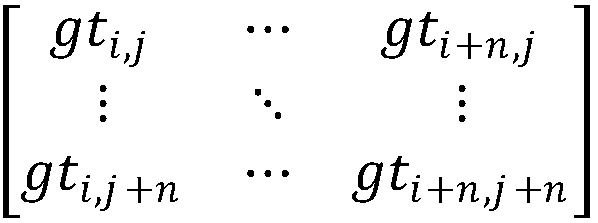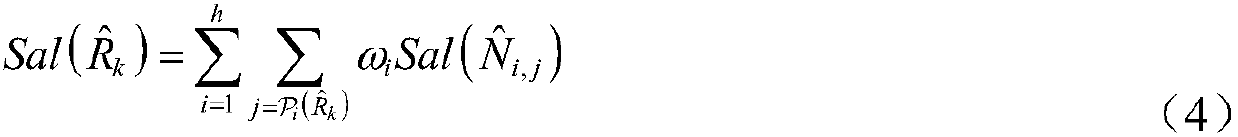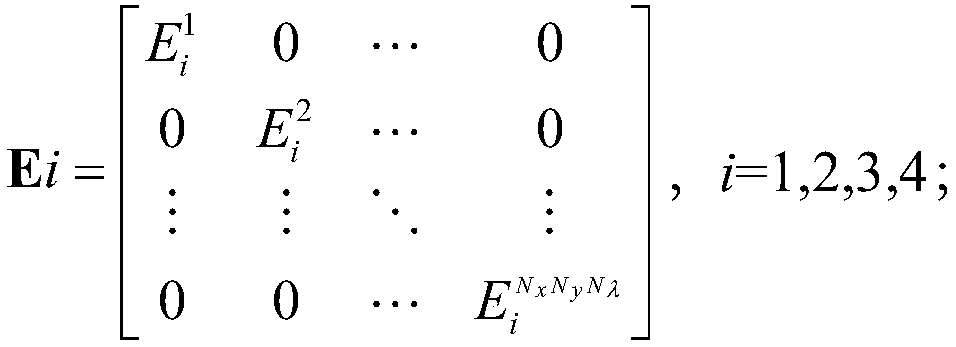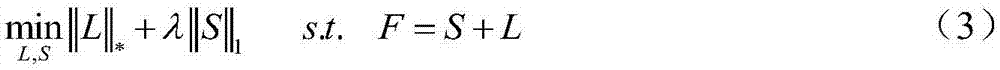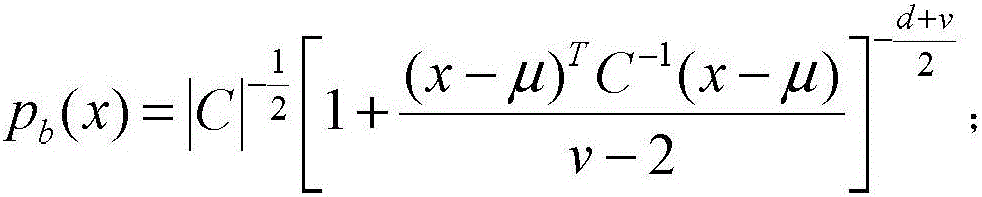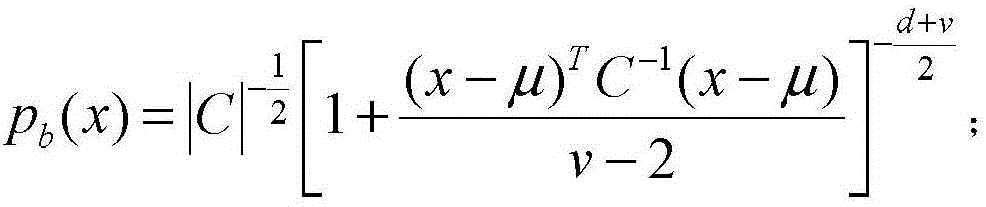Patents
Literature
170 results about "Spectral dimension" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
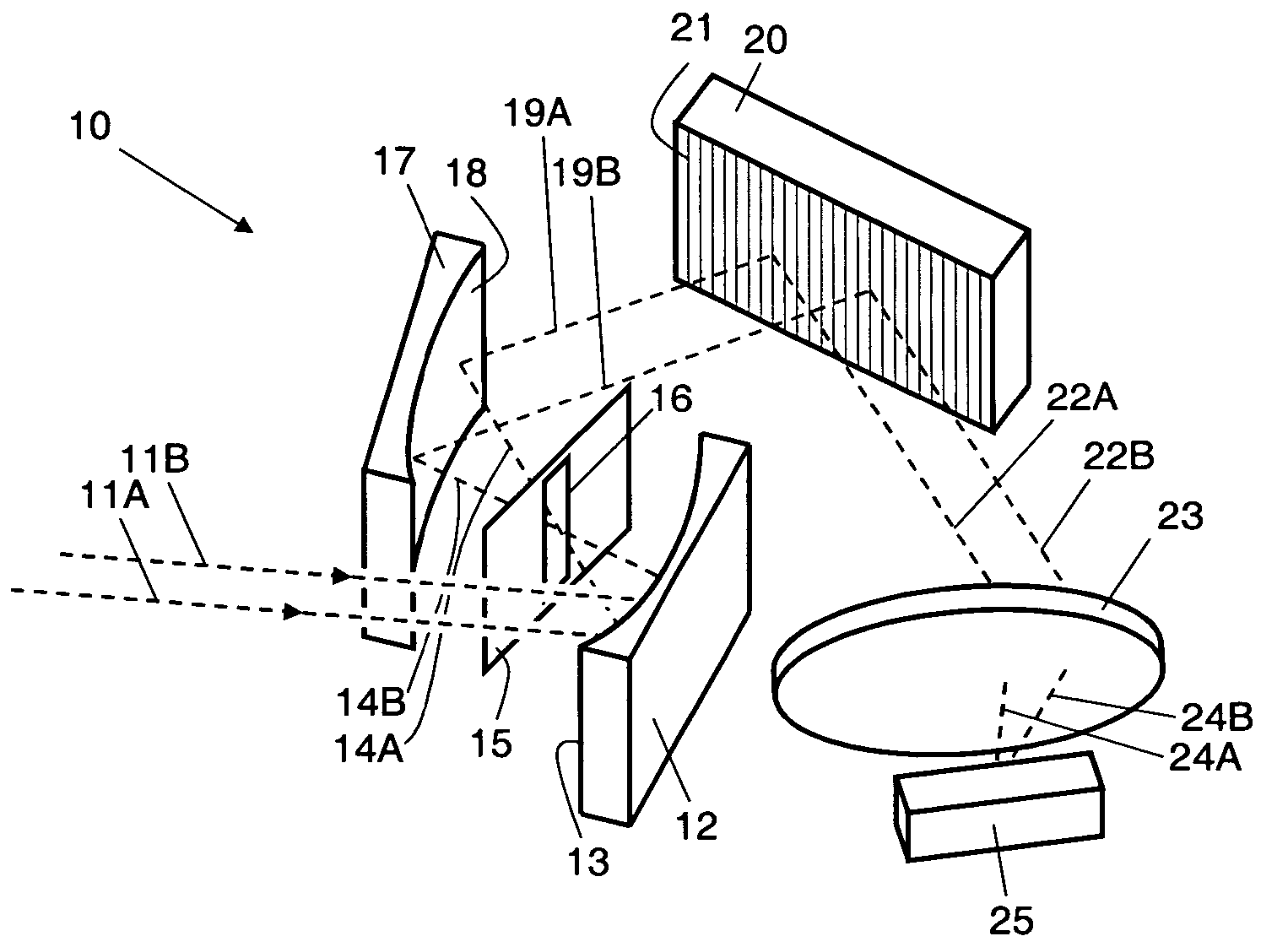
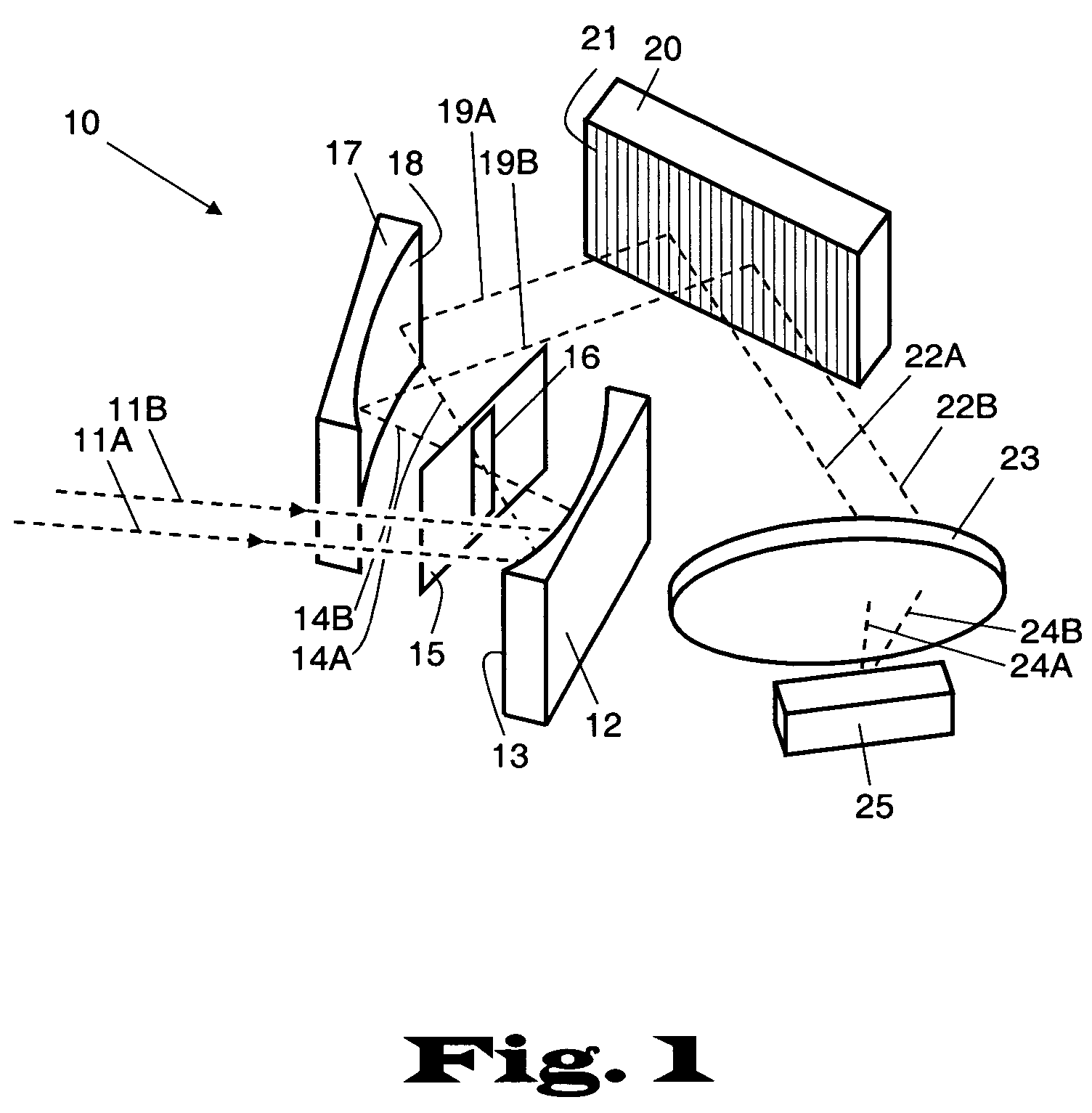
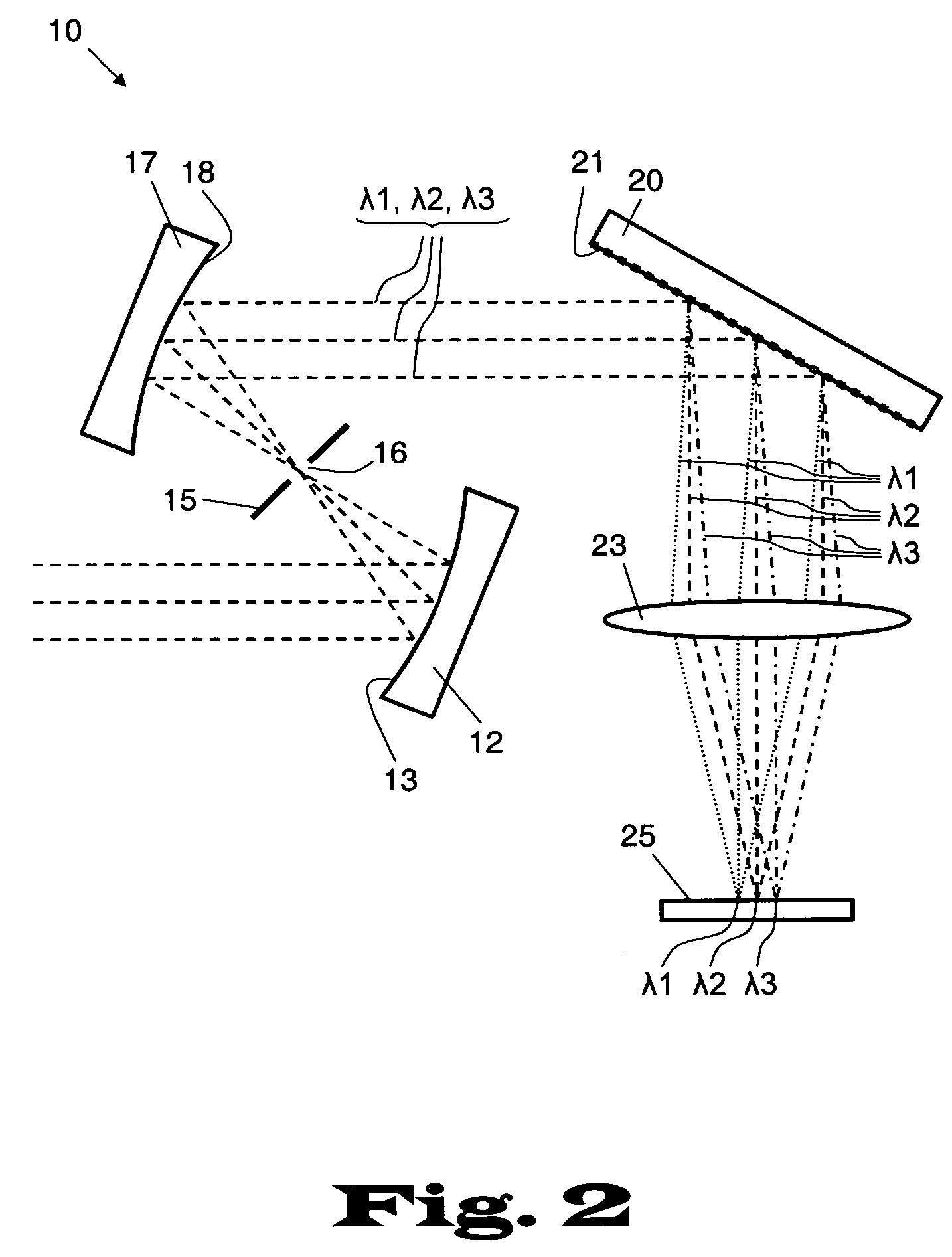
Spectral imaging system
InactiveUS20050151965A1Wide rangeIncrease calibration rangeRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationData acquisitionSpectral dimension
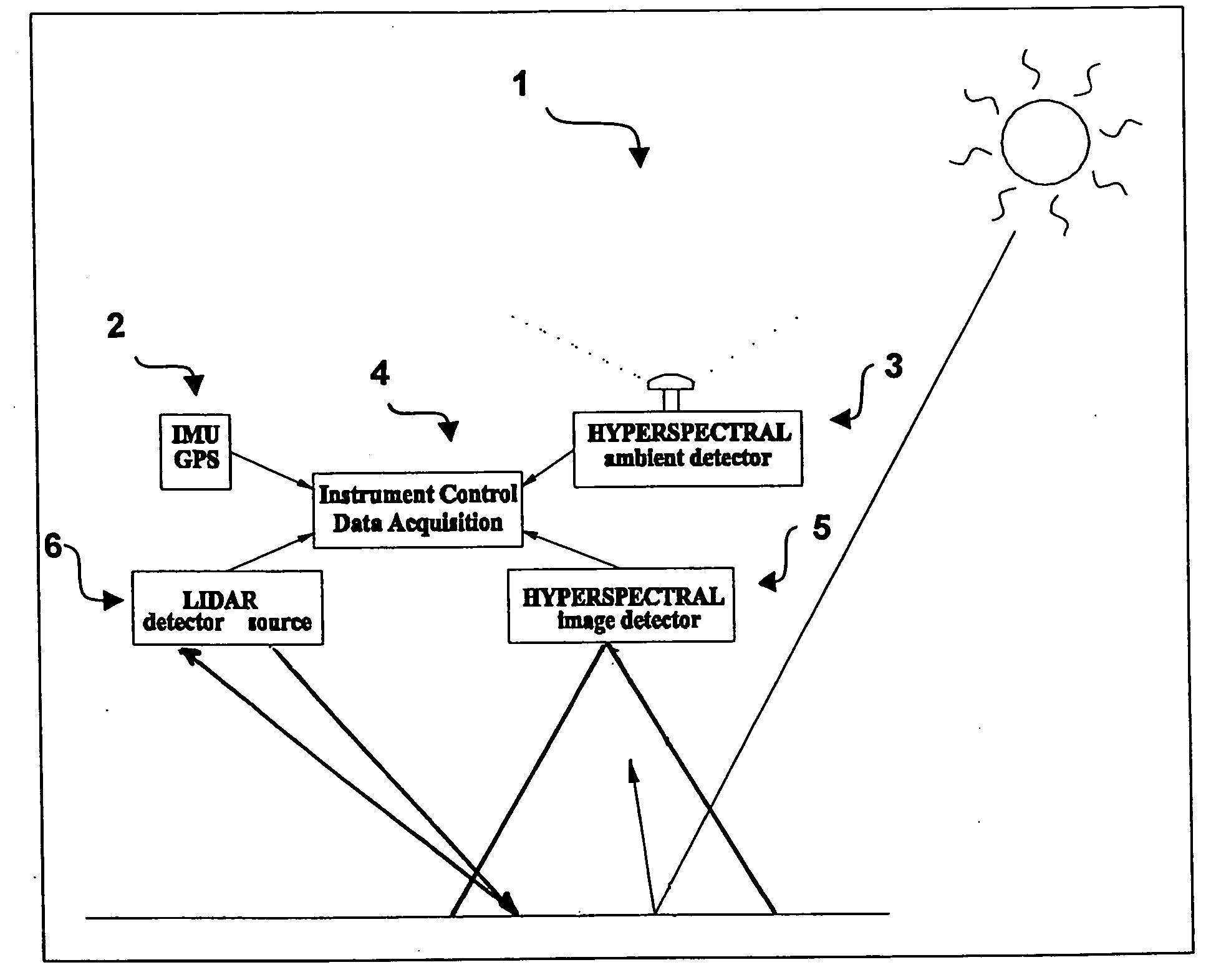
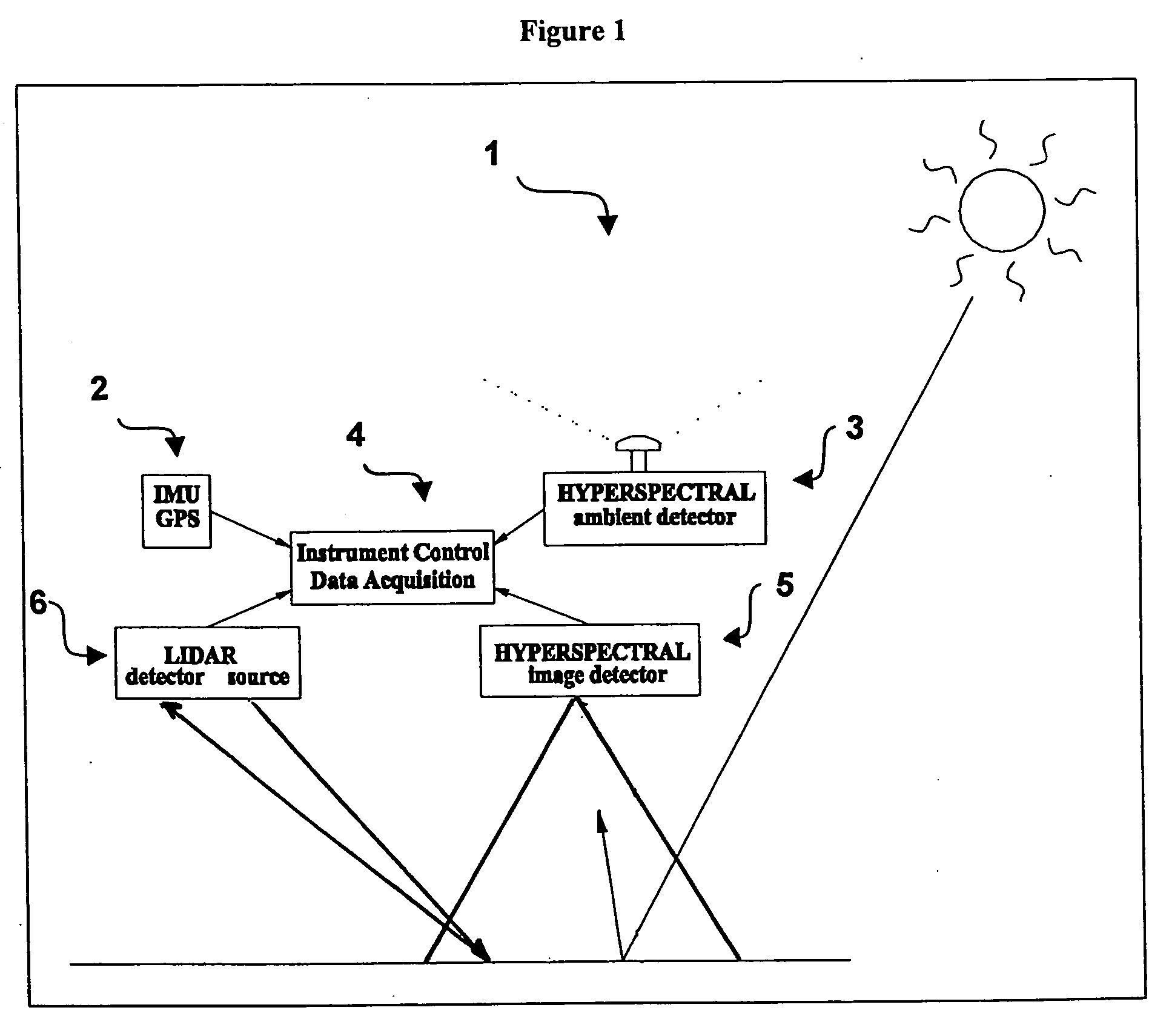
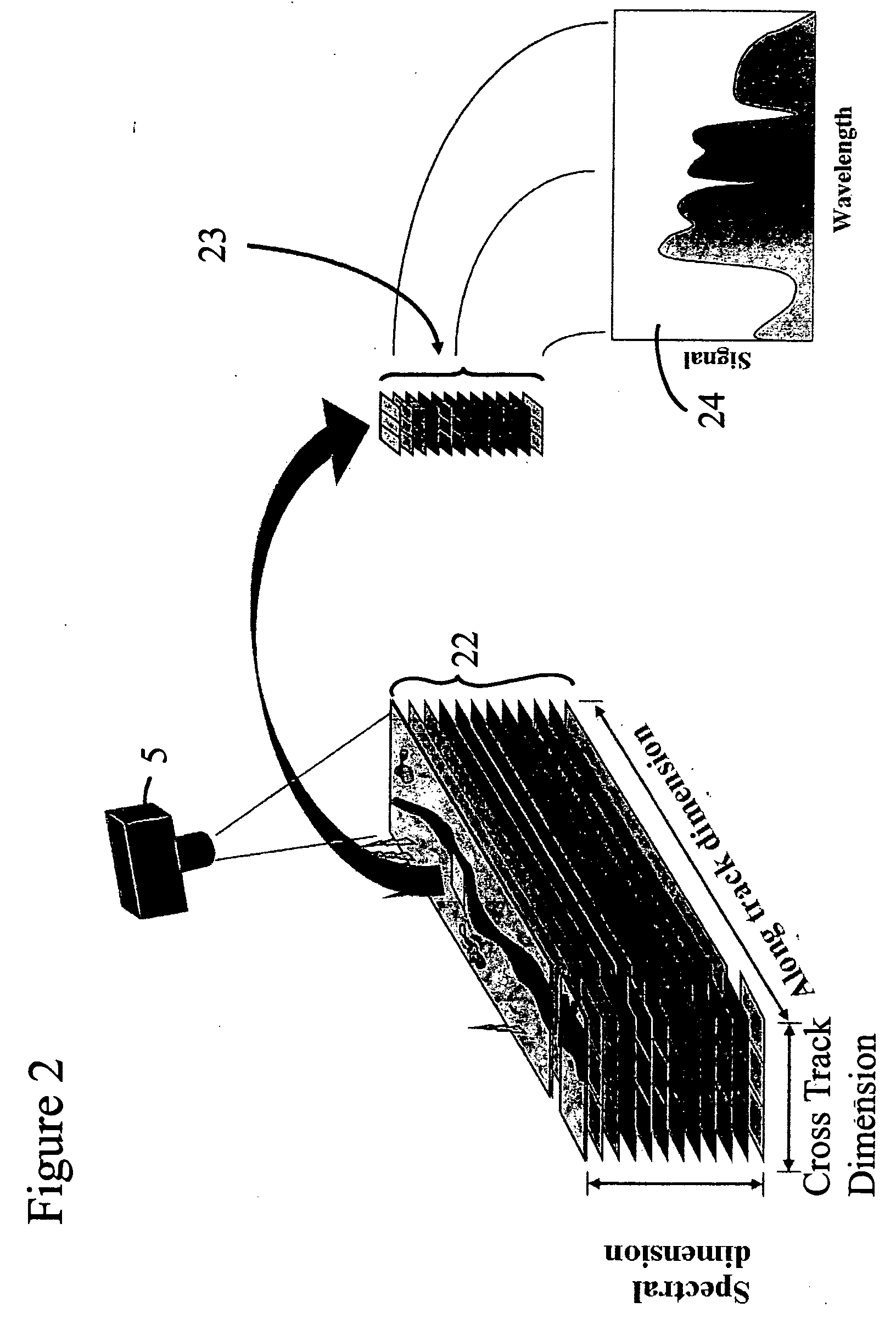
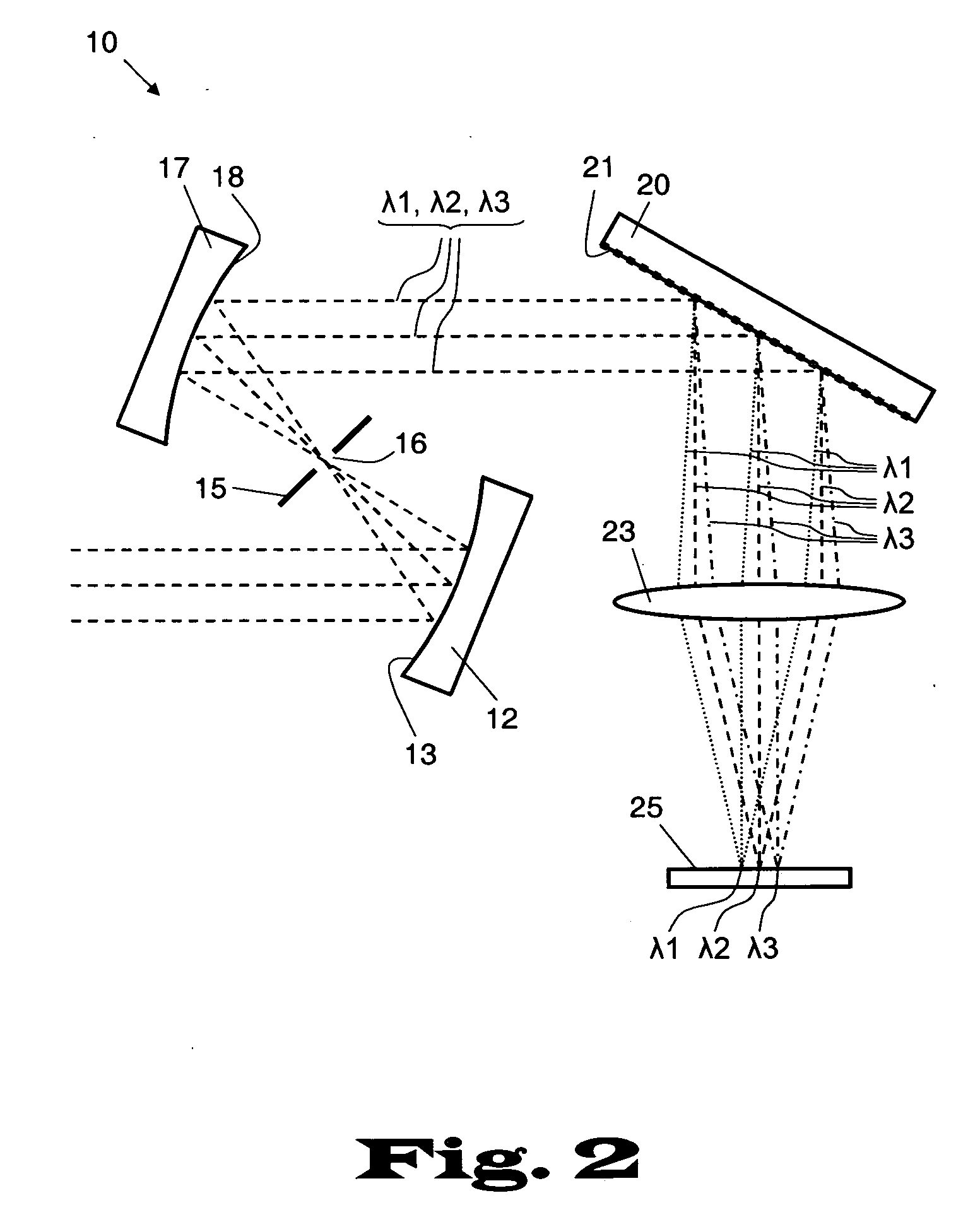
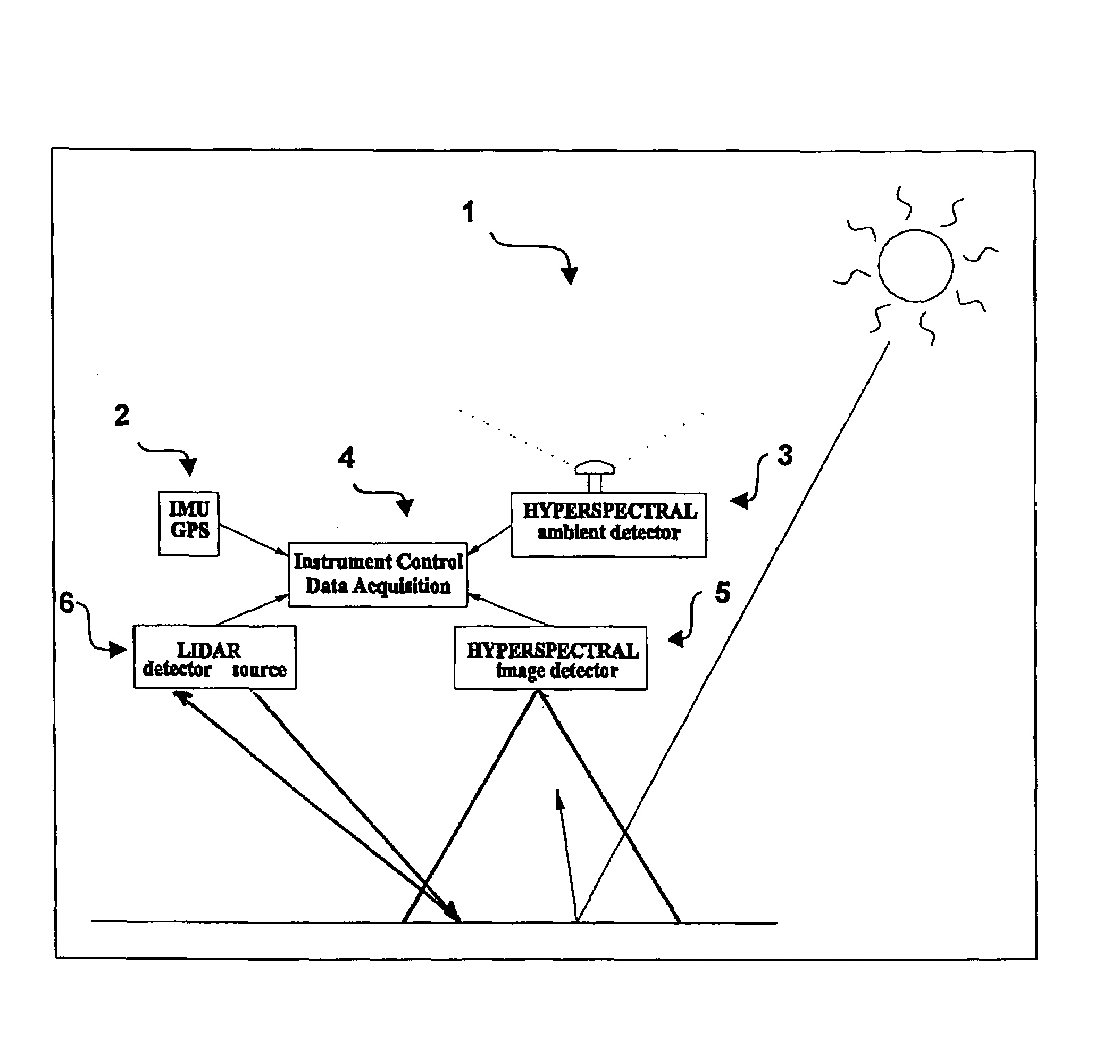
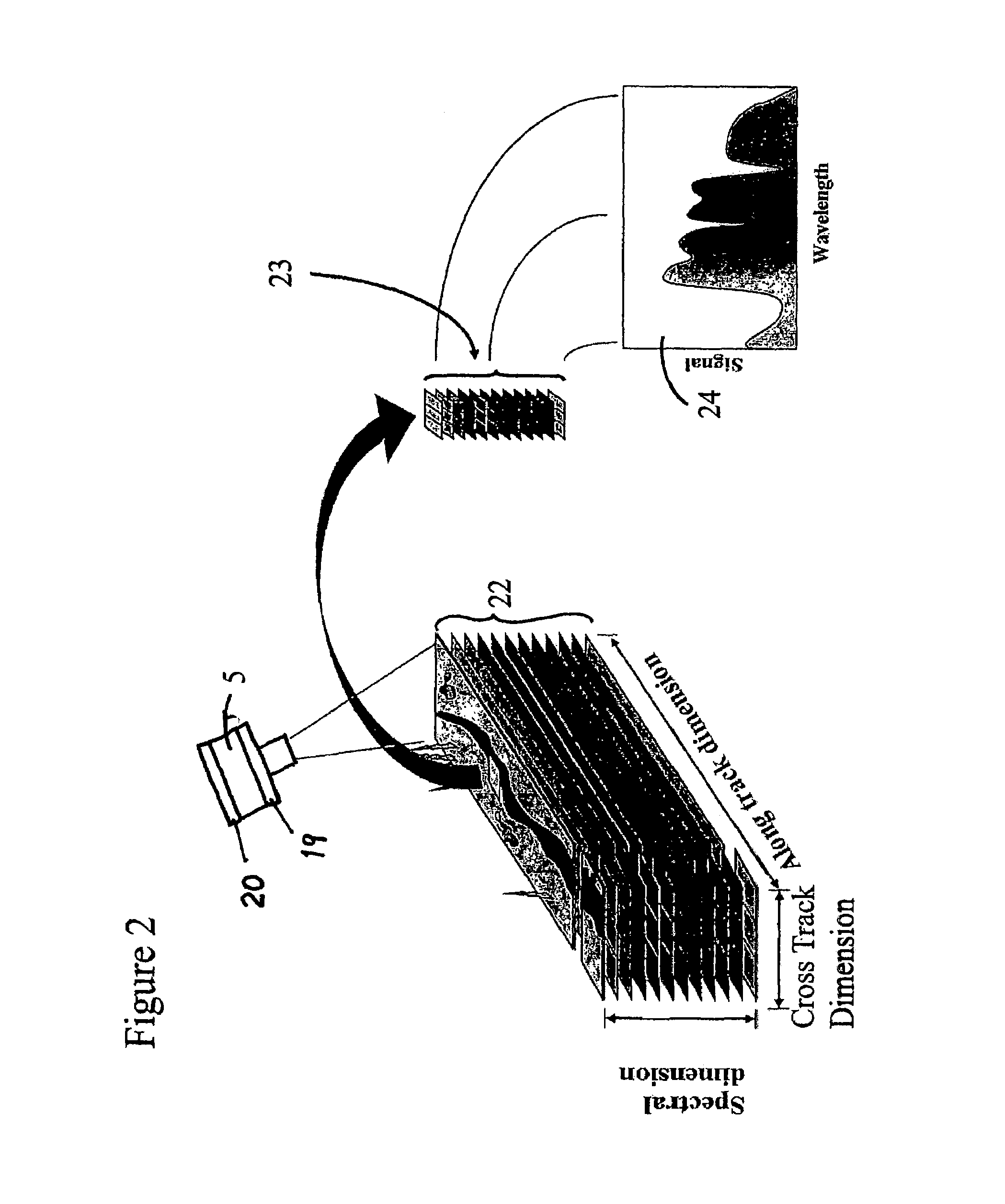
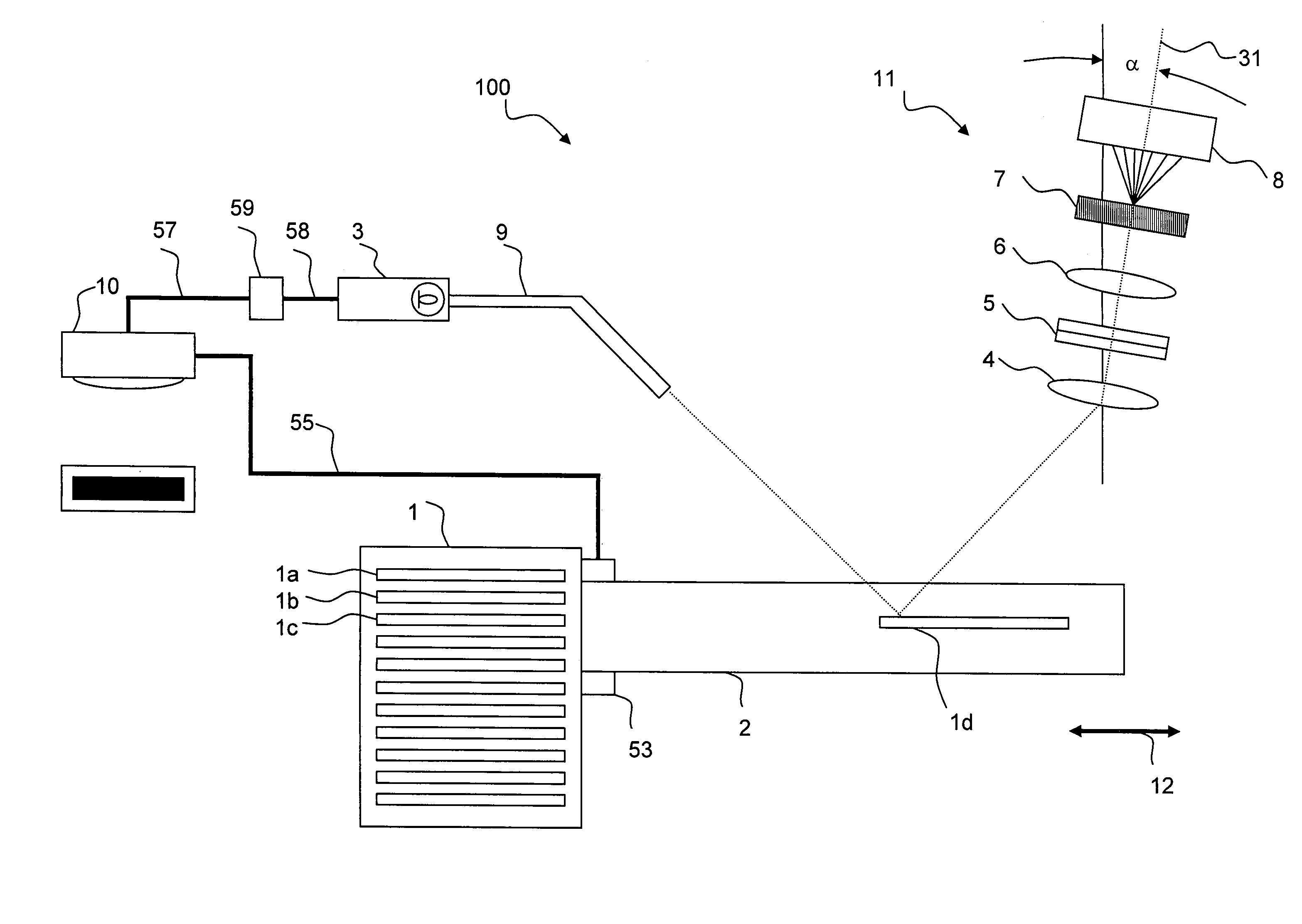
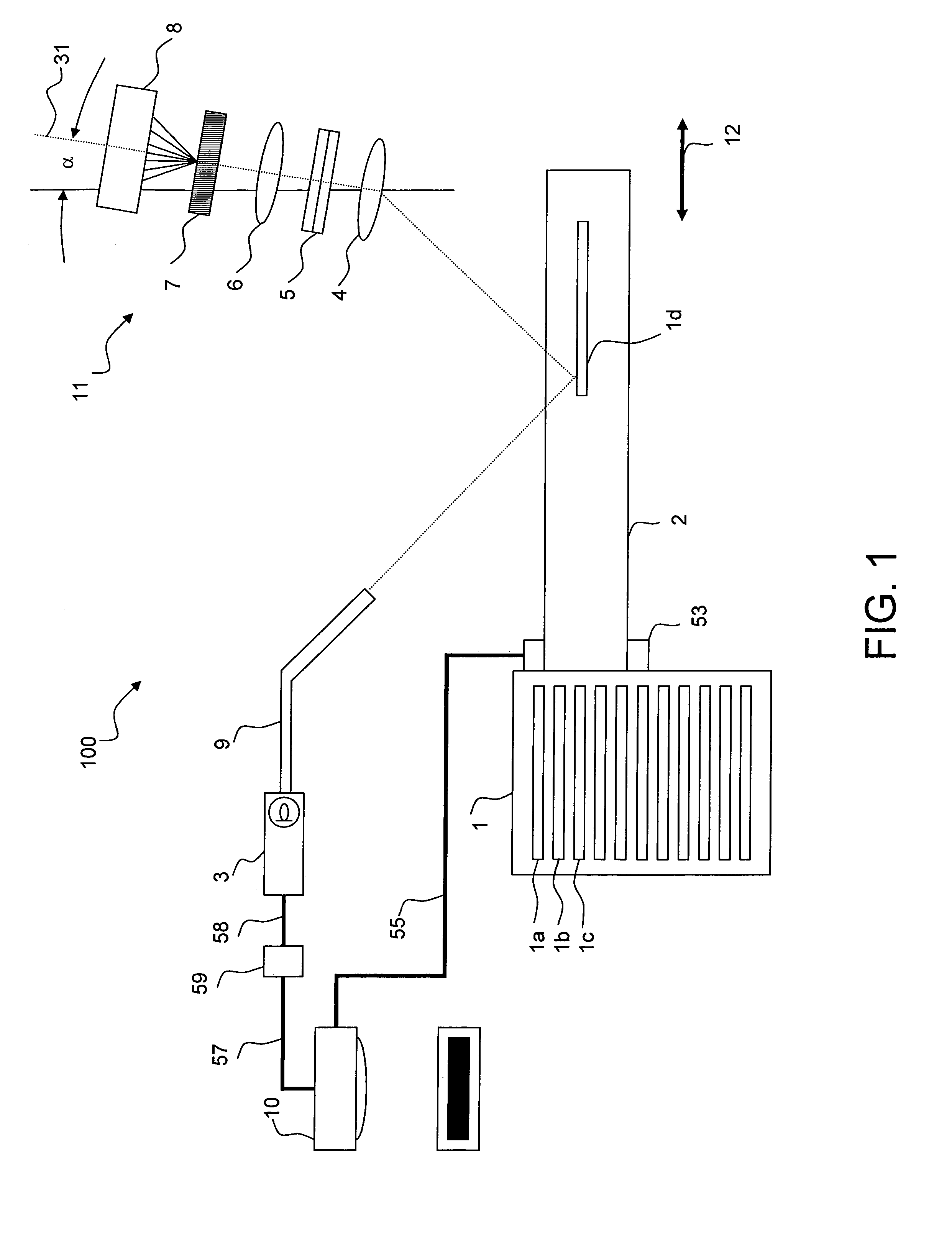
An imaging system and methods for resolving elements of interest through and obscuring environment by removing undesired signals from the intervening, obscuring environment is disclosed. A passive hyperspectral imaging sensor is calibrated and integrated into a system having a positioning and attitude detection system and an instrument control and data acquisition system that records data from sensors in a three-dimensional data cube having two spatial dimensions and a spectral dimension. Either an active detection and ranging system or a look-up-table approach or both are used to remove the noise generated by the intervening, obscuring environment from the data relevant to the elements of interest.
Owner:EATHON INTELLIGENCE
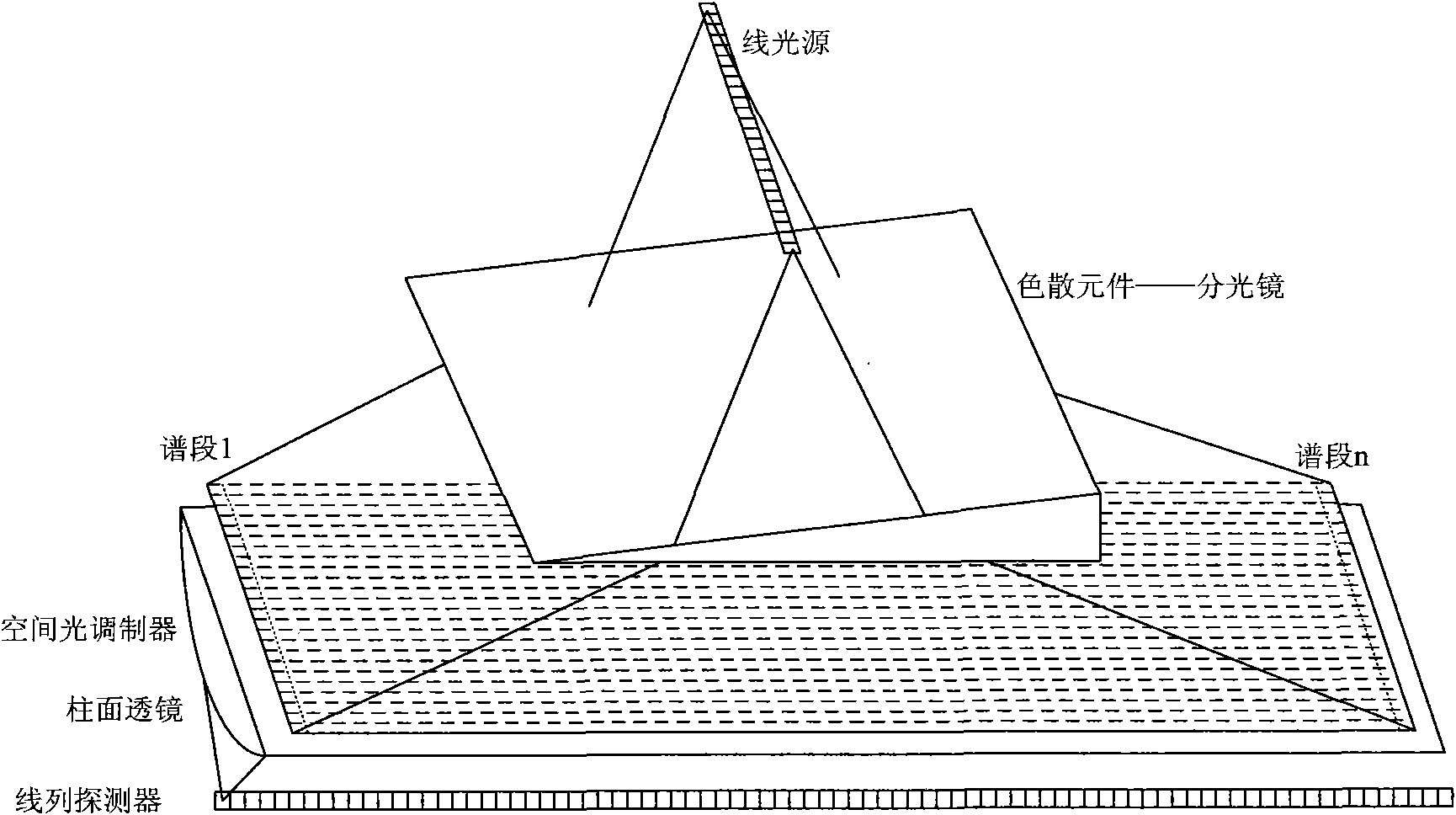
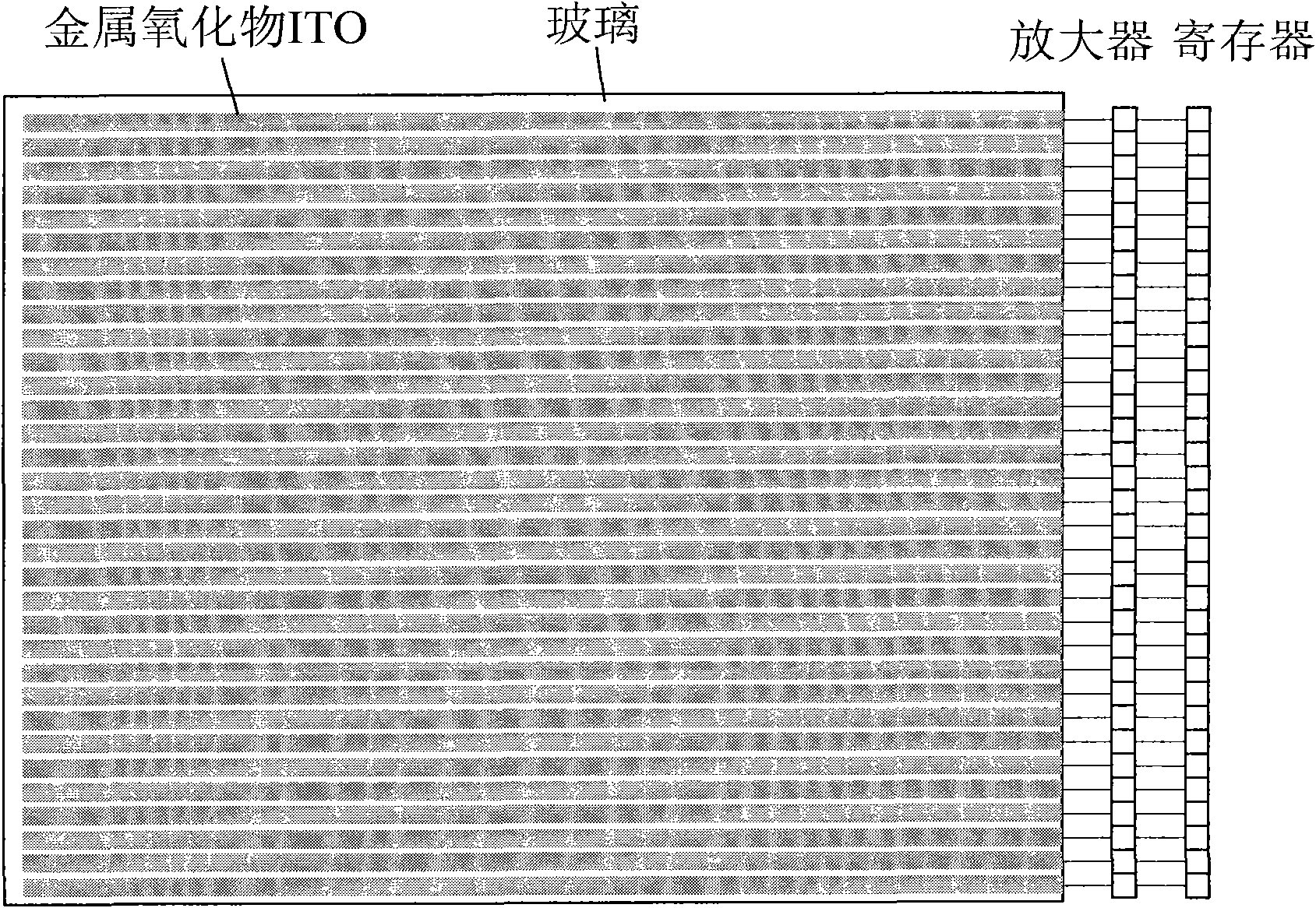
Hyperspectral imager and imaging method based on compressive sensing
InactiveCN101893552AReduce sampling costsReduce computing costSpectrum investigationColor/spectral properties measurementsSpatial light modulatorSpectral dimension
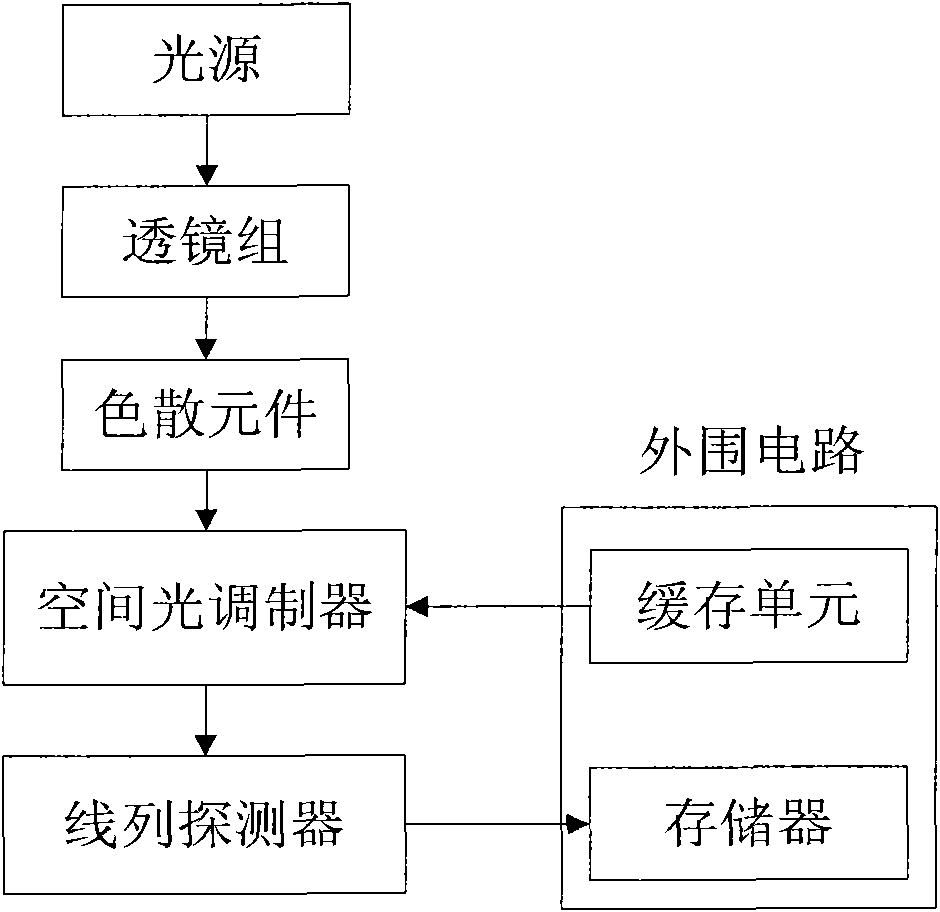
The invention discloses a hyperspectral imager and an imaging method based on compressive sensing, mainly solving the problem that the existing hyperspectral imager has high sampling rate and high sensor realization difficulty. The imager comprises a battery of lens, a dispersive device, a spatial light modulator, a linear detector and a peripheral circuit. The acquired linear light source is split in the space through the dispersive device to form the plane light source formed by spatial dimension and spectral dimension. The plane light source converges again in the direction of spatial dimension after being modulated by the spatial light modulator to form the linear light source formed by spectral dimension. The linear detector completes sampling and quantizing. The imaging method is characterized by utilizing the obtained hyperspectral compressive observation vector to obtain the hyperspectral images through grouping and reconstitution. The hyperspectral imager improves the average reconstitution accuracy of each spectrum by utilizing the joint sparse characteristic among the hyperspectral spectra, has the advantages of simple structure and low cost and is suitable for compressive sensing and imaging of hyperspectra.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Scalable imaging spectrometer
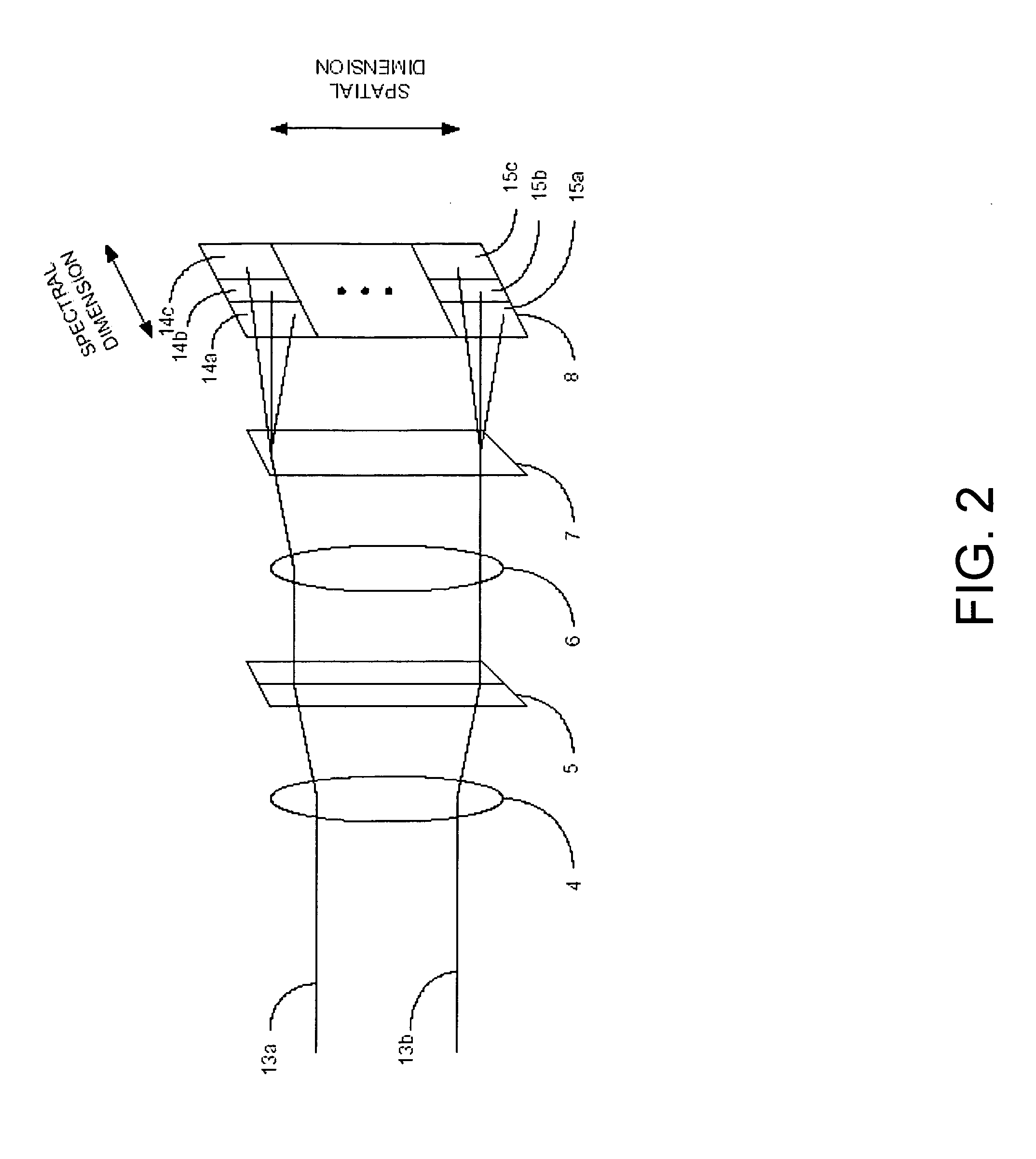
A scalable imaging spectrometer, using anamorphic optical elements to form an intermediate focus in only one dimension. Light reflects off an object to form an incident beam. The beam reflects off an anamorphic objective mirror to form a line focus at a slit. At the slit, the beam is focused along the spectral dimension, but remains substantially collimated along the spatial dimension. The beam is then recollimated in the spectral dimension by a second anamorphic mirror, reflects off a diffraction grating, passes through a lens, and is brought to focus on a two dimensional detector, which produces both spectral and spatial information about the object. Because there is no intermediate focus in the spatial dimension, there are no off-axis aberrations from the anamorphic mirrors, and the field of view may be substantially increased over prior art spectrometers in the spatial dimension.
Owner:RESONON
Spectral imaging system
InactiveUS7369229B2Increase calibration rangeAccurate detectionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationFull spectral imagingData acquisition
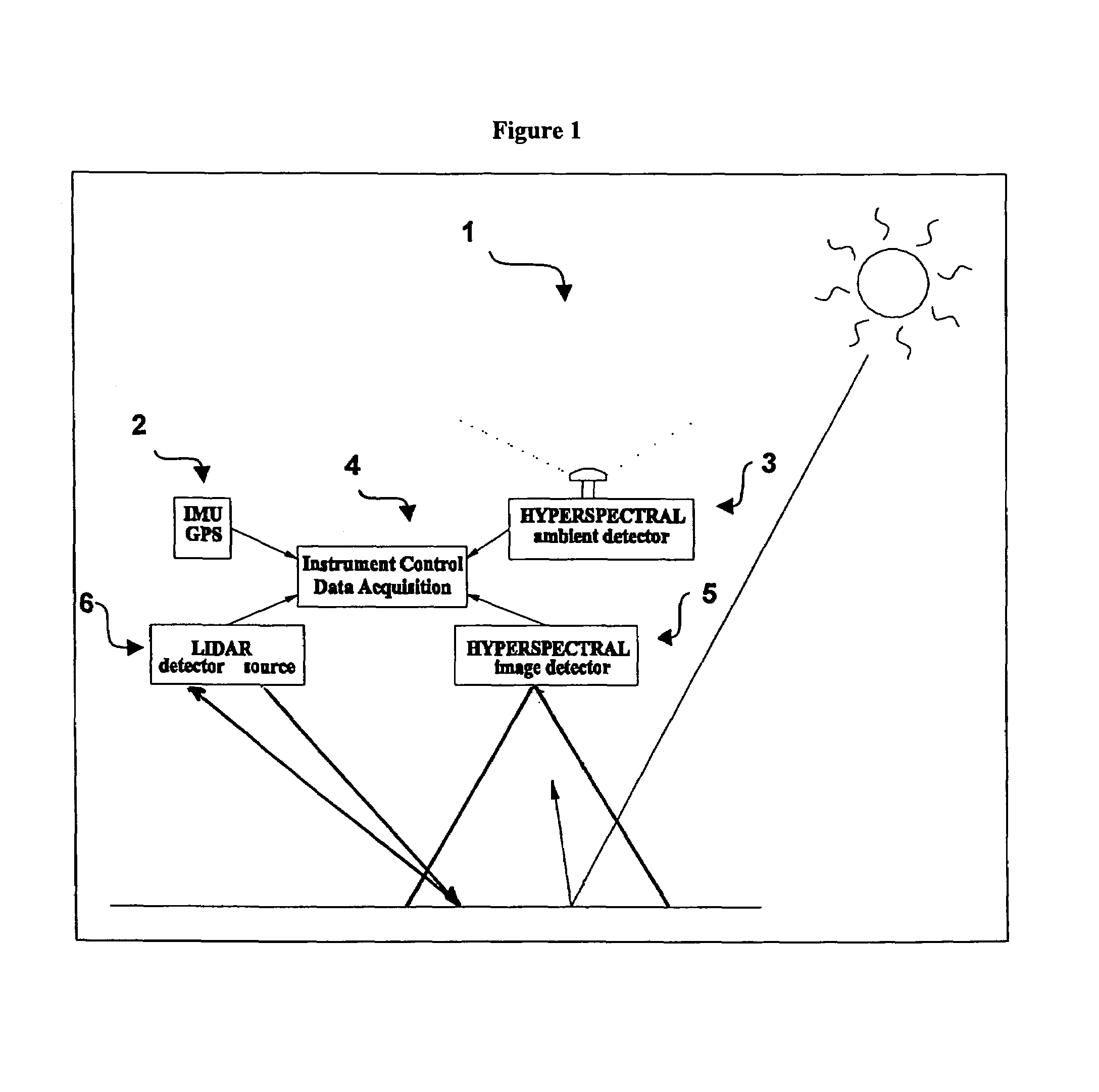
An imaging system and methods for resolving elements of interest through and obscuring environment by removing undesired signals from the intervening, obscuring environment is disclosed. A passive hyperspectral imaging sensor is calibrated and integrated into a system having a positioning and attitude detection system and an instrument control and data acquisition system that records data from sensors in a three-dimensional data cube having two spatial dimensions and a spectral dimension. Either an active detection and ranging system or a look-up-table approach or both are used to remove the noise generated by the intervening, obscuring environment from the data relevant to the elements of interest.
Owner:EATHON INTELLIGENCE
Scalable imaging spectrometer
A scalable imaging spectrometer, using anamorphic optical elements to form an intermediate focus in only one dimension. Light reflects off an object to form an incident beam. The beam reflects off an anamorphic objective mirror to form a line focus at a slit. At the slit, the beam is focused along the spectral dimension, but remains substantially collimated along the spatial dimension. The beam is then recollimated in the spectral dimension by a second anamorphic mirror, reflects off a diffraction grating, passes through a lens, and is brought to focus on a two dimensional detector, which produces both spectral and spatial information about the object. Because there is no intermediate focus in the spatial dimension, there are no off-axis aberrations from the anamorphic mirrors, and the field of view may be substantially increased over prior art spectrometers in the spatial dimension.
Owner:RESONON
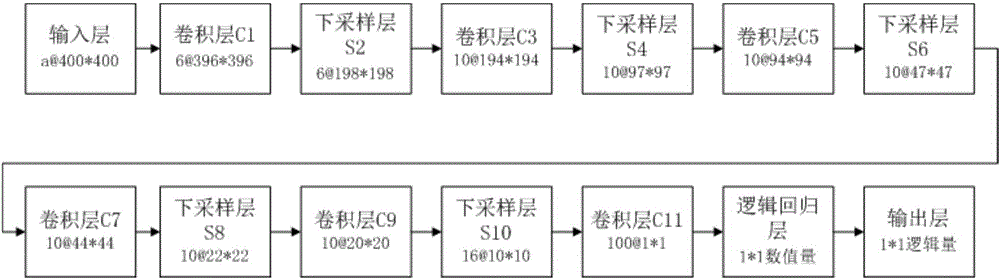
Gastrointestinal tumor microscopic hyper-spectral image processing method based on convolutional neural network
InactiveCN106097355AIncrease the amount of informationImprove efficiencyImage enhancementImage analysisBatch processingHyperspectral image processing
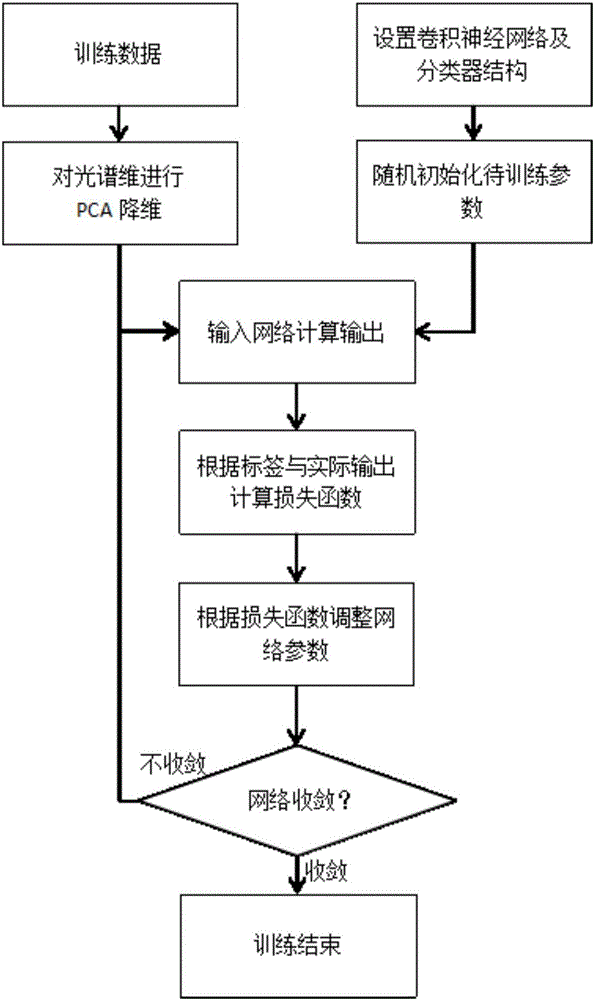
The invention discloses a gastrointestinal tumor microscopic hyper-spectral image processing method based on a convolutional neural network, comprising the following steps: reducing and de-noising the spectral dimension of an acquired gastrointestinal tissue hyper-spectral training image; constructing a convolutional neural network structure; and inputting obtained hyper-spectral data principal components (namely, a plurality of 2D gray images, which are equivalent to a plurality of feature maps of an input layer) as input images into the constructed convolutional neural network structure using a batch processing method, and by taking a cross entropy function as a loss function and using an error back propagation algorithm, training the parameters in the convolutional neural network and the parameters of a logistic regression layer according to the average loss function in a training batch until the network converges. According to the invention, the dimension of a hyper-spectral image is reduced using a principal component analysis method, enough spectral information and spatial texture information are retained, the complexity of the algorithm is reduced greatly, and the efficiency of the algorithm is improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Multi-spectral imaging
InactiveCN102472664ASpectrum investigationRadiation controlled devicesMultispectral imageSpectral dimension
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Hyperspectral image classification method based on convolutional neural network and spatial spectrum information fusion
InactiveCN107909015AEfficient extractionReduce complexityScene recognitionNeural learning methodsImage resolutionSpectral dimension
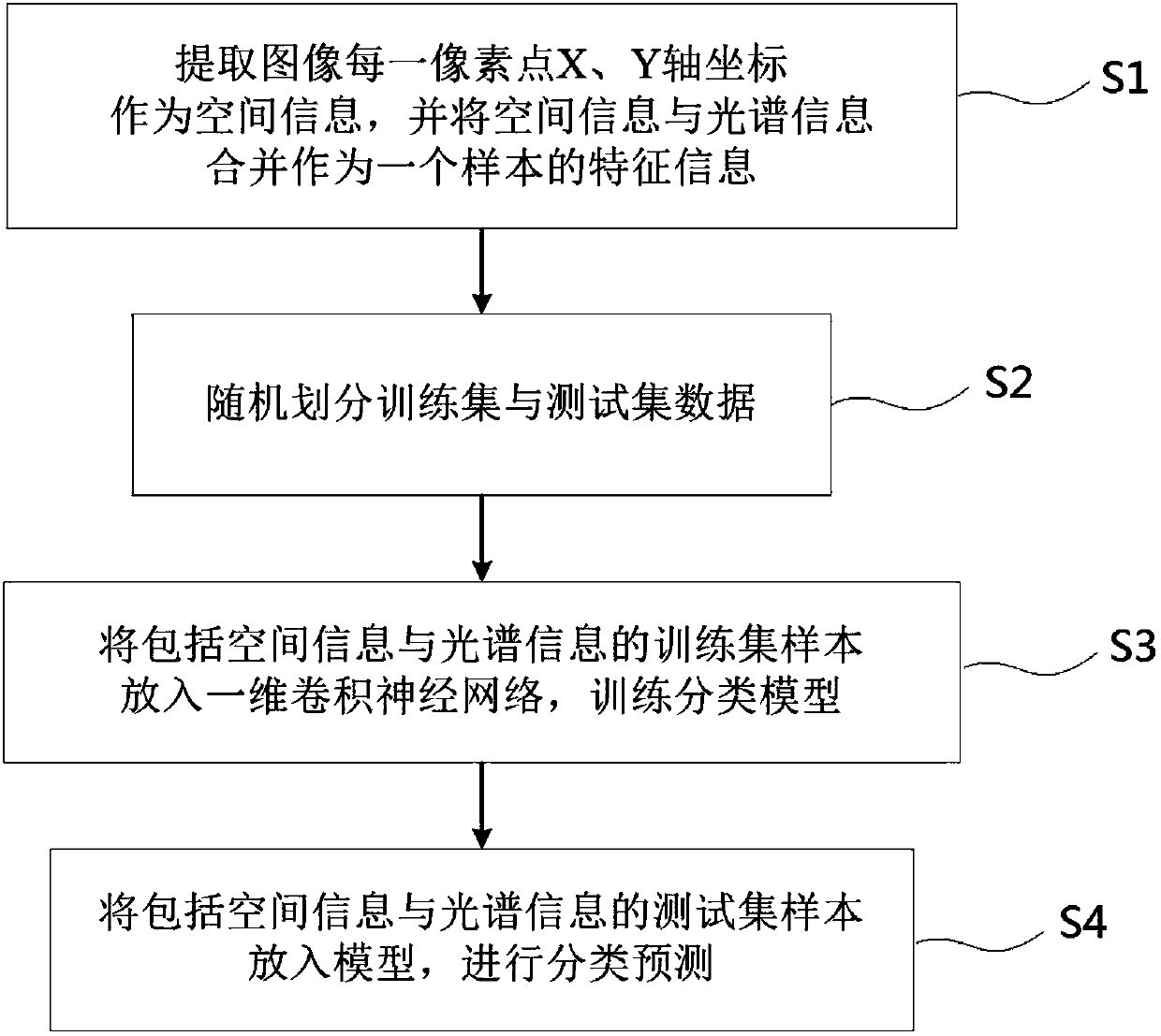
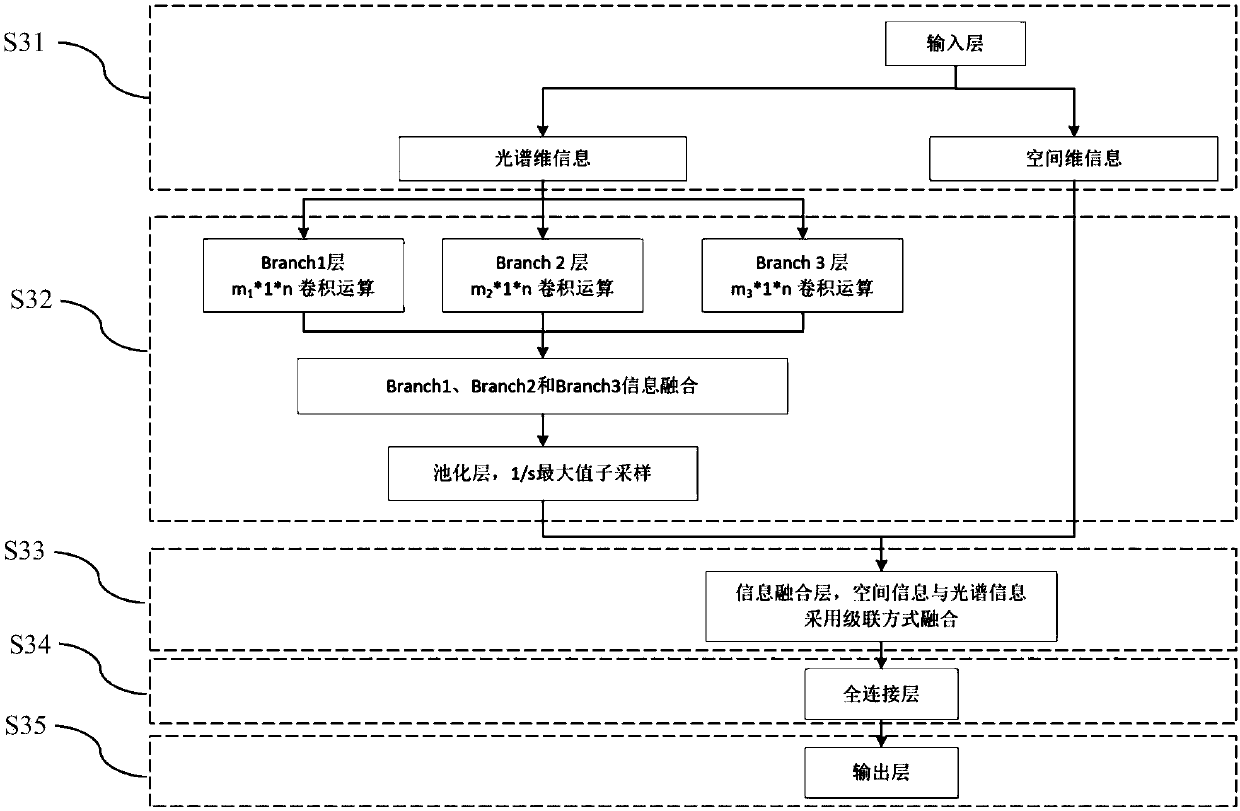
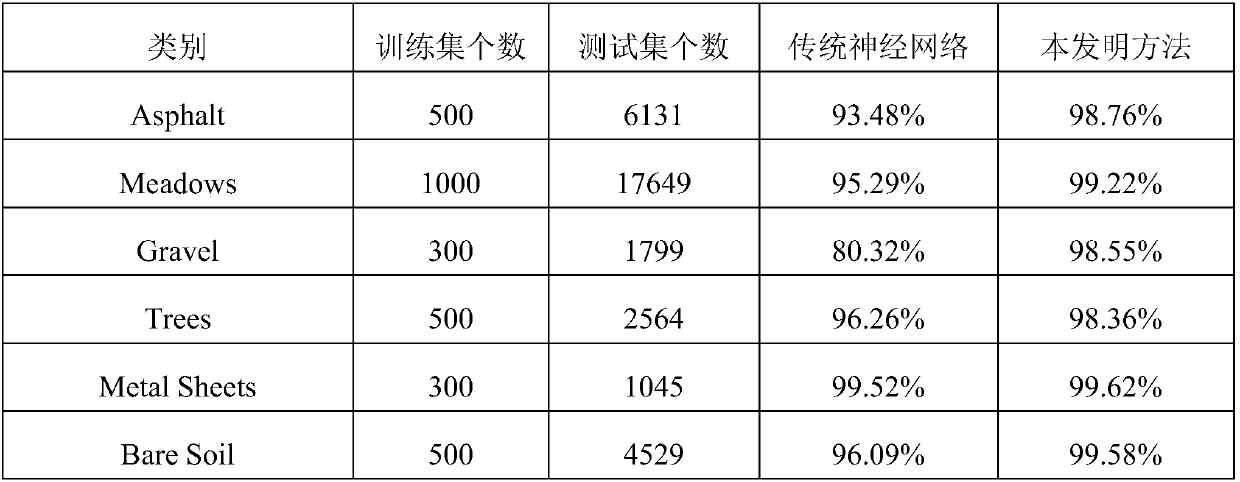
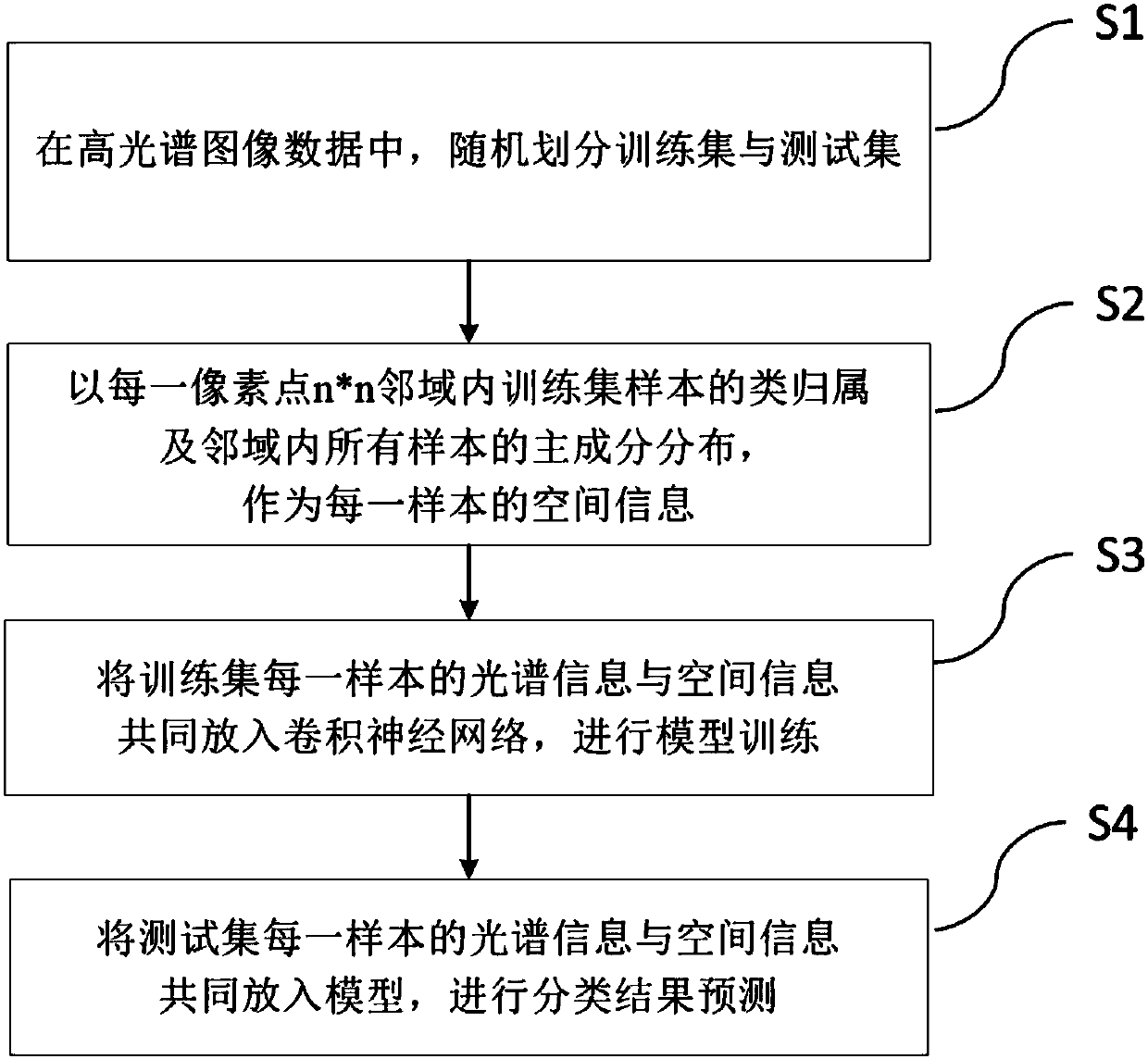
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on a convolutional neural network and spatial spectrum information fusion. The method comprises the steps that S1 X and Y axiscoordinates of each pixel point of a hyperspectral image are extracted as spatial information, and the spatial information and spectral information are combined as the feature information of a sample; S2 training set and test set data are randomly divided; S3 training set samples including the spatial information and the spectral information are put into a one-dimensional convolutional neural network to train a classification model; and S4 the training set samples including the spatial information and the spectral information are put into the classification model for classification prediction. The convolutional neural network uses convolution kernels of different sizes to carry out convolution operation, which can effectively extract feature information with different resolutions in the spectral dimension of a hyperspectrum. In addition, the spectral dimension information and the spatial dimension information are input into the neural network to learn simultaneously. The feature of dual high resolutions of the hyperspectrum is fully used. The algorithm structure is simple, and the classification accuracy can be significantly improved.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with sparse spectral sampling and interleaved dynamic shimming
InactiveUS7683614B2Maximize efficiencyMaximize sensitivityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientSpectral dimension
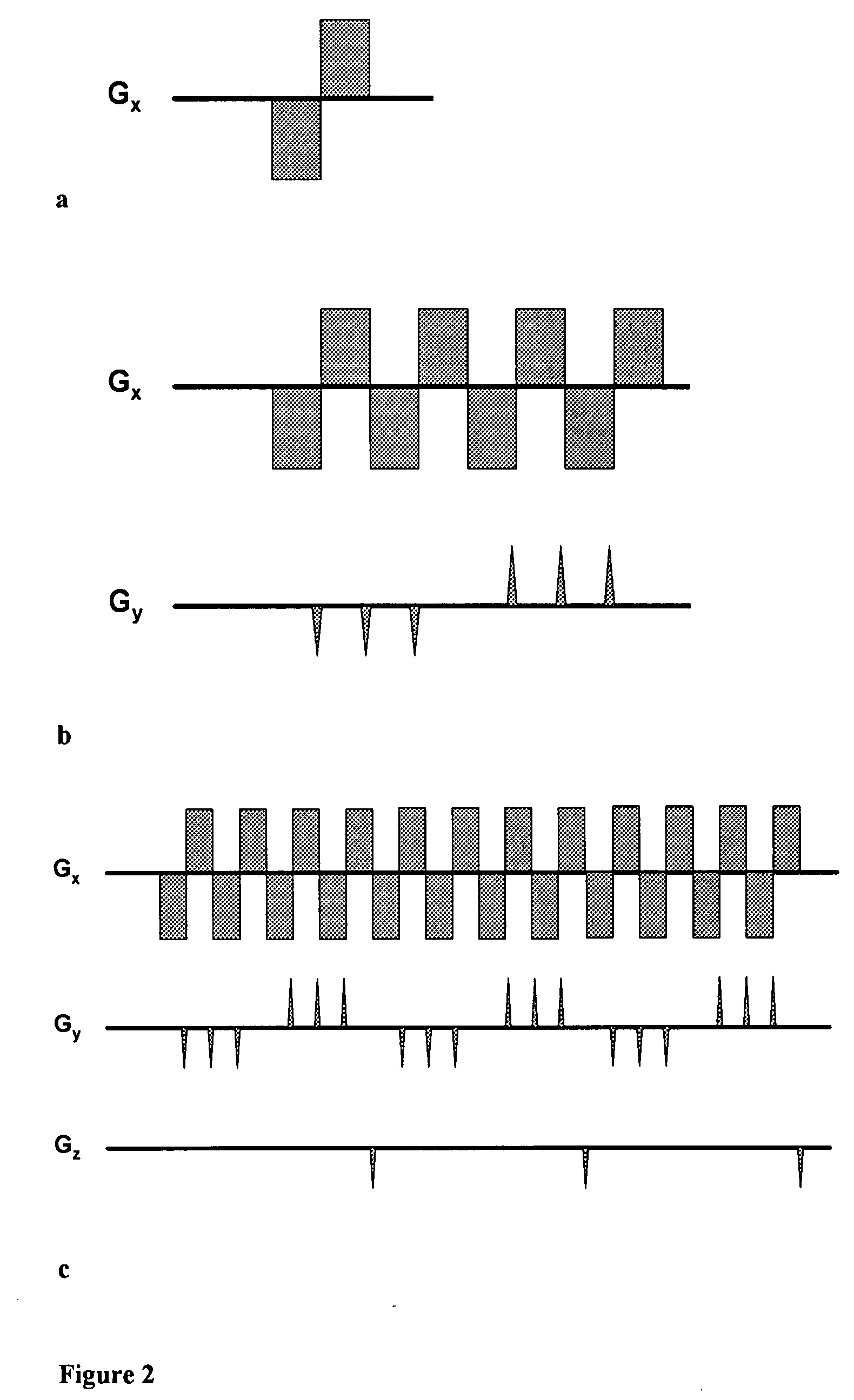
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with up to three spatial dimensions and one spectral dimension. Interleaving dynamically switched magnetic field gradients into the spectroscopic encoding scheme enables multi-region shimming in a single shot to compensate the spatially varying spectral line broadening resulting from local magnetic field gradients. The method also employs sparse spectral sampling with controlled spectral aliasing and nonlinear sampling density to maximize encoding speed, data sampling efficiency and sensitivity.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Multiple-label fluorescence imaging using excitation-emisssion matrices
InactiveUS20060007439A1Maximize throughputImprove reading speedRaman/scattering spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryFluorescenceSpectral dimension
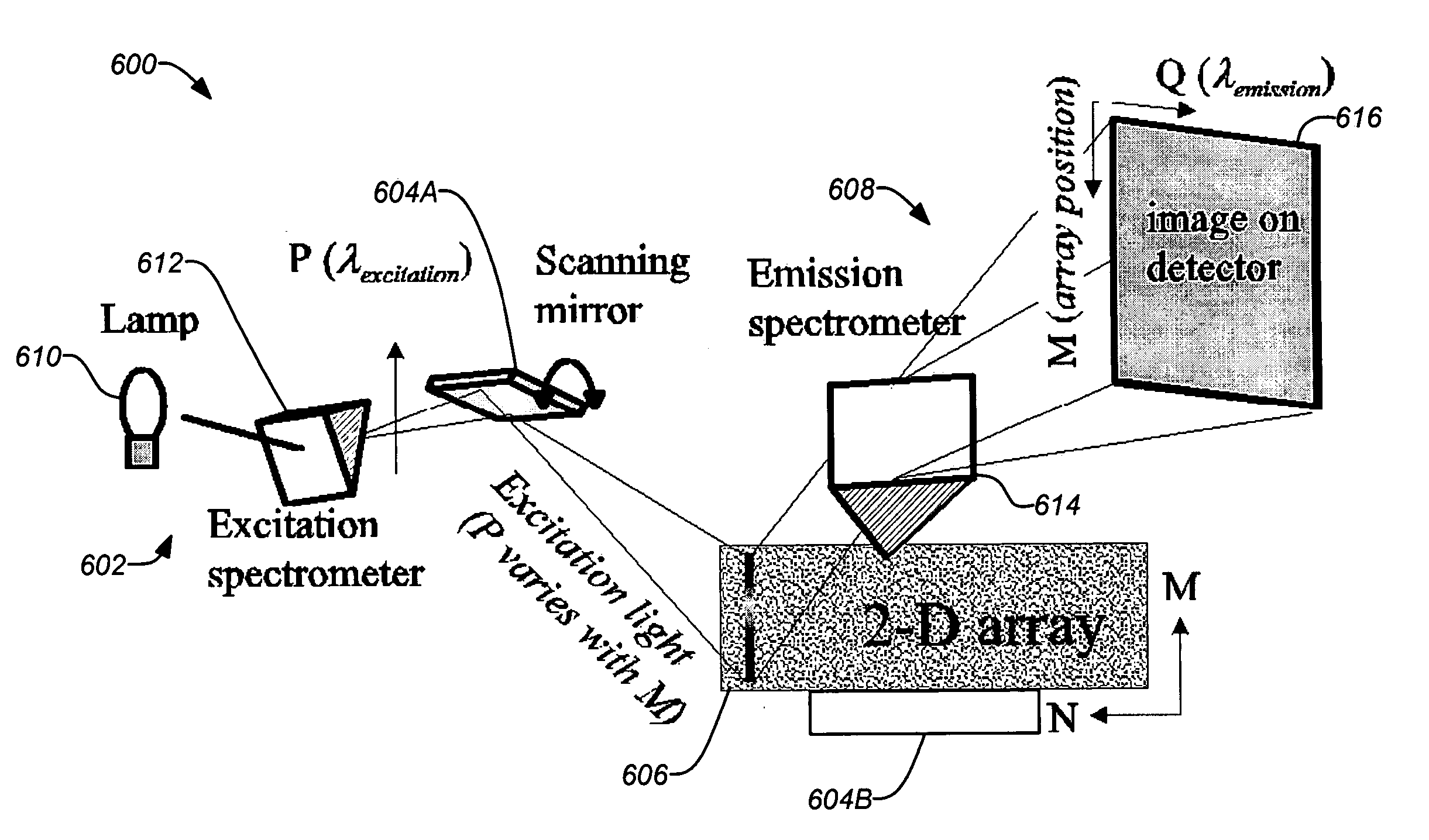
Methods and devices are disclosed which apply an excitation-emission matrix (EEM) to a heterogeneous, two-dimensional sample, allowing a considerably larger number of emitting, e.g. fluorescent, labels to be used simultaneously. This may be accomplished by employing a spectroscopic method of excitation-emission matrices which allows discrimination of species with similar emission spectra, and also allows positive identification of energy transfer between emitting species. The methods and devices may employ a novel excitation-light scanning technique which allows imaging of the emission from the heterogeneous sample both in two spatial dimensions (length and width) and in two spectral dimensions (excitation and emission wavelength). This light scanning technique maximizes the throughput of excitation light, increasing the sensitivity and hence the reading speed of the instrument.
Owner:CORCORAN TIMOTHY C
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with sparse spectral sampling and interleaved dynamic shimming
InactiveUS20070252597A1Maximize encoding speedMaximize data sampling efficiencyMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientSpectral dimension
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with up to three spatial dimensions and one spectral dimension. Interleaving dynamically switched magnetic field gradients into the spectroscopic encoding scheme enables multi-region shimming in a single shot to compensate the spatially varying spectral line broadening resulting from local magnetic field gradients. The method also employs sparse spectral sampling with controlled spectral aliasing and nonlinear sampling density to maximize encoding speed, data sampling efficiency and sensitivity.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Determining wafer orientation in spectral imaging
Devices and methods for determining wafer orientation in spectral imaging are described. The devices and methods generate an image of a wafer that includes at least one spectral dimension. One or more properties are determined from the spectral dimension, and a map is generated based on the property. The generated map is compared to at least one other map, and data or information of the comparison is used to locate a region of the wafer, for example a measurement pad or other structure.
Owner:FILMETRICS
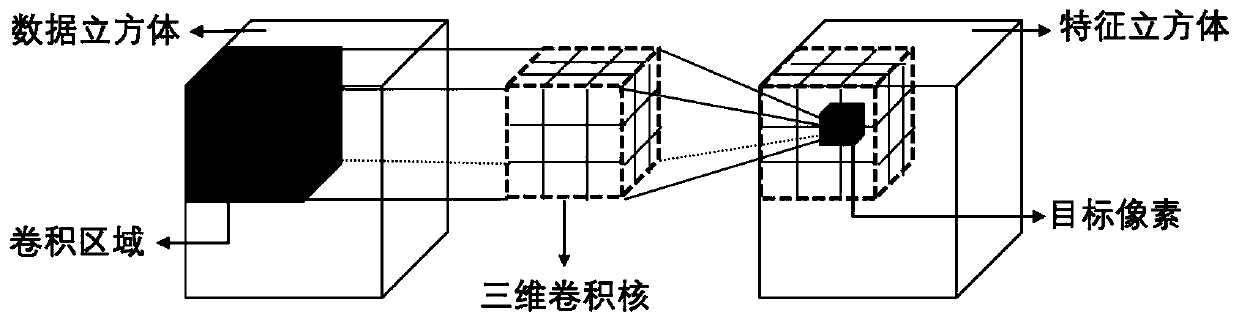
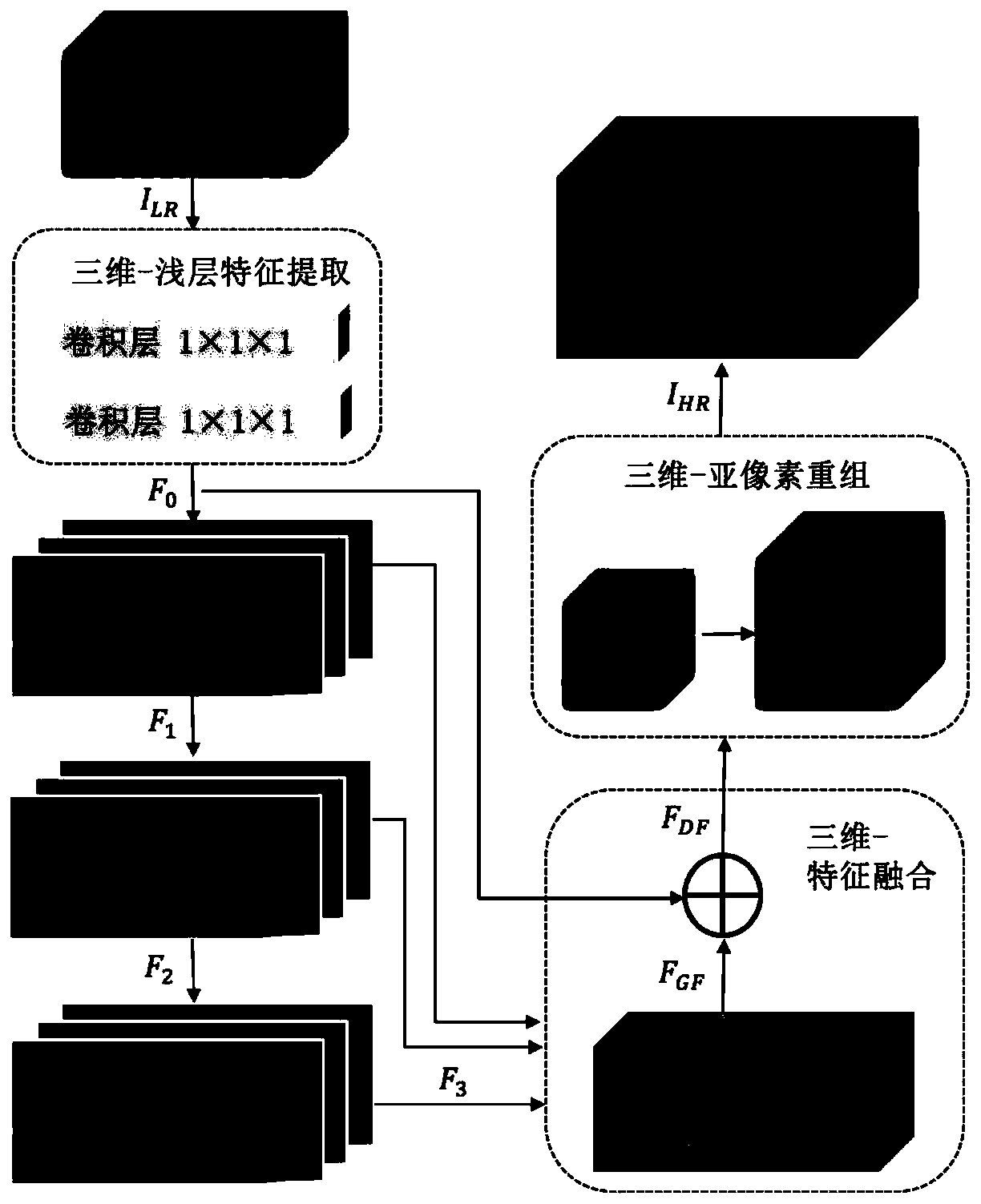
A hyperspectral image super-resolution restoration method based on a 3D convolutional neural network
InactiveCN109903255AReduce the number of featuresSolve the problem of excessive accumulation of feature numbersImage enhancementGeometric image transformationRestoration methodHigh resolution image
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image super-resolution restoration method based on a 3D convolutional neural network. According to the technical scheme, the 3D residual dense network is characterized by comprising 3D convolution kernel to convolve the hyperspectral image spectral dimension and 3D sub-pixel recombination to enlarge the image and reconstruct the high-resolution image part, and unifying the two parts in the deep convolutional neural network framework 3D-RDN; hierarchical characteristics of the convolutional layer are fully utilized through structures such as residual dense blocks, and super-resolution restoration of the hyperspectral image is achieved. At present, when an existing method based on deep learning is applied to a hyperspectral image, the characteristics of the hyperspectral image are not fully considered, and therefore it is difficult to effectively utilize rich spectral dimension information of the hyperspectral image to reconstruct a high-resolutionimage. According to the method, all spatial spectrum information of the hyperspectral image is fully utilized, efficient super-resolution restoration is achieved, and the PSNR value is superior to that of an existing method.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
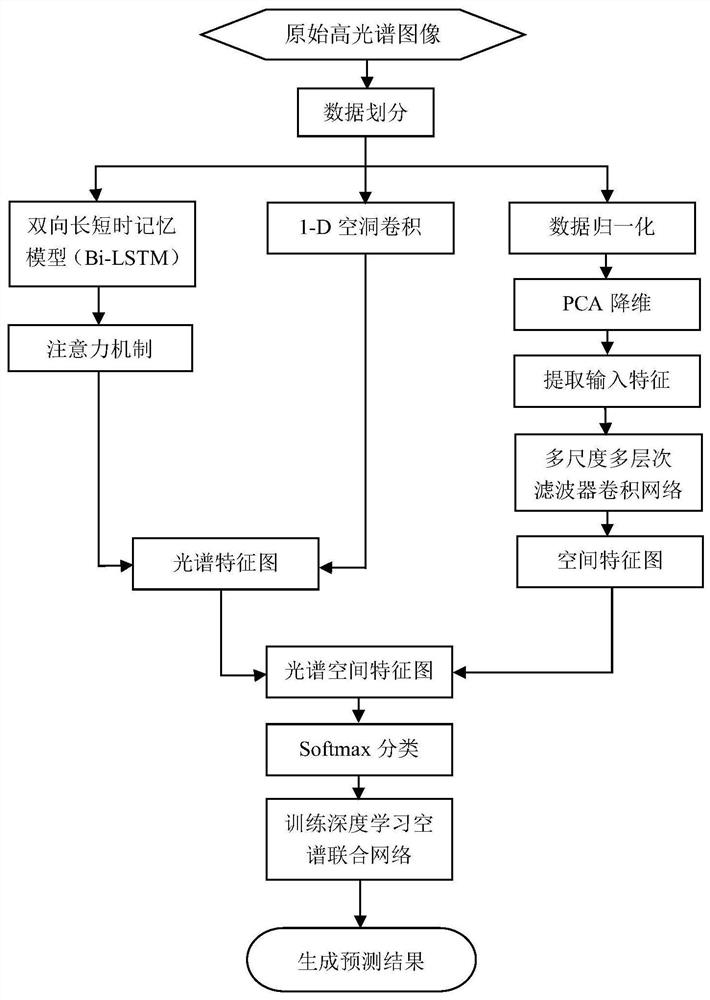
Hyperspectral image classification method based on deep learning space-spectrum joint network
ActiveCN111914907ARich discriminative featuresDiscriminant features fineCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesDimensionality reductionTerm memory
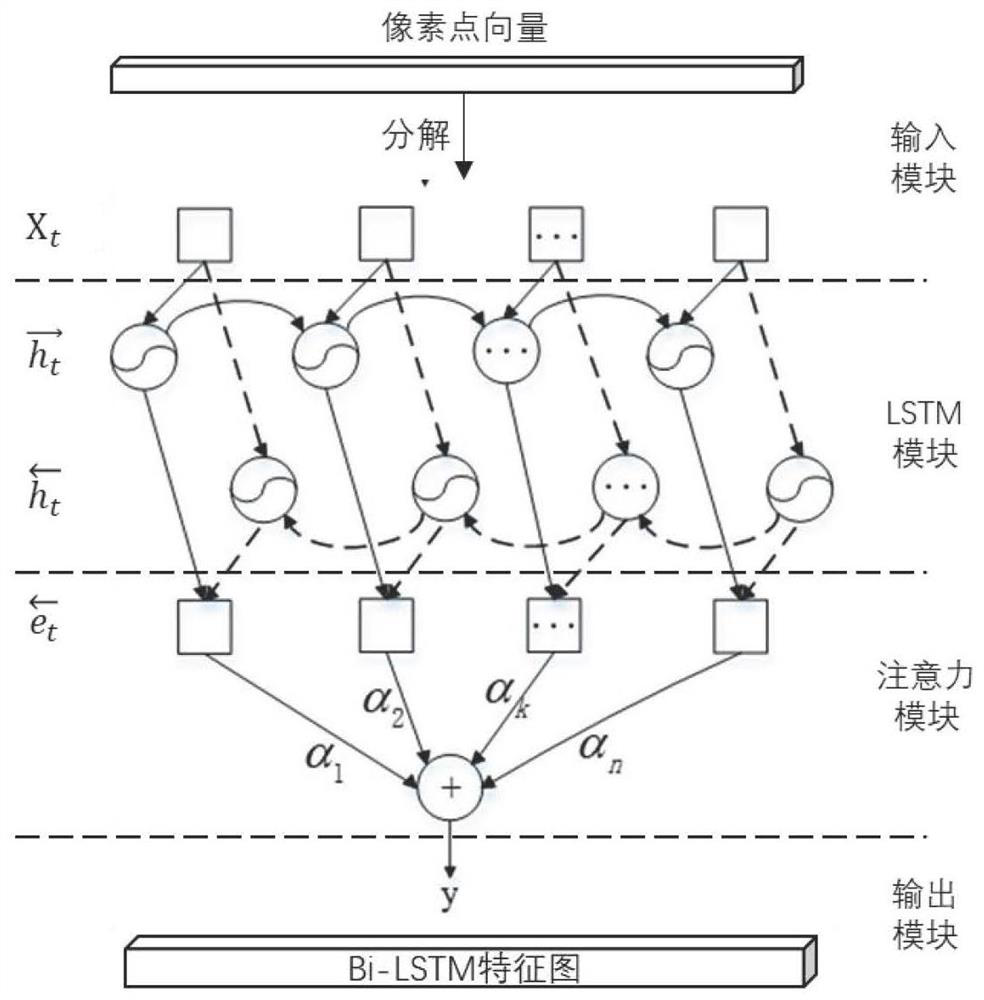
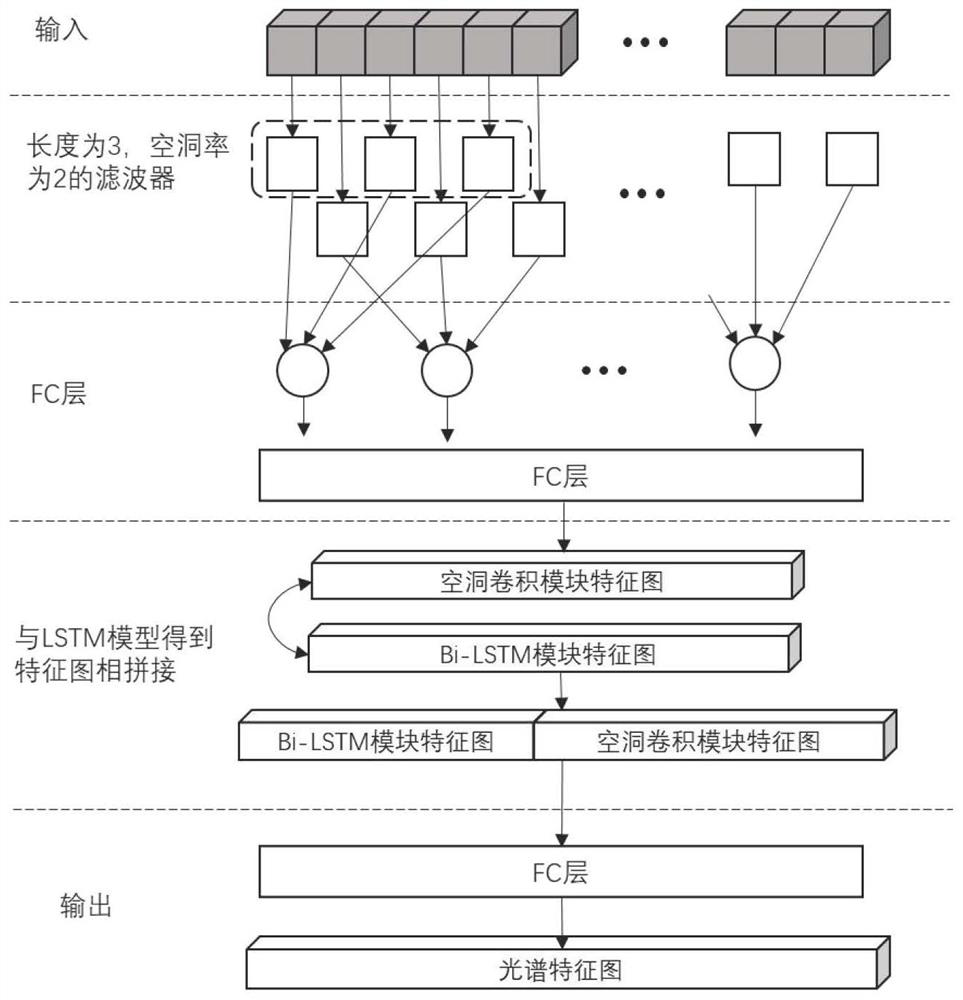
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image classification method based on a deep learning space-spectrum joint network, and the method comprises the steps: firstly carrying out the data partitioning of an original hyperspectral image, and then training the deep learning space-spectrum joint network through a small amount of label data; simultaneously carrying out spectral dimension feature extraction processing on the input hyperspectral original image by a bidirectional long-short-term memory model with an attention mechanism and a 1D hole convolutional neural network to obtain a final spectral feature map; performing data normalization processing on an input image, performing PCA dimension reduction, extracting input features, sending the input features into a multi-scale multi-levelfilter convolutional network to extract spatial features, and performing global average pooling layer processing to obtain a final spatial feature map; and finally, carrying out classification by combining the trained network parameters. According to the method, spectral dimension features and spatial features are processed separately, richer and more effective spectral feature maps and richer feature expressions can be obtained, and the classification precision is further improved.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with real-time correction of motion and frequency drift, and real-time shimming
InactiveUS20070265520A1Suppress signalReduce sensitivityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSpectral patternObject motion
This invention relates to localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and to magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) of the proton NMR signal, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) method to measure a single volume of interest and to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with at least one spectral dimension and up to three spatial dimensions. MRS and MRSI are sensitive to movement of the object to be imaged and to frequency drifts during the scan that may arise from scanner instability, field drift, respiration, and shim coil heating due to gradient switching. Inter-scan and intra-scan movement leads to line broadening and changes in spectral pattern secondary to changes in partial volume effects in localized MRS. In MRSI movement leads to ghosting artifacts across the entire spectroscopic image. For both MRS an MRSI movement changes the magnetic field inhomogeneity, which requires dynamic reshimming. Frequency drifts in MRS and MRSI degrade water suppression, prevent coherent signal averaging over the time course of the scan and interfere with gradient encoding, thus leading to a loss in localization. It is desirable to measure object movement and frequency drift and to correct object motion and frequency drift without interfering with the MRS and MRSI data acquisition.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Hyperspectral remote sensing data classification method based on ensemble learning
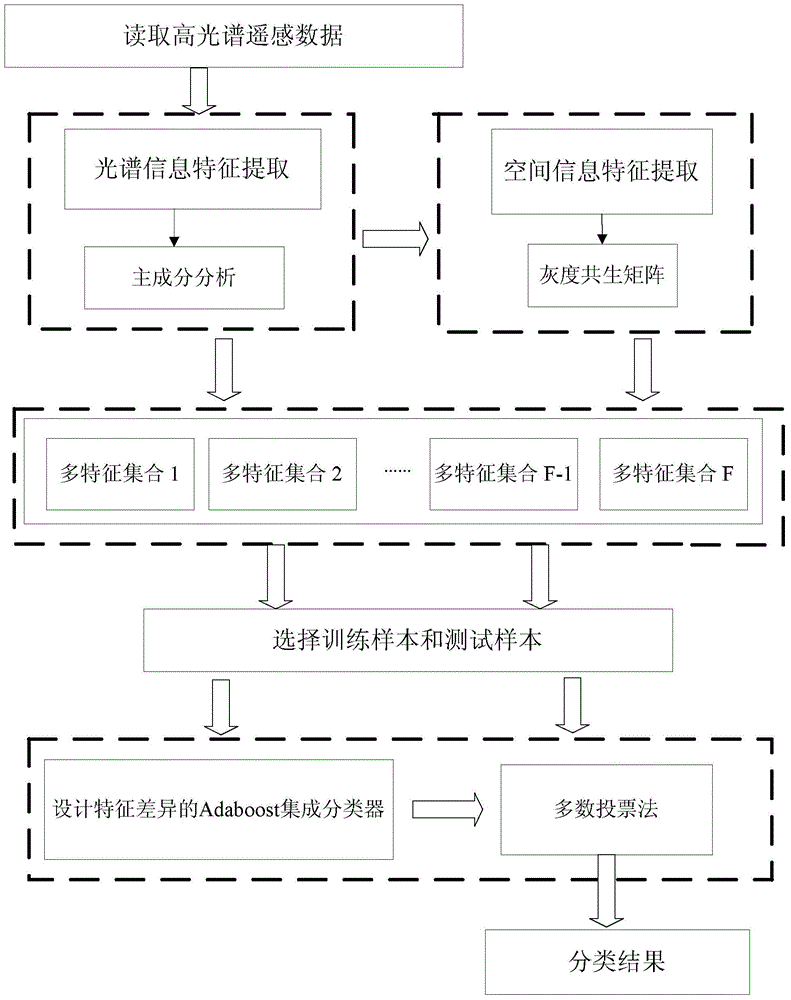
InactiveCN104021396AReduce the impact of classification accuracyGood serviceScene recognitionSensing dataHyperspectral data classification
The invention discloses a hyperspectral remote sensing data classification method based on ensemble learning, belonging to the technical field of spectral data classification and aiming at solving the problem of low data classification precision caused by the fact that an existing hyperspectral data classification method is used for classifying data from the aspect of spectral dimensions. The hyperspectral remote sensing data classification method comprises the following steps: firstly, reading hyperspectral remote sensing data to obtain spectral characteristics and spatial characteristics of hyperspectral remote sensing data; integrating the spectral characteristics and the spatial characteristics to obtain a multiple characteristic set; determining a marking sample and selecting training samples and testing samples according to the multiple characteristic set; designing an Adaboost integration and classification frame of characteristic difference based on an ensemble learning method, and training with the training sample to obtain F weak classifiers; and classifying the testing samples by the F weak classifiers. The hyperspectral remote sensing data classification method is used for classifying hyperspectral remote sensing data.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Hyperspectral image classification method based on neighborhood information deep learning
ActiveCN107798348AEliminate the "pitting" effectImprove continuityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesHyperspectral data classificationSpectral dimension
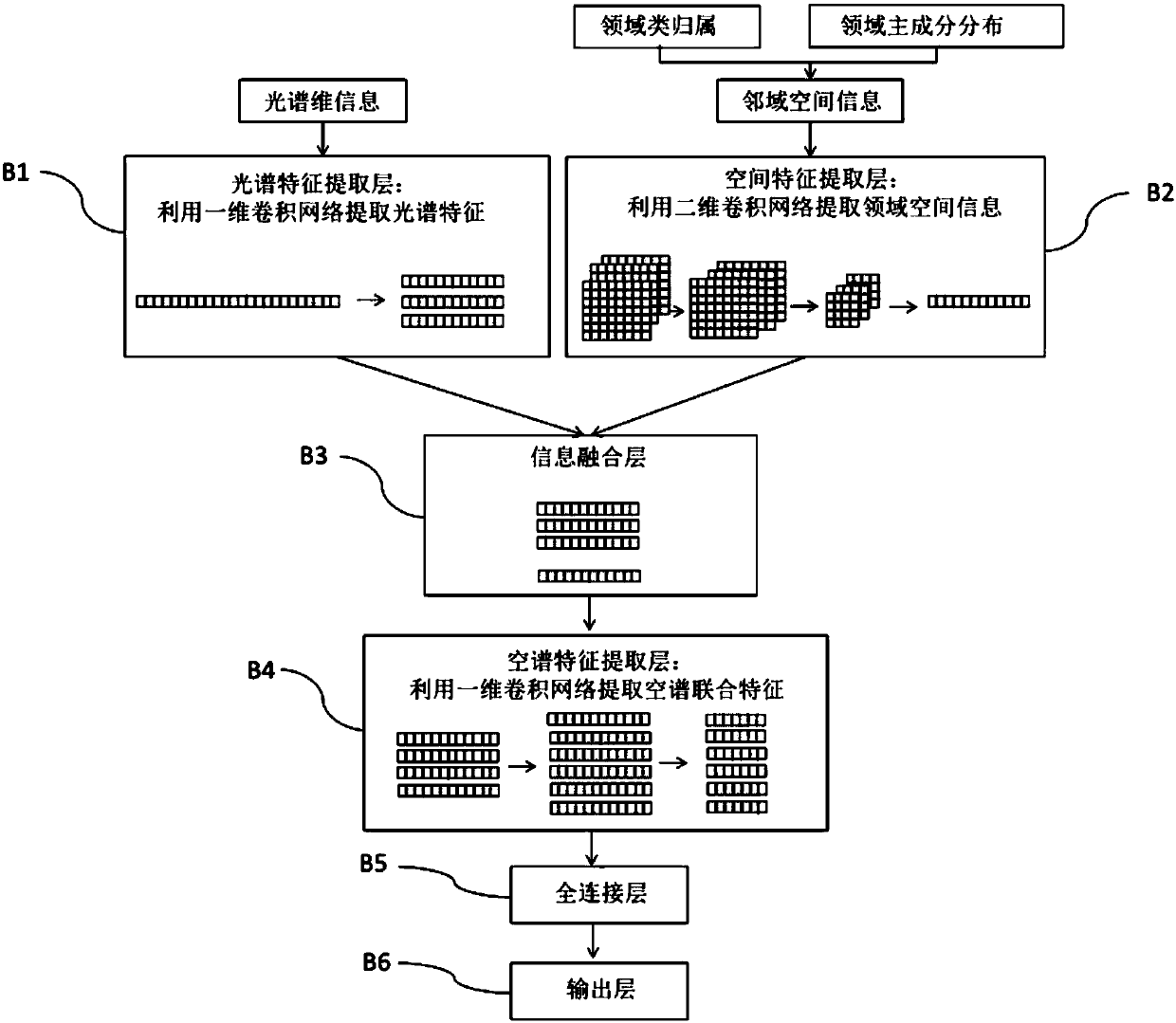
The invention discloses a hyperspectral data classification method based on neighborhood information deep learning. The method comprises the steps of randomly dividing hyperspectral image data into atraining set and a test set; taking class attribution of the training set samples in the n * n neighborhood of each pixel point and the score of a front one main component of all the samples in the n* n neighborhood as the spatial information of each sample, putting the spectral information and the spatial information of each sample of the training set into a convolution neural network for modeltraining, putting the spectrum information and the space information of each sample of the test set into the model for classification result prediction. According to the method, the class attributionof the training set of each pixel point in the n * n neighborhood in a picture and the main component distribution of all the samples in the neighborhood serve as spatial information, spatial featureextraction is carried out on the neighborhood image through a two-dimensional convolution neural network, and fusion with the spectral dimension information is then conducted. The classification precision can be remarkably improved. The method has a good application prospect in the field of hyperspectral data classification.
Owner:INST OF INTELLIGENT MFG GUANGDONG ACAD OF SCI
Hyperspectral image camouflage target detection method based on deep learning
PendingCN111368712ARealize location classificationGood for camouflaged target detectionOptical detectionScene recognitionPattern recognitionData set
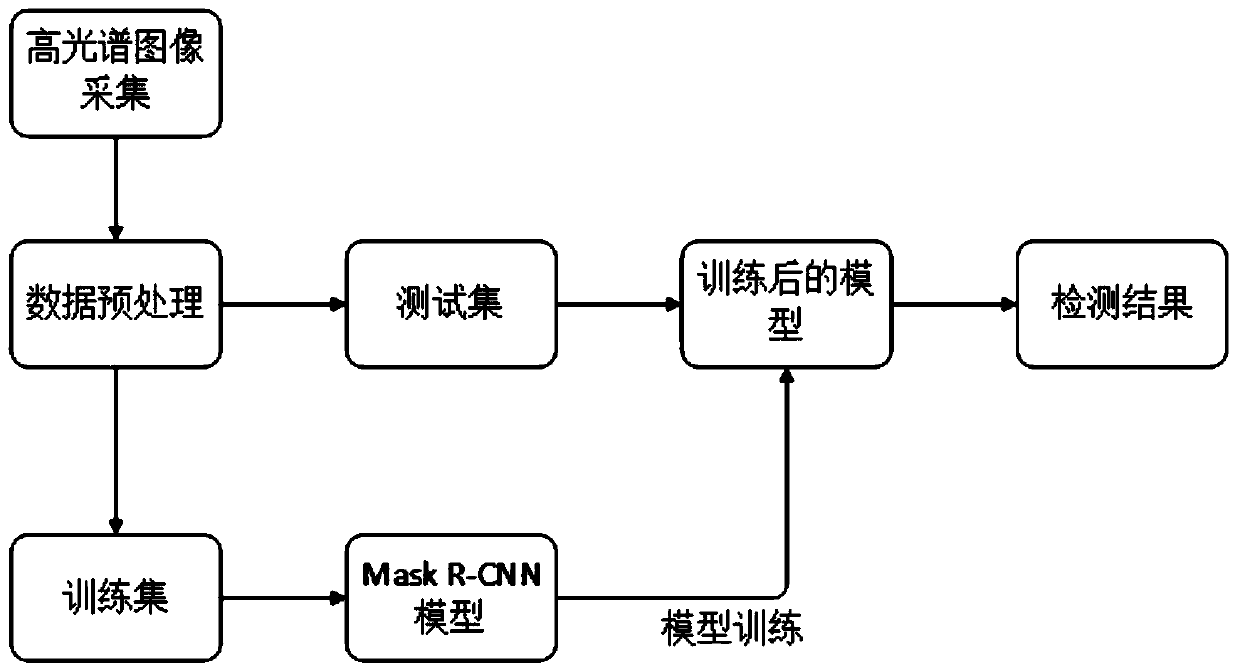
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image camouflage target detection method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the following steps: a, constructing a hyperspectral data set: collecting, preprocessing, dividing and marking the hyperspectral data set, and obtaining a training data set and a test data set; b, constructing a target detection model: using an open-source Mask R-CNN model, adjusting the Mask R-CNN model for an input hyperspectral data set, and constructing the target detection model; c, model training: training the target detection model constructed in the step b by using a training data set; and d, testing the model: detecting and identifying the test data set by using the target detection model trained in the step c. According to the invention, the target detection model based on deep learning is used, and the spectral dimension and spatial dimension information of the hyperspectral image is used at the same time, thereby achieving the positioning and classification of camouflage targets.
Owner:SICHUAN JIUZHOU ELECTRIC GROUP
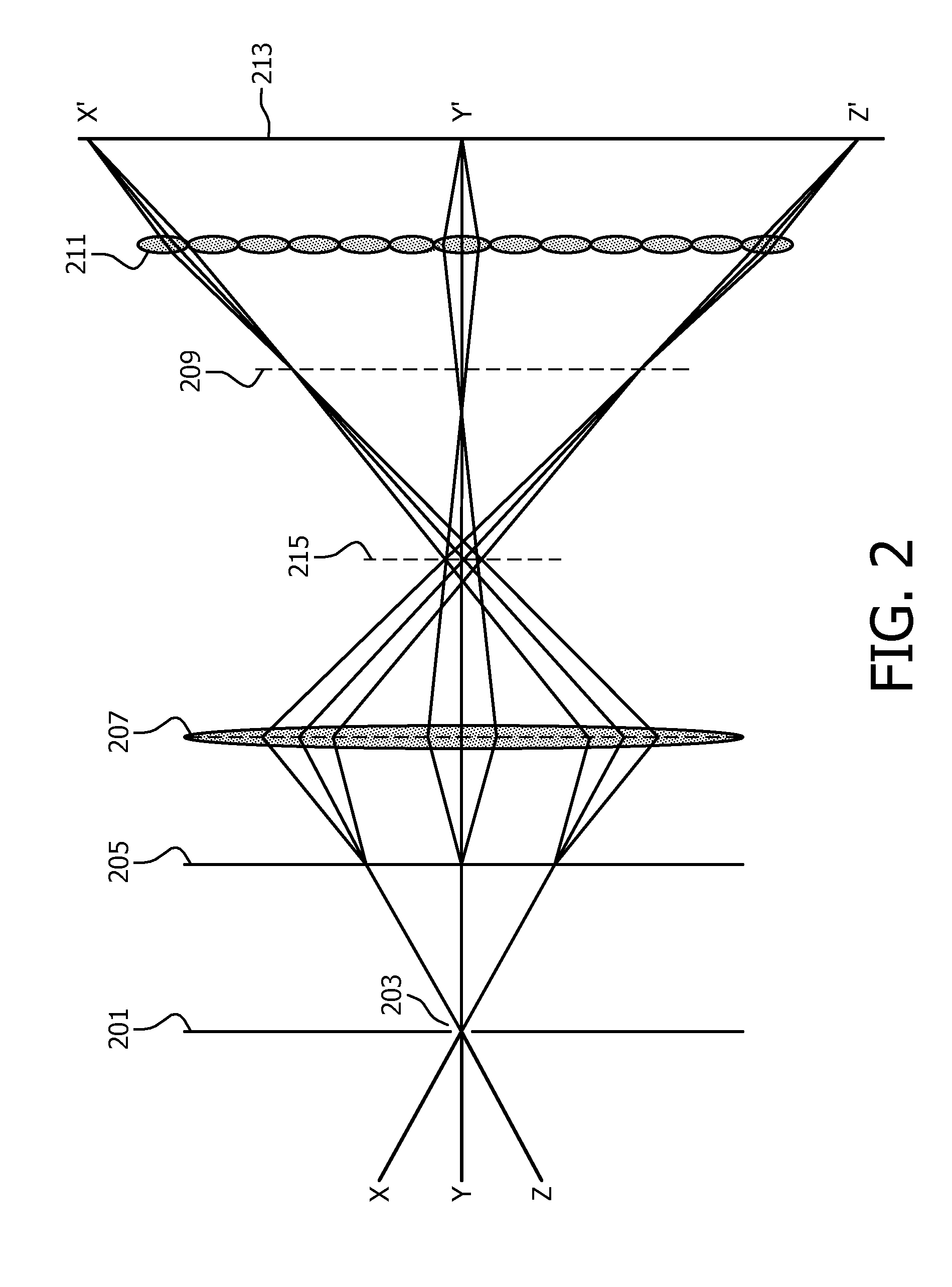
Multi-spectral imaging
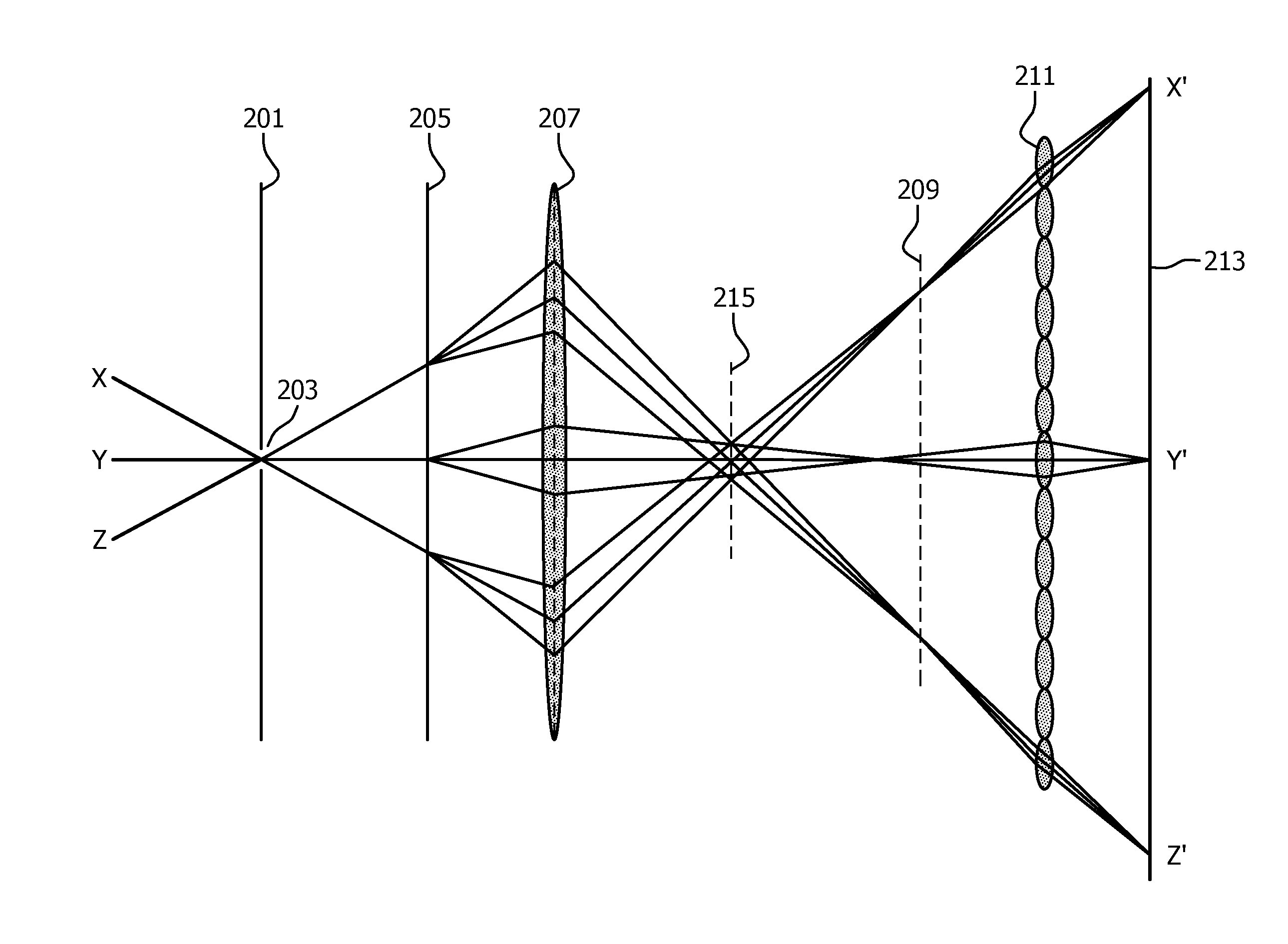
ActiveUS20120127351A1Improve timing performanceHigh resolutionSignal generator with single pick-up deviceRadiation controlled devicesMultispectral imageSpectral dimension
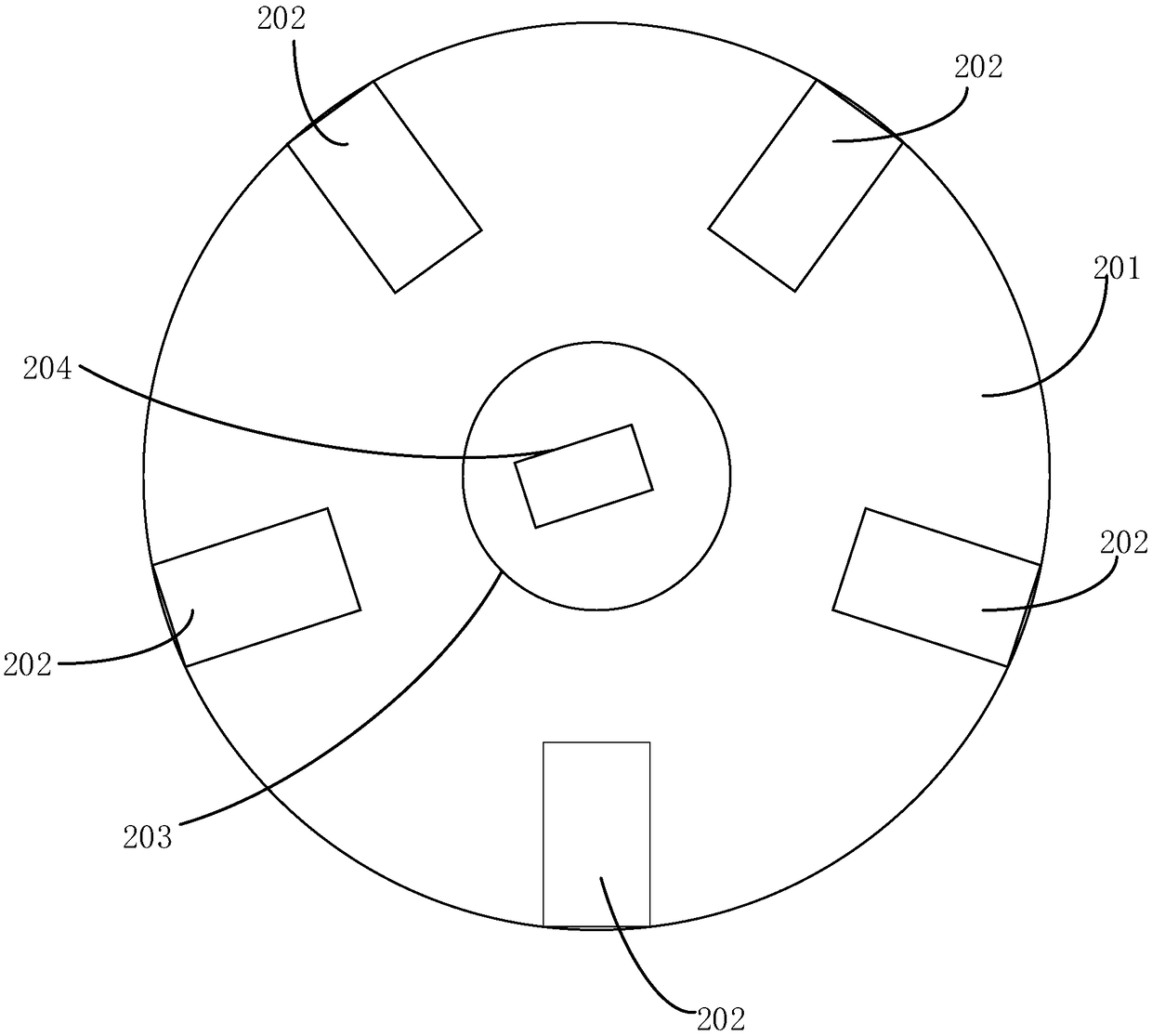
A multi-spectral camera comprises a blocking element (201) having at least one hole (203) allowing light through. A dispersive element (205) spreads light from the at least one hole (203) in different wavelength dependent directions and a lens (207) focuses light from the dispersive element (205) on an image plane (209). A microlens array (211) receives light from the lens (207) and an image sensor (213) receives the light from the microlens array (211) and generates a pixel value signal which comprises incident light values for the pixels of the image sensor (213). A processor then generates a multi-spectral image from the pixel value signal. The approach may allow a single instantaneous sensor measurement to provide a multi-spectral image comprising at least one spatial dimension and one spectral dimension. The multi-spectral image may be generated by post-processing of the sensor output and no physical filtering or moving parts are necessary.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Remote sensing image restoration method combining wave-band clustering with sparse representation
ActiveCN103020912ACorrecting Poor Recovery SituationsAvoid insufficientImage enhancementRelevant informationImage resolution
The invention provides a remote sensing image restoration method combining wave-band clustering with sparse representation. In order to improve the spatial resolution of a hyperspectral remote sensing image, according to the characteristics of rich spectral dimension information of the hyperspectral image and different noise strength of different wave bands, a multiband image restoration model is built, the wave bands are mutually restrained and complemented by the aid of high similarity of the wave bands and redundant information, and finally, the high-quality hyperspectral image is obtained. Firstly, the wave bands of the hyperspectral image are clustered, and a large number of wave bands are divided into a small number of categories with large relevant information difference. Secondly, a cluster of wave bands in the same category is built into an integral variation training multiband dictionary by the compressive sensing theory, and the dictionary is used for completing image restoration. Relevancy of a plurality of wave bands is sufficiently used for restoring target images, the spectral characteristics of the target images are kept, and restoration results have higher spatial information and spectral information keeping performance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
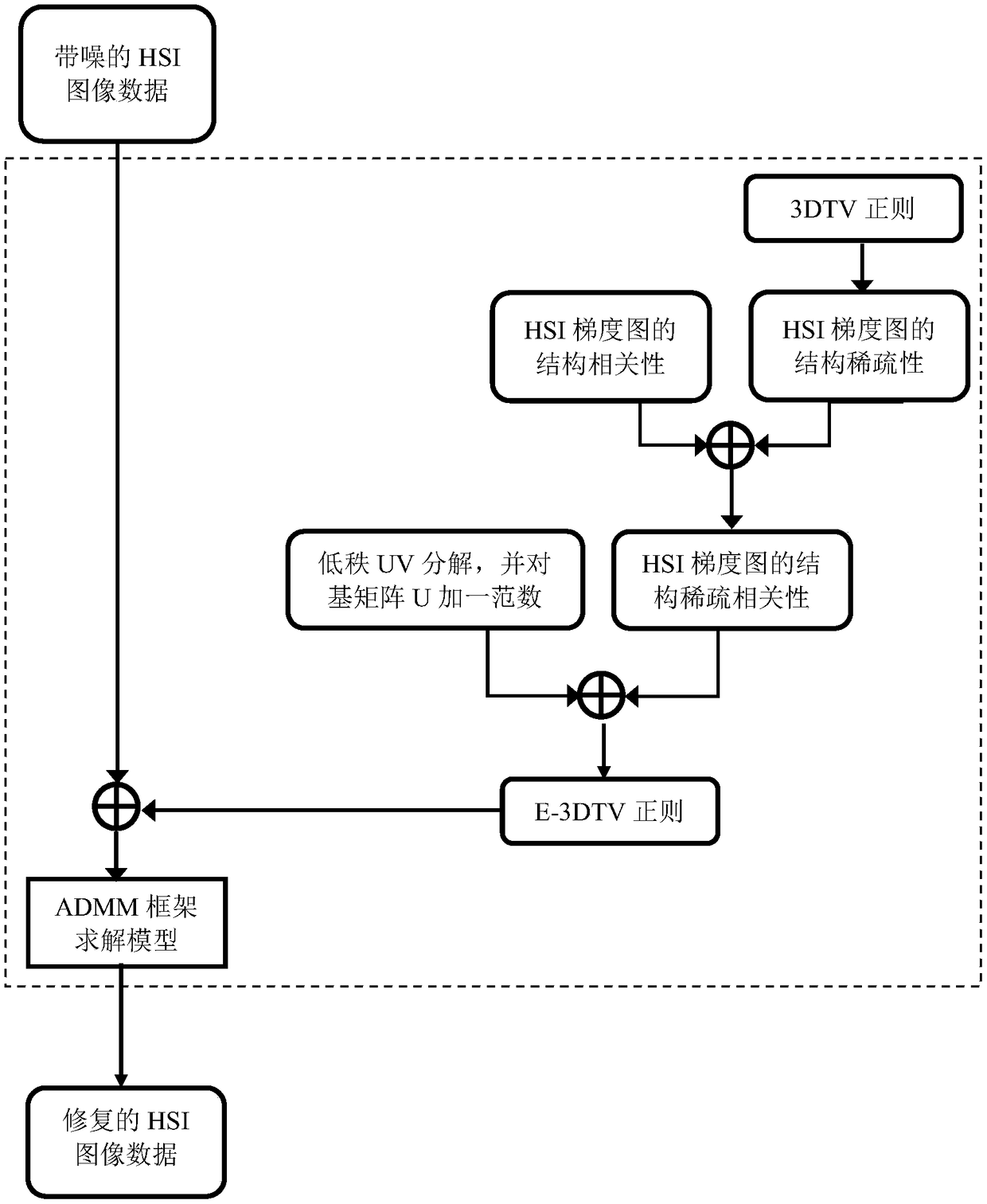
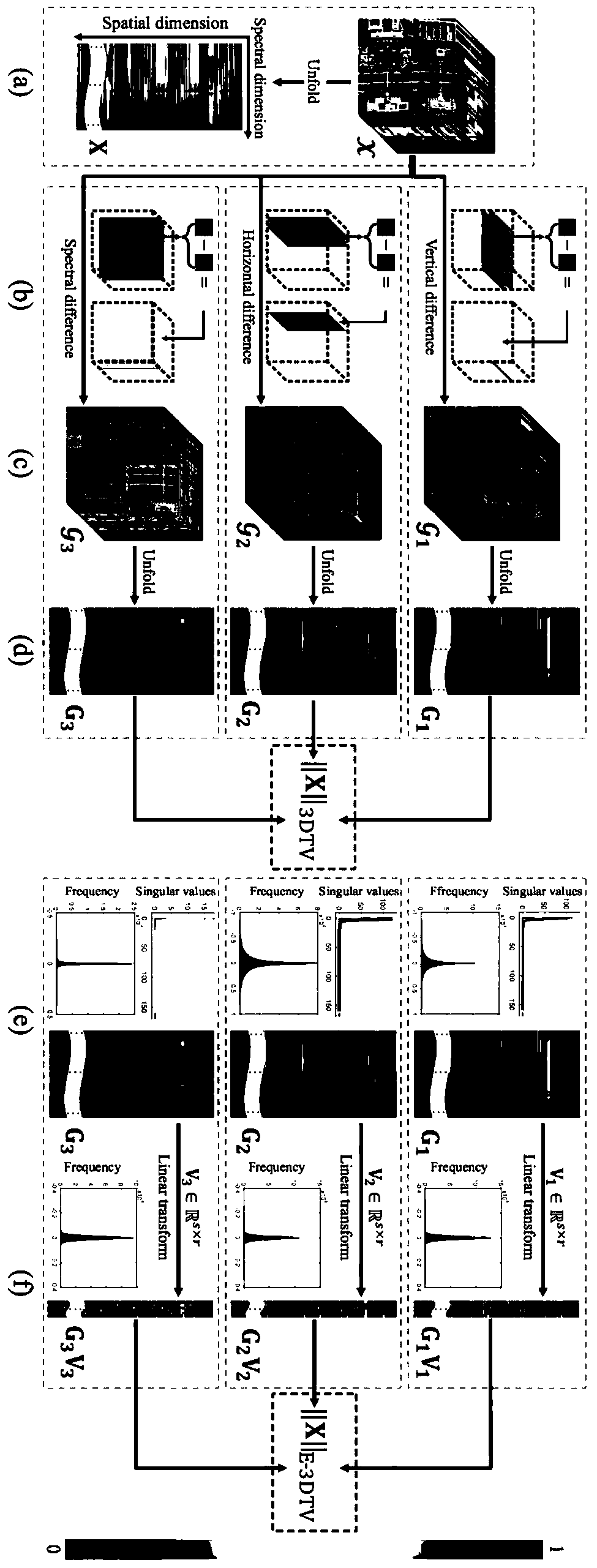
A hyperspectral image inpainting method based on E-3DTV regularity
A hyperspectral image inpainting method based on E-3DTV regularity is provided. The method comprises the steps of expanding the original three-dimensional hyperspectral data with noise into matrix along the spectral dimension, and initializing the matrix representation of the noise term and the hyperspectral data to be repaired, and other model variables and parameters under the ADMM framework; performing differential operation on the hyperspectral data to be repaired along horizontal, vertical and spectral dimensions to obtain three gradient maps in different directions, which are expanded into matrices along the spectral dimensions; decomposing the gradient graph matrices in three directions by low rank UV, and constraining the basis matrices of the gradient graph by sparsity to obtain E-3DTV regularity; adding the E-3DTV regularity to the data to be repaired, writing out the optimization model, using the ADMM framework to solve iteratively; obtaining the restoration image and noisewhen the iteration is stable. The invention performs denoising and compression reconstruction on the hyperspectral image data, and improves the enhancement of the traditional 3DTV so as to give consideration to the structural correlation and sparsity of the gradient image, thereby overcoming the defect that the traditional 3DTV can only depict the sparsity of the gradient image and ignores the correlation.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Video imaging method, system, apparatus and storage medium based on hybrid camera
ActiveCN109167924ASolve technical problems with low resolutionHigh resolutionTelevision system detailsColor television detailsWide fieldImage resolution
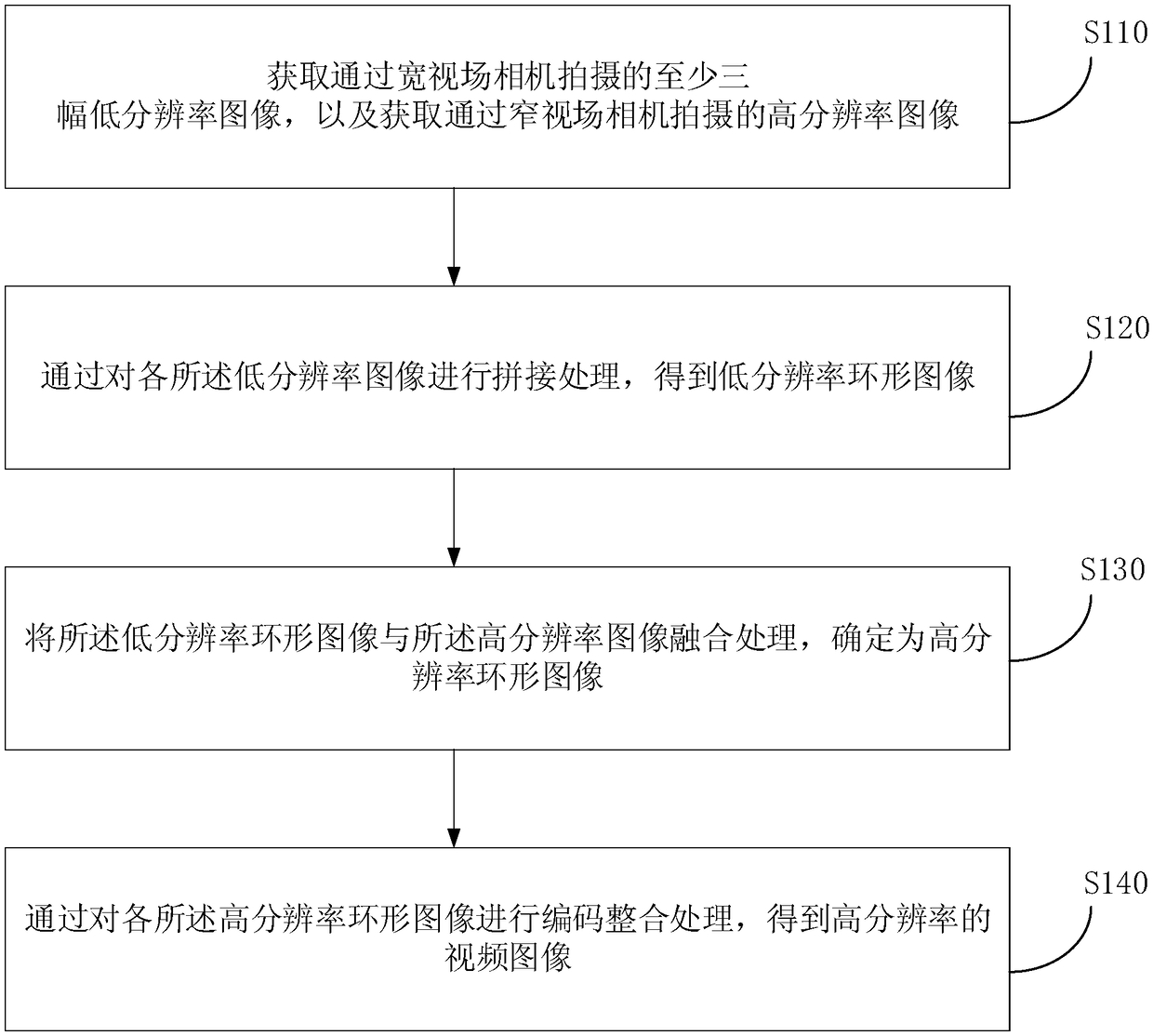
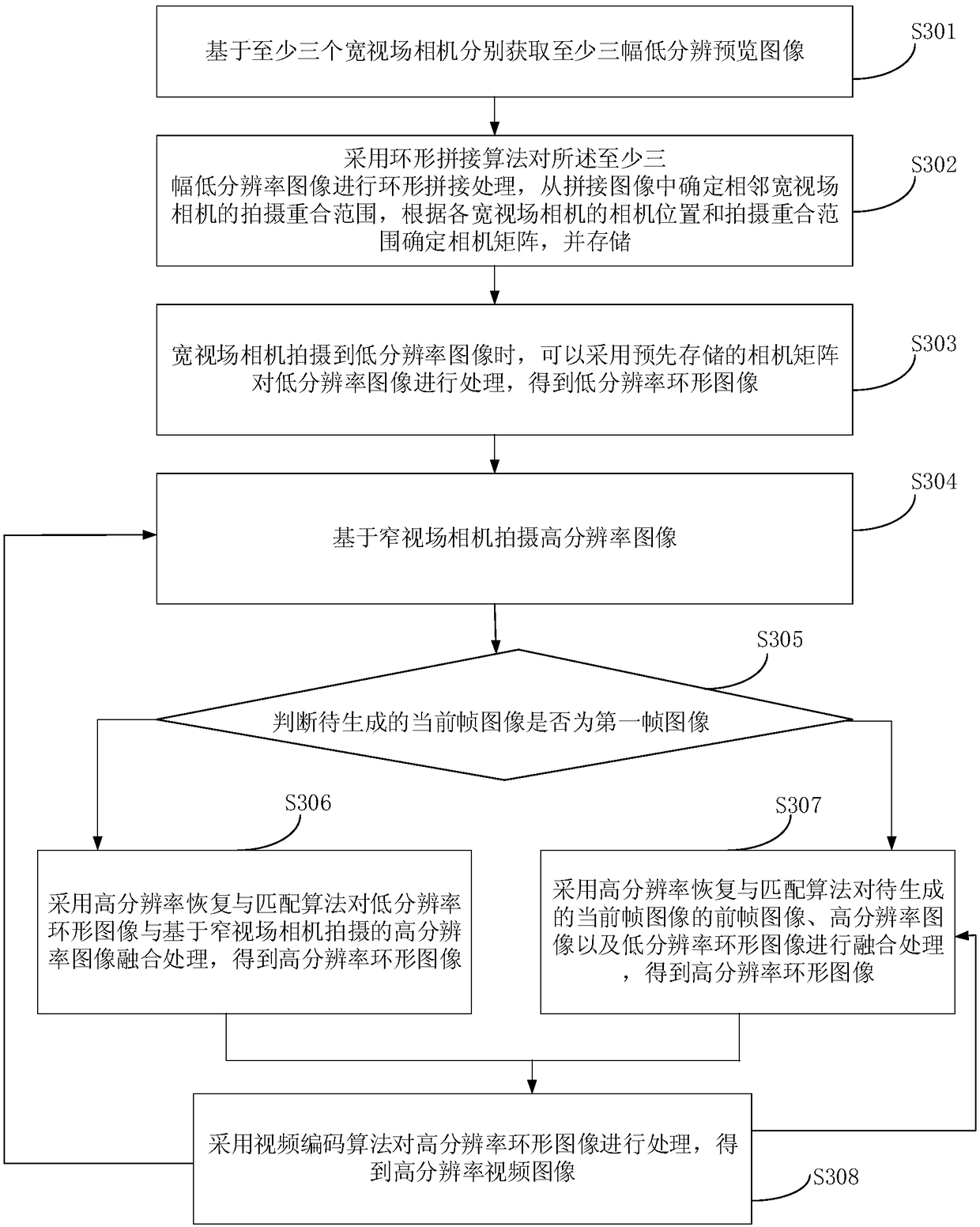
The embodiment of the invention discloses a video imaging method, a system, an apparatus and a storage medium based on a hybrid camera. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring at least three low-resolution images captured by a wide-field camera and acquiring high-resolution images captured by a narrow-field camera; obtaining a high-resolution image captured by a narrow-field camera; obtaining a low-resolution image by mosaic that low-resolution images; fusing the low-resolution annular image and the high-resolution image to determine a high-resolution annular image; obtaining a high-resolution video image by encoding and integrating each of the high-resolution ring images. The technical proposal of the embodiment of the invention realizes that the high-resolution image and thelow-resolution image taken by the narrow-field camera and the wide-field camera respectively are combined together and a series of algorithms are adopted to process the high-resolution image and the low-resolution image to obtain the video image with gigapixel level resolution. The resolution of the video image and the technical effect of the spectral dimension are improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Hyperspectral image saliency object detection method based on spectral gradient and hierarchical structure
ActiveCN107274416ASmall amount of calculationImage enhancementImage analysisSaliency mapImage segmentation
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image saliency object detection method based on a spectral gradient and a hierarchical structure, so as to solve the technical problem of large calculation amount of the existing hyperspectral image saliency object detection method. According to the technical scheme, a spectral gradient map is firstly generated; an image segmentation region is then generated; a saliency detection model based on an image hierarchical structure is built; a saliency calculation method based on Background priors and edge features is then built; and a saliency map result is calculated. Through calculating the spectral gradient on a spectral dimension of the original hyperspectral image, the spectral gradient features of the image are extracted, and adverse effects caused by uneven illumination are weakened. A simple linear iterative clustering algorithm (SLIC) is used to generate super pixels, the hyperspectral image is segmented, the calculation process is accelerated, the saliency is measured through calculating the spectral feature contrast between segmentation areas, and the calculation amount is small.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
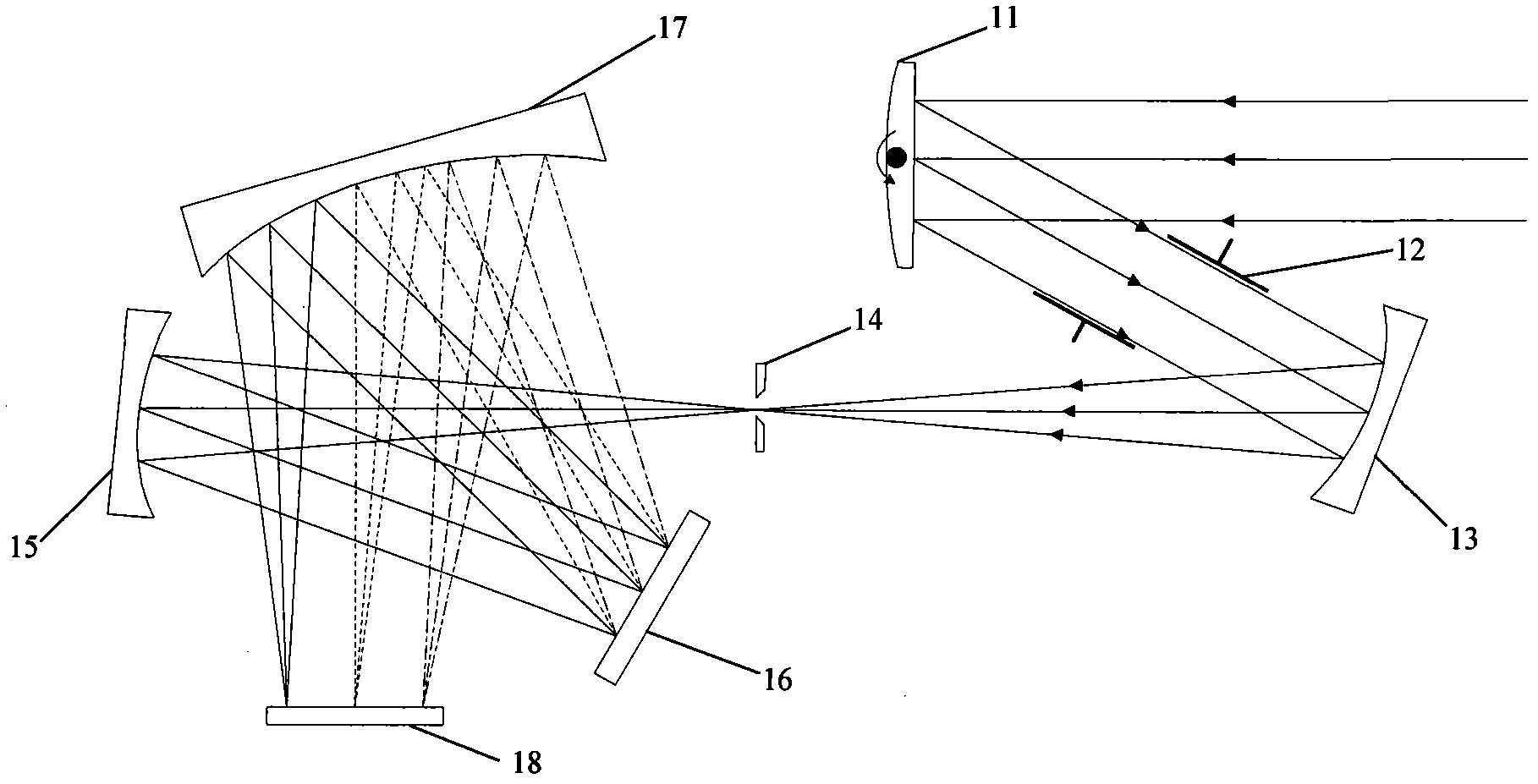
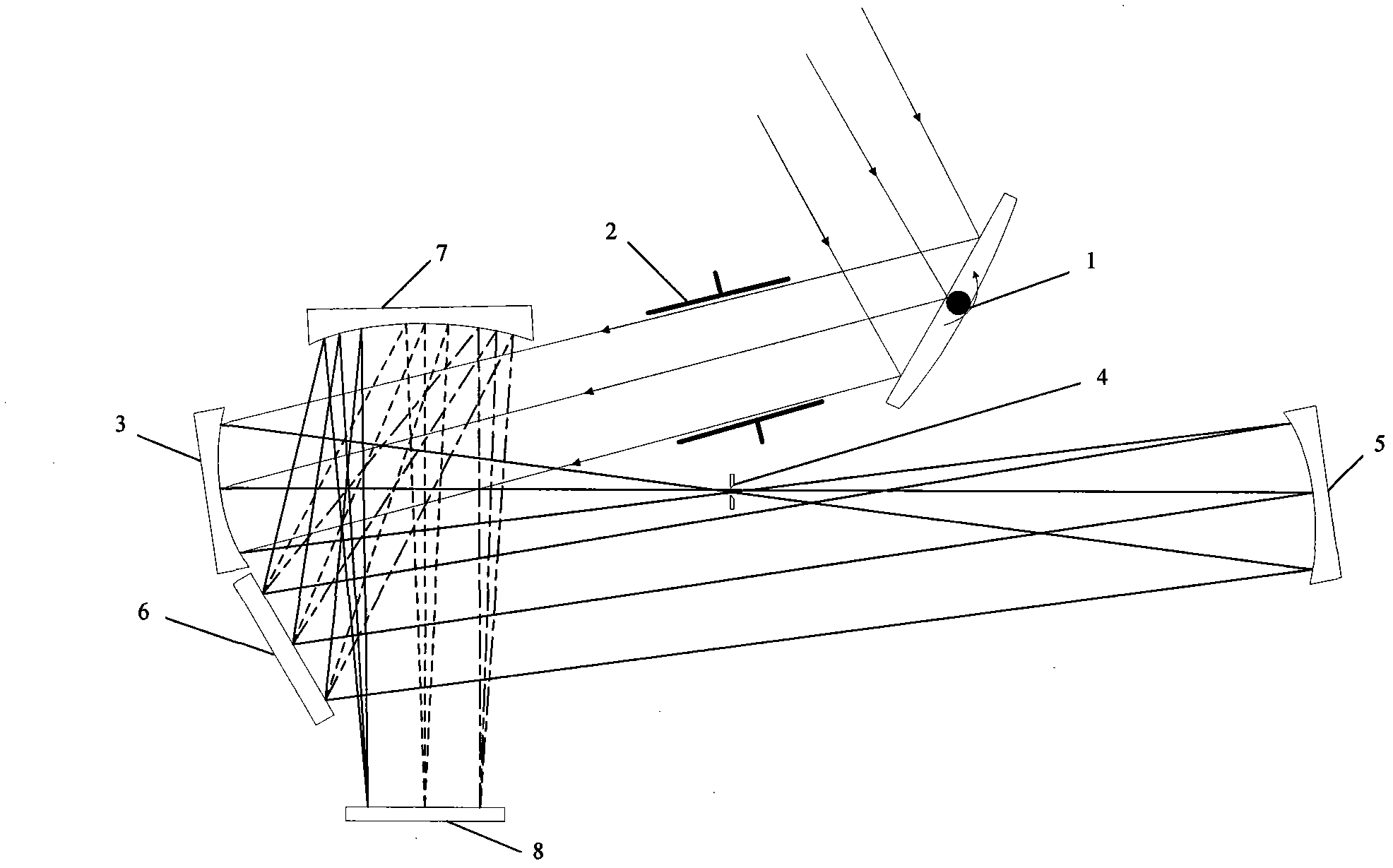
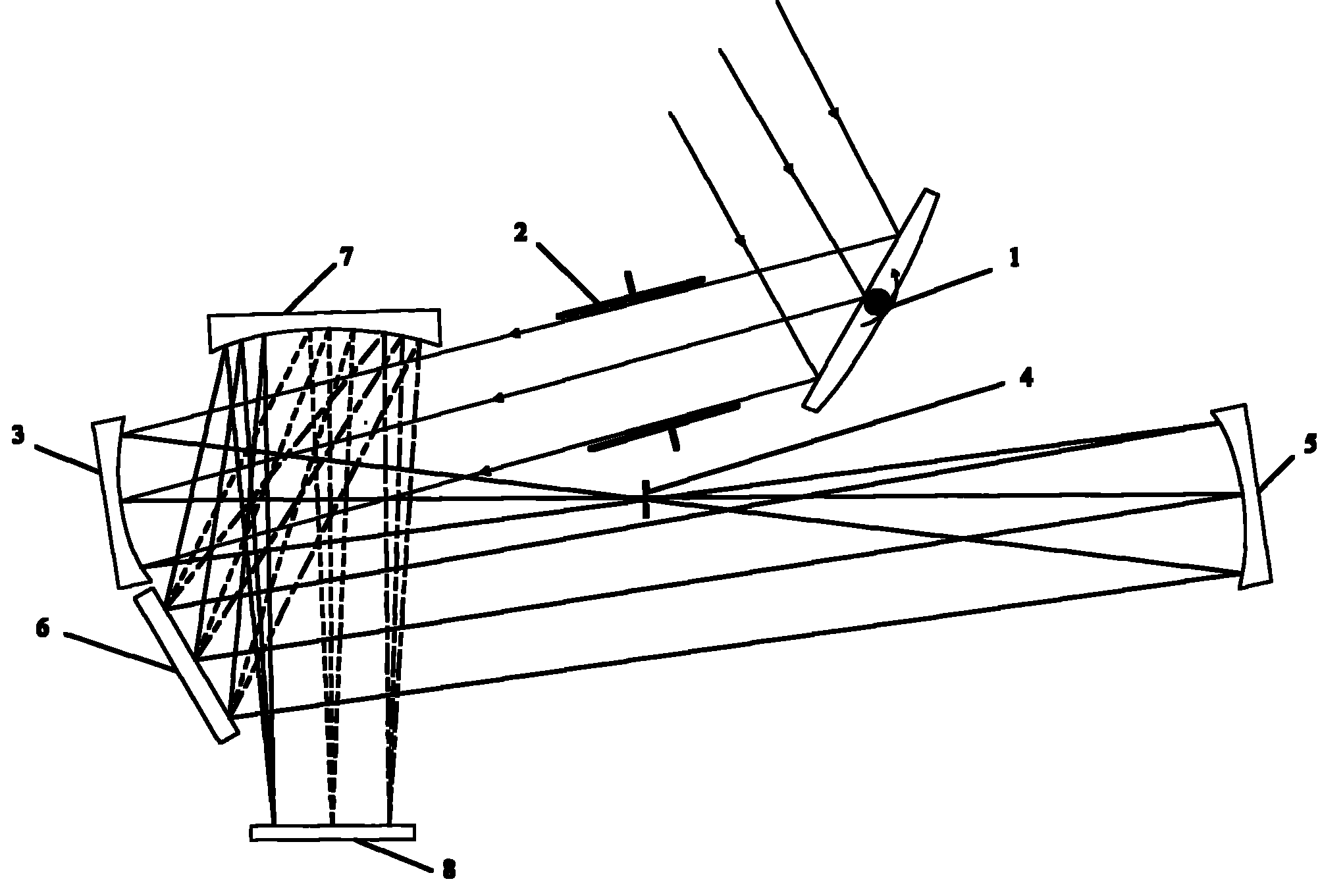
Light path structure of scanning and imaging spectrometer
InactiveCN101975610AIncrease distanceReduce off-axis angleRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationGratingHigh reflectivity
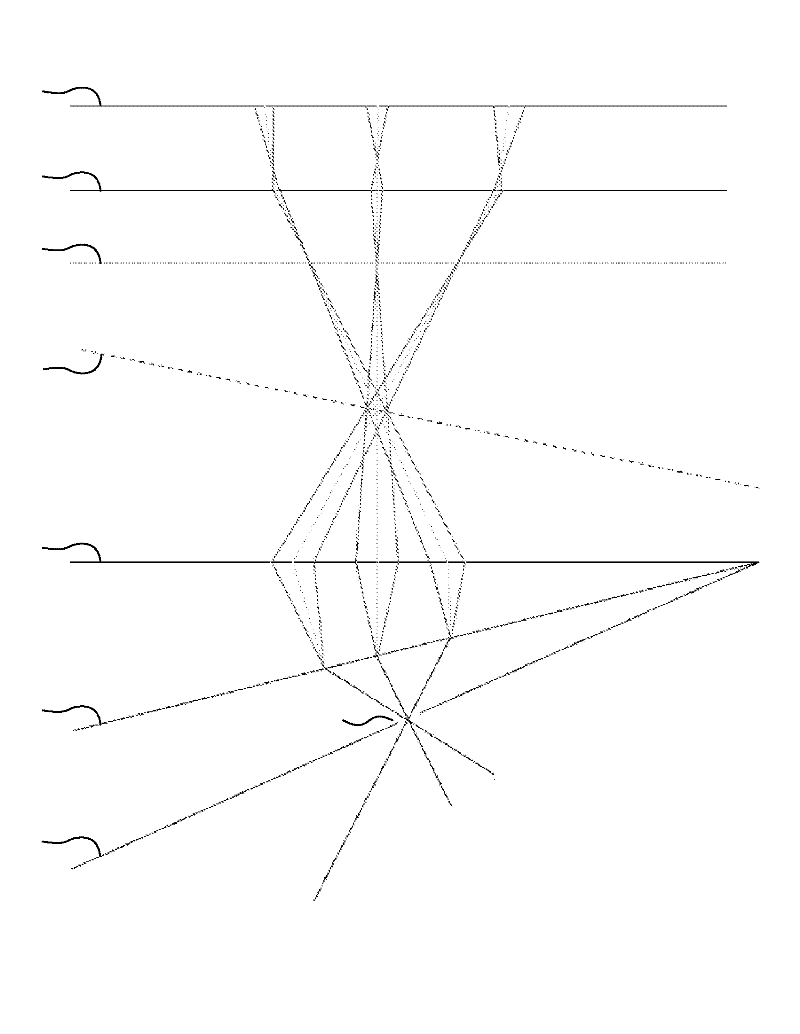
The invention relates to a light path structure of a scanning and imaging spectrometer, comprising a scanning mirror (1), a diaphragm (2), a telescope objective (3), a collimator objective (5), a raster (6) and a focusing objective (7). The scanning mirror (1) is used for reflecting incident light from a target, the diaphragm (2) is used for selecting light in a certain FOV (Field Of View) to enter the spectrometer, the telescope objective (3) is used for focusing light passing through the diaphragm in a silt (4), the collimator objective (5) is used for reflecting light passing through the silt to the raster (6) which is used for splitting light, and the focusing objective (7) is used for focusing the split light on the photosurface of a detector (8) for spectroscopic imaging. Spectral data in a two-dimensional space can be acquired through the scanning of the scanning mirror (1) on spectral dimensions. The spectrometer adopts all-reflective type optical elements, and all the reflecting elements are respectively coated with a high-reflectivity film. The light path structure is structurally characterized in that the space is shared by a telescopic imaging light path and a spectroscopic imaging light path, an off-axis angle between the optical elements is reduced on a basis of keeping the original system size and the spectral resolution and the imaging resolution of the spectrometer are greatly improved.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
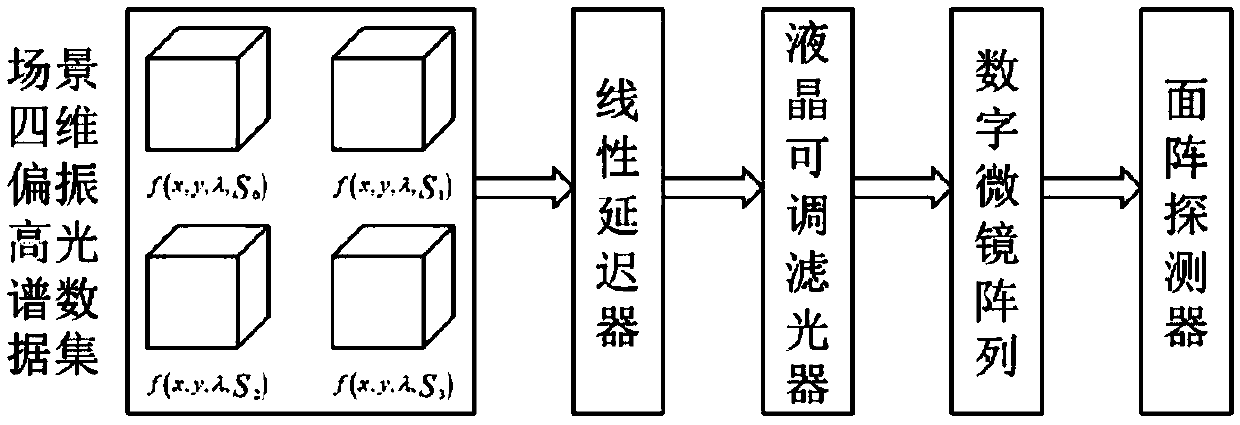
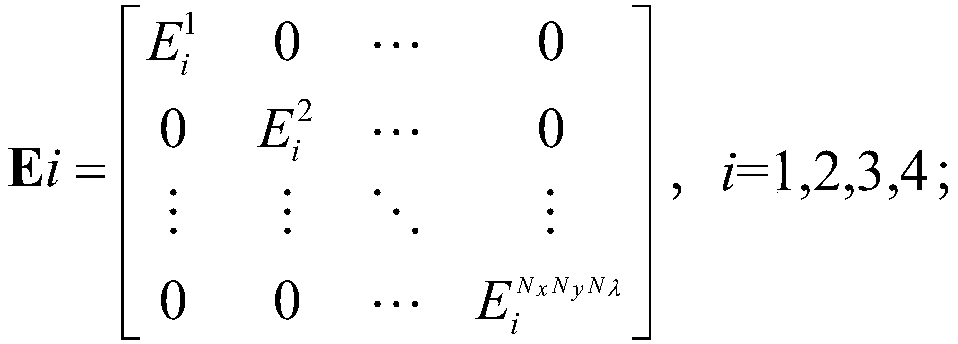
LCTF-based full-polarization hyperspectral compressed sensing imaging system and method
ActiveCN108955887AReduce sampling redundancyImprove sampling efficiencyRadiation pyrometryPolarisation spectroscopySpectral dimensionLength wave
The invention discloses an LCTF-based full-polarization hyperspectral compressed sensing imaging system and an LCTF-based full-polarization hyperspectral compressed sensing imaging method. The LCTF-based full-polarization hyperspectral compressed sensing imaging system comprises a linear retarder, a liquid crystal tunable optical filter, a digital micro mirror array and an area array detector, wherein a Mueller matrix of the linear retarder is designed such that absolute values of first two elements of each column are different; the linear retarder and the liquid crystal tunable optical filter realize polarization dimension compression jointly; the liquid crystal tunable optical filter switches L different center wavelengths, outputs images in each band, and realizes spectral dimension compression; the digital micro mirror array encodes the images of each band, and realizes spatial dimension coding compression; and an original image is detected by means of the area array detector after sequentially passing through the linear retarder, the liquid crystal tunable optical filter and the digital micro mirror array, so as to obtain an image containing full Stokes parameters. By applying the LCTF-based full-polarization hyperspectral compressed sensing imaging system and the LCTF-based full-polarization hyperspectral compressed sensing imaging method, compression reconstruction ofthe full Stokes parameters of the original image can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
System and method for high-resolution spectroscopic imaging
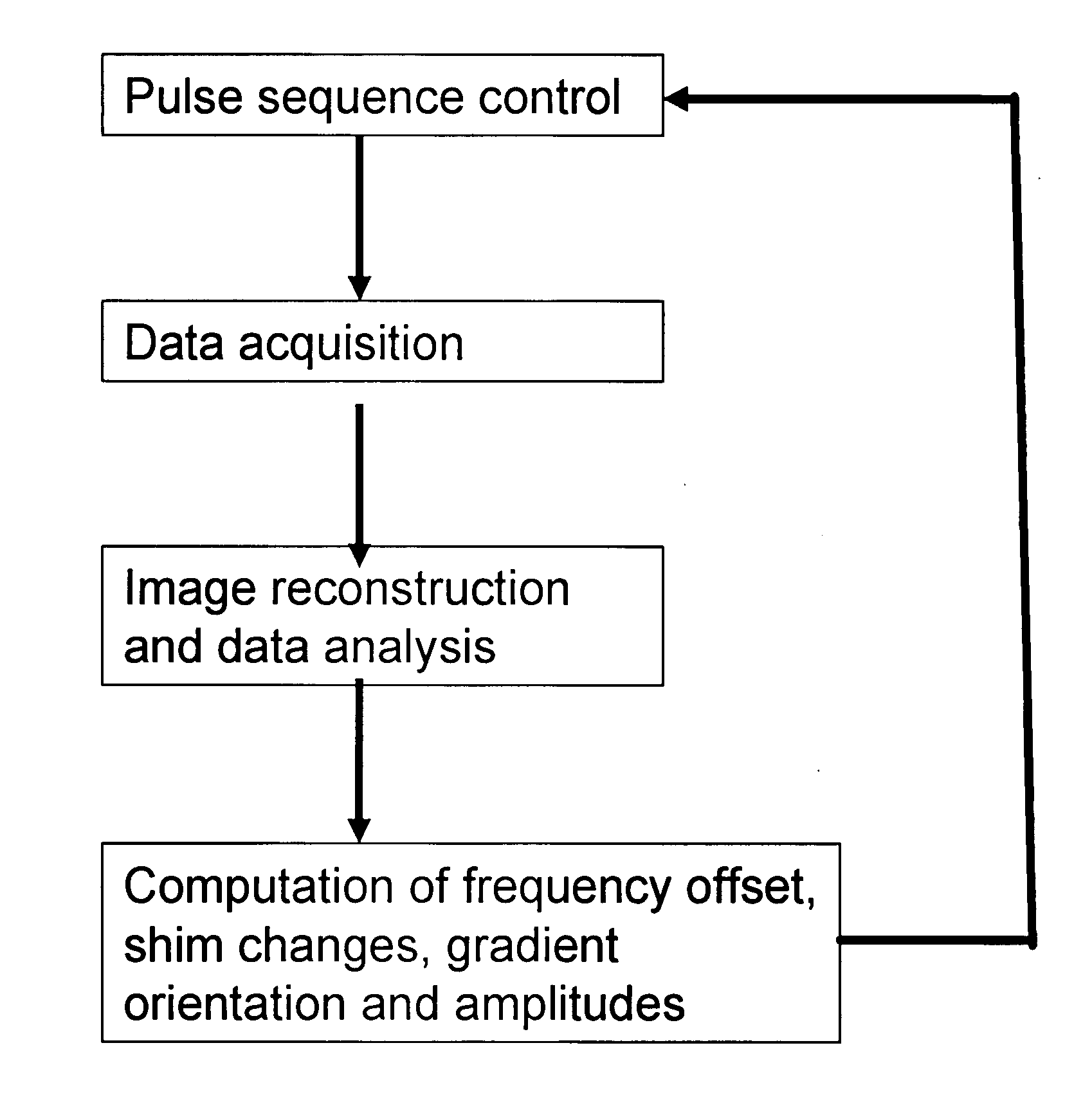
ActiveUS20160202336A1Data acquisition time can be shortenedHigh resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBiological testingData setSubspace model
A new method is developed to accelerate high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). The method is built on a low-dimensional subspace model exploiting the partial separability of high-dimensional MRSI signals and uses this subspace model for data acquisition, processing, and image reconstruction. Specifically for two and three dimensional MRSI with one spectral dimension, this method sparsely samples the corresponding (k,t)-space in two complementary data sets, one with dense temporal sampling and high signal-to-noise ratio but limited k-space coverage and the other with sparse temporal sampling but extended k-space coverage. The reconstruction is then done by estimating a set of temporal / spectral basis functions and the corresponding spatial coefficients from these two data sets. The proposed subspace model can be further extended to incorporate multiple signal components for nuisance signal removal in 1H-MRSI and more generalized reconstruction methods. The resulting imaging technique can be used for high-resolution MRSI of different nuclei. It will be useful for high-resolution metabolic imaging with many exciting applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
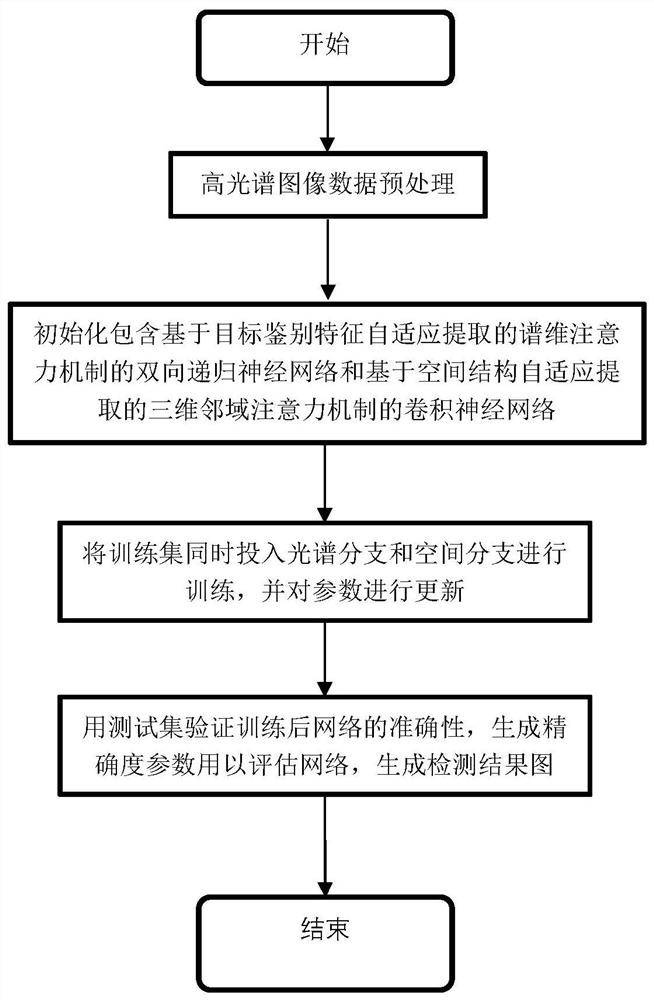
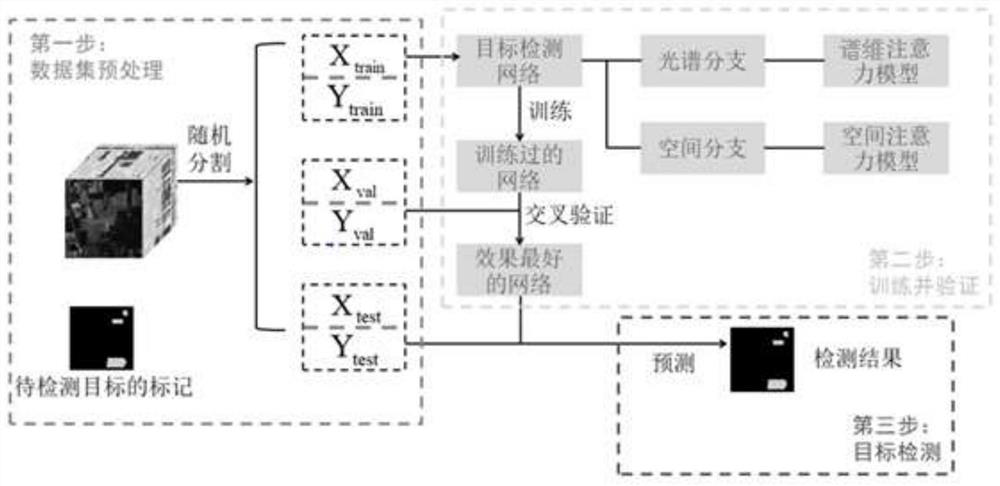
Hyperspectral image target detection method and system based on spectral dimension and spatial cooperation neighborhood attention
InactiveCN112116563AImprove object detection accuracyImprove generalization abilityImage enhancementImage analysisActivation functionData set
The invention discloses a hyperspectral image target detection method and system based on spectral dimension and spatial cooperation neighborhood attention. The method comprises the following steps: generating a 3D cube set; respectively taking a bidirectional recurrent neural network of spectral dimension neighborhood attention mechanism based on target identification feature self-adaptive extraction and convolutional neural network of three-dimensional neighborhood attention mechanism based on spatial structure self-adaptive extraction as spectral branch and spatial branch to respectively extract spectral features and spatial features of hyperspectral image for cascade generation; forming spatial-spectral cooperation characteristics to obtain an optimal network model; and obtaining a target detection result of the network to the data set through an activation function according to the spatial-spectral cooperation characteristics. through a neighborhood attention mechanism of spectrumdimension and space cooperation, the neural network can adaptively learn and acquire space-spectrum cooperation features, the interdependence relationship between discriminative spectrum features andsimilar space features is better mined, the generalization ability is high, and high target detection precision can be obtained.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Hyperspectral batch-type nondestructive detection method and system for quality of agricultural and livestock products
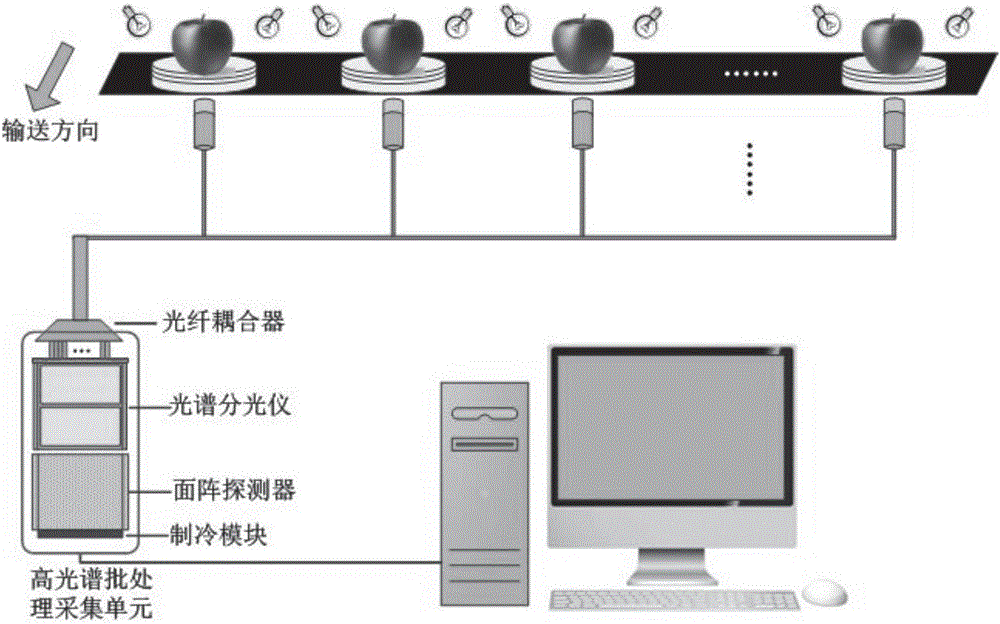
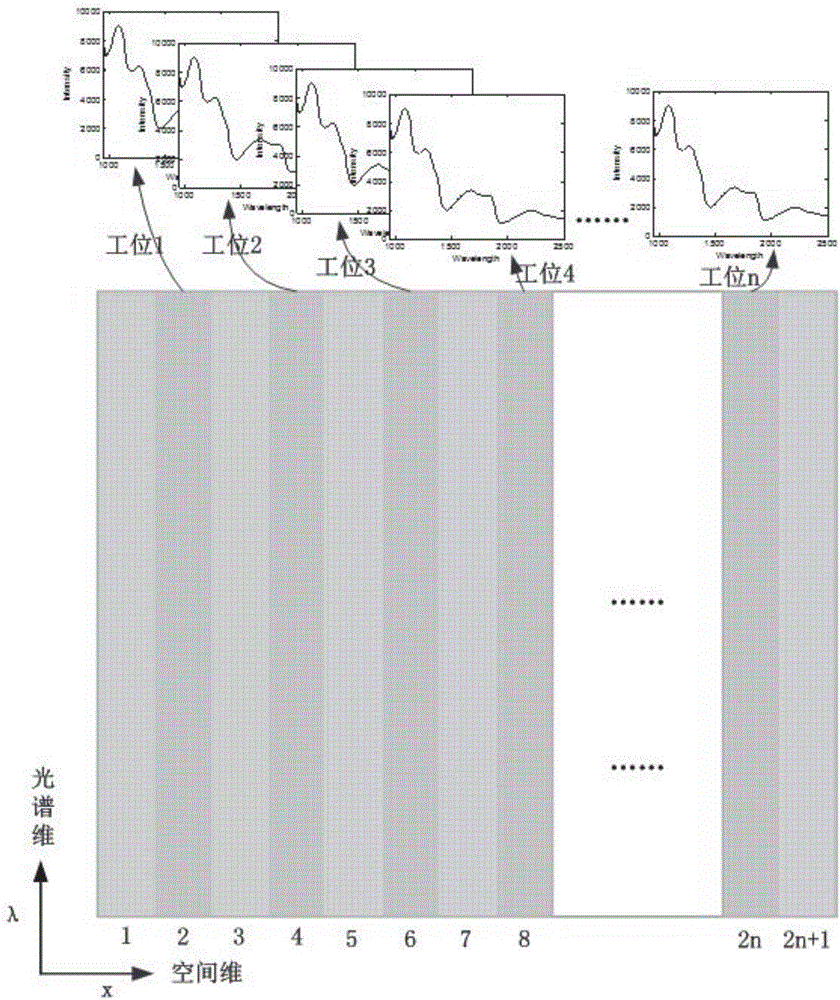
ActiveCN105973839ASolve the bottleneck problem of detecting speed limitDetection speedMaterial analysis by optical meansFiberEngineering
The invention discloses a hyperspectral batch-type nondestructive detection method and system for quality of agricultural and livestock products. The method comprises: presetting the number of single hyperspectral batch-type samples, determining the number of coupling fibers, and further determining the size and arrangement of the fibers; establishing a correspondence of each fiber with spatial-dimension and spectral-dimension photosensitive regions on an area array detector, and establishing a correspondence of a fiber corresponding detection sample with a near-infrared spectral signal responsively acquired by the assigned photosensitive region of the detector; establishing a quality detection model using quality indexes of the batch-type detection samples and near-infrared spectrum acquired by the detector; subjecting samples to be detected to batch feeding, acquiring near-infrared spectrums of the samples, substituting to the quality detection model, outputting the quality indexes of the samples to be detected respectively to finish hyperspectral batch-type rapid destructive detection for the quality of agricultural and livestock products. The detection speed limit problem and model transfer bottleneck problems can be broken through for the detection of the quality of agricultural and livestock products.
Owner:上海陆华光电科技有限公司
Matrix factorization-based hyperspectral image saliency target detection method
ActiveCN107316309AReduce adverse effectsAvoid the problem of uneven partitioningImage enhancementImage analysisMatrix decompositionPattern recognition
The invention provides a matrix factorization-based hyperspectral image saliency target detection method. According to the method, the spectral gradients of an original hyperspectral image are calculated in spectral dimension, the spectral gradient features of the image are extracted, and therefore, adverse effects caused by illumination are eliminated, and at the same time, an image feature matrix is constructed; matrix low-rank sparse decomposition is performed on the image feature matrix, so that a low-rank matrix corresponding to a background part and a sparse matrix corresponding to a saliency target are obtained; and therefore, the problem of nonuniformity of block division in a salient object can be solved, and saliency target detection is realized with decreased computational complexity.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
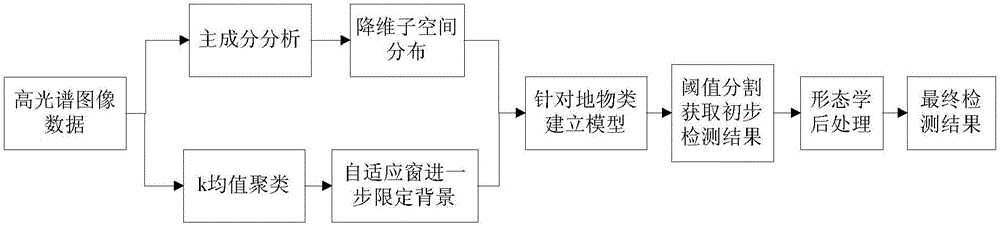
Clustered adaptive window based hyperspectral image abnormality detection method
ActiveCN106600602AHigh precisionEfficient detectionImage enhancementImage analysisHyperspectral image processingPrincipal component analysis
The invention provides a clustered adaptive window based hyperspectral image abnormality detection method which belongs to the hyperspectral image processing field with the object of solving the problem with the consistence of the hyperspectral image background restricted by an existing background model structuring method. The steps of the method are as follows: conducting analysis on the main components of spectral dimensions of hyperspectral image and generating spectral subspace; generating adaptive windows for each to-be-detected pixel wherein each of the generated adaptive window is a binary matrix whose center is superposed with the to-be-detected pixel and the pixel in the matrix represented by one indicates the pixel as one in the homogeneous background area of the hyperspectral image while the pixel in the matrix represented by zero indicates the pixel as one in the non-homogeneous background area of the hyperspectral image; using the analysis result of the main components and an elliptical contour model to estimate the background logarithmic likelihood of the adaptive window to detect the abnormal image elements and generate a preliminary matrix for detection result; and using the morphological filtering for post-treatment and obtaining the final result of the detection matrix. The invention is used to detect the abnormity of a hyperspectral remote sensing image.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com