Patents
Literature
159results about How to "Increase erasing speed" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
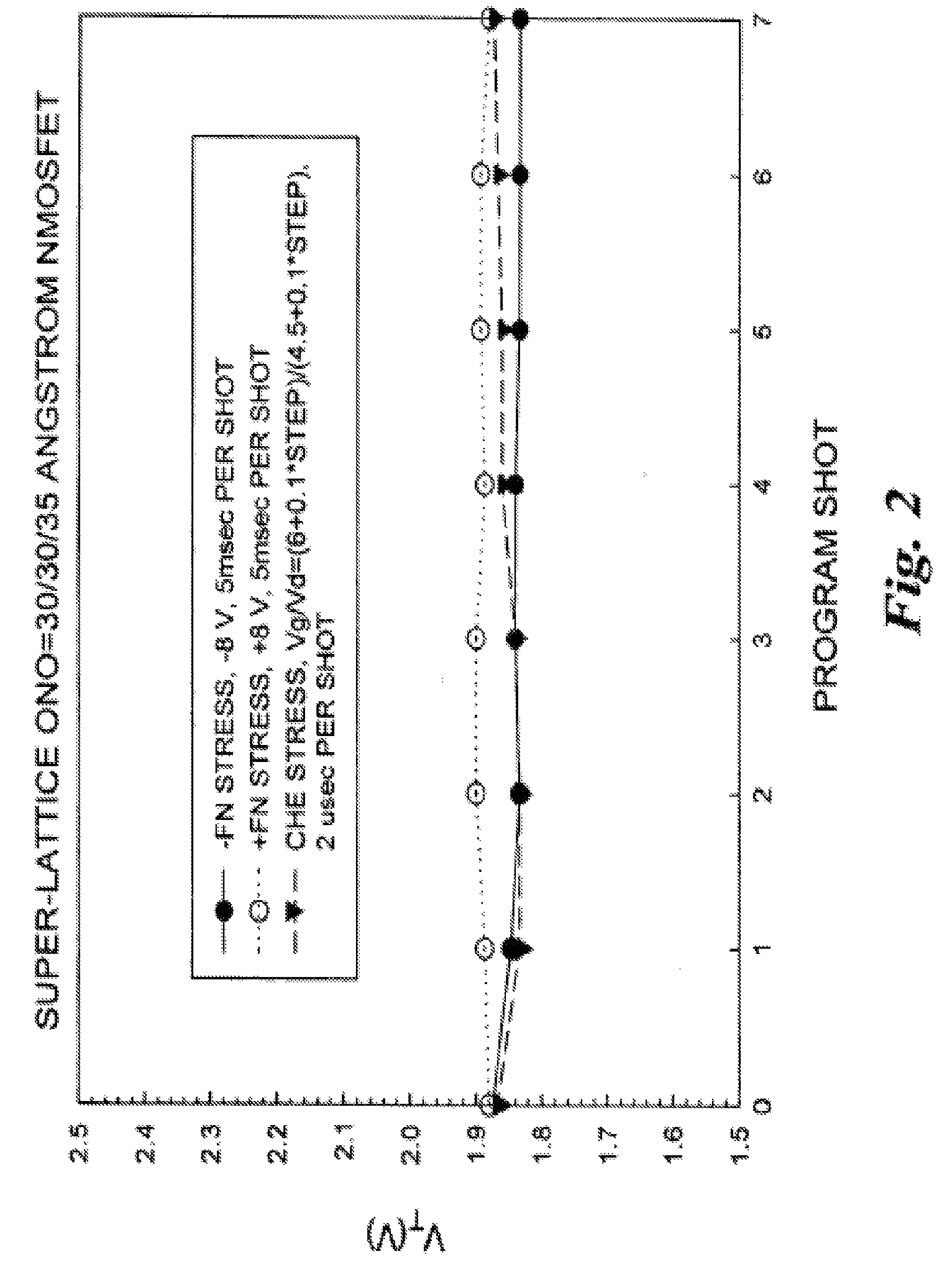
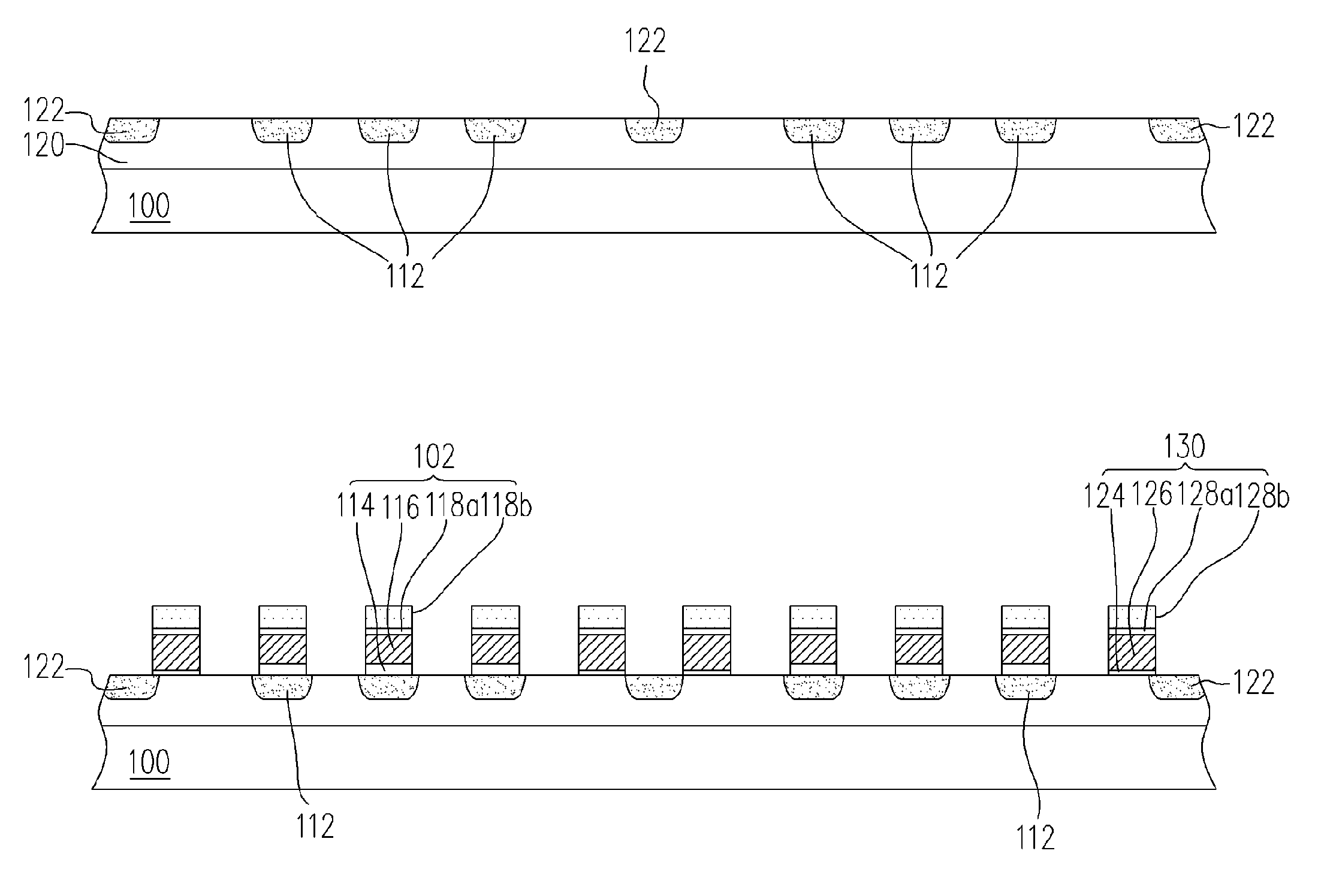
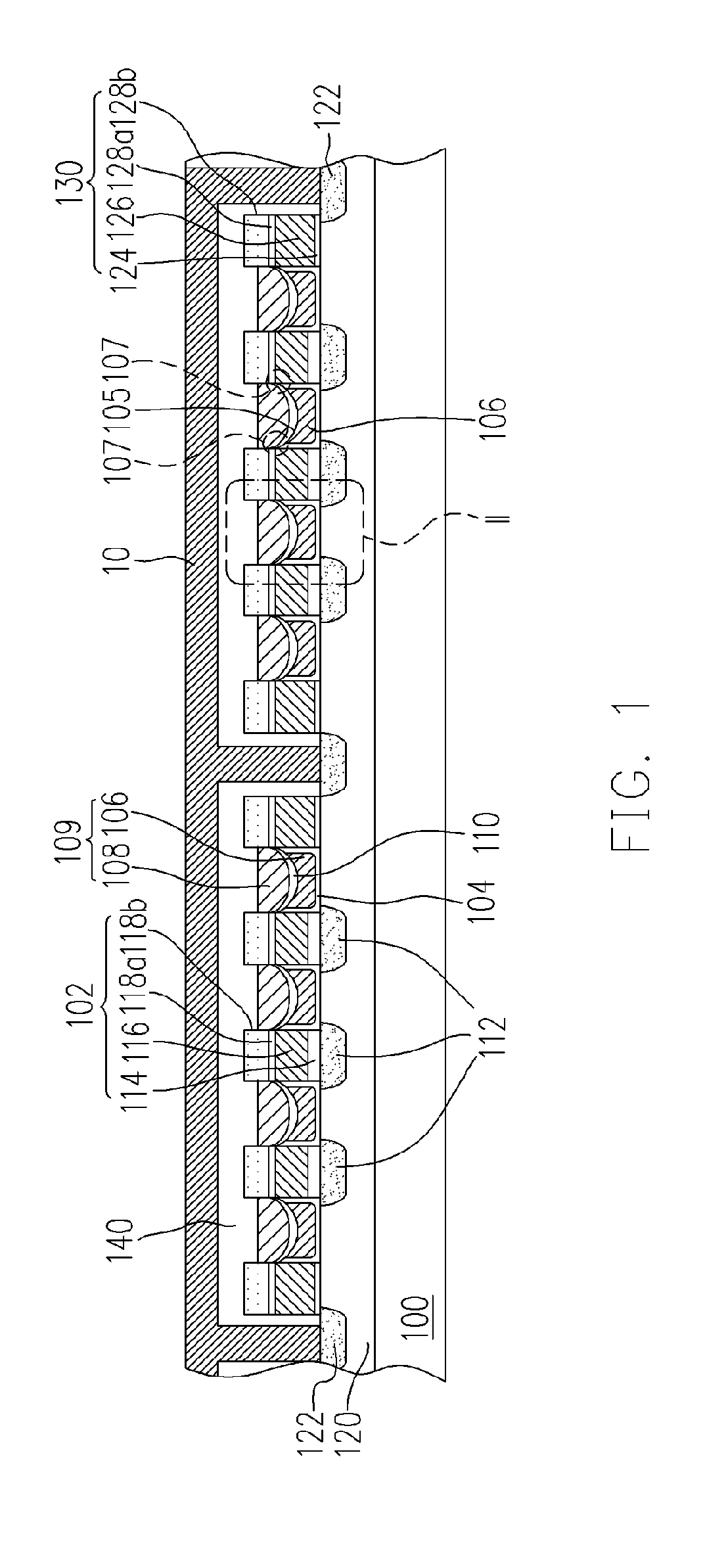
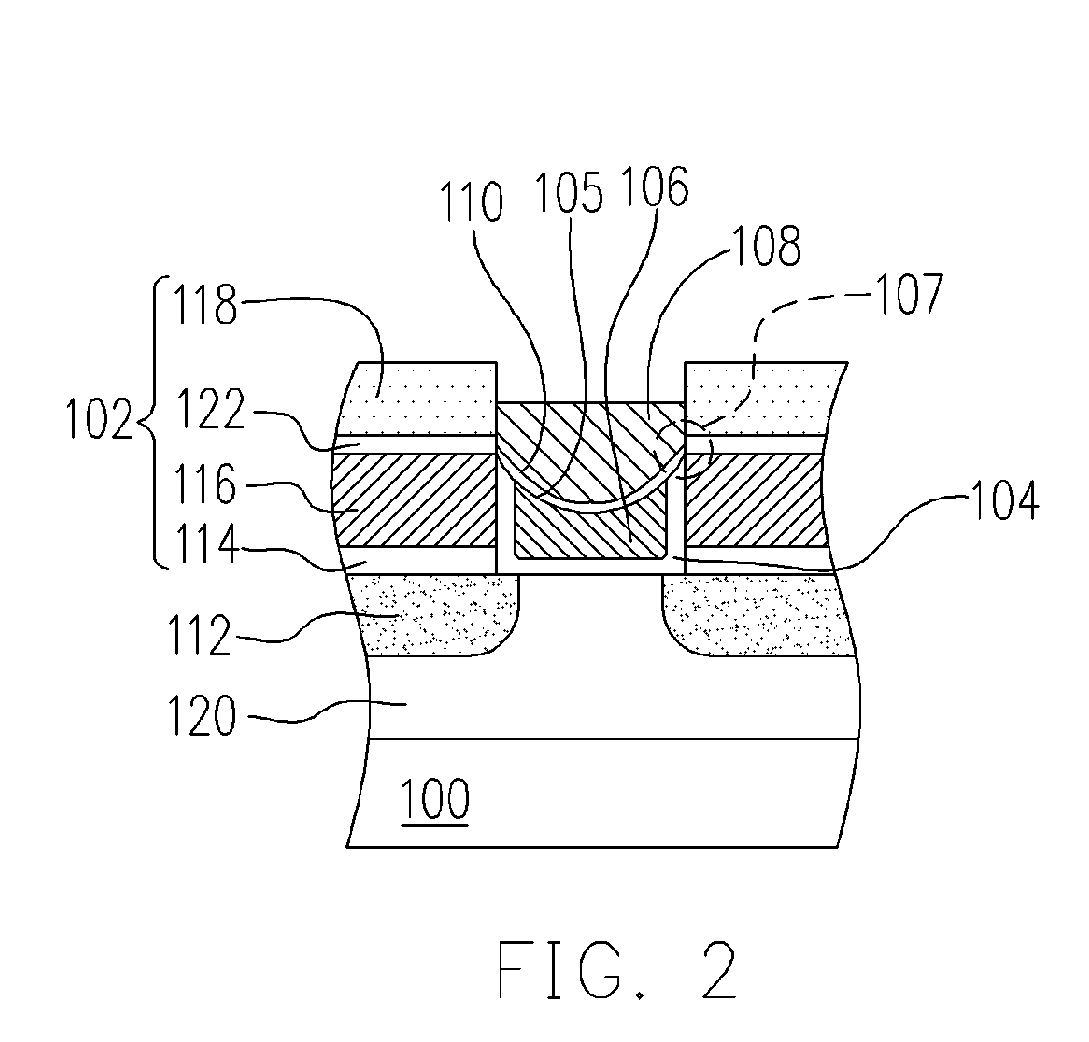
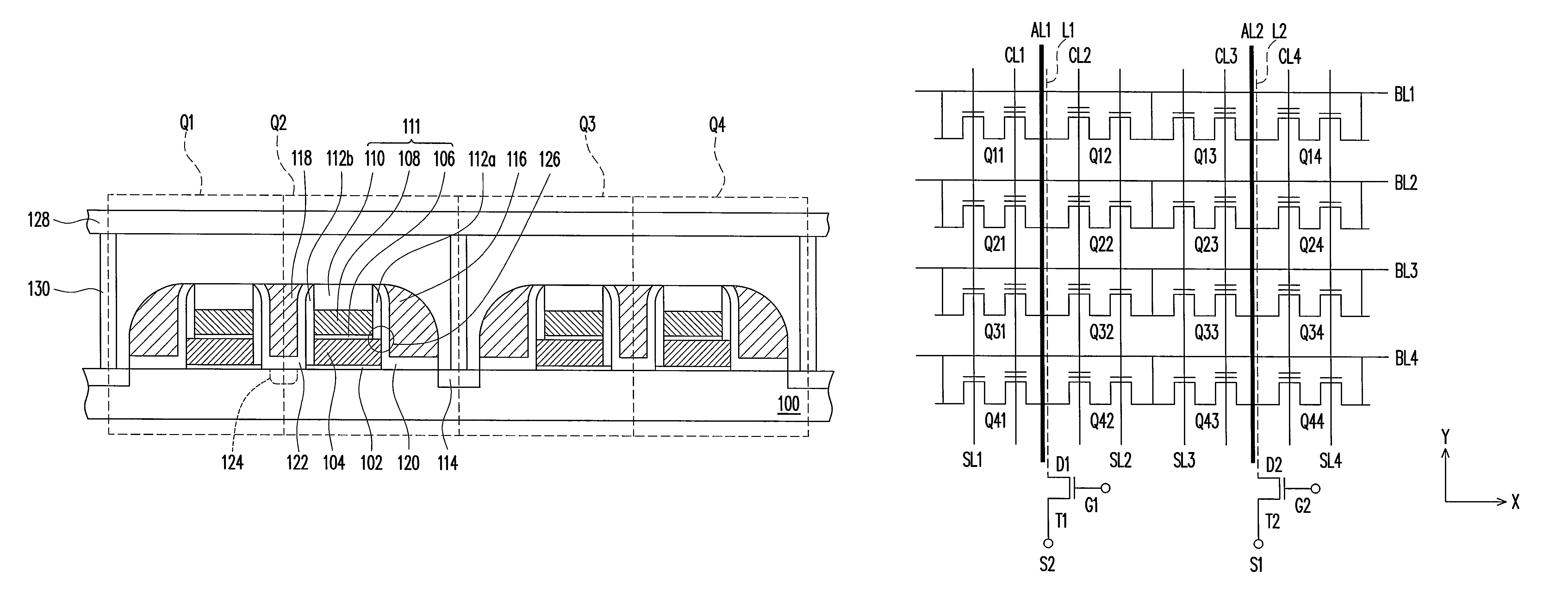
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
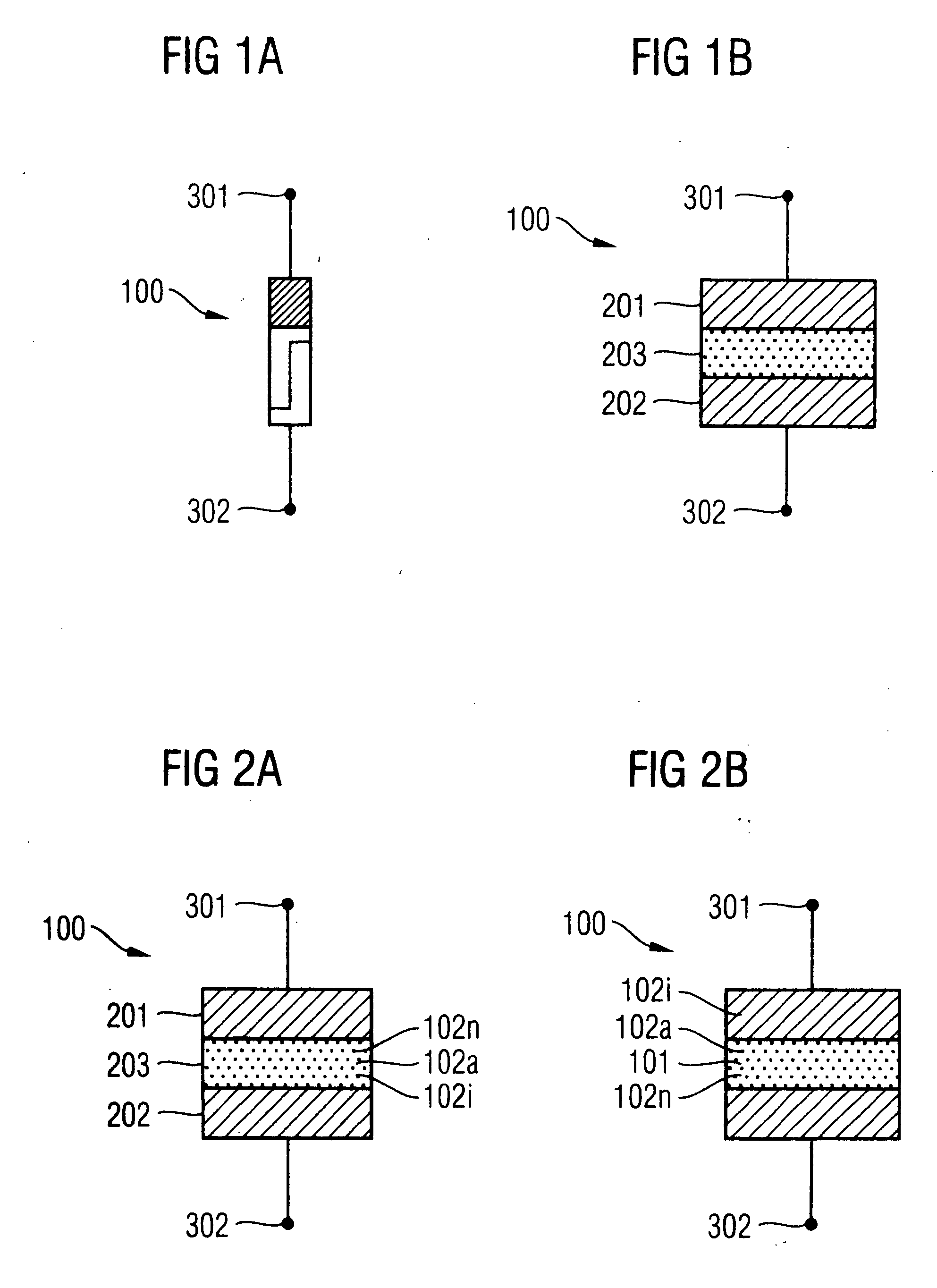
ActiveUS20060202261A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesEngineeringDielectric structure
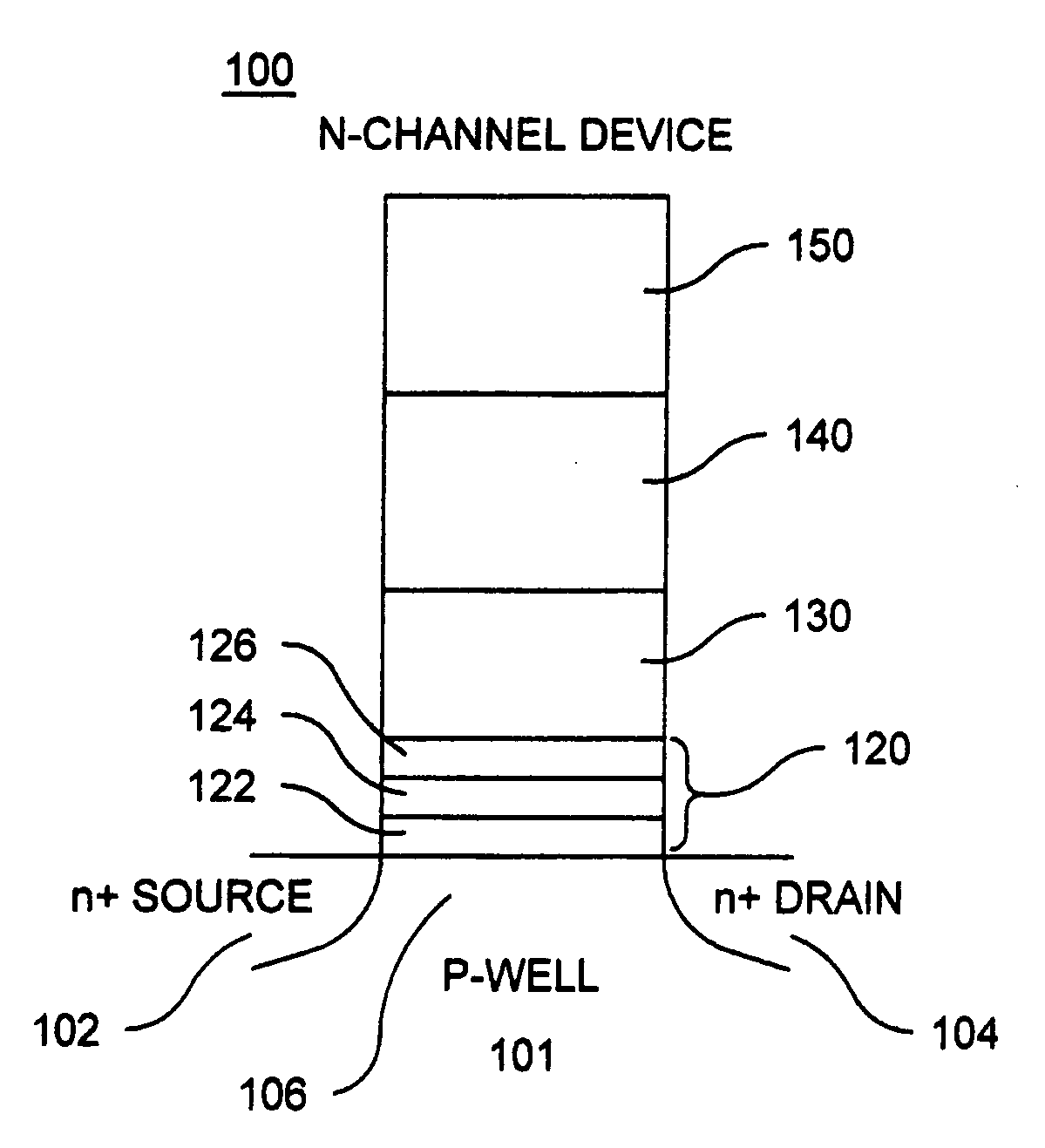
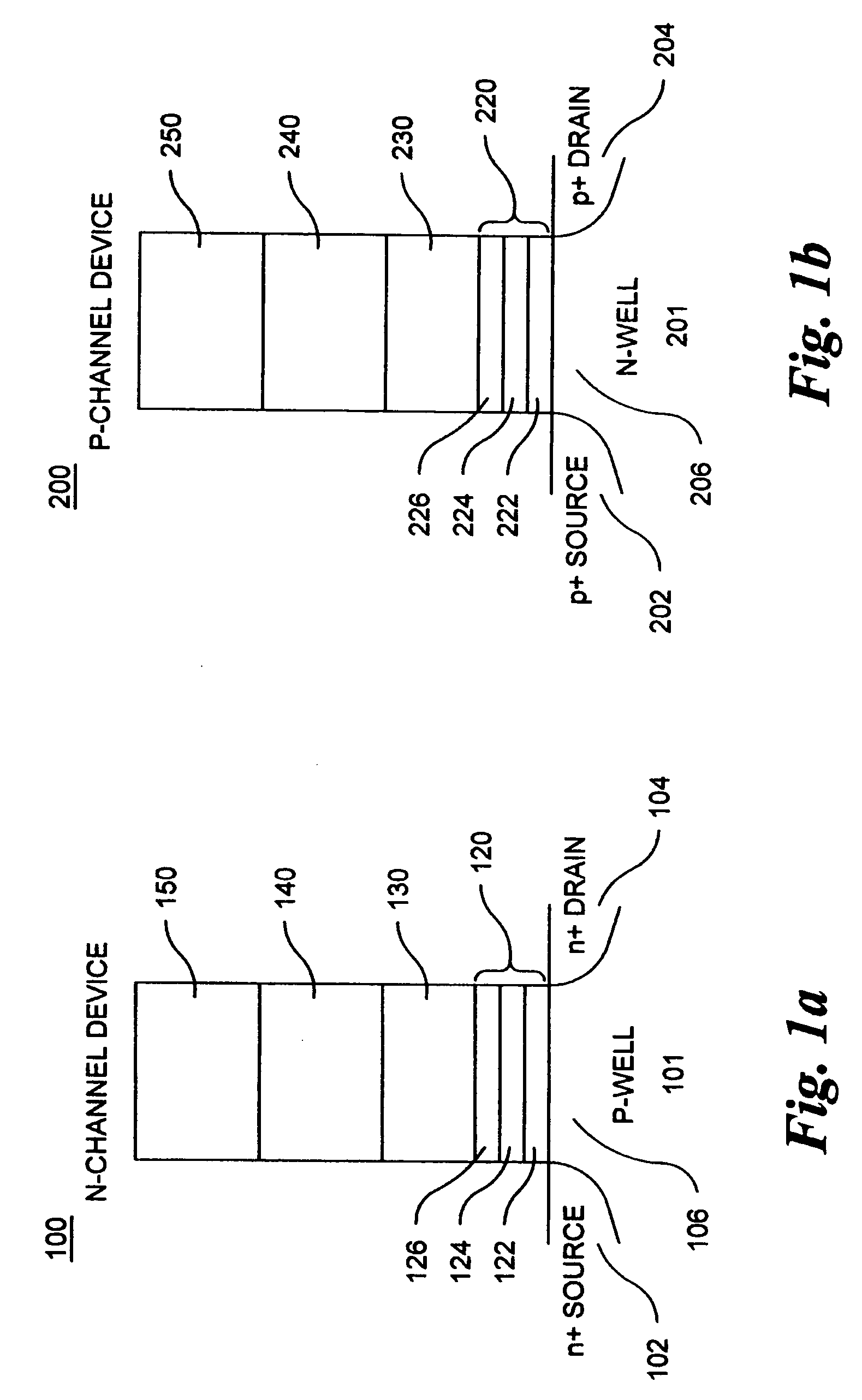
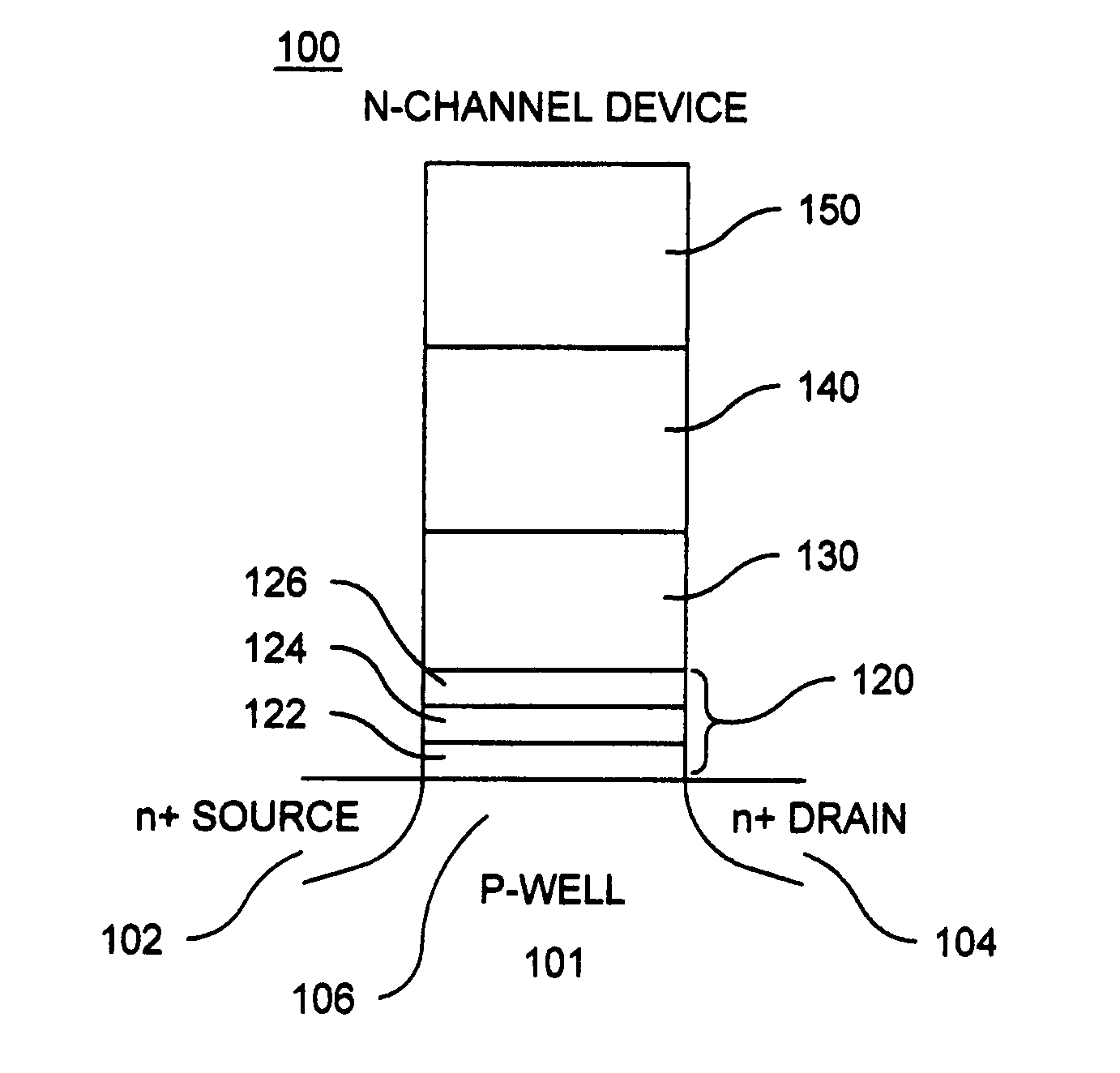
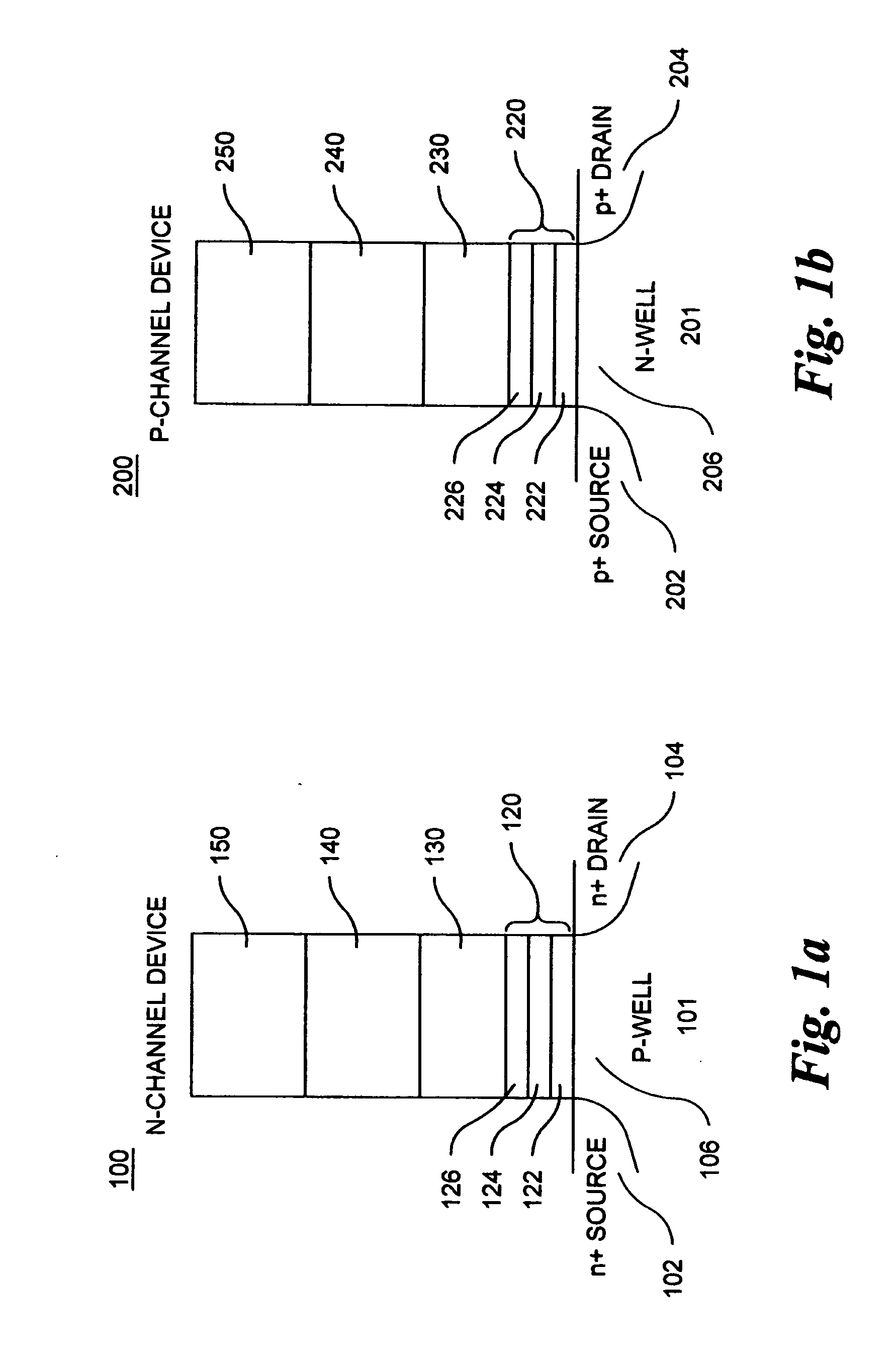
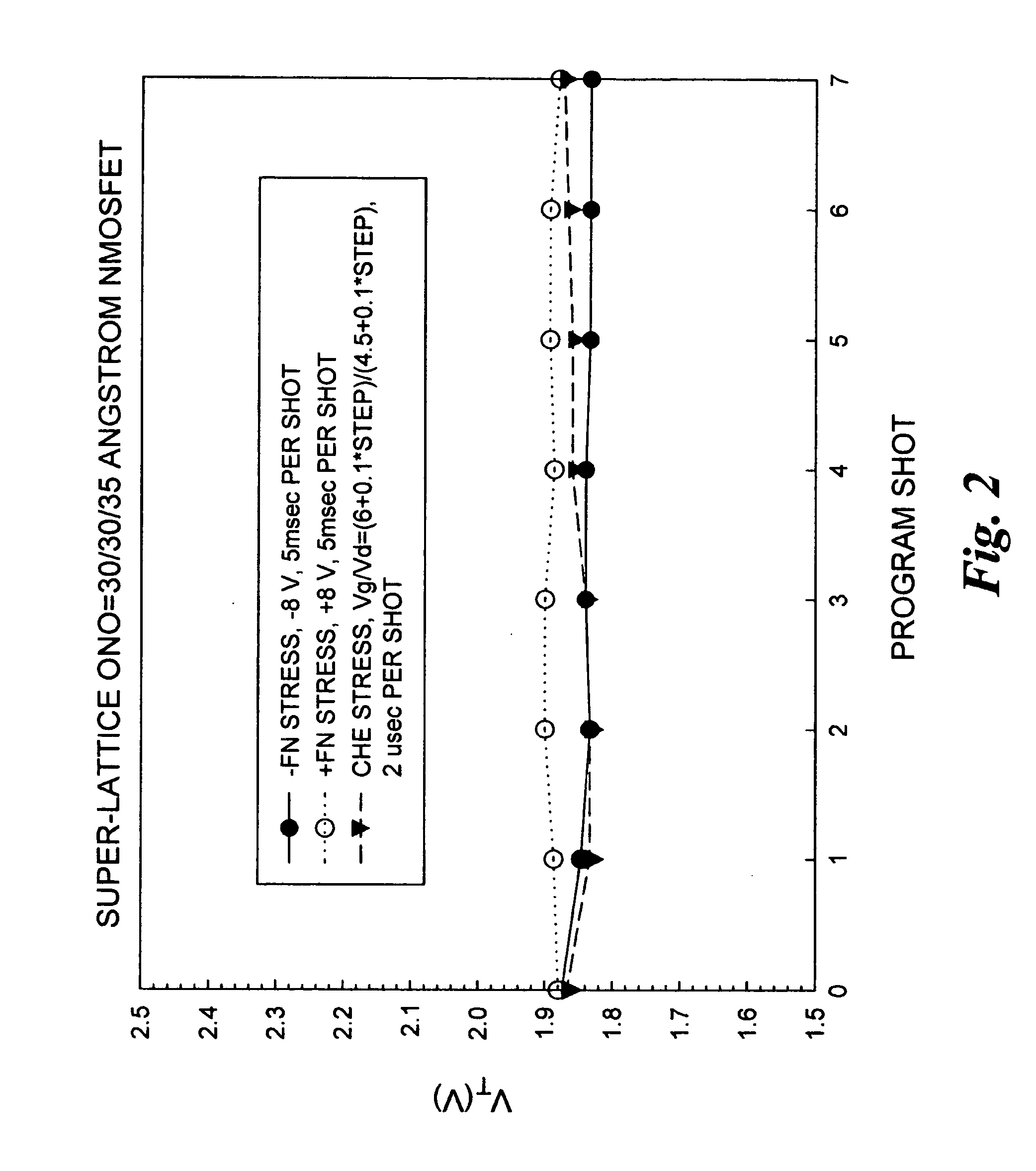
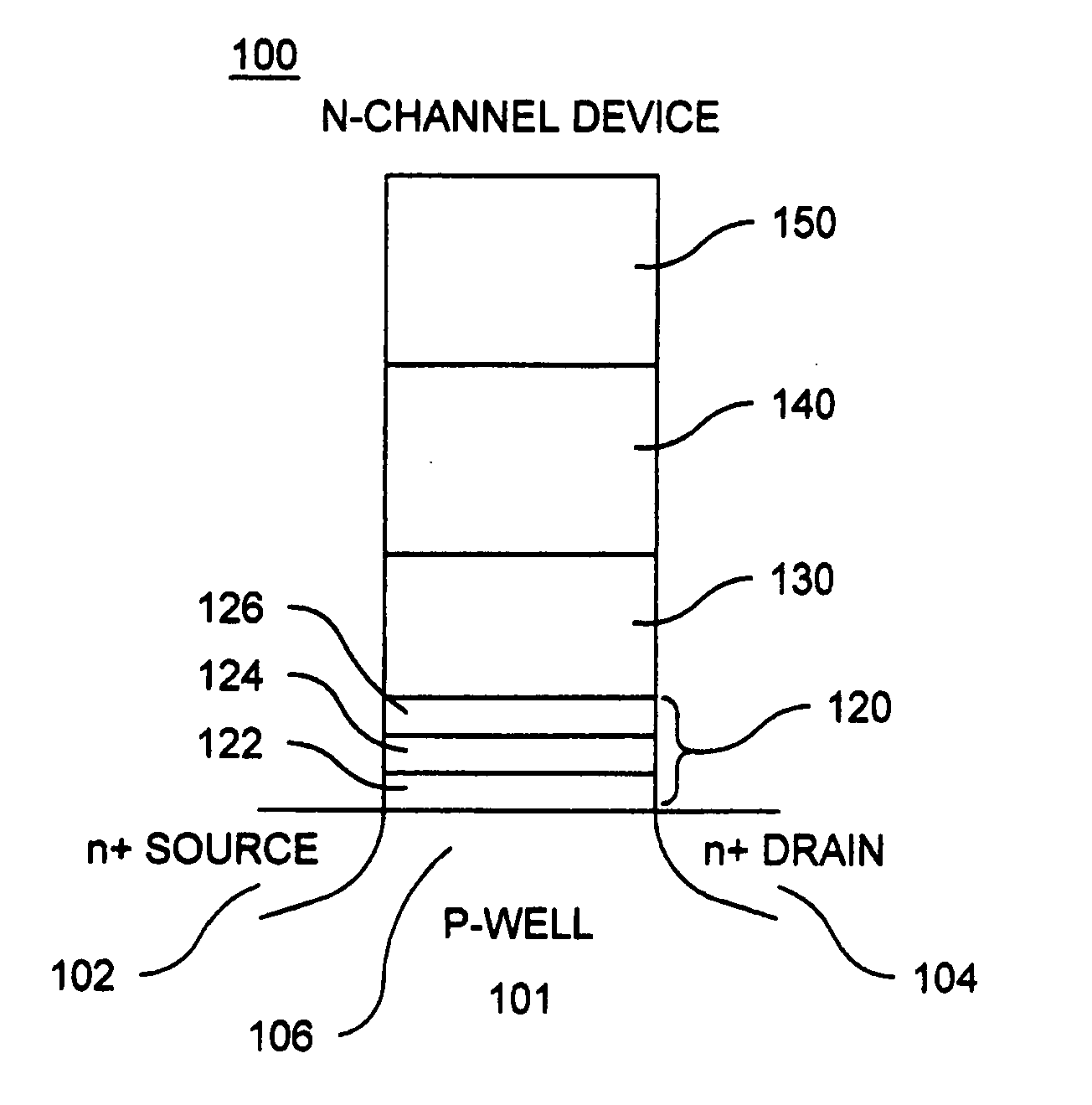
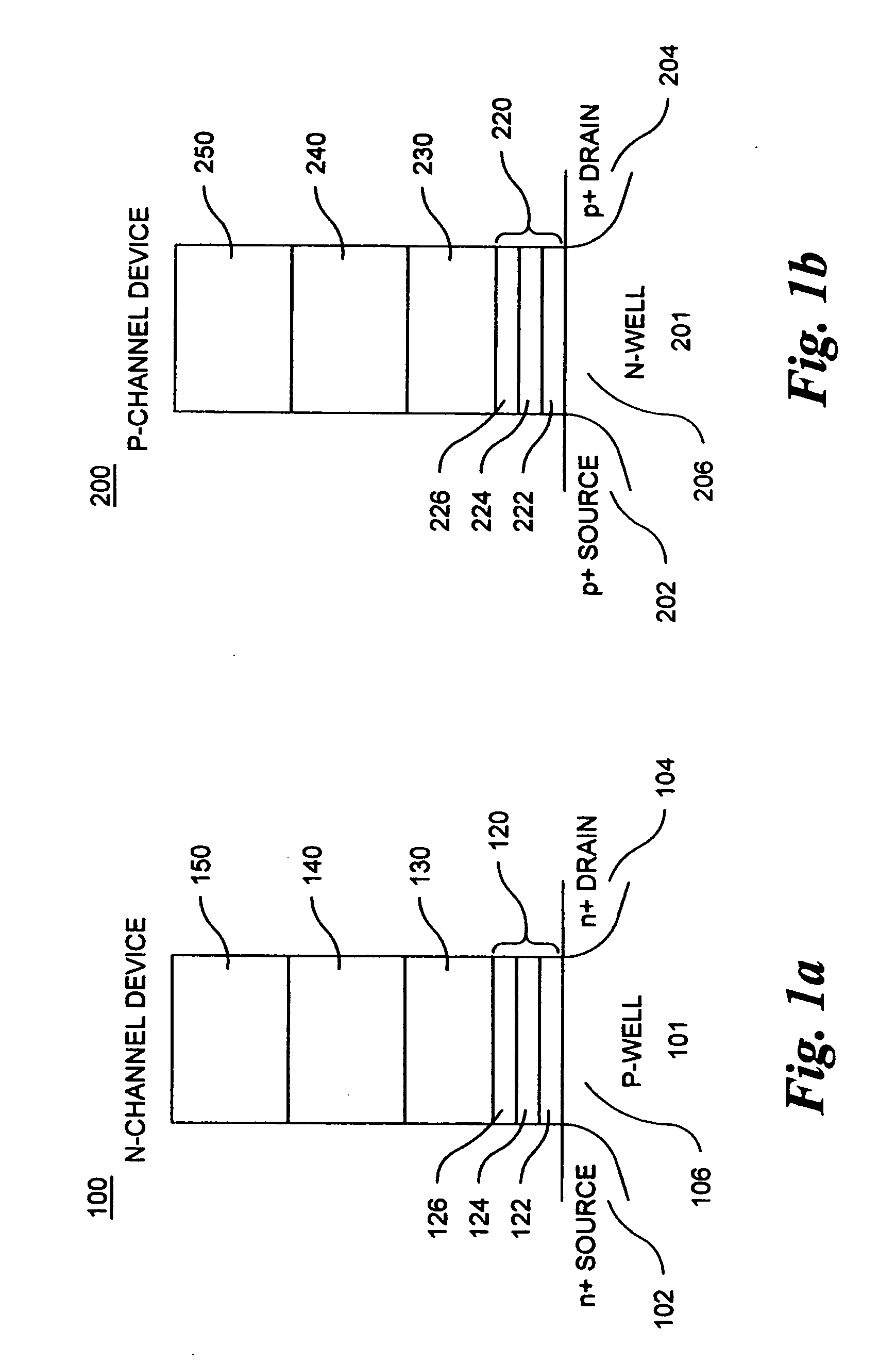
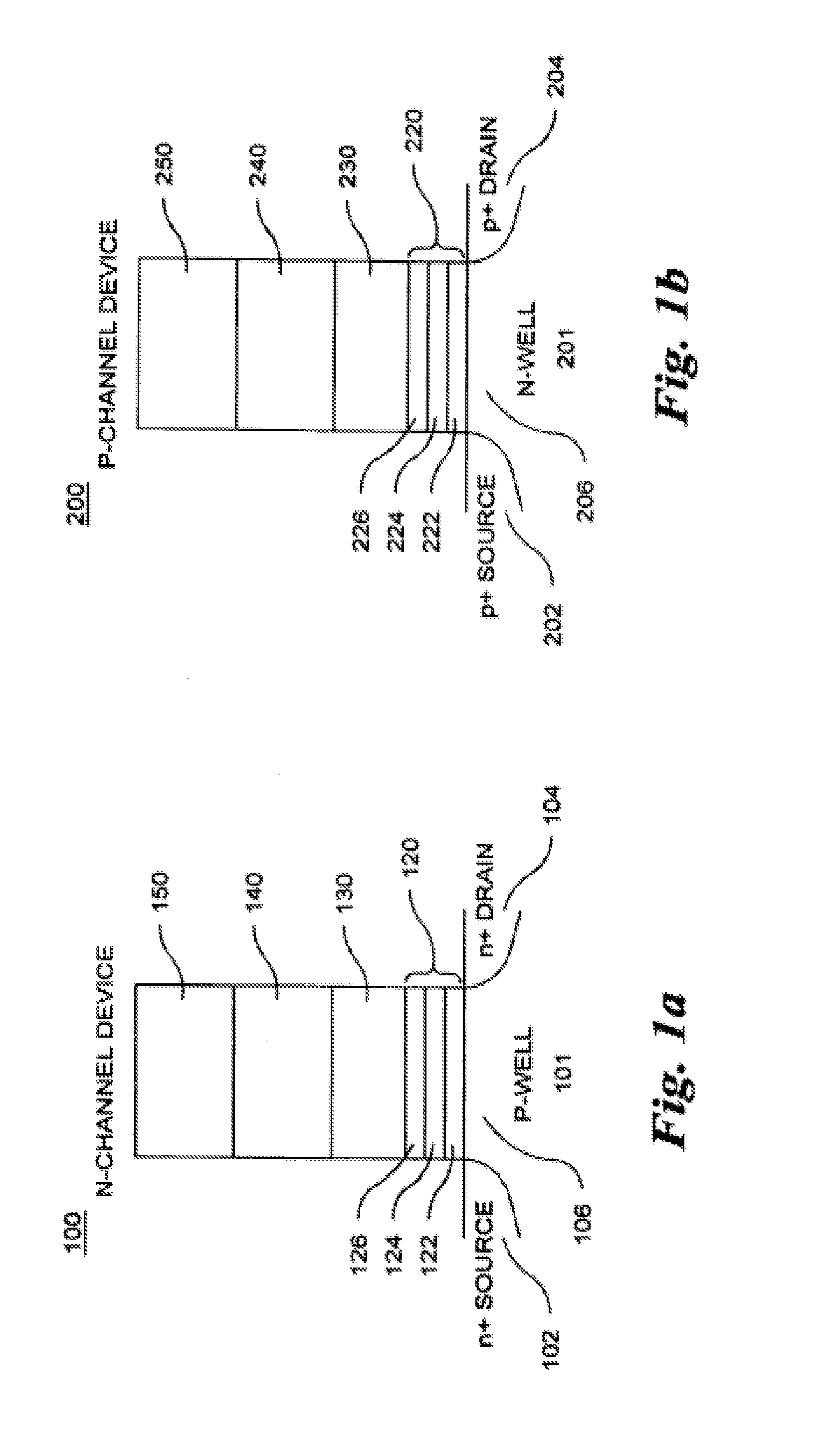
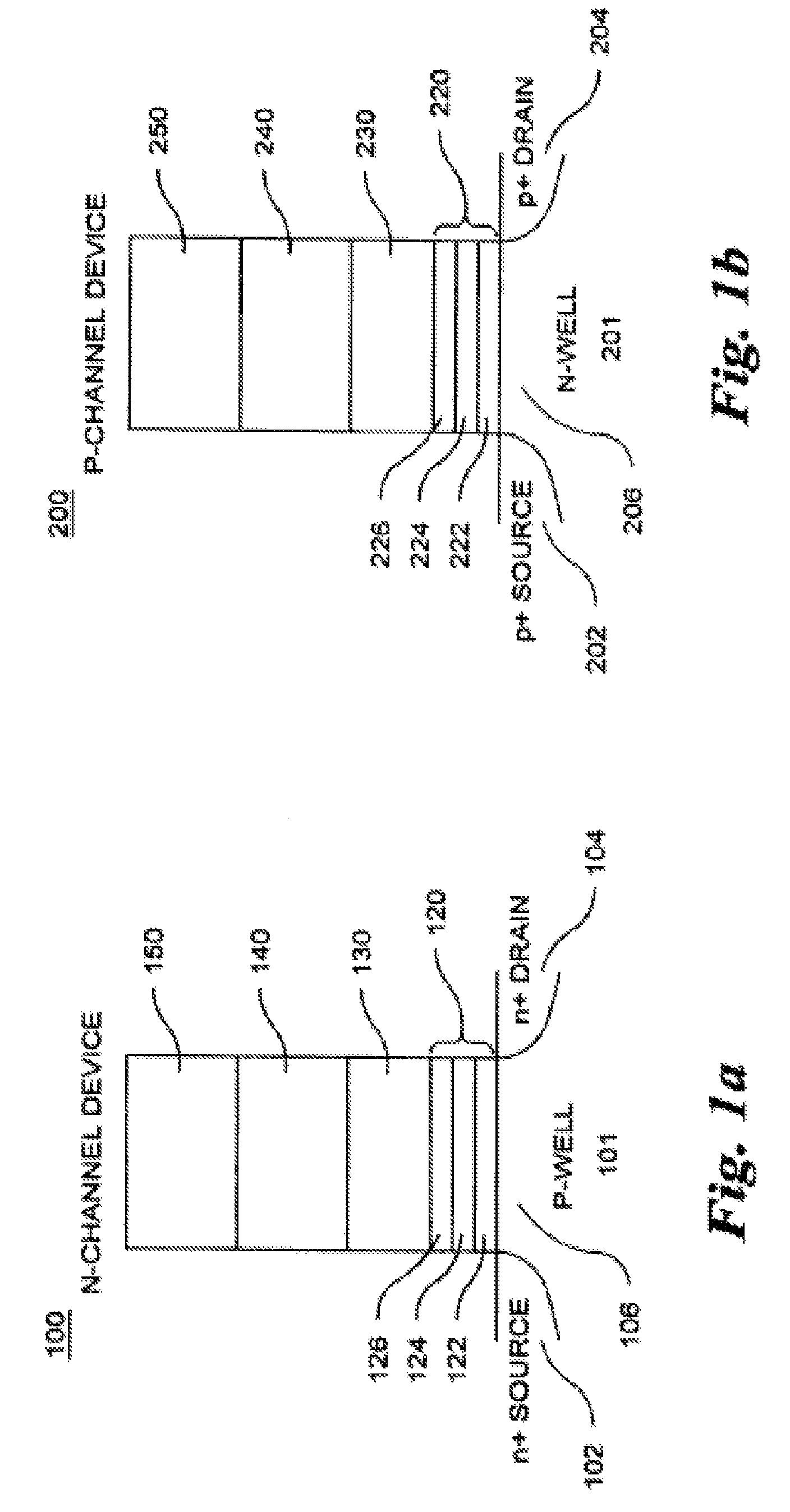
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS20060198190A1Easy to optimizeEasy to eraseSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
InactiveUS20060198189A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowRead-only memoriesDigital storageDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS20060202252A1Easy to optimizeEasy to eraseSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesTunnel barrierEngineering
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD +1
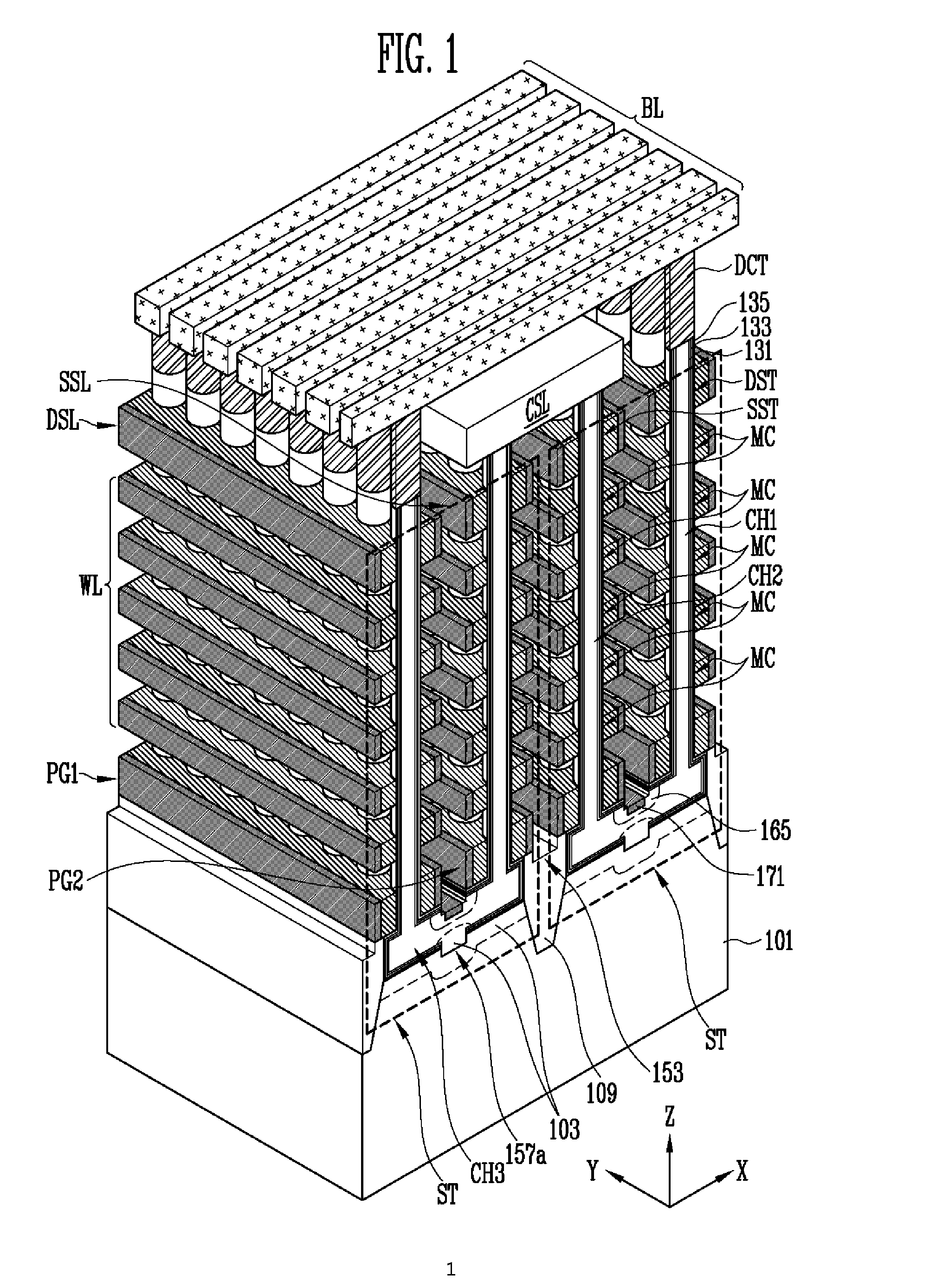
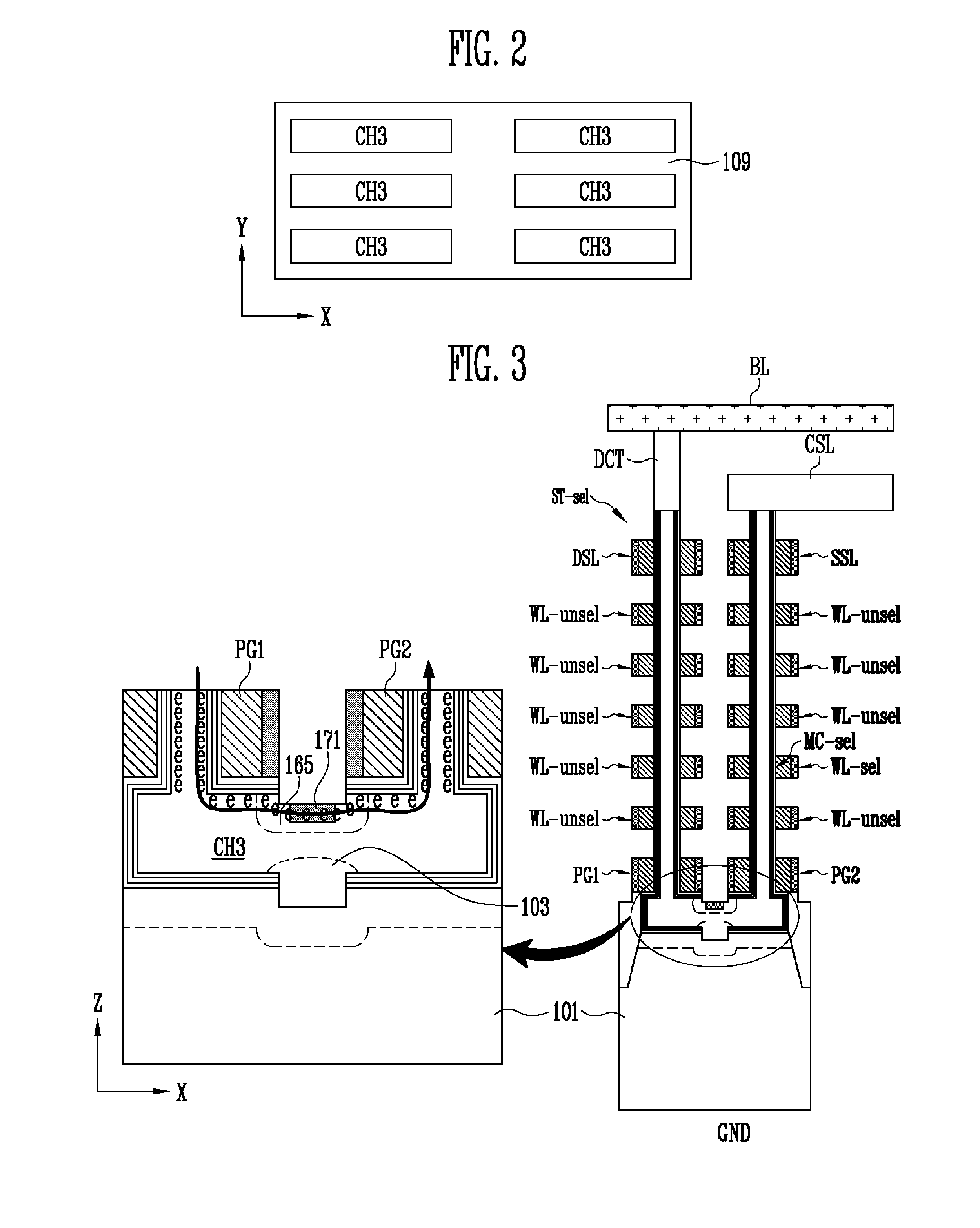
Non-volatile memory device and method of manufacturing the same
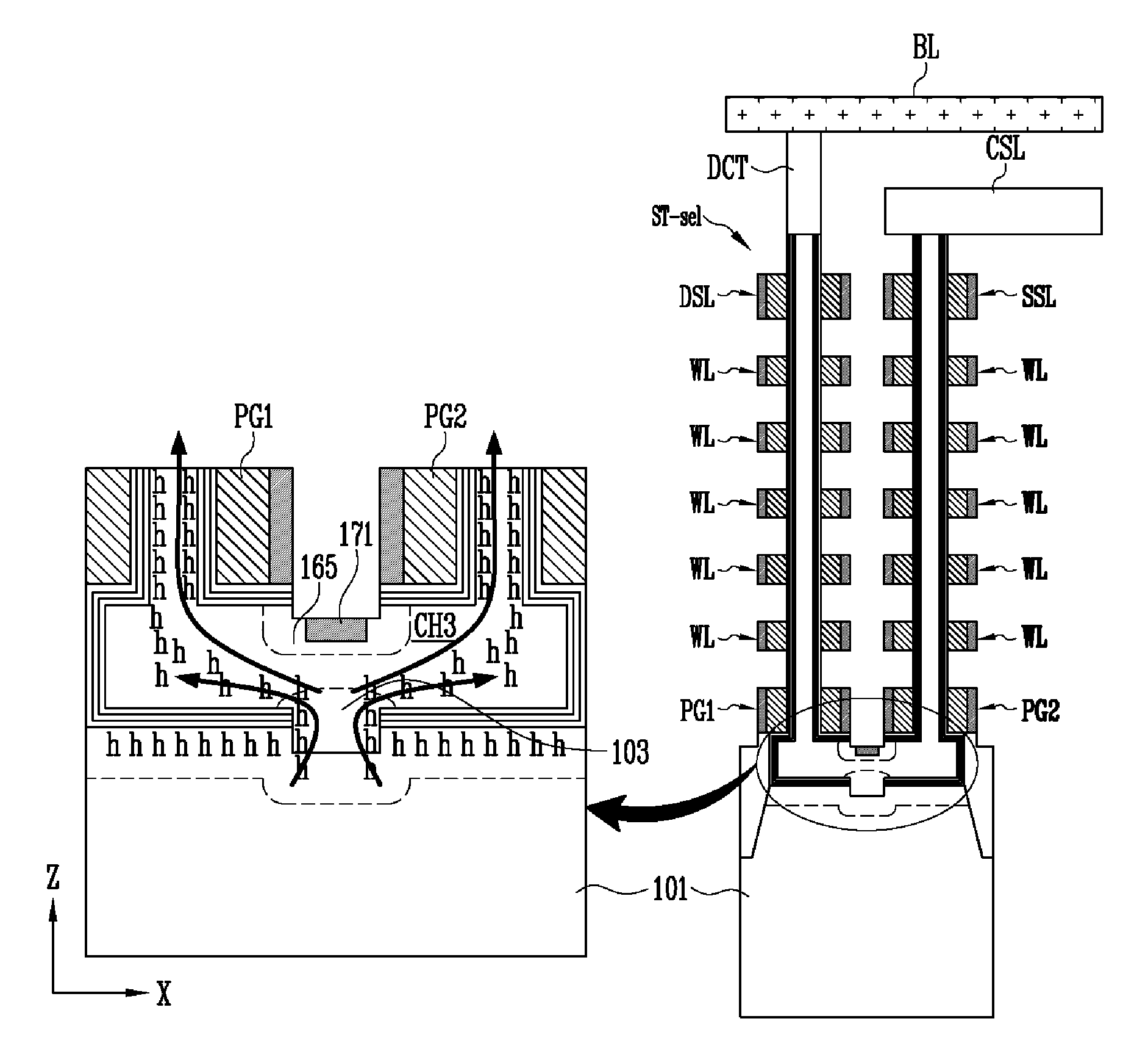
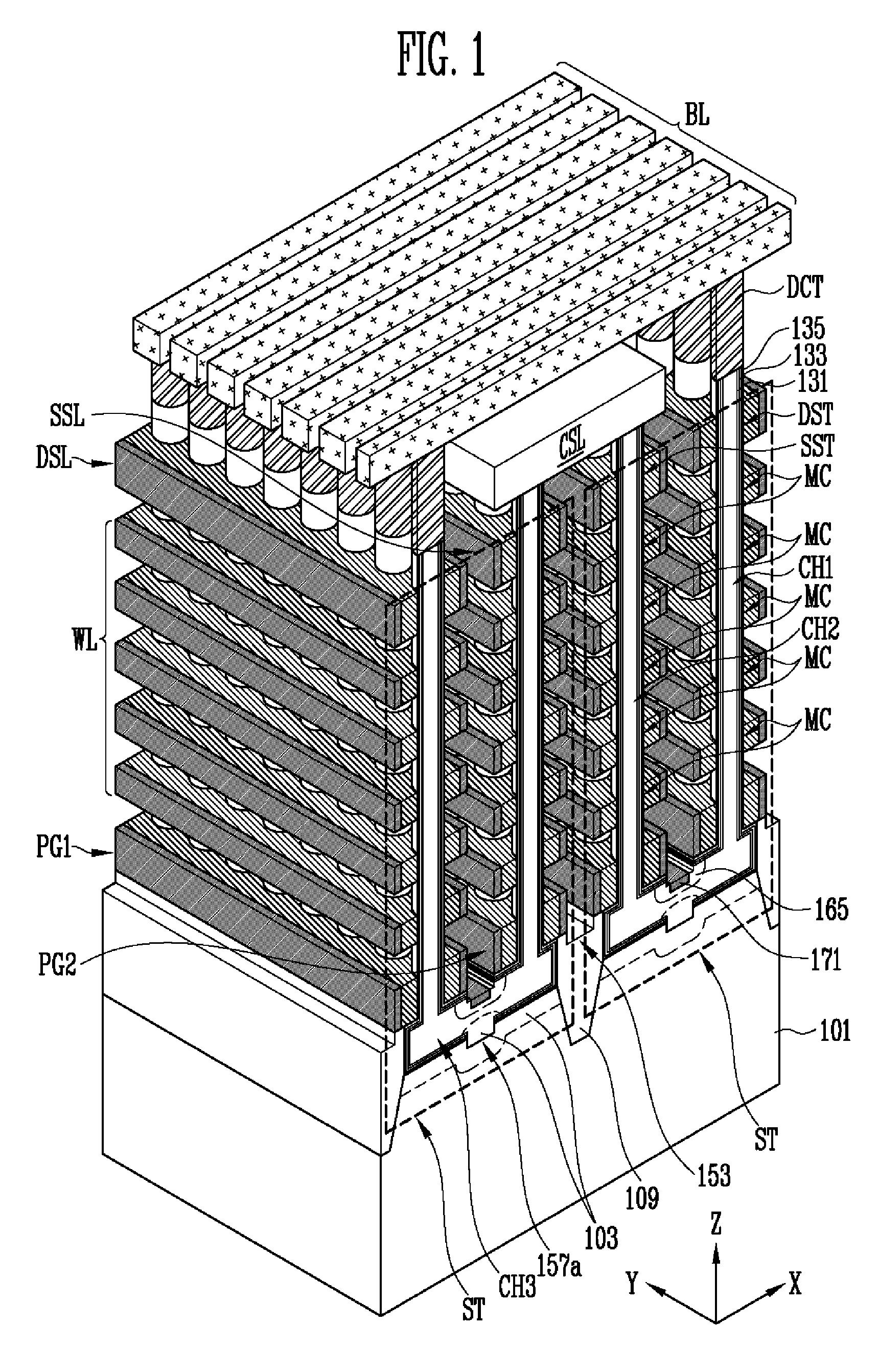
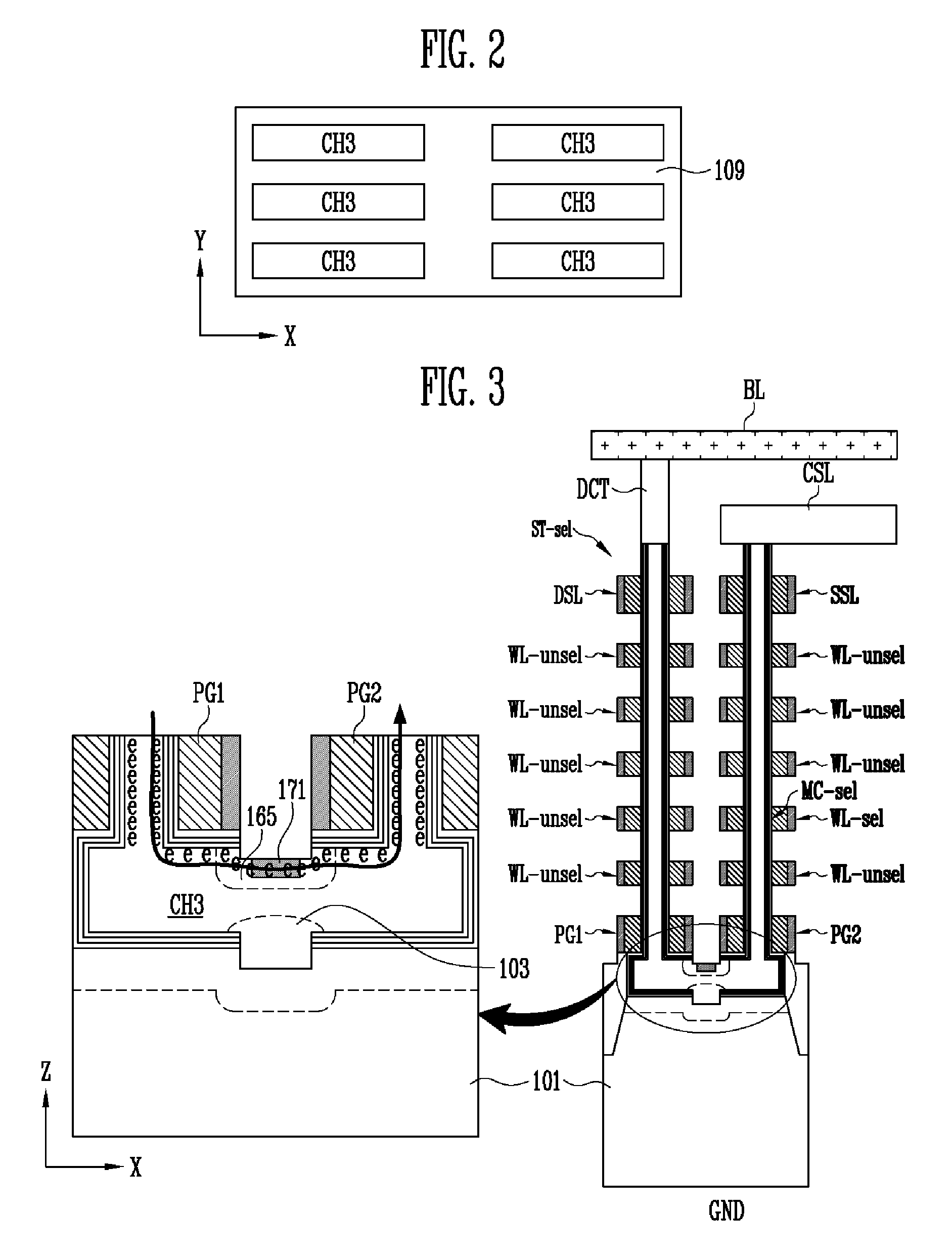
ActiveUS20130009235A1Increase erasing speedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesMemory cellMechanical engineering
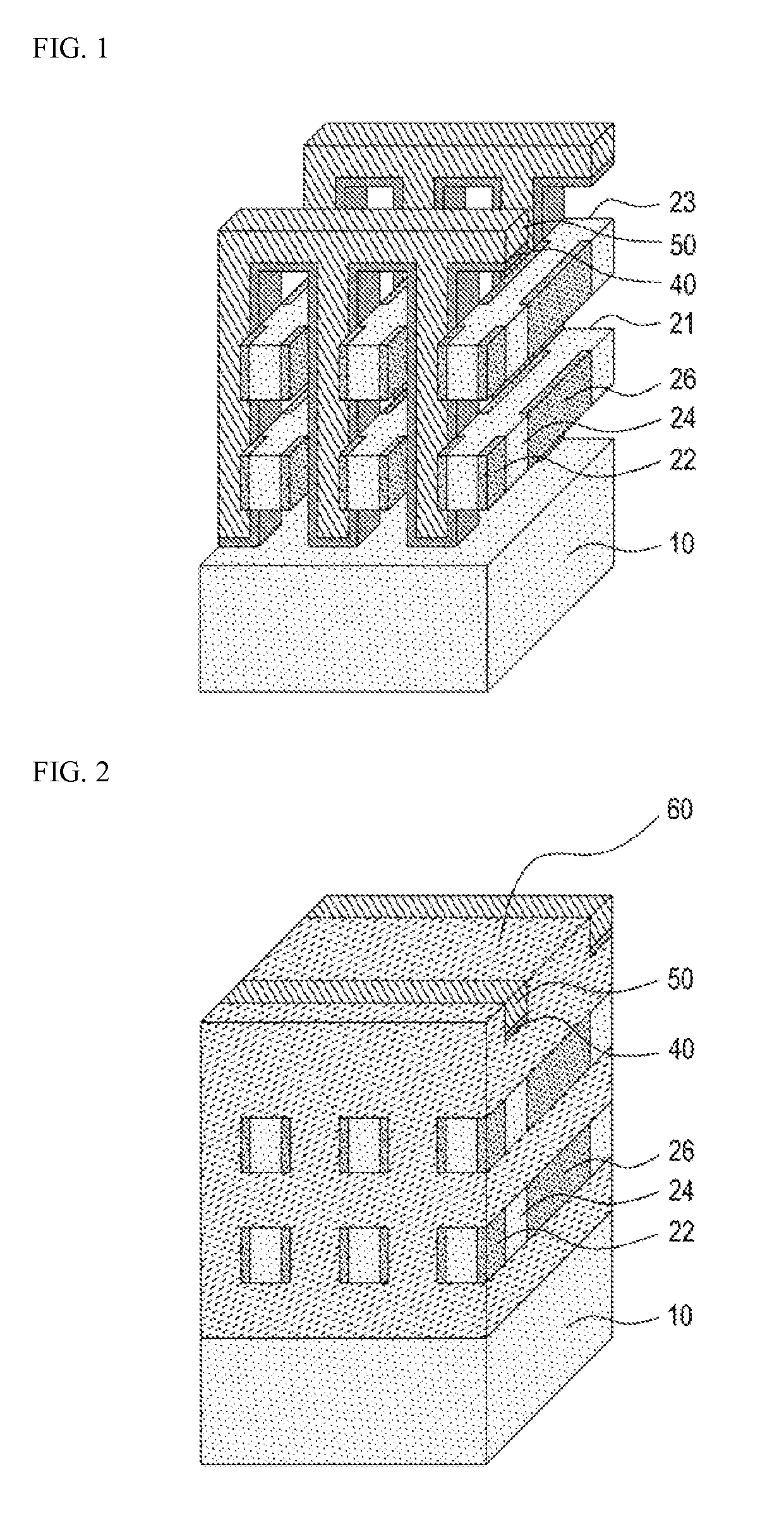
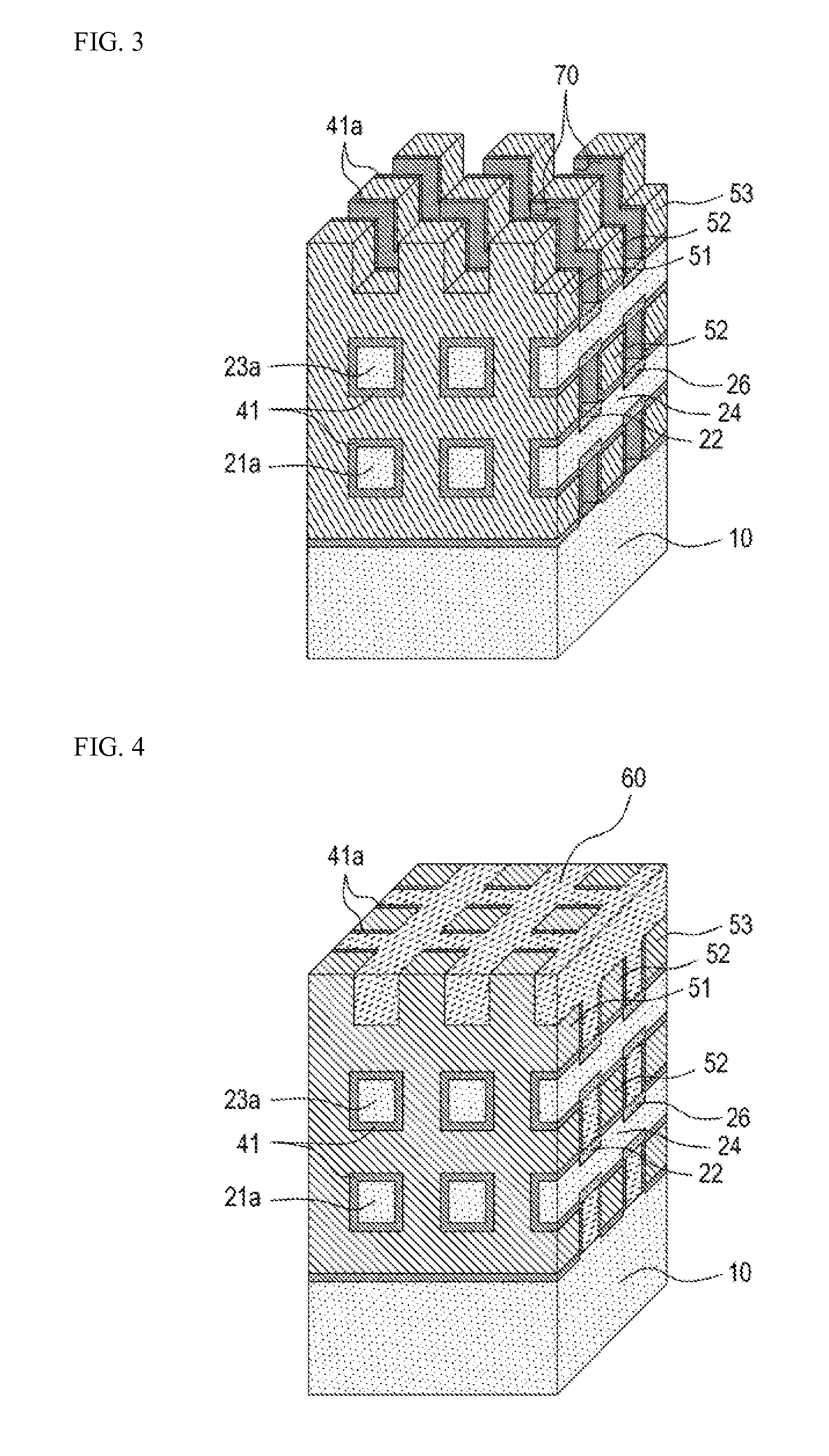
A non-volatile memory device includes first and second vertical channel layers generally protruding upwardly from a semiconductor substrate substantially in parallel; a first gate group configured to include a plurality of memory cell gates which are stacked substantially along the first vertical channel layer and are isolated from each other with an interlayer insulating layer interposed substantially between the memory cell gates; a second gate group configured to include a plurality of memory cell gates which are stacked substantially along the second vertical channel layer and are isolated from each other with the interlayer insulating layer interposed substantially between the memory cell gates; a pipe channel layer configured to couple the first and the second vertical channel layers; and a channel layer extension part generally extended from the pipe channel layer to the semiconductor substrate and configured to couple the pipe channel layer and the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device and data writing method
InactiveUS20070195590A1Provide effectDeterioration in programmingElectric analogue storesRead-only memoriesBit lineElectricity
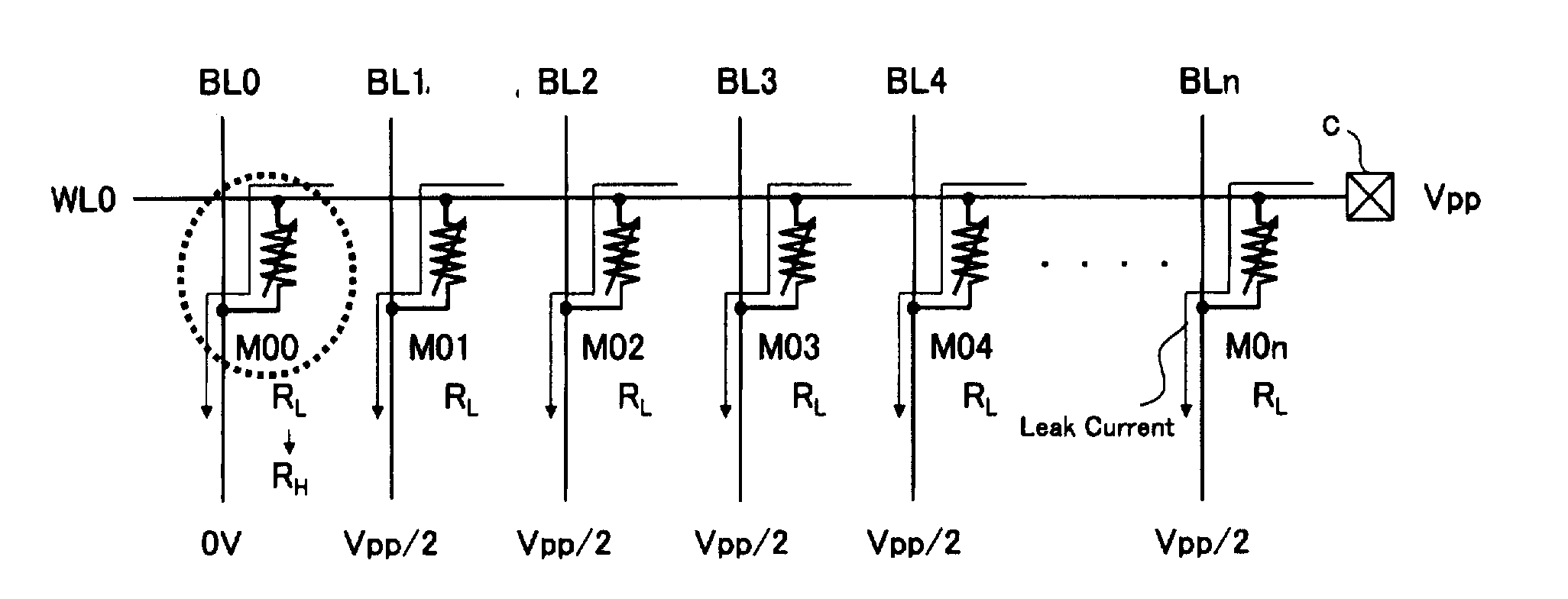
The invention provides a data writing method for writing data sequentially in a cross-point memory cell array having a variable resistive element whose electric resistance is changed by application of an electric stress. When data is sequentially written in memory cells in the same row or column, the writing order of the memory cells to be written is determined according to the length from an electric connection point to a selected memory cell to be written and the increase / decrease direction of the electric resistance of each selected memory cell changed by data writing, the electric connection point being between a write voltage applying circuit, which applies a data writing voltage to a same wiring of the selected word line or bit line connected to the selected memory cell, and the same wiring, and the data writing is executed based on the determined writing order.
Owner:XENOGENIC DEV LLC
Silicon on insulator and thin film transistor bandgap engineered split gate memory
ActiveUS20080175053A1Large thermal budgetLarge lateral diffusionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectric structureBand-gap engineering
Memory cells comprising thin film transistor, stacked arrays, employing bandgap engineered tunneling layers in a junction free, NAND configuration. The cells comprise a channel region in a semiconductor strip formed on an insulating layer; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising a multilayer structure including at least one layer having a hole-tunneling barrier height lower than that at the interface with the channel region; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer Arrays and methods of operation are described.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
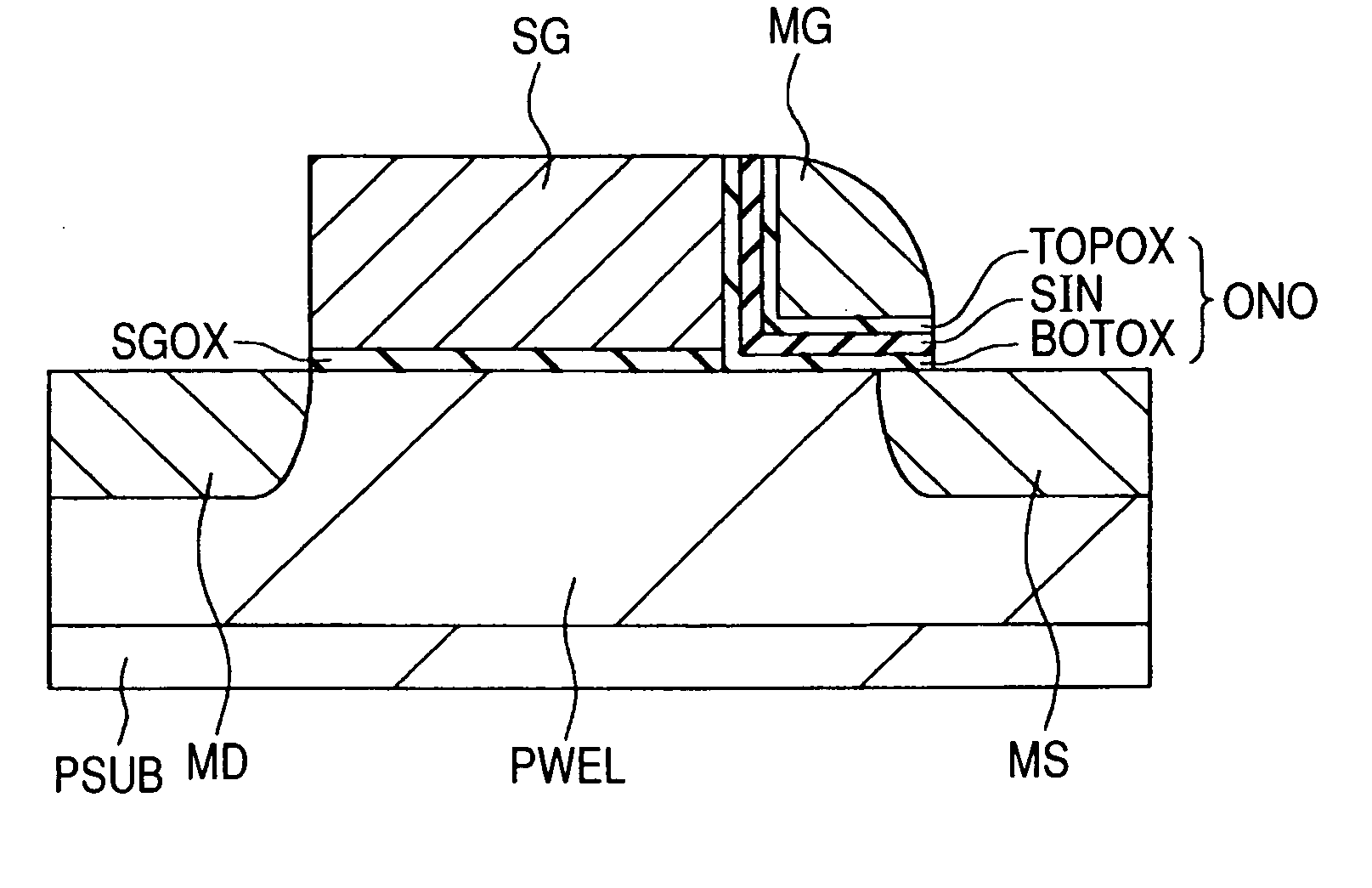
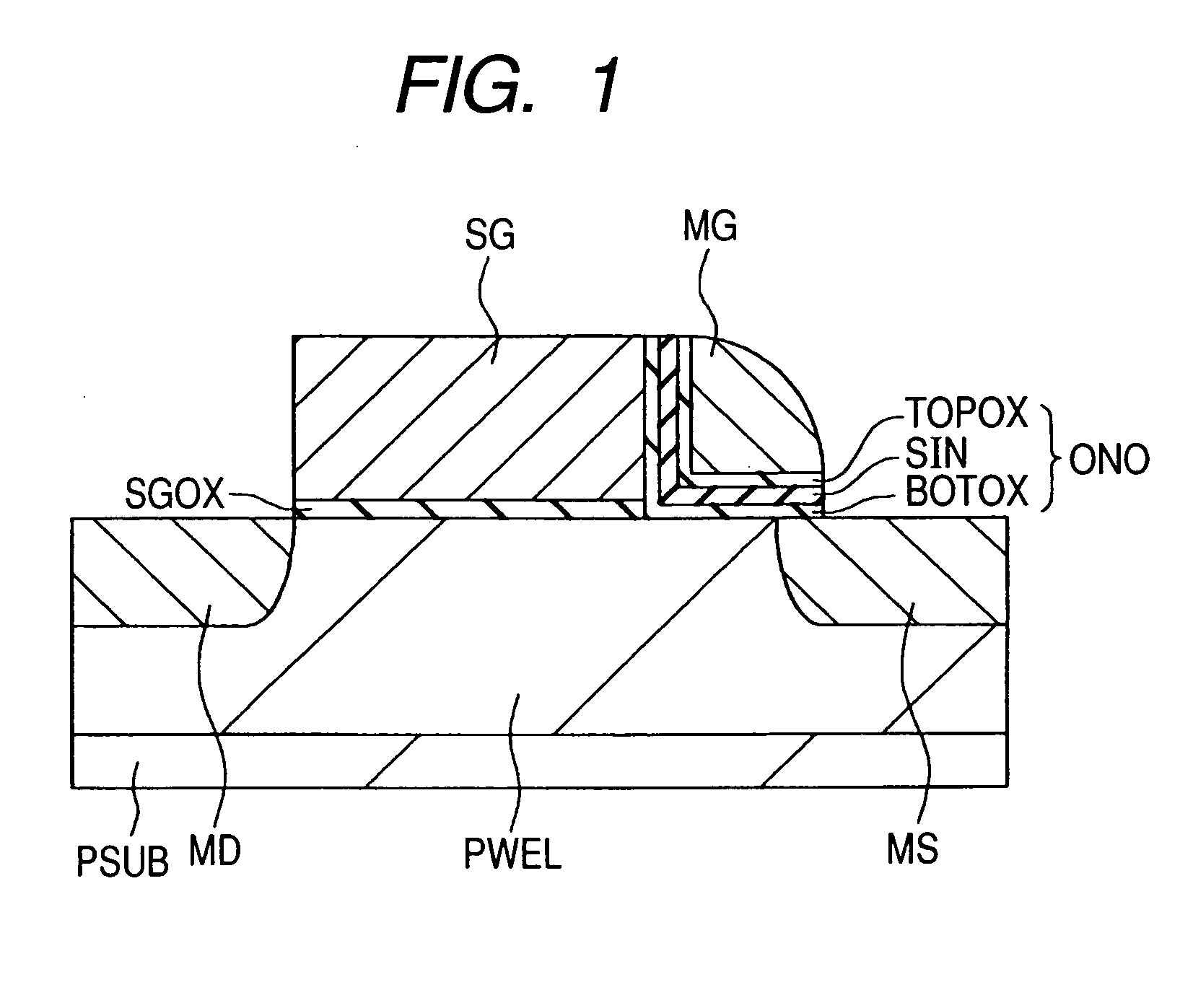
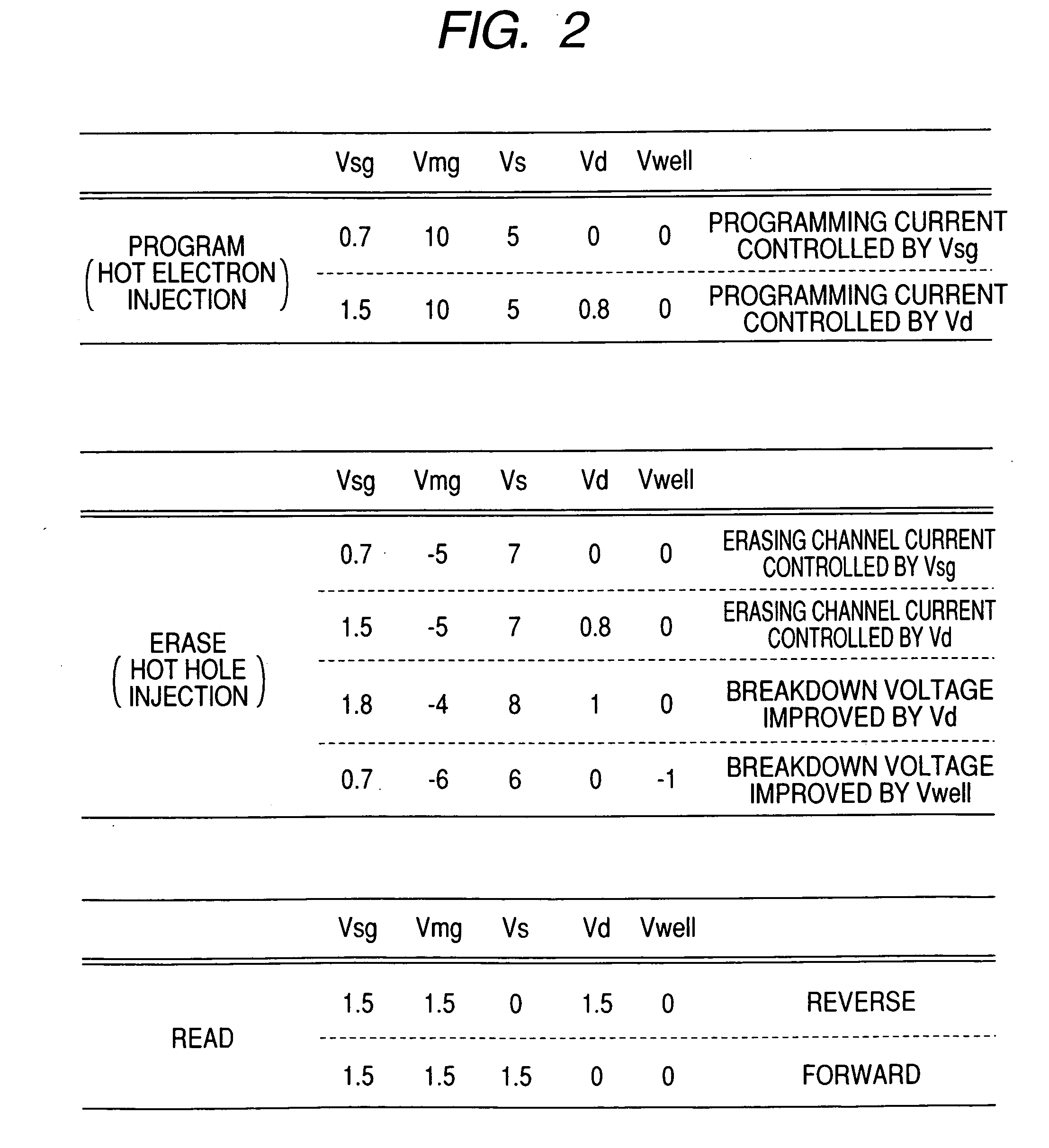
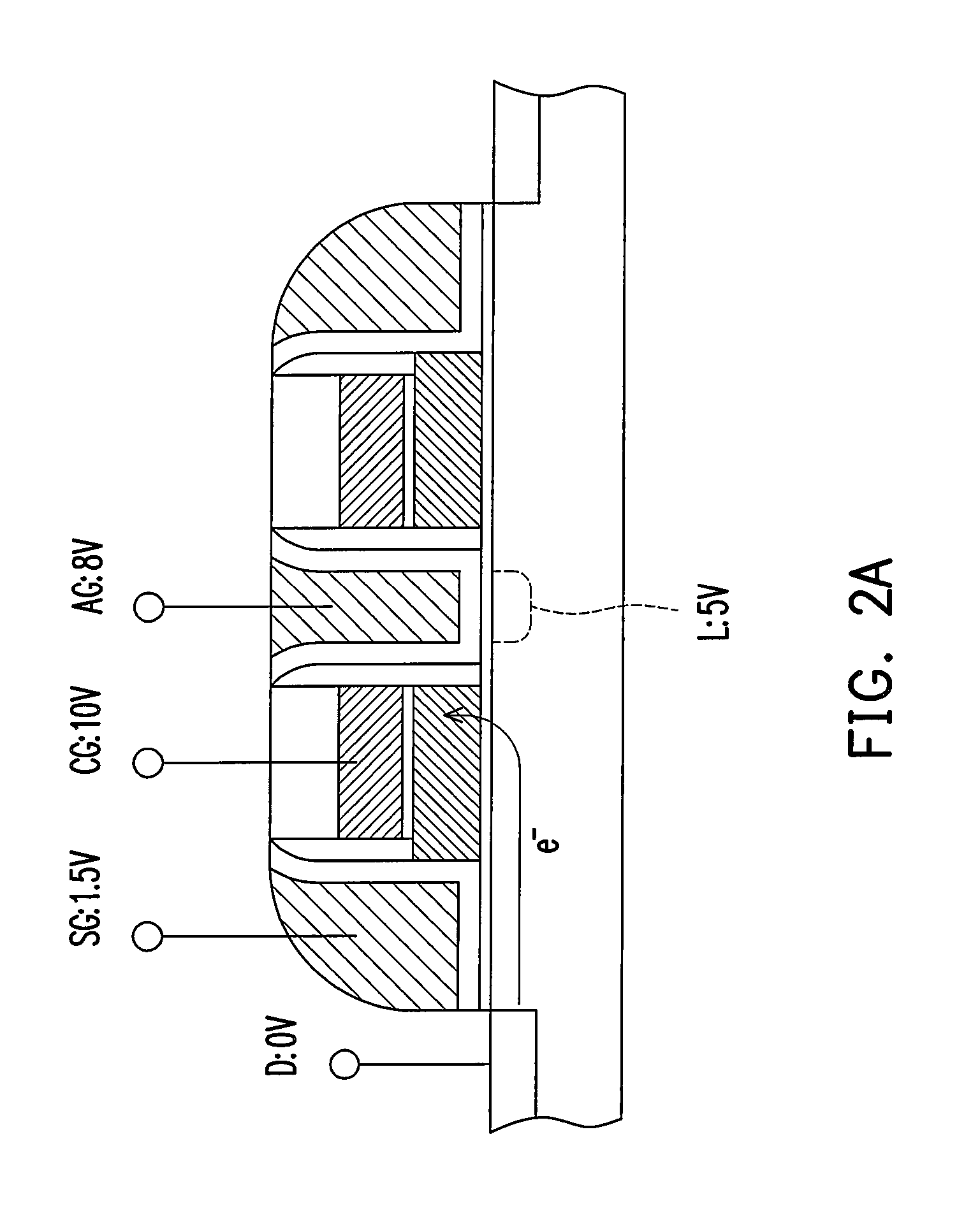
ActiveUS6972997B2Improve performanceImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesElectron flowImpact ionization
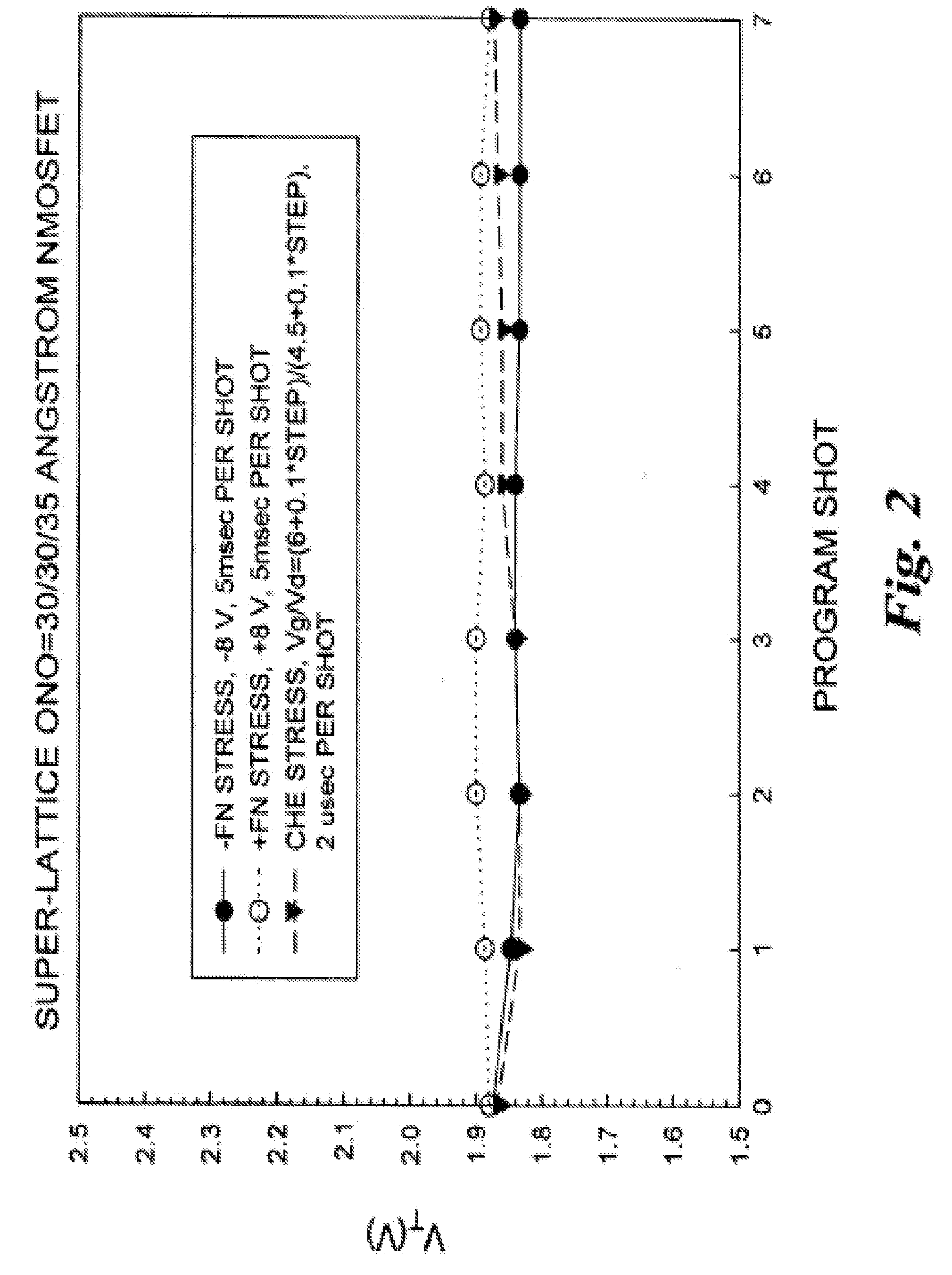
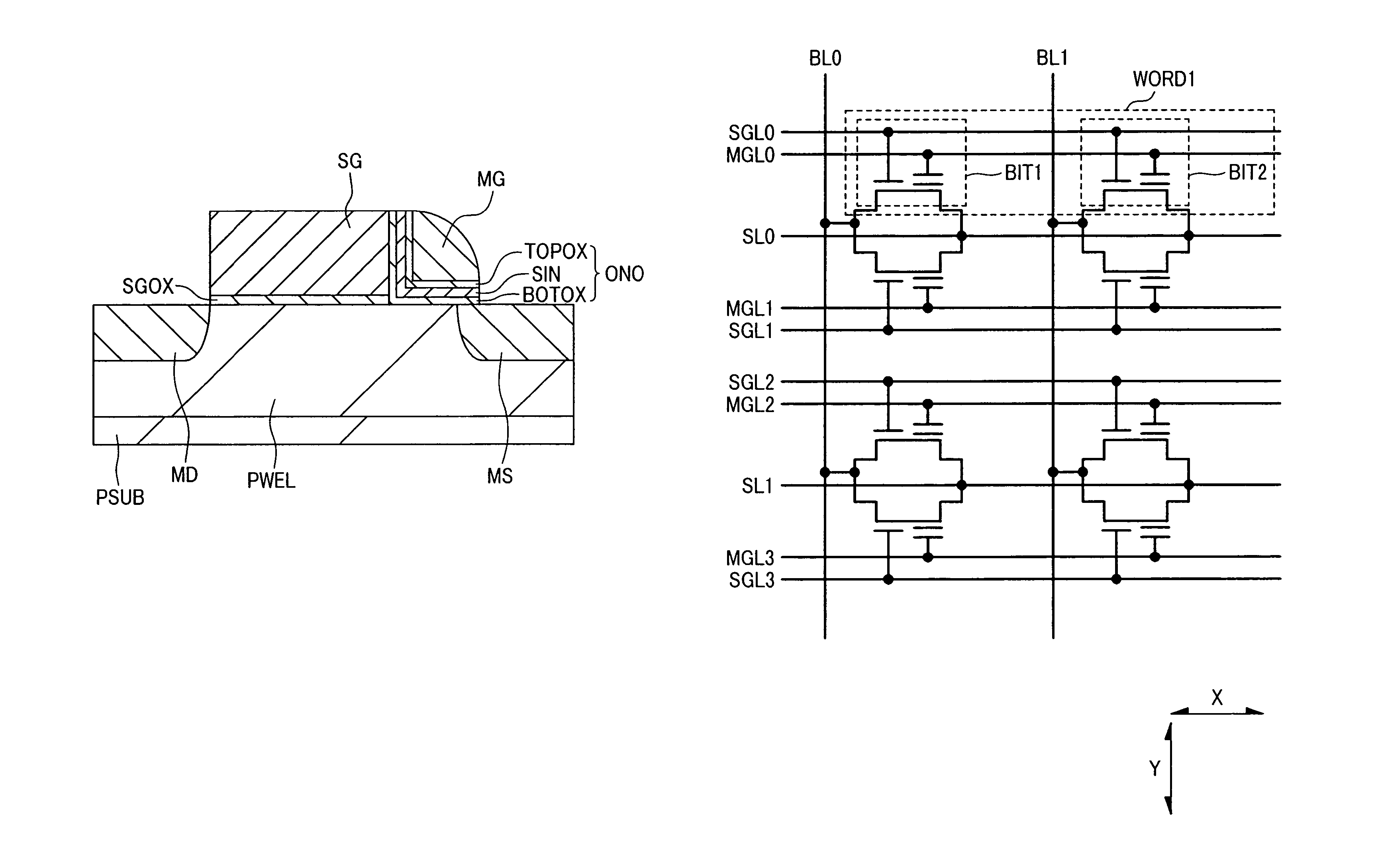
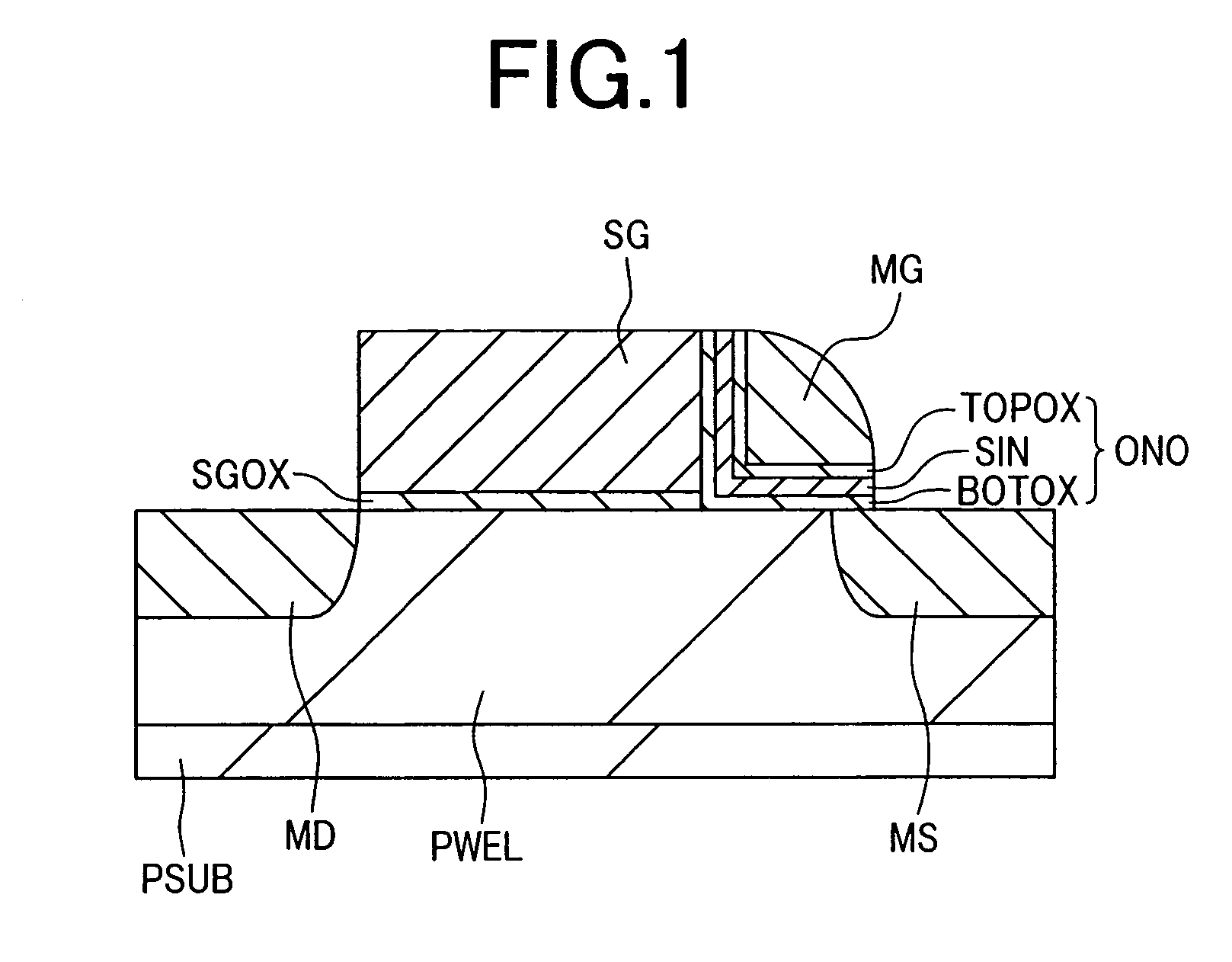
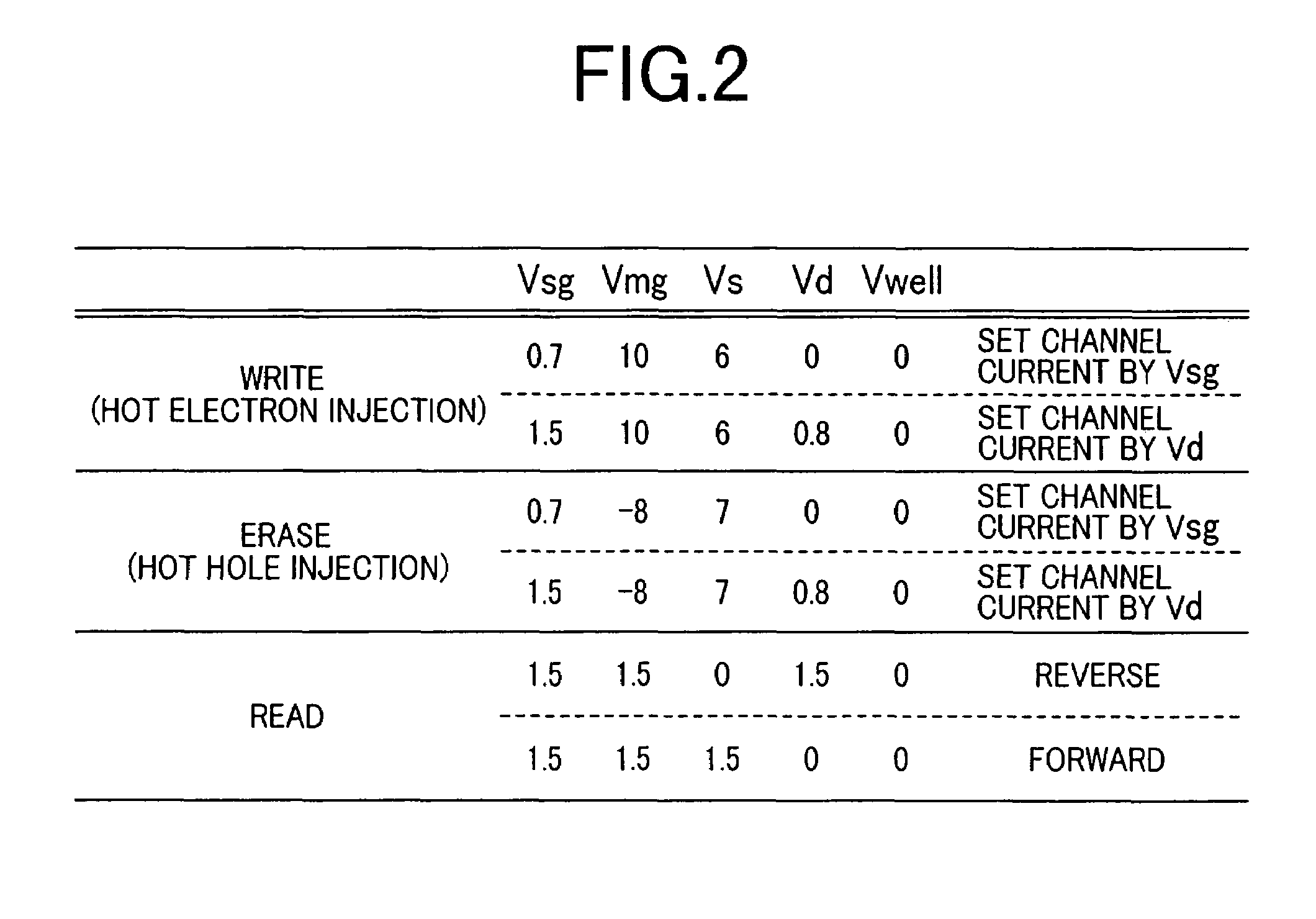
Characteristics of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device are improved. The memory cell comprises: an ONO film constituted by a silicon nitride film SIN for accumulating charge and by oxide films BOTOX and TOPOX disposed thereon and thereunder; a memory gate electrode MG disposed at an upper portion thereof; a select gate electrode SG disposed at a side portion thereof through the ONO film; a gate oxide film SGOX disposed thereunder. By applying a potential to a select gate electrode SG of a memory cell having a source region MS and a drain region MD and to the source region MS and by accelerating electrons flowing in a channel through a high electric field produced between a channel end of the select transistor and an end of an n-type doped region ME disposed under the memory gate electrode MG, hot holes are generated by impact ionization, and the hot holes are injected into a silicon nitride film SIN by a negative potential applied to the memory gate electrode MG, and thereby an erase operation is performed.
Owner:TESSERA ADVANCED TECH
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20050230736A1Improve performanceImprove reliabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesGate insulatorCondensed matter physics
In a situation where a memory cell includes an ONO film, which comprises a silicon nitride film for charge storage and oxide films positioned above and below the silicon nitride film; a memory gate above the ONO film; a select gate, which is adjacent to a lateral surface of the memory gate via the ONO film; a gate insulator positioned below the select gate; a source region; and a drain region, an erase operation is performed by injecting holes generated by BTBT into the silicon nitride film while applying a positive potential to the source region, applying a negative potential to the memory gate, applying a positive potential to the select gate, and flowing a current from the drain region to the source region, thus improving the characteristics of a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
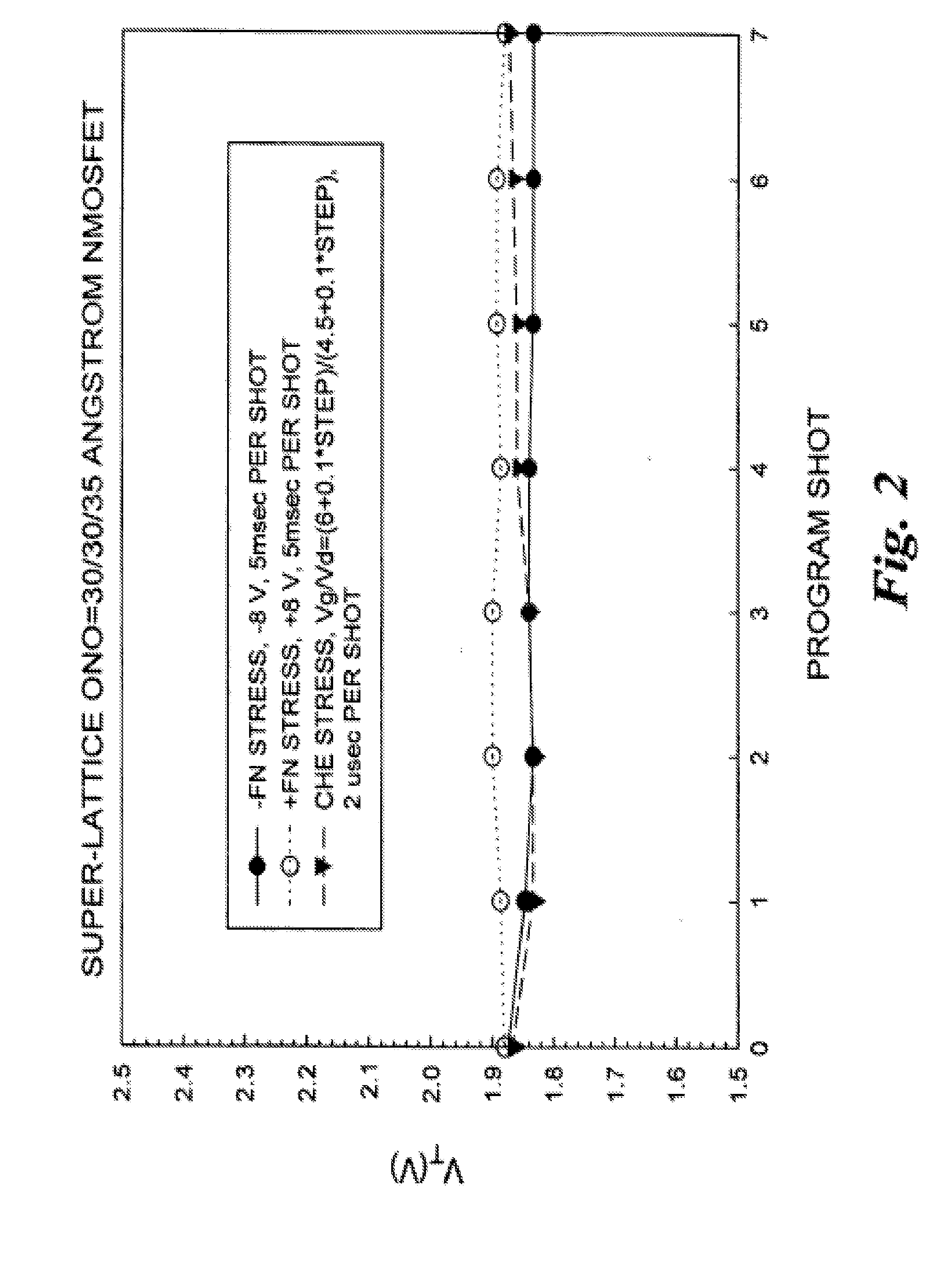
Methods of operating bandgap engineered memory
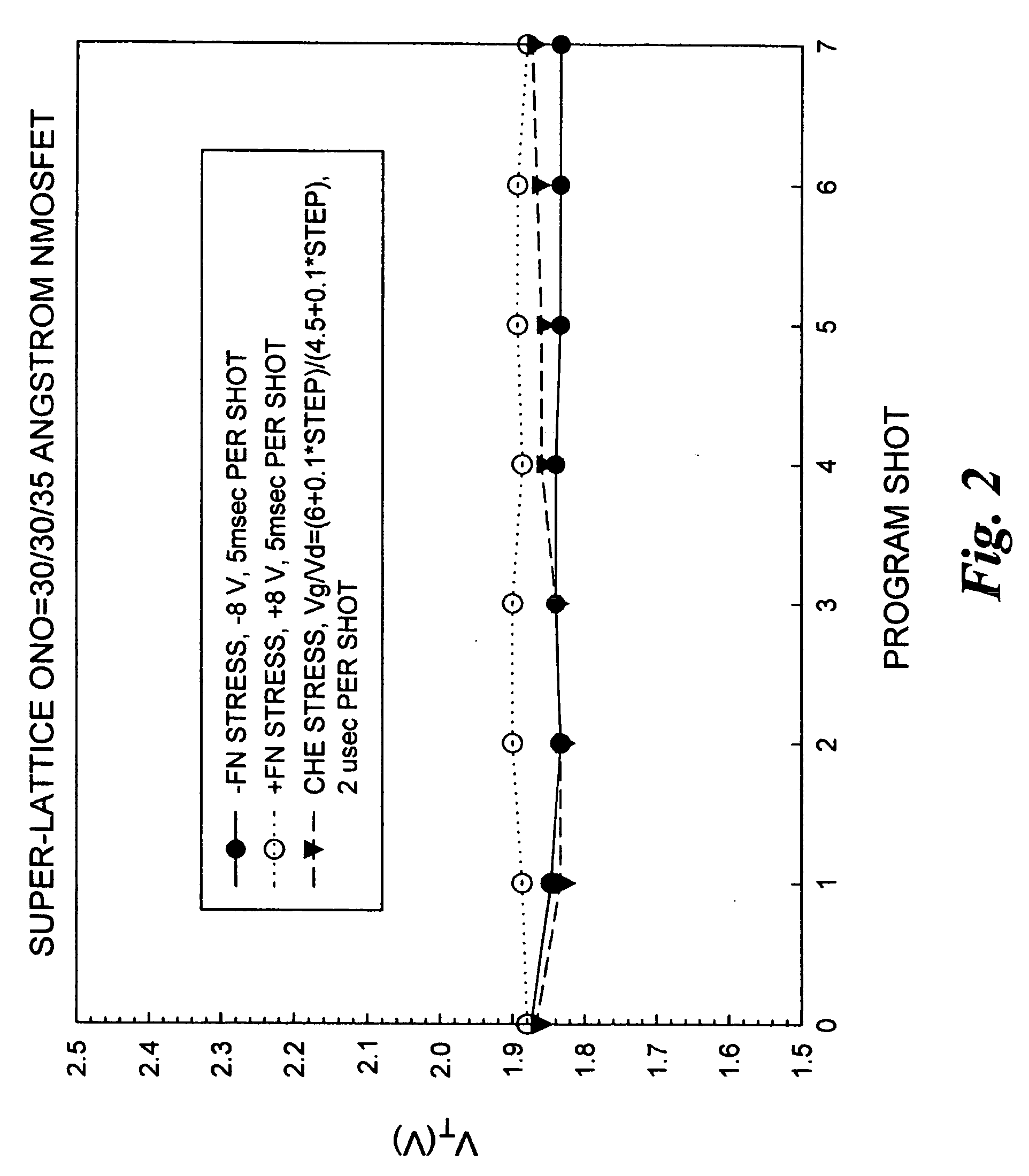
ActiveUS20070268753A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a hole-tunneling barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Silicon on insulator and thin film transistor bandgap engineered split gate memory
ActiveUS8482052B2Large operating windowEasy to operateTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric structureSemiconductor
Thin film transistor memory cells are stackable, and employ bandgap engineered tunneling layers in a junction free, NAND configuration, that can be arranged in 3D arrays. The memory cells have a channel region in a semiconductor strip formed on an insulating layer, a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure having a multilayer structure including at least one layer having a hole-tunneling barrier height lower than that at the interface with the channel region, a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure, an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer, and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
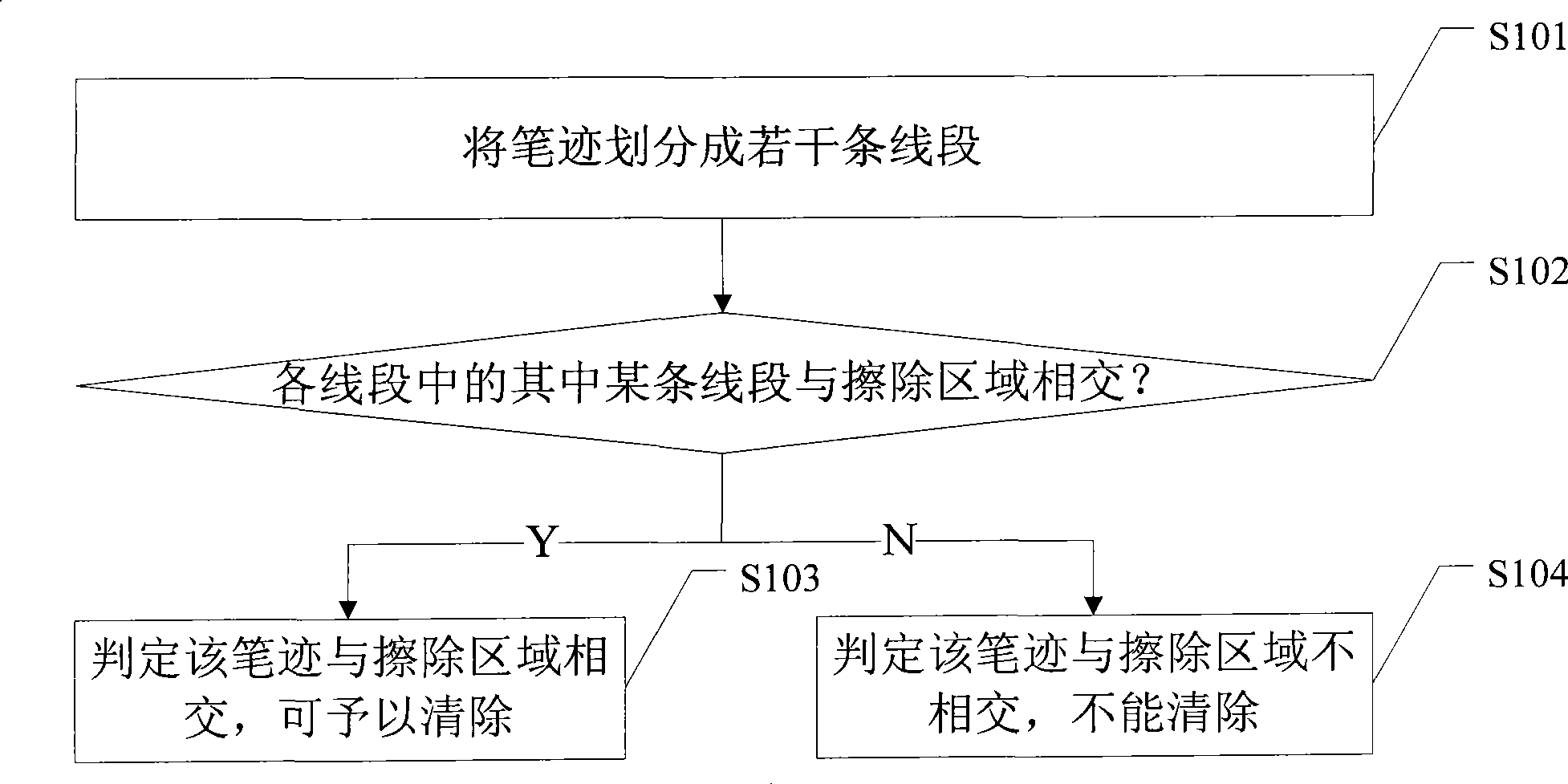
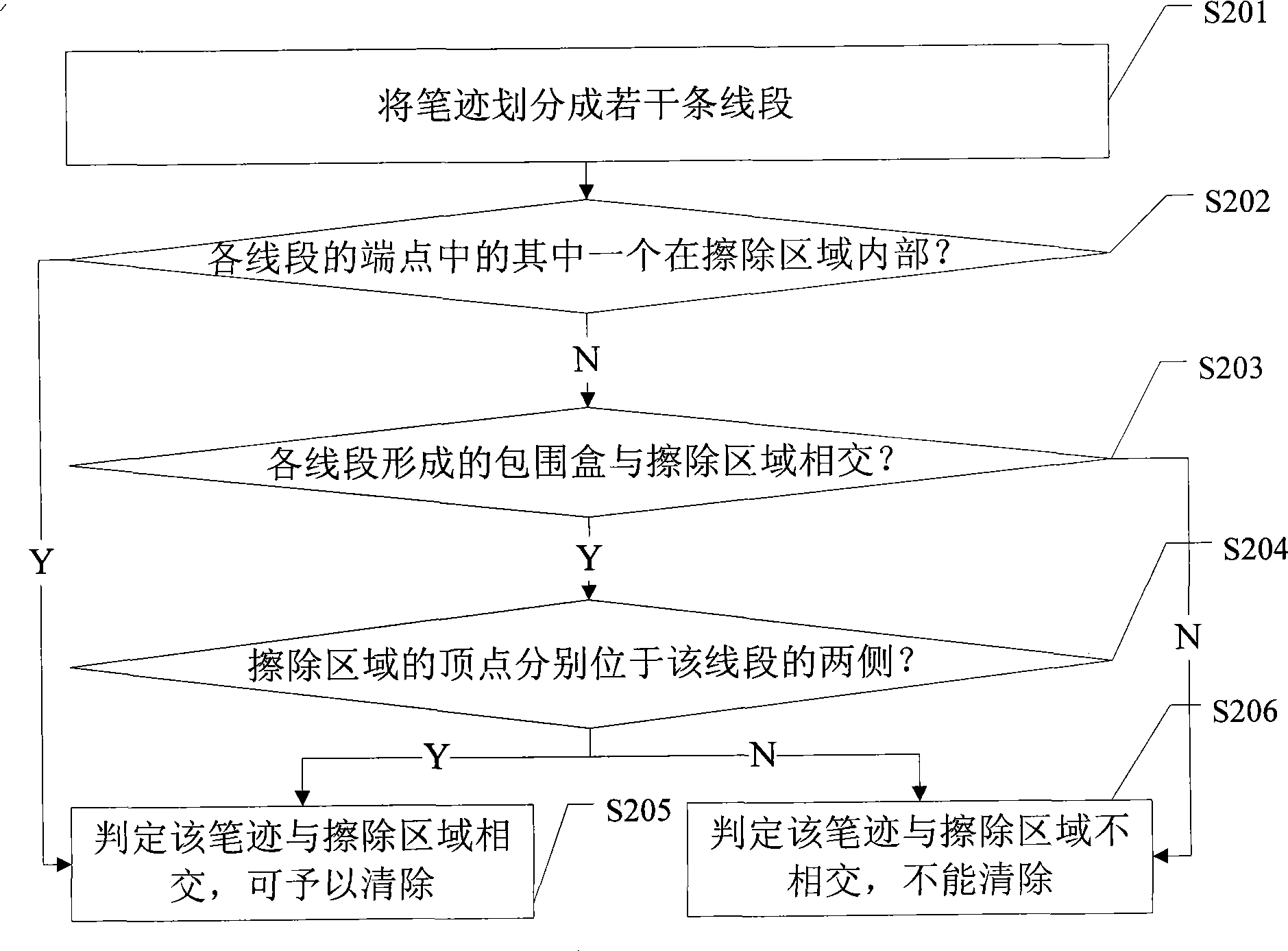
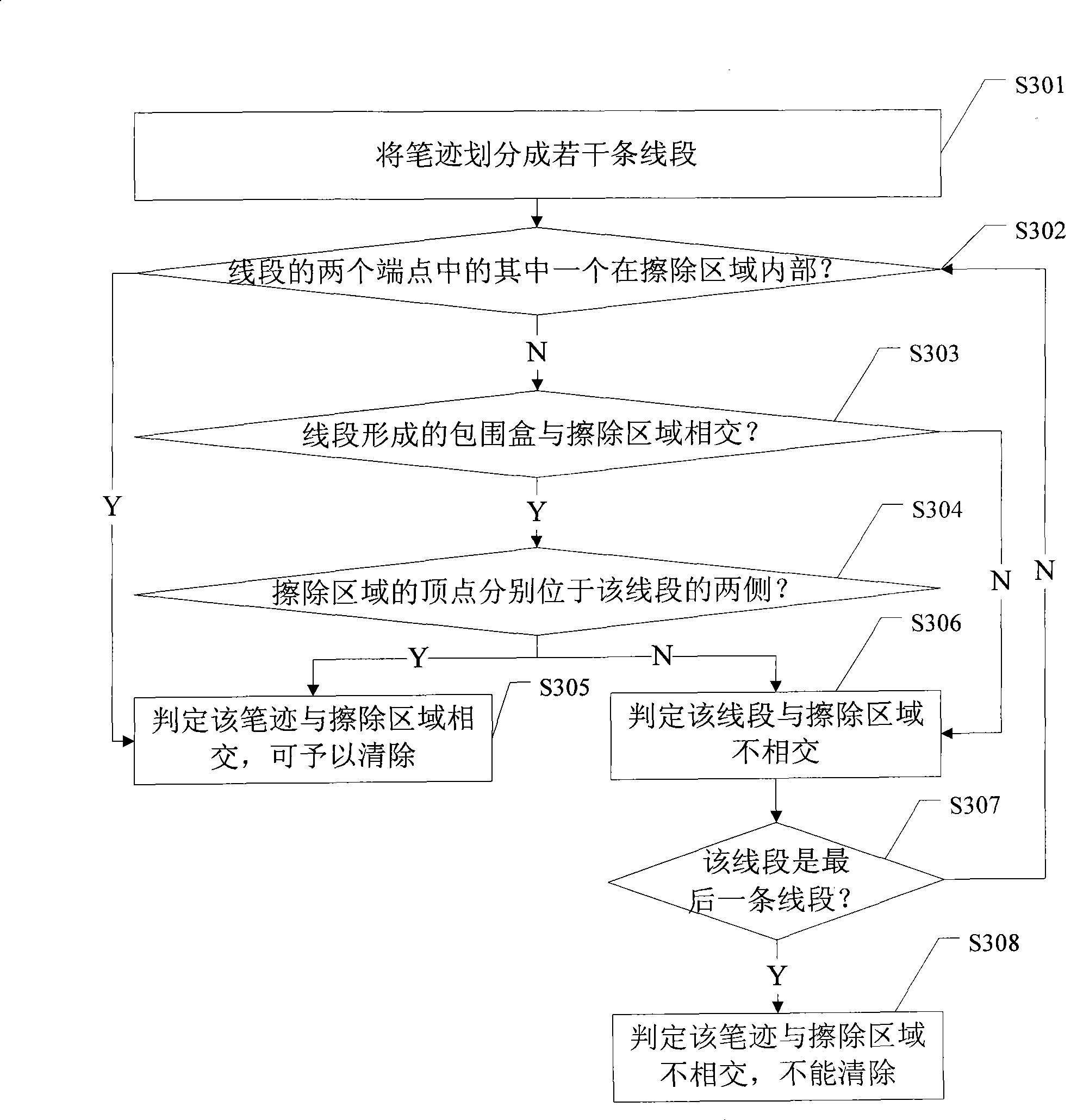
Handwriting erasing method and apparatus
InactiveCN101477694AIncrease erasing speedImprove erase effect2D-image generationHandwritingComputer hardware
Owner:GUANGDONG VTRON TECH CO LTD
Bandgap engineered split gate memory
ActiveUS20070267687A1Easy to eraseLarge operating windowTransistorSolid-state devicesDielectric structureCondensed matter physics
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a hole-tunneling barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Method and device for driving solid electrolyte cells
InactiveUS20060203430A1High densityFast switching speedLiquid electrolytic capacitorsSolid-state devicesElectrical switchingElectrolyte
An electrical switching device comprises a switching element and a heating device for heating the switching element. The switching element comprises a first electrode, a second electrode, and an electrolyte layer arranged between and contact-connected to the first and second electrode. The switching element is configured to establish a conducting path between the first and second electrodes via the electrolyte layer by conduction elements having diffused from the first electrode into the electrolyte layer.
Owner:INFINEON TECH AG
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20050095769A1Increase ratingsIncrease erasing speedRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMemory arraySemiconductor memory
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of realizing optimized erasing operation in a memory array configuration in which a plurality of pages correspond to and are connected to each of a plurality of word lines and higher speed of the erasing operation. In a flash memory, the erasing operation is performed by an erasing method of erasing a plurality of pages arbitrarily selected in a lump. In a two-page erasing mode, page erasure, page pre-erasure verification, page rewriting process, page pre-rewriting verification, and page upper end determining process are performed in order. The method realizes, particularly, (1) suppression of the number of erase verification times to the minimum by performing erase verification only on arbitrary one even-numbered or odd-numbered page in the pages to be erased in consideration of variations in the erasing characteristic, and (2) prevention of erroneous determination of the upper end of erasure since it is unnecessary to set a memory cell to be rewritten every rewrite verification by continuously executing the rewriting process page by page.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Non-volatile memory cells, memory arrays including the same and methods of operating cells and arrays
ActiveUS7642585B2Easy to eraseLarge operating windowTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsMemory cellDielectric structure
Memory cells comprising: a semiconductor substrate having a source region and a drain region disposed below a surface of the substrate and separated by a channel region; a tunnel dielectric structure disposed above the channel region, the tunnel dielectric structure comprising at least one layer having a small hole-tunneling-barrier height; a charge storage layer disposed above the tunnel dielectric structure; an insulating layer disposed above the charge storage layer; and a gate electrode disposed above the insulating layer are described along with arrays thereof and methods of operation.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD +1
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory with erase gate and its manufacturing method
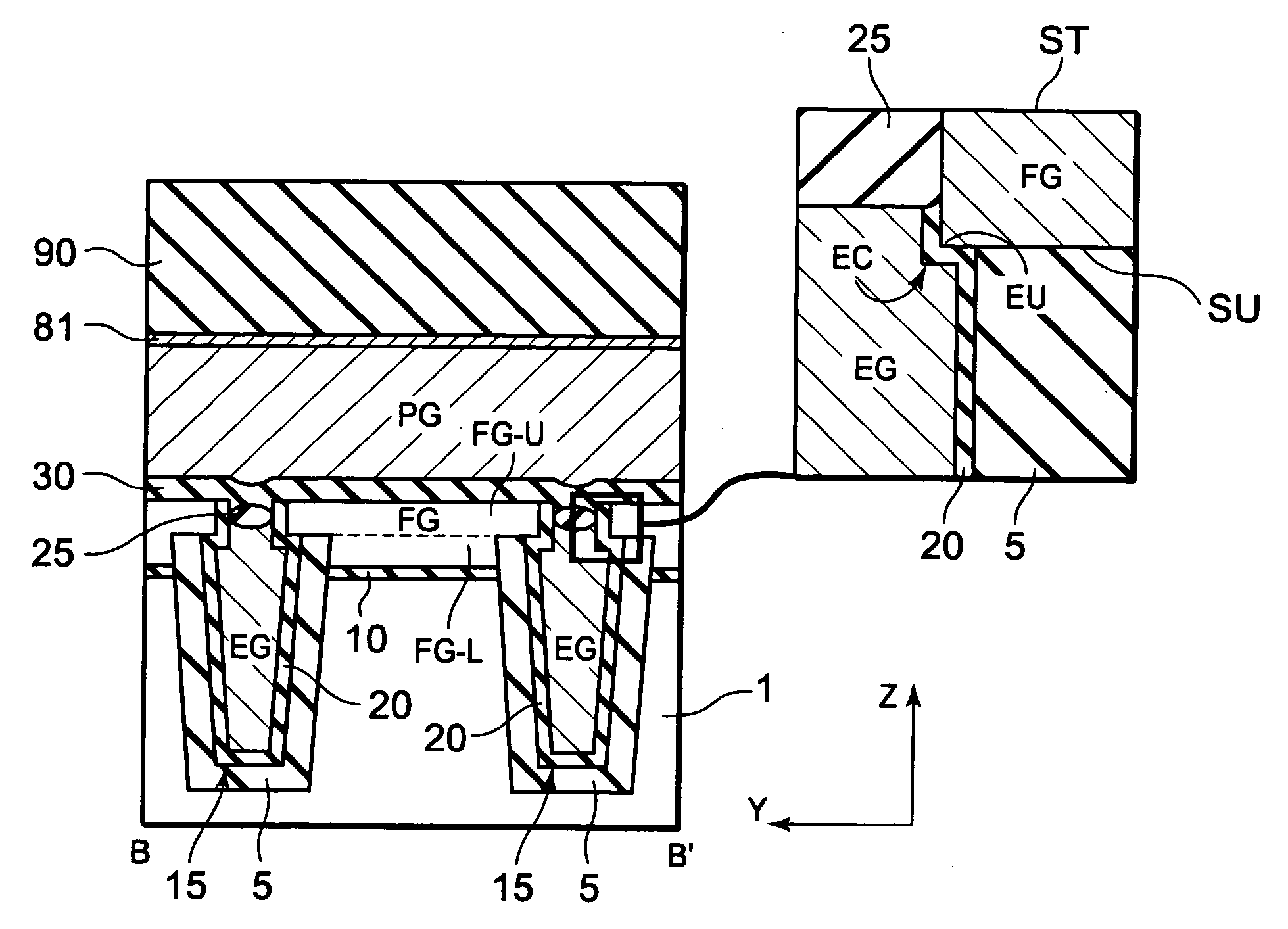
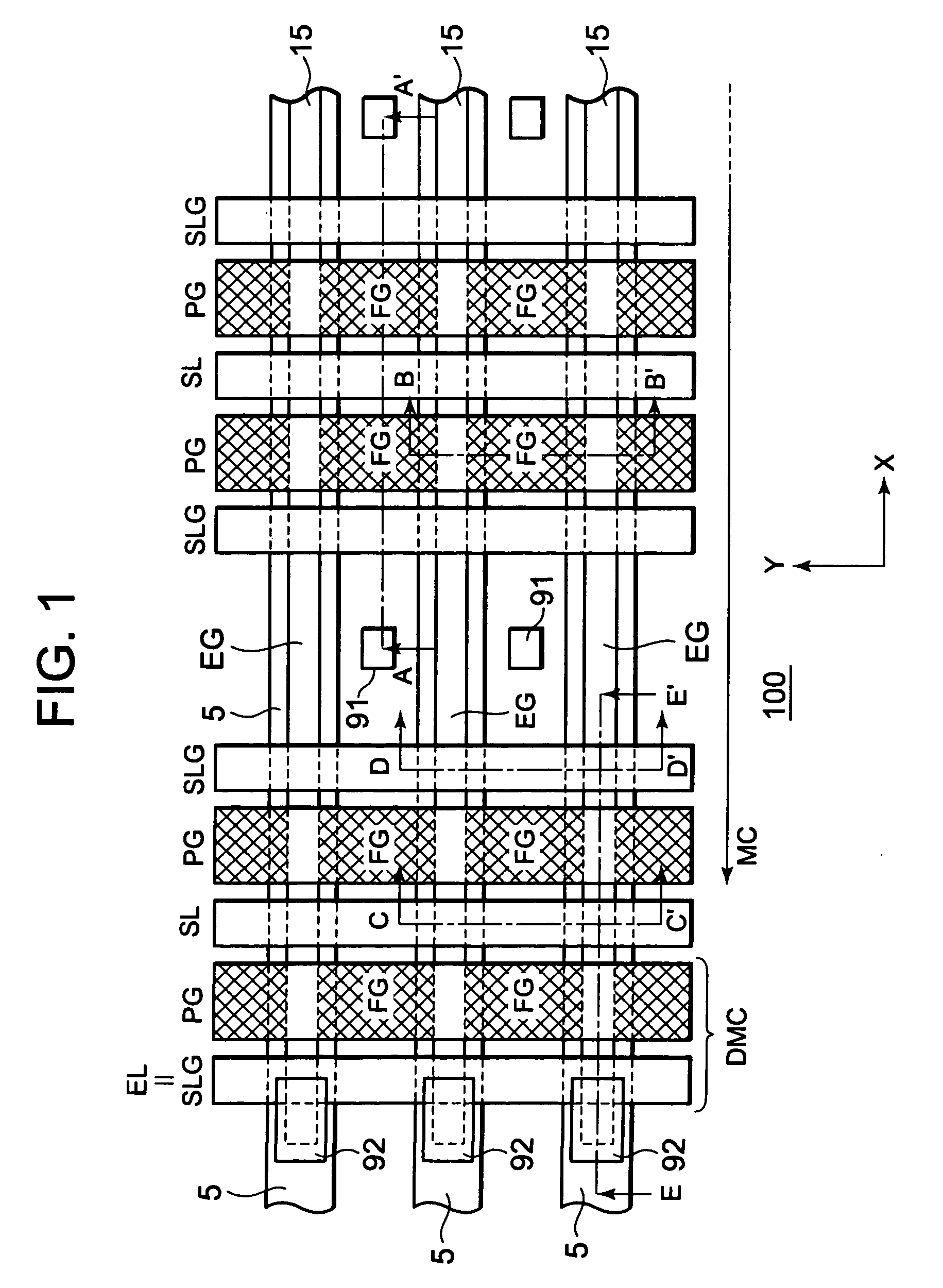
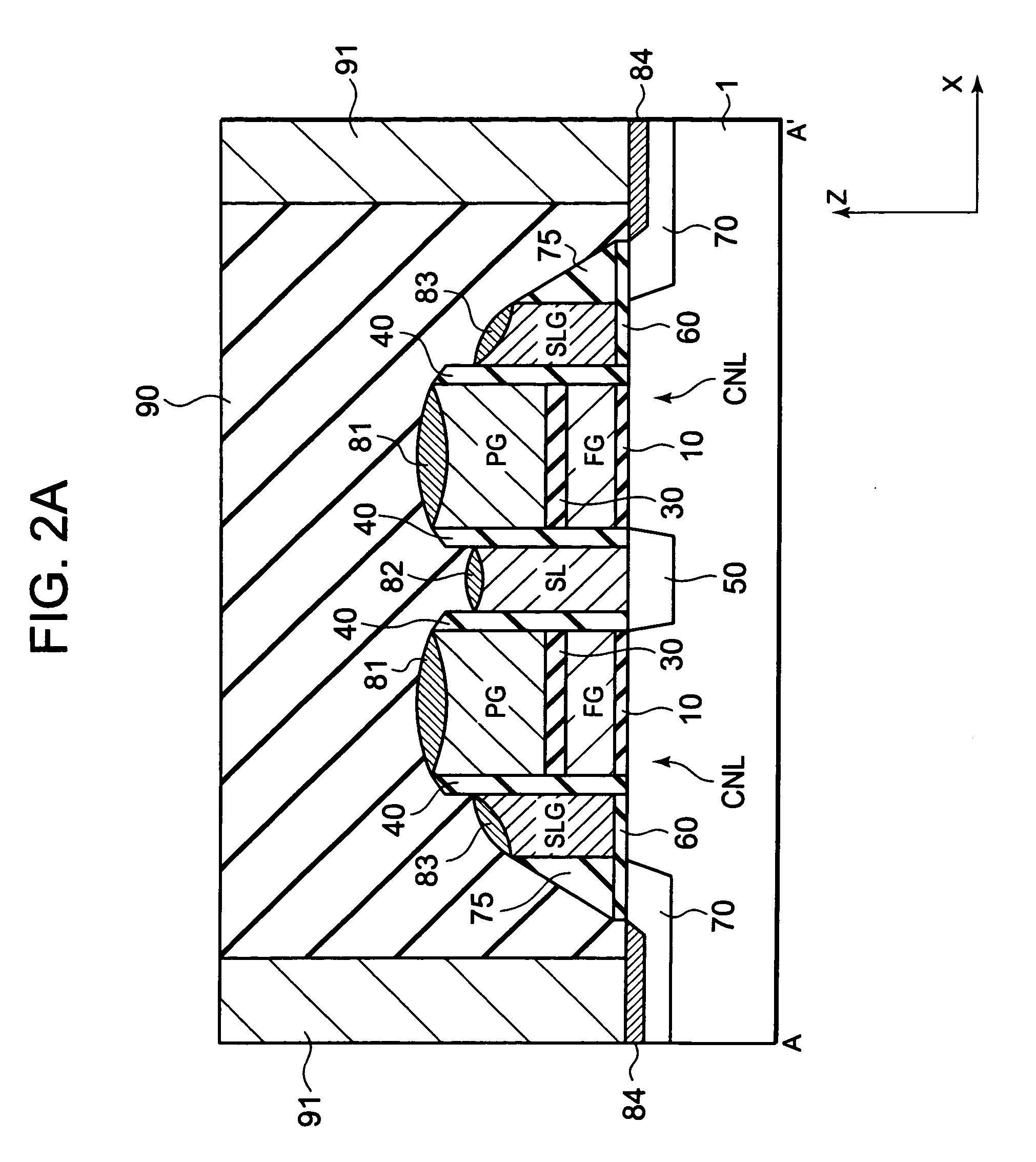
InactiveUS20090166708A1Improve erase efficiencySpeed up erasure operationSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductorSemiconductor memory
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor substrate, a select gate formed above the semiconductor substrate, a floating gate formed above the semiconductor substrate and an erase gate positioned lower than an upper surface of the floating gate, and opposite an edge of a lower surface of the floating gate.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
ActiveUS20070070707A1Increase erasing speedArea of memory prevented increasingSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCapacitanceCoupling
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device for storing data by accumulating charge in a floating gate includes a plurality of MOS transistors sharing the floating gate. In the device, a PMOS is used for coupling during writing and an n-type depletion MOS (DMOS) is used for coupling during erasure. Coupling of channel inversion capacitance by the PMOS is used for writing and coupling of depletion capacitance by the n-type DMOS is used for erasure, thereby increasing the erase speed without increase of area, as compared to a conventional three-transistor nonvolatile memory element.
Owner:PANASONIC SEMICON SOLUTIONS CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of realizing optimized erasing operation in a memory array
InactiveUS6958940B2Increase ratingsIncrease erasing speedRead-only memoriesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMemory arraySemiconductor memory
A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of realizing optimized erasing operation in a memory array configuration in which a plurality of pages correspond to and are connected to each of a plurality of word lines and higher speed of the erasing operation. In a flash memory, the erasing operation is performed by an erasing method of erasing a plurality of pages arbitrarily selected in a lump. In a two-page erasing mode, page erasure, page pre-erasure verification, page rewriting process, page pre-rewriting verification, and page upper end determining process are performed in order. The method realizes, particularly, (1) suppression of the number of erase verification times to the minimum by performing erase verification only on arbitrary one even-numbered or odd-numbered page in the pages to be erased in consideration of variations in the erasing characteristic, and (2) prevention of erroneous determination of the upper end of erasure since it is unnecessary to set a memory cell to be rewritten every rewrite verification by continuously executing the rewriting process page by page.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Integrated circuit memory with fast page mode verify
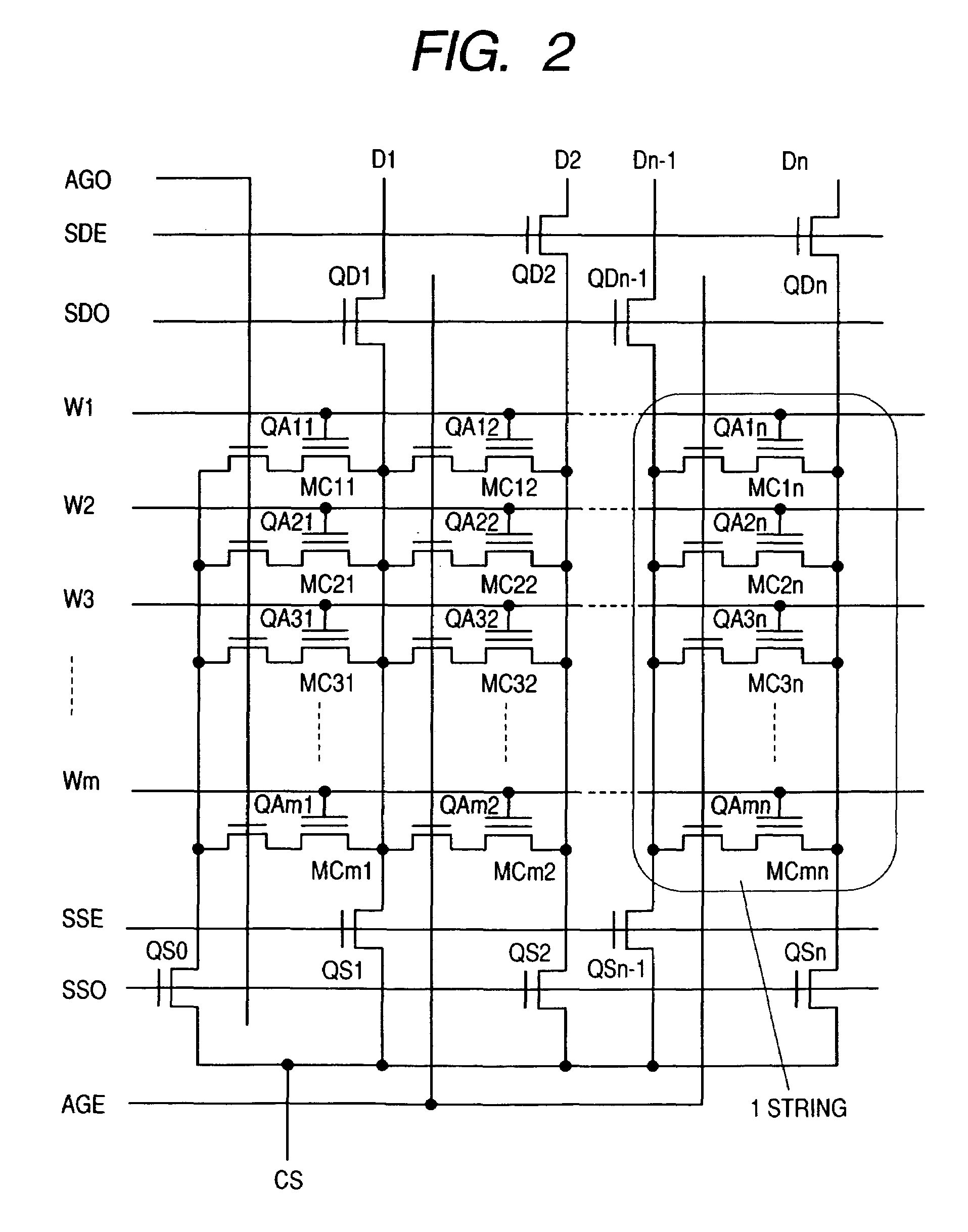
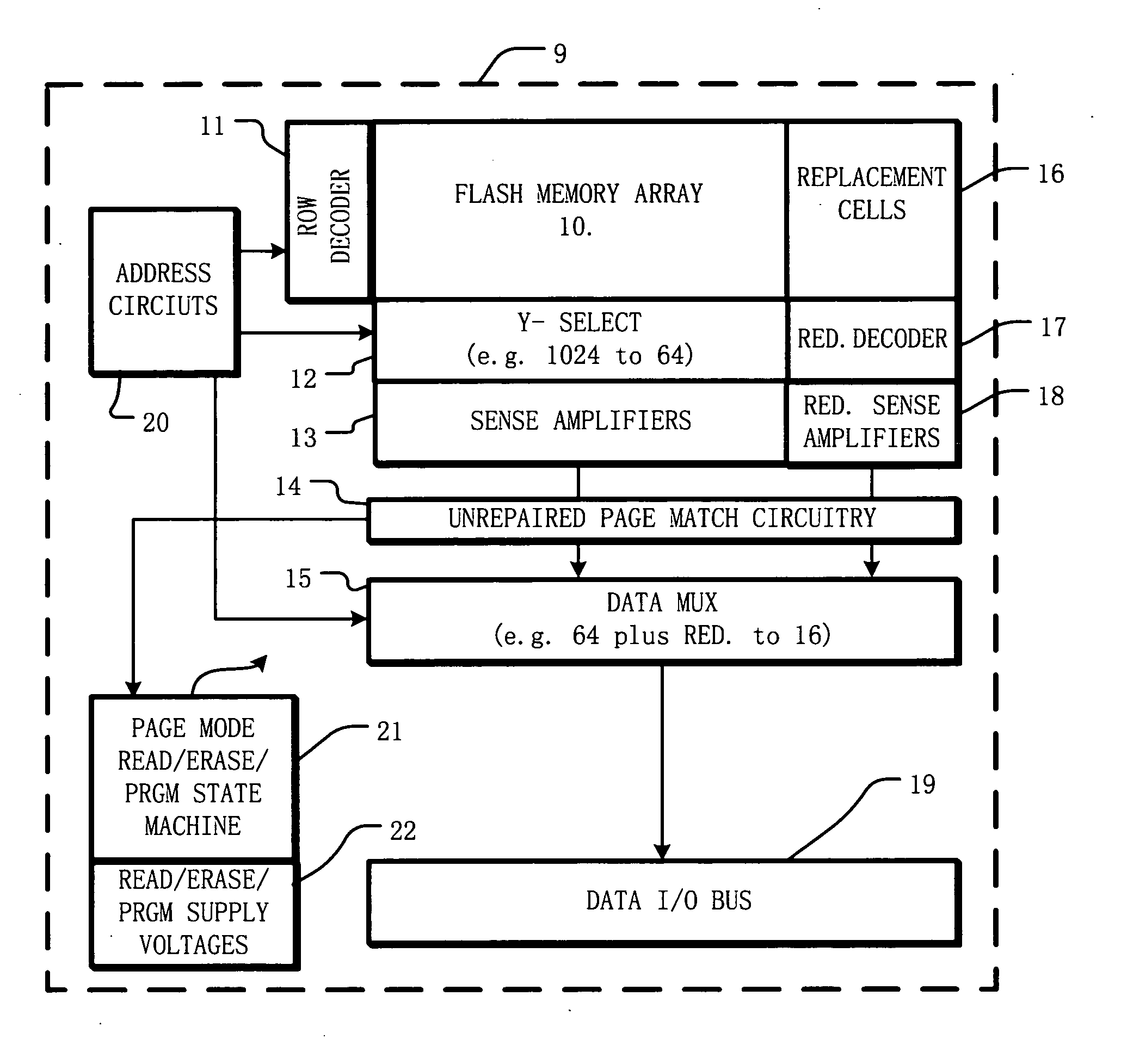
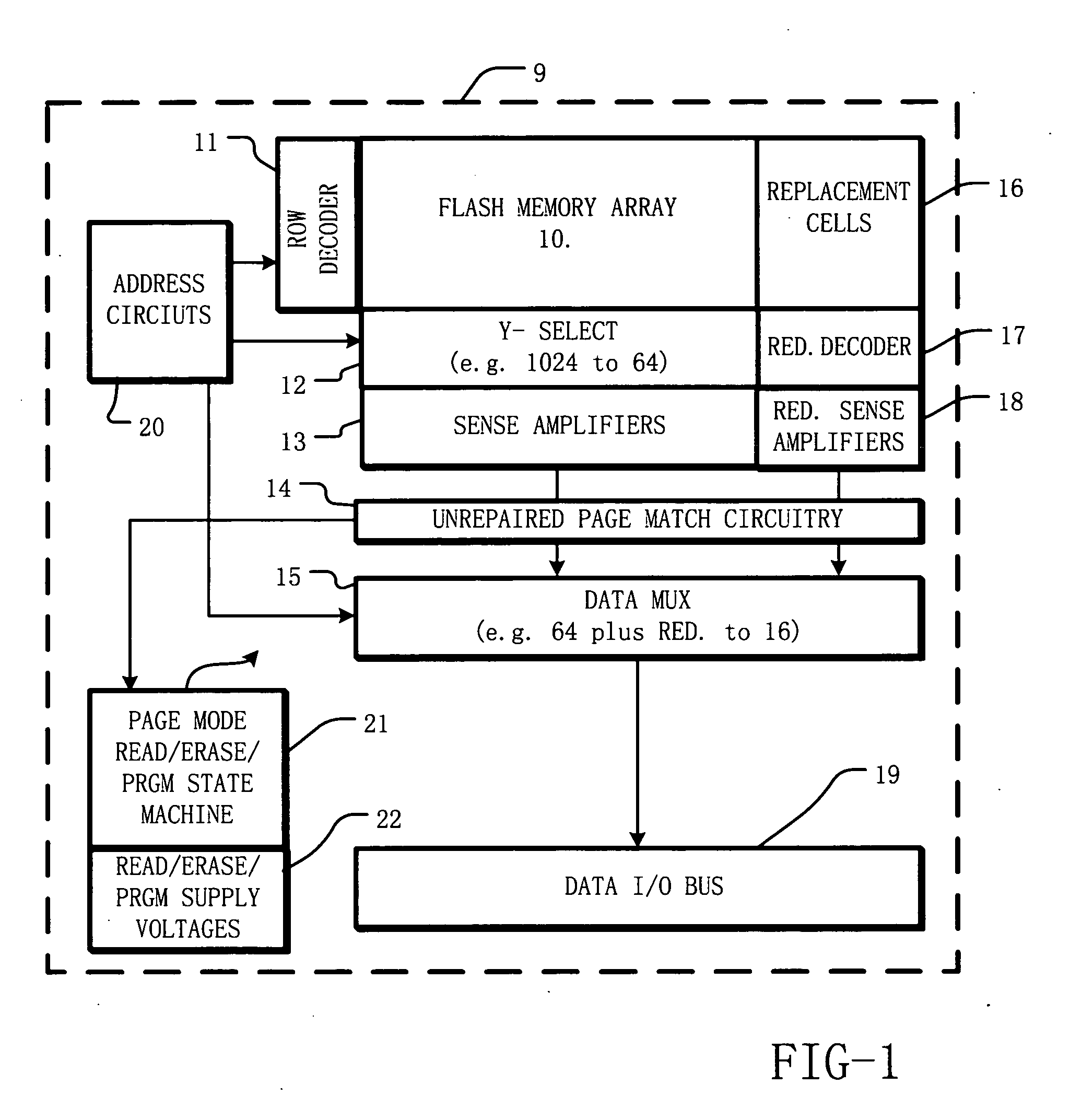
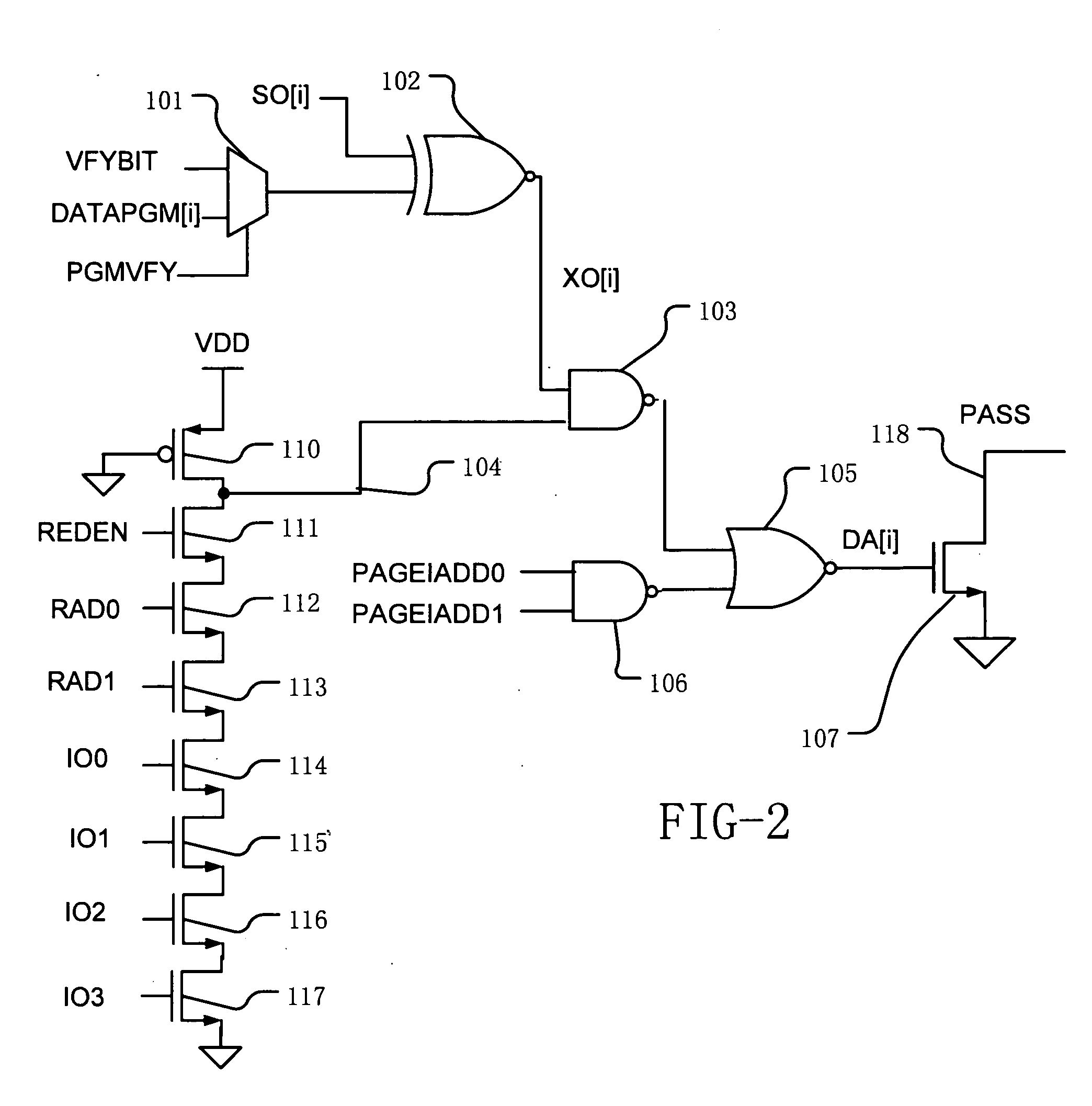
ActiveUS20050276129A1Accelerated programIncrease erasing speedRead-only memoriesDigital storageIntegrated circuitBit line
A method for operating an integrated circuit memory device includes applying a verify procedure in which the page of data and one or more bits from a set of replacement cells are matched with a pattern in parallel to indicate a verify result, where the page of data is “unrepaired” and may include one or more bits from defective bit lines. While matching to indicate a verify result, the one or more bits from defective bit lines in the page are masked. Flash memory and other memory devices implement the method.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Thermally assisted dielectric charge trapping flash
ActiveUS8488387B2Improve staminaEffective endurance of the device can be greatly improvedRead-only memoriesDiodeElectricityPower flow
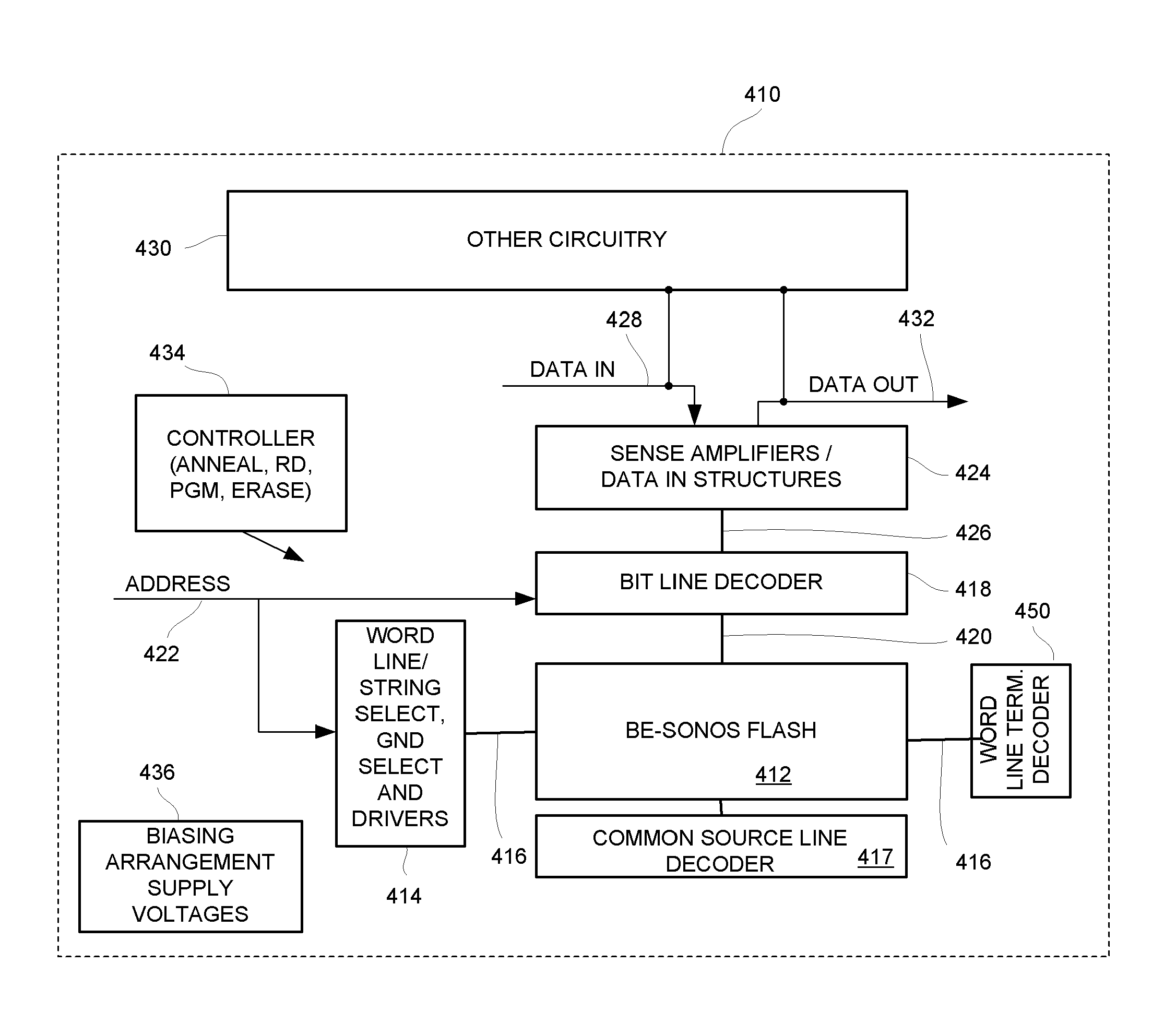
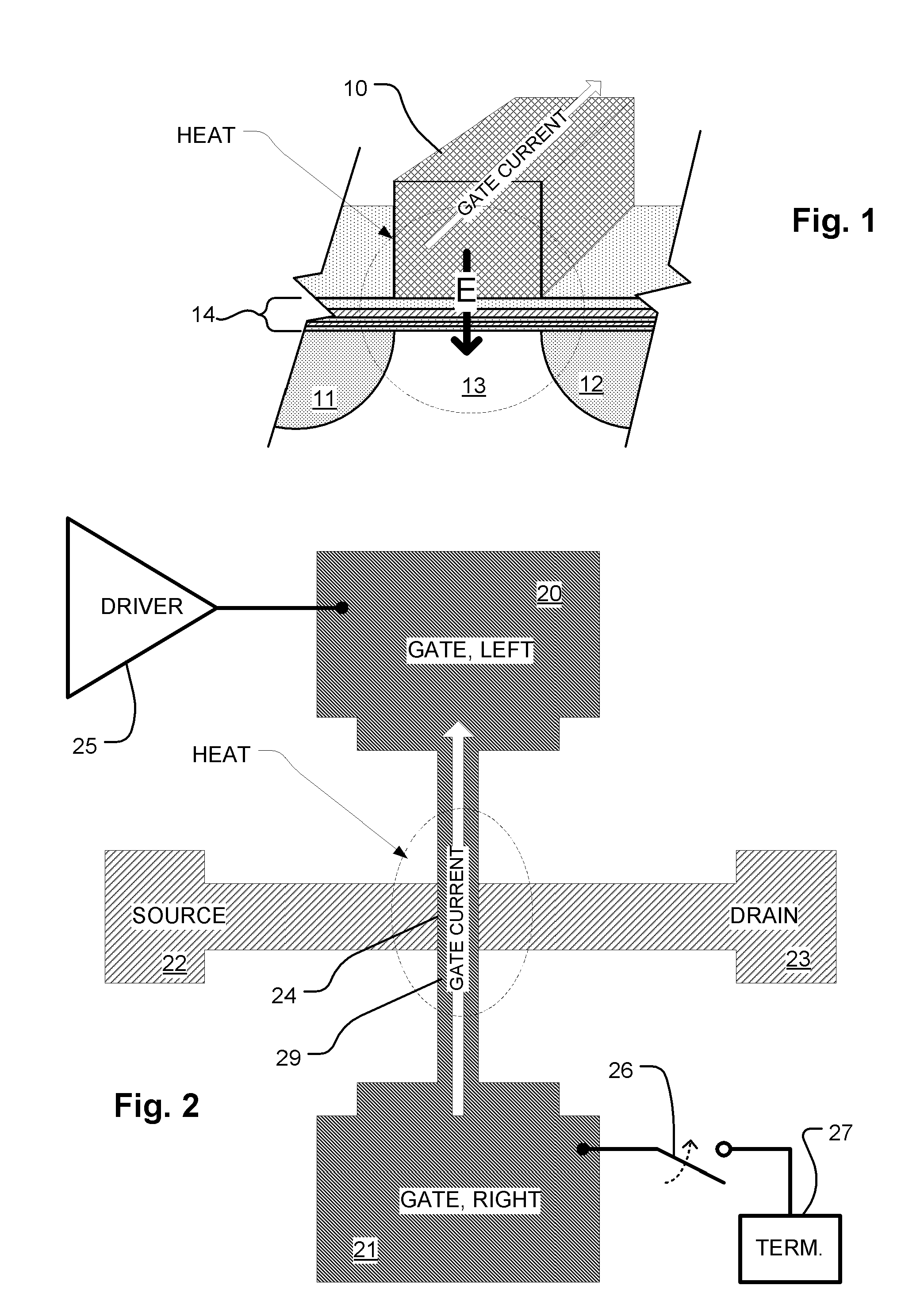
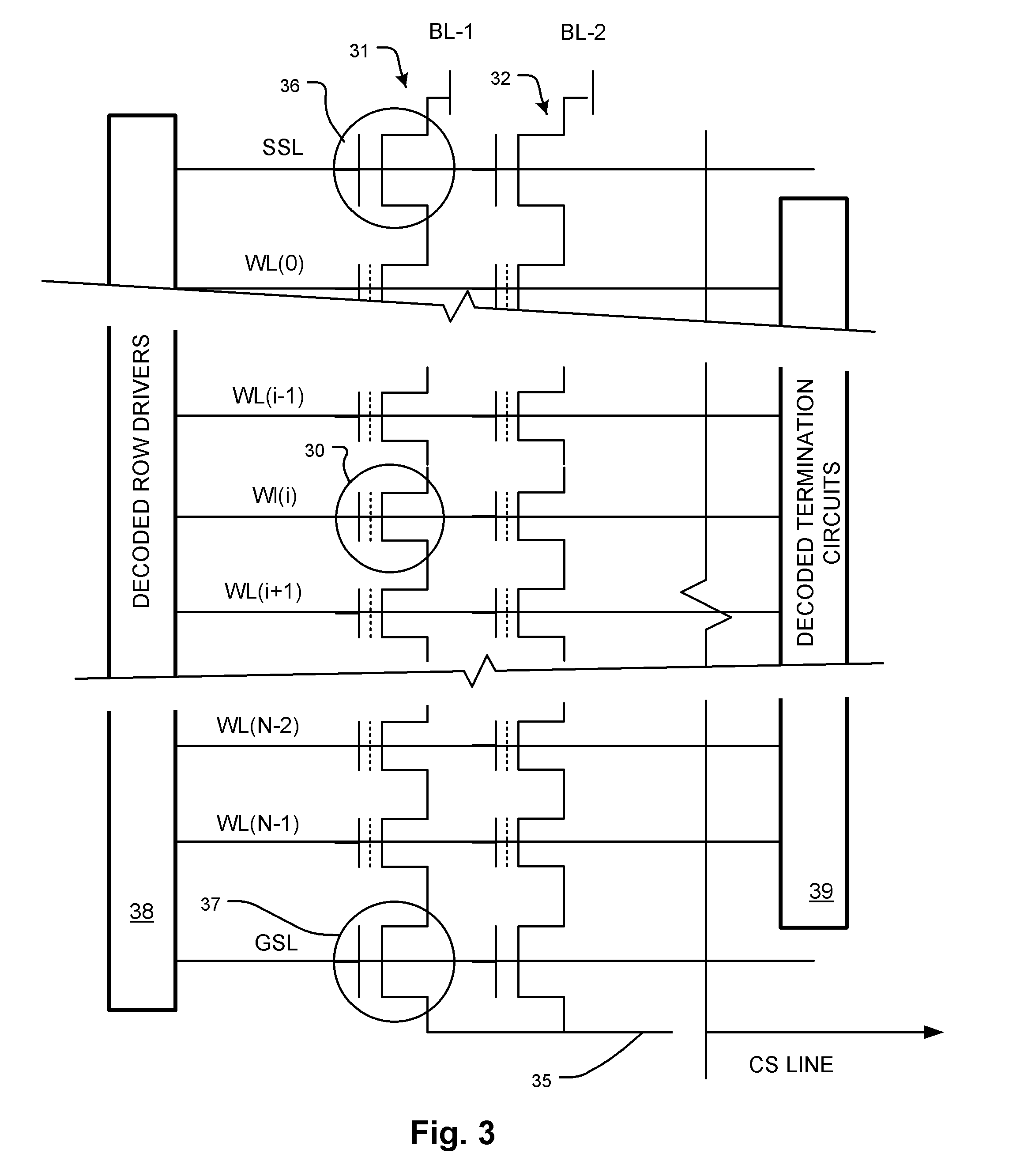
A memory device includes an array of dielectric charge trapping structures memory cells including word lines and bit lines. Control circuitry is coupled to the array arranged to control read, program and erase operations. A controller is arranged with supporting circuitry thermally annealing charge trapping structures in the memory cells in the array. Word line drivers and word line termination circuits can be used to induce current flow on the word lines to induce heat for the annealing. The thermal annealing can be applied interleaved with normal operations for recover from cycling damage. Also, the thermally annealing can be applied during mission functions like erase, to improve performance of the function.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Semiconductor device having stacked array structure, NAND flash memory array using the same and fabrication thereof
ActiveUS20120117316A1Increase widthImprove controllabilitySolid-state devicesMemory adressing/allocation/relocationDevice materialEngineering
The present invention relates to a semiconductor device, a memory array and a fabrication method thereof, and more particularly to a semiconductor device having a stacked array structure (referred to as a STAR structure: a STacked ARray structure) applicable to not only a switch device but also a memory device, a NAND flash memory array using the same as a memory device and a fabrication method thereof.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
Nonvolatile memory erase method and device
ActiveCN103426474AShorten the timeReduce the risk of Over ProgramRead-only memoriesGate voltageOperating system
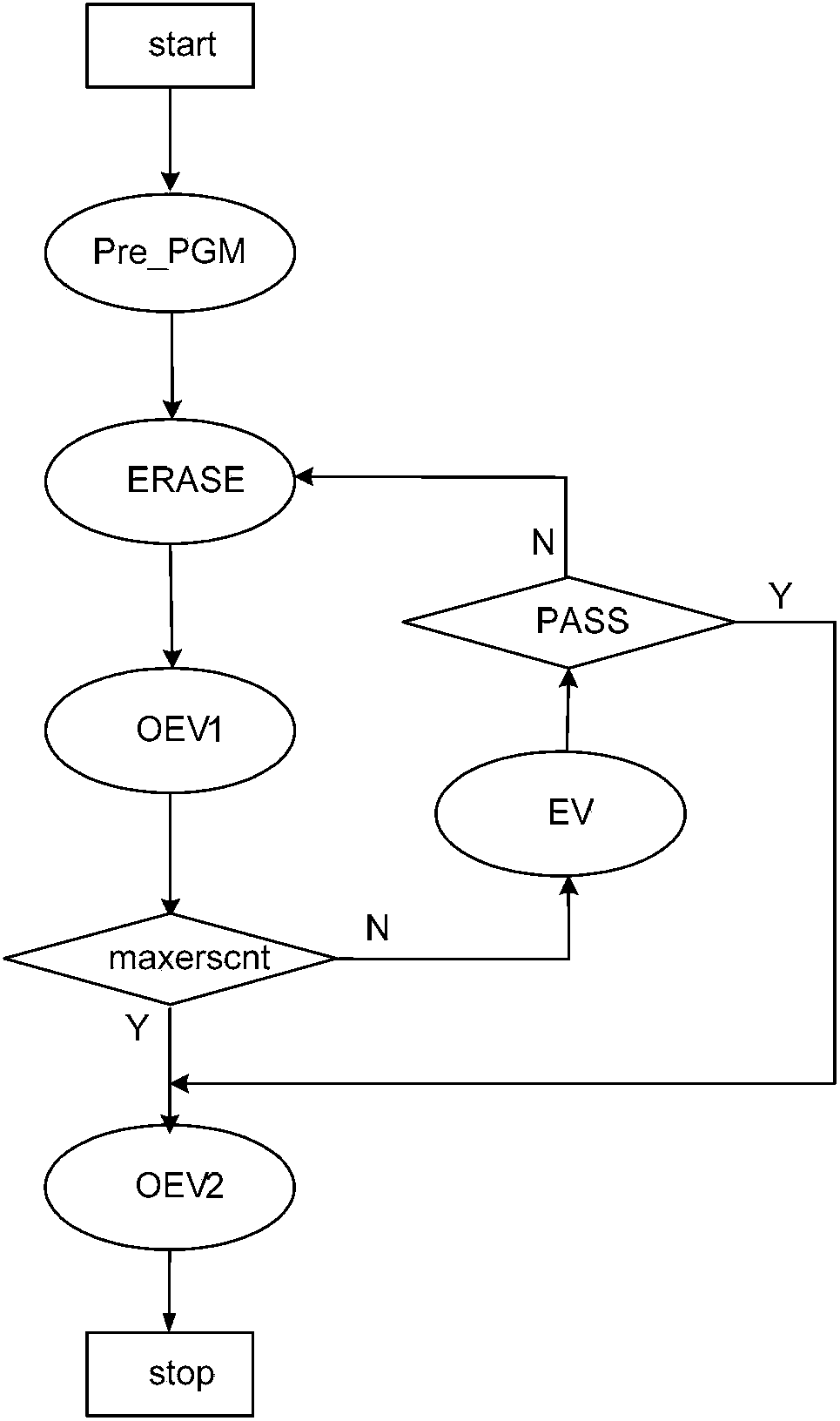
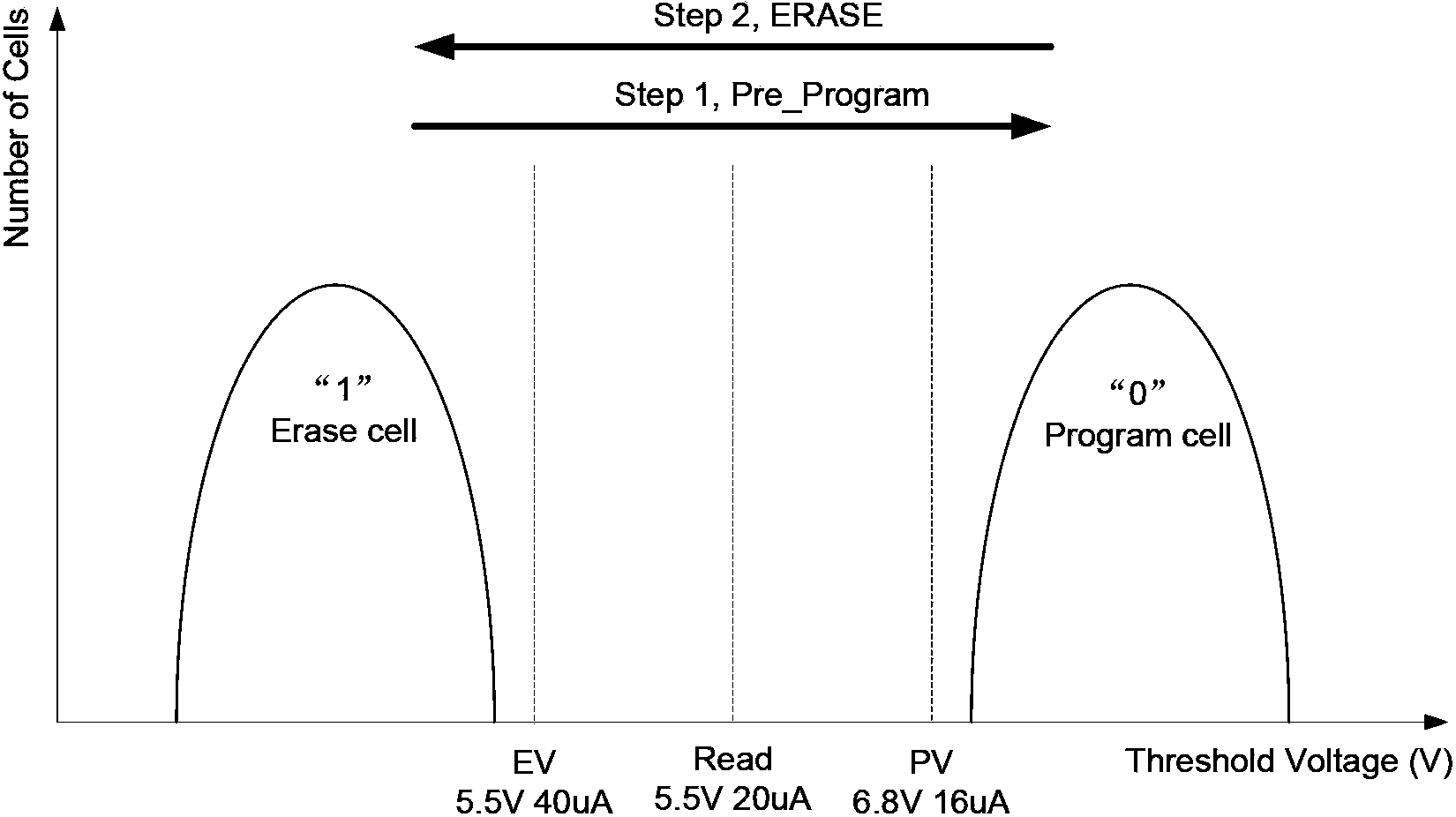
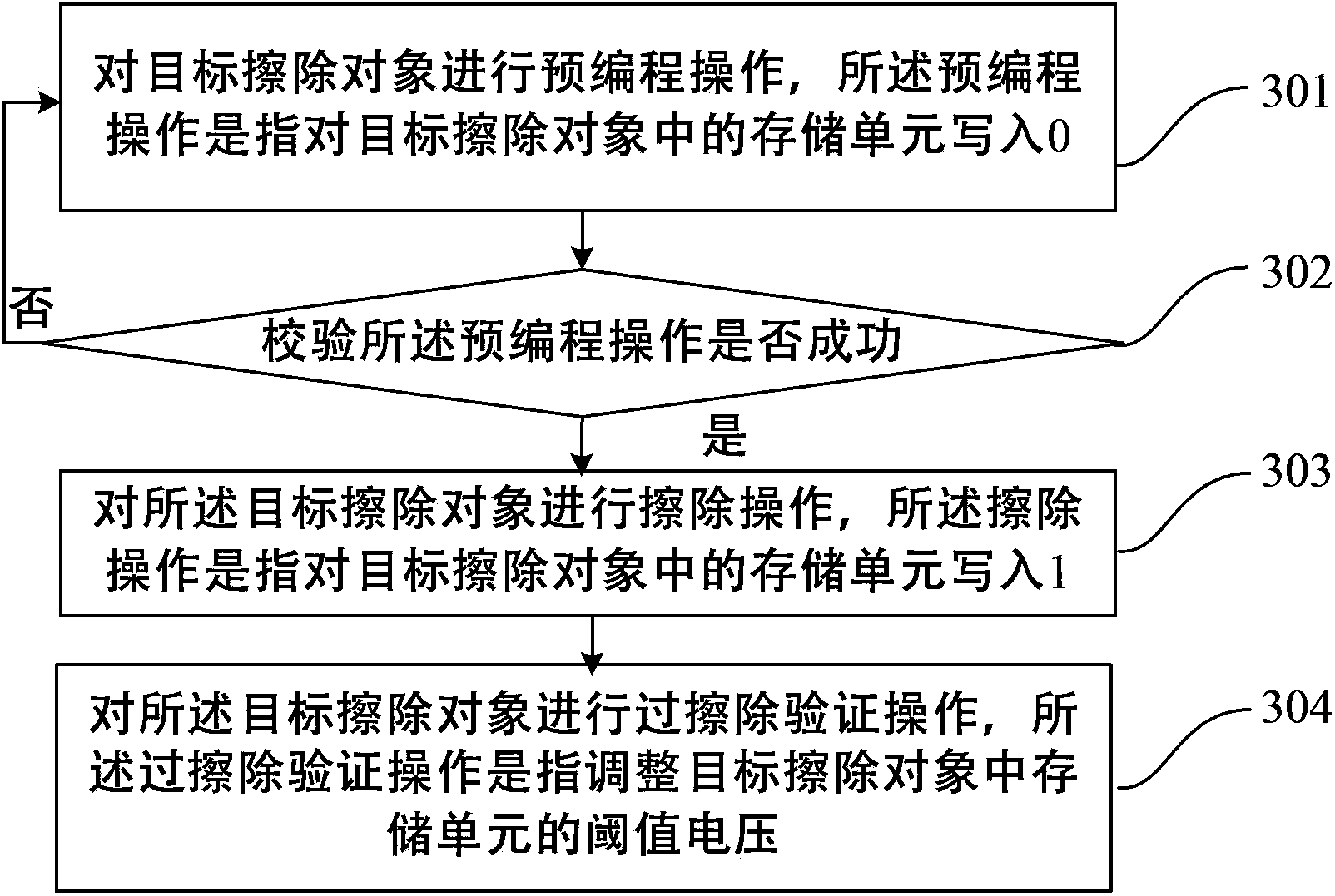
The invention discloses a nonvolatile memory erase method and a nonvolatile memory erase device. The method comprises the steps that: a target erasing target is subjected to a preprogramming operation, wherein the preprogramming operation is that 0 is written into memory units of the target erase object; whether the preprogramming operation is successful is examined, wherein the examining is that whether currents of the memories in the target erase object processed through the preprogramming operation under a certain gate voltage are all smaller than a target current value which is a current value with current margin; if the preprogramming operation is successful, a next step is executed, and if not, the progress is turned back to the execution of the preprogramming operation; the target erase object is subjected to an erase operation, wherein the erase operation is that 1 is written into memory units of the target erase object; and the target erase object is subjected to an over-erase examine operation, wherein the over-erase examine operation is that threshold voltage of memory units in the target erase object is adjusted. With the method and device provided by the invention, nonvolatile memory erase speed can be improved, and memory performance can be improved.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
Preparation method of high-speed low-power-consumption phase change memory
ActiveCN102447061AReversible phase change functionWork fasterSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhase-change memoryInsulation layer
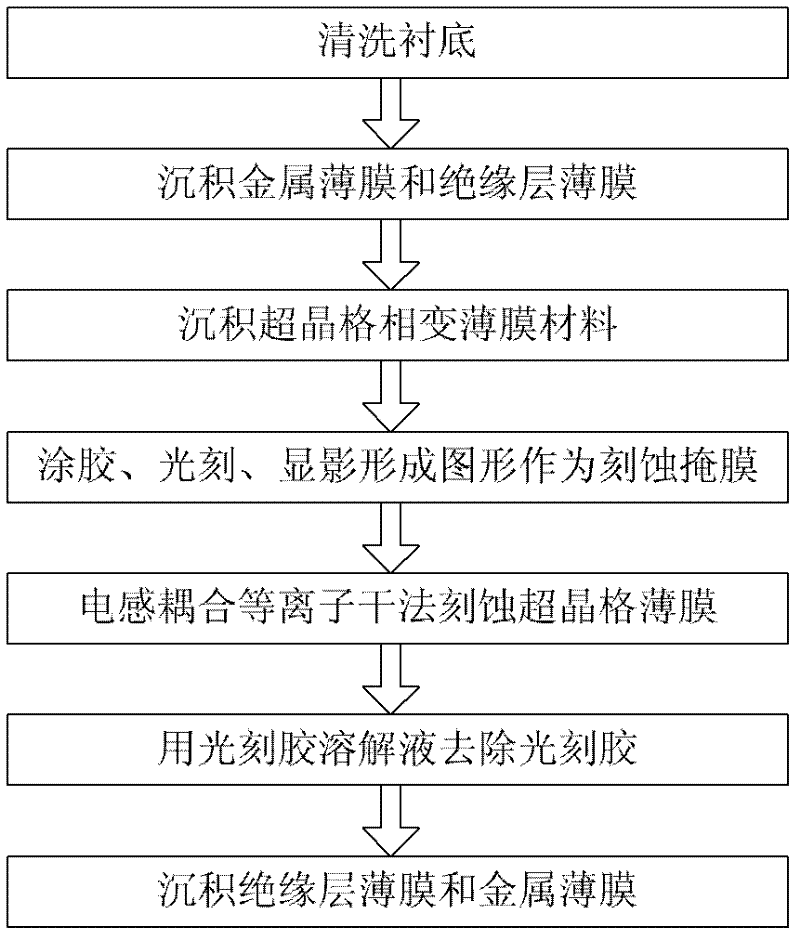
The invention discloses a preparation method of a high-speed low-power-consumption phase change memory. In the method, a superlattice film material with rapid phase change speed and low heat conductivity is used as a phase change material, and an inductive coupling plasma dry method is used to etch the material so as to form a phase change memory unit with good appearance, steep and straight side wall and good consistency. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: (1) washing a substrate; (2) successively depositing a metal film and an insulation layer film; (3) depositing a superlattice film phase change material; (4) gluing and photoetching to form photoresist serving as an etched mask; (5) etching the superlattice film material with inductive coupling plasma etching equipment; (6) removing the etched mask; and (7) successively depositing an insulation layer film and a metal film. According to the invention, the prepared phase change memory has high speed and low power consumption through utilizing the characteristics of the inductive coupling plasma dry method etching on the superlattice phase change film material, such as anisotropism, consistency and the like; and the preparation method disclosed by the invention can be well applied to superintegrated and large-scale industrialized production.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
NAND flash memory cell row and manufacturing method thereof
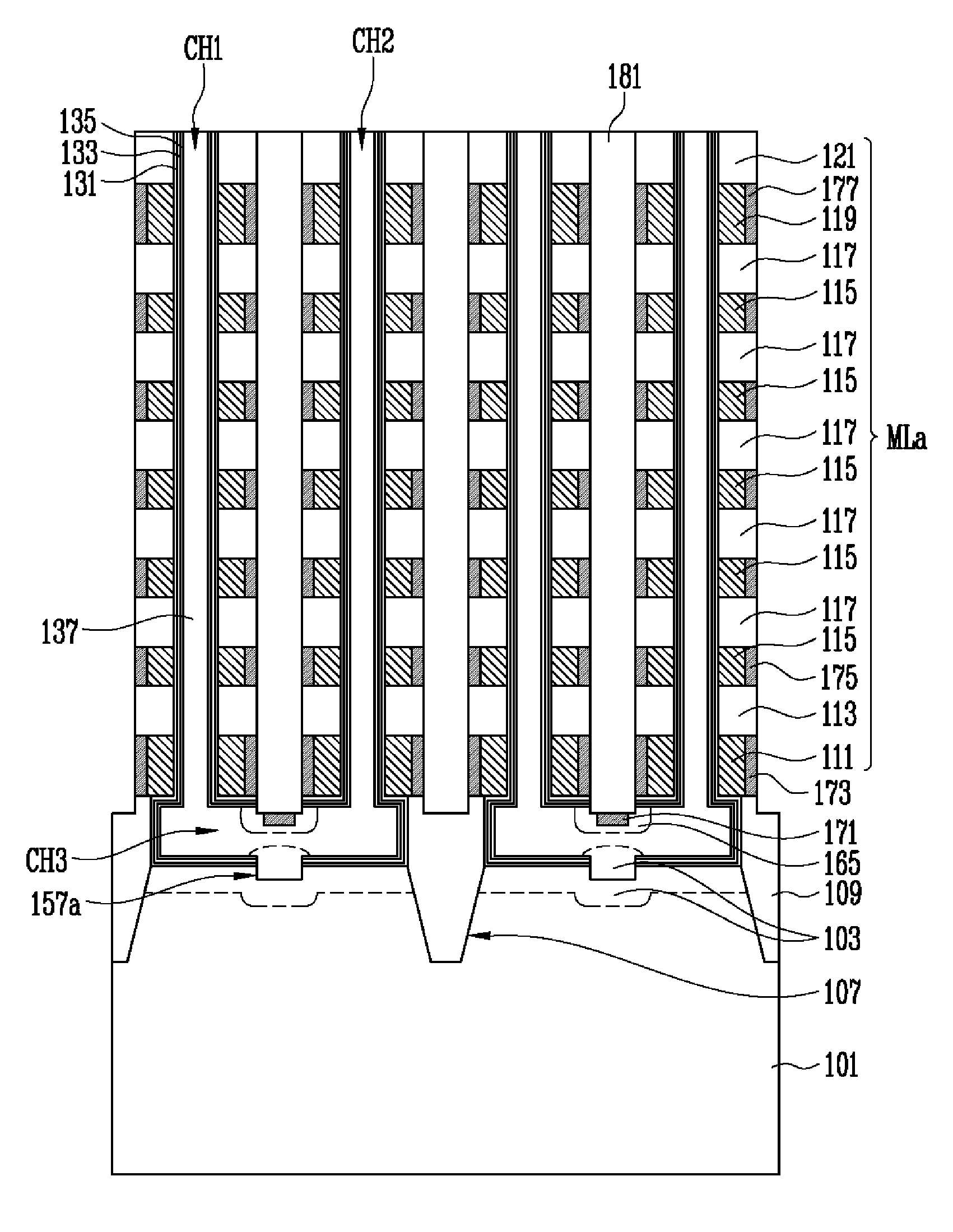
ActiveUS20060040440A1Improve memory performanceIncrease erasing speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricEngineering
A NAND flash memory cell row includes first and second stacked gate structures, control and floating gates, inter-gate dielectric layer, a tunnel oxide layer, doping regions and source / drain regions. The first stacked gate structures has an erase gate dielectric layer, an erase gate and a first cap layer. Each of the second stacked gate structure has a select gate dielectric layer, a select gate and a second cap layer. The control gate is between each of the first stacked gate structures, and between each of the second stacked gate structures and the adjacent first stacked gate structure. The floating gate is between the control gate and substrate. The inter-gate dielectric layer is disposed between the control and floating gates. The tunnel oxide is between the floating gate and substrate. The doping regions are disposed under the first stacked gate structure, and the source / drain regions are in the exposed substrate.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
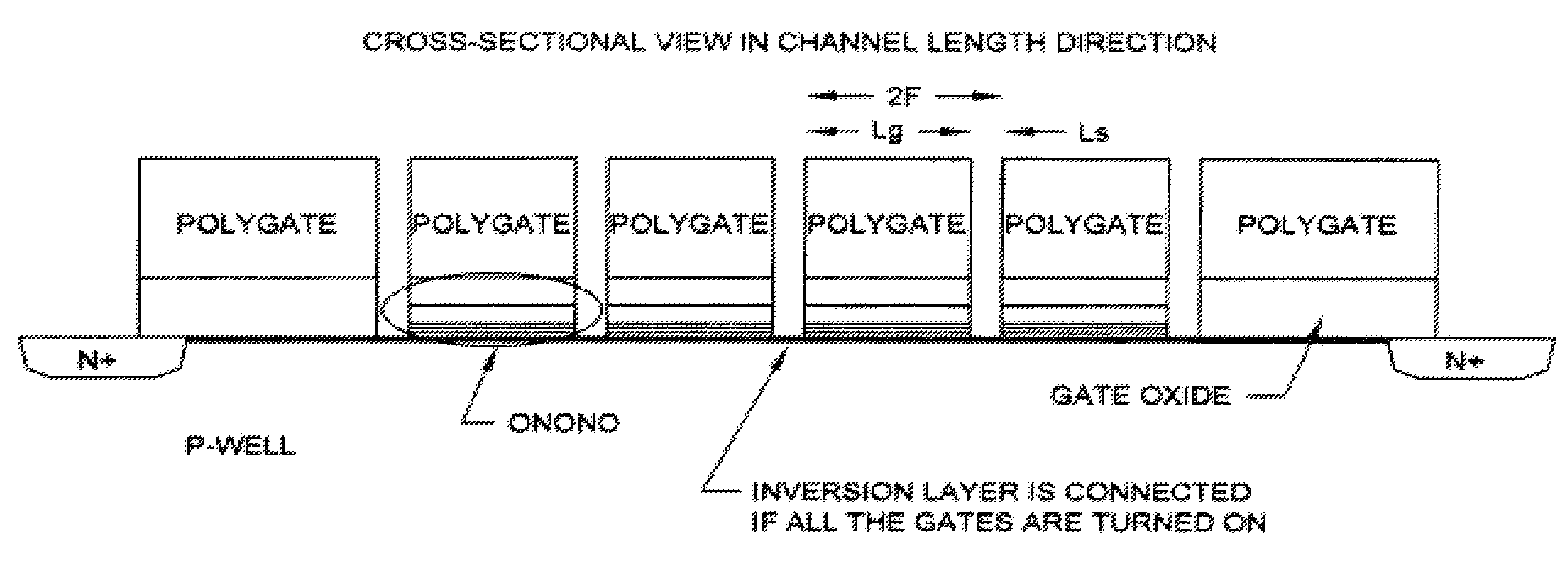
Multi-level non-volatile memory
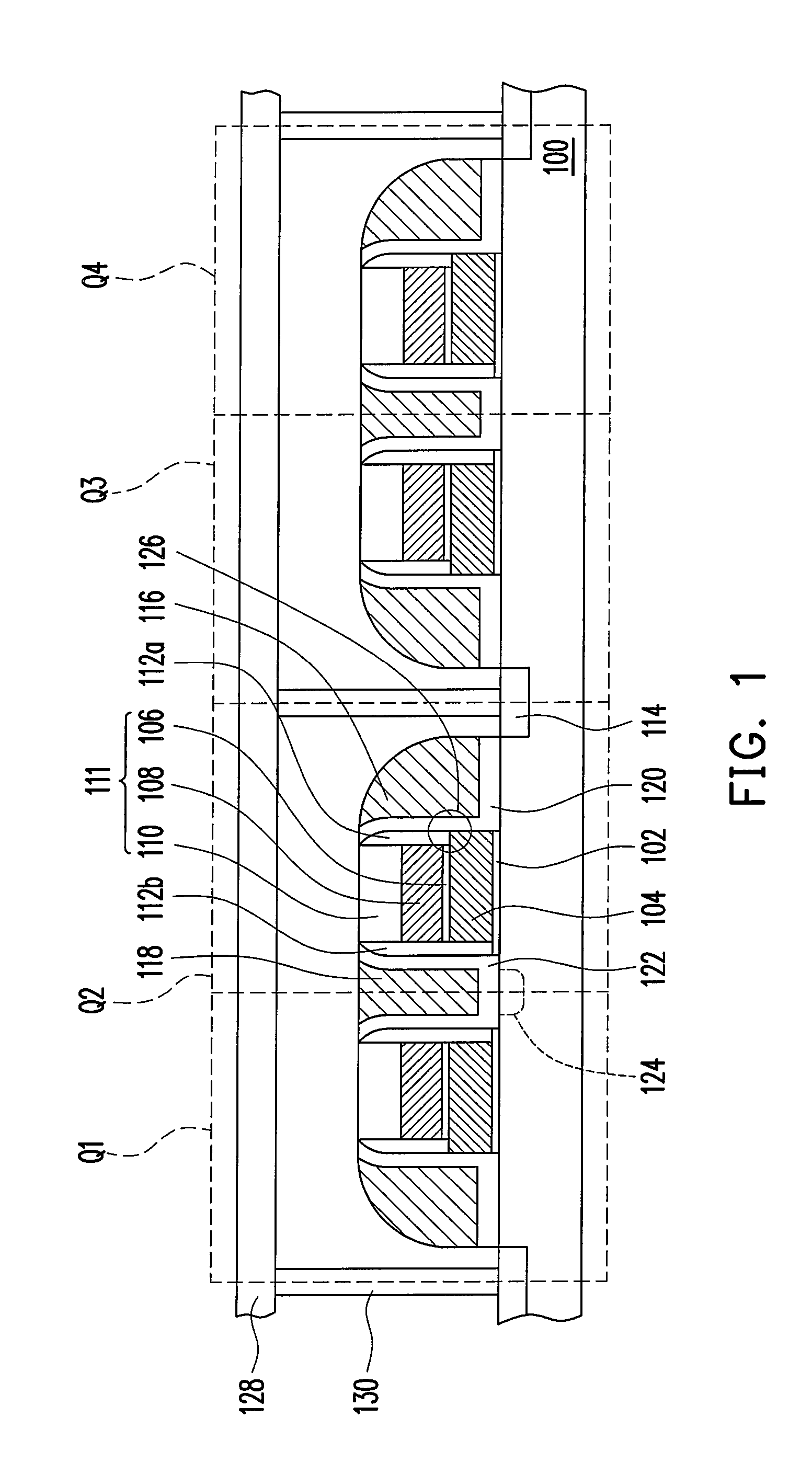
ActiveUS7518912B2Improve equipment reliabilitySimple processTransistorSolid-state devicesEngineeringNon-volatile memory
A multi-level non-volatile memory including a memory cell disposed on a substrate is provided. The memory cell includes a control gate, a charge storage layer, a doped region, a select gate, and an assist gate. The control gate is disposed on the substrate. The charge storage layer is disposed between the control gate and the substrate. The doped region is disposed in the substrate at the first side of the control gate. The select gate is disposed on the sidewall of the first side of the control gate and on the substrate between the control gate and the doped region. The assist gate is disposed on the sidewall of the second side of the control gate. An inversion layer is formed in the substrate below the assist gate when a voltage is applied to the assist gate.
Owner:POWERCHIP SEMICON MFG CORP
Split-gate memory device and forming method thereof
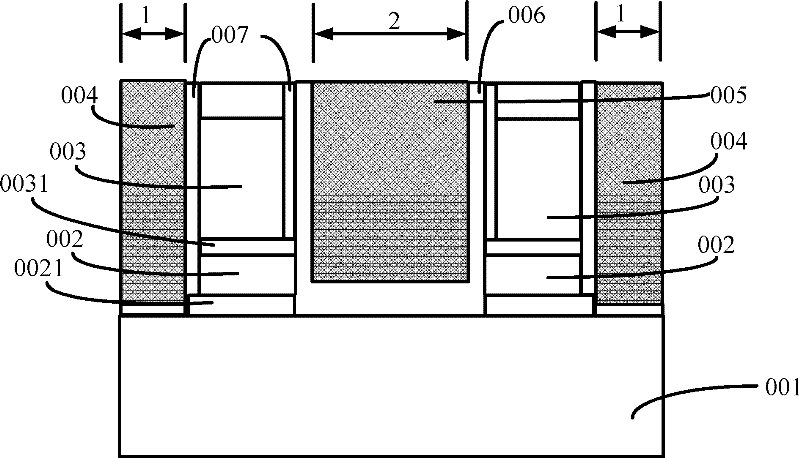
InactiveCN102543885AReduce widthIncrease erasing speedSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSilicon oxideElectrical and Electronics engineering
The invention provides a forming method of a split-gate memory device. The forming method comprises the steps of: providing a substrate; forming two control gates on the substrate, wherein a region between the two control gates is an erasing gate region, and a region outside the two control gates is a word line region; forming a side wall and a sacrifice side wall which is arranged on the side surface of the side wall; using the sacrifice side wall as a mask to form a floating gate; removing the sacrifice side wall; and forming a tunneling oxide and an erasing gate, wherein the erasing gate and the floating gate have lateral overlapped parts. The invention additionally provides the split-gate memory device. By forming the lateral protruding part of the floating gate and enabling the erasing gate and the floating gate to have the lateral overlapped parts, the overlapped parts can effectively reduce the width of the potential barrier of the tunneling oxide and can improve information erasing speed. By etching a silicon oxide layer and a silicon nitride layer in one step to form a dual-layer side wall and using the dual-layer side wall as a gap layer between word lines and the floating gate, the process of the gap layer is simplified, the uniformity of the gap layer is improved and the writing uniformity is improved.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Erasing method and device for non-volatile memory
ActiveCN101923900AShorten the timeIncrease erasing speedRead-only memoriesNon-volatile memoryMemory block
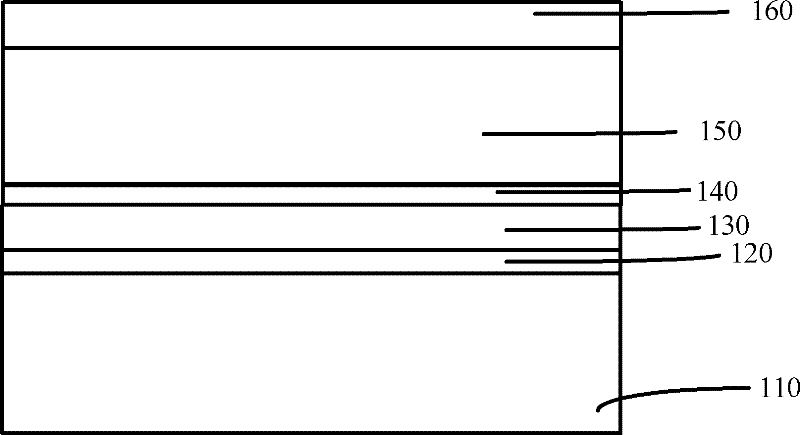
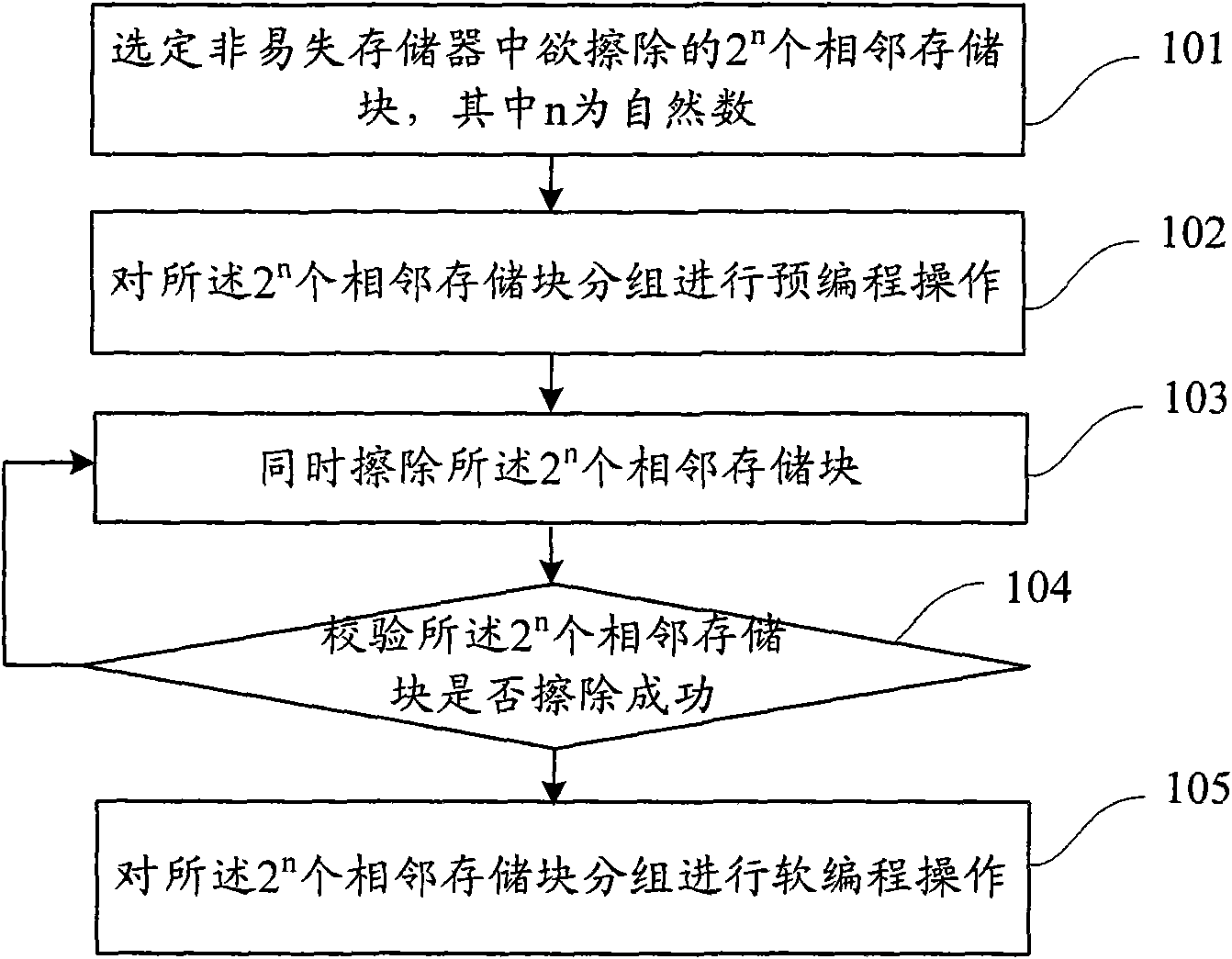
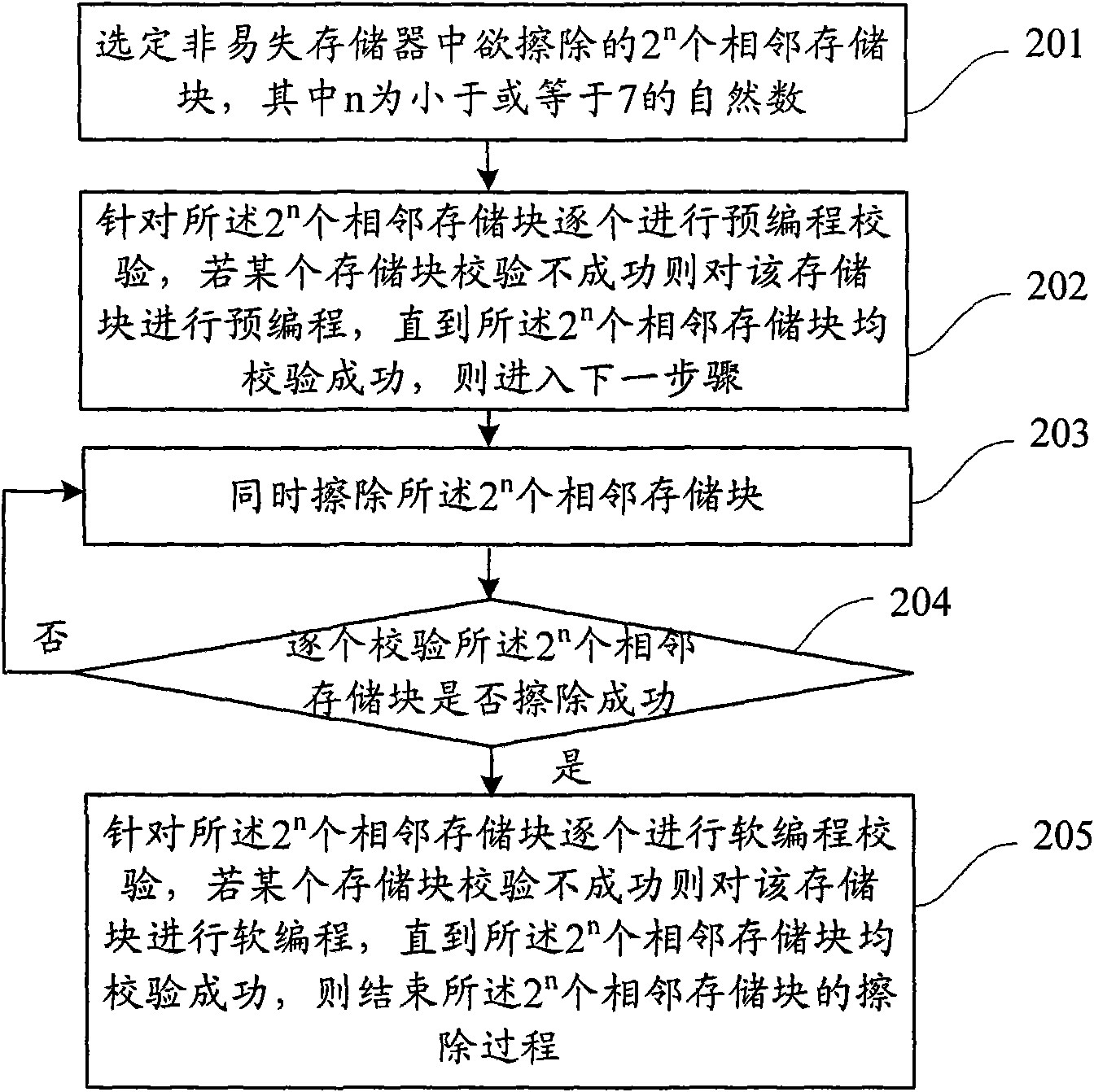
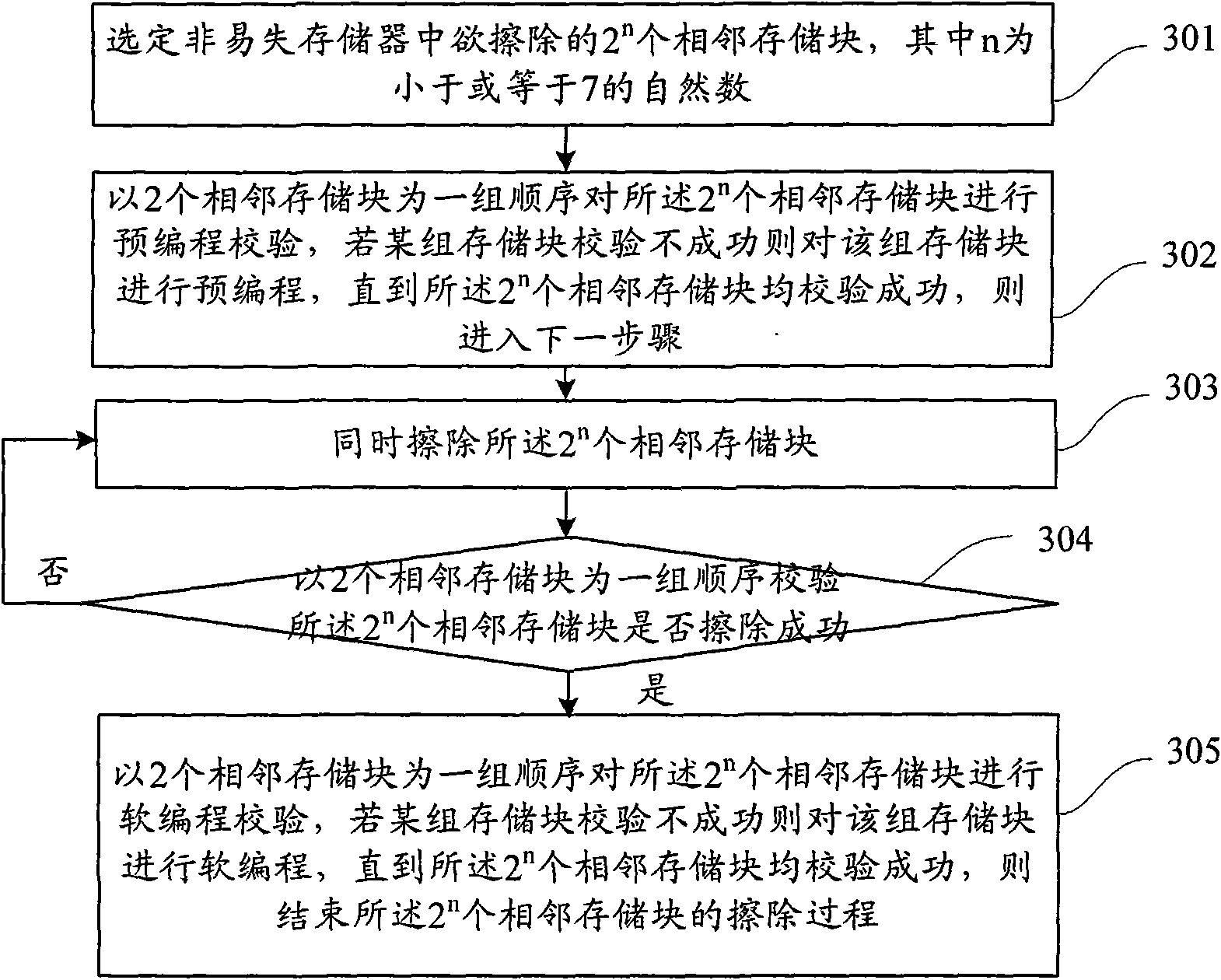
The invention discloses an erasing method for a non-volatile memory. The method comprises the following steps of: selecting a target, namely, selecting 2n to-be-erased adjacent memory blocks in the non-volatile memory, wherein n is a natural number; performing pre-programming operation, namely, pre-programming the 2n adjacent memory blocks in groups; erasing, namely, simultaneously erasing the 2n adjacent memory blocks; checking the erasing, namely, checking whether the 2n adjacent memory blocks are successfully erased in groups, if so, performing soft programming operation, and otherwise, returning to the erasing step; and performing the soft programming operation, namely, performing the soft programming operation on the adjacent memory blocks in groups. The method can save erasing time and improve erasing speed and erasing efficiency.
Owner:GIGADEVICE SEMICON (BEIJING) INC
Drawn line erasing method and drawn line erasing device
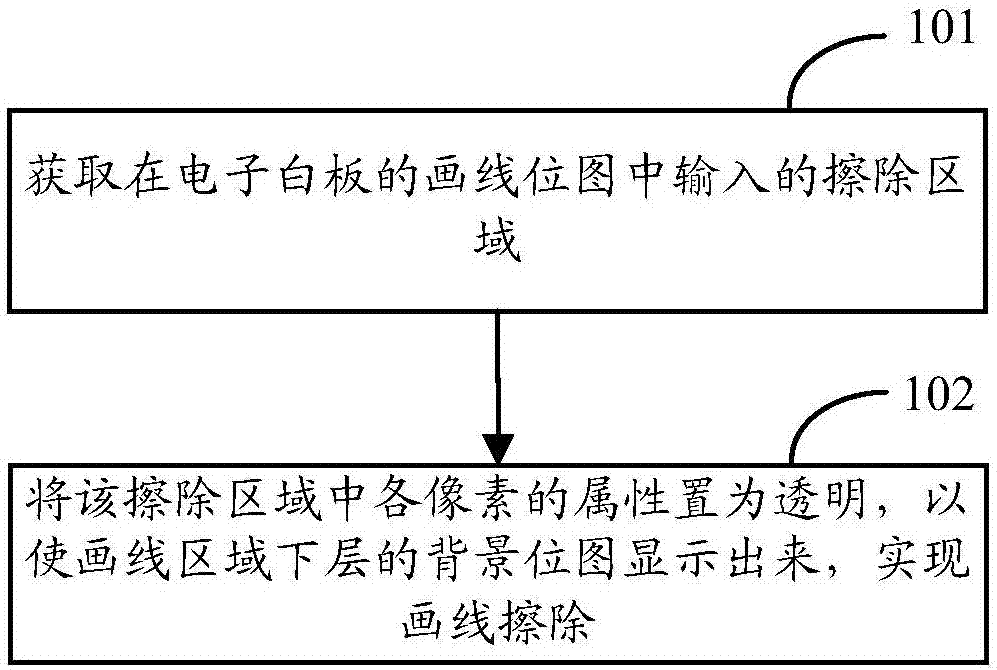
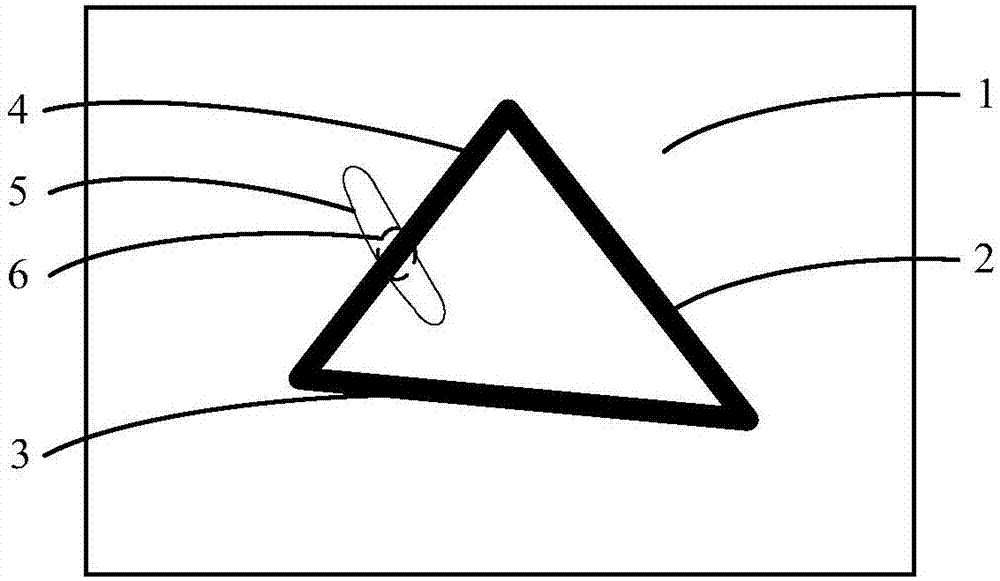
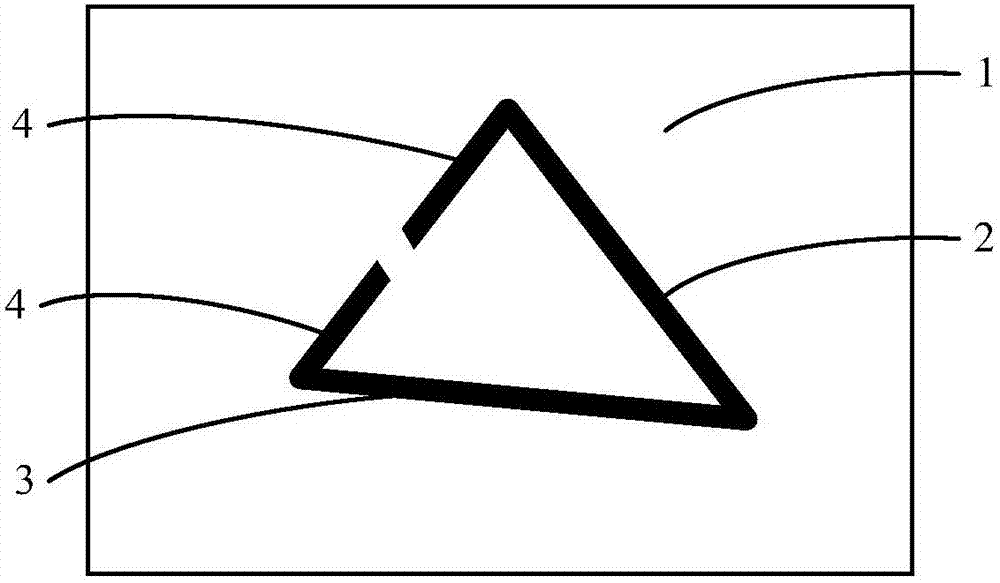
InactiveCN106910232AIncrease erasing speedImprove user experienceModifying/creating image using manual inputWhiteboardComputer science
The application provides a drawn line erasing method and a drawn line erasing device. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring an erasing area input to a drawn line bitmap of an electronic whiteboard; and setting the attribute of the pixels in the erasing area as transparent to display a background bitmap under the drawn line area, thus erasing drawn lines. According to the application, interface display of the electronic whiteboard is realized through superposed display of the drawn line bitmap and the background bitmap. For erasing, the attribute of the pixels in the erasing area of the electronic whiteboard is directly set as transparent so that the background bitmap under the drawn line area is displayed. There is no need to calculate an intersection area of the erasing area and the drawn line area and modify the pixels in the intersection area in order to update the display interface. An intersection area calculation process is omitted. The erasing speed of drawn lines is increased. The user experience is enhanced.
Owner:HISENSE VISUAL TECH CO LTD
Non-volatile memory device and method of manufacturing the same
ActiveUS20150099338A1Increase erasing speedSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesMemory cellMechanical engineering
A non-volatile memory device includes first and second vertical channel layers generally protruding upwardly from a semiconductor substrate substantially in parallel; a first gate group configured to include a plurality of memory cell gates which are stacked substantially along the first vertical channel layer and are isolated from each other with an interlayer insulating layer interposed substantially between the memory cell gates; a second gate group configured to include a plurality of memory cell gates which are stacked substantially along the second vertical channel layer and are isolated from each other with the interlayer insulating layer interposed substantially between the memory cell gates; a pipe channel layer configured to couple the first and the second vertical channel layers; and a channel layer extension part generally extended from the pipe channel layer to the semiconductor substrate and configured to couple the pipe channel layer and the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:MIMIRIP LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com