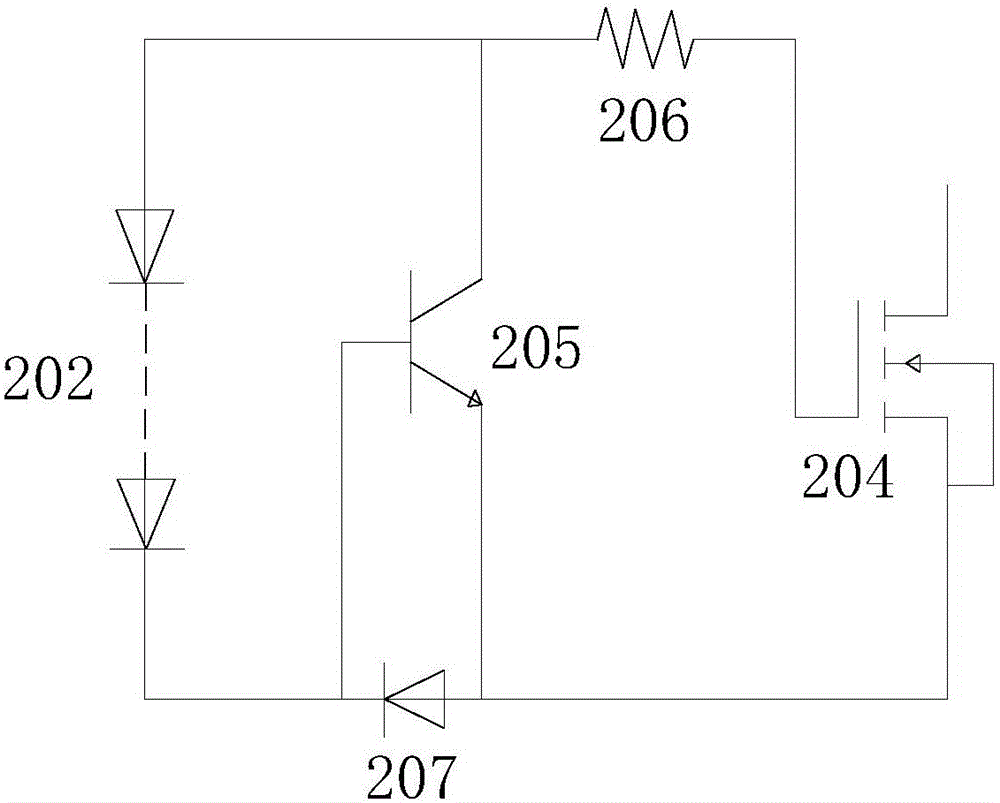Patents
Literature
35results about How to "Stable bias voltage" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
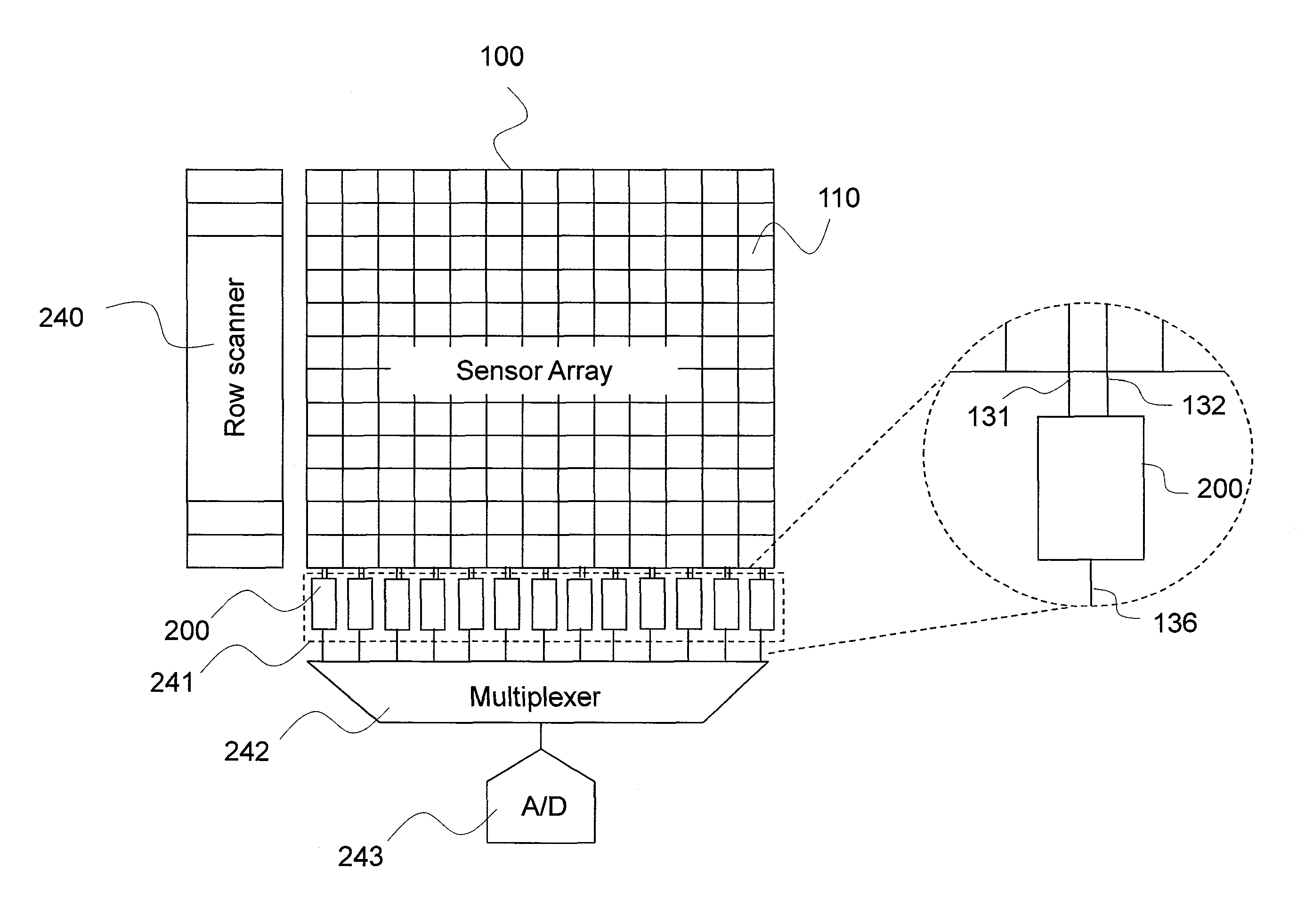
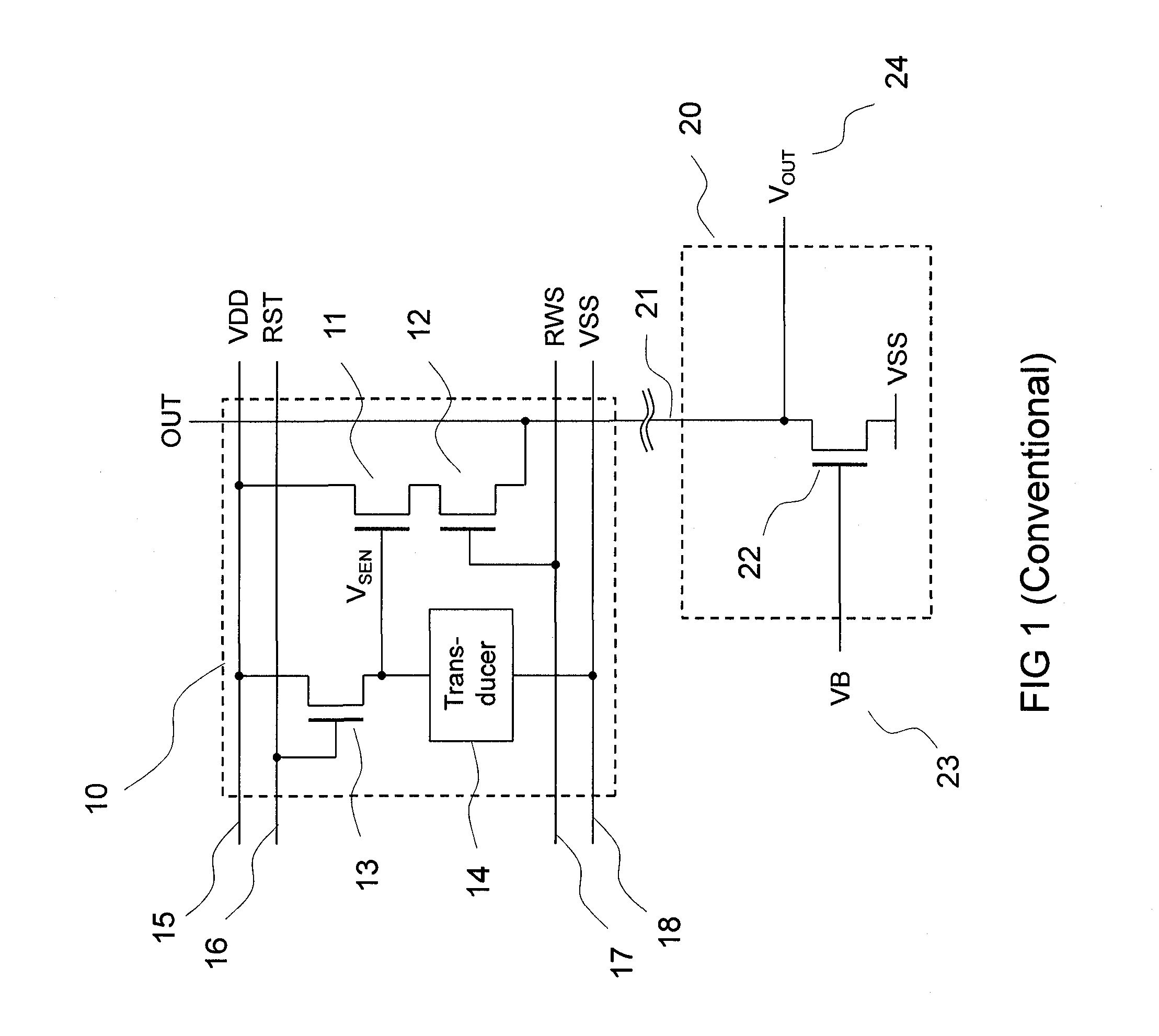
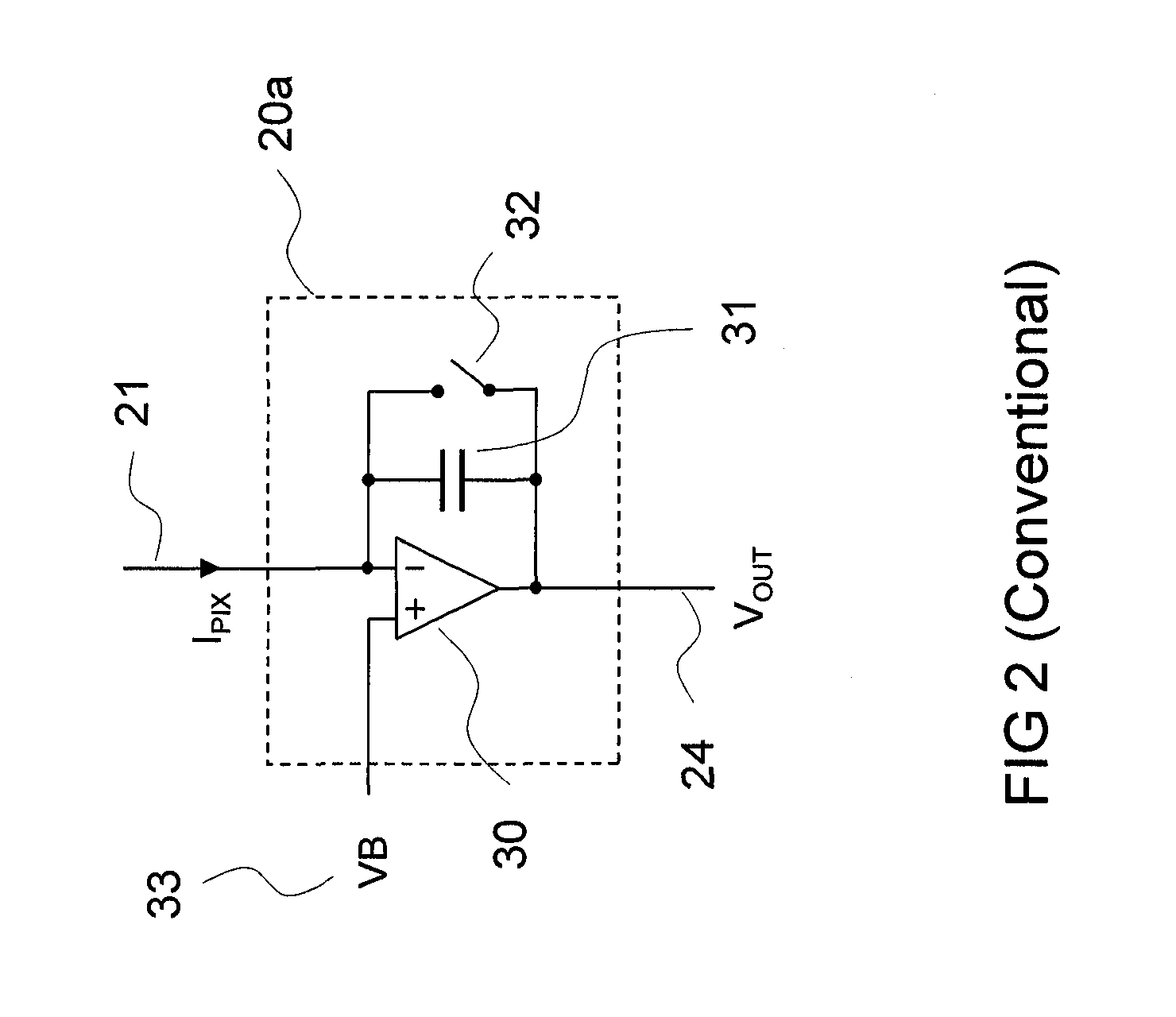
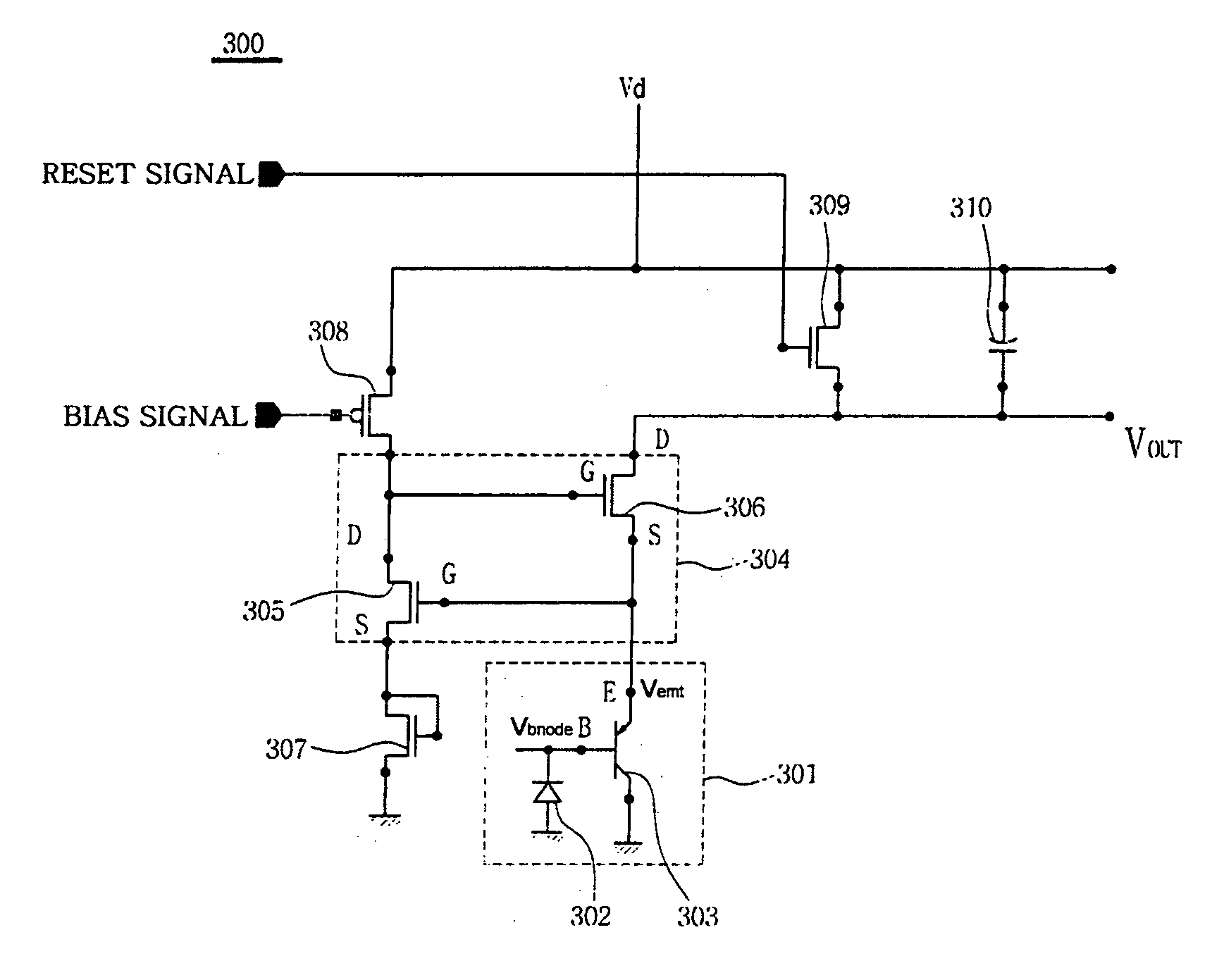
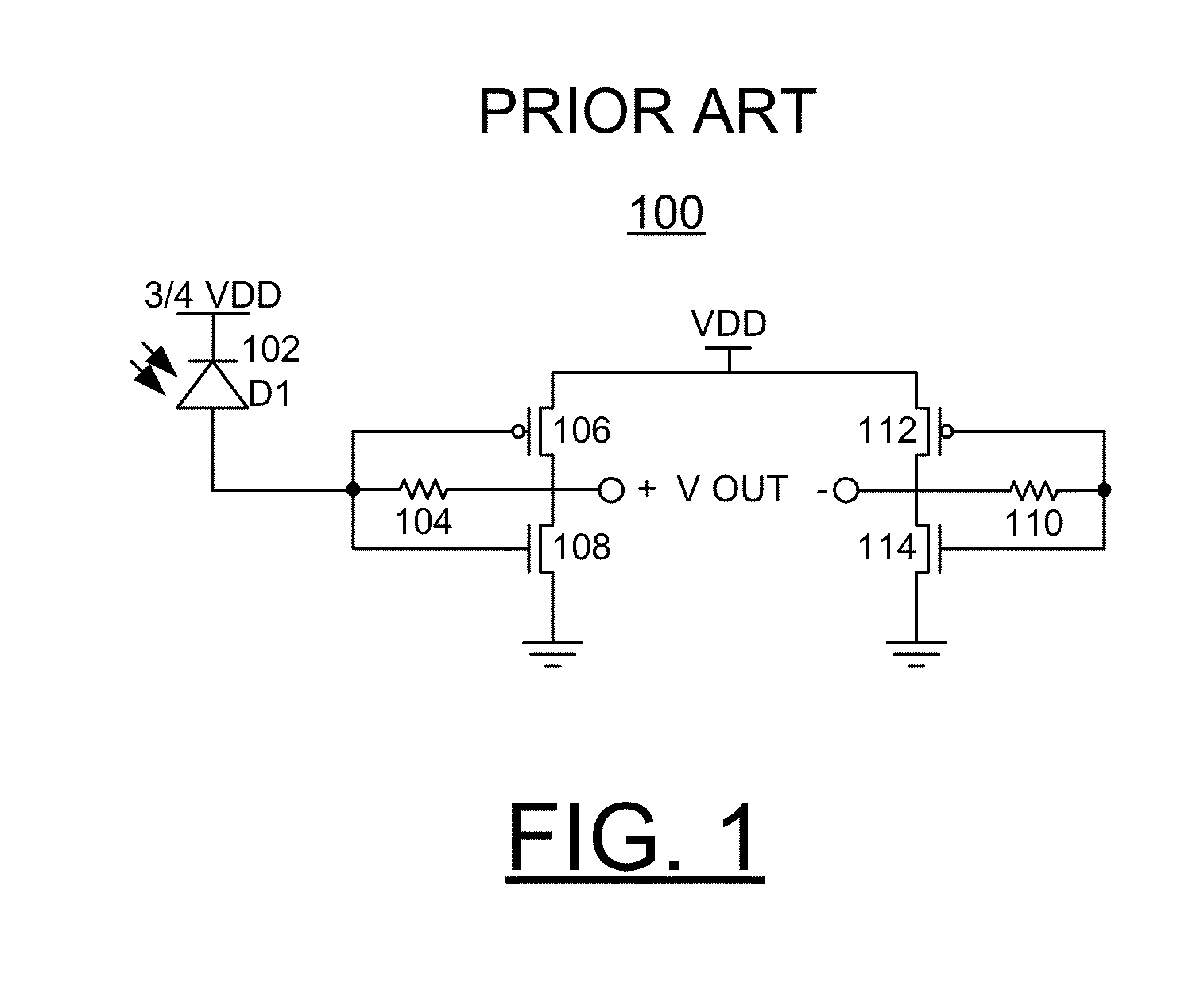
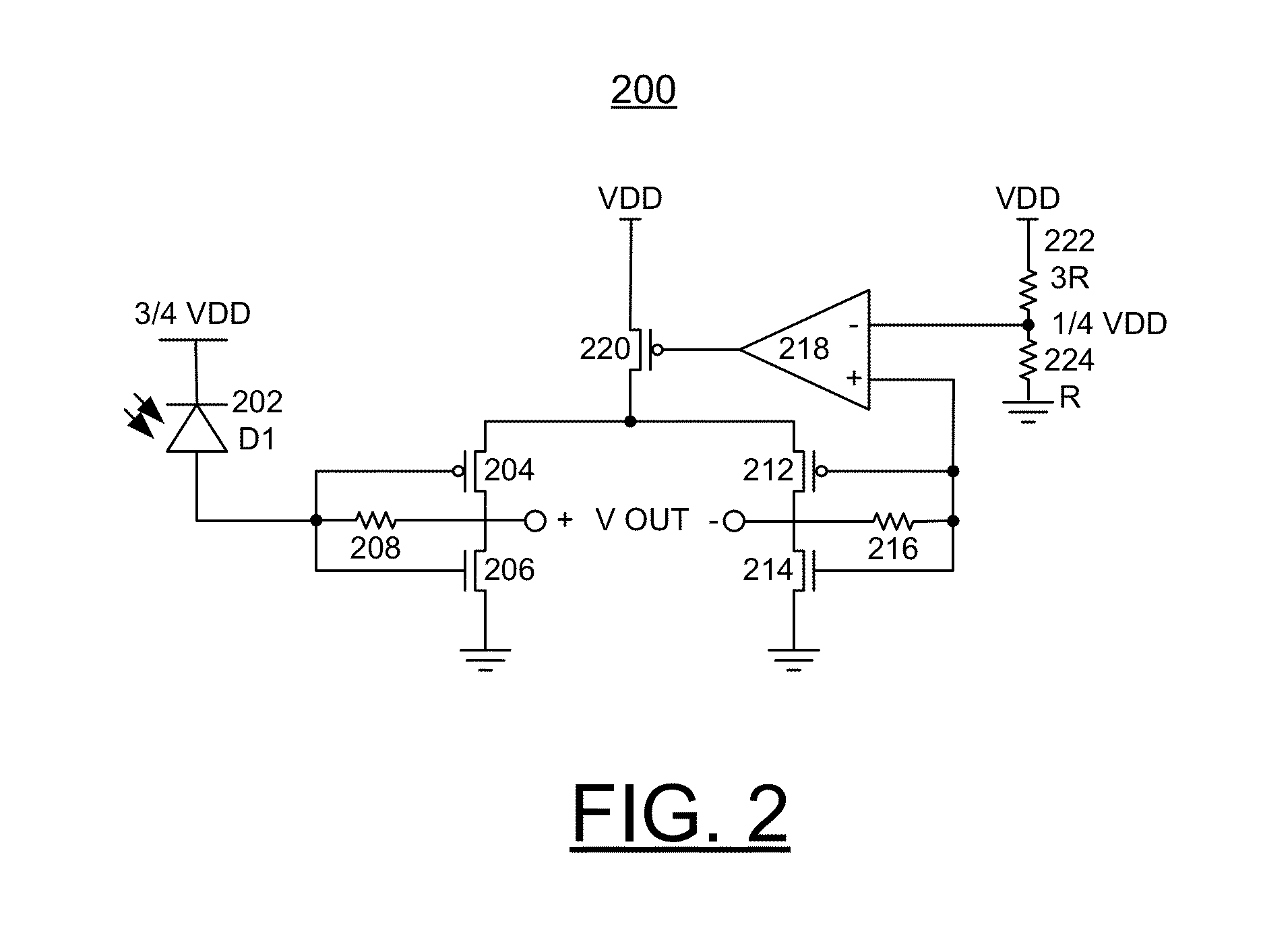
Sensor array with high linearity
InactiveUS20130082936A1Stable bias voltageReduce dependenceTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSensor arrayPower flow
A sensor array includes a plurality of pixel sensor circuits; and a current-mode readout circuit to sample signals generated in each pixel sensor circuit; and addressing circuitry to individually select each pixel sensor circuit. Each pixel sensor circuit includes: a transducer and an amplifying element coupled to the transducer and configured to output a signal current which varies as a function of a measured physical property. The current-mode readout circuit includes: a sense signal line coupled to each of the amplifying elements in order to monitor the voltage presented across the amplifying element of the selected pixel sensor circuit; a drive signal line coupled to an output of each of the amplifying elements in order to provide a constant bias voltage to the amplifying element of the selected pixel sensor circuit; and a current conveyor circuit coupled to the sense signal line and drive signal line.
Owner:SHARP KK
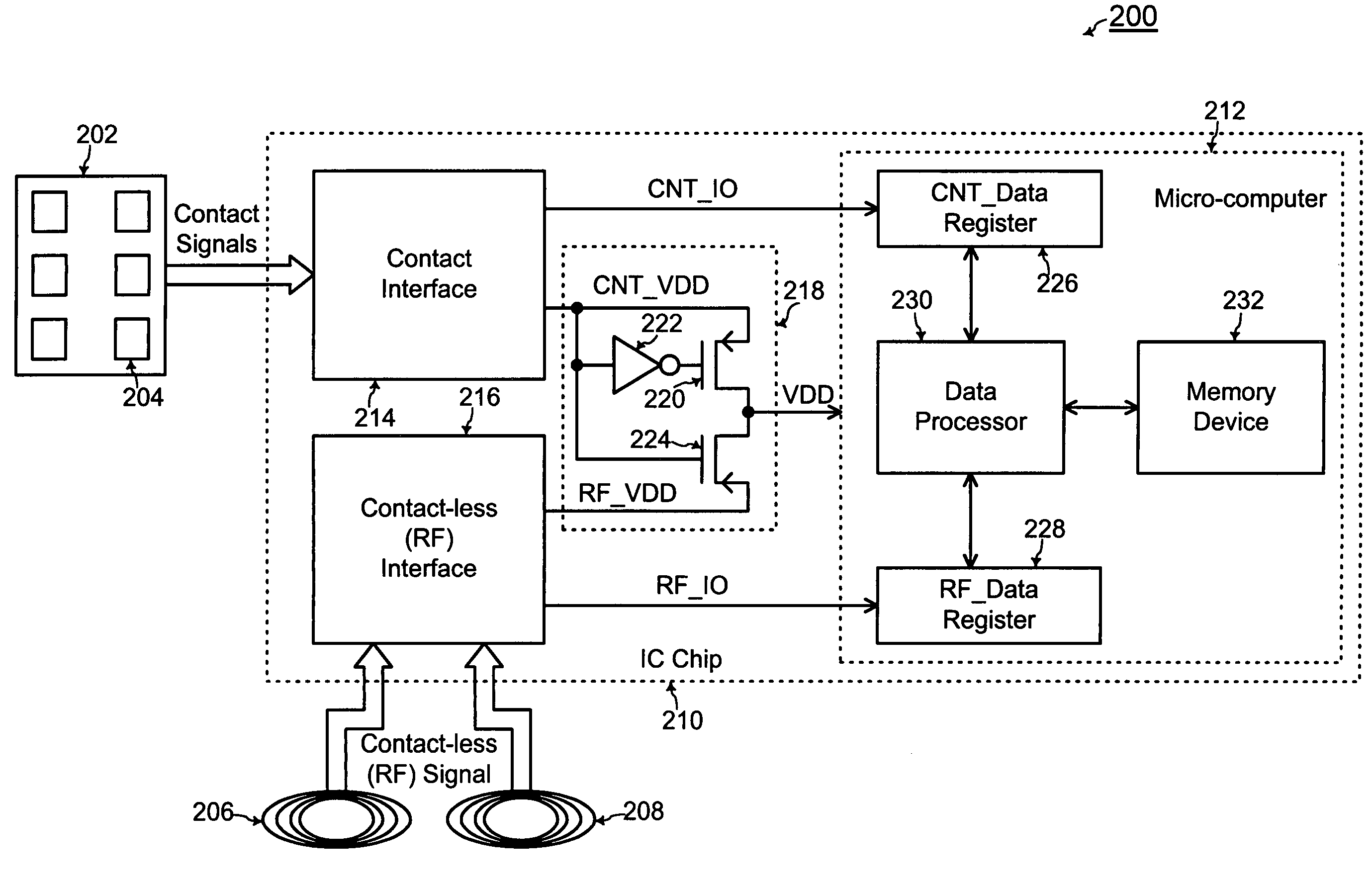
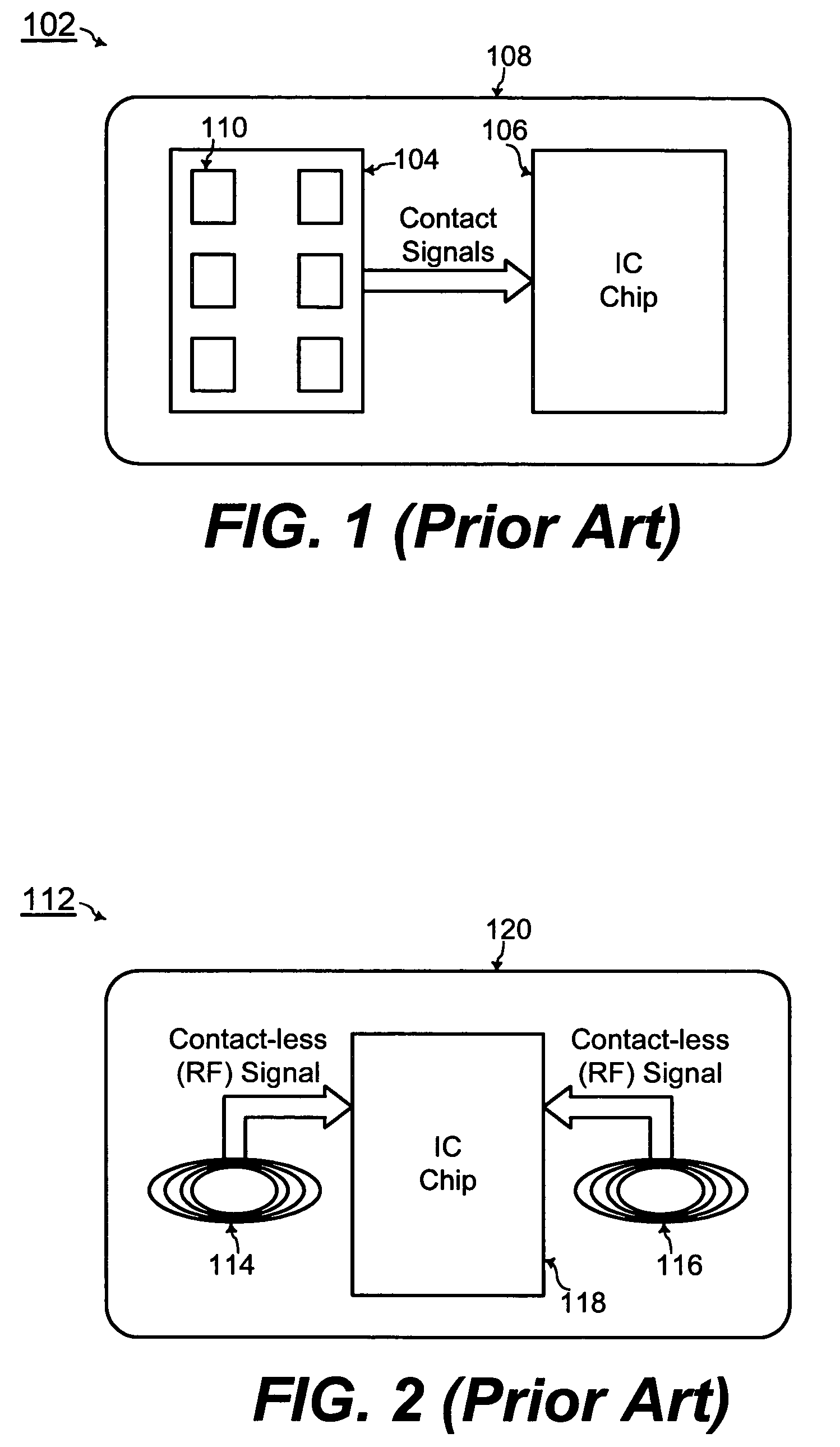
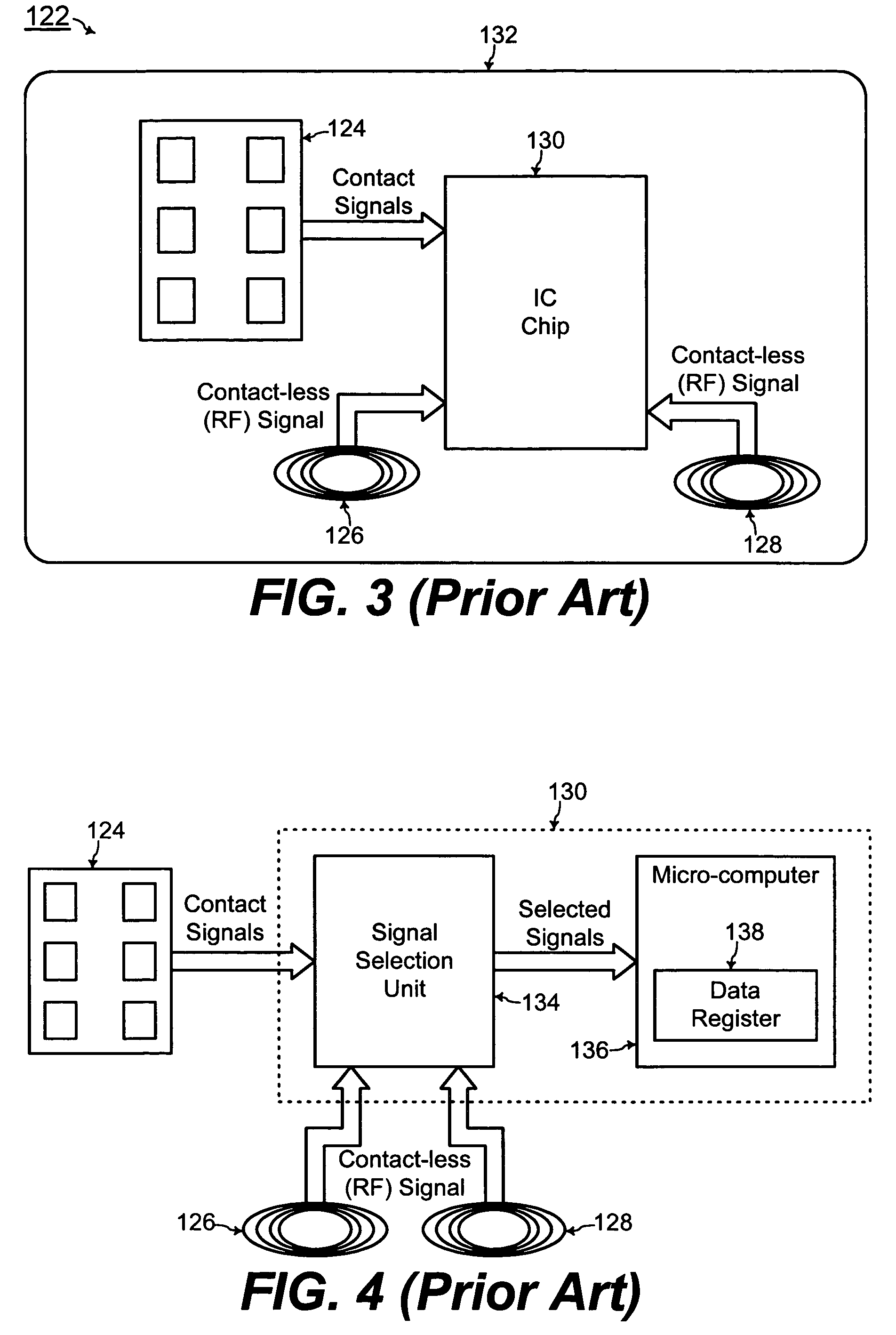
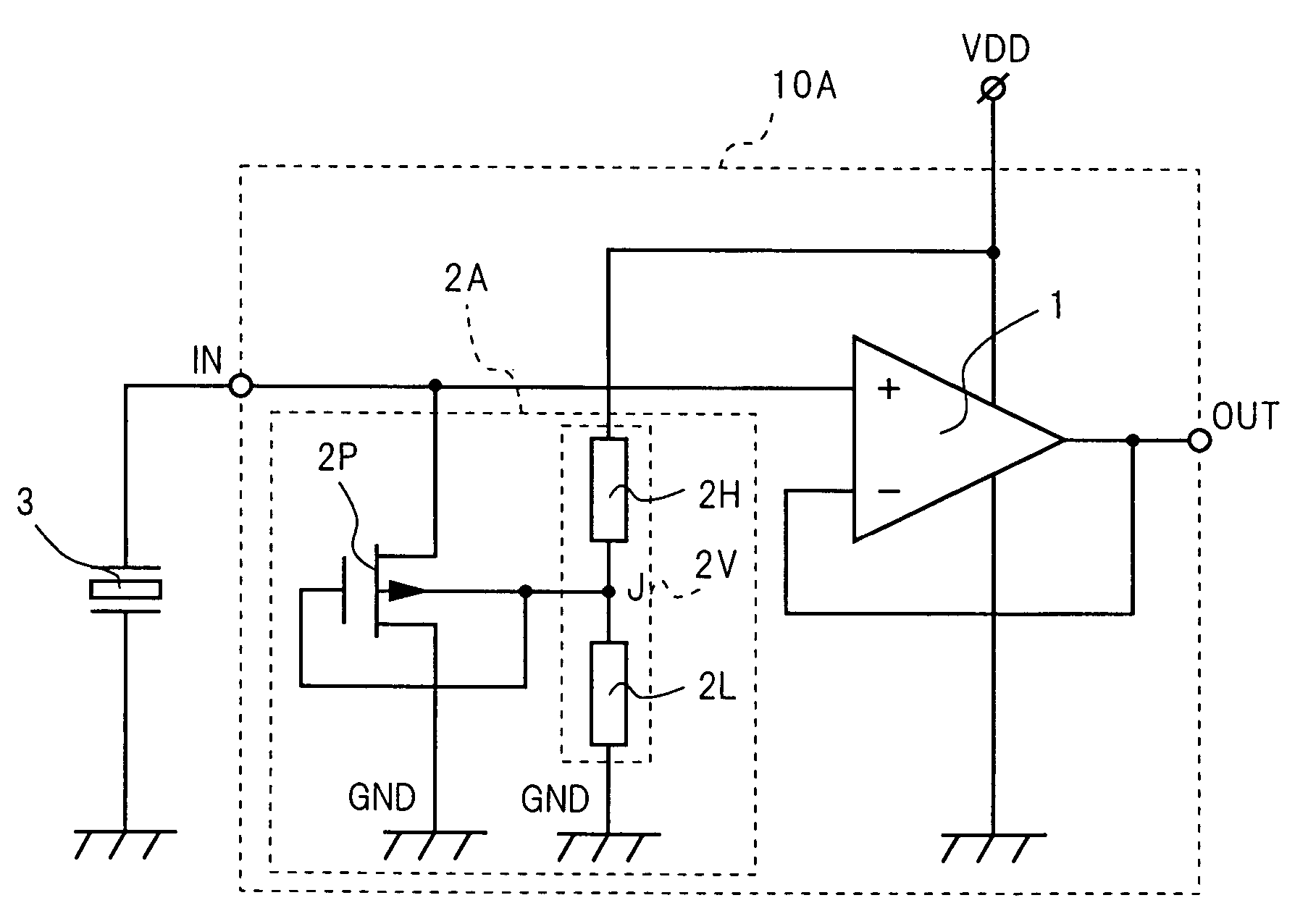
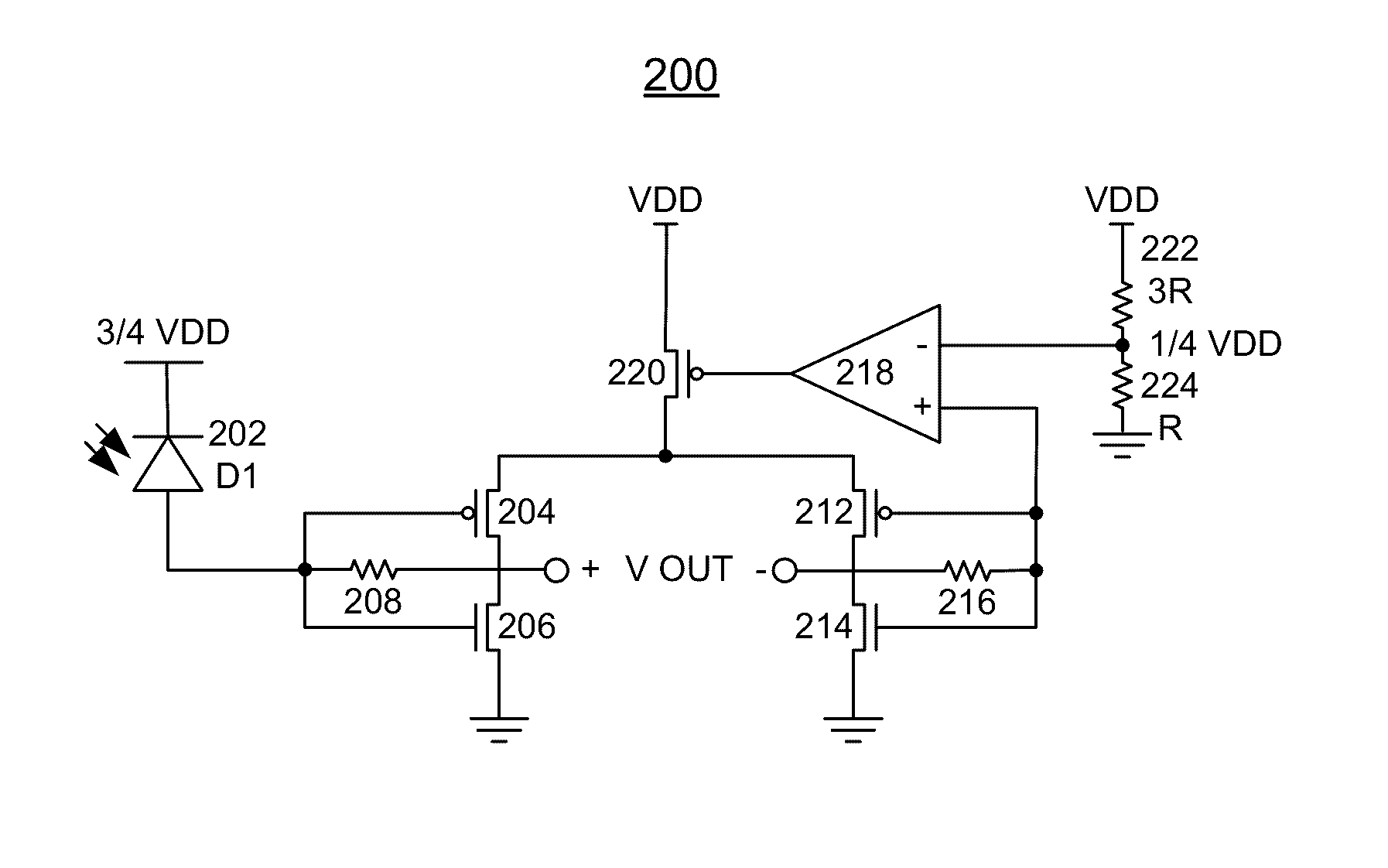
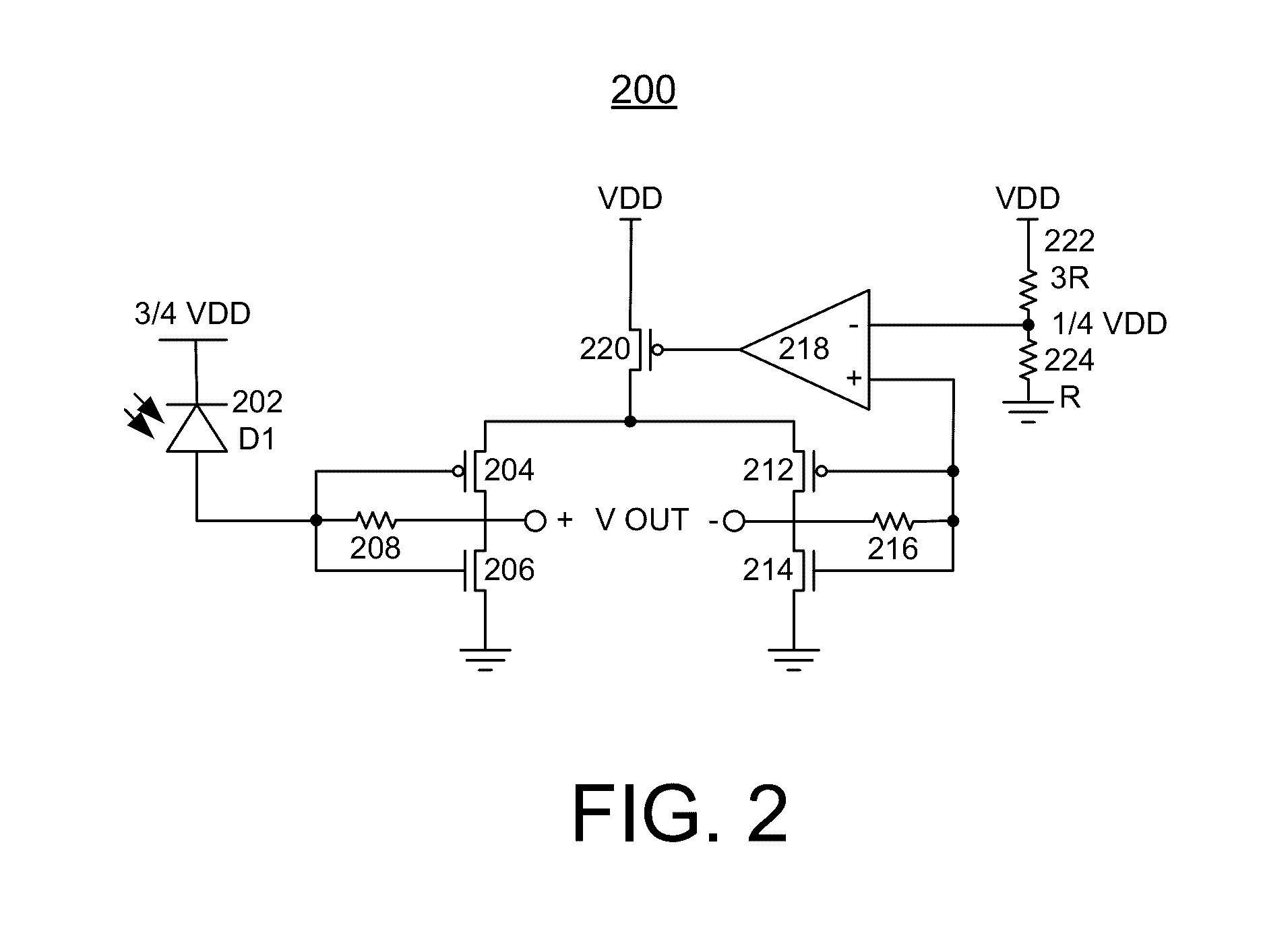
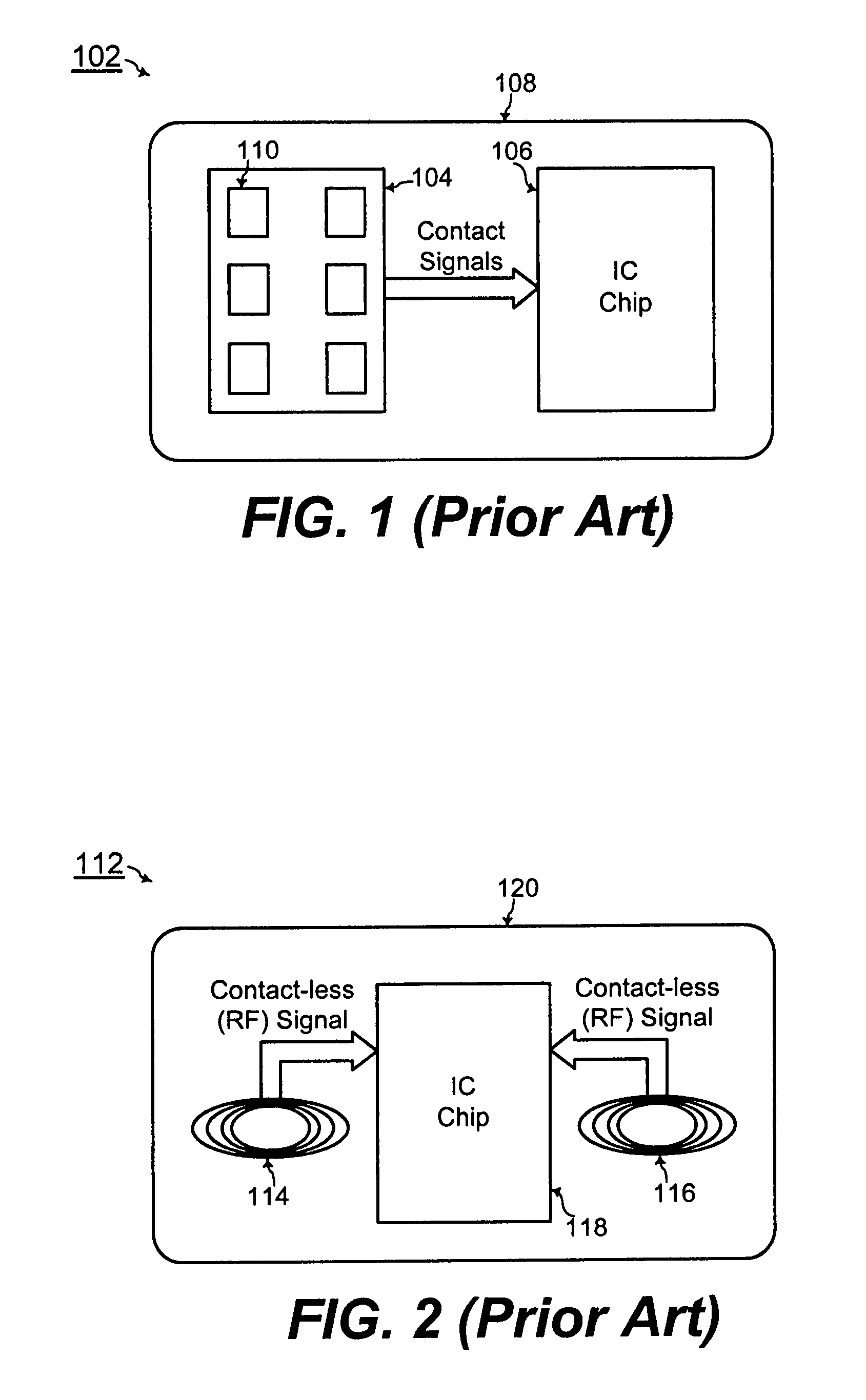
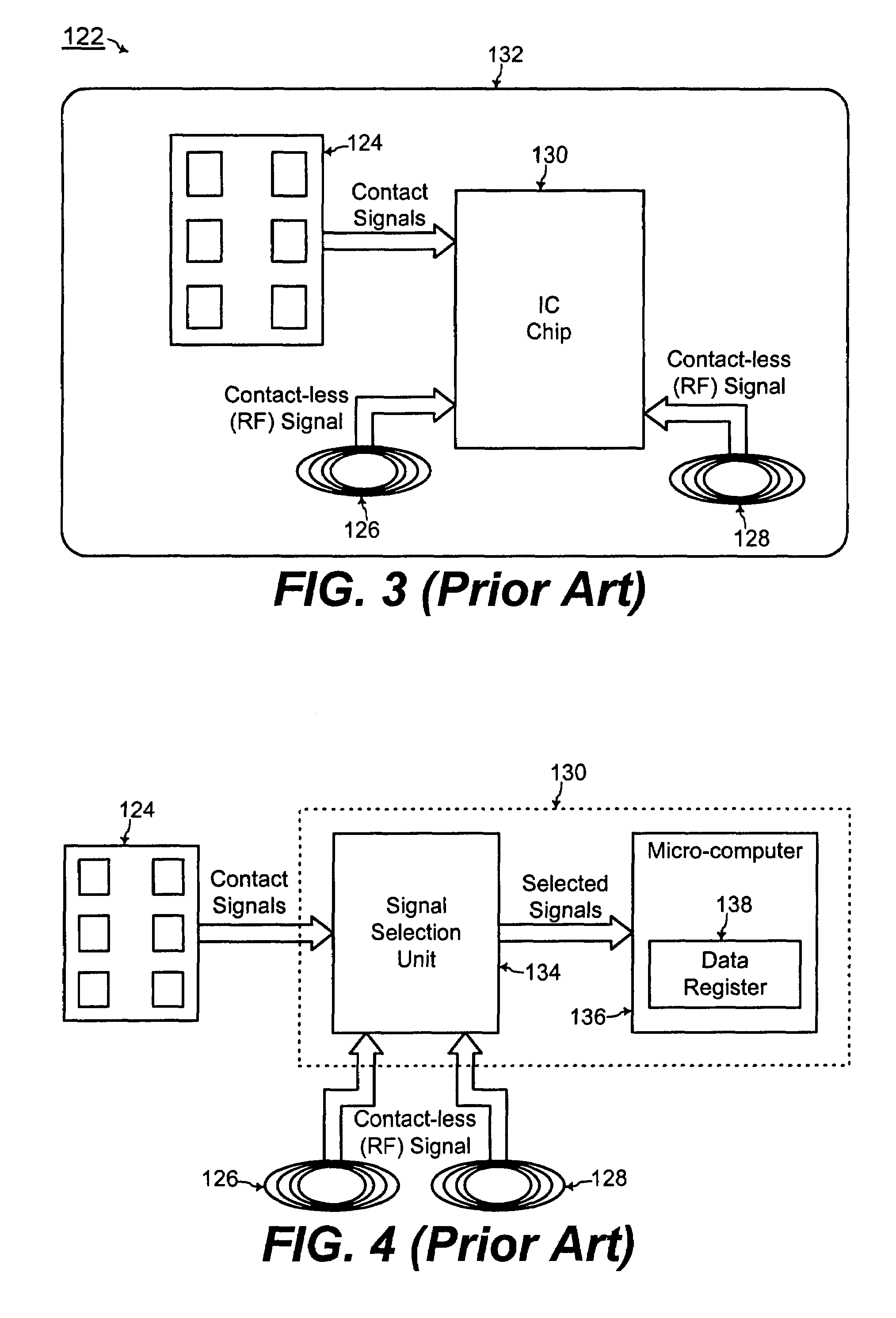
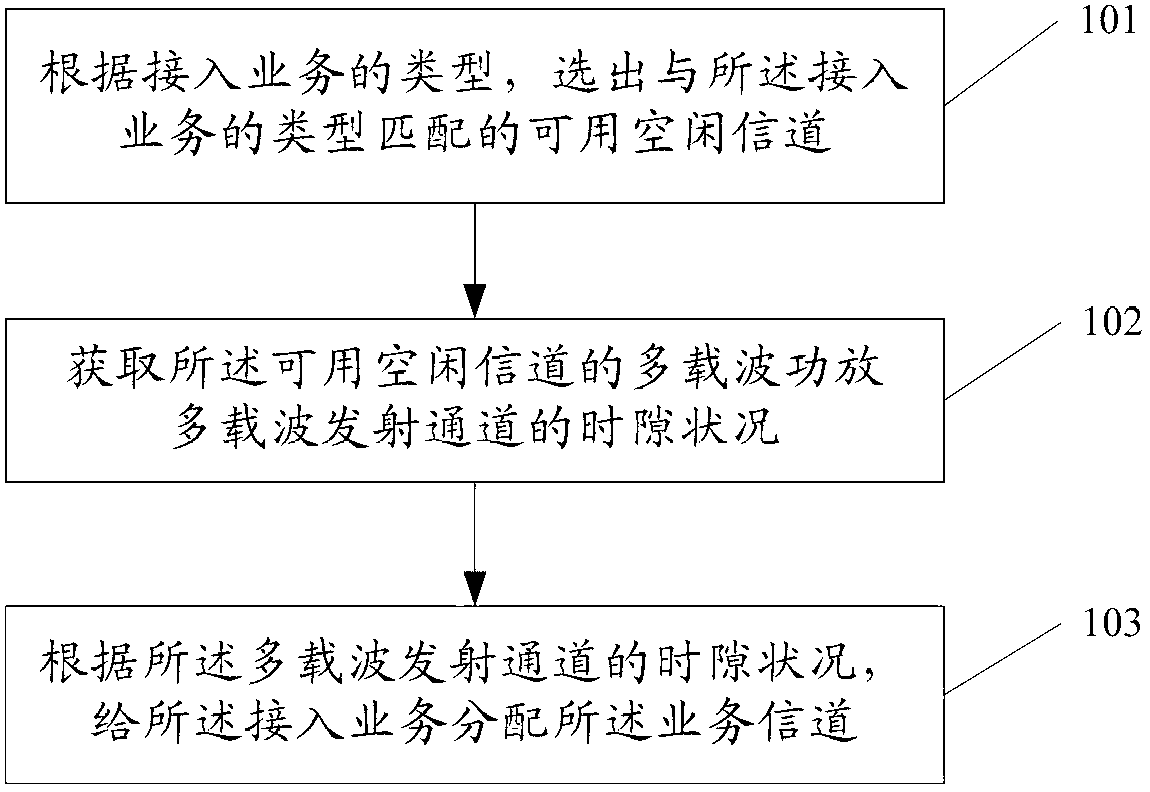
Chip card with simultaneous contact and contact-less operations
ActiveUS7246750B2Stable bias voltageCo-operative working arrangementsSensing record carriersMicrocomputerMicro computer
A chip card receives and processes what-ever combination of contact data and contact-less data is available to allow multiple functionalities for the chip card. A micro-computer of the chip card is adapted to simultaneously receive and process contact data from a contact interface and contact-less data from a contact-less interface. In addition, the chip card includes a power voltage selector for selecting a contact bias to supply power to the micro-computer when-ever the contact bias voltage is available since the contact bias voltage is more stable than a contact-less bias voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
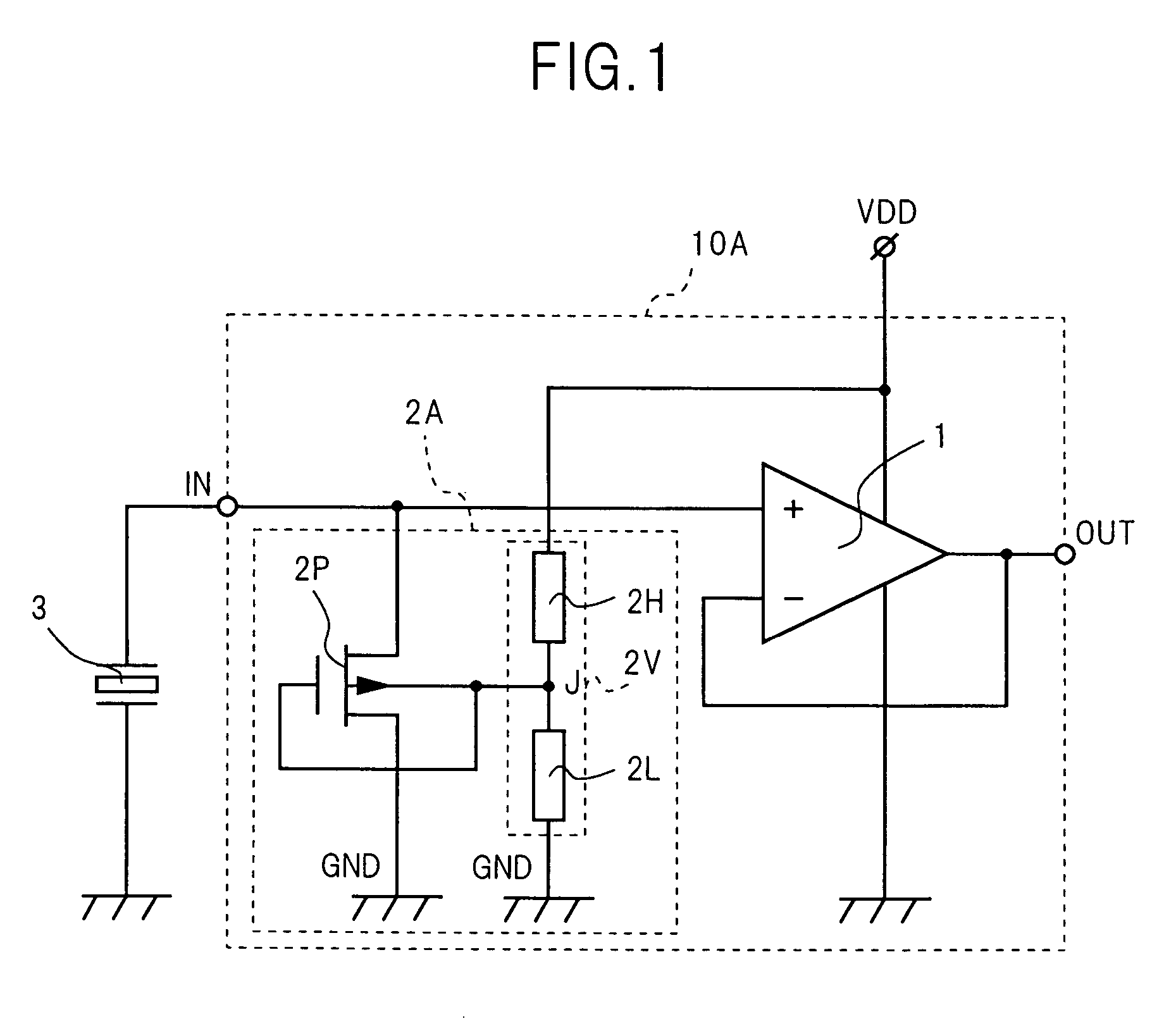
Amplification device with a bias circuit
InactiveUS7119622B2Improve toleranceStable bias voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationLow frequency amplifiersMOSFETAudio power amplifier
An operational amplifier amplifies a signal received through its input terminal connected directly to a piezoelectric device. A bias voltage generating section includes a voltage divider between the power supply terminal and the ground terminal. The drain and source of a p-channel MOSFET are connected to the input terminal of the operational amplifier and the ground terminal. Since the voltage divider applies a bias voltage to the gate and the backgate, the p-channel MOSFET maintains the OFF state. Since a drain-backgate parasitic diode clamps the drain potential to the bias voltage, the bias voltage is applied to the input terminal of the operational amplifier. Then, the drain-backgate resistance is extremely high. The p-channel MOSFET is embedded on a substrate together with other circuits of the amplification device. Thus, the amplification device with an extremely high input impedance is configured as a single integrated circuit.
Owner:COLLABO INNOVATIONS INC
Self-biased high-speed receiver
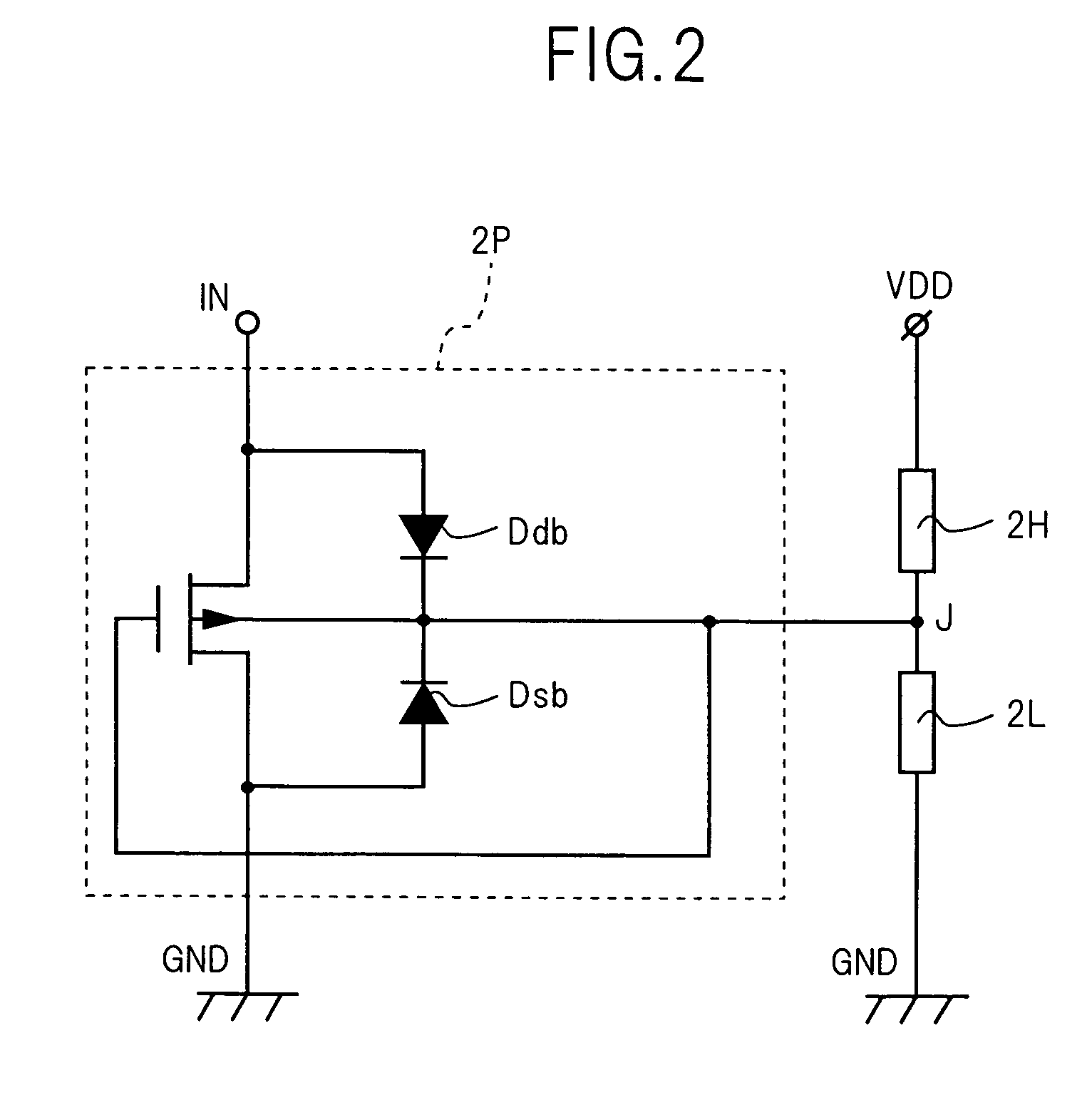
InactiveUS7349681B2Stable bias voltageMinimize the numberResonant long antennasReliability increase in field effect transistorsVoltage referenceTransistor
A self-biased high-speed receiver is described. The receiver is powered by one power supply with the core operation voltage and one power supply with the IO operation voltage. The receiver is self-biased to provide a stable bias voltage. A reference voltage and an IO signal are applied on the receiver so that the difference is amplified. Thick oxide transistors are used to increase the operation voltage of the transistors. Native thick oxide transistors are used so that the receiver can work with low command mode input.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Implementing enhanced bias configuration for CMOS inverter based optical transimpedance amplifier
ActiveUS9490757B2OptimizationStable bias voltageAmplifiers controlled by lightPower inverterAudio power amplifier
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Chip card with simultaneous contact and contact-less operations
A chip card receives and processes what-ever combination of contact data and contact-less data is available to allow multiple functionalities for the chip card. A micro-computer of the chip card is adapted to simultaneously receive and process contact data from a contact interface and contact-less data from a contact-less interface. In addition, the chip card includes a power voltage selector for selecting a contact bias to supply power to the micro-computer when-ever the contact bias voltage is available since the contact bias voltage is more stable than a contact-less bias voltage.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
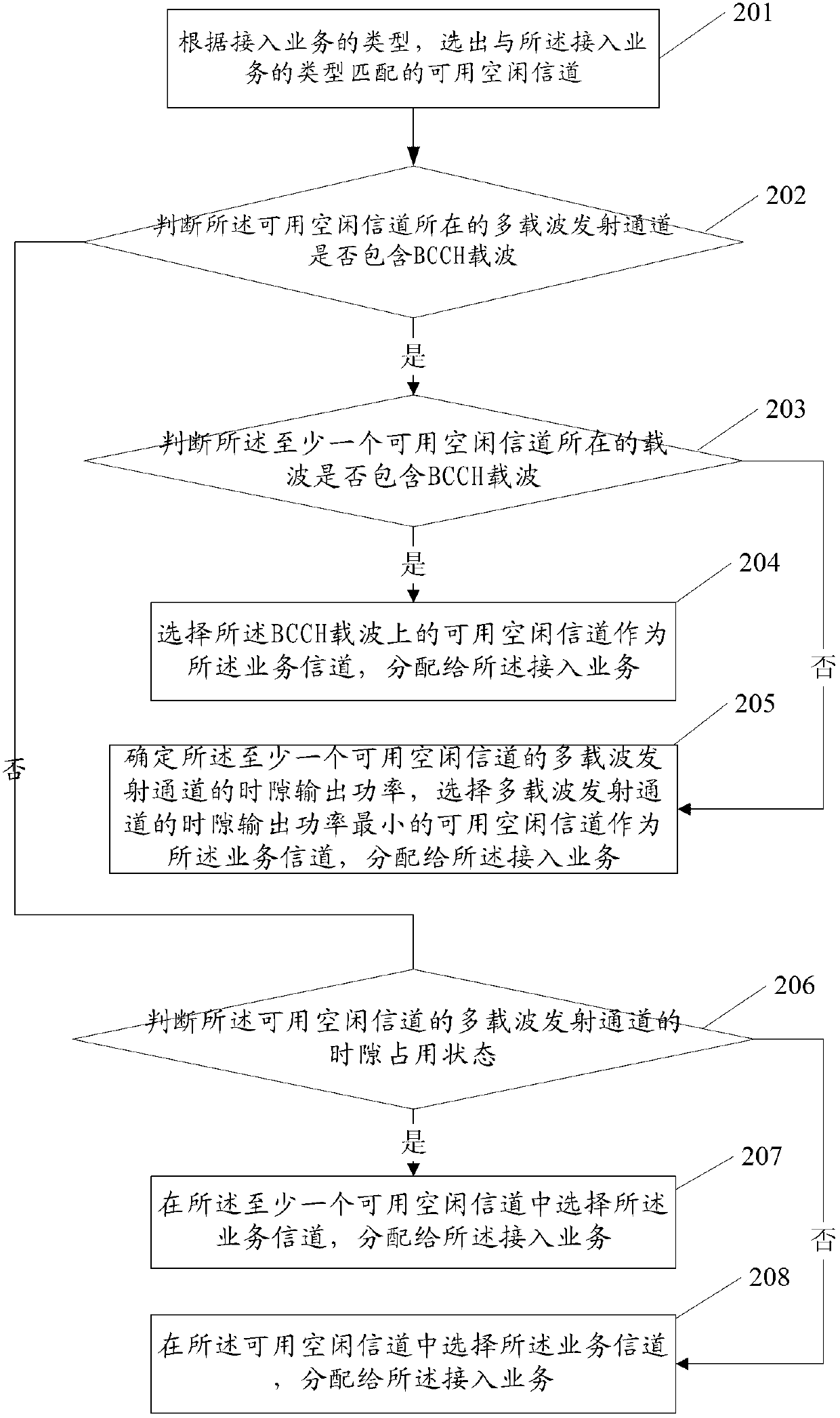
Method and apparatus for traffic channel assignment
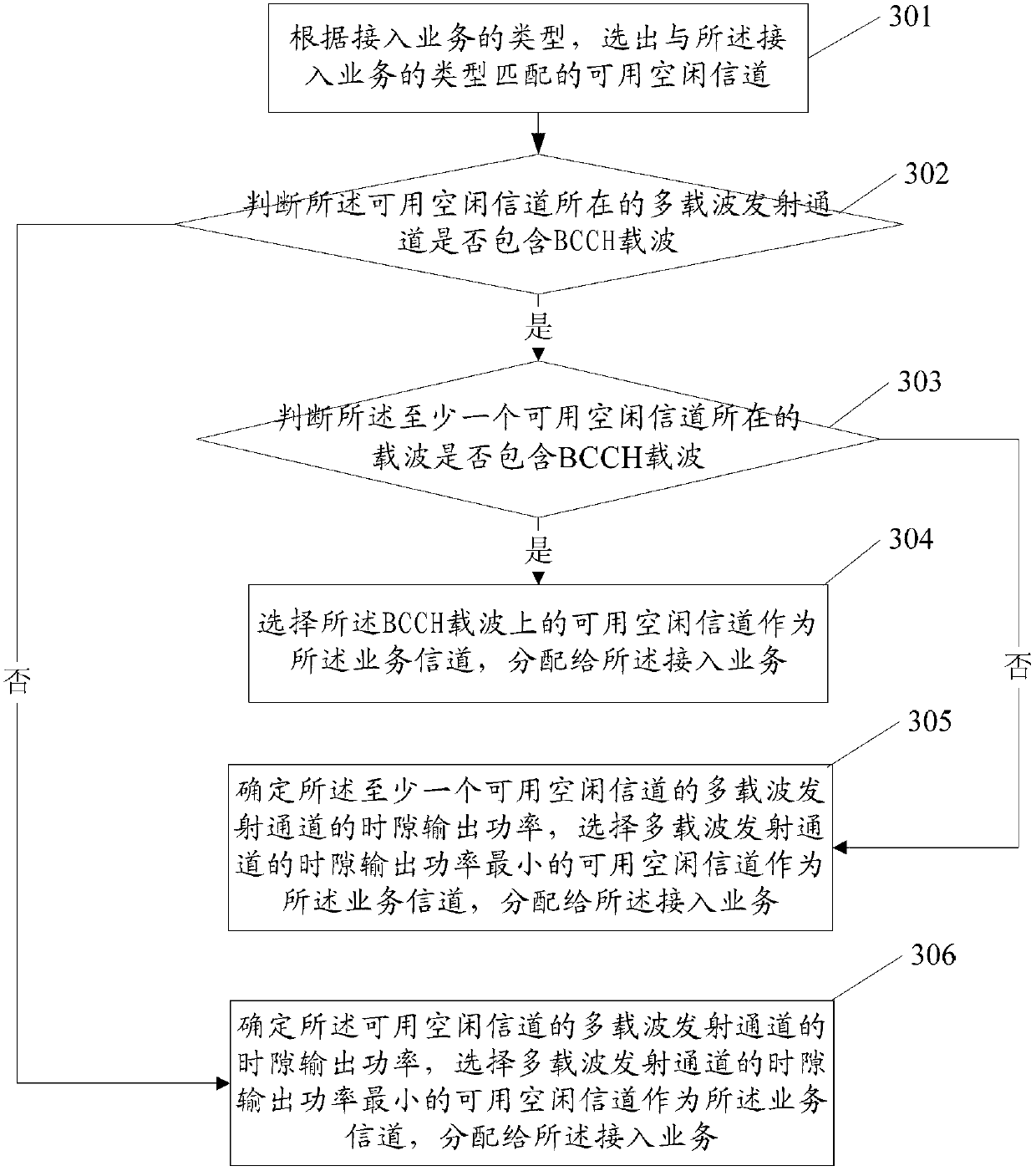
InactiveCN102870482AEasy accessStable output powerEnergy efficient ICTPower managementIdle channelMulti carrier
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus for a traffic channel assignment. The method comprises: based on an accesse service type, selecting available idle channels matching with the accesse service type; obtaining the time slot condition of the multi-carrier transmitting channel of the available idle channels matching with the accesse service type; and according to the channel slot condition of said multi-carrier transmitter, assigning the traffic channel to the access traffic. By using embodiments of the present invention, it is possible to take full advantage of multi-carrier energy-saving technologies, and greatly enhance energy-saving effect of multi-carrier base stations.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
High-speed BDI-type pixel unit circuit
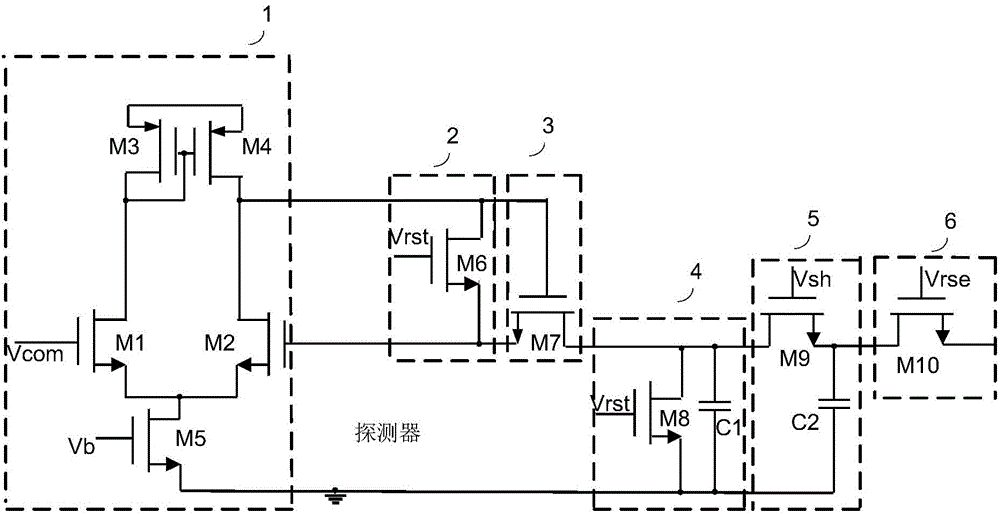
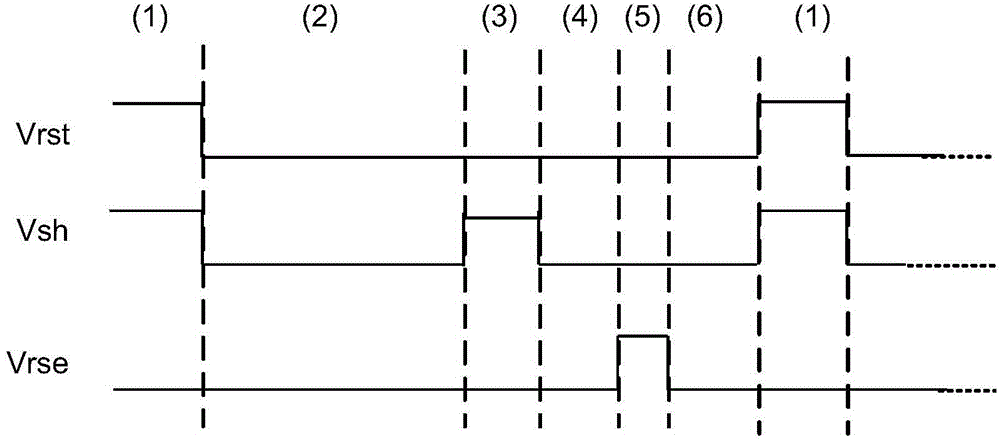
InactiveCN104065890AReduce power consumptionHigh speedTelevision system detailsColor television detailsStable stateNegative feedback
A high-speed BDI-type pixel unit circuit comprises an input amplifier, a detector bias reset circuit, an injection pipe, an integration / reset control circuit, a sample hold circuit and a transmission circuit, wherein the input amplifier, the detector bias reset circuit, the injection pipe, the integration / reset control circuit, the sample hold circuit and the transmission circuit are connected in sequence. A difference amplifier with a current mirror serving as a load is adopted by the input amplifier, a detector bias voltage is rapidly reset to be in a stable state by the detector bias reset circuit in a reset state, the injection pipe forms a negative feedback mode, integration is conducted on an output signal of the infrared detector in the integration state of the integration / reset control circuit, and an integration capacitor is reset in the reset state. The sample hold circuit is used for collecting and holding integration voltages and the transmission circuit is used for receiving output of the sample hold circuit.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Detection circuit for auto detecting avalanche magnitude of voltage of avalanche photodiode and method
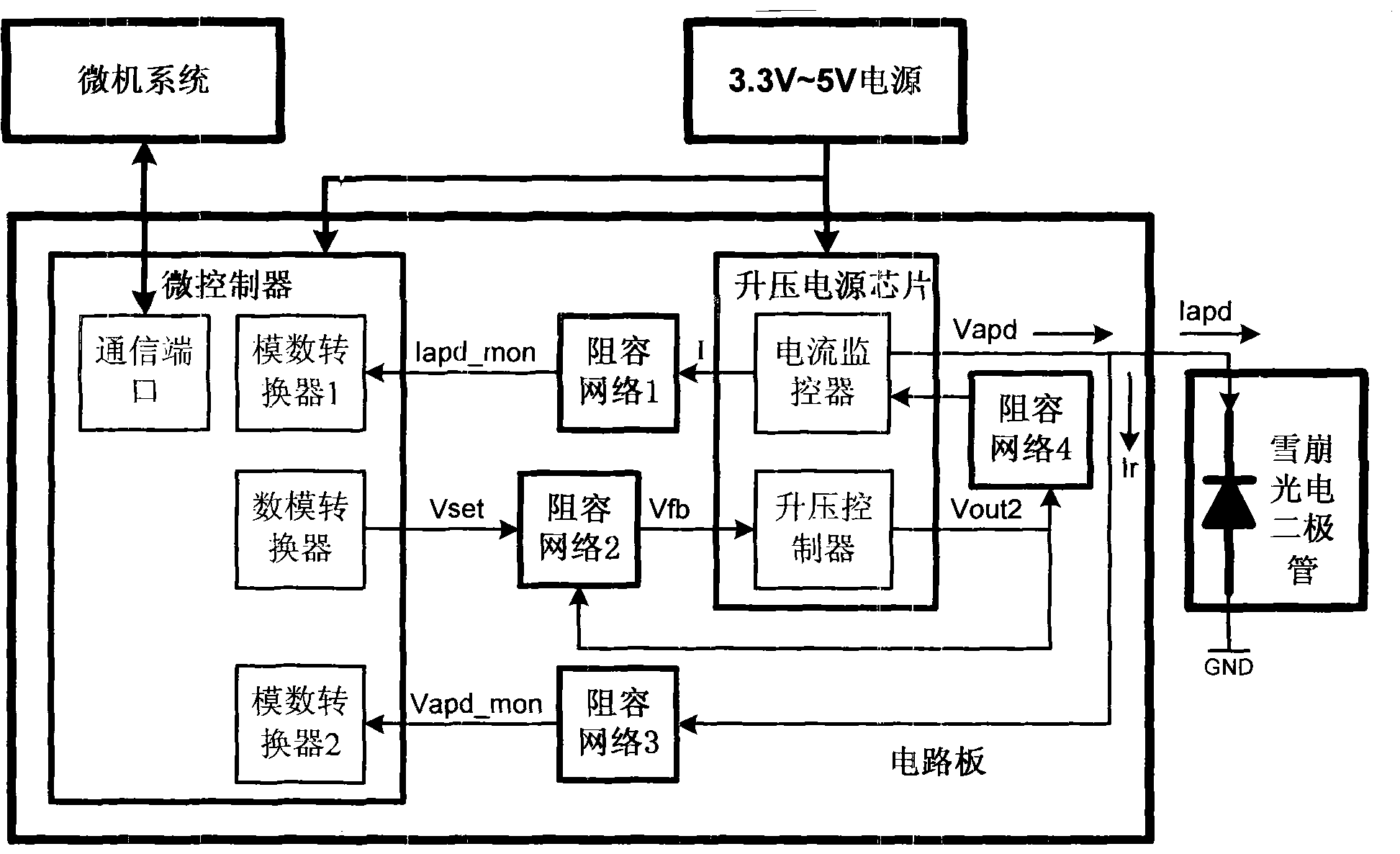
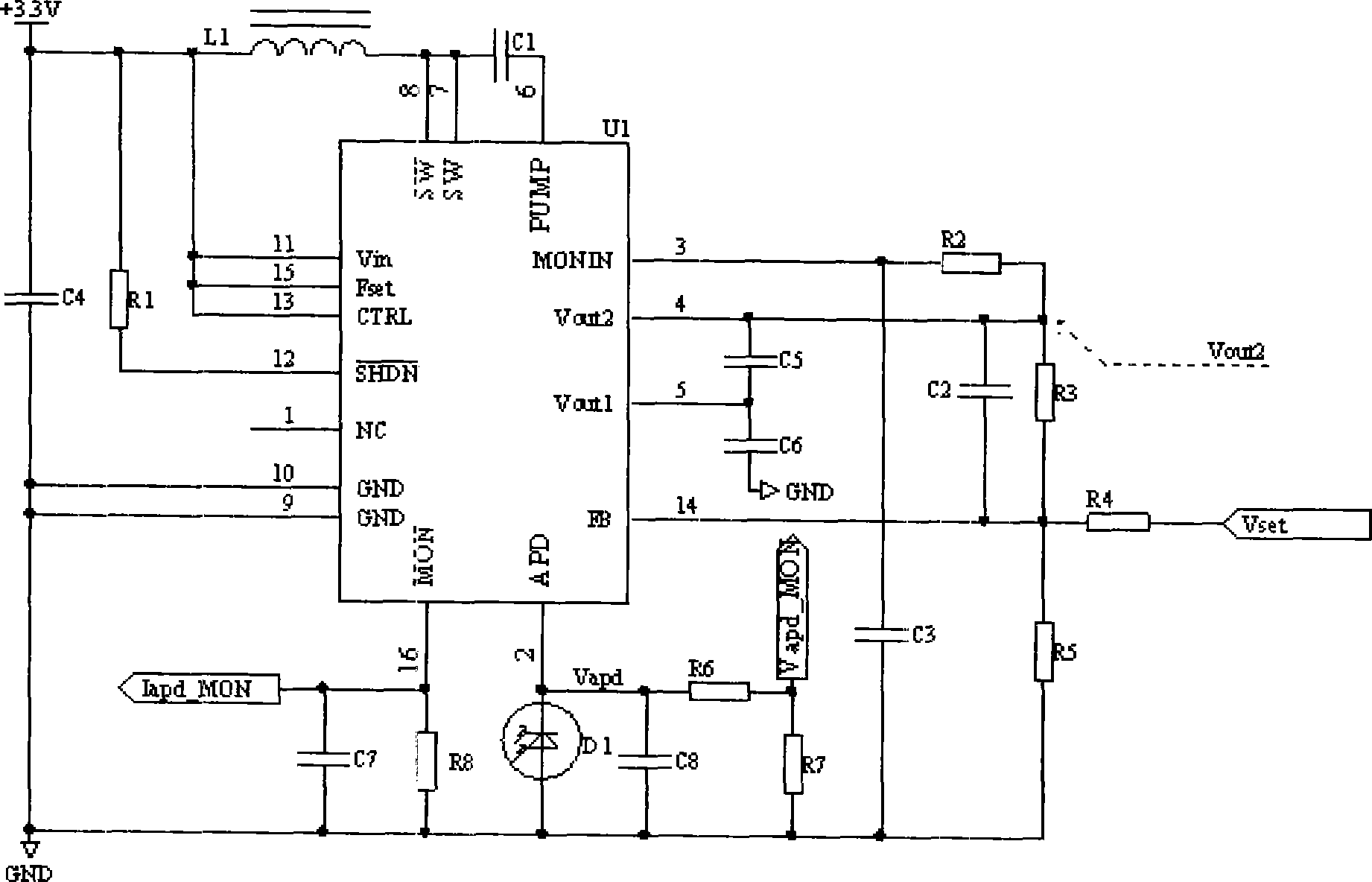
InactiveCN101387658BEasy to operateReduce the difficulty of operationCurrent/voltage measurementIndividual semiconductor device testingMicrocontrollerAutomatic control
Owner:SUPERXON (CHENGDU) TECH LTD
Differential amplifier
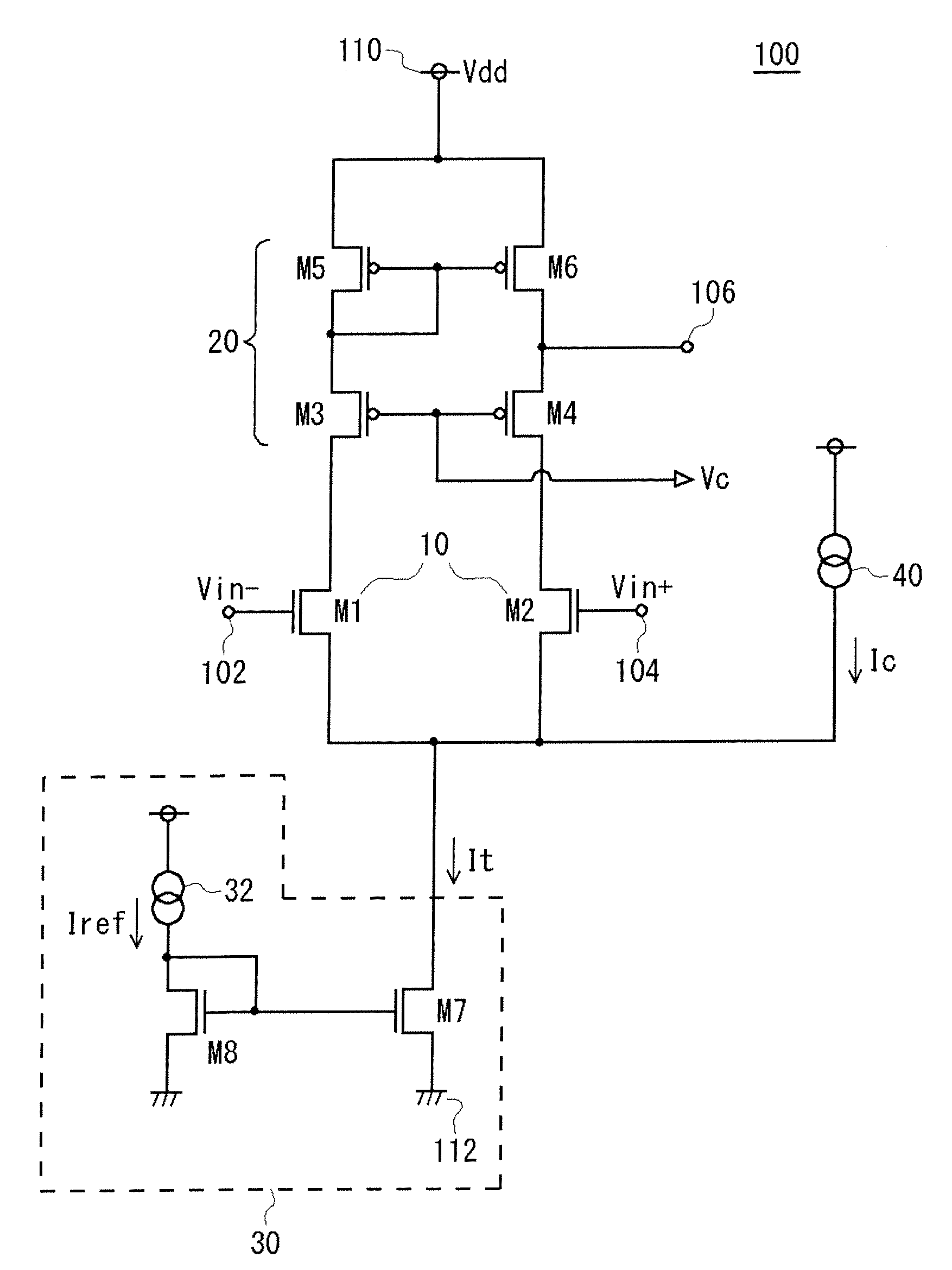
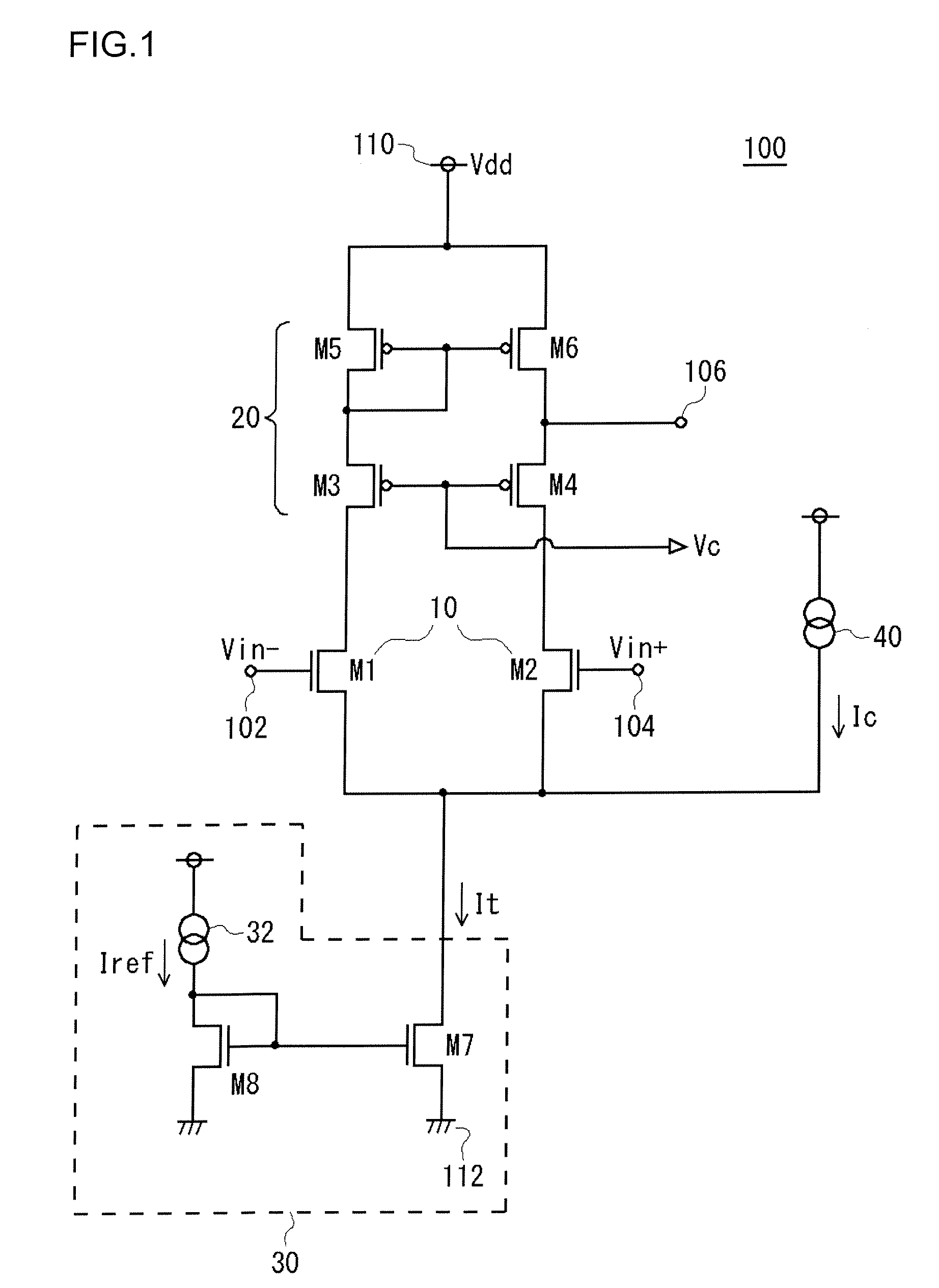
InactiveUS20080290942A1Increase speedReduce circuit costDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesCascode current mirrorEngineering
A cascode current mirror circuit is connected as an active load to the input differential pair. A tail current source supplies a tail current to the input differential pair. A constant current source is connected in parallel with the input differential pair, and supplies a constant current to the tail current source. The constant current supplied by the constant current source is set to a value at which a transistor is not cut off.
Owner:ADVANTEST CORP
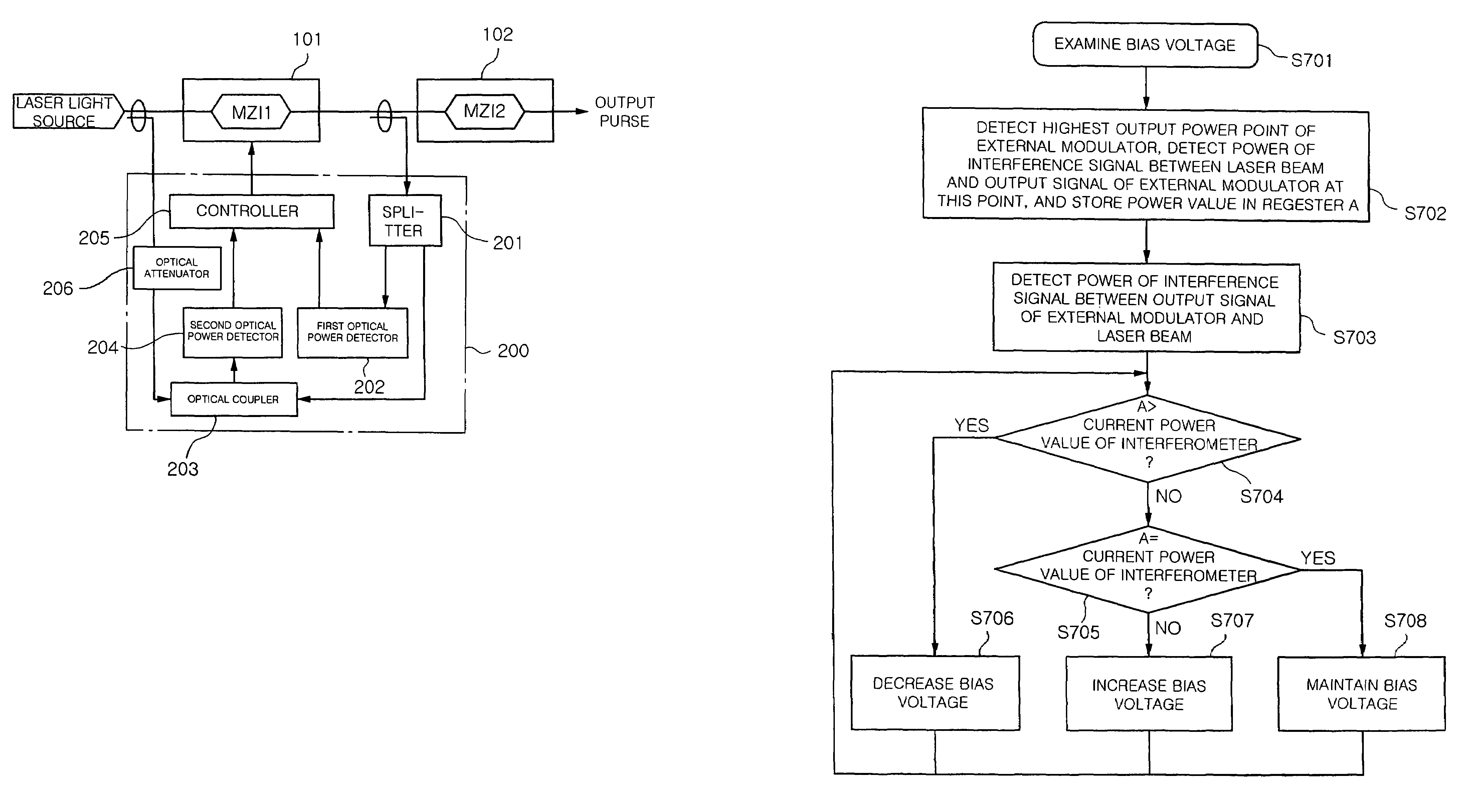
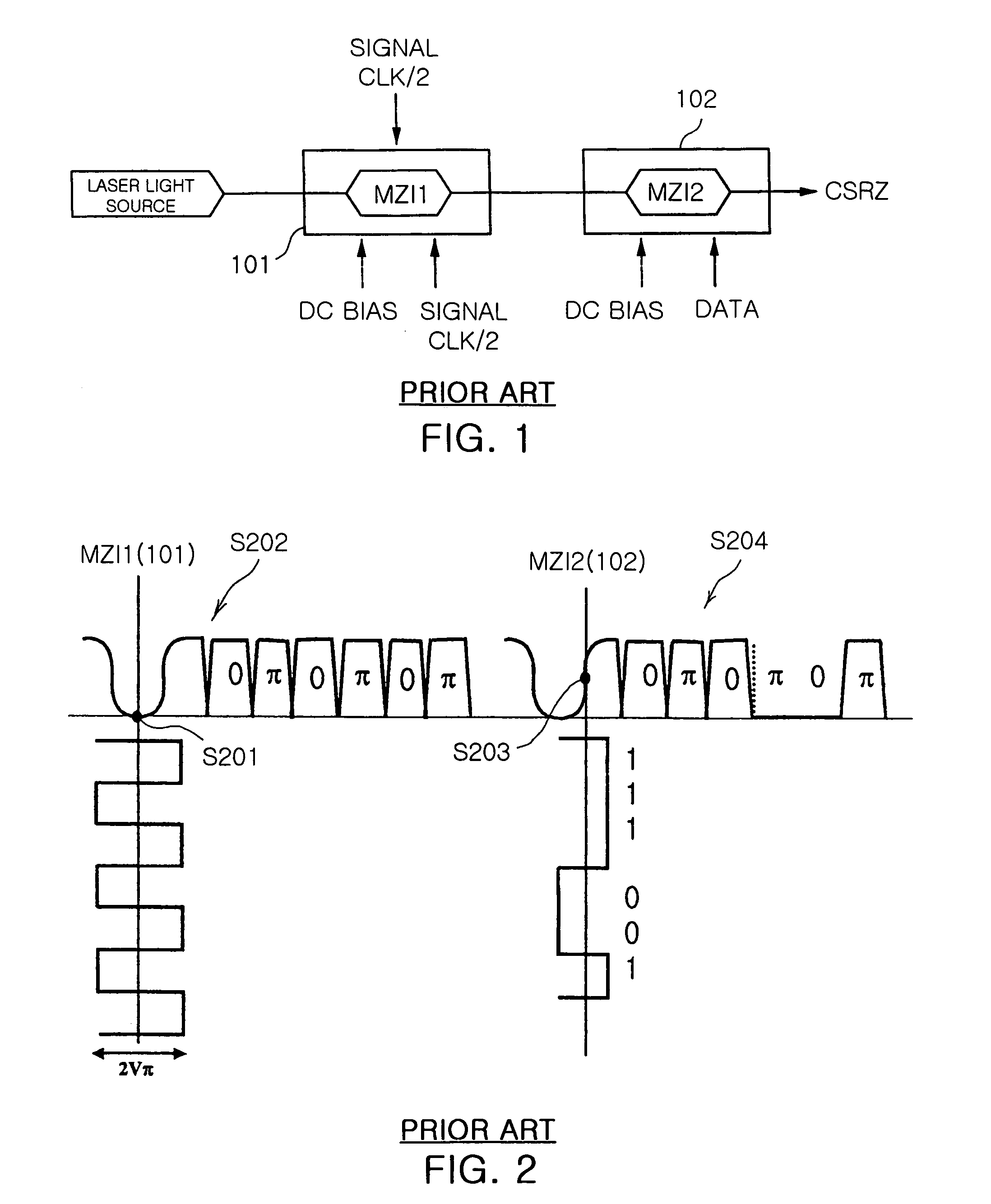
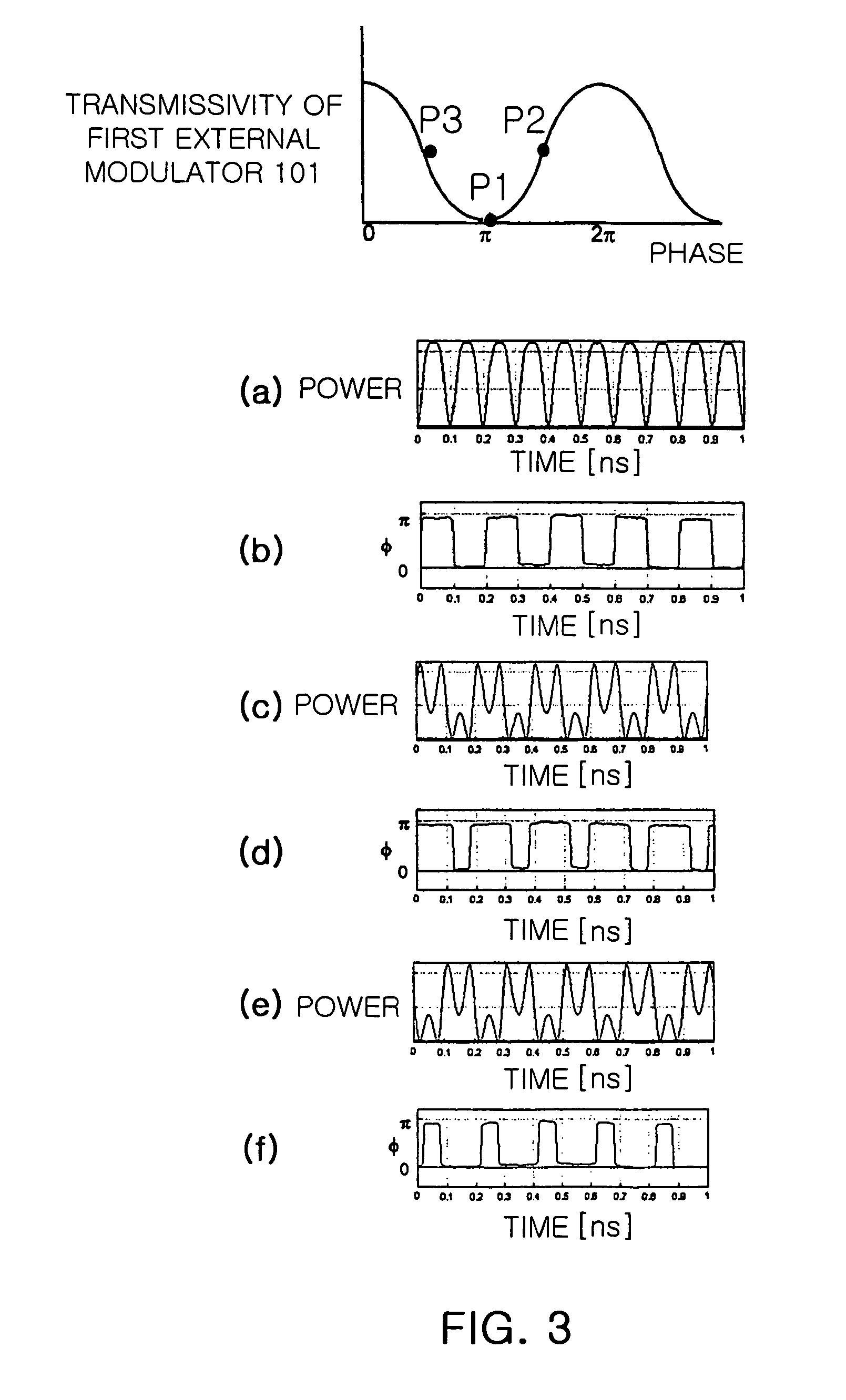
Apparatus and method for automatically correcting bias voltage for carrier suppressed pulse generating modulator
InactiveUS7075694B2Stable bias voltageOptical transmission with multiple stagesBurial vaultsPhase variationCarrier signal
The present invention relates to an apparatus and method for automatically correcting a bias voltage for a carrier suppressed pulse generating modulator using the phase distribution of the output pulses, which automatically detects an optimal bias voltage for the carrier suppressed pulse generating modulator and stabilizes the bias voltage.In the bias voltage automatic correction method and apparatus of the present invention, an optimal bias voltage for the modulator is set to a bias voltage that is obtained when mean power of an optical signal output from the modulator is highest. The varying direction of the bias voltage is detected on the basis of the phase variations in the output optical signal of the modulator according to the bias voltage variations is detected, and the bias voltage is corrected oppositely to the varying direction of the bias voltage.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Circuit structure used for driving silicon-based avalanche photodiode
InactiveCN105827236AReduce noiseReduce power consumptionPower reduction in field effect transistorsLogic circuits using opto-electronic devicesIsolation effectField-effect transistor
The invention relates to a circuit structure for driving a silicon-based avalanche photodiode, which includes a photovoltaic diode array, a silicon-based avalanche photodiode, a charge and discharge management circuit, a field effect transistor, a high-voltage bias circuit and a bias voltage setting circuit; The two ends of the input end of the charging and discharging management circuit are connected to the positive and negative poles of the photovoltaic diode array; the two ends of the output end of the charging and discharging management circuit are connected to the gate and source of the field effect transistor; The drains of the effect transistors are connected; the output end of the high-voltage bias circuit is connected with the cathode of the silicon-based avalanche photodiode, and the output end of the bias voltage setting circuit is connected with the input end of the high-voltage bias circuit; the beneficial effects of the present invention are: the The response speed of the circuit structure is fast, the dark current is extremely low when there is no light, the light-current gain is high, the control circuit has a good isolation effect, the circuit power consumption is low, and the circuit structure is relatively simple.
Owner:合肥汇芯半导体科技有限公司
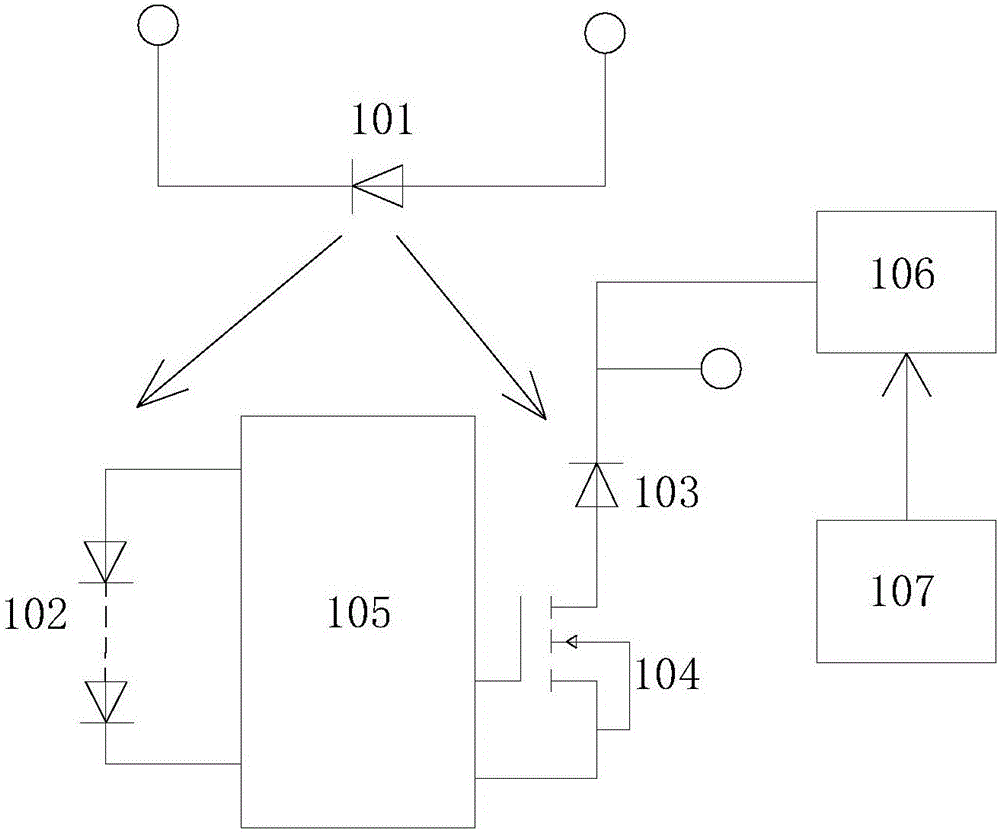
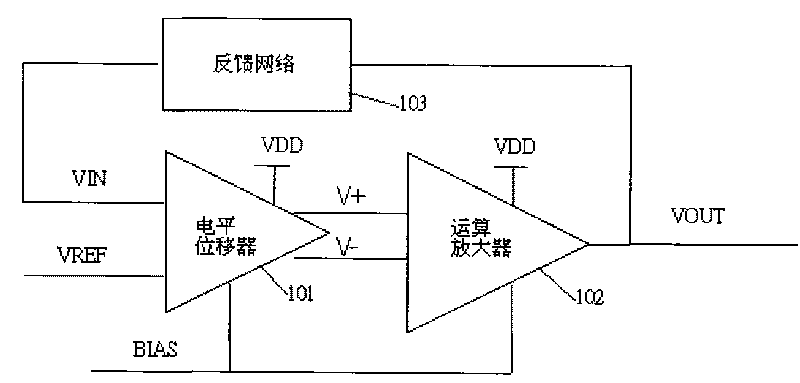
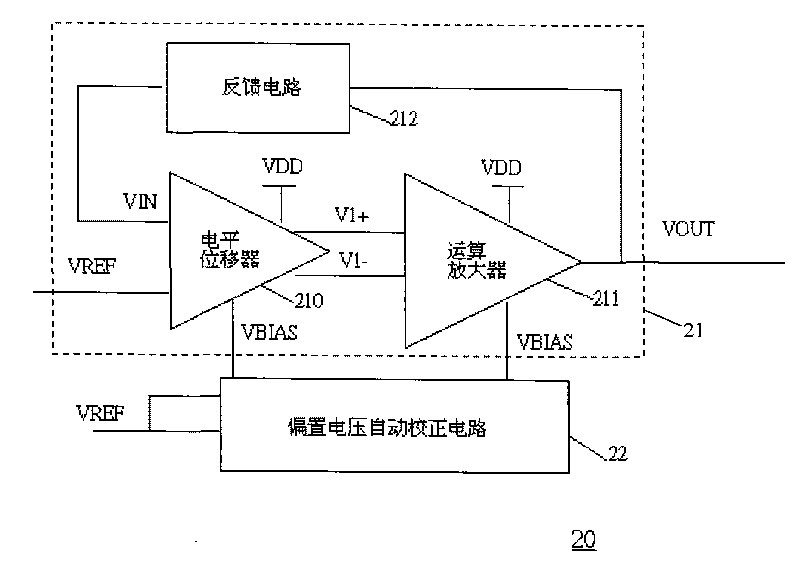
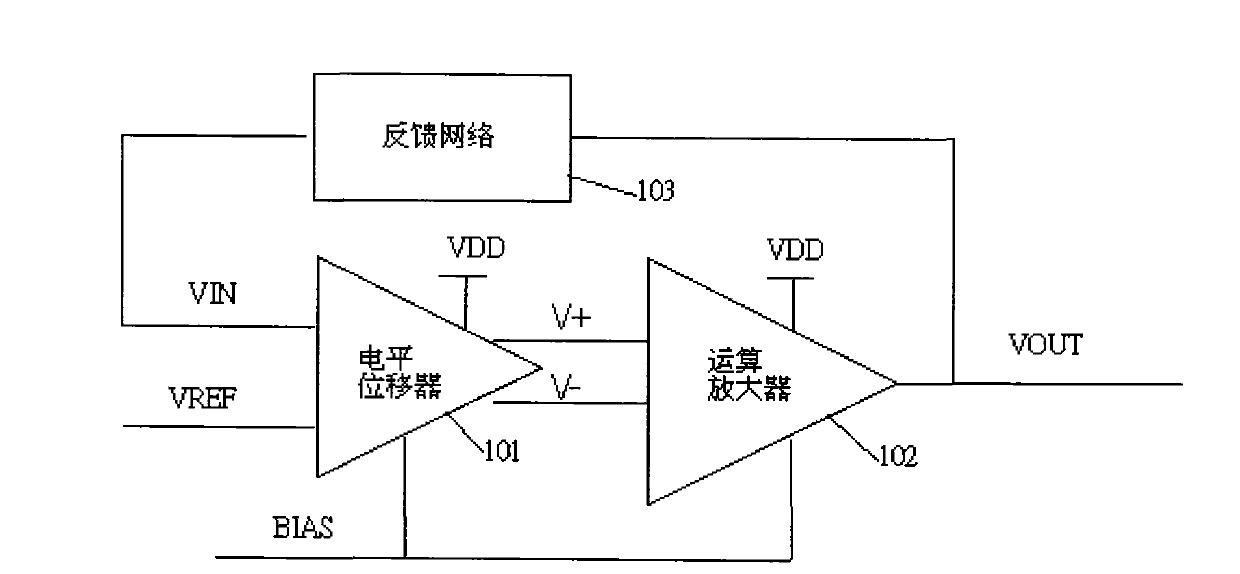
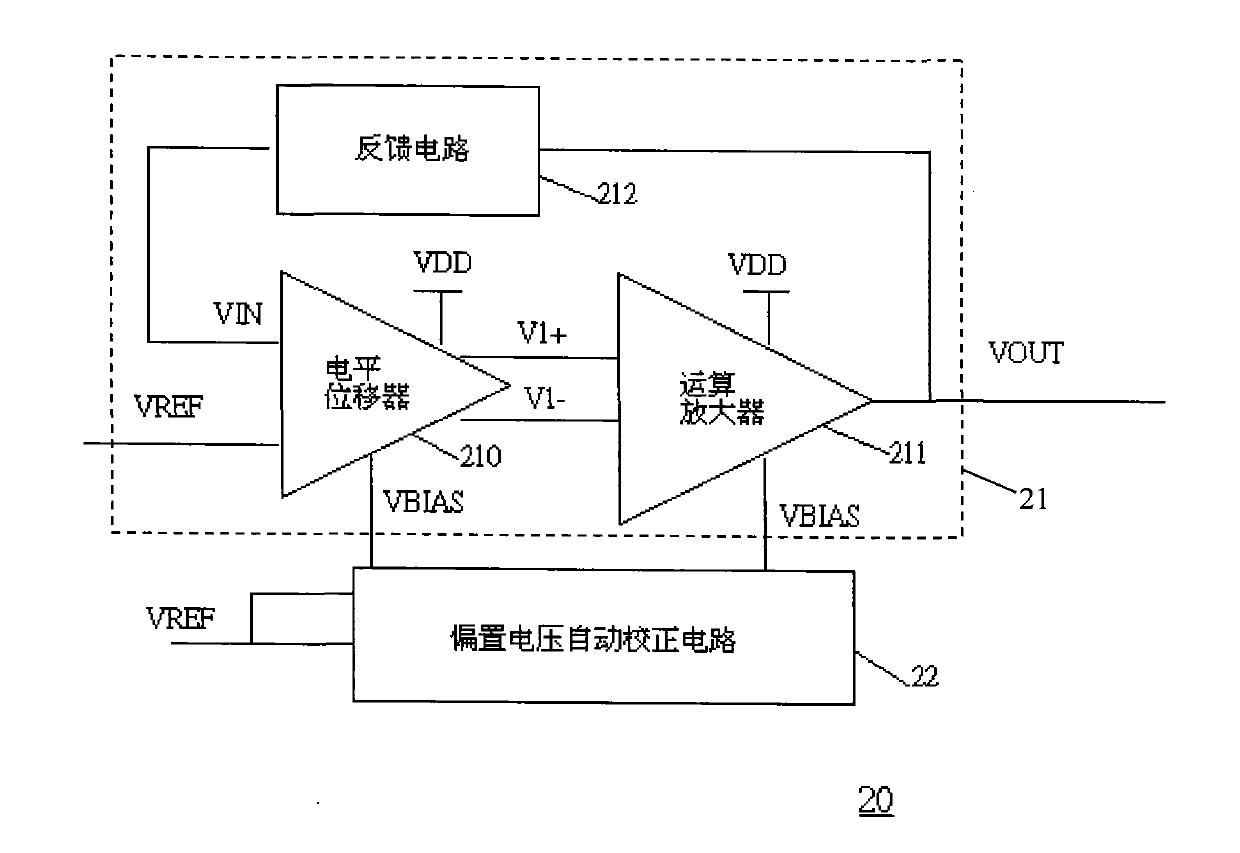
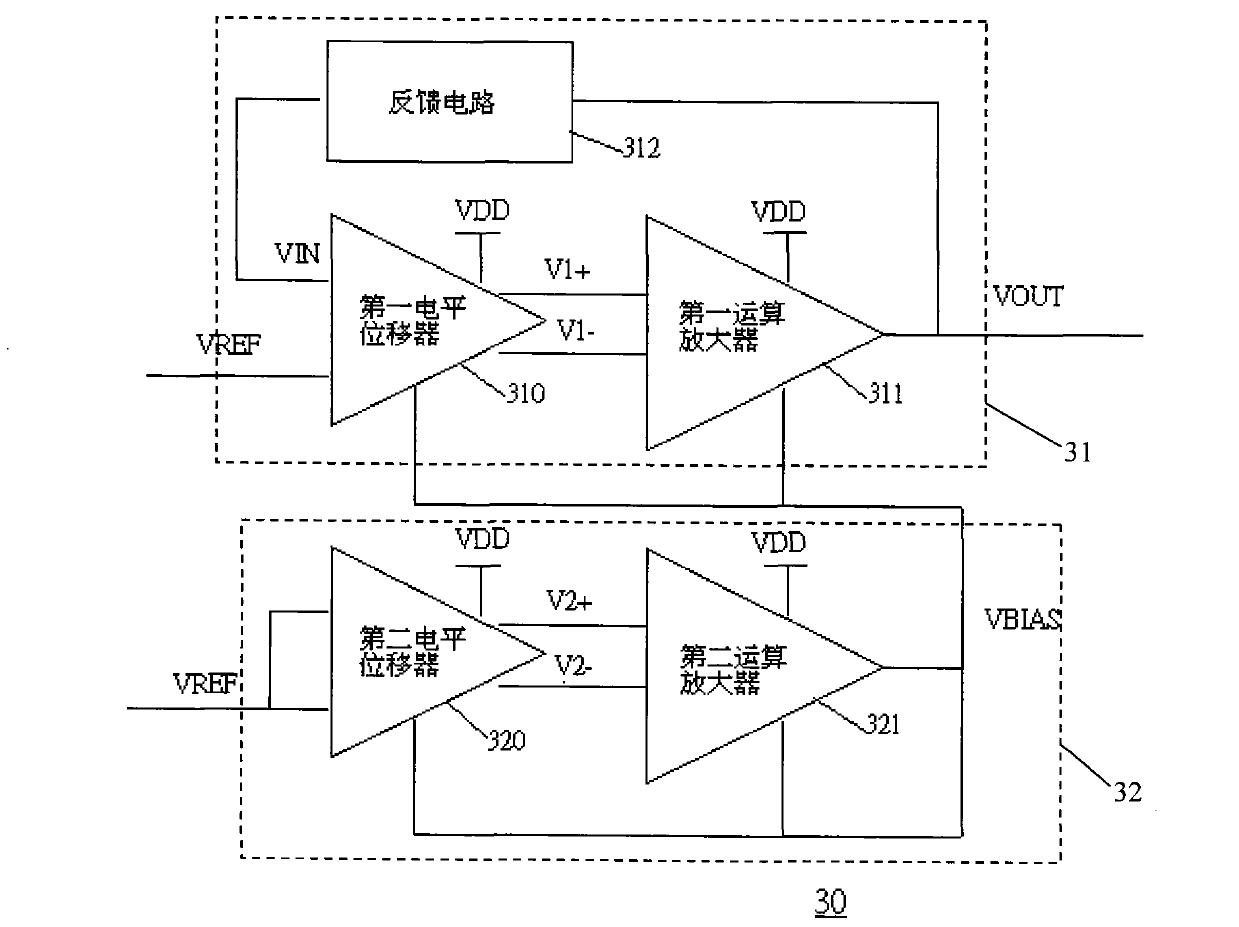
Auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit
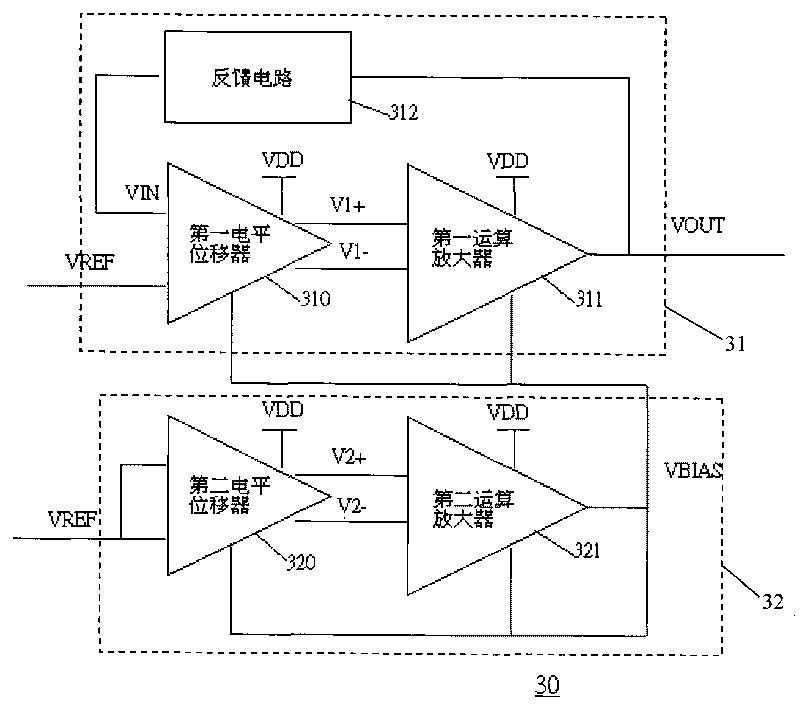
ActiveCN101763133AImprove performanceStable bias voltageElectric variable regulationAudio power amplifierFeedback circuits
The invention discloses an auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit. The auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit comprises a first level shifter, a first operational amplifier and a bias voltage automatic correcting circuit, wherein the first level shifter is used for generating a first two-difference voltage; the first operational amplifier is connected with the first level shifter voltage; the firstoperational amplifier amplifies the first two-difference voltage and outputs an output voltage, and the output voltage is simultaneously connected to a feedback circuit; the feedback network samples the output voltage and outputs a feedback voltage to the first level shifter; and the bias voltage automatic correcting circuit is used for converting the variations of the technological parameters ofthe first level shifter into a differential voltage and outputting the differential voltage to the first level shifter and the first operational amplifier, thereby providing a bias voltage. The auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit does not need to use the fixed bias voltage and can automatically obtain a stable bias voltage by utilizing the bias voltage automatic correcting circuit, so that the output voltage is free from the effects of the technological parameters, and the performance of the voltage stabilizing circuit is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Ka-Band MMIC (monolithic microwave integrated circuit) low-noise amplifier
PendingCN107612514AReduced frequency response peaksReduce spikesAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceLinearity
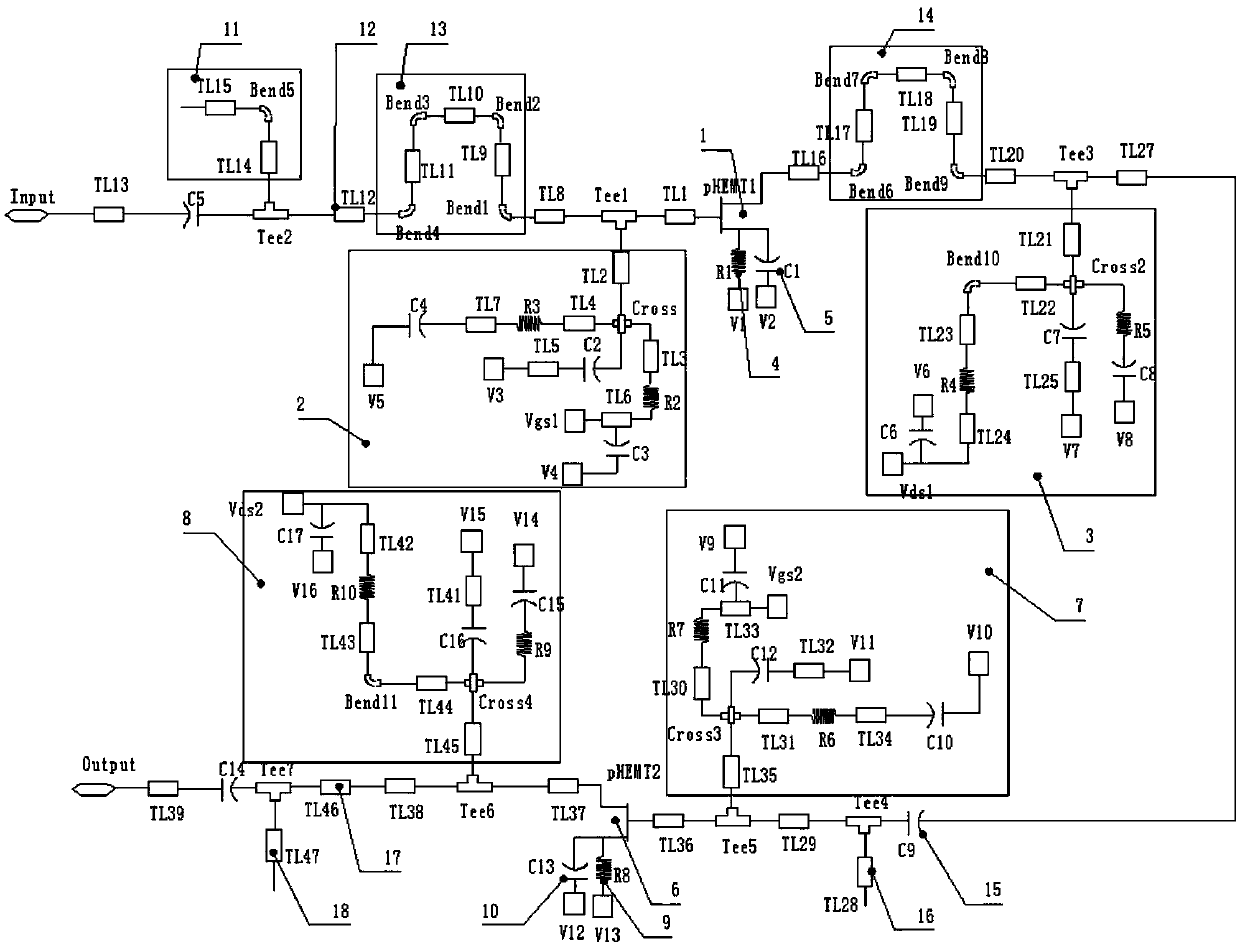
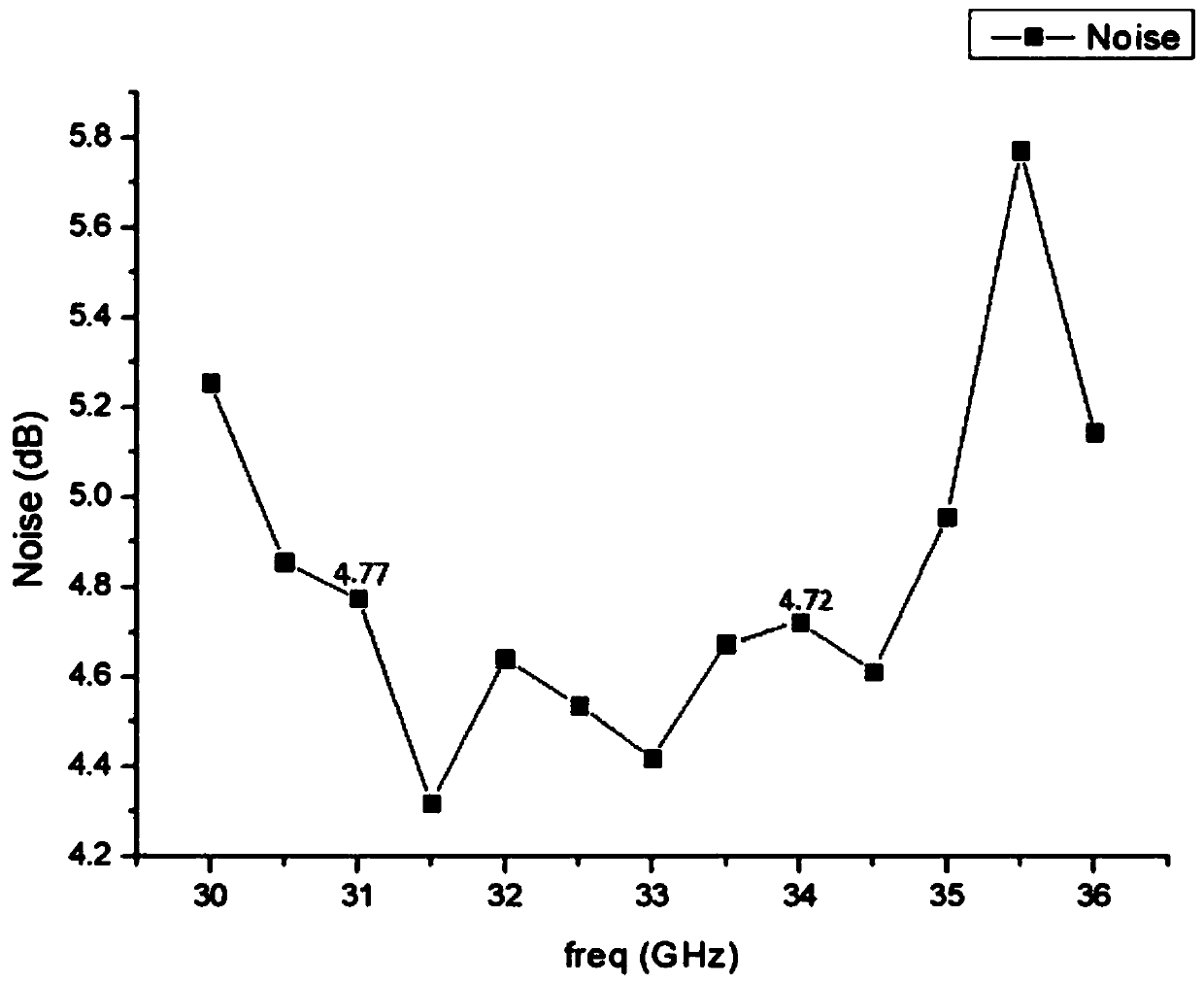
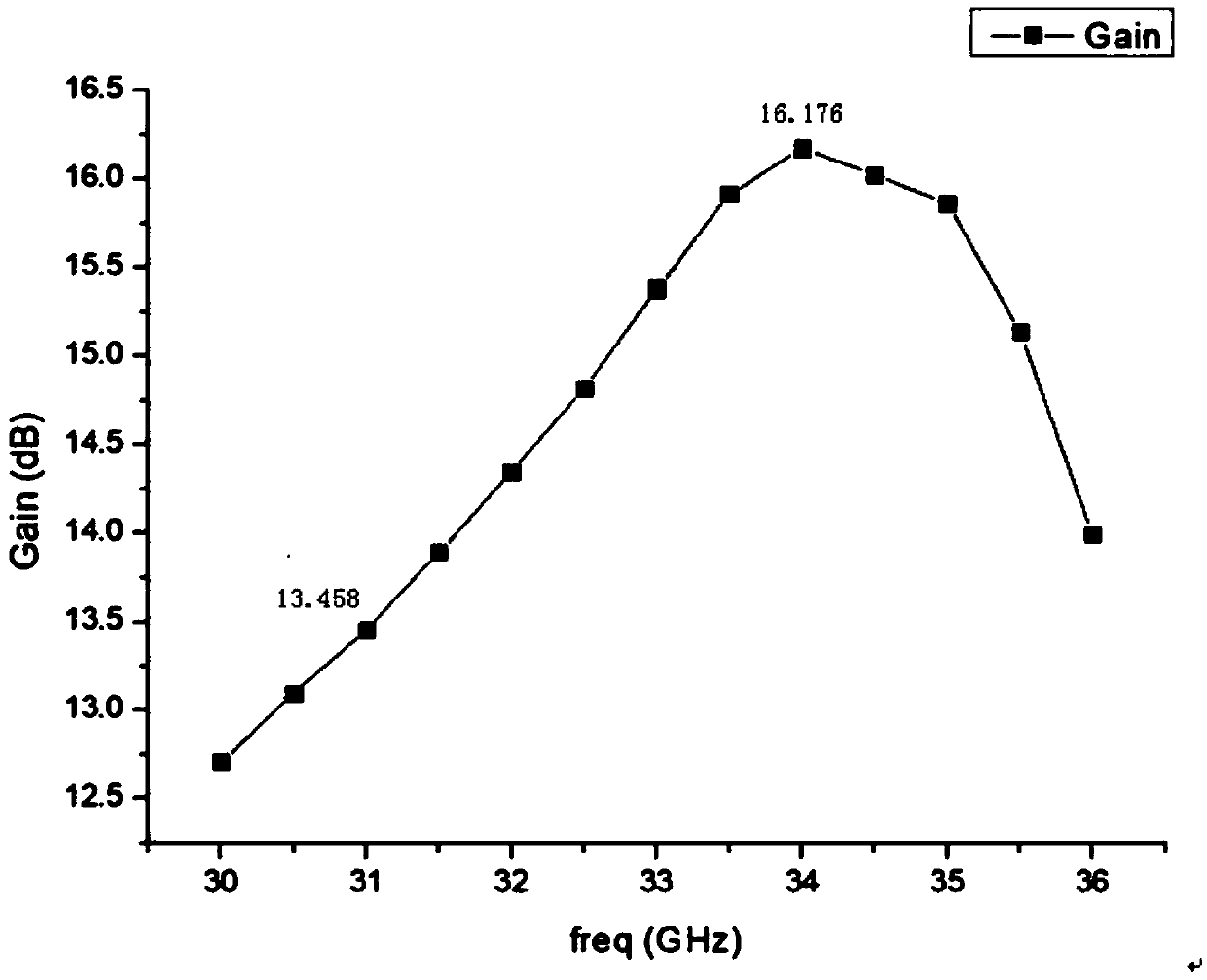
The invention relates to a Ka-band MMIC (monolithic microwave integrated circuit) low-noise amplifier and mainly solves the technical problem that the prior art has high noise coefficient, poor in-band gain flatness and poor linearity. The Ka-band MMIC low-noise amplifier comprises a two-stage amplifier, a gamma / 4 transmission wire structure and a three-stage matching network, the two-stage amplifier comprises a primary field-effect transistor amplifier, a primary gate bias network, a primary drain bias network, a primary source resistor ad primary source capacitor parallel network, a secondary amplifier, a secondary gate bias network, a secondary drain bias network, and a secondary source resistor and capacitor parallel network, the gamma / 4 transmission wire structure comprises a first transmission wire mesh connected with the primary gate bias network and a second transmission wire mesh connected with the primary drain bias network; by using the above technical scheme, the problem iswell solved; the Ka-band MMIC low-noise amplifier is applicable to the field of Ka-band communications.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH +1
Photo cell and a gain control method thereof
InactiveUS20050189476A1Simple designImprove light effectiveness and sensitivityVehicle arrangementsTelevision system scanning detailsCMOS sensorTerminal voltage
A photocell used with an optical mouse, a CMOS sensor of a digital camera module, or a scanner includes a photo element in which a feedback circuit to maintain a base terminal voltage of the photo element constant, is not directly connected to a base terminal to control the voltage to directly maintain an emitter terminal voltage so that a stable bias voltage is generated compared to a conventional photo element. The photocell includes a stepping element to increase the voltage applied to the base terminal of the photocell, thereby improving sensitivity of the photocell and increasing effectiveness of light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD
Implementing enhanced bias configuration for CMOS inverter based optical transimpedence amplifier
ActiveUS20160226455A1OptimizationStable bias voltageAmplifiers controlled by lightPower inverterAudio power amplifier
A method and circuit are provided for implementing an enhanced bias configuration for CMOS inverter based optical Transimpedance Amplifiers (TIAs). An operational amplifier is provided in a feedback configuration that forces an input of the CMOS inverter to a set voltage level by regulation of the inverter power supply. A photo-detector sees a more stable bias voltage, and the responsivity of the photo-detector is more robust and the TIA has improved performance across process corners.
Owner:IBM CORP
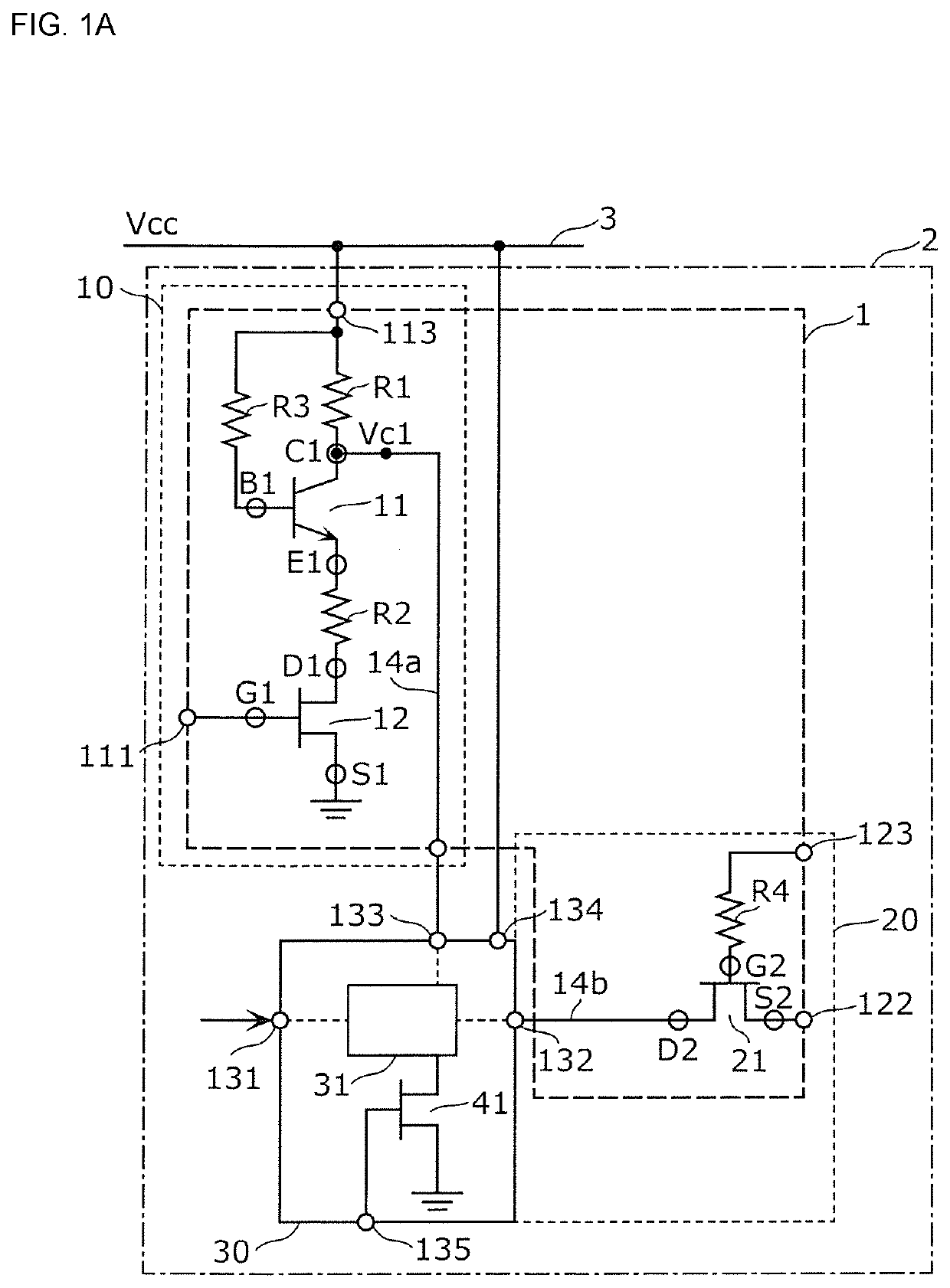
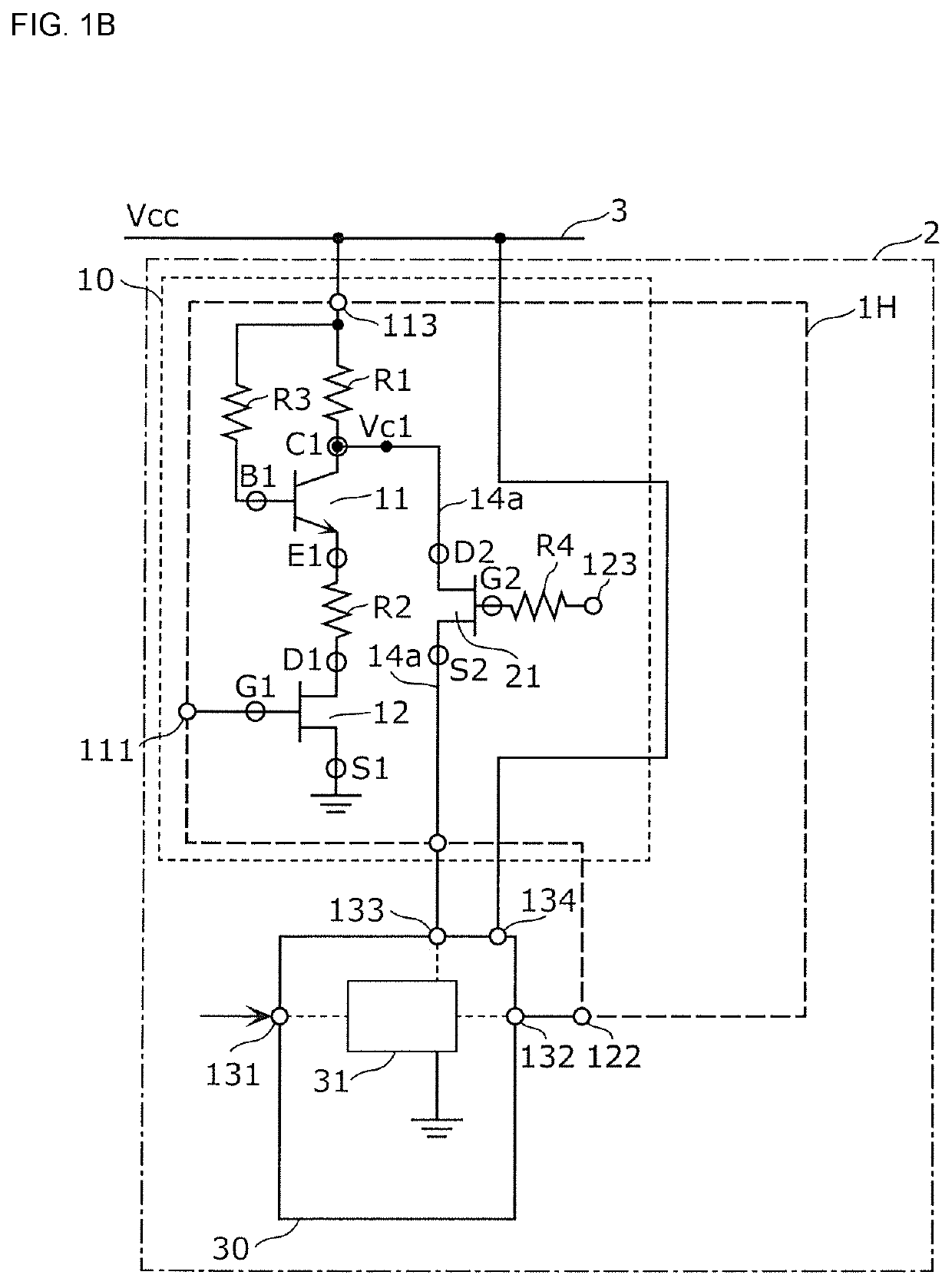
Bias circuit and electronic circuit
ActiveUS20210218395A1Stable bias voltageTransistorAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDetector circuitsSoftware engineering
A bias circuit supplies bias voltage to a linear detector circuit. The bias circuit includes a transistor including a collector terminal, an emitter terminal, and a base terminal; a resistance element having one end connected to the collector terminal and the other end connected to a power line and the base terminal; a resistance element having one end connected to the emitter terminal; a transistor that switches between connection and disconnection between the resistance element and ground; collector voltage extended lines that transmit voltage corresponding to collector voltage as the bias voltage; and a transistor that is arranged on a path of one of the collector voltage extended lines and that switches between connection and disconnection between an output terminal of the linear detector circuit and the collector terminal.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
A Logarithmic Response Ultra-High Speed Infrared Focal Plane Pixel Readout Unit Circuit
ActiveCN112326044BMinimizeMeet temperature measurement application requirementsPyrometry using electric radation detectorsUltra high speedMemory cell
The invention discloses a logarithmic response ultra-high-speed infrared focal plane pixel readout unit circuit, which includes an operational amplifier, a subthreshold state MOS tube, a buffer stage and a storage unit array, and the output end of the operational amplifier is connected to the subthreshold state MOS tube. The gate terminal and the input of the buffer stage, the source terminal of the MOS transistor in the subthreshold state is connected to the negative input terminal of the operational amplifier and the input terminal of the detector, the drain terminal of the MOS transistor in the subthreshold state is connected to the bias voltage, and the positive terminal of the operational amplifier input is connected to the bias voltage. The output terminal of the buffer stage is connected to the input terminal of the memory cell array. The operational amplifier and the sub-threshold state MOS tube are connected in a negative feedback loop. The sub-threshold state MOS tube detects the photocurrent signal of the detector to realize the logarithmic transformation from the photocurrent signal to the sub-threshold state MOS gate-source voltage. The buffer stage will The logarithmic response voltage buffers the output, and the memory cell array stores the signal values of the detector signal at different times sequentially at high speed, and has the measurement capability of ultra-high speed and extremely wide temperature range.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PHYSICS
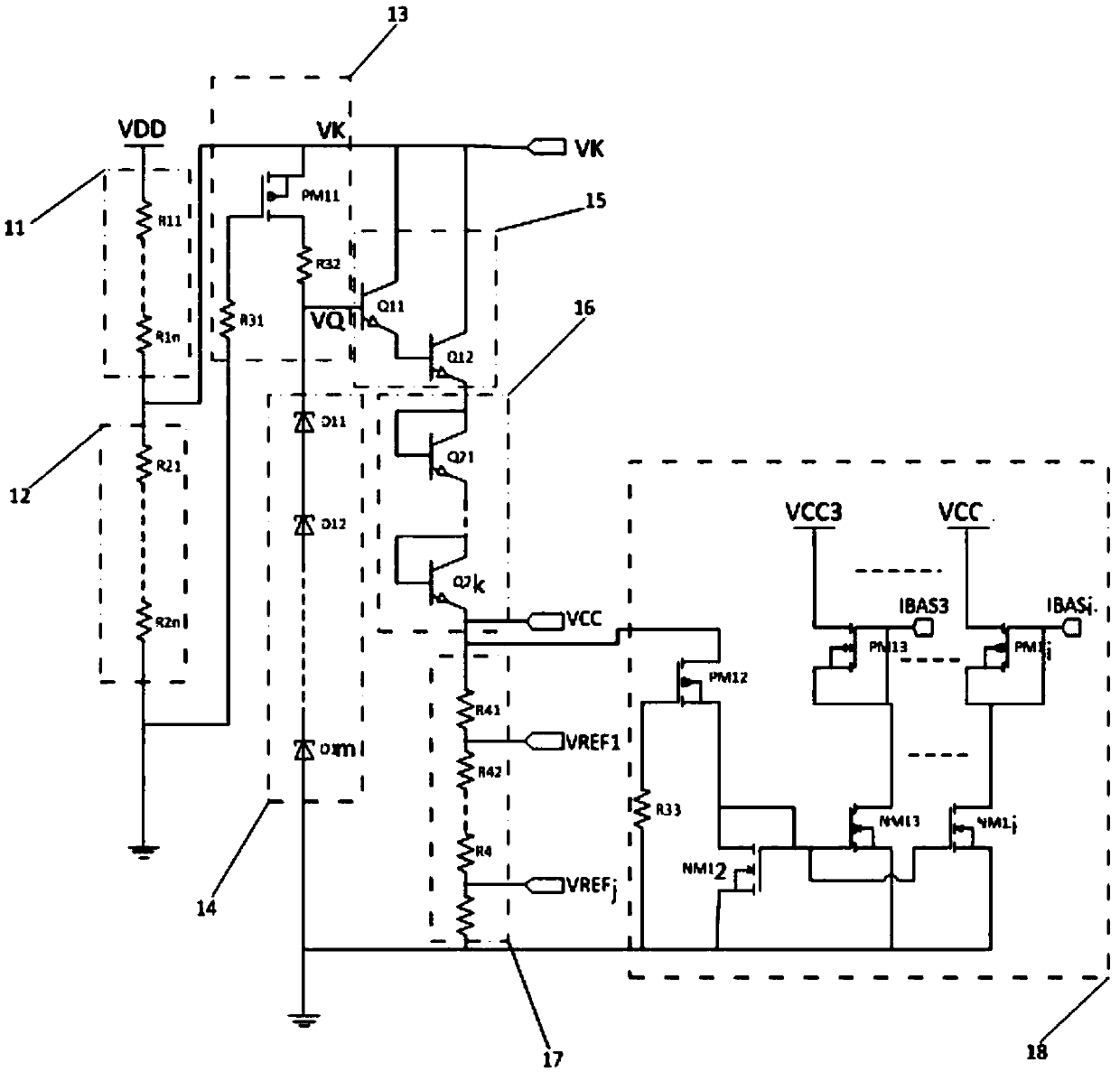
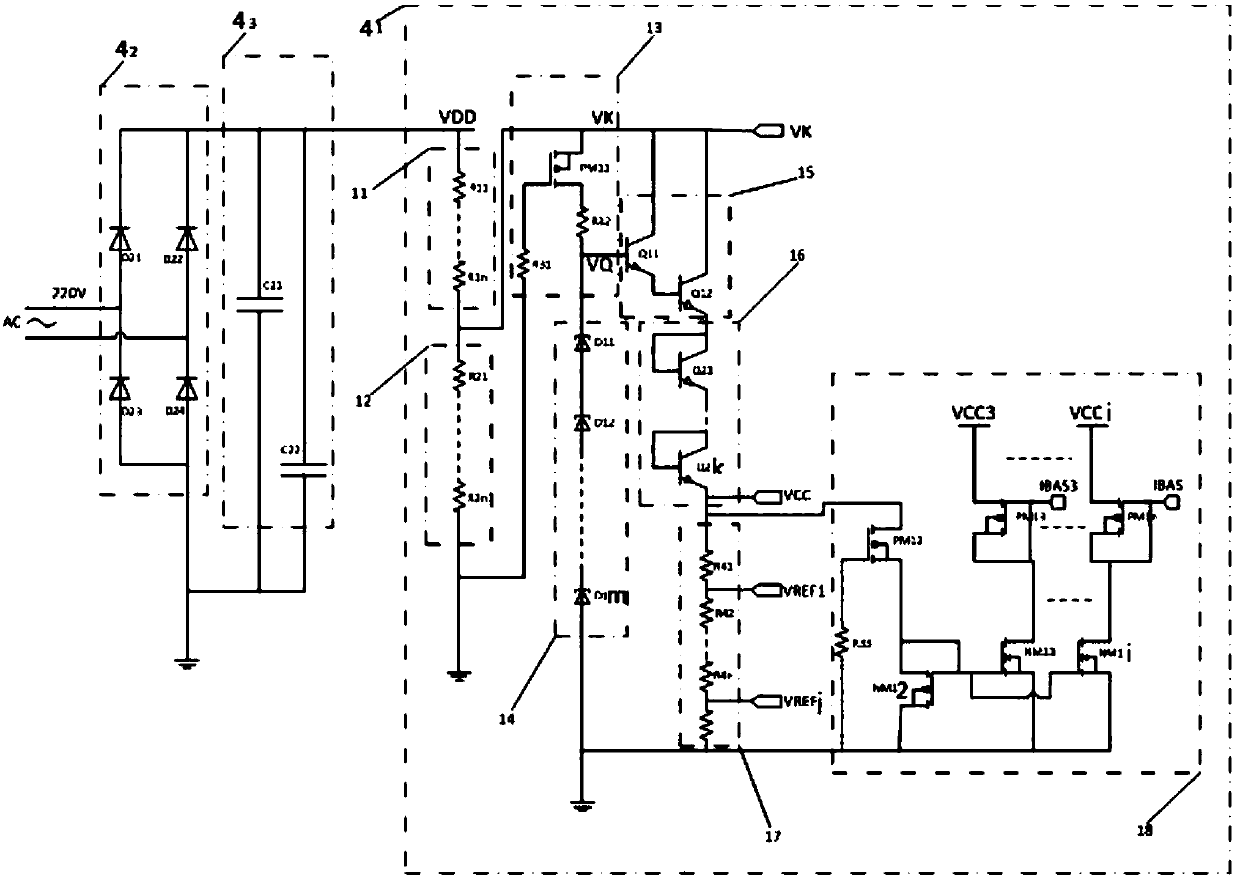
Step-down voltage dividing bias circuit based on in-well high-voltage high-precision polycrystalline resistor
ActiveCN109687869AHighly integratedReduce areaPhysical parameters compensation/preventionElectrical resistance and conductanceLow voltage
The invention discloses a step-down voltage dividing bias circuit based on an in-well high-voltage high-precision polycrystalline resistor. The bias circuit includes two high-voltage-resistance high-precision polycrystalline resistor voltage dividing circuits, voltage self-bias circuits, bipolar composite triodes, series connection voltage dividing triodes, a series connection resistor voltage dividing circuit and a current bias circuit. The two high-voltage-resistance high-precision polycrystalline resistor voltage dividing circuits are in series connection, and are used for obtaining high voltage from a high-voltage port VDD, and obtaining sampling voltage VK after voltage dividing and step-down; stable voltage VQ is generated after the sampling voltage VK passes through the voltage self-bias circuits for voltage regulation; constant low-voltage bias voltage VCC is output after the stable voltage VQ passes through the bipolar composite triodes and the series connection voltage dividing triodes for voltage step-down and fine-adjustment; reference voltage VREF of various values is obtained after the constant bias voltage VCC passes through the series connection resistor voltage dividing circuit for voltage dividing; and at the same time, the current bias circuit utilizes the constant bias voltage VCC to produce multiple stable bias currents IBAS. An entire bias circuit networkincreases a circuit integration degree, reduces a chip area, and reduces costs.
Owner:58TH RES INST OF CETC
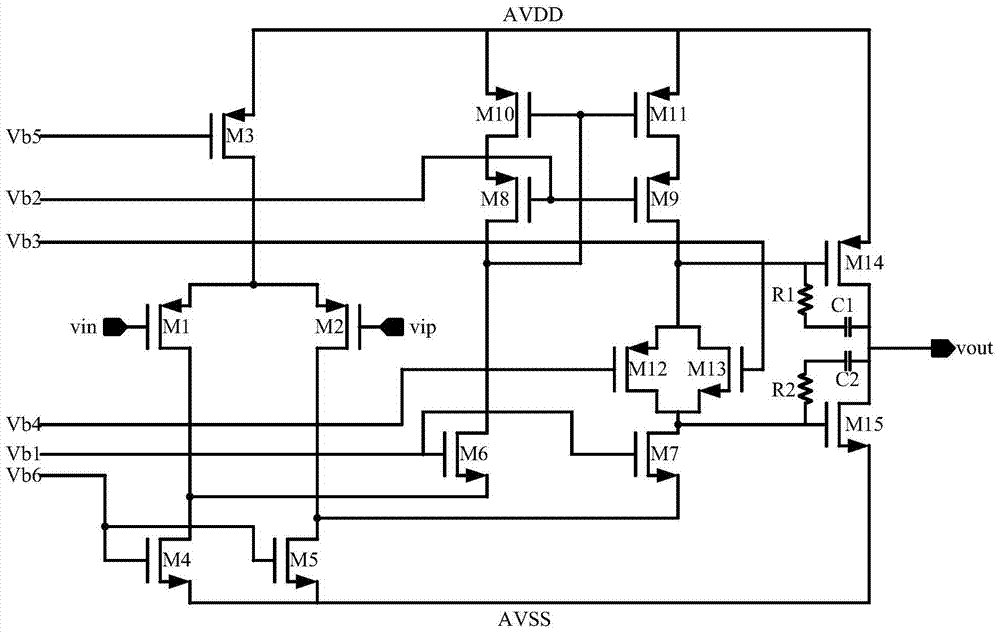
Operational Amplifier
ActiveCN104639071BStable bias voltageStrong drivePush-pull amplifiersPhase-splittersPush–pull outputClosed loop feedback
The invention discloses an operational amplifier, which includes a two-stage amplifying circuit and a bias circuit. The folded cascode amplifying circuit of the first stage can provide a high gain of more than 90dB for the circuit, and the push-pull output circuit of the second stage has Good drive capability, the bias voltage of the amplifying circuit is provided by the bias circuit using the bandgap reference circuit, which can make the bias voltage of the circuit very stable, and the characteristics of high gain and stable bias can make the circuit of the present invention be applied to high precision closed-loop feedback system.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Signal amplification circuit and active bias circuit
ActiveCN111200407AReduce the starting voltageRealize the zoom functionPower amplifiersAmplifier detailsRadio frequencyOperational amplifier
The embodiment of the invention provides a signal amplification circuit and an active bias circuit. The signal amplification circuit comprises the active bias circuit and a radio frequency amplification circuit; the active bias circuit comprises a first branch circuit and a second branch circuit connected with the first branch circuit in parallel; the second branch circuit comprises an operationalamplifier; and the active bias circuit outputs bias voltage through the operational amplifier; and the radio frequency amplification circuit is connected with the active bias circuit and is used foramplifying an input signal input into the signal amplification circuit under the action of the bias voltage. According to the invention, the dependence of the active bias circuit on the power supply voltage can be reduced, so that the starting voltage of the whole circuit is reduced; the starting work can be realized under lower power supply voltage; stable bias voltage is input into the radio frequency amplification circuit; and the amplification function of the radio frequency amplification circuit is realized.
Owner:GUANGZHOU HUIZHI MICROELECTRONICS
APD bias control circuit, photoelectric receiving circuit and bias control method
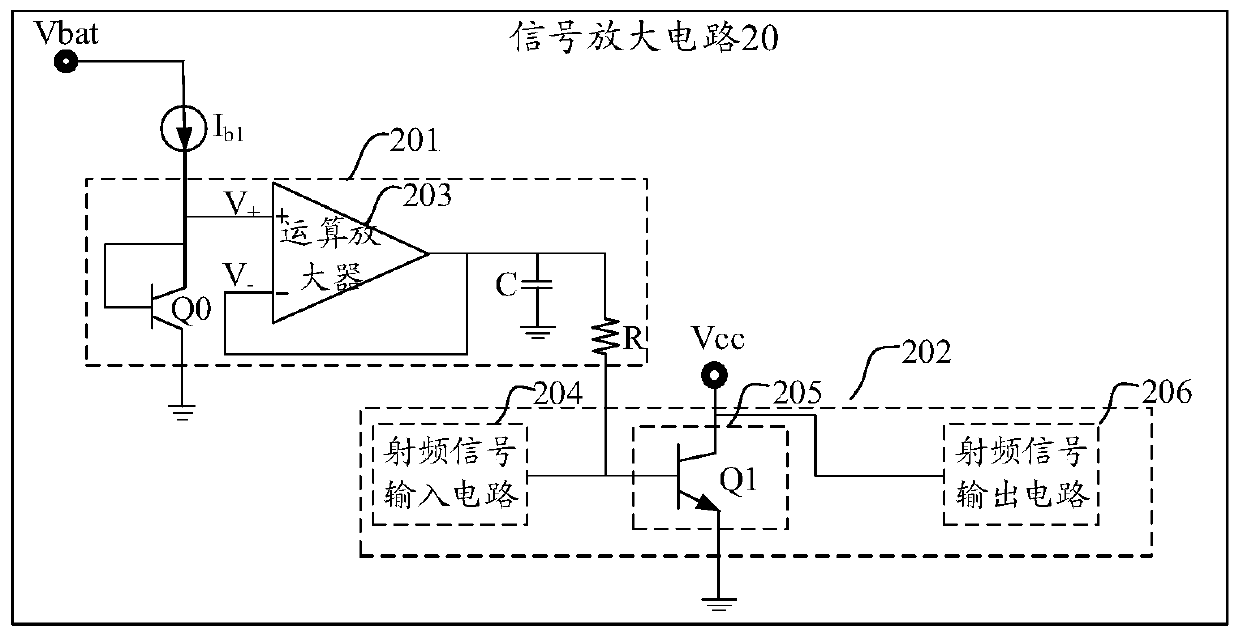
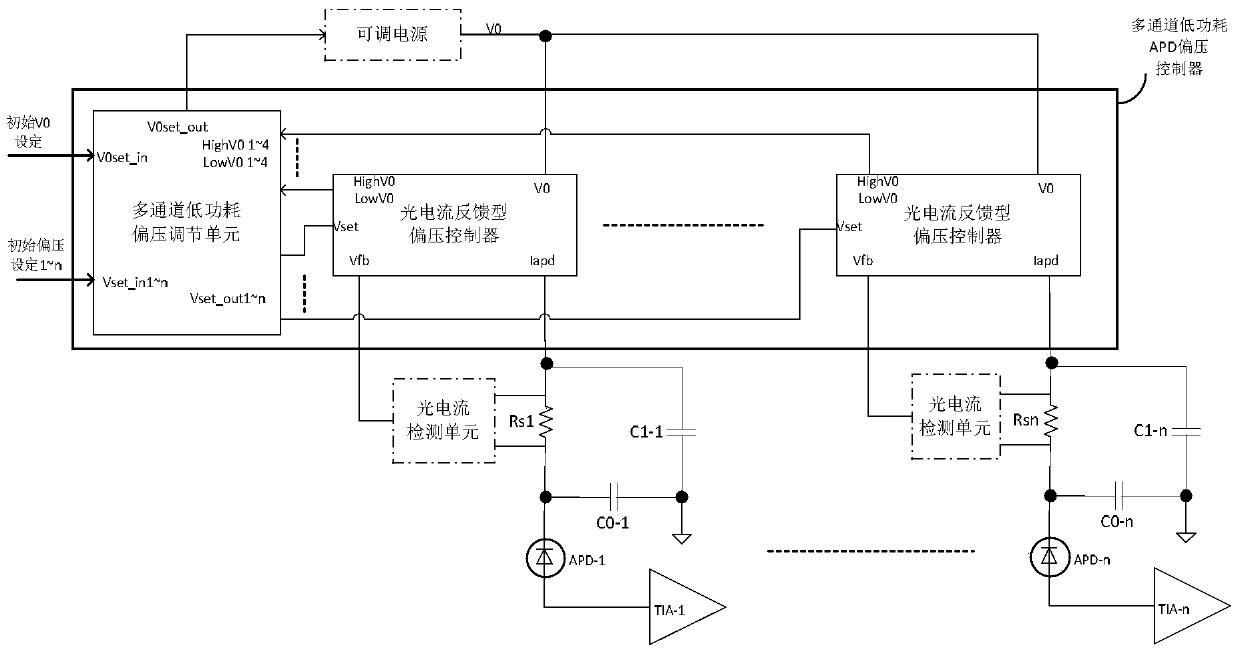
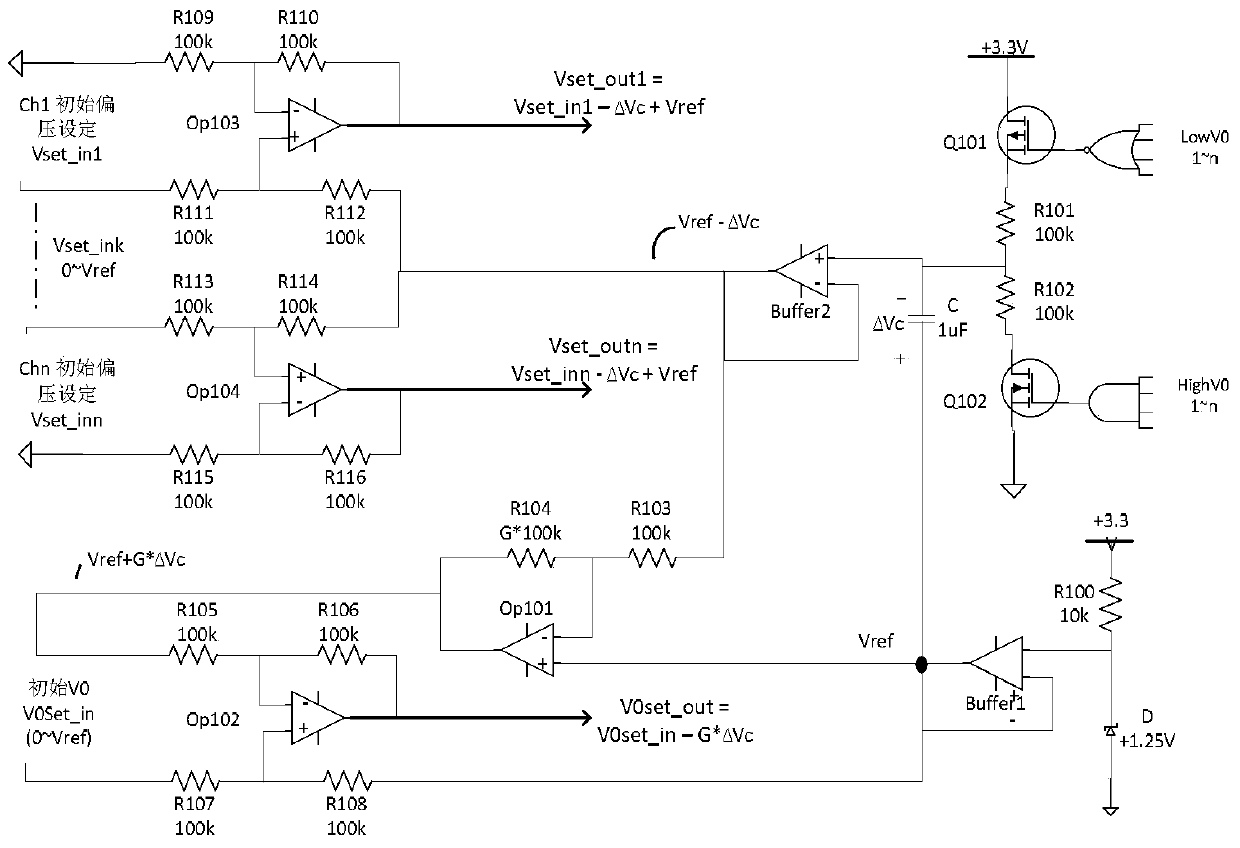
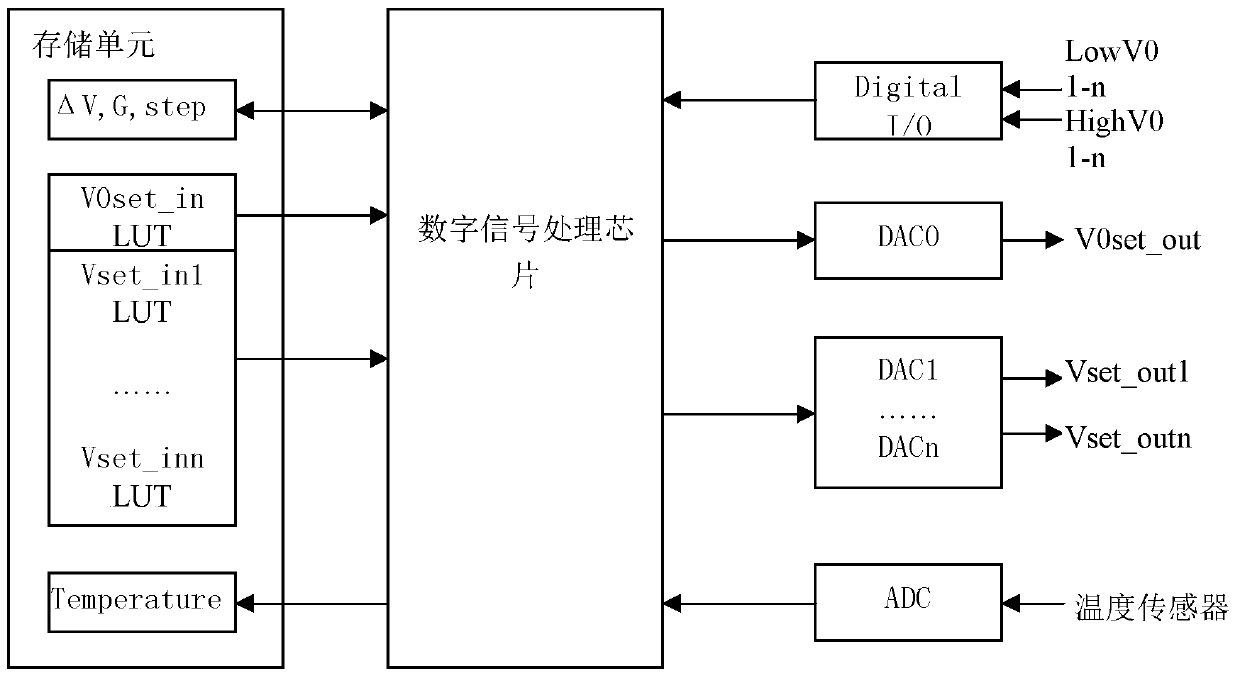
ActiveCN107342741BStable bias voltageMeet miniaturization requirementsAmplifiers controlled by lightElectromagnetic receiversControl signalMiniaturization
The invention provides an APD bias control circuit, a photoelectric receiving circuit and a bias control method. The APD bias control circuit comprises a bias regulation unit and a plurality of bias controllers, wherein the bias regulation unit is used for generating a supply voltage control signal and a bias control signal of each APD according to overvoltage state indication information and undervoltage state indication information transmitted by each bias controller; the plurality of bias controllers are connected with the plurality of APDs, used for receiving light current strength voltage signals corresponding to light current signals passing through the APDs connected with the bias controllers, and generating load voltage of the APDs connected with the bias controllers according to current supply voltage, the light current strength voltage signal and the bias control signal of a power module. According to the technical scheme of the circuits and method provided by the invention, the characteristics of few circuit element, low overall circuit power consumption and small wiring space occupied by circuit elements are achieved, and the requirement of miniaturization of the circuits is met, while multi-channel low power consumption APD bias control is achieved.
Owner:INNOLIGHT TECHNOLOGY (SUZHOU) LTD
Biasing circuit of power amplifier
InactiveCN102594271AStable bias voltageMeet needsAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention provides a biasing circuit of a power amplifier. The biasing circuit at least comprises a voltage generating module and a direct current biasing buffer outputting module, wherein the voltage generating module is connected with an external biasing voltage and used for processing the external biasing voltage to output stable voltage output, and the direct current biasing buffer outputting module is connected to an output end of the voltage generating module and used for outputting the stable voltage to the power amplifier through an emitter-follower in a manner of direct current buffer and providing a larger current to the power amplifier. The biasing circuit not only can provide the stable biasing voltage to the power amplifier so as to inhibit the biasing current of the power amplifier from changing greatly with temperature, but also can provide larger biasing current to the power amplifier so as to better meet the requirement of the power amplifier.
Owner:刘轶
MEMS microphone biasing circuit and MEMS microphone
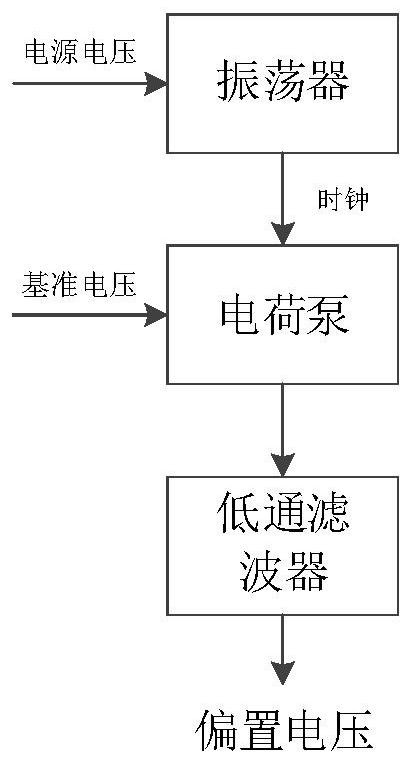
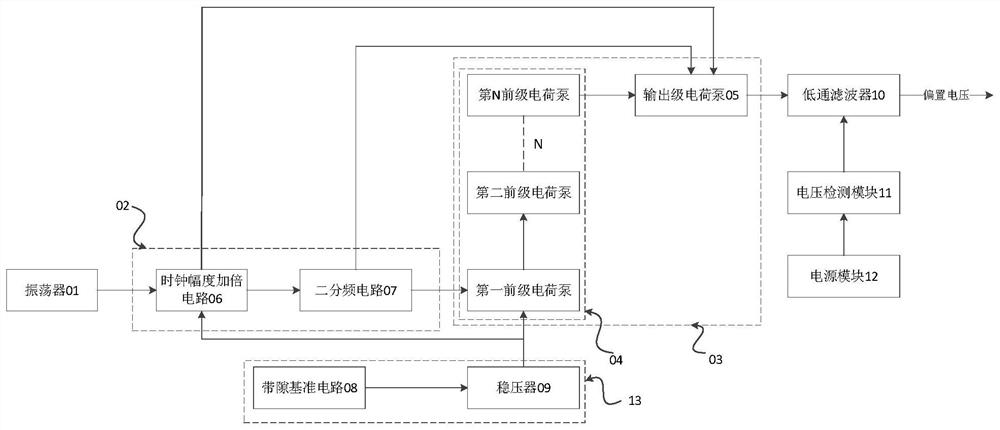
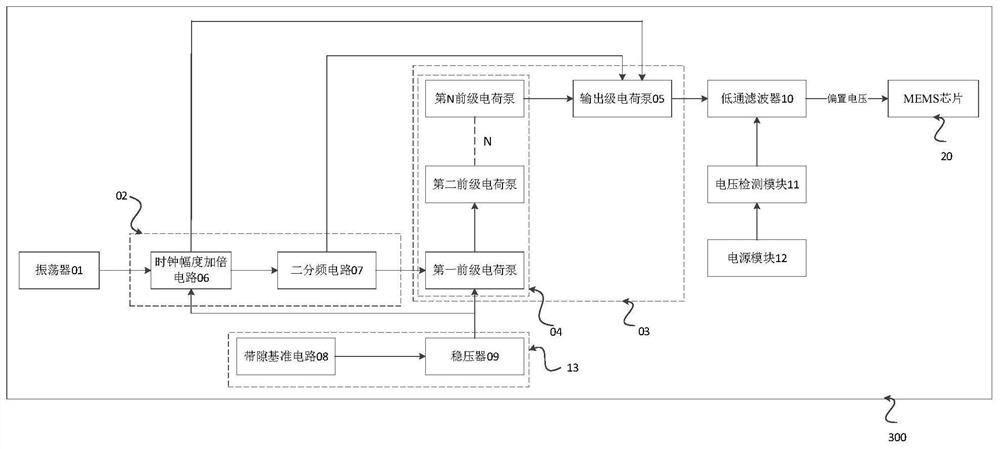
The invention relates to an MEMS microphone biasing circuit which is characterized by comprising an oscillator, a clock amplitude adjusting module, a reference voltage module and a charge pump set, the output end of the oscillator is connected with the input end of the clock amplitude adjusting module, and the oscillator is used for sending a clock signal to the clock amplitude adjusting module; the output end of the clock amplitude adjusting module is connected with the charge pump set, and the clock amplitude adjusting module is used for adjusting the amplitude of the clock signal; the reference voltage module is connected with the charge pump set and used for providing input voltage for operation of the charge pump set. The charge pump set comprises a preceding-stage charge pump and an output-stage charge pump, the preceding-stage charge pump is located at the input end of the charge pump set, the output-stage charge pump is located at the output end of the charge pump set, and the charge pump set is used for outputting bias voltage to be processed. And stable bias voltage can be output, so that the MEMS microphone has good sensitivity.
Owner:GOERTEK MICROELECTRONICS CO LTD
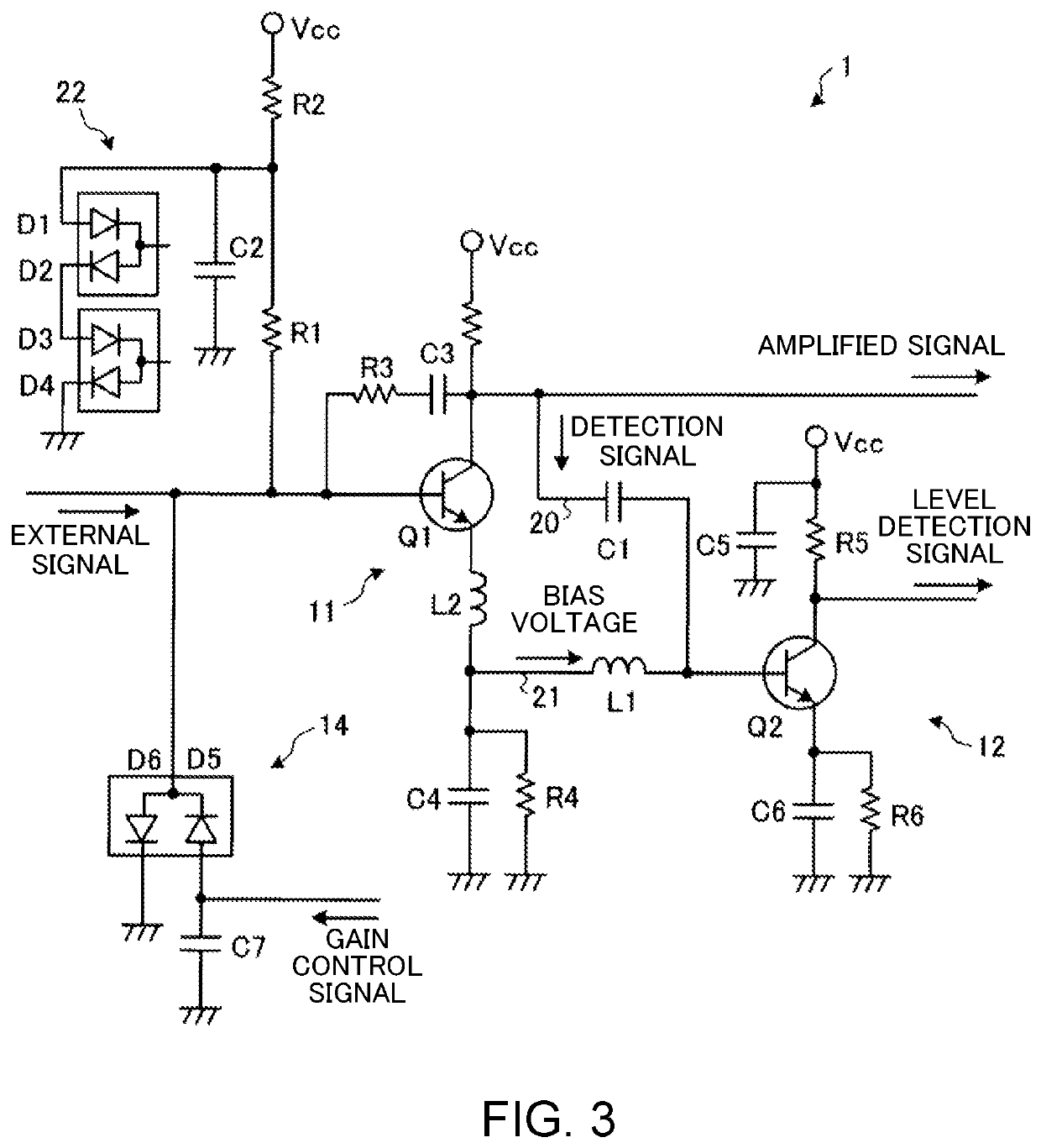
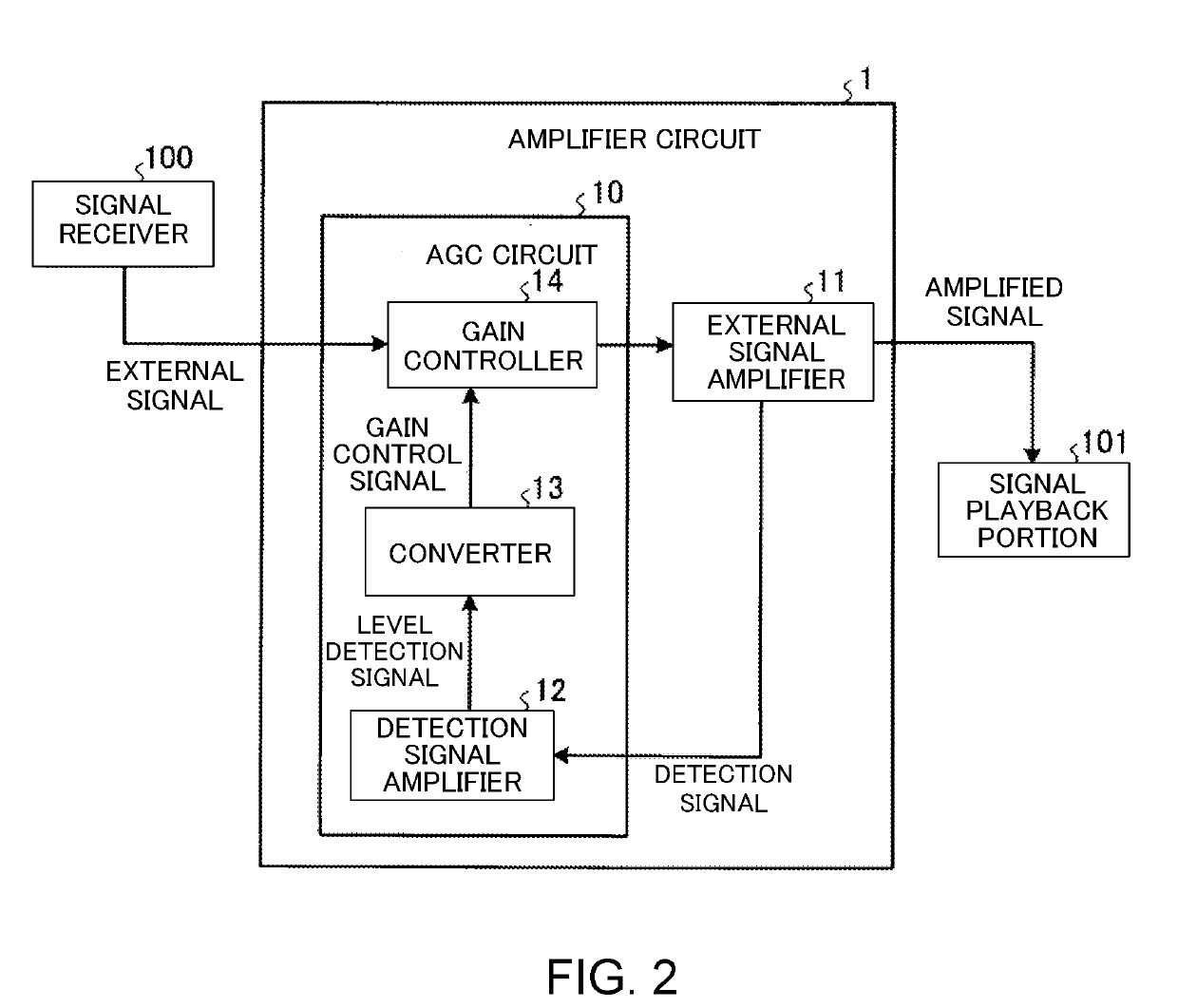
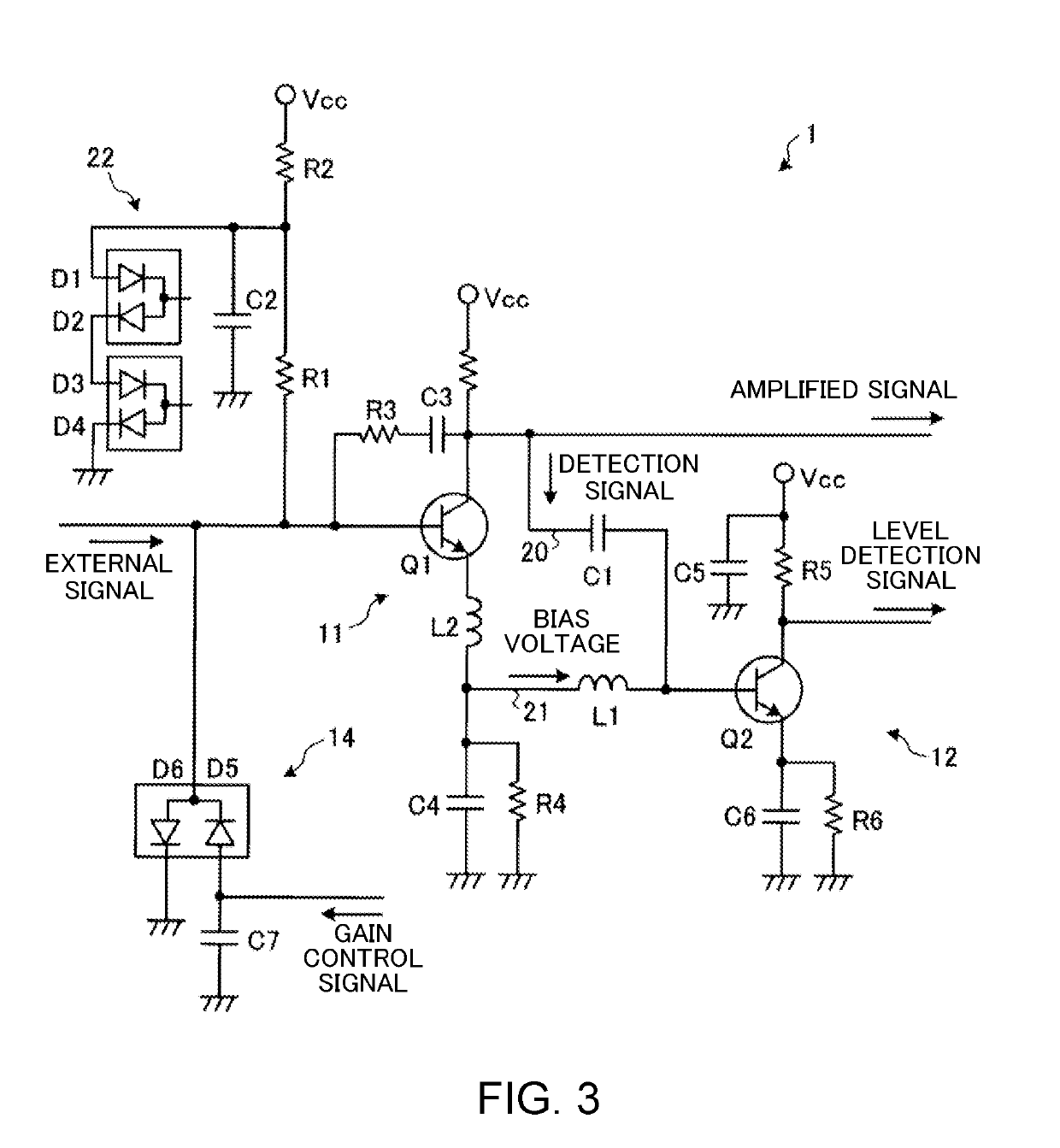
Amplifier circuit
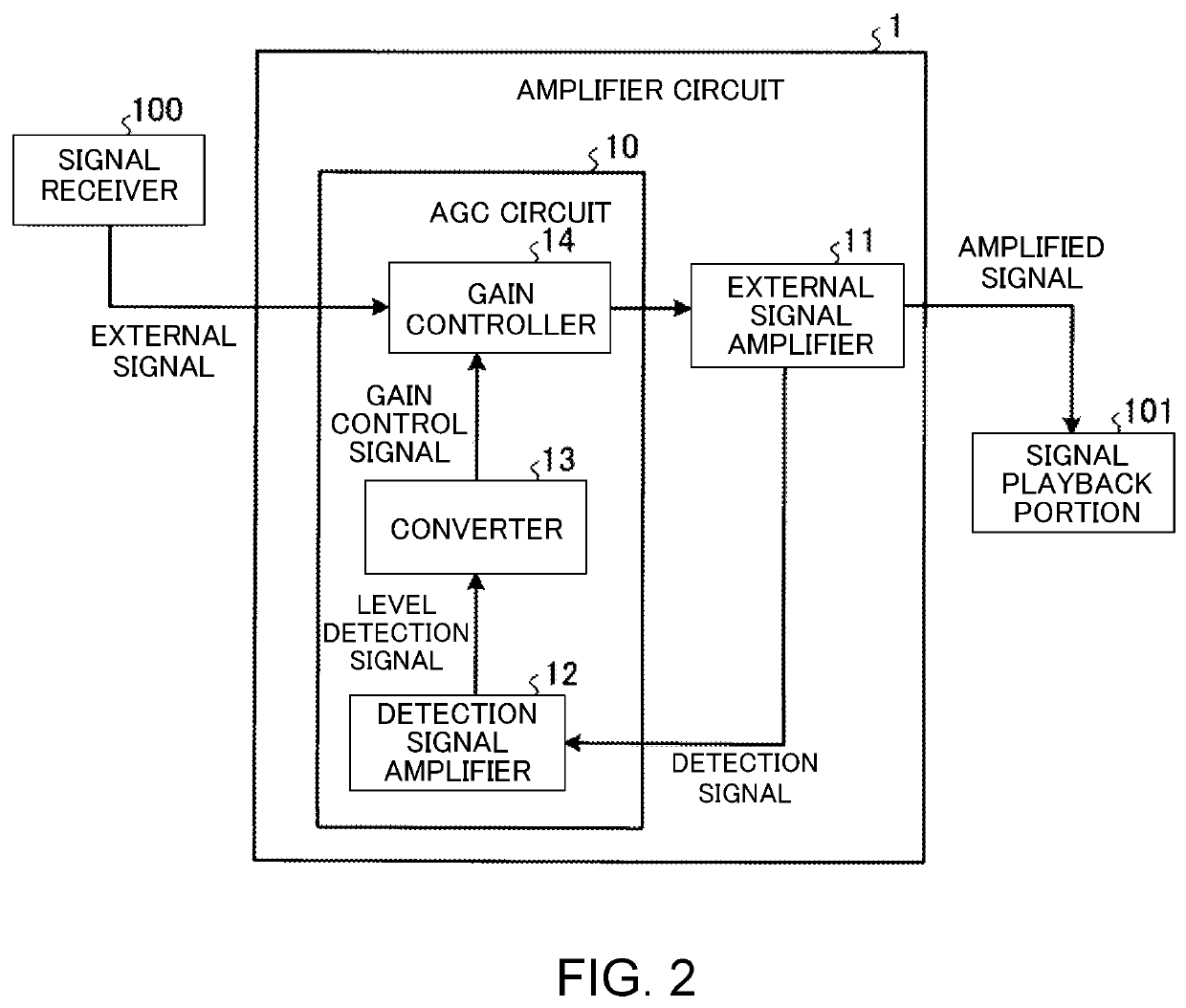
ActiveUS10715086B2Adequate levelStable bias voltageNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersSoftware engineeringHemt circuits
An amplifier circuit includes a first transistor, a second transistor, a first pathway and a second pathway. The first transistor amplifies an external signal that is input from outside the amplifier circuit. The second transistor amplifies a detection signal that detects a level of the external signal. The first pathway is connected between a collector of the first transistor and a base of the second transistor to supply the detection signal that is output from the collector of the first transistor to the base of the second transistor. The second pathway is connected between an emitter of the first transistor and the base of the second transistor to supply a bias voltage from the emitter of the first transistor to the base of the second transistor.
Owner:DENSO TEN LTD
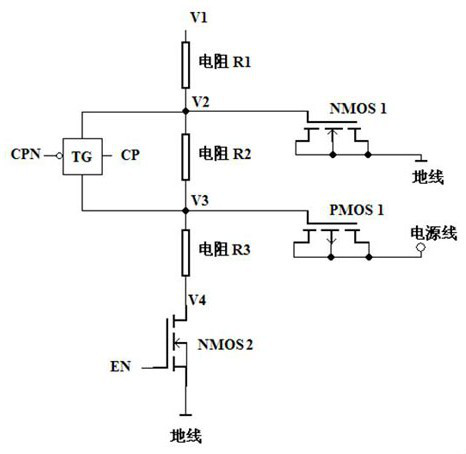
A circuit structure for lcd driving bias voltage
ActiveCN107170420BHighly integratedReduce areaStatic indicating devicesElectronic switchingTransmission gateHemt circuits
The invention discloses a circuit structure for LCD driving bias voltage, comprising resistor R1, resistor R2, resistor R3, a first NMOS transistor, a second NMOS transistor, a PMOS transistor and a transmission gate TG. The output ends of the resistor R1 are respectively It is connected to one end of the transmission gate TG, the input end of the resistor R2 and the input end of the first NMOS tube, and the output end of the resistor R2 is respectively connected to the other end of the transmission gate TG, the input end of the resistor R3 and the input end of the PMOS tube. The output end of R3 is connected to the input end of the second NMOS transistor. By adopting NMOS tube and PMOS tube, the present invention has stable bias voltage, good effect, simple structure, high circuit integration, small occupied chip area and low cost.
Owner:SHENZHEN HANGSHUN CHIP TECH DEV CO LTD
Bias circuit
ActiveCN113721691AStable bias voltageAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationPower amplifiersHemt circuitsControl theory
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD
Start circuit and voltage stabilizing circuit with start circuit
ActiveCN103440009BStable bias voltageImprove performanceElectric variable regulationElectrical resistance and conductanceLinear regulator
The invention discloses a start circuit which comprises a first NMOS (N-Mental-Oxide-Semiconductor) tube, a first resistor, a second resistor, a second NMOS tube and a third NMOS tube, wherein a grid electrode of the first NMOS tube is connected with a drain electrode and then is connected with a starting current source, and a source electrode of the first NMOS tube is earthed; one end of the first resistor is connected with the grid electrode of the first NMOS tube, and the other end of the first resistor is used as a bias voltage output end; a source electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with bias voltage, and a drain electrode of the second NMOS tube is connected with the second resistor; a grid electrode of the third NMOS tube is connected with a drain electrode and then is connected with a bias current source, a grid electrode of the third NMOS tube is connected with that of the second NMOS tube, and a source electrode of the third NMOS tube is connected with constant voltage. The invention further discloses a voltage stabilizing circuit with the start circuit. According to the voltage stabilizing circuit, the bias voltage is used as reference input voltage of a linear regulator, power supply voltage is generated to supply power to a bandgap reference source, and bandgap reference voltage is generated by the bandgap reference source, so as to be used as reference and then be fed back to regulate the bias voltage in the start circuit, so that the accurate and stable power supply voltage can be obtained to be used for internal circuits in a chip.
Owner:SILLUMIN SEMICON CO LTD
Auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit
ActiveCN101763133BImprove performanceStable bias voltageElectric variable regulationFeedback circuitsOperational amplifier
The invention discloses an auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit. The auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit comprises a first level shifter, a first operational amplifier and a bias voltage automatic correcting circuit, wherein the first level shifter is used for generating a first two-difference voltage; the first operational amplifier is connected with the first level shifter voltage; the firstoperational amplifier amplifies the first two-difference voltage and outputs an output voltage, and the output voltage is simultaneously connected to a feedback circuit; the feedback network samples the output voltage and outputs a feedback voltage to the first level shifter; and the bias voltage automatic correcting circuit is used for converting the variations of the technological parameters ofthe first level shifter into a differential voltage and outputting the differential voltage to the first level shifter and the first operational amplifier, thereby providing a bias voltage. The auto-bias voltage stabilizing circuit does not need to use the fixed bias voltage and can automatically obtain a stable bias voltage by utilizing the bias voltage automatic correcting circuit, so that the output voltage is free from the effects of the technological parameters, and the performance of the voltage stabilizing circuit is enhanced.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
Amplifier circuit
ActiveUS20190190454A1Automatic controlAdequate levelNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsHigh frequency amplifiersSoftware engineeringHemt circuits
An amplifier circuit includes a first transistor, a second transistor, a first pathway and a second pathway. The first transistor amplifies an external signal that is input from outside the amplifier circuit. The second transistor amplifies a detection signal that detects a level of the external signal. The first pathway is connected between a collector of the first transistor and a base of the second transistor to supply the detection signal that is output from the collector of the first transistor to the base of the second transistor. The second pathway is connected between an emitter of the first transistor and the base of the second transistor to supply a bias voltage from the emitter of the first transistor to the base of the second transistor.
Owner:DENSO TEN LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com