Signal amplification circuit and active bias circuit
A technology of signal amplifying circuit and bias circuit, which is applied to parts of amplifying devices, amplifiers, power amplifiers, etc., to achieve the effect of reducing dependence, realizing the amplification function, and reducing the starting voltage
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
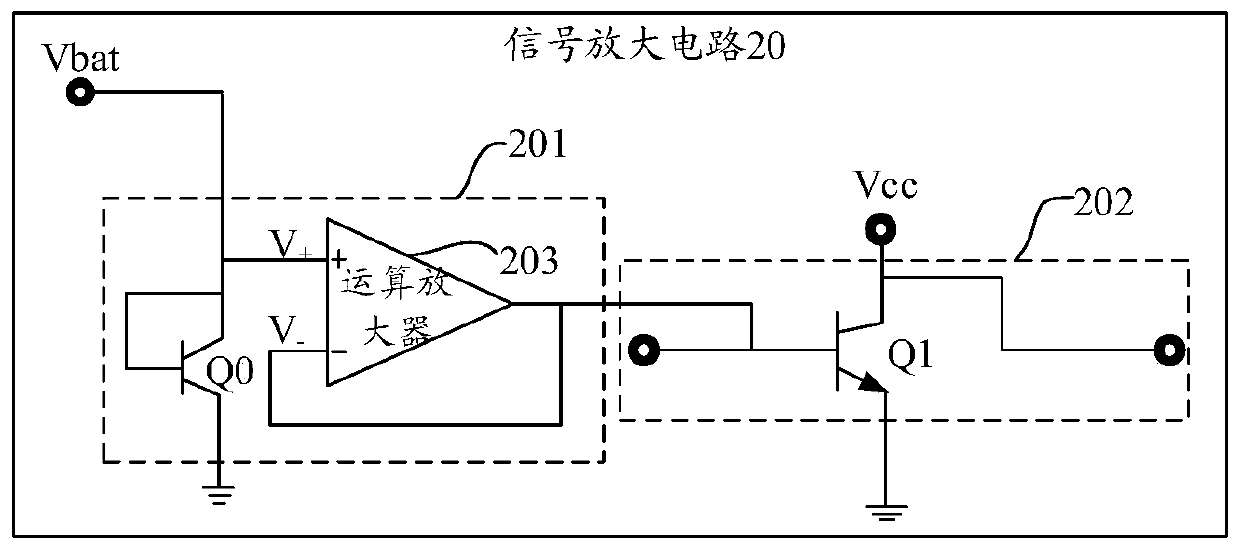
[0046] Such as figure 2 Shown is an optional circuit diagram of the signal amplifying circuit provided in the embodiment of the present application, and the signal amplifying circuit 20 includes an active bias circuit 201 and a radio frequency amplifying circuit 202 .
[0047] The active bias circuit 201 includes a first branch and a second branch connected in parallel with the first branch, the second branch includes an operational amplifier 203, and the active bias circuit 201 passes the operation Amplifier 203 outputs a bias voltage.
[0048] The first branch is formed by a first transistor Q0, and the emitter set of the first transistor Q0 is grounded. Here, the first transistor Q0 may be an NPN transistor or a PNP transistor. Taking Q0 as an NPN transistor as an example, the base and collector of the transistor Q0 in the first branch are short-circuited, and it is used as a diode in the circuit to provide the bias current output by the entire active bias circuit.
[004...
Embodiment 2
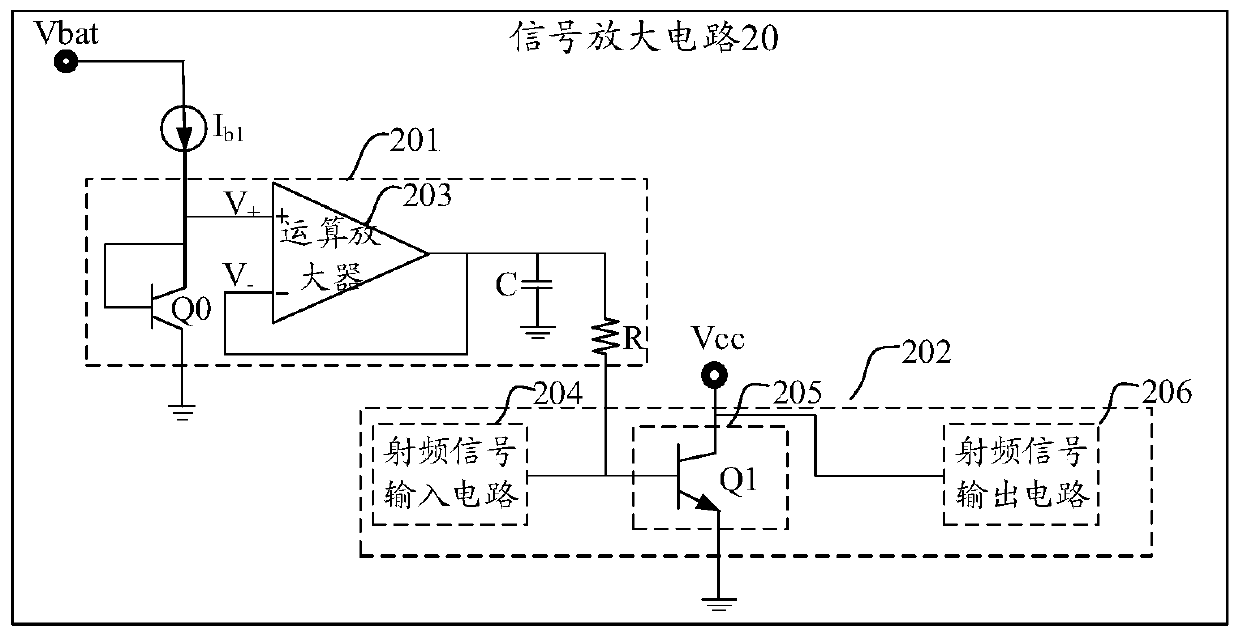
[0055] Such as image 3 Shown is another optional circuit diagram of the signal amplifying circuit provided by the embodiment of the present application. The signal amplifying circuit 20 includes an active bias circuit 201 and a radio frequency amplifying circuit 202 .
[0056] The active bias circuit 201 includes a first branch and a second branch connected in parallel with the first branch, the second branch includes an operational amplifier 203, and the active bias circuit 201 passes the operation Amplifier 203 outputs a bias voltage.
[0057] The first branch is composed of a first transistor Q0, and the emitter set of the first transistor Q0 is grounded, and the first transistor Q0 is used to realize the current output function in the bias circuit.
[0058] The second branch is used to provide a bias voltage to the RF amplifier circuit 202 .
[0059] In some embodiments, the active bias circuit 201 also includes a constant current source I b1 ; The constant current sou...
Embodiment 3
[0069] An embodiment of the present application provides a signal amplifying circuit, and the signal amplifying circuit includes an active bias circuit and a radio frequency amplifying circuit. The active bias circuit includes a first branch and a second branch connected in parallel with the first branch, the second branch includes an operational amplifier 203, and the active bias circuit outputs through the operational amplifier 203 Bias voltage; the first branch is used to realize the current output function in the bias circuit. The second branch is used to provide a bias voltage to the RF amplifier circuit 202 .
[0070] Such as Figure 4 Shown is a circuit diagram of an operational amplifier provided in the embodiment of the present application, and the operational amplifier 203 in the second branch includes a first voltage stabilizing branch 401 and a second voltage stabilizing branch 402 .
[0071] The first voltage stabilizing branch 401 includes a first transistor Q5...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com