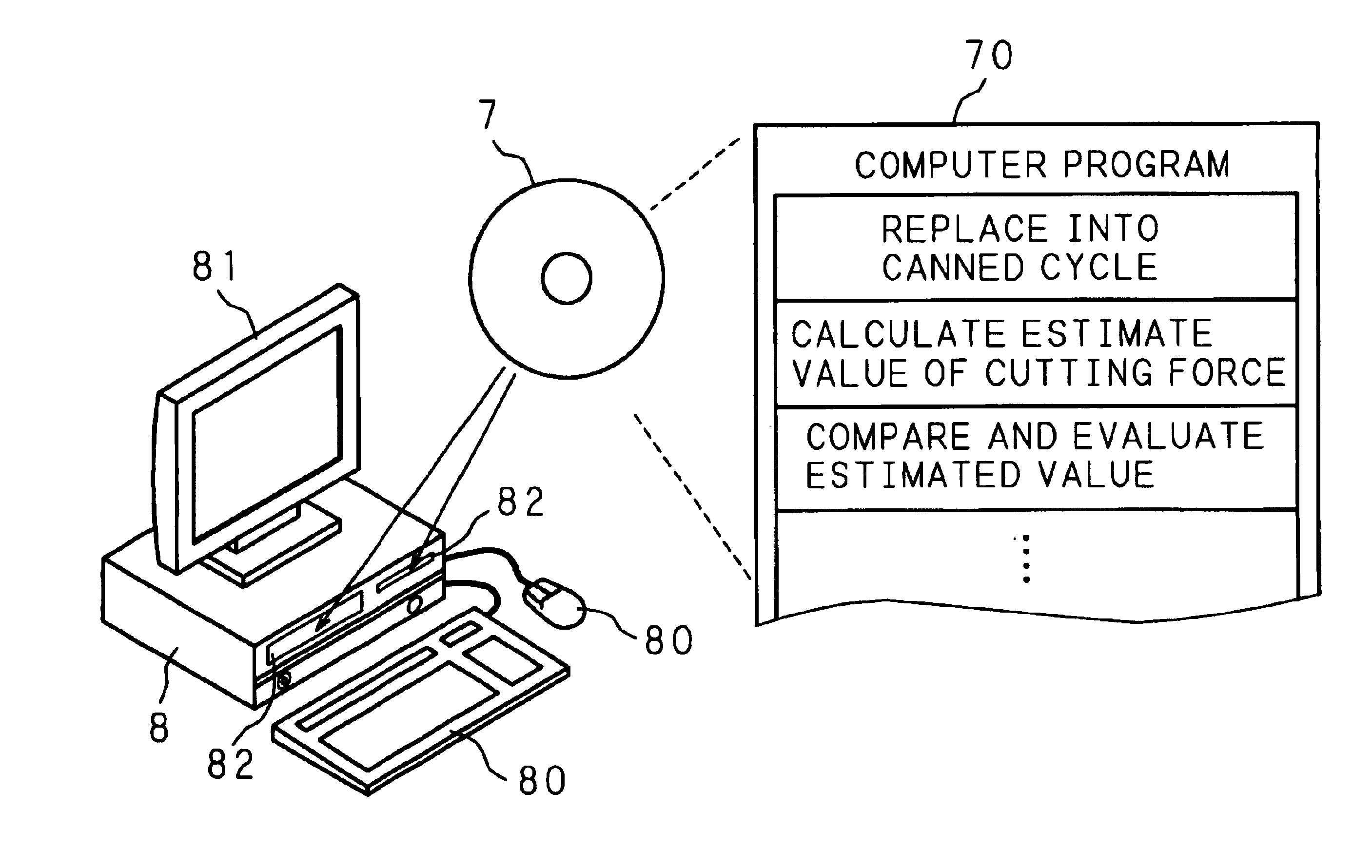
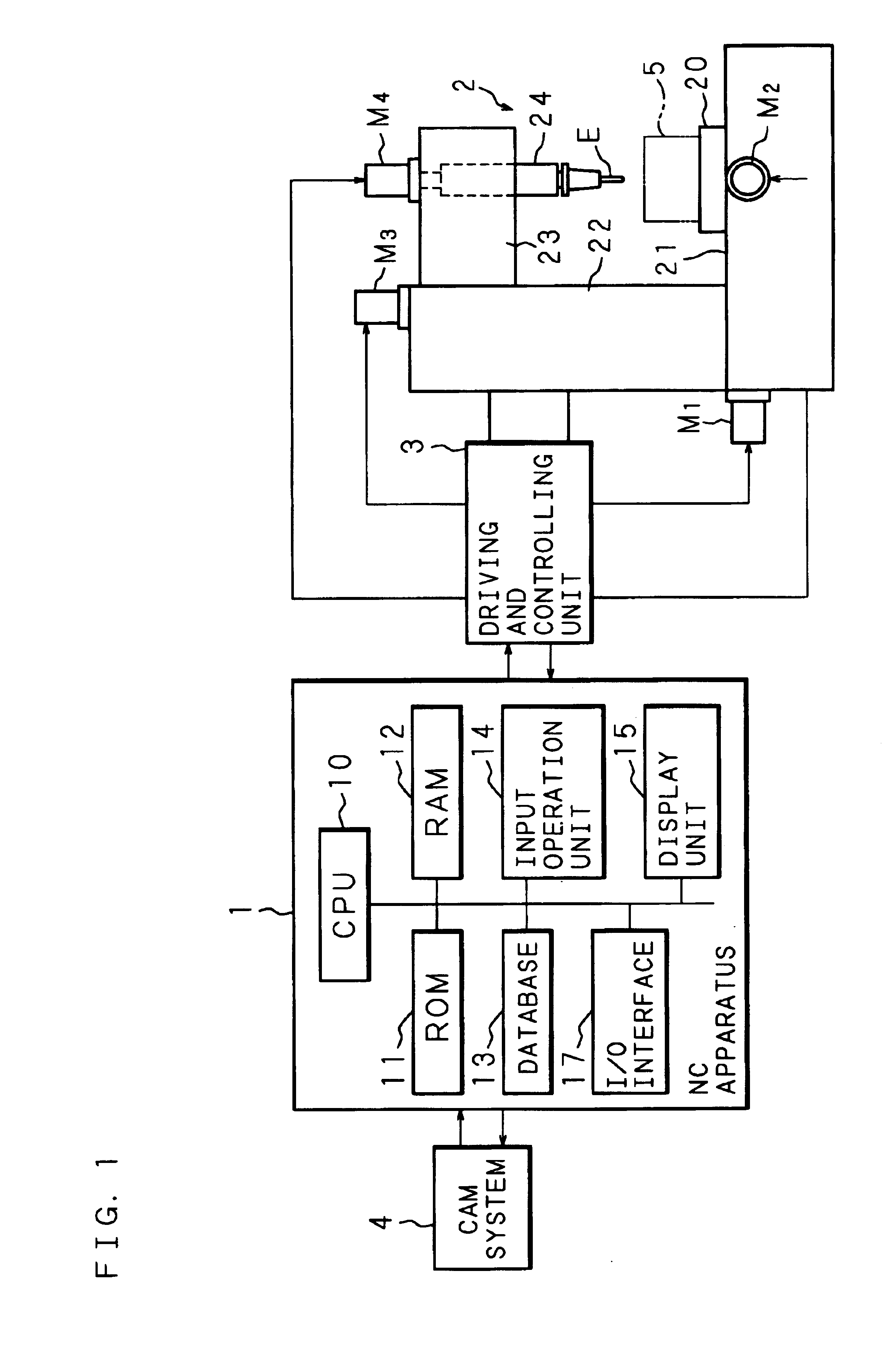
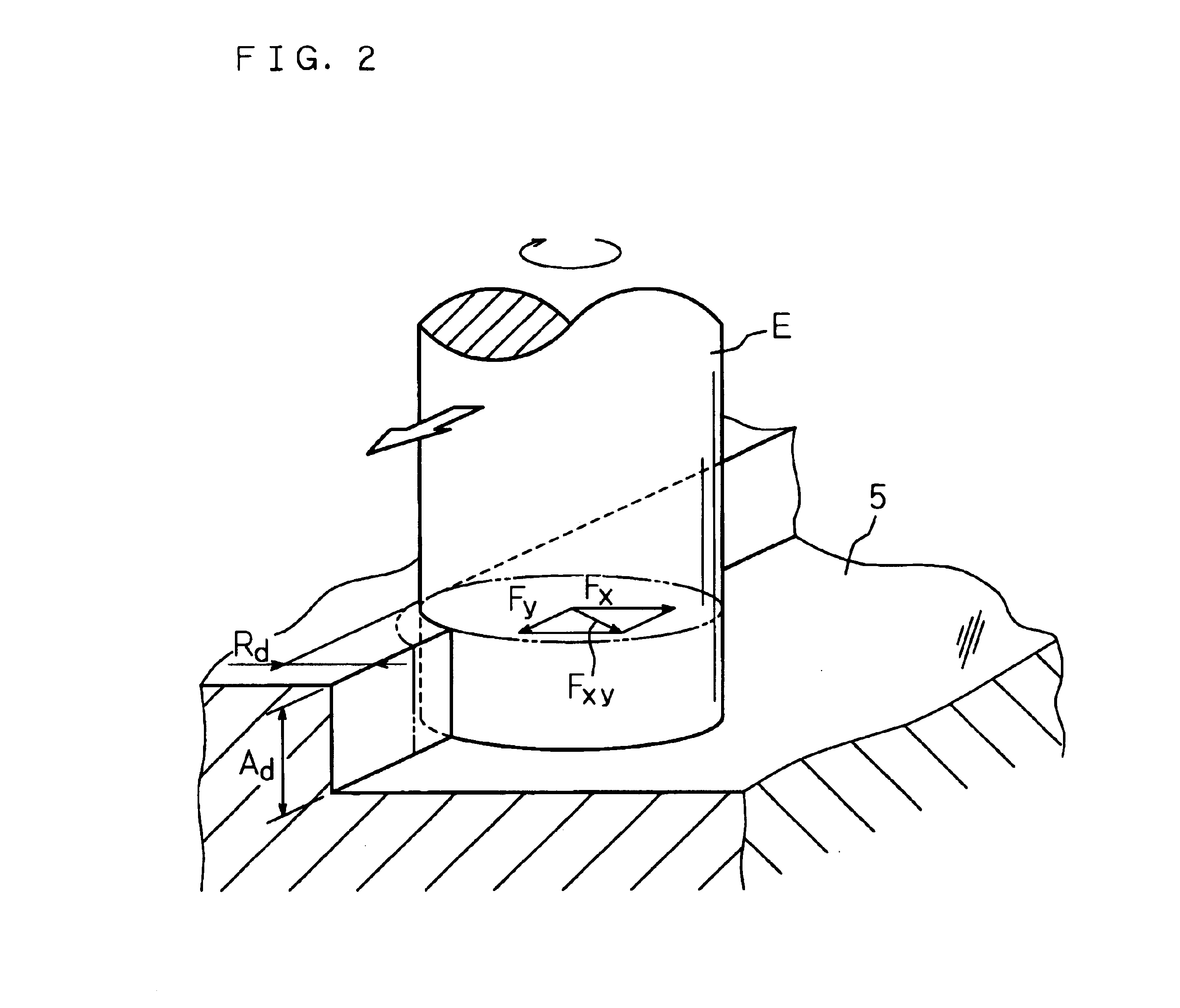
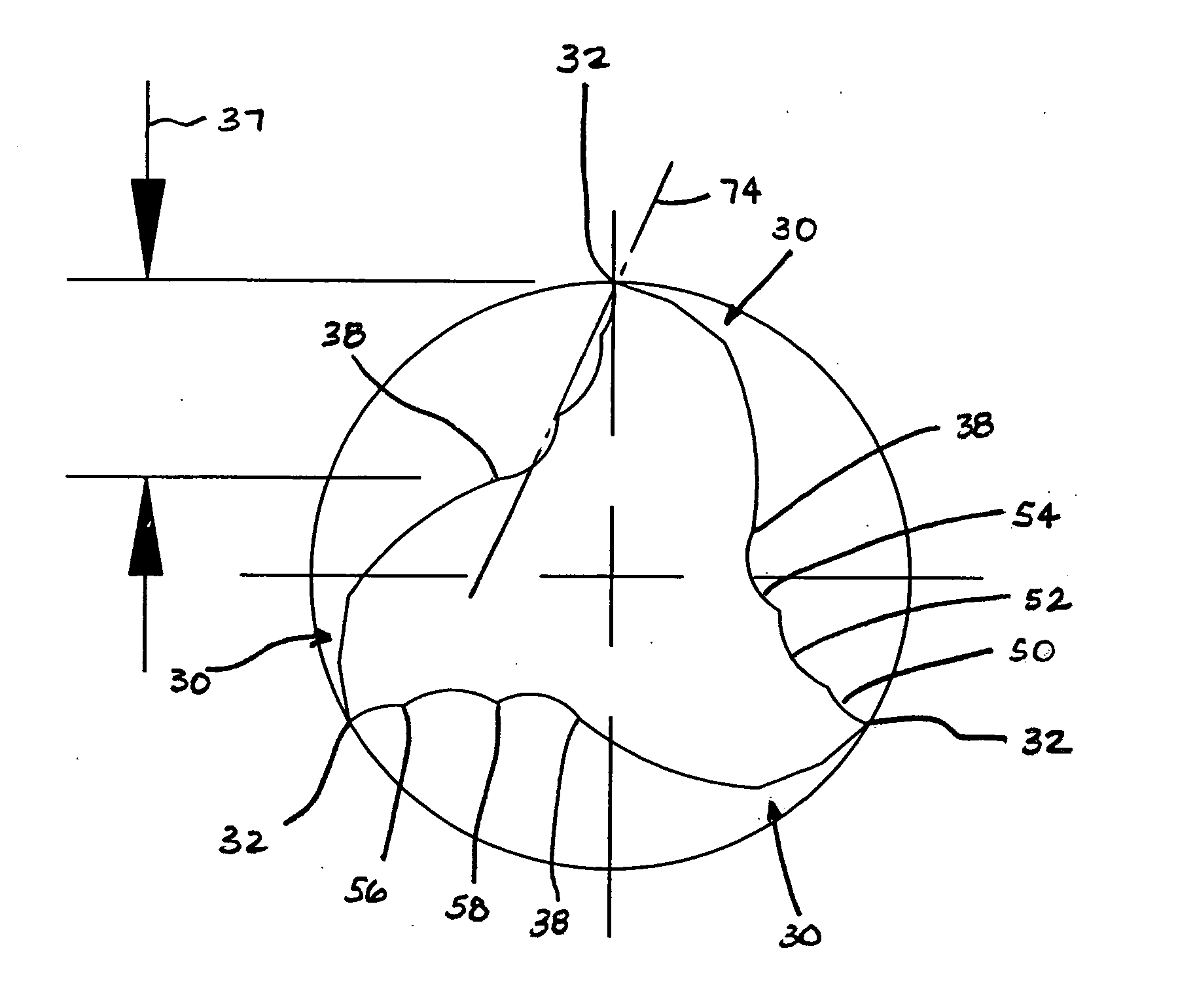
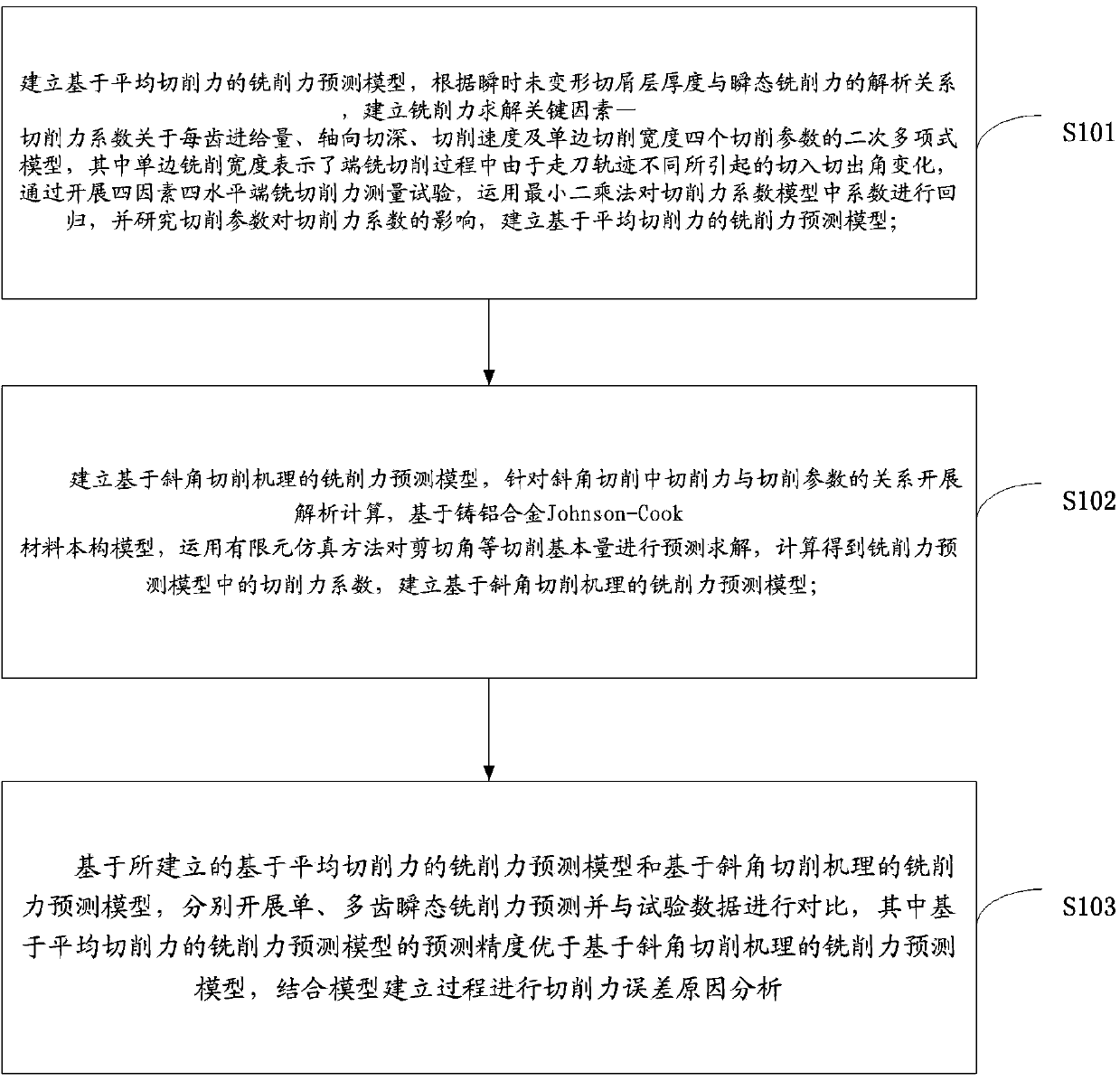
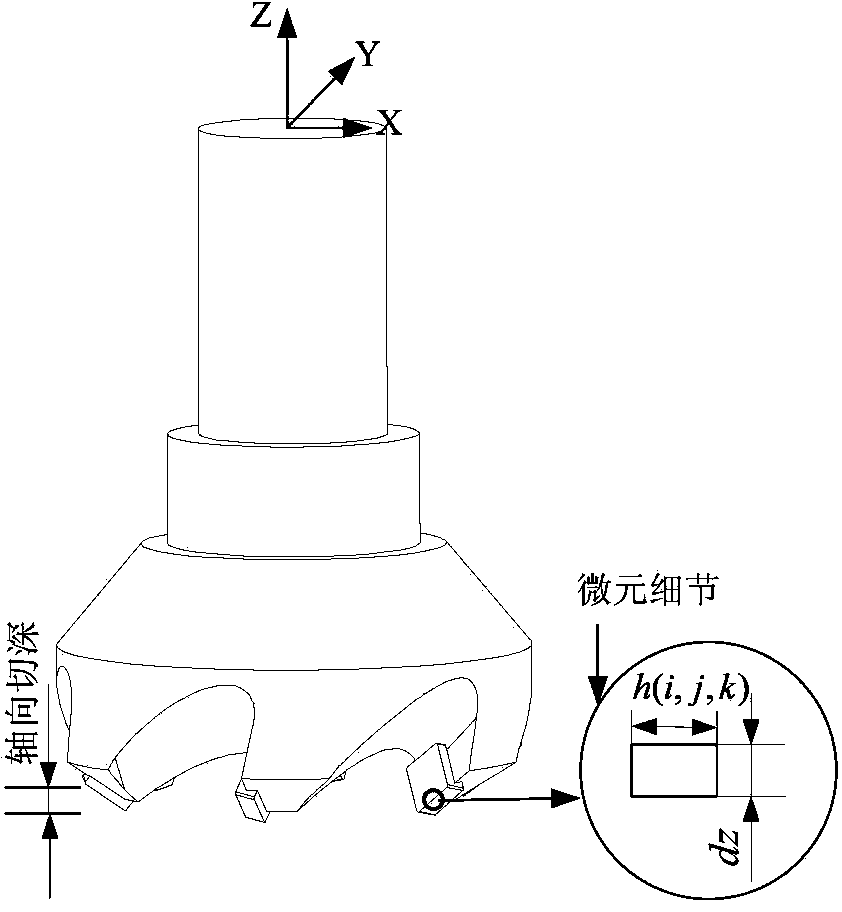
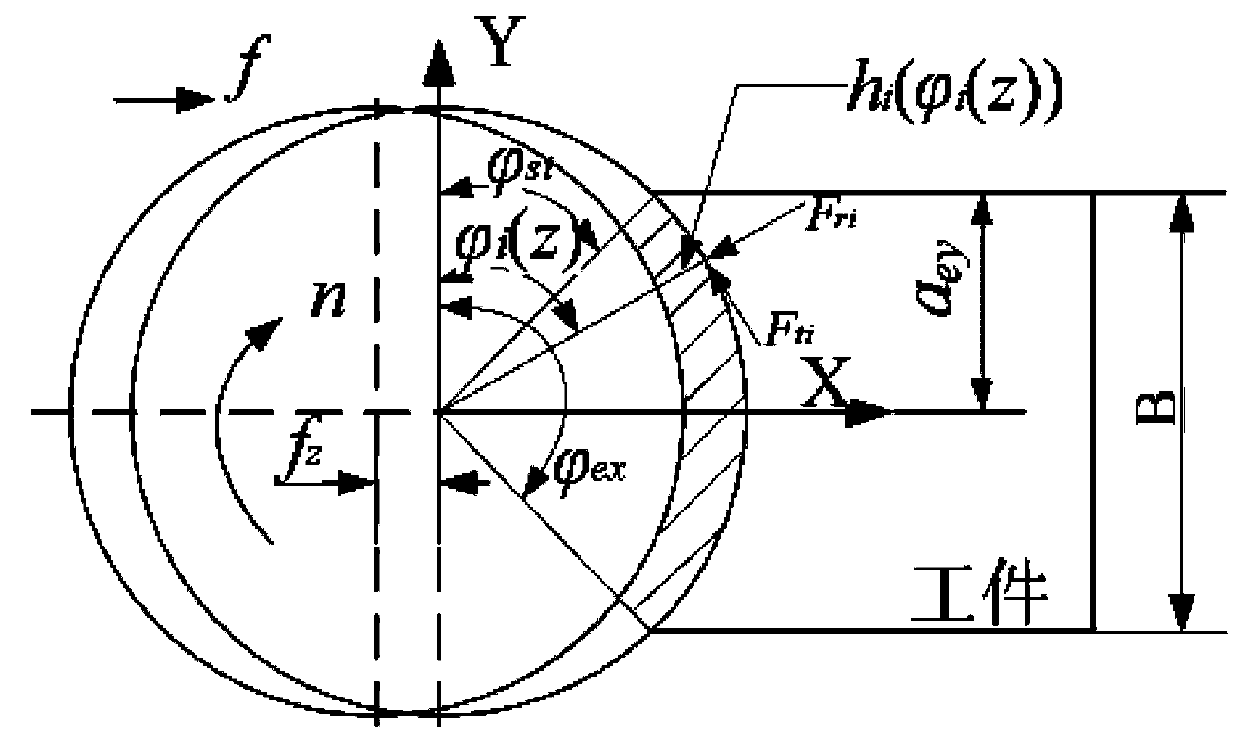
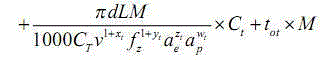Patents
Literature
757 results about "End mill" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
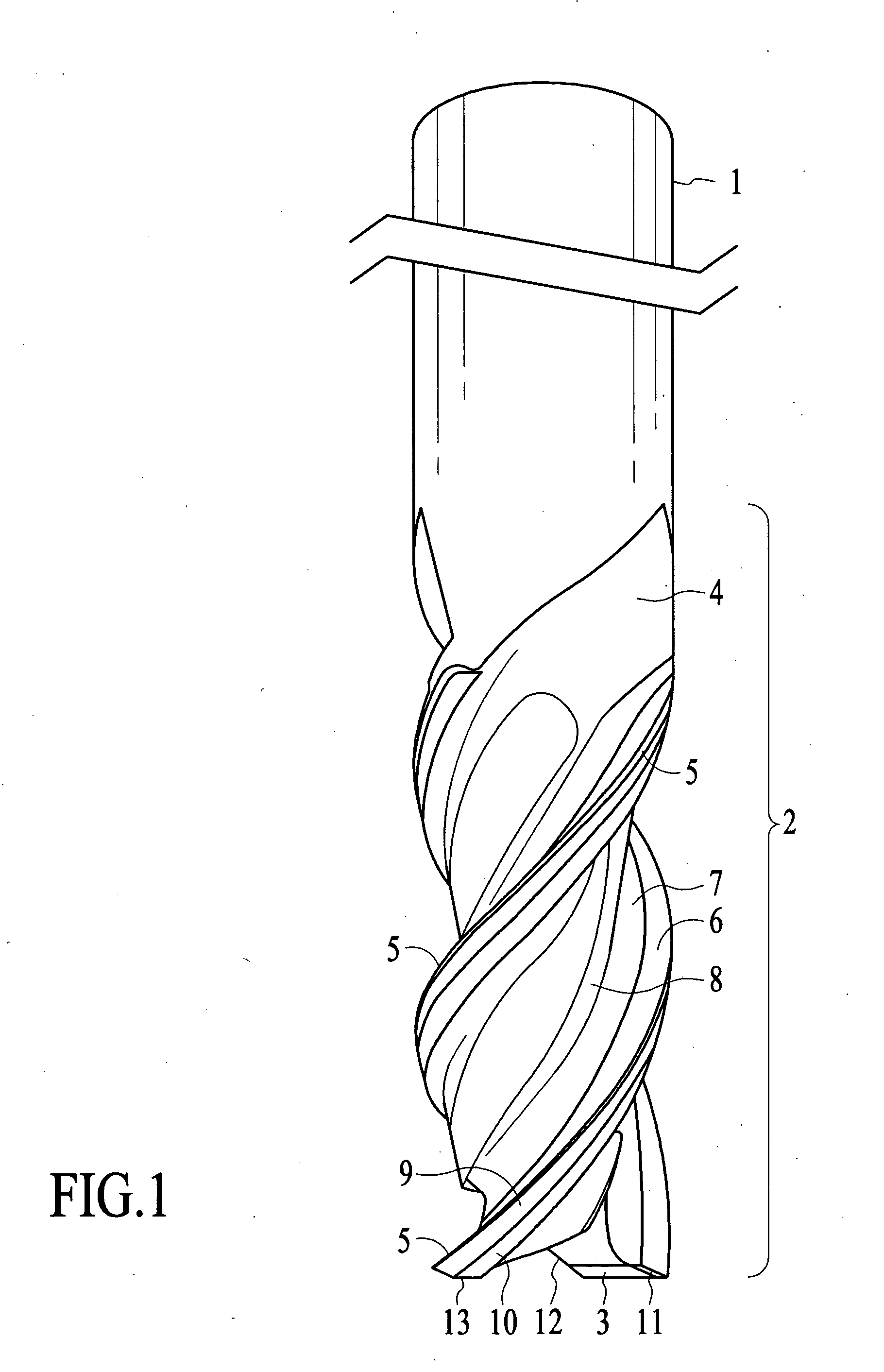
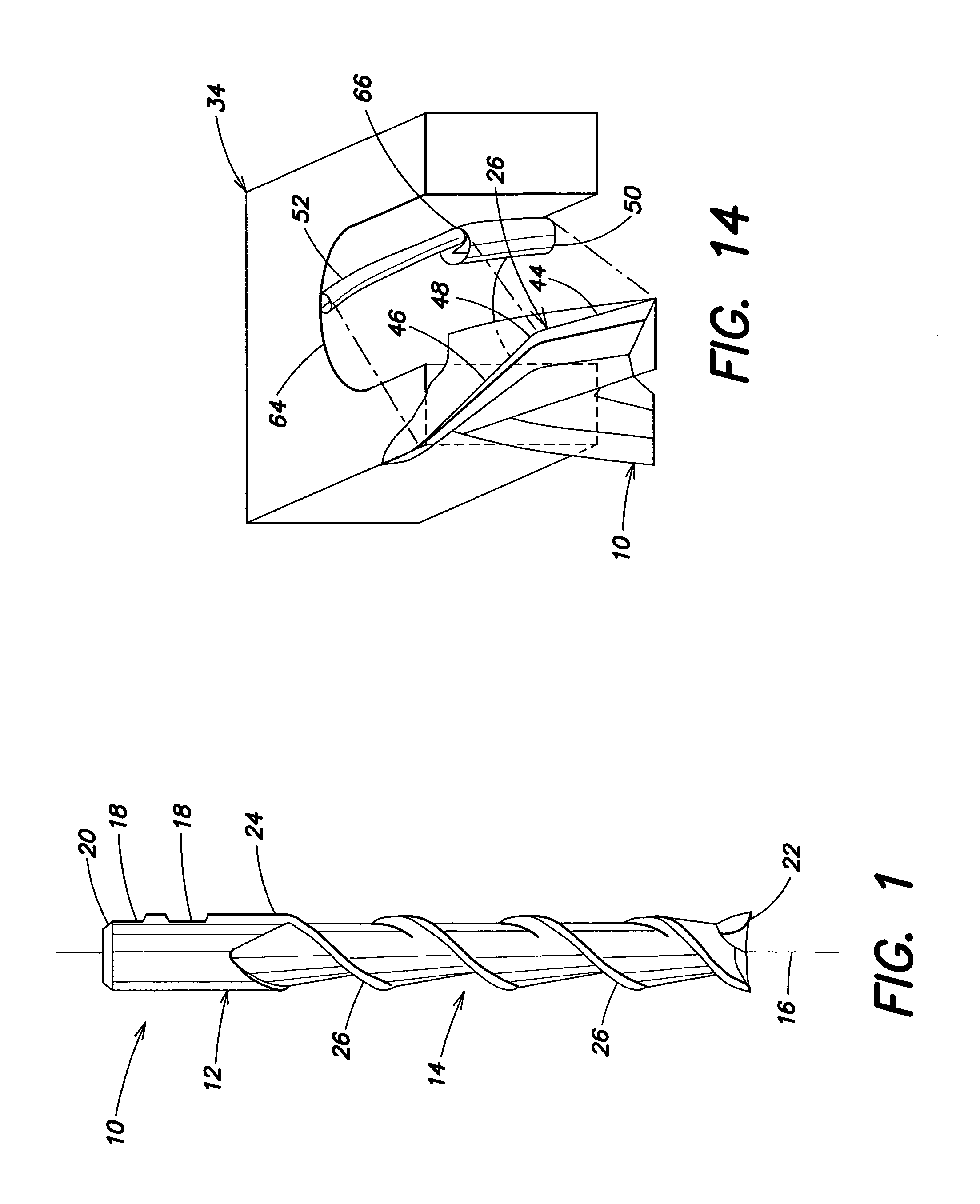
An end mill is a type of milling cutter, a cutting tool used in industrial milling applications. It is distinguished from the drill bit in its application, geometry, and manufacture. While a drill bit can only cut in the axial direction, a milling bit can generally cut in all directions, though some cannot cut axially.
Method for manufacturing a golf club face
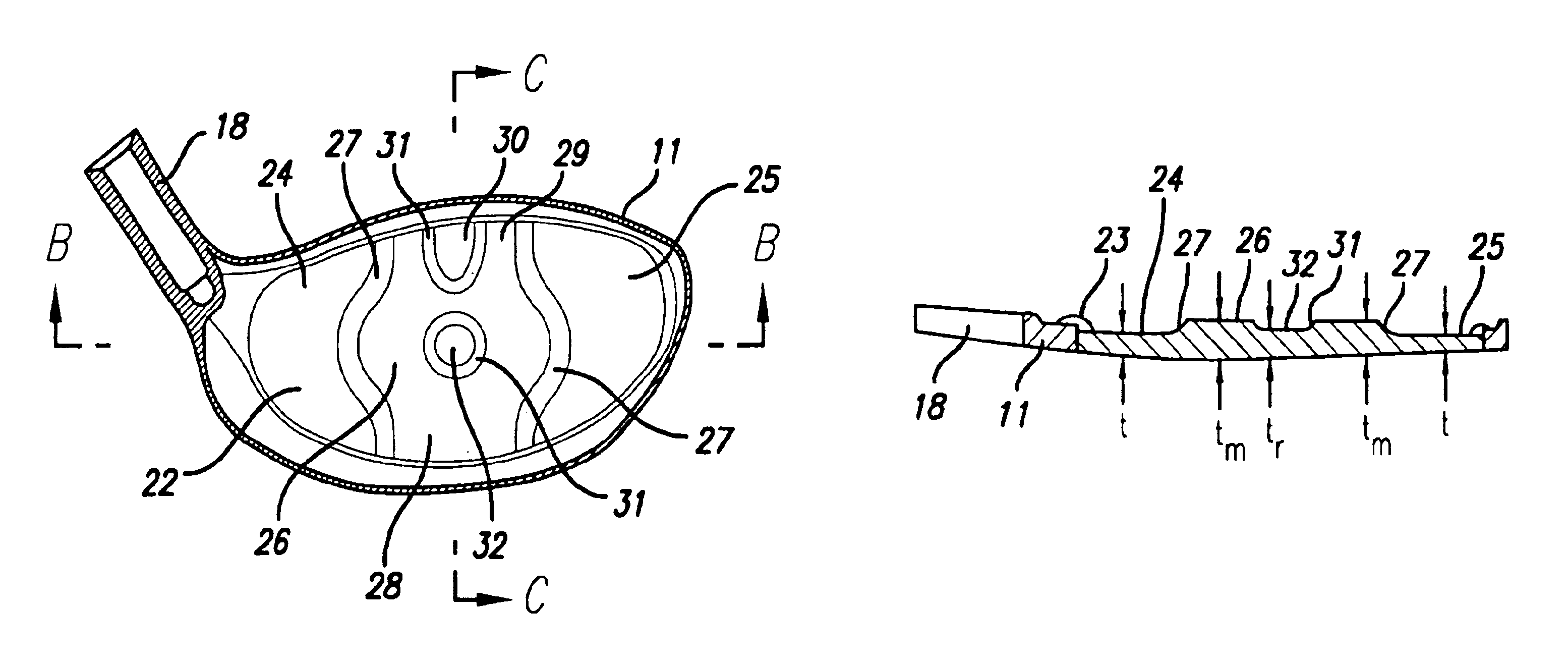
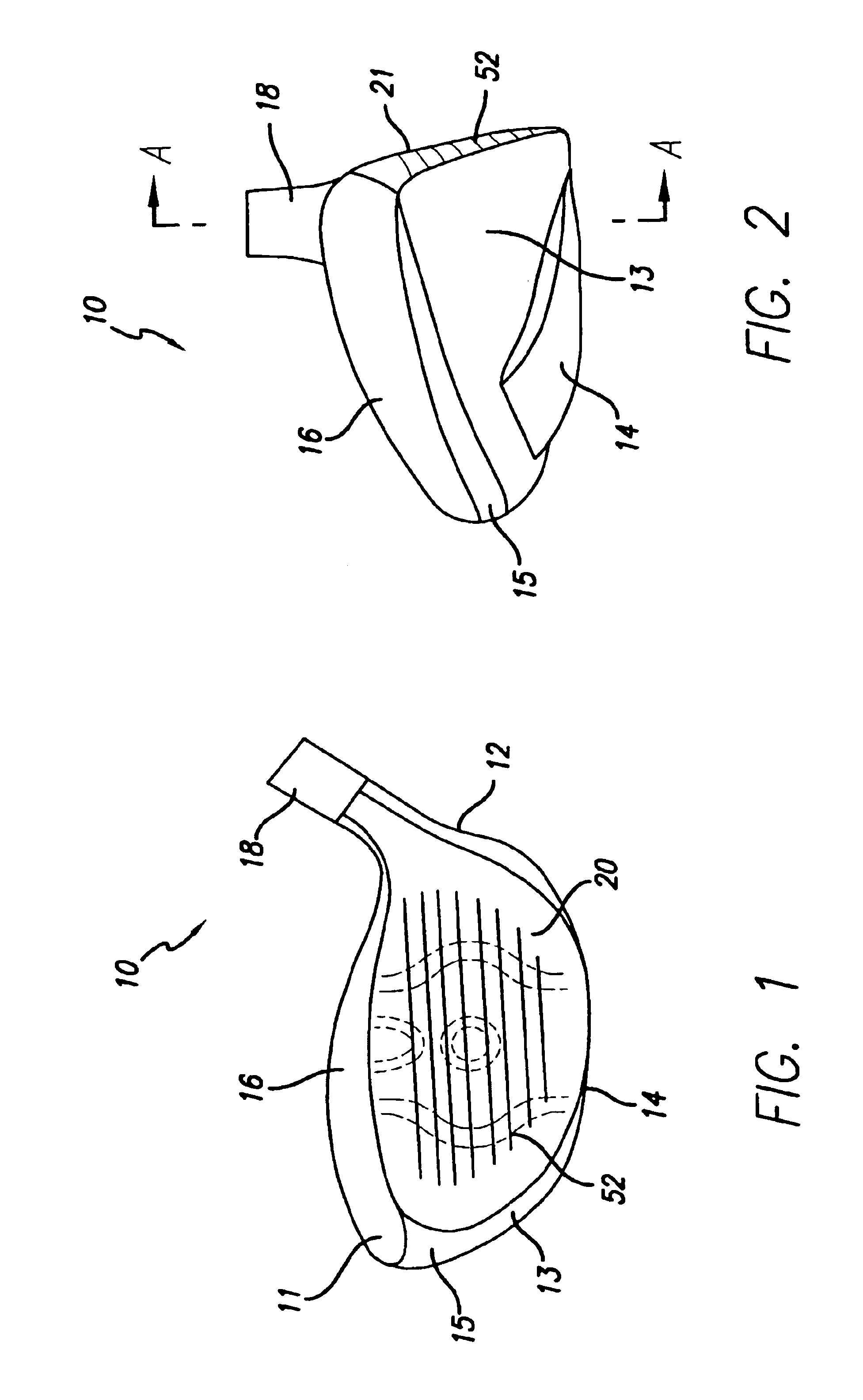
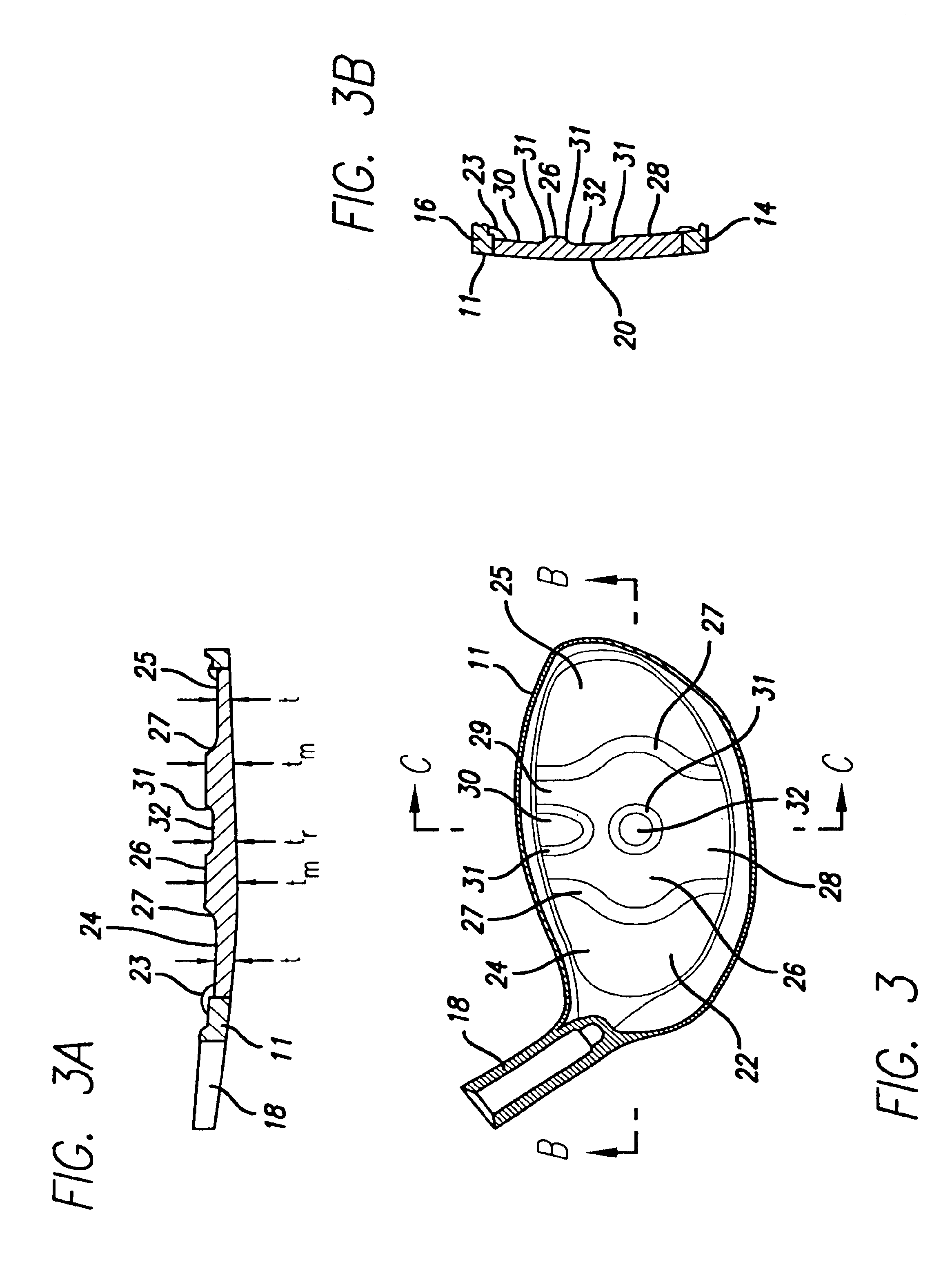
InactiveUS6904663B2Large thickness variationImprove performanceGolf clubsRacket sportsVariable thicknessAsymmetric face
A method of manufacturing a face plate for a golf club head is presented to provide face having substantial thickness variation for enhanced performance. The method includes the steps of providing a rolled sheet of metal material having an initial thickness and forming a blank having a prescribed outer shape from the material. The method also includes machining a second side of the blank such that the resulting face plate has a variable thickness. The machining is such that the plate has a first thickness less than or equal to the initial thickness, a second thickness less than the first thickness and a third thickness less than the second thickness. The machining is performed over a substantial portion of the surface area of the second side. Either a CNC lathe or milling machine may be used; however, for an axisymmetric face thickness a CNC lathe is preferred and for an asymmetric face thickness a CNC end mill is preferred. The club head may be a wood-type or iron, and titanium or steel alloys may be used.
Owner:TAYLOR MADE GOLF
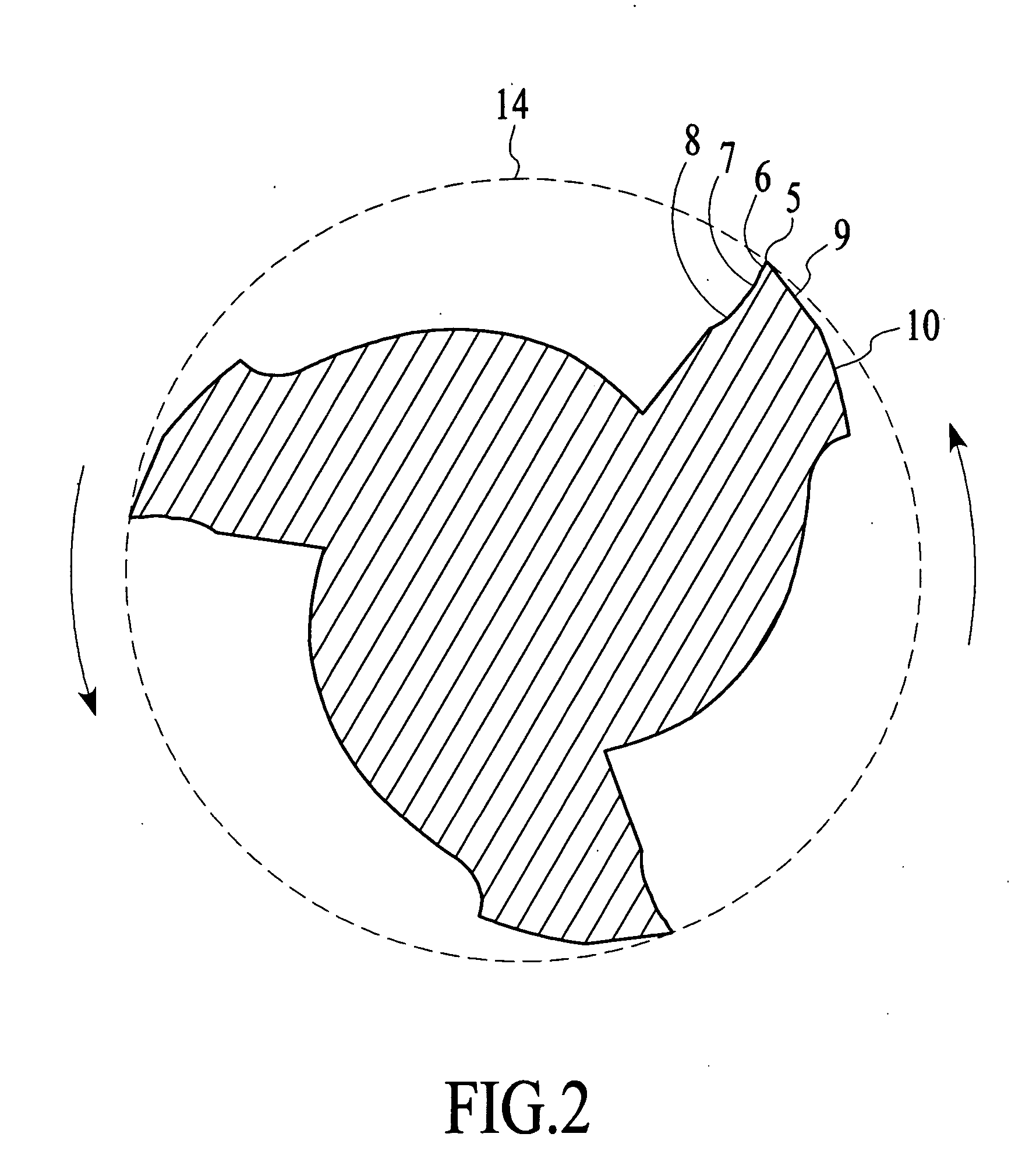
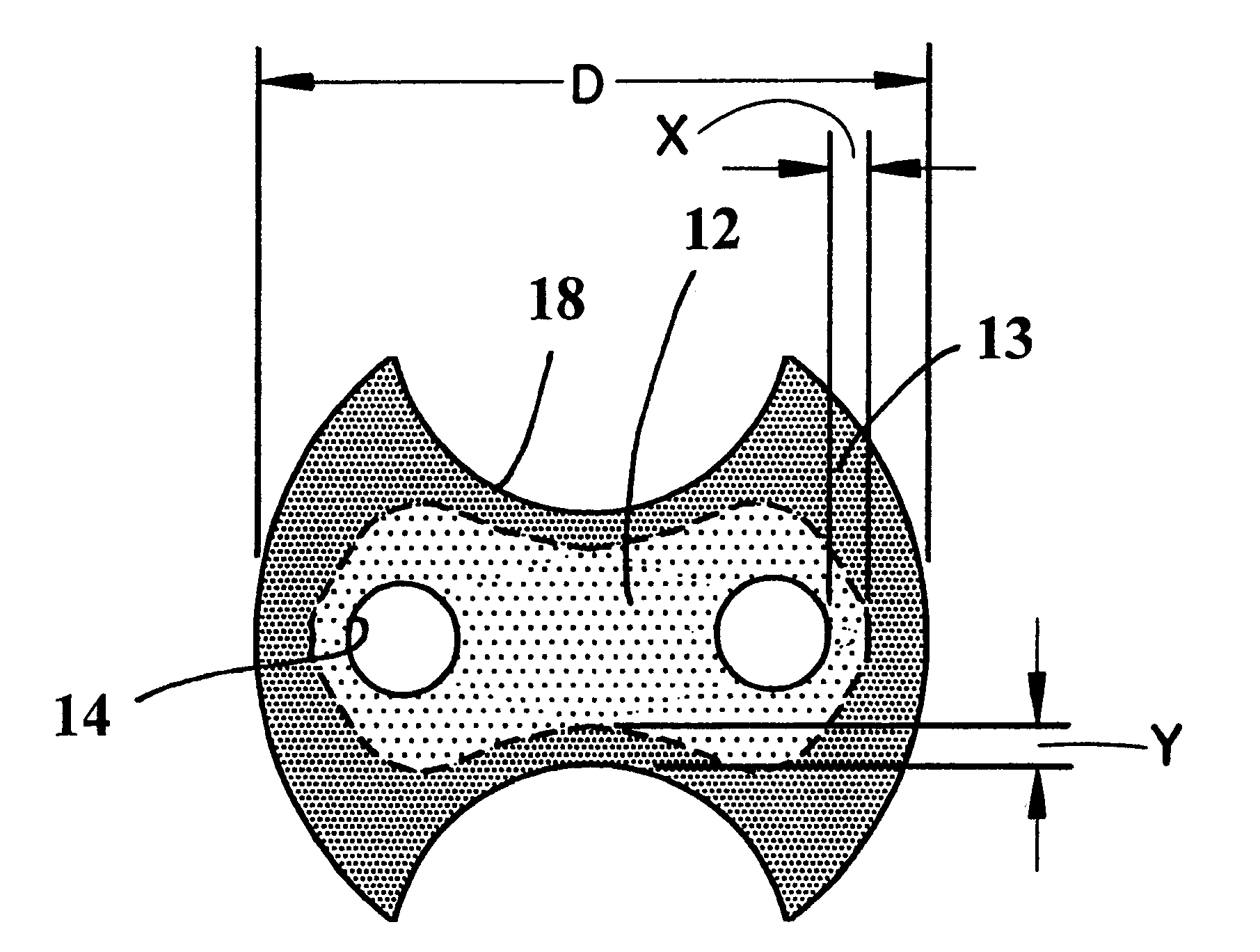
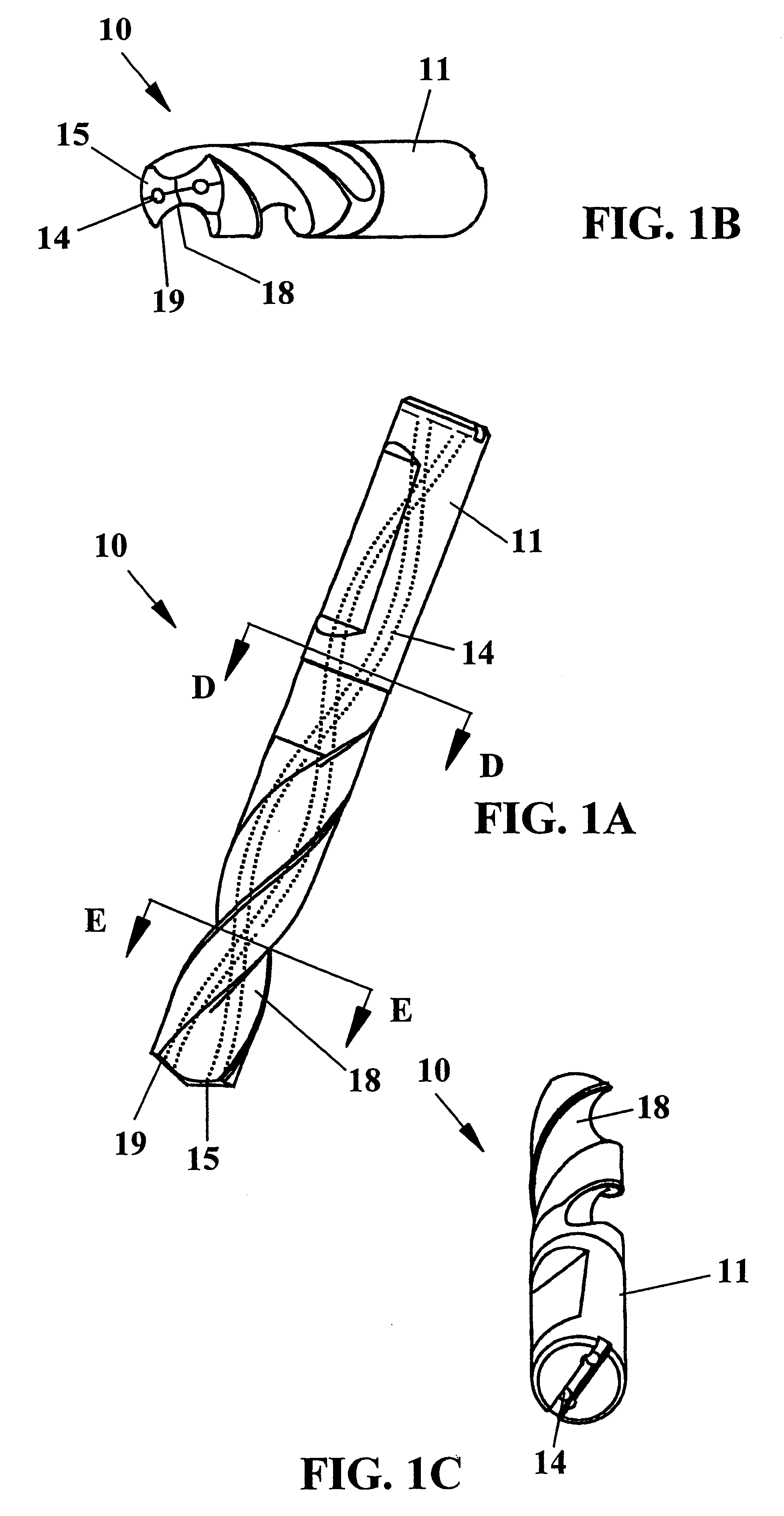
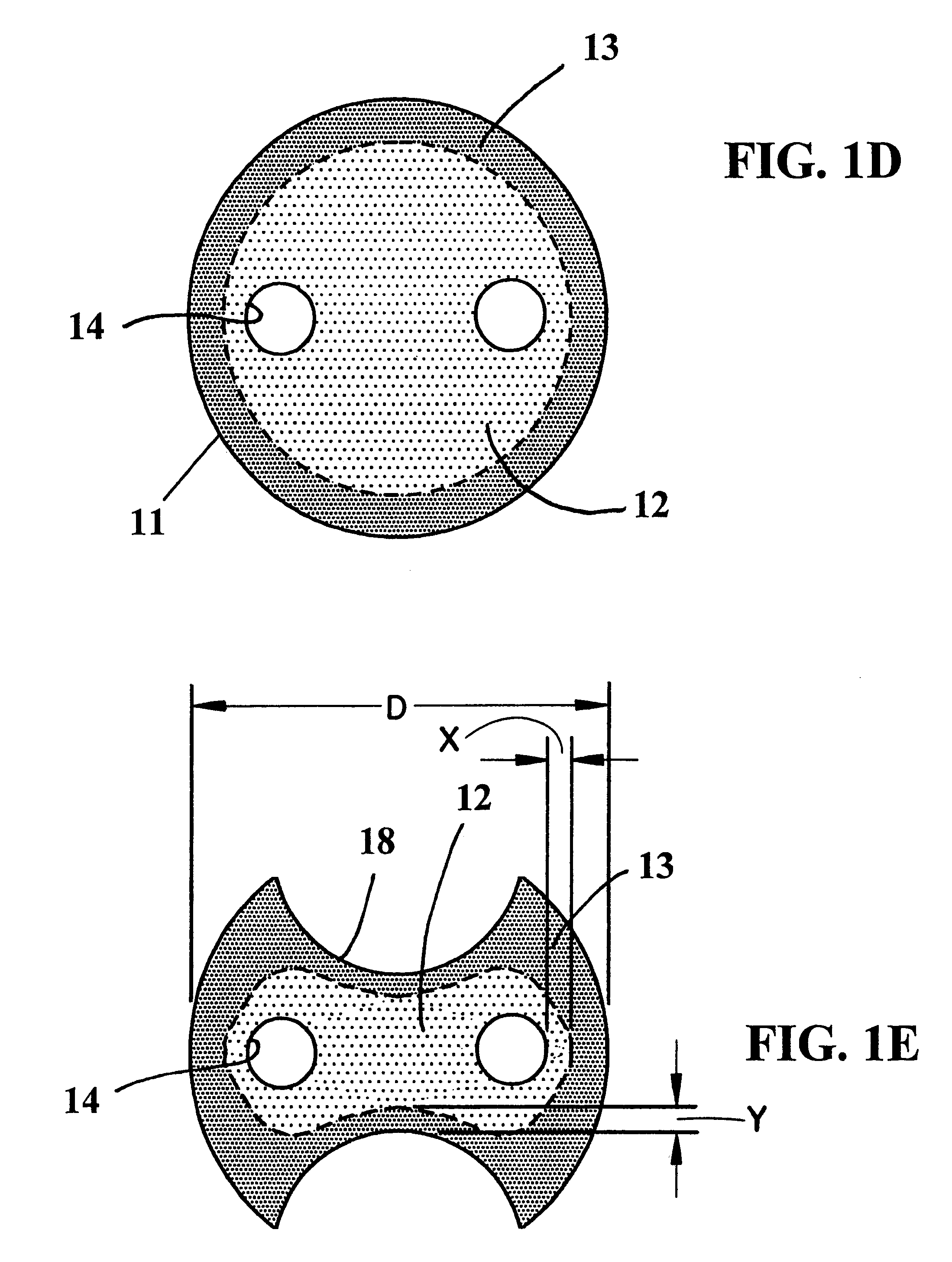
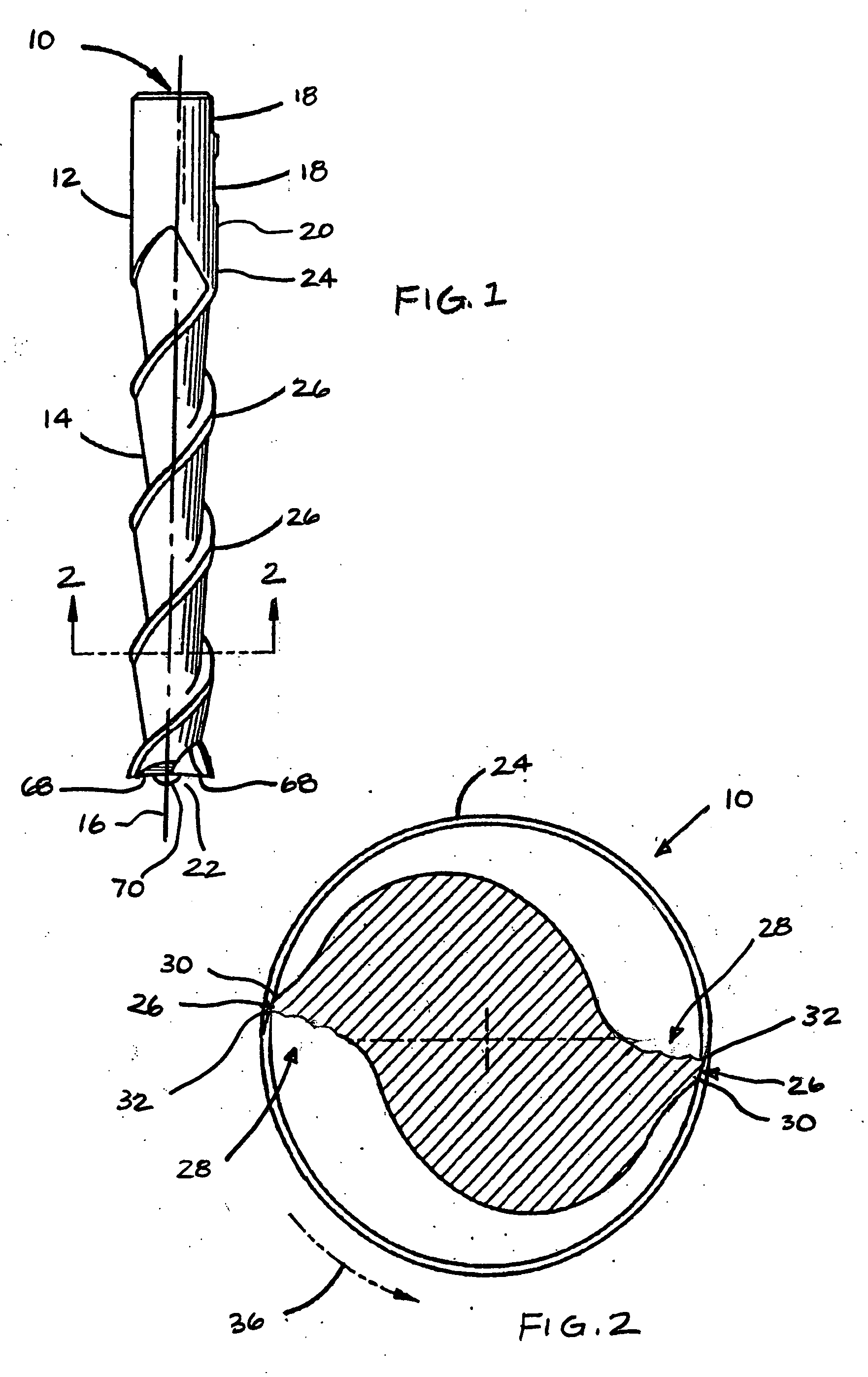
End mill
InactiveUS20060067797A1Aggressive and deep cutLess forceMilling cuttersWorkpiecesUltra fineEngineering
An end mill with a peripheral margin which increases in width from the terminal end of the tool to the shank portion of the tool. The end mill also has a tooth face made up of three tooth-face walls The depth of the tool face gradually decreases from the terminal end to the shank portion of the tool. The end mill also has an end cutting face which includes a flat, narrow land at the outmost region of the end cutting end. The end mill has chip breakers with rounded peripheral corners. The end mill can be made up of ultra-fine micro grain tungsten carbide with a cobalt content which varies throughout the length of the tool.
Owner:CALAMIA GUY ALLEN
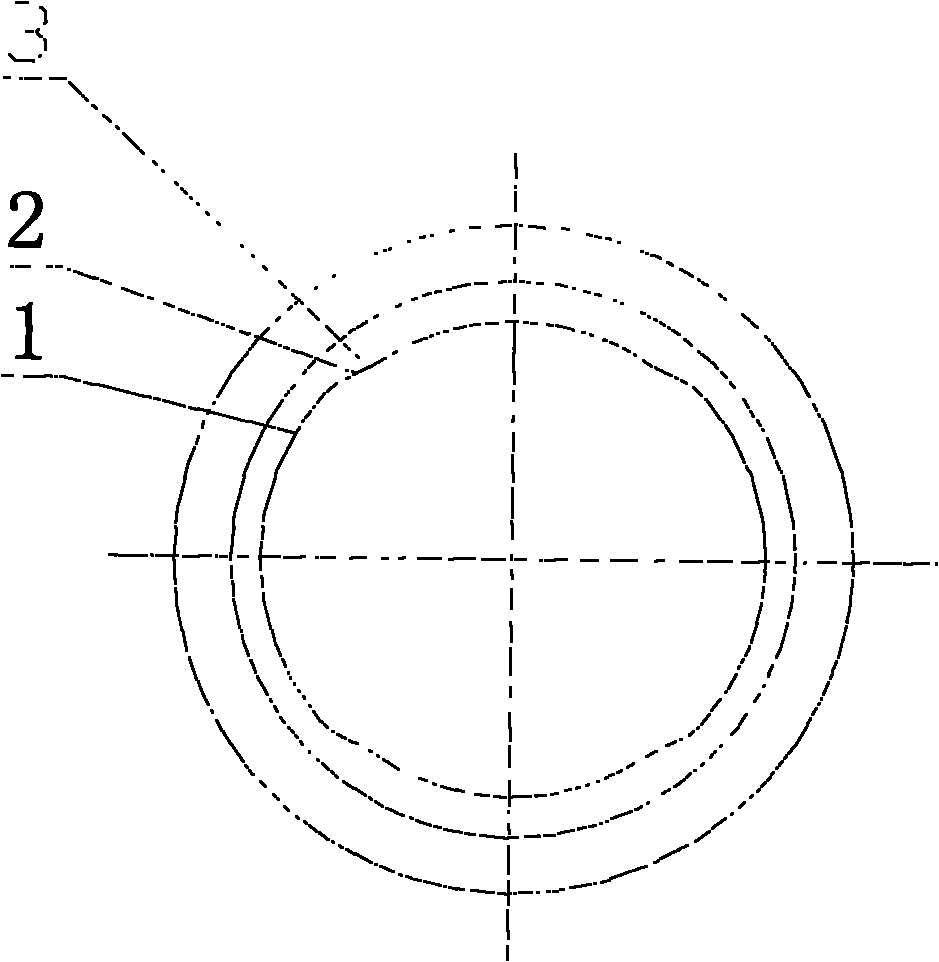
Radius end mill having radius edge enhanced in resistance to chipping and fracture
InactiveUS6846135B2Suppress chipping and fractureHigh-feed cuttingMilling cuttersWorkpiecesEngineeringCurve line
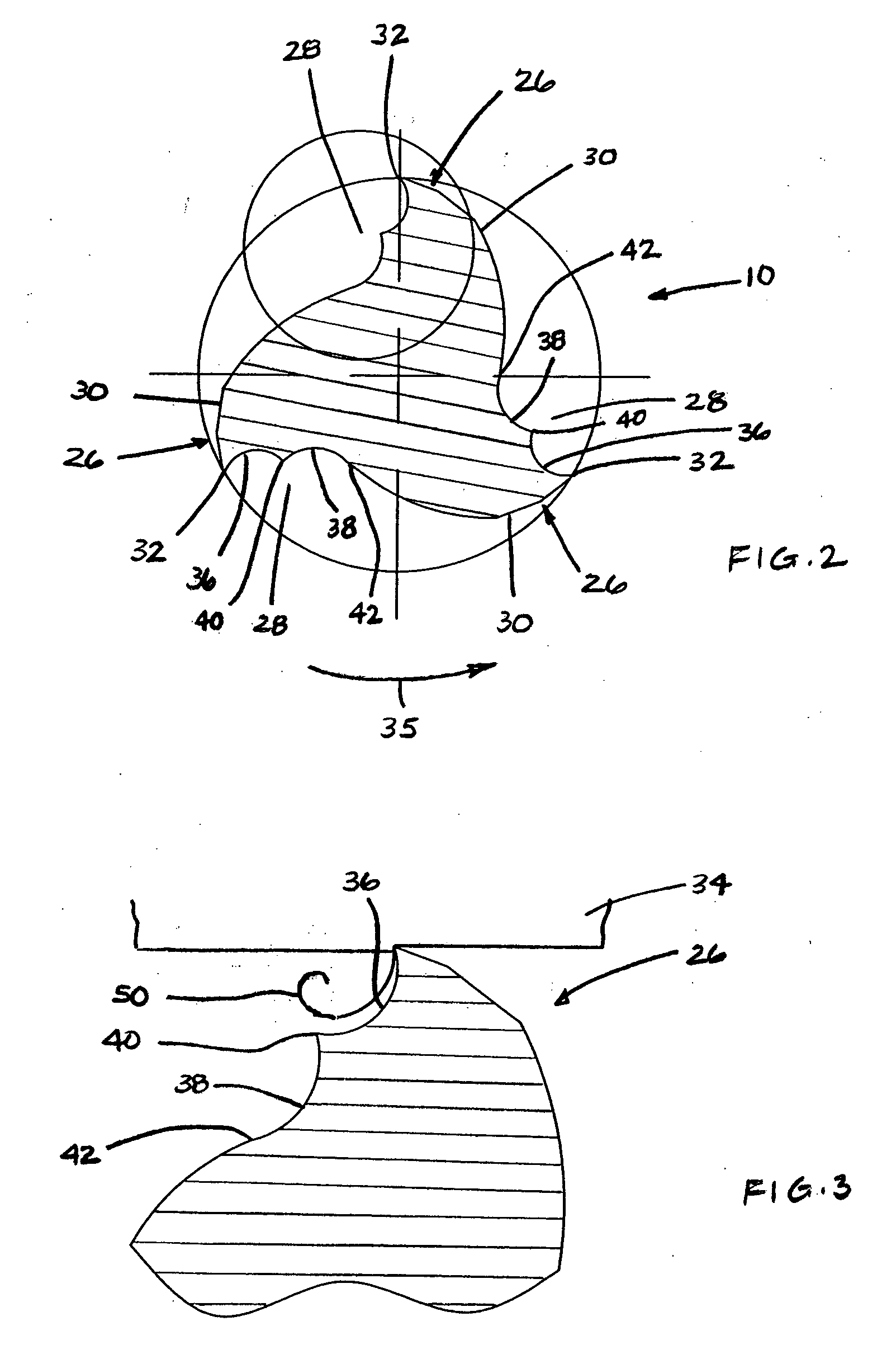
In a radius end mill having a bottom edge formed on the end face thereof, a radius edge designed in a substantially quarter arc shape and formed at a corner portion thereof, and an outer peripheral edge formed spirally on the side surface thereof, the bottom edge and the radius edge being continuously connected to each other at a connecting point A while the radius edge is continuously connected to each other at a connecting point B, when a view taken along a plane that passes through the connecting points A and B and crosses a rake face of the radius edge is represented by an R cross-sectional view, the rake face of the radius edge is designed to have a convex curved line extending from the connecting point A to the connecting point B in the R cross-sectional view.
Owner:HITACHI TOOL ENG LTD
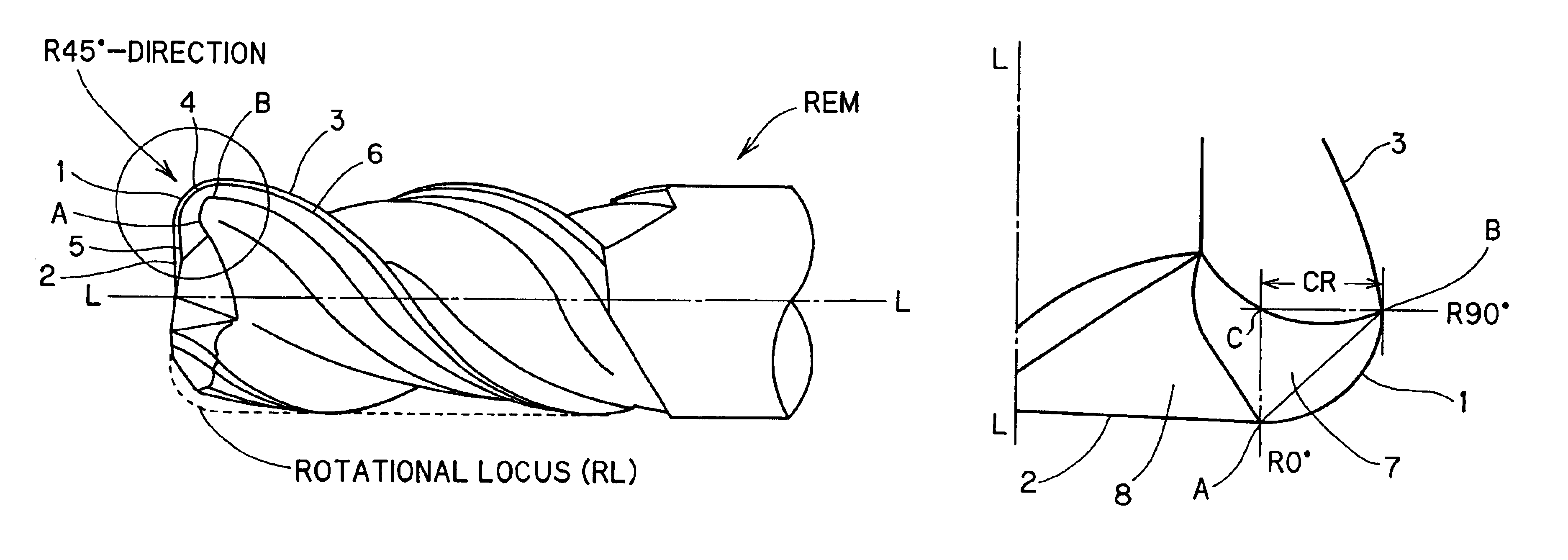
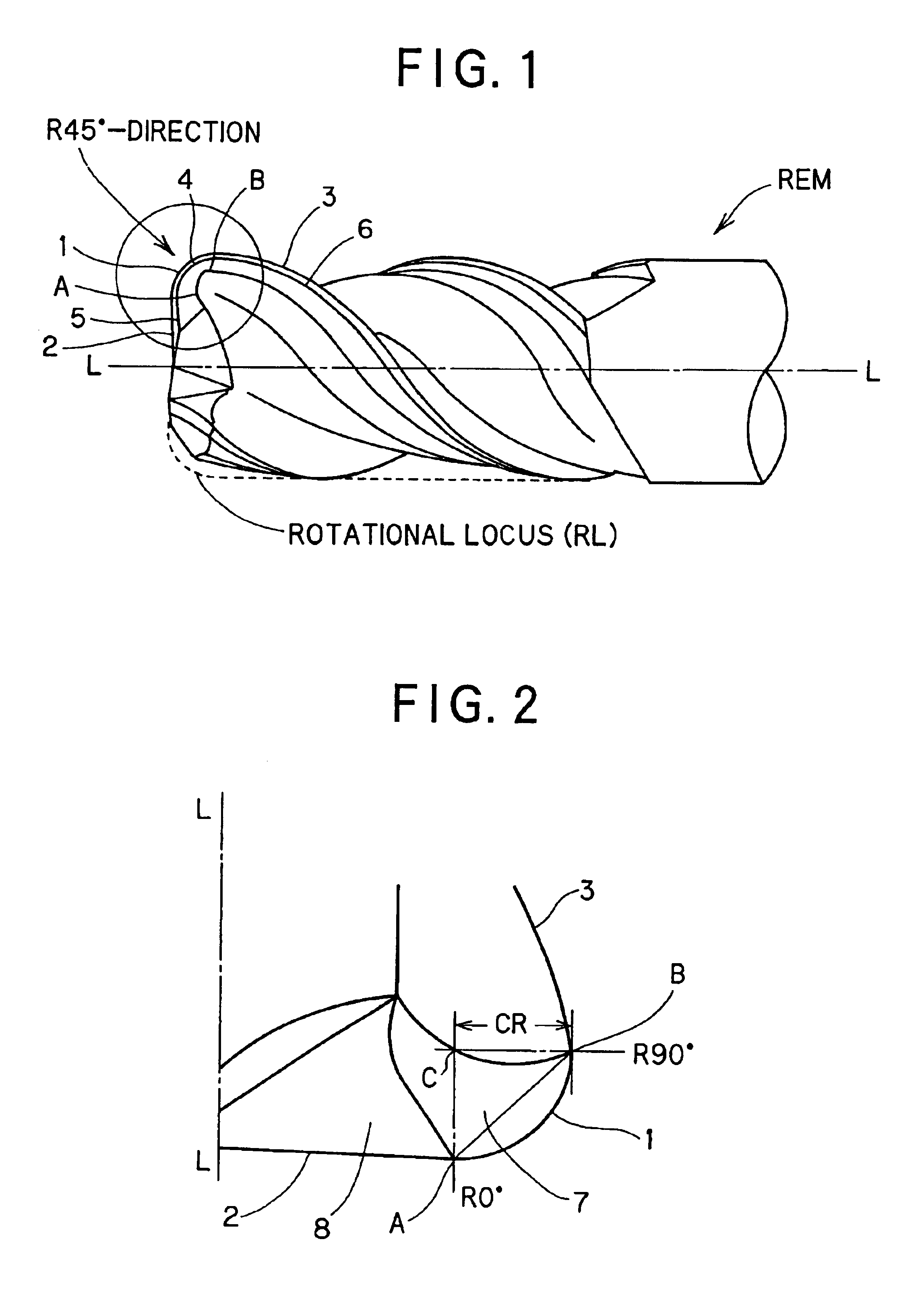
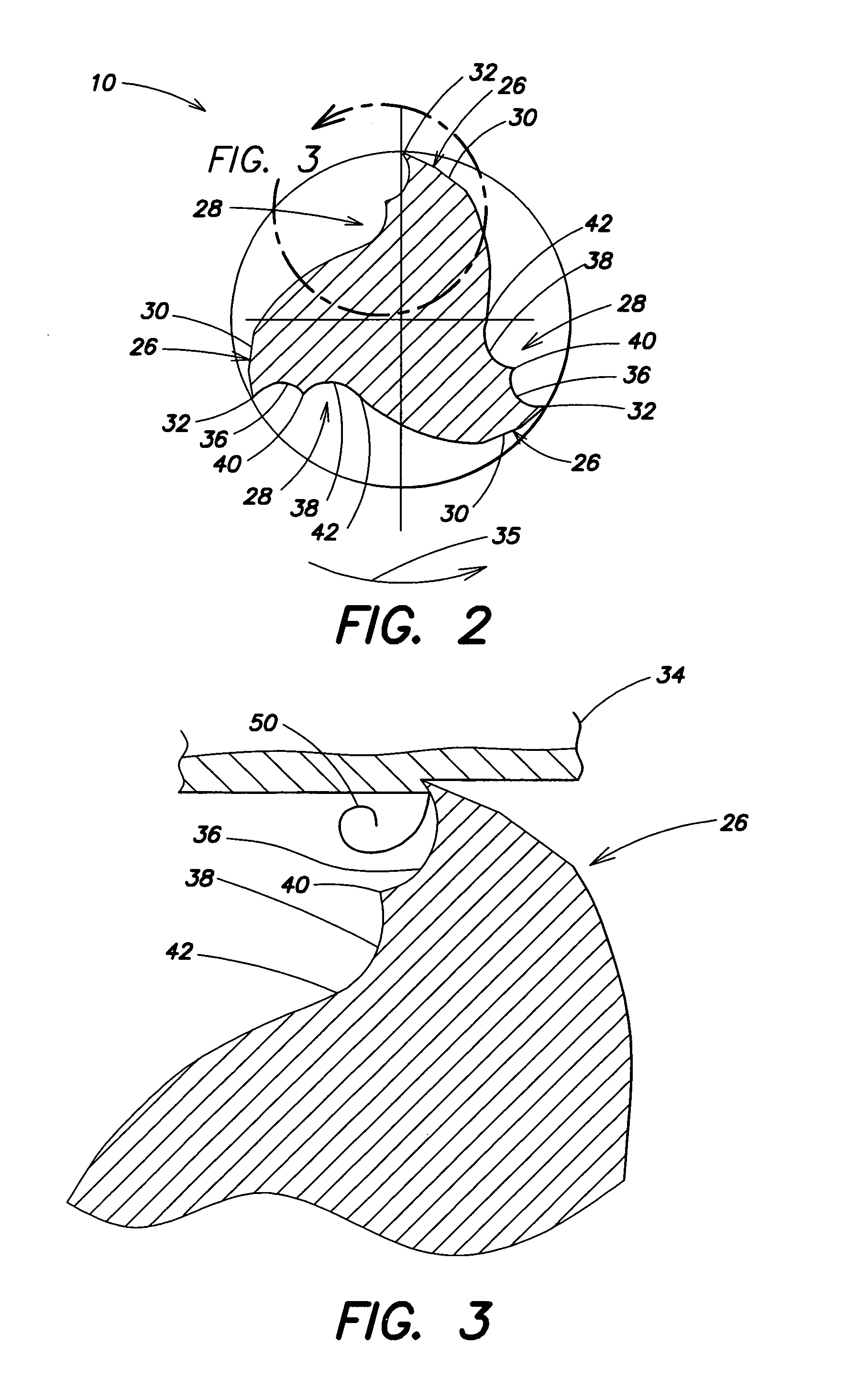
Rotary cutting tool
ActiveUS20070154272A1Overcome disadvantagesMilling cuttersAdverse effect compensationFluteRadial plane
A rotary cutting tool or end mill is provided, the tool comprising a plurality of pairs of diametrically-opposed, symmetrical, helical flutes formed in a cutting portion of the tool body, wherein the pitch between at least one pair of adjacent helical flutes is less than or greater than the pitch of at least one other pair of adjacent helical flutes in at least one radial plane along the axial length of the flutes, a plurality of peripheral cutting edges, wherein at least one of the peripheral cutting edges has a radial rake angle different from radial rake angle of a peripheral cutting edge of a different helical flute.
Owner:KYOCERA SGS PRECISION TOOLS INC
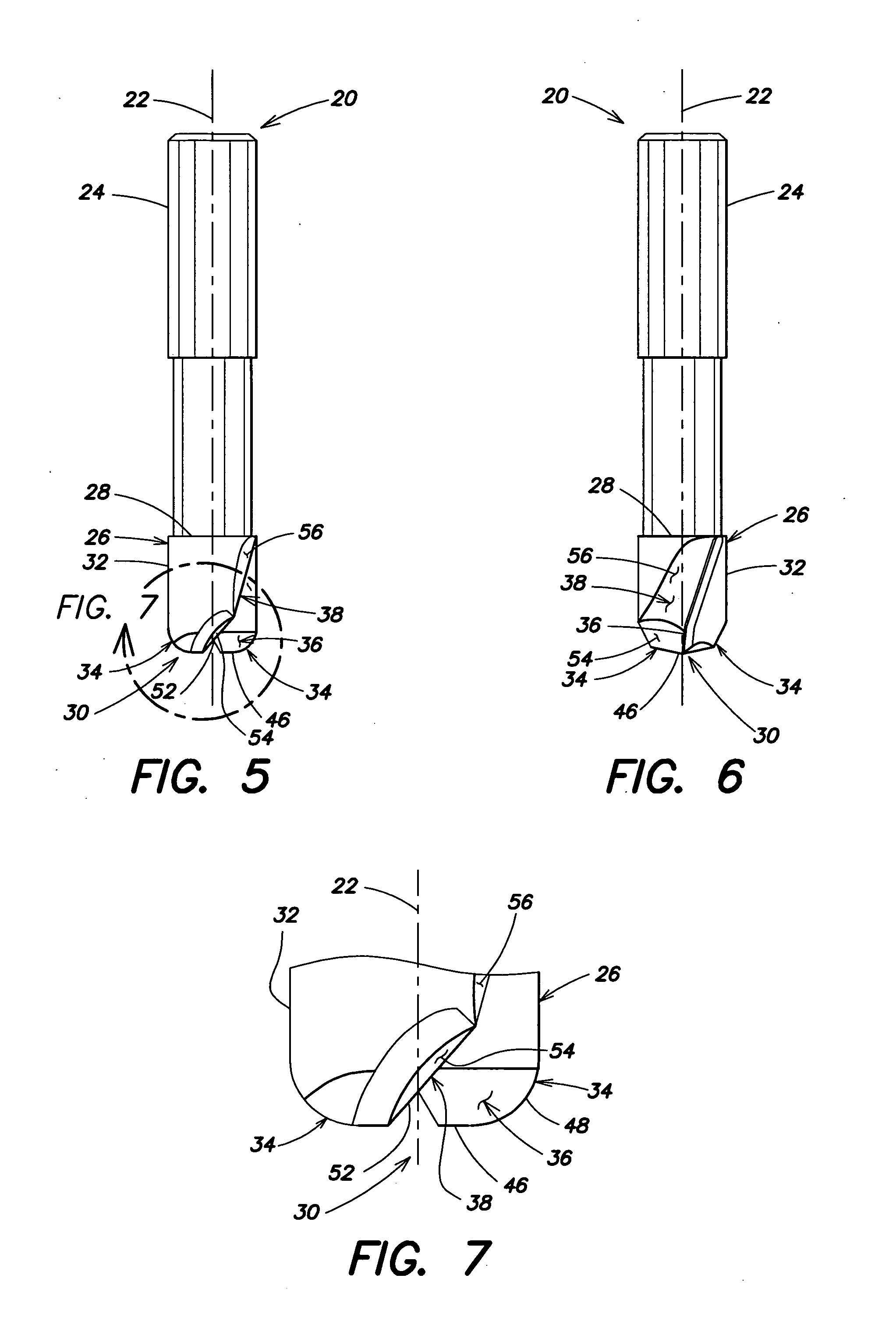
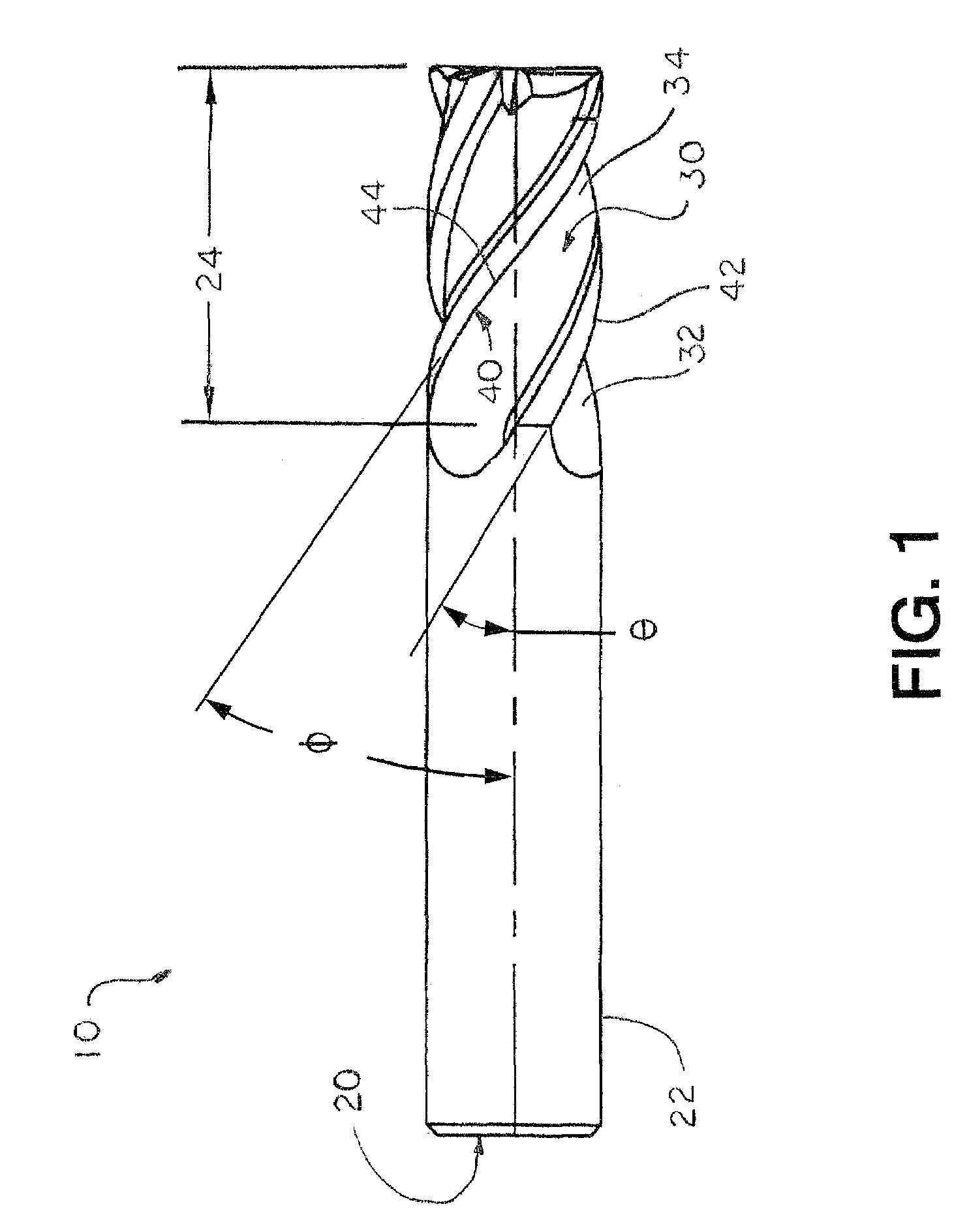
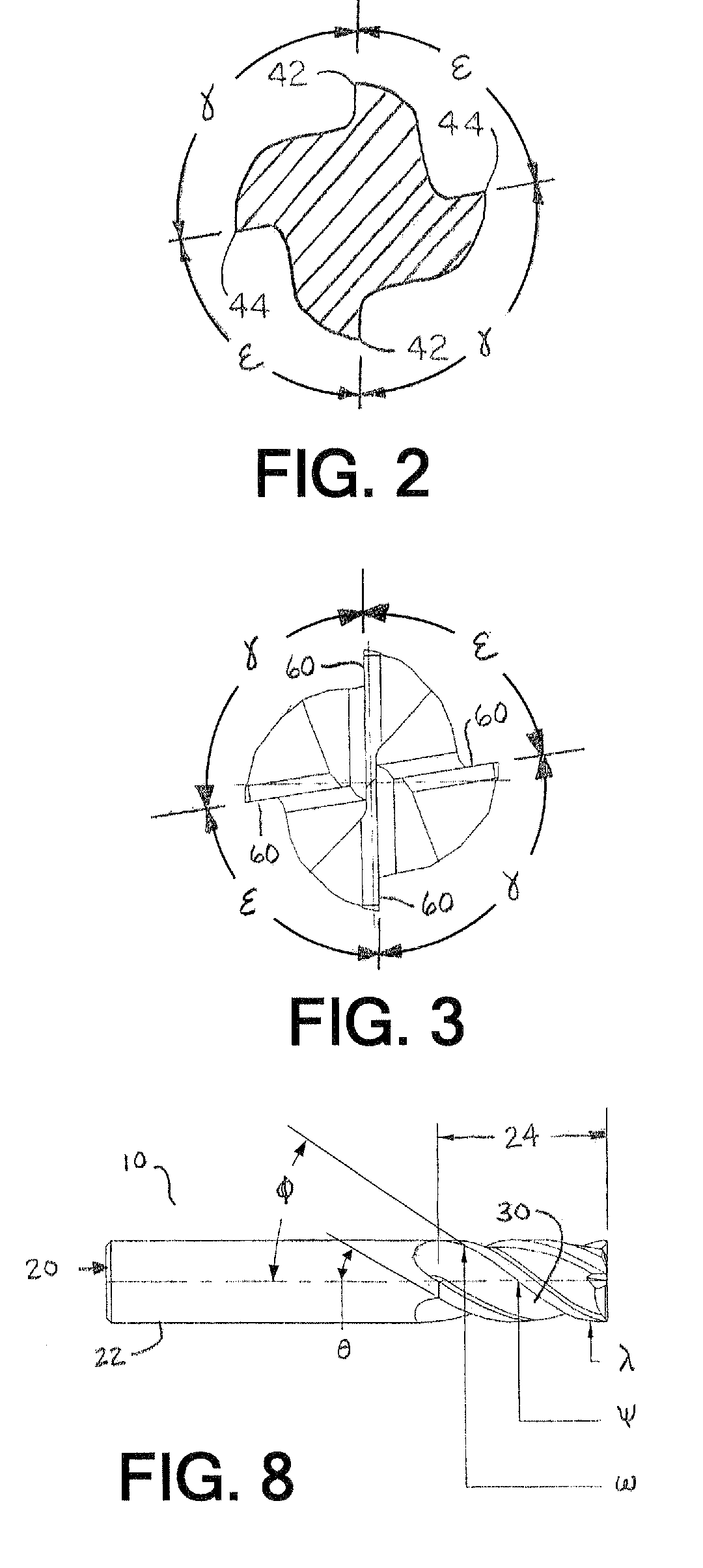
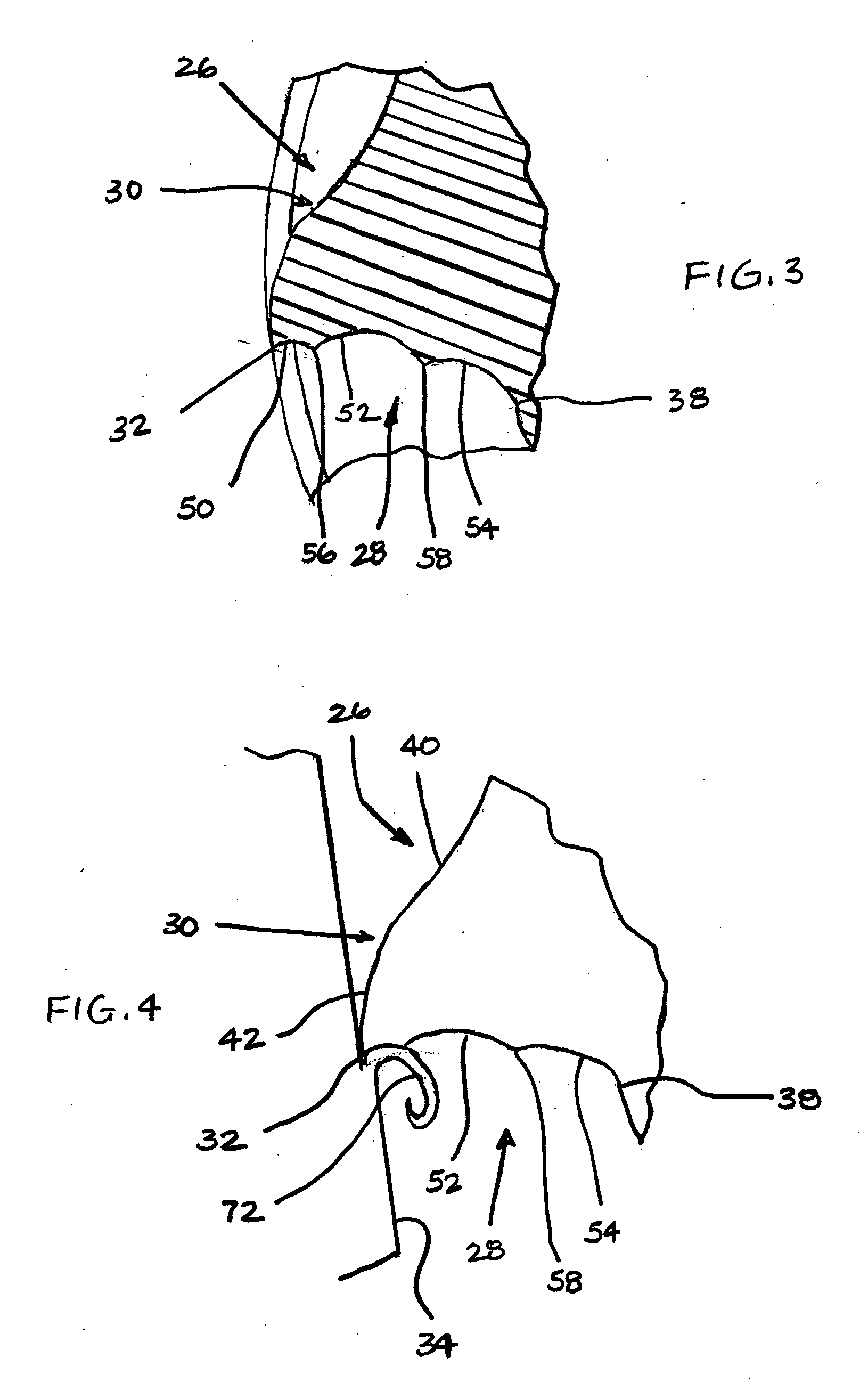
End-mill tool with multiple cutting edges
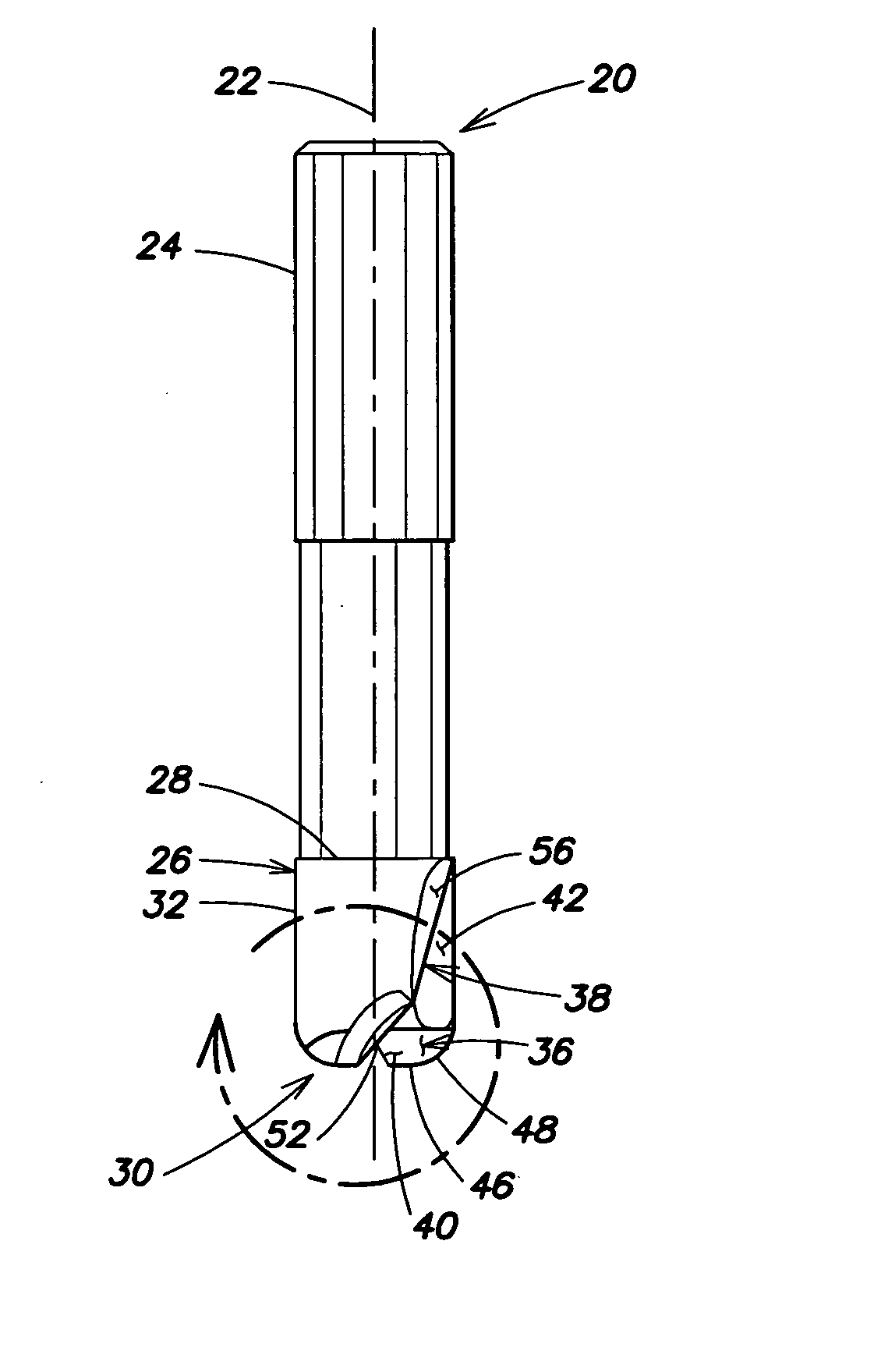
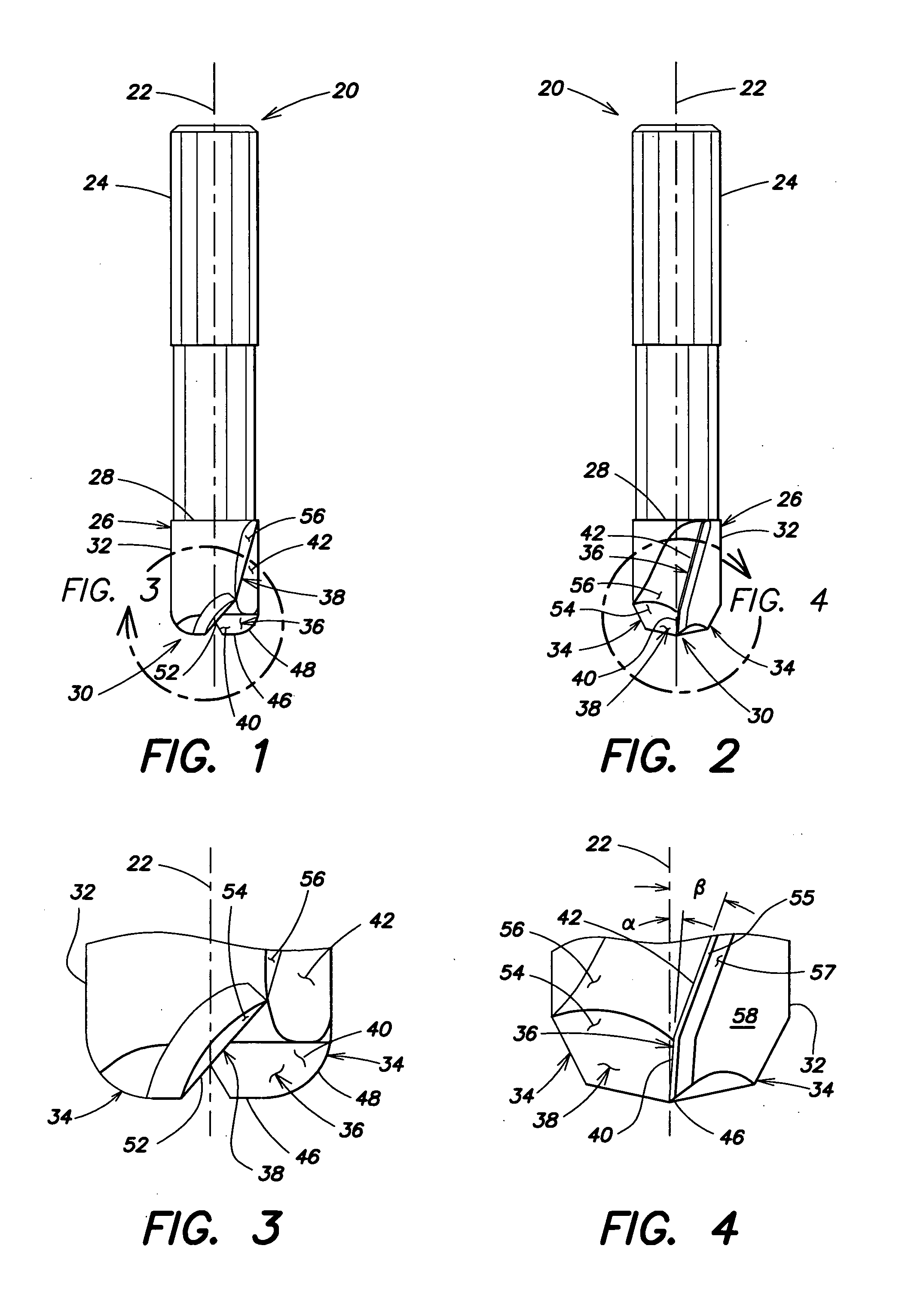
The present invention provides an end-mill tool which includes a shank, a point, and a main body portion located intermediate the shank and the point. A first flute is formed on the main body portion along a first helix. A second flute is formed on the main body portion along a second helix. The first and second flutes preferably extend helically along the body of the tool. Two distinct helical cutting surfaces are defined by the first flute and the second flute. The point of the tool includes two additional cutting edges formed by ears extending outward from the point of the tool adjacent the first flute and the second flute.
Owner:WARDELL LON J
Cutting tool and track guidance system
ActiveUS6966731B2Quickly attachableQuickly removableMulti-purpose machinesProfiling/shaping machinesGuidance systemMilling cutter
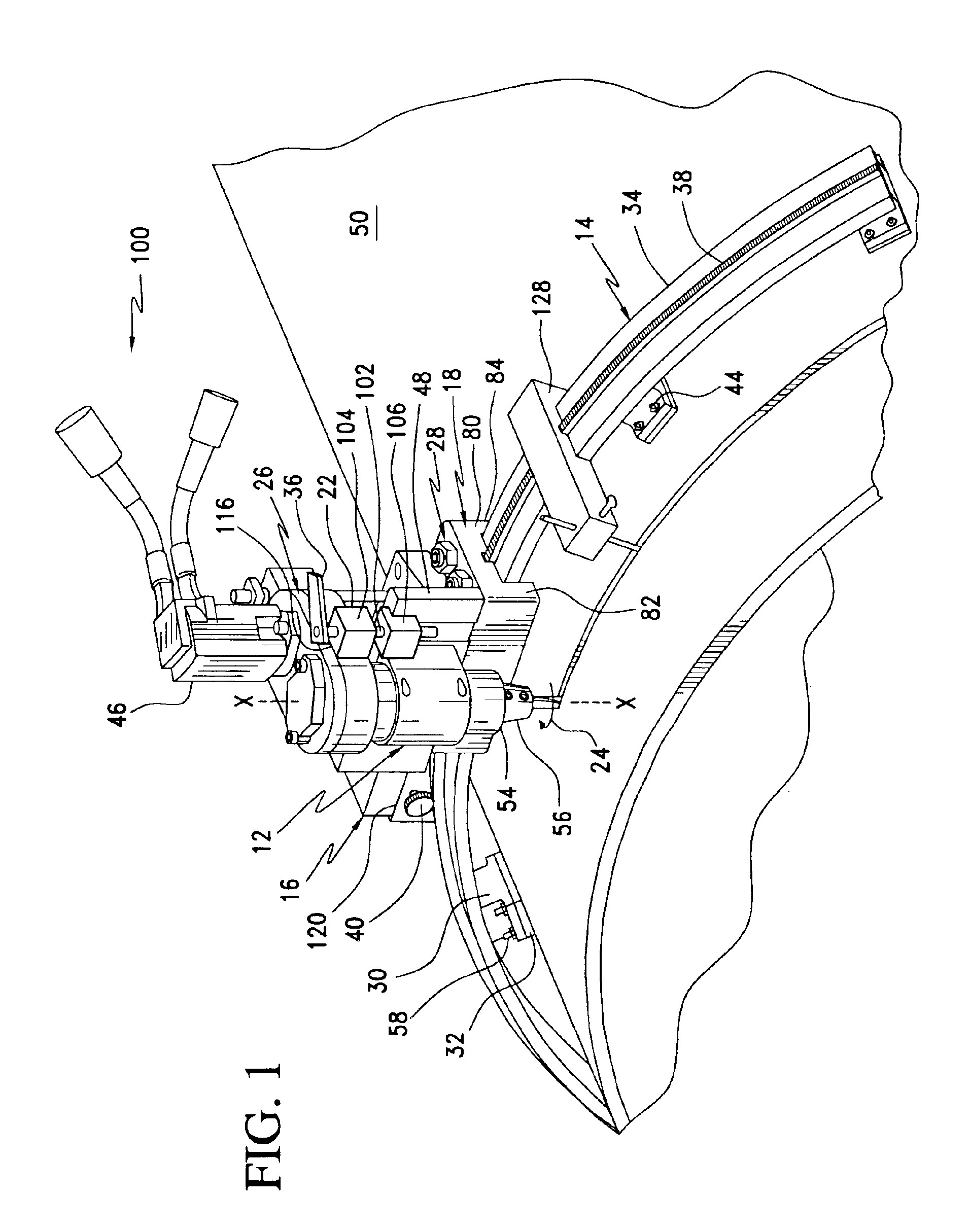
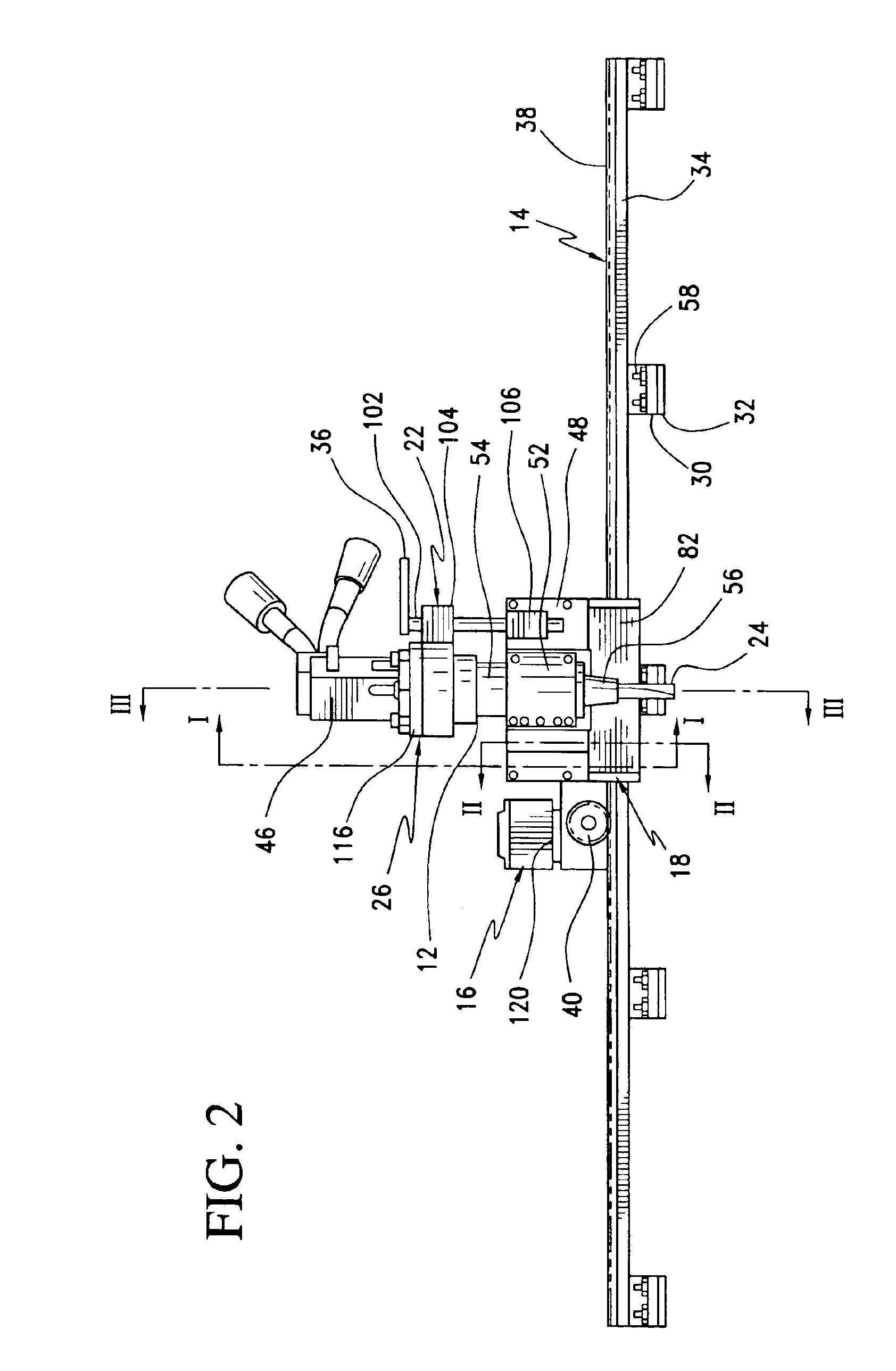
A cutting tool and track system includes a multi-segment track assembly configured to be removably attached to a surface of a workpiece, a carriage assembly configured to ride along the track assembly, a carriage drive mechanism arranged to drive the carriage assembly along the track assembly, a cutting tool assembly connected to the carriage assembly, and a tool driving system connected to the cutting tool assembly. The cutting tool assembly rotatably supports an end mill type cutting tool that may be driven in a radial cutting plane about the axis of a tubular workpiece or along a workpiece surface. A method is provided for cutting a workpiece wherein a cutting tool assembly rotatably supports an end mill mounted for travel along a predetermined transport path in a cutting plane about a central axis of the workpiece wherein the end mill is first fed through the wall thickness of the workpiece and the cutting tool assembly is moved along the transport path in the cutting plane to cut the workpiece.
Owner:TRI TOOL INC
Rotary cutting tool having irregular insert orientation
A rotary cutting tool such as a helical end mill, having pockets arranged to overcome harmonic vibrations. The tool has at least two and in one embodiment all three of three spacing irregularities. In the first irregularity, columns of pockets, typically associated with flutes, are staggered circumferentially out of even spacing. In a preferred embodiment having three flutes, the flutes are mostly not centered on one hundred twenty degree intervals. In the second irregularity, at least some pockets are arranged at different radial rake angles. In the third irregularity, at least some pockets are arranged at different axial rake angles.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
End-mill tool with high and low helical flutes and related method for rough cutting and finishing a workpiece
An end-mill tool has at least one low helix angle flute, or primary flute) and at least two low helix angle flutes, or secondary flutes. The primary and secondary flutes intersect to define a plurality of compound helical cutting surfaces. Each of the compound cutting surfaces includes a cutting edge having a leading portion formed adjacent one of the primary flutes and a trailing portion formed adjacent one of the secondary flutes.
Owner:WARDELL LON J
Double-sided ball end mill cutting insert and tool therefor
A double-sided ball end mill includes a body having a generally hemispherical forward end portion and a rearward end portion. The forward end portion includes insert-receiving pockets and chip pockets. A cutting insert can be mounted within each insert-receiving pocket. The cutting insert includes a first substantially planar surface, a second substantially planar surface, a first curvilinear side surface, a second curvilinear side surface, a first pair of cutting edges formed at an intersection between the first substantially planar surface and the first and second curvilinear side surfaces, and a second pair of cutting edges formed at an intersection between the second substantially planar surface and the first and second curvilinear side surfaces. The first and second planar surfaces are substantially parallel to each other, and the cutting insert is mirror symmetric about all three axes.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
End mill for orbital drilling of fiber reinforced plastic materials
A center or non-center cutting end mill for orbital drilling of fiber reinforced plastic (FRP) materials includes a shank, a neck, a cutting head and two or more flutes. The end mill has a tool geometry with the following features: a dish angle between about 2 degrees to about 6 degrees; a helix angle between about 5 degrees to about 18 degrees; an end teeth radial rake angle between about 0 degrees and about 15 degrees; a peripheral teeth radial rake angle between about 8 degrees and about 16 degrees; a gashing axial rake angle between about 3 degrees to about 10 degrees; and a primary clearance angle between about 10 degrees to about 18 degrees. The end mill is made from a tungsten carbide substrate with cemented cobalt in a range between about 3 to 10 wt. % and a diamond coating having a thickness in a range between about 8 to 20 μm.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
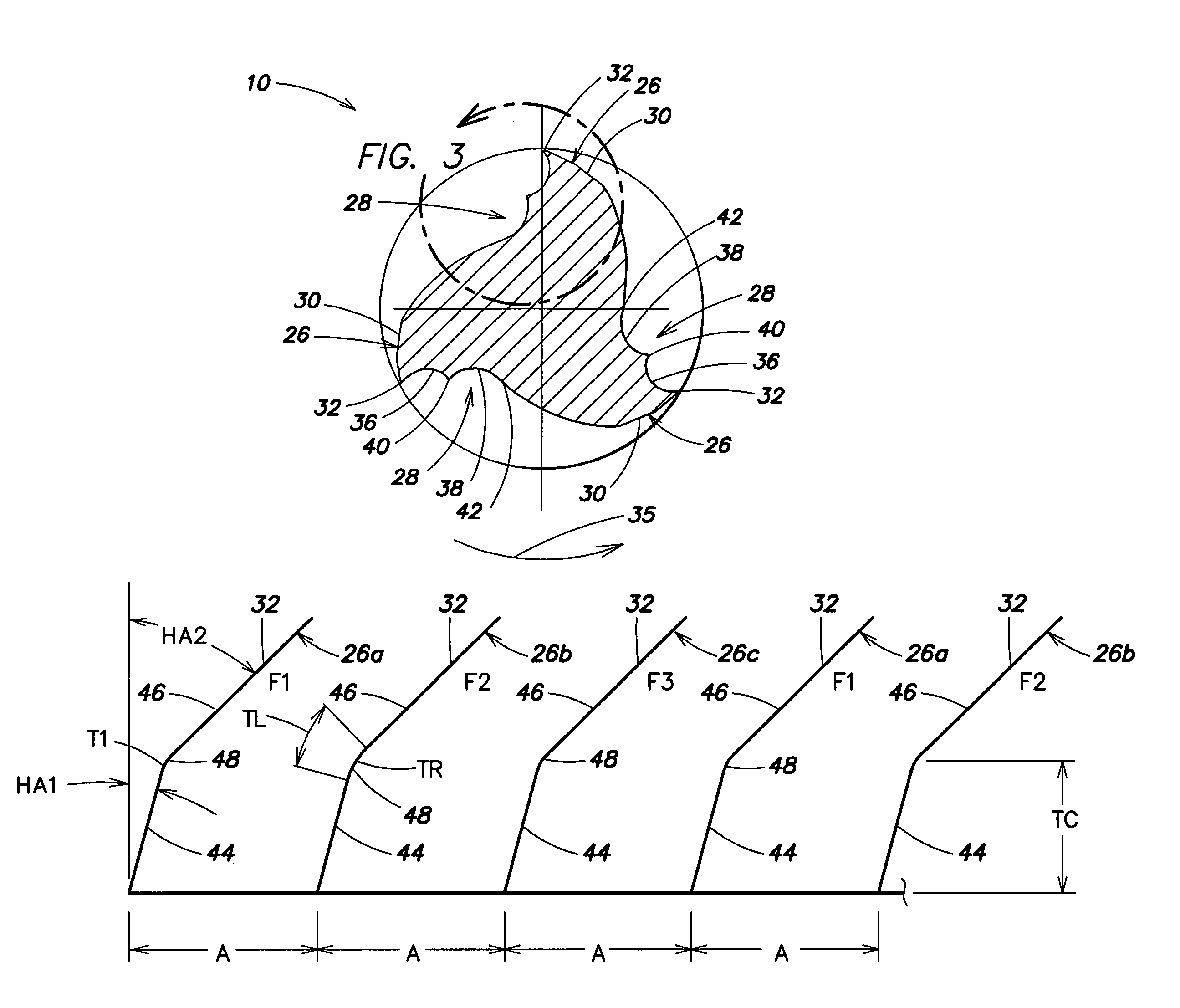
Helical flute end mill with multi-section cutting edge
ActiveUS20060045637A1Desirable performanceEasy chip removalMilling cuttersShaping cuttersFluteEngineering
An end mill is provided that includes a shank section and a fluted section. One or more helical teeth are disposed along an outer surface of the fluted section. Each helical tooth has a cutting surface and a relief wall that intersect to form an angle defining a helical cutting edge. The cutting surface of each helical tooth includes a first section, a second section, and a take-off peak disposed between the first section and second section. The cutting edge of each helical tooth includes a first portion having a first constant angle, and a second portion having a second constant angle unequal to the first constant angle, and an arcuate transition section connecting the first portion and second portion. Some embodiments of the present invention include more portions than the aforesaid first and second portions.
Owner:BERKSHIRE PRECISION TOOL
BP and GA based blade machining cutting quantity optimization selection method
InactiveCN105160059AImprove calculation accuracyImprove accuracyGenetic modelsForecastingAviationResearch Object
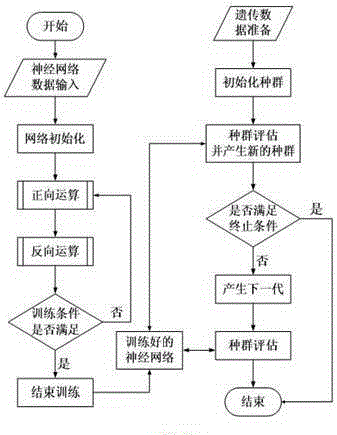
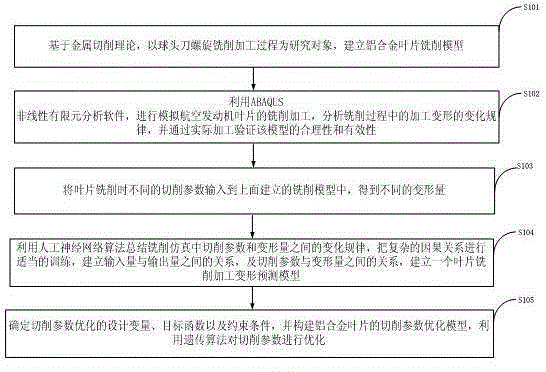
The invention discloses a BP and GA based blade machining cutting quantity optimization selection method. The method comprises: establishing an aluminum alloy blade milling model by taking a spiral milling process of a ball end mill as a research object; simulating milling of blades of an aeroengine by using ABAQUS nonlinear finite element analysis software; summing up a change pattern between a cutting parameter and a deformation amount in milling simulation and a relationship between the cutting parameter and the deformation amount by using an artificial neural network algorithm, and establishing a blade milling deformation prediction model; and determining a design variable, a target function and a constraint condition for cutting parameter optimization, constructing a cutting parameter optimization model of aluminum alloy blades, and optimizing the cutting parameter by using a genetic algorithm. According to the method, the functional relationship between the deformation amount and the cutting parameter is established, and the cutting parameter optimization model is established, thereby providing a reasonable and quick cutting parameter selection method to guide actual production.
Owner:XIAN TECH UNIV
Multi-axis curved surface type numerically-controlled method for machining complicated curved surface part
ActiveCN103537743AImprove cutting efficiencySmall residualAutomatic control devicesFeeding apparatusNumerical controlMilling cutter
The invention discloses a multi-axis curved surface type numerically-controlled method for machining a complicated curved surface part. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the axis of a cutter can be arranged according to the directions of longitude and latitude normal lines for forming a curved surface, an inclined angle is adjusted to generate a cutter path, and the machining efficiency and the part surface smoothness can be improved. The numerically-controlled method can be realized by the following technical scheme: a part is fixed in a rotary center of a five-shaft machine tool; a curved surface is reconstructed according to the curvature change, the normal line direction of the curved surface and a machining path; a space change of an axis vector of the cutter is controlled by adjusting the front inclined angle and the side inclined angle of a cutter shaft of a flat-bottom end mill so that the cutter always keeps that a cutter tip participates in curved surface cutting in the five-axis continuous cutting process; a curved surface projection machining manner is adopted in the programming process so that the mill can carry out multi-axis linked milling machining according to the curvature change of the curved surface; the axis of the cutter is similar with a relatively small front inclined angle alpha overlapped to the normal line direction of the cutter path and a side inclined angle is set as 0; the axis of the cutter is kept vertical to the direction of the machining path to implement a five-axis linked machining numerical control procedure.
Owner:四川泛华航空仪表电器有限公司
End Mill Having A Symmetric Index Angle Arrangement For Machining Titanium
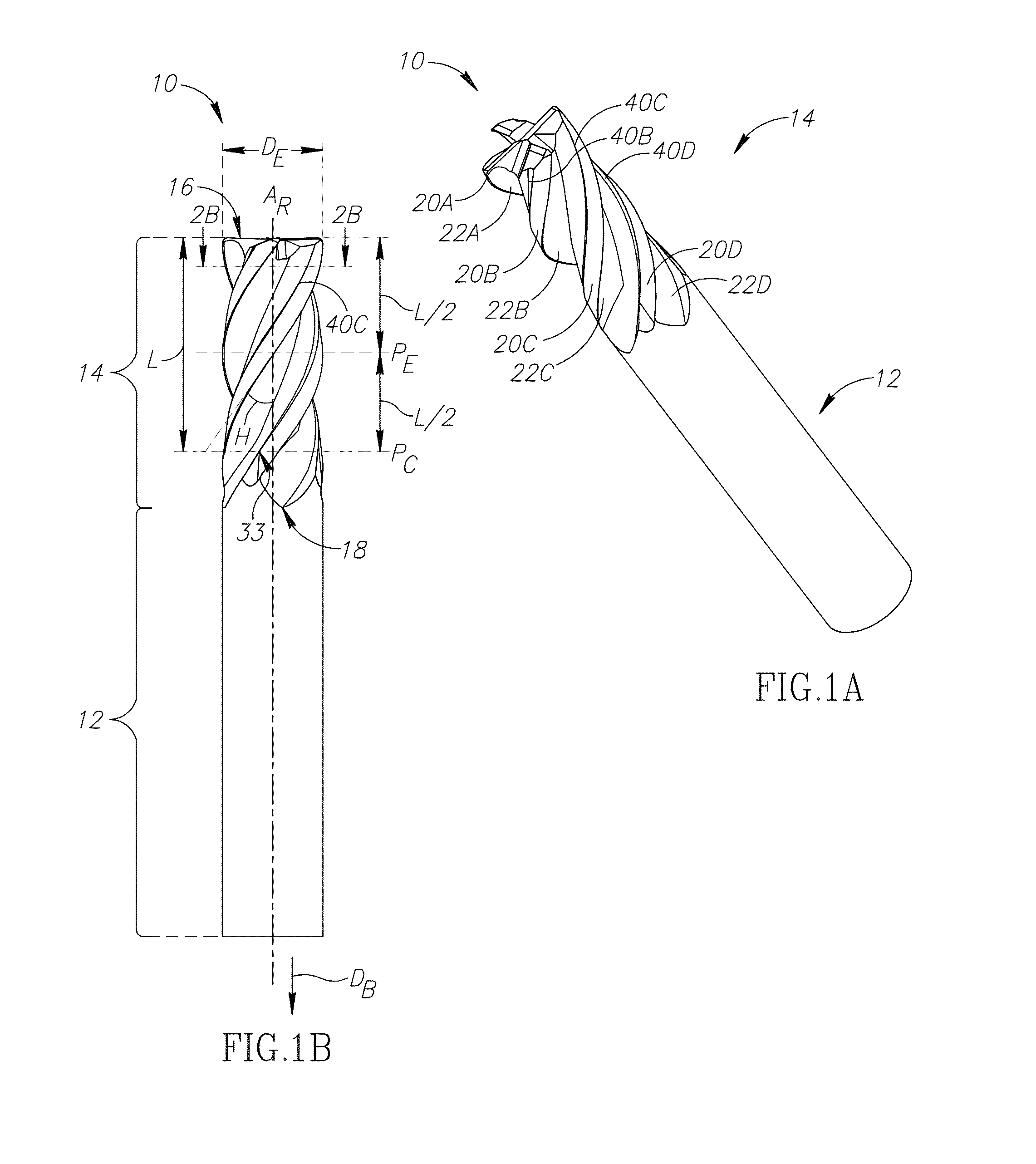
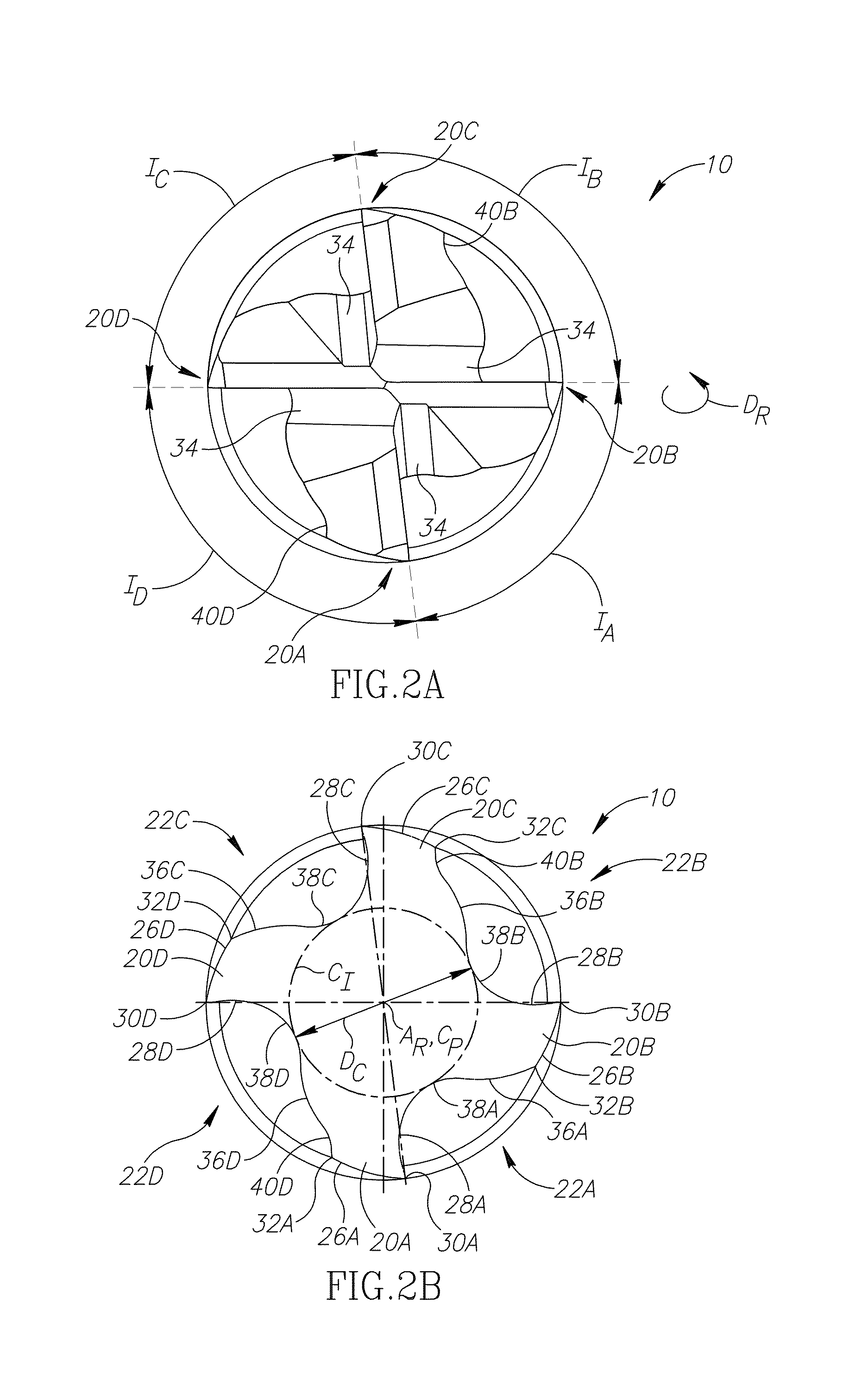
An end mill for machining titanium includes a cutting portion having blunt cutting edges alternated with flutes. Each flute includes, in order from the cutting edge, a rake surface, a concavely shaped bending portion, a convexly shaped ejecting portion and a tooth relief edge. The convexly shaped ejecting portion has an ejection height E, which is measurable between an apex of the ejecting portion to an imaginary straight line extending from a nadir of the adjacent bending portion of the flute to the adjacent tooth relief edge. In a plane perpendicular to a rotation axis of the end mill, the ejection height E and a cutting portion diameter DE, fulfill the condition 0.010DE<E<0.031DE.
Owner:ISCAR LTD
Multiple-axis cutting toroidal end mill
InactiveUS20060045639A1Increases effective machining of machineLower capability requirementsMilling cuttersShaping cuttersRotational axisMilling cutter
A one-piece toroidal end mill having an axis of rotation is provided. The end mill includes a shank section and a fluted section. The shank section extends along the axis of rotation. The fluted section extends along the axis of rotation, and has a first end, an outer surface, and a plurality of teeth. The first end is integrally attached to the shank section. Each of the plurality of teeth has a cutting surface and a shoulder surface. The cutting surface includes a cutting edge. The shoulder surfaces intersect with one another to form a center void disposed between the cutting surfaces.
Owner:BERKSHIRE PRECISION TOOL
Tool for chip removal machining
InactiveUS6402439B1Drawback can be obviatedDrawbacks of the known technique are eliminatedWood turning toolsTransportation and packagingMilling cutterWear resistant
A tool such as a drill or end mill has a central portion formed of a relatively tough hard material connected to an outer peripheral portion formed of relatively wear resistant hard material, i.e., the outer peripheral portion is more brittle and wear resistant than the central portion. The chip flutes of the tool are disposed only in the outer peripheral portion and thus are formed entirely of relatively wear resistant hard material.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
Modeling method for milling surface appearance of workpiece
The invention discloses a modeling method for milling the surface appearance of a workpiece, belonging to the field of digital milling. The modeling method comprises the steps of carrying out dispersing treatment on the cutting edge of a ball-end mill according to cutting movement locus of a milling cutter; establishing infinitesimal cutting locus equation of the cutting edge of the ball-end mill, wherein the surface appearance of the cutting locus equation is formed by the outermost side locus in the established locus equation; determining corresponding cutter turning angle range for milling the outermost side locus by judging the cutting infinitesimal position angle range corresponding to the outermost side locus; calculating corresponding milling time for milling the locus by combining with angular rotation speed obtained through a cutter spindle rotation speed; and obtaining the outermost side milling locus through a helical lag angle at the cutting infinitesimal position, thus obtaining the surface appearance of the milling workpiece. The modeling method can solve the generation problem on the surface appearance of the workpiece in milling process.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
Rotary cutting tool
A rotary cutting tool or end mill is provided, the tool comprising a plurality of pairs of diametrically-opposed, symmetrical, helical flutes formed in a cutting portion of the tool body, wherein the pitch between at least one pair of adjacent helical flutes is less than or greater than the pitch of at least one other pair of adjacent helical flutes in at least one radial plane along the axial length of the flutes, a plurality of peripheral cutting edges, wherein at least one of the peripheral cutting edges has a radial rake angle different from radial rake angle of a peripheral cutting edge of a different helical flute.
Owner:KYOCERA SGS PRECISION TOOLS INC
Cylinder head stud removal tool
InactiveUS20050204542A1Efficient removalDrilling/boring measurement devicesWorkpiecesCylinder headEngineering
A method and apparatus for the removal of a broken stud from a cylinder head, and rehabilitation thereof, includes a precise alignment block for attachment to at least two intact studs or stud bores of a cylinder head for alignment of a pilot port over the broken stud. Further holes in the block along the length of the block match a stud pattern of a cylinder head of pre-determined stud spacing. The apparatus comprises a series of replaceable steady pilots and corresponding rotary tools in pairs, including an end mill and cooperating milling pilot for flat or concave milling of the end of the broken stud; a drill bit and cooperating drilling pilot for drilling the end of the broken stud; and a tap and cooperating threaded tapping pilot to form new threads in the cylinder head for accepting a new replacement stud. Optionally, a threaded coil insert can be used in the newly prepared stud bore, having outer threads matching the new threads and having inner threads matching a replacement stud.
Owner:PITTMAN BERNARD
Carbide end mill and cutting method using the end mill
ActiveUS20120020749A1Improve featuresExtended service lifeMilling cuttersAdverse effect compensationCarbideEnd mill
Provided is a long life carbide end mill which can perform stable cutting in high-efficiency machining such as die machining and parts machining. A cutting method using such an end mill is also provided. When a certain wavy or nicked peripheral cutting edge is considered a reference peripheral cutting edge with reference phases in a pitch of the reference peripheral cutting edge, wherein the distance of each reference phase is an amount corresponding to a value obtained by dividing the pitch of the nicks or waveform of each peripheral cutting edge by the number of the cutting edges; and the phase of at least one of the remaining peripheral cutting edges is deviated in the direction of the tool axis from the corresponding reference phase by an amount corresponding to 5% or less (excluding 0%) of the pitch.
Owner:HITACHI TOOL ENG LTD
NC program generating method, NC apparatus, computer memory product, and computer program product
InactiveUS6942436B2Improve accuracyImprove efficiencyAutomatic control devicesComputer controlCutting forceComputer memory
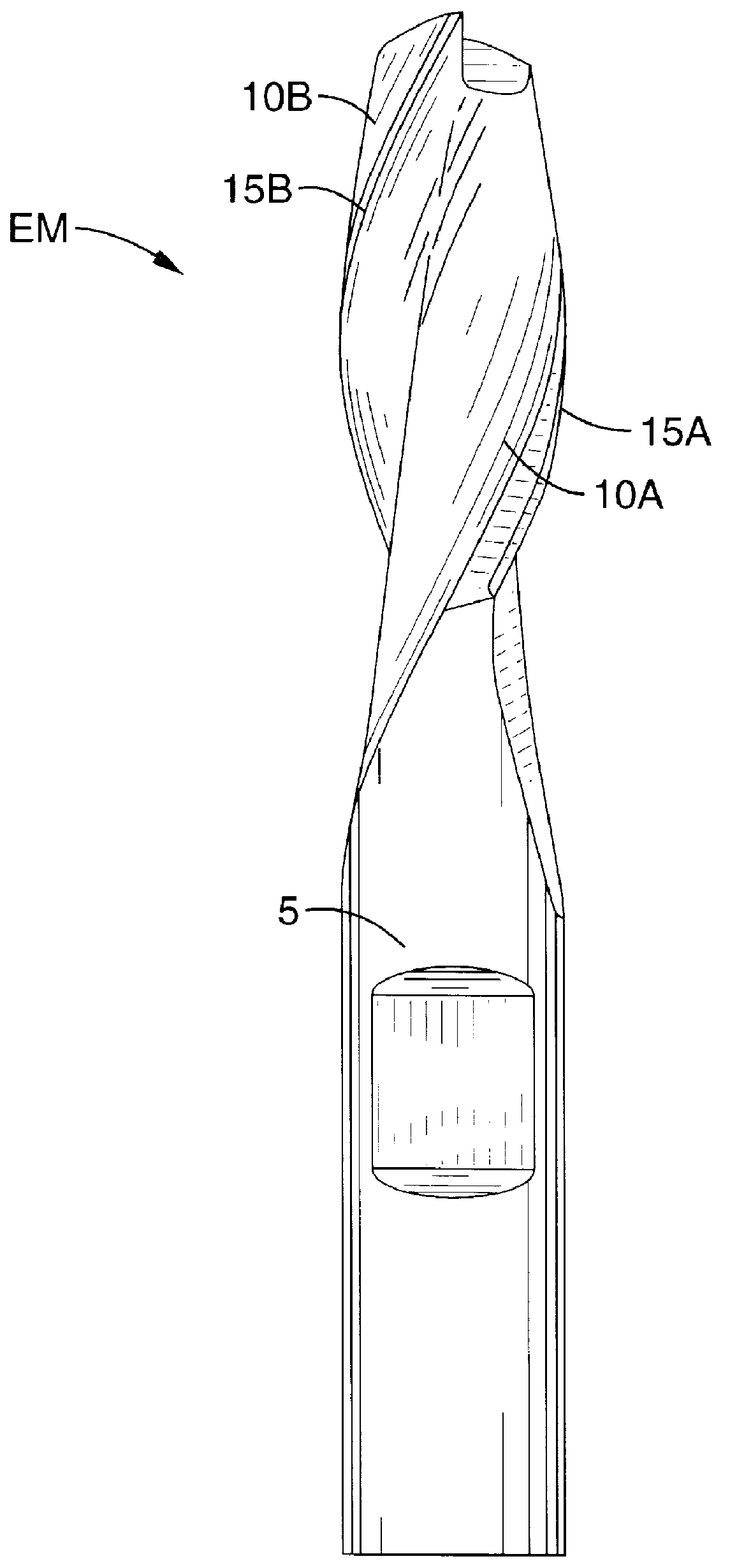
An NC apparatus 1 replaces a required machining shape of a workpiece 5 with a predetermined canned machining cycle depending on a specification of machining conditions including a machining start point, a machining end point, and the size of an end mill E to be used. Calculation of an estimated value of cutting force exerted on the end mill E fed along the assumed tool path during the replaced canned machining cycle is repeated until a predetermined comparison and evaluation result is obtained in comparison with a predetermined appropriate value. Accordingly, the tool path of the end mill E together with the feed rate in each portion of the tool path is determined. This permits generation of an NC program which is used in a NC machine equipped with an end mill serve as a cutting tool, and which optimizes the tool path of the end mill together with the feed rate in each portion of the tool path such as to achieve high machining efficiency and accuracy.
Owner:KAKINO YOSHIAKI +4
Helical flute end mill with multi-section cutting surface
A rotary cutting end mill is provided. The end mill includes a shank section and a fluted section. The fluted section has a first end integrally attached to the shank section, a second end, and an outer surface. One or more helical teeth are disposed along the outer surface of the fluted section. Each helical tooth has a cutting surface and a relief wall that intersect to form an angle defining a helical cutting edge. The helical cutting edge defines an outer circumferential cutting path. The cutting surface includes first, second, and third sections, and first and second take-off peaks. The first take-off peak is disposed between the first section and second section. The second take-off peak is disposed between the second section and the third section.
Owner:DAUPHIN PRECISION TOOL
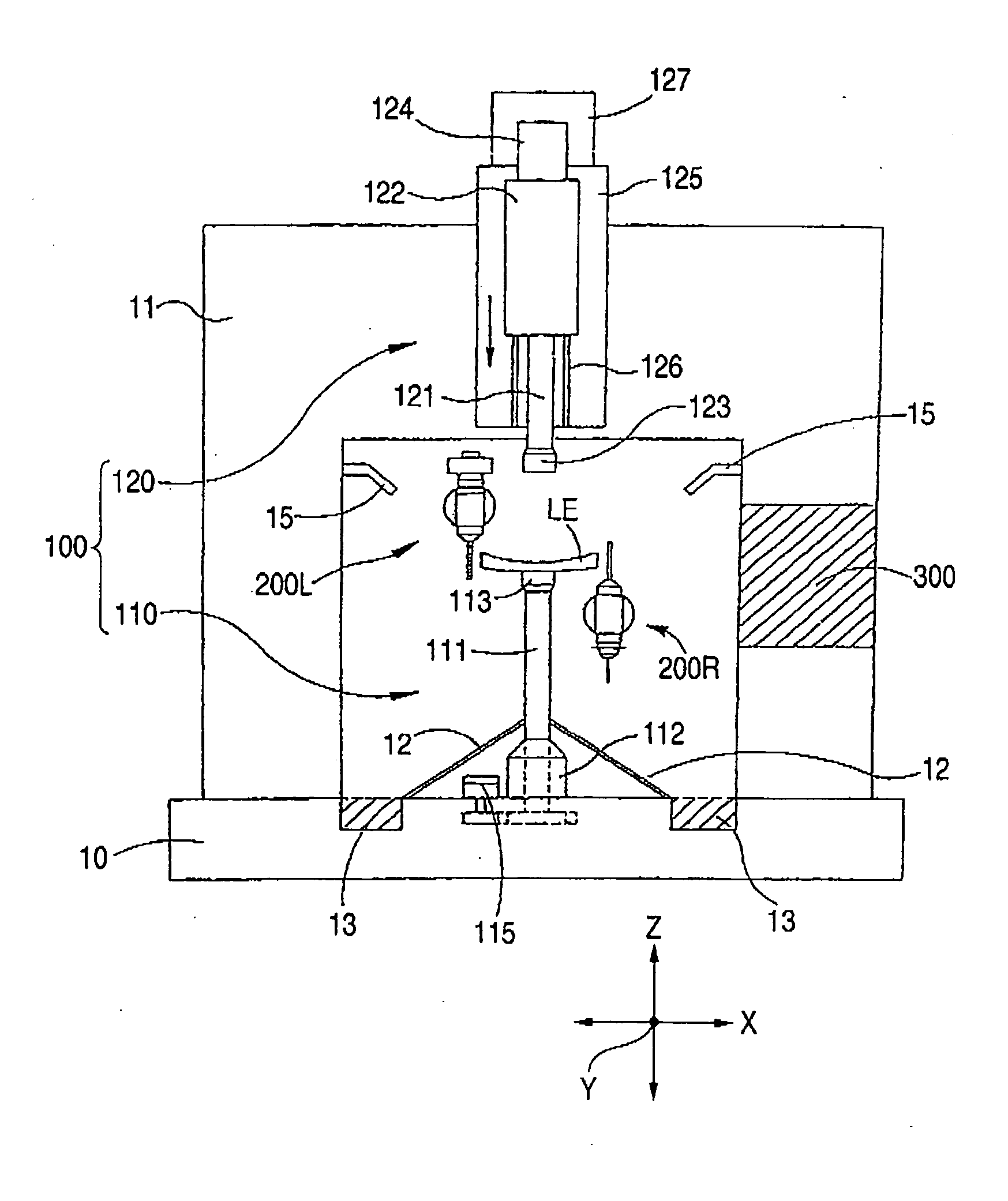
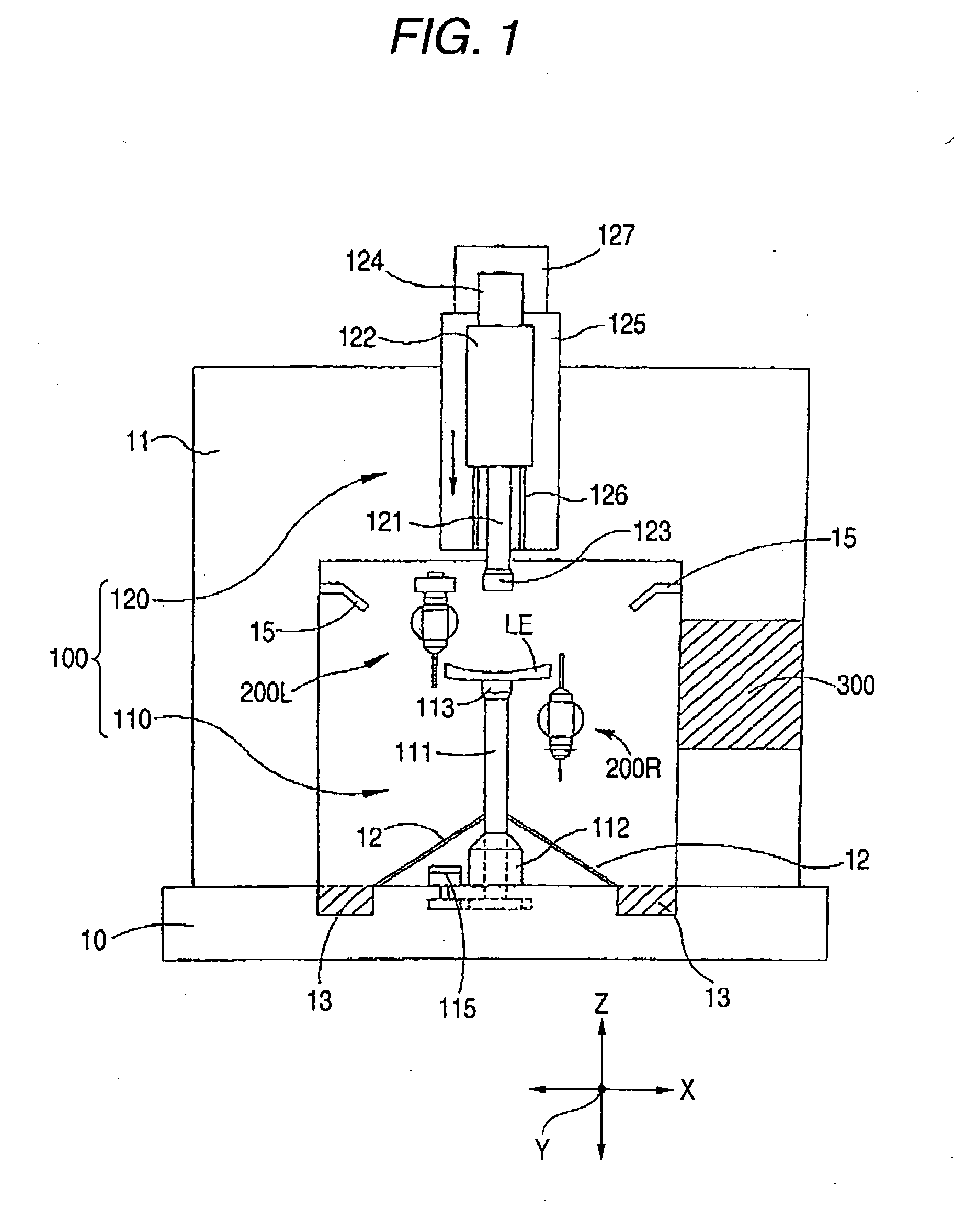
Eyeglass lens processing apparatus
An eyeglass lens processing apparatus for processing a periphery of an eyeglass lens, the apparatus includes: a lens chuck shaft that holds and rotates the lens; an end mill that processes the periphery of the lens; an end mill tilting unit that varies a tilt of the end mill with respect to the lens chuck shaft; an end mill moving unit that relatively moves the end mill with respect to the lens held by the lens chuck shaft; a target lens shape input unit that inputs an target lens shape; a lens measuring unit that detects a position of a processing edge of the lens based on the input target lens shape; a memory that stores a beveling shape including a beveling tilt angle on a front surface side of the lens and a beveling tilt angle on a rear surface side of the lens; and a control unit that controls the end mill tilting unit and the end mill moving unit to perform a roughing process on the lens using the end mill based on the input target lens shape and to perform a beveling process on the roughing-processed lens using the end mill based on the detected position of the processing edge and the stored beveling shape.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
A milling tool with cooperating projections and recesses between the cutting insert and the holder
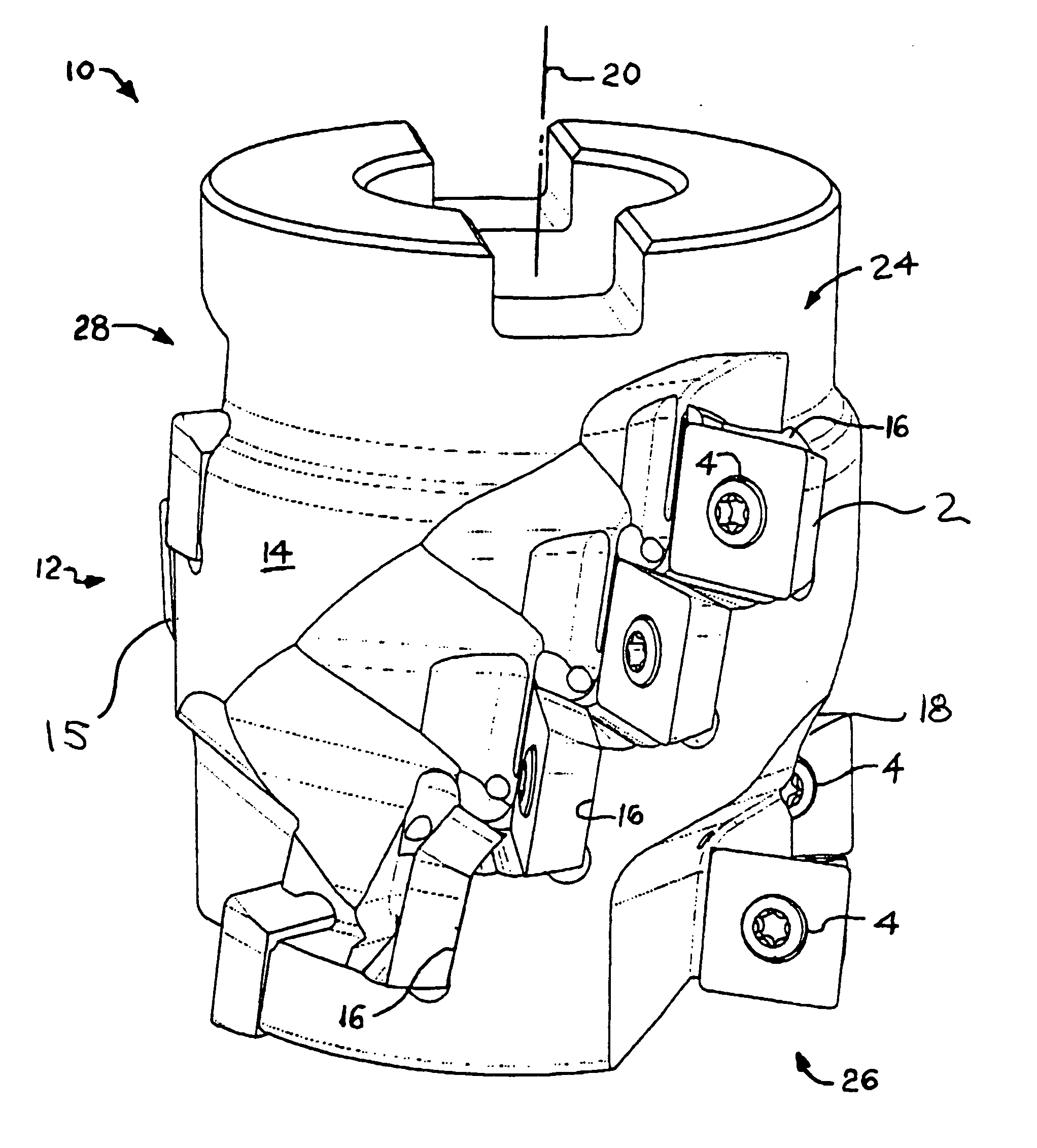
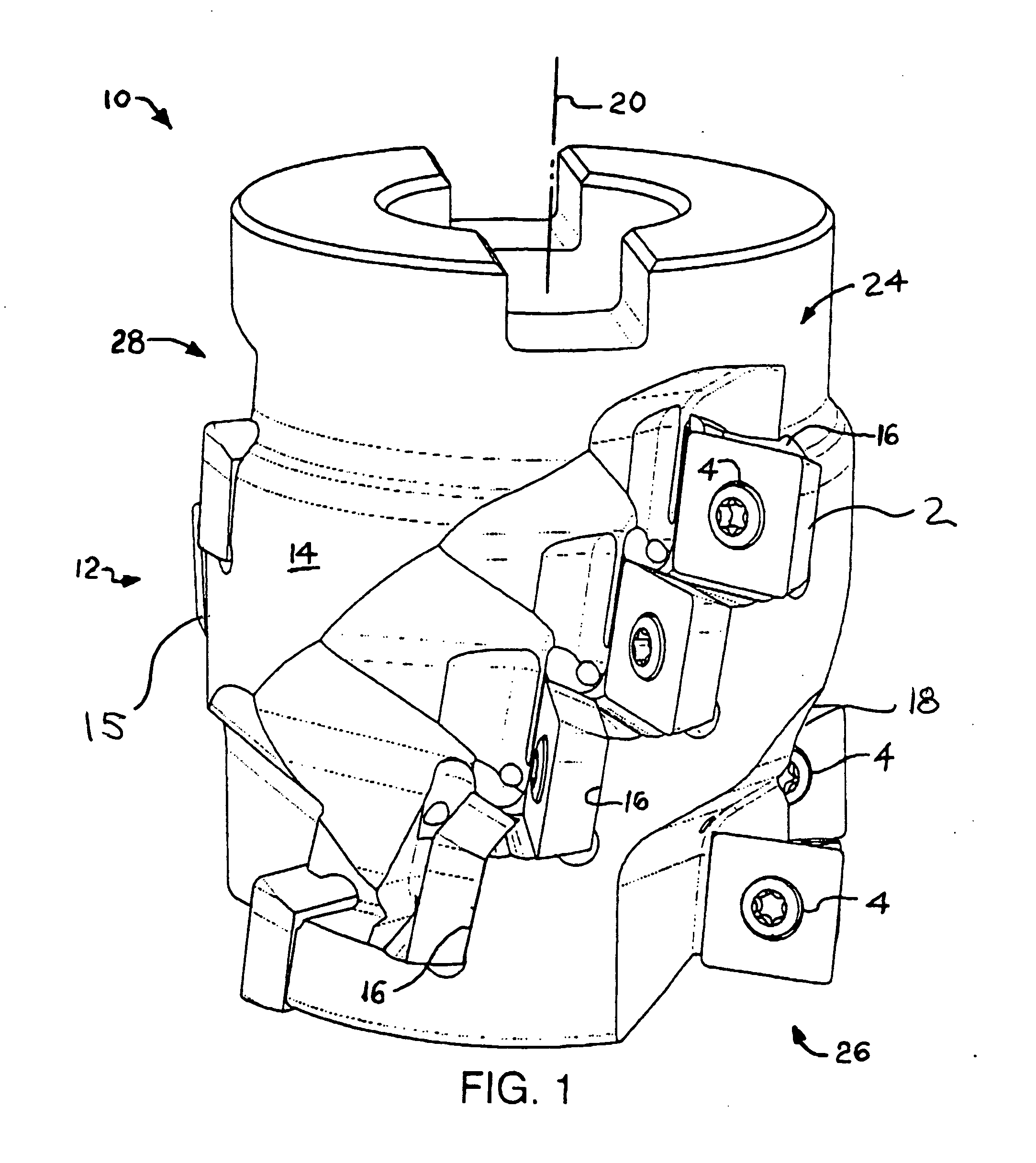
ActiveUS20060056926A1Precise positioningTransportation and packagingMilling cuttersMilling cutterEngineering
The present invention relates to an indexable cutting insert for an end mill for machining of contours in a workpiece and to a milling tool. The cutting insert is asymmetrical in respect of a line through a hole in the cutting insert. The cutting insert includes two cutting edge portions. Each cutting edge portion comprises of a substantially straight cutting edge and a curved cutting edge along respective intersecting lines between a clearance surface and a chip surface. The curved cutting edges have different lengths. The cutting insert includes recesses in a bottom side of the cutting insert. The recesses are arranged on both sides of and at different distances from the hole of the cutting insert.
Owner:SECO TOOLS AB
Construction method of aluminium alloy material end milling-cutting force and cutting processing deformation model
The invention discloses a construction method of an aluminium alloy material end milling-cutting force and cutting processing deformation model. According to the construction method, a milling-cutting force prediction model on the basis of an average cutting force is established; a milling-cutting force prediction model on the basis of an inclined cutting mechanism is established; on the basis of the established milling-cutting force prediction model on the basis of the average cutting force and the established milling-cutting force prediction model on the basis of the inclined cutting mechanism, single-tooth and multi-tooth transient milling-cutting force predictions are respectively carried out and obtained data is compared with testing data; an aluminum alloy material milling-cutting processing deformation model is established; on the basis of a real number encoded adaptive genetic algorithm, a flatness error of an end milled surface is predicted; the construction method has the important research significance for researching the processing deformation mechanism.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Numerical control milling process method of thin-walled part die cavity
InactiveCN101780557AGuaranteed stabilityImprove processing efficiencyMilling cuttersMilling equipment detailsNumerical controlMilling cutter
The invention belongs to the numerical control process technology and relates to an improvement to the numerical control milling process method of the thin-walled part die cavity. The method comprises the following steps: installing and clamping an thin-walled part, selecting a mechanical clamped cutter and an end milling cutter, measuring parameter, selecting a programming origin and cutting parameters, determining the cutter position of the mechanical clamped cutter, measuring the length difference of the end milling cutter and the mechanical clamped cutter, roughing a insert bit mechanically-clamped numerical control milling cutter, finishing a high-speed steel end milling cutter, etc. The invention is characterized in that the cutting parameters are as follows: the cutting depth of the mechanical clamped cutter is 0.4-0.6mm, the cutting depth of the end milling cutter is equal to the depth of the thin-walled part die cavity; the cutting speed of the mechanical clamped cutter is 1500-2500rpm, the cutting speed of the end milling cutter is 400-600rpm; and the feeding amount of the mechanical clamped cutter is 700-1200mm / min, and the feeding amount of the end milling cutter is 300-500mm / min. The numerical control milling process method of the invention has high working efficiency, and can ensure the working size precision of the thin-walled part, obtain lower surface roughness, eliminate size distortion of the part and increase the product quality.
Owner:AVIC HUIYANG AVIATION PROPELLER
Helical flute end mill with multi-section cutting edge
An end mill is provided that includes a shank section and a fluted section. One or more helical teeth are disposed along an outer surface of the fluted section. Each helical tooth has a cutting surface and a relief wall that intersect to form an angle defining a helical cutting edge. The cutting surface of each helical tooth includes a first section, a second section, and a take-off peak disposed between the first section and second section. The cutting edge of each helical tooth includes a first portion having a first constant angle, and a second portion having a second constant angle unequal to the first constant angle, and an arcuate transition section connecting the first portion and second portion. Some embodiments of the present invention include more portions than the aforesaid first and second portions.
Owner:BERKSHIRE PRECISION TOOL
Machining process of axial-flow type turbine blade
The invention discloses a machining process of an axial-flow type turbine blade. The machining process of the axial-flow type turbine blade comprises the following steps that two side faces are machined on a square blank stock through an end face end mill on an ordinary milling machine through two process of rough milling and finish milling, another two side faces are machined with the two machined side faces as base planes, and then the two end faces are machined through the end face end mill; a steam outlet side face is machined on one side face through two process of rough milling and finish milling, the position, close to the steam outlet side face, of the blade root end face is marked as C, a face which forms an acute angle with the steam outlet side face and is adjacent to the steam outlet side face is marked as N and is the inner radial surface, and the other three side faces are machined to be a parallelogram through rough milling and finish milling; central holes are drilled in the blade root end face and the blade crown end face; the blade type is roughly milled through the end face end mill, the blade root is roughly milled, and finally the blade crown is roughly milled; then the blade is installed on a five-axis numerical control machining center for alignment and is machined in a finish mode; a process head at the blade root end face is roughly sawn through a sawing machine; the turbine blade is detected according to the requirements of a drawing.
Owner:南京赛达科技有限公司
Method for preparing a cutting edge on an end mill
InactiveUS6105467AEasy to prepareReduce debrisMetal-working drilling toolsMilling cuttersMilling cutterEnd mill
A method of increasing the length of time a tool maintains sharp cutting edges utilizes the steps of manufacturing the tool with the cutting edges ground sharp and then partially dulling, to a lighter or heavier extent, those previously ground sharp cutting edges. Often the partial dulling is accomplished by means of applying a brush wheel to the selected cutting edges.
Owner:ROBBJACK CORP
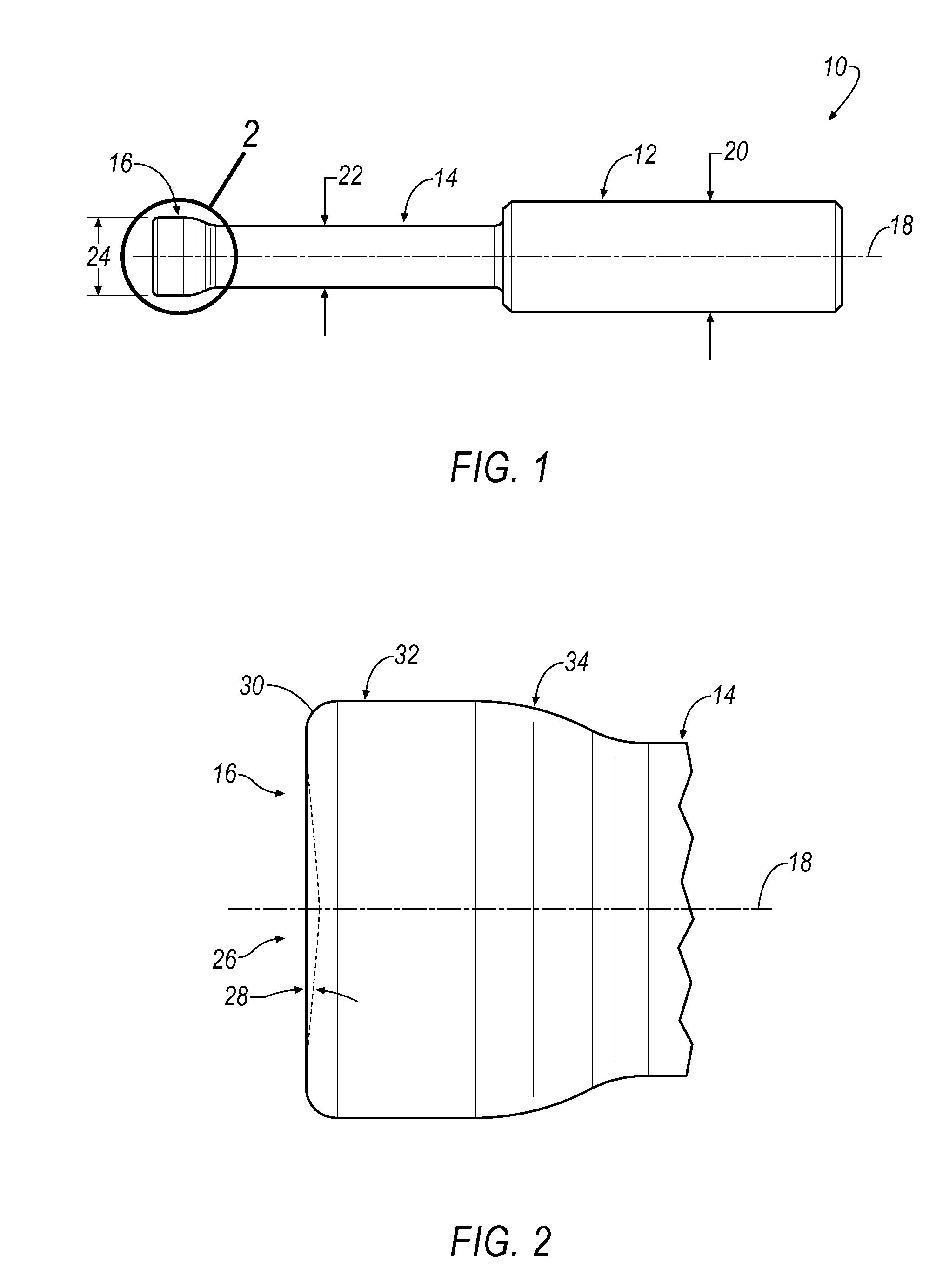
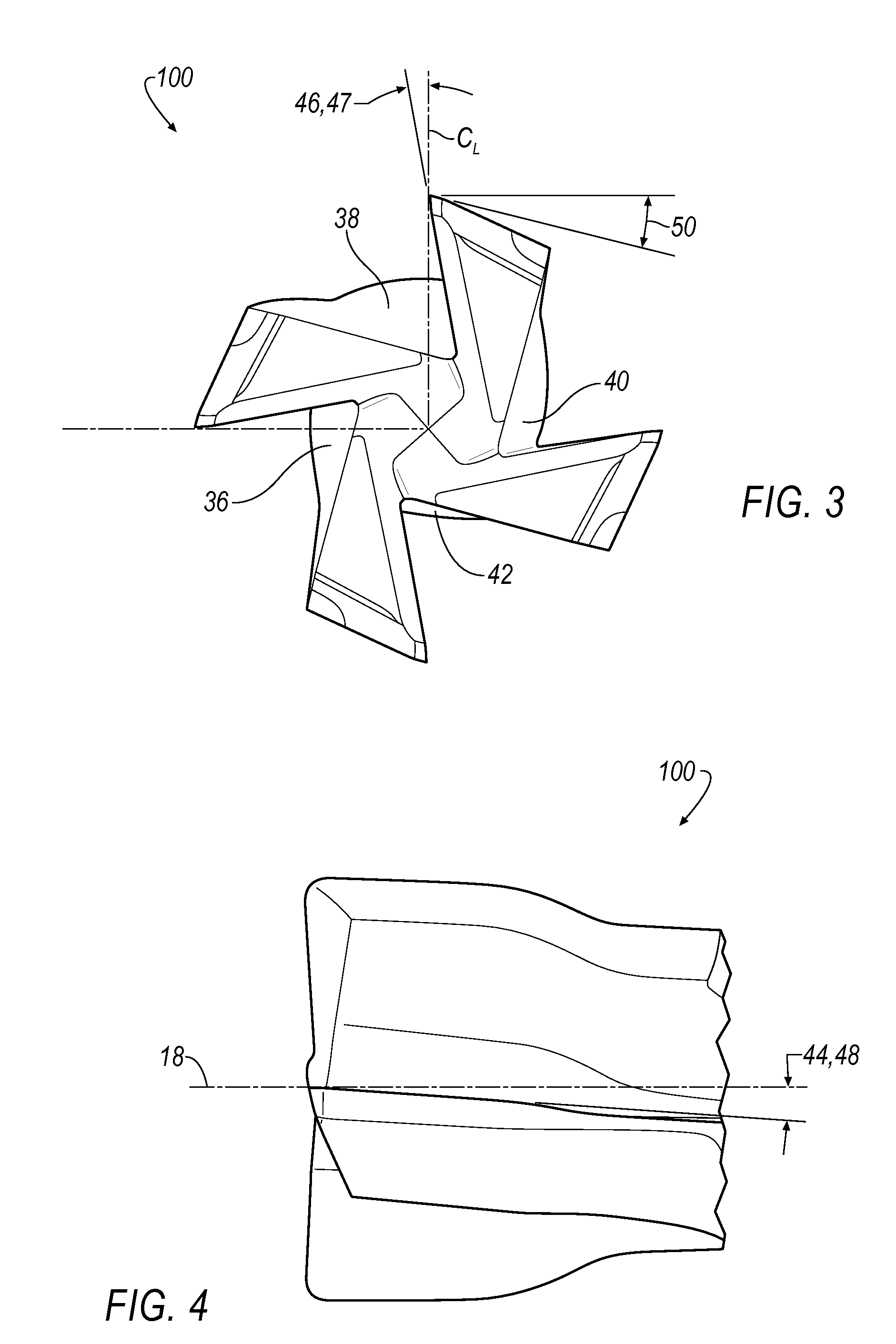
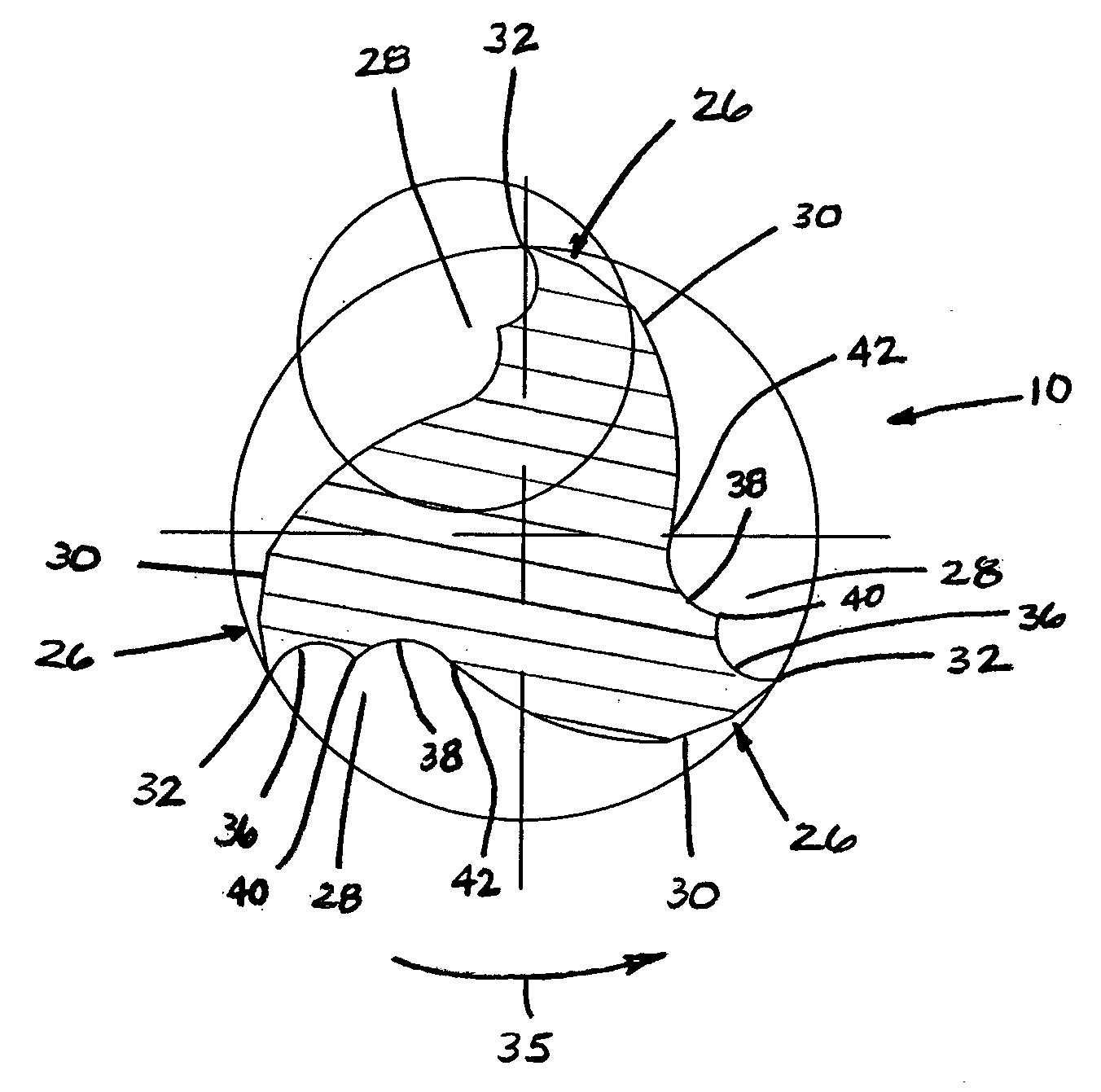
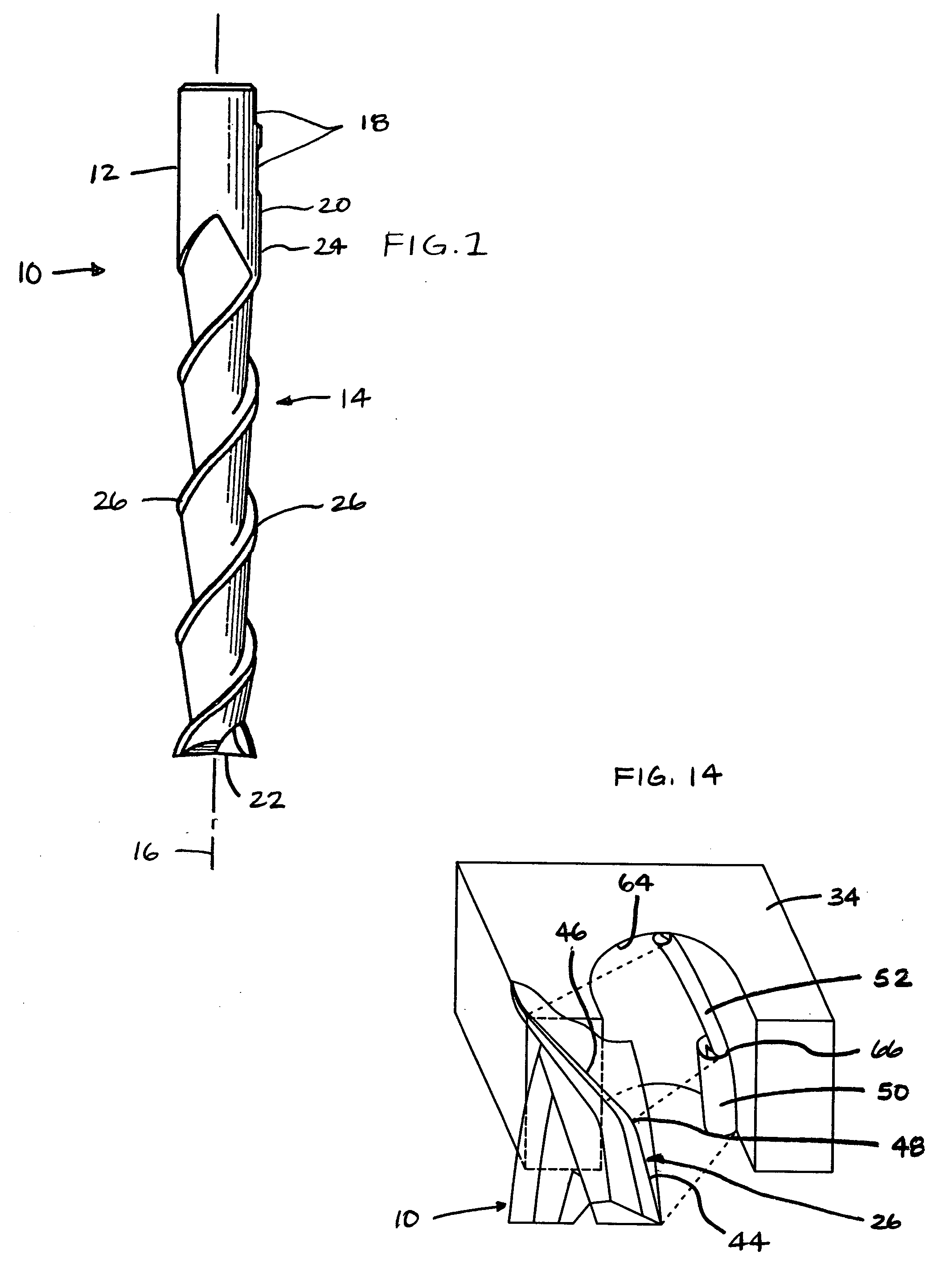
End mill
ActiveUS20080219782A1Improved cutting edgeAvoid chippingMilling cuttersShaping cuttersRotational axisMilling cutter
An end mill is provided having an axis of rotation, a shank section and a fluted section, each extending along the axis of rotation, and a plurality of helical teeth. The fluted section has a first end attached to the shank section and a second end. The plurality of helical teeth is disposed within the fluted section. Each helical tooth has a cutting edge, a relief surface, a cutting surface, and an edge preparation surface. The edge preparation surface is contiguous with the cutting edge of the respective tooth.
Owner:BERKSHIRE PRECISION TOOL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com