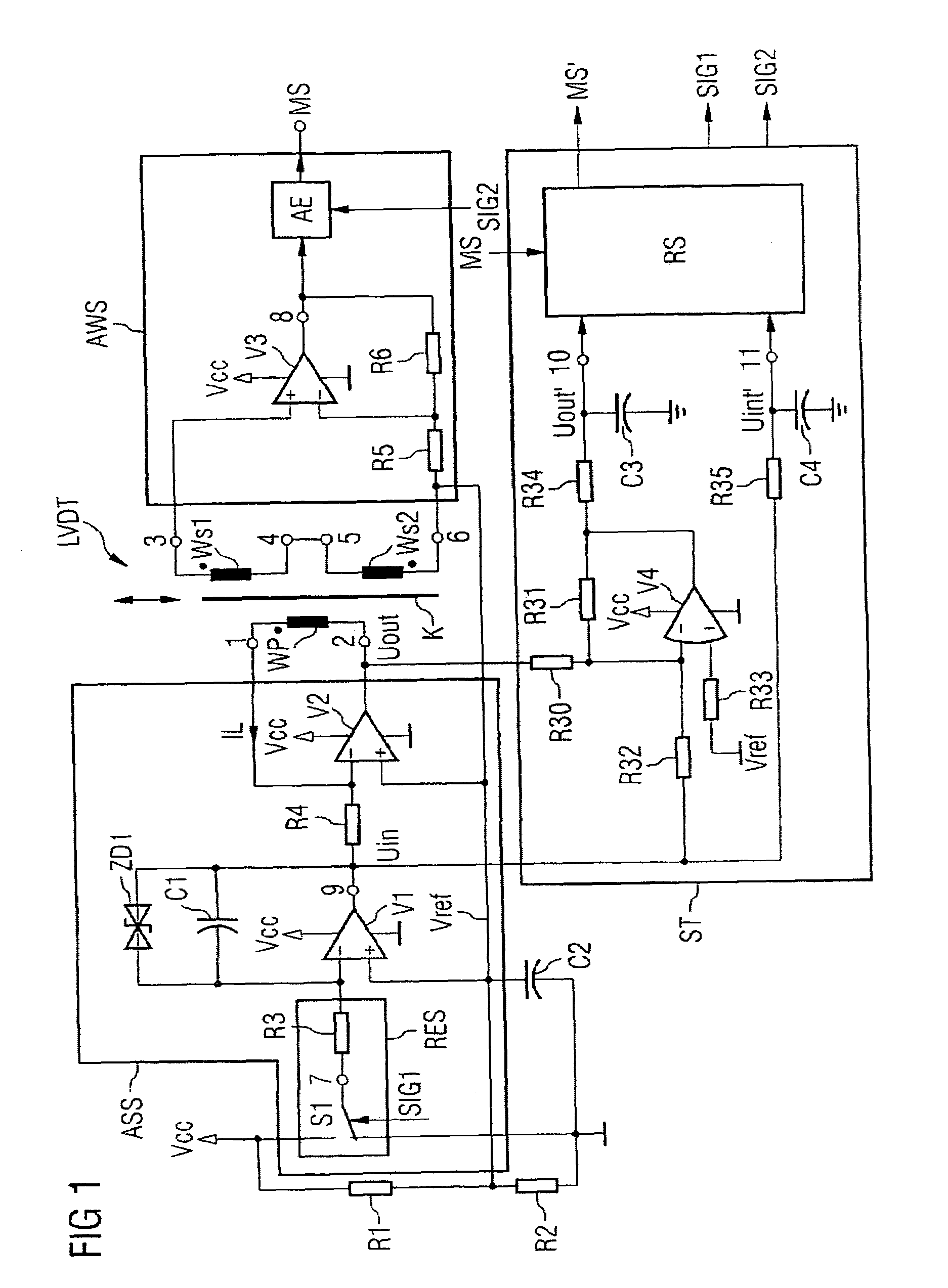
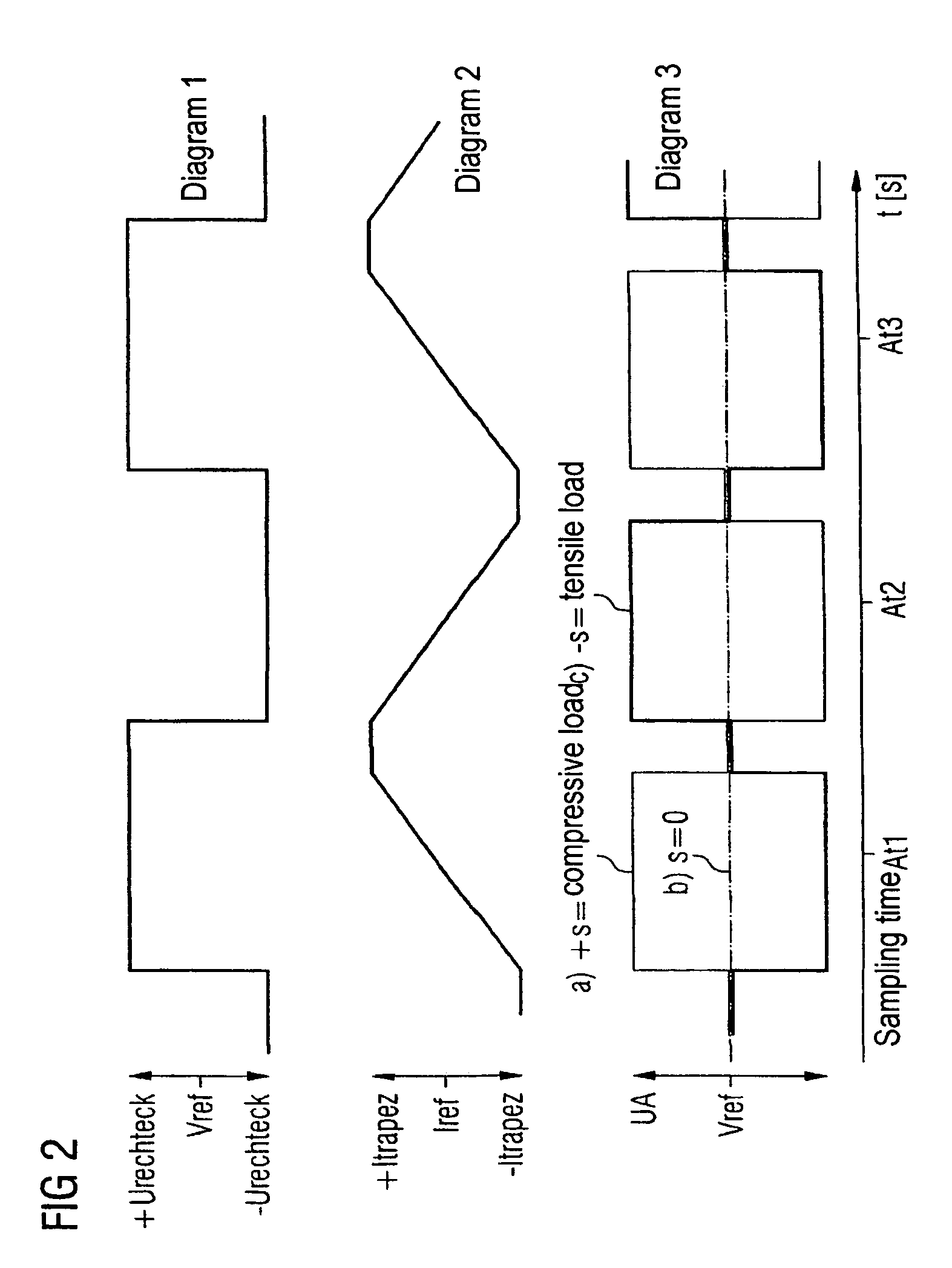
Circuit arrangement with a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) as a displacement sensor or force sensor
InactiveUS7053603B2Accurate measurementMinimal costElectric signal transmission systemsForce measurementLinear variable differential transformerElectrical resistance and conductance
In a circuit arrangement having a linear variable differential transformer as a displacement sensor or force sensor, having a selection circuit which is connected to the primary coil of the transformer and which provides an output current for triggering the primary coil, and having an analysis circuit which is connected to the secondary coils of the transformer and which provides a message signal, a control circuit used for triggering the selection circuit and the analysis circuit and for processing the measurement signal provided by the analysis circuit is connected to the primary coil in order to calculate the temperature of the circuit arrangement, and is configured such that it determines the temperature-dependent ohmic resistance of the primary coil and calculates from it the temperature and corrects accordingly the measurement signal provided by the analysis circuit.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Conditioning circuit of linear variable differential transformer (LVDT)
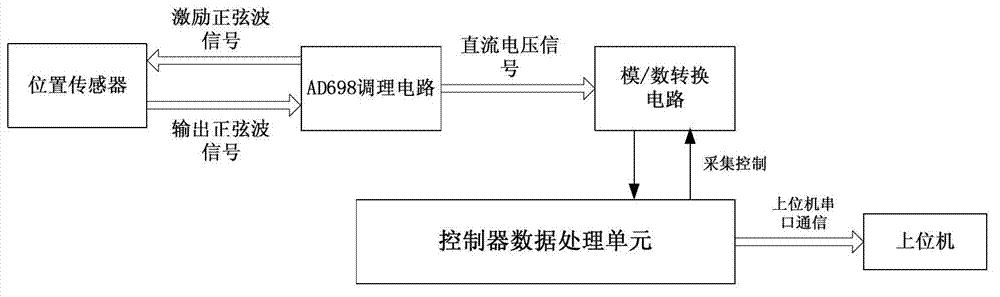
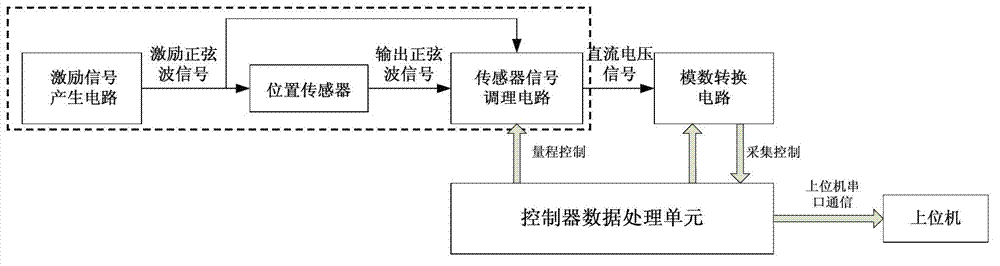
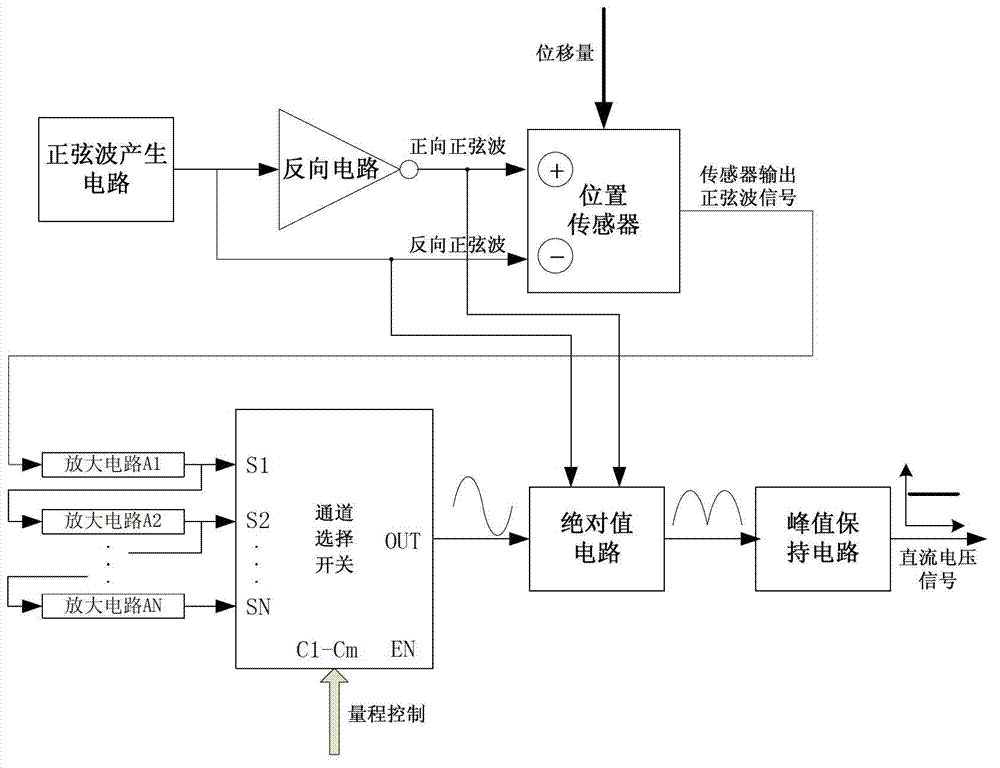
ActiveCN102768008ASmall temperature driftLow costUsing electrical meansLinear variable differential transformerEngineering
The invention discloses a conditioning circuit of a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT). The conditioning circuit comprises a half-bridge position sensor, an analog-digital conversion circuit, a controller data processing unit, an upper computer, a sine wave generating circuit, an inverting circuit, an amplifying circuit, a channel selector switch, an absolute value circuit and a peak holding circuit, wherein the analog-digital conversion circuit is connected with the upper computer through the controller data processing unit; one path of the output end of the sine wave generating circuit is connected with the positive input end of the position sensor through the inverting circuit, and the other path of the output end of the sine wave generating circuit is connected with the positive input end of the position sensor; the output end of the position sensor is connected with the input end of the channel selector switch through the amplifying circuit; the output end of the channel selector switch is connected with the input end of the peak holding circuit through the input end and the output end of the absolute value circuit; and the output end of the peak holding circuit is connected with the input end of the analog-digital conversion circuit. The conditioning circuit consisting of discrete components has the advantages of low temperature excursion and low cost.
Owner:绍兴中轴自动化设备有限公司
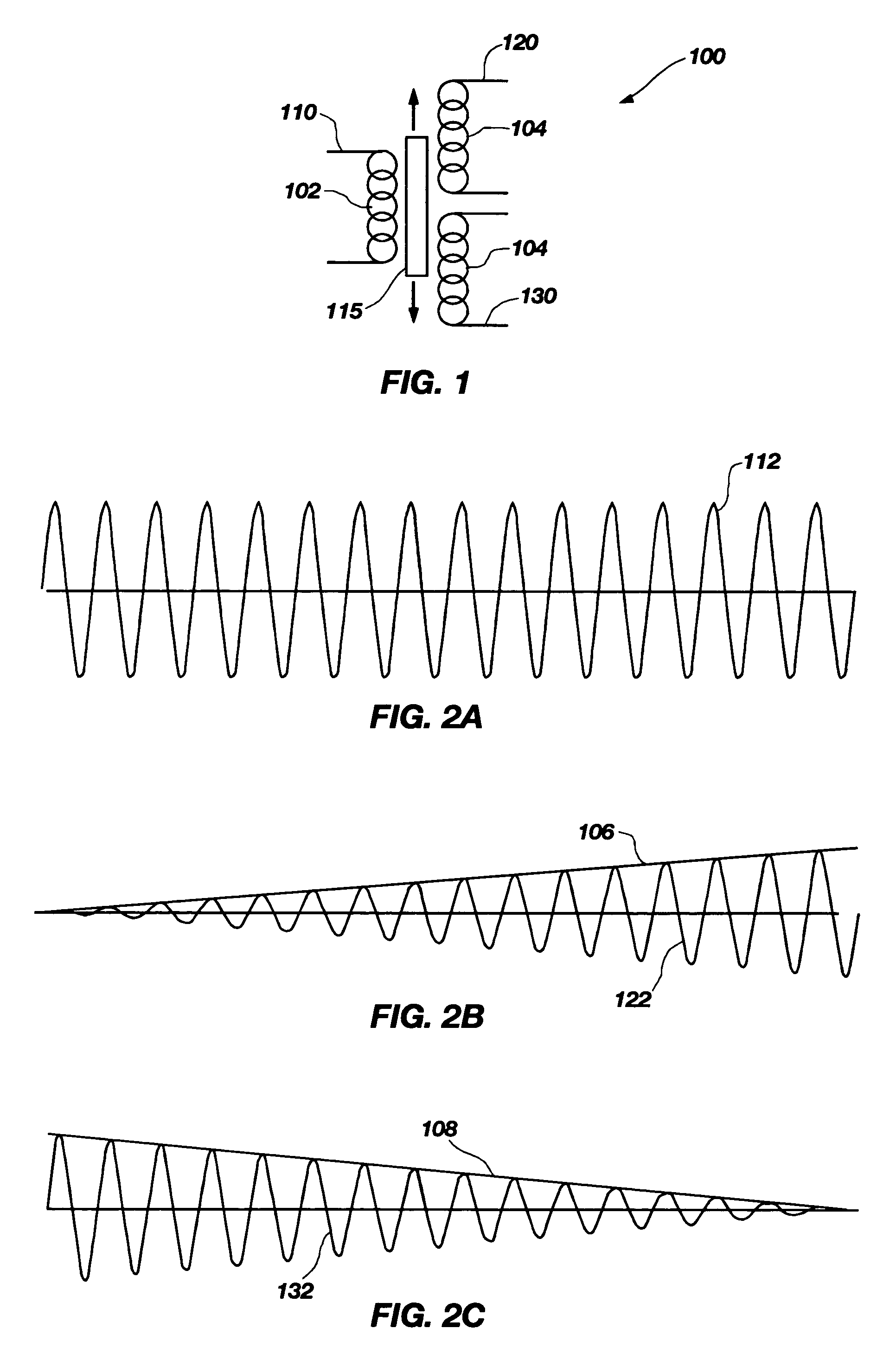
Improved linear variable differential transformer for high-accuracy posotion survey
InactiveCN1483136AReduce or eliminate noiseReduce length scaleUsing electrical meansNanotechnologyLinear variable differential transformerAtomic force microscopy
A transducer that reduces noise, increases sensitivity, and improves the time response of a linear variable differential transformer (LVDT). The device replaces the primary coil and the high permeability ferromagnetic core of conventional LVDTs with a primary wound around a moving non-ferromagnetic core. In addition to reducing or eliminating Barkhausen noise, this approach reduced or eliminated a number of other undesirable effects in conventional LVDTs including excessive eddy current heating in the core, non-linearities associated with high permeability materials and the length scale of the flux circuit. These improvements are coupled with improved LVDT signal conditioning circuitry. The device is also an actuator and may be used to convert differential voltages into force. Devices with these improvements have numerous applications, including molecular force measurements, atomic force microscopy and manipulation technology, lithographic manufacturing, nanometer scale surface profiling and other aspects of nanotechnology.
Owner:ASYLUM RES
Linear variable differential transformers
ActiveUS20120032768A1Transformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsTransformers/inductances magnetic coresLinear variable differential transformerNuclear engineering
Linear variable differential transformers include a core comprising a non-ferromagnetic material and a ferromagnetic material, and a coil assembly including an axial bore within which the core is disposed and through which the core axially translates.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
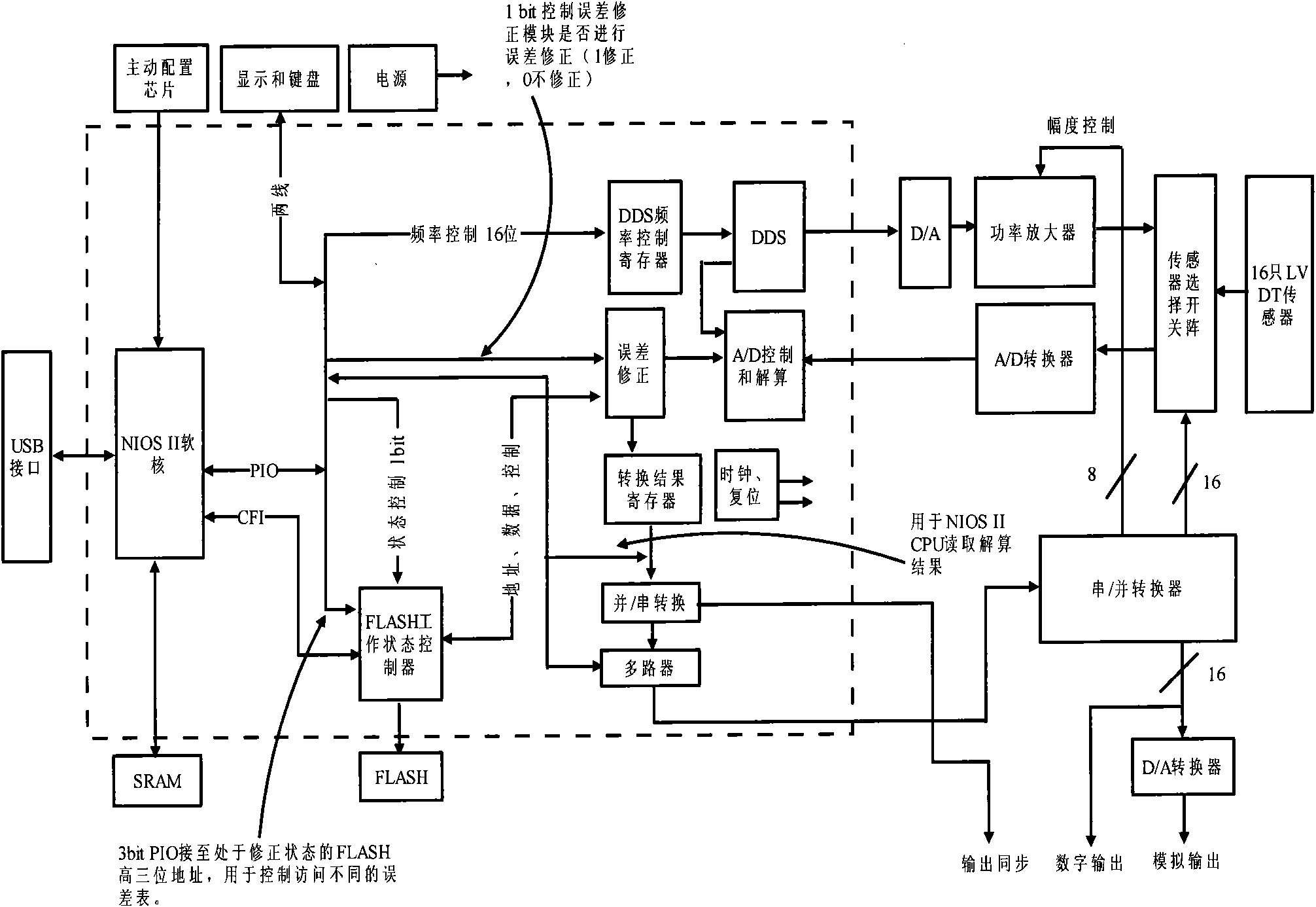
Measurement circuit and measuring method of LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer)
ActiveCN106370096AAchieve outputFew influencing factorsElectric/magnetic position measurementsUsing electrical meansLinear variable differential transformerSignal conditioning circuits
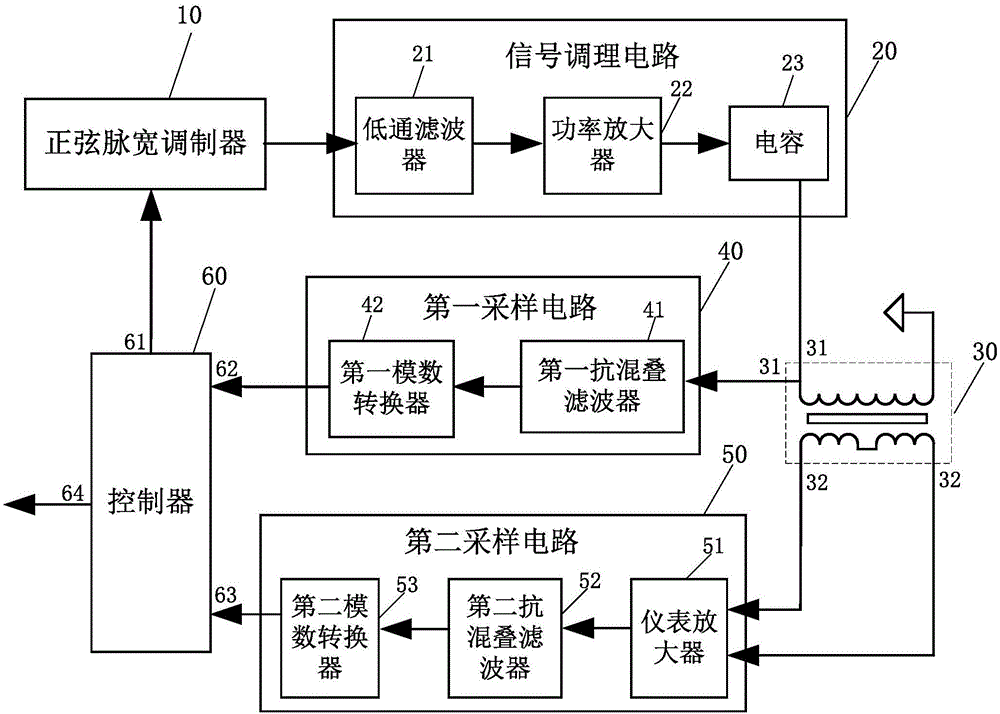
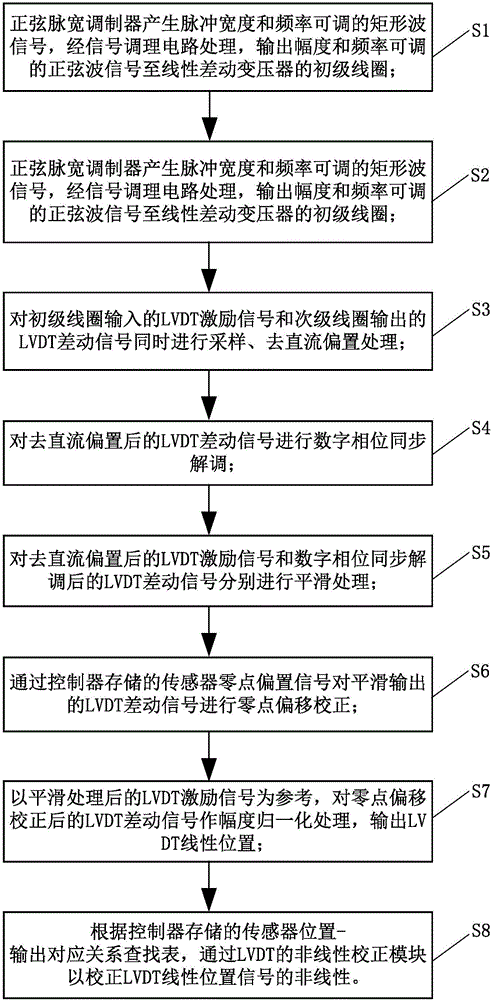
The invention discloses a measurement circuit of an LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer). The measurement circuit comprises a sinusoidal pulse width modulator, a signal conditioning circuit, a linear variable differential transformer, a first sampling circuit, a second sampling circuit and a controller; the sinusoidal pulse width modulator is used for outputting pulse width and frequency-adjustable rectangular wave signals; the input end of the signal conditioning circuit is connected with the sinusoidal pulse width modulator; the signal conditioning circuit outputs amplitude and frequency adjustable sinusoidal wave signals; the primary coil of the linear differential transformer is connected with the output end of the signal conditioning circuit to receive the sinusoidal wave signals as LVDT excitation signals; the secondary coil of the linear differential transformer outputs LVDT differential signals; the input end of the first sampling circuit is connected with the primary coil; the input end of the second sampling circuit is connected with the secondary coil; and the controller is connected with the output end of the first sampling circuit and the output end of the second sampling circuit and is used for performing amplitude normalization processing to output an LVDT linear position. With the measurement circuit of the LVDT, relatively complicated analog circuit parameter adjustment is avoided, zero-point residual voltage, phase drift and sensor nonlinearity can be effectively compensated. The measurement circuit has the advantages of high stability and can reduce measurement errors.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Tubular ovality testing
InactiveUS6862099B2Investigating moving sheetsUsing mechanical meansLinear variable differential transformerMeasurement device
A system for measuring diameter (inner and / or outer) of a tubular, the system in at least certain aspects including at least one linear distance measuring device with respect to which a tubular to be measured is movable, the at least one linear distance measuring device including a detector for detecting a surface of the tubular, the detector movably mounted to mount apparatus, the detector movable longitudinally along the surface of the tubular and movable axially in response to variation in diameter of the tubular, a rotatable head rotatable with respect to the tubular either outside of it or within it, the mount apparatus secured to the rotatable head, at least one signal production apparatus secured to the mount apparatus or head, and in communication with the linear distance measuring device, the at least one signal production apparatus for producing a signal indicative of distance between said detector and a known point, and transmitting apparatus for transmitting said signals to processing equipment for determining diameter of the tubular; and in certain aspects the linear distance measuring device is a laser device, electronic measurement device, acoustic measurement device, infrared measurement device, or linear variable differential transformer device.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
General closed-loop control system for providing positive and negative constant flow sources for aircraft engines
InactiveCN103605393AImprove compatibilityIncrease output impedanceElectric variable regulationLinear variable differential transformerLoop control
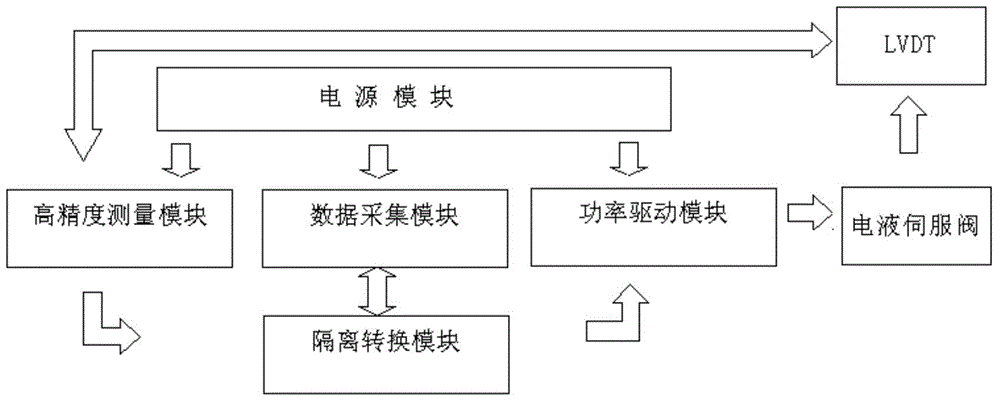
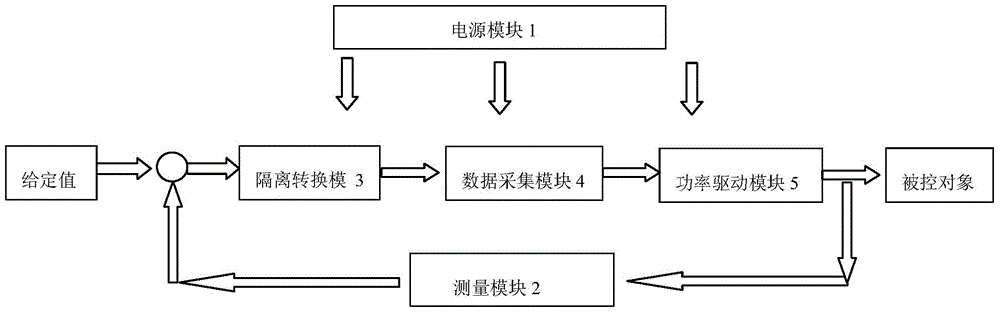
The invention belongs to the technical field of engine control and particularly relates to a practical aircraft engine fuel electronic control system. A general closed-loop control system for providing positive and negative constant flow sources for aircraft engines is mainly applied to performance adjustment and static testing for an engine with an electro-hydraulic servo valve being served as an electro-hydraulic conversion device and can be used for primarily calibrating steady state characters of the engine. According to the general closed-loop control system for providing the positive and negative constant flow sources for the aircraft engines, a high-precision measuring module which provides excitation signals for an LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) collects a current position of the LVDT, a preset instruct state of the closed-loop system is changed, PID (Proportion Integration Differentiation) calculation is performed on the current position and a preset position of the LVDT under a closed-loop control state, and the flow of the engine is controlled. The closed-loop control system needs to maintain current values to be at steady state values during a testing process.
Owner:BEIJING HANGKE ENGINE CONTROL SYST SCI & TECH
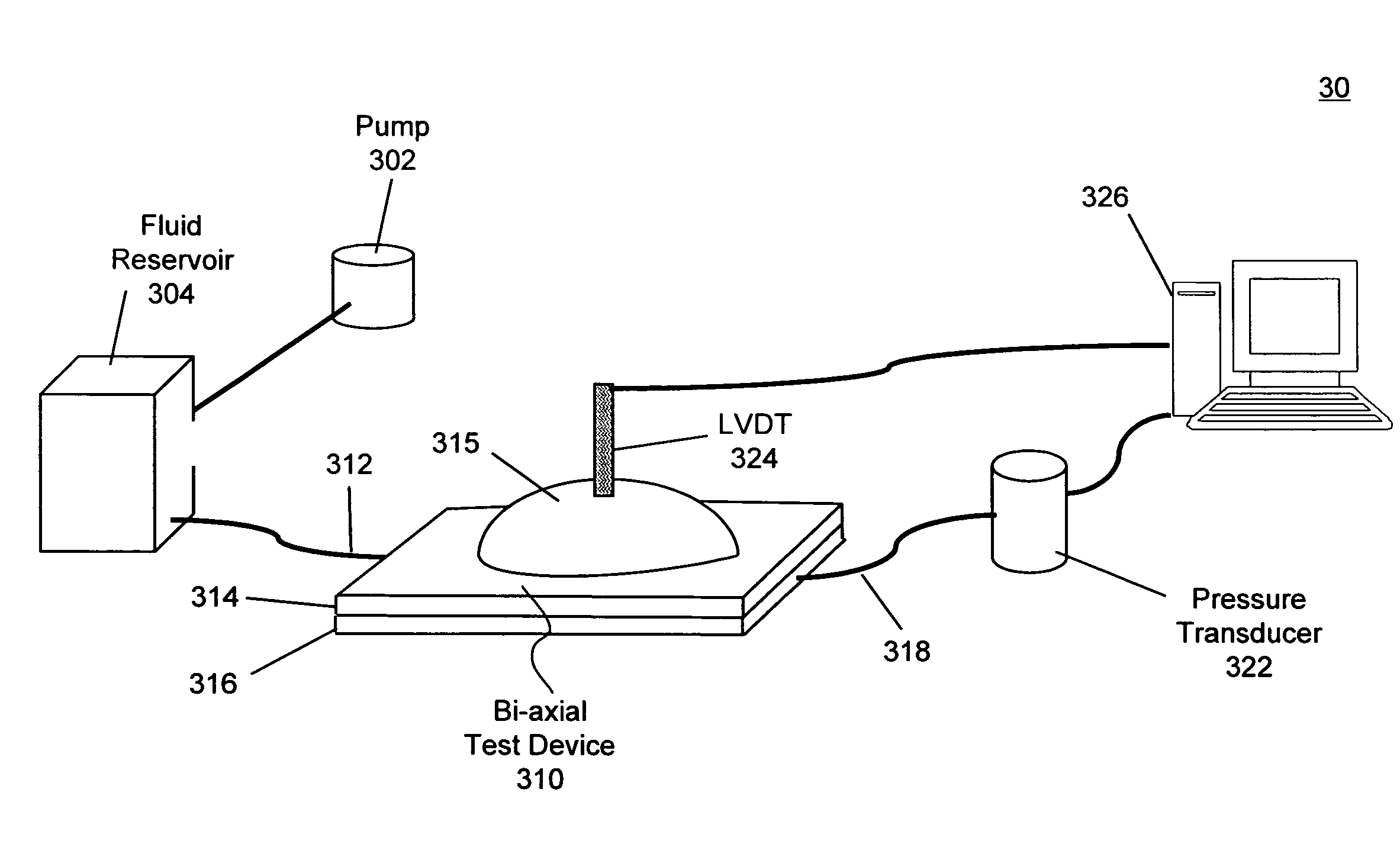
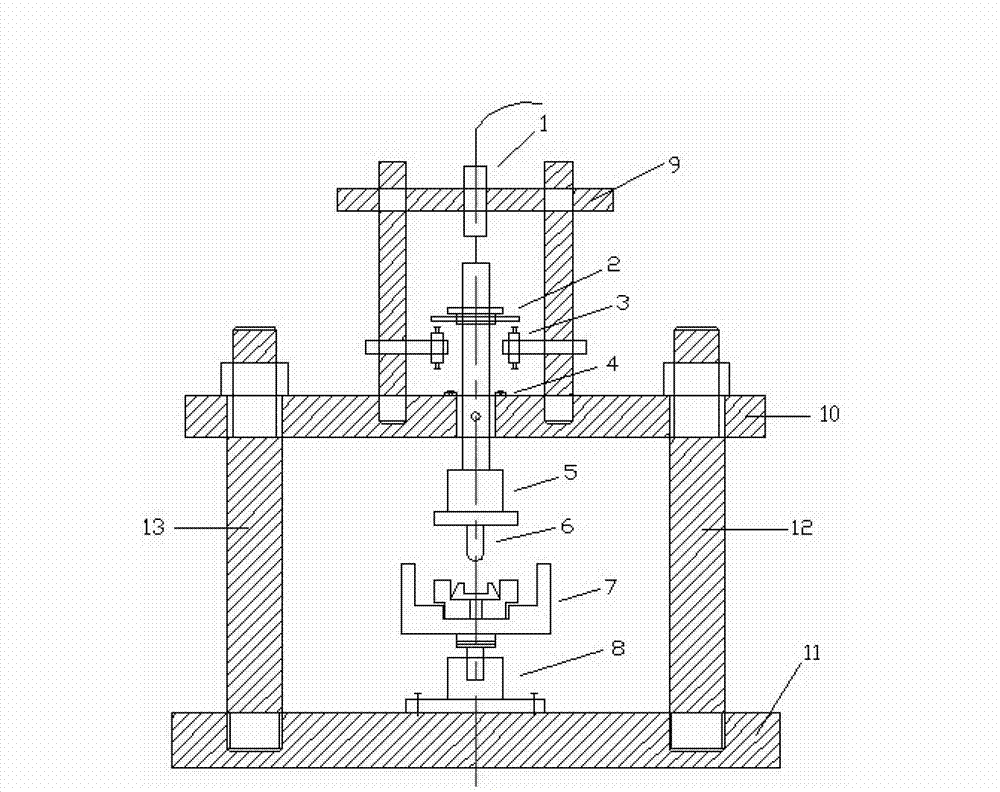
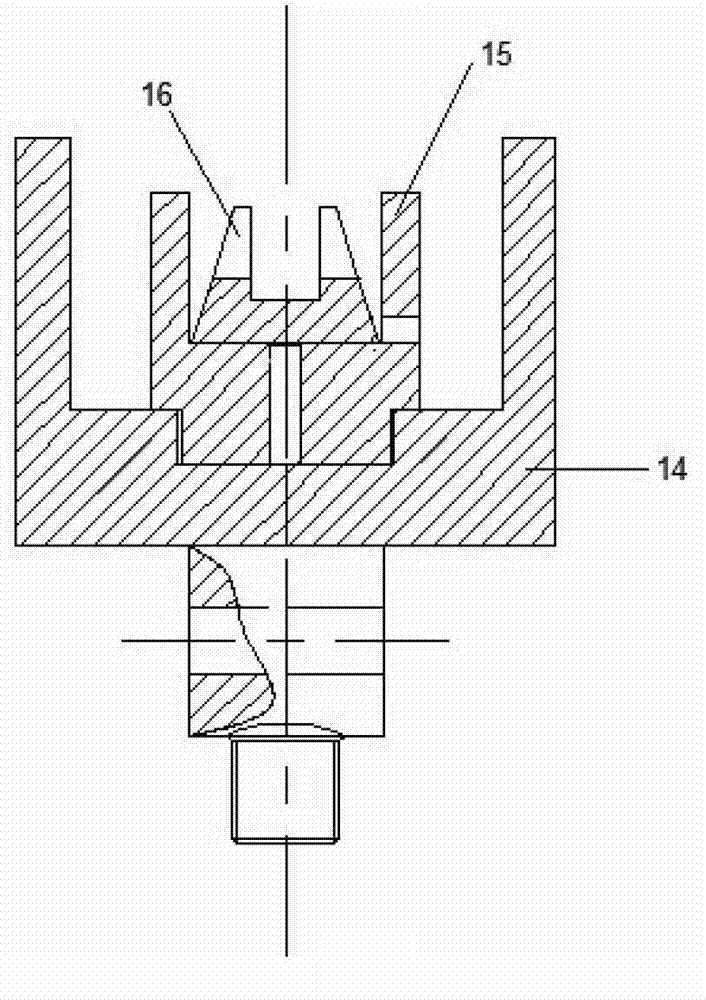
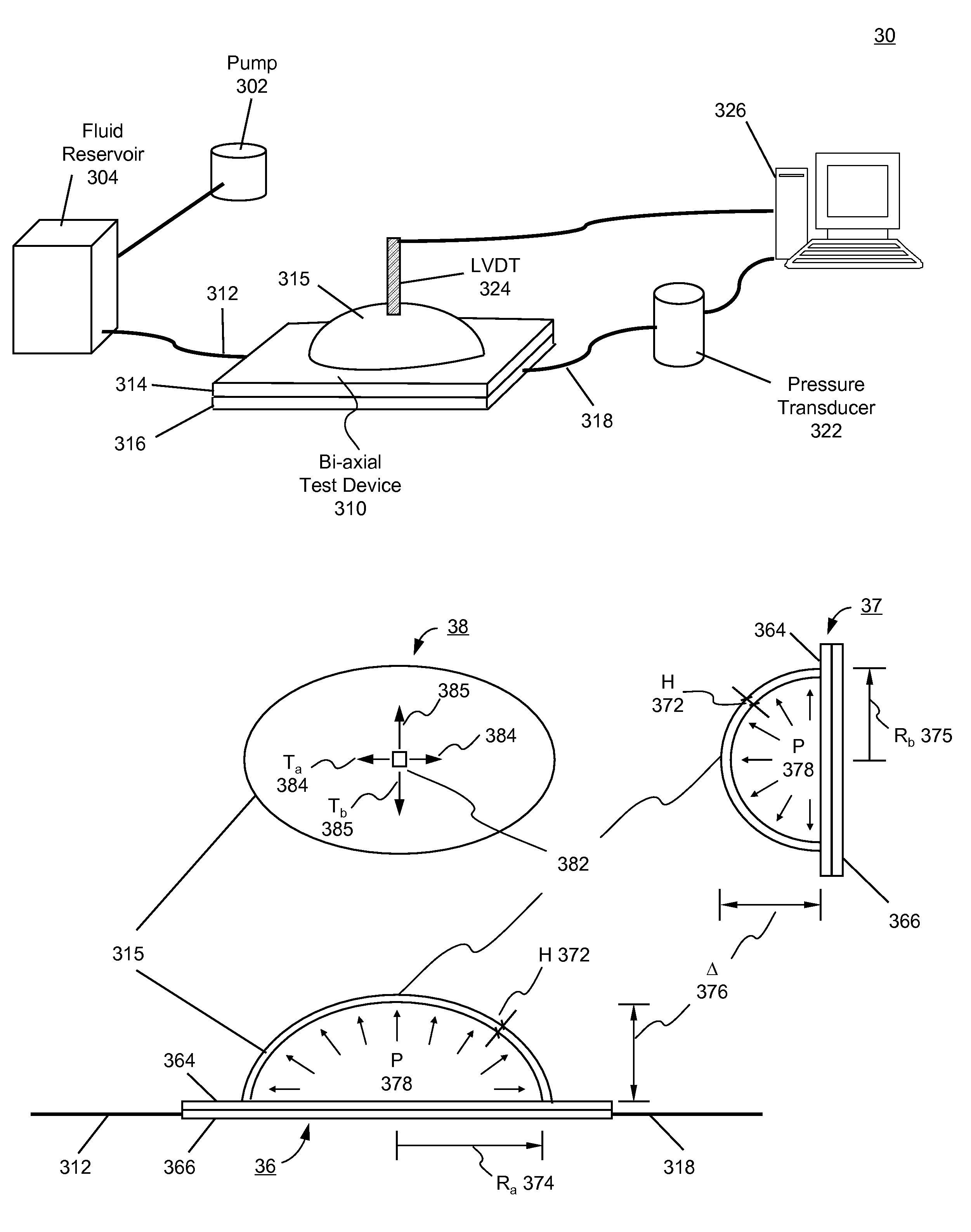
Determination of elastomer material properties for the Mullins effect using a bi-axial test device
ActiveUS7472602B1Measurement arrangements for variableMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesElastomerLinear variable differential transformer
Systems and methods for determining material properties of elastomers for the Mullins effect are described. In one aspect of the present invention, material properties of an elastomer membrane specimen are obtained using a system comprising a bi-axial test device, a pump, a fluid reservoir, a linear variable differential transformer, a pressure transducer and a computer. The bi-axial test device comprises a top plate and a bottom plate. The top plate has a circular hole configured to allow the specimen to be expanded up by pressures of the inflating fluids. The circular hole is so dimensioned that the specimen can be expanded with a substantially low pressure. The bottom plate is a solid plate configured with a fluid intake at one side and a fluid outlet at the other end. The fluid intake is connected to the fluid reservoir. Fluids stored in the fluid reservoir are pumped into the bi-axial test device by the pump. The fluid outlet is connected to the pressure transducer.
Owner:ANSYS
Cartilage creep mechanical performance testing device
InactiveCN103926158AQuick clampingQuick changeInvestigating material ductilityConstant loadLinear variable differential transformer
The invention discloses a cartilage creep mechanical performance testing device. The device wholly adopts a symmetrical double-layered bracket structure and comprises a central shaft, a movable test sample platform, a first bracket and a second bracket. The movement of the central shaft is controlled by a straight-line bearing with a flange and the speed of the central shaft is controlled by a hydraulic buffer arranged on the first bracket; a weight tray is fixedly disposed on the hydraulic buffer; the top of the central shaft is provided with an LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) displacement sensor; a pressure head is arranged at the bottommost end of the central shaft and a pressure sensor is arranged at the position which is tightly close to the pressure head; and the movable test sample platform formed by a test sample groove and a test sample groove bracket is fixedly disposed on a bottom support of the second bracket. The device disclosed by the invention is simple in structure, low in cost and convenient to measure; and in a whole testing process, a computer is used for detecting signals from the pressure sensor and the displacement sensor and can measure the variation of displacement-time of a test sample under a constant load in a simulated body fluid environment, and the variation of pressure-displacement of the test sample under a constant loading speed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Determination of elastomer material properties for the Mullins effect using a bi-axial test device
ActiveUS7533577B1Measurement arrangements for variableMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesLinear variable differential transformerElastomer
Systems and methods for determining material properties of elastomers for the Mullins effect are described. In one aspect of the present invention, material properties of an elastomer membrane specimen are obtained using a system comprising a bi-axial test device, a pump, a fluid reservoir, a linear variable differential transformer, a pressure transducer and a computer. The bi-axial test device comprises a top plate and a bottom plate. The top plate has an elliptical shape hole configured to allow the specimen to be expanded up by pressures of the inflating fluids. The hole is so dimensioned that the specimen can be expanded with a relatively low pressure. The bottom plate is a solid plate configured with a fluid intake at one side and a fluid outlet at the other end. The fluid intake is connected to the fluid reservoir. Fluids stored in the fluid reservoir are pumped into the bi-axial test device by the pump. The fluid outlet is connected to the pressure transducer.
Owner:ANSYS
High sensitivity displacement measuring device using linear variable differential transformer
InactiveUS6489760B2Increased displacement amplificationReduce gapElectric signal transmission systemsElement comparisonLinear variable differential transformerMeasurement device
The present invention is intended to provide a ultra-precision high sensitivity displacement measuring device which has such a high resolution as to be able to make submicron measurement.According to the invention, there is provided a displacement measuring device with high resolution, comprising: an electromagnetic system (10) which forms a closed loop of magnetic blocks (17,19) and which houses primary coil bundles (11) and secondary coil bundles (13) for forming magnetic fields within said closed loop of magnetic blocks (17,19); plate springs (20) which include displacement input parts (21) and displacement output zones (24) fixed to the cores (14) having the secondary coils wound around them and which act to guide so that the displacement output zones (24) can output the displacement amplified in proportional to the displacement input to the displacement input parts (21); and a supporting mechanism (30) for supporting the displacement input parts (21) of said plate springs (20) so that the displacement may be input only in one axial direction.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Testing device for determining compression creepage performance of microelectronic packing welding spots
ActiveCN103528896ASuitable for testing needsHigh measurement accuracyMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesUsing optical meansLinear variable differential transformerTest sample
The invention discloses a testing device for determining compression creepage performance of microelectronic packing welding spots, belonging to the field of testing on the mechanical performance of materials. A main body of the testing device comprises an environmental box, a sample stand, a locating mechanism and a loading mechanism, wherein the upper half part of the sample stand is arranged in the environmental box, a load rod of the loading mechanism is fixedly connected with a supporting disc after sequentially penetrating through a supporting table top, the sample stand, a test sample and an upper pressure plate, and a weight tray is arranged at the lower part of the load rod. In testing, the environment box enables the test sample to reach an experimental temperature, the loading mechanism applies pressure stress load to the test sample, and an optical displacement meter mechanism or an LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) displacement meter mechanism is used for recording the displacement variation of the test sample in testing. The testing device enables the test sample to be located accurately and loaded uniformly, and the experiment accuracy can be improved. The working conditions of the microelectronic packing welding spots under conditions of different temperatures and pressure loads can be simulated through regulating the temperature of the environmental box and the number of loaded weights so as to obtain creepage data under corresponding working conditions, and especially, the testing device can meet testing demands of practical microelectronic products in production.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Testing device for measuring radial deformation of single-axis compression rock at high temperature
InactiveCN109946170ASolve the problem of radial deformationGuaranteed stabilityMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMeasurement deviceAxial pressure
The invention discloses a testing device for measuring the radial deformation of single-axis compression rock at a high temperature and belongs to laboratory testing equipment. The testing device comprises an axial pressure exerting device, a heating temperature control device, a radial displacement measurement device and a temperature / displacement acquisition device, wherein radial displacement of a test sample is mainly tested under a high temperature condition by enabling a quartz rod to penetrate through a heating device to prop against the middle position of the test sample, connecting the quartz rod with an external LVDT (Linear Variable Differential Transformer) displacement sensor and by using the high temperature resistant quartz rod as a medium. By adopting the device, high temperature (1000 DEG C) single-axis rock mechanical testing under a long-term condition can be achieved, real-time dynamic acquisition on radial deformation can be achieved, and the device is simple and reliable, good in long-term stability and good in automatism.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIV OF TECH
Testing device and method for simulating stratum cavities caused by subway shield tunnel construction
InactiveCN104792966ASolve difficult-to-simulate problemsControl formation timeEarth material testingElectrical resistance and conductanceLinear variable differential transformer
The invention discloses a testing device and method for simulating stratum cavities caused by subway shield tunnel construction. The testing device comprises a cavity model, a test model case (8), a heating control device (7), a test soil mass (9), an LVDT (linear variable differential transformer) displacement meter (10), a steel tunnel model (11) with a hole, a switch valve (13) and a measuring cylinder (14), wherein the cavity model is used for simulating irregular stratum cavities and comprises a polyurethane liquid bag (3), a resistance wire (4), a first conduit (5) and a second conduit (6), the resistance wire (4) penetrates through the second conduit (6) on the polyurethane liquid bag (3) to be connected to the heating control device (7), and the heating control device (7) performs heating control on the resistance wire. With the adoption of the testing device and method for simulating the stratum cavities caused by subway shield tunnel construction, the problems that the stratum cavities are difficult to simulate and cavity shapes cannot be controlled in existing model tests can be better solved.
Owner:SOUTHWEST JIAOTONG UNIV
Integrated linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) displacement sensor for measuring micro strain of pile foundation
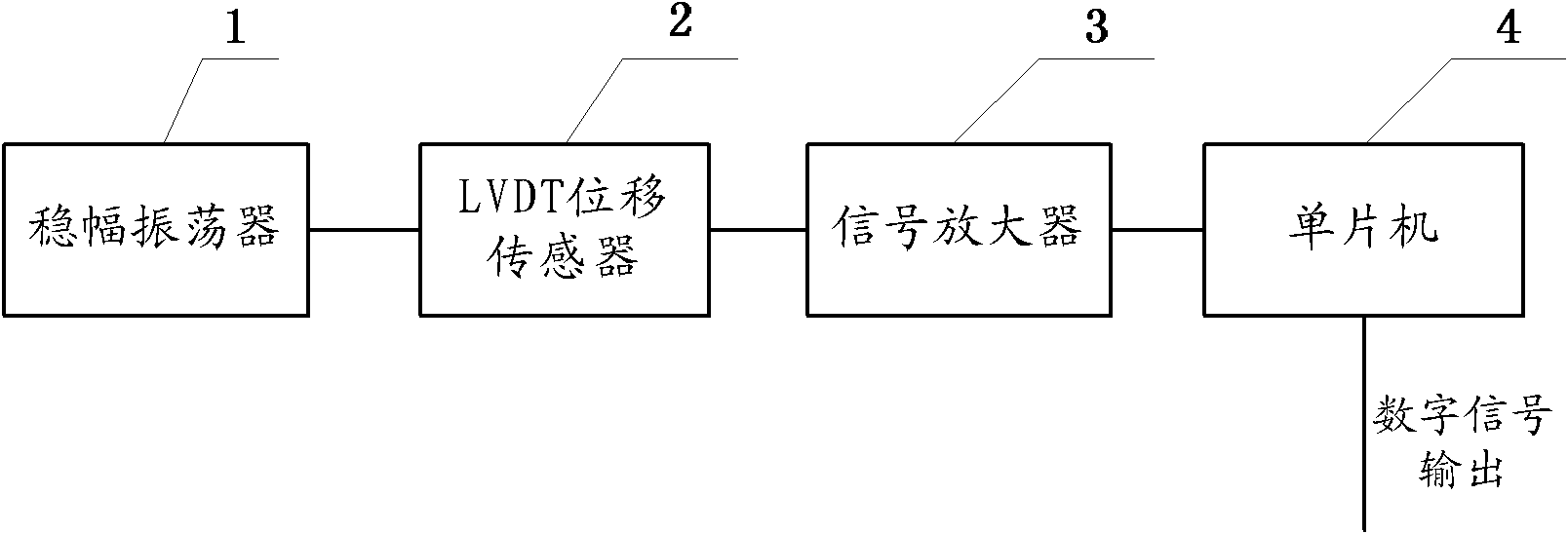
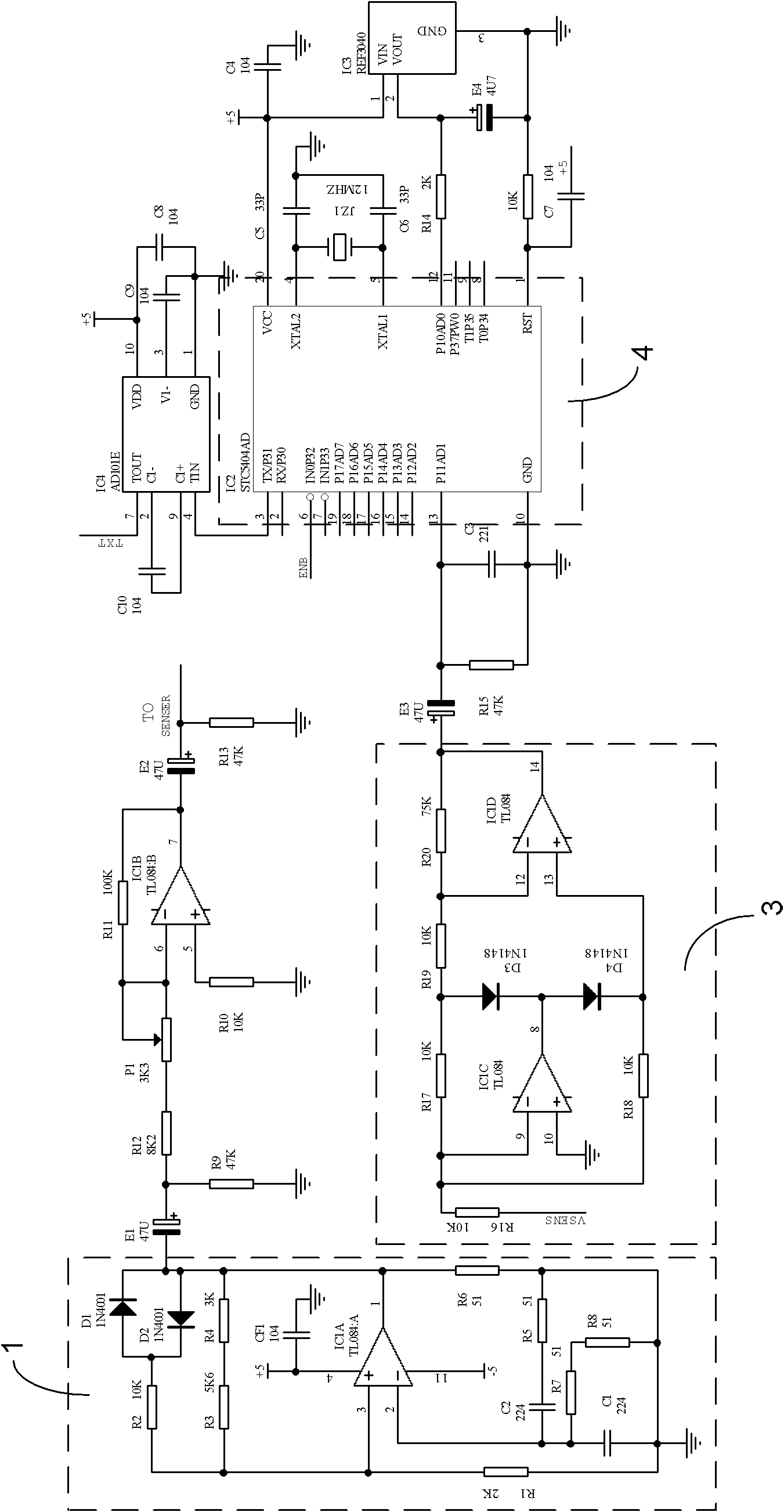
InactiveCN102620643AStrong common mode rejectionEnhanced inhibitory effectUsing electrical meansElectrical/magnetic solid deformation measurementMicrocomputerMicrocontroller
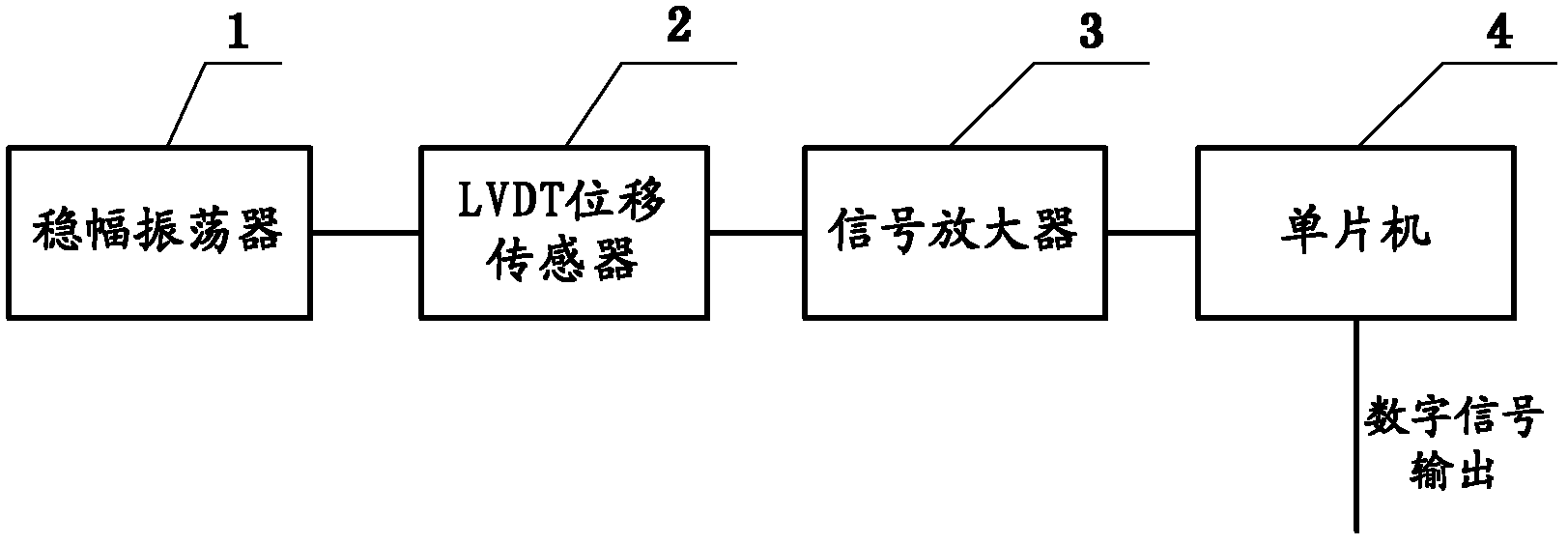
The invention discloses an integrated linear variable differential transformer (LVDT) displacement sensor for measuring micro strain of a pile foundation. The integrated LVDT displacement sensor comprises a fixed amplitude oscillator, a LVDT displacement sensor, a signal amplifier and a single chip microcomputer, wherein the excitation signal input end of the LVDT displacement sensor is connected with the output end of the fixed amplitude oscillator; the detection signal output end of the LVDT displacement sensor is connected with the input end of the signal amplifier; and the acquisition voltage signal input end of the single chip microcomputer is connected with the output end of the signal amplifier. The LVDT displacement sensor has extremely high common-mode rejection capability, for instance, temperature change parameters are converted into common modulus in output response of the displacement sensor, so that the integrated LVDT displacement sensor has high rejection capability for the common modulus such as temperature change, cannot be influenced by temperature drift almost, can directly output displacement without secondary transformation calculation and has extremely fine measurement resolution and linearity.
Owner:李建国
Linear variable differential transformer type sensor and winding method
ActiveCN106767953AIncrease the itineraryAnd constant valueConverting sensor output electrically/magneticallyLinear variable differential transformerEngineering
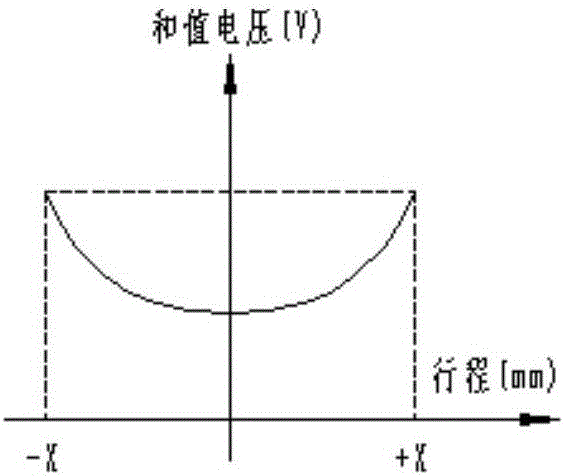
The invention belongs to the field of linear variable differential transformer type sensors, and relates to a linear variable differential transformer type sensor and a winding method. The sensor is characterized in that along the axial direction of a coil spool (3), the coil density of a secondary coil A is gradually increased, the coil density of a secondary coil B is reduced, the secondary coil A and the secondary coil B are arranged around the whole coil spool (3), the coil total numbers of the secondary coil A and the secondary coil B are basically the same in any segment of the coil spool (3), and discrete coils are employed so that manual winding is facilitated. According to the linear variable differential transformer type sensor coil winding method, the measuring range ratio is high, the usage efficiency of the coil spool of the sensor is improved, constant sum-value voltage is output, and online monitoring of the sensor is facilitated.
Owner:JINCHENG NANJING ELECTROMECHANICAL HYDRAULIC PRESSURE ENG RES CENT AVIATION IND OF CHINA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com