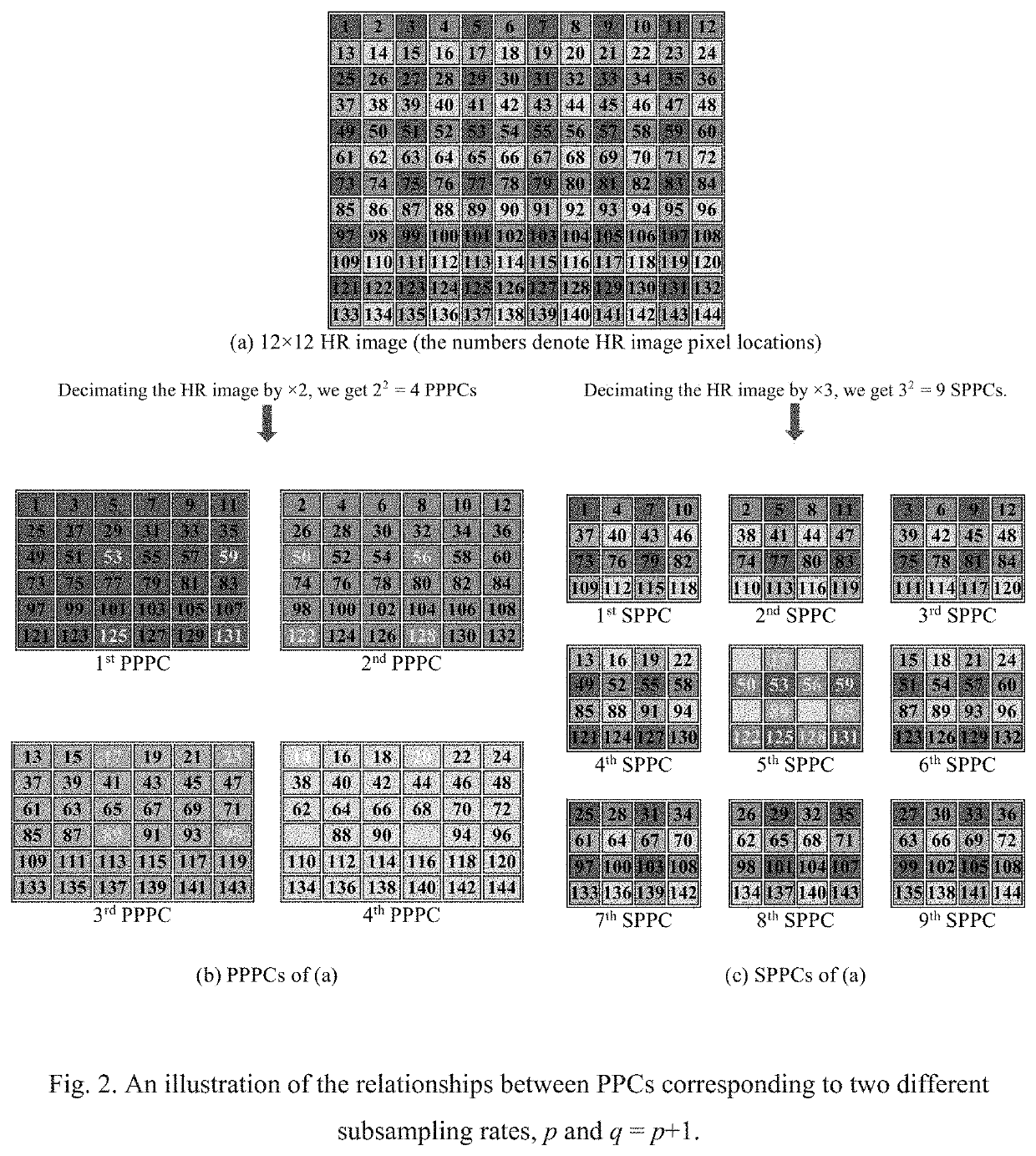
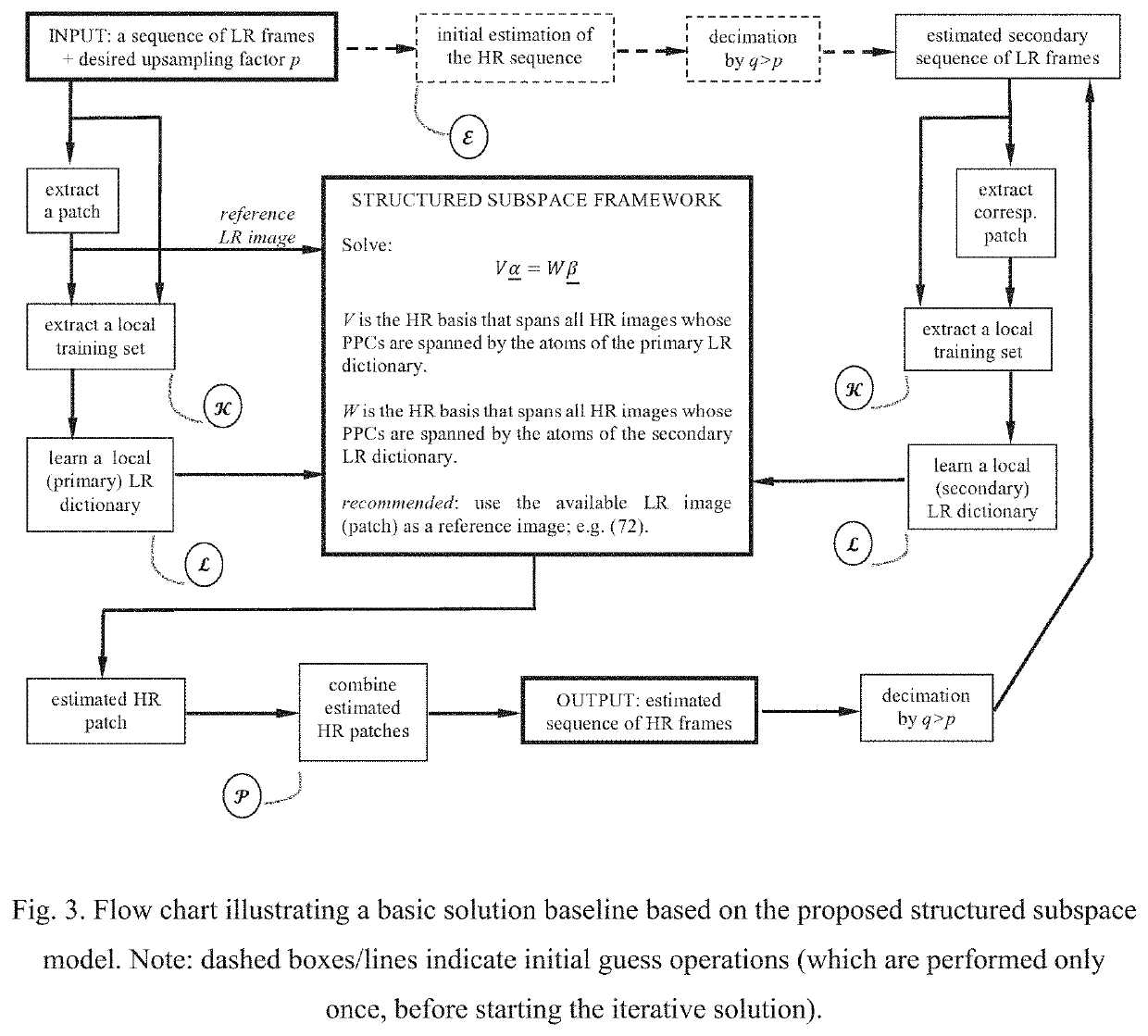
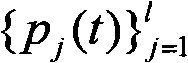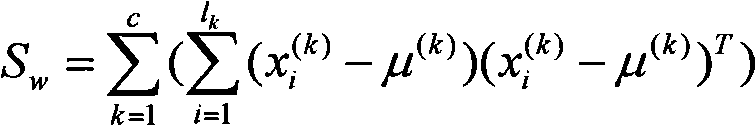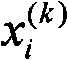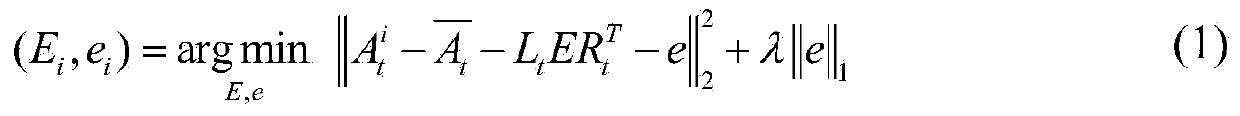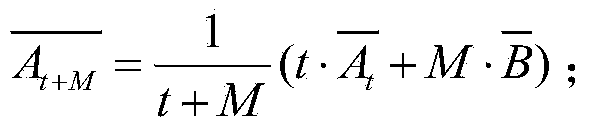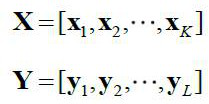Patents
Literature
46 results about "Subspace model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
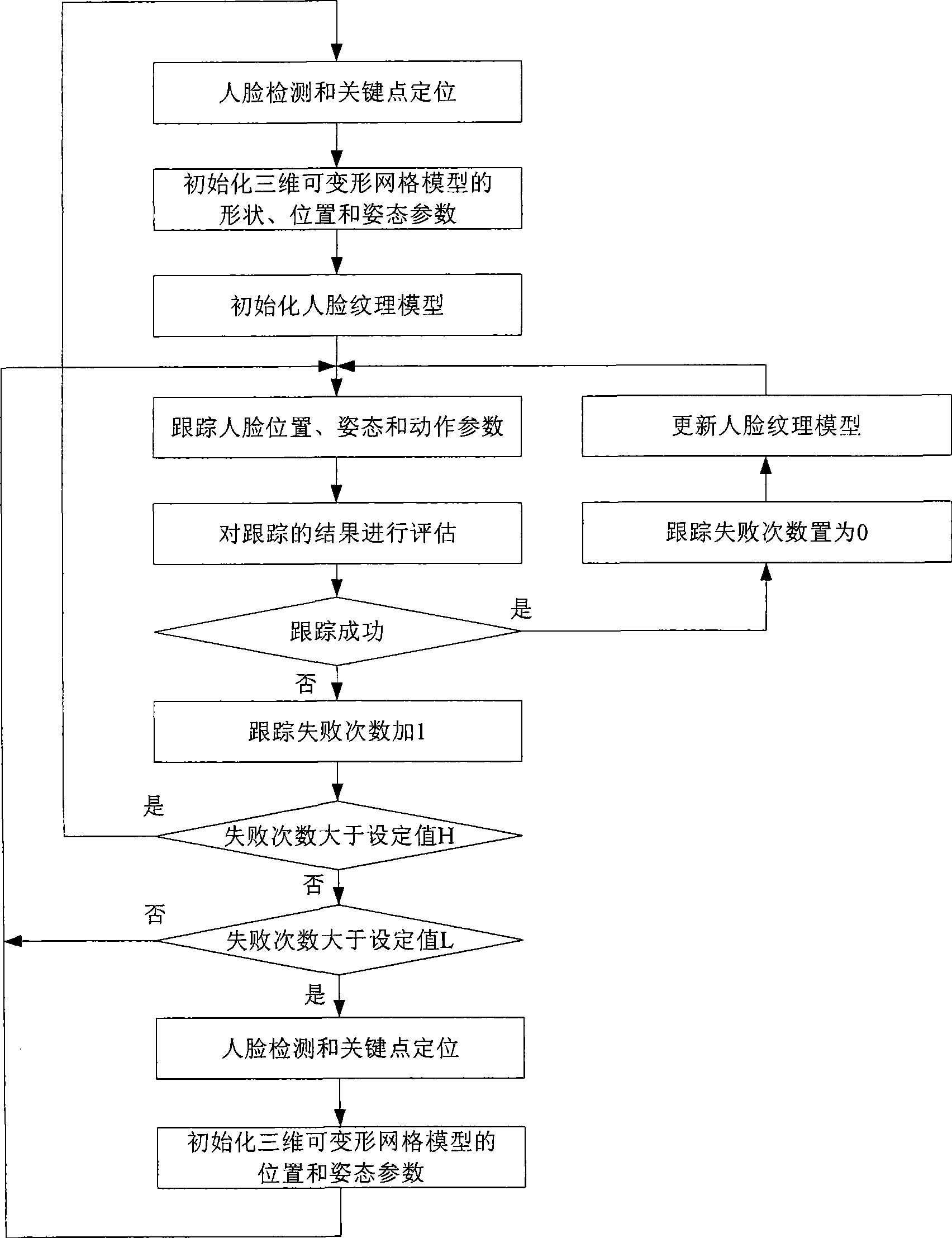
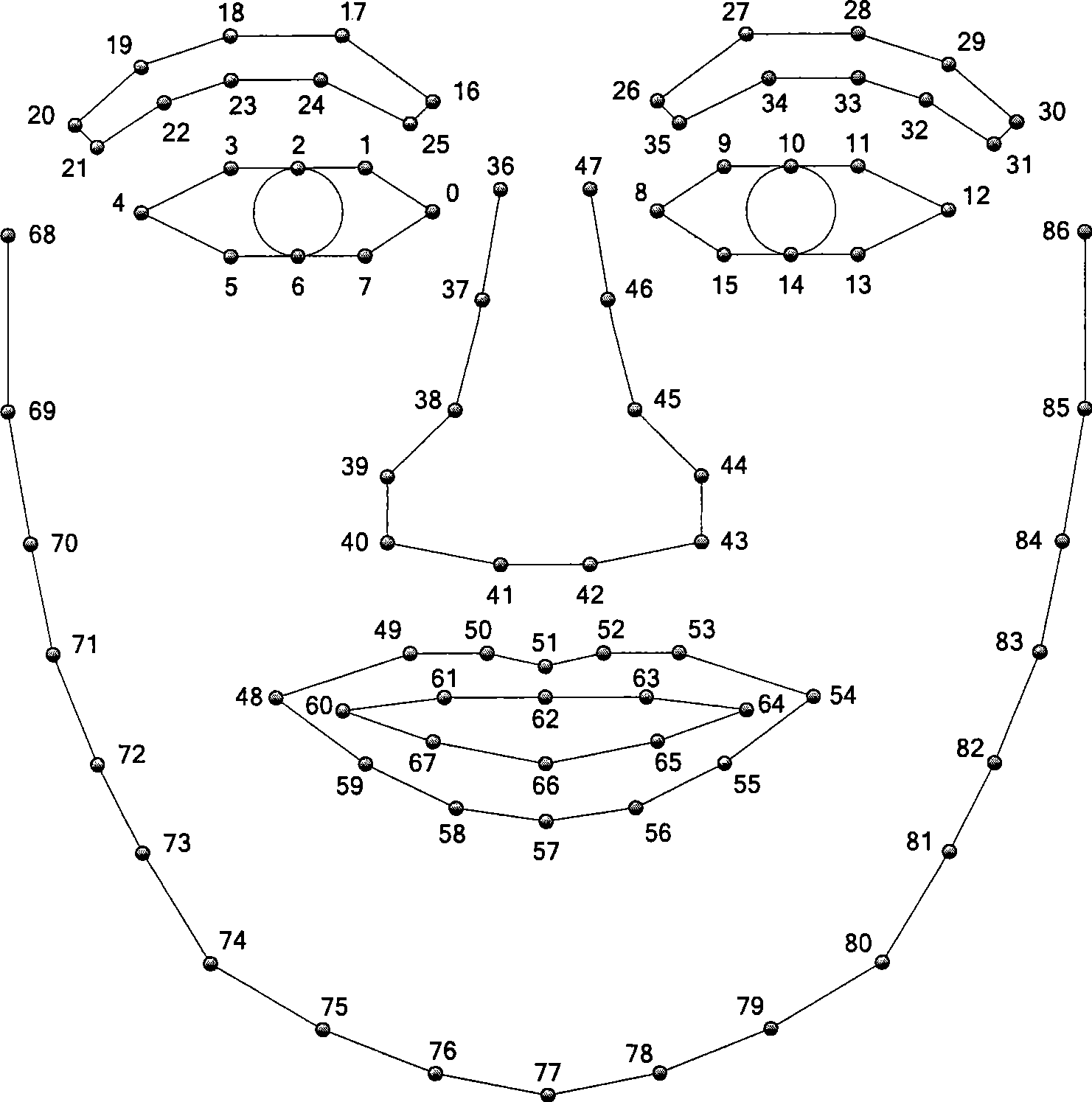
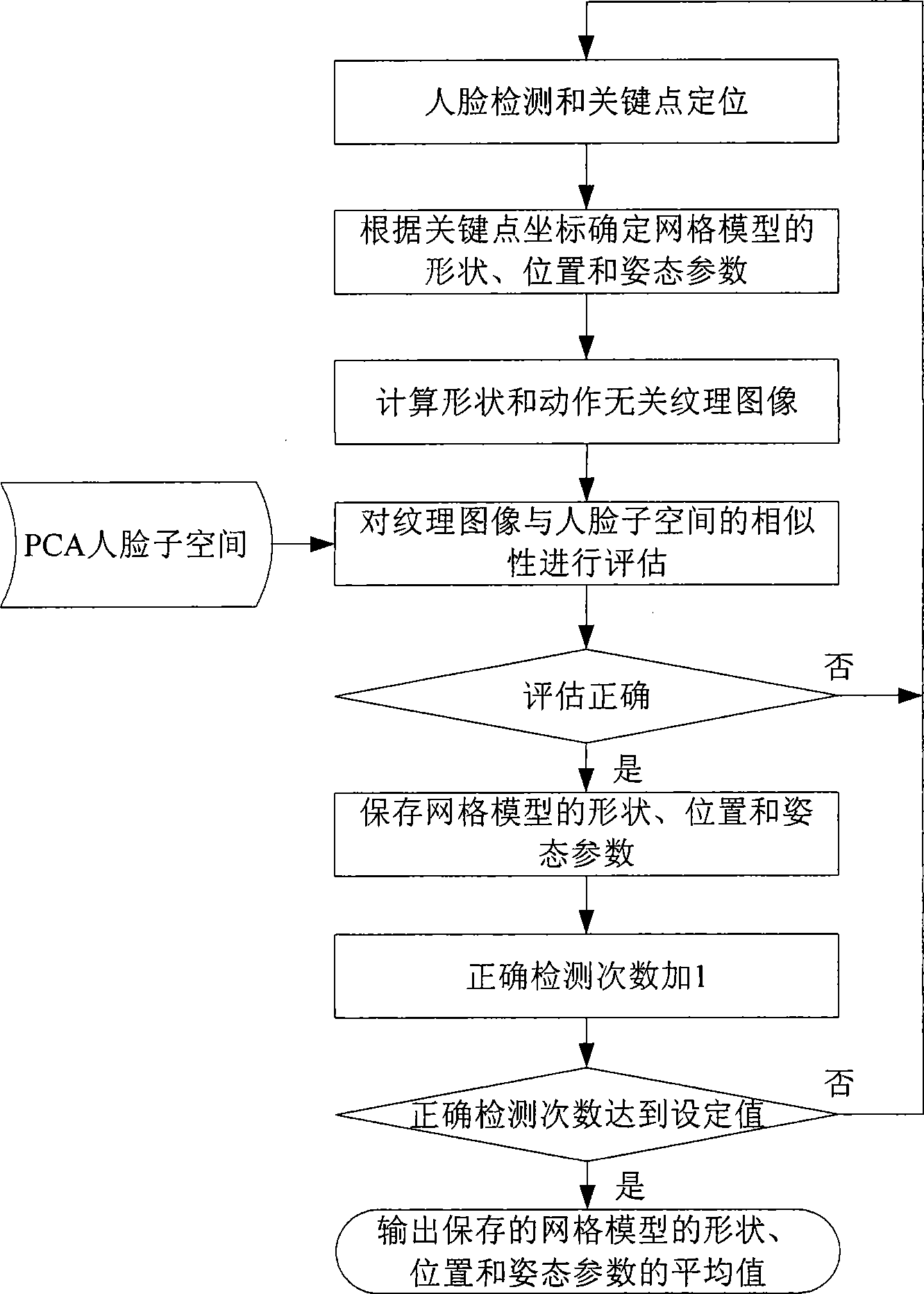
Three-dimensional human face action detecting and tracing method based on video stream
InactiveCN101499128AImplement automatic detectionGuaranteed robustnessCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionCrucial point
The invention provides a method for detecting and tracing three-dimension face action based on video stream. The method include steps as follows: detecting face and a key point position on the face; initializing the three-dimension deformable face gridding module and face texture module used for tracing; processing real time, continuous trace to the face position, gesture and face action in follow video image by using image registering with two modules; processing evaluation to the result of detection, location and tracking by using a PCl face sub-space, if finding the trace is interrupted, adopting measure to restore trace automatically. The method does not need to train special user, has wide head gesture tracing range and accurate face action detail, and has certain robustness to illumination and shelter. The method has more utility value and wide application prospect in the field, such as human-computer interaction, expression analysis, game amusement.
Owner:INST OF AUTOMATION CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
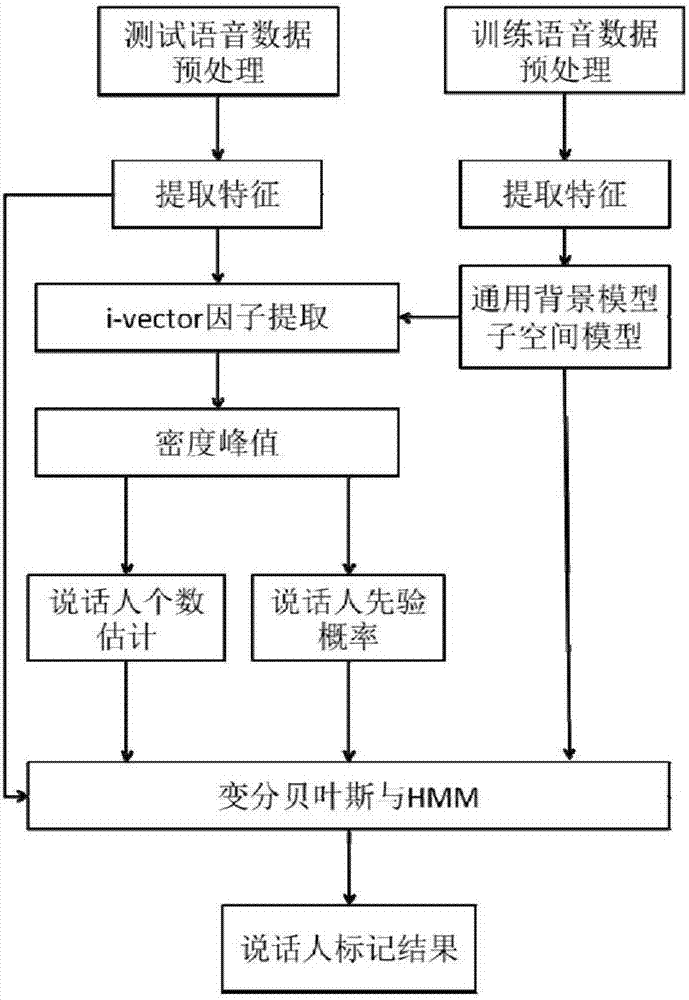
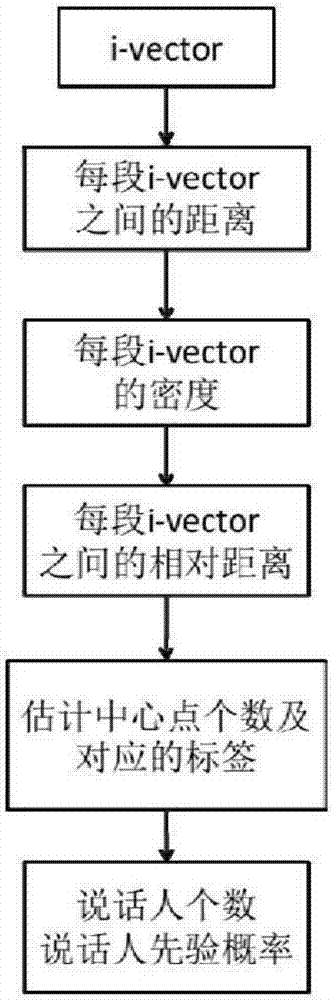
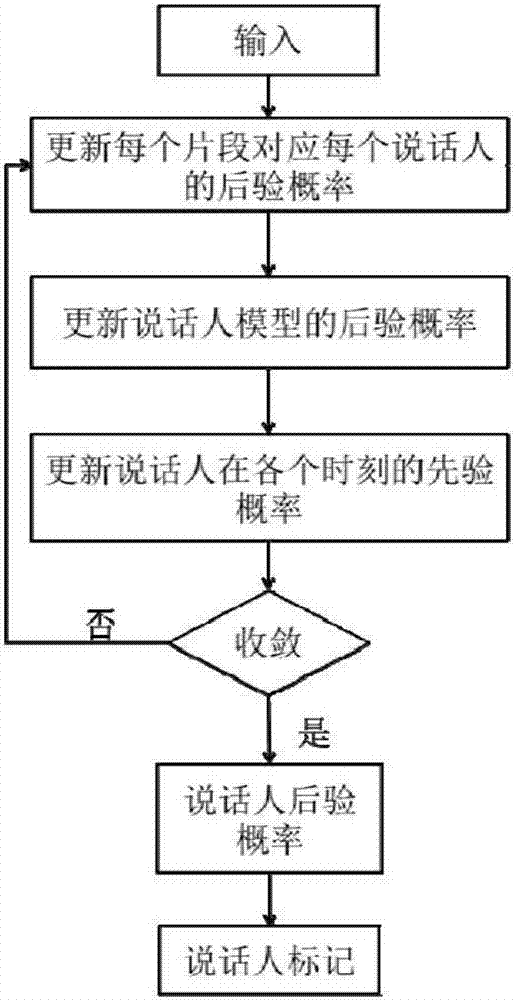
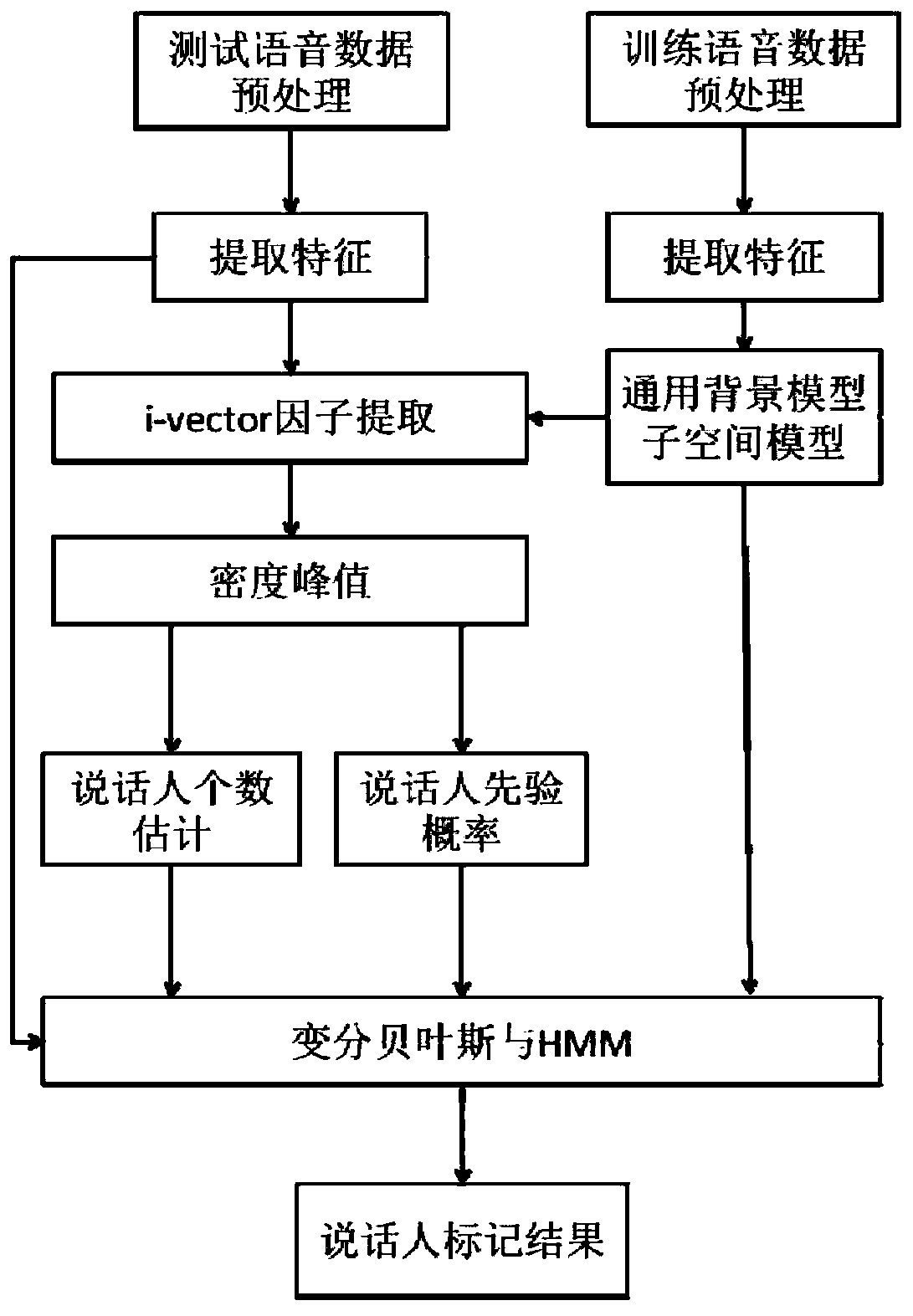
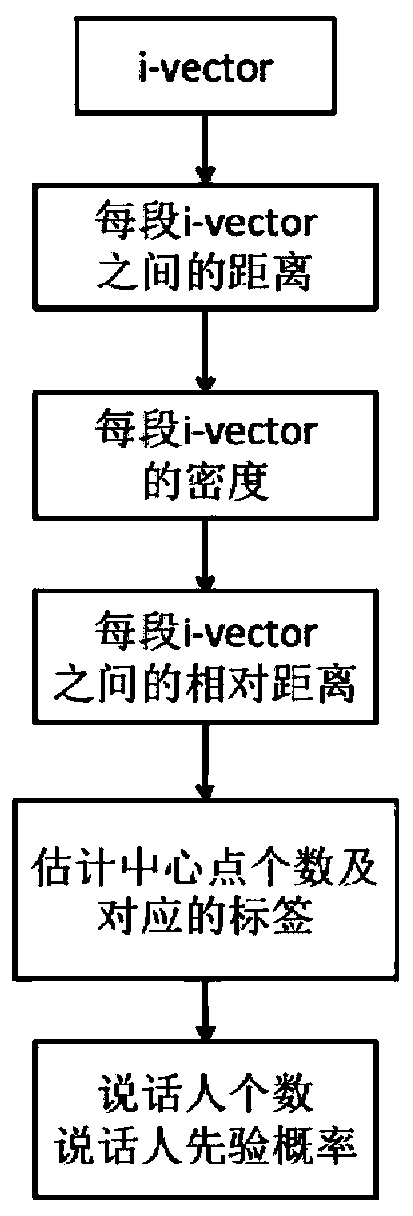
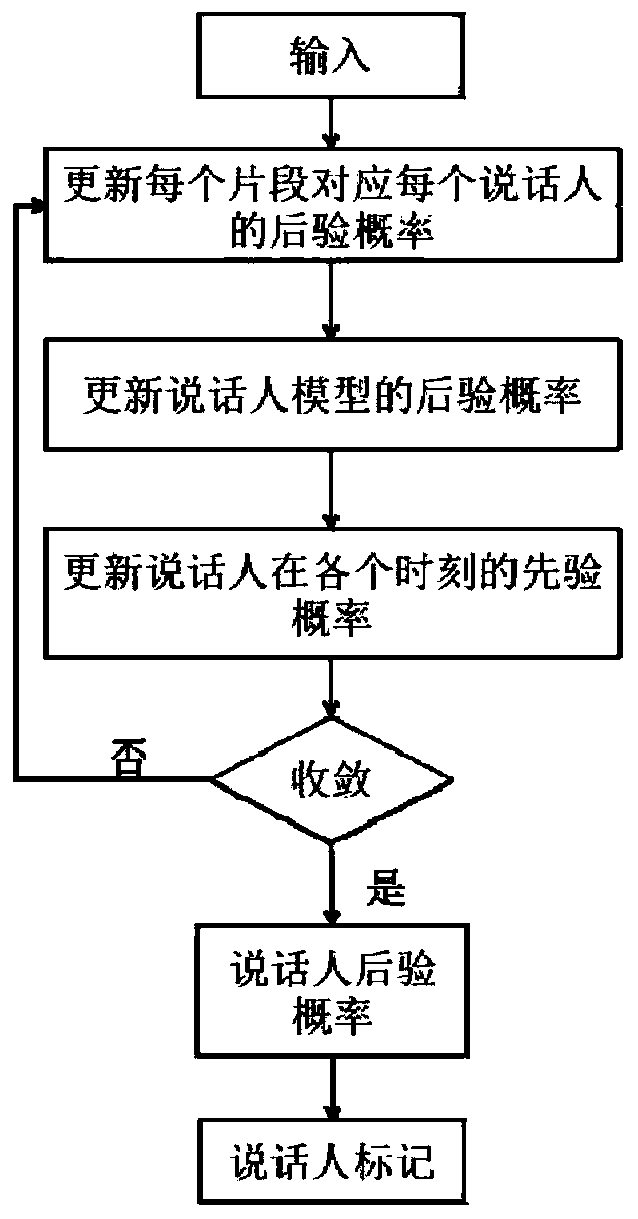
Speaker marking method and system based on density peak value clustering and variational Bayes
ActiveCN106971713AImprove accuracyImprove stabilitySpeech recognitionCluster algorithmSubspace model
The invention provides a speaker marking method and system based on density peak value clustering and variation Bayes, and belongs to the field of voiceprint identification and mode identification. The method includes: firstly establishing a training voice database, and obtaining a general background model and a subspace model; then obtaining an i-vector factor of each fragment of to-be-detected voice data through an i-vector factor extraction method; and obtaining the number of speakers of the to-be-detected voice data and the prior probabilities of the speakers at each moment by employing a density peak value clustering algorithm, performing iterative estimation on the posterior probability of each speaker corresponding to each fragment by employing variational Bayes, and obtaining a speaker marking result. According to the method and system, problems of uncertainty of estimation of initial values of the number of the speakers and the prior probability of each speaker at each moment and large deviation generated by easy influence of the initial values on the speaker marking performance in the prior art are solved, and the accuracy, the stability and the flexibility of speaker marking are improved.
Owner:北京华控智加科技有限公司
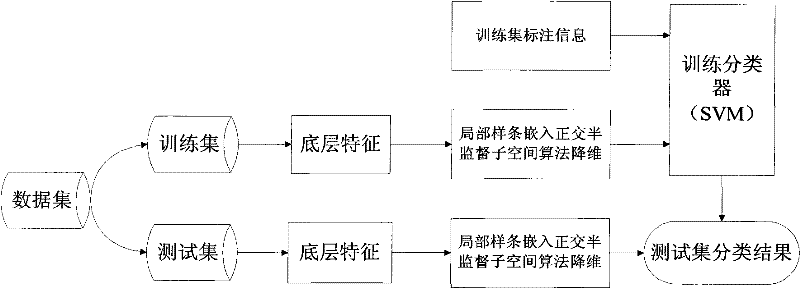
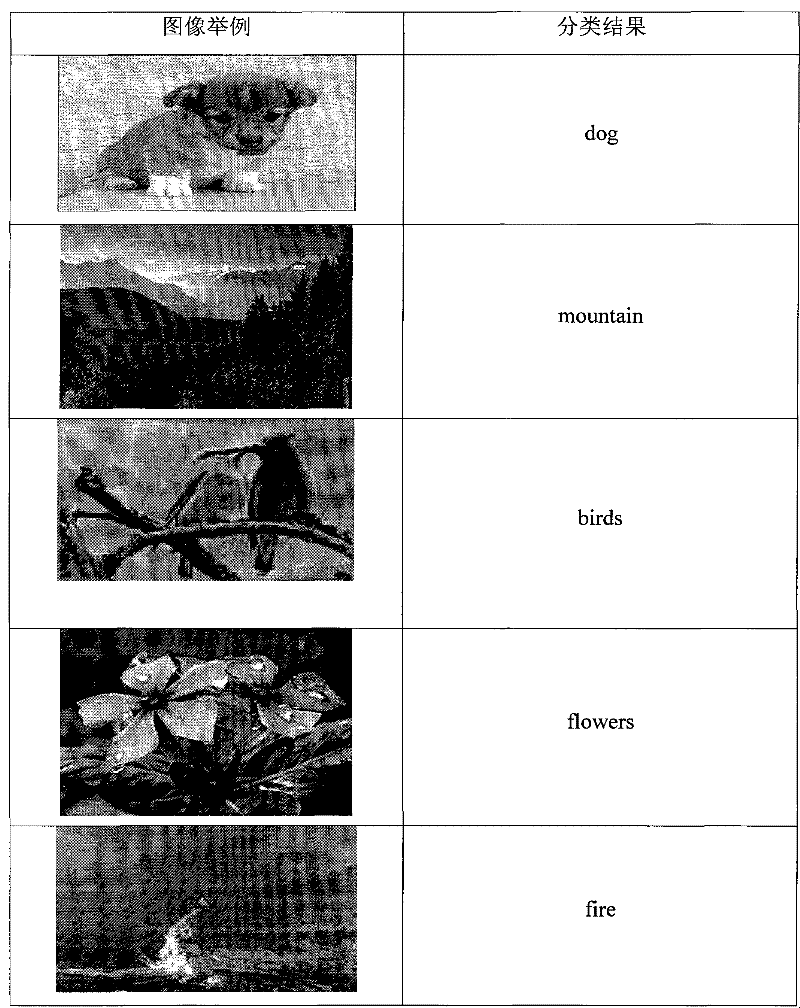
Local spline embedding-based orthogonal semi-monitoring subspace image classification method
InactiveCN101916376APreserve the eigenstructure of the manifold spaceAvoid difficultiesCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixData set
The invention discloses a local spline embedding-based orthogonal semi-monitoring subspace image classification method. The method comprises the following steps of: 1) selecting n samples serving as training sets and the balance serving as testing sets from image data sets, wherein the training sets comprise marked data and unmarked data; 2) building an extra-class divergence matrix and an intra-class divergence matrix by using the marked data; (3) training data characteristic space distribution by using a whole and building a Laplacian matrix in a local spline embedding mode; 4) according to a local spline, embedding an orthogonal semi-monitoring subspace model, and searching a projection matrix to perform dimensionality reduction on the original high dimension characteristic; 5) building a classifier for the training samples after the dimensionality reduction by using a support vector machine; and 6) performing the dimensionality reduction on the testing sets by using the projection matrix and classifying the testing sets after the dimensionality reduction by using the classifier. In the method, the information, such as image sample marking, characteristic space distribution and the like, is fully utilized; potential semantic relevance among image data can be found out; and image semantics can be analyzed and expressed better.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
End-to-end three-dimensional human face reconstruction method based on depth neural network
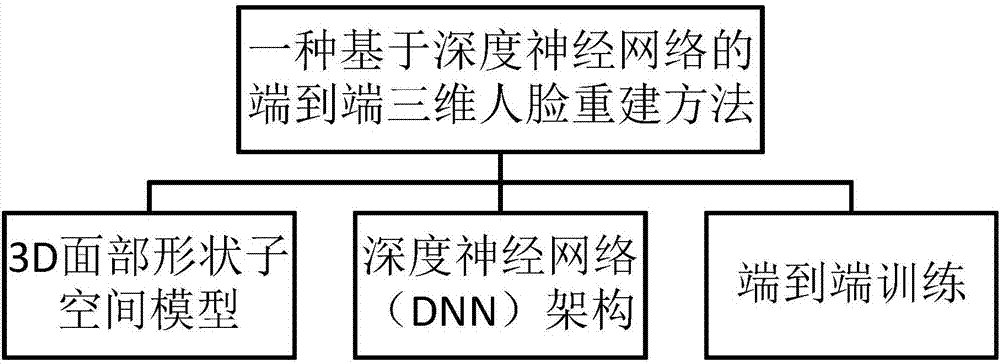
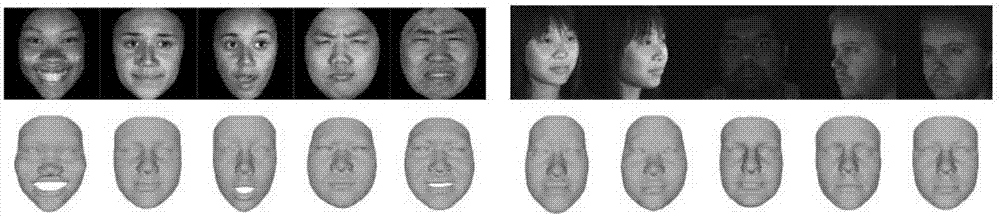
The invention proposes an end-to-end three-dimensional human face reconstruction method based on a depth neural network, and the method mainly comprises the contents: a 3D face shape subspace model, the depth neural network (DNN) configuration and end-to-end training. The process comprises the steps: employing the 3D face shape subspace model, and enabling a 3D face to serve as a linear combination of shapes and mixed-shape base lines; adding a sub-convolution neural network (fusion CNN) to a face model based on a VGG network for regression of expression parameters; adding a multitask learning loss function for identity parameter prediction and expression parameter prediction, wherein the input of the DNN in the end-to-end training is a two-dimensional image, and the output consists of an identity parameter vector and an expression parameter vector. According to the invention, the method solves a problem of impact caused by the posture, expression and illumination changes in a face image, and avoids the loss of the depth information in a process of image collection. Meanwhile, the method simplifies the frame, reduces the calculation cost, and improves the reconstruction precision and the recognition robustness.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
Layered integrated Gaussian process regression soft measurement modeling method
ActiveCN107451101AStrong generalizationRealize online estimationCharacter and pattern recognitionComplex mathematical operationsSubspace modelPrincipal component analysis
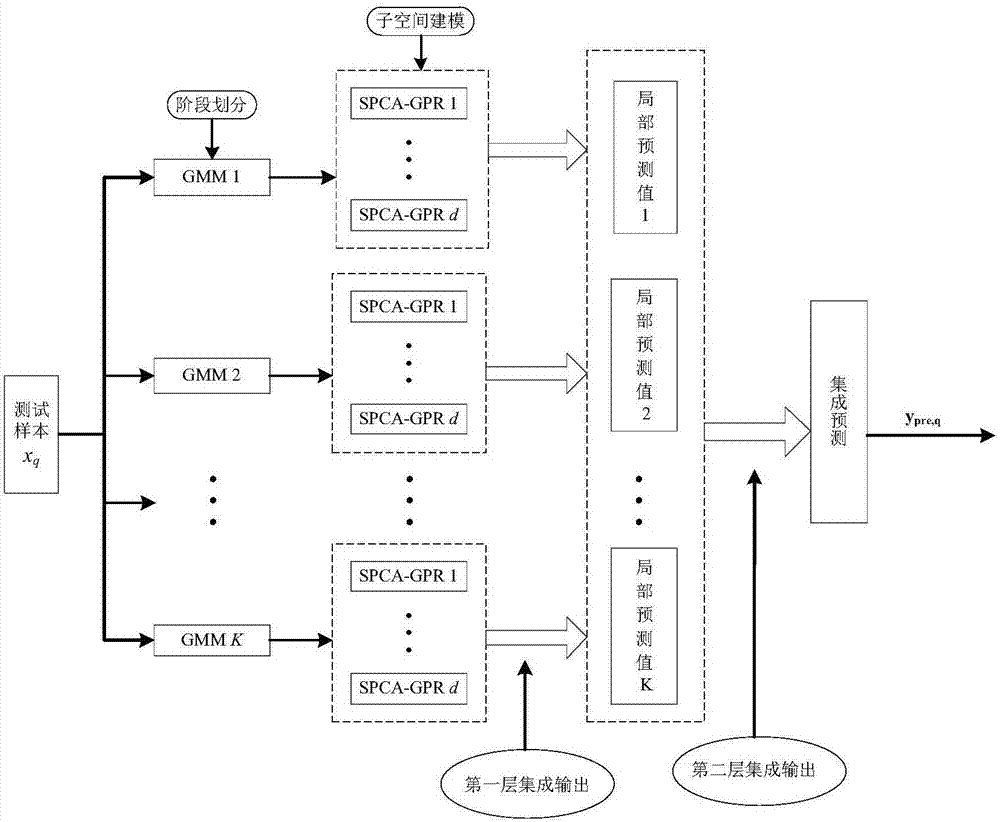
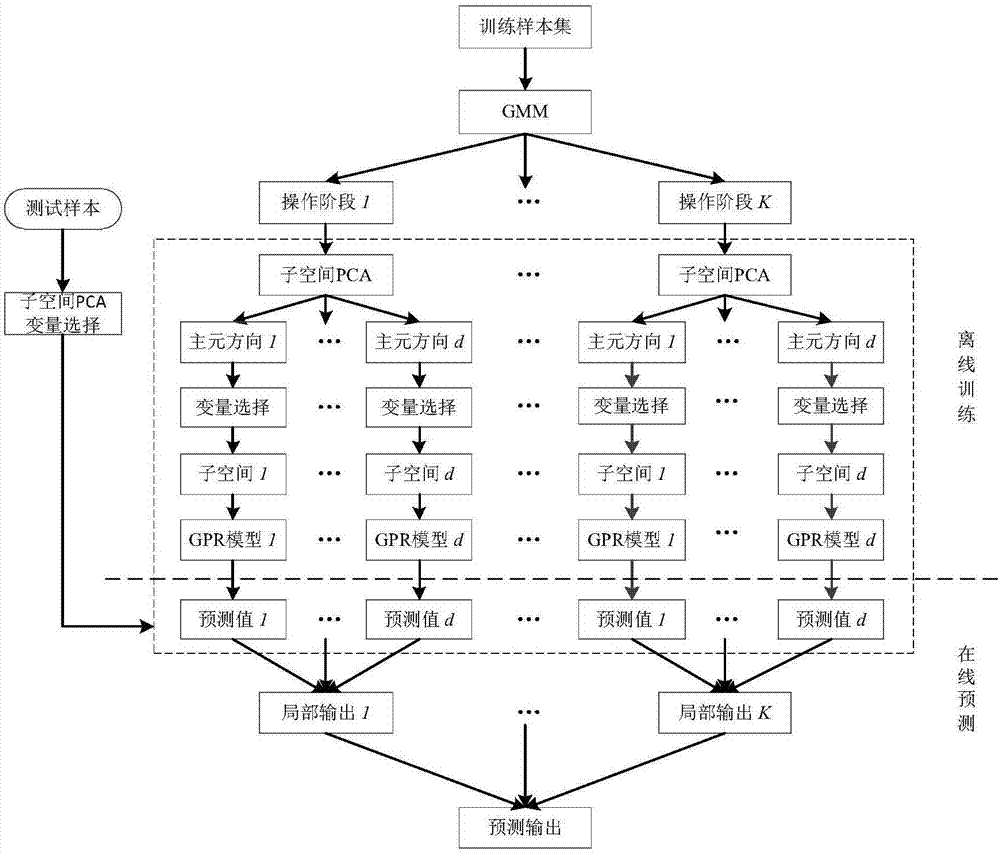
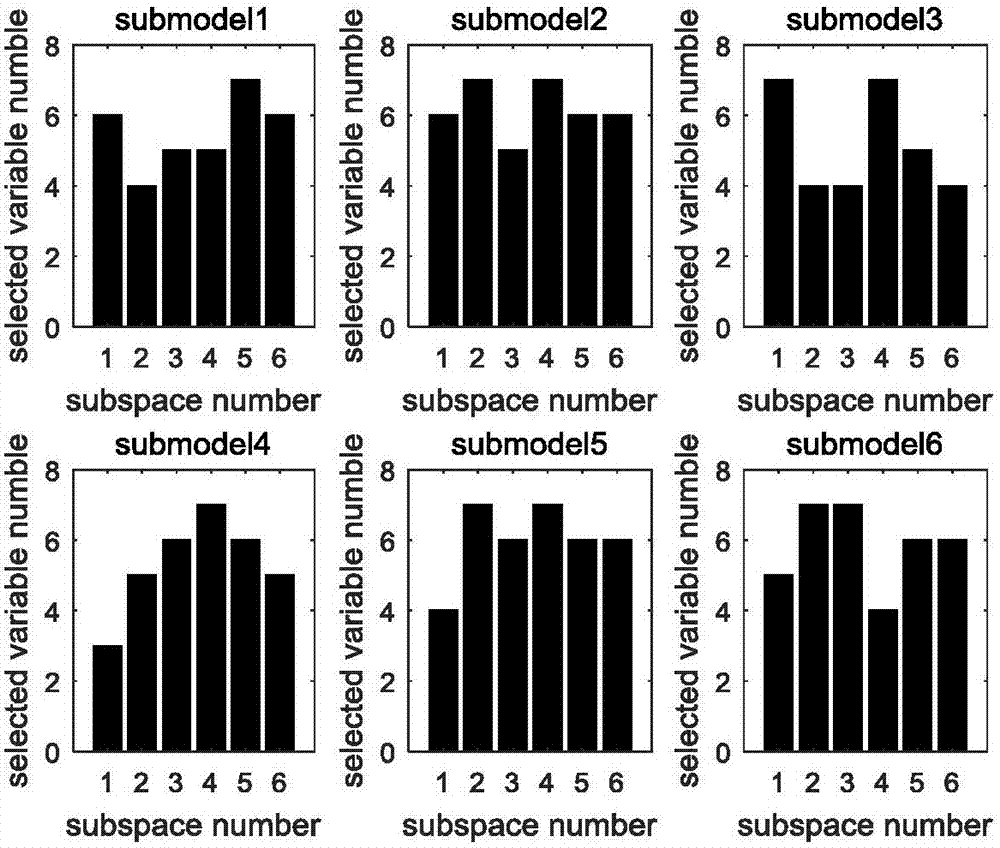
The invention discloses a layered integrated Gaussian process regression soft measurement modeling method used for a complex changeable multi-stage chemical process. The layered integrated Gaussian process regression soft measurement modeling method is an on-line multi-model strategy. A Gaussian mixture model is employed to identify different stages of the process, principal component analysis is carried out on data in each stage, on the basis of the contribution degree of each auxiliary variable in the principal element space, data in each mode is divided into several subspaces, and a corresponding Gaussian process regression soft measurement model is established. When new data comes around, variable selection is carried out by means of subspace PCA, and on the basis of the soft measurement model which is established off line, the prediction output of each model can be obtained. By carrying out mean value fusion on outputs of subspace models, first layer integrated output, i.e., local prediction output in each mode can be obtained, finally new data obtained according to calculation is attached to the posterior probability of each different stage, and local prediction in each mode is fused by means of the posterior probability to obtain second layer integrated output. Key variables can be accurately predicted, and therefore the product quality is improved, and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
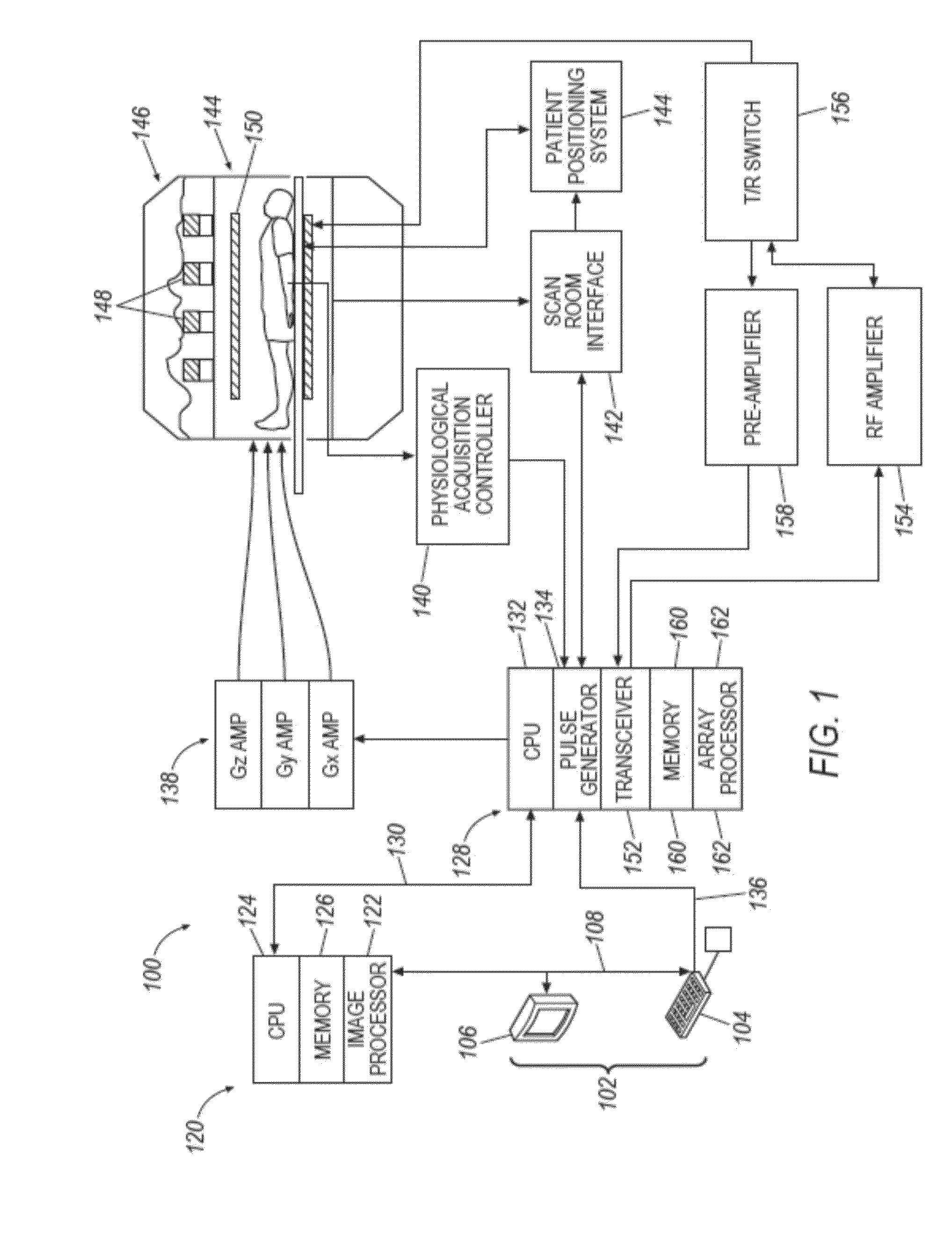
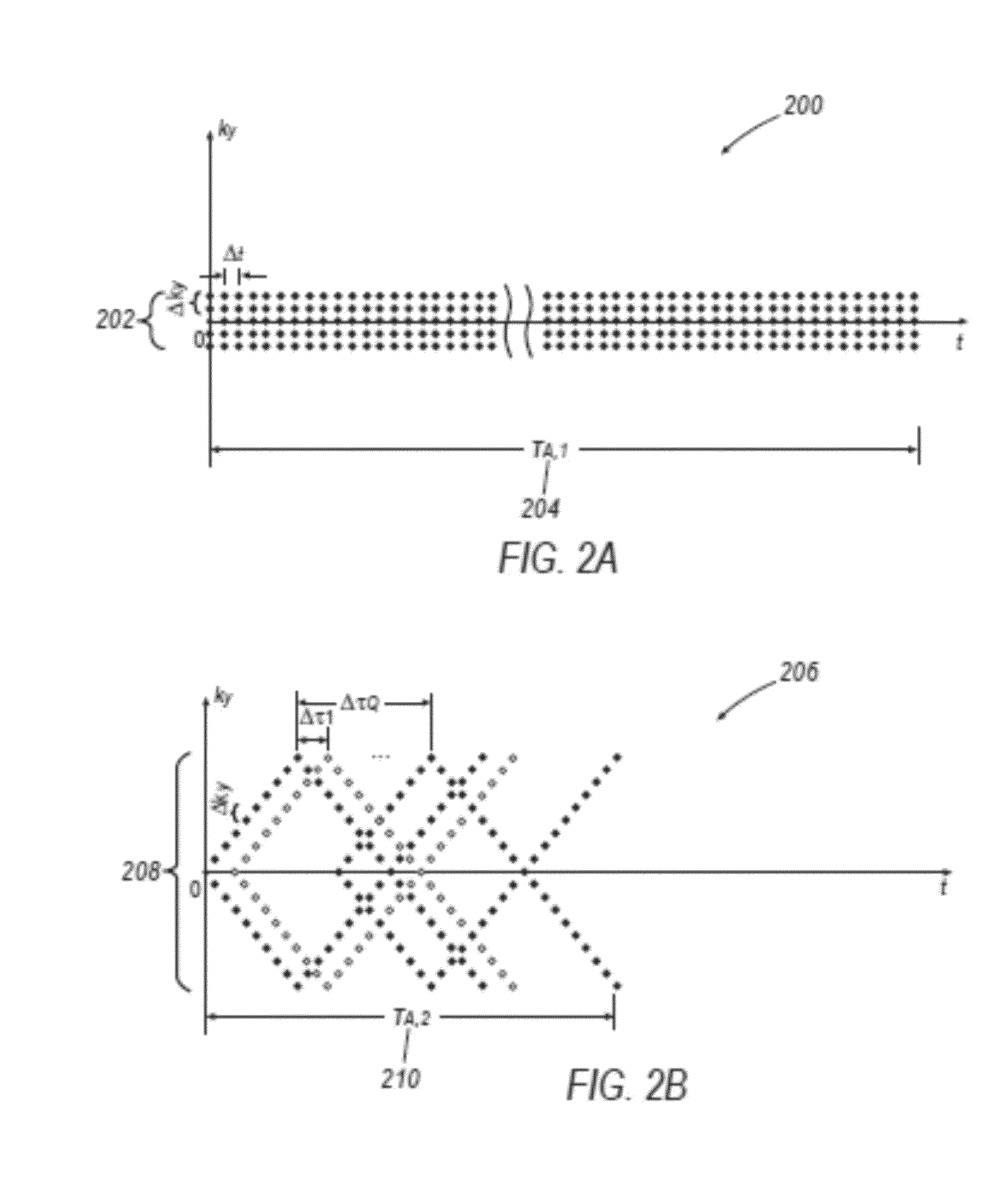
System and method for high-resolution spectroscopic imaging
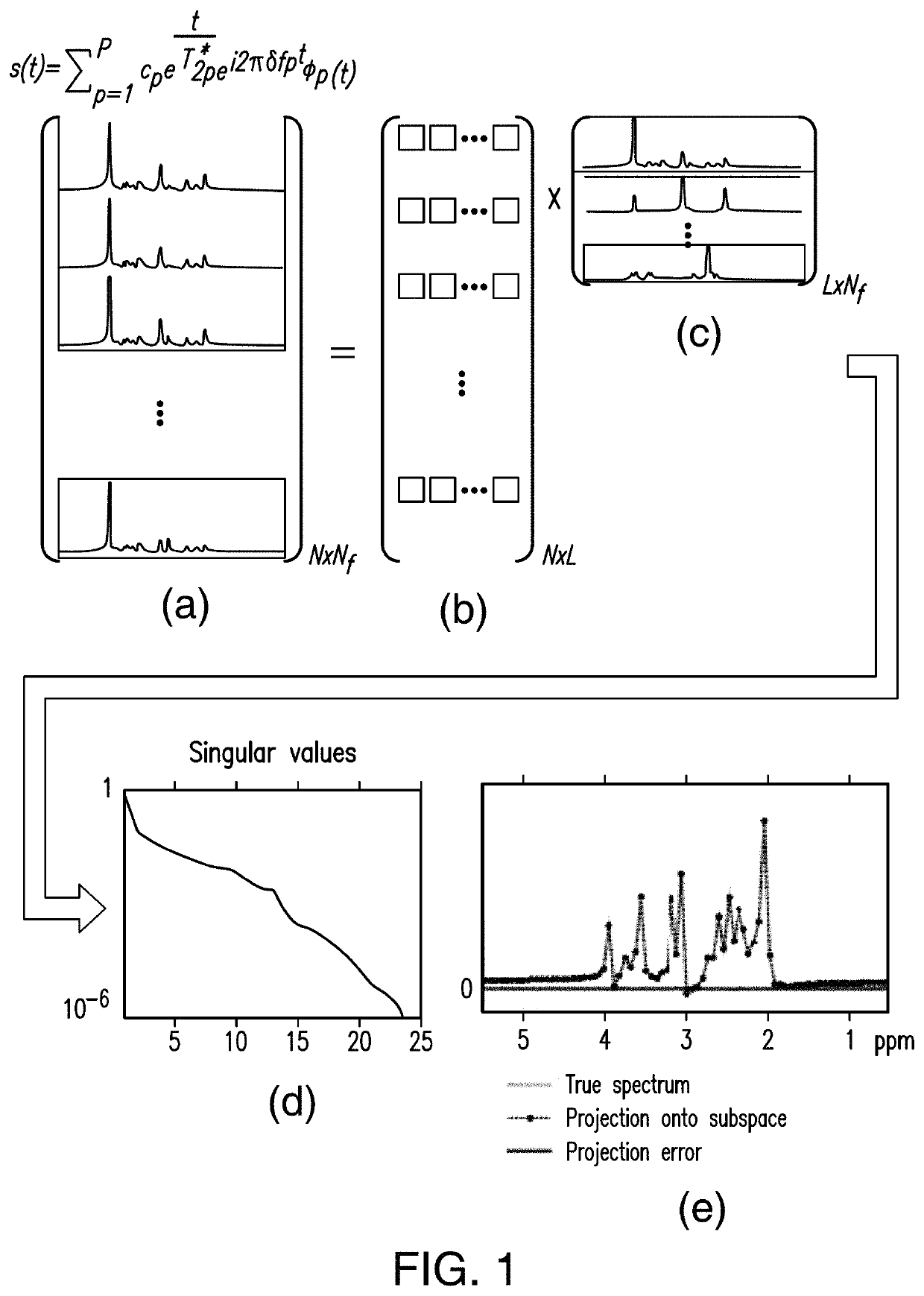
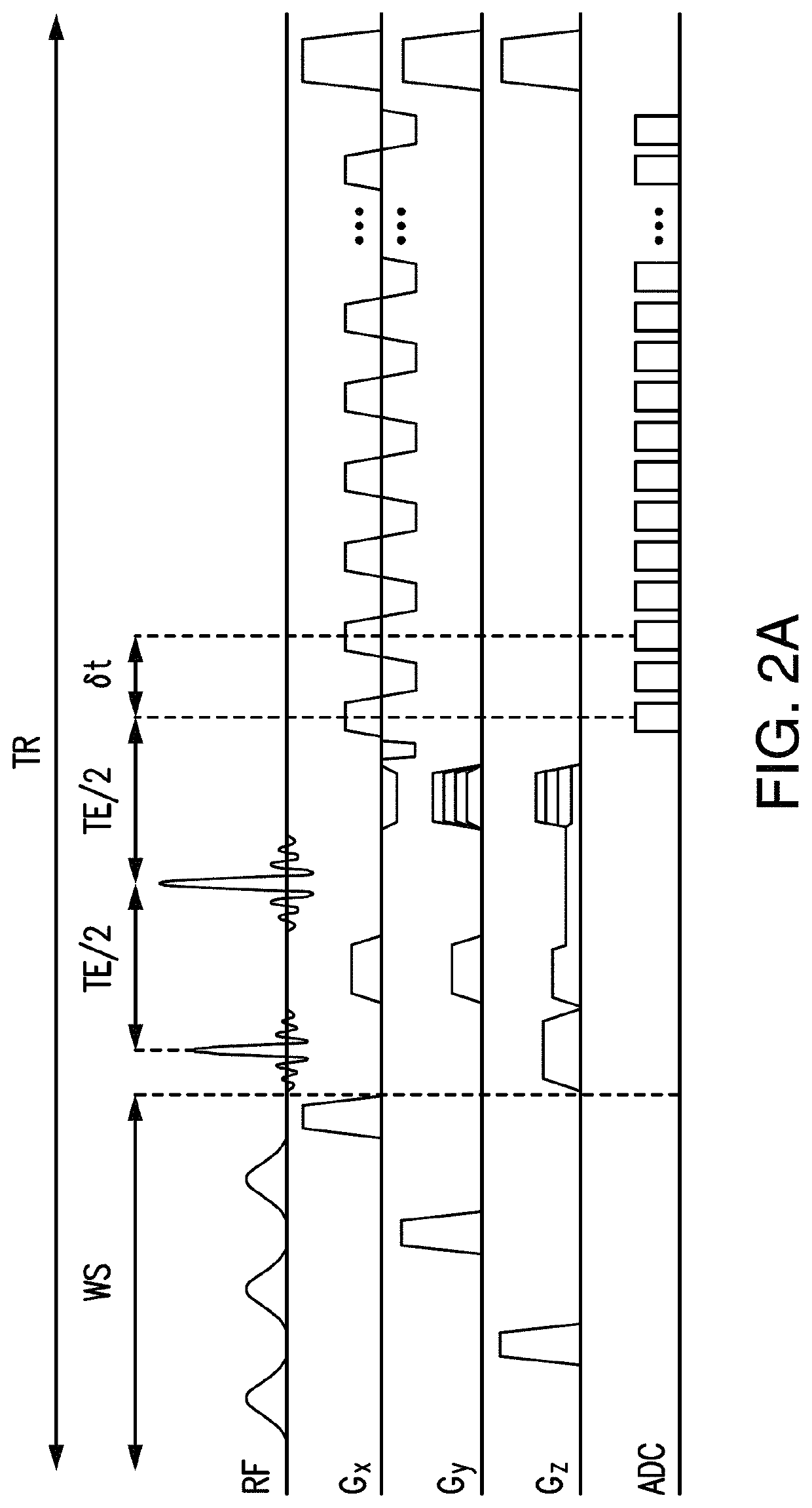
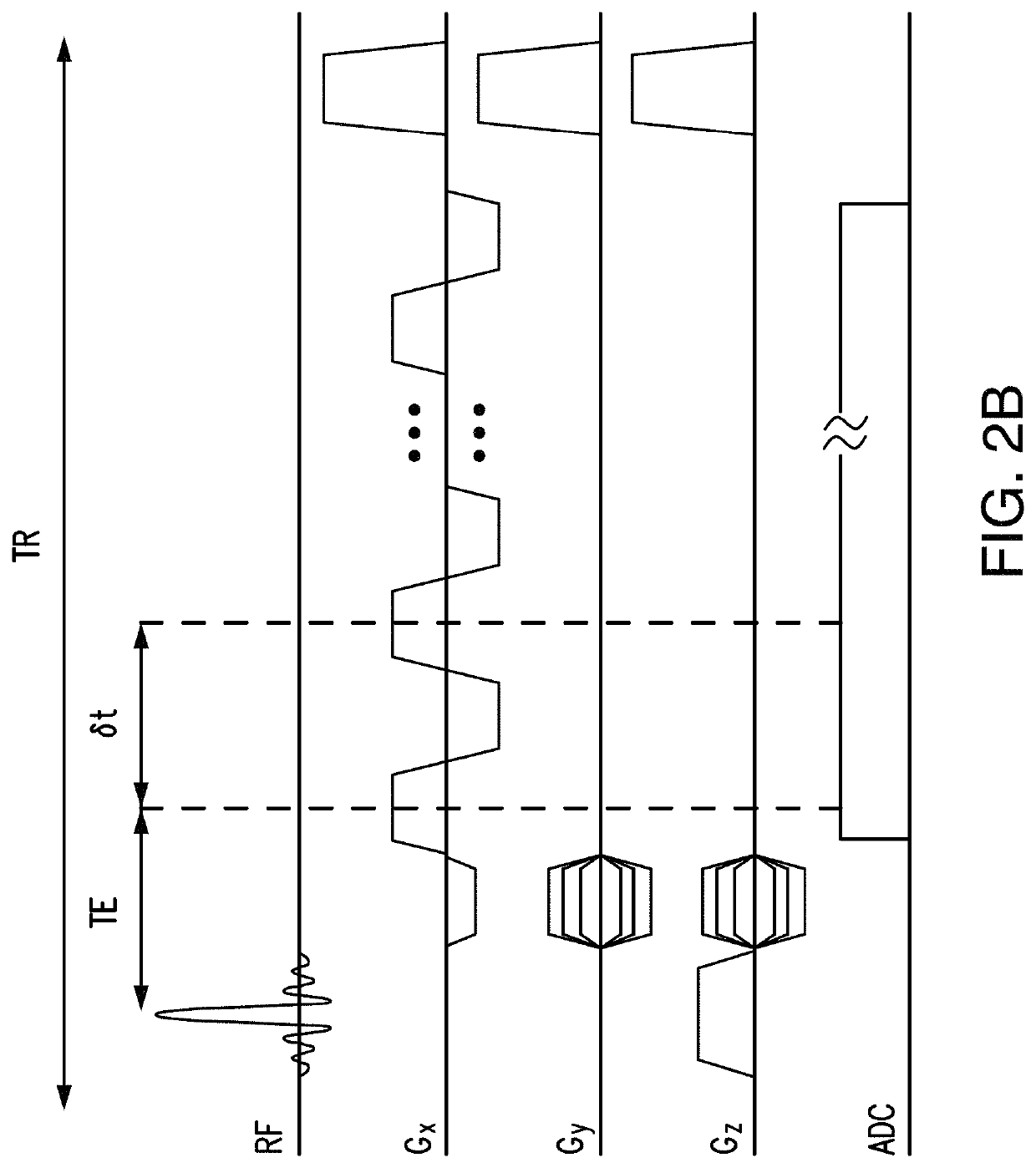
ActiveUS20160202336A1Data acquisition time can be shortenedHigh resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBiological testingData setSubspace model
A new method is developed to accelerate high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). The method is built on a low-dimensional subspace model exploiting the partial separability of high-dimensional MRSI signals and uses this subspace model for data acquisition, processing, and image reconstruction. Specifically for two and three dimensional MRSI with one spectral dimension, this method sparsely samples the corresponding (k,t)-space in two complementary data sets, one with dense temporal sampling and high signal-to-noise ratio but limited k-space coverage and the other with sparse temporal sampling but extended k-space coverage. The reconstruction is then done by estimating a set of temporal / spectral basis functions and the corresponding spatial coefficients from these two data sets. The proposed subspace model can be further extended to incorporate multiple signal components for nuisance signal removal in 1H-MRSI and more generalized reconstruction methods. The resulting imaging technique can be used for high-resolution MRSI of different nuclei. It will be useful for high-resolution metabolic imaging with many exciting applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
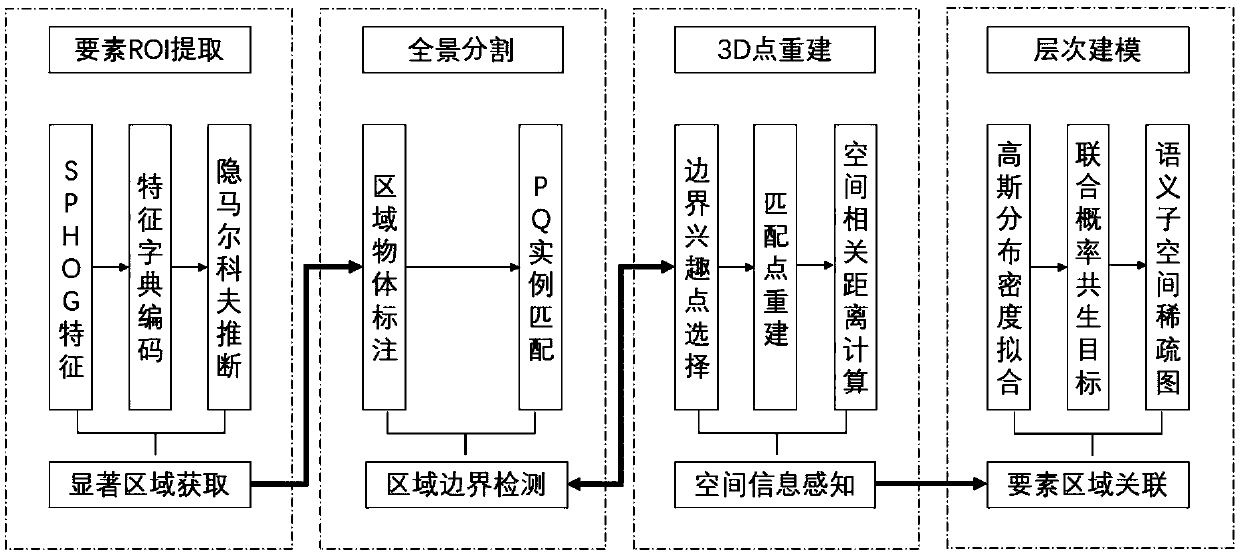
Method and system for realizing combined semantic hierarchical connection model based on panoramic area scene perception
ActiveCN110533048AThe area boundary is highly accurate and completeInternal combustion piston enginesCharacter and pattern recognitionElement spaceSubspace model
The invention discloses a method and a system for realizing a combined semantic hierarchical connection model based on panoramic area scene perception. The system comprises an ROI extraction module, apanoramic region segmentation module, a spatial information acquisition module and a multi-level modeling module; the ROI extraction module is in segmentation connection with a target instance and transmits target salient region information; the panoramic region segmentation module is connected with the interest point 3D reconstruction module and transmits region boundary information; the spatialinformation acquisition module is connected with the semantic subspace model and transmits region position correlation information, and the multi-level modeling module outputs spatial semantics and correlation degree information of each region. On the basis that the ROI is obtained through region significance for panoramic segmentation, on the premise that interest points are extracted for geometric reconstruction and element space semantic information association, multi-level modeling of scene perception is achieved according to analysis of probability symbiosis of scene composition elements.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
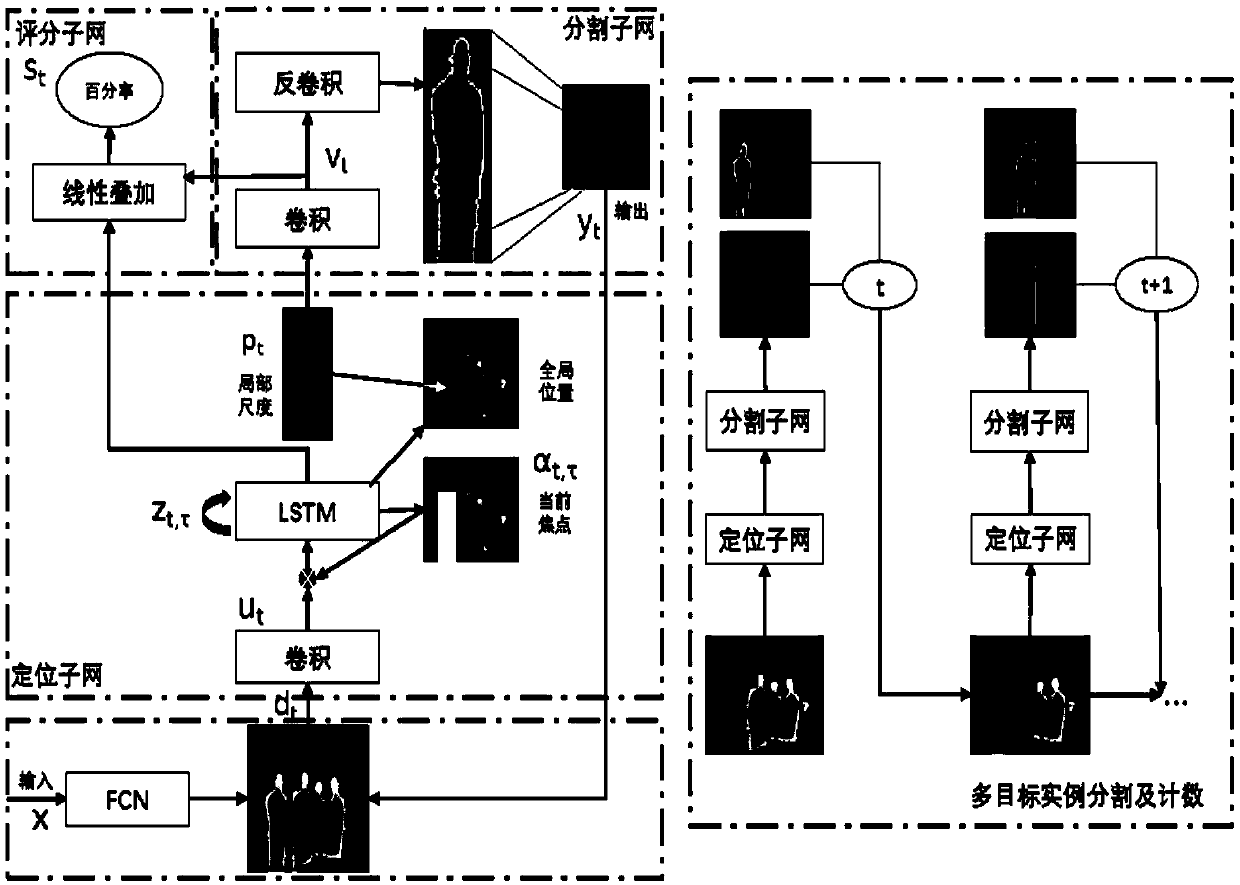
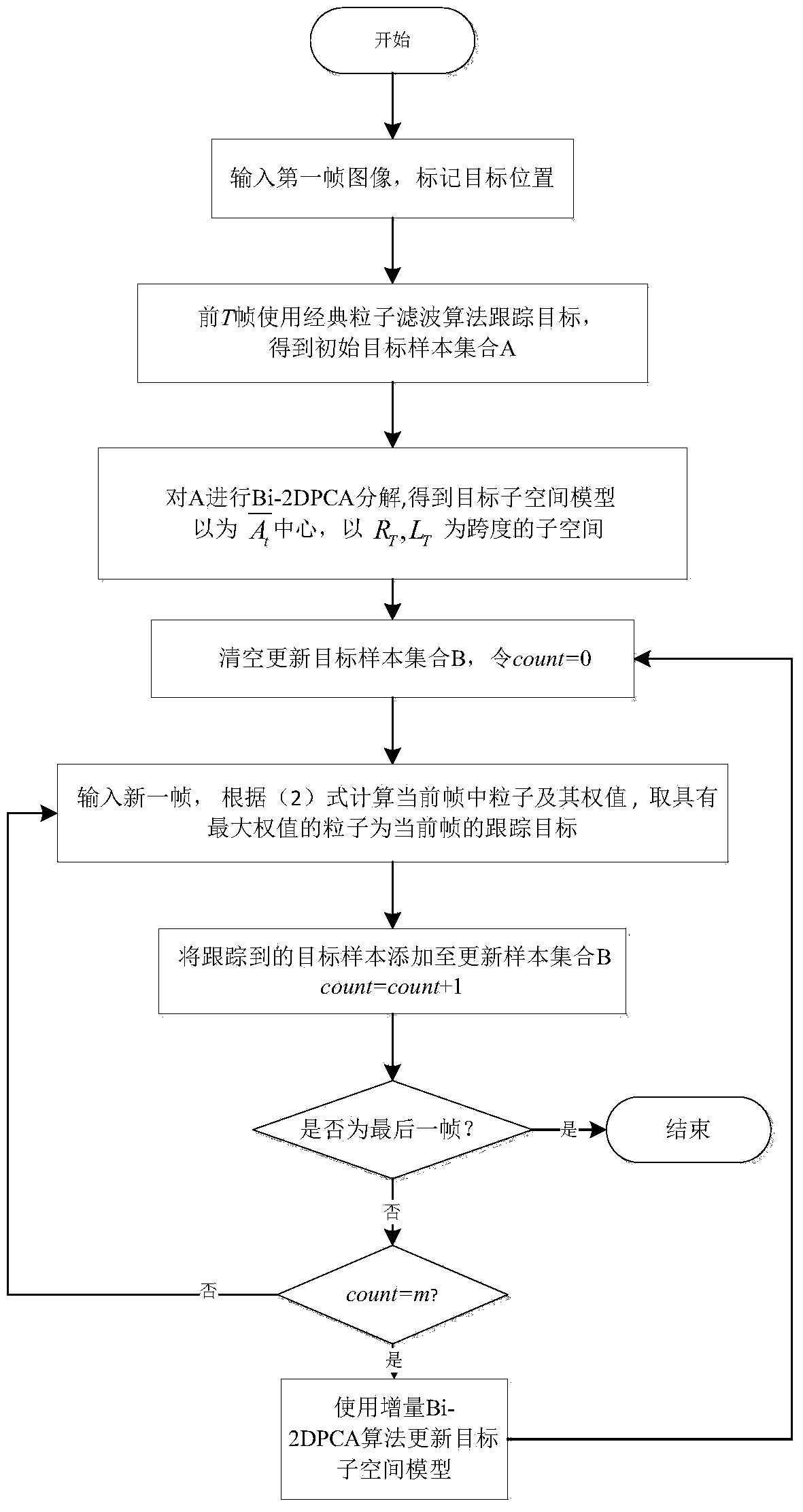
Online target tracking method based on increment bilateral two-dimensional principal component analysis (Bi-2DPCA) learning and sparse representation
ActiveCN103473790AEasy to handleFast and Accurate UpdatesImage analysisKernel principal component analysisSubspace model
The invention relates to an online target tracking method based on increment bilateral two-dimensional principal component analysis (Bi-2DPCA) learning and sparse representation, and provides an increment Bi-2DPCA learning algorithm capable of rapidly and accurately updating a target sub-space model to reflect an appearance change of a target in a tracking process. Aiming at the problem that the target is frequently blocked and polluted by noise in the tracking process to cause that the tracking effect becomes worse, according to the method disclosed by the invention, a Bi-2DPCA-based sub-space model is embedded below a sparse representation frame, so that interferences to target positioning and target sub-space model updating caused by blocking and noise are furthest removed. Meanwhile, a novel method for calculating visual similarity is used. By adopting the method, energy distribution of Bi-2DPCA when an image is presented is considered, and is more accurate in comparison with a classical reconstruction error; tracking is achieved under a Bayesian inference framework; the target state is estimated by using a particle filtering algorithm.
Owner:NANTONG JUJIU NEW MATERIAL SCI & TECH CO LTD
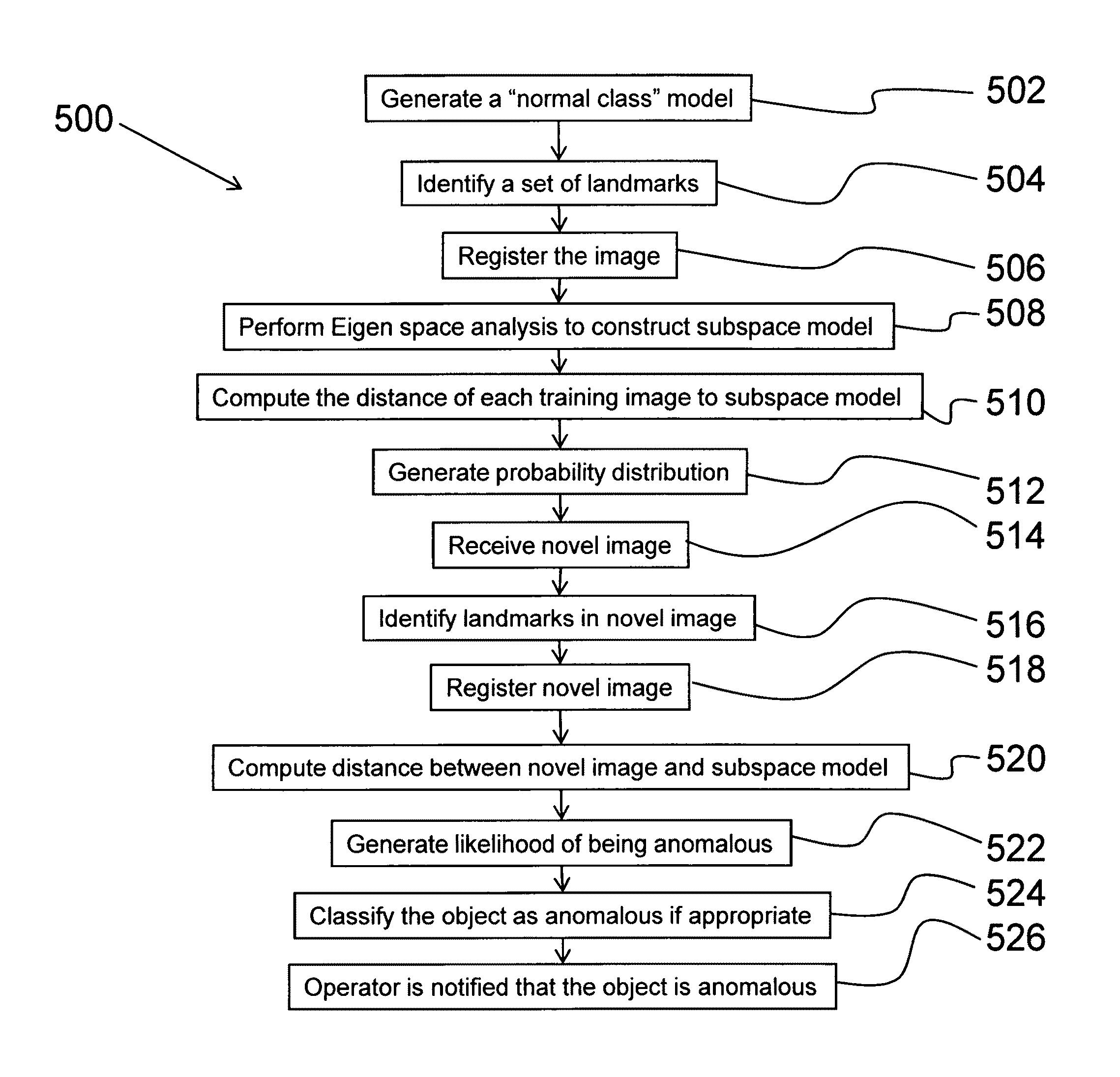
System for anomaly detection using sub-space analysis
ActiveUS8116575B1Drawing from basic elementsCharacter and pattern recognitionAnomaly detectionSubspace model
Described is a system for anomaly detection to detect an anomalous object in an image, such as a concealed object beneath a person's clothing. The system is configured to generate a subspace model for a normal class using training images. The normal class represents normal objects in a common class. The system receives a novel image having an object in the common class. A set of geometric landmarks are identified in the object in the novel image for use in registering the image. The novel image is registered by warping the image so that the geometric landmarks coincide in the novel image and the training images, resulting in a warped novel image having an object. Thereafter, the system determines if the object in the warped novel image is anomalous by measuring the distance of the warped novel image from the subspace model. Finally, if anomalous, an operator is notified accordingly.
Owner:HRL LAB
Industrial data driving prediction control method based on subspace identification
InactiveCN107179689AImprove practicalitySolving nonlinear time-varying problemsAdaptive controlRecursive modelSubspace model identification
The invention discloses an industrial data driving prediction control method based on subspace identification. The industrial data driving prediction control method includes steps of (1) calculating the predication model output and obtaining the predication output expressed by the predication increment according to the subspace model identification; (2) for the nonlinear time-varying characteristic, adopting the adaptive prediction control method of an online recursion identification model and updating the predication error of the before-after predication output and the process output through comparison to determine whether the predication model needs to be updated; and 3) performing constraint processing and for the physical constraints in the system, solving the problem by means of standard secondary programming and reducing the solution computational complexity by means of Lagrange daily functions. The industrial data driving prediction control method has the advantages of good practicality, high control precision, and simplified calculation.
Owner:STAR (CHONGQING) INTELLIGENT EQUIP TECH RES INST CO LTD
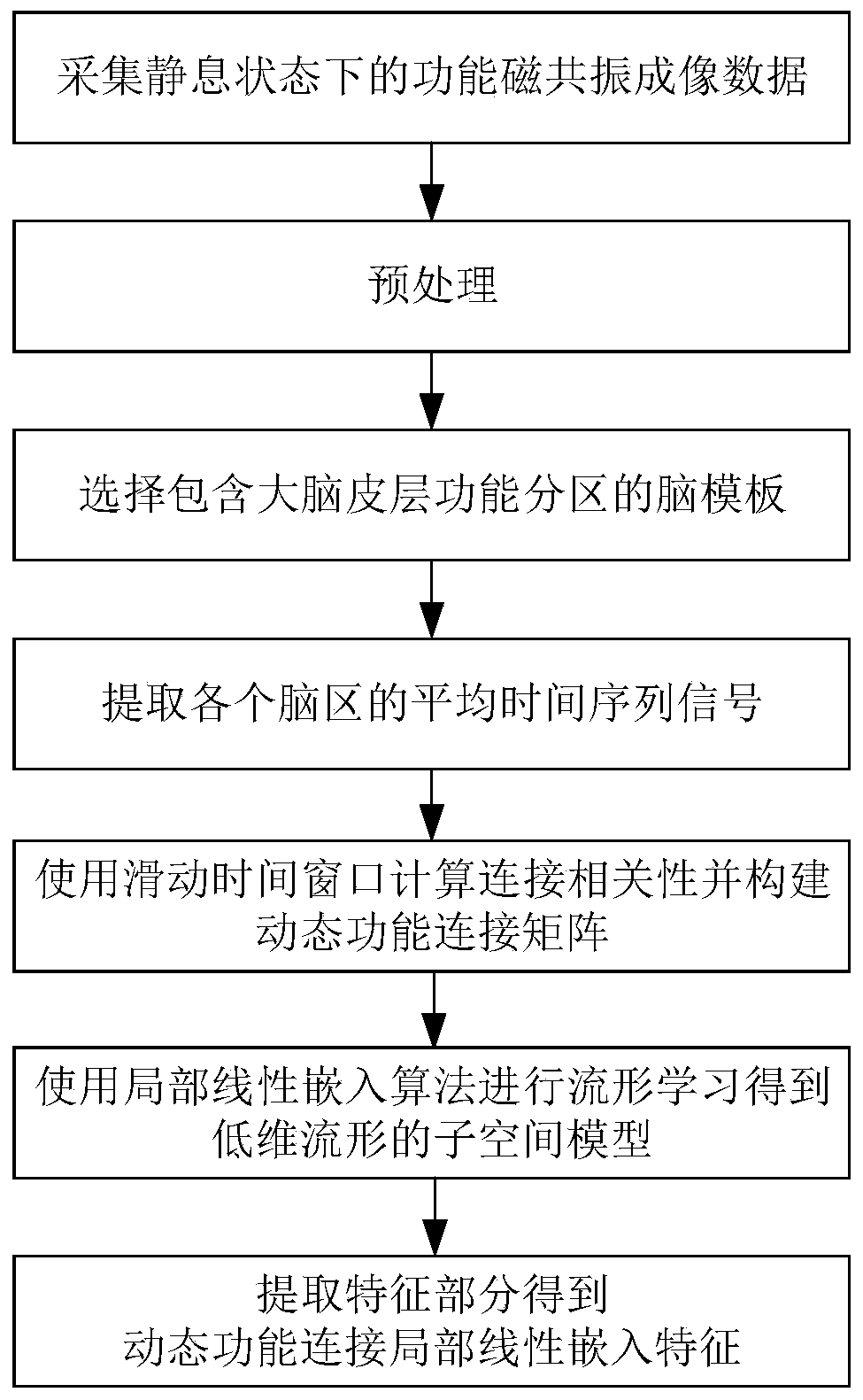
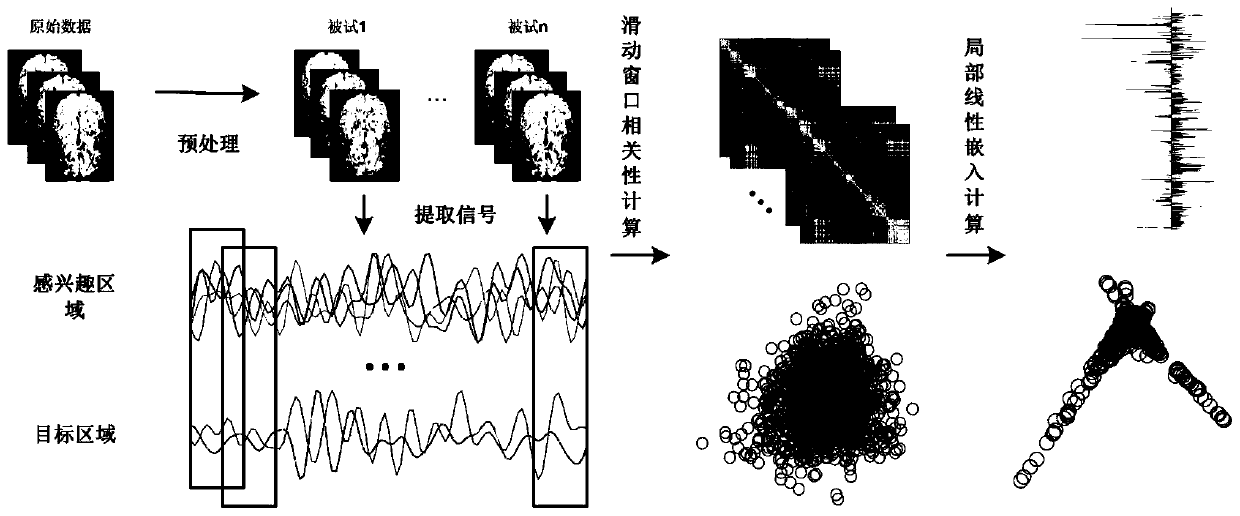
Dynamic function connection local linear embedded feature extraction and brain state classification method and system
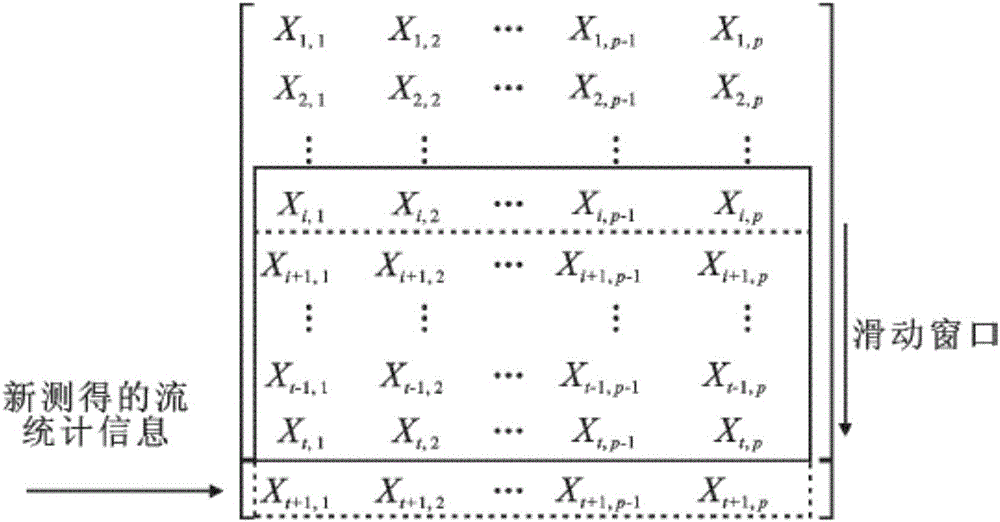
InactiveCN110232332AGood processing effectQuick calculationCharacter and pattern recognitionSliding time windowOriginal data
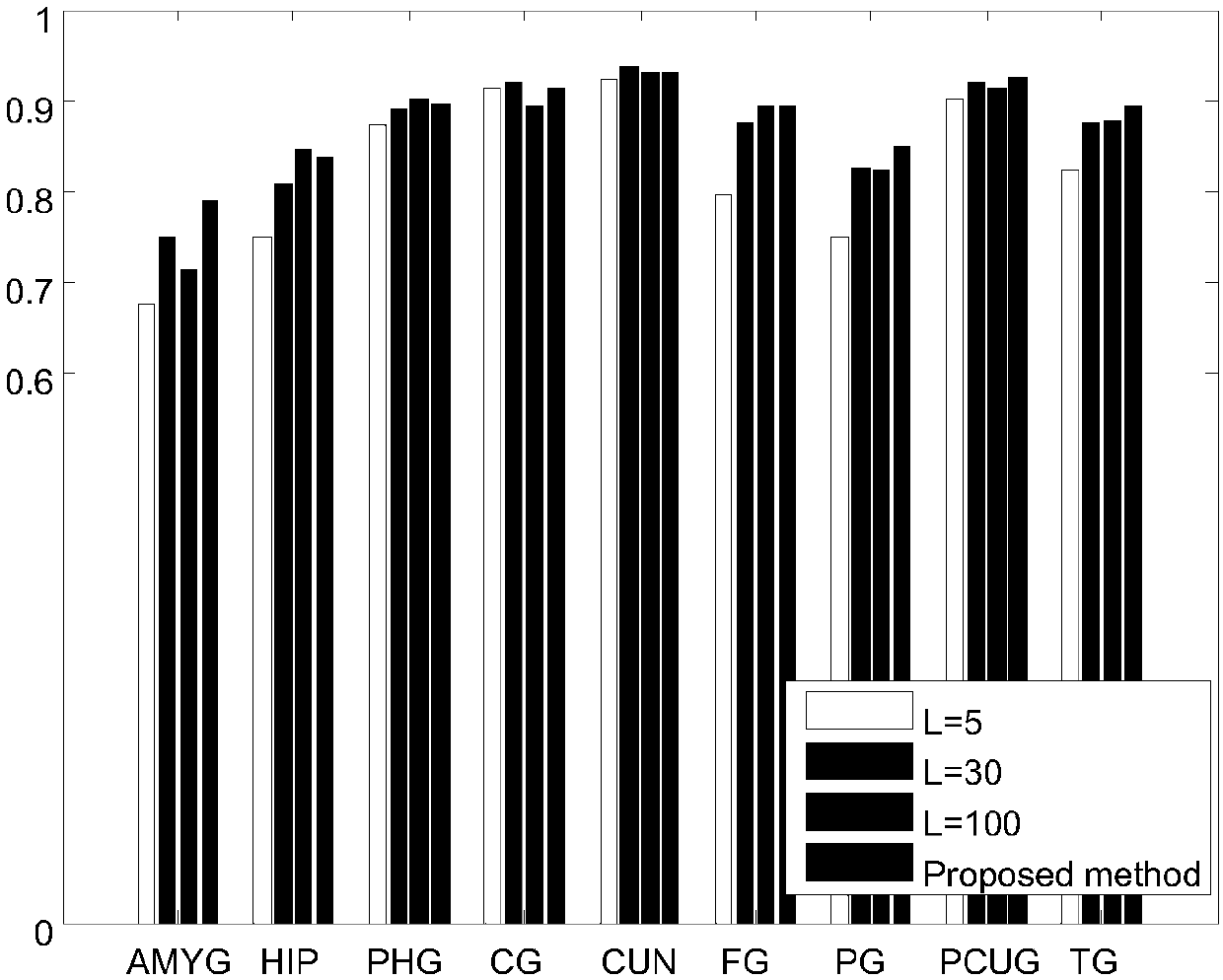
The invention discloses a dynamic function connection local linear embedded feature extraction and brain state classification method and system. The dynamic function connection local linear embedded feature extraction method comprises the following steps: collecting functional magnetic resonance imaging data in a resting state; after preprocessing, extracting an average time sequence signal of each brain region through a brain template; calculating and constructing a dynamic function connection matrix by using a sliding time window, and taking the dynamic function connection matrix as to-be-processed high-dimensional brain dynamic description original data; and carrying out manifold learning on the dynamic function connection matrix by using a local linear embedding algorithm to obtain a low-dimensional manifold subspace model, and extracting a feature part in the low-dimensional manifold subspace model to obtain a dynamic function connection local linear embedding feature. For the dynamic function connection local linear embedded feature extraction method, the feature extraction method is rapid in calculation and ideal in data processing effect, can construct significant crowd feature description, does not depend on the absolute value of the amplitude of an imaging signal, is migratable between different MRI machines, is excellent in classification and discrimination performance, and can conveniently utilize a machine learning model to realize brain state classification.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF DEFENSE TECH
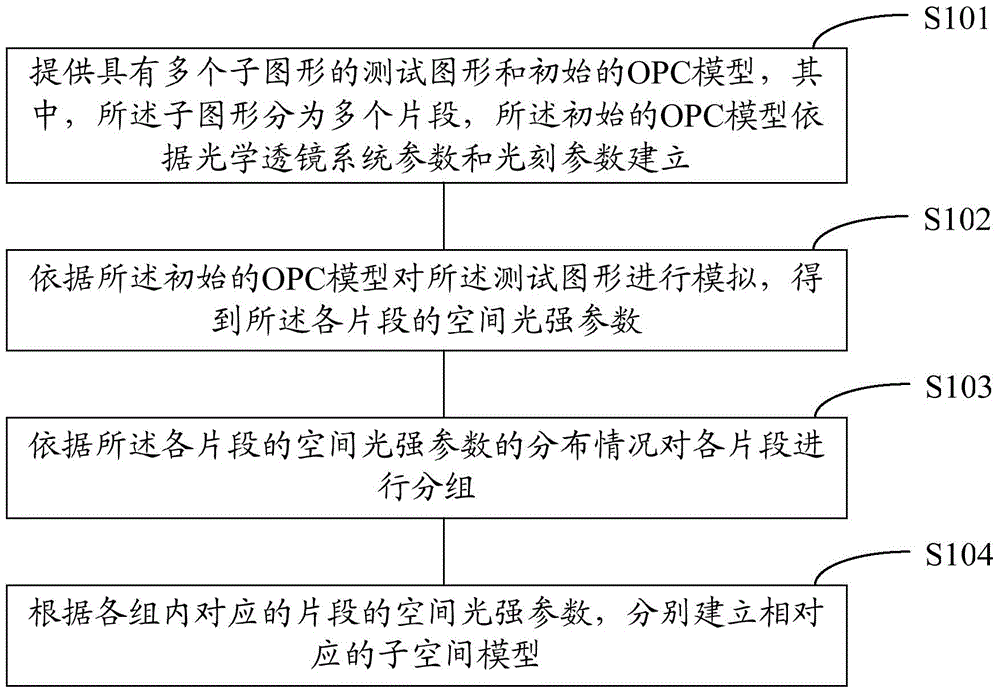
Method for establishing OPC model and optical proximity correction method for user target graphs
ActiveCN104614930AQuality improvementReduce calibration timeOriginals for photomechanical treatmentGraphicsLithographic artist
The invention relates to a method for establishing an OPC model and an optical proximity correction method for user target graphs, wherein the method for establishing the OPC model comprises the following steps: providing a test graph having several sprite graphics and an initial OPC model, wherein the sprite graphics can be divided into several fragments, establishing the initial OPC model according to an optical system parameter and a lithography parameter; simulating the test graph according to the initial OPC model to obtain the space light intensity parameter of each fragment; grouping the fragments according to the distribution condition of the space light intensity parameter of each fragment; respectively establishing a corresponding sub-space model according to space light intensity parameter of the fragment corresponding to each group, by aiming at different space light intensity parameters of the sprite graphics in the test graph, respectively employing the different sub-space models for performing optical proximity correction to effectively increase the subsequent formed graphics quality on wafer.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
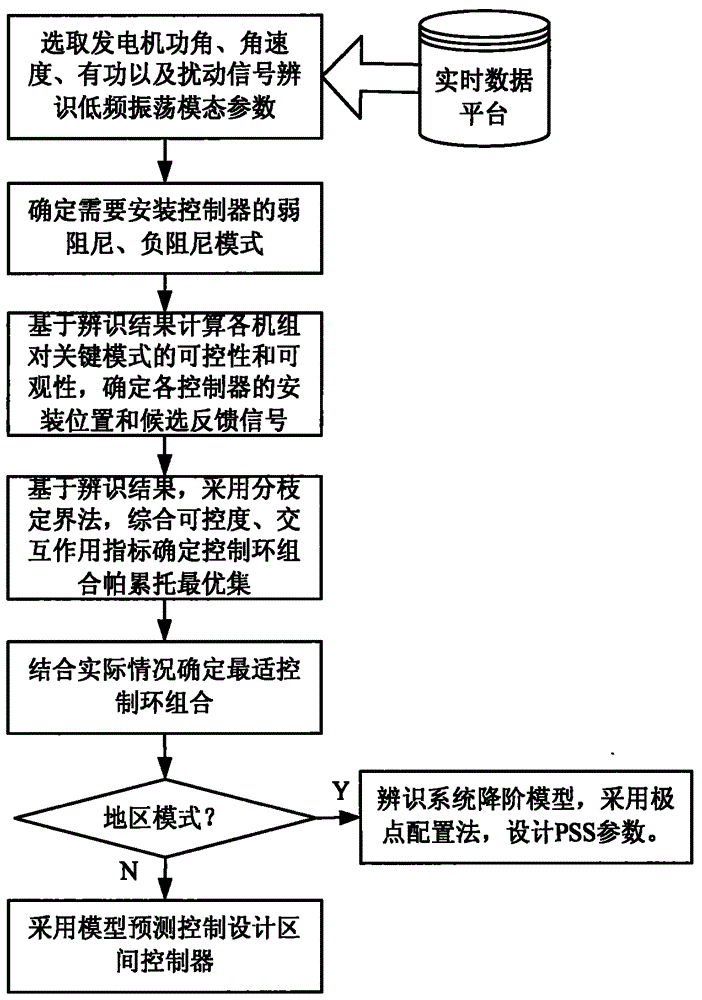
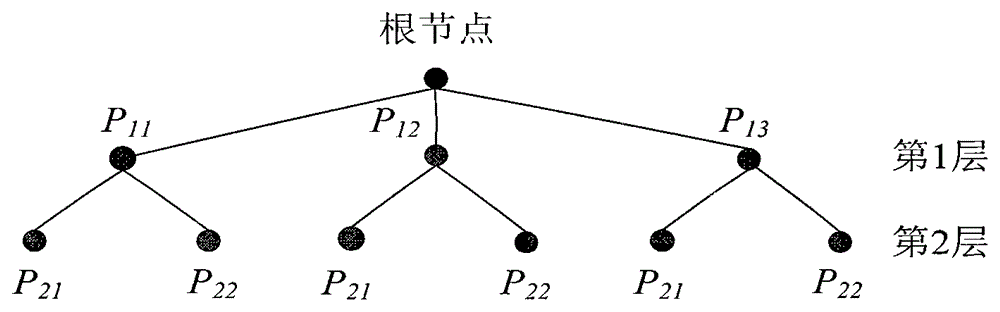
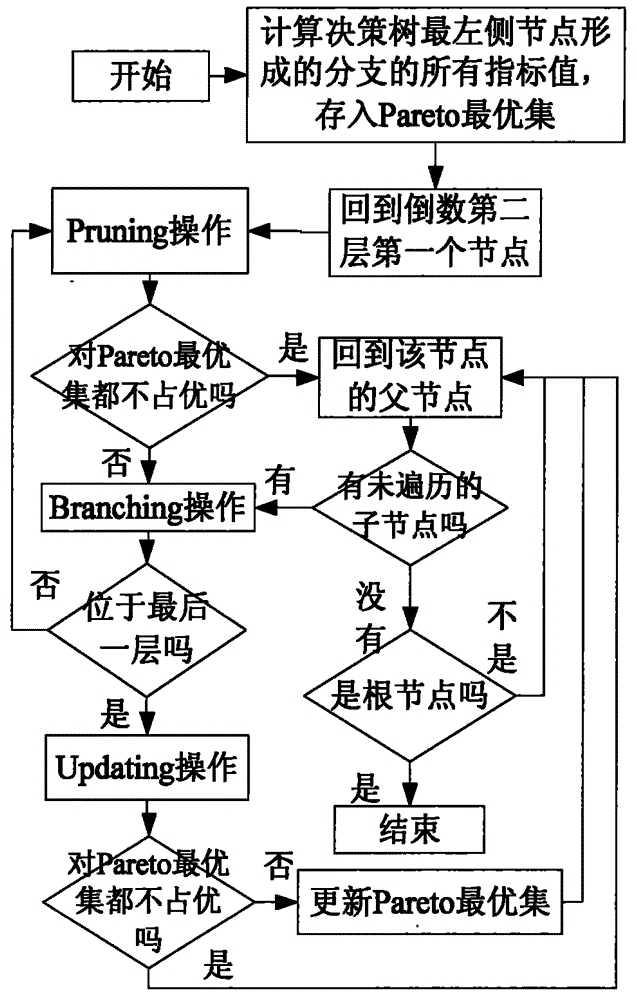
WAMS-based low-frequency oscillation decentralized controller design method considering interaction
ActiveCN105281347AReduce complexityReduce dependencePower oscillations reduction/preventionInteraction controlSubspace model identification
The invention discloses a WAMS-based low-frequency oscillation decentralized controller design method considering interaction which can be applied to low-frequency oscillation control of a power system. The method comprises the steps of: acquiring modal information by integrating multiple identification results; identifying controllability and observability by adopting a state subspace model identification method (N4SID), and determining installation positions of controllers and candidate feedback signals; transferring functional matrix definition according to MIMO for identification and solution row by row, calculating a highly-controllable low-interaction control loop combination by utilizing a branch and bound method, and converting a complex multi-controller coordination design problem into a simple decentralized controller independent design problem; designing a PSS for a region pattern by adopting an identification-based pole placement method, and designing the controllers for an interval pattern by adopting a model prediction control method. The good control effects of the two types of independently designed controllers verify effectiveness of the WAMS-based low-frequency oscillation decentralized controller design method. The WAMS-based low-frequency oscillation decentralized controller design method provides a new idea for designing a multi-damping controller based on identification coordination.
Owner:NORTH CHINA ELECTRIC POWER UNIV (BAODING)
Extended target sensitivity detector and system during subspace signal mismatch
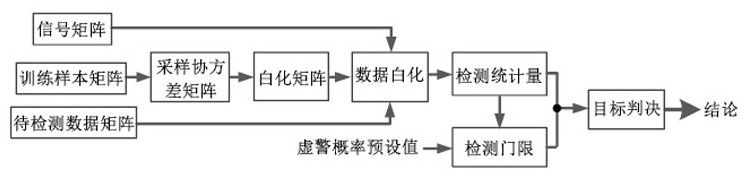
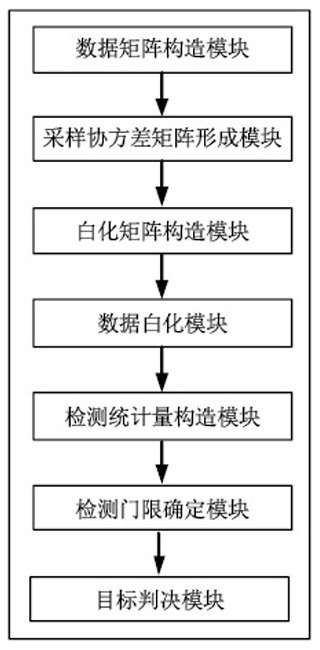
InactiveCN112558034AConstant false alarm characteristicSuppress interferenceWave based measurement systemsAlgorithmSubspace model
The invention relates to an extended target sensitivity detector and a system during subspace signal mismatch, and the method comprises the steps: firstly constructing a to-be-detected data matrix, asignal matrix and a training sample matrix, then constructing a sampling covariance matrix through the training sample matrix, and then constructing a whitening matrix through the sampling covariancematrix; whitening the to-be-detected data matrix and the signal matrix by utilizing the whitening matrix, constructing a detection statistic by utilizing the whitened data matrix, determining a detection threshold by utilizing the detection statistic and a false alarm probability, finally comparing the detection statistic with the detection threshold, and judging whether a target exists or not. Onthe basis of the self-adaptive detection idea, mismatch sensitive target detection under signal mismatch is achieved, the method is suitable for extended target detection based on a subspace model, and the detector has the constant false alarm characteristic and does not need independent constant false alarm processing.
Owner:AIR FORCE EARLY WARNING ACADEMY
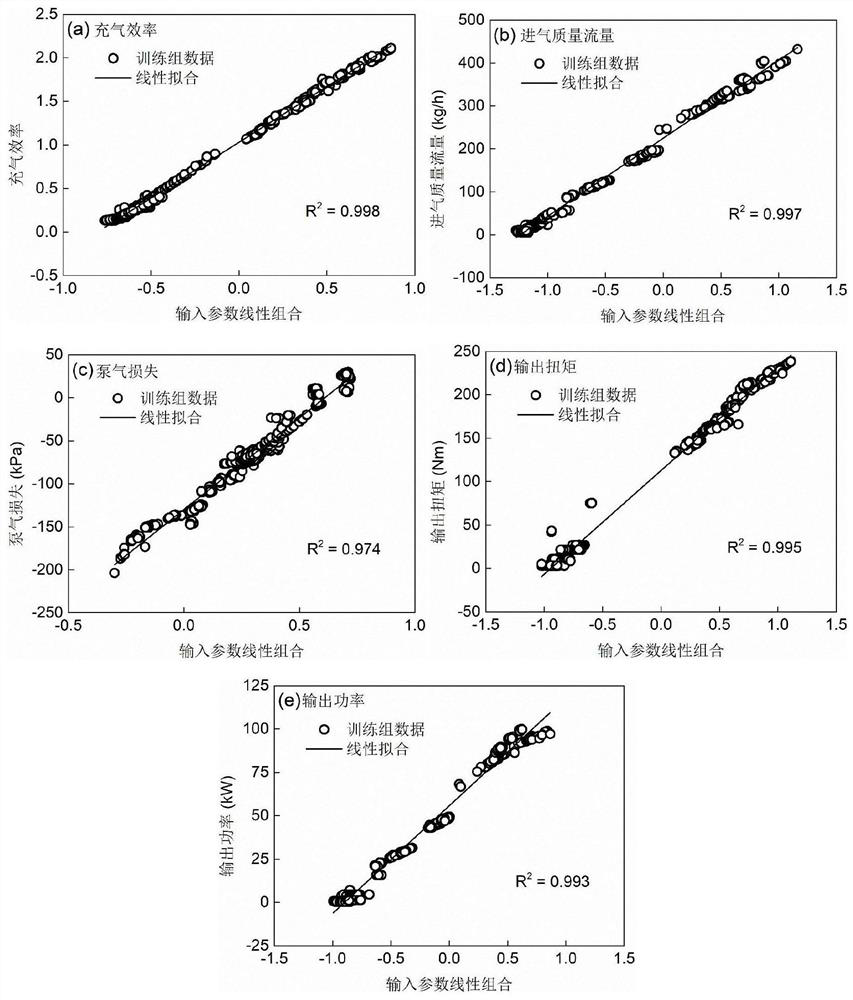
Automobile engine performance prediction and auxiliary calibration method and system
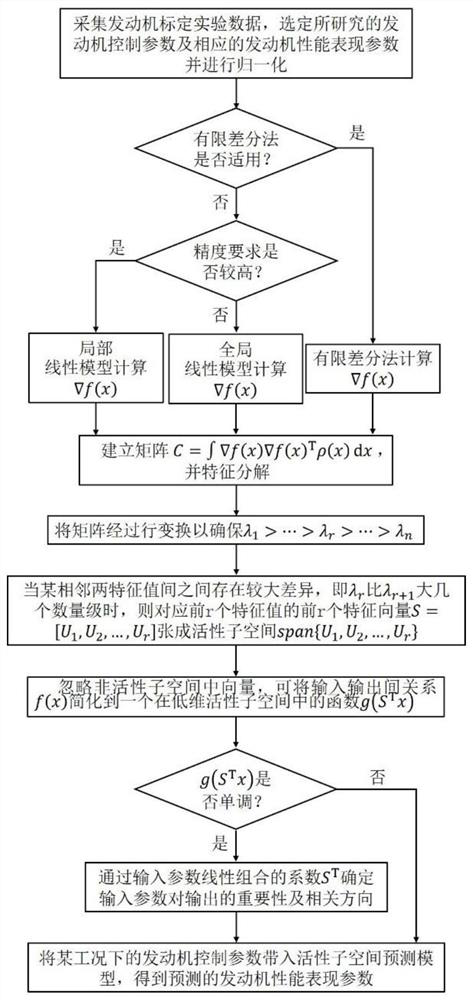
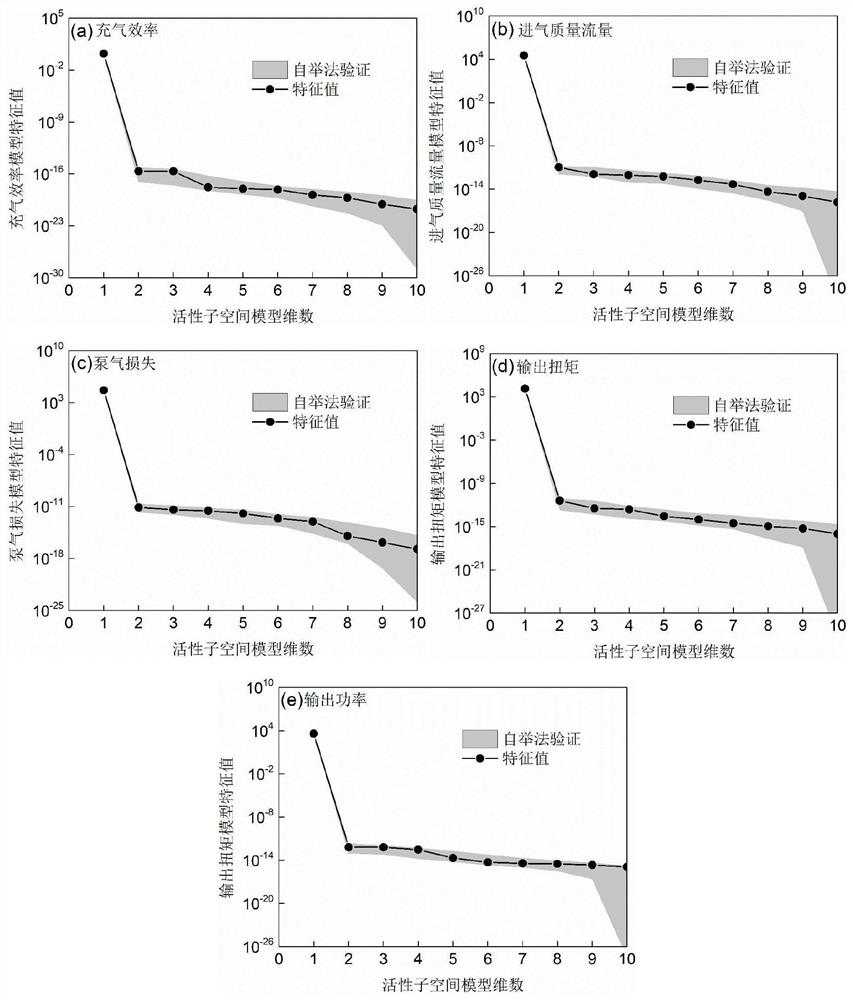
ActiveCN111651913ASave time and costImprove performanceGeometric CADDesign optimisation/simulationSensitive analysisSubspace model
The invention provides an automobile engine performance prediction and auxiliary calibration method and system, and the method comprises the steps: M1, collecting engine calibration experiment data, and selecting a researched engine control parameter and a corresponding engine performance expression parameter; M2, establishing an active subspace prediction model according to the selected researched engine control parameters and the corresponding engine performance expression parameters; and M3, substituting the engine control parameters under the preset working condition into the active subspace prediction model to obtain predicted engine performance expression parameters so as to achieve an auxiliary calibration effect, wherein the active subspace prediction model is a model based on datadimension reduction, and dimension reduction is carried out on a complex database. The active subspace model established by the invention can predict the operation condition of the engine to reduce the experimental workload on one hand, and can be used for sensitivity analysis of each control parameter of the engine to guide subsequent performance optimization work on the other hand.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
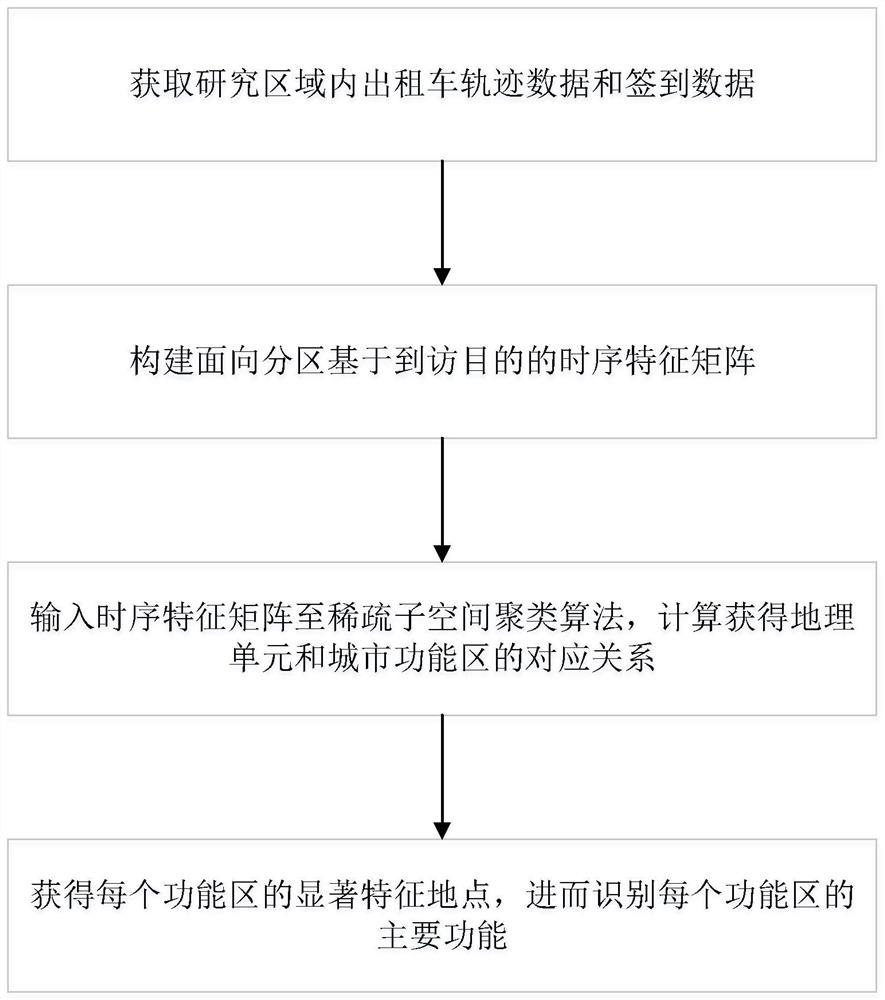
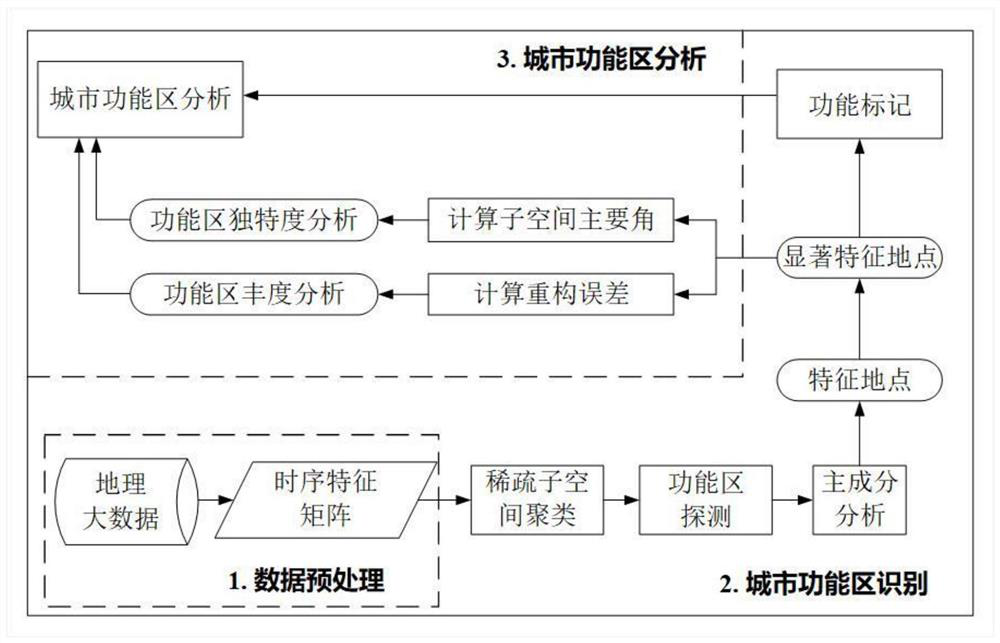
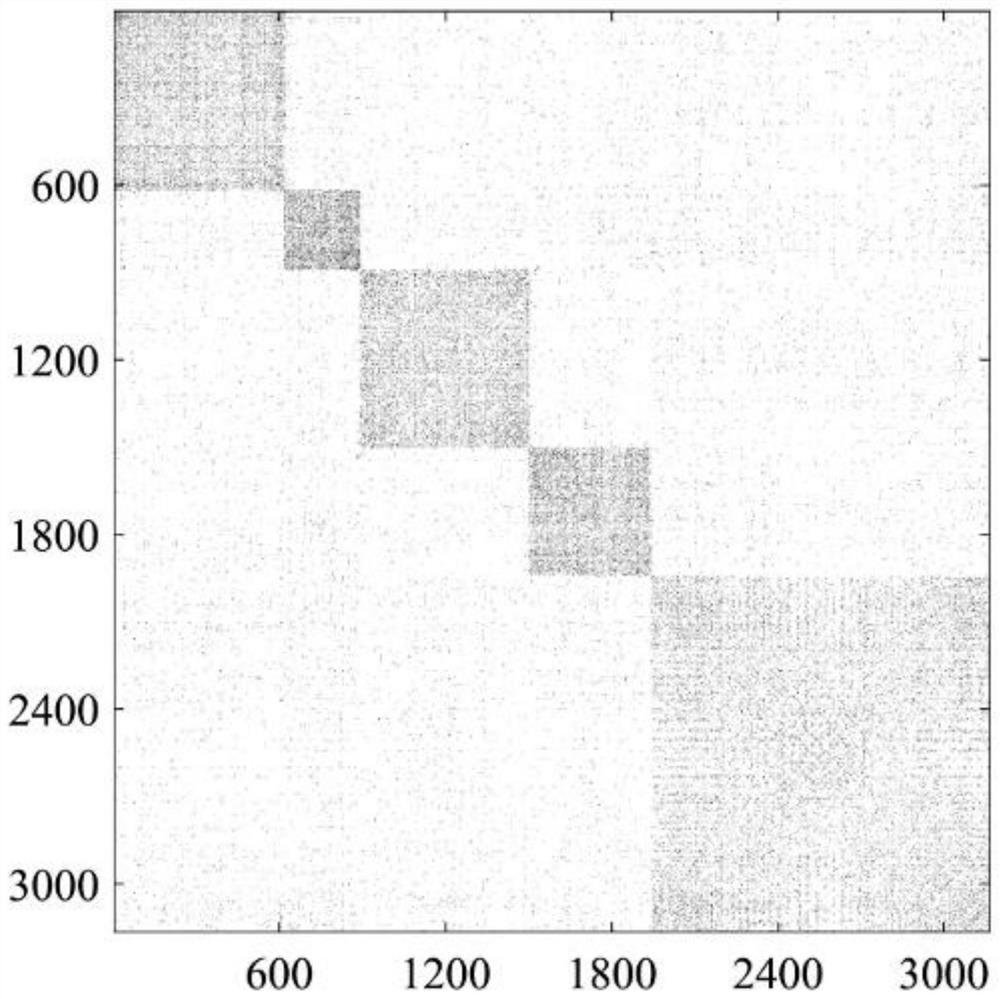
Urban functional area identification method based on multi-subspace model
ActiveCN111651502ACharacter and pattern recognitionGeographical information databasesSubspace modelEngineering
The invention discloses an urban functional area identification method based on a multi-subspace model. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining taxi track data and sign-in data in a research area; constructing a partition-oriented time sequence feature matrix C based on a visiting purpose; inputting the time sequence characteristic matrix C to a sparse subspace clustering algorithm, and calculating and obtaining a corresponding relationship between the geographic unit and the urban functional area; and obtaining a significant feature location of each functional area, and further identifying a main function of each functional area. According to the method, human activity information provided by geographic big data is utilized; the model based on the multiple subspaces overcomesthe defects in the prior art, can recognize the urban functional areas more accurately, analyzes the uniqueness and abundance of each functional area based on the geometrical properties of the subspaces, and provides fine quantitative index indication for the management and development of the urban functional areas.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
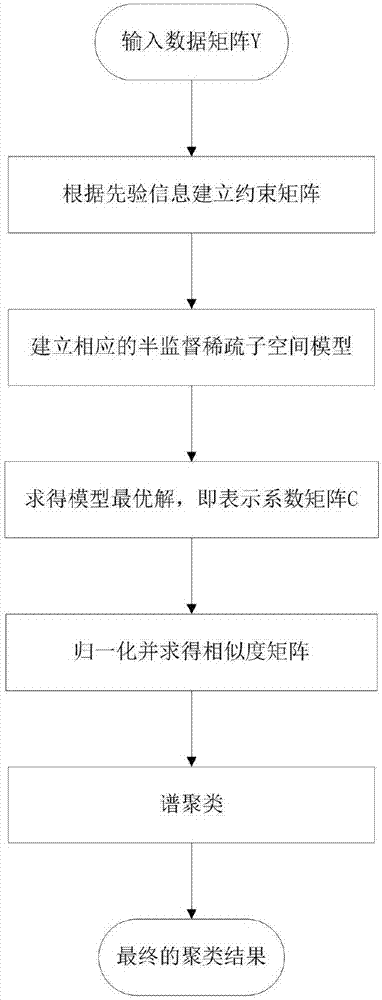
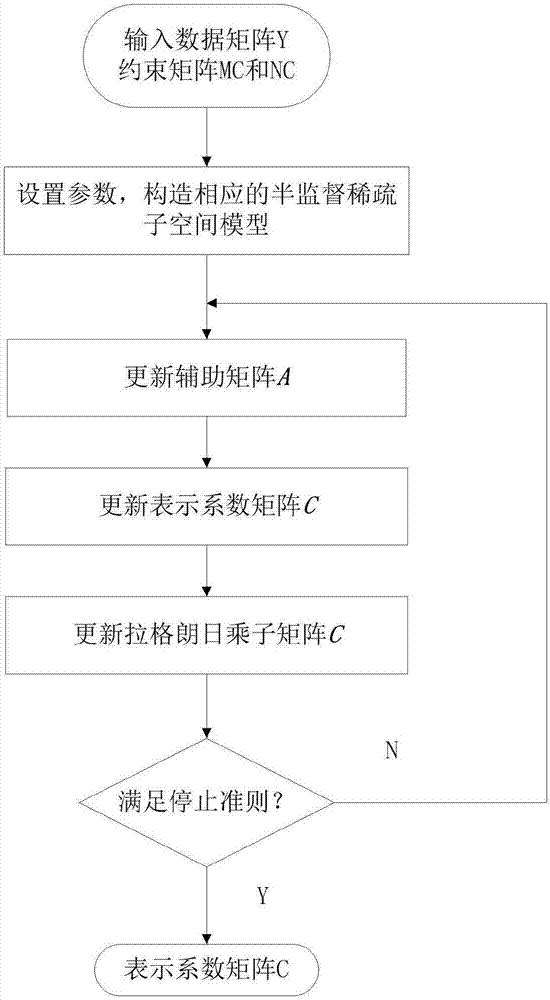
Sparse subspace clustering algorithm based on semi-supervision
InactiveCN106951920APreserve clustering accuracyImprove applicabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionPrior information
The invention discloses a sparse subspace clustering algorithm based on semi-supervision. The sparse subspace clustering algorithm comprises the steps that data prior information is converted into a constraint matrix suitable for a sparse subspace model in the form of point pair constraint; interference of flag-free bits is eliminated in the form of Hadamard product, the state of the coefficient represented by different constraint conditions is also considered and corresponding constraint terms are established; and a semi-supervised sparse subspace model of two hard threshold and soft threshold forms is established by using the constraint terms, and a semi-supervised framework is accordingly established on the sparse subspace clustering algorithm. The clustering accuracy of the sparse subspace algorithm can still be maintained by the algorithm without prior information. Meanwhile, the performance advantages of the sparse subspace clustering algorithm are also absorbed so that the high-dimensional clustering problem containing interference information data can be directly and effectively processed, the clustering performance is ensured to be effectively enhanced under the condition of less known prior information and thus the algorithm applicability can be increased.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
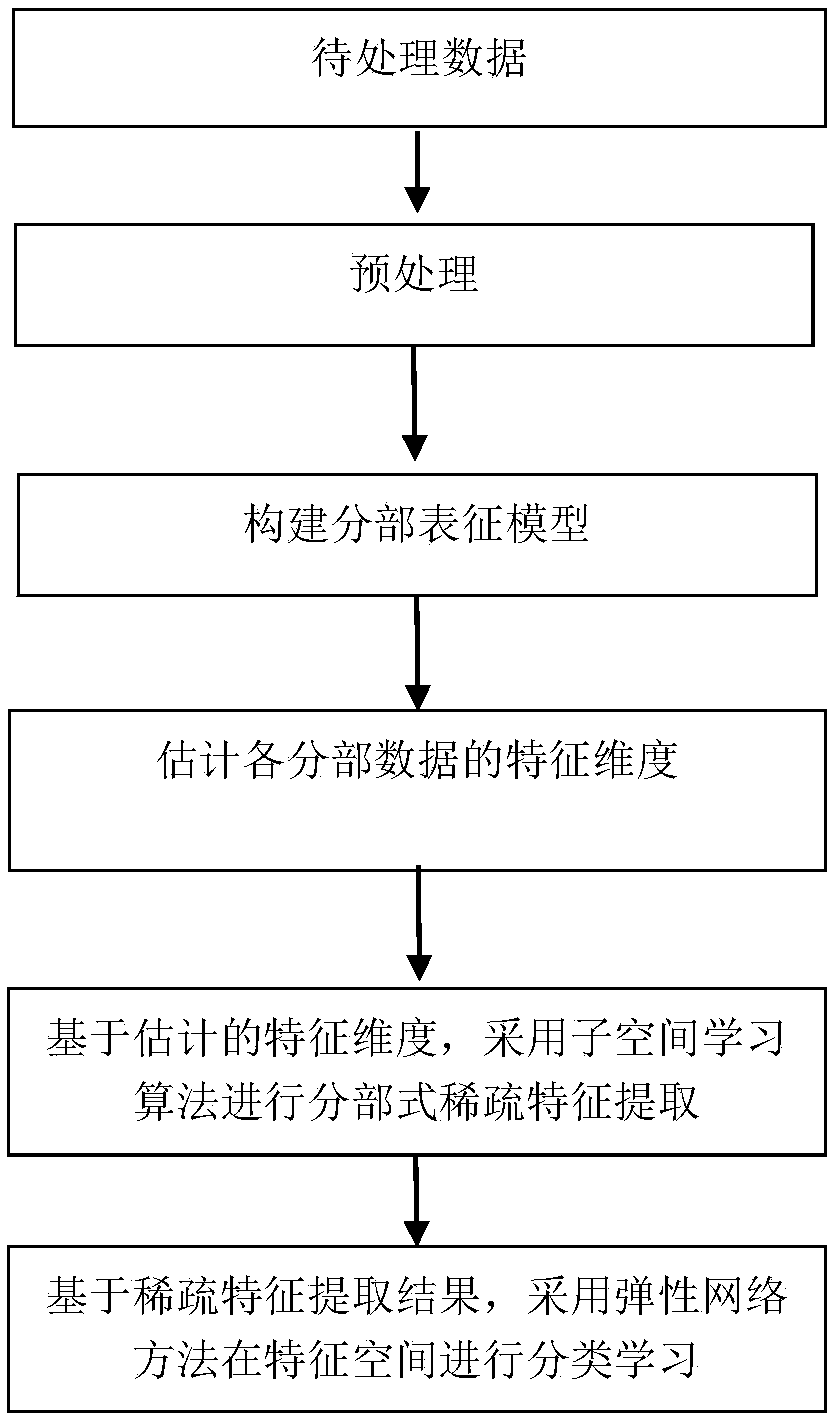
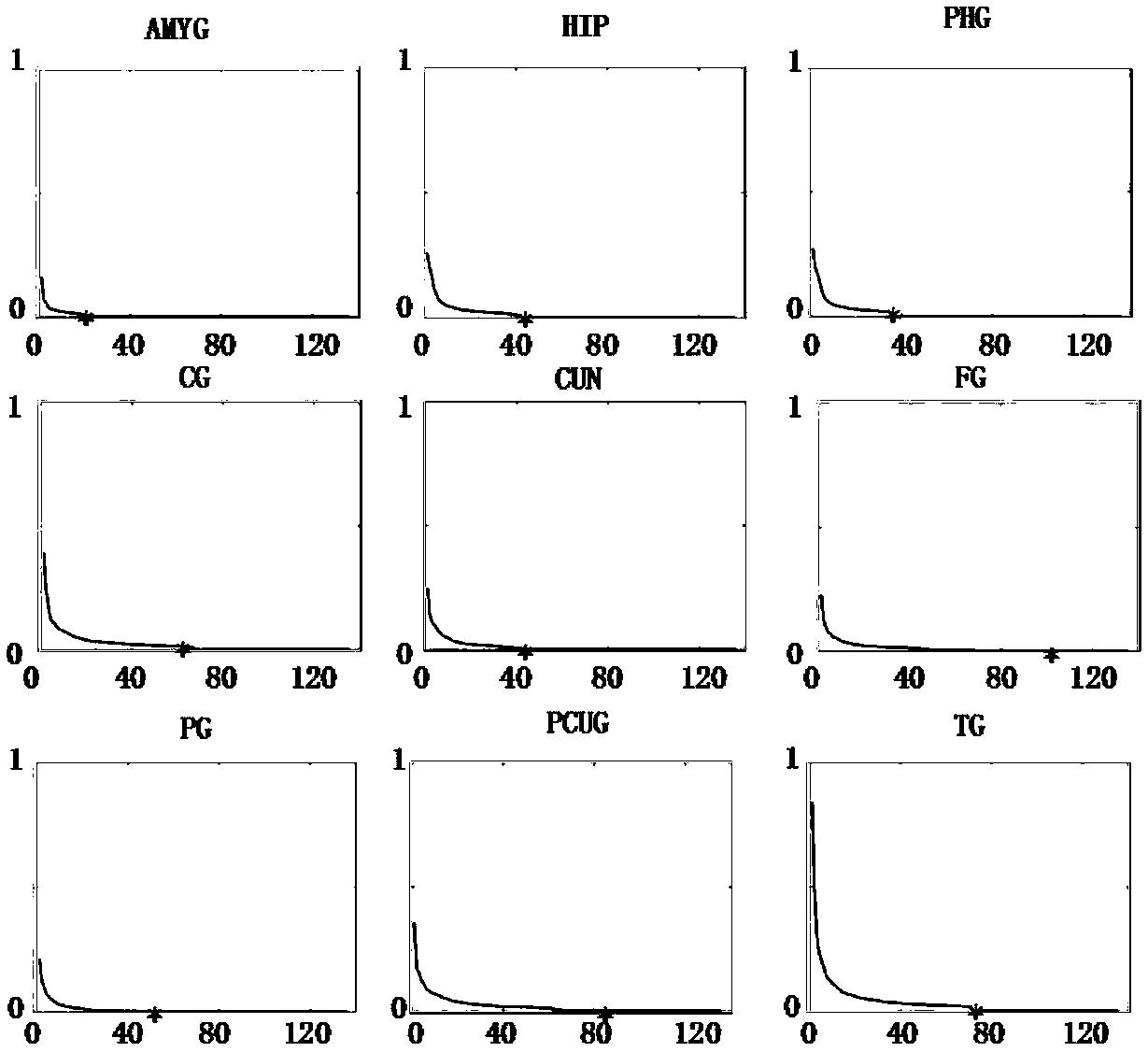
Subsection subspace model-based sparse feature extraction and classification method
ActiveCN107316065AValid reservationImprove efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognitionElastic networkSingular value decomposition
The present invention relates to a feature extraction and classification method for high-dimensional data, in particular to a subsection type subspace model-based sparse feature extraction and classification method. The method includes the following steps that: training data to be processed and test data are preprocessed separately, a spatial identification function is constructed, and a subsection characterization model is constructed; singular value decomposition is performed on the training data of each subsection, and feature dimensionalities corresponding to each subsection are estimated; sparse feature extraction is performed on the training data of the subsections through adopting a subspace learning method and on the basis of the estimated feature dimensionalities; and classification learning is performed on the test data in a feature space through using an elastic network method and on the basis of a sparse feature extraction result, so that a final classification result is obtained. With the subsection type subspace model-based sparse feature extraction and classification method of the invention adopted, the accuracy of the feature dimensionality estimation and feature extraction of local sub-regions can be effectively improved with a relatively small number of samples, and the efficiency and accuracy of existing high-dimensional data classification learning can be effectively improved.
Owner:刘艳
System and method for high-resolution spectroscopic imaging
Various embodiments accelerate high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). Various embodiments are built on a low-dimensional subspace model exploiting the partial separability of high-dimensional MRSI signals. For two and three dimensional MRSI with one spectral dimension, various embodiments sparsely sample the corresponding (k,t)-space in two complementary data sets, one with dense temporal sampling and high signal-to-noise ratio but limited k-space coverage and the other with sparse temporal sampling but extended k-space coverage. The reconstruction is then done by estimating a set of temporal / spectral basis functions and the corresponding spatial coefficients from these two data sets. The imaging technique of various embodiments can be used for high-resolution MRSI of different nuclei.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
SDN-based flow detection method
InactiveCN106330625AThe method is simpleImprove detection accuracyData switching networksData streamSubspace model
The invention relates to an SDN-based flow detection method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining the network flow detection rule; obtaining attribute information of the message of a first data stream, judging whether the attribute information is matched with the obtained network flow detection rule, if the attribute information is matched with the safety rule, executing the next step, if the attribute information is not matched with the safety rule, determining that the network flow is normal; building a sub-space model, and computing a flow threshold value E according to the sub-space model; accessing the information item of the OpenFlow exchanger flow list through an SDN network controller, and obtaining the communication flow Q arriving the exchanger; and comparing the flow threshold value E with the communication flow Q, if E is smaller than or equal to Q, presenting that the network flow is normal, otherwise the network flow is abnormal. The SDN-based flow detection method is capable of detecting the safety of the internal flow of the network, and effectively improving the detection accuracy for DDoS attack generated in the SDN network.
Owner:STATE GRID ANHUI ELECTRIC POWER +2
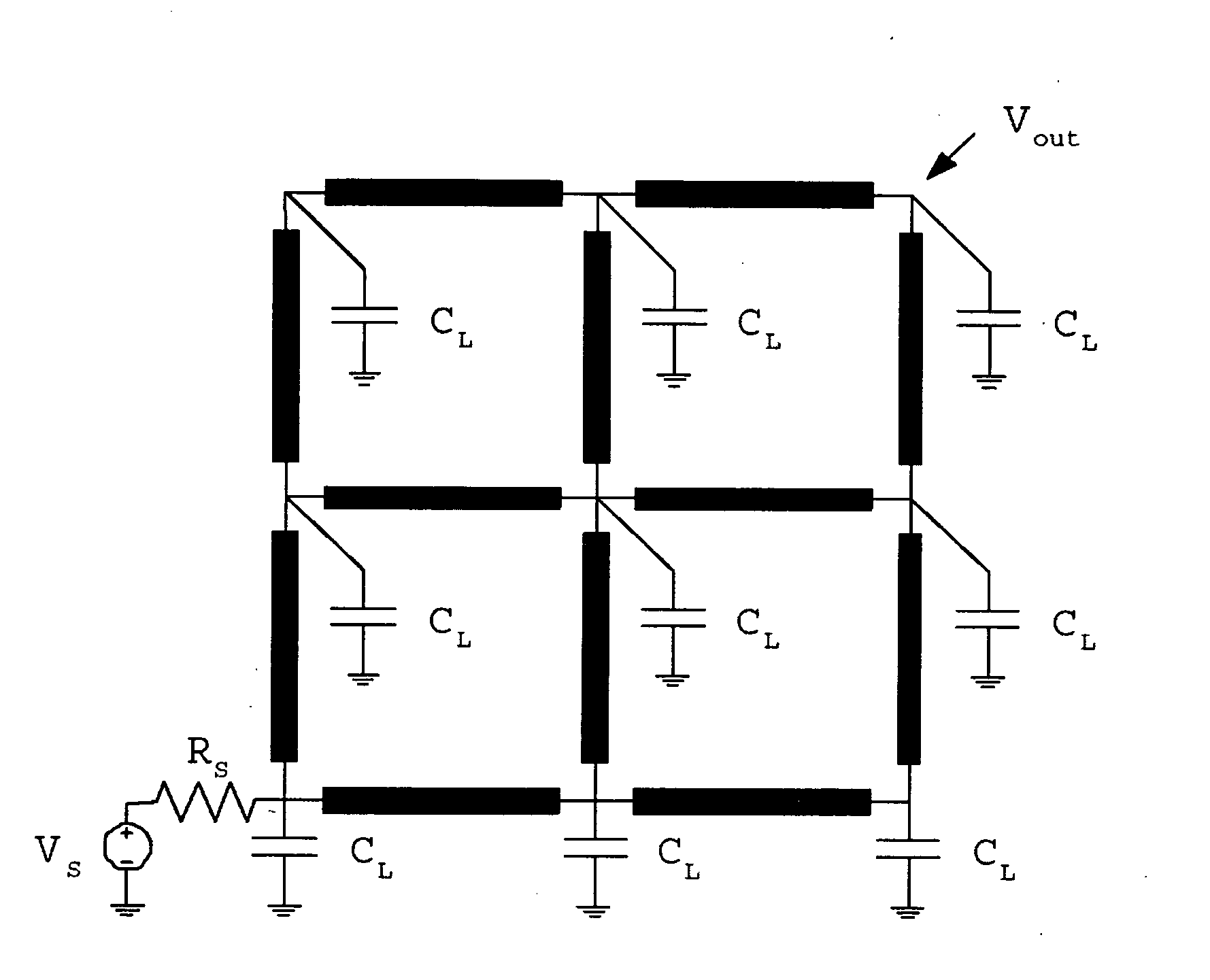
Interconnect model-order reduction method
InactiveUS20070033549A1The process is fast and accurateEfficiently provideDetecting faulty computer hardwareComputer aided designSubspace modelReduced order
An interconnect model-order reduction method for reduction of a nano-level semiconductor interconnect network as an original interconnect network by using iteration-based Arnoldi algorithms disclosed. The method is performed based on a projection method and has become a necessity for efficient interconnect modeling and simulations. To select order of the reduced-order model that can efficiently reflect essential dynamics of the original interconnect network, a residual error between transfer functions of the original interconnect network and the reduced interconnect model may be considered as a reference in determining if the iteration process should end, analytical expressions of the residual error being derived herein. Furthermore, the approximate transfer function of the reduced interconnect model may also be expressed as an addition of the original interconnect model and some additive perturbations. A perturbation matrix is only related with resultant vectors at a previous step of the Arnoldi algorithm. Therefore, the residual error information may be taken as a reference for the order selection scheme used in Krylov subspace model-order algorithm.
Owner:CHANG GUNG UNIVERSITY
Feature subspace integration method for biological cell microscope image classification
ActiveCN103902997AImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionKernel principal component analysisBiological cell
The invention discloses a feature subspace integration method for biological cell microscope image classification. The method comprises the following steps: features of biological cell microscope images to be classified are extracted; a feature subspace model is constructed for three extracted image features of the biological cell microscope images by using the kernel principal component analysis (KPCA) to make each type of biological cell microscope images has three feature subspaces; three image features are reconstructed for the biological cell microscope images to be classified by adopting each type of three trained feature subspaces to obtain the reconstruction result of each feature subspace in each type on the image features to be classified, and the classification confidence of the classified images on each type is obtained through the comparison between the reconstruction result of each feature subspace and the originally-extracted image feature vectors; and the images to be classified are classified into the type having the highest confidence. According to the method, the feature dimension can be effectively reduced, the diversity of integration classifiers can be improved, and the classification effect can be further improved.
Owner:XIAN JIAOTONG LIVERPOOL UNIV
Image upsampling by learning pairs of low-resolution dictionaries using a structured subspace model
ActiveUS20210019561A1Improve dynamic rangeIncrease speedGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionPattern recognitionSubspace model
Owner:CICADA IMAGING INC
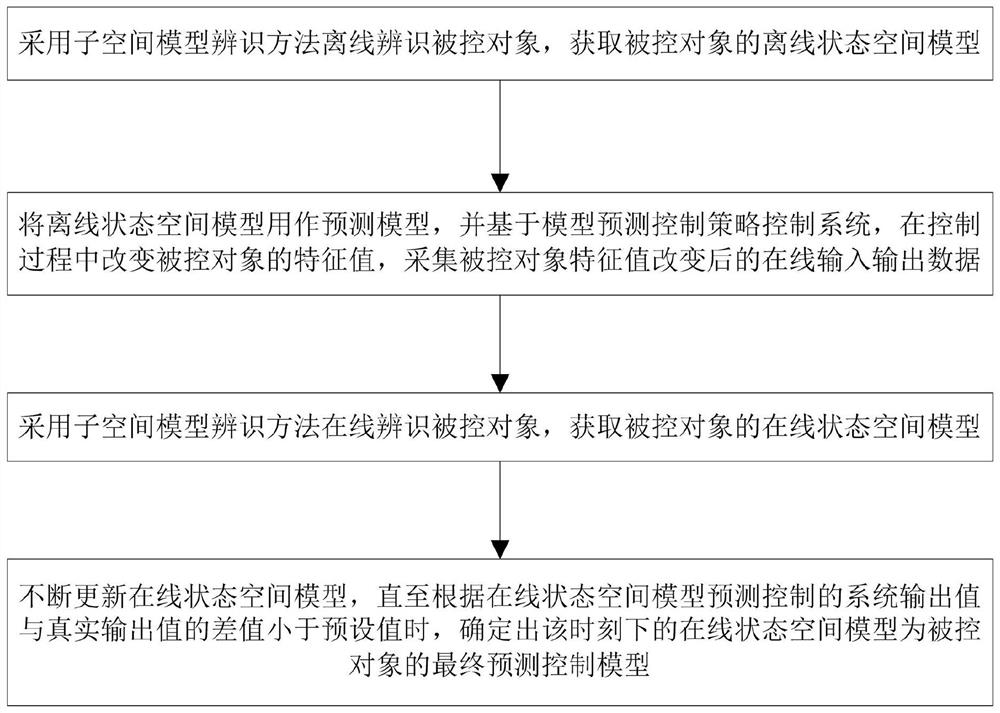
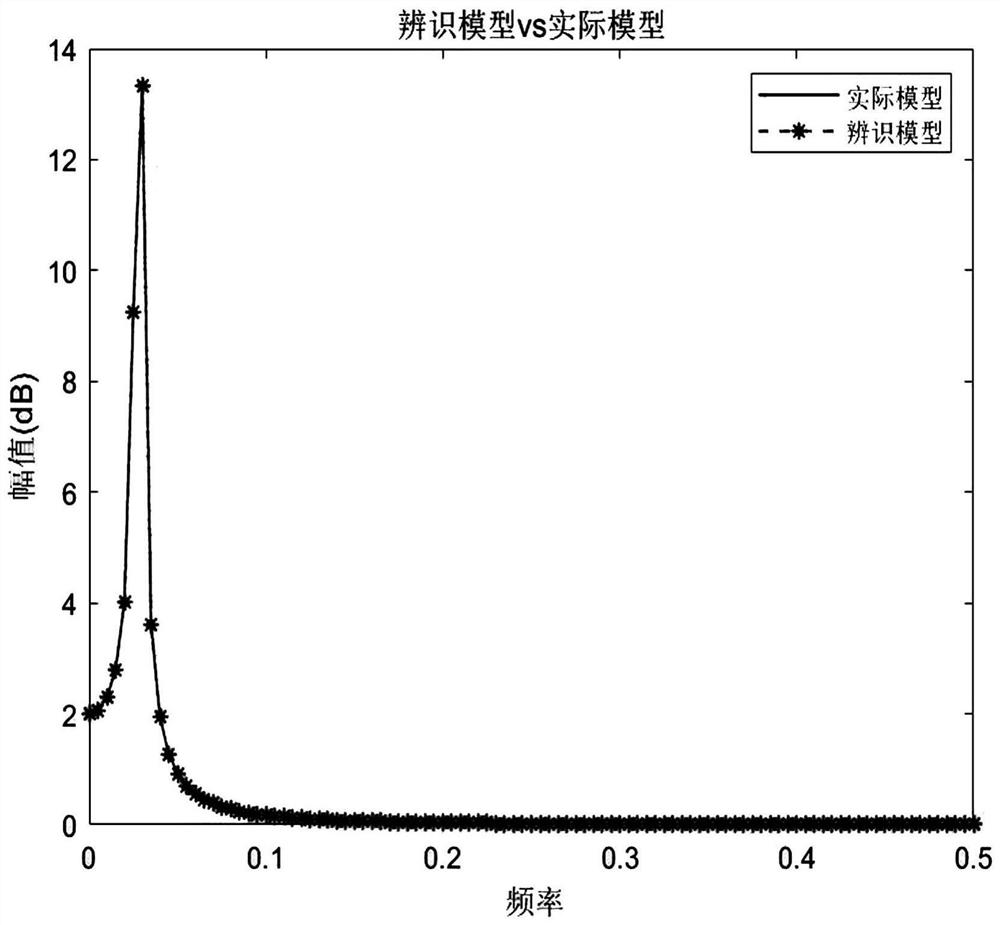
Subspace model identification prediction control method based on data driving
PendingCN114077195AIdentification stabilityGuaranteed uptimeAdaptive controlSubspace model identificationAlgorithm
The invention relates to a subspace model identification prediction control method based on data driving, and the method comprises the steps: carrying out offline identification on a controlled object through a subspace model identification method, and obtaining an offline state space model; taking the obtained off-line state space model as a prediction model, controlling the system based on a model prediction control strategy, changing a characteristic value of a controlled object, and collecting on-line input and output data after the characteristic value of the controlled object is changed; identifying the controlled object online through a subspace model identification method, and obtaining an online state space model; and updating the online state space model until the difference value between the system output value controlled according to the online state space model and the real output value of the controlled object is smaller than a preset value. According to the method, under the condition that a system model is unknown, the coefficient of a state space system matrix is obtained through the subspace model identification method, on this basis, the controlled object is controlled, the model is updated, finally, the model of the controlled object is identified accurately and operates stably, and a good operation state is achieved.
Owner:苏州益声瑞机器人科技有限公司
Local spline embedding-based orthogonal semi-monitoring subspace image classification method
InactiveCN101916376BPreserve the eigenstructure of the manifold spaceAvoid difficultiesCharacter and pattern recognitionHat matrixData set
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Brain-computer information fusion classification method and system for shared subspace learning
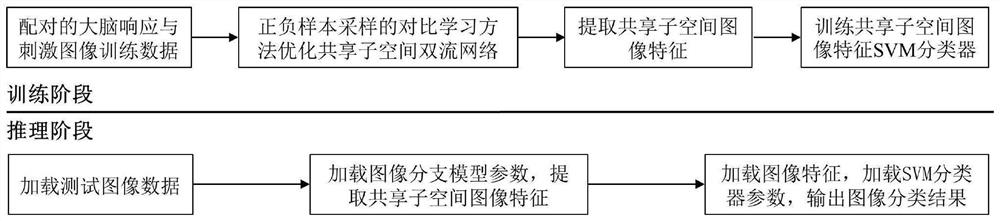
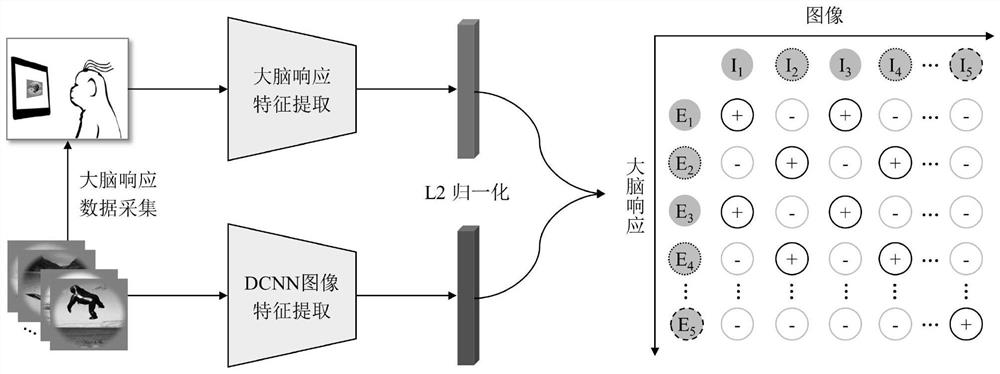
PendingCN114742092ACreativeEfficient migrationCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesSubspace modelClassification methods
The invention belongs to the technical field of brain-computer interface technology application, and discloses a brain-computer information fusion classification method and system for shared subspace learning, and the brain-computer information fusion classification method comprises a training stage and a reasoning stage. In the training stage, paired images and brain response data are utilized, shared subspace model parameters of the images and brain responses are optimized through a contrast learning strategy of positive and negative sample sampling, and an image classifier is trained; in the reasoning stage, image features are extracted for classification, and the application target of the whole brain-computer information fusion classification system is achieved. According to the brain-computer information fusion classification system based on shared subspace learning, the shared subspace can be trained in an end-to-end mode, efficient migration of brain cognitive information is achieved, and the performance of an image classification task in a complex open scene is improved; through the application that the brain is not in the loop, the efficiency and the stability in the practical application are improved, and the method has a wide application prospect under a new normal form of brain-computer information cooperative work.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Abnormity monitoring method for non-stationary nonlinear industrial process
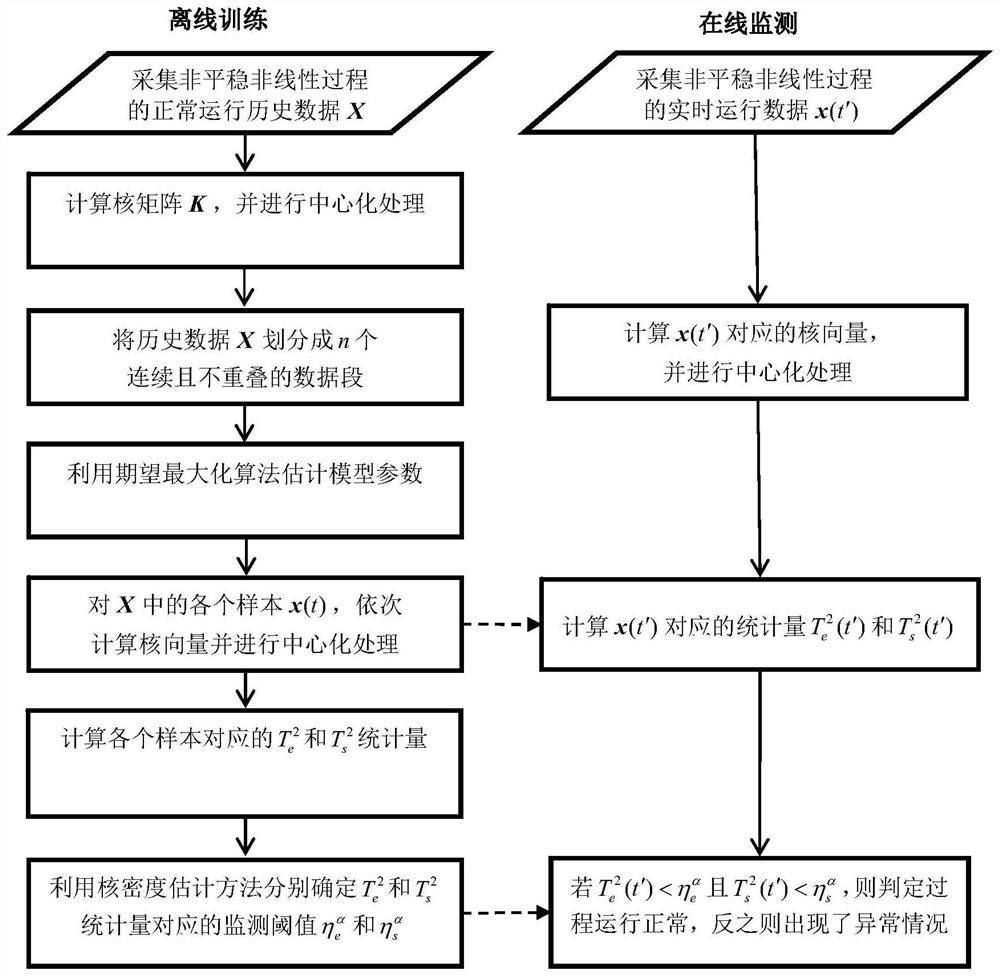
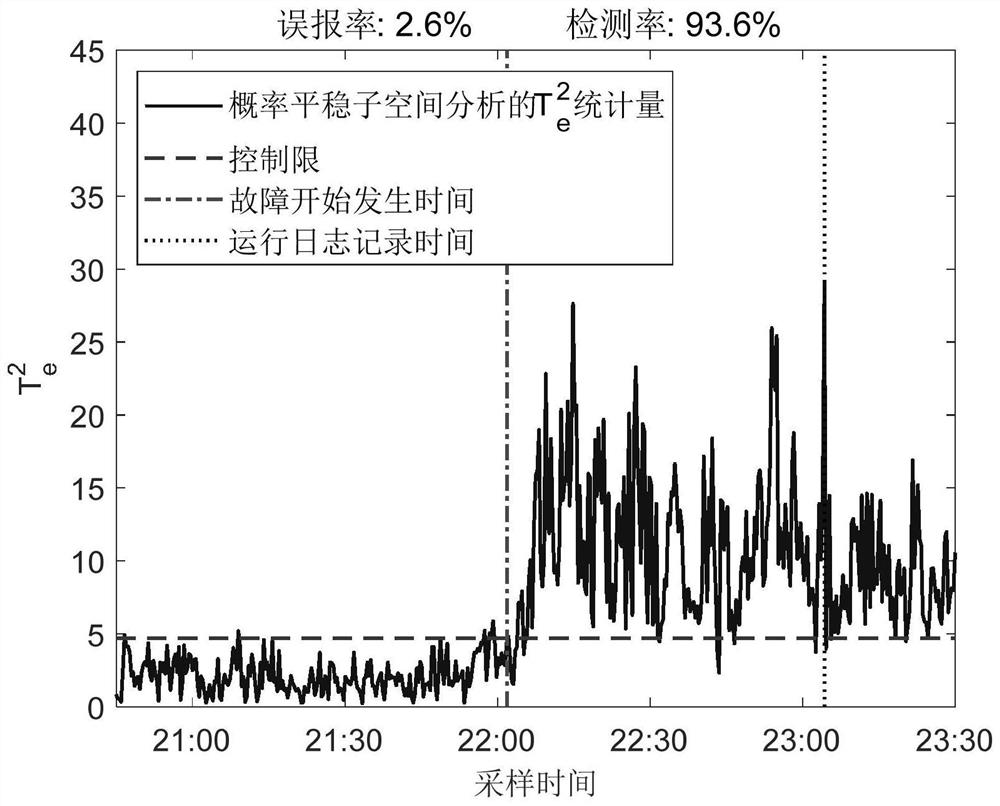
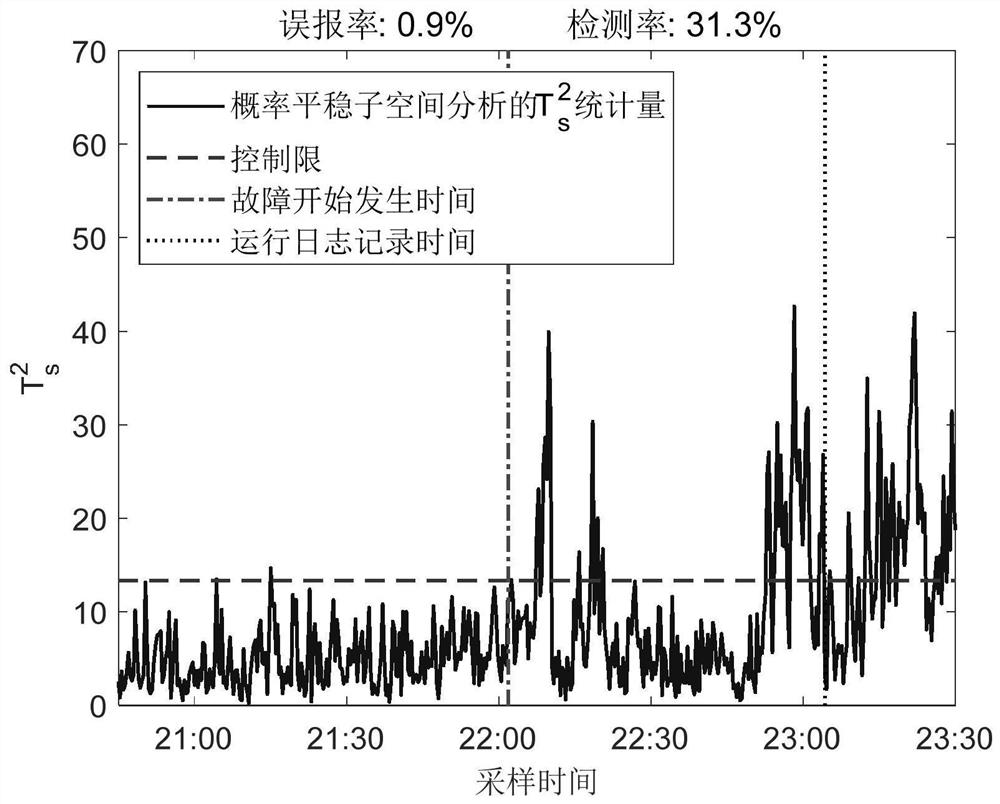
InactiveCN113806918ADesign optimisation/simulationProbabilistic CADExpectation–maximization algorithmSubspace model
The invention discloses an anomaly monitoring method for a non-stationary nonlinear industrial process, and belongs to the field of industrial process anomaly monitoring. On the basis of probabilistic stationary subspace analysis, a kernel probability stationary subspace analysis method is provided by using a kernel skill, and non-stationary and nonlinear characteristics of a complex industrial process can be processed at the same time. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, mapping nonlinear data to a high-dimensional feature space, and establishing a linear model in the high-dimensional feature space; secondly, estimating parameters of the model by using an expectation maximization algorithm; by introducing a kernel skill, realizing a parameter learning process by using a kernel function without knowing an explicit expression of nonlinear mapping. Based on a kernel probability stationary subspace model, two detection indexes are proposed for monitoring a non-stationary nonlinear industrial process. Compared with an original probabilistic stationary subspace analysis method, the non-linear relation in the measured variables can be effectively extracted, and therefore the method is more suitable for monitoring the non-stationary industrial process with the non-linear characteristic at the same time.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Cartoon animation generation method with combination of hand drawing style
InactiveCN108109190AGenerate efficientlyRetain original featuresAnimationCartoon animationViewpoints
The invention provides a cartoon animation generation method with the combination of a hand drawing style. The method includes following steps: (1) firstly constructing three-dimensional grids and a skeleton subspace model of a role by employing a hand drawing; (2) then creating a group of viewpoint relevant models matched with multi-viewpoint hand drawings with the combination of posture reconstruction and a differential domain grid deformation algorithm; and (3) finally combining the hand drawing style with an input motion sequence through motion annotation and a heuristic generalization algorithm to enable the generated animation to maintain original characteristics of the motion sequence. According to the animation generated by employing the method, the original characteristics of themotion sequence are maintained, the drawing style of hand drawing is reflected, and the method can effectively generate cartoon role animation representing the hand drawing style.
Owner:佛山市晴天视觉数字科技有限公司
Speaker labeling method and system based on density peak clustering and variational Bayesian
ActiveCN106971713BImprove accuracyImprove stabilitySpeech recognitionCluster algorithmSubspace model
Owner:北京华控智加科技有限公司
System and method for ultrafast magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging using learned spectral features
ActiveUS11079453B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMetaboliteSubspace model
A new method is developed for ultrafast, high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) using learned spectral features. The method uses Free Induction Decay (FID) based ultrashort-TE and short-TR acquisition without any solvent suppression pulses to generate the desired spatiospectral encodings. The spectral features for the desired molecules are learned from specifically designed “training” data by taking into account the resonance structure of each compound generated by quantum mechanical simulations. A union-of-subspaces model that incorporates the learned spectral features is used to effectively separate the unsuppressed water / lipid signals, the metabolite signals, and the macromolecule signals. The unsuppressed water spectroscopic signals in the data can be used for various purposes, e.g., removing the need of additional auxiliary scans for calibration, and for generating high quality quantitative tissue susceptiability mapping etc. Simultaneous spatiospectral reconstructions of water, lipids, metabolite and macromolecule can be obtained using a single 1H-MRSI scan.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com