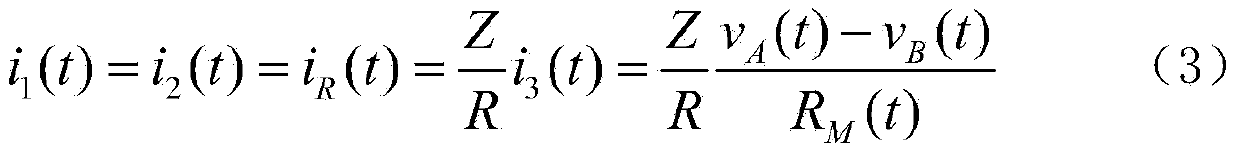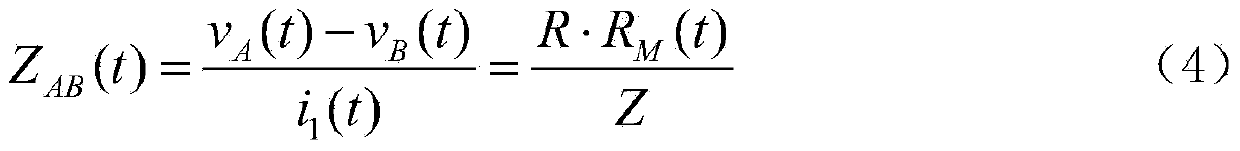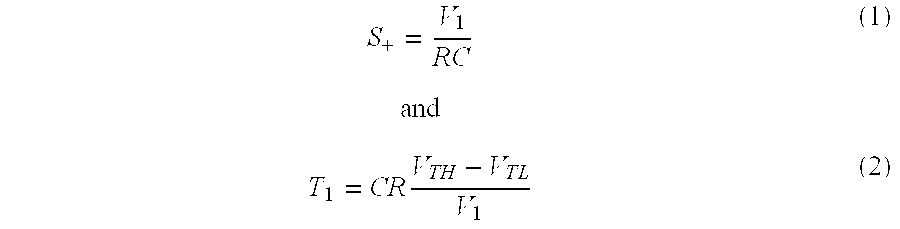Patents
Literature
85 results about "Current conveyor" patented technology
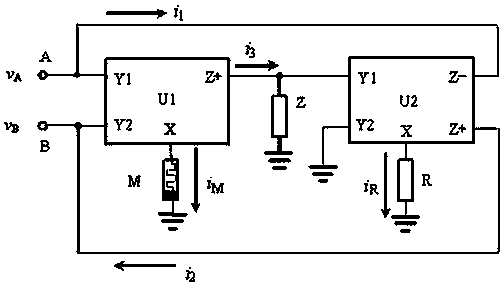
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
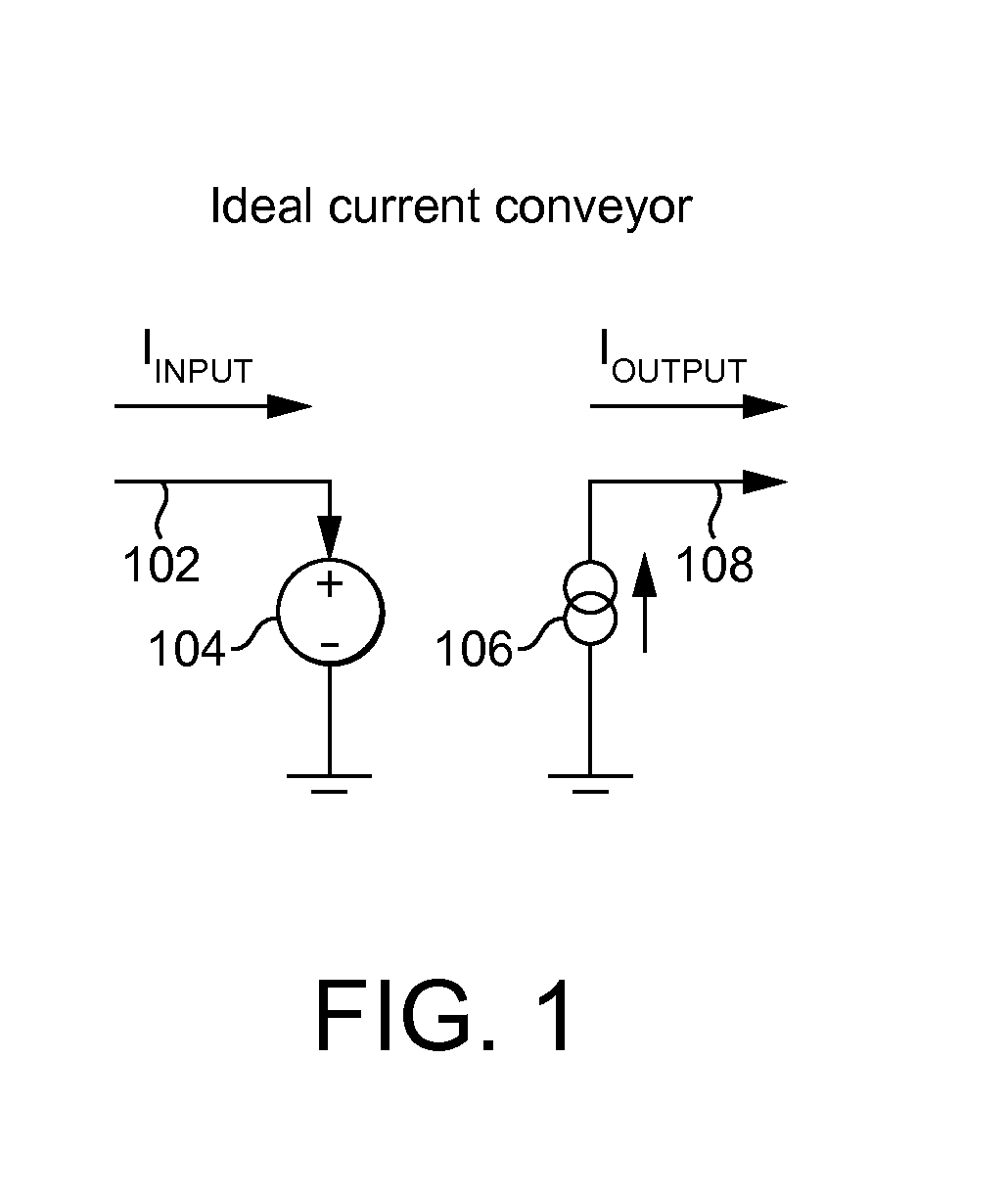
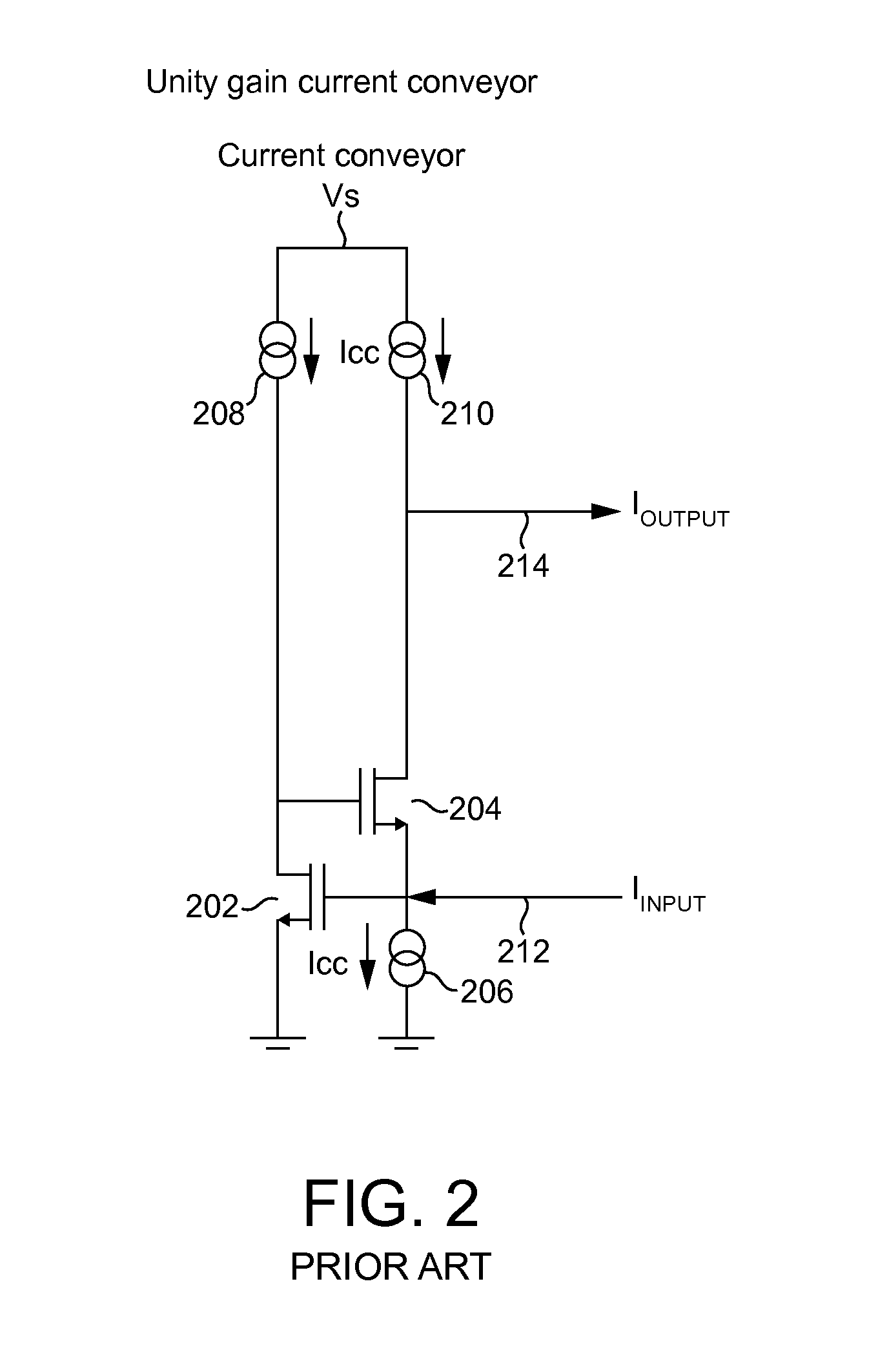
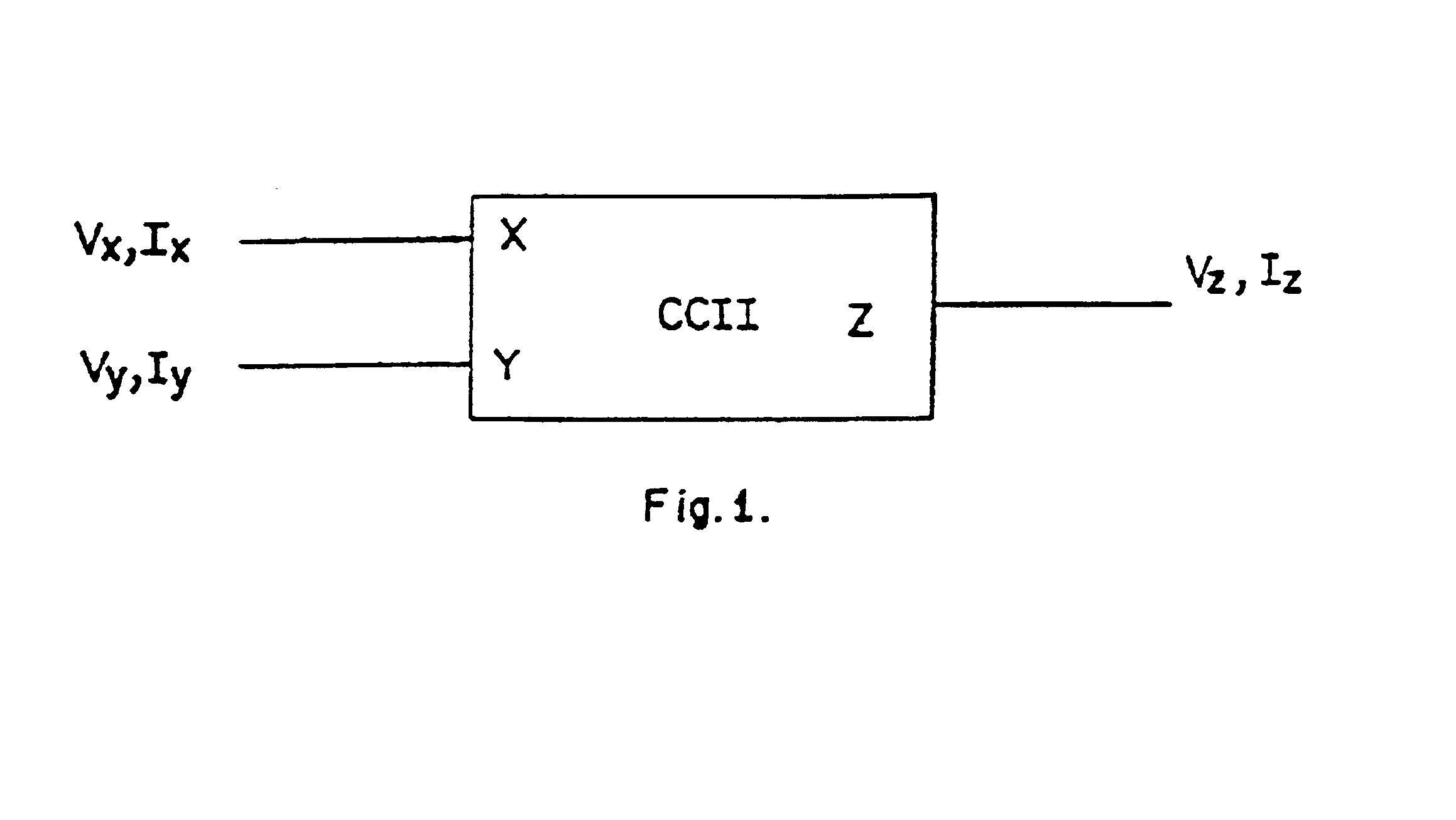
A current conveyor is an abstraction for a three terminal analogue electronic device. It is a form of electronic amplifier with unity gain. There are three versions of generations of the idealised device, CCI, CCII and CCIII. When configured with other circuit elements, real current conveyors can perform many analogue signal processing functions, in a similar manner to the way op-amps and the ideal concept of the op-amp are used.
Sensor array with high linearity
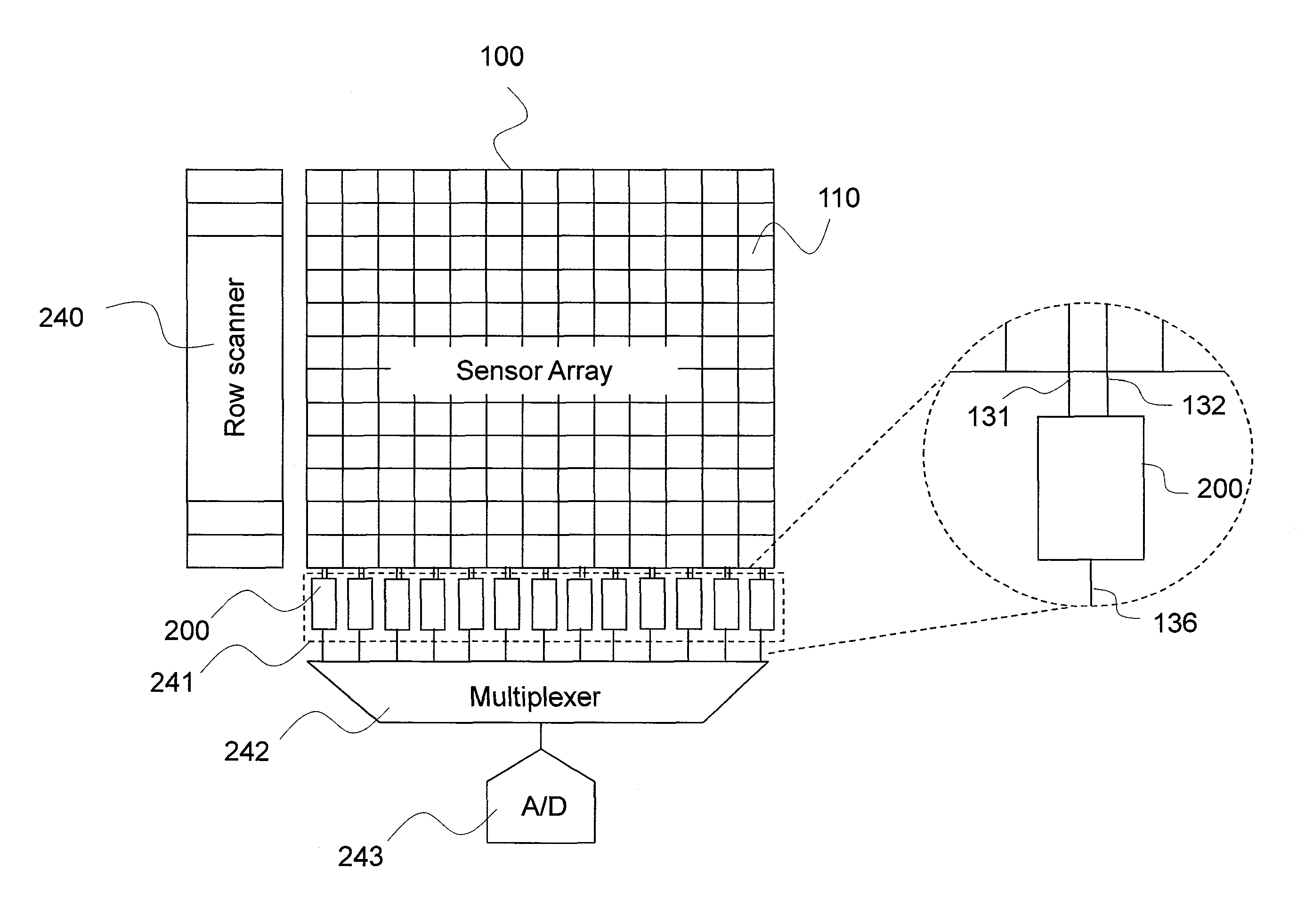
InactiveUS20130082936A1Stable bias voltageReduce dependenceTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesSensor arrayPower flow
A sensor array includes a plurality of pixel sensor circuits; and a current-mode readout circuit to sample signals generated in each pixel sensor circuit; and addressing circuitry to individually select each pixel sensor circuit. Each pixel sensor circuit includes: a transducer and an amplifying element coupled to the transducer and configured to output a signal current which varies as a function of a measured physical property. The current-mode readout circuit includes: a sense signal line coupled to each of the amplifying elements in order to monitor the voltage presented across the amplifying element of the selected pixel sensor circuit; a drive signal line coupled to an output of each of the amplifying elements in order to provide a constant bias voltage to the amplifying element of the selected pixel sensor circuit; and a current conveyor circuit coupled to the sense signal line and drive signal line.
Owner:SHARP KK
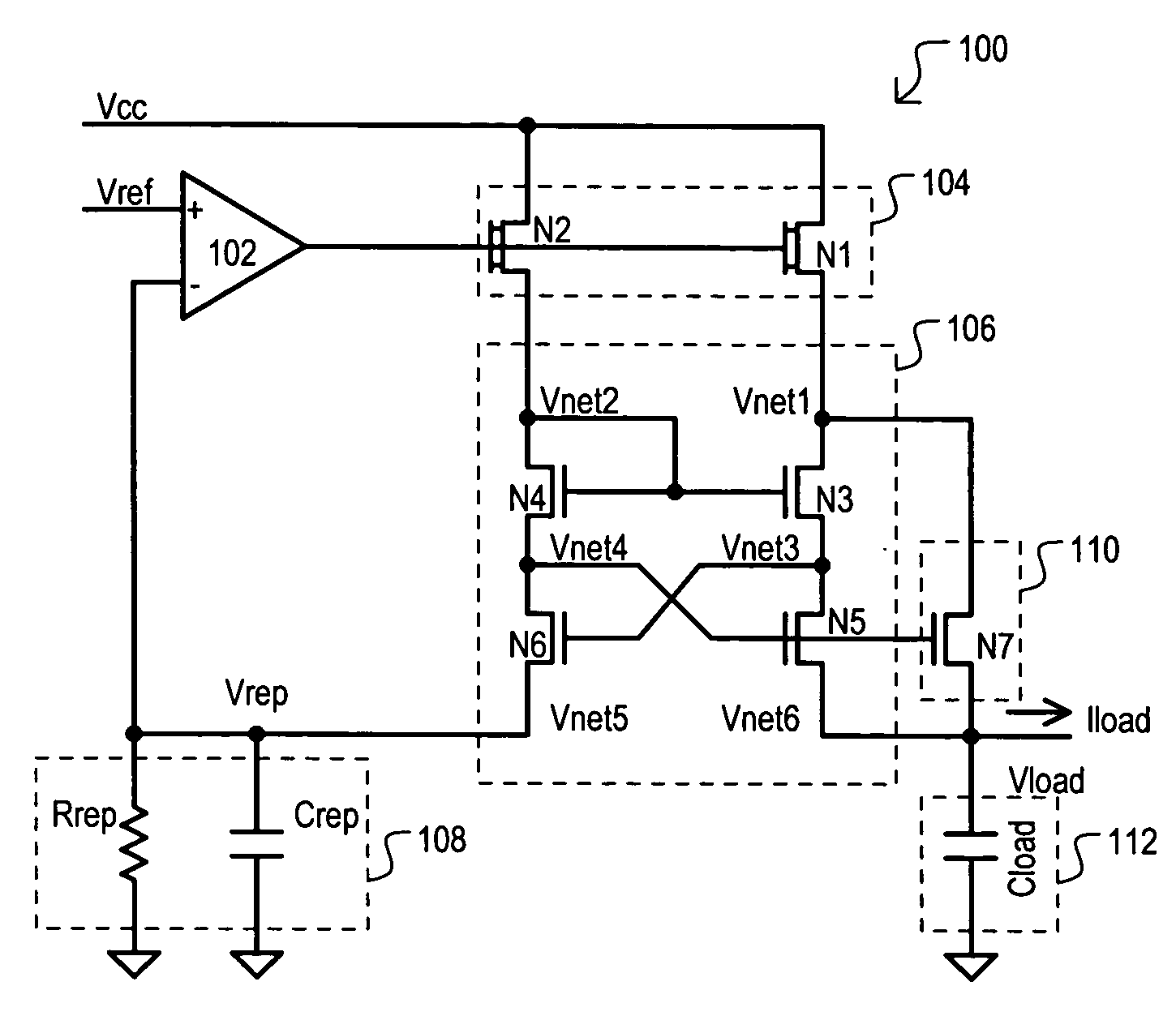
Replica biased voltage regulator
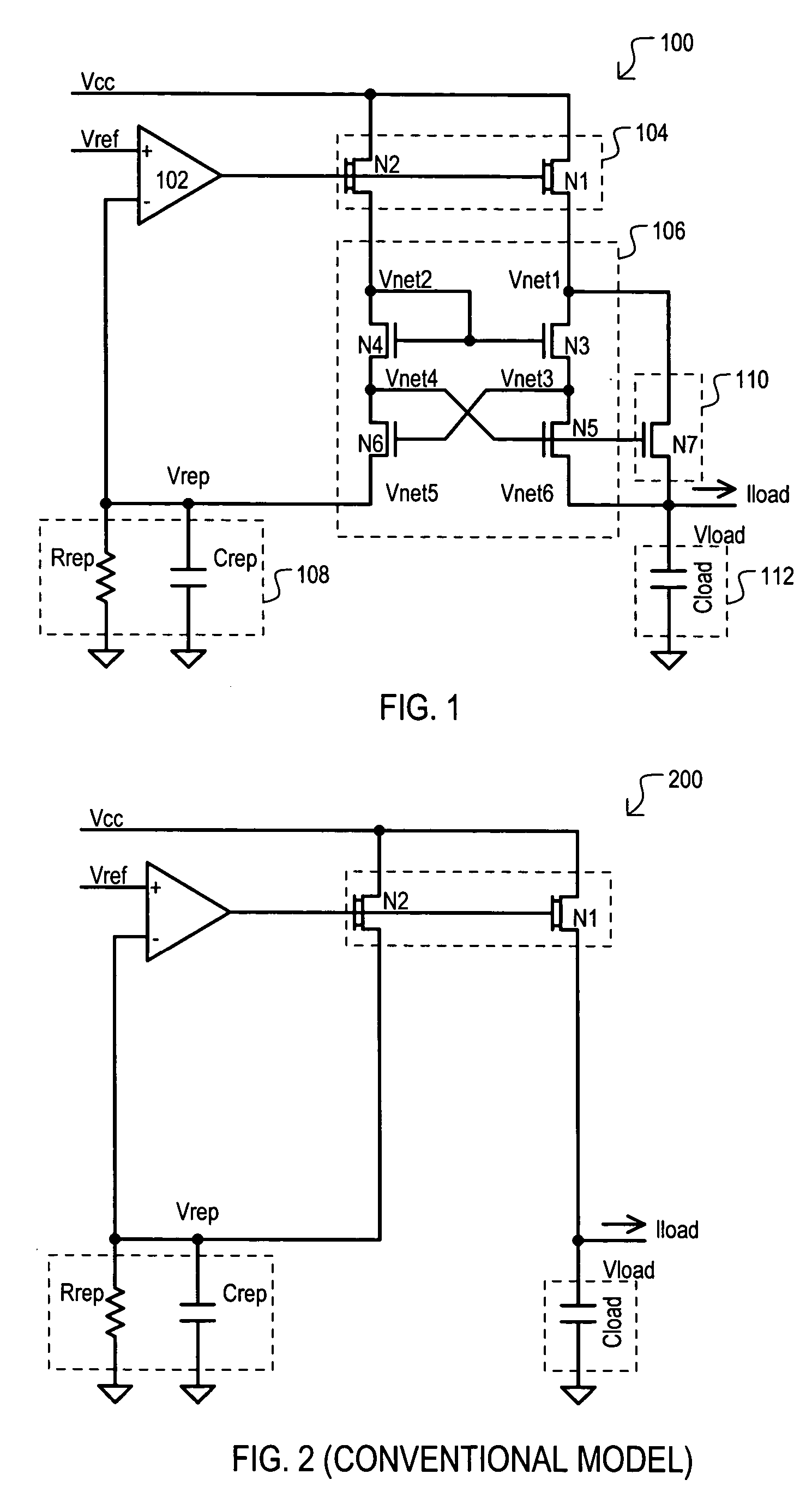
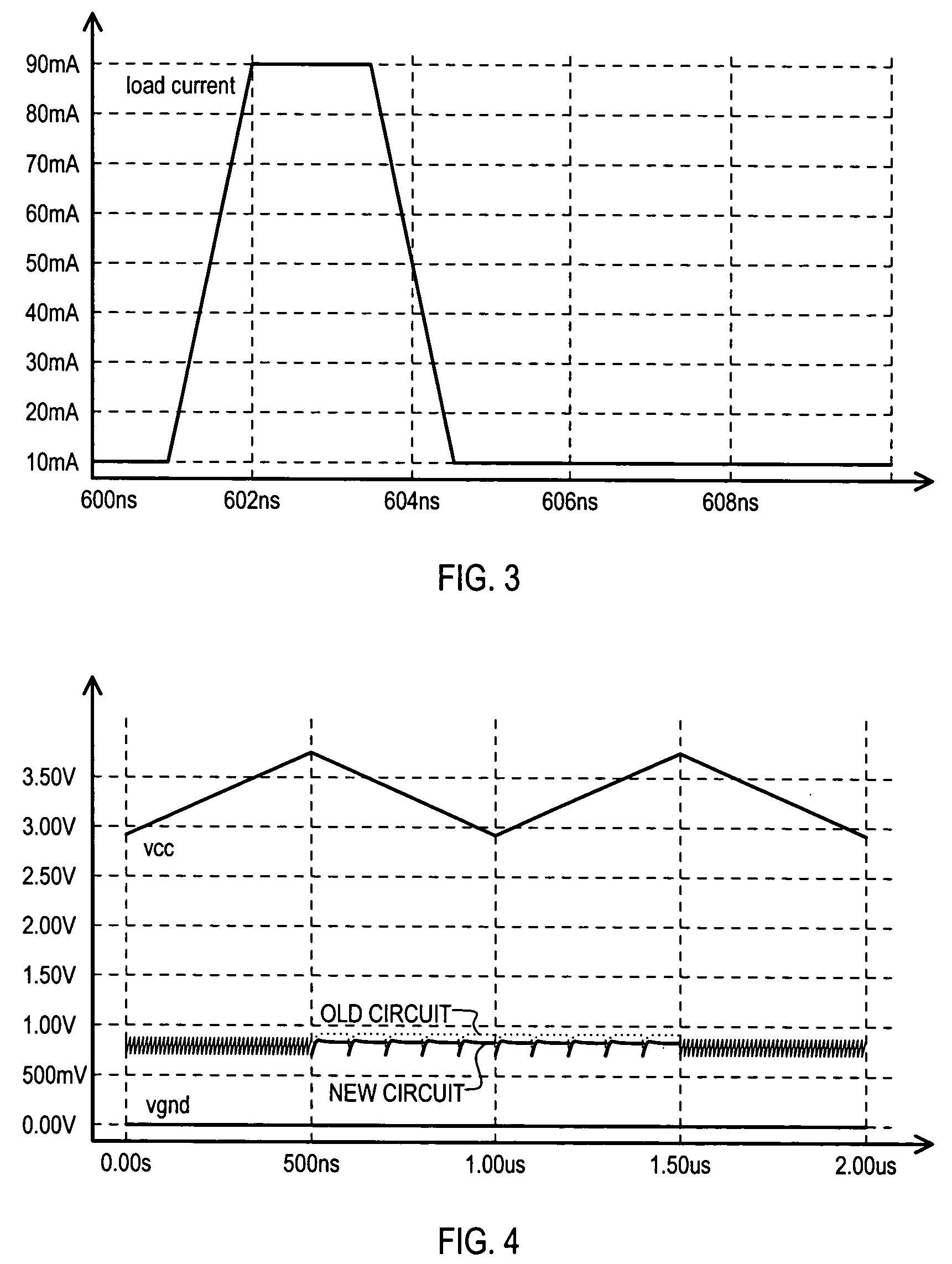
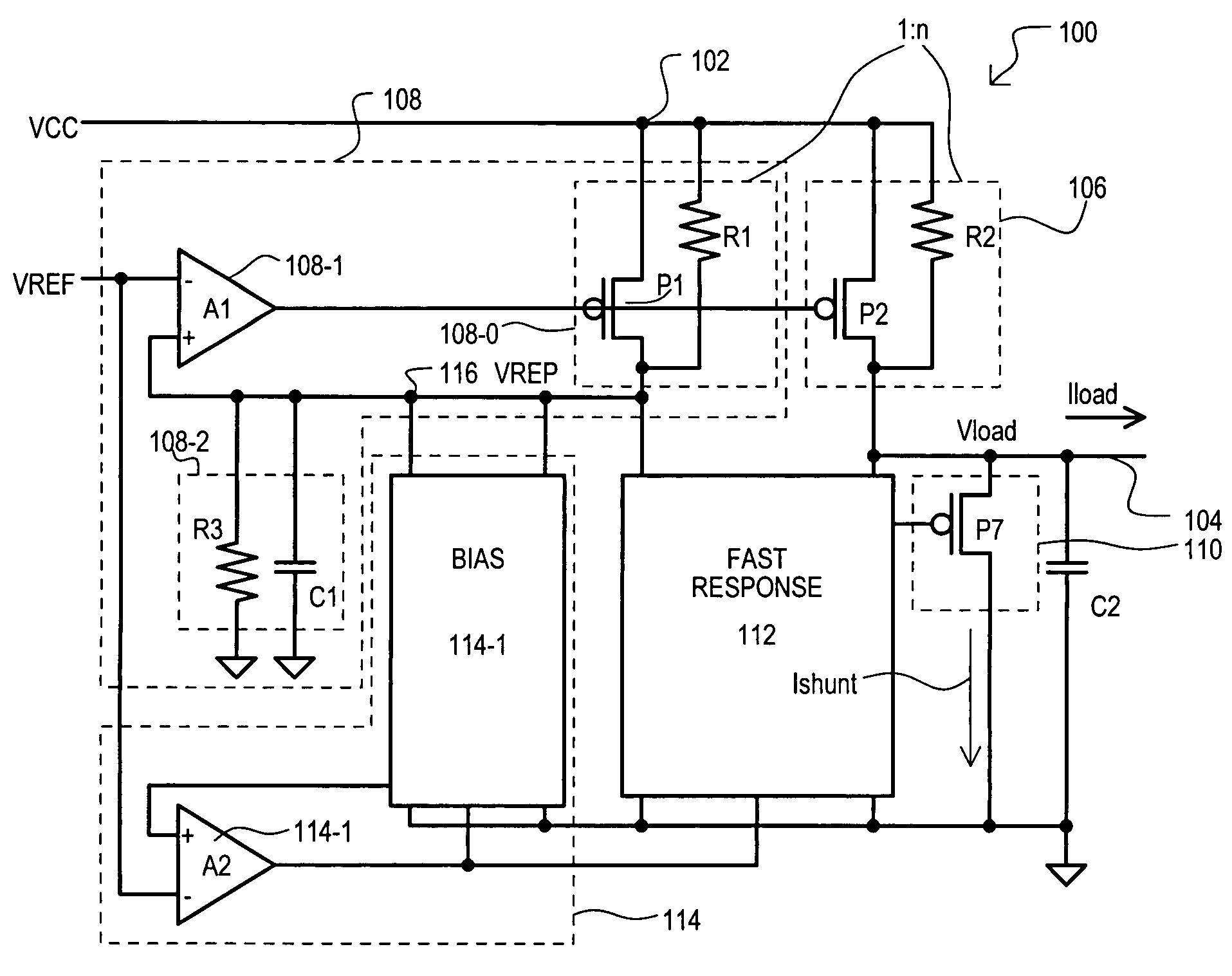
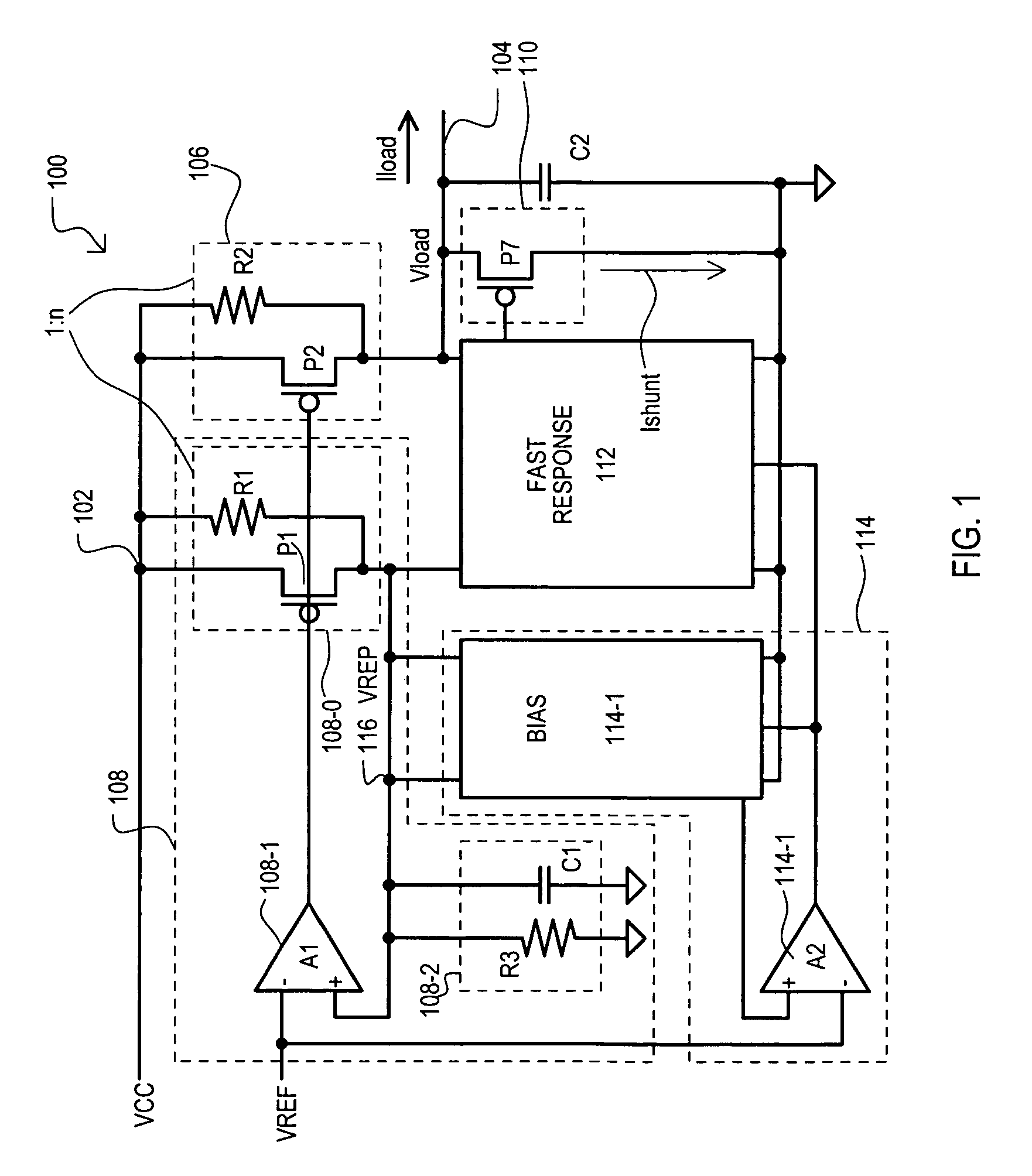
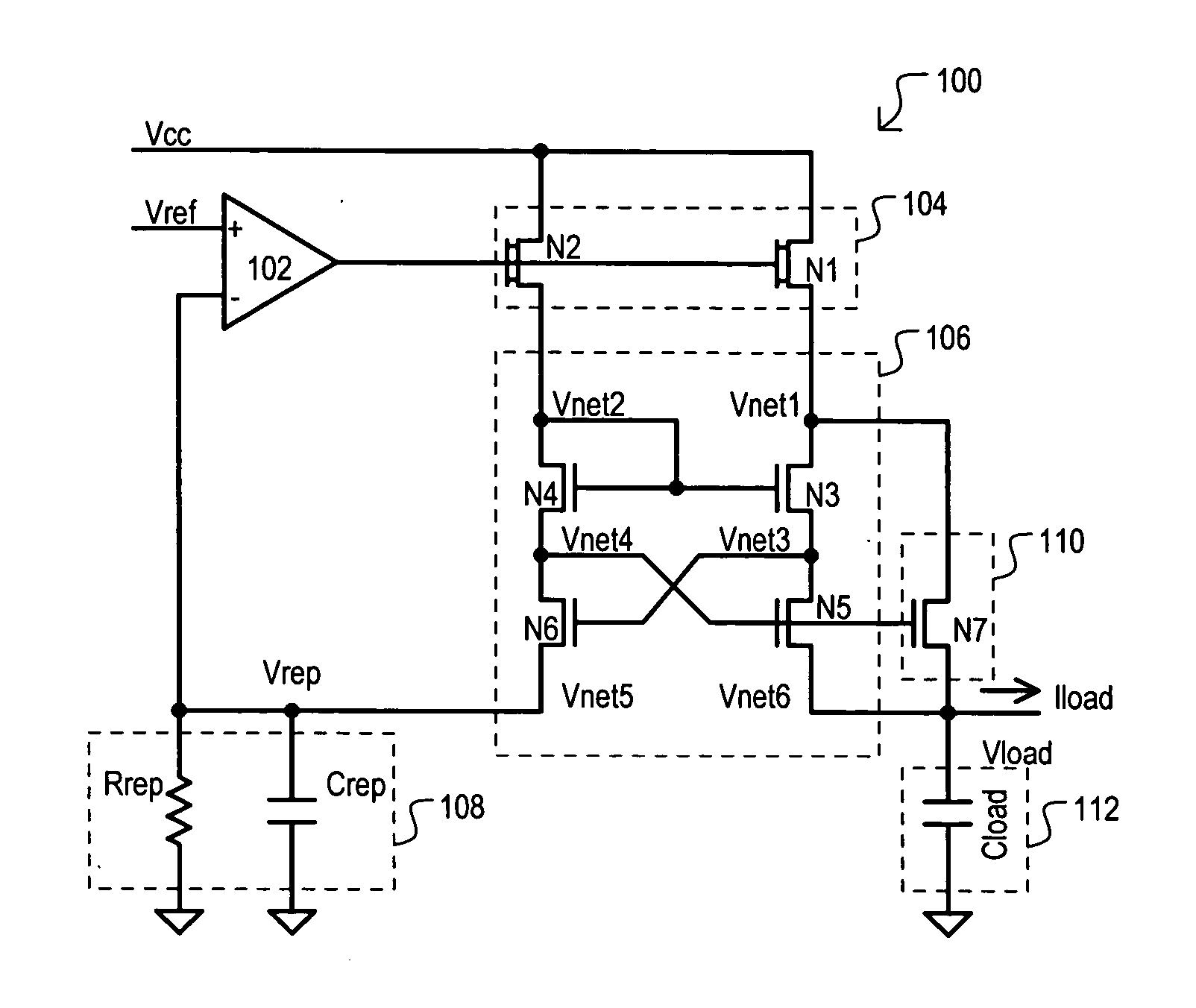
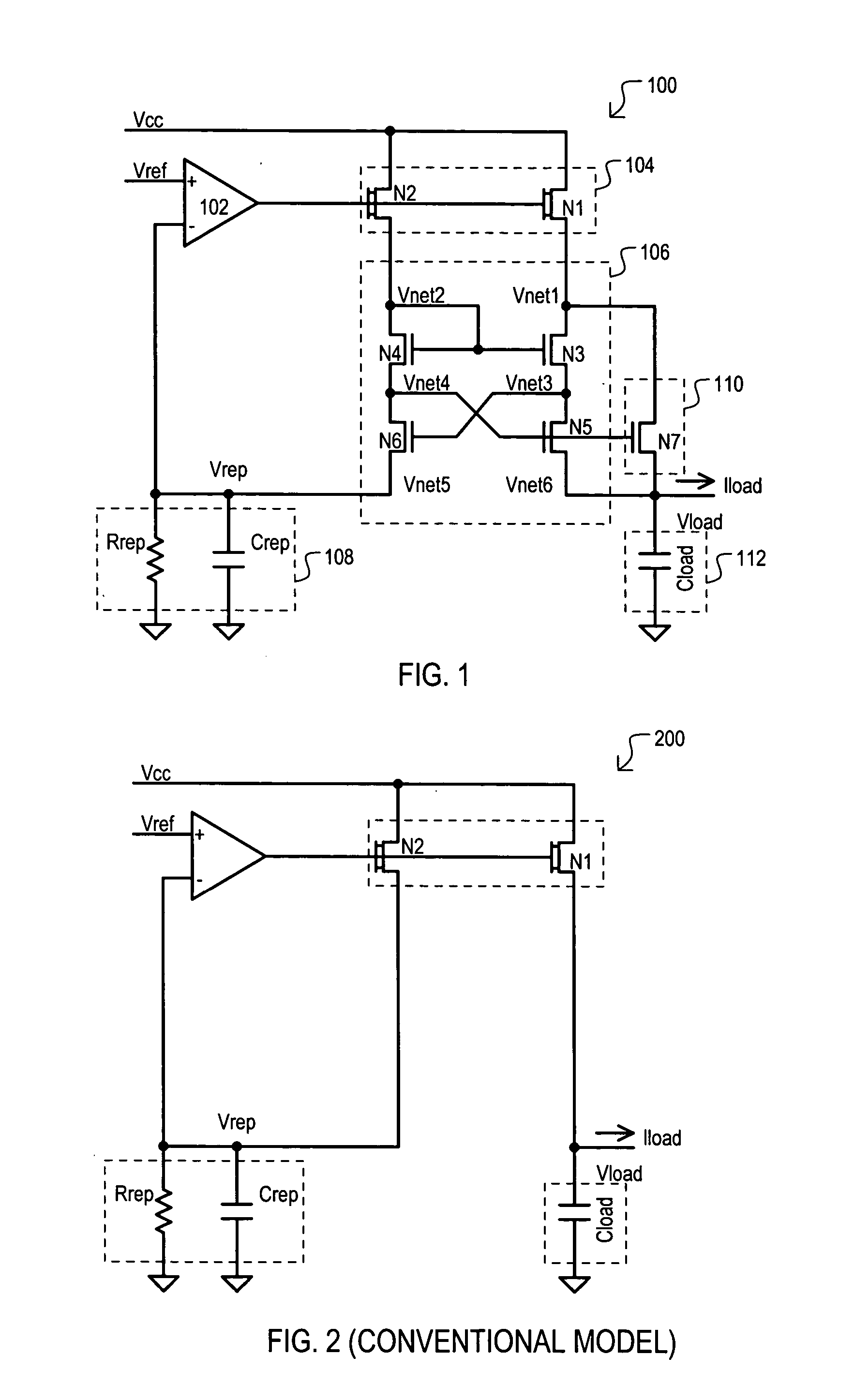
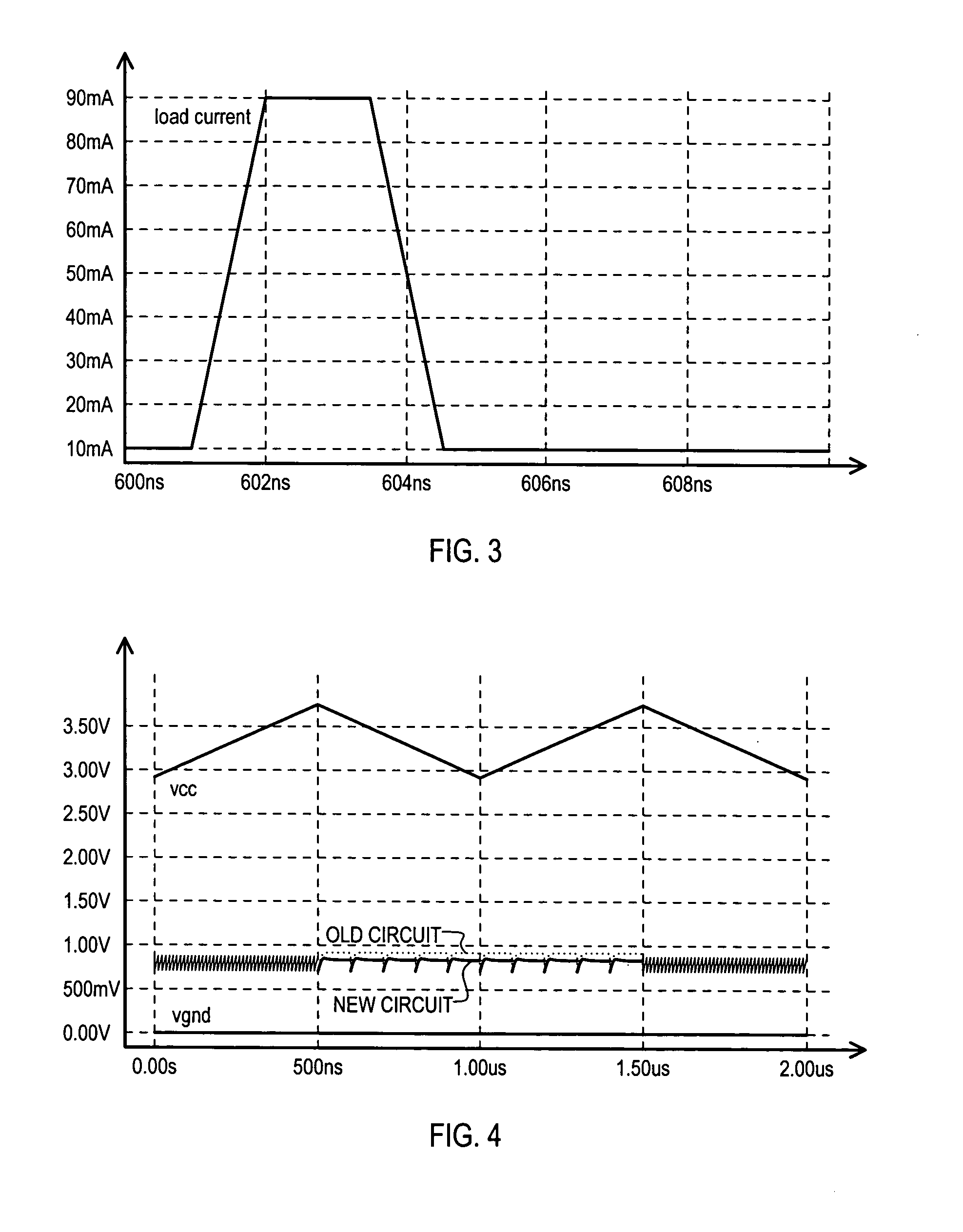
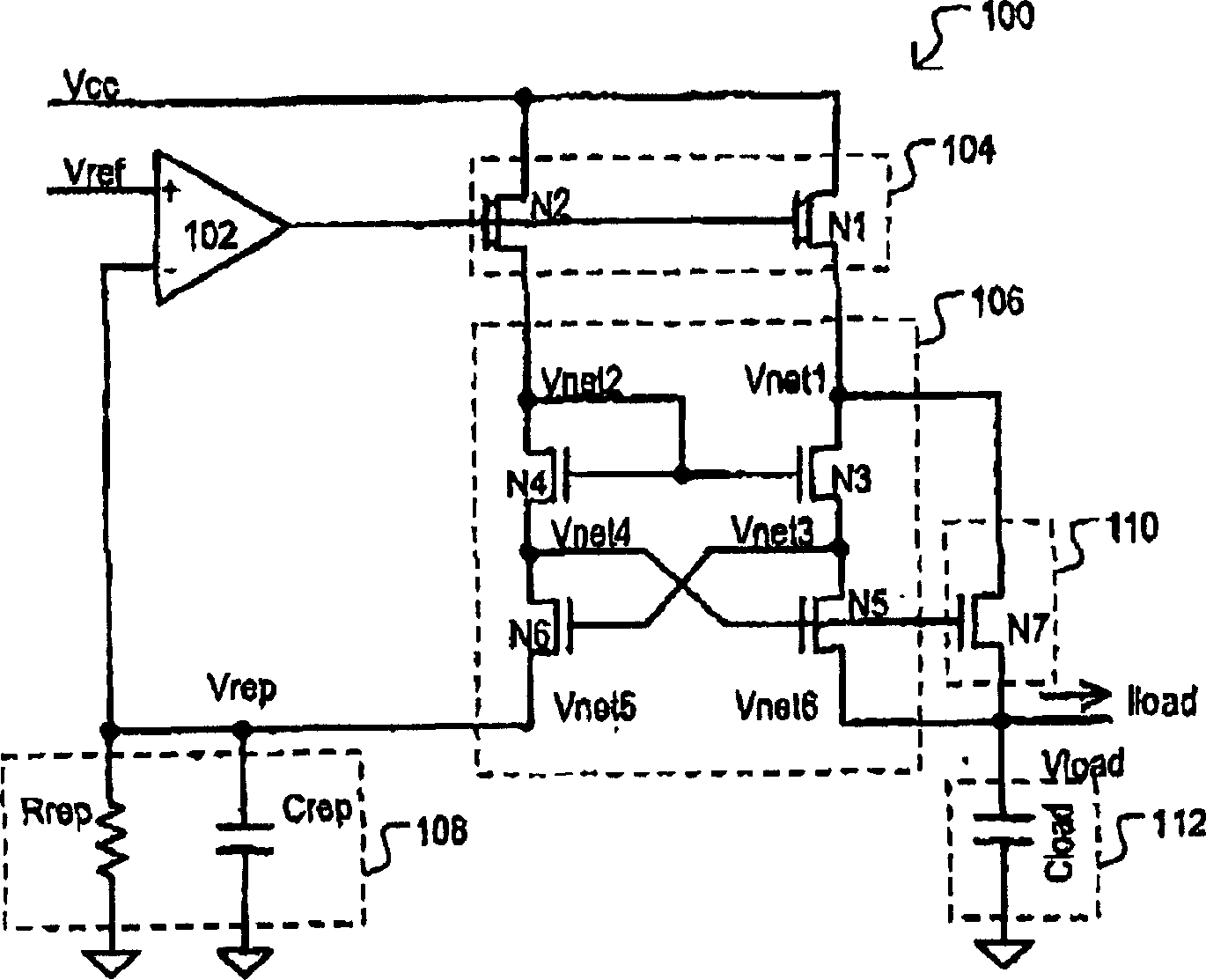
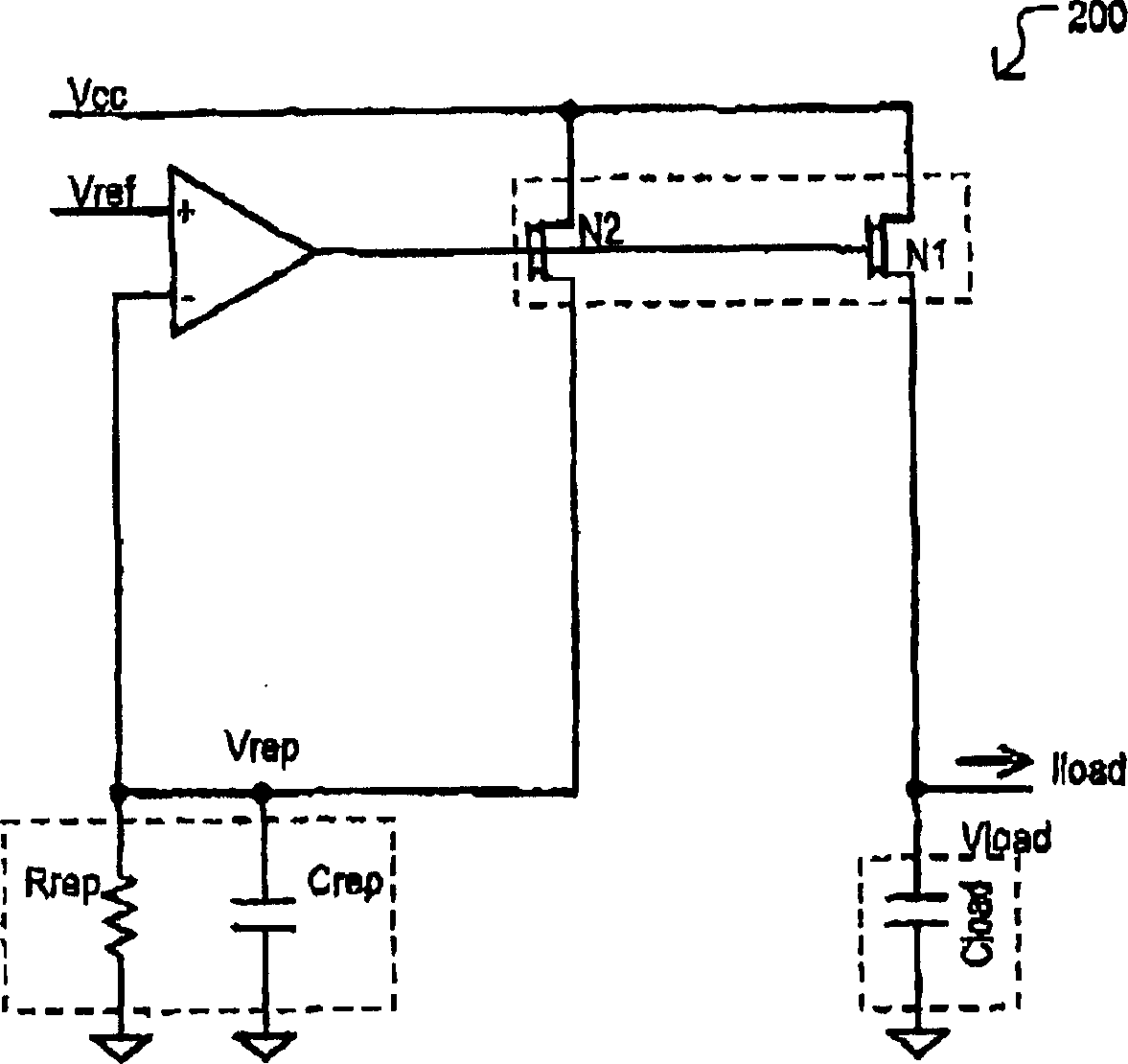
A replica biased voltage regulator circuit (100) is disclosed that provides high frequency response via local positive feedback and low frequency response via a negative feedback loop. A voltage regulator circuit (100) can include current conveyor (106) that essentially forces an output voltage (Vload) to follow a replica voltage (Vrep). An operational amplifier (102) can provide negative feedback by controlling current supplied to the current conveyor (104) based on a comparison between a reference voltage (Vref) and the replica voltage (Vrep).
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Systems and methods for programming large-scale field-programmable analog arrays
ActiveUS20060261846A1Good flexibilitySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsCapacitanceTransistor array
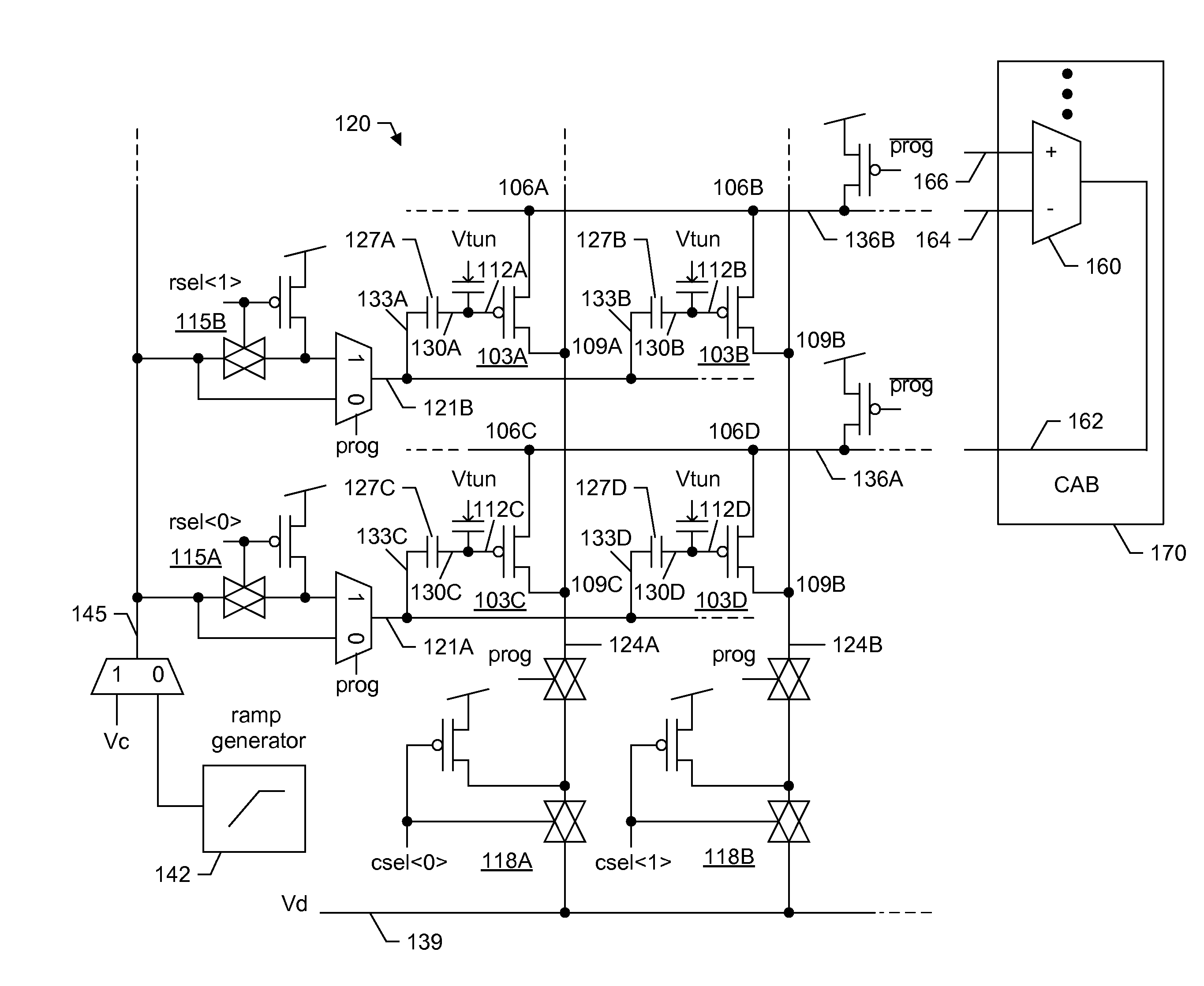
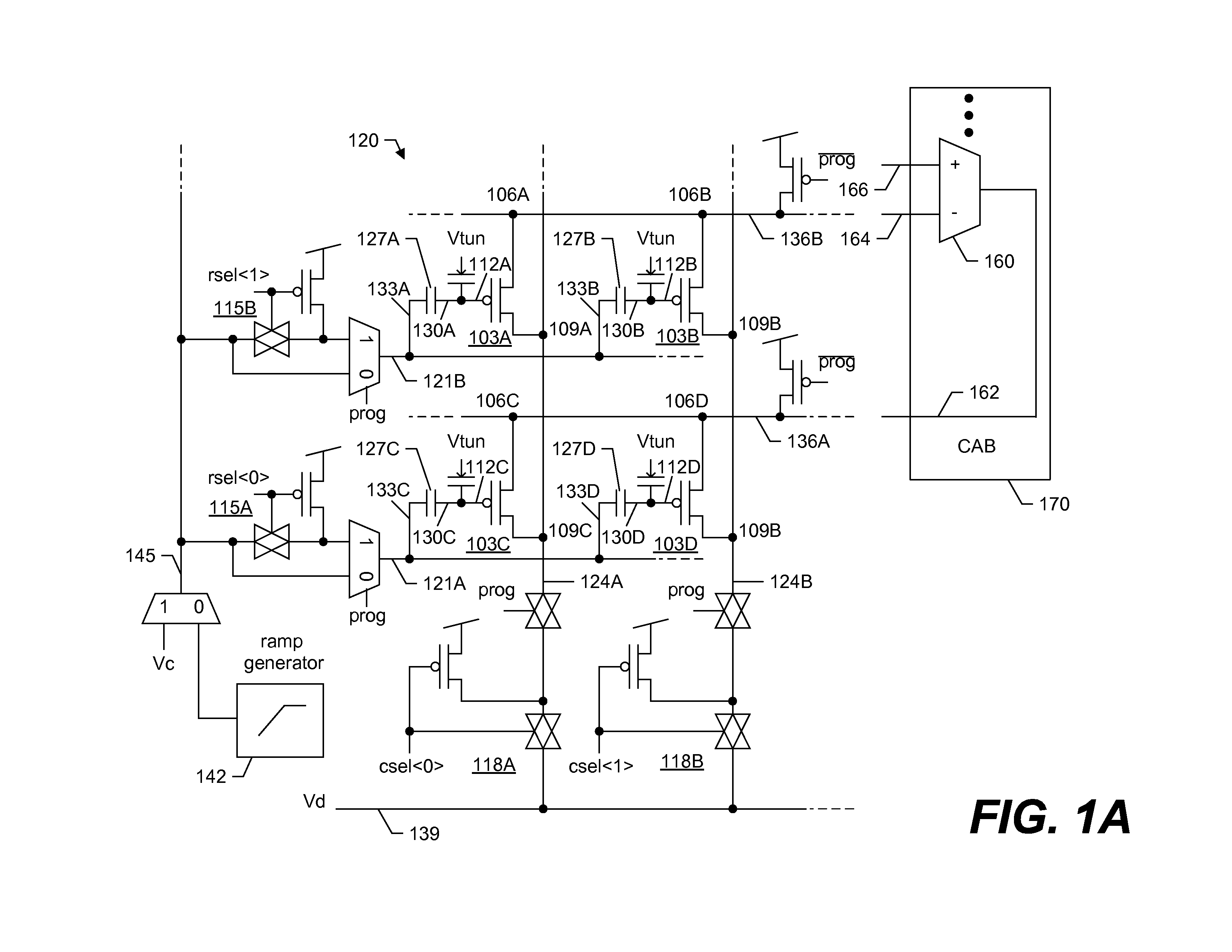
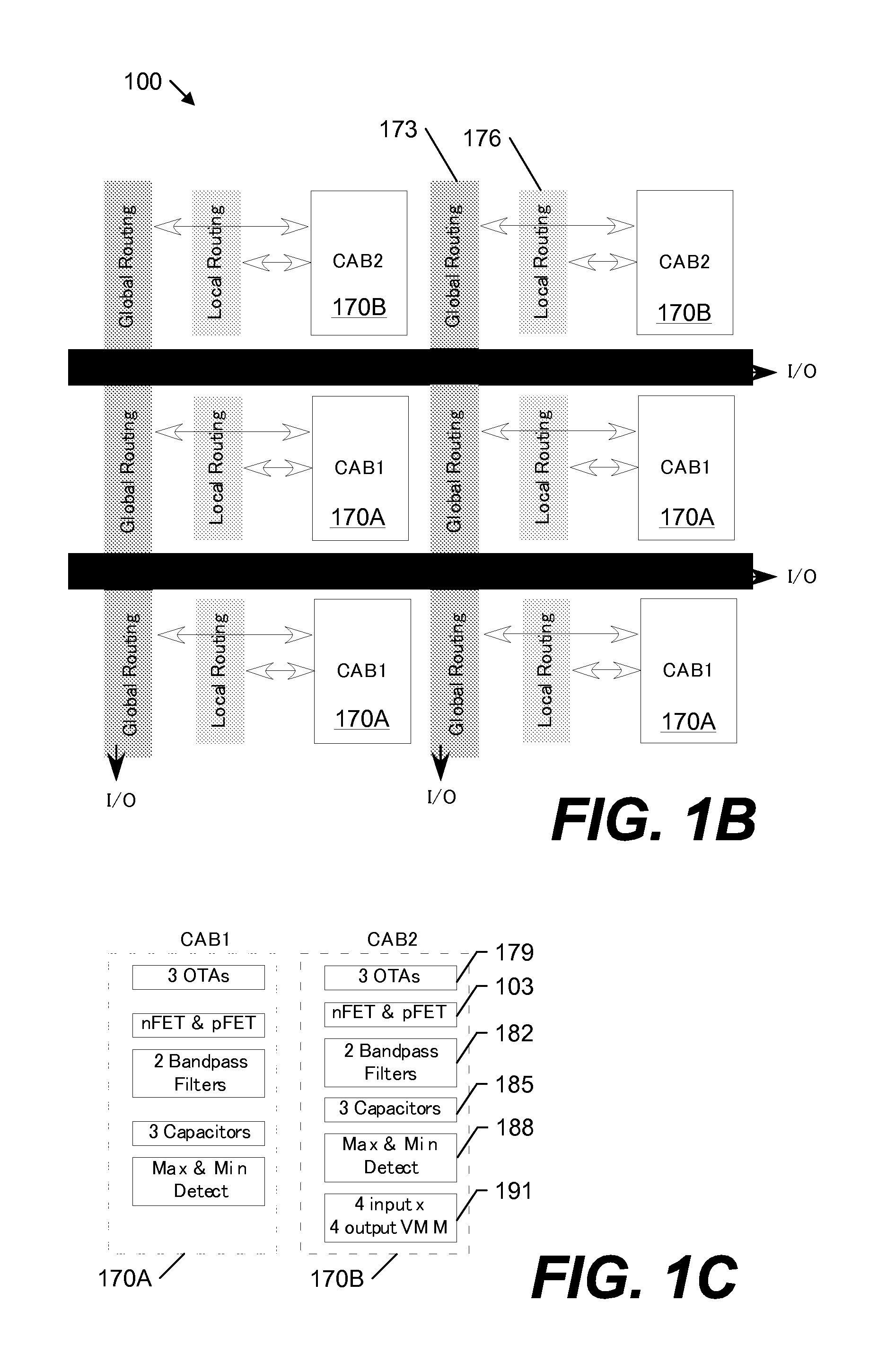
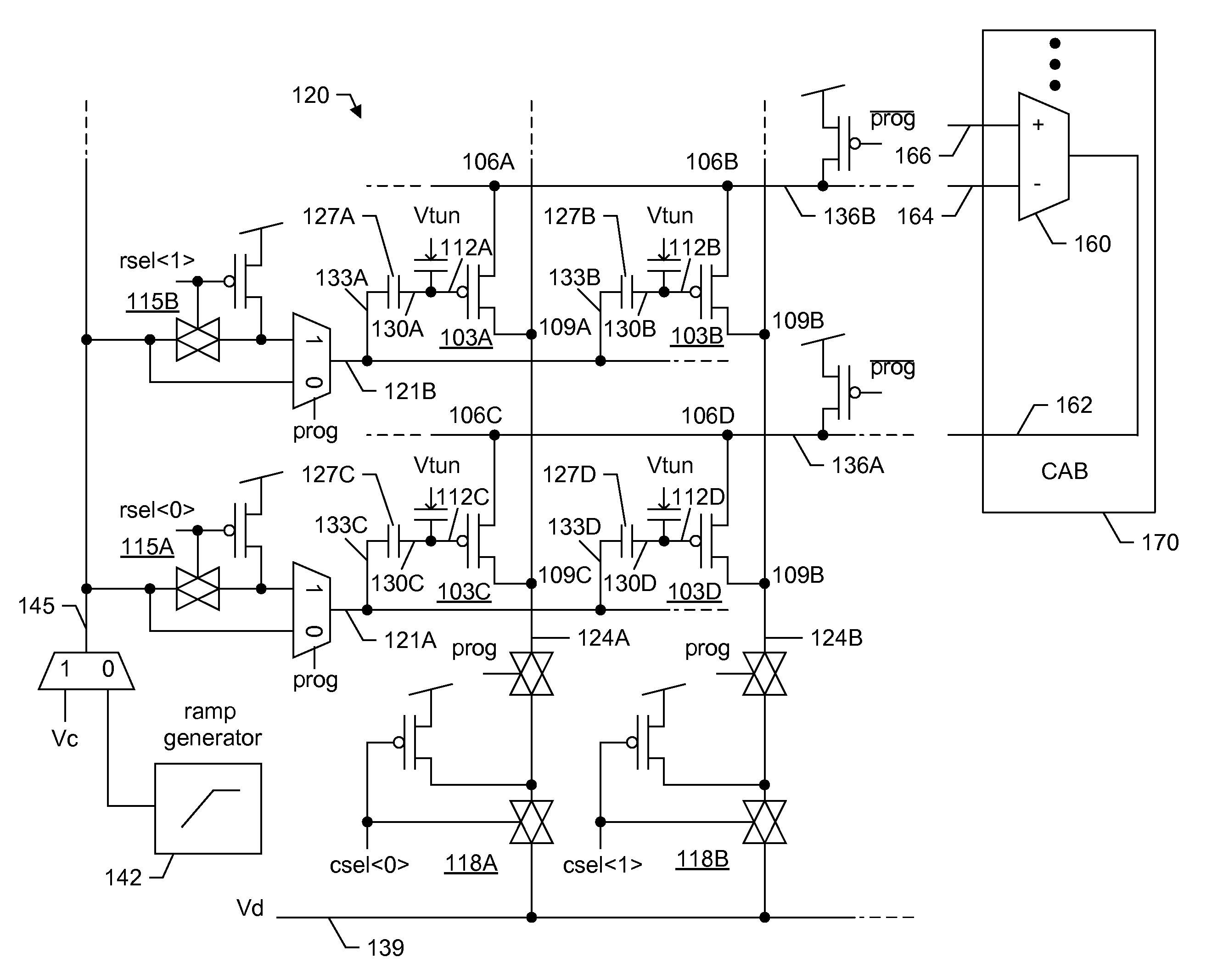
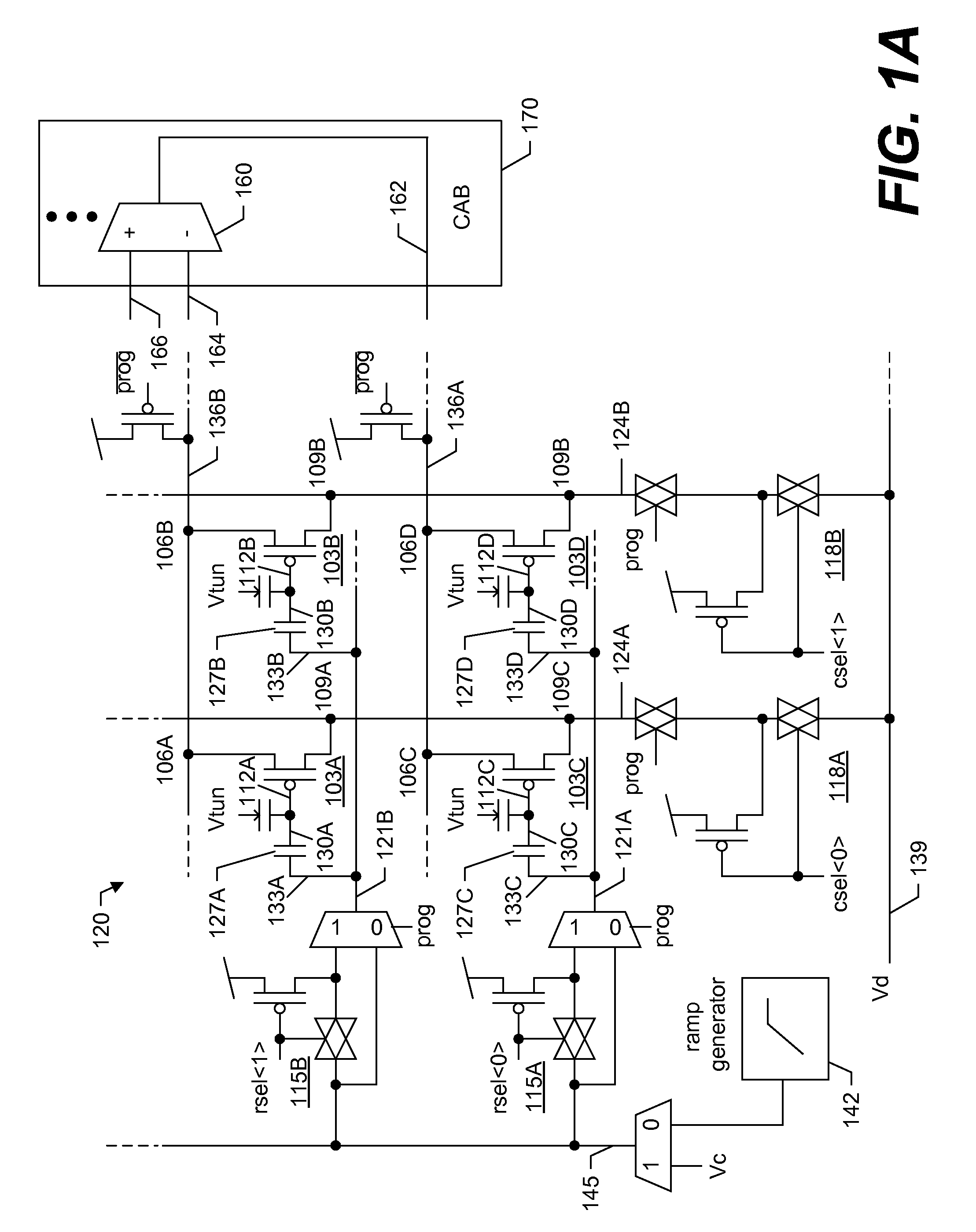
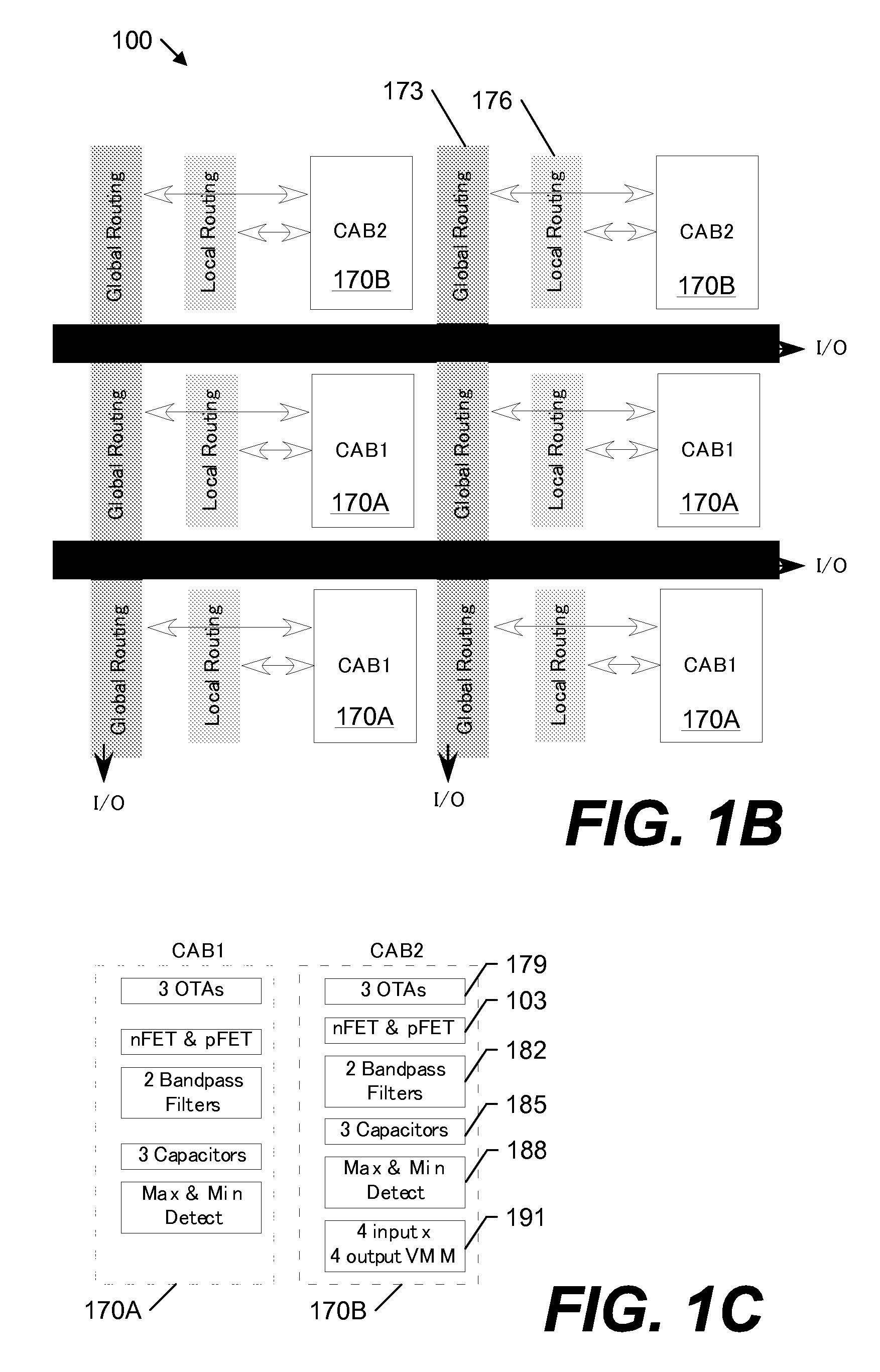
A large-scale field-programmable analog array (FPAA) for rapidly prototyping analog systems and an arbitrary analog waveform generator. The large-scale FPAA includes a floating-gate transistor array and a plurality of computational analog blocks (CABs), which may be adapted to set bias voltages for operational transconductance amplifiers (OTAs), adjust corner frequencies on the capacitively coupled current conveyors, set multiplier coefficients in vector-matrix multipliers, and a variety of other operations. The floating-gate transistors may be used as switch elements, programmable resistor elements, precision current sources, and programmable transistors. Accordingly, the floating-gate transistors within the array allow on-chip programming of the characteristics of the computational elements, while still maintaining compact CABs. The arbitrary analog waveform generator may include programmable floating-gate MOS transistors for use as analog memory cells to store samples of the waveforms.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Chua's circuit and it's use in hyperchaotic circuit
InactiveUS20050134409A1Minimal useNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsNetwork simulating negative resistancesState variableEngineering
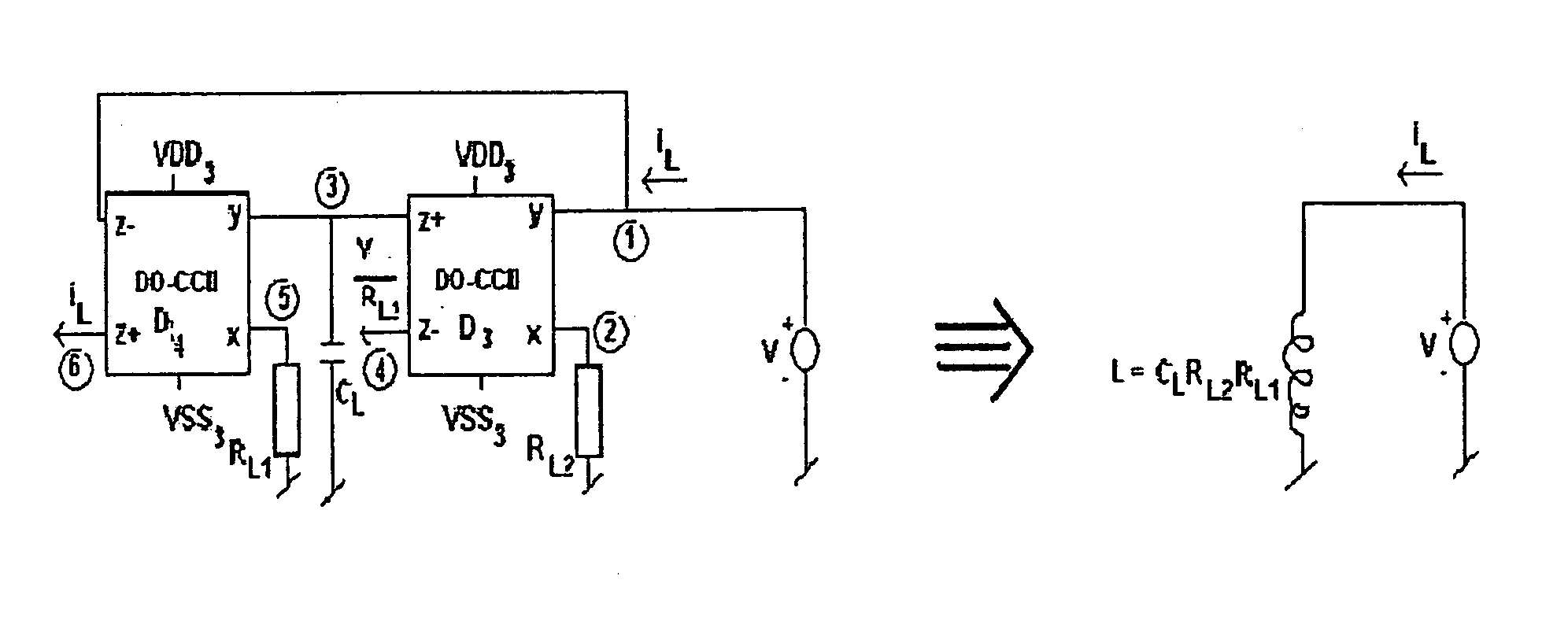
The present invention provides an improved Chua's circuit providing current mode operation, access to all state variables, minimum use of grounded passive elements, and freedom from passive component matching comprising a dual output current conveyer based inductor having one grounded terminal, a capacitor connected across the second terminal of said inductor, a resistor having one terminal connected to the second terminal of said inductor, the second terminal of said resistor connected to one terminal of a second capacitor the other end of which is grounded, and a pair of dual output current conveyers connected together to form a 2-terminal negative resistance having one terminal connected to ground and the second terminal connected to the second terminal of said resistance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
Switch reluctance motor memory sensor model modeling method
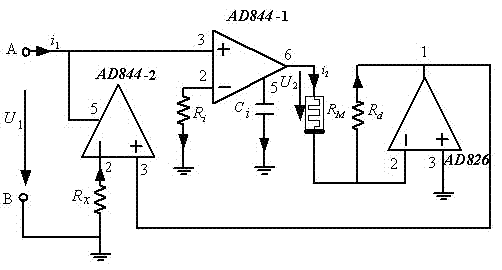
ActiveCN103095191AImprove optimal designReduce hardware costsElectronic commutation motor controlAC motor controlCapacitanceHemt circuits
Provided is a switch reluctance motor memory sensor model modeling method. A switch reluctance motor memory sensor circuit model is formed by two current conveyors AD844, an operational amplifier AD826, a memristor, a capacitor and three resistors. The modeling method makes a basis for circuit hardware modeling of a switch reluctance motor system model, is beneficial for match direct simulation of a switch reluctance motor system, enables physical phenomena in a simulation system to be similar with an actual switch reluctance motor system, and has important theoretical value and wide application prospects. The modeling method is simple, can improve static and dynamic properties of a system, and achieves real-time simulation and real-time control of the switch reluctance motor system.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH
Shunt type voltage regulator
InactiveUS7262586B1Lower average currentSpeed regulation responseElectric variable regulationShunt typesVoltage regulation
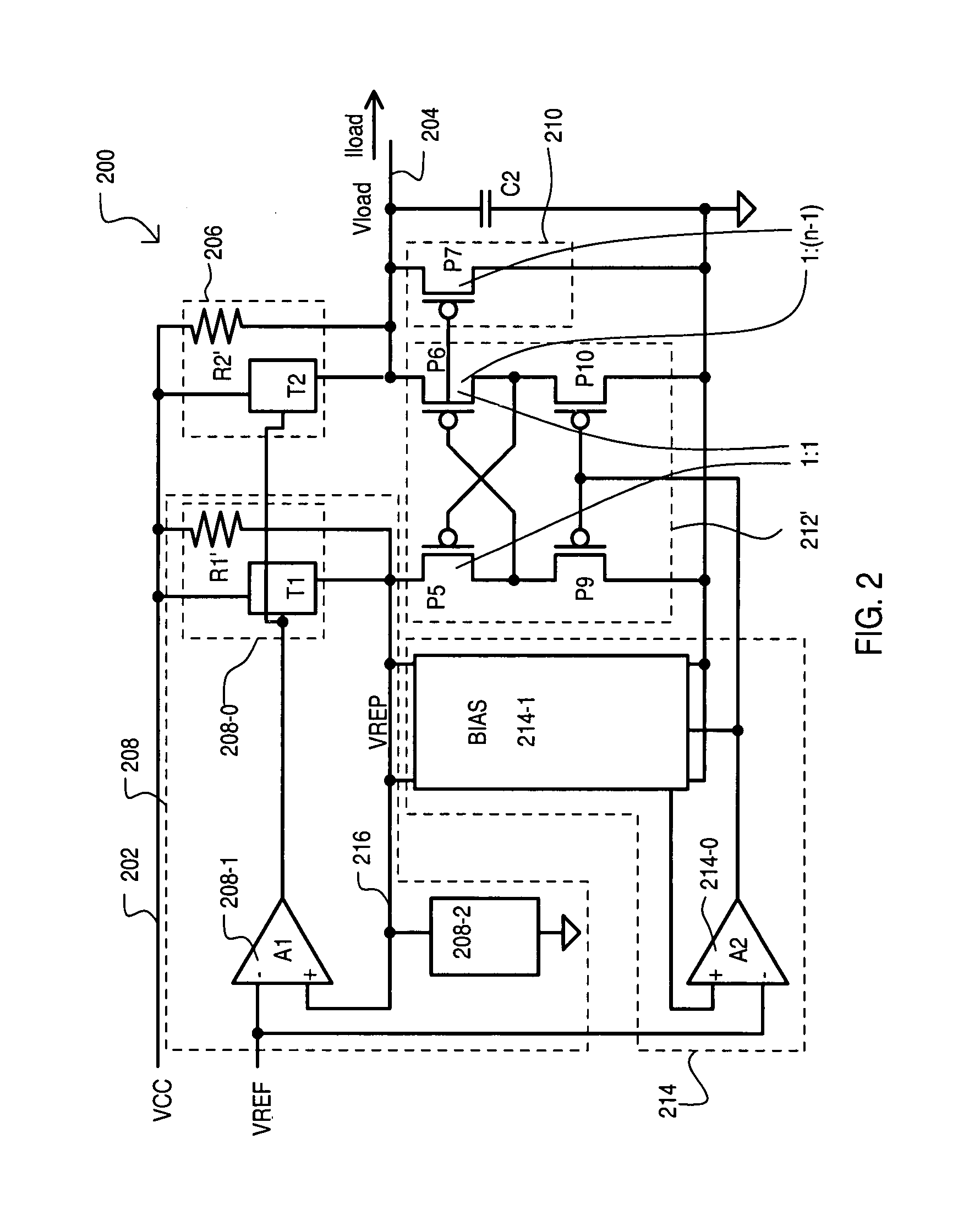
A shunt type voltage regulator circuit (300) can include a load supply circuit (306) and feedback circuit (308-0) that provide impedance modulated according to a first feedback circuit (308), thus limiting power consumption at higher power supply ranges. In addition, a faster regulation response can be provided by a current conveyor circuit (312′) that can force the voltage at a regulated load node (304) to match that at a replication node (316).
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Floating memory capacitor and memory inductor simulator based on memory resistor
The invention discloses a floating memory capacitor and memory inductor simulator based on a memory resistor. The floating memory capacitor and memory inductor simulator based on the memory resistor comprises a first differential difference current conveyor, a second differential difference current conveyor, the memory resistor, a resistor and a reactance element, wherein the X end of the first differential difference current conveyor is connected with the ground after being connected with the memory resistor, one input end of the second differential difference current conveyor is connected with the ground, the other input end of the second differential difference current conveyor is connected with the in-phase current output end of the first differential difference current conveyor and one end of the reactance element, the other end of the reactance element is connected with the ground, the X end of the second differential difference current conveyor is connected with the ground after being connected with the resistor, the in-phase current output end and the reverse current output end of the second differential difference current conveyor are connected with two input ends of the first differential difference current conveyor respectively. The floating memory capacitor and memory inductor simulator based on the memory resistor has the advantages that the simulator can effectively replace an actual memory capacitor and memory inductor to design a circuit, voltage at the two ends of the memory capacitor and voltage at the two ends of the memory inductor are not limited, and the simulator can be connected with other electronic elements flexibly.
Owner:XIANGTAN UNIV
Replica biased voltage regulator
ActiveUS20050134242A1Low frequency regulationElectric variable regulationEngineeringVoltage reference
A replica biased voltage regulator circuit (100) is disclosed that provides high frequency response via local positive feedback and low frequency response via a negative feedback loop. A voltage regulator circuit (100) can include current conveyor (106) that essentially forces an output voltage (Vload) to follow a replica voltage (Vrep). An operational amplifier (102) can provide negative feedback by controlling current supplied to the current conveyor (104) based on a comparison between a reference voltage (Vref) and the replica voltage (Vrep).
Owner:MONTEREY RES LLC
Systems and methods for programming large-scale field-programmable analog arrays
ActiveUS7439764B2Good flexibilitySolid-state devicesLogic circuits using elementary logic circuit componentsTransistor arrayCapacitance
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
Class AB enhanced transconductance source follower
ActiveUS7151410B2Maintaining large bandwidthReduce voltageAmplifier combinationsAmplifier detailsLow voltageCascode
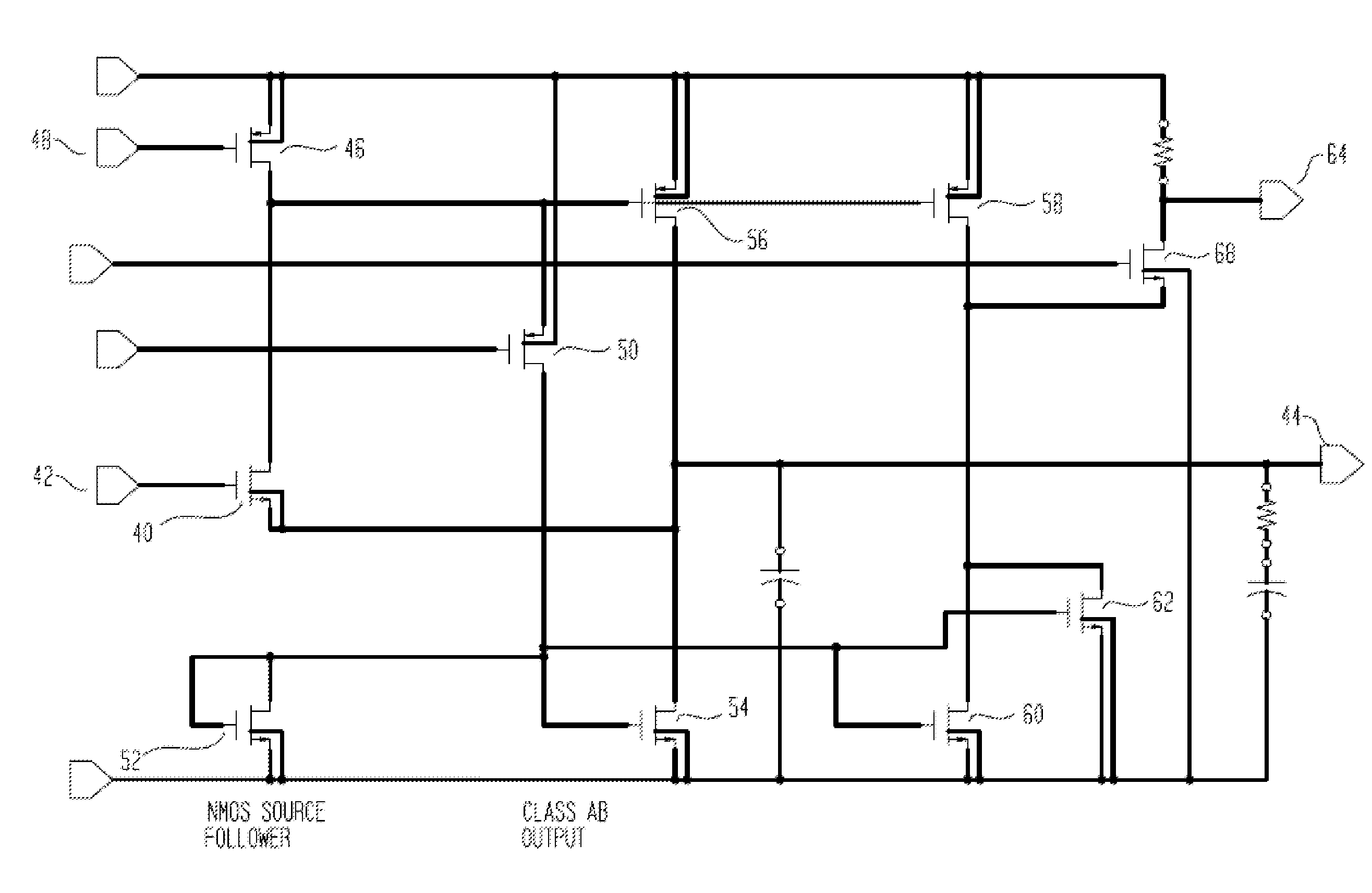
A low voltage, high bandwidth, enhanced transconductance, source follower circuit constructed from MOS FET devices, which operates in a class AB mode. The drain current of the source follower is sensed with a folded cascode device. The sensed current is multiplied by a common source device of same type (NMOS or PMOS) as the source follower, and directed to the output load. Over limit current load at the source follower drain is sensed by a common source device of the opposite type (NMOS or PMOS), which also supplies the necessary extra current to the output load. This allows the device to supply significantly more than the quiescent current in both sourcing and sinking the output. Average power consumption for driving a given load is significantly reduced, while maintaining the large bandwidth of traditional source follower designs, and the capability for use in either voltage regulators or in a current conveyor.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
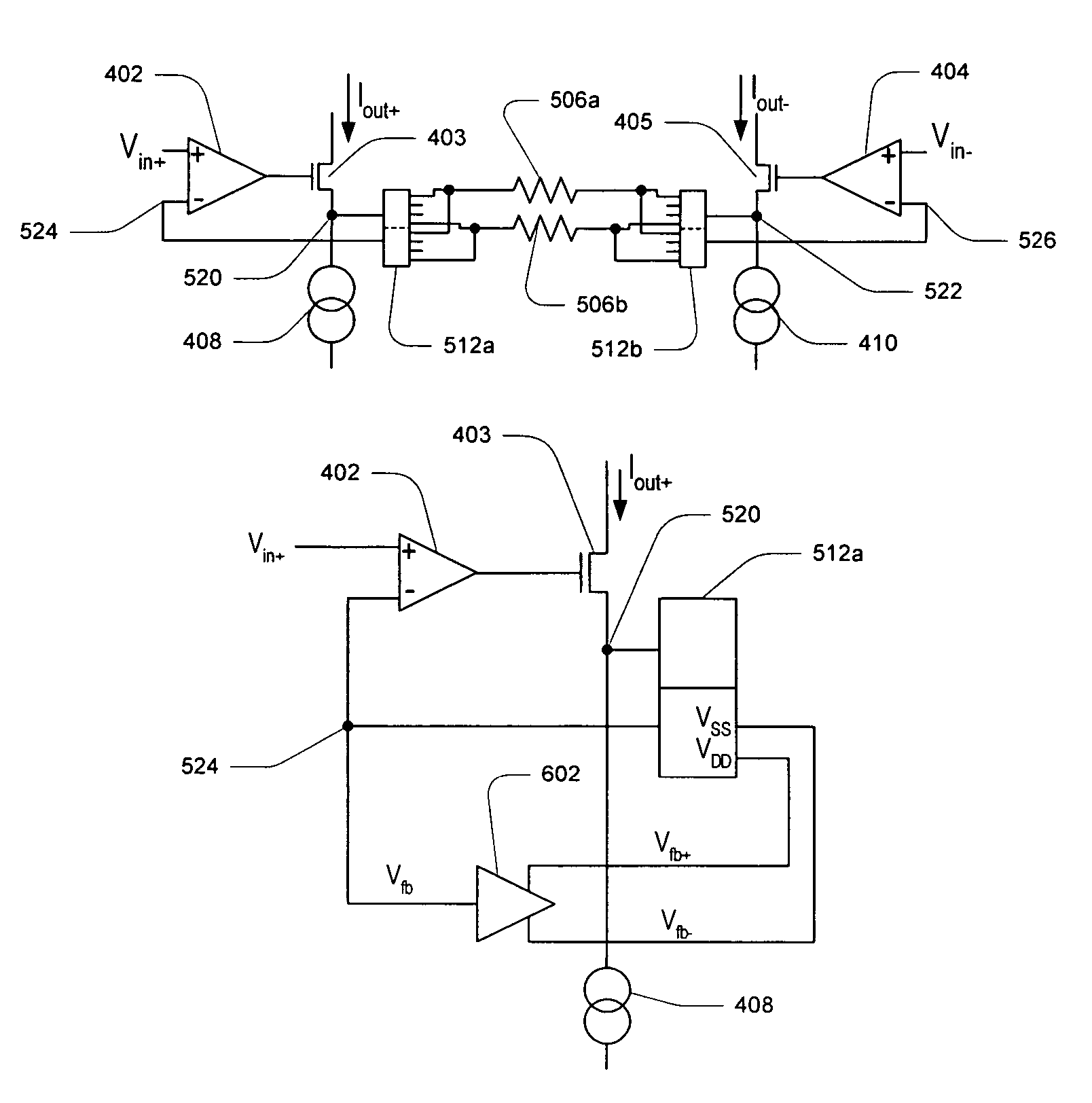
Programmable gain instrumentation amplifier with improved gain multiplexers
ActiveUS7215197B2Accurate trackingGain controlDifferential amplifiersInstrumentation amplifierAudio power amplifier
In one embodiment, a programmable gain instrumentation amplifier comprises an input stage configured with a differential precision current conveyor circuit. The current conveyor circuit may be implemented with operational amplifiers coupled to gain-setting resistors, with double-multiplexers configured on each end of the gain-setting resistors. In a first set of embodiments, the double-multiplexers may be bootstrapped, whereby the power supplies of each double-multiplexer may track the signals on the output pin of a respective sense-multiplexer component of the double-multiplexer. In a second set of embodiments, the power supplies may alternatively track the op-amp differential output during non-overload conditions, or the op-amp common-mode output at a gain resistor center tap during overload conditions. Corresponding bootstrap circuits may be designed for both sets of embodiments, the bootstrap circuits coupling to the respective tracking node or nodes in either case.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Four-input transconductance amplifier for fully differential Gm-C filter
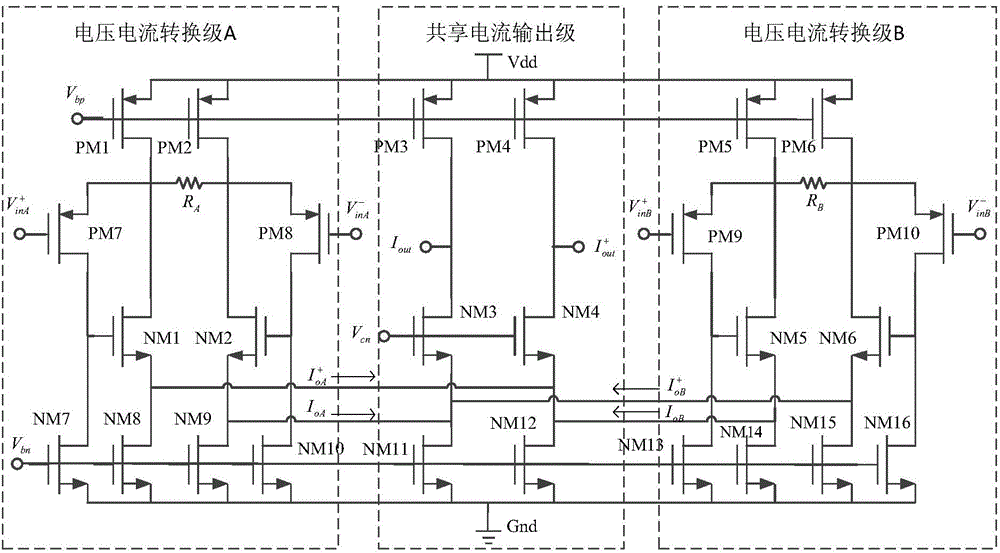
ActiveCN104660194AReduce power consumptionNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsDifferential amplifiersAudio power amplifierEngineering
The invention discloses a four-input transconductance amplifier for a fully differential Gm-C filter. The four-input transconductance amplifier comprises a voltage-current conversion stage A, a voltage-current conversion stage B and a sharing current output-stage circuit. The four-input transconductance amplifier adopts a highly linear transconductance amplifier based on a current conveyor and consists of the voltage-current conversion stages and the current output stage, and output of the two fully differential voltage-current conversion stages is connected in parallel to share the current output stages, so that a four-input two-output transconductance amplifier is realized. Compared with a conventional realizing mode of directly connecting two same transconductance amplifiers in parallel, a function of adding and subtracting differential output current is directly realized, and the power consumption of the current output stages is reduced. Meanwhile, compared with the conventional realizing mode, the Gm-C filter disclosed by the invention has the same frequency characteristics.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Chua's circuit and it's use in a hyperchaotic circuit
ActiveUS20050242906A1Minimal useNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsNetwork simulating negative resistancesState variableEngineering
The present invention provides an improved Chua's circuit providing current mode operation, access to all state variables, minimum use of grounded passive elements, and freedom from passive component matching comprising a dual output current conveyer based inductor having one grounded terminal, a capacitor connected across the second terminal of said inductor, a resistor having one terminal connected to the second terminal of said inductor, the second terminal of said resistor connected to one terminal of a second capacitor the other end of which is grounded, and a pair of dual output current conveyers connected together to form a 2-terminal negative resistance having one terminal connected to ground and the second terminal connected to the second terminal of said resistance.
Owner:STMICROELECTRONICS PVT LTD
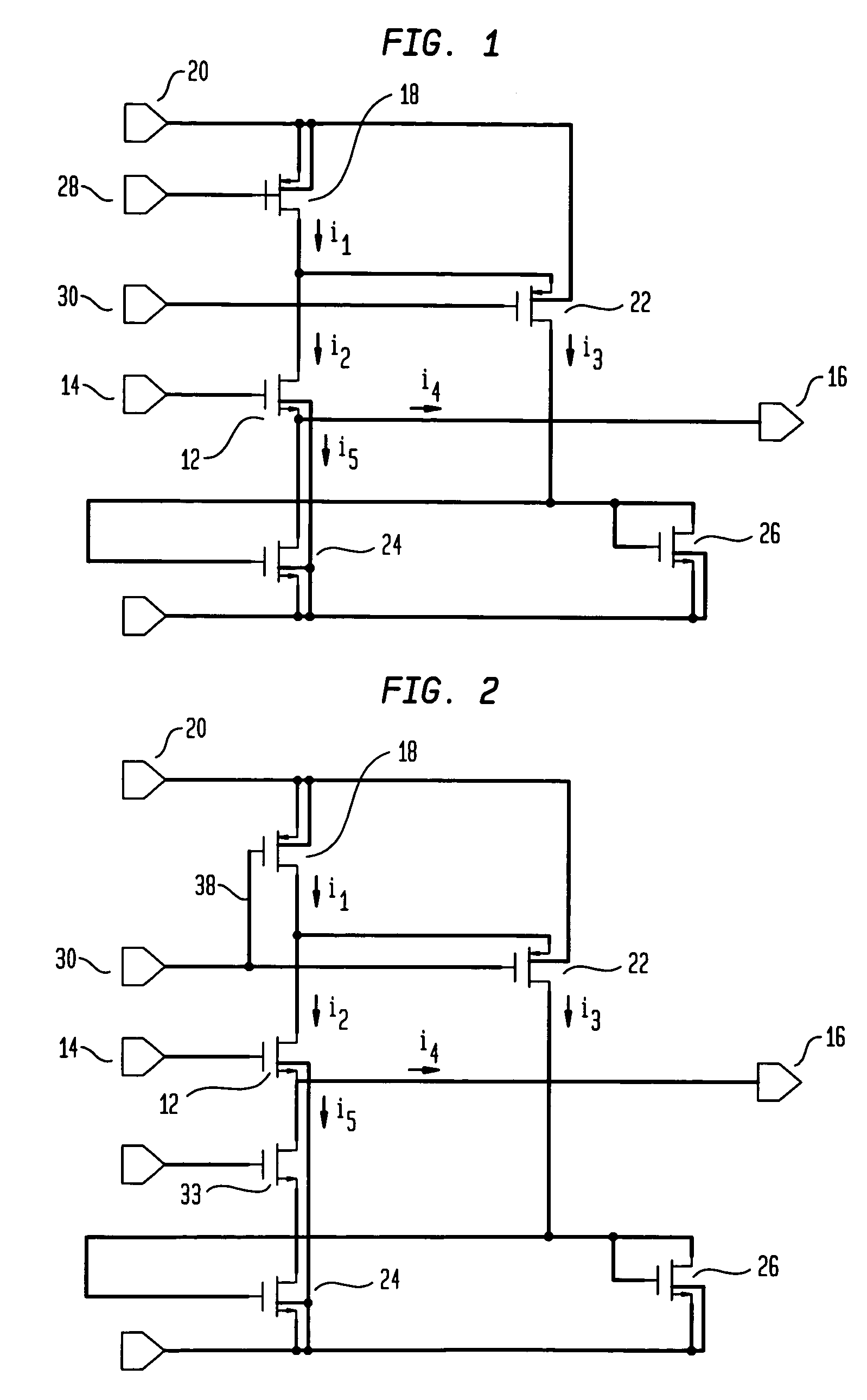
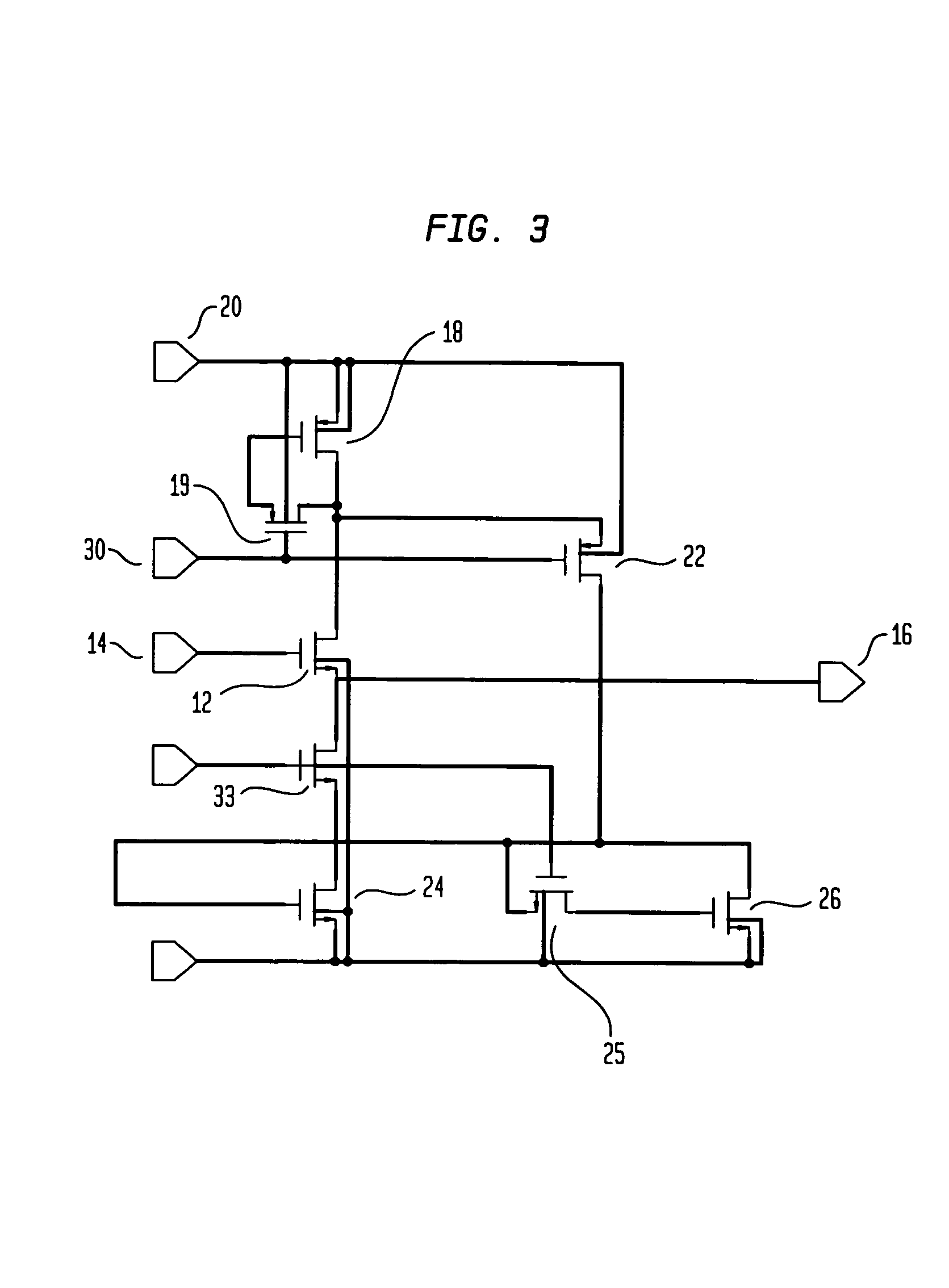
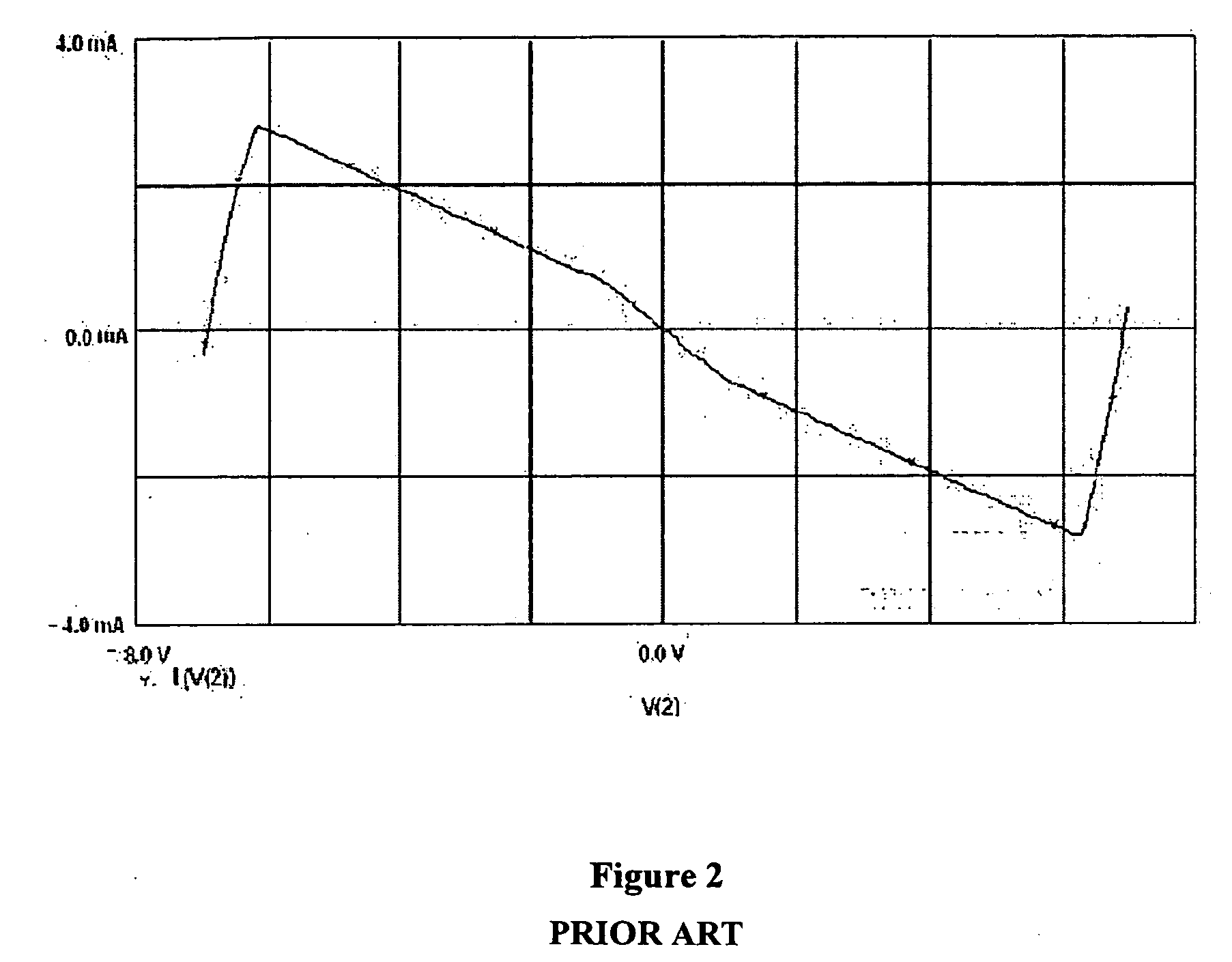
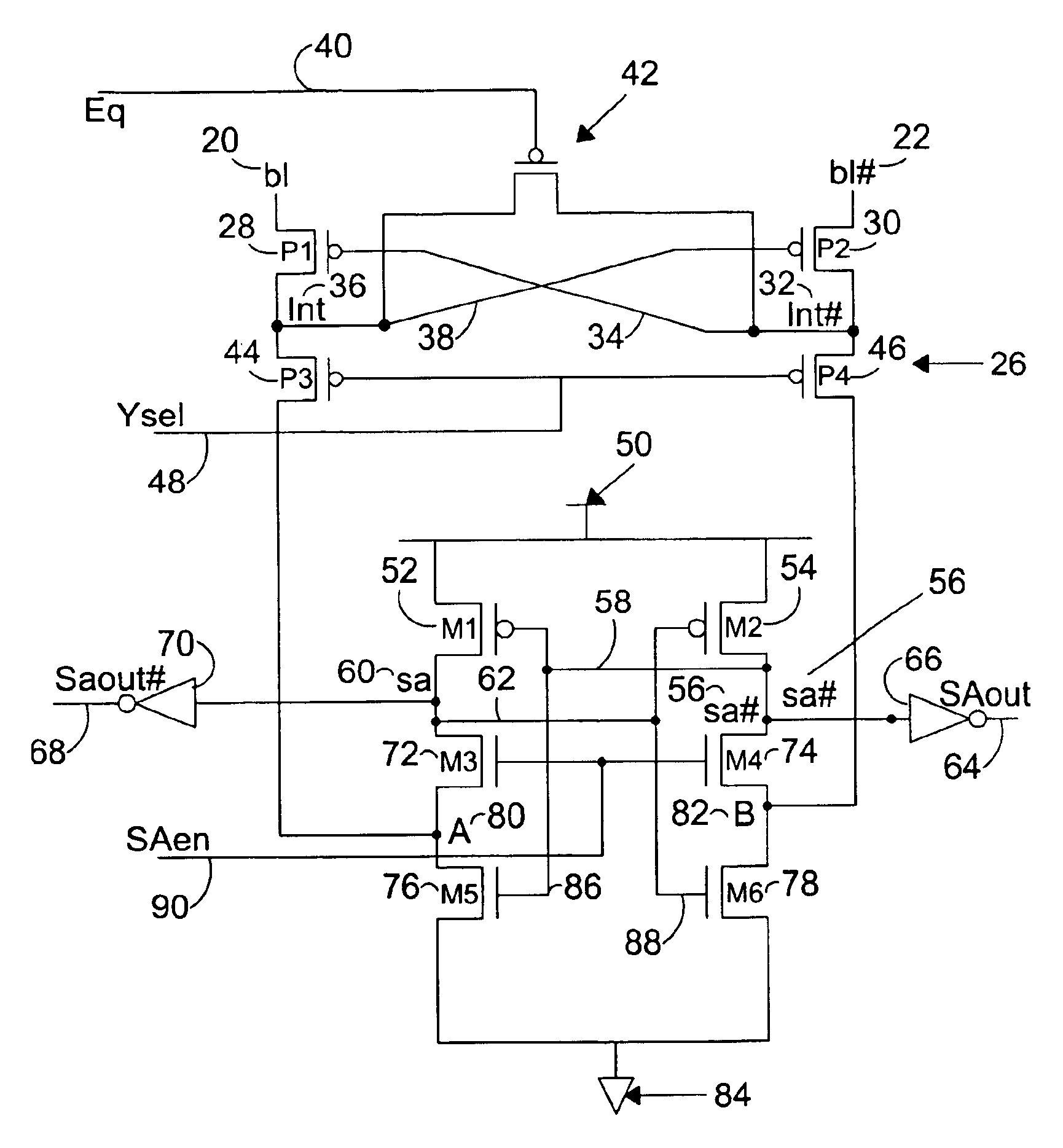
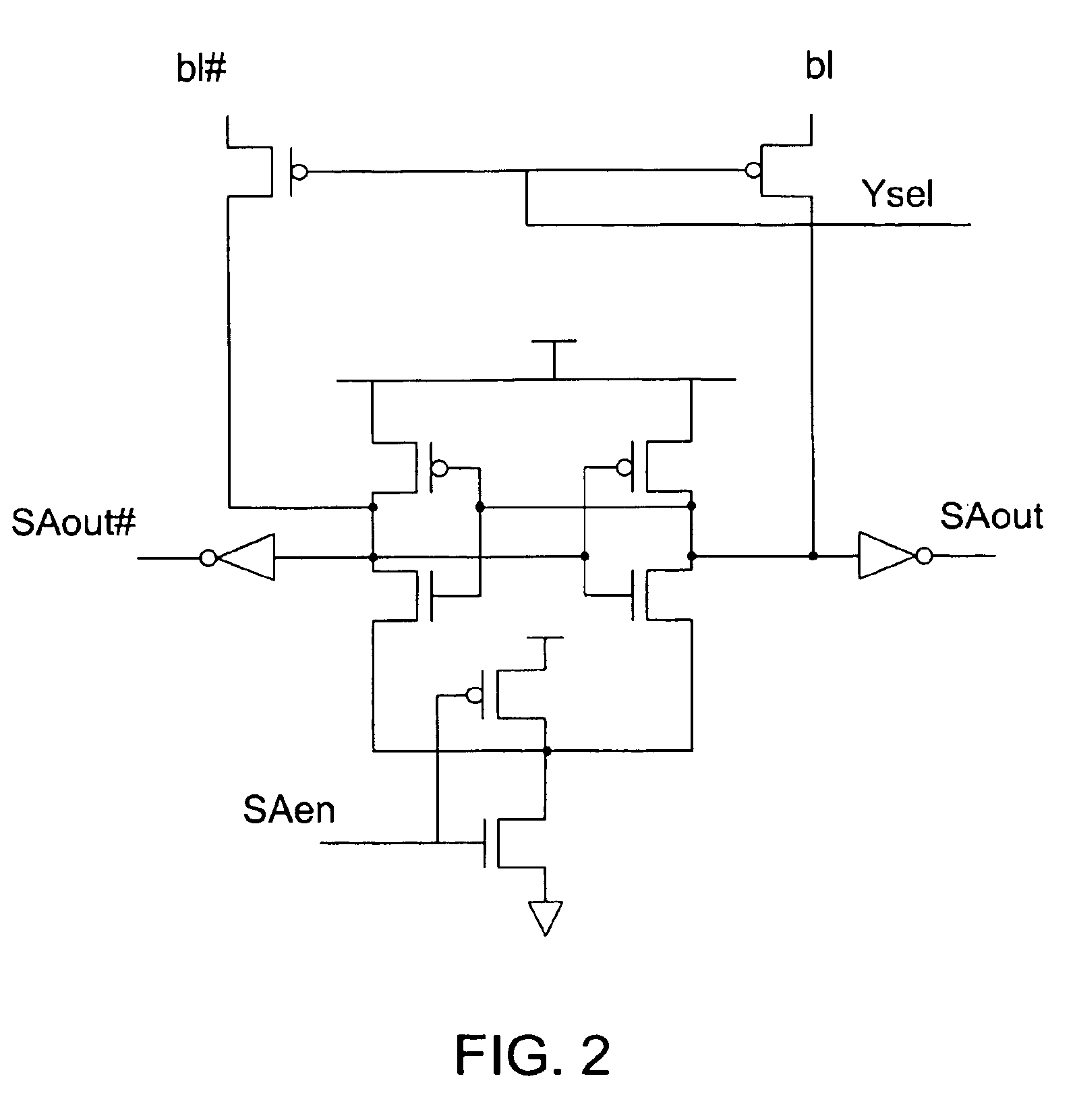
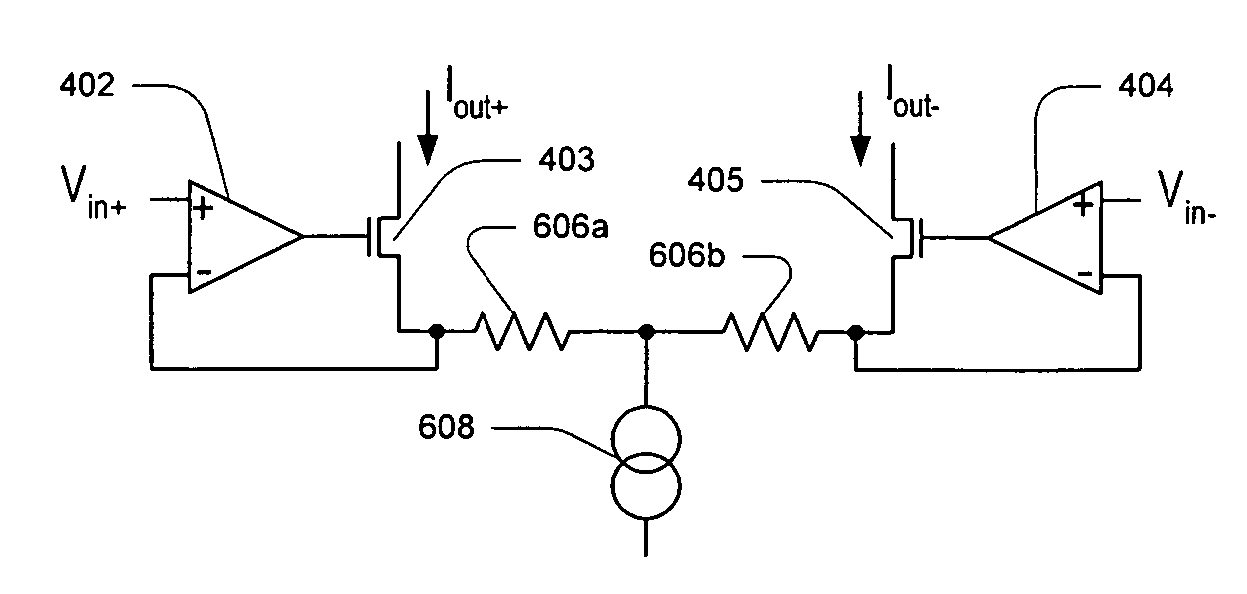
Differential current sense amplifier
A high-performance, low energy amplifier circuit for the detection and amplification of a voltage differential includes a current conveyor and a sense amplifier. The current conveyor includes a pair of cross-linked transistors and a pair of pass transistors. The sense amplifier includes four transistors forming a cross-linked current sense amplifier. The current sense amplifier detects a current differential between complementary bit lines, develops a differential voltage based on the current differential, amplifies the differential voltage and outputs the amplified differential voltage.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Very low power analog compensation circuit
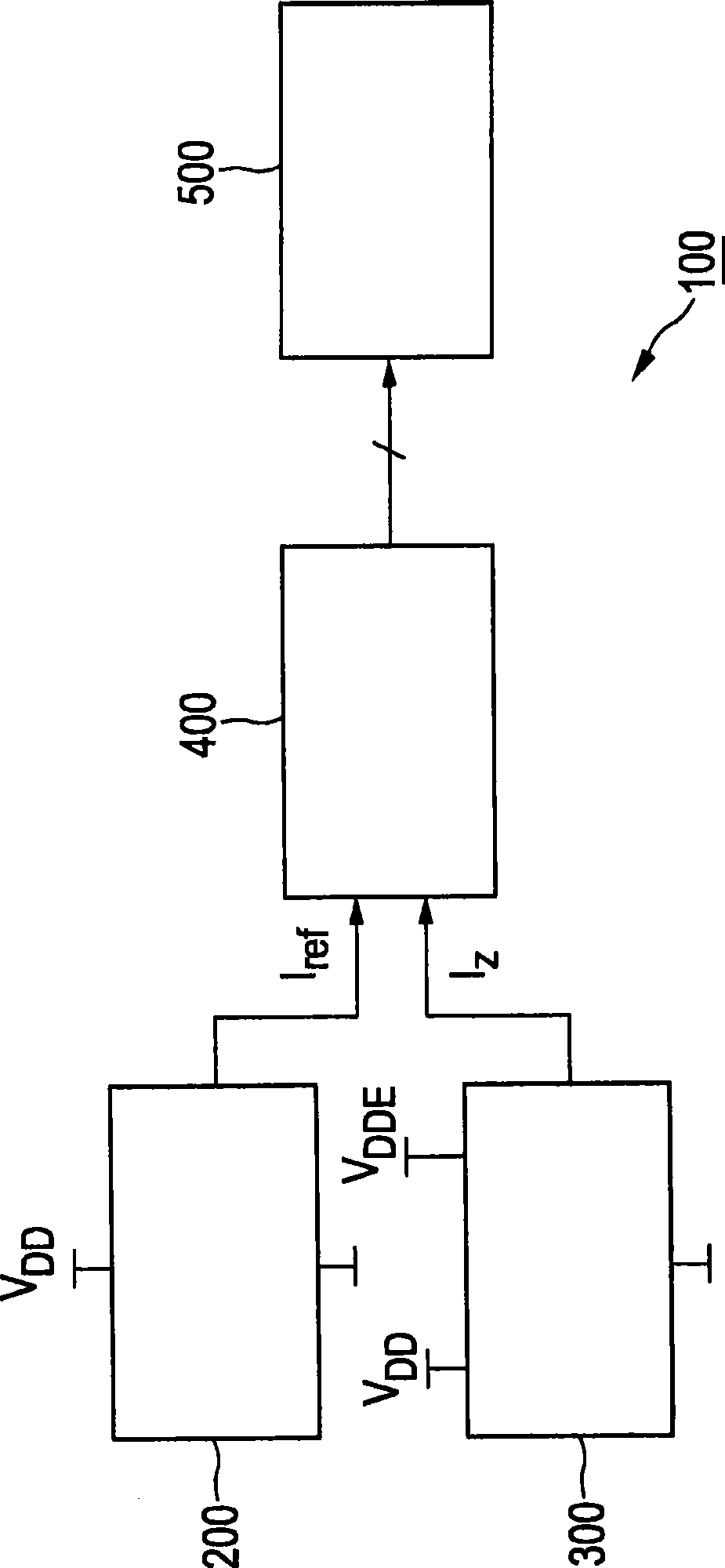
InactiveCN101485088AReliability increasing modificationsPower supply linesReference currentLow voltage
The present invention relates to a compensation circuit for providing compen- sation over PVT variations within an integrated circuit. Using a low voltage reference current source, the compensation circuit generates directly, from an on-chip reference low voltage supply (VDD), a reference current (Iref) that is constant over PVT variations, whereas a detection current (Iz) that is variable over PVT variations is generated by a sensing circuit, which is based on a current conveyor, from a low voltage supply (VDDE-VDD) applied across a single diode-connected transistor (M10) corresponding to a voltage difference between two reference low voltage supplies. Both currents (Iref, Iz) are then compared inside a current mode analog-to-digital converter that outputs a plurality of digital bits. These digital bits can be subsequently used to compensate for PVT variations in an I / O buffer circuit.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
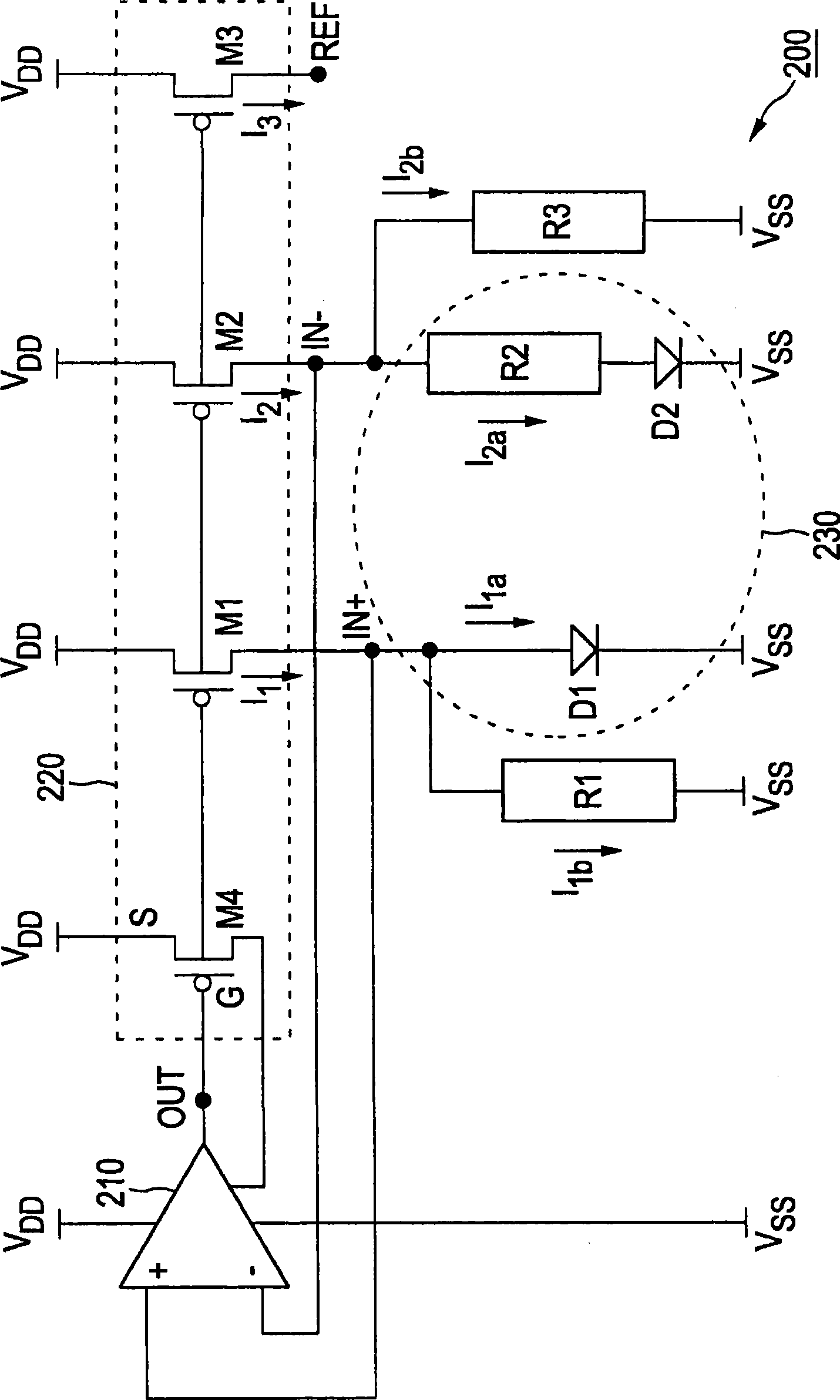
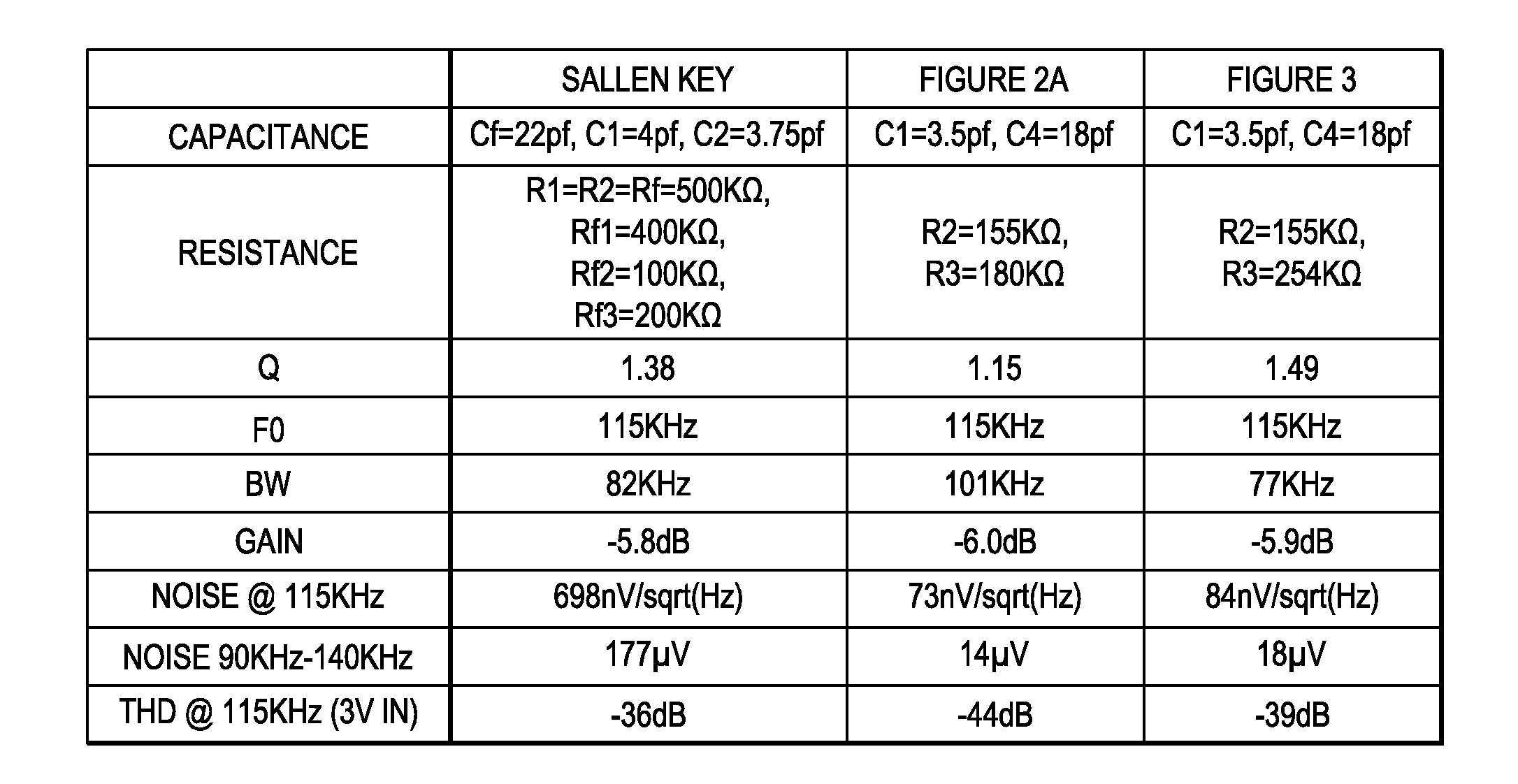
Low noise capacitive sensor with integrated bandpass filter
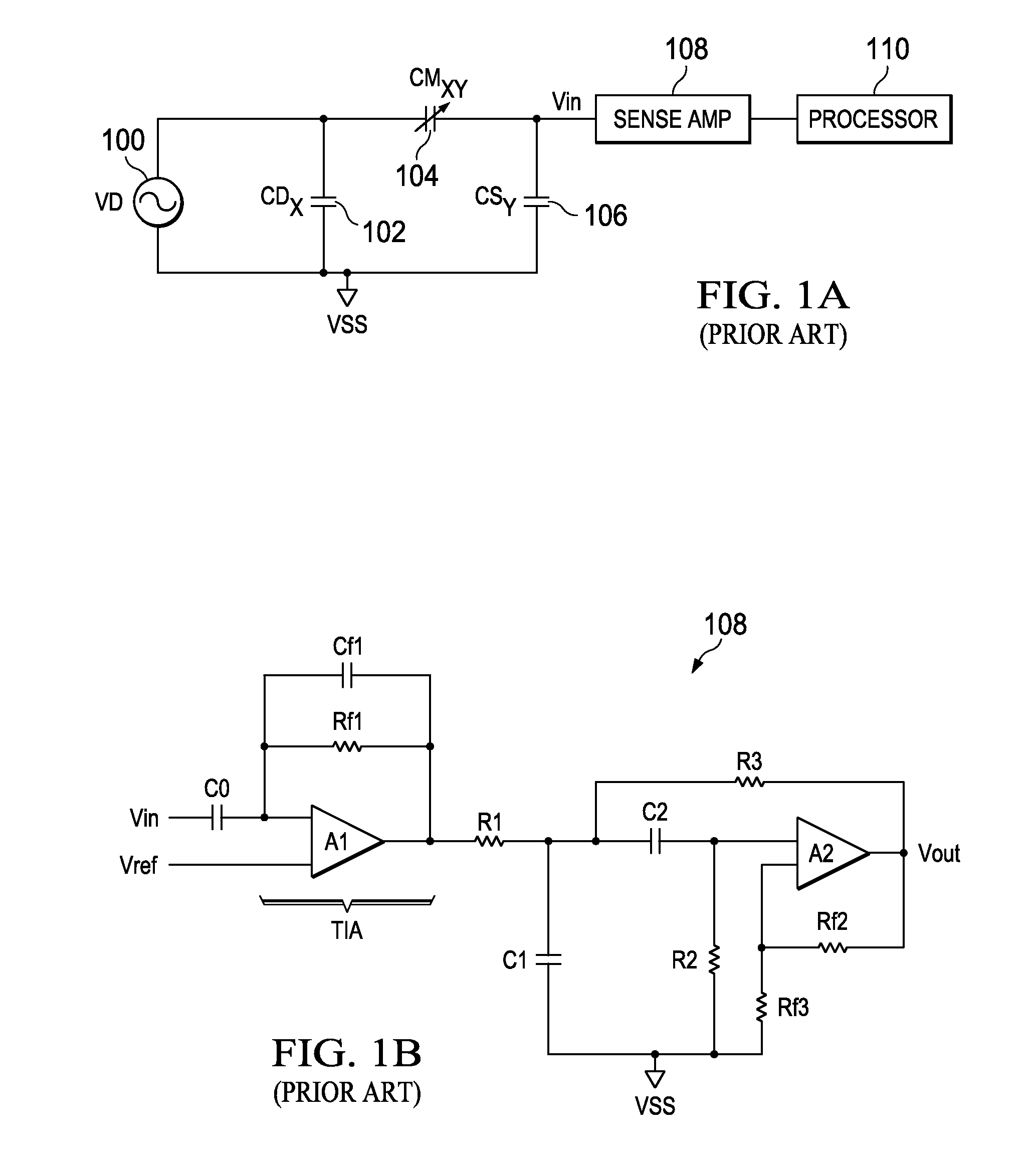
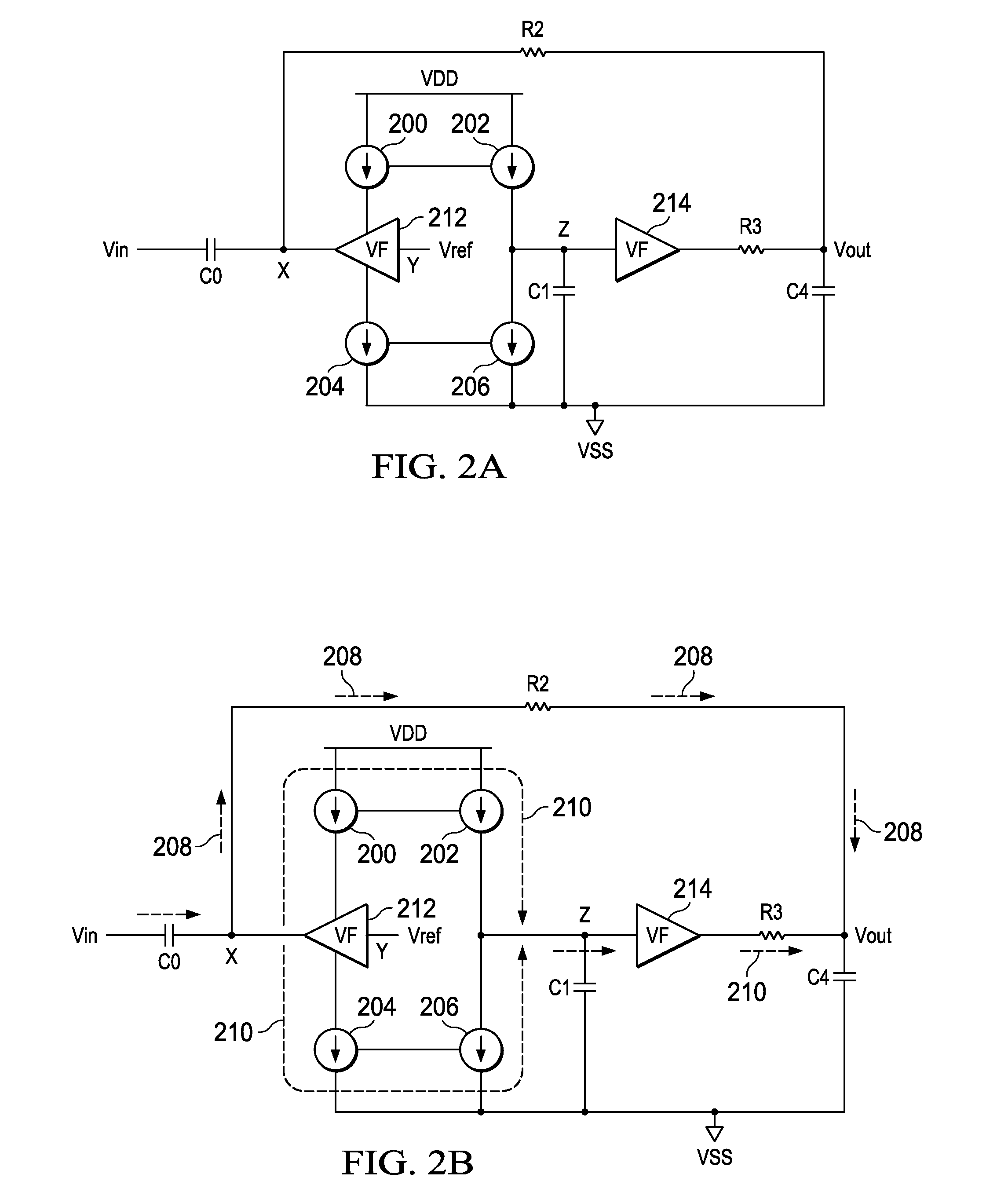
A bandpass sense amplifier circuit (FIG. 2A) is disclosed. The circuit includes a capacitor (C0) having a first terminal coupled to receive an input signal (Vin) and a second terminal. A current conveyor circuit (200-206,212) has a third terminal (X) coupled to the second terminal of the capacitor and a fourth terminal (Z) arranged to mirror a current into the third terminal. A voltage follower circuit (214) has an input terminal coupled to the fourth terminal of the current conveyor circuit and an output terminal.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
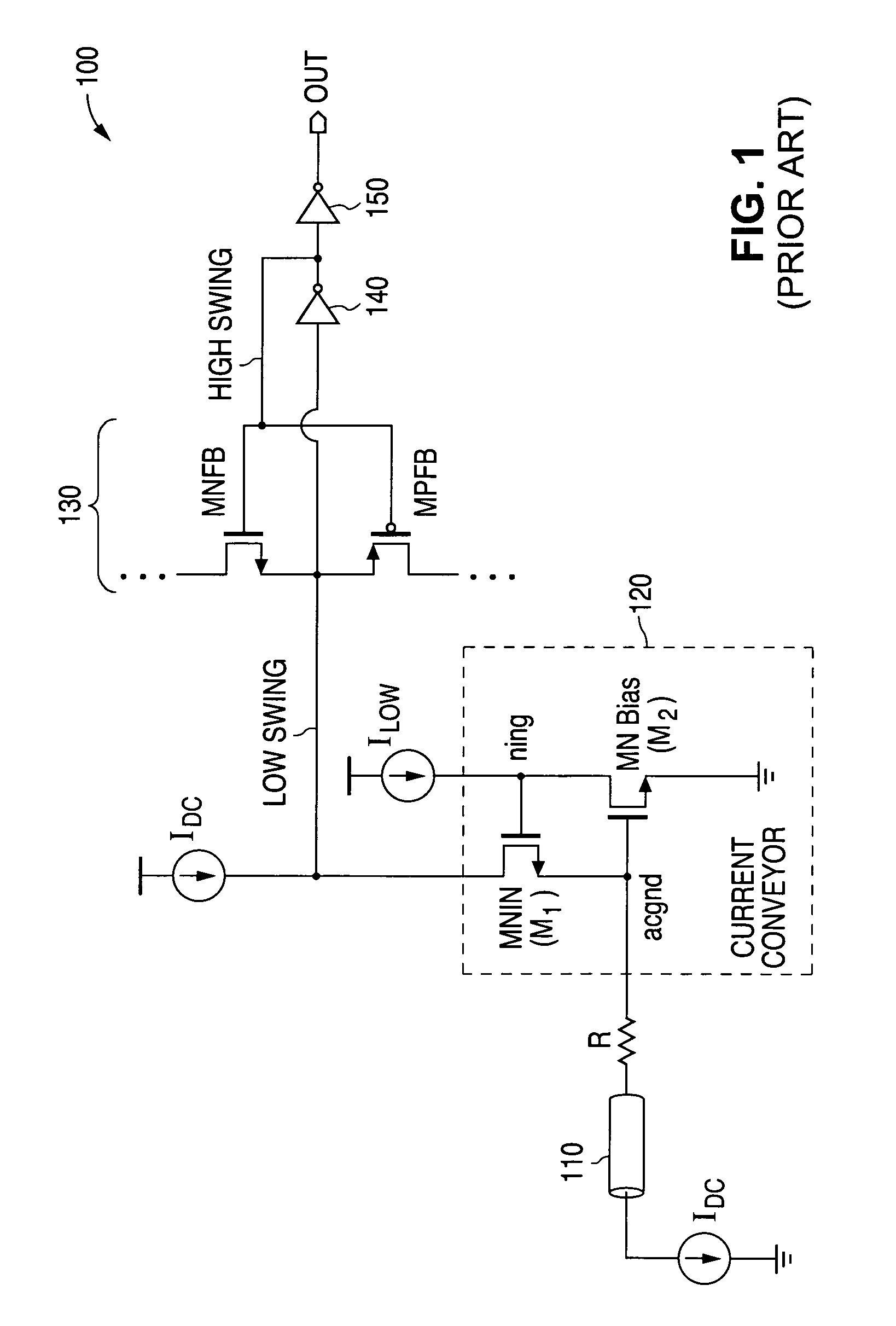
Current conveyor circuit with improved power supply noise immunity
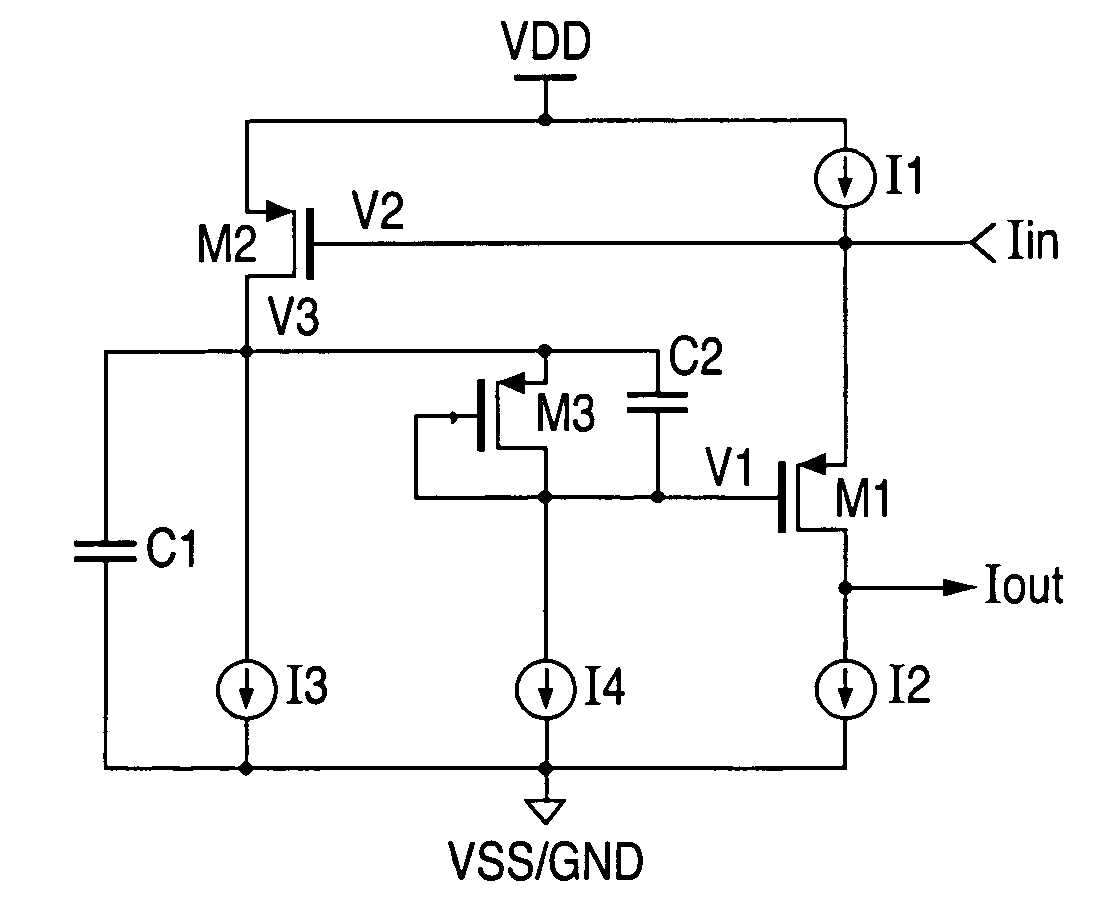
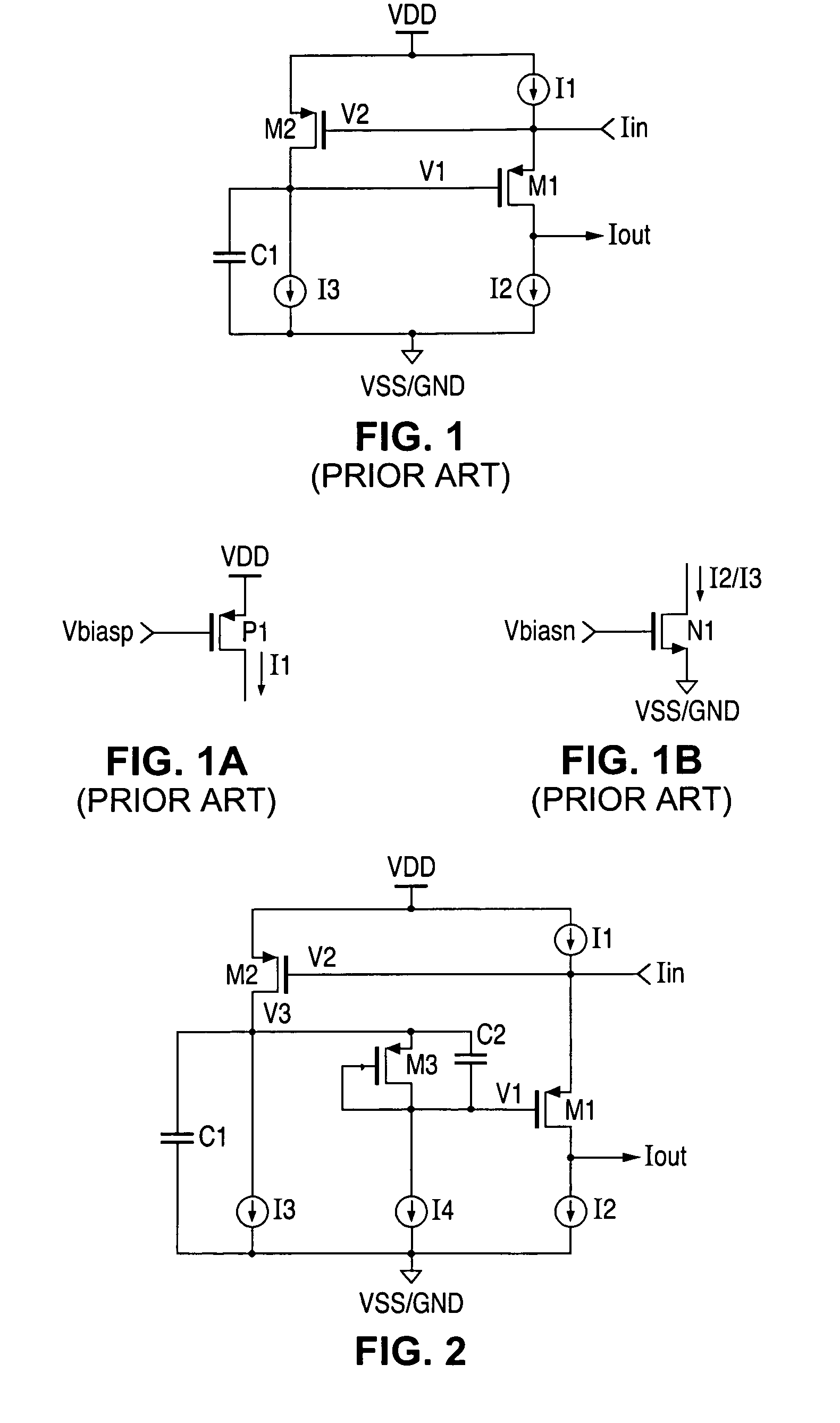
ActiveUS7193456B1Improved power supply noise immunityIncreases magnitudeAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationElectronic switchingVoltageCurrent conveyor
A current conveyor circuit with improved power supply noise immunity. Additional biasing circuitry causes the nominal biasing potential applied to the output circuit to be increased, thereby producing a corresponding increase in the magnitude of noise voltage needed to appear on the power supply before the output signal becomes affected.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Process deviation tolerating and reading interference eliminating reading amplifying circuit
ActiveCN104134452AReduce read disturbanceReduce the impact of process variationRead-only memoriesDigital storageProcess deviationsLoad circuit
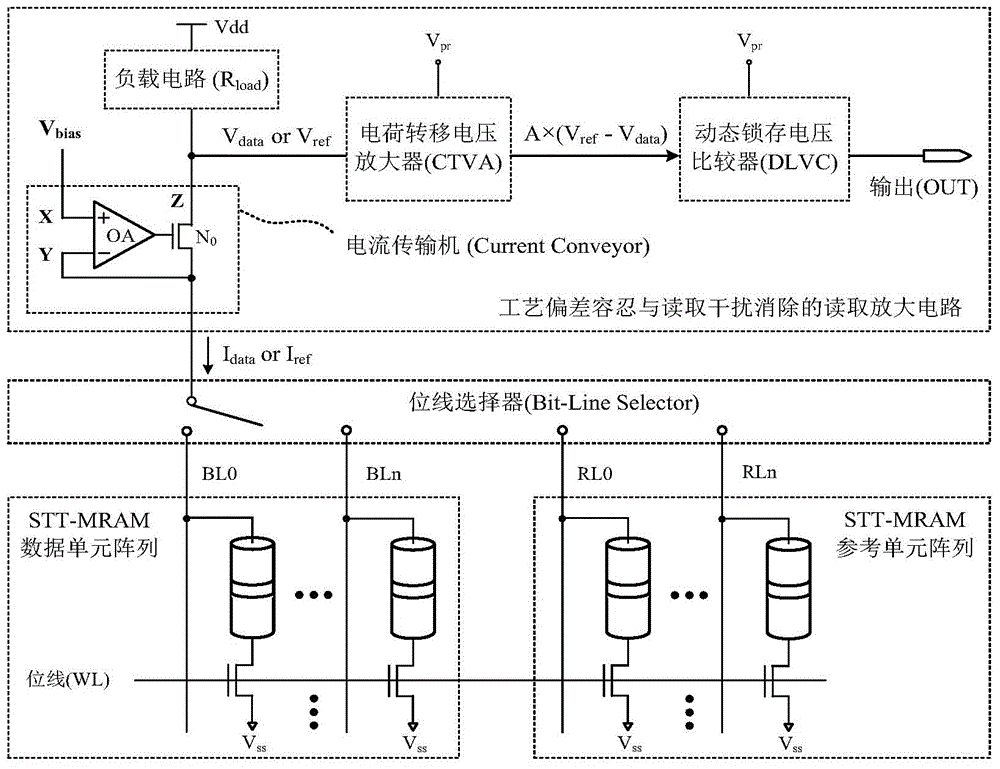
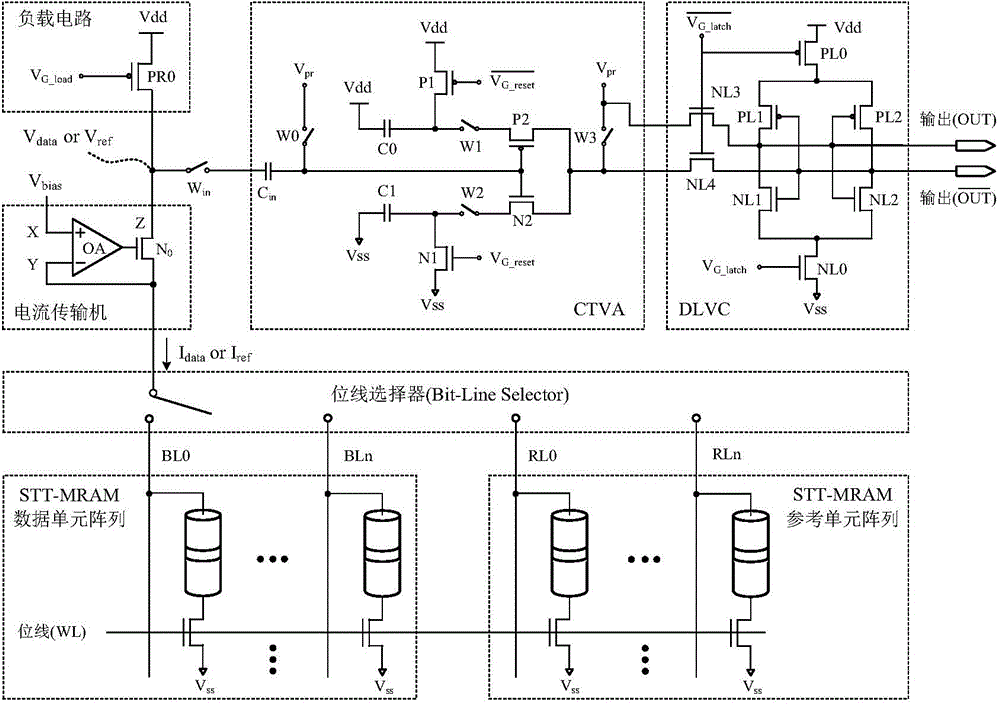
The invention provides a process deviation tolerating and reading interference eliminating reading amplifying circuit, which consists of a current conveyor, a load circuit, a charge transferring voltage amplifier and a dynamic latch voltage comparator, wherein one input end Y of the current conveyor is connected with an STT-MRAM (Spin Transfer Torque Magnetic Random Access Memory) data unit array to be read and an STT-MRAM reference unit array to be read through a bit line selector; the other input end X of the current conveyor is connected with an external bias voltage V<bias>; the output end Z of the current conveyor is simultaneously connected with the load circuit and the input end of the charge transferring voltage amplifier; the other end of the load circuit is connected with a power supply voltage source Vdd; the output end of the charge transferring voltage amplifier is connected with the input end of the dynamic latch voltage comparator; and the output end of the dynamic latch voltage comparator outputs final read binary data signals. The reading amplifying circuit provided by the invention has the advantages that the problem of conflict between the reading interference and the reading judging allowance in the STT-MRAM technology is solved, and the reading reliability of an STT-MRAM is improved.
Owner:致真存储(北京)科技有限公司
Replica biased voltage regulator
The invention discloses a replica biased voltage regulator circuit (100) that provides high frequency response via local positive feedback and low frequency response via a negative feedback loop. A voltage regulator circuit (100) can include current conveyor (106) that essentially forces an output voltage (Vload) to follow a replica voltage (Vrep). An operational amplifier (102) can provide negative feedback by controlling current supplied to the current conveyor (104) based on a comparison between a reference voltage (Vref) and the replica voltage (Vrep).
Owner:CYPRESS SEMICON CORP
Programmable gain instrumentation amplifier with improved gain multiplexers
ActiveUS20060038614A1Accurate trackingGain controlDifferential amplifiersInstrumentation amplifierAudio power amplifier
In one embodiment, a programmable gain instrumentation amplifier comprises an input stage configured with a differential precision current conveyor circuit. The current conveyor circuit may be implemented with operational amplifiers coupled to gain-setting resistors, with double-multiplexers configured on each end of the gain-setting resistors. In a first set of embodiments, the double-multiplexers may be bootstrapped, whereby the power supplies of each double-multiplexer may track the signals on the output pin of a respective sense-multiplexer component of the double-multiplexer. In a second set of embodiments, the power supplies may alternatively track the op-amp differential output during non-overload conditions, or the op-amp common-mode output at a gain resistor center tap during overload conditions. Corresponding bootstrap circuits may be designed for both sets of embodiments, the bootstrap circuits coupling to the respective tracking node or nodes in either case.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
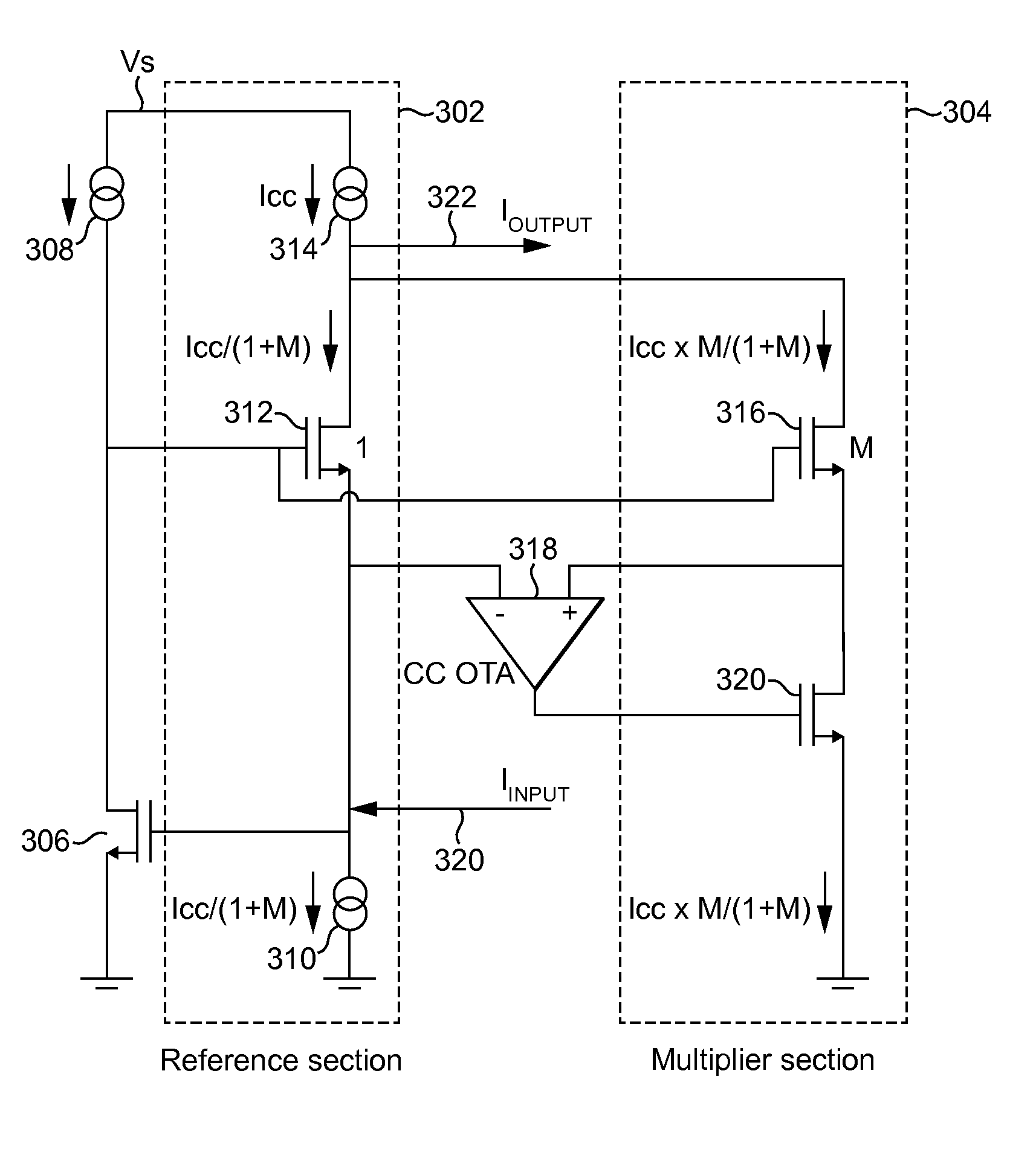
Multiplying current conveyor for amplifier
ActiveUS20150214898A1Power amplifiersAmplifier modifications to raise efficiencyAudio power amplifierEngineering
A circuit having a first transistor being a common gate connected transistor and a second transistor, the second transistor being M times the size of the first transistor, the first and second transistors having commonly connected gates and commonly connected drains, wherein an apparatus is provided to regulate the source voltage of the second transistor to track the source voltage of the first transistor, wherein the current gain of the circuit is M+1.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
Differential structure programmable gain instrumentation amplifier
ActiveUS7327189B2Increase computing speedImprove output swingDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Instrumentation amplifier
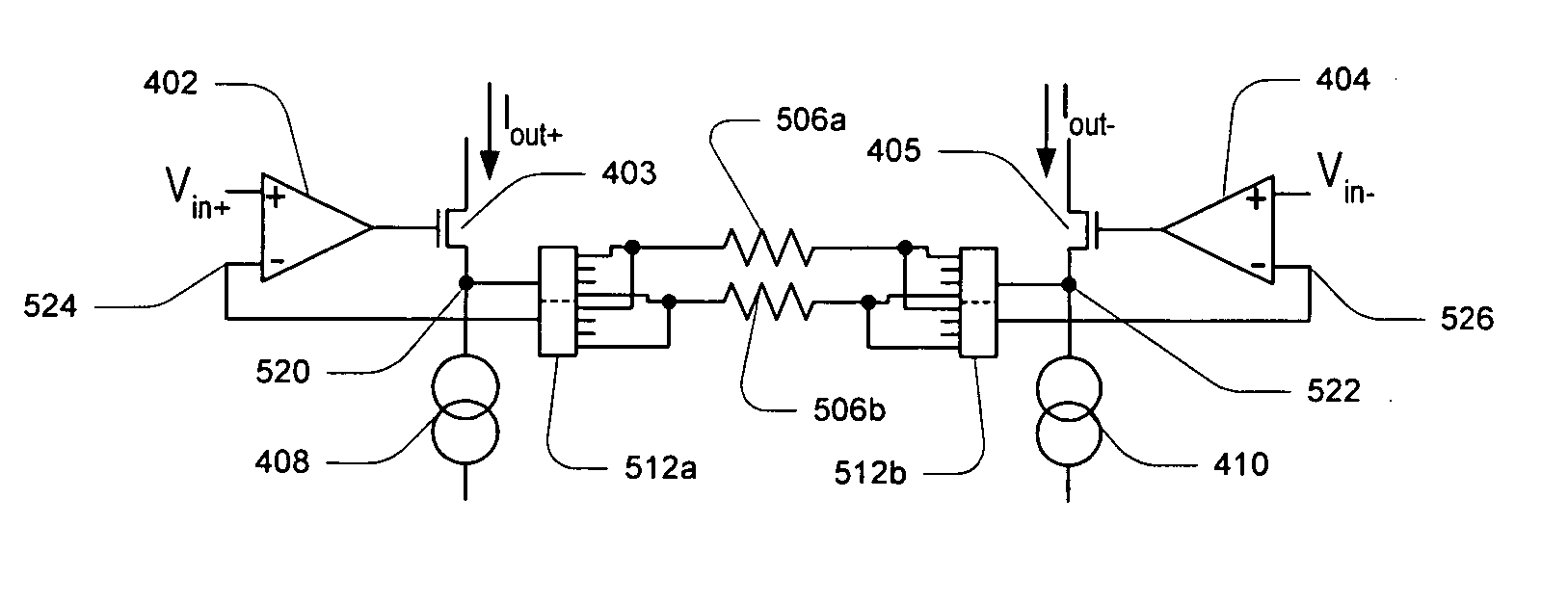
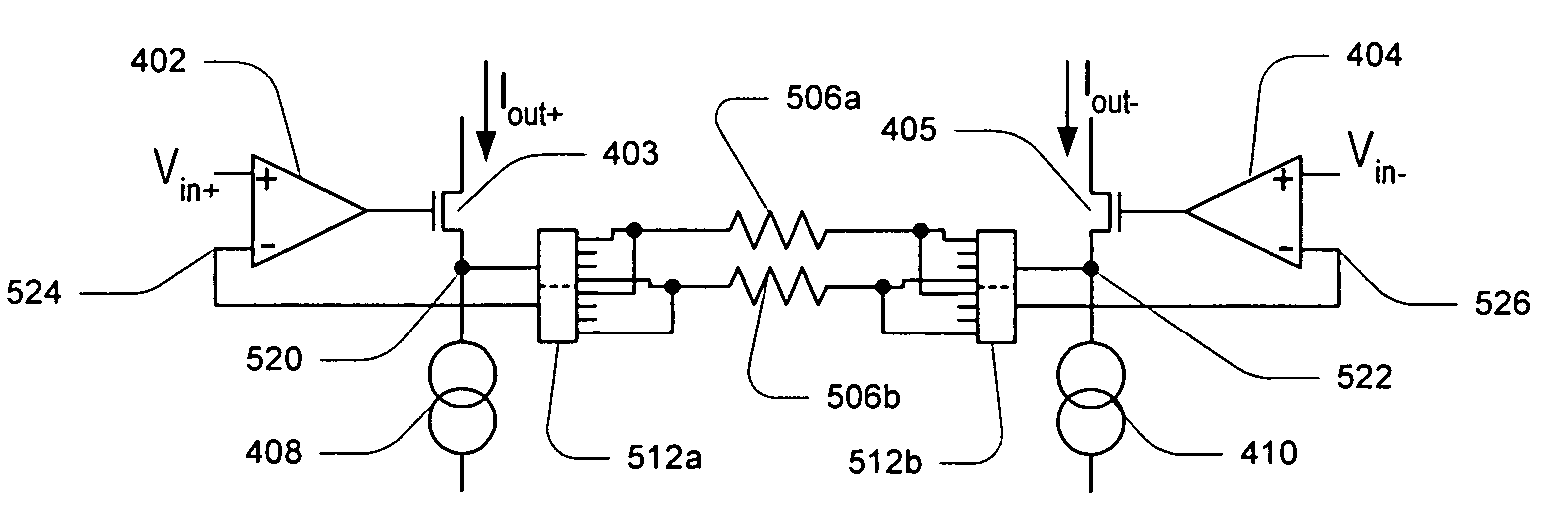
In one embodiment, a programmable gain instrumentation amplifier (PGIA) comprises a pair of current conveyors, each current conveyor having a respective sense node and a respective voltage input, with a gain-setting resistor coupled between the respective sense nodes, and current being sensed on both sides of the gain setting resistor. In one embodiment, each current conveyor comprises a corresponding operational amplifier (op-amp) having a non-inverting input configured as the respective voltage input that may receive a respective input voltage signal, an output and an inverting input, with a respective current conveying element, which may be a FET, configured in a feedback loop between the output and the inverting input. Each current conveyor may be configured to sense a corresponding current flowing through its respective FET, with the corresponding currents forming a differential output current of the PGIA. The respective input voltage signals received by the respective voltage inputs may form a differential input voltage of the PGIA. In one set of embodiments, the PGIA may be implemented with a differential voltage output, leading to an increased output swing for higher signal-to-noise ratio and increased symmetry for a higher common mode rejection ratio.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
Noise cancellation circuit and operating method thereof
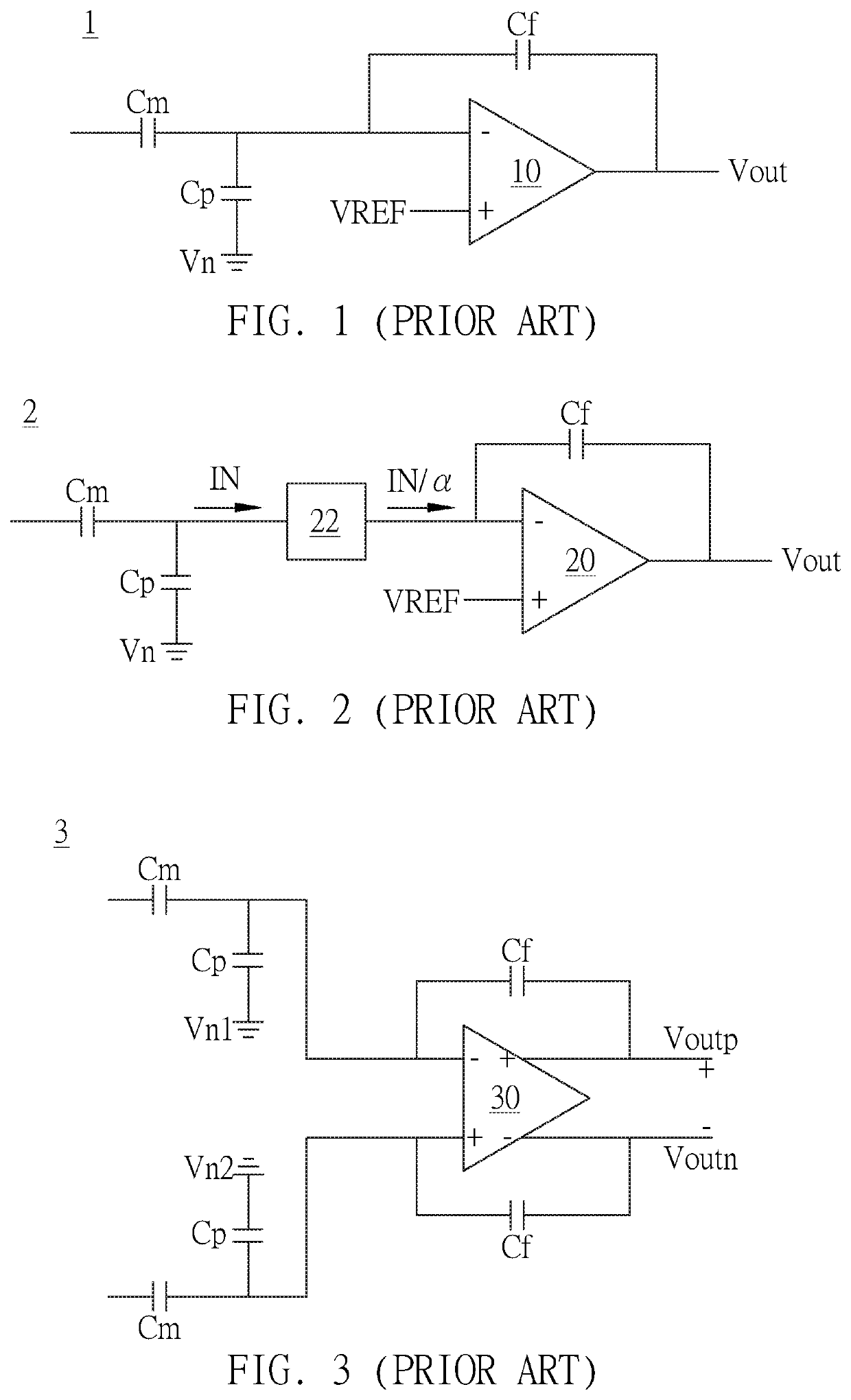
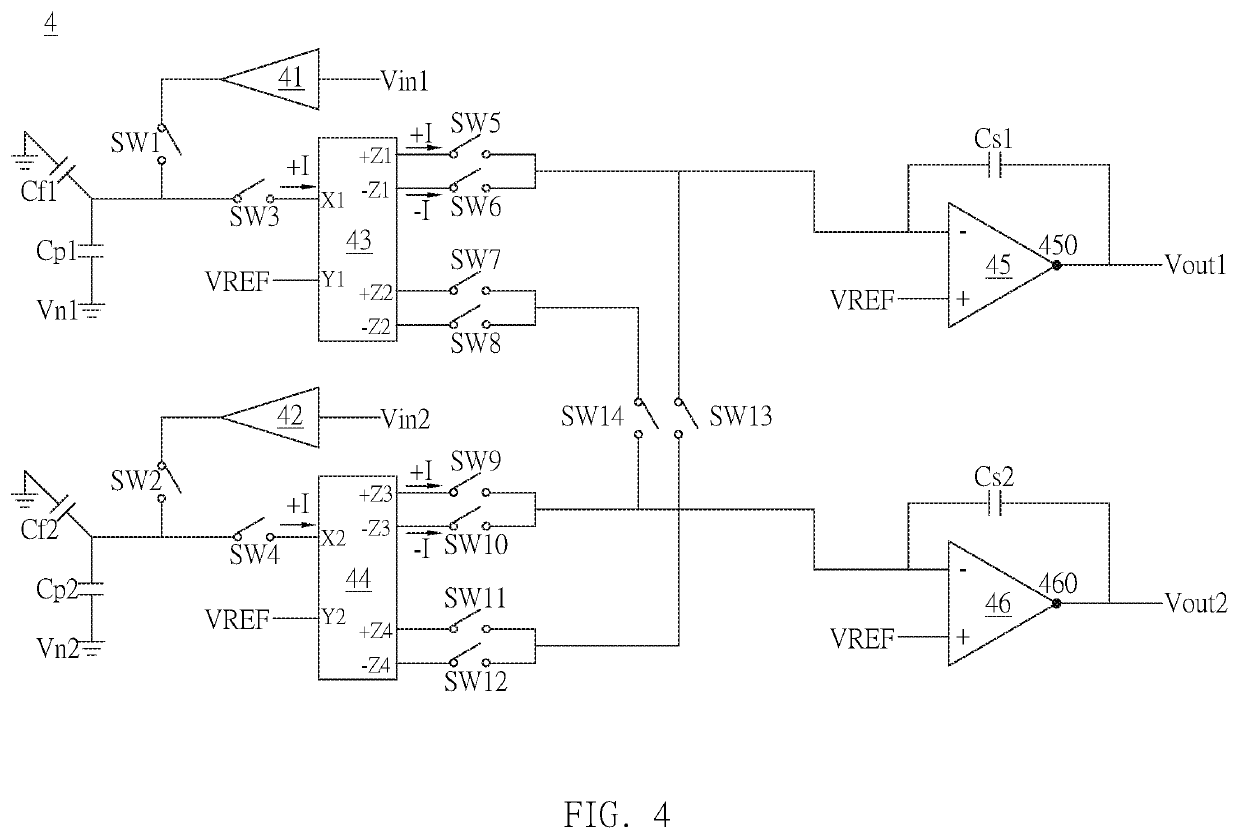
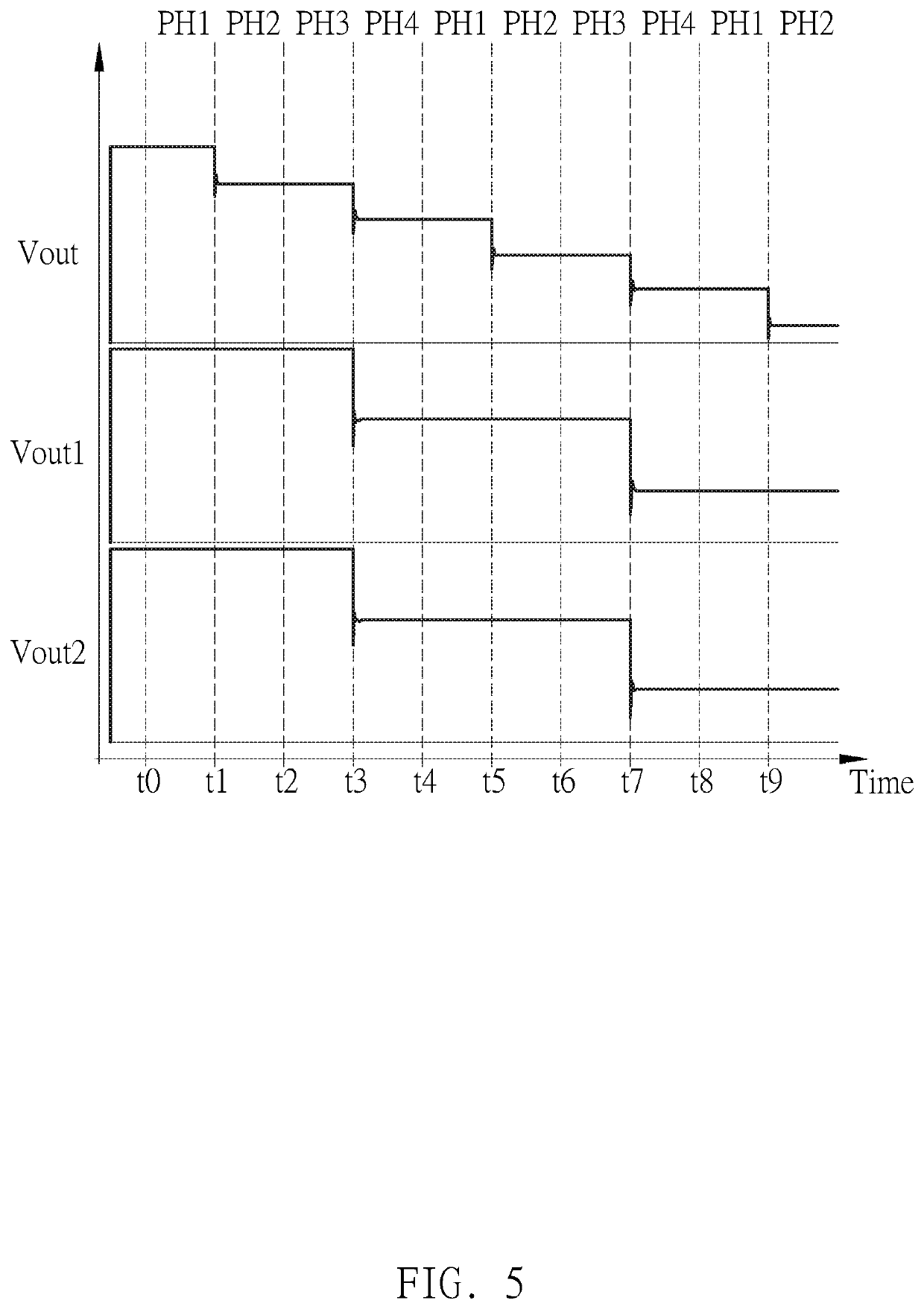
InactiveUS20200220544A1Improve accuracyCancel noiseCapacitance measurementsElectronic switchingSoftware engineeringHemt circuits
A noise cancellation circuit includes a first switch to a fourteenth switch, a first / second analog buffer, a first / second feedback capacitor, a first / second parallel capacitor, a first / second current conveyor, a first / second operation amplifier and a first / second series capacitor. In a first phase, the first switch and second switch are turned on and the remaining switches are not turned on. In a second phase, the third to fifth switches, the eighth to ninth switches and the twelfth to fourteenth switches are turned on and the remaining switches are not turned on. In a third phase, the first switch and the second switch are turned on and the remaining switches are not turned on. In a fourth phase, the third to fifth switches, the seventh switch, the tenth switch and the twelfth to fourteenth switches are turned on and the remaining switches are not turned on.
Owner:RAYDIUM SEMICON
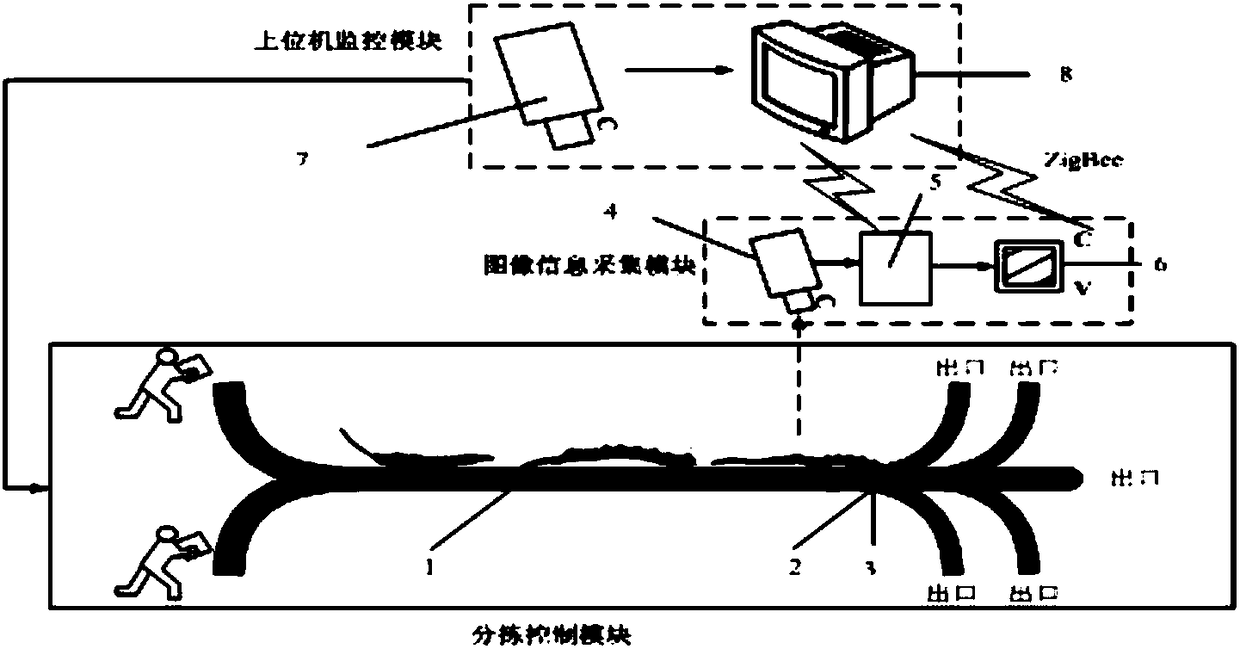
Intelligent sorting system of caterpillar fungus and utilization method of intelligent sorting system
ActiveCN108311411AImprove recognition efficiencyImprove recognition accuracyNeural architecturesSortingCamera lensLiquid-crystal display
The invention provides an intelligent sorting system of caterpillar fungus and a utilization method of the intelligent sorting system. The intelligent sorting system comprises a conveyor belt, a motor, a sliding shoe, a camera lens, a microprocessor, an LCD (Liquid Crystal Display), an upper computer camera lens and an upper computer, wherein the conveyor belt is used for conveying the caterpillarfungus needing to be sorted; the motor is used for controlling the conveyor belt to operate; the sliding shoe is used for sorting the caterpillar fungus of a corresponding path opening; the camera lens is located above the sorting path opening and is used for acquiring a caterpillar fungus image; the microprocessor is connected with a camera through a serial port and is used for transplanting OpenCV to carry out image processing; a caterpillar fungus type is identified through a convolutional neural network based on a SUPF algorithm; graded sorting is carried out through Canny edge detectionand a Hu matrix algorithm and the sliding shoe is controlled to carry out sorting; the LCD is used for displaying acquired caterpillar fungus information; the upper computer camera lens is used for monitoring a sorting condition and feeding the sorting condition back to the upper computer in real time; the upper computer is used for displaying a current sorting condition in real time and acquiringthe quantity of the caterpillar fungus on the current conveyor belt through image processing, so as to control the speed of the motor. The intelligent sorting system provided by the invention can beused for identifying and positioning the caterpillar fungus with different species and different grades and the sorting error rate is reduced.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF SCI & TECH
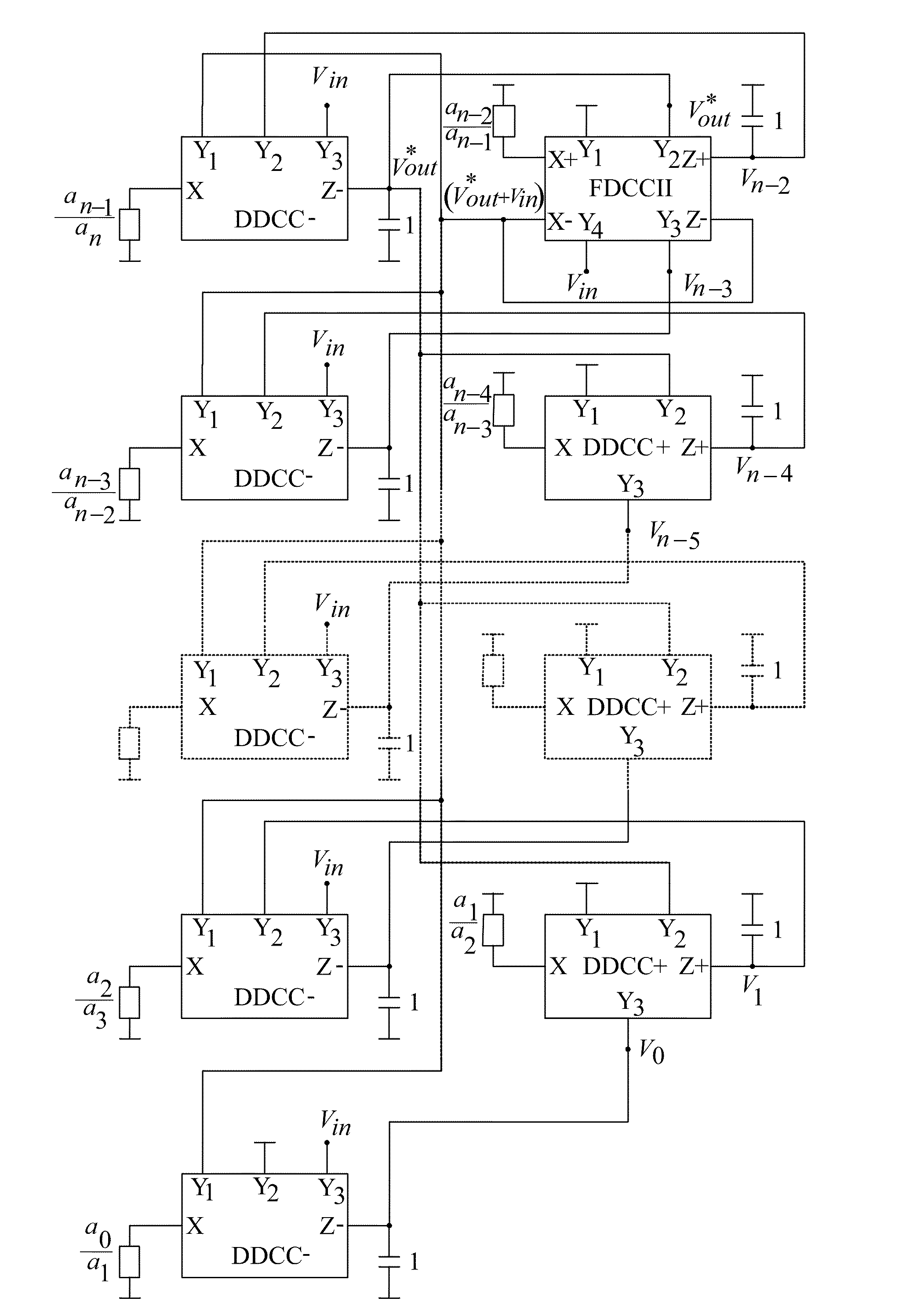
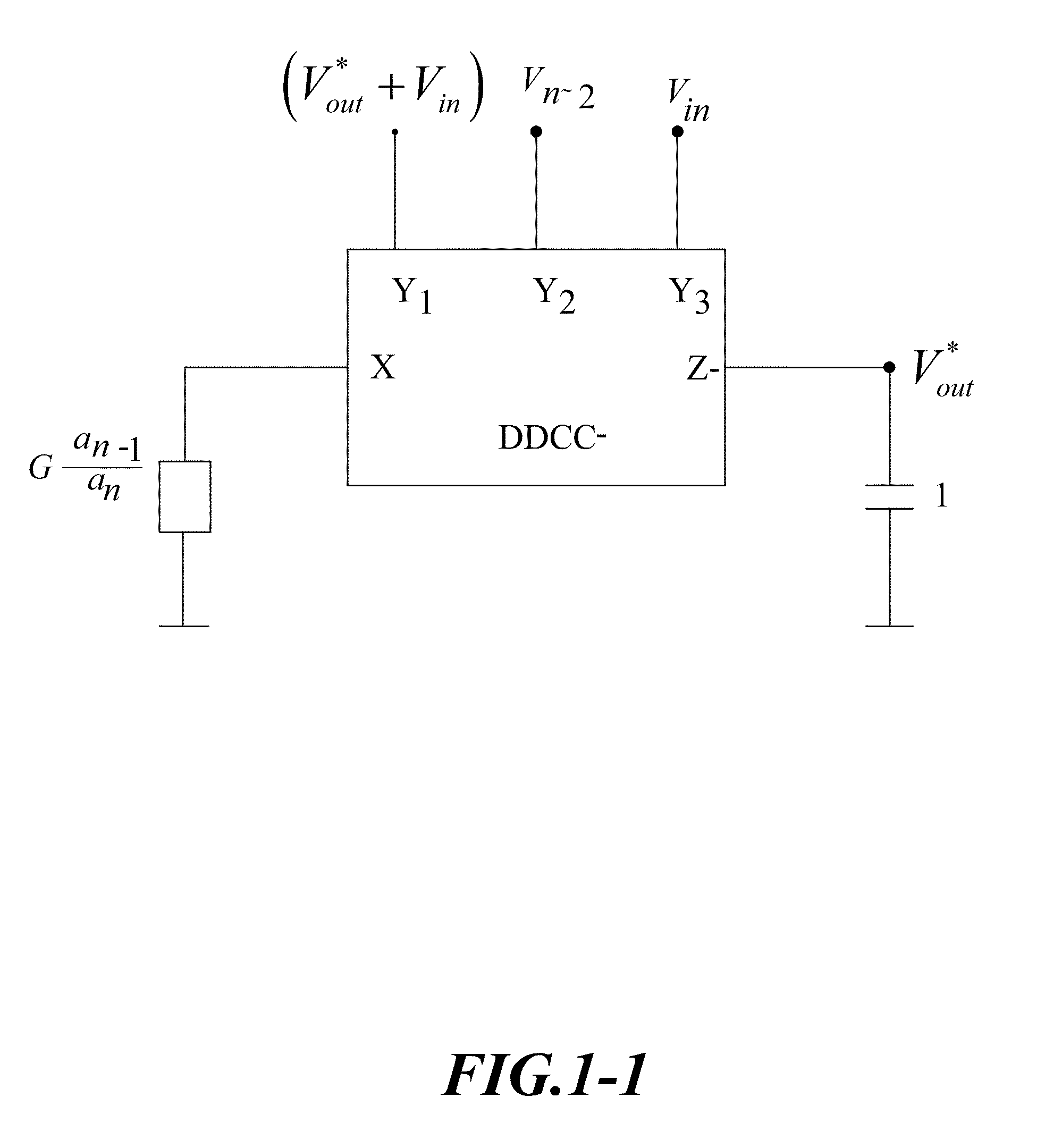
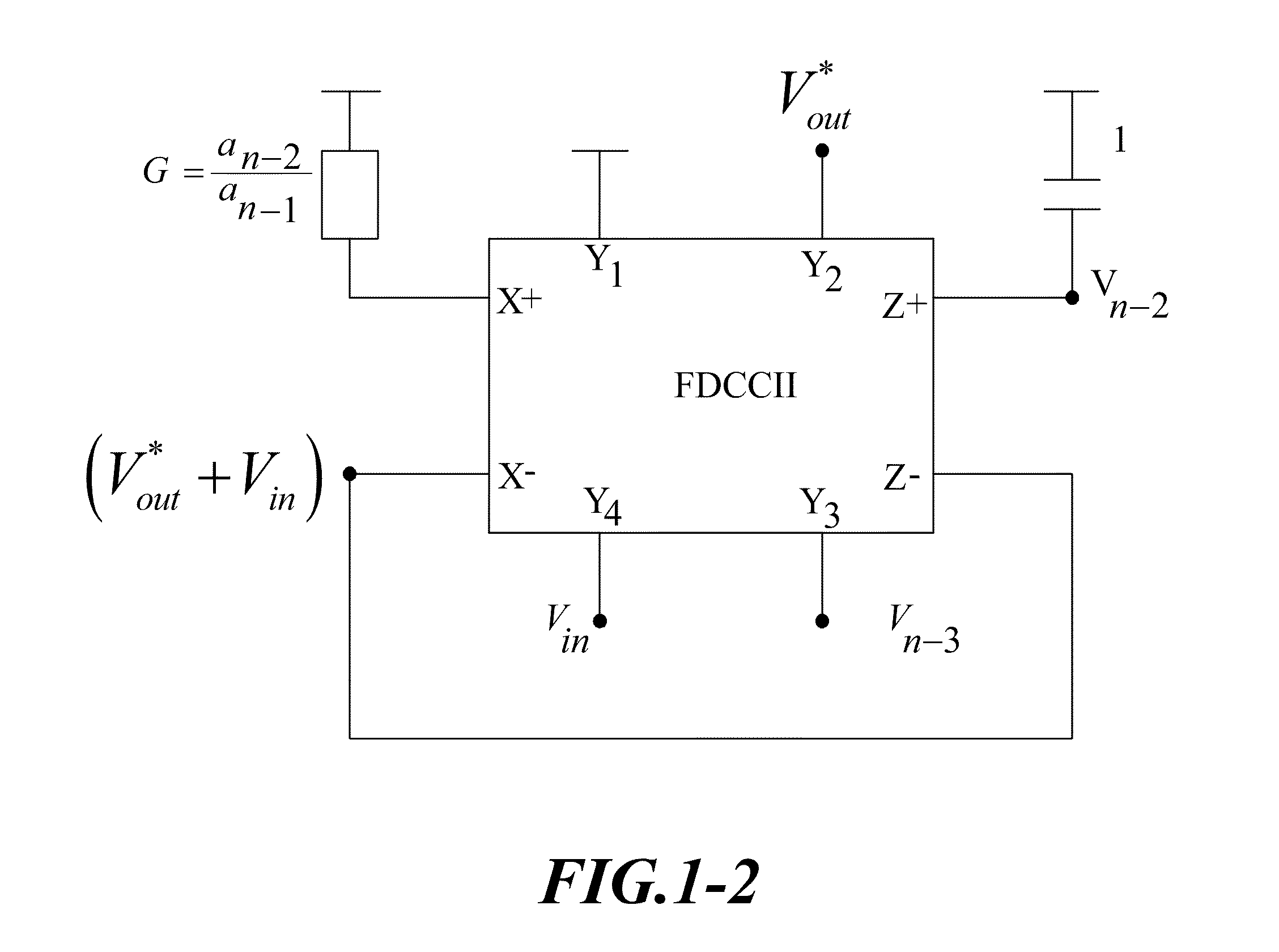
DDCC and FDCCII-Grounded Resistor and Capacitor Filter Structures
InactiveUS20100005430A1Simple filter structureReduce parasitismComputer aided designSoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationElectrical resistance and conductanceIntegrator
A voltage-mode nth-order differential difference current conveyor (DDCC) and fully differential current conveyor (FDCCII)-resistor and capacitor filter structures are proposed using a new effective analytical synthesis method (ASM), a succession of innovative algebra operations until a set of simple equations are produced, which are then realized using n integrators and a constraint sub-circuitry, A new ASM can effectively carry out (i) use of all the grounded capacitors and grounded resistors, and (ii) employment of the minimum number of active and passive components and then enjoys the low sensitivities, lower parasitics, power consumption, noise, and smaller chip area leading to simultaneously achieving two important features: (i) higher output performance and (ii) lower cost, without tradeoff. Moreover, the component value variations of all the relative sensitivities have the same incremental percentage or decrement.
Owner:CHUNG YUAN CHRISTIAN UNIVERSITY
Current mode active device-based wideband radio frequency mixer
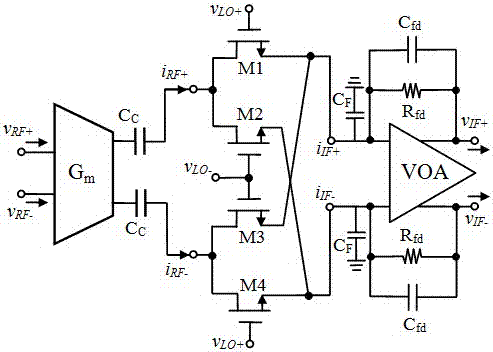
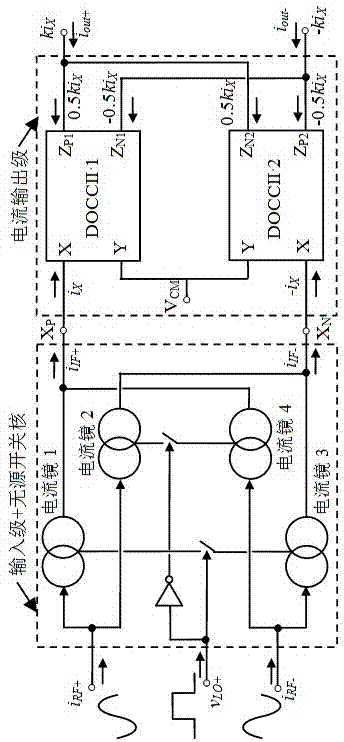
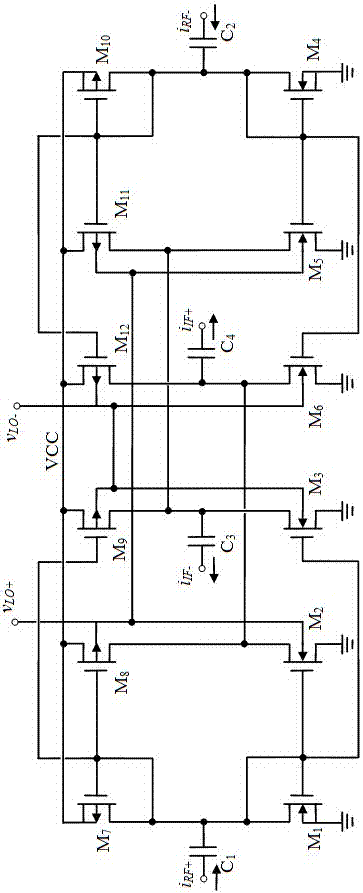
ActiveCN106877821AImprove conversion gainImprove linearityModulation transference balanced arrangementsPhase currentsEngineering
The present invention discloses a current mirror and DOCCII (dual-output current conveyor)-based wideband radio mixer. The wideband radio mixer provided by the invention is composed of a dual-NMOS-PMOS current mirror mixing unit and a current output stage; four dual-NMOS-PMOS current mirrors embedded with local oscillation signals vLO+ / - are combined together so as to form the dual-NMOS-PMOS current mirror mixing unit; the dual-NMOS-PMOS current mirror mixing unit is used for executing the input stage and passive switch core of the mixer and is equivalent to the double-balance topological structure of a traditional active Gilbert mixer; the in-phase current output ends and anti-phase current output ends of two dual-output current conveyors are in cross coupled connection with each other, so that the current output stage can be formed; and the current output stage is adopted as the transimpedance amplifier of a conventional passive mixer; and the current output stage has very low input impedance and high output impedance and is used for achieving the amplification of output current signals which have been subjected to pre-frequency conversion and effectively driving a next-stage circuit. According to the wideband radio mixer provided by the invention, inductive passive components are not required. The wideband radio mixer can simultaneously have the advantages of the active Gilbert mixer and the passive mixer.
Owner:常州联讯信息科技有限公司
Differential structure programmable gain instrumentation amplifier
ActiveUS20060038615A1Easy to switchImprove output swingDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesAudio power amplifierInstrumentation amplifier
In one embodiment, a programmable gain instrumentation amplifier (PGIA) comprises a pair of current conveyors, each current conveyor having a respective sense node and a respective voltage input, with a gain-setting resistor coupled between the respective sense nodes, and current being sensed on both sides of the gain setting resistor. In one embodiment, each current conveyor comprises a corresponding operational amplifier (op-amp) having a non-inverting input configured as the respective voltage input that may receive a respective input voltage signal, an output and an inverting input, with a respective current conveying element, which may be a FET, configured in a feedback loop between the output and the inverting input. Each current conveyor may be configured to sense a corresponding current flowing through its respective FET, with the corresponding currents forming a differential output current of the PGIA. The respective input voltage signals received by the respective voltage inputs may form a differential input voltage of the PGIA. In one set of embodiments, the PGIA may be implemented with a differential voltage output, leading to an increased output swing for higher signal-to-noise ratio and increased symmetry for a higher common mode rejection ratio.
Owner:NATIONAL INSTRUMENTS
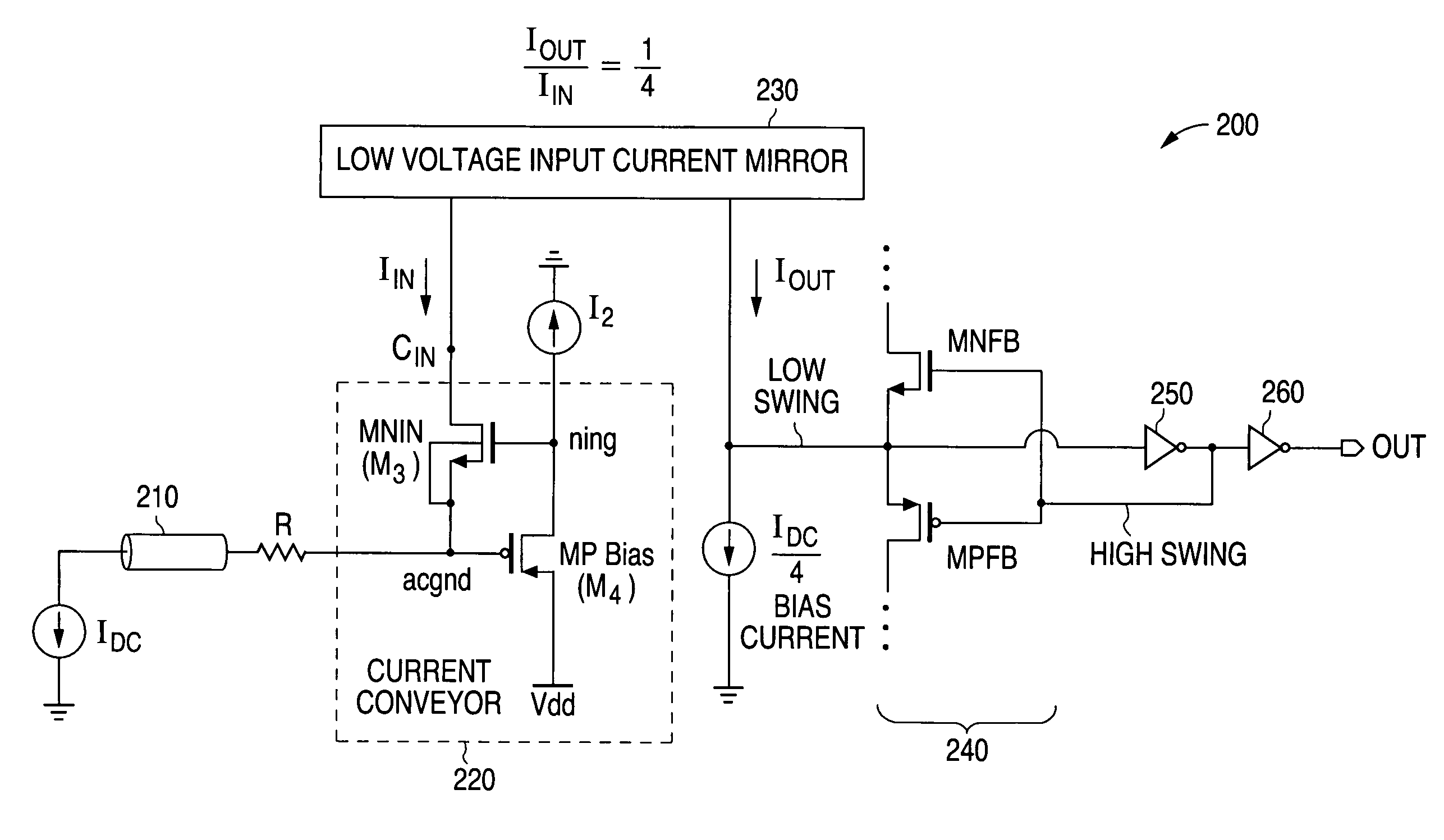
System and method for providing a high input common mode current conveyor
ActiveUS7764115B1Increase rangeAffecting functionalityAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesElectric variable regulationLow voltageEngineering
A system and method is disclosed for providing an improved current conveyor circuit in a mobile pixel link (MPL) receiver that can provide an increased input common mode voltage to allow a greater tolerance of noise on a transmission line. The current conveyor circuit comprises (1) a PMOS transistor with a source coupled to an operating voltage Vdd and a drain that is coupled to a current source, and (2) an NMOS transistor with a source coupled to an input terminal of the current conveyor circuit and a drain coupled to a low voltage input current mirror. The current conveyer circuit increases the range of the common mode voltage of the receiver without adversely affecting the functionality of the receiver.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Simulated circuit layout for low voltage, low paper and high performance type II current conveyor
InactiveUS6931605B2Easy to useHigh swing capabilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesMOSFETLow voltage
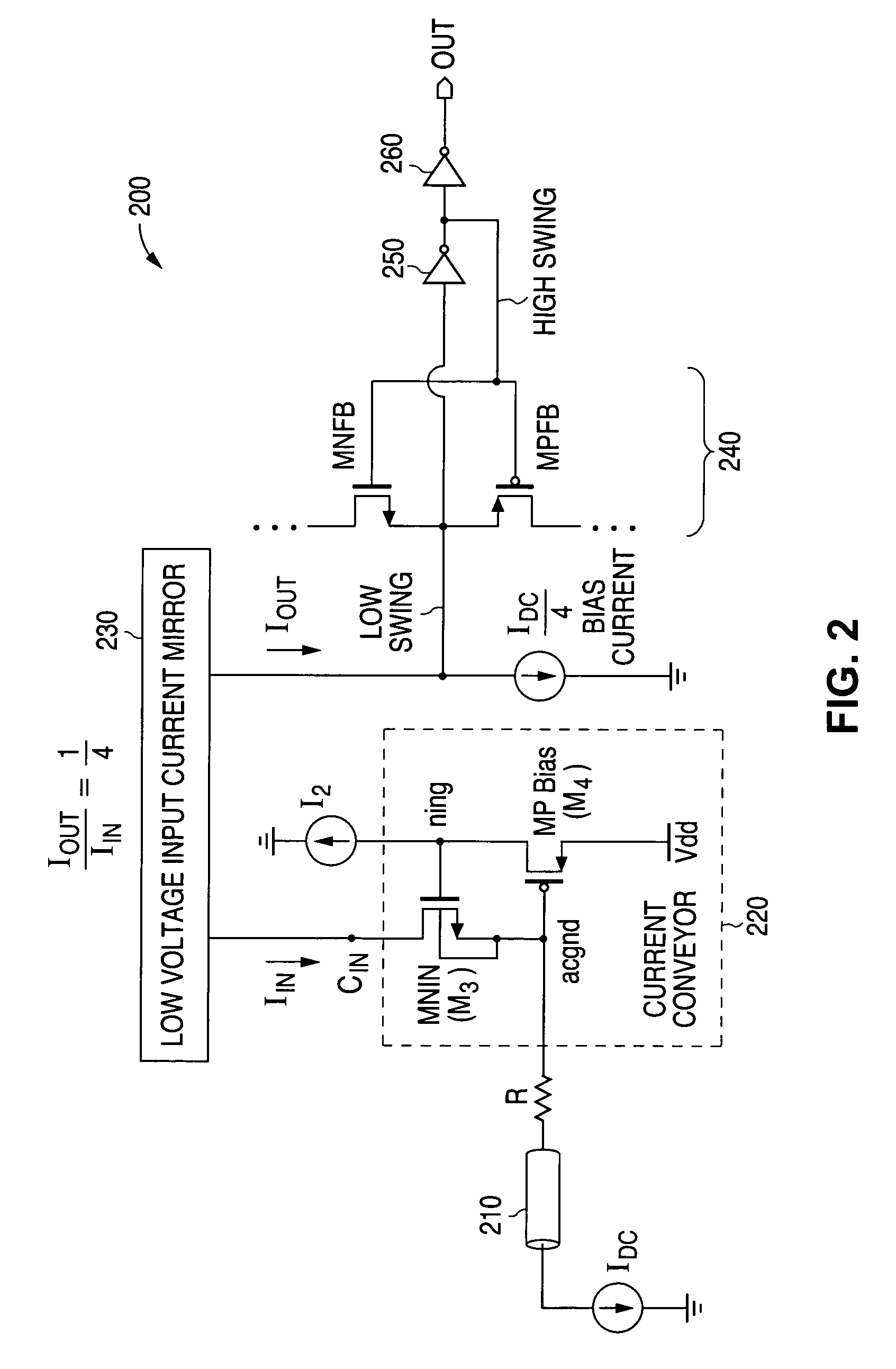
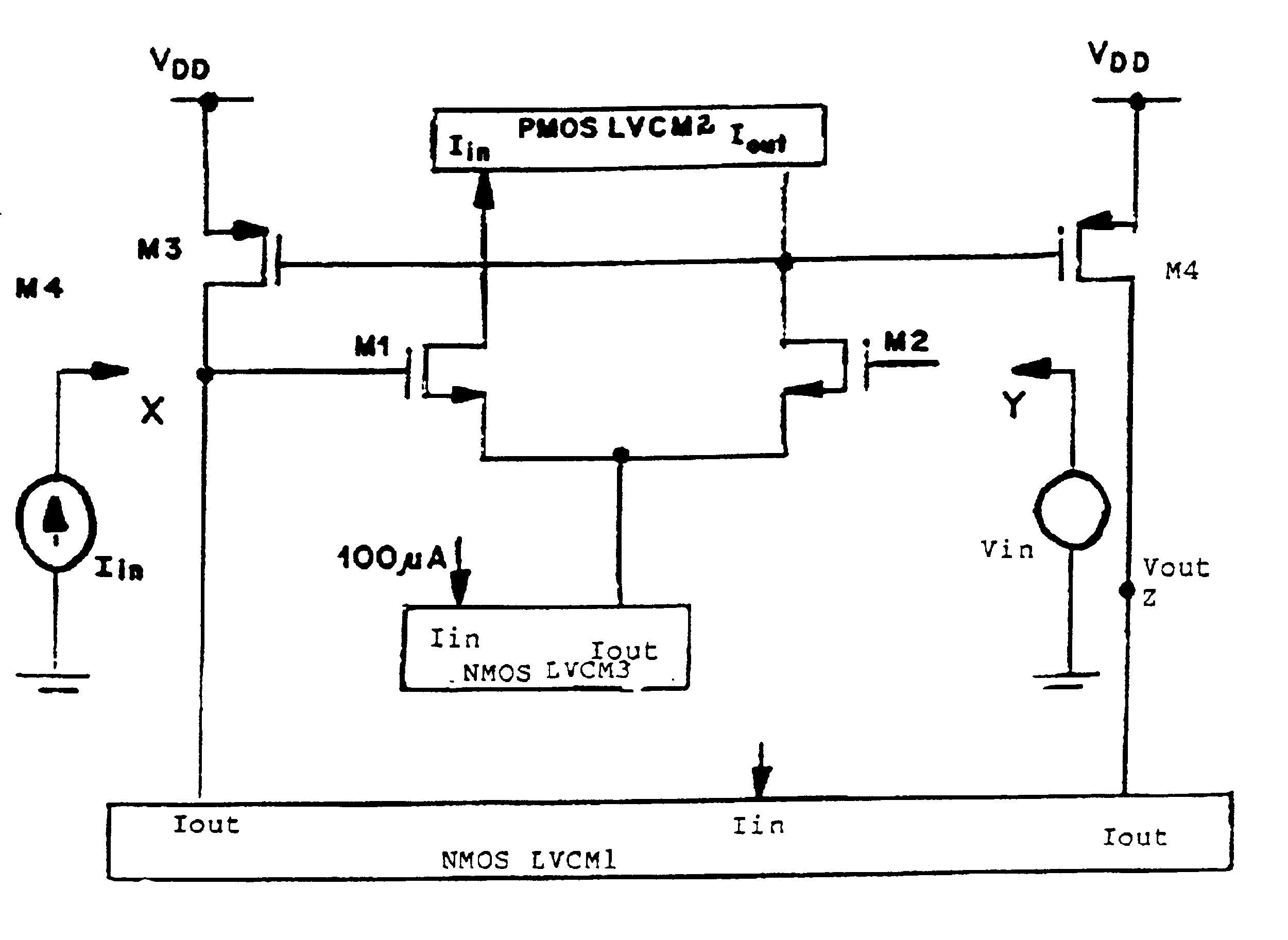
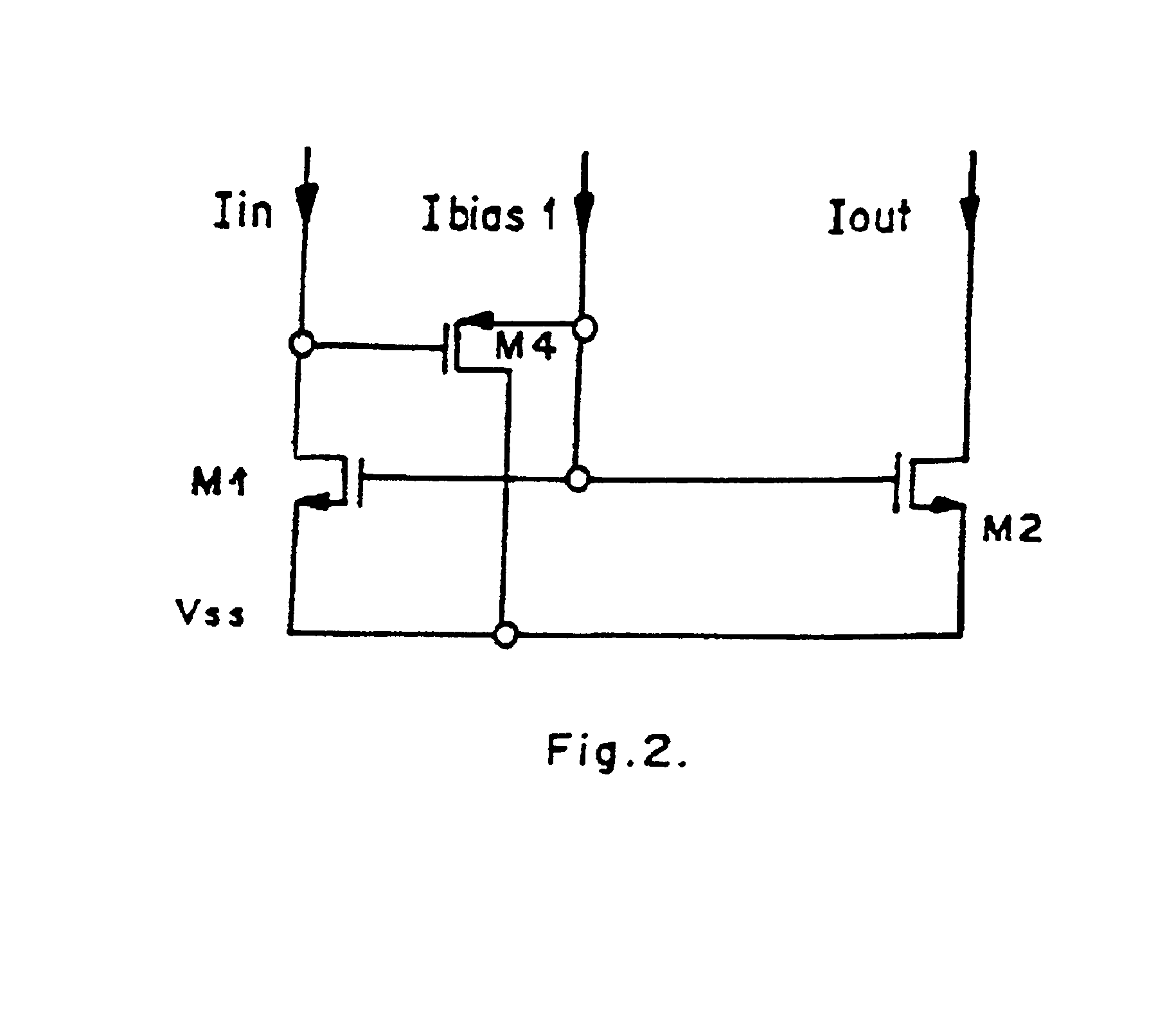
The present invention relates to a current conveyor circuit capable of operating at very low voltages, said circuit comprising: three LVCM's and four MOSFETS, wherein LVCM1 provides a constant bias current to flow through M3, if port X is kept open and the difference between the bias current and the injected current flows through M3 if a current is injected into port X, which gets reflected at port Z due to the action of LVCM1, M3 and M4, LVCM2 maintains the drain currents of M1 and M2 constant, and LVCM3 maintains a constant tail current in the circuit.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
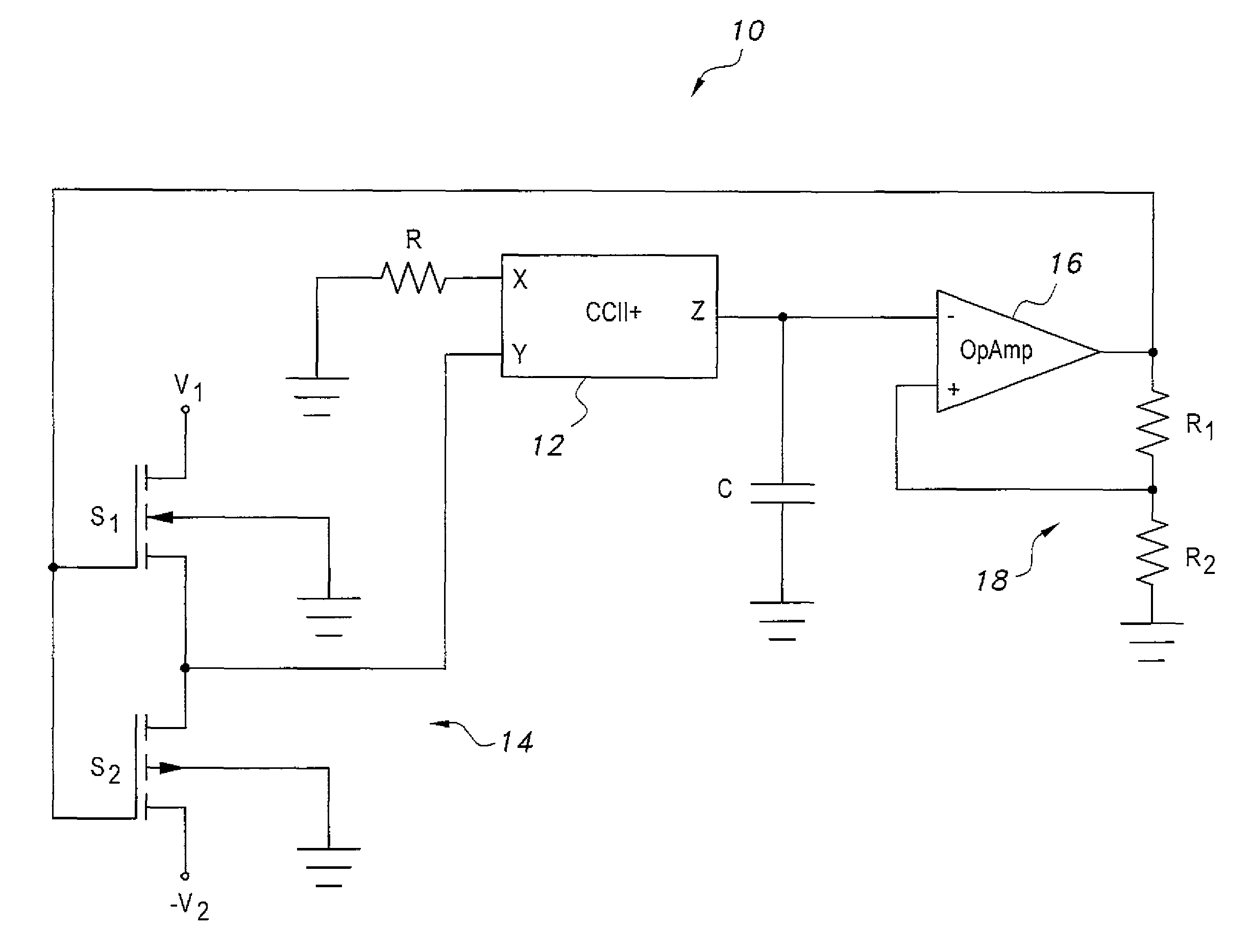
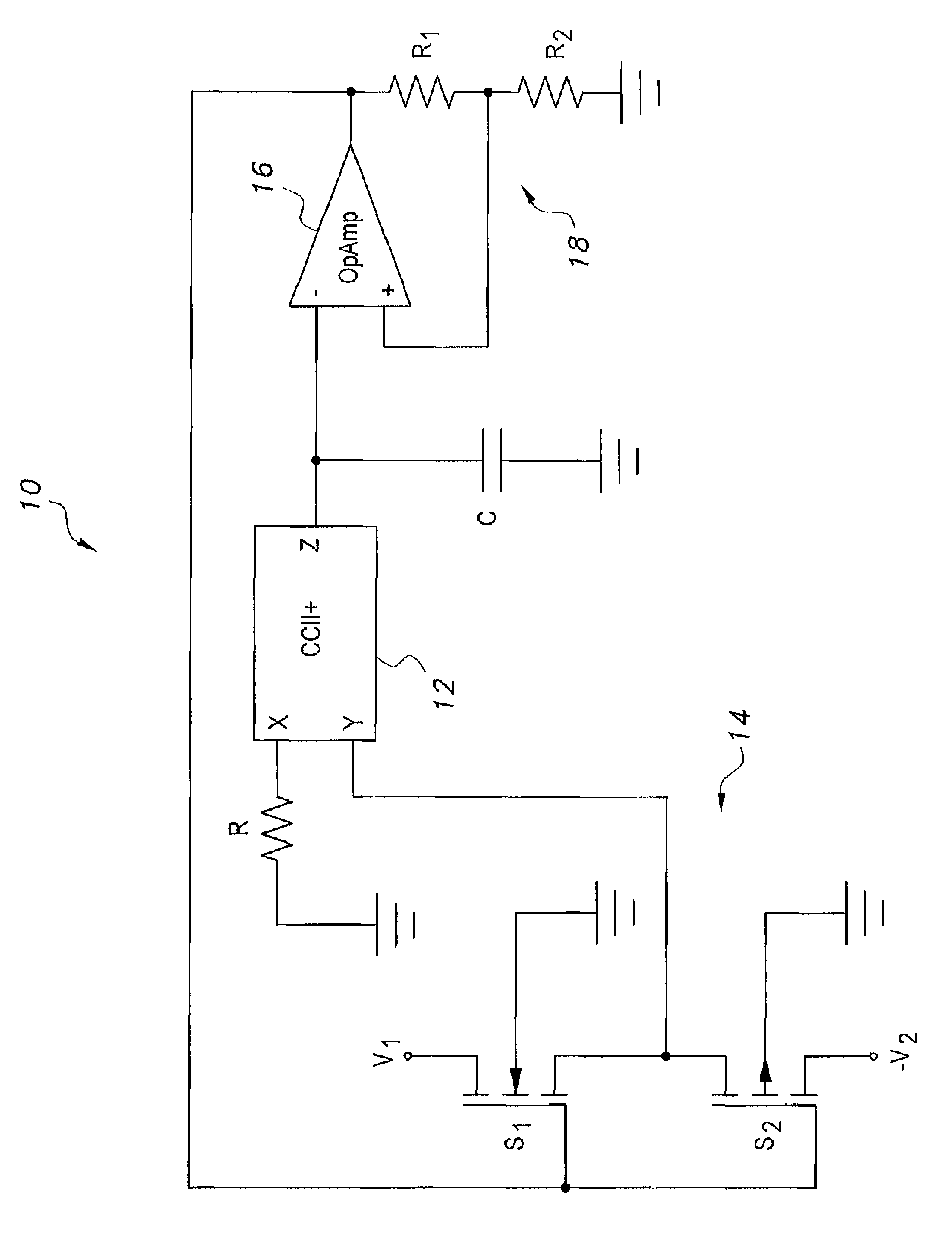
Voltage-controlled dual-slope square and triangular waveform generator
The voltage-controlled dual-slope square and triangular waveform generator is an electronic circuit that includes a plus-type second-generation current conveyor operably connected to a single operational amplifier. At the input stage to the operational amplifier, two metal-oxide semiconductor (MOS) transistors are configured as switches. Three resistors and a grounded capacitor are included in the electronic circuit, thereby maintaining a low component count. The leading and trailing slopes of the waveform are independently adjustable by selection of the voltages V1 and V2 that are selectively connectable to the y-input of the CCII+ via switching action of the MOS transistors. The frequency of the waveform is adjustable via the voltage divider ratio between the output and noninverting input of the operational amplifier. The simple and elegant nature of the circuit design provides a low-cost waveform generator that can be adjusted both for frequency and for independent leading edge and trailing edge slopes.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com