Patents
Literature
49 results about "NvSRAM" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
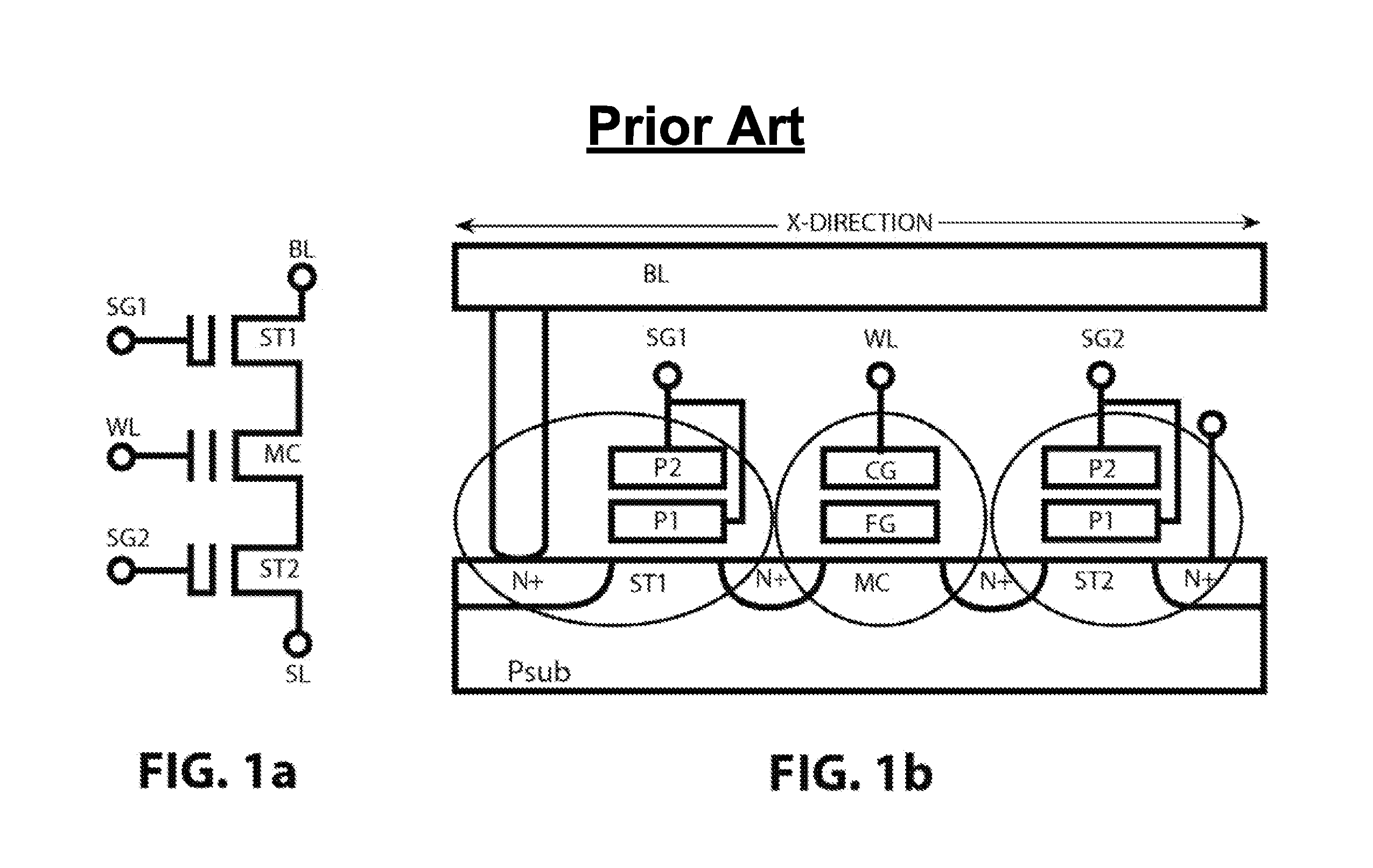
NvSRAM is a type of non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM). It is similar in operation to static random-access memory (SRAM). nvSRAM is one of the advanced NVRAM technologies that is fast replacing the BBSRAMs; battery-backed static random-access memory, especially for applications that need battery free solutions and long term retention at SRAM speeds. nvSRAMs are used in a wide range of situations—networking, aerospace, and medical, among many others —where the preservation of data is critical and where batteries are impractical.
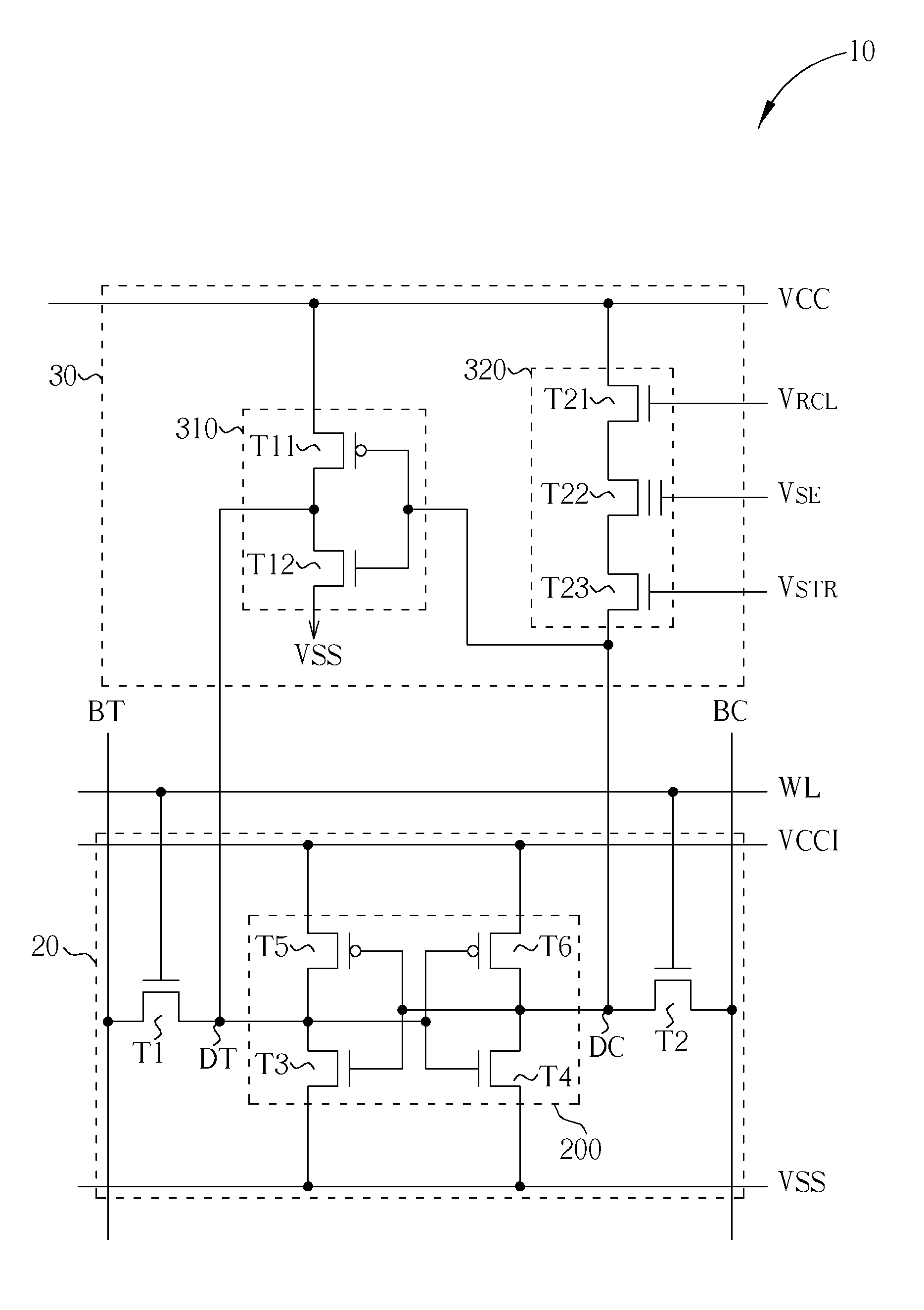
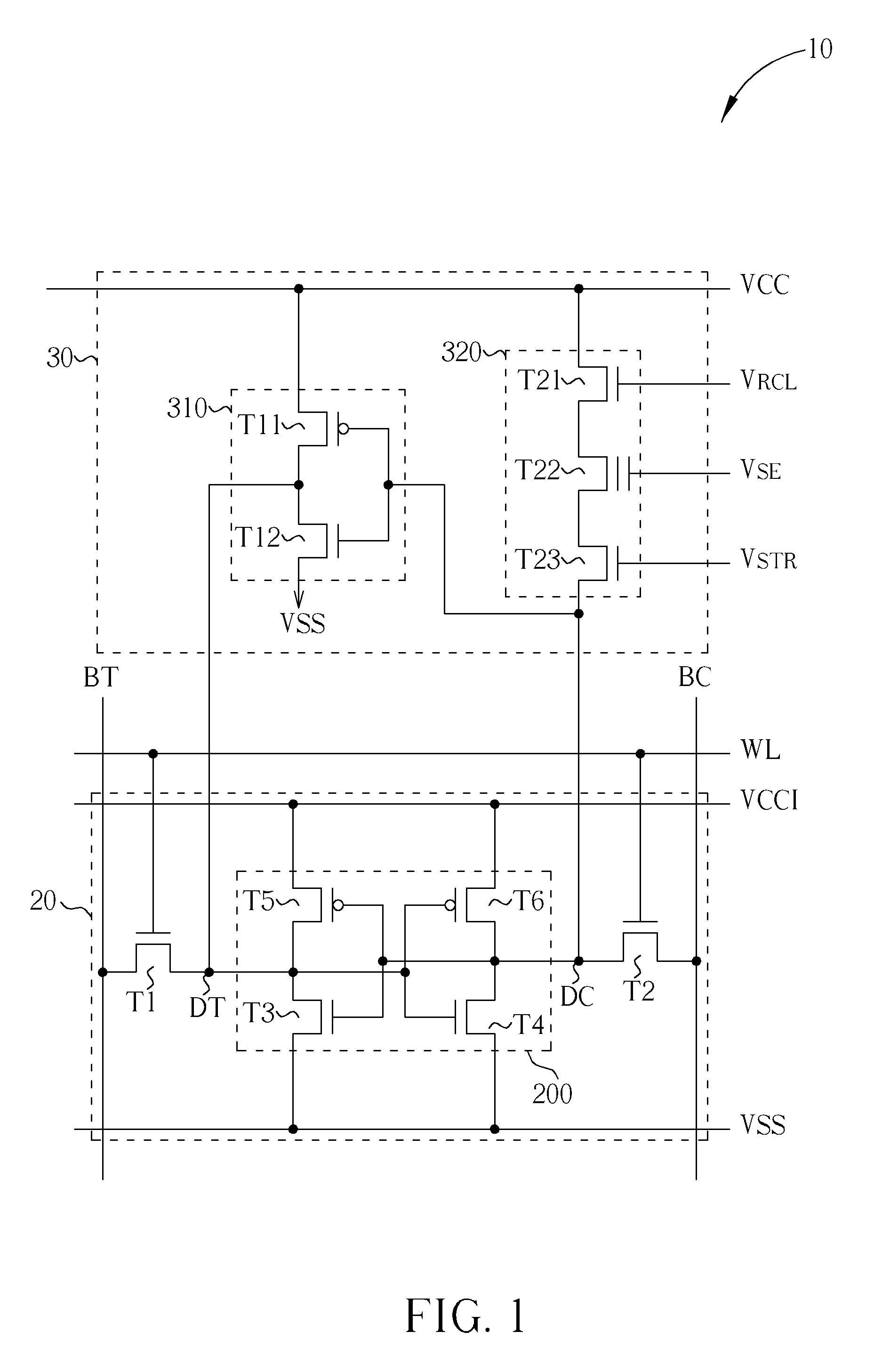
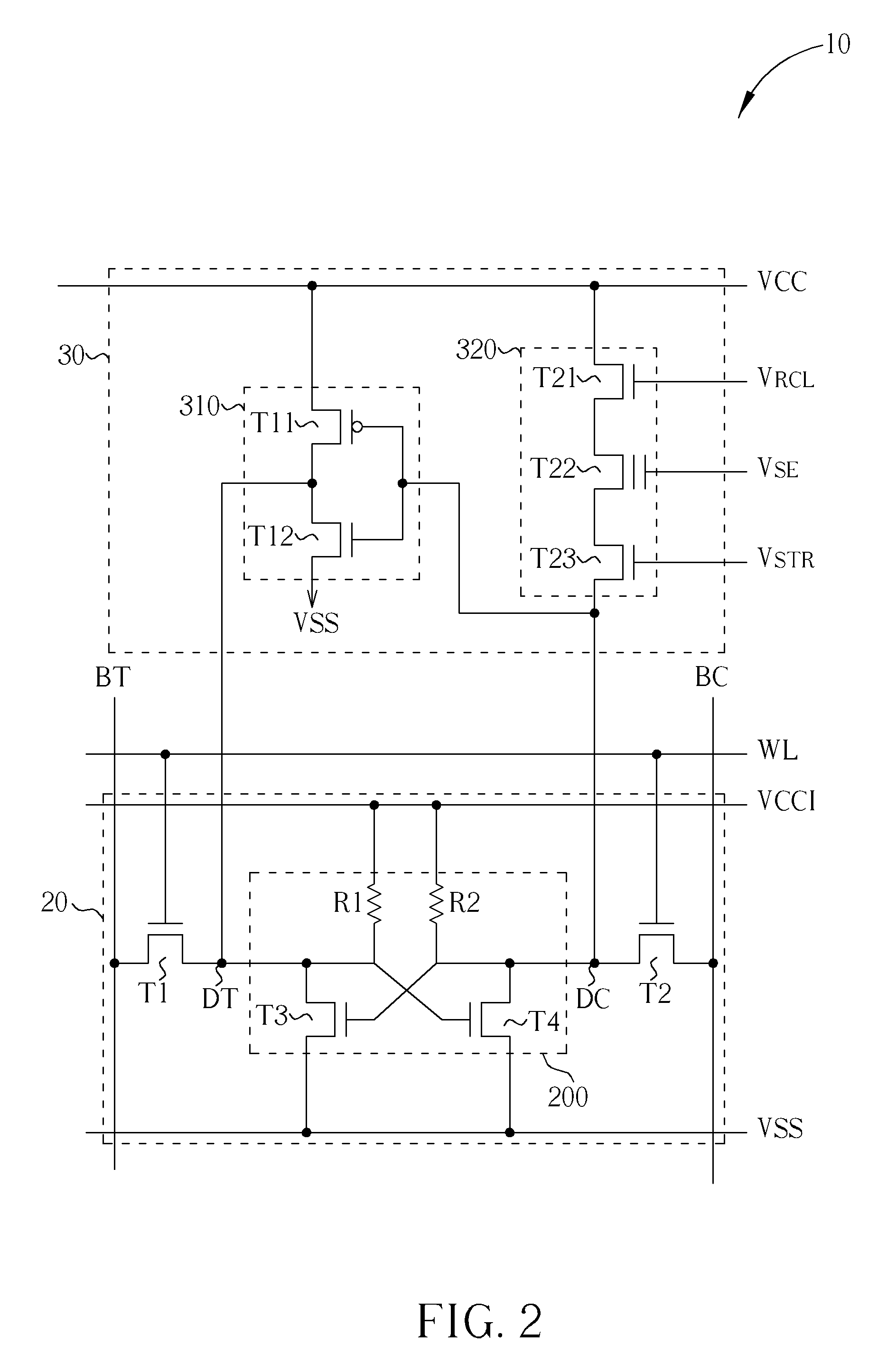
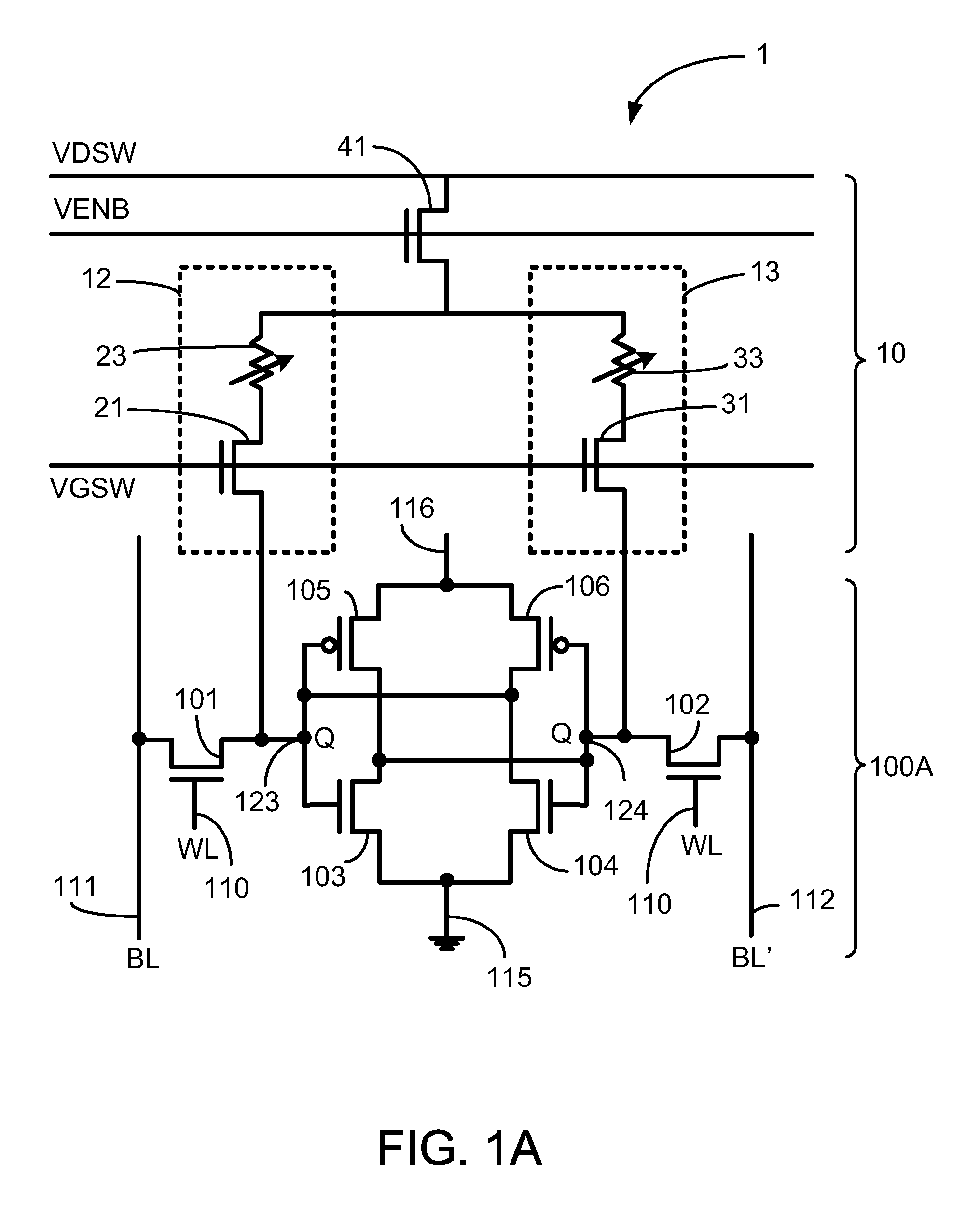
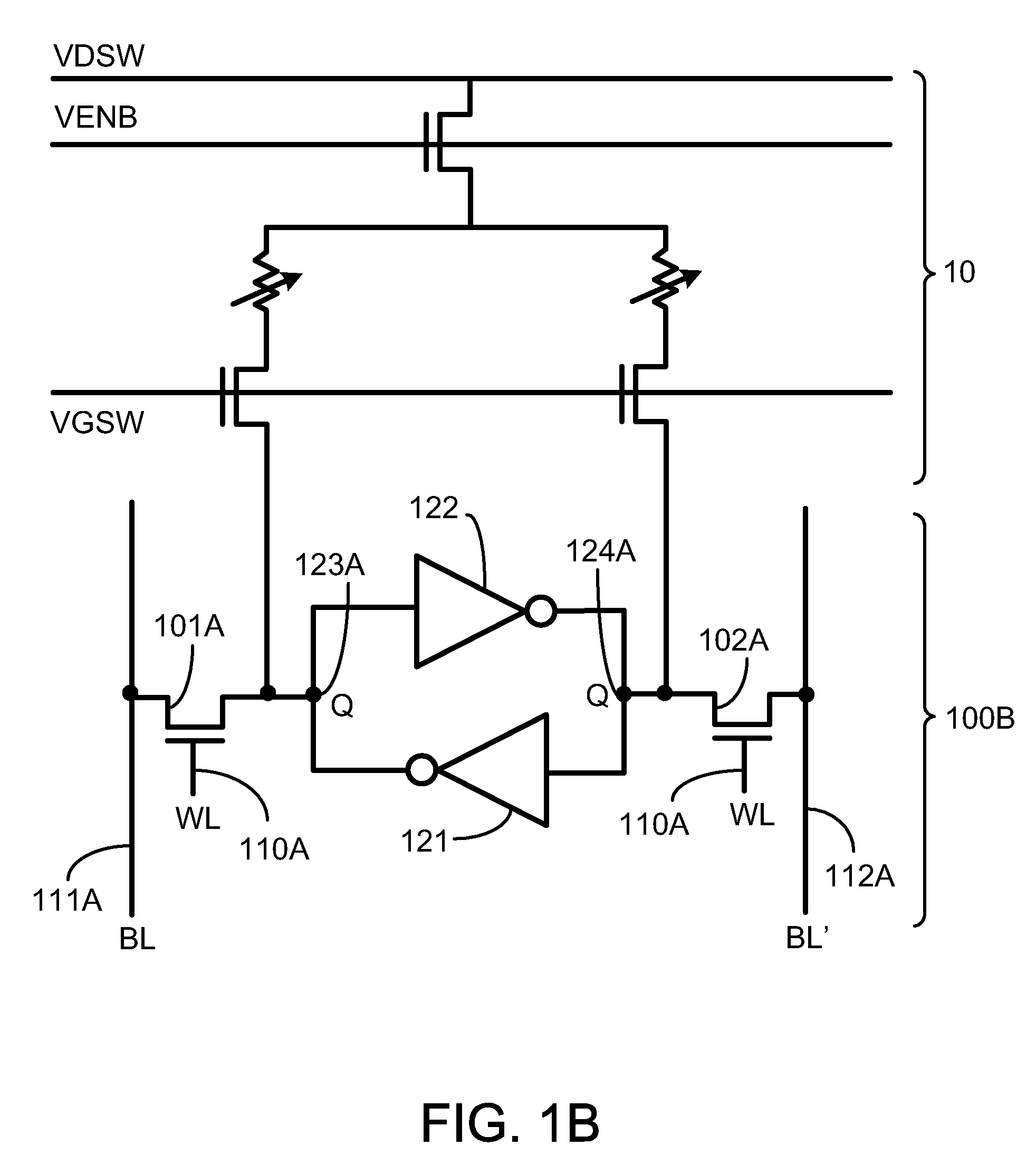
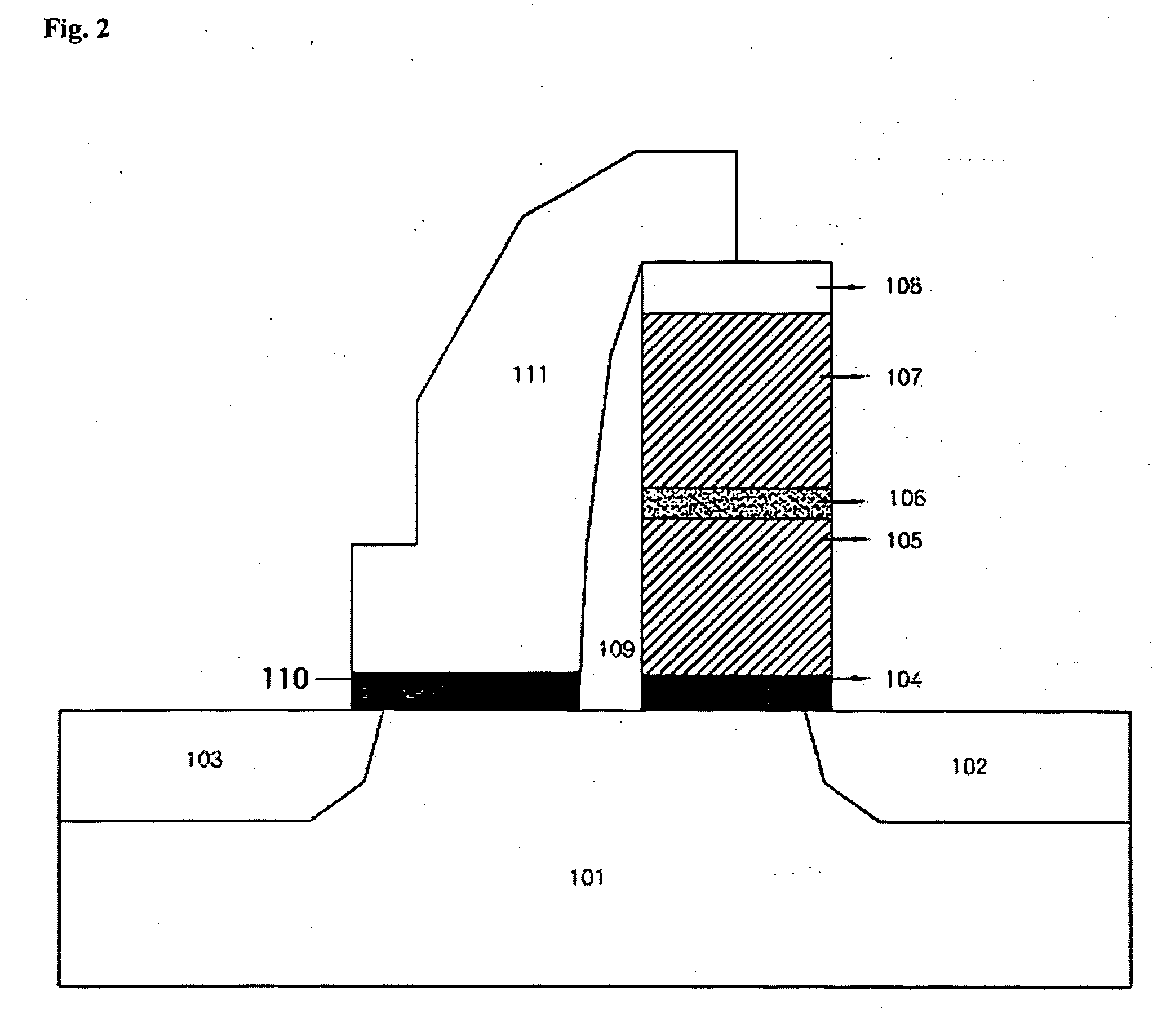
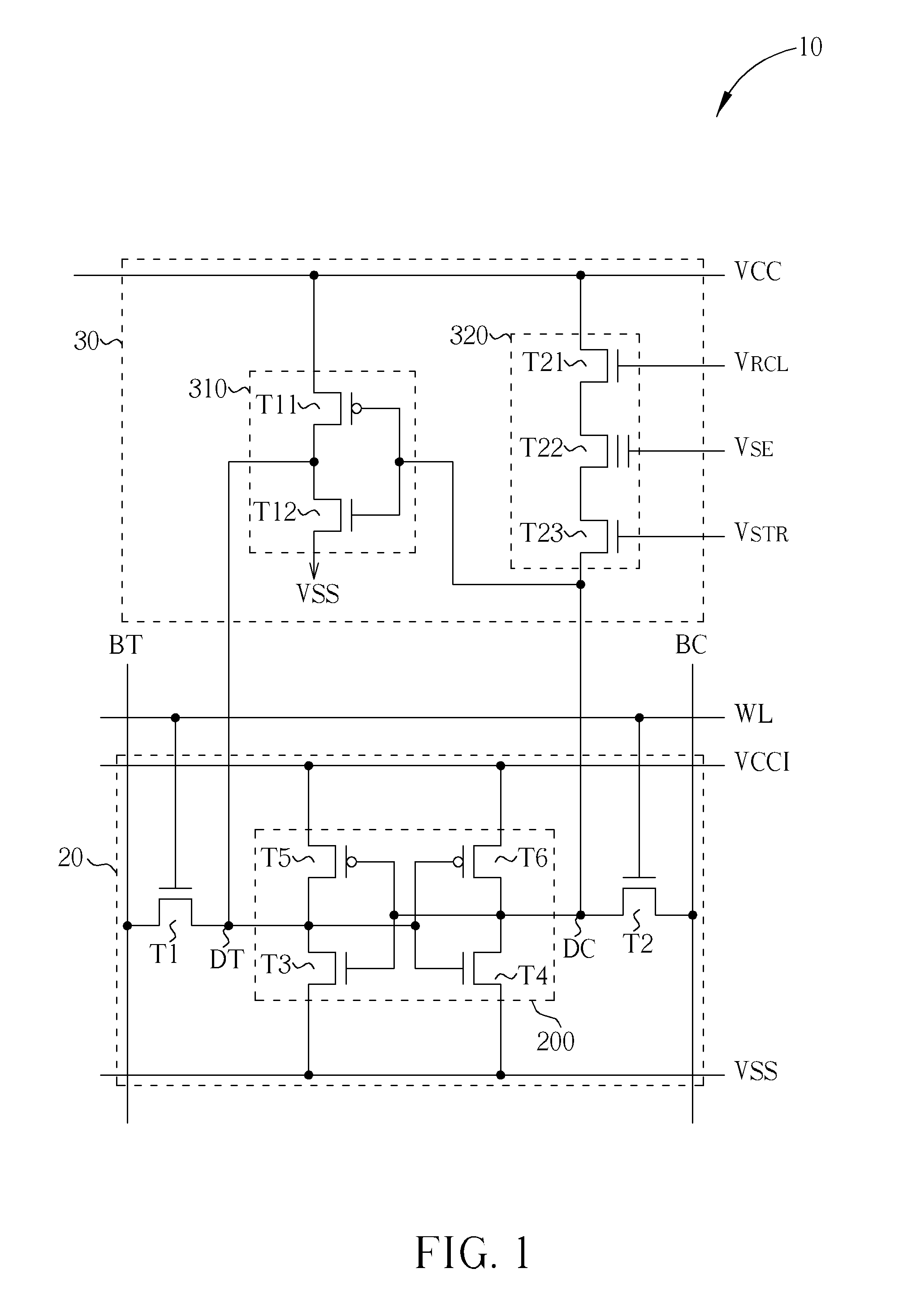
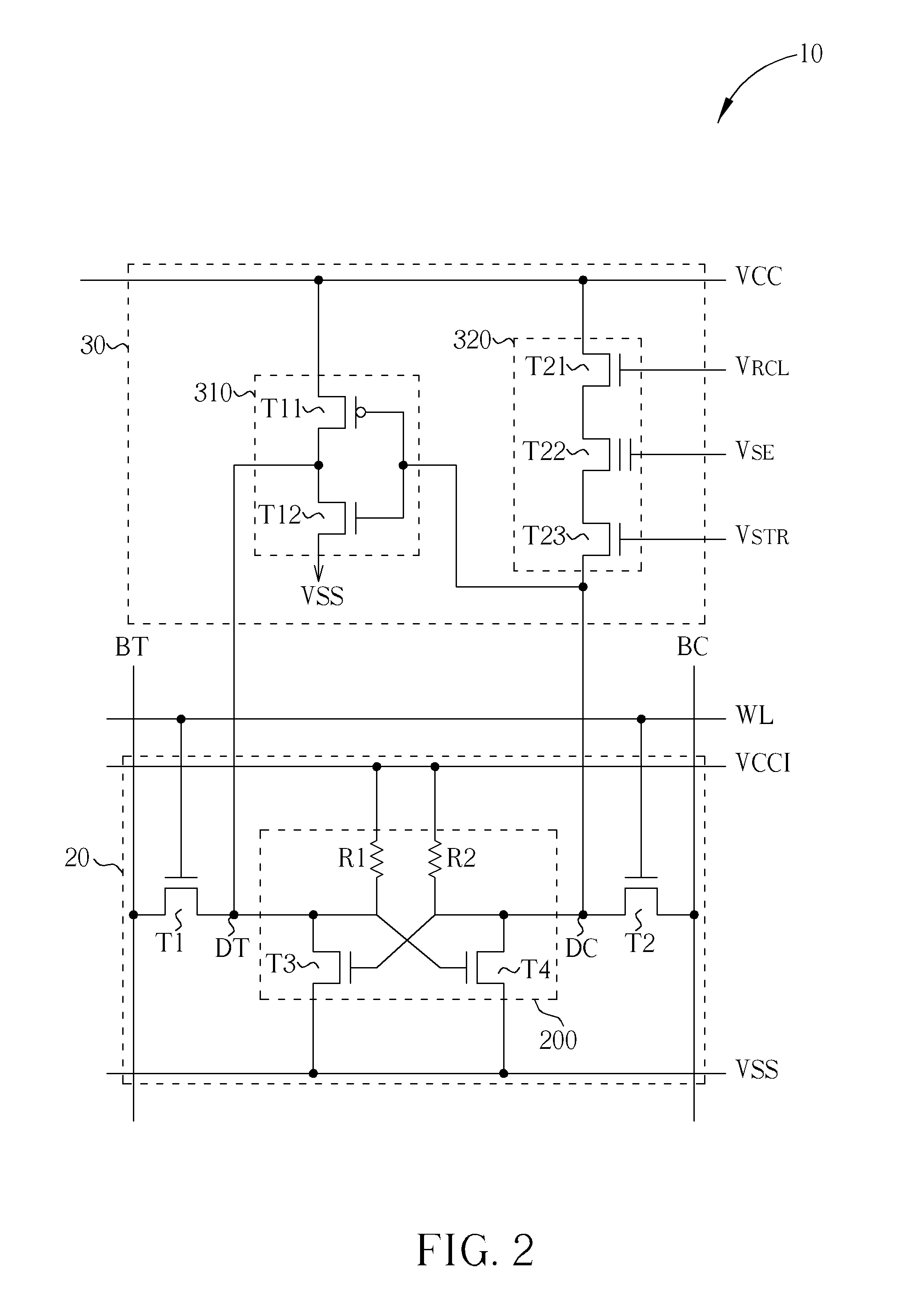
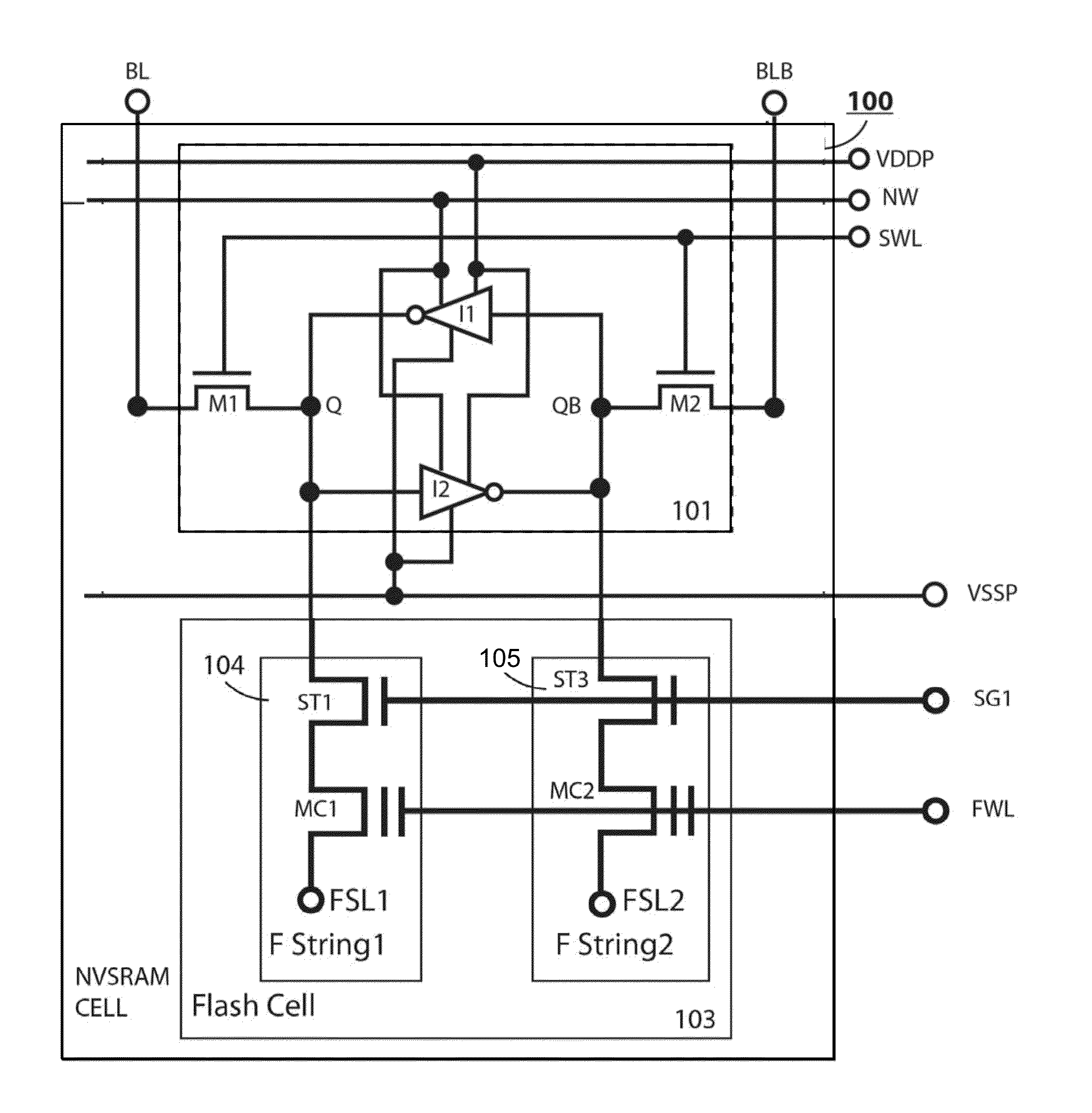
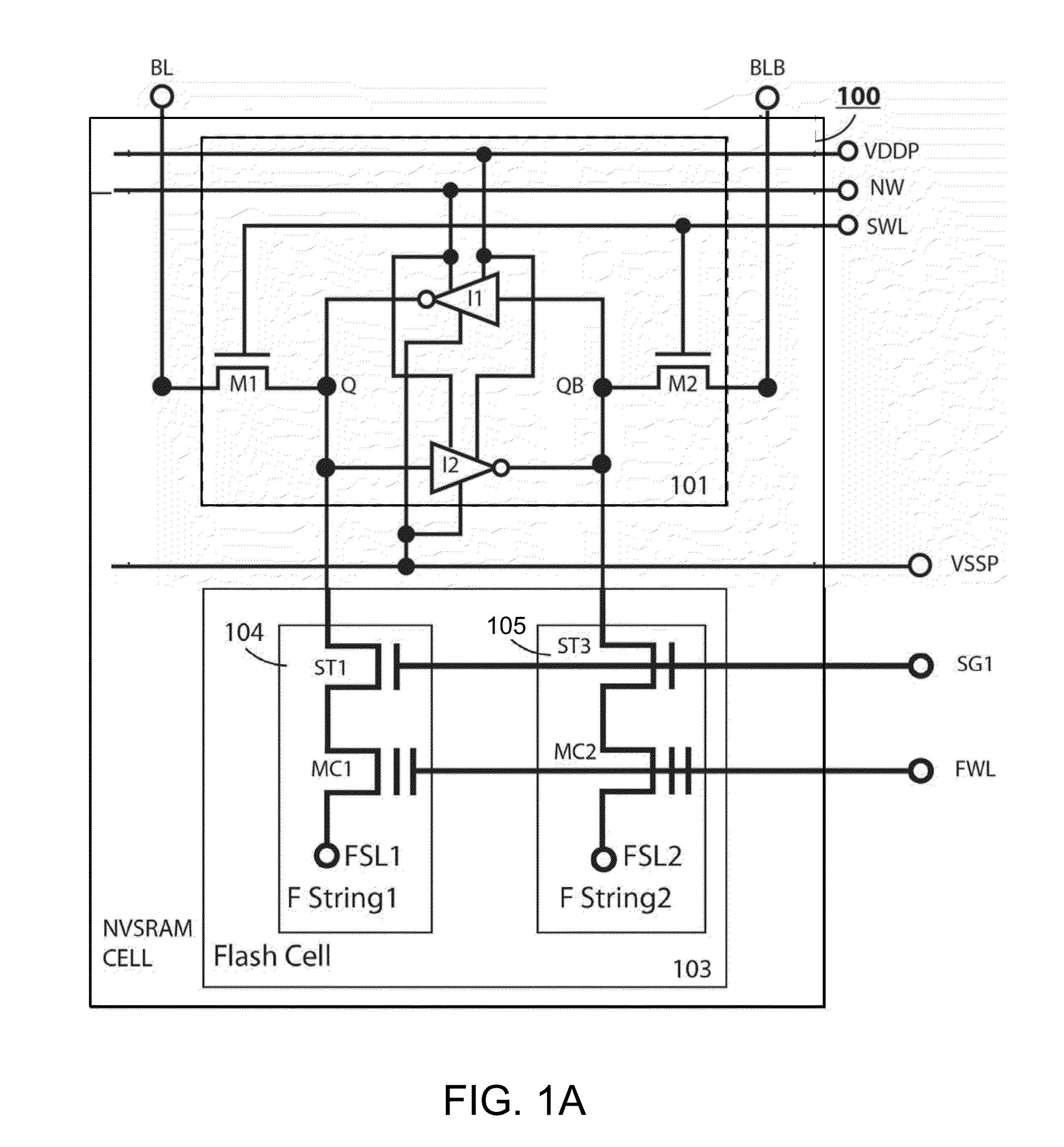
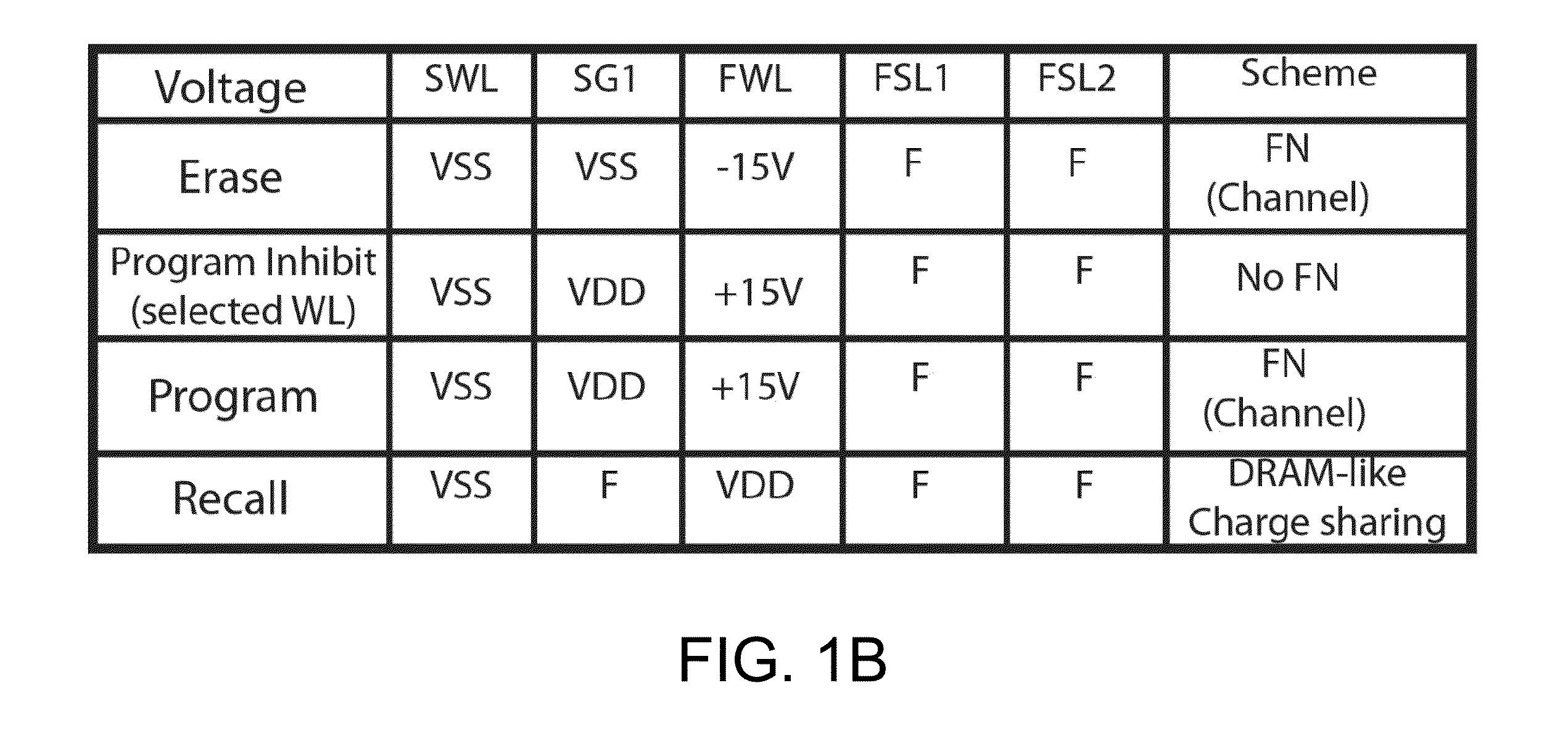
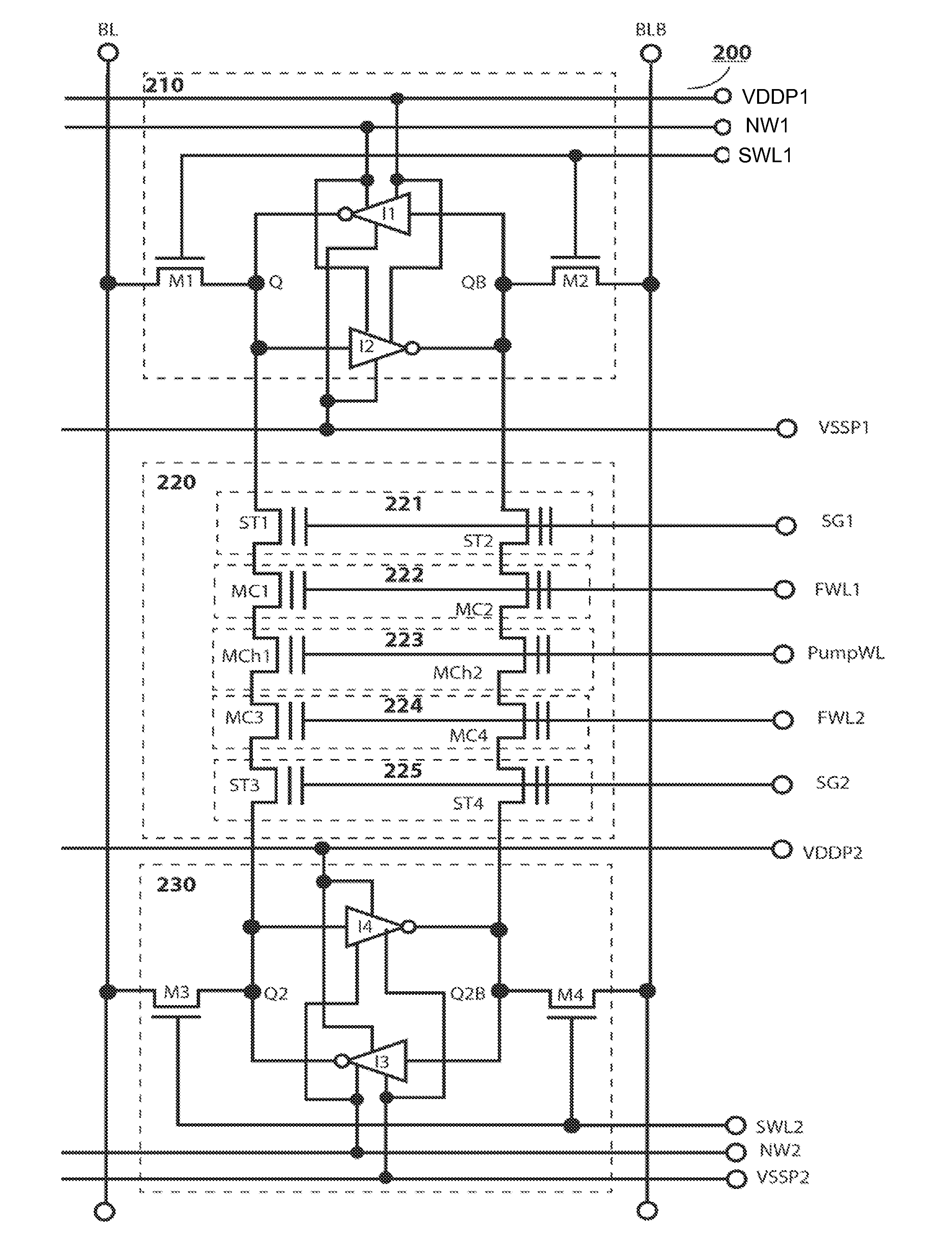
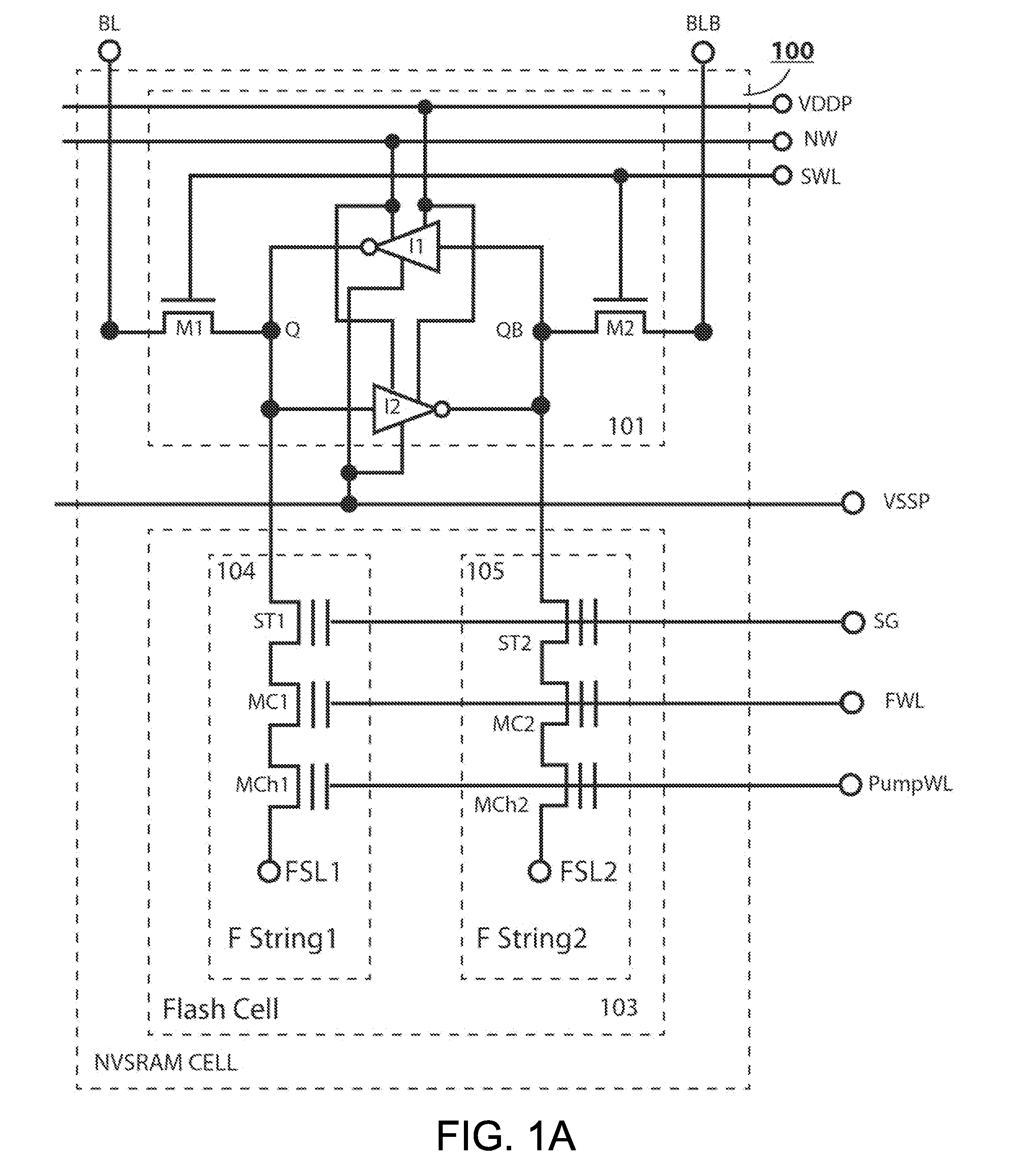
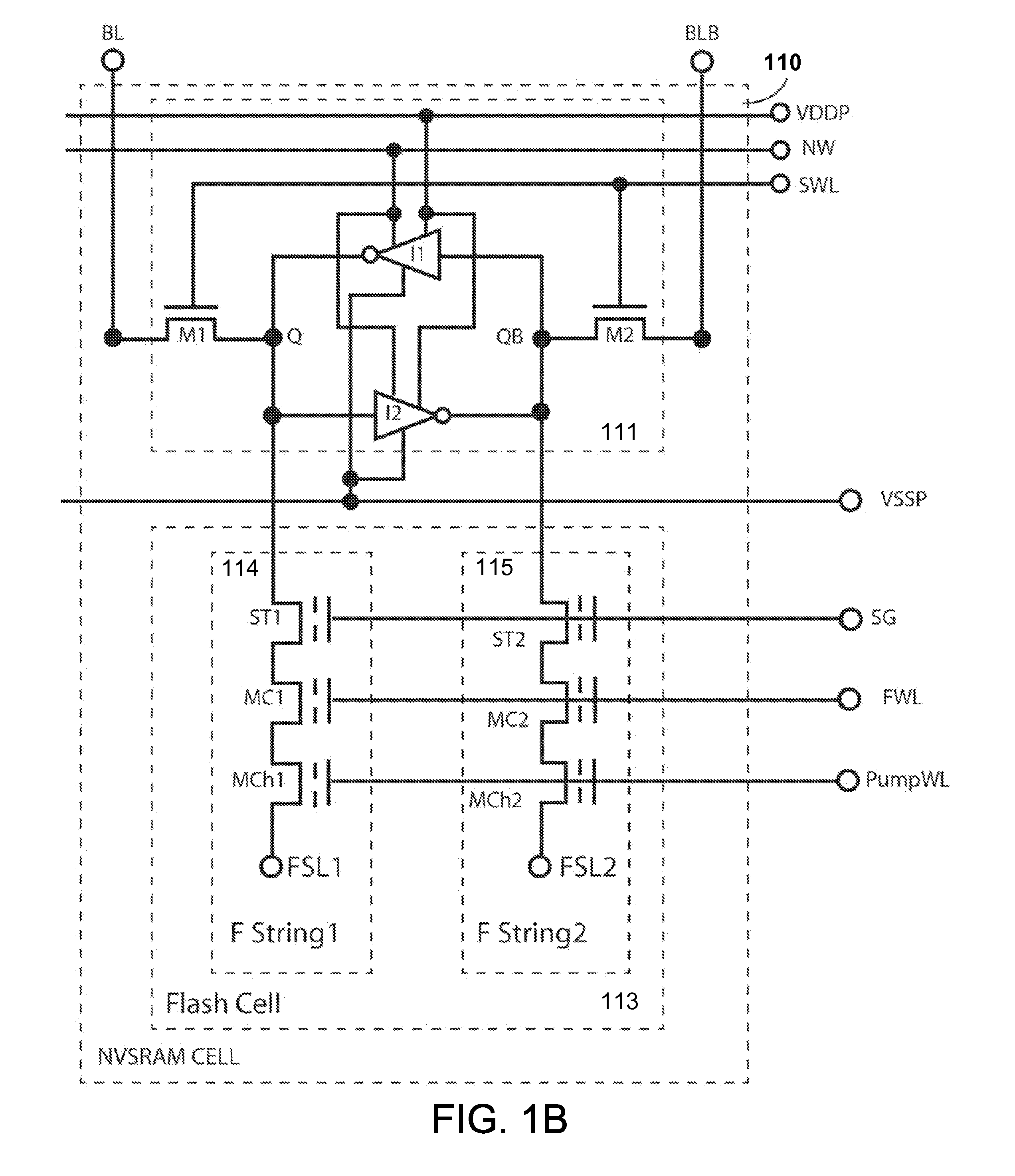
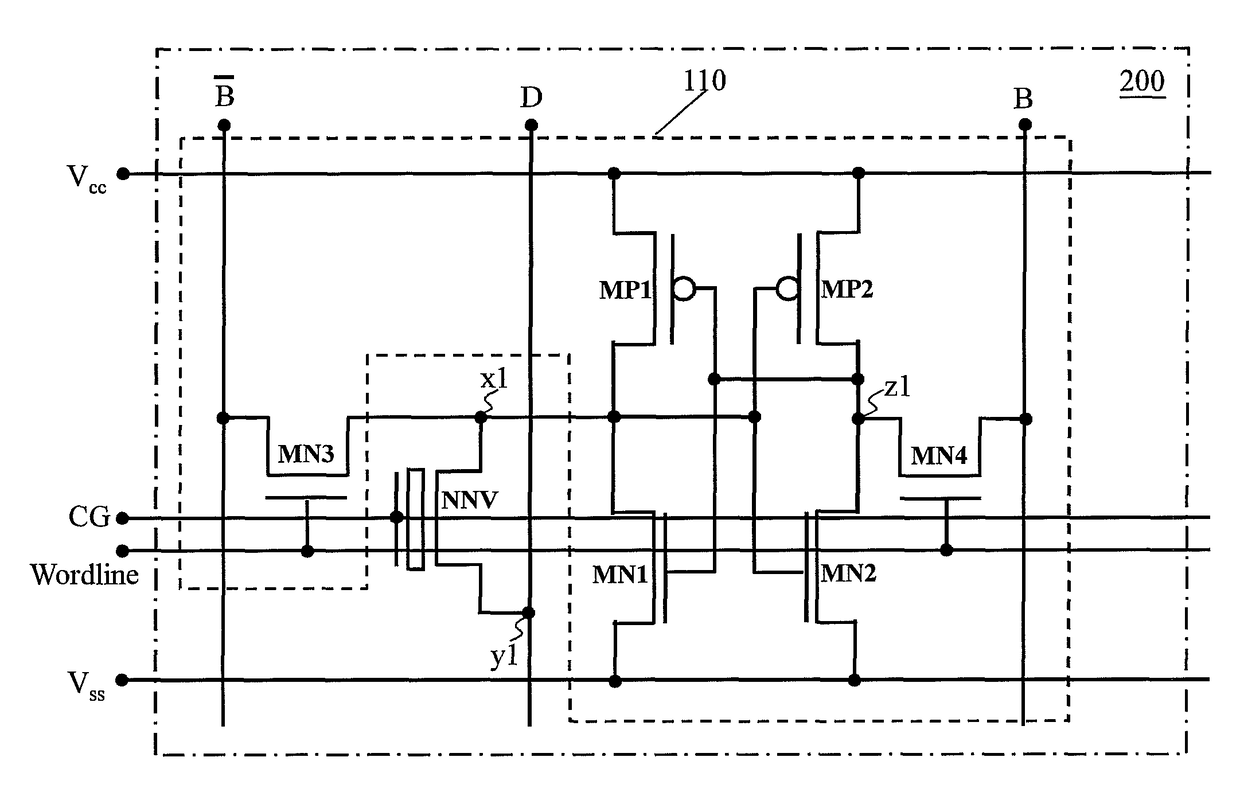
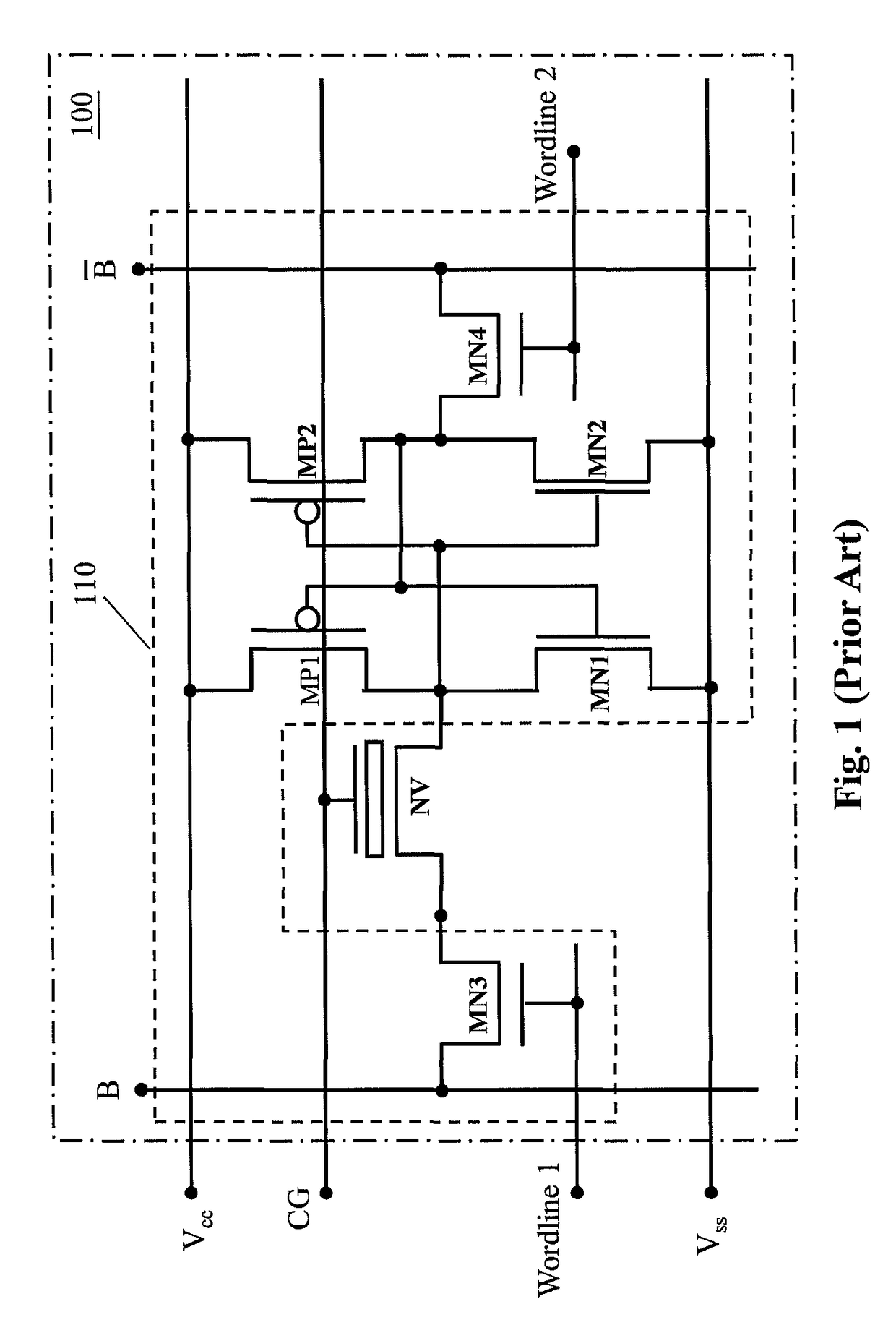
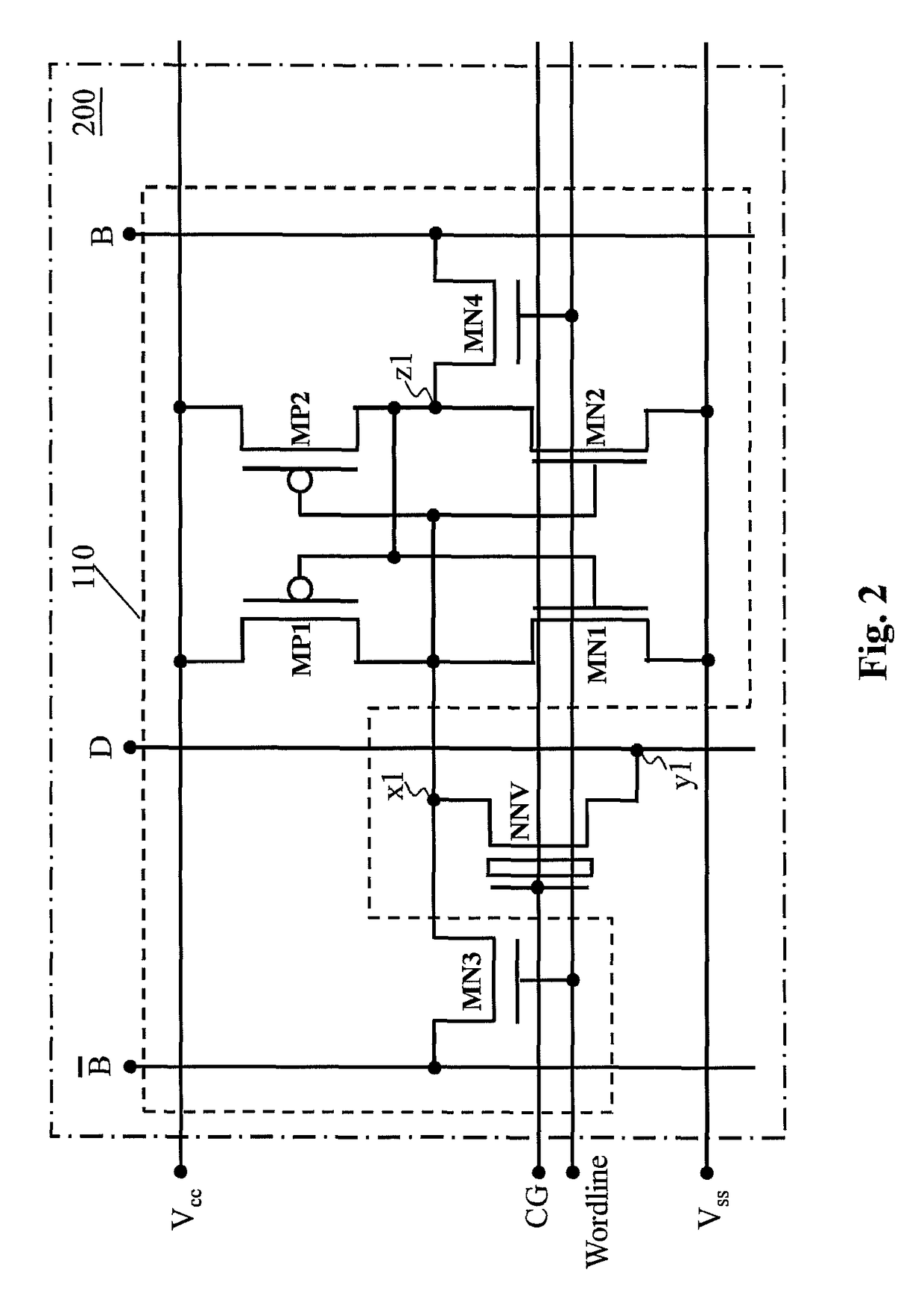
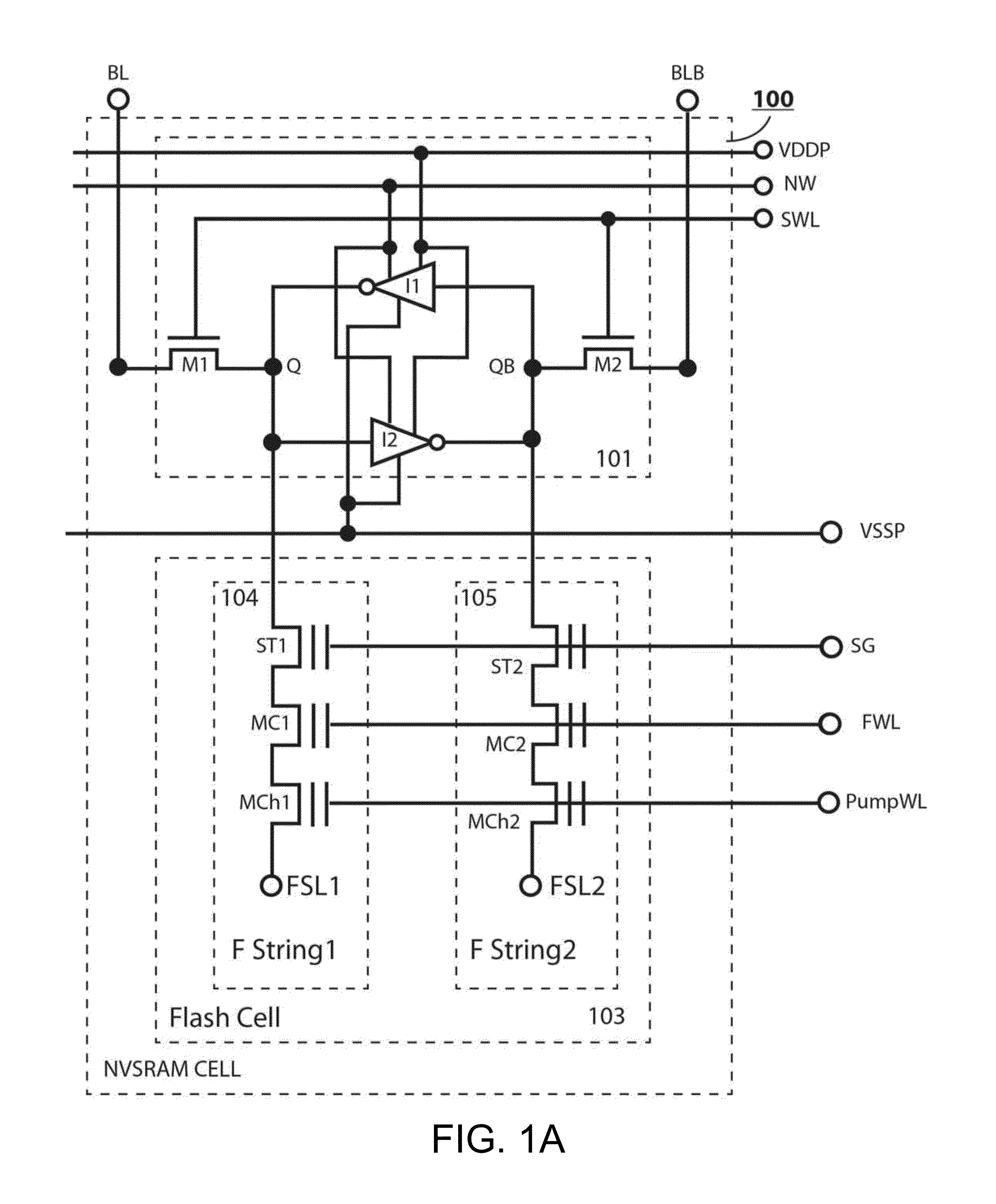
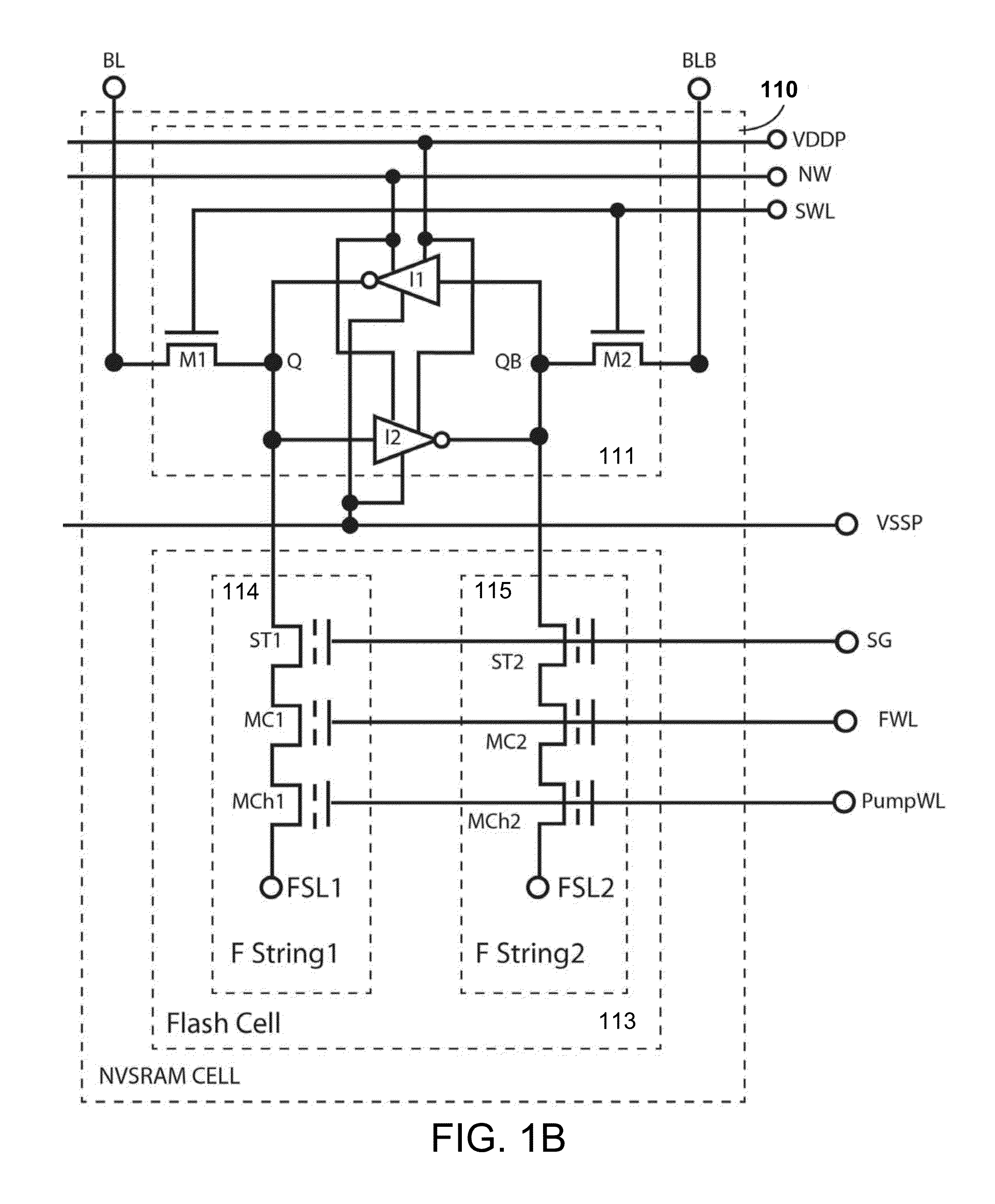
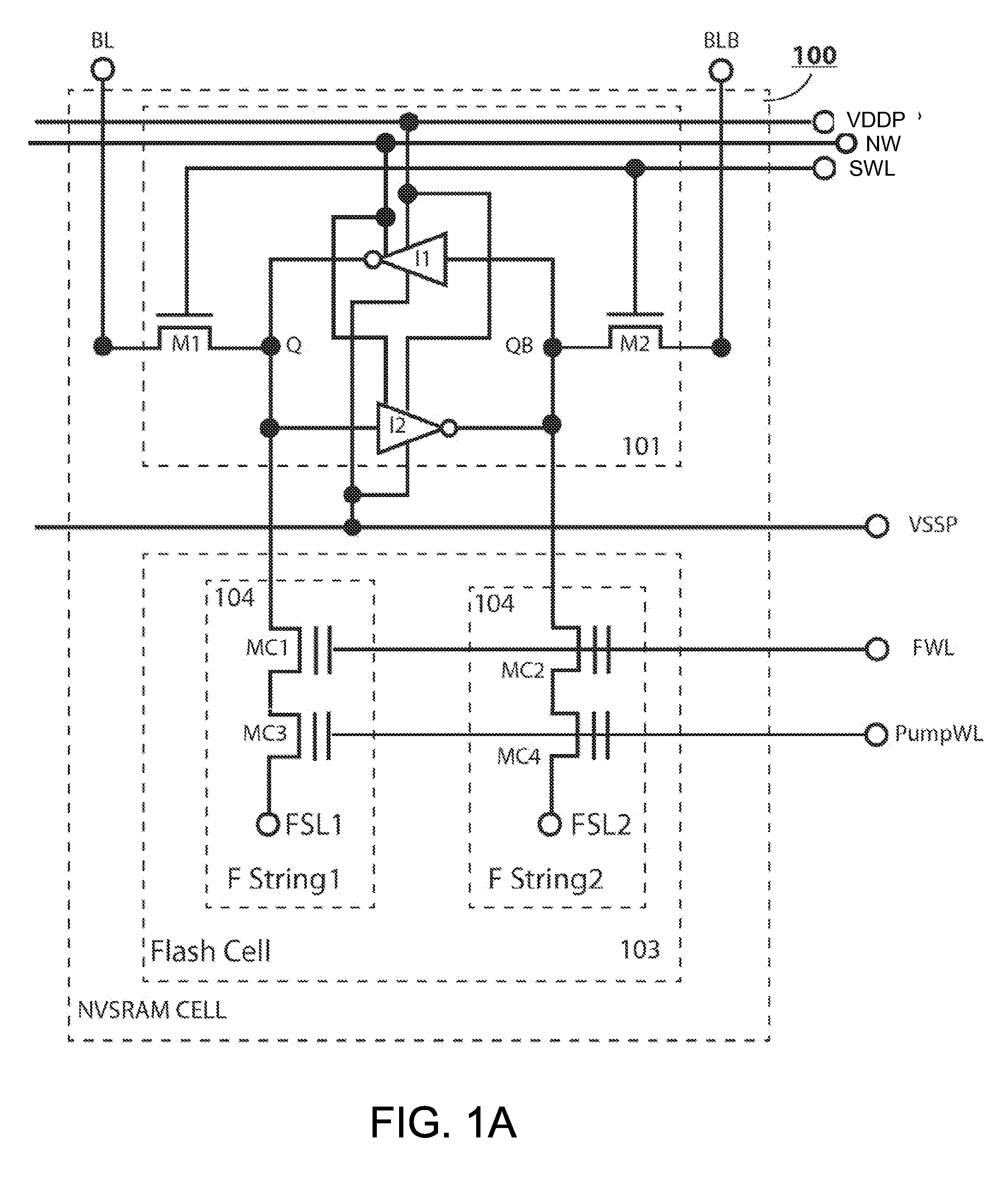
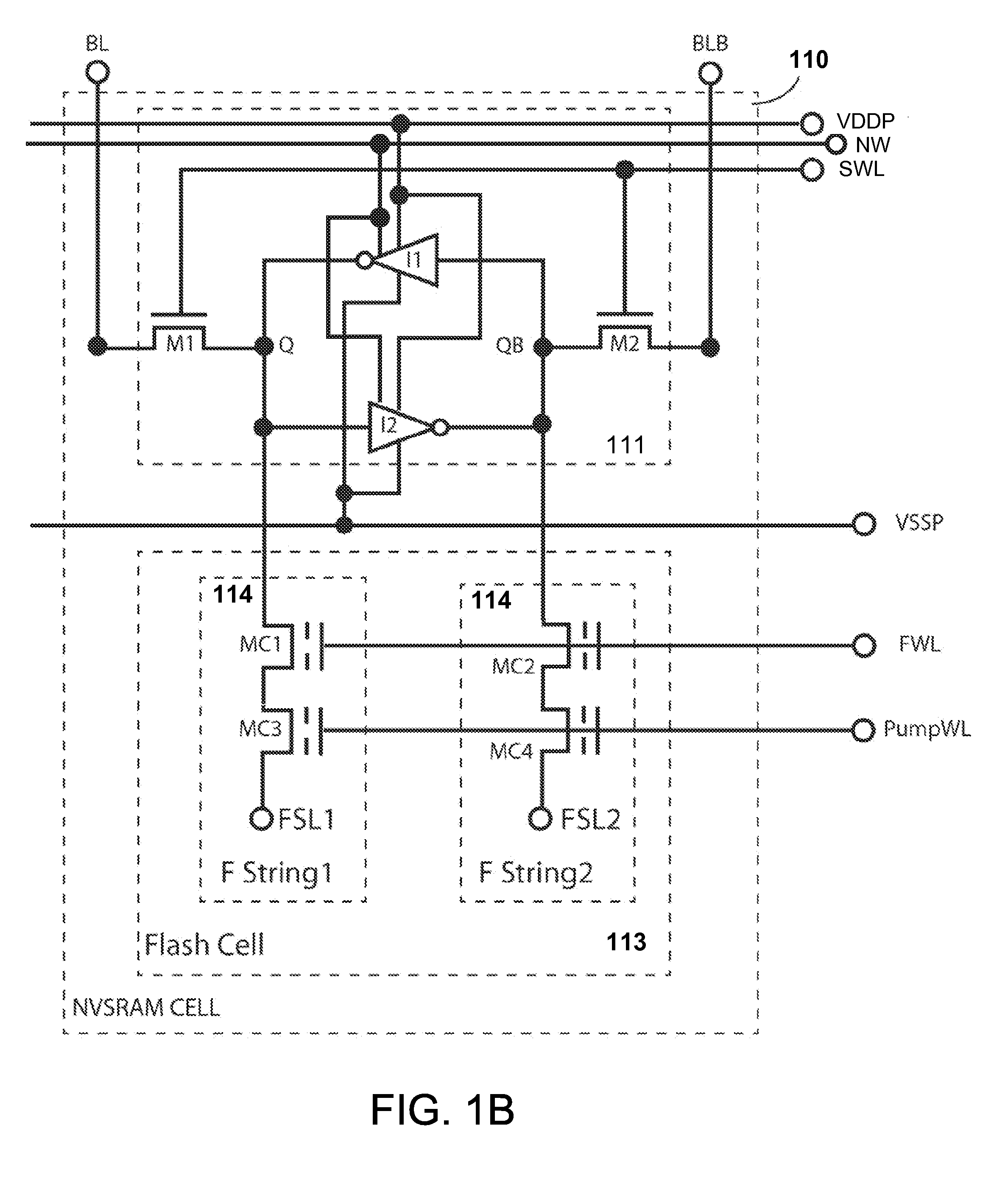
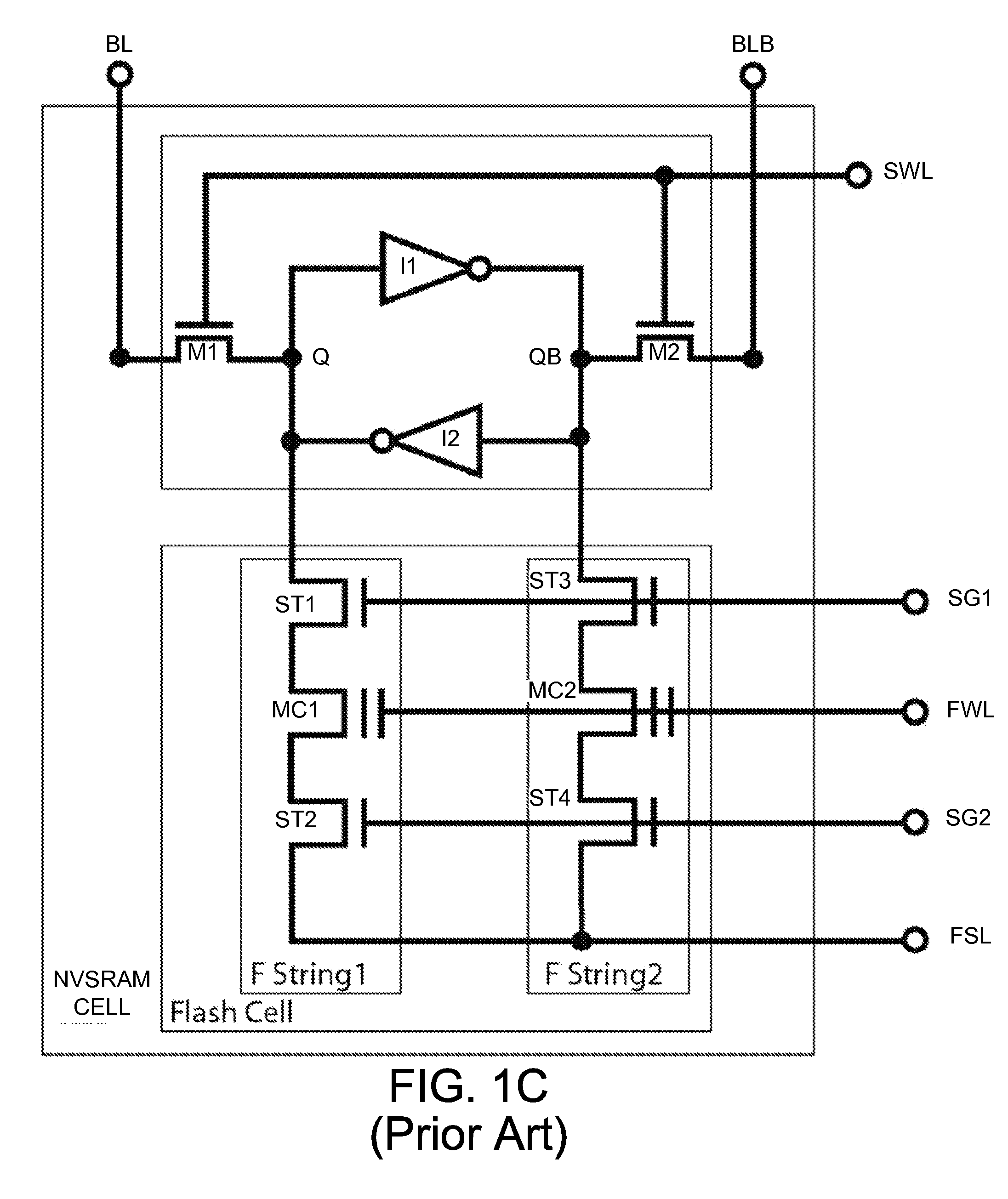
Non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) device
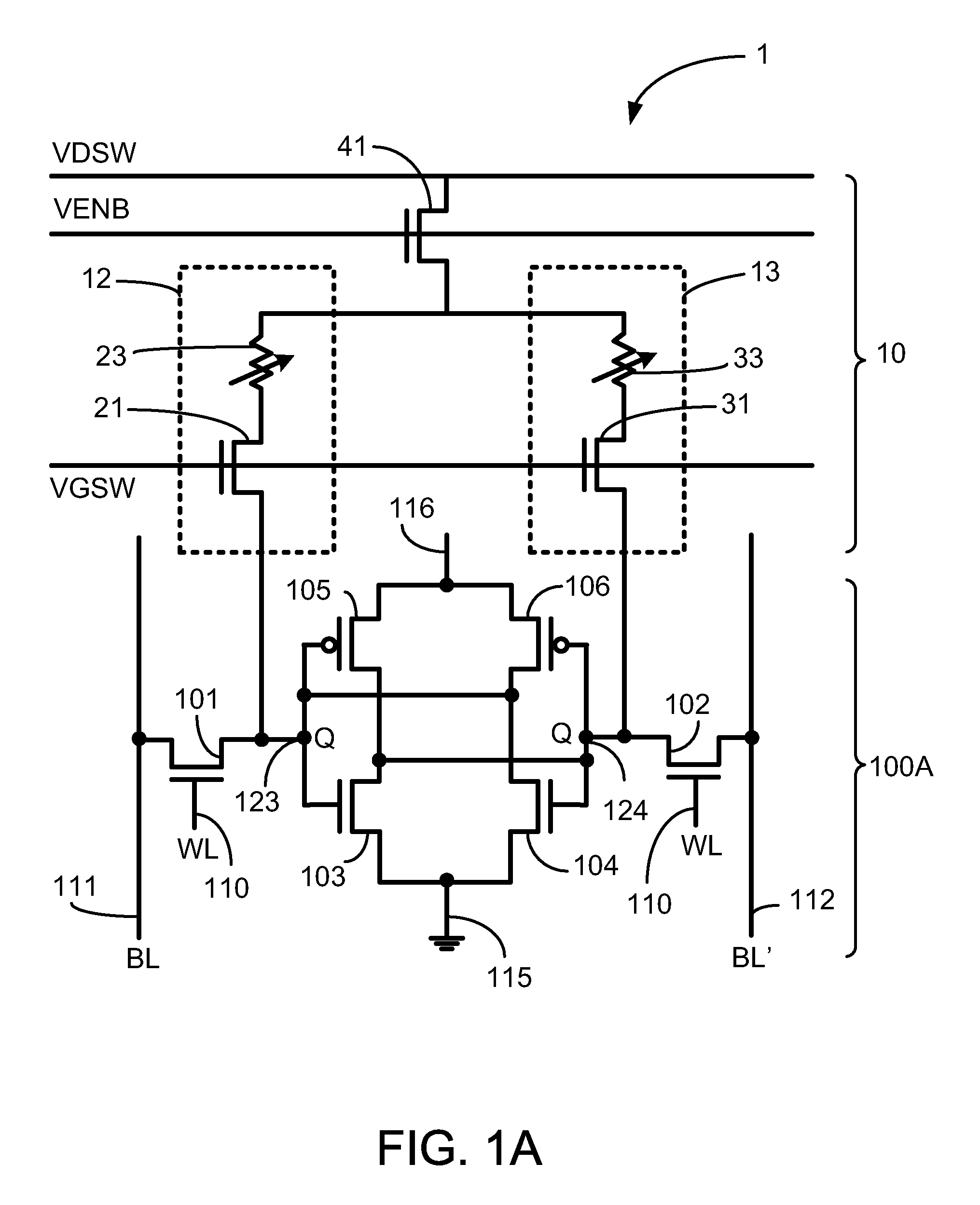
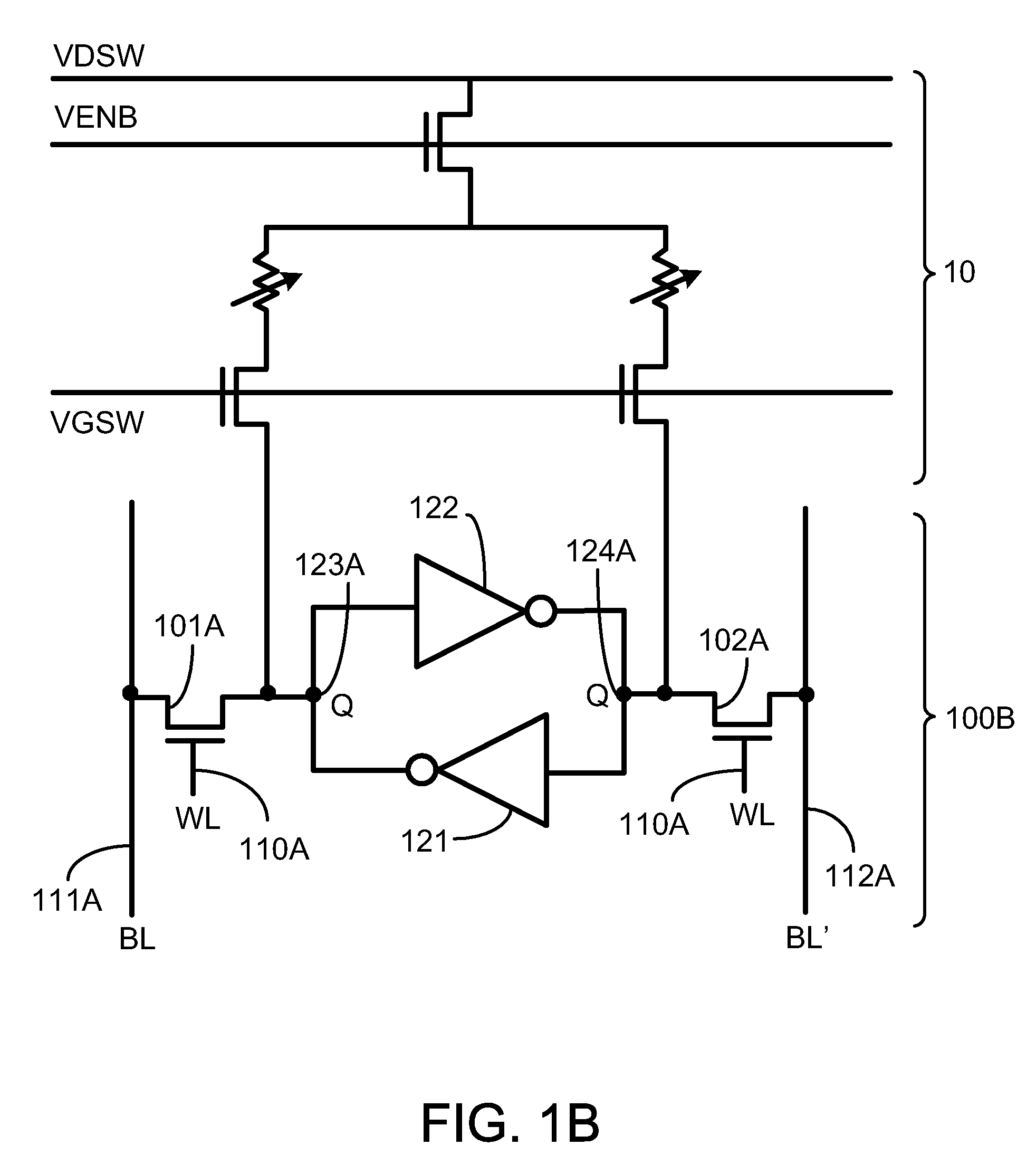
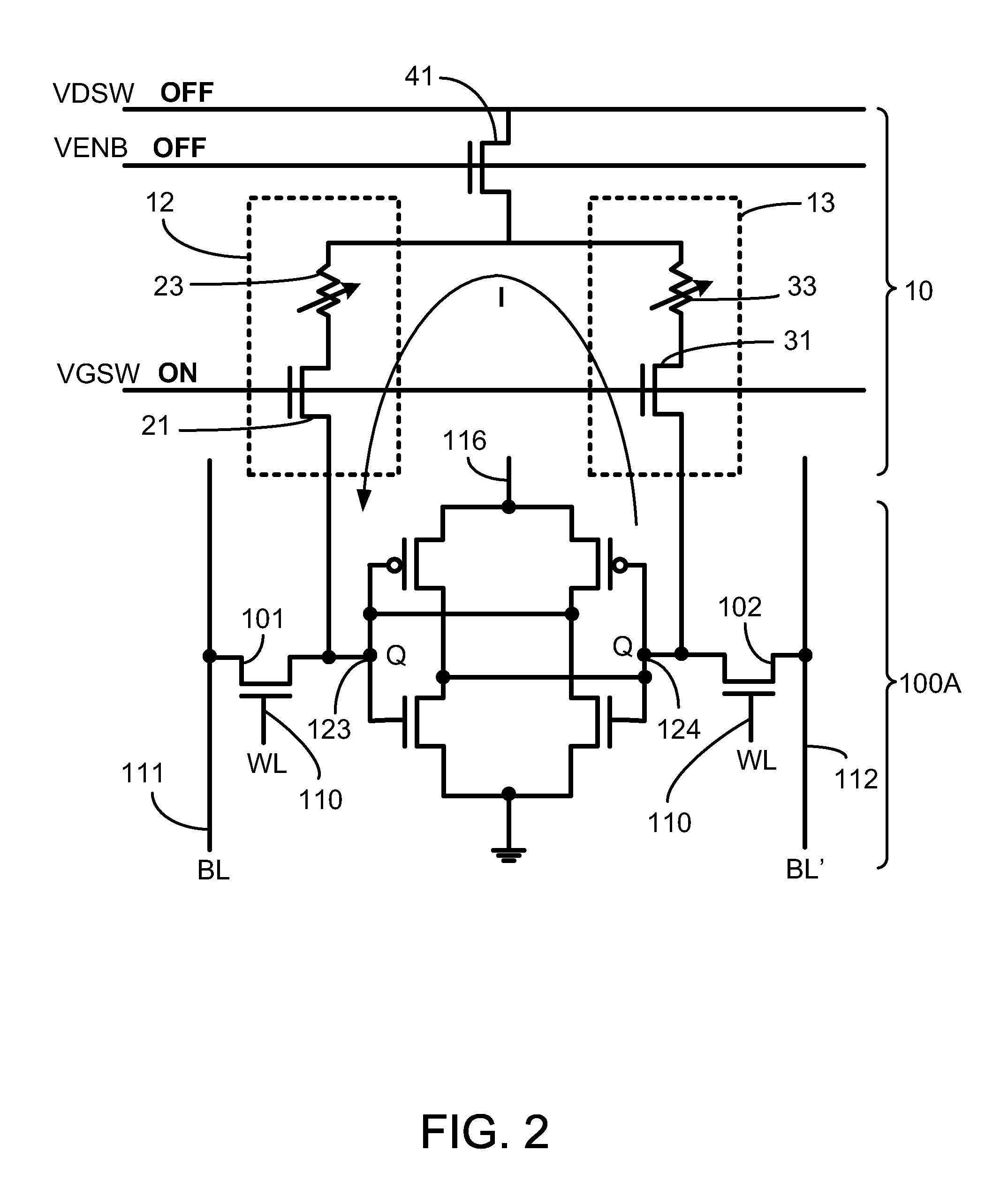
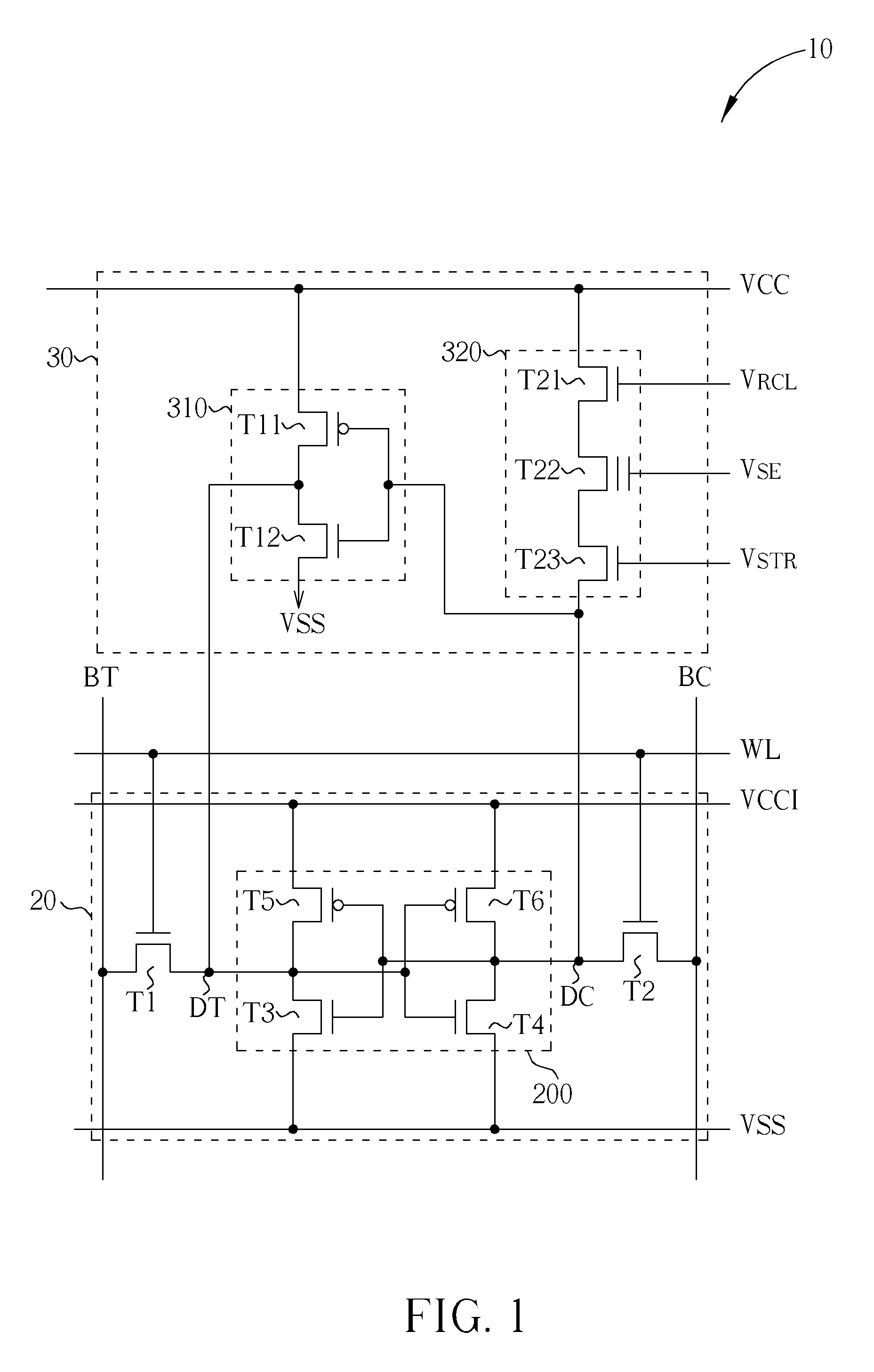
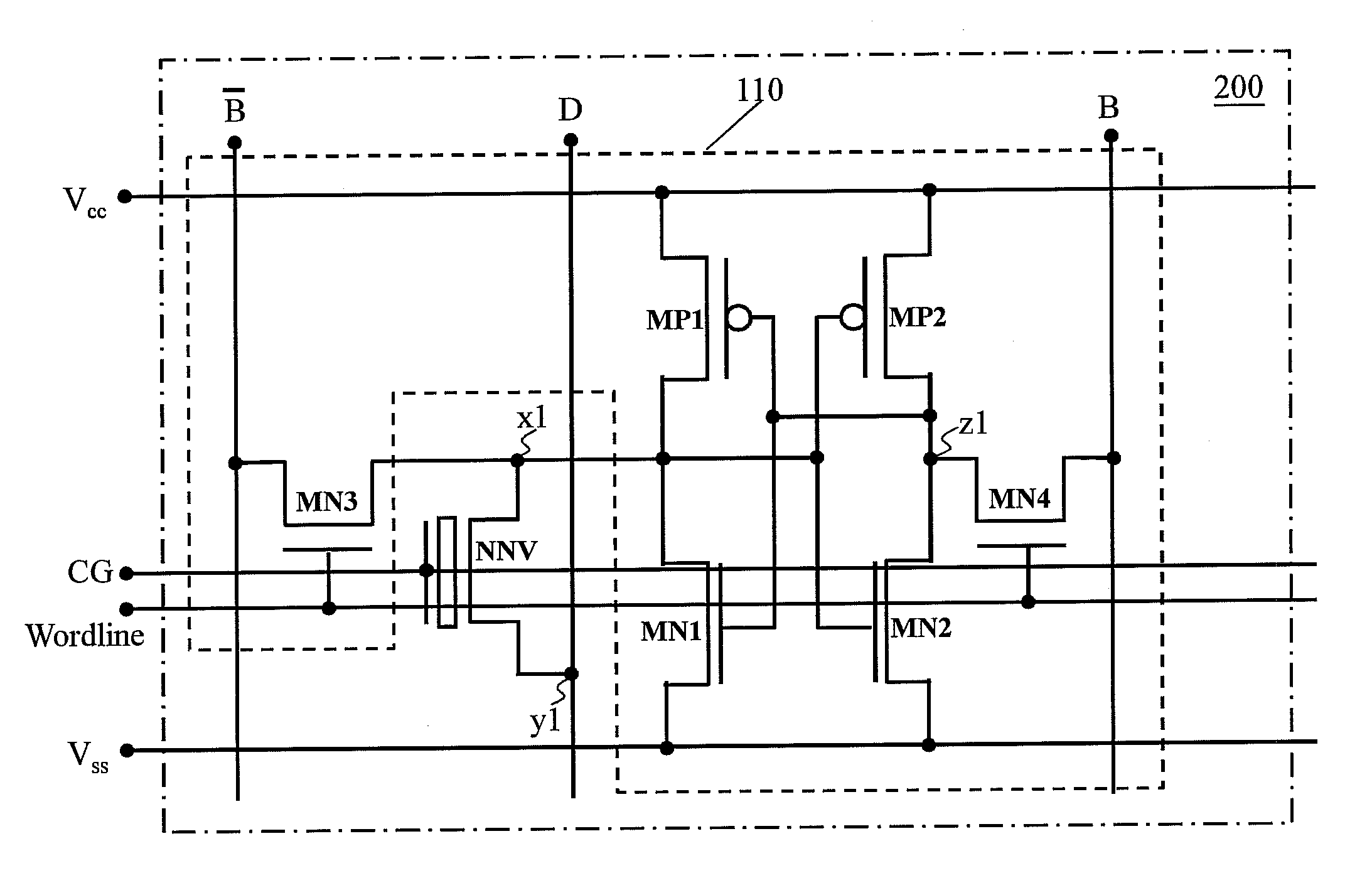
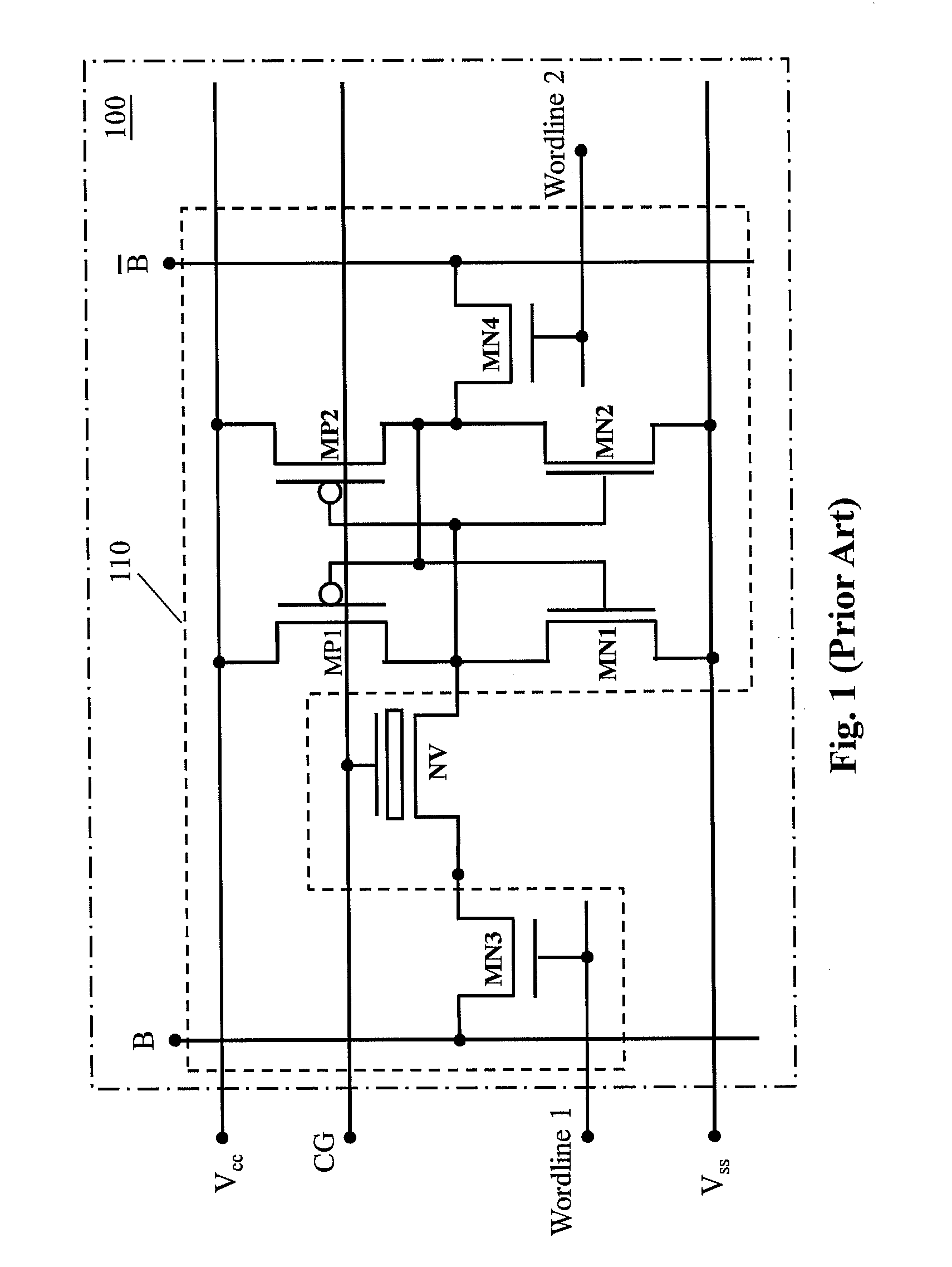
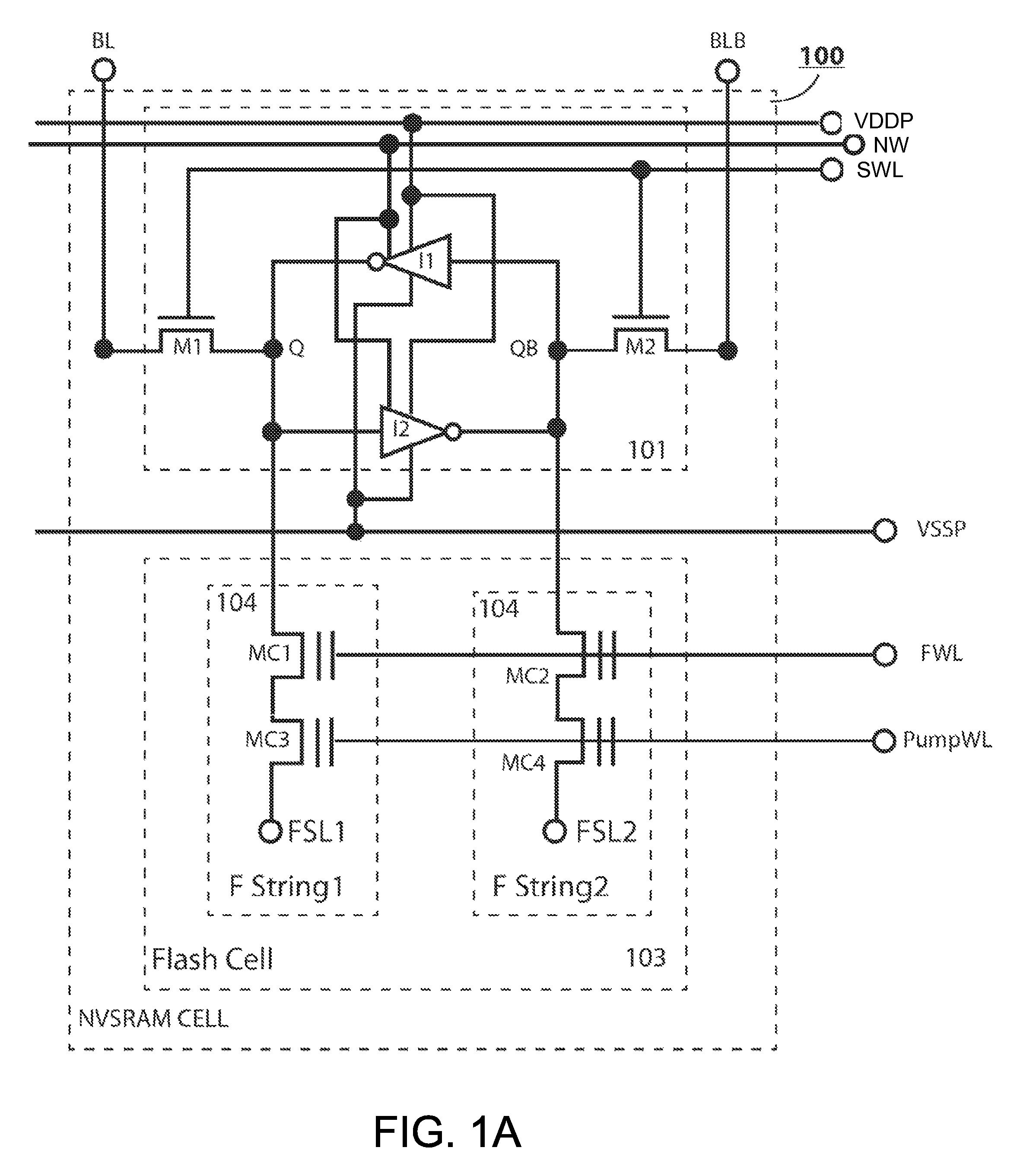
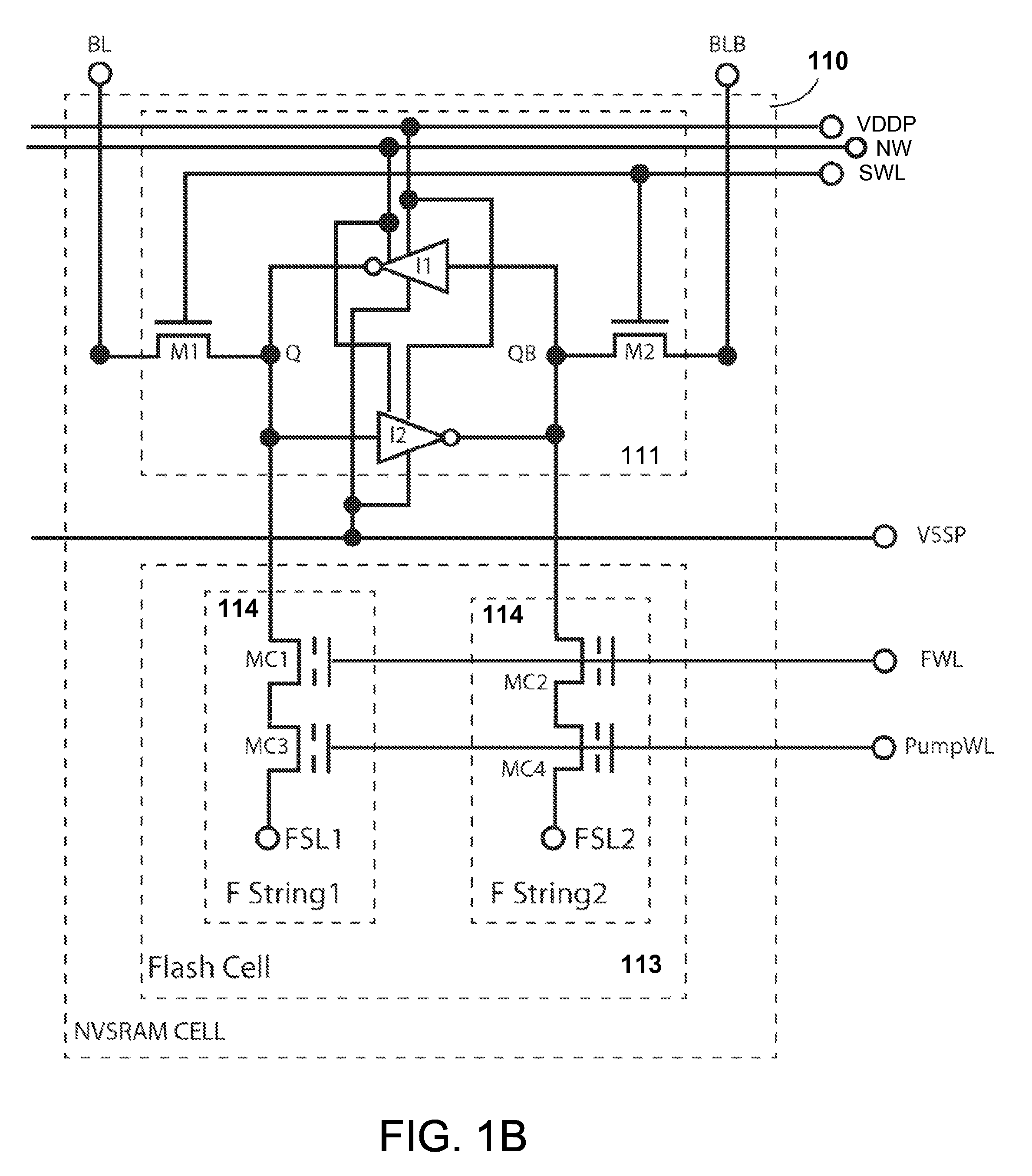
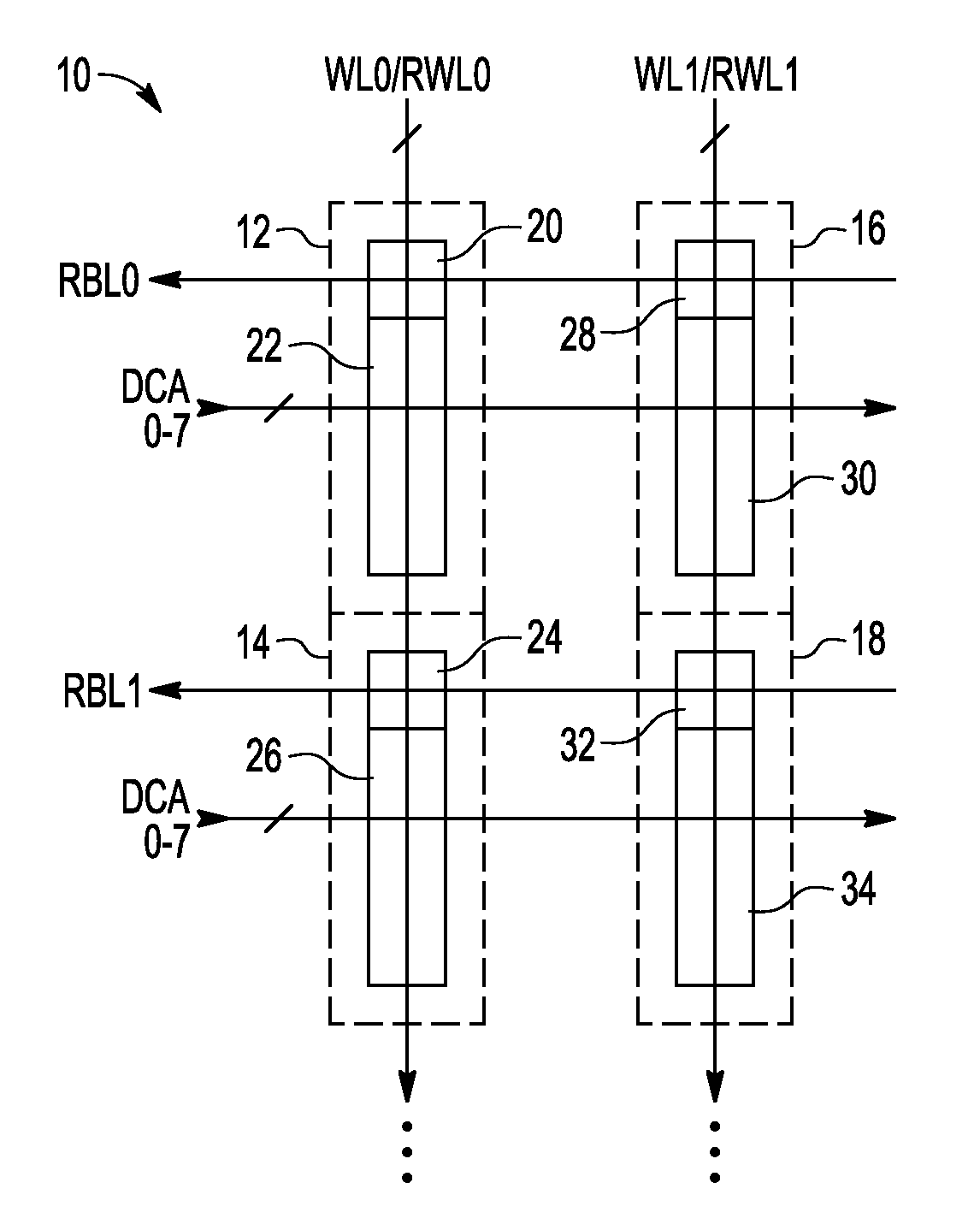
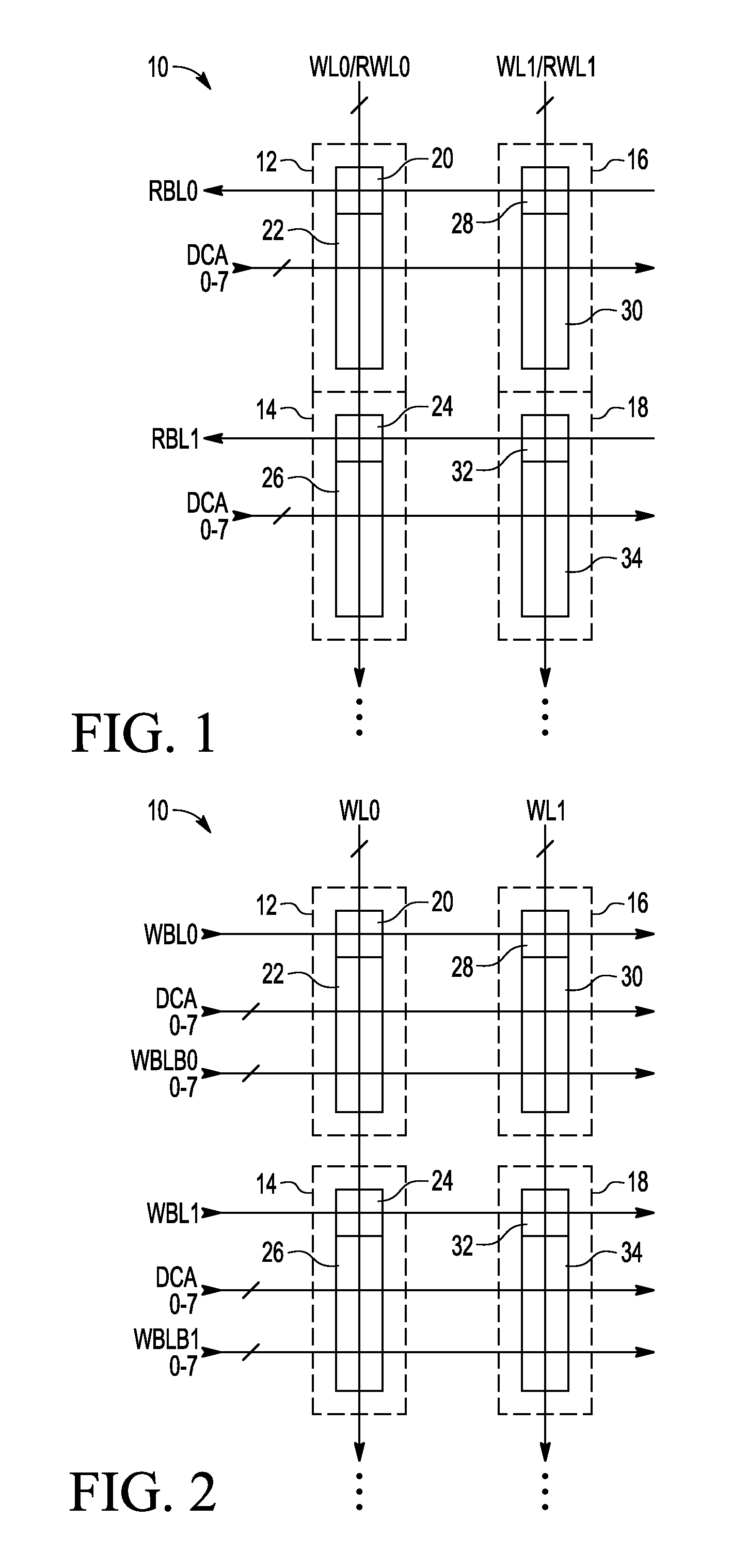
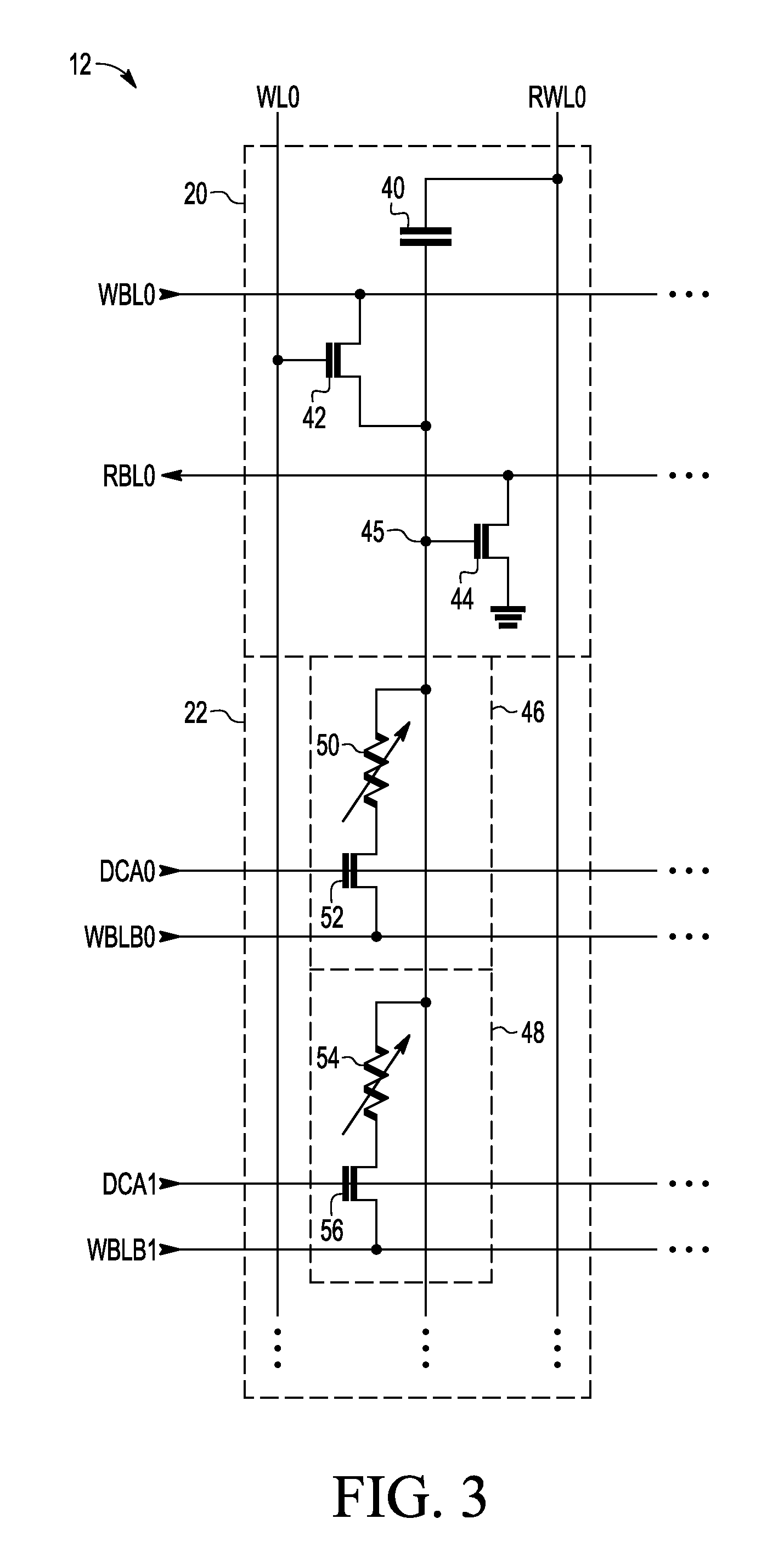
A non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) device includes a volatile circuit and a non-volatile circuit. Under normal operations when an external power is supplied, the volatile circuit can provide fast data access. When the power supply is somehow interrupted, the non-volatile circuit can provide data backup using an inverter circuit and a non-volatile erasable programmable memory (NVEPM) circuit, thereby retaining data previously stored in the volatile circuit.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
nvSRAM having variable magnetic resistors
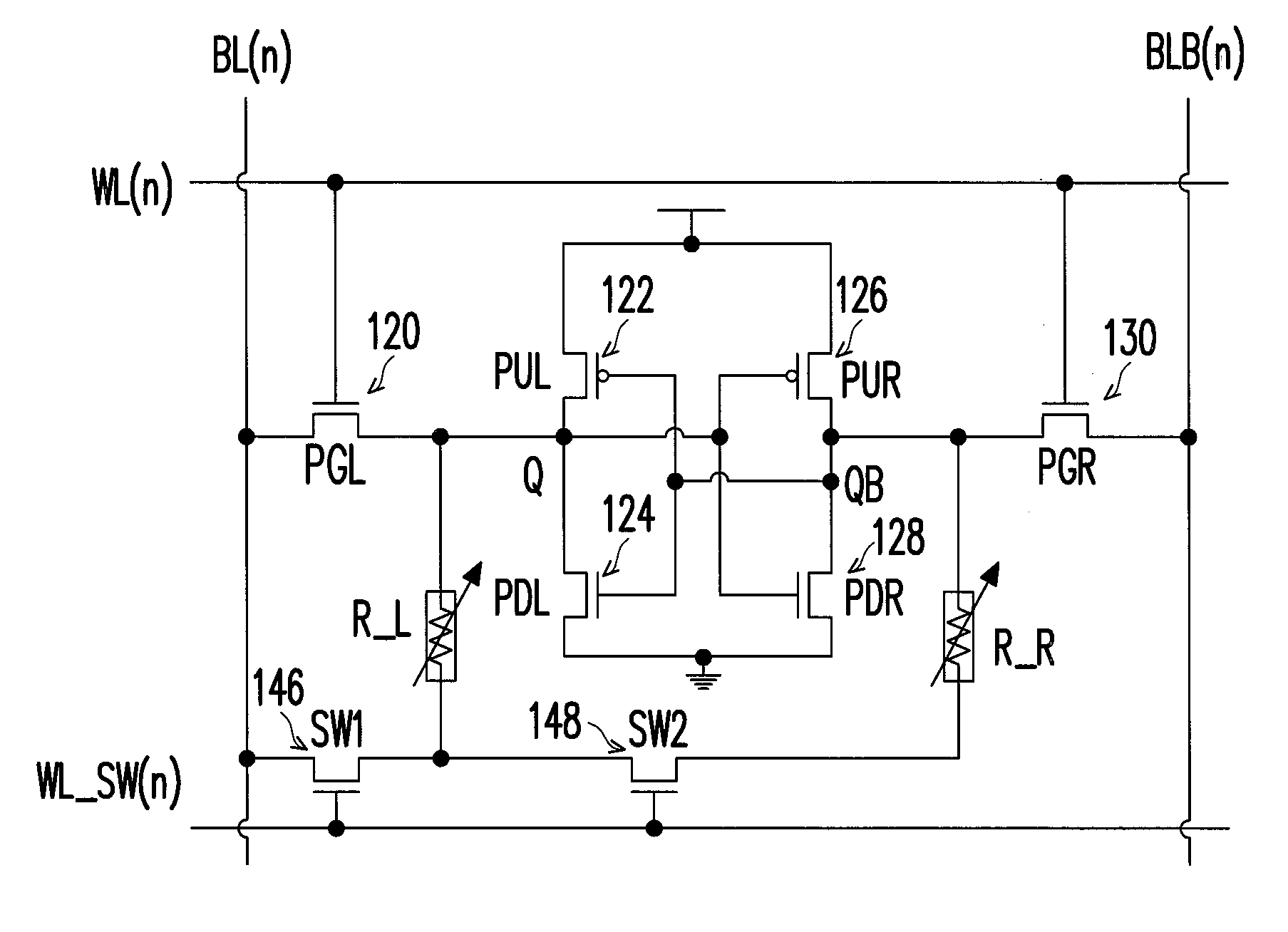
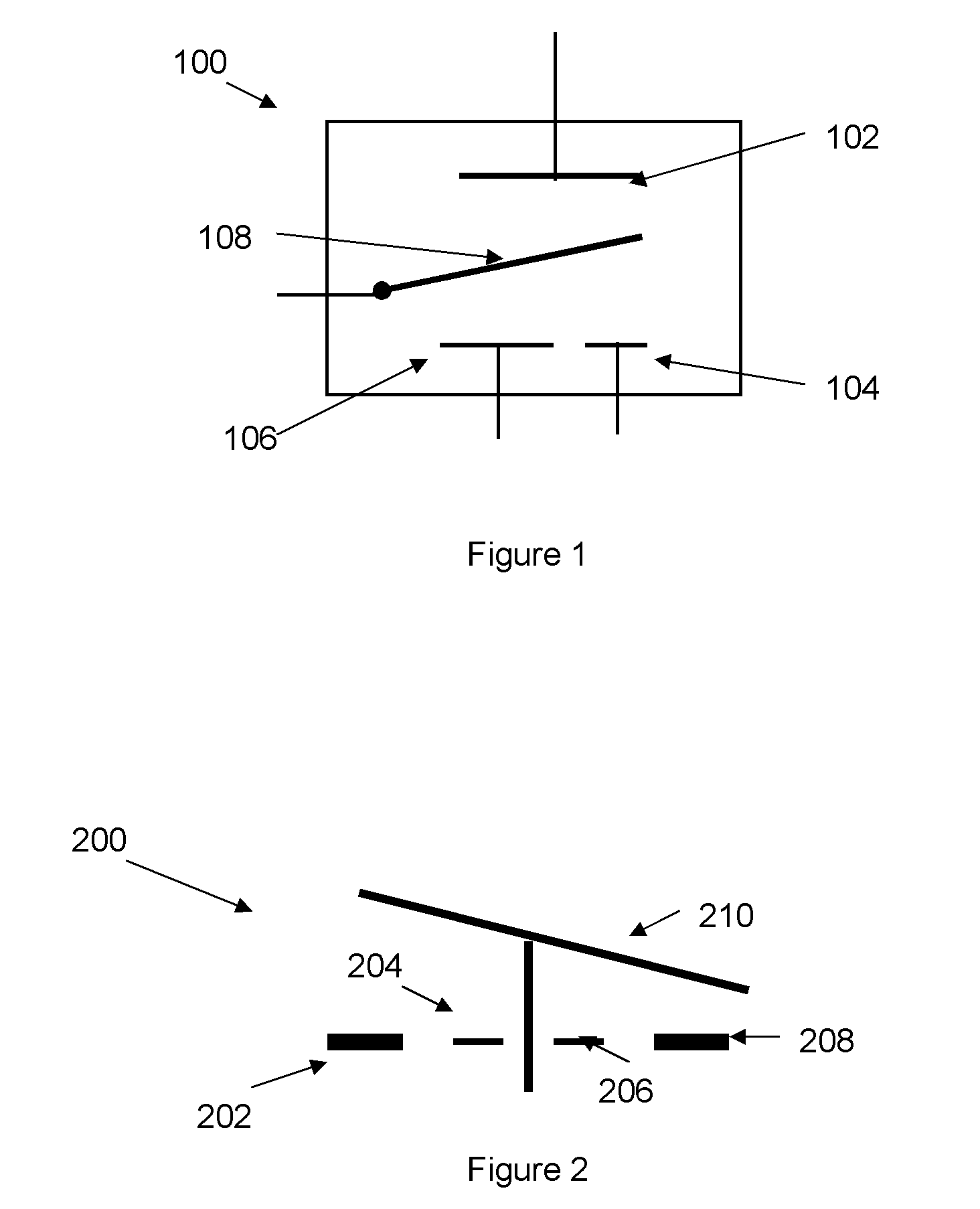
Non-volatile static random access memory (nvSRAM) that has a six transistor static random access memory (6T SRAM) cell electrically connected to a non-volatile random access memory (nvRAM) cell. The nvRAM cell has first and second variable magnetic resistors and first, second and third transistors.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Semiconductor device
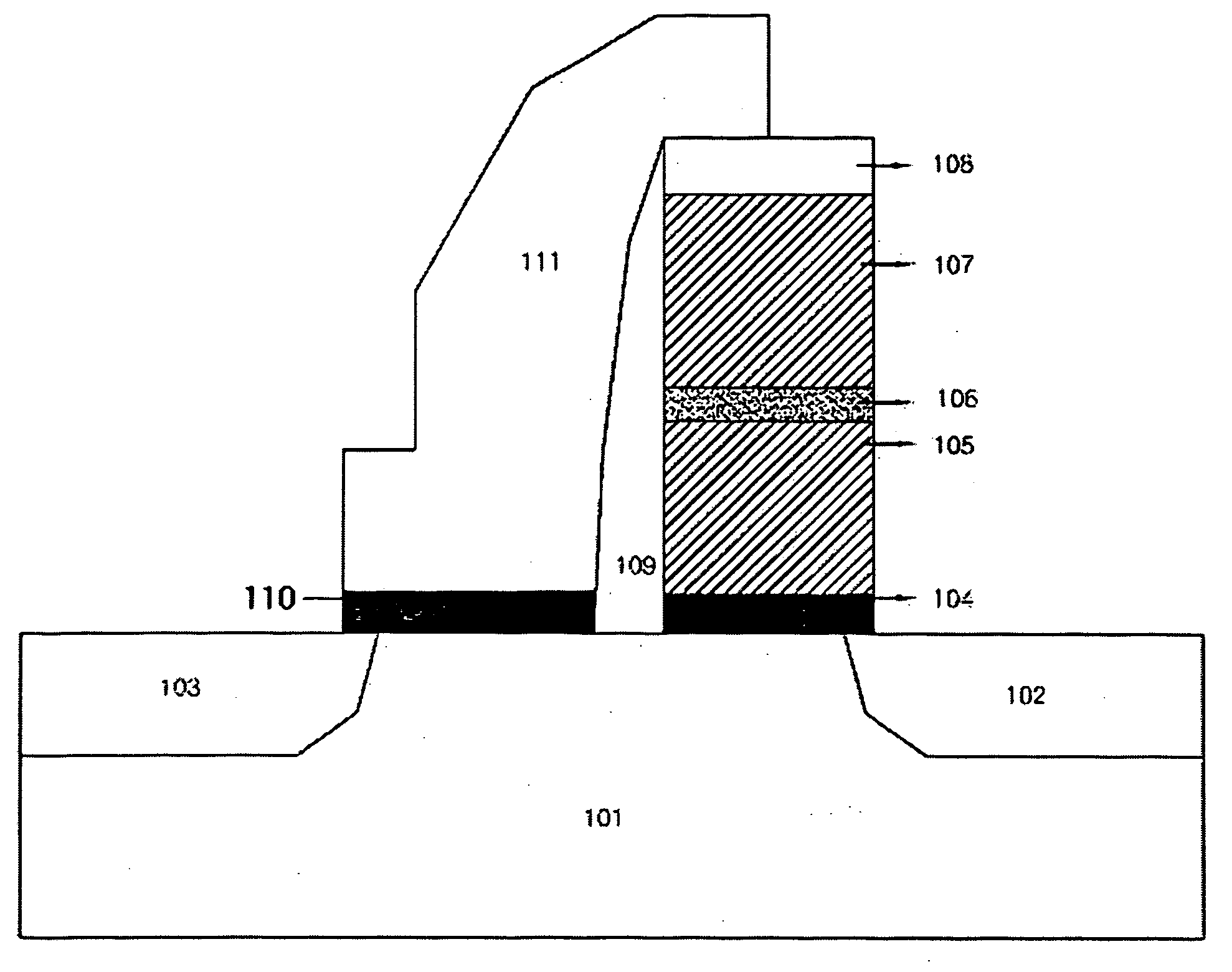
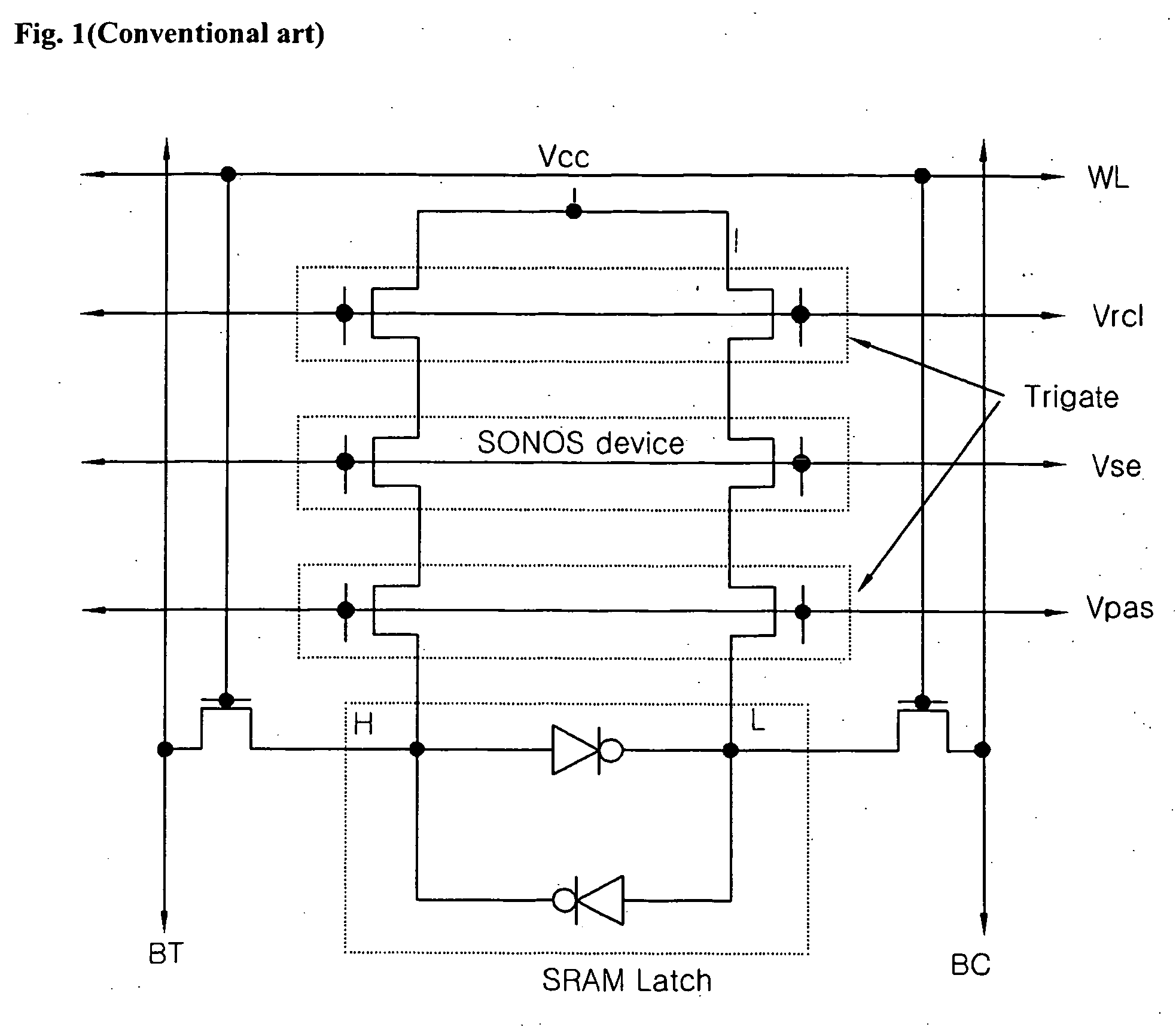
An nvSRAM having a stacked oxide layer is disclosed. A disclosed device comprises: two NMOS transistors and two PMOS transistors for an SRAM latch; two NMOS pass gates for reading and writing a HIGH condition and a LOW condition that are formed in the SRAM latch; and two floating gate NVM devices of split gate structure for storing the HIGH condition and the LOW condition that are stored in the SRAM latch when the power is off.
Owner:DONGBU ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Nonvolatile static random access memory cell and memory circuit
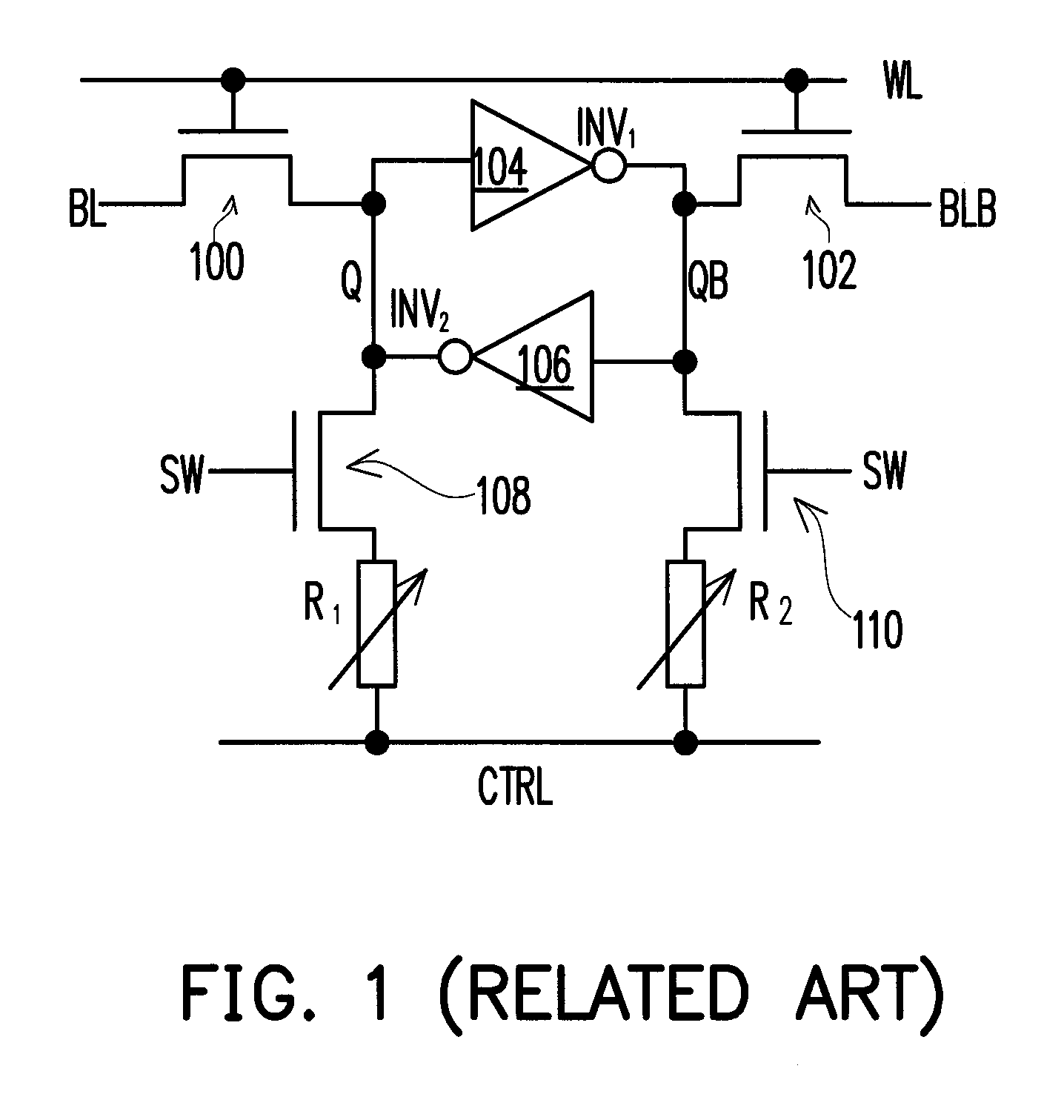
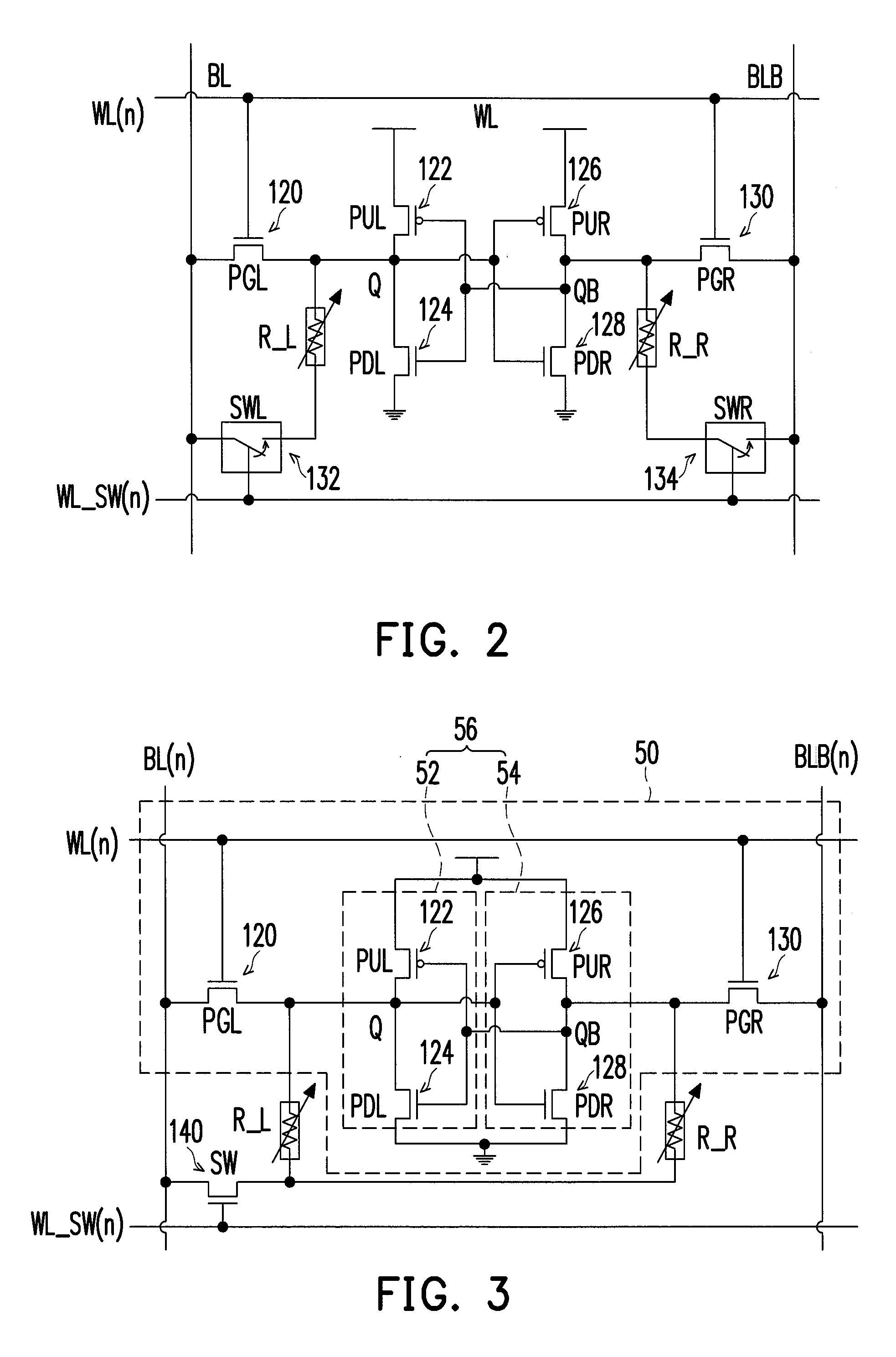
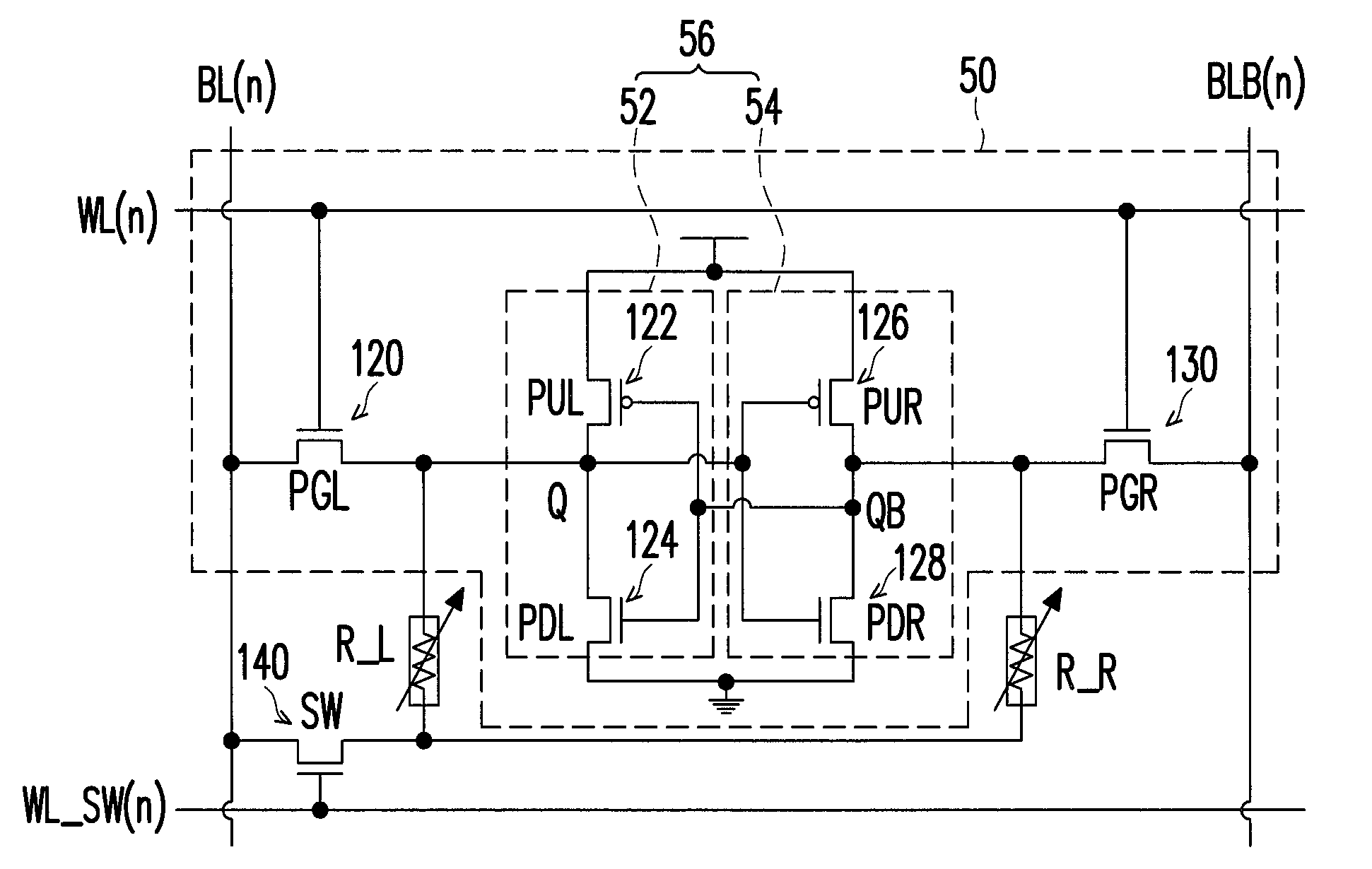
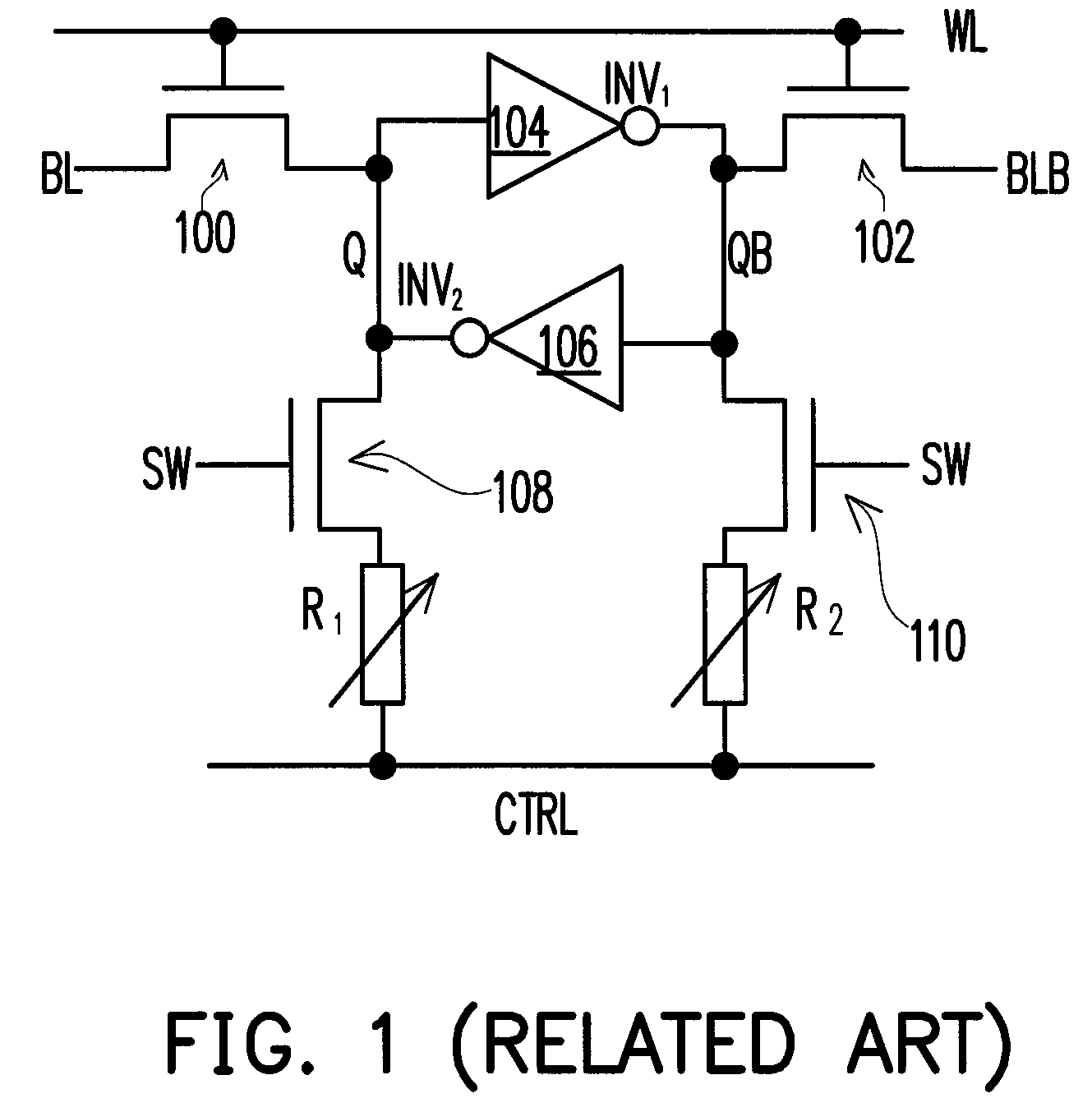
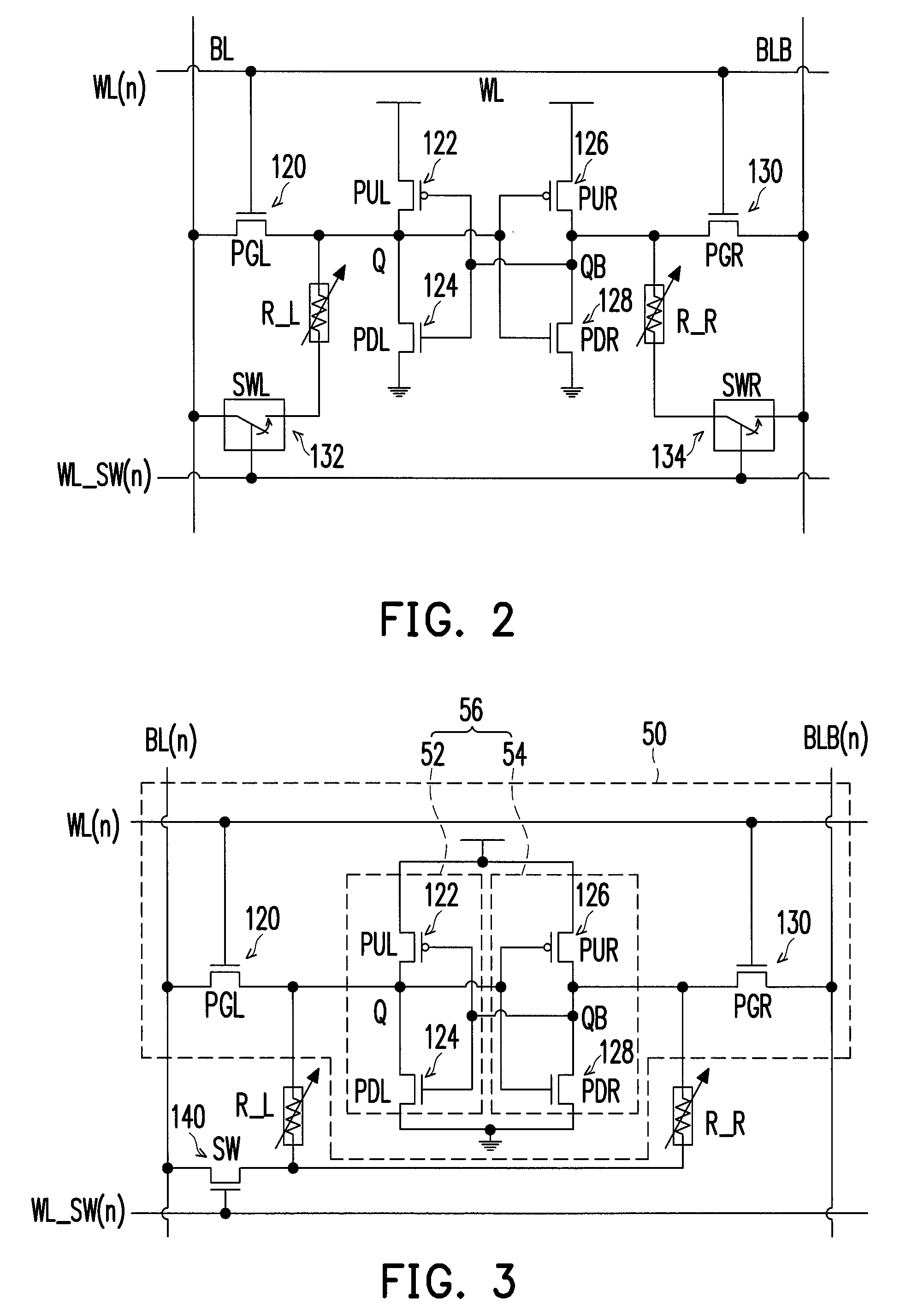
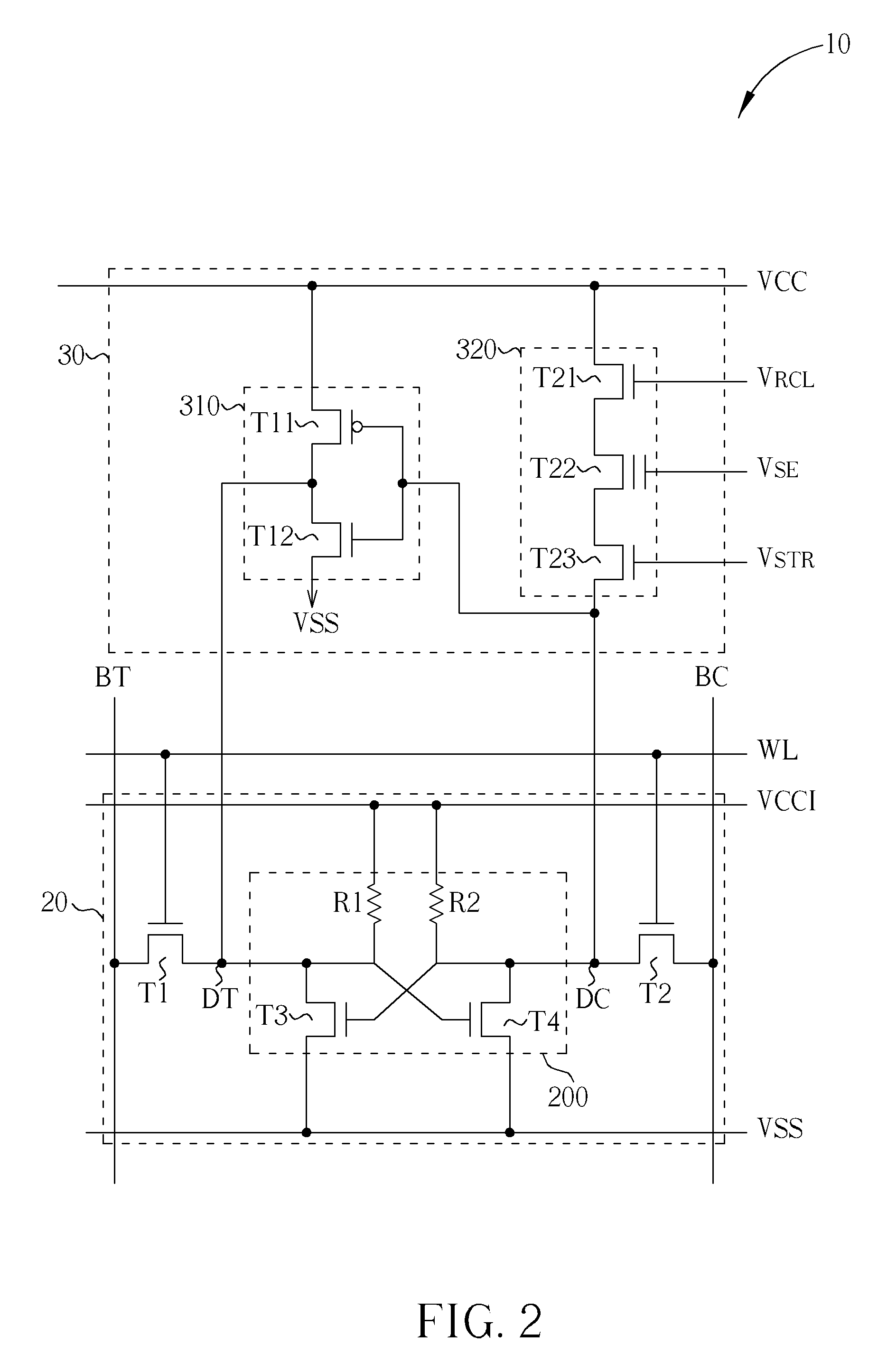
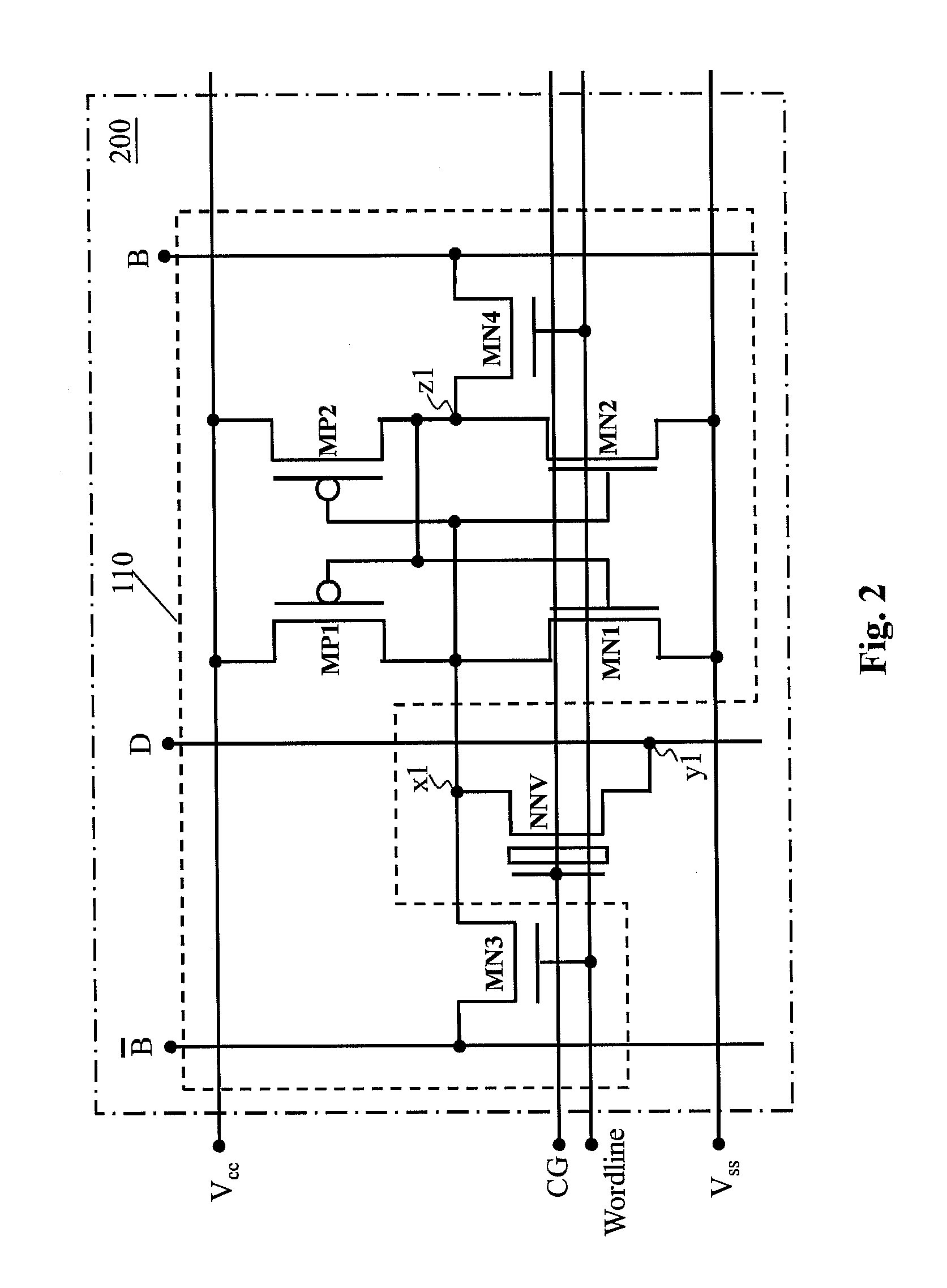
A non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) cell including a static random access circuit, first storage device, a second storage device, and a switch unit is provided. The static random access circuit has a first terminal and a second terminal respectively having a first voltage and a second voltage. Stored data in the first storage device and the second storage device are determined by the first voltage and the second voltage. The first storage device and the second storage device respectively have a first connection terminal and a second connection terminal. The switch unit is respectively coupled to the second connection terminals of the first storage device and the second storage device, and is controlled by a switching signal of a switch line to conduct the first storage device and the second storage device to a same bit line or a same complementary bit line.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
nvSRAM HAVING VARIABLE MAGNETIC RESISTORS
Non-volatile static random access memory (nvSRAM) that has a six transistor static random access memory (6T SRAM) cell electrically connected to a non-volatile random access memory (nvRAM) cell. The nvRAM cell has first and second variable magnetic resistors and first, second and third transistors.
Owner:SEAGATE TECH LLC
Computer remote control method and system
ActiveCN101038561AFix bugsEasy to controlProgram loading/initiatingRedundant operation error correctionOperational systemRemote control
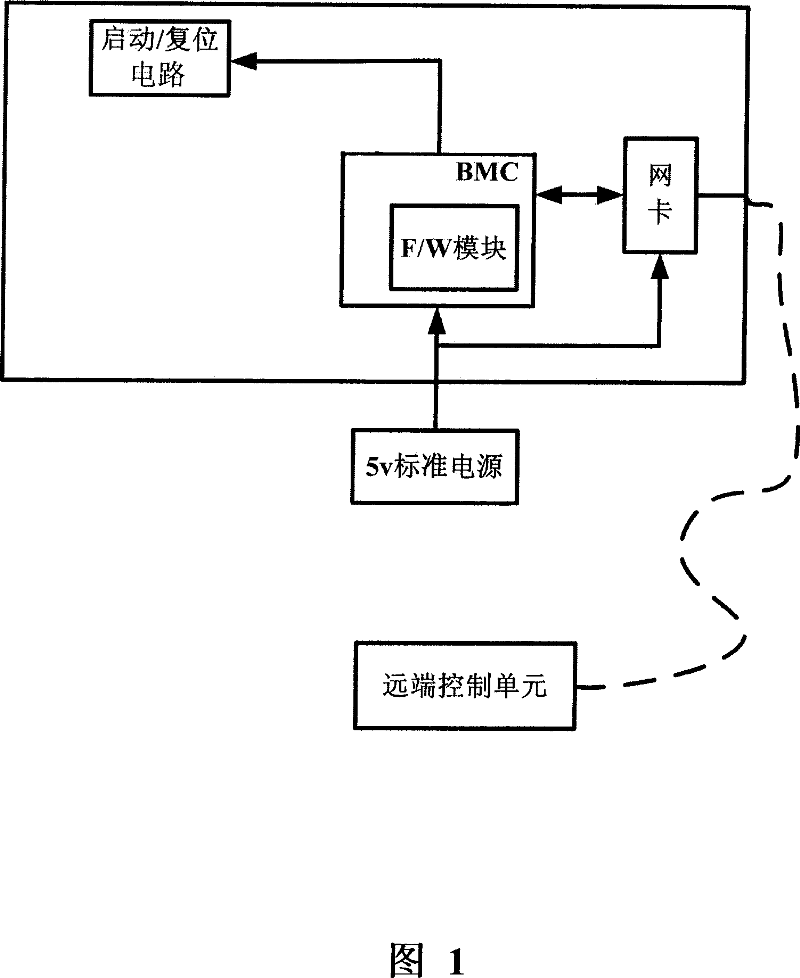
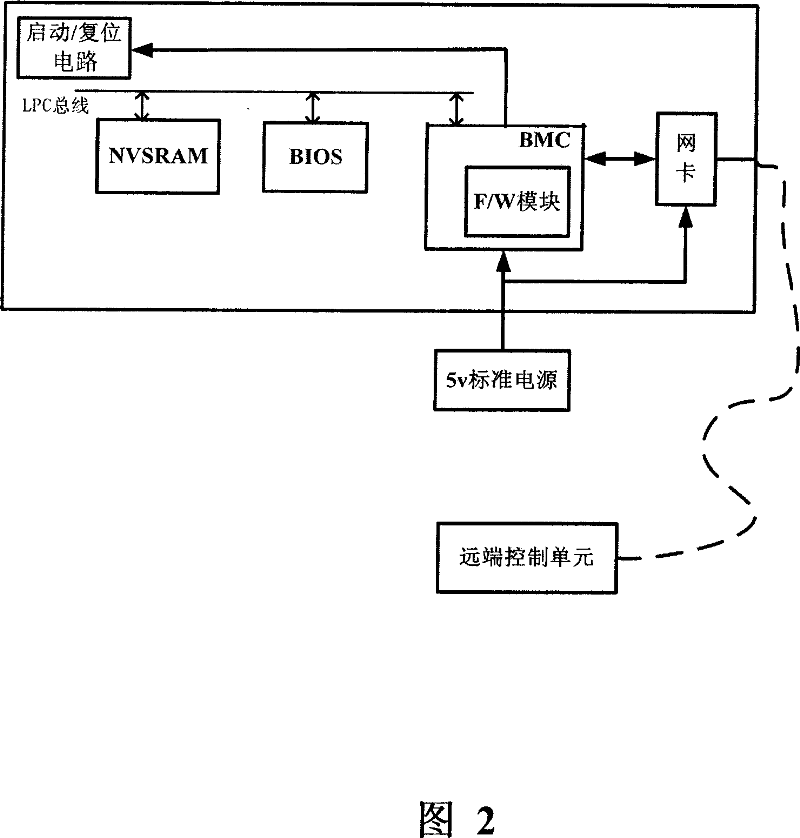
The invention relates to a computer remote control method and a computer system, wherein a remote communication module is employed to communicate, and a starting bit zone of a bit zone loading module is changed and a restart / or start command is sent to the computer; the starting bit zone is checked by a basic input and output system, if the starting bit zone is set as a bit zone for starting the second operation system, then the second operation system in a storage apparatus will be started; then the computer can be operated by a running second operation system. Said remote communication module is a BMC chip, said bit zone storage module is a F / W module of the BMC chip; and said storage apparatus is a nonvolatile memory NVSRAM. By using the scheme, a remote complete control can be implemented, the remote diagnosis and network function of the second operation system can restore and re-install the operation system and repair the operation system malfunctions apart from the physical damage of the motherboard.
Owner:LENOVO (BEIJING) CO LTD
Nonvolatile static random access memory cell and memory circuit
A non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) cell including a static random access circuit, first storage device, a second storage device, and a switch unit is provided. The static random access circuit has a first terminal and a second terminal respectively having a first voltage and a second voltage. Stored data in the first storage device and the second storage device are determined by the first voltage and the second voltage. The first storage device and the second storage device respectively have a first connection terminal and a second connection terminal. The switch unit is respectively coupled to the second connection terminals of the first storage device and the second storage device, and is controlled by a switching signal of a switch line to conduct the first storage device and the second storage device to a same bit line or a same complementary bit line.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
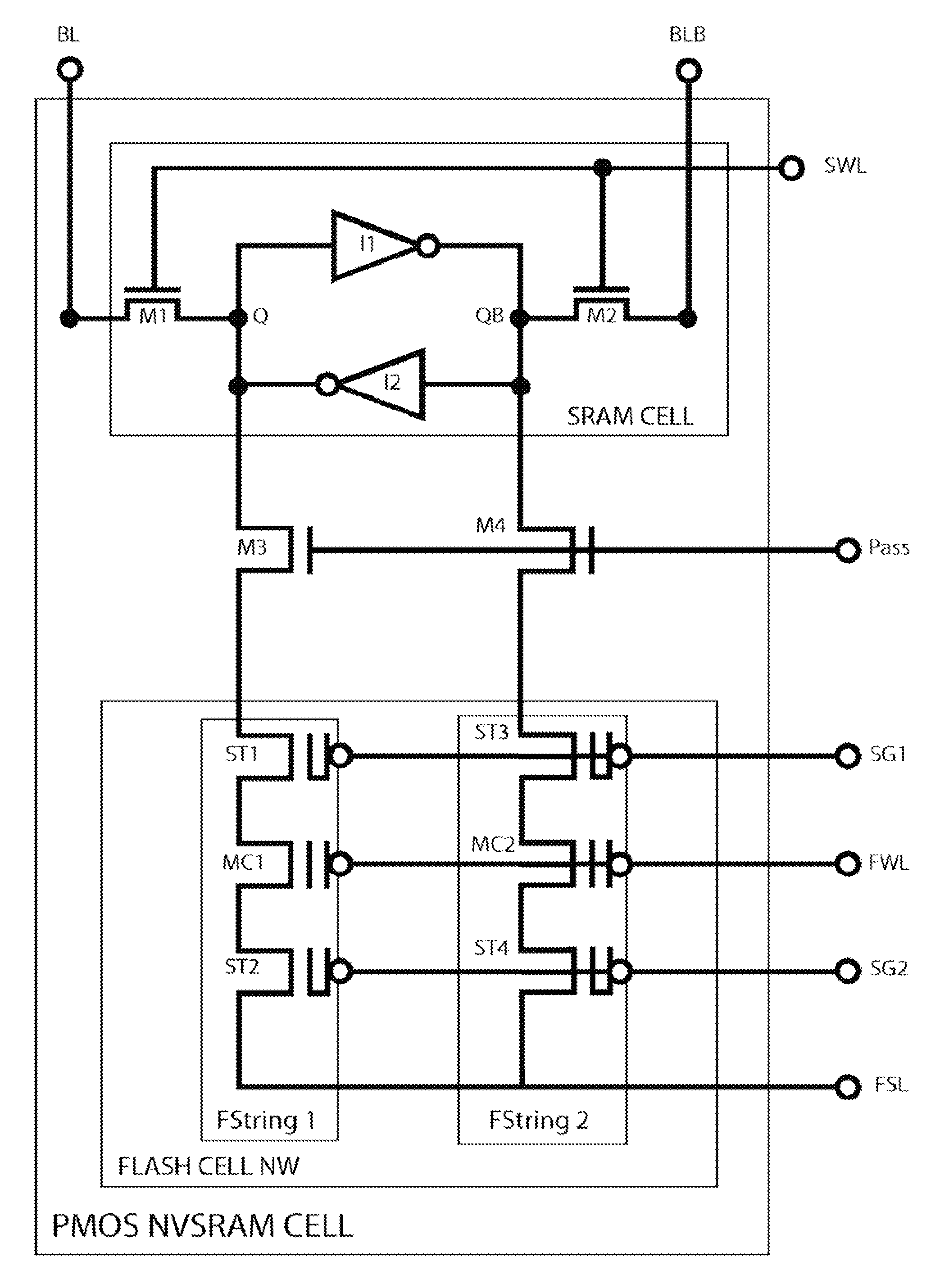
Low-voltage fast-write PMOS nvsram cell
InactiveUS20140050025A1Junction breakdown can be preventedImprove the coupling ratioRead-only memoriesDigital storageLow voltageComputer science
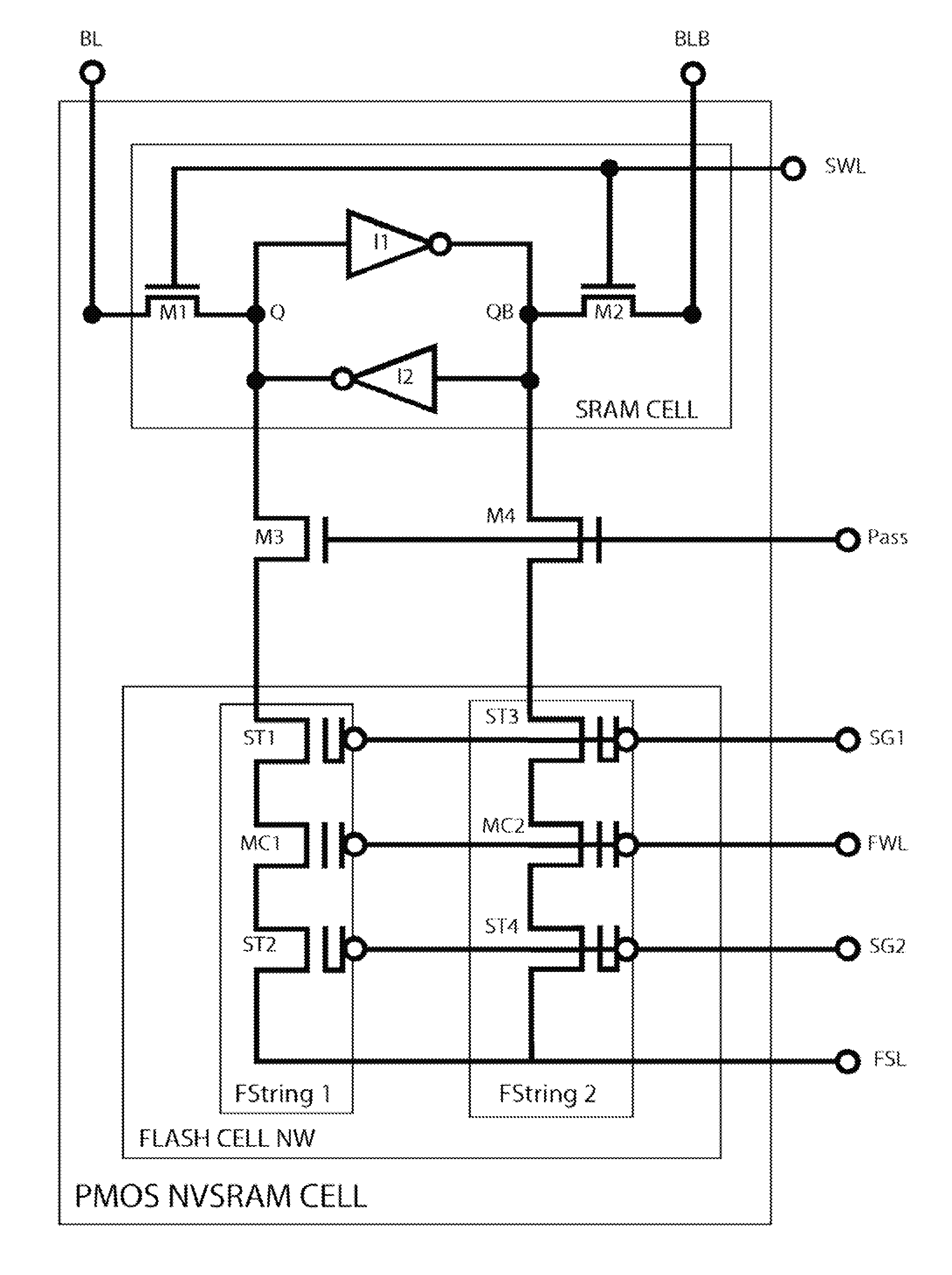
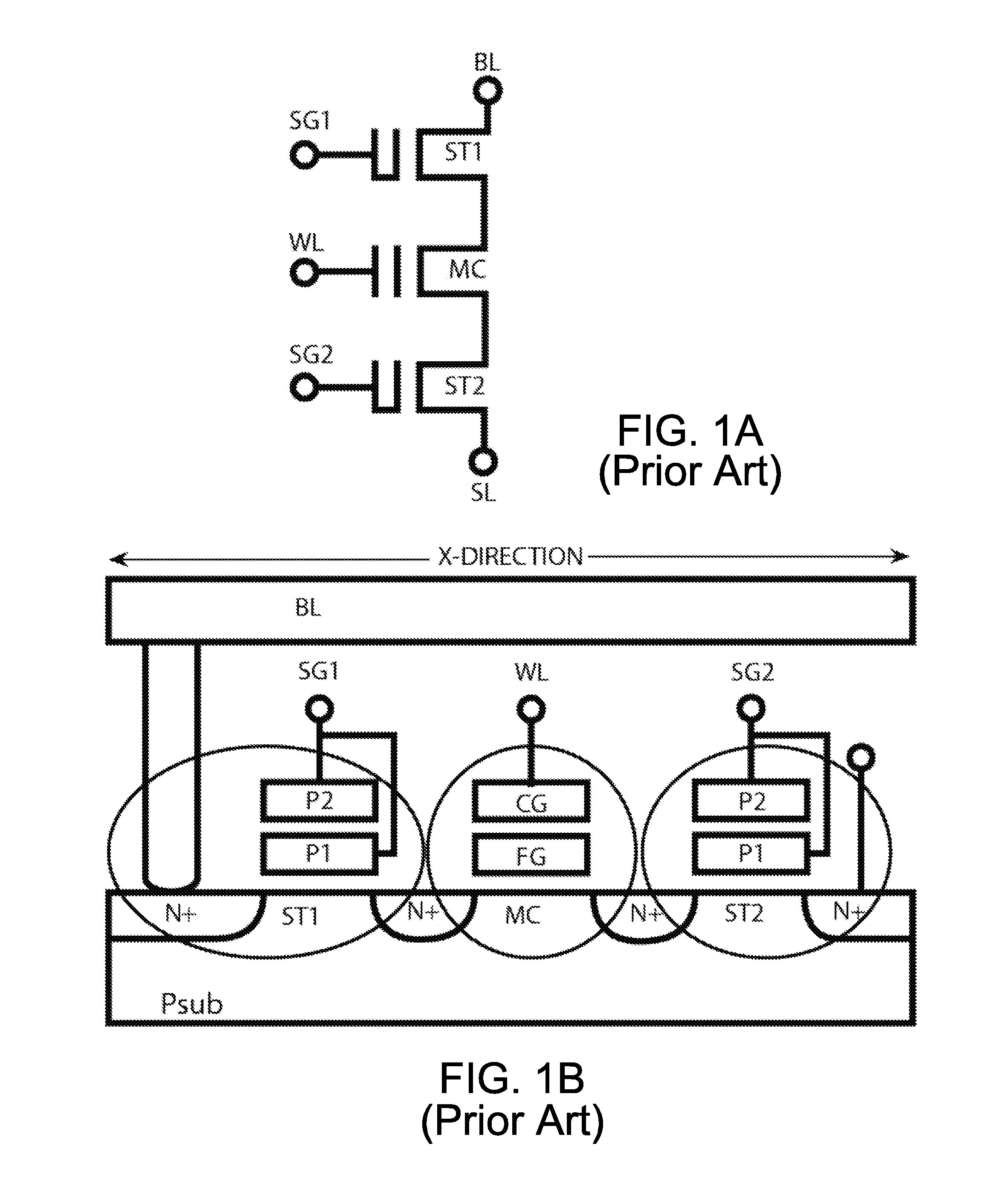
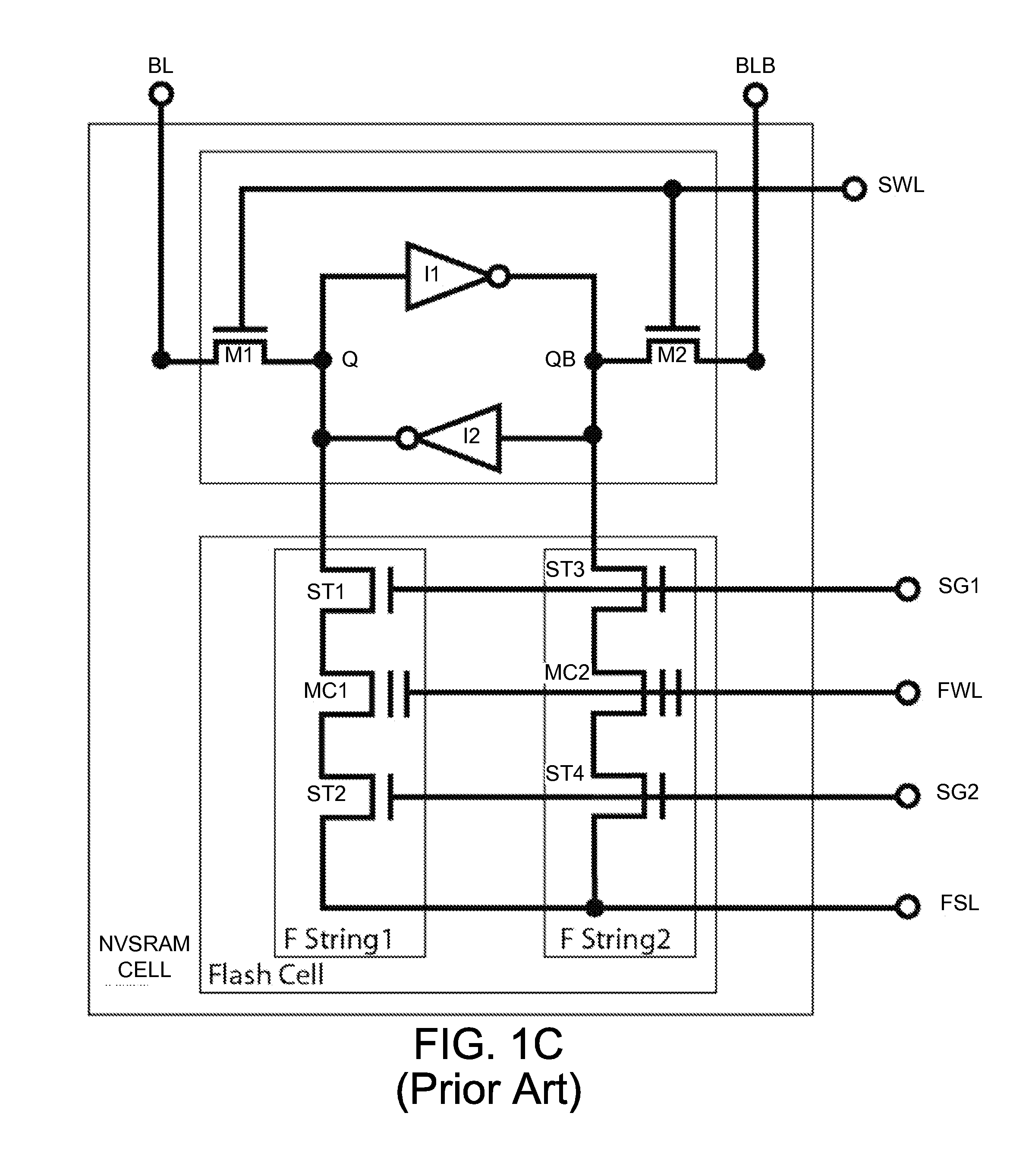
This invention discloses a low-voltage fast-write 12T or 14T PMOS NVSRAM cell structure which comprises a 6T LV SRAM cell and one pairs of two 3T or 4T HV PMOS Flash strings. Due to reverse threshold voltage definition of PMOS and NMOS flash cell, this PMOS NVSRAM cell has the advantage over the NMOS NVSRAM cell to have the same data polarity between SRAM and Flash pairs during the data writing operation. In addition, this PMOS NVSRAM's PMOS Flash cell uses similar low-current FN-tunneling scheme as NMOS NVSRAM, thus the fast data program and erase can be achieved in a big density up to 100 Mb simultaneously. As a result, low power voltage operation of NVSRAM with 1.2V VDD can be much easier to be designed without coupling the FSL line to any VDD level during the flash data loading into SRAM cell during a power-on period.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Non-volatile static random access memory (nvsram) device
A non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) device includes a volatile circuit and a non-volatile circuit. Under normal operations when an external power is supplied, the volatile circuit can provide fast data access. When the power supply is somehow interrupted, the non-volatile circuit can provide data backup using an inverter circuit and a non-volatile erasable programmable memory (NVEPM) circuit, thereby retaining data previously stored in the volatile circuit.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
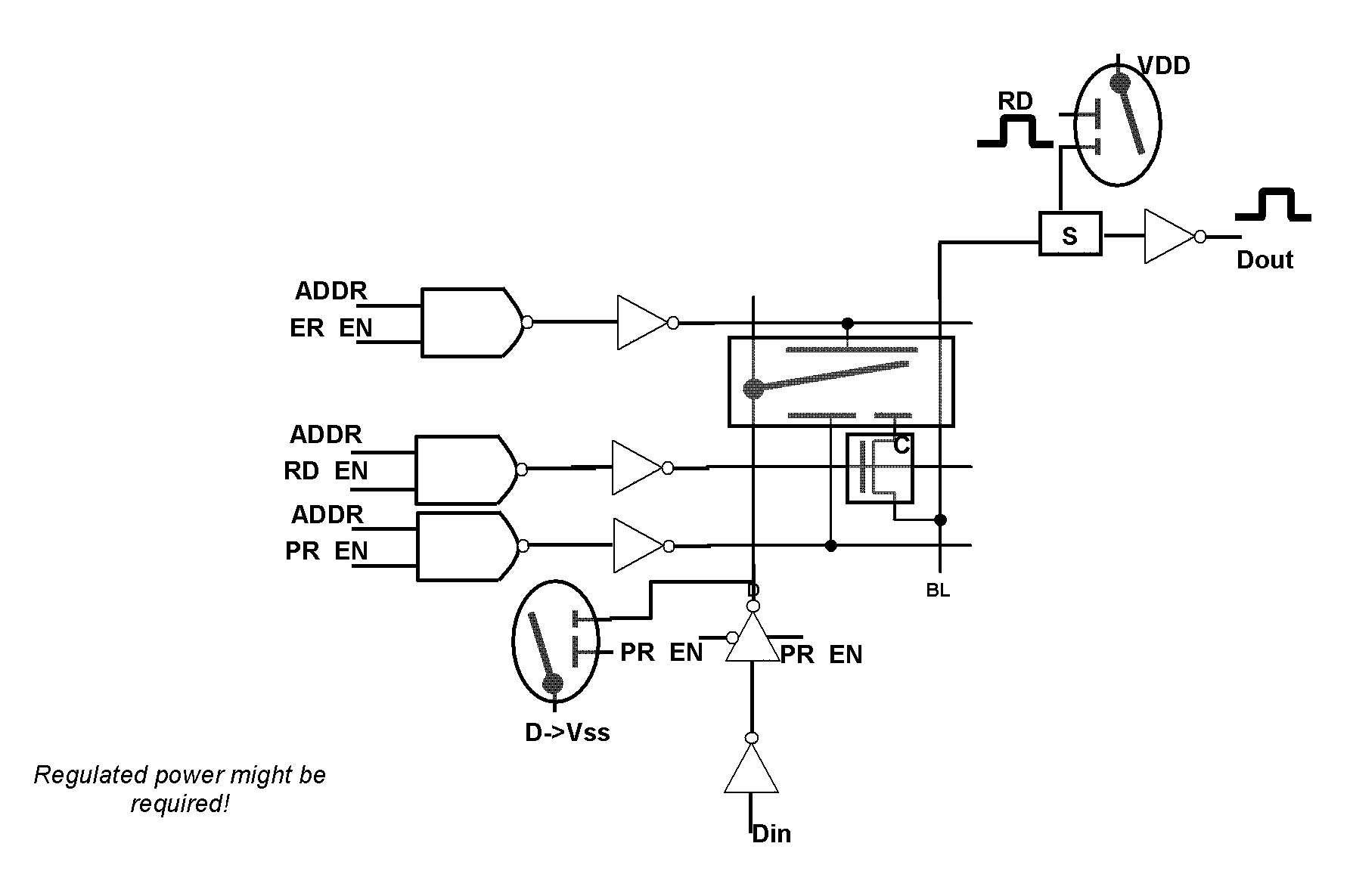
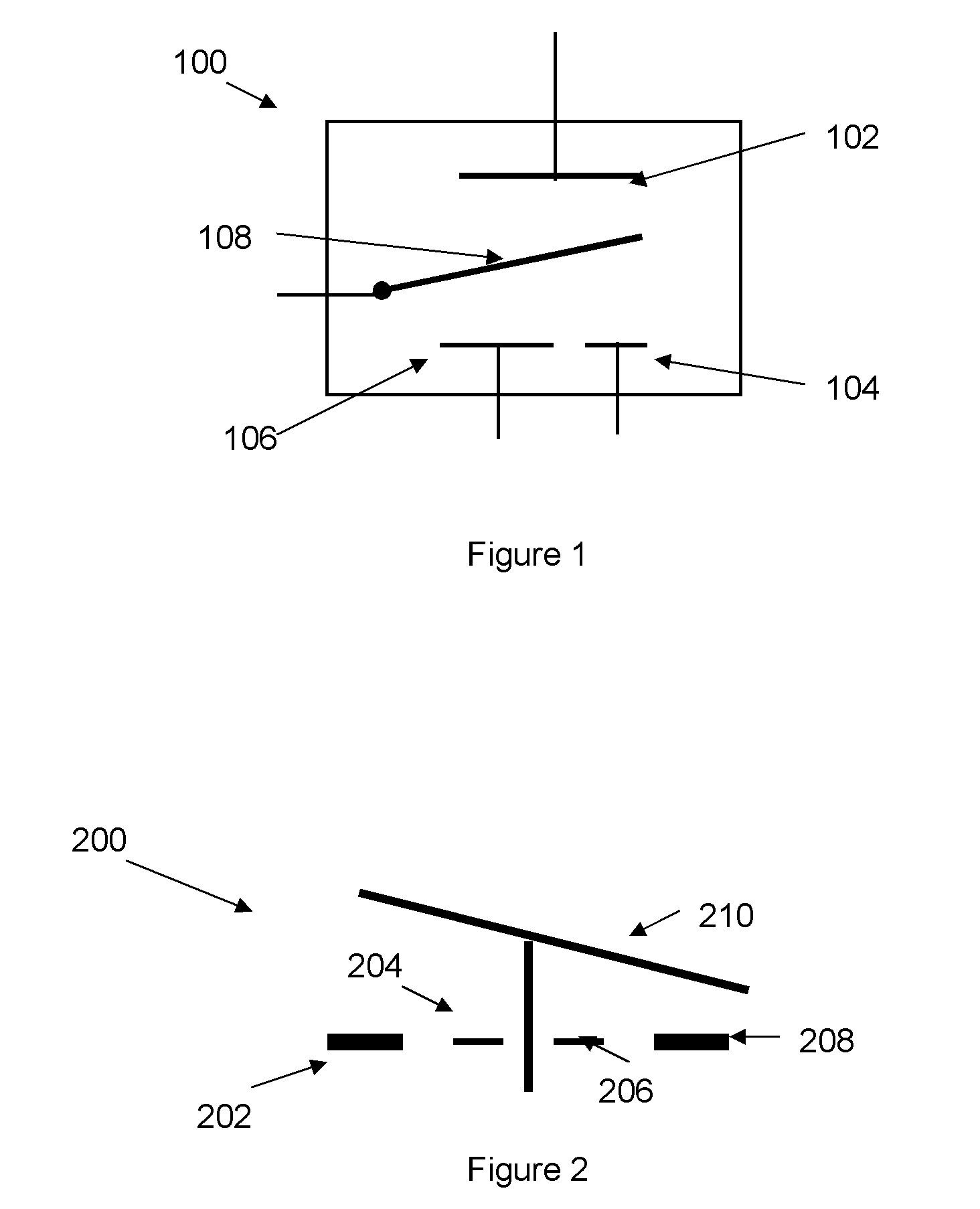
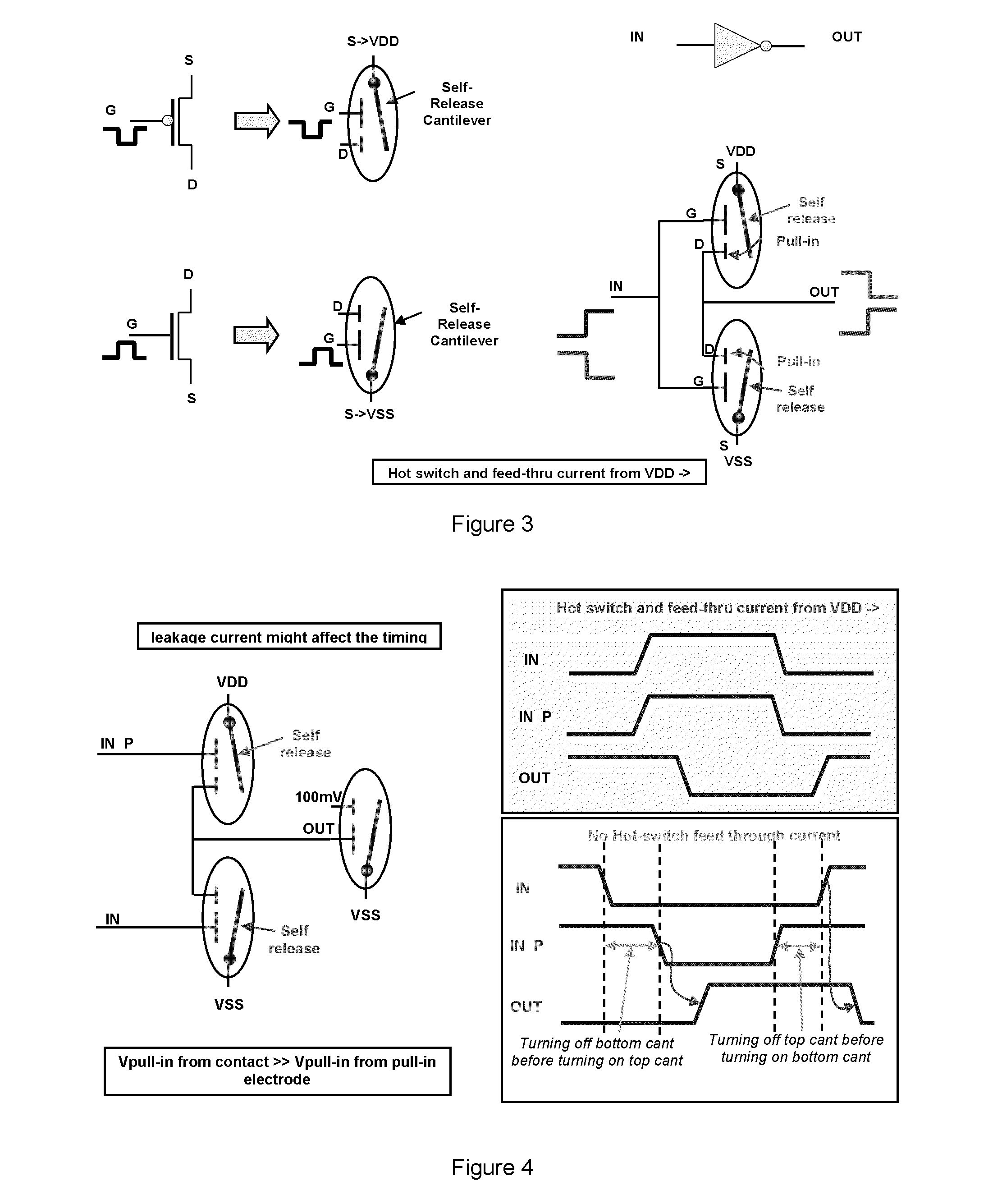
Binary Logic Utilizing MEMS Devices
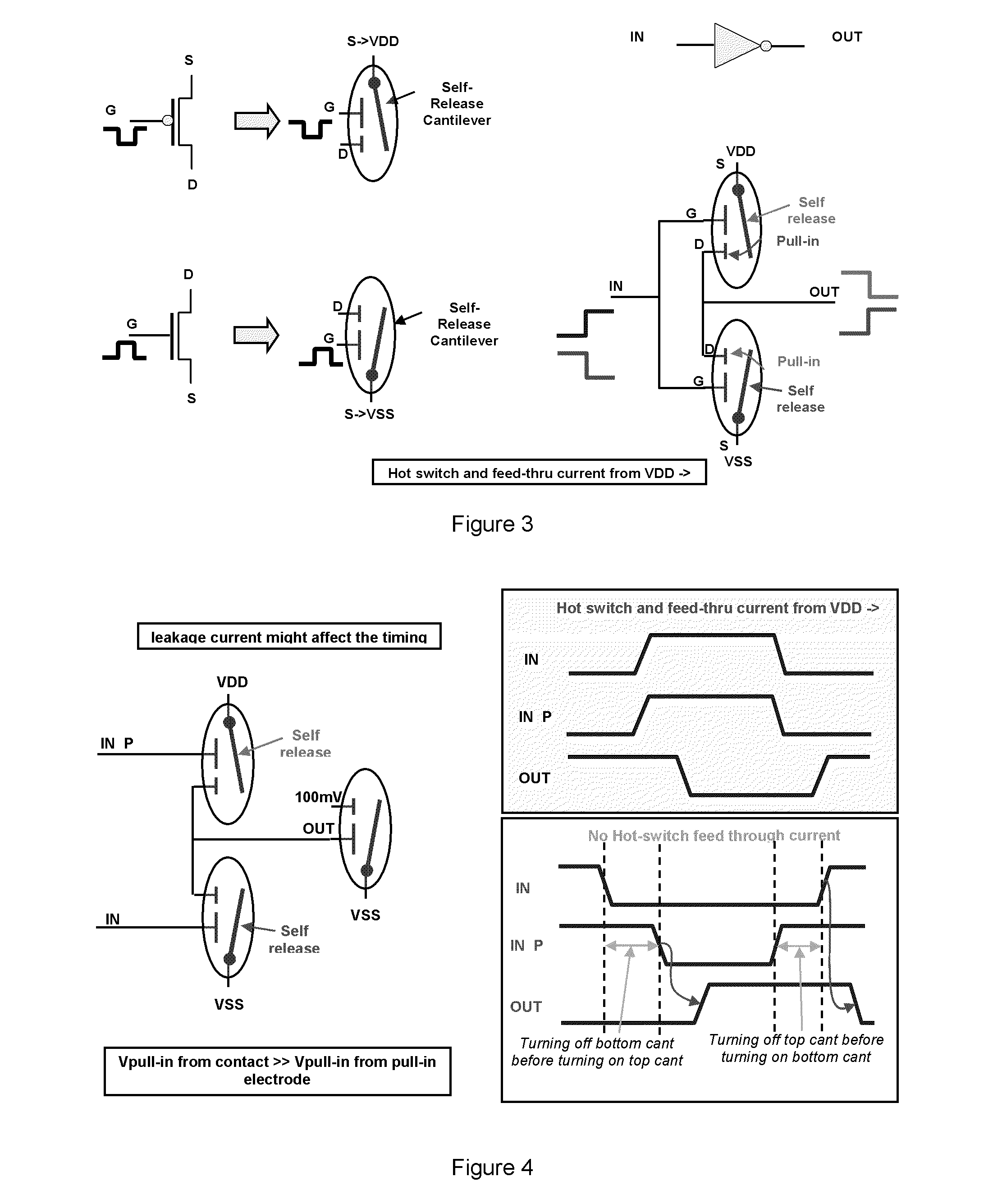
ActiveUS20110002168A1Space utilizationNecessitating useRead-only memoriesDigital storageNvSRAMTransistor
Embodiments disclosed herein generally relate to switches that utilize micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS). By replacing transistors in many devices with switches such as MEMS switches, the devices may be used for logic applications. MEMS switches may be used in devices such as FPGAs, NAND devices, nvSRAM devices, AMS chips and general memory logic devices. The benefit of utilizing MEMS devices in place of transistors is that the transistors utilize more space on the chip. Additionally, the MEMS devices can be formed in the BEOL without having any negative impacts on the FEOL or necessitating the use of additional layers within the chip.
Owner:QORVO US INC
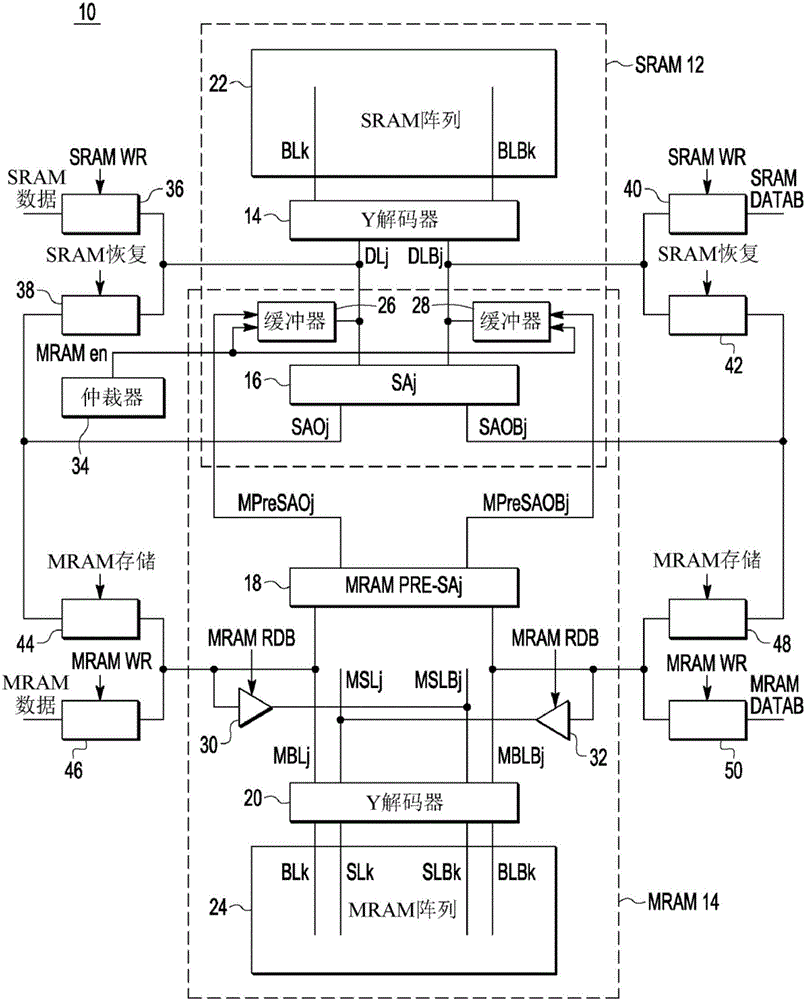
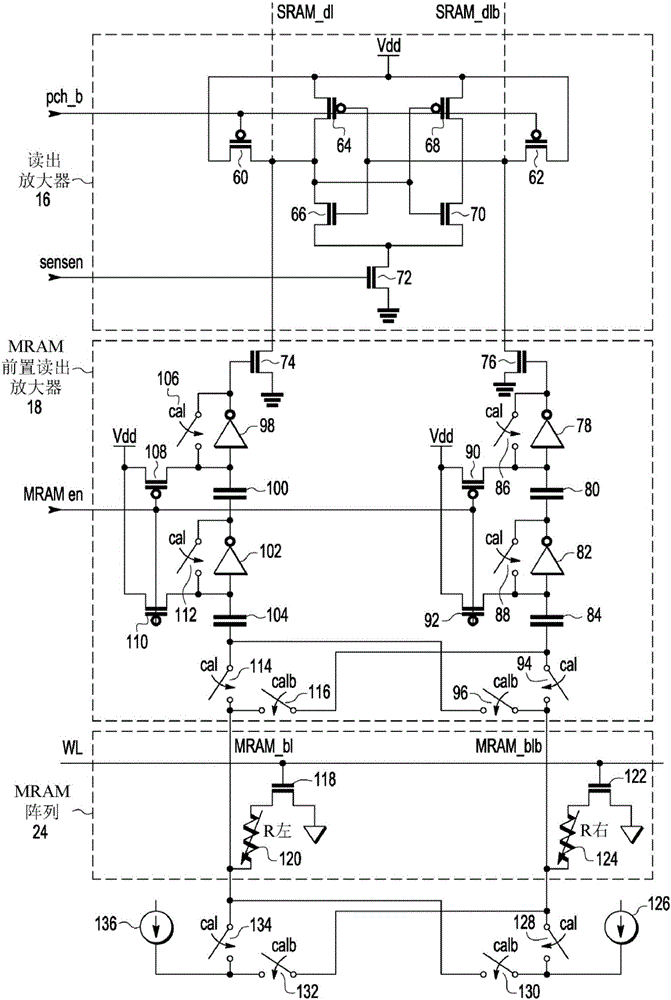
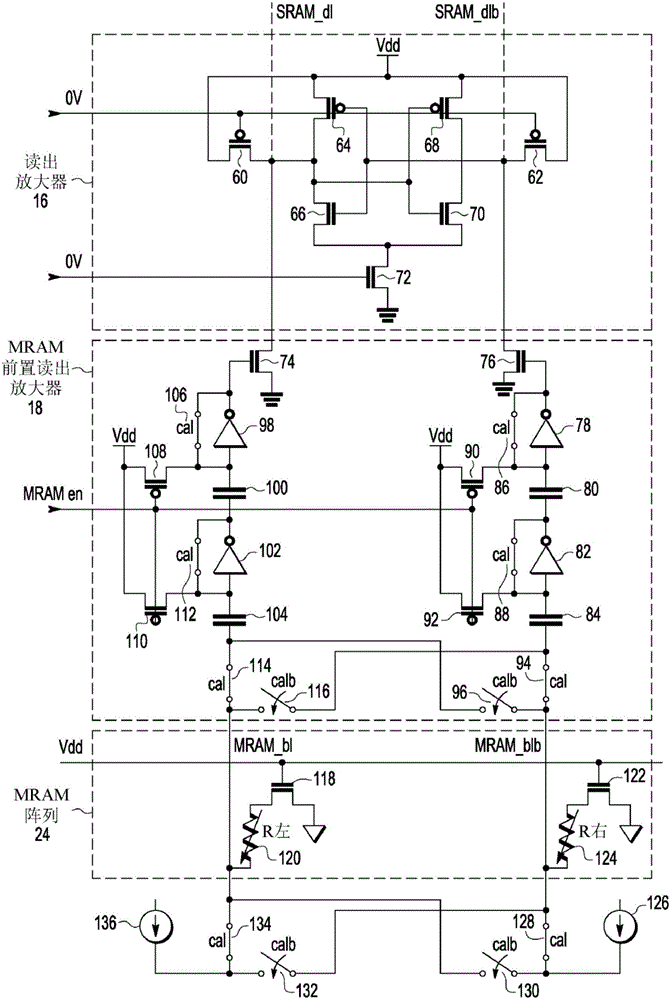
Nonvolatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) system having a static random access memory (SRAM) array and a resistive memory array
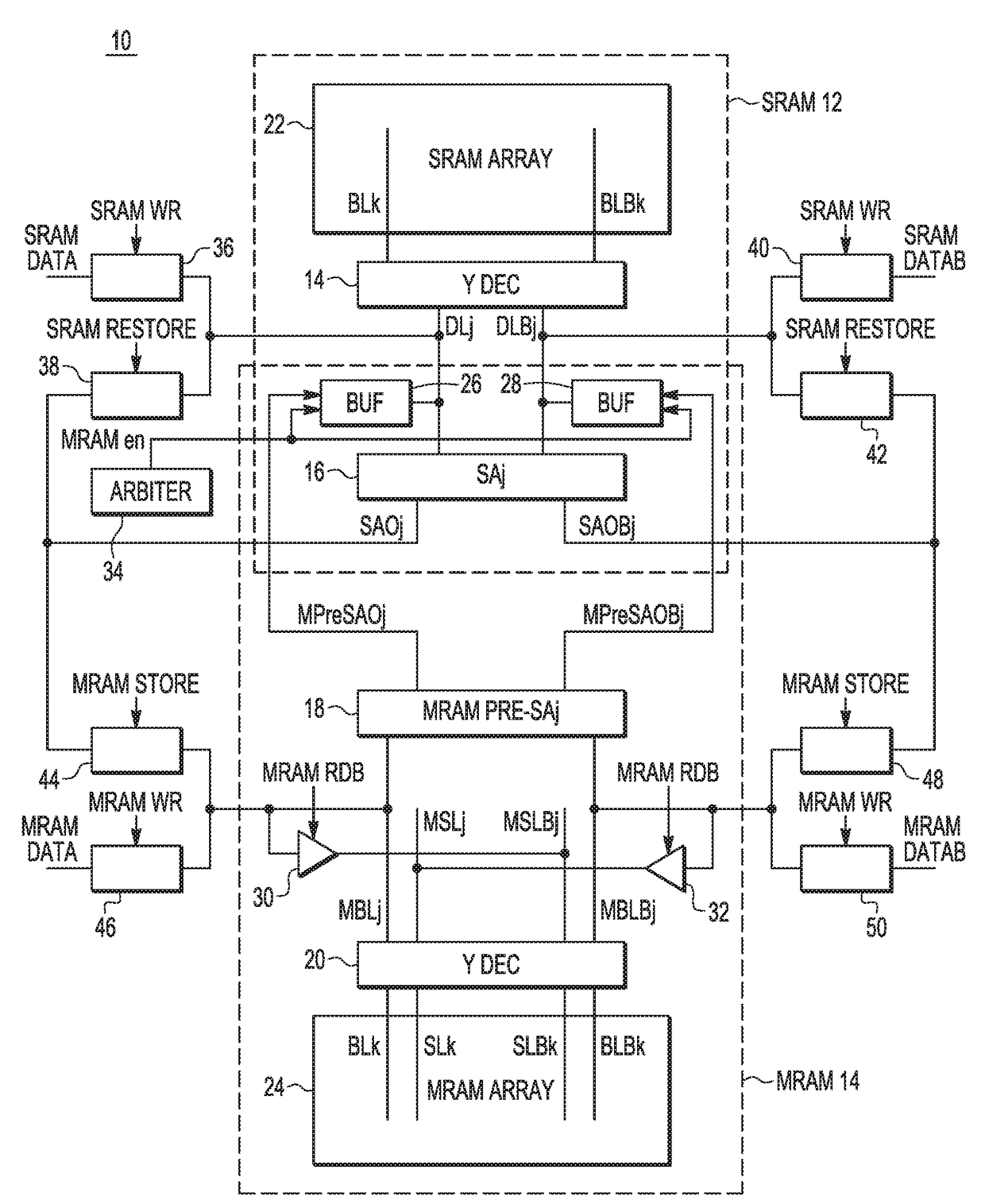
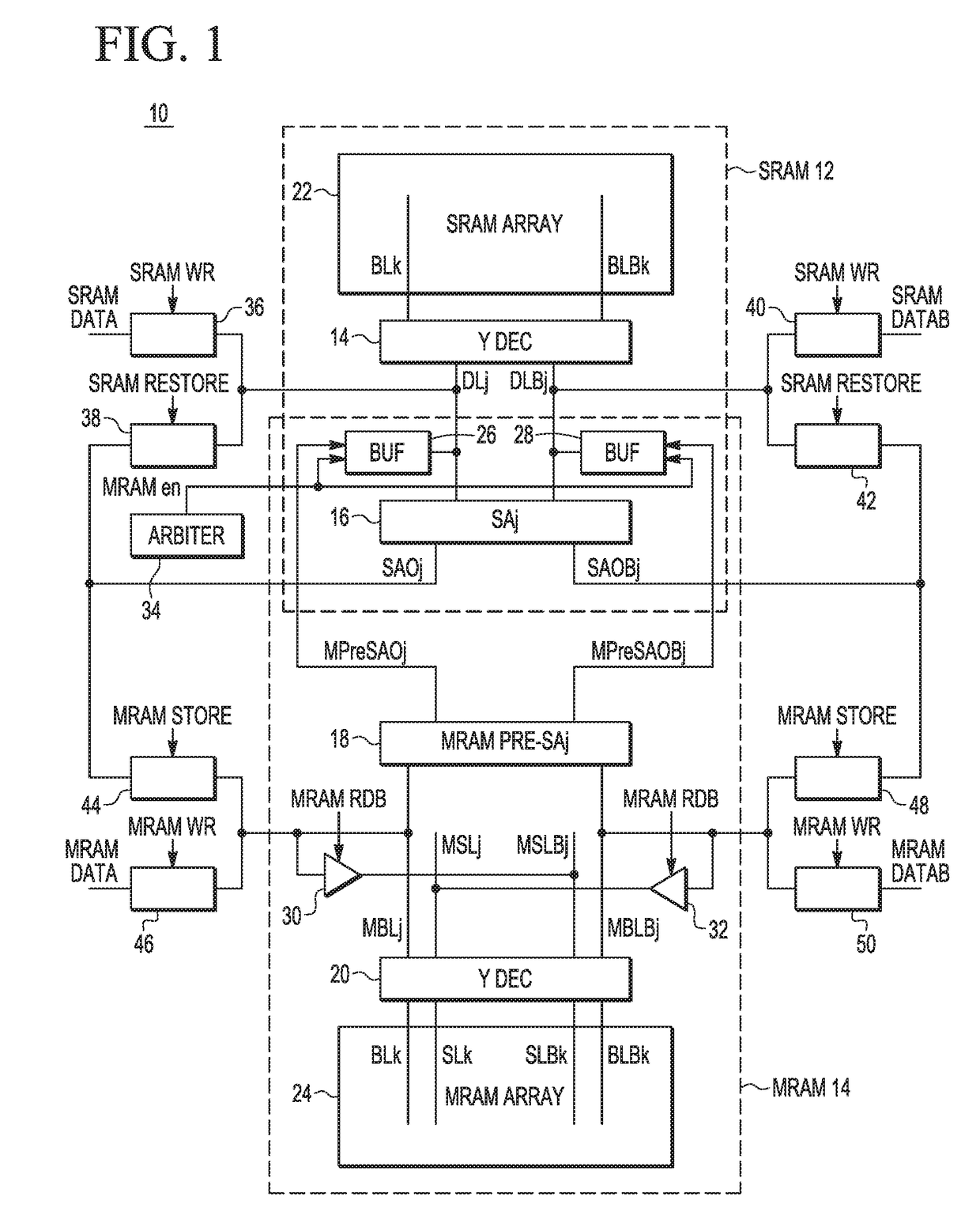
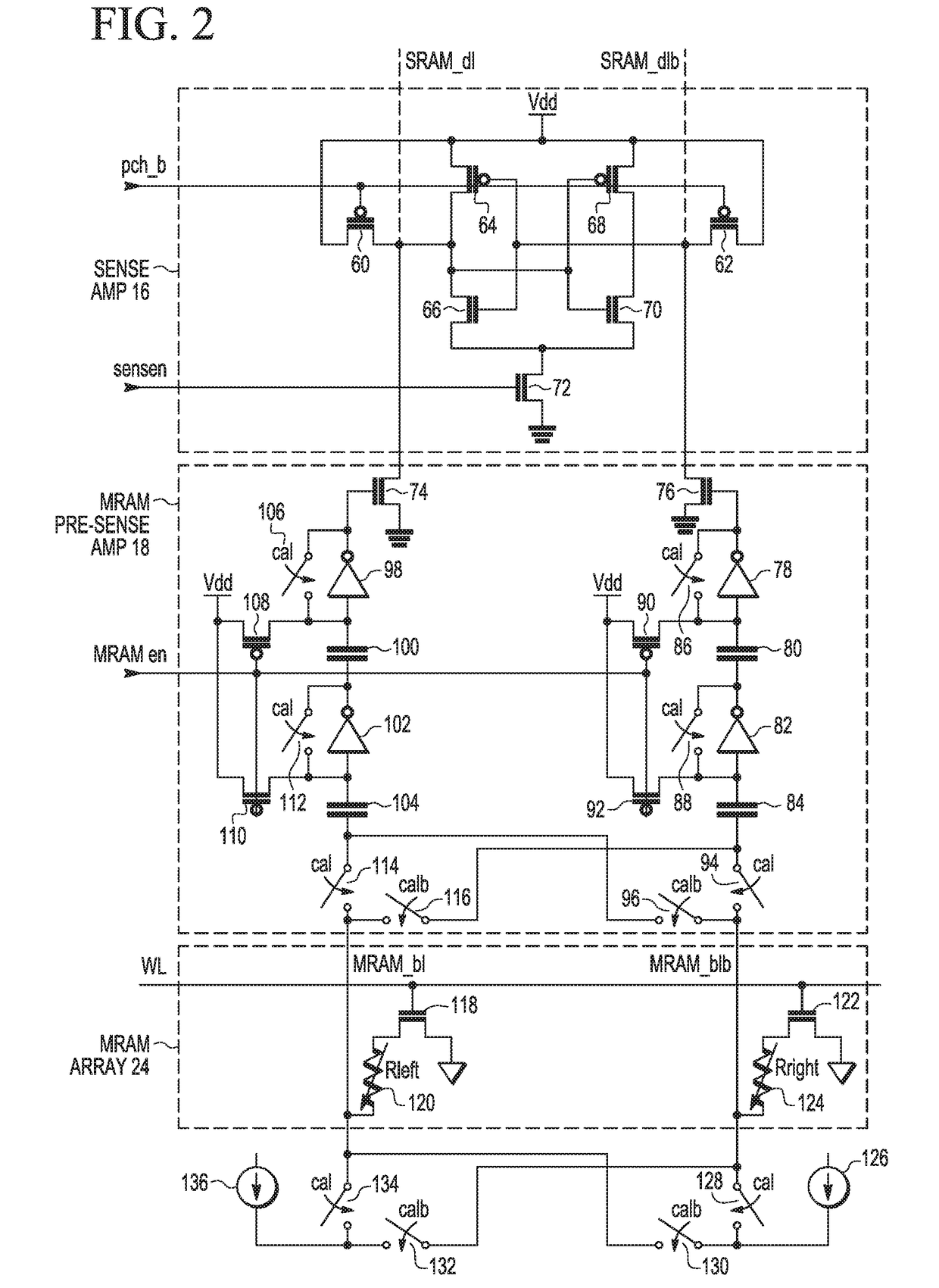
ActiveUS9640256B1Electric analogue storesSolid-state devicesStatic random-access memoryAudio power amplifier
An integrated circuit (IC) device includes a static random access memory (SRAM) array, and a resistive memory (resistive memory) array. A first set of programmable resistive elements in the resistive memory array are used to store data from memory cells in the SRAM array. Sense amplifier circuitry is couplable to the SRAM array and the resistive memory array. An arbiter is configured to assert an resistive memory enable signal to couple the sense amplifier circuitry to the resistive memory array and decouple the sense amplifier circuitry from the SRAM array during a resistive memory read operation, and to couple the sense amplifier to the SRAM array and decouple the sense amplifier circuitry from the resistive memory array during an SRAM read operation.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Low-voltage fast-write nvsram cell
InactiveUS20130294161A1Improve performanceQuickly and correctly programmedRead-only memoriesDigital storageTrappingLow voltage
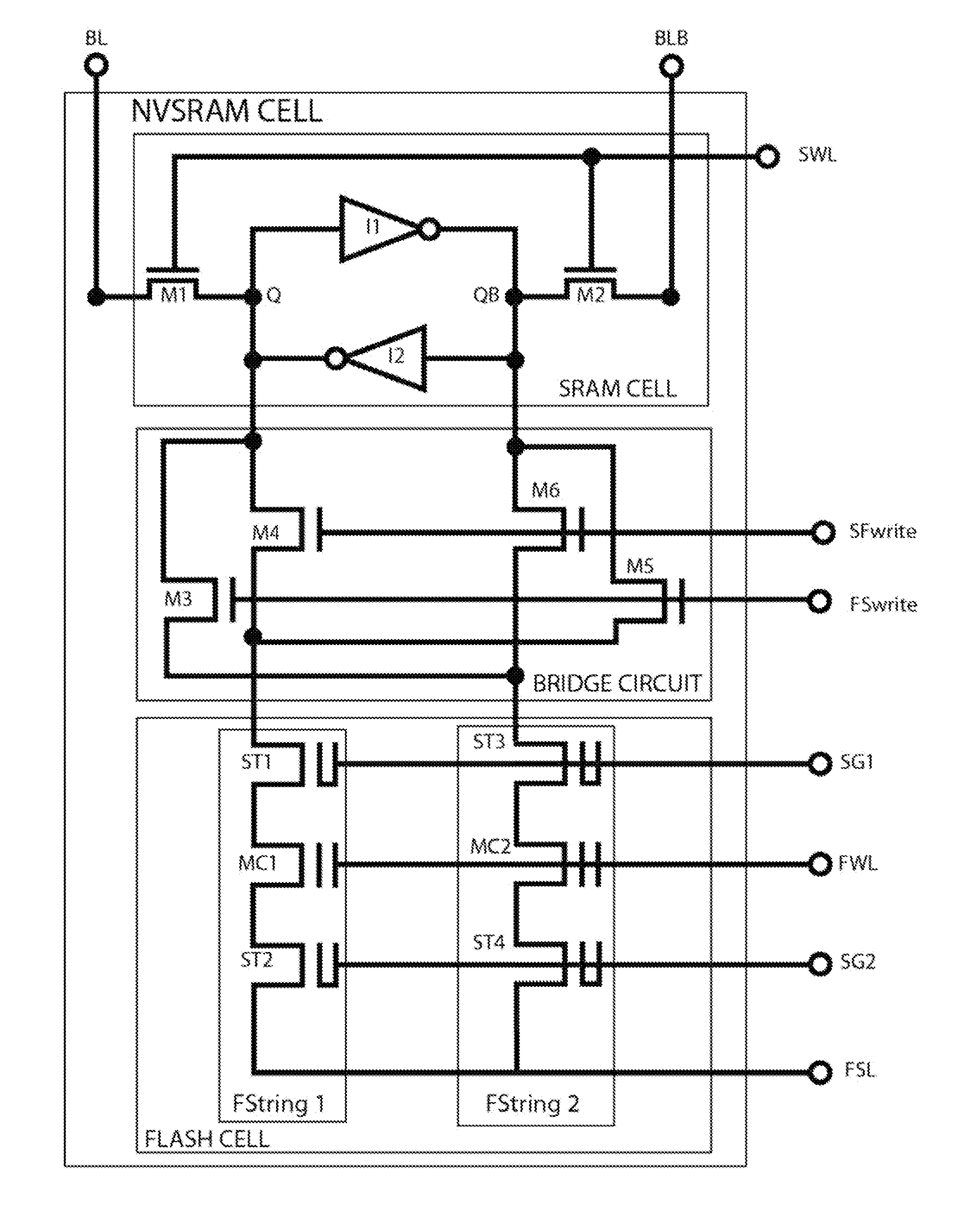
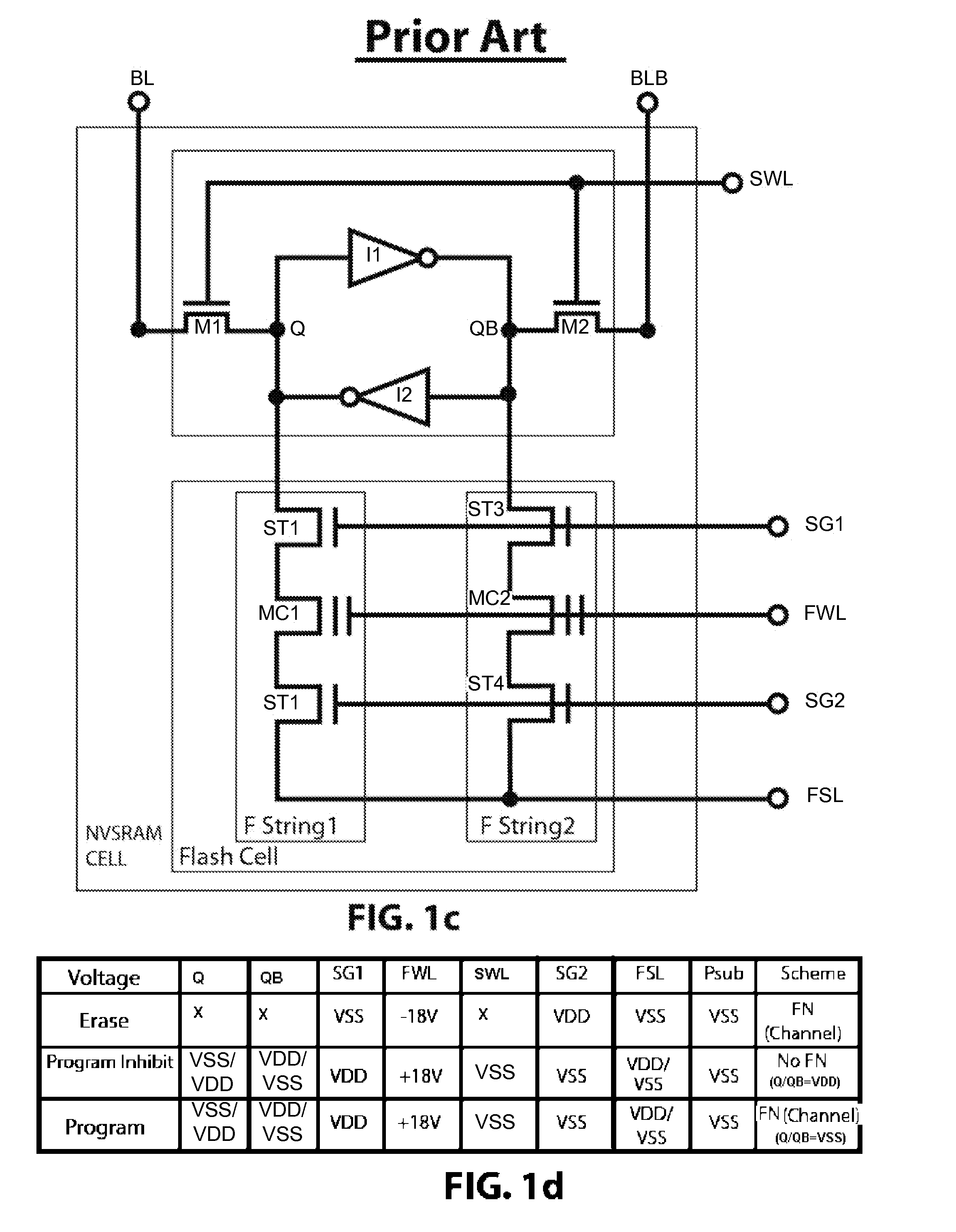
This invention discloses several embodiments of a low-voltage fast-write NVSRAM cells, made of either of a 2-poly floating-gate type flash cell or a 1-poly charge-trapping SONOS or MONOS flash cell with improvement by adding a Bridge circuit. This Bridge circuit is preferably inserted between each LV 6T SRAM cell and each HV Flash cell that comprises one paired complementary Flash strings. The Flash strings can be made of either 2T or 3T Flash strings. The tradeoff of using either a 2T or a 3T Flash string is subject to the gate area penalty and required design specs. One improvement for adding the Bridge circuit into the NVSRAM cell is to ensure the data writing between Flash cell and SRAM cell with the same polarity and to allow the operation down to low 1.2V Vdd.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Non-volatile static random access memory (nvsram) device
A non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) device includes a volatile circuit and a non-volatile circuit. Under normal operations when an external power is supplied, the volatile circuit can provide fast data access. When the power supply is somehow interrupted, the non-volatile circuit can provide data backup using an inverter circuit and a non-volatile erasable programmable memory (NVEPM) circuit, thereby retaining data previously stored in the volatile circuit.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
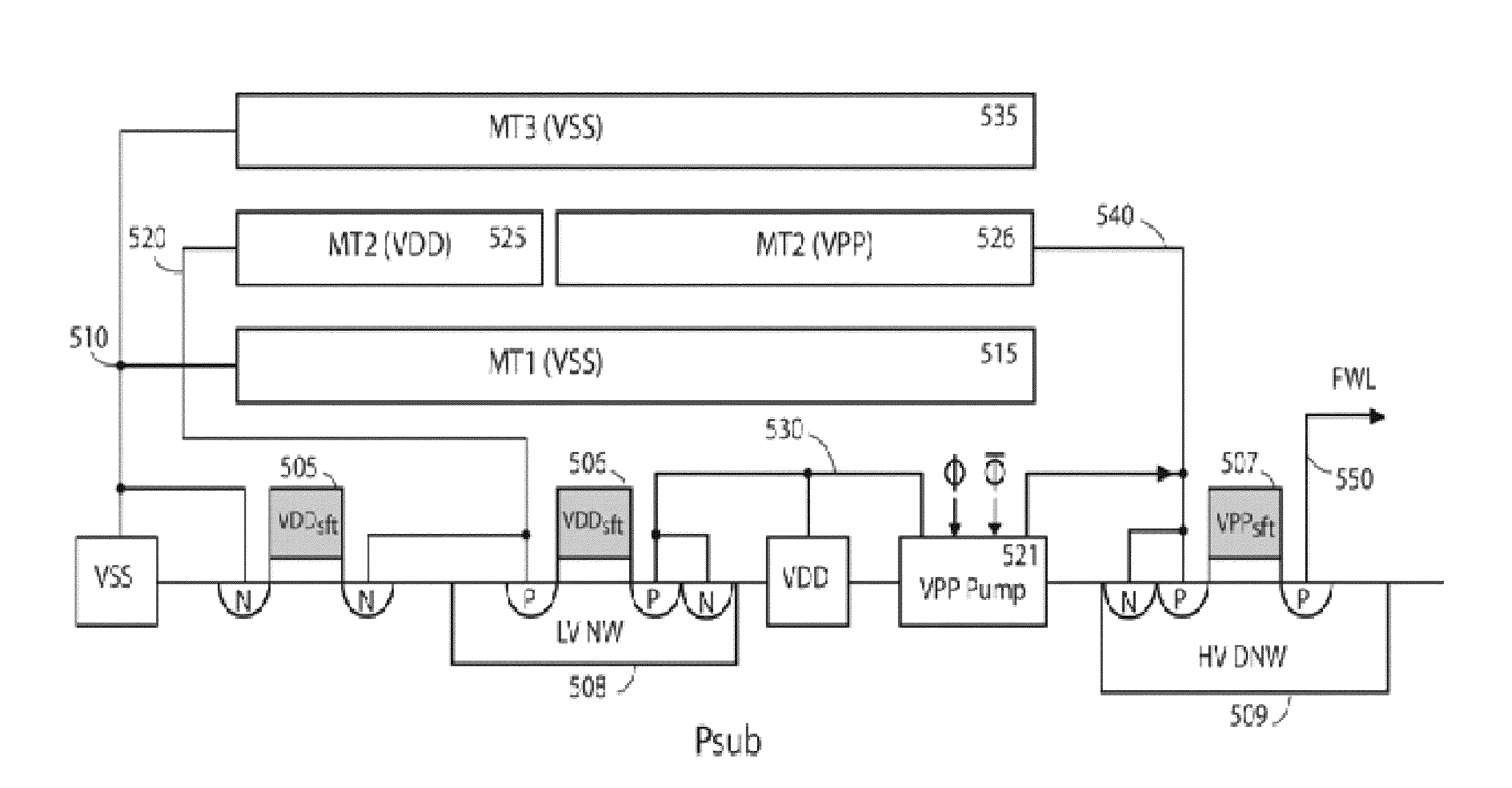
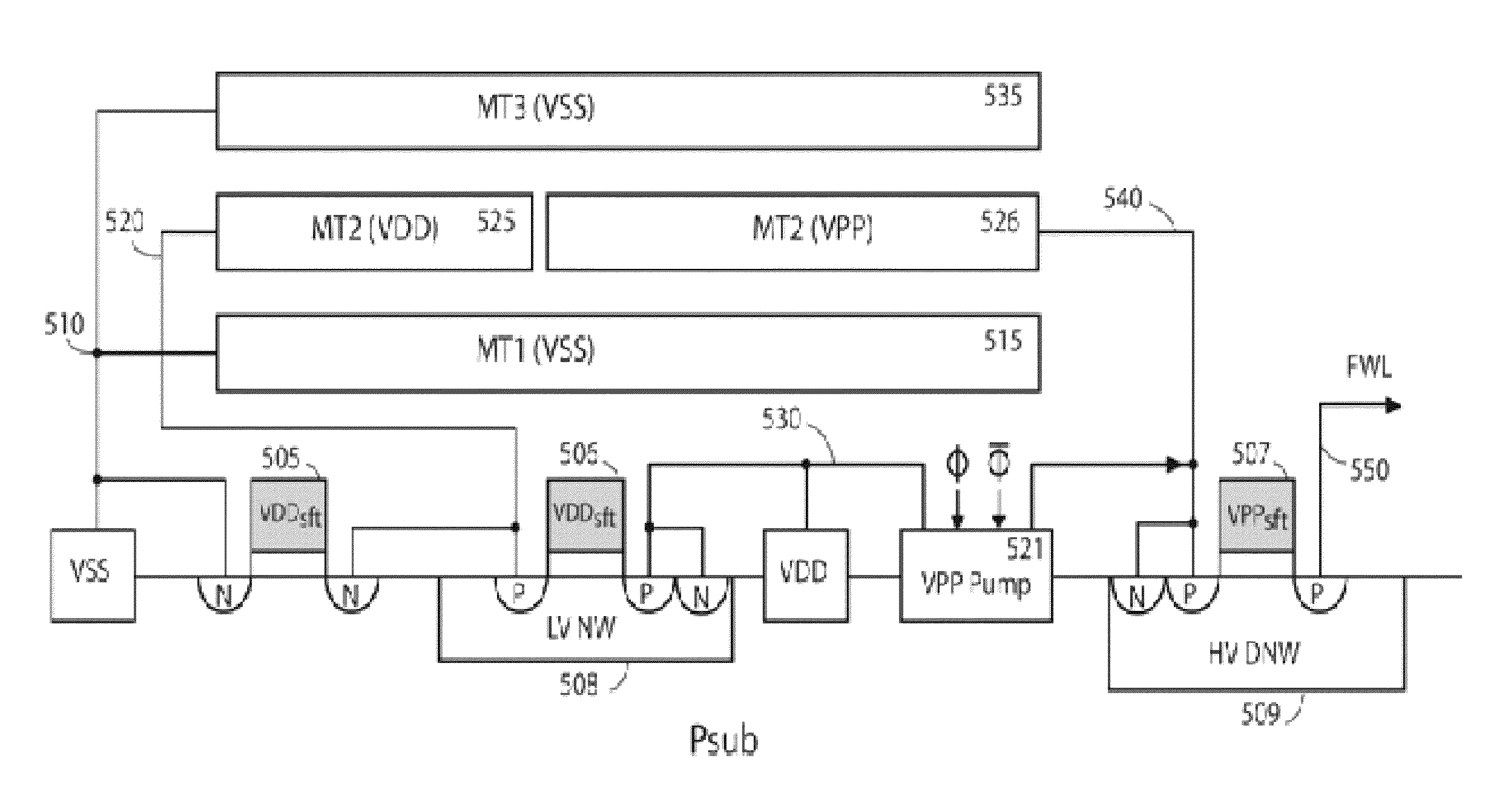
On-chip HV and LV capacitors acting as the second back-up supplies for nvsram auto-store operation
InactiveUS20140104946A1Reduce frequency of oscillatorRapid paceRead-only memoriesDigital storageMemory chipCapacitance
Two on-chip capacitors including one HV capacitor VPPcap and one LV VCC capacitor VCCcap are built over a NVSRAM memory chip as a back-up second power supplies for each NVSRAM cell, regardless of 1-poly, 2-poly, PMOS or NMOS flash cell structures therein. The on-chip HV and LV capacitors are preferably made from one or more MIM or MIP layers for achieving required capacitance. A simplified VCC power system circuit without a need of a State machine designed for performing only one NVSRAM Program operation without Erase operations is proposed for initiating NVSRAM's Auto-Store operation without using any off-chip Vbat and Vcap. During the Auto-Store operation, all HV pumps and oscillators associated with the two on-chip capacitors are shut off once VCC voltage drop is detected by a VCC detector to be below 80% of regular VDD level.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
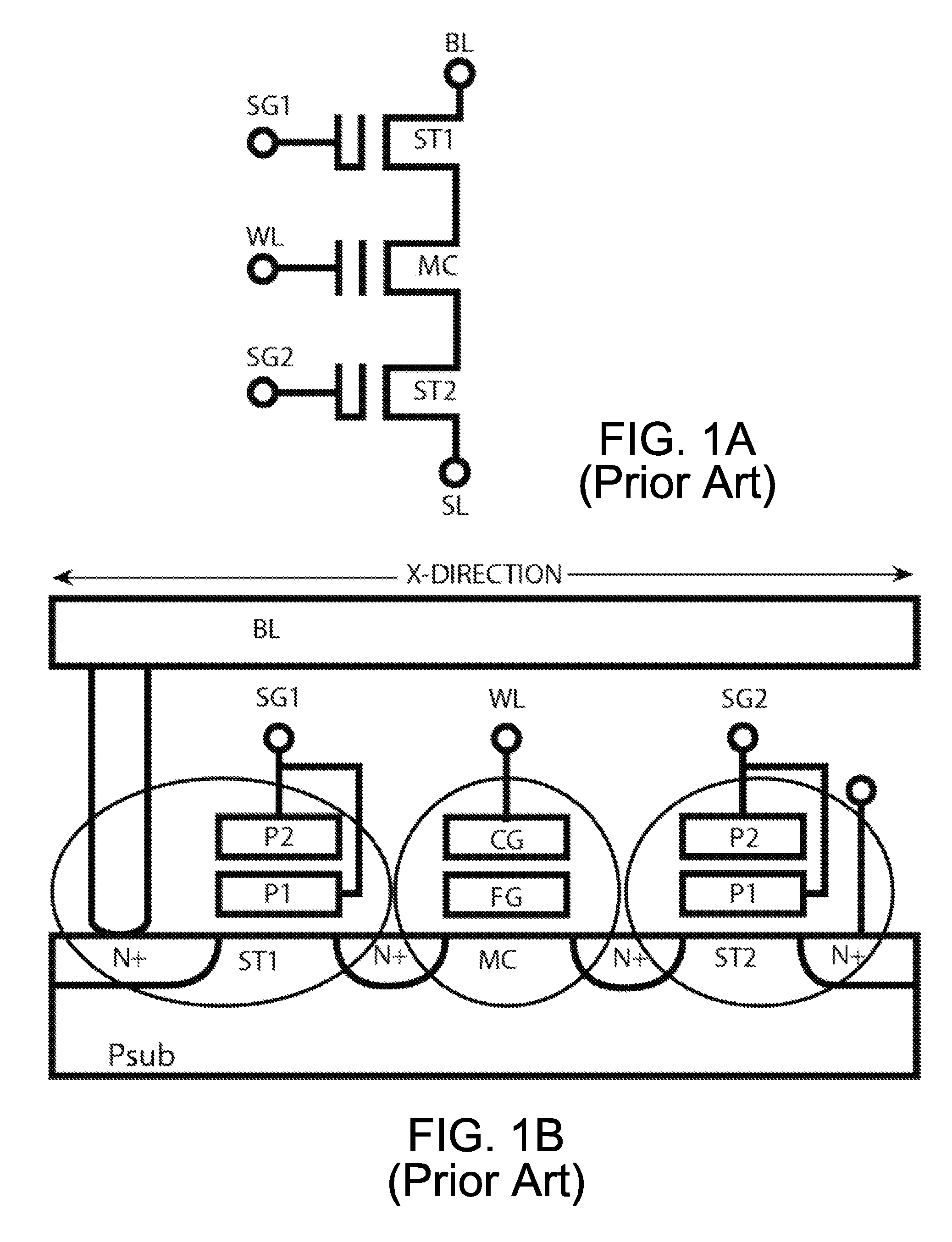
10t nvsram cell and cell operations
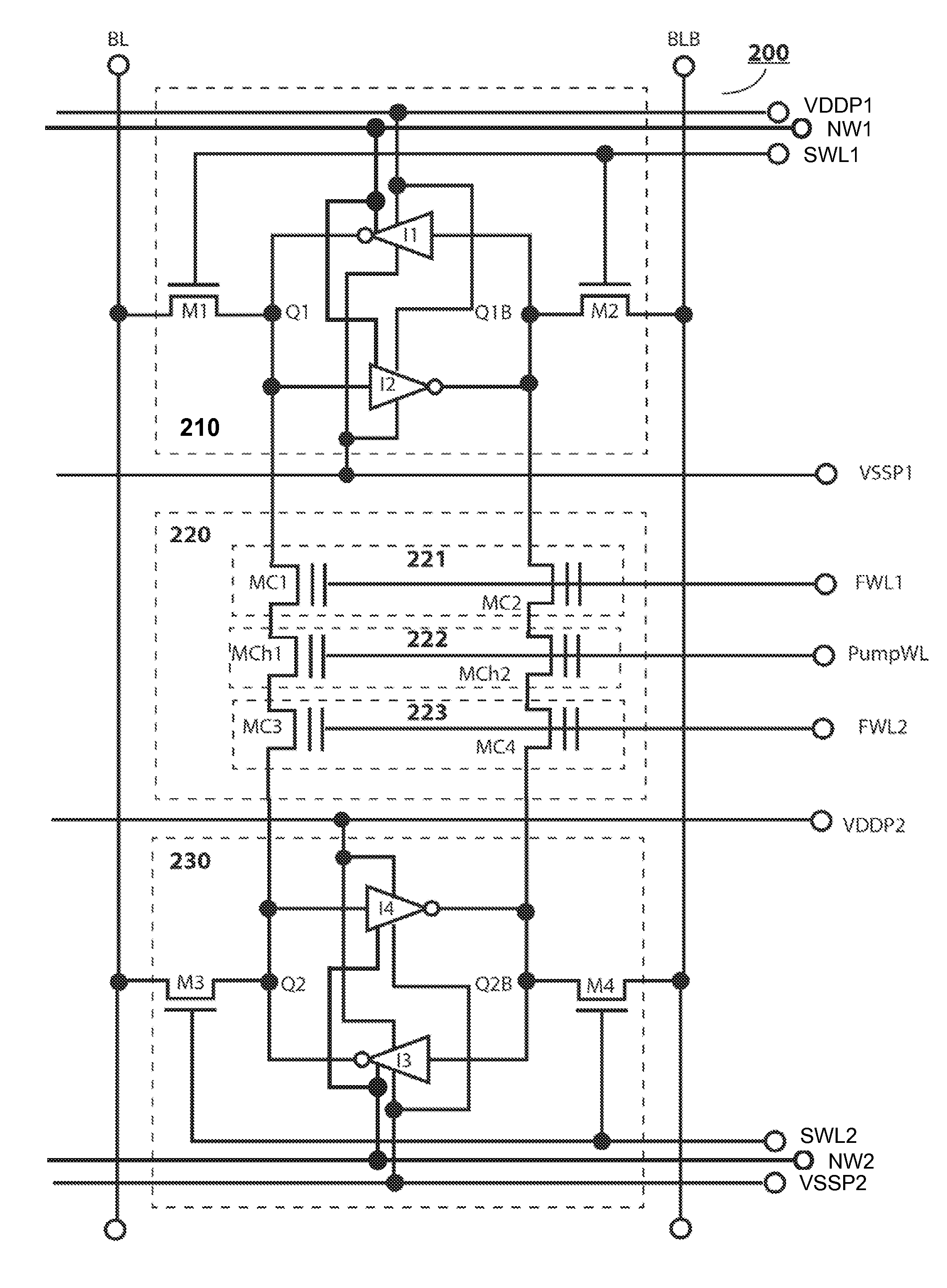
A 10T NVSRAM cell is provided with a bottom HV NMOS Select transistor in each 3T FString removed from traditional 12T NVSRAM cell. A Recall operation by reading a stored ΔVt state of flash transistors into each SRAM cell uses a charge-sensing scheme rather than the current-sensing scheme, with all other key operations unchanged. The Recall operation works under any ramping rate of SRAM's power line voltage and Flash gate signal which can be set higher than only Vt0 or both Vt0 and Vt1. Alternatively, the Store operation can use a current charging scheme from a Fpower line to the paired Q and QB nodes of each SRAM cell through a paired Flash Voltage Follower that stored ΔVtp≧1.0V. The Recall operation in this alternative embodiment is to use a 7-step approach with the FN-channel erase, FN-channel program and FN-edge program schemes, including 2-step SRAM amplification.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
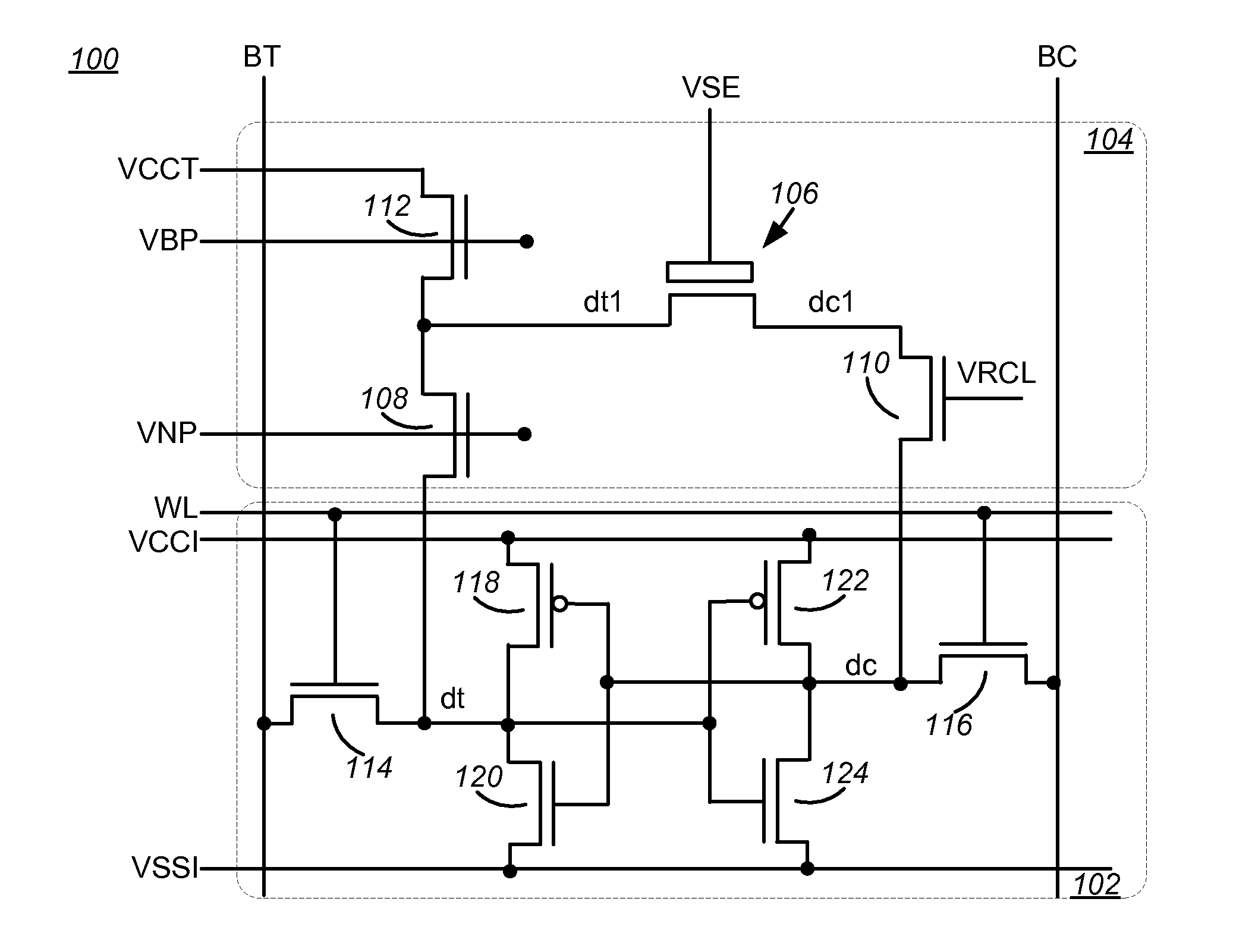
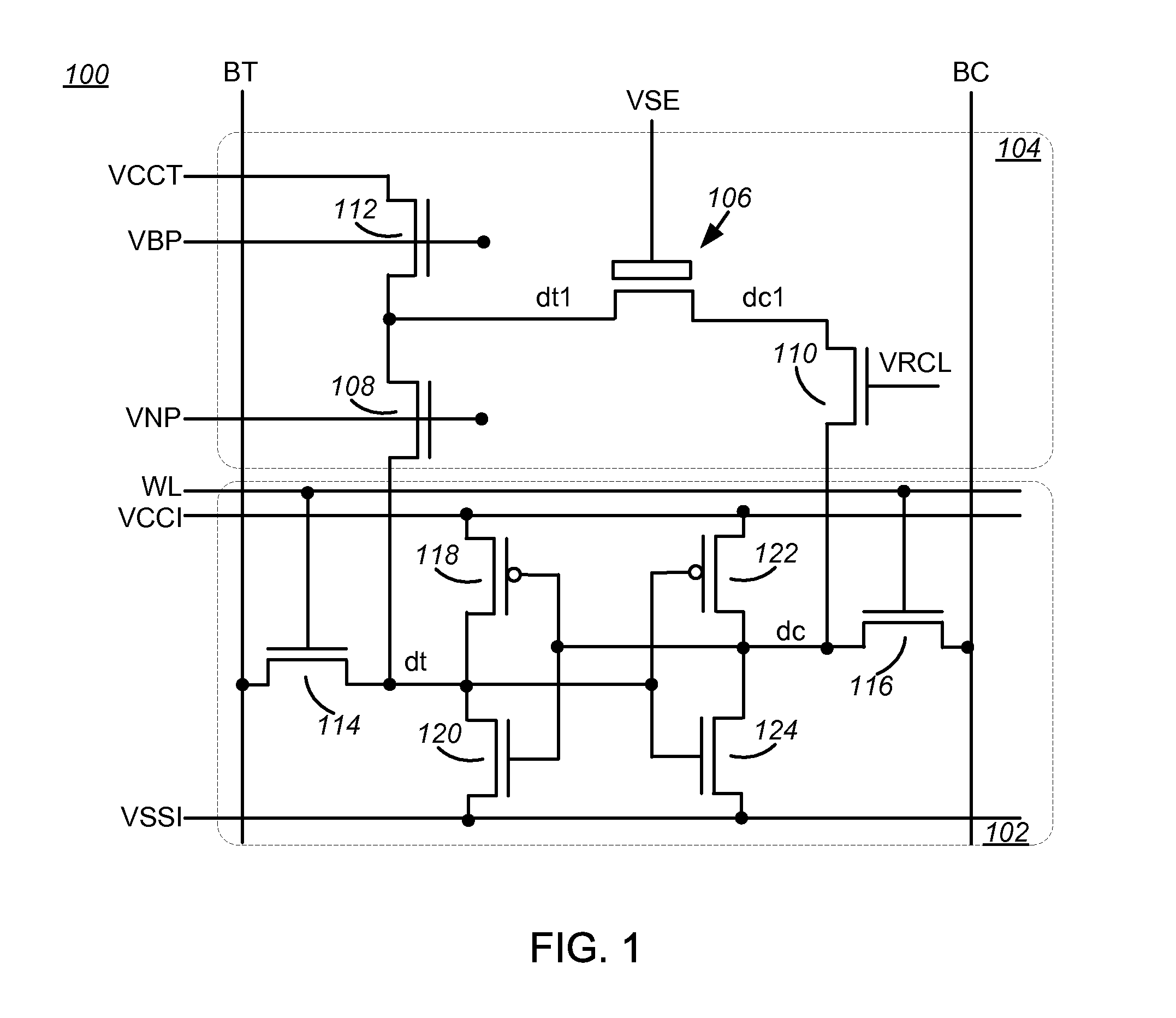
Nvsram cells with voltage flash charger
The present invention discloses two preferred embodiments of a 12 T NVSRAM cell with a flash-based Charger and a pseudo 10 T NVSRAM cell with one shared Flash-based Charger. The Flash-based Charger can be made of a 2-poly floating-gate type or a 1-poly charge-trapping SONOS / MONOS flash type, regardless of PMOS type or NMOS type. In an alternative embodiment, the Store operation of above two preferred NVSRAM cell use a DRAM-like charge-sensing scheme with Flash cell configured into a voltage follower associated with Flash Charger and 2-step SRAM amplification technique to amplify the threshold level difference ΔVt stored in the paired Flash transistors. The ΔVt can be detected as low as 1V when the coupled charges through the Flash charger are sufficient by ramping a gate control of the Flash Charger as high as VPP or by increasing the channel length for the Flash Charger.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
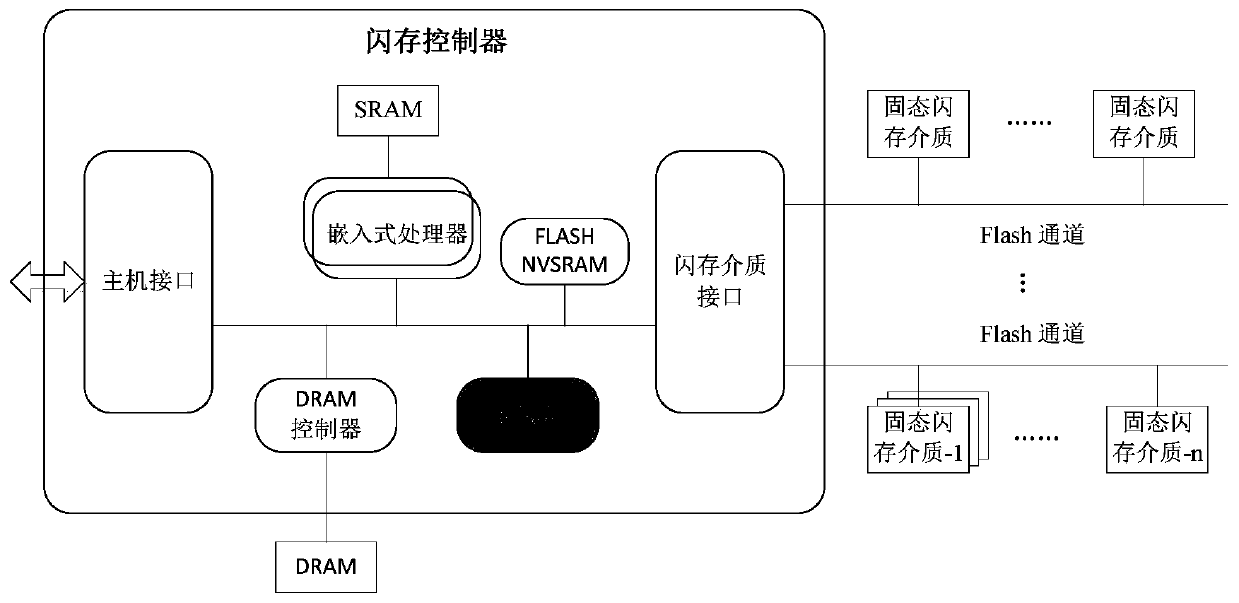
A reconfigurable computing storage fusion flash memory control system
PendingCN109947694AReduce movementWith programmableEnergy efficient computingArchitecture with single central processing unitControl storeControl system
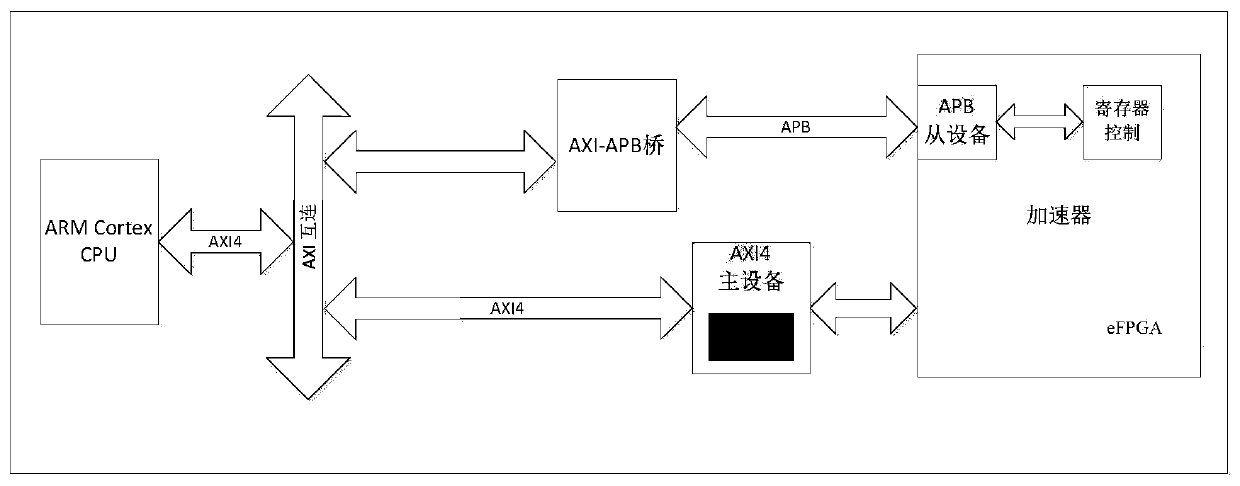
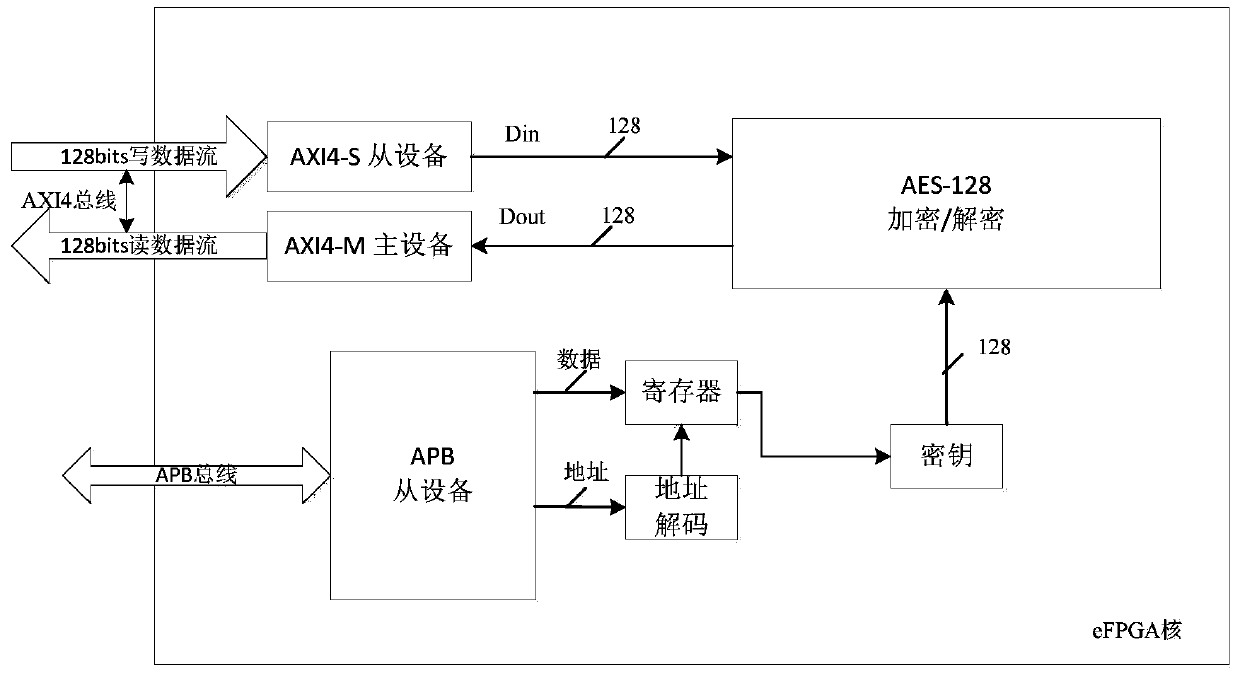
The invention discloses a reconfigurable computing storage fusion flash memory control system which comprises a host interface, a flash memory medium interface, an embedded processor, a cache and storage controller, an on-chip FLASH, an NVSRAM and an embedded FPGA, and all hardware modules are mounted on an internal bus and communicate through the internal bus. And the embedded FPGA is used for calculating hardware acceleration of tasks, generating a bit stream file in a software environment and reburning the bit stream file, changing the internal structure of the embedded FPGA, arranging andwiring the embedded FPGA, realizing different functions and realizing a reconfigurable hardware acceleration function. The method solves the problems of bandwidth wall and high power consumption caused by separation of calculation and storage and the technical problem of chip tape-out function solidification, has the advantages of being programmable, flexible in design, capable of achieving onlineupgrading and secondary development and the like, and can achieve calculation in storage, reduce data movement and reduce power consumption; and the chip hardware is reconfigurable and supports realization of different functions.
Owner:上海威固信息技术股份有限公司
Non-volatile static random access memory devices and methods of operations
Non-Volatile Static Random Access Memory (NVSRAM) cell devices applying only one single non-volatile element embedded in a conventional Static Random Access Memory (SRAM) cell are disclosed. The NVSRAM cell devices can be integrated into a compact cell array. The NVSRAM devices of the invention have a read / write speed of a conventional SRAM and non-volatile property of a non-volatile memory cell. The methods of operations for the NVSRAM devices of the invention are also disclosed.
Owner:SYNERGER INC
Pseudo-8T NVSRAM cell with a charge-follower
InactiveUS8971113B2Small sizeIncrease channel lengthRead-only memoriesDigital storageParasitic capacitanceNvSRAM
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Nonvolatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) system having static random access memory (SRAM) array and resistive memory array
ActiveCN107437426AElectric analogue storesDigital storageStatic random-access memoryAudio power amplifier
An integrated circuit (IC) device includes a static random access memory (SRAM) array, and a resistive memory (resistive memory) array. A first set of programmable resistive elements in the resistive memory array are used to store data from memory cells in the SRAM array. Sense amplifier circuitry is couplable to the SRAM array and the resistive memory array. An arbiter is configured to assert an resistive memory enable signal to couple the sense amplifier circuitry to the resistive memory array and decouple the sense amplifier circuitry from the SRAM array during a resistive memory read operation, and to couple the sense amplifier to the SRAM array and decouple the sense amplifier circuitry from the resistive memory array during an SRAM read operation.
Owner:NXP USA INC
On-chip HV and LV capacitors acting as the second back-up supplies for NVSRAM auto-store operation
InactiveUS9001583B2Improve efficiencySimplify the solution stepsRead-only memoriesDigital storageMemory chipCapacitance
Two on-chip capacitors including one HV capacitor VPPcap and one LV VCC capacitor VCCcap are built over a NVSRAM memory chip as a back-up second power supplies for each NVSRAM cell, regardless of 1-poly, 2-poly, PMOS or NMOS flash cell structures therein. The on-chip HV and LV capacitors are preferably made from one or more MIM or MIP layers for achieving required capacitance. A simplified VCC power system circuit without a need of a State machine designed for performing only one NVSRAM Program operation without Erase operations is proposed for initiating NVSRAM's Auto-Store operation without using any off-chip Vbat and Vcap. During the Auto-Store operation, all HV pumps and oscillators associated with the two on-chip capacitors are shut off once VCC voltage drop is detected by a VCC detector to be below 80% of regular VDD level.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
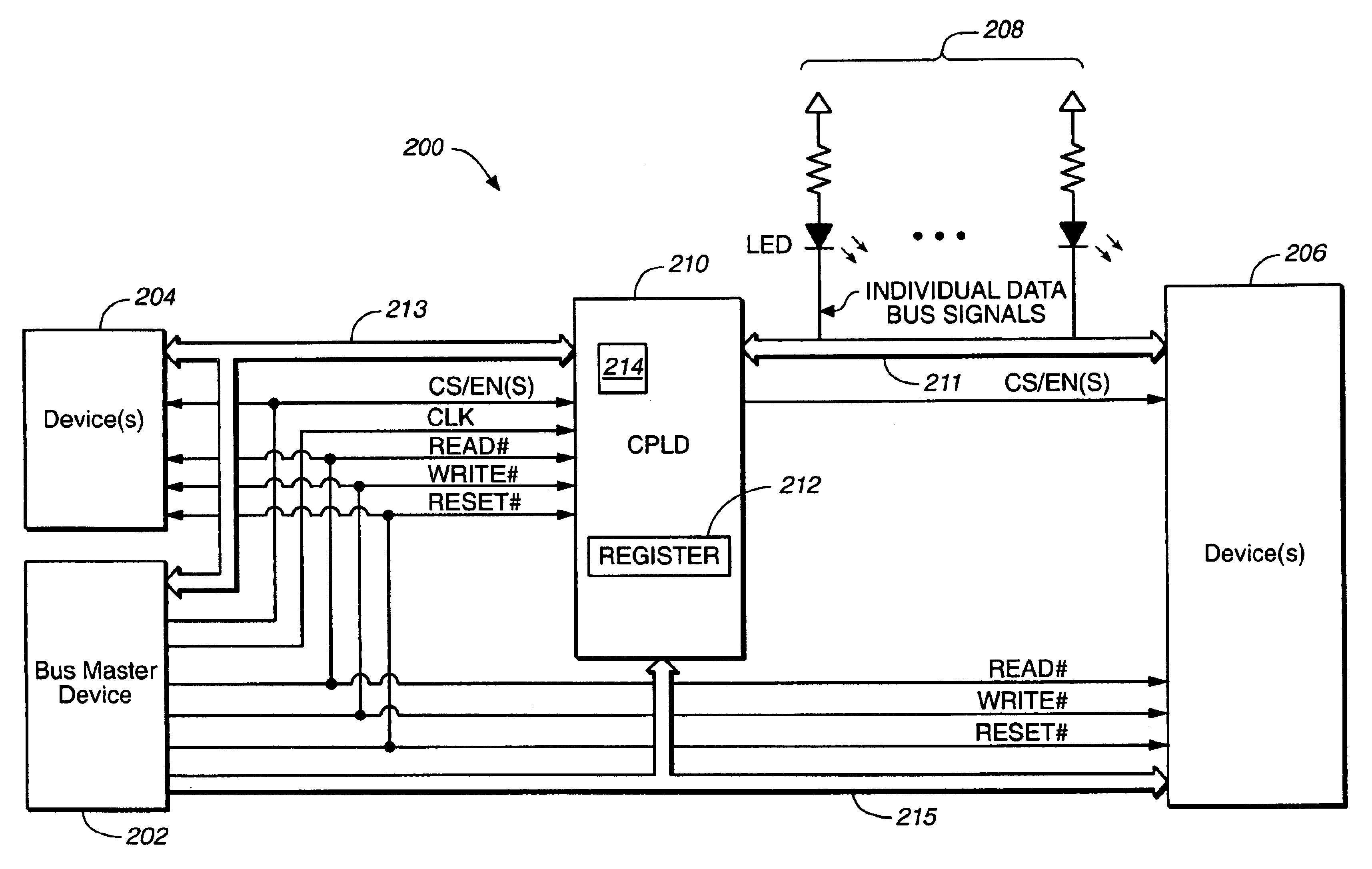
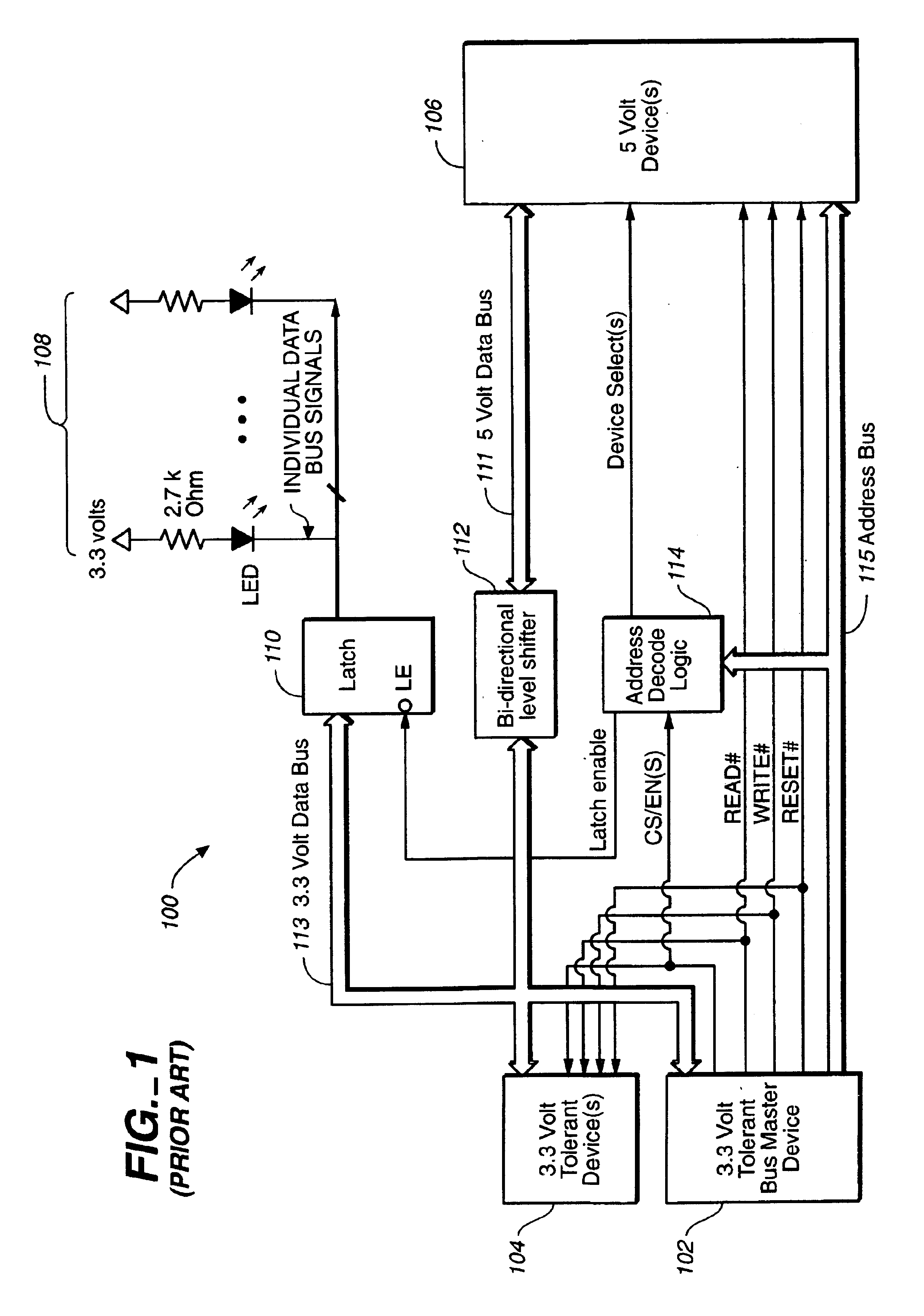
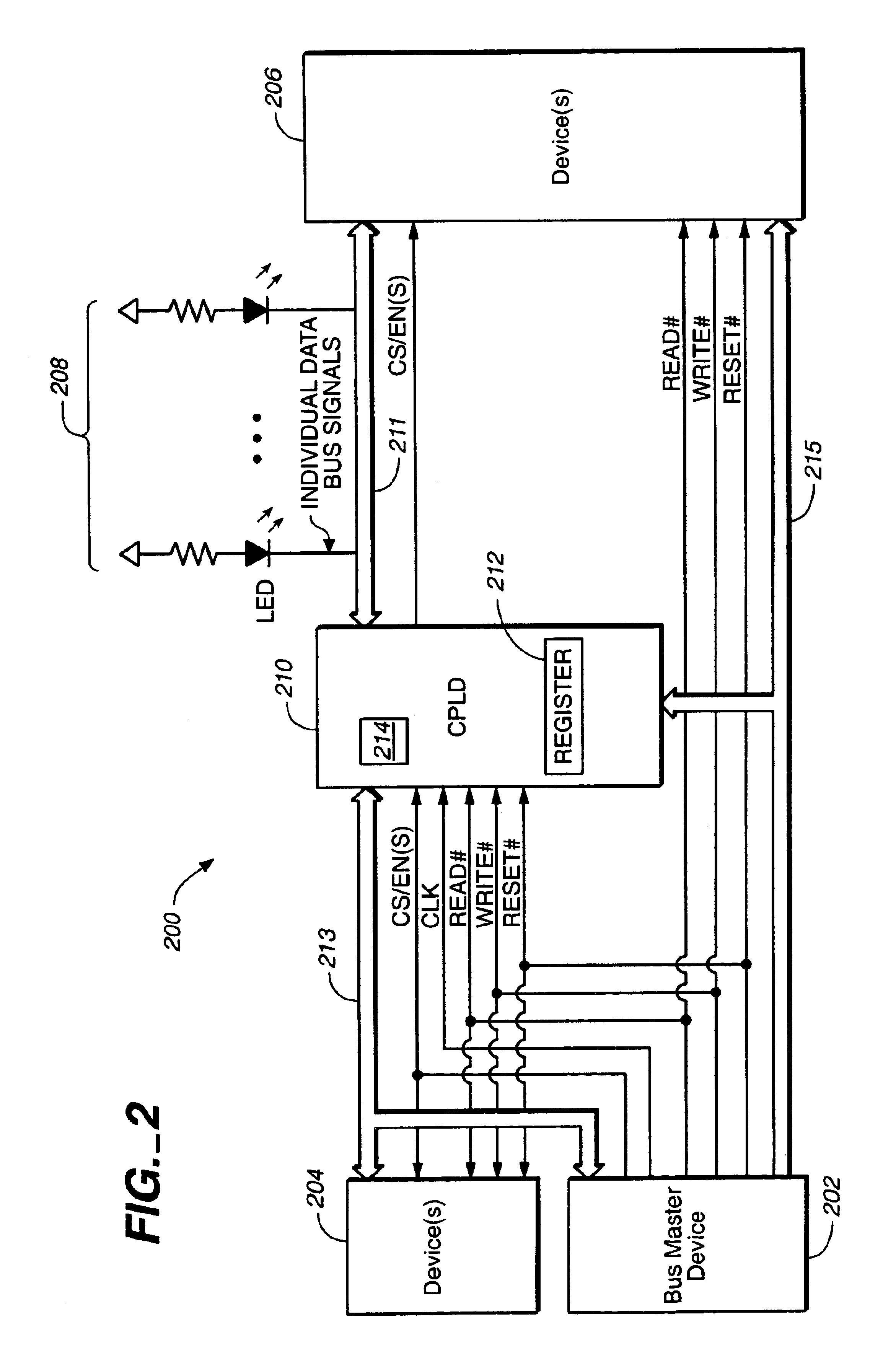
Method and apparatus for transferring data between data buses
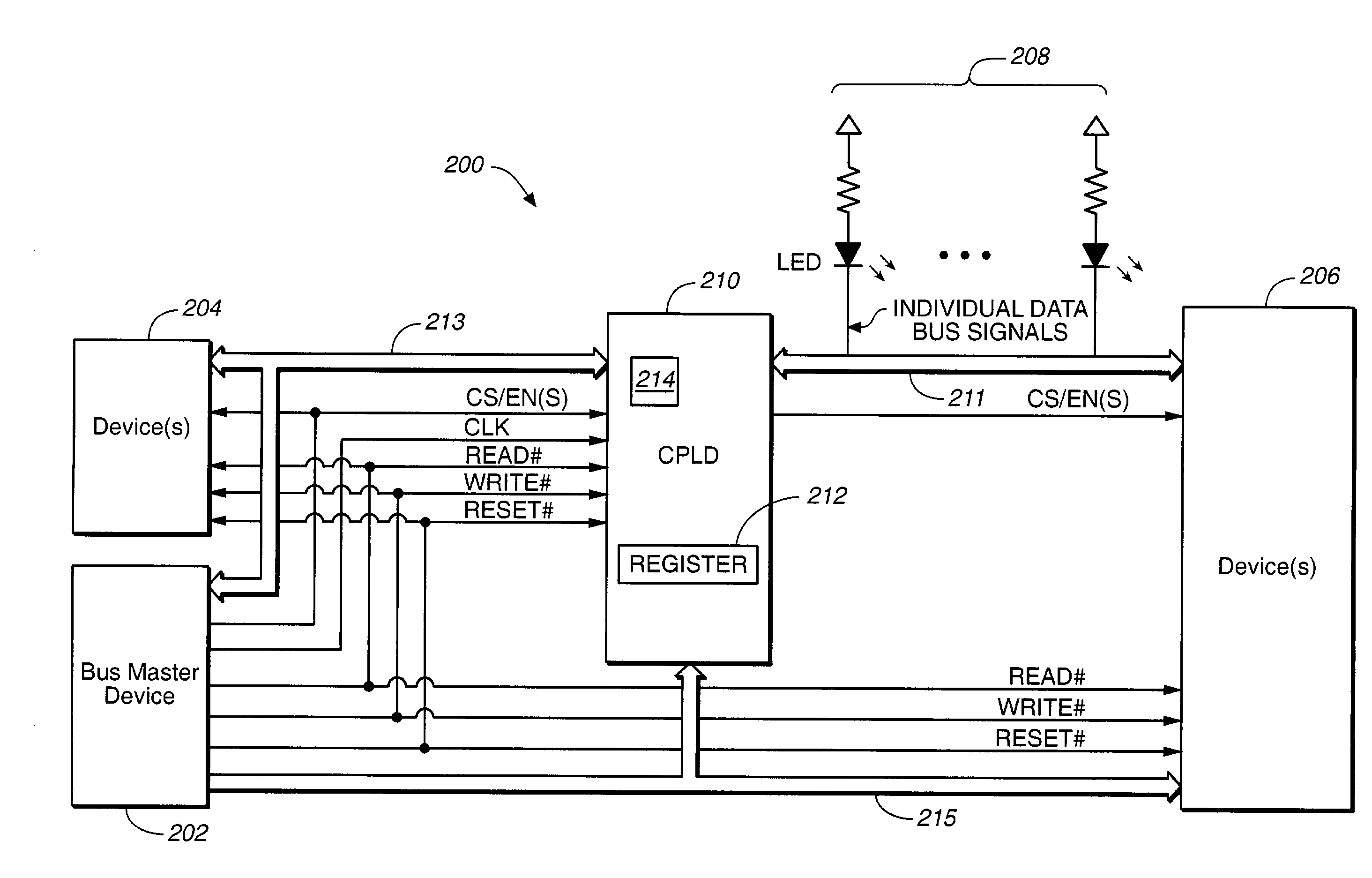
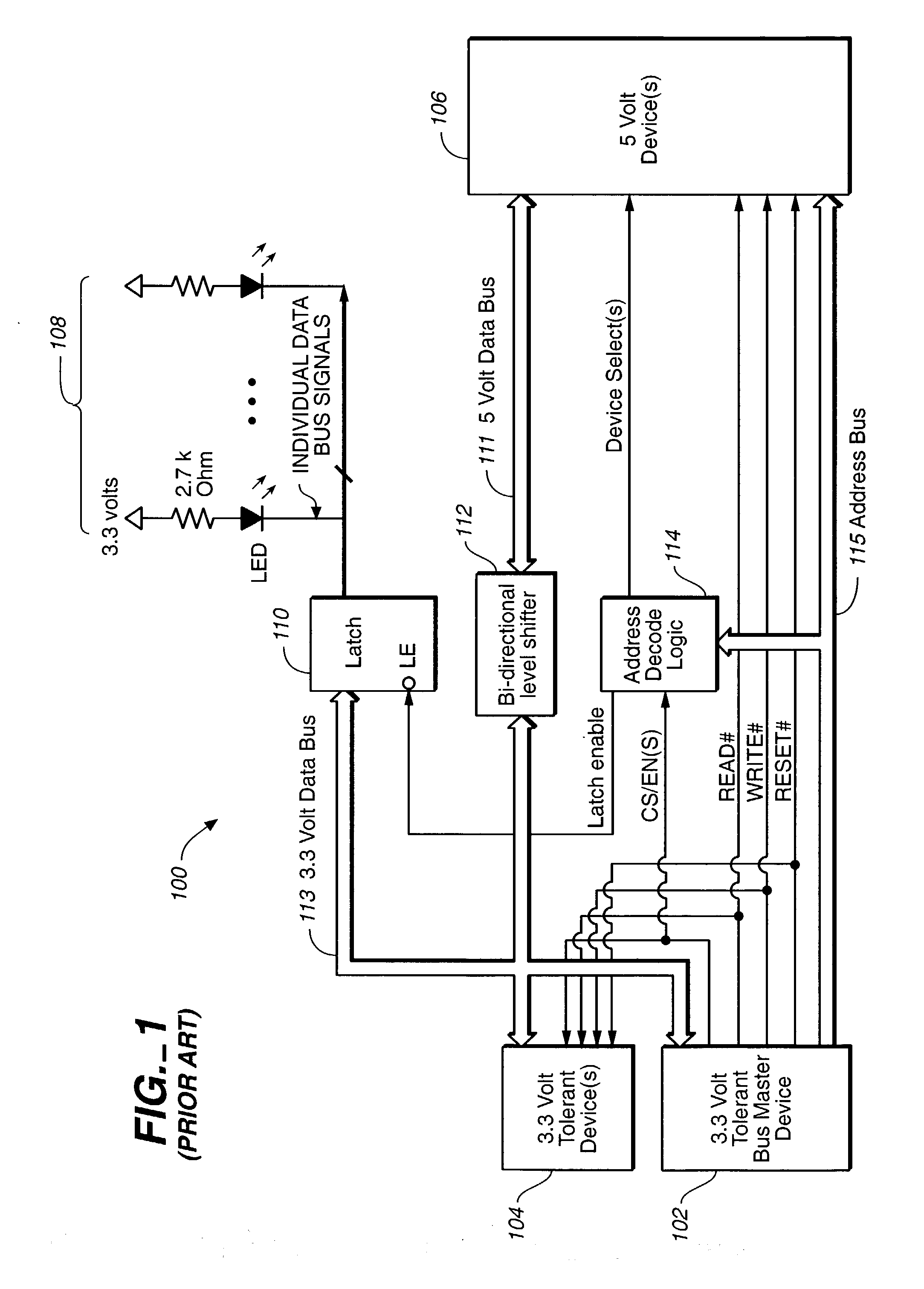
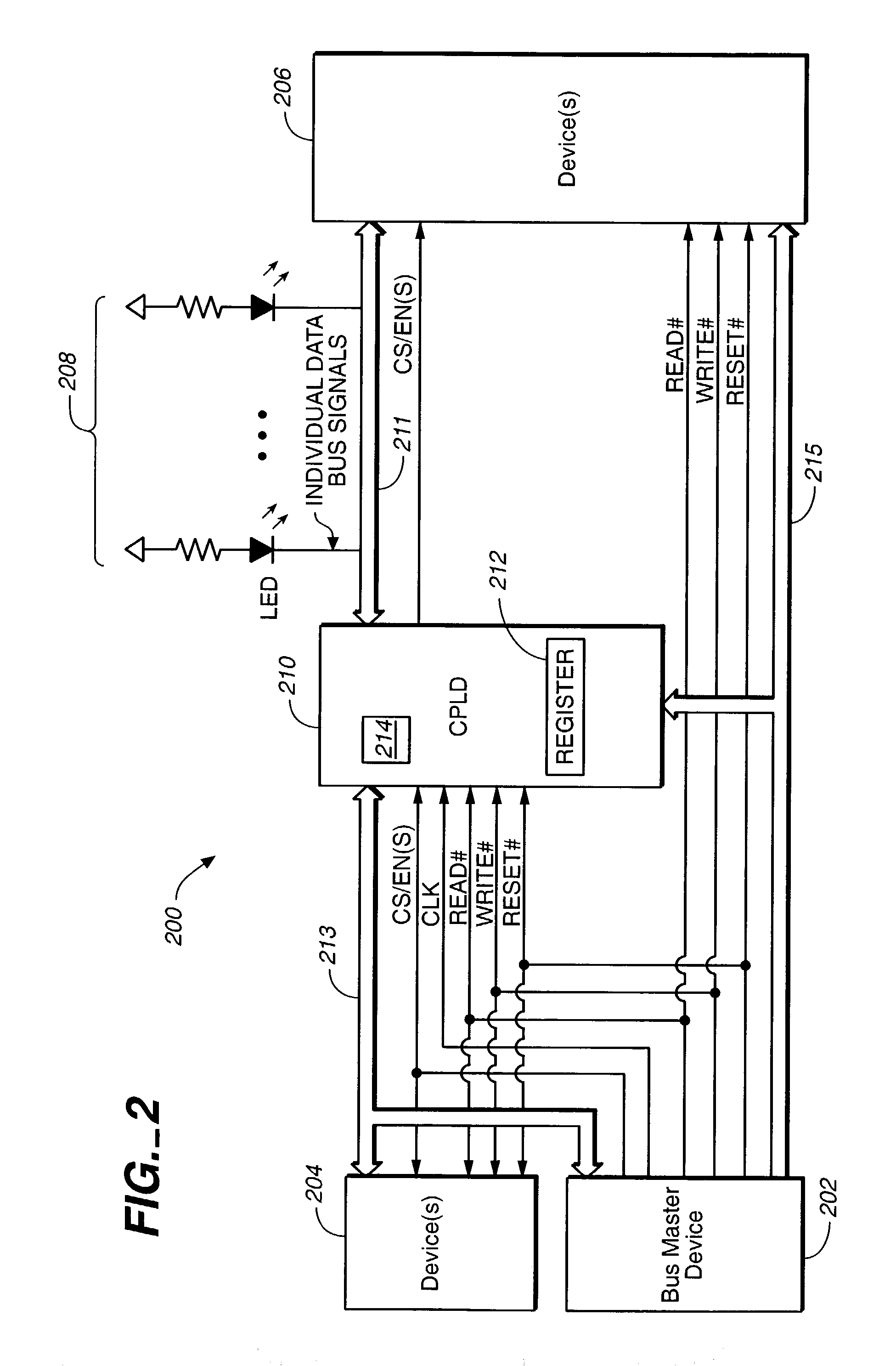
InactiveUS20040061528A1Shorten the counting processReduce power consumptionElectric digital data processingLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsMultiplexingNvSRAM
Systems and methods for transferring data. A circuit transfers information between two buses using different signal voltage levels and multiplexes signals applied to the second bus over multiple devices coupled thereto. The data on a first data bus is transferred at a first voltage level and the data on a second data bus is transferred at a second voltage level. For example, the first data bus may transfer data at 3.3V and the second data bus may transfer data at 5V. A logic device (e.g., a CPLD) is connected between the first and the second data buses for transferring the data between the first and second voltage levels. The logic device is also configured for multiplexing the data with the second voltage level between first and second devices (e.g., one or more LEDs and / or NVSRAMs) connected to the second data bus.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Binary logic utilizing MEMS devices
Embodiments disclosed herein generally relate to switches that utilize micro-electromechanical systems (MEMS). By replacing transistors in many devices with switches such as MEMS switches, the devices may be used for logic applications. MEMS switches may be used in devices such as FPGAs, NAND devices, nvSRAM devices, AMS chips and general memory logic devices. The benefit of utilizing MEMS devices in place of transistors is that the transistors utilize more space on the chip. Additionally, the MEMS devices can be formed in the BEOL without having any negative impacts on the FEOL or necessitating the use of additional layers within the chip.
Owner:QORVO US INC
NVSRAM cells with voltage flash charger
InactiveUS8976588B2Reducing flash cell threshold level differenceEasy to operateRead-only memoriesDigital storageTrappingEngineering
The present invention discloses two preferred embodiments of a 12T NVSRAM cell with a flash-based Charger and a pseudo 10T NVSRAM cell with one shared Flash-based Charger. The Flash-based Charger can be made of a 2-poly floating-gate type or a 1-poly charge-trapping SONOS / MONOS flash type, regardless of PMOS type or NMOS type. In an alternative embodiment, the Store operation of above two preferred NVSRAM cell use a DRAM-like charge-sensing scheme with Flash cell configured into a voltage follower associated with Flash Charger and 2-step SRAM amplification technique to amplify the threshold level difference ΔVt stored in the paired Flash transistors. The ΔVt can be detected as low as 1V when the coupled charges through the Flash charger are sufficient by ramping a gate control of the Flash Charger as high as VPP or by increasing the channel length for the Flash Charger.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
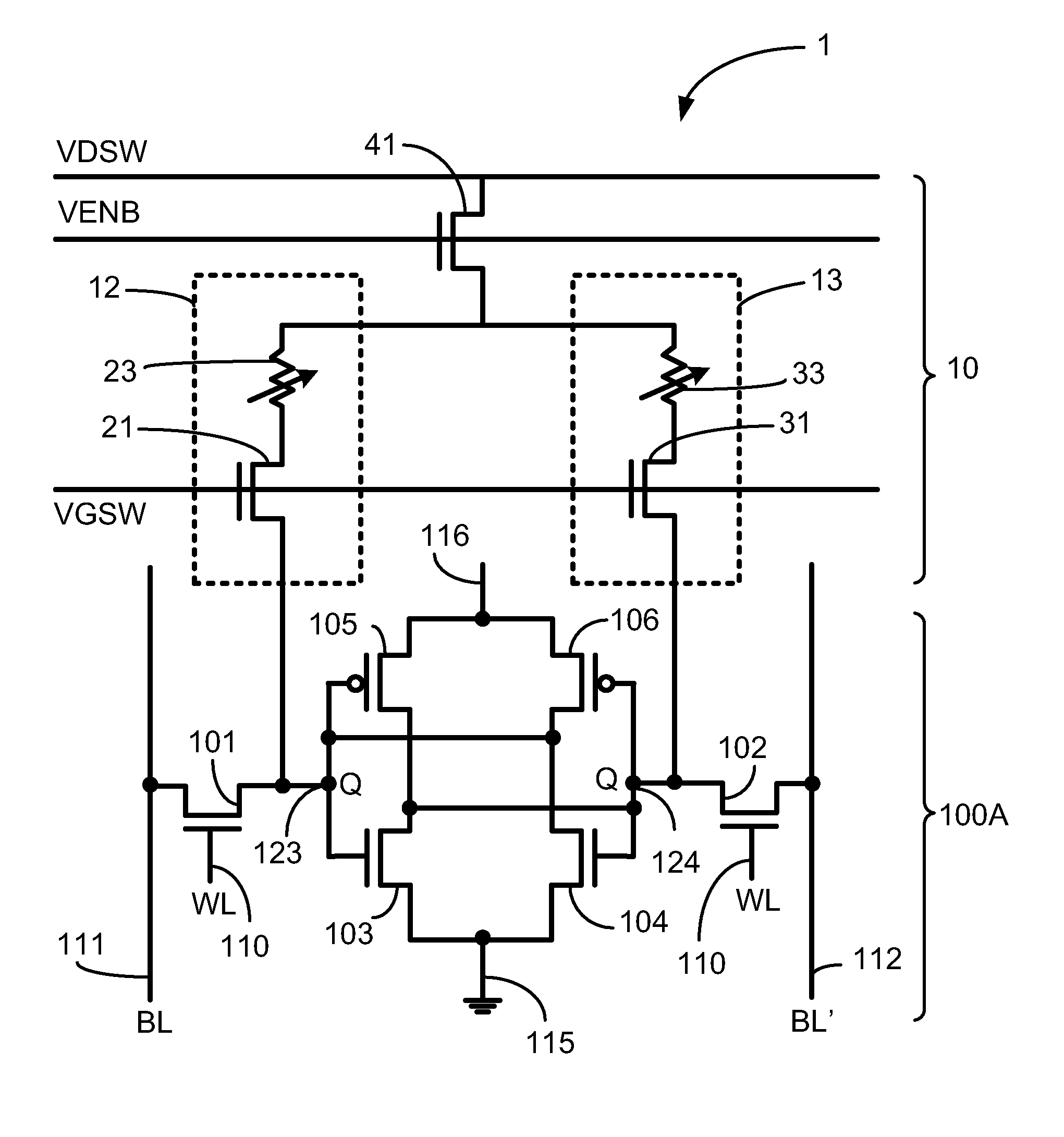
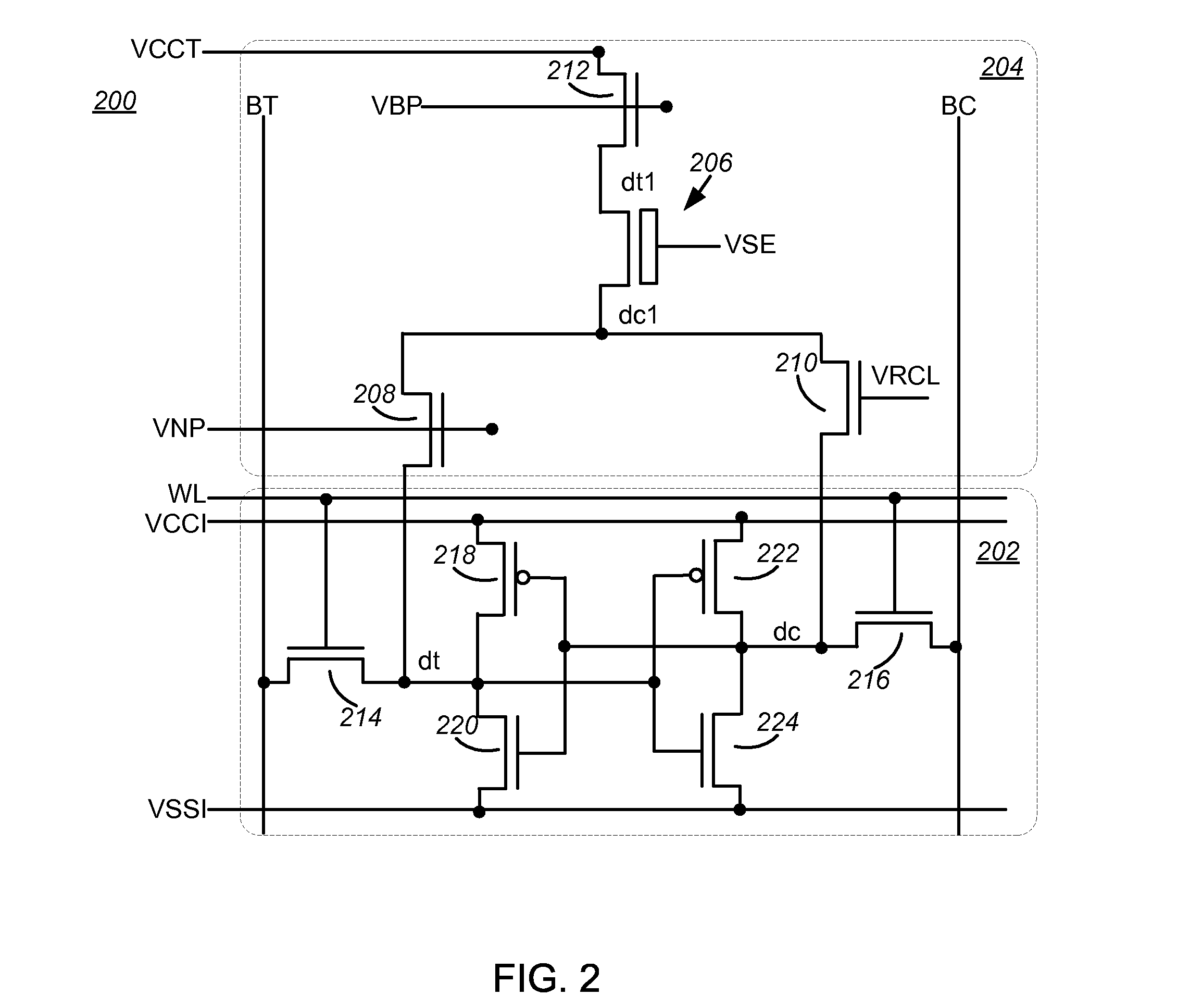
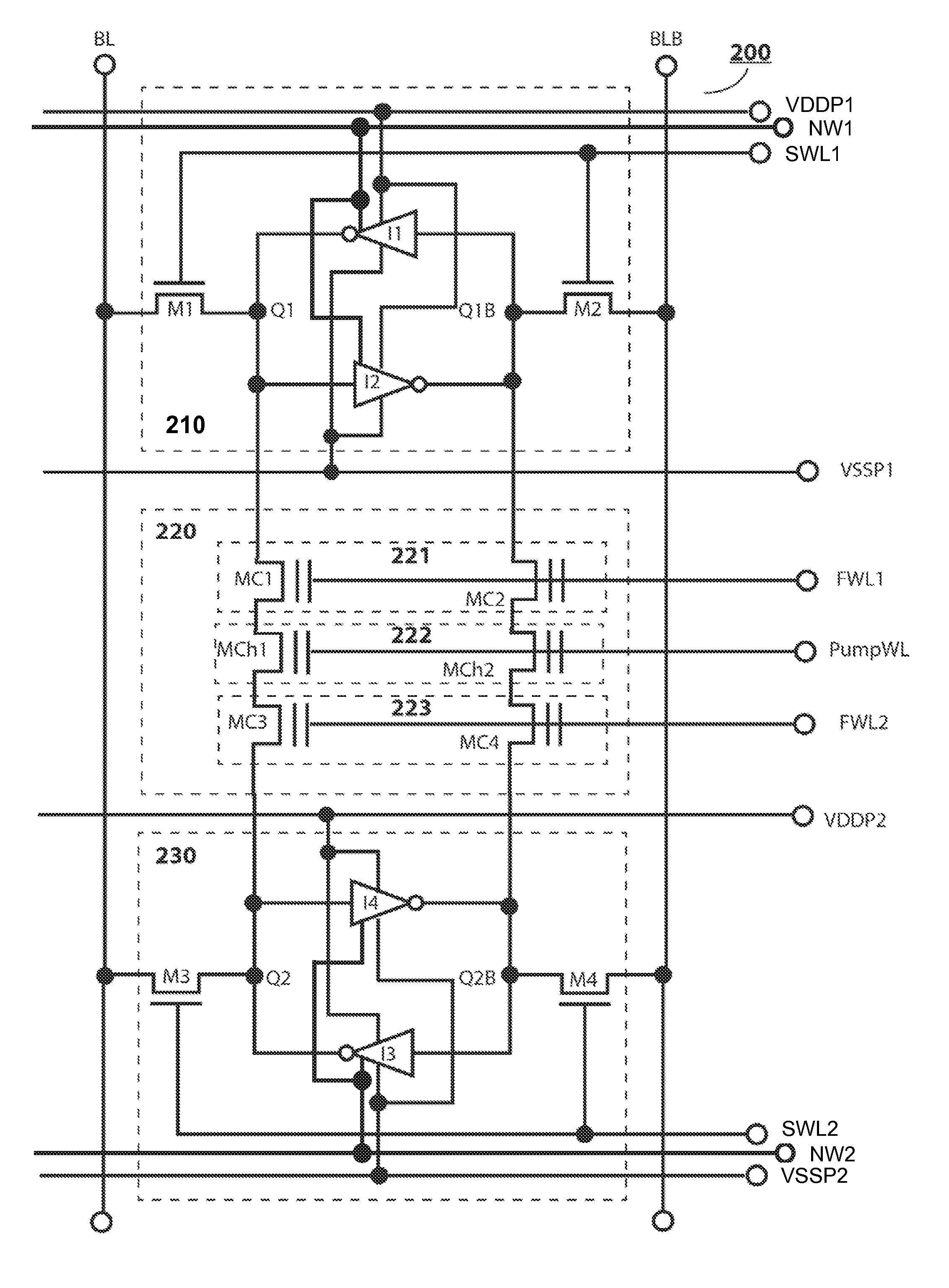
10T Non-Volatile Static Random-Access Memory
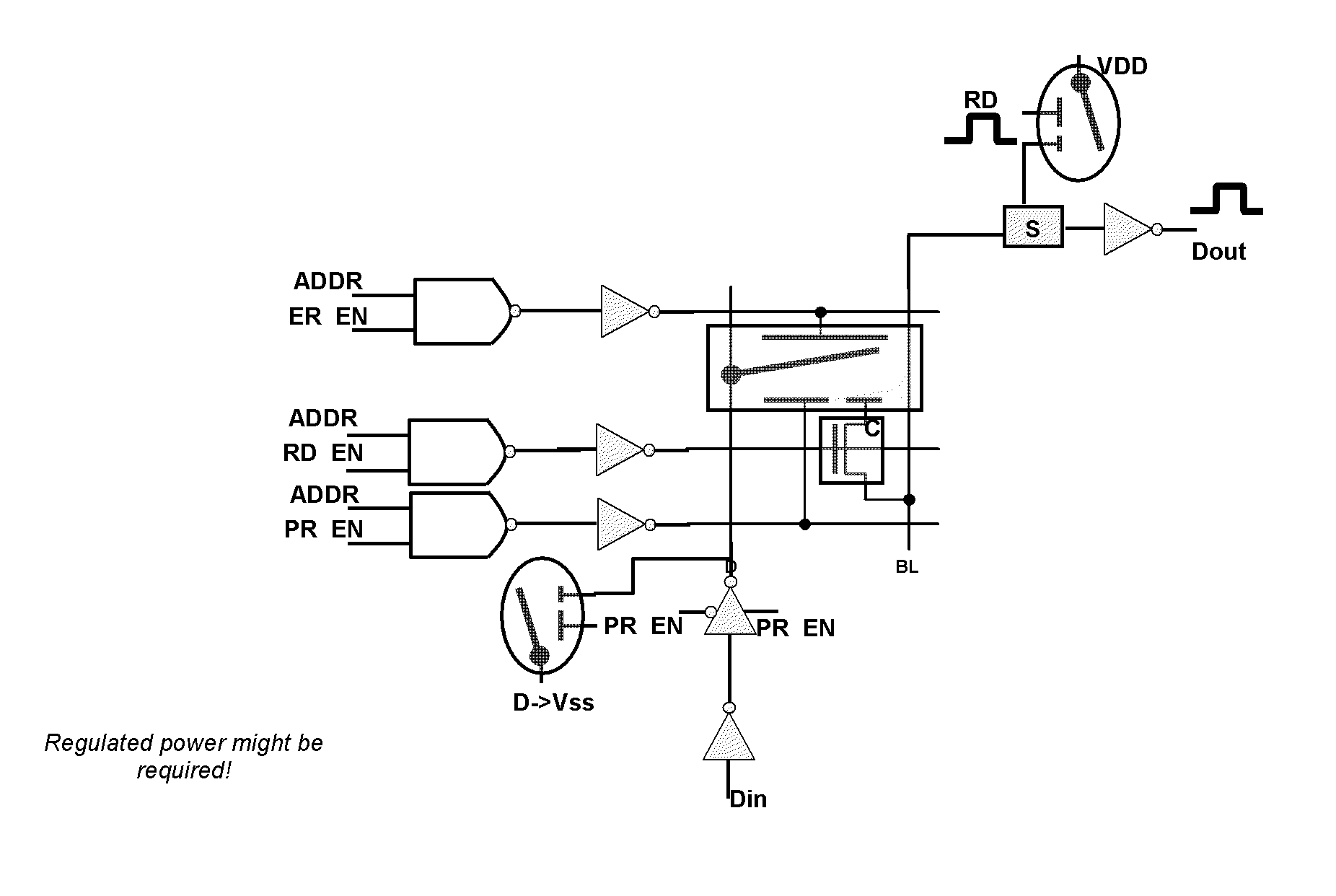
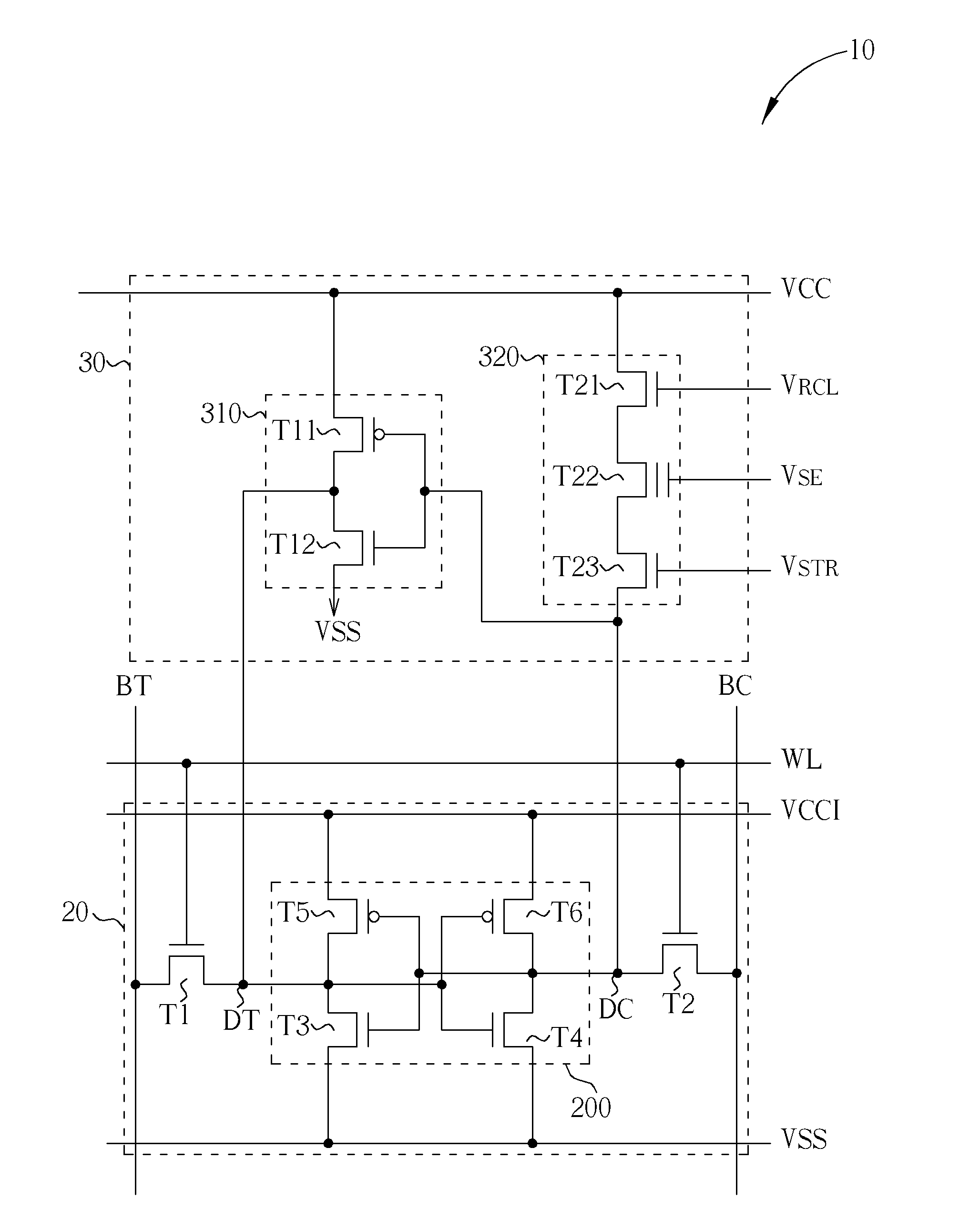
A memory including an array of nvSRAM cells and method of operating the same are provided. Each nvSRAM cell includes a volatile charge storage circuit, and a non-volatile charge storage circuit including exactly one non-volatile memory (NVM) element, a first transistor coupled to the NVM element through which data true is coupled to the volatile charge storage circuit, a second transistor coupled to the NVM element through which a complement of the data is coupled to the volatile charge storage circuit and a third transistor through which the NVM element is coupled to a positive voltage supply line (VCCT). In one embodiment, the first transistor is coupled to a first node of the NVM element, the second transistor is coupled to a second node of the NVM element and the third transistor is coupled between the first node and VCCT. Other embodiments are also disclosed.
Owner:INFINEON TECH LLC
Method and apparatus for transferring data between data buses
InactiveUS6930514B2Reduce power consumptionShorten the counting processElectric digital data processingLogic circuit coupling/interface arrangementsMultiplexingNvSRAM
Systems and methods for transferring data. A circuit transfers information between two buses using different signal voltage levels and multiplexes signals applied to the second bus over multiple devices coupled thereto. The data on a first data bus is transferred at a first voltage level and the data on a second data bus is transferred at a second voltage level. For example, the first data bus may transfer data at 3.3V and the second data bus may transfer data at 5V. A logic device (e.g., a CPLD) is connected between the first and the second data buses for transferring the data between the first and second voltage levels. The logic device is also configured for multiplexing the data with the second voltage level between first and second devices (e.g., one or more LEDs and / or NVSRAMs) connected to the second data bus.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
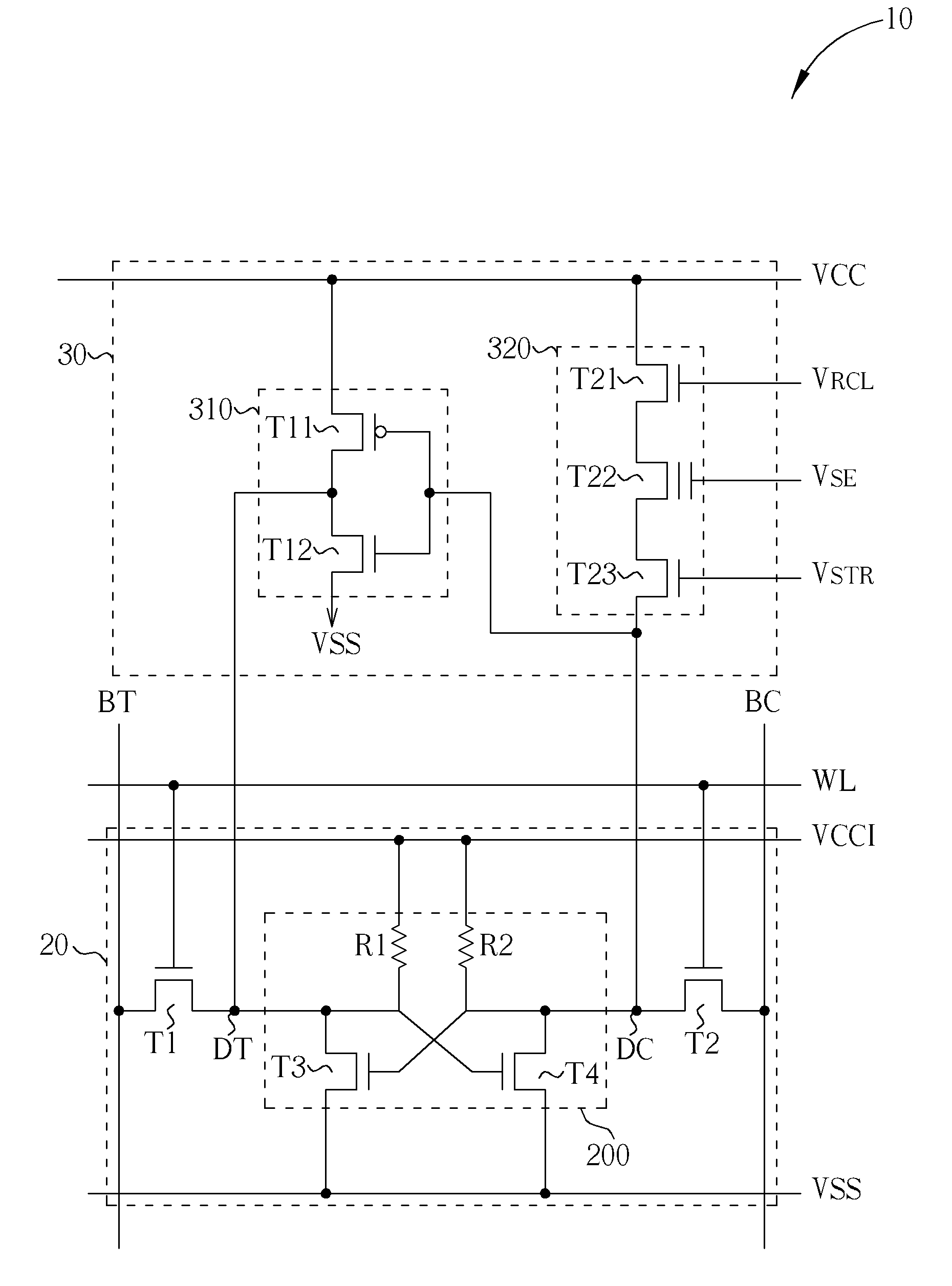
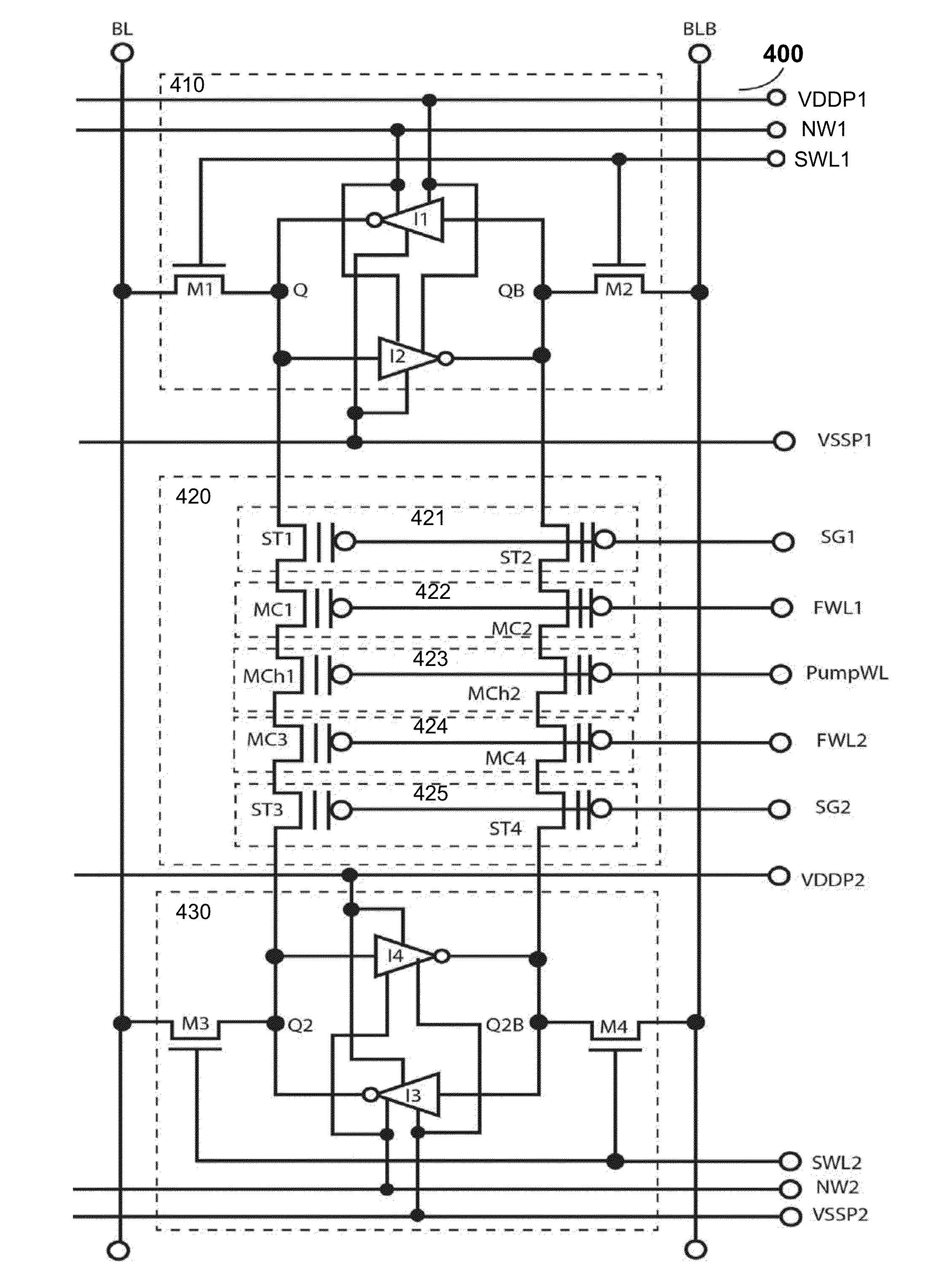
Non-volatile static random access memory (NVSRAM) having a shared port
A nonvolatile memory device includes a shared port block, a plurality of decoded address signals, a read signal, and a read word line. The shared port block includes a shared port communicatively coupled to a block, the block comprising a plurality of memory cells, wherein the shared port is operable to sense a voltage level at each of the plurality of memory cells. The plurality of decoded address signals are communicatively coupled to the block. Each of the plurality of decoded address signals is operable to enable a corresponding one of the plurality of memory cells. The read signal is communicatively coupled to the shared port. The read signal is operable to enable a read operation associated with the block. The read word line signal is communicatively coupled to the shared port block. The read word line signal is operable to enable the read operation.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Pseudo-8t nvsram cell with a charge-follower
The present invention discloses a 10T NVSRAM cell with a 6T SRAM cell with 4T Flash cell with one dedicated Flash-based Charger. In addition, a Pseudo-8T NVSRAM cell with a shared Flash-based Charger between two adjacent 8T NVSRAM cells at top and bottom in cell layout is also disclosed to further reduce cell size by 20%. As opposed to the prior art of 12T NVSRAM cell, the Store operation of the above two preferred embodiments use a DRAM-like charge-sensing scheme with Flash cell configured into a voltage follower ensured by the Flash-based Charger to obtain the final ΔVQ-QB>0.2V at Q and QB nodes of each SRAM cell to cover all the mismatched of parasitic capacitance in flash cell devices and layout for a reliable amplification by ramping up SRAM's VDD line and ramping down SRAM's VSS line.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Low-voltage fast-write PMOS NVSRAM cell
InactiveUS9177644B2Improve the coupling ratioShorten the timeRead-only memoriesDigital storageLow voltageNvSRAM
This invention discloses a low-voltage fast-write 12T or 14T PMOS NVSRAM cell structure which comprises a 6T LV SRAM cell and one pairs of two 3T or 4T HV PMOS Flash strings. Due to reverse threshold voltage definition of PMOS and NMOS flash cell, this PMOS NVSRAM cell has the advantage over the NMOS NVSRAM cell to have the same data polarity between SRAM and Flash pairs during the data writing operation. In addition, this PMOS NVSRAM's PMOS Flash cell uses similar low-current FN-tunneling scheme as NMOS NVSRAM, thus the fast data program and erase can be achieved in a big density up to 100 Mb simultaneously. As a result, low power voltage operation of NVSRAM with 1.2V VDD can be much easier to be designed without coupling the FSL line to any VDD level during the flash data loading into SRAM cell during a power-on period.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com