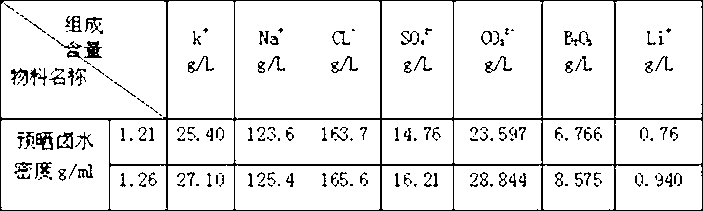
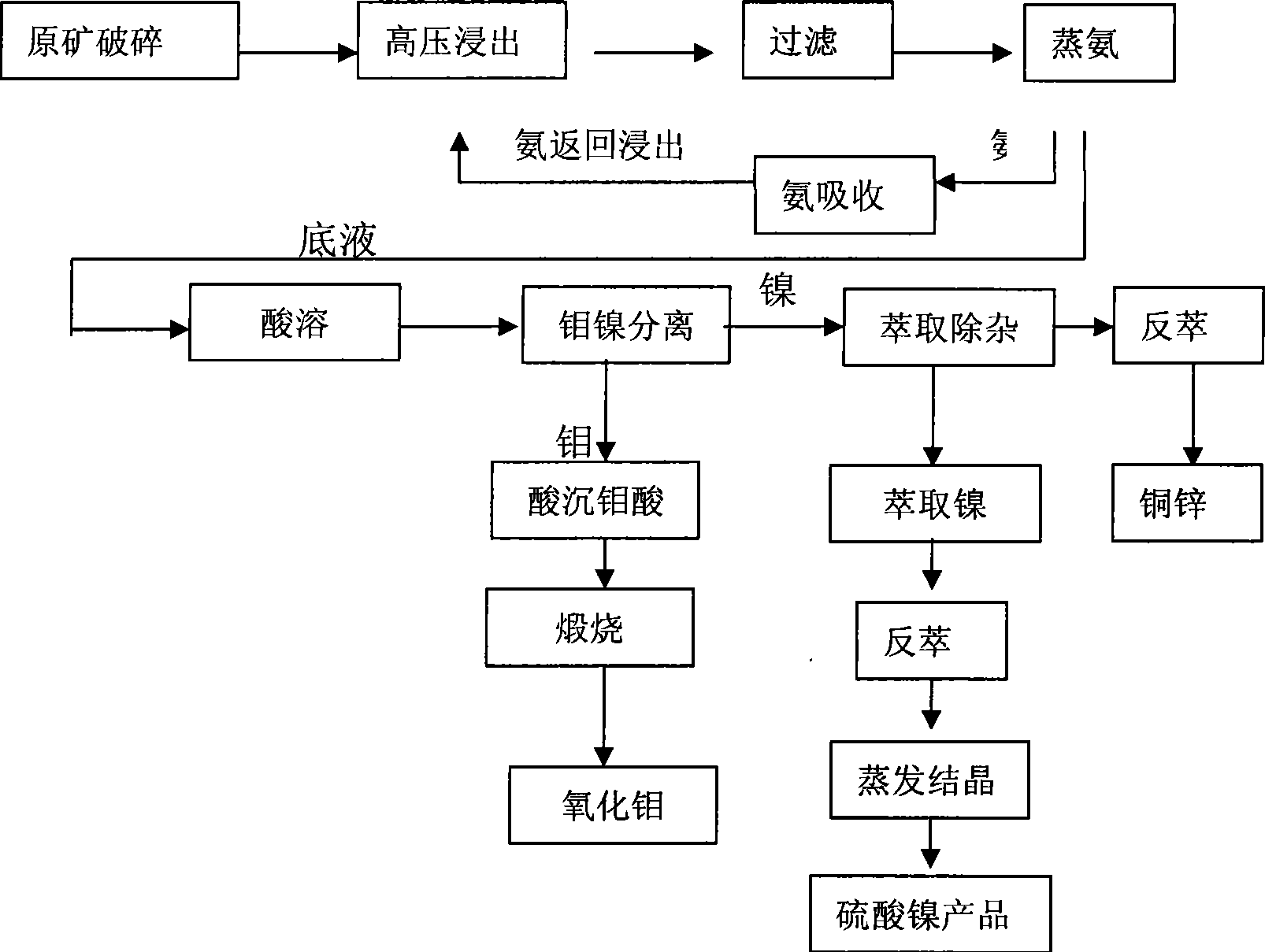
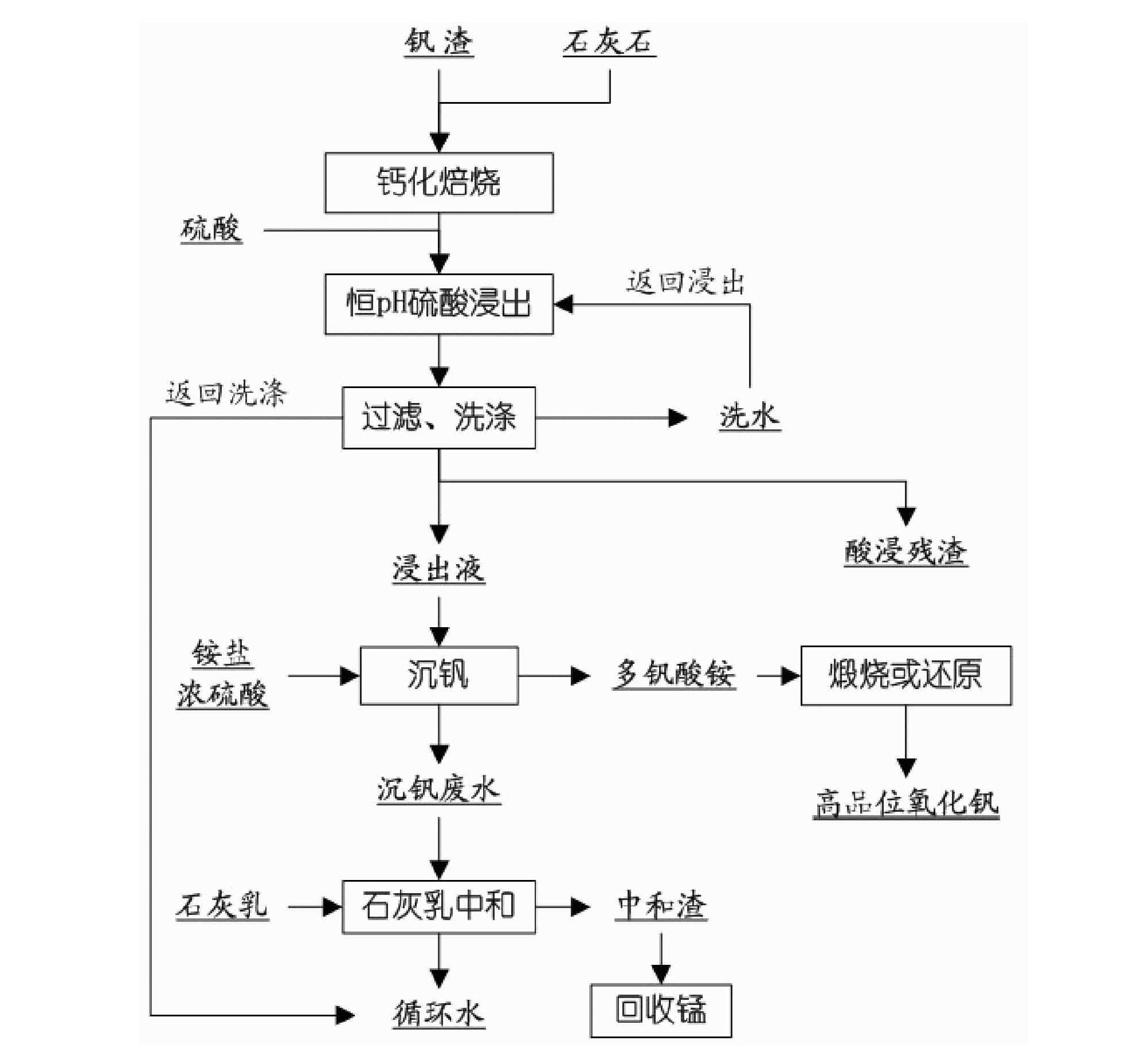
Patents
Literature
191results about How to "Improve overall recovery" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
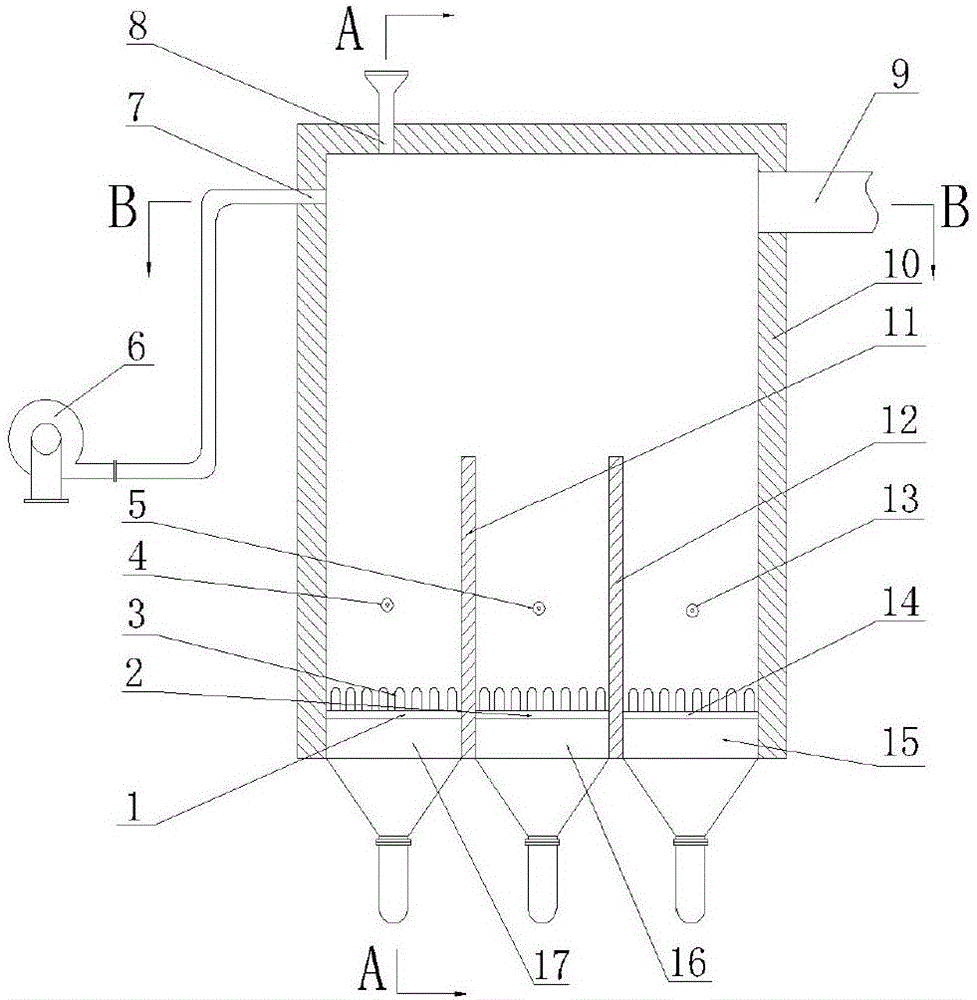
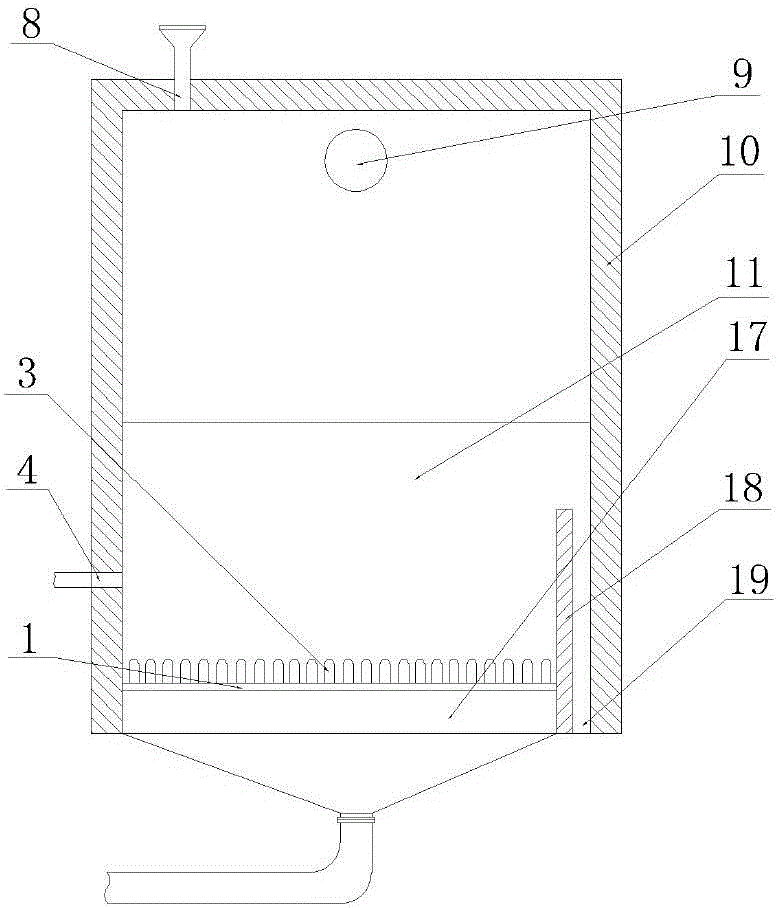
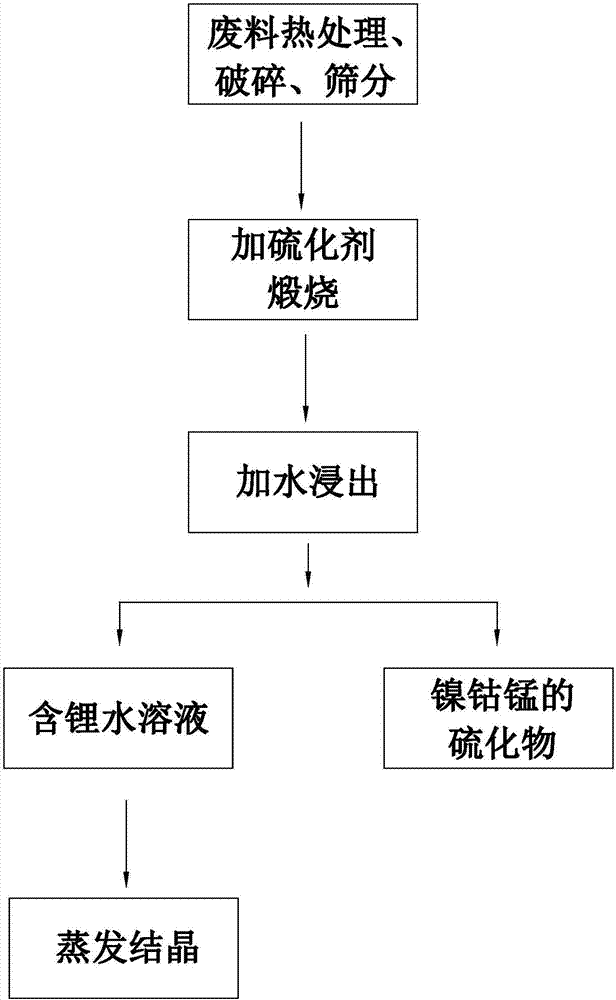
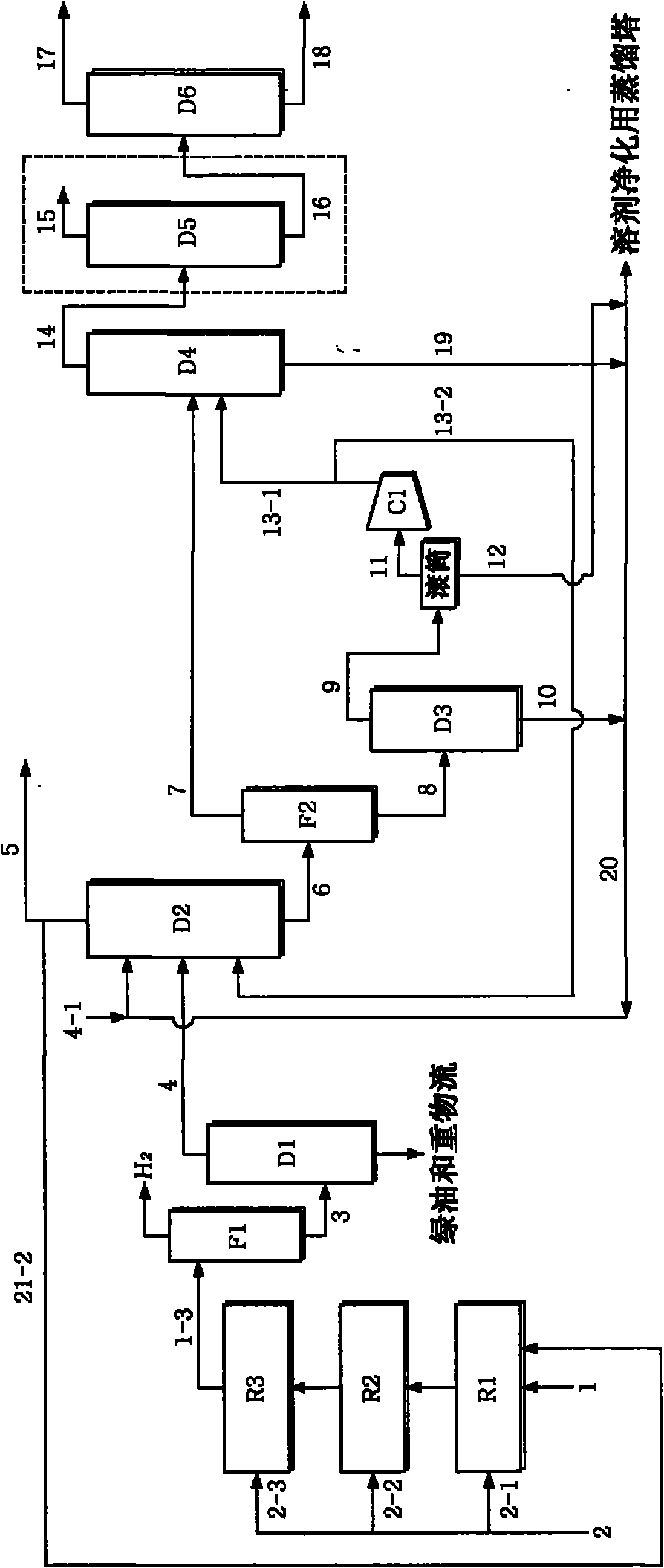
Recycling and harmless treatment method for cyaniding tailing slurry
ActiveCN101759274AIncrease contact areaToxicWaste water treatment from quariesWater contaminantsSlagGas phase
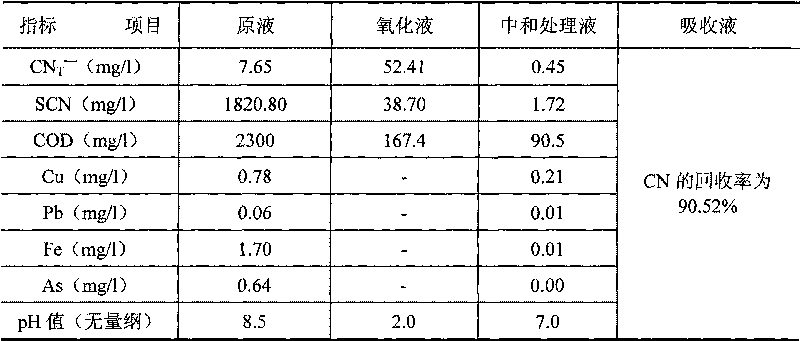
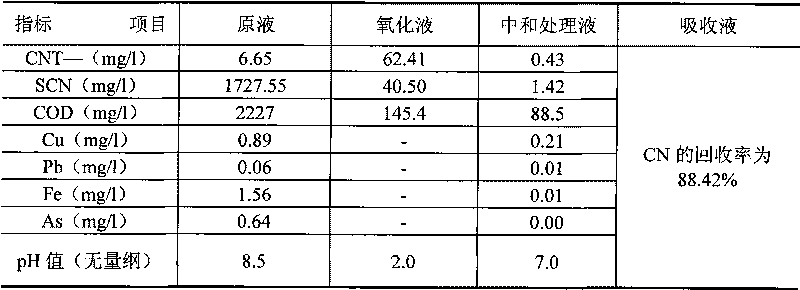
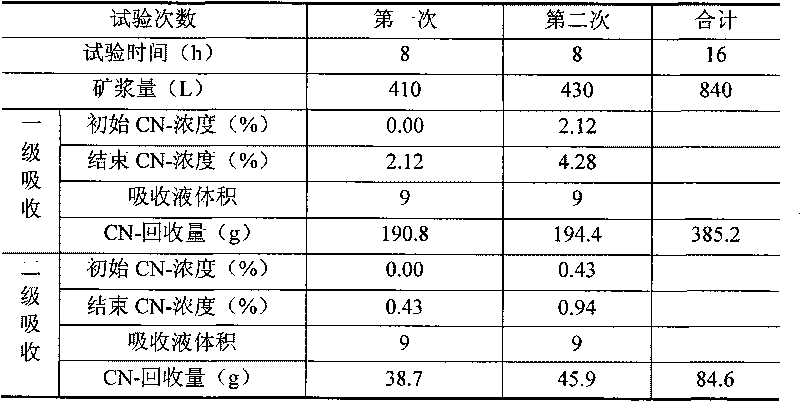
The invention discloses a recycling and harmless treatment method for cyaniding tailing slurry. In the method, the cyaniding tailing slurry containing cyanogen, thiocyanate, heavy metal and arsenic and liquid containing hydrogen peroxide are subjected to direct mixing treatment; the method utilizes high specific surface area of micro-fine granular ore to add the contact opportunity between the thiocyanate and the hydrogen peroxide and the contact area between gas phase and liquid phase through surface adsorption to accelerate a speed of oxidation-reduction reaction and an acidifying and stripping speed, utilizes metallic substances contained in slag to accelerate the reaction rate of the oxidation-reduction reaction without the addition of catalyst, and can reduce cost; meanwhile, in neutralization, Fe3+ in the slag is utilized to meet the requirement of arsenic precipitation without the addition of an arsenic precipitation reagent; when residual cyanides is removed from the hydrogen peroxide liquid, the hydrogen peroxide liquid and cyano complexes which are difficult to remove through the oxidation-reduction reaction form sediment so that the residual thiocyanate is further removed; the method can make the conversion rate of the thiocyanate in the ore slurry more than or equal to 88 percent; and compared with the treatment of filter pressing clear liquid of homogeneous ore slurry, the total reclaiming rate can be increased by over 20 percent.
Owner:CHANGCHUN GOLD RES INST +1
Method for directly producing high-purity electronic level cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste
ActiveCN102061390AMeet high purity requirementsImprove overall recoveryProcess efficiency improvementTotal recoveryGoethite
The invention provides a method for directly producing high-purity electronic level cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste, in particular a process for producing cobaltous sulfate by using cobalt-containing waste. The method comprises the steps of: checking and classifying raw materials, wet-milling and size-mixing, acid-decomposing, filtering, washing, separating, and extracting copper sponge. The method is characterized by also comprising the steps of: removing iron with a goethite process, extracting P2O4 and removing impurities, separating nickel from cobalt, extracting N235, purifying, concentrating and crystallizing. The high purity electron level cobaltous sulfate is directly regenerated by using various kinds of cobalt wastes, the requirement of the modern high-technology industry on high purity of the cobaltous sulfate is met; the total recovery of the cobalt is higher than or equal to 98 percent; various usable elements can be comprehensively recycled, and coppersponge, tungsten carbide, iron hydroxide and nickel carbonate can be regenerated while the electronic level cobaltous sulfate as a main product is regenerated. The invention has the advantages of comprehensively utilizing waste cobalt resources, recycling the wastes, improving the enterprise benefit, and being beneficial to the development of energy conservation, emission reduction, environment protection and circular economy.
Owner:HUNAN JINYUAN NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
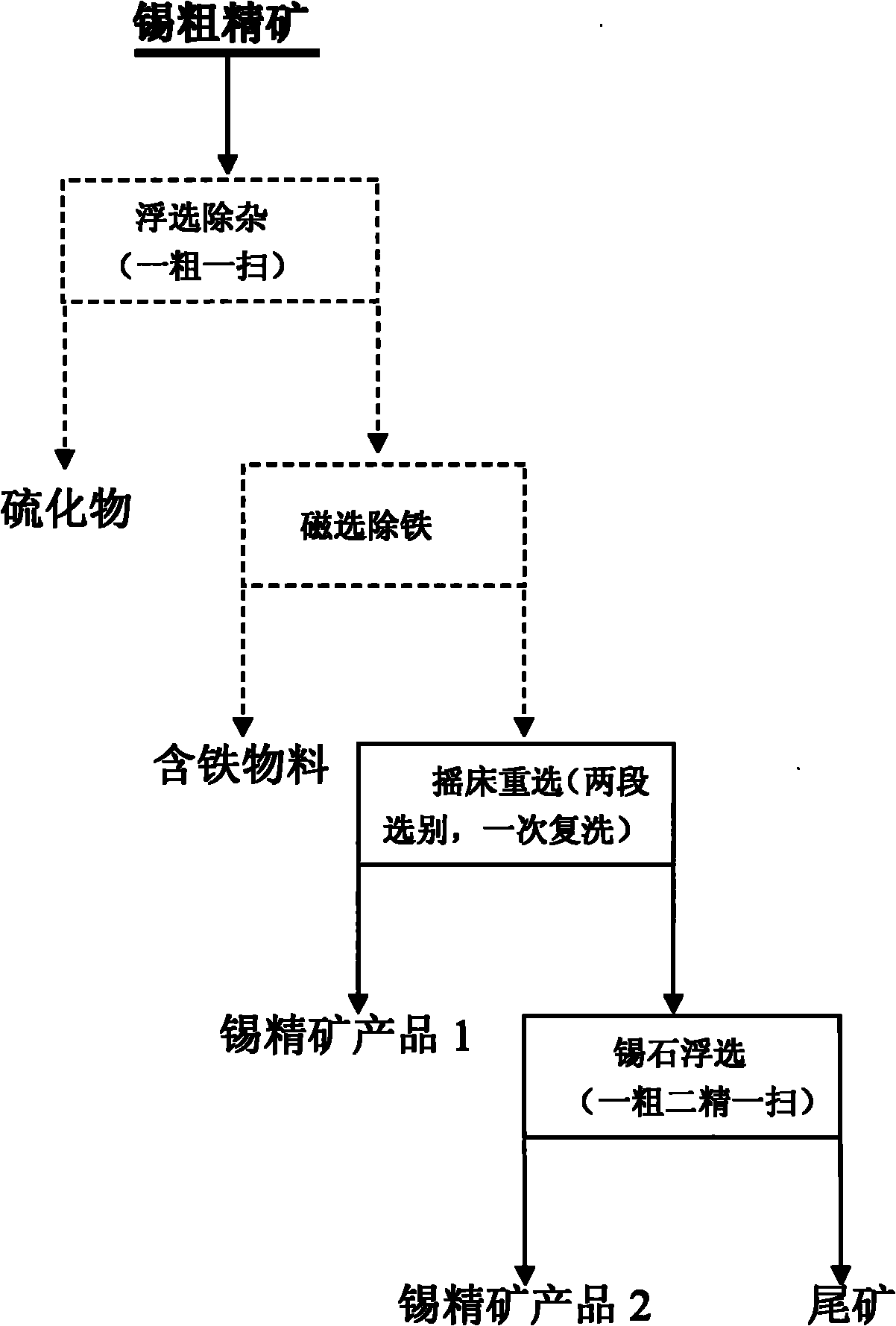
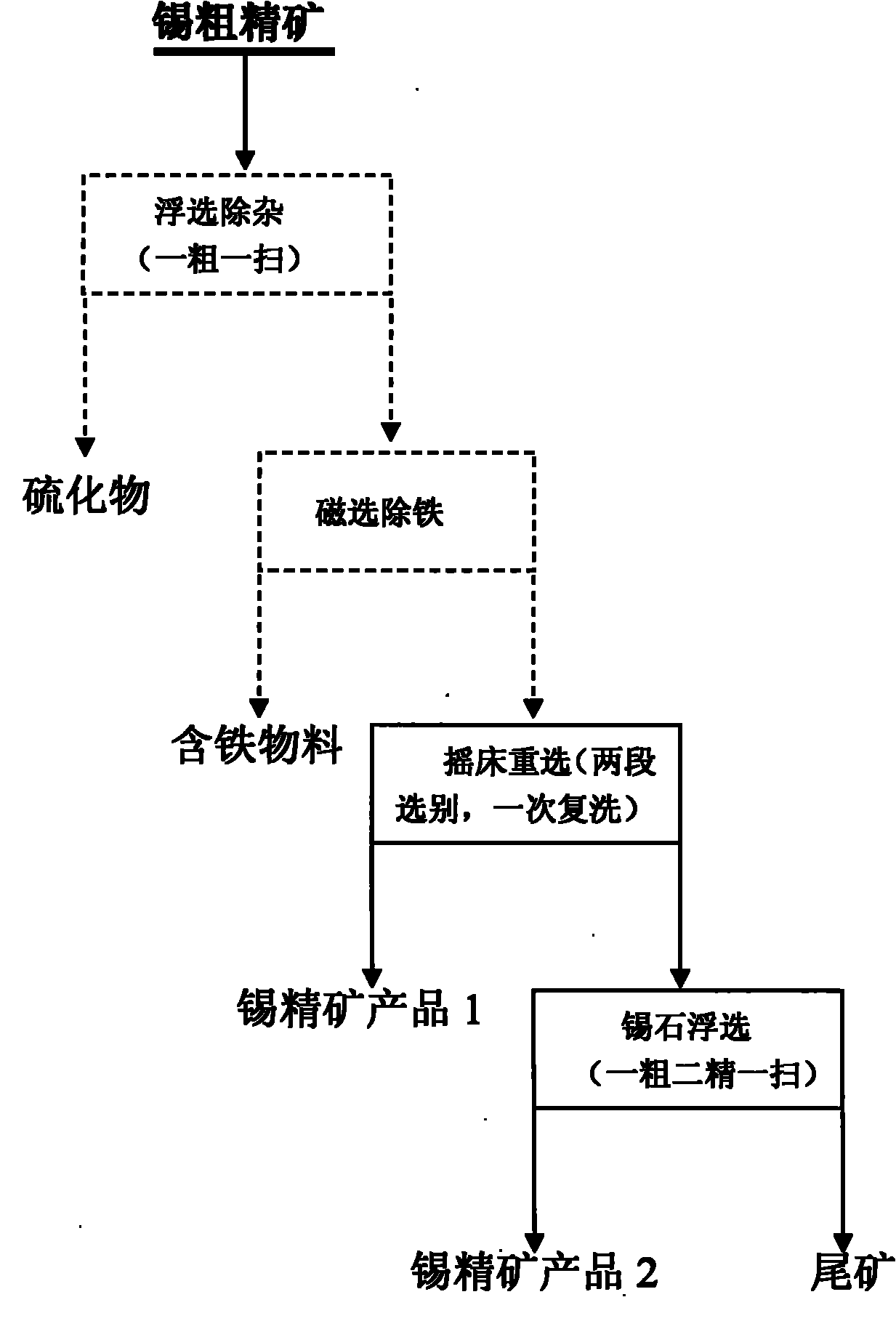
Improved method for cleaning tin rough concentrate
InactiveCN101920222AIncrease profitImprove overall recoveryFlotationWet separationNonferrous metalImproved method
The invention relates to a method for cleaning tin-containing rough concentrate, which belongs to the technical field of nonferrous metal beneficiation and metallurgy. The method comprises the following processing steps of: performing pulp-mixing on the tin-containing rough concentrate, controlling the weight percentage concentration of the pulp to be between 20 and 25 percent and feeding the pulp into a table concentrator to perform gravity concentration so as to obtain a tin concentrate product 1, of which the tin content is between 40 and 45 percent; and grinding gravity tailings, of which the tin content is less than 2 percent, until 60 to 80 percent of ore can pass through a sieve of 400 meshes, performing the pulp-mixing until the weight percentage concentration of the pulp is between 40 and 60 percent and performing flotation to obtain a tin concentrate product 2, of which the tin content is between 30 and 40 percent. The method can obtain a high-grade qualified tin concentrate product and a second-grade tin concentrate product, has the advantage of efficiently recycling tin metal and can be applied to a tin raw ore treatment process as well as the development and utilization of tin pile-up tailings.
Owner:YUNNAN TIN GROUP HLDG
Process for extracting and separating coenzyme Q10 from mushroom dregs
The invention discloses a process for extracting and preparing high-purity coenzyme Q10 from mushroom dregs. The mushroom dregs serve as raw materials to be subjected to percolation extraction, and a coenzyme Q10 percolation extracting solution is obtained; the coenzyme Q10 percolation extracting solution is subjected to multilevel extraction for purification, and raffinate is obtained; the raffinate is subjected to crystallization treatment, finally, the high-purity coenzyme Q10 with the purity reaching 98% or above is obtained, and the yield is 95% or above. The whole process is simple, reliable and easy to operate and achieve, and parameters are convenient to control.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
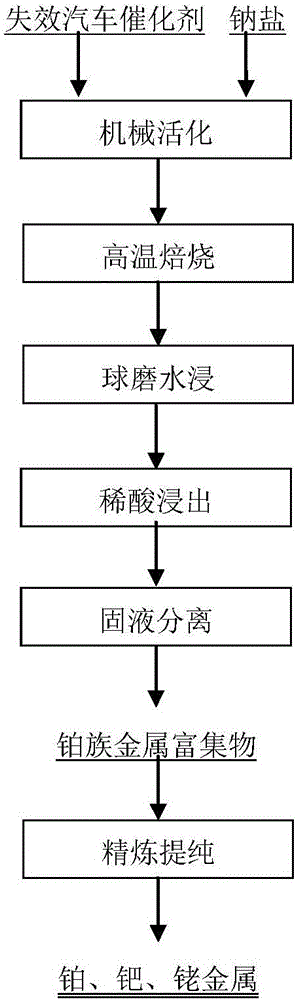
Method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts
ActiveCN106011477AHigh reactivityFully dispersedProcess efficiency improvementWater immersionBiological activation
The invention discloses a method for recycling platinum group metal from ineffective automobile catalysts. The method includes the steps of (1) mechanical activation, (2) high-temperature roasting, (3) ball-milling water immersion, (4) diluted acid leaching and (5) platinum group metal refining. Platinum group metal enriched products obtained in the step (4) are processed according to existing refining processes, so that platinum group metal products are obtained. The ineffective automobile catalysts are processed through the method of combining mechanical activation, sodium salt roasting, water immersion and acid leaching, the reaction activity of materials is improved through mechanical activation, phase transformation of catalyst carrier components occurs due to sodium salt roasting, insoluble residues are enriched with the platinum group metal after water immersion and acid leaching, and separation between carriers and the platinum group metal is achieved. Equipment needed for the method is conventional metallurgical equipment, the technological process is simple, industrial implementation is easy, and the total recovery rate of the platinum group metal is larger than 98%.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF PRECIOUS METALS
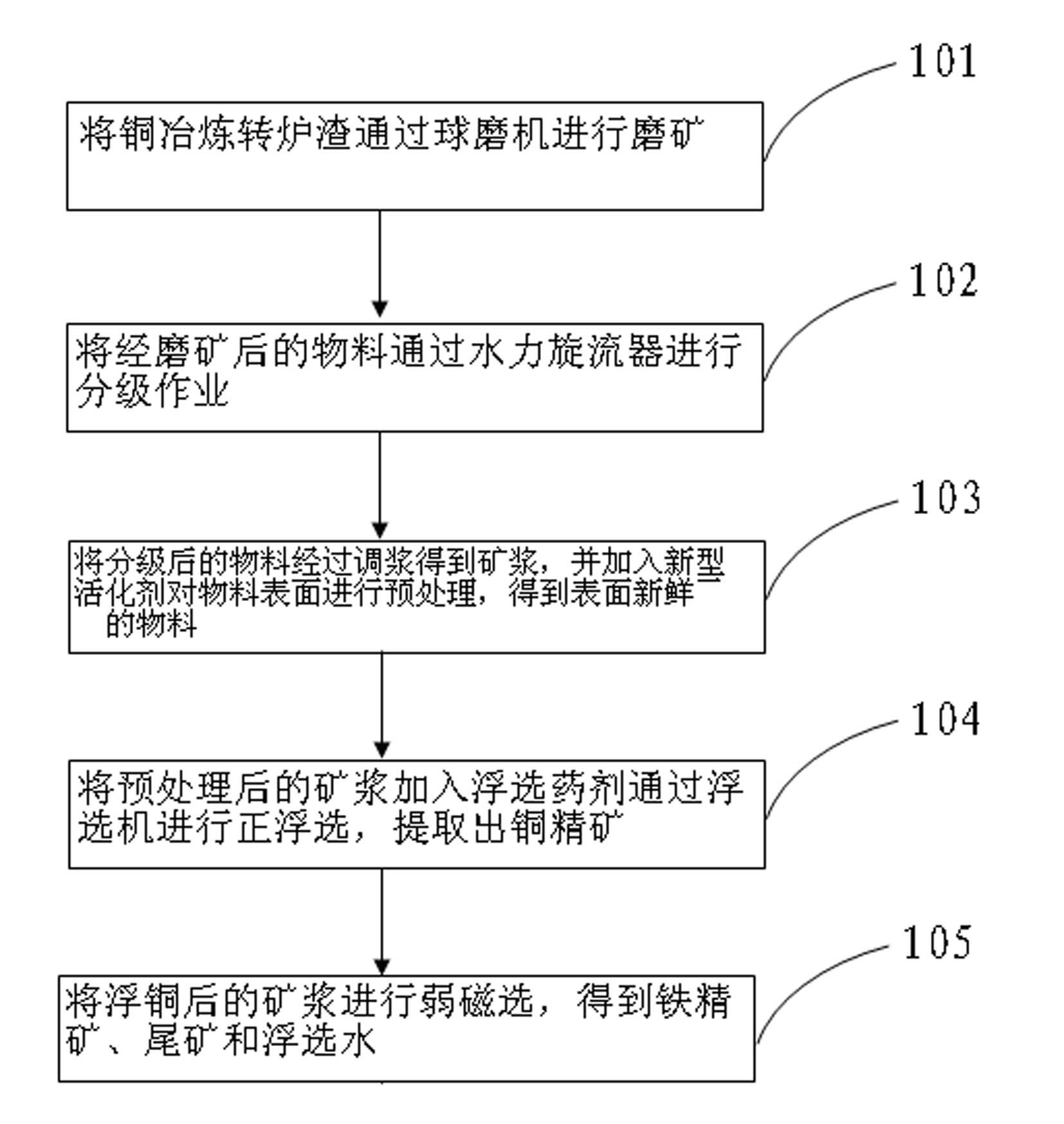
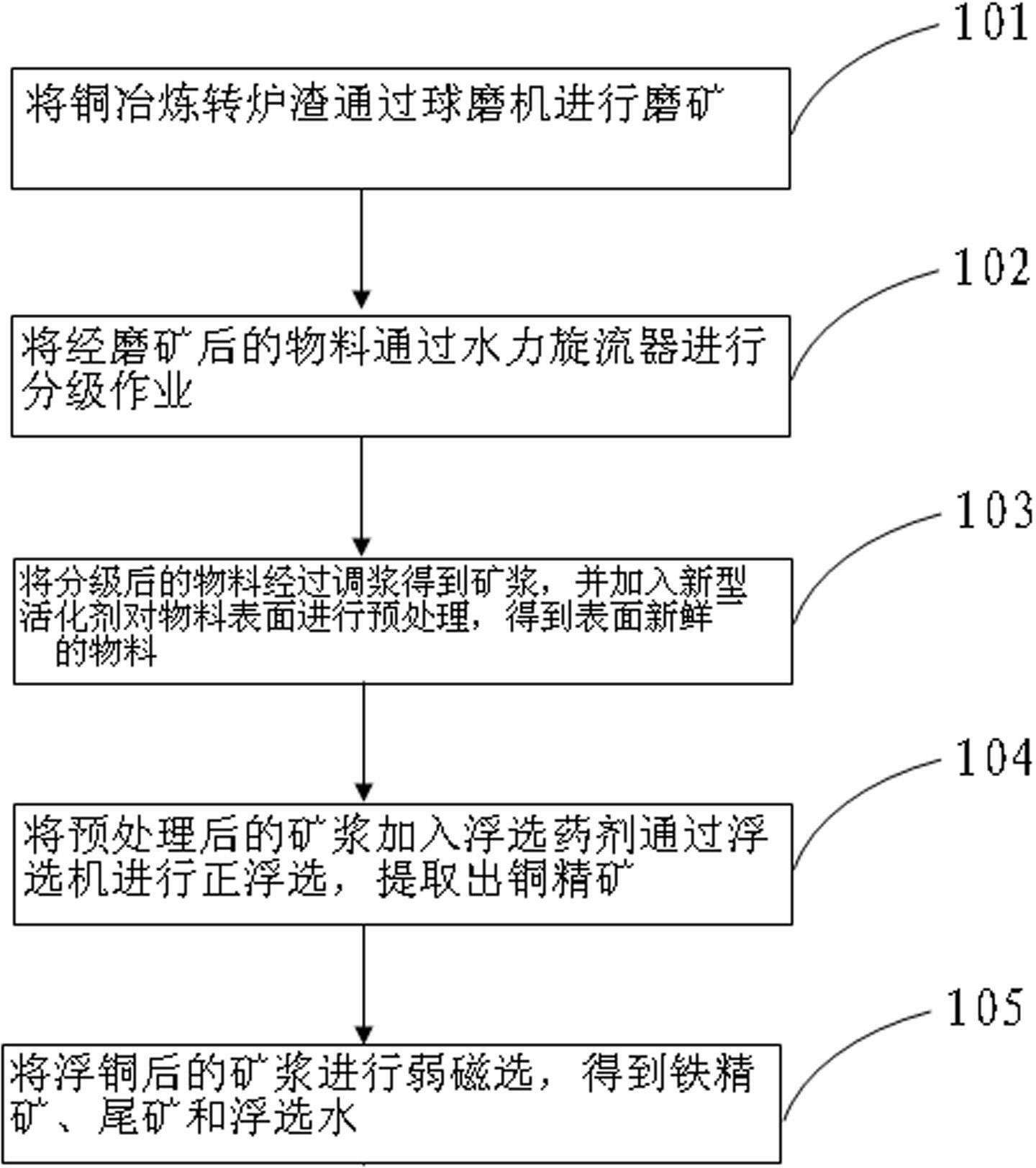
Extracting method for copper in slag of copper smelting converter
The invention relates to an extracting method for copper in slag of a copper smelting converter. The extracting method comprises the following steps of: crushing the slag of the copper smelting converter, and grinding the slag by using a ball mill; classifying grinded materials; subjecting classification-qualified materials to floatation, and adding activating agent for the pretreatment of the materials; and adding floating agent into the pretreated materials, and subjecting the materials to positive floatation by using a flotation machine so as to extract copper concentrate. When the copper extracting method is adopted, recovery rate of copper is increased, high-level copper concentrate is obtained, cost is saved, and content of the copper in tailings is within 0.2%; and moreover the process is simple.
Owner:YANTAI XINHAI MINING MACHINERY
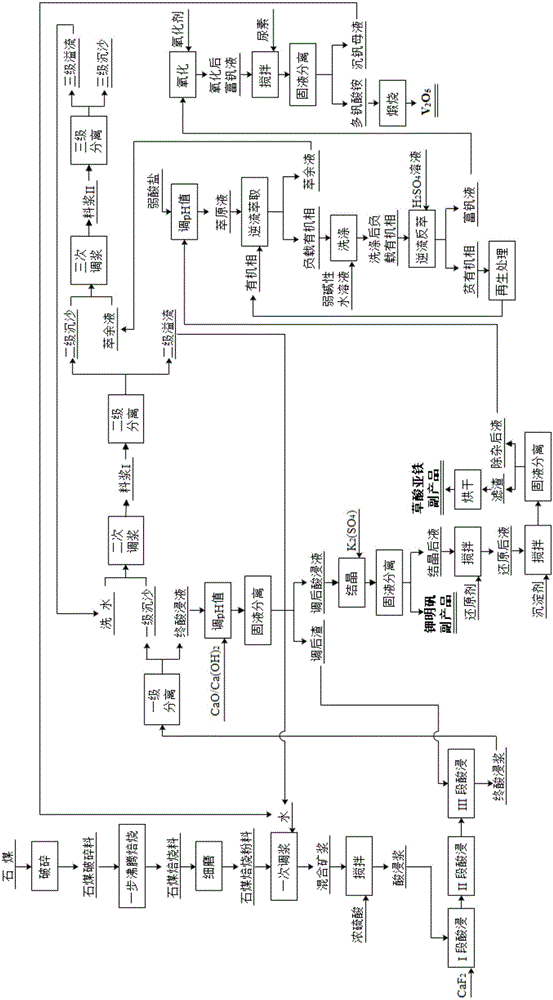
Method for preparing high-purity vanadium pentoxide by use of stone coal one-step method
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity vanadium pentoxide by use of a stone coal one-step method. The technical solution is as follows: a fluidized bed furnace for one-step roasting of stone coal is adopted to perform one-step fluidized bed roasting on the stone coal; roasted materials are leached in three segments, final pickling slurry is subjected to primary separation so as to obtain final pickle liquor, secondary overflow is returned to be subjected to primary size mixing, and tertiary overflow is returned to be subjected to secondary size mixing; the pH value of the final pickle liquor is regulated, and slags obtained after regulation are returned to a segment III so as to be leached; the regulated pickle liquor is crystallized to obtain a potassium alum byproduct; after crystallization, the liquid is subjected to reduction and precipitation-based impurity removal, and filter residues are dried to obtained a ferrous oxalate byproduct; after impurity removal, pH value regulation is performed on the liquid by use of weak acid salt, then counter-current extraction is performed on the liquid, and extraction raffinate is returned to be subjected to tertiary size mixing; after being washed, the loaded organic phase is subjected to countercurrent reverse extraction; a lean organic phase is regenerated and then is returned to be extracted; after a vanadium-rich solution is oxidized, urea is added, stirring is performed, the obtained molybdenum precipitation mother solution is returned to be subjected to primary size mixing, and ammonium polyorthovanadate is calcinated to prepare vanadium pentoxide. The method has the characteristics of short process flow, less pollution, low energy consumption, less chemical usage, high vanadium recovery rate and high product purity.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
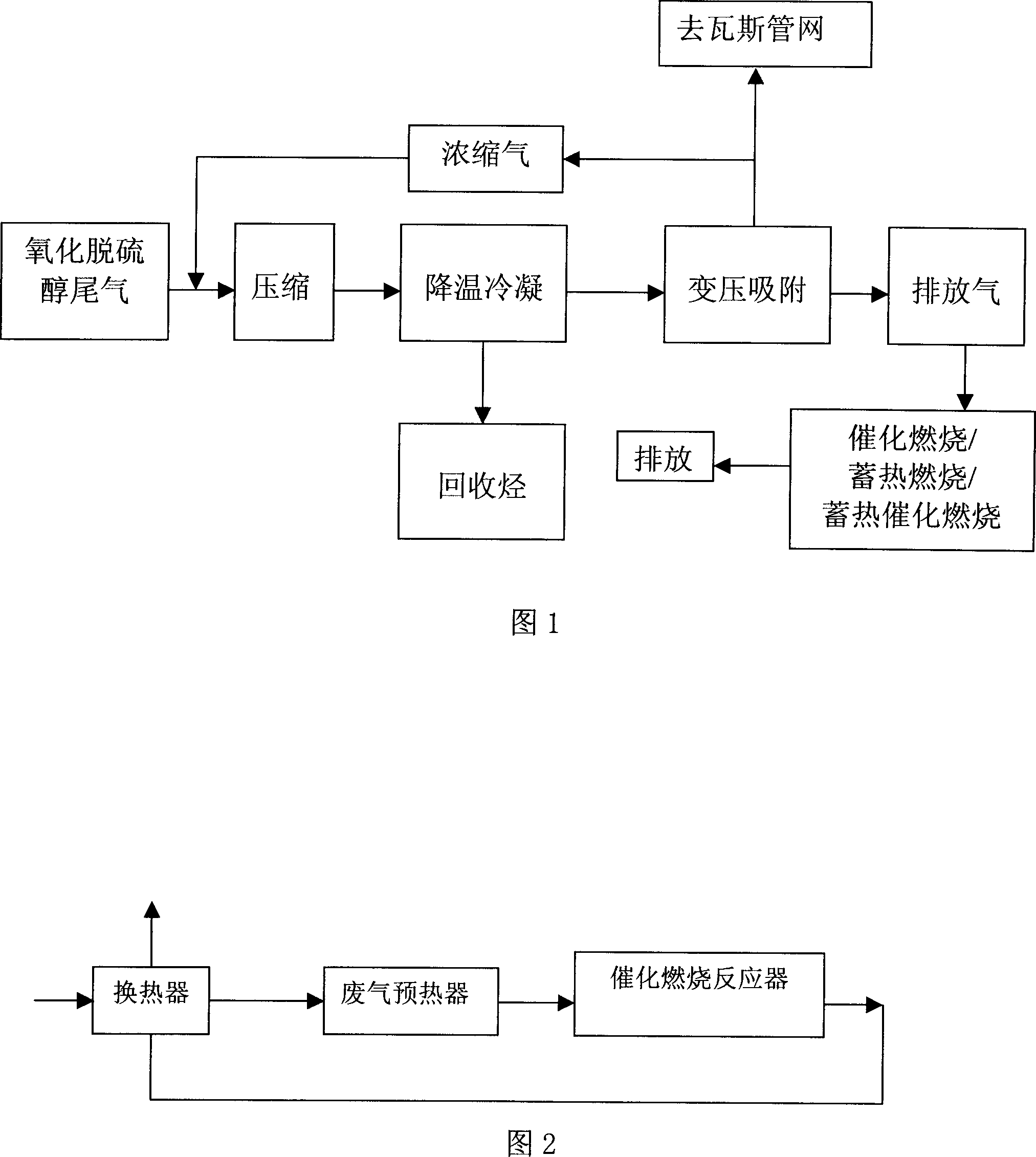
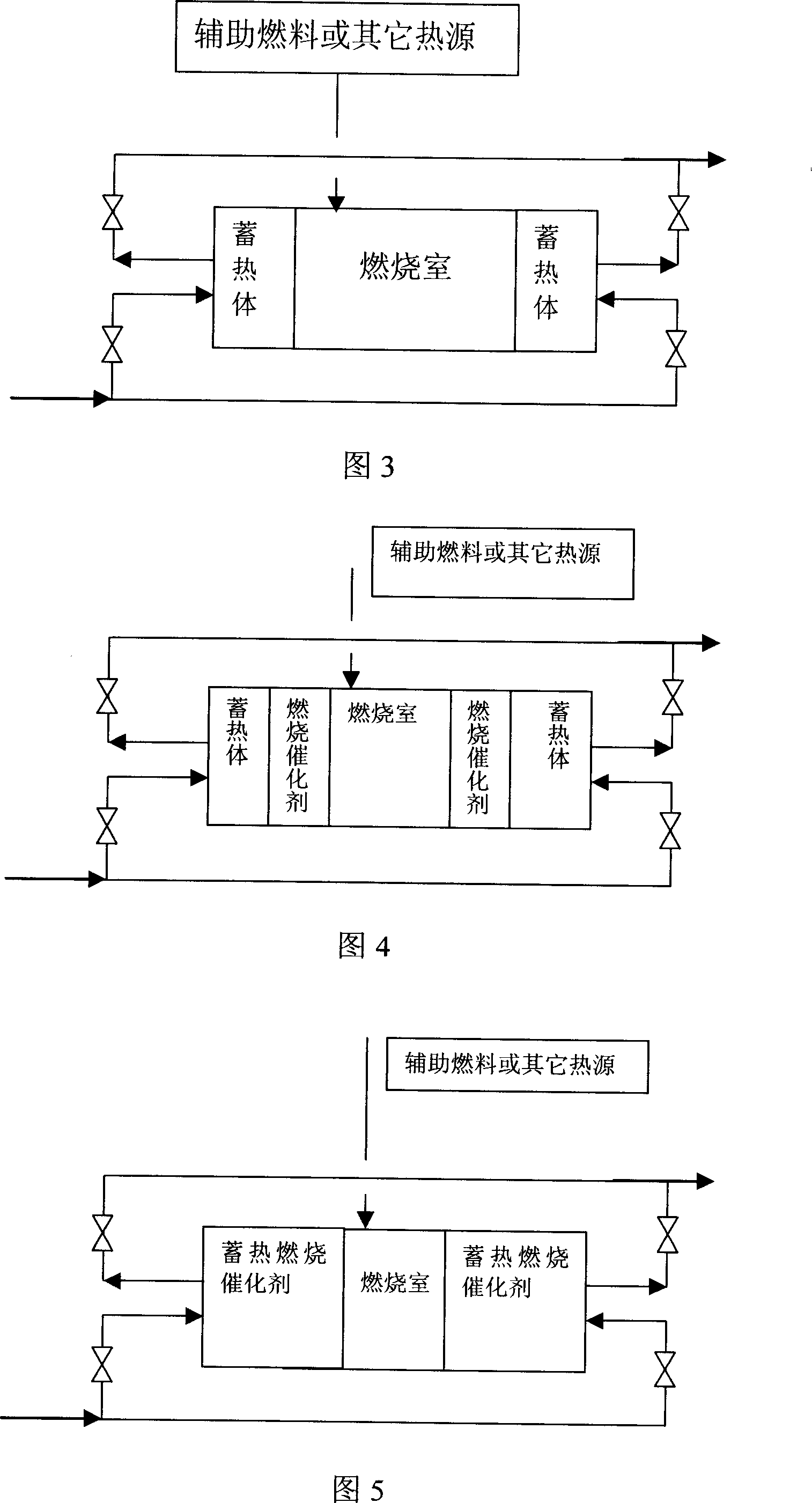
Method for processing light hydrocarbons oxidation sweetening tail gas
ActiveCN1951534AHigh recovery rateRealize adsorption recoveryDispersed particle separationVapor condensationCatalytic combustionLight hydrocarbons
The invention relates to a method for processing the oxidization desulfuration tail gas of hydrocarbons. Wherein, it compresses the tail gas; uses circulate cooling water to reduce the temperature; and recycles the condensed hydrocarbons; the discharge gas is absorbed; the concentrated gas is circulated to the compression and condensation or discharge into gas tube; the discharges gas can be discharged directly or burnt. The invention has high recycle rate and low cost.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
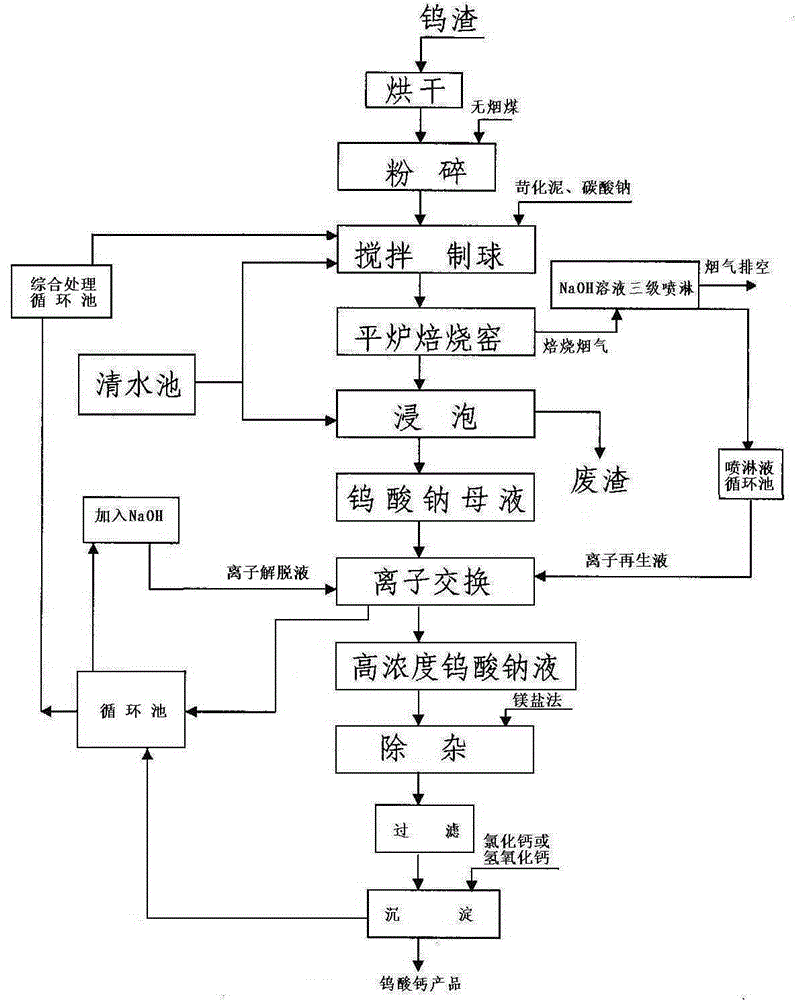
Technology for producing tungsten trioxide by prilling and roasting of tungsten slag
The invention discloses a technology for producing tungsten trioxide by prilling and roasting of tungsten slag. The technology is characterized by comprising the following steps of: (1) baking tungsten slag and then adding blind coal, mixing and crushing the tungsten slag and the blind coal, and then adding lime mud, sodium carbonate and water, priling in a priling disc to prepare the mixed tungsten slag balls; (2) putting the mixed tungsten slag balls into an open hearth kiln to carry out semi-enclosed insulated roasting so as to obtain a tungsten slag clinker; (3) soaking the tungsten slag clinker, and carrying out ion exchange to obtain high-concentration sodium tungstate mother liquor; (4) removing the impurity of the high-concentration sodium tungstate mother liquor, and then filtering, precipitating, leaching the sediment, dewatering and baking the sediment to obtain a calcium tungstate product. The tungsten slag, the blind coal, the lime mud and recycling wastewater are adopted as roasting agents to replace soda ash and burning acid with high price and large consumption for the traditional technology-wet firing method, so that the tungsten production cost of each metal ton is reduced by***, and the transformation rate of WO3 is improved by 25%; the chronic diseases of sodium-process rotary kiln roasting and caking shovel kiln stop production are successfully solved, and about 50% of energy consumption is saved on the traditional technology and wet firing production.
Owner:陈检辉
Method for recycling associated rhenium resources from sandstone-type uranium deposit in-situ leaching uranium exploration process adsorption tail liquid
ActiveCN106148737AReduce consumptionImprove overall recoveryProcess efficiency improvementRheniumIon-exchange resin
The invention discloses a method for recycling associated rhenium resources from sandstone-type uranium deposit in-situ leaching uranium exploration process lean resin. Sandstone-type uranium deposits are added into a sulfuric acid solution containing an oxidizing agent. After vibration soaking is carried out for a period at a certain temperature, anion exchange resin is used for adsorbing uranium and rhenium in leachate. After the resin is saturated, an ammonium nitrate solution is used for desorbing the uranium in the resin. The lean resin returns to the adsorption process after transforming. The desorbed uranium concentrated solution is precipitated by adopting sodium hydroxide, the rhenium in the resin is desorbed, the concentrated ammonium rhenate solution is obtained, and ammonium rhenate products are obtained after recrystallization. The method is simple in process and capable of realizing large-scale production easily. The products are high in purity, the overall recovery rate of the rhenium in the leachate reaches 80% or above, reagents used in the process are environmentally friendly, and remarkable social benefits and economical benefits are achieved.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF TECH
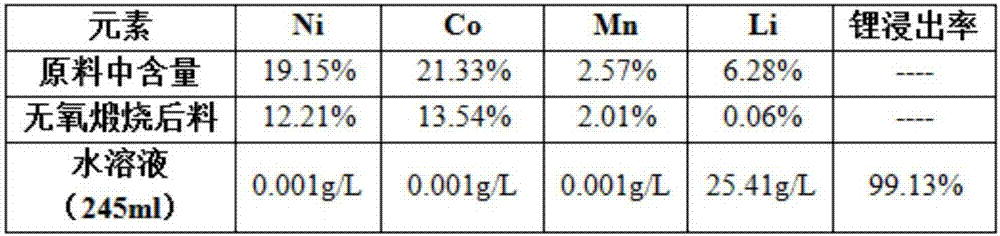
Method for recovering lithium from waste lithium batteries
InactiveCN107221724AImprove overall recoveryEasy to separateWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingManganeseEconomic benefits
The invention discloses a method for recovering lithium from waste lithium batteries. The method comprises the following steps: subjecting the positive electrode materials of waste lithium batteries and a sulfuration agent, carrying out calcining and then carrying out solid-liquid separation so as to separate a lithium-containing aqueous solution. According to the invention, the sulfuration-calcining method is employed for recovery of the lithium-containing aqueous solution; in the lithium-containing aqueous solution having undergone filtering once, the concentration of lithium is 15 g / L or above; the total recovery rate of lithium is as high as 97.43% or above; and good separation effect on lithium and nickel-cobalt-manganese is obtained. The method provided by the invention is applicable to comprehensive recovery of waste batteries, suitable for large-scale production and free of environmental pollution, and produces considerable economic benefits.
Owner:HUNAN BRUNP RECYCLING TECH +1
Process for 1,3-butadiene separation from crude C4 stream with acetylene converter
ActiveCN101821361AReduce accumulation timeReduce logistics lossDistillation purification/separationTreatment with hydrotreatment processesVinylacetyleneButene
Disclosed is a method of recovering 1,3 -butadiene from a C4 stream containing butane, isobutane, 2-butene, 1-butene, isobutene, butadiene and acetylene. The process of recovering highly pure 1,3 -butadiene includes acetylene conversion for selectively converting acetylene through liquid-phase hydrogenation, so that the acetylene content is decreased to 70 wt ppm or less, and 1,3 -butadiene extraction using an extractive distillation column, a pre-separator, a solvent stripping column, a solvent recovery column, and a purification column. Through the acetylene conversion, the concentration of vinylacetylene is decreased to 70 wt ppm or less, after which 1,3-butadiene is recovered using only one extractive distillation column, thereby considerably decreasing the degree of utility and the loss of streams in the course of extraction. The number of units necessary for the process is decreased, thus remarkably reducing the time during which impurities can accumulate in a processing unit.
Owner:SK INNOVATION CO LTD
Process for recovering distillation waste liquid generated by producing 1,4-butanediol
InactiveCN103274898AHigh recovery rateImprove overall recoveryOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationDistillationButanediol
The invention relates to a process for recovering distillation waste liquid generated by producing 1,4-butanediol and belongs to the technical field of recycling of organic waste liquid in the industrial production. According to the invention, the distillation waste liquid generated in the process of producing 1,4-butanediol by a Reppe method is used as a raw material; drained wastewater is used as an extracting agent; sodium sulfate is used as a salting-out agent; sulfuric acid is used as a catalyst for depolymerizing reaction; and by a circulating process of salting-out-extraction, reduced pressure batch distillation separation and depolymerizing reaction, various products in the distillation waste liquid, such as 1,4-butanediol, butanol and 3-tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol are recovered. The process disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that various products can be recovered, the recovery rate of the products is high and the recovery economic benefits are good; the process sufficiently utilizes waste liquid resources and is beneficial to environment protection; the process is simple, reaction conditions are mild, equipment is conventional and recovery cost is low; and the process has a wide application range and is convenient to popularize and apply. The process can be widely applied to recycling of the organic waste liquid in the industrial production and is particularly suitable for recycling the waste liquid generated in the process of producing 1,4-butanediol by the Reppe method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
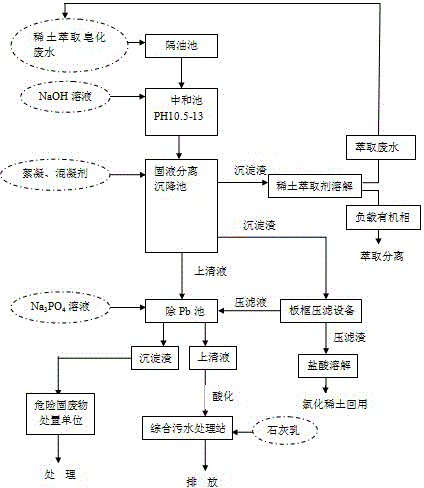
Technology of removing lead and recycling rare earth from saponified wastewater generated during process of rare earth extraction
ActiveCN105087964AEfficient removalAchieve recyclingProcess efficiency improvementFiltrationLead phosphate
The invention discloses a technology of removing lead and recycling rare earth from saponified wastewater generated during the process of rare earth extraction. The technology comprises the following steps: (a) making saponified wastewater which is generated during the process of rare earth extraction go through an oil separation tank to remove the oil; (b) adding a NaOH solution, adjusting the pH to 10.5-13, and separating the solid and the liquid to obtain a supernate containing lead and rare earth precipitate; (c) subjecting the precipitate to plate-frame pressure filtration to obtain press filtrate and pressure-filtered residues; or dissolving the rare earth precipitate by hydrochloric acid or an acidic extractant to obtain a chlorinated rare earth solution, and the extracting rare earth from the chlorinated rare earth solution; (d) adding a Na3PO4 solution into the supernate and / or the press filtrate to obtain lead phosphate precipitate and supernate, wherein the content of total Pb in the supernate is not more than 0.2 mg / L; (e) press-filtering the precipitate, stacking the precipitate together, handing over the precipitate to factories, which has the qualification to process the dangerous solid wastes; acidifying the supernate, adding lime milk to remove the excess PO4<3->, then discharging the wastewater, wherein the content of total Pb in saponified wastewater is not more than 0.2 mg / L, the discharged wastewater can meet the requirements of Pollutant Discharge Standards Of Rare Earth Industry, and at the same time, the rare earth in the wastewater is effectively recycled.
Owner:GUANGDONG ZHUJIANG RARE EARTHS
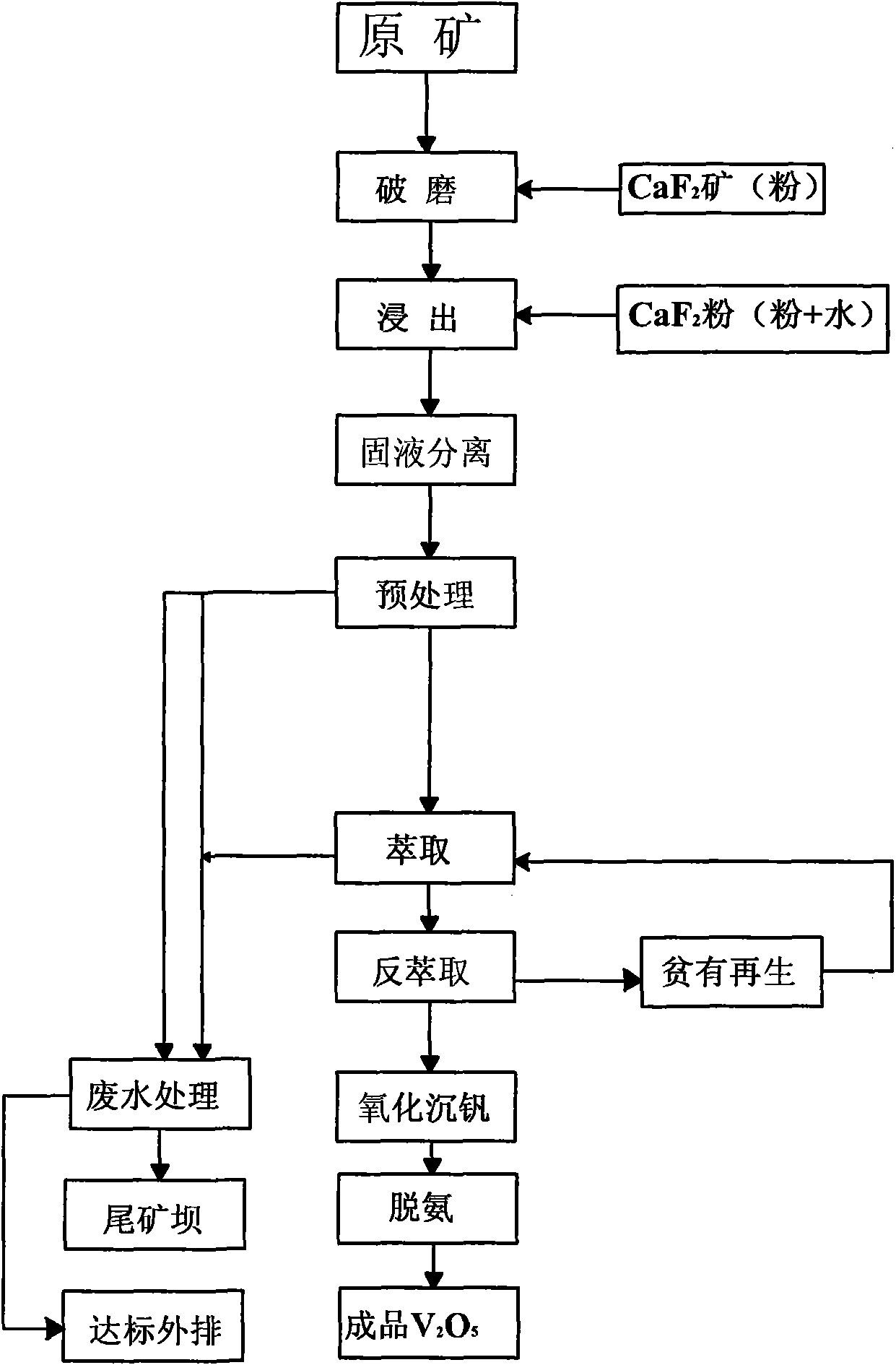
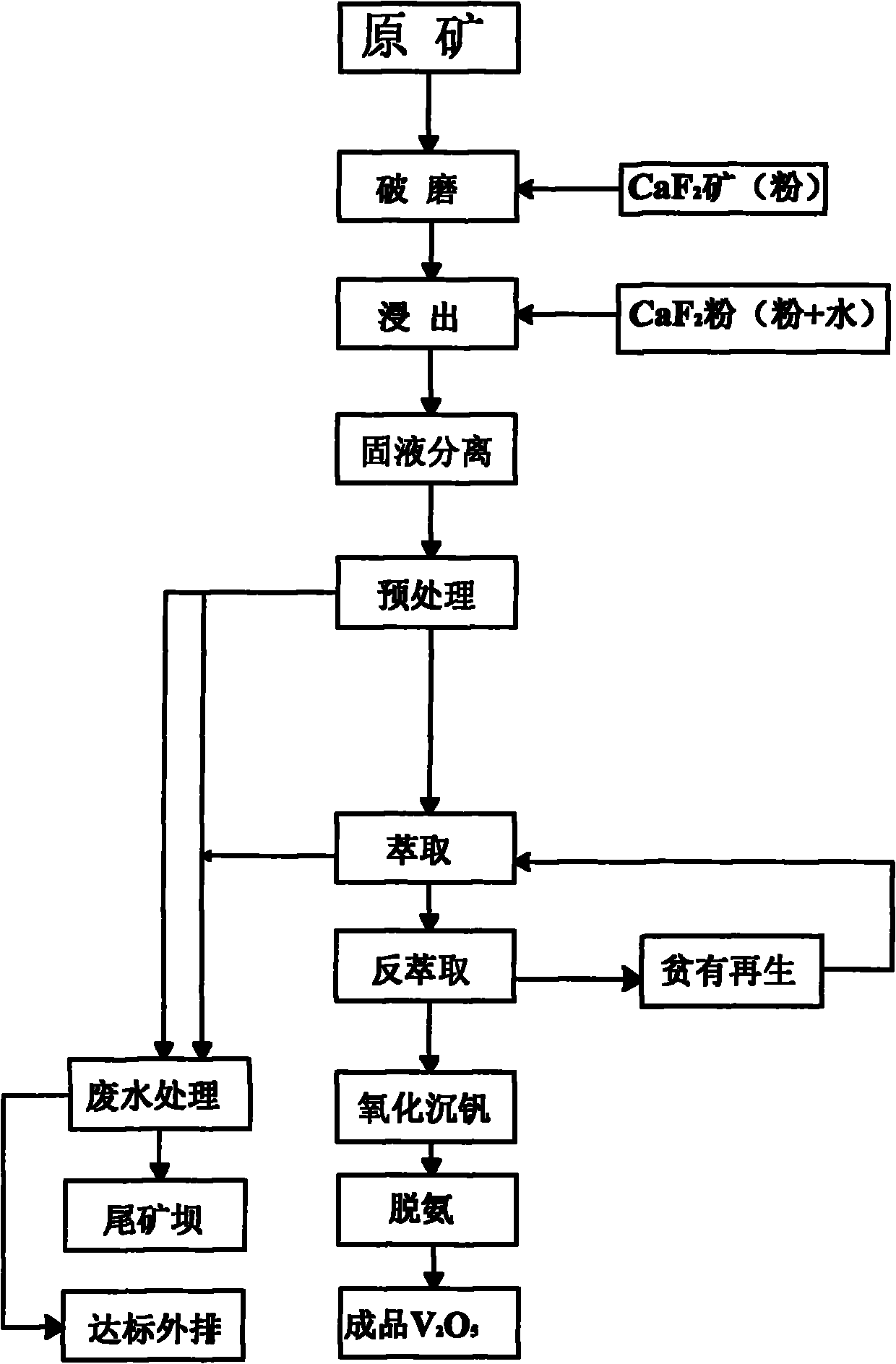
Process for extracting vanadium from stone coal by acid method by using leaching agent
InactiveCN101845560AImprove overall recoveryOvercome the disadvantage of low recovery rateProcess efficiency improvementGrain treatmentsCoalLeaching rate
The invention discloses a process for extracting vanadium from stone coal by an acid method by using a leaching agent. The process comprises the following steps of: rude ore crushing, acid leaching, liquid-solid separation, solution pretreatment, extraction and back-extraction, oxidization of the vanadium precipitation, and red vanadium deamination, wherein a CaF2-containing leaching agent is added in the step of rude ore crushing or / and acid leaching and pulping; and the weight ratio of rude ore to CaF2 is 100:1-8. Due to the adoption of the process, the technical problem that the leaching rate of vanadium-containing stone coal is low is solved; the leaching rate is high; specific yield is improved; and unit cost is saved.
Owner:SHANYANG YINHUA MINING
Molybdate additive and polycrystalline silicon or monocrystalline silicon cutting fluid containing same
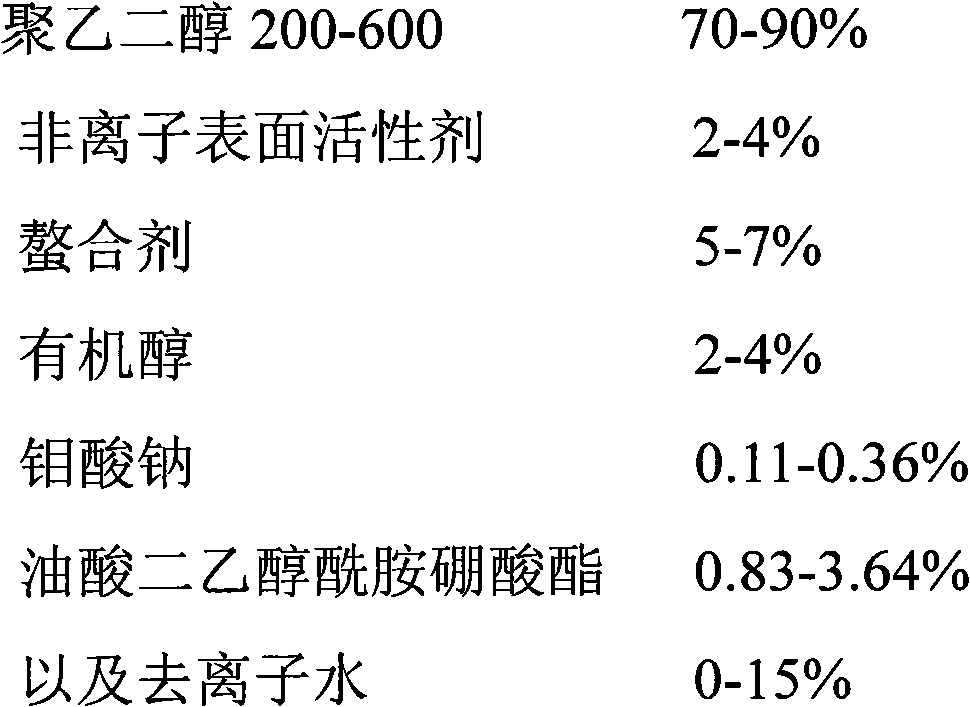
ActiveCN102041137AExcellent technical performanceImprove cutting effectAdditivesPolyethylene glycolLubrication
The invention discloses a molybdate additive, which is a mixture of sodium molybdate and oleic diethanolamide borate ester according to a mass ratio of 1:5-1:20. The invention also discloses polycrystalline silicon or monocrystalline silicon cutting fluid, which comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 30 to 90 percent of polyethylene glycol 100-1000, 0.5 to 5 percent of nonionic surfactant, 1 to 10 percent of chelant, 0.5 to 5 percent of organic alcohol, 1 to 5 percent of molybdate additive and 0 to 67 percent of deionized water. The cutting fluid overcomes the defects of complicated preparation process, high cost, environmental pollution and the like of the conventional polycrystalline (monocrystalline) silicon cutting fluid, has excellent technical characteristics, high repeatability and stable quality, can shorten disorderly closedown time, effectively solves the problem of redeposit of cuttings and abrasive powder, integrates penetration, lubrication, cooling, cleaning and antirust performance, and is nontoxic and harmless, low in cost and high in total yield.
Owner:SHANGHAI EMPEROR OF CLEANING HI TECH
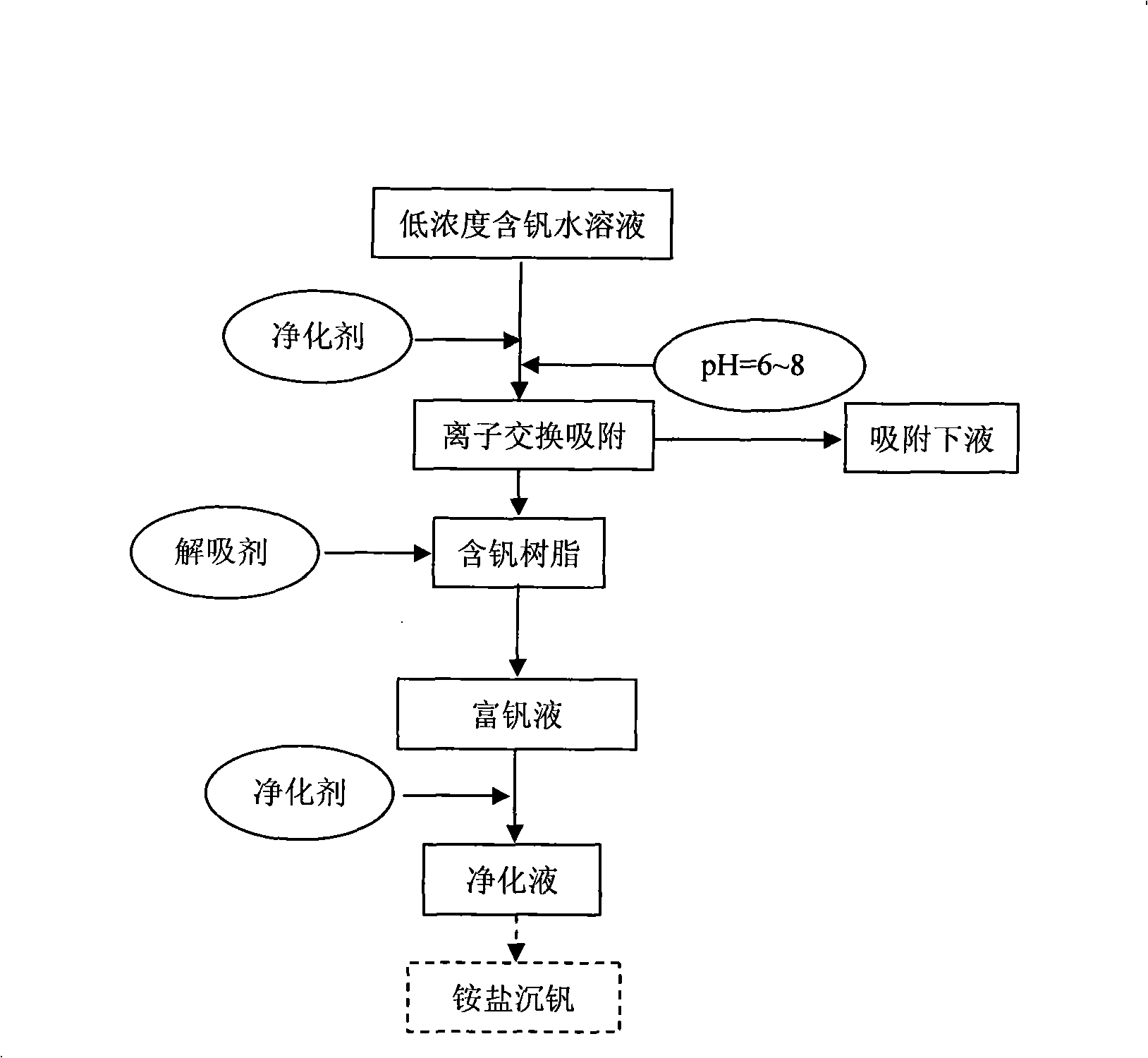
Method for purifying and enriching low-concentration vanadium-containing water solution
InactiveCN101260467ASimple purification processReduce dosageProcess efficiency improvementDesorptionIon exchange
The invention relates to a method for purifying and enriching a low concentration water solution with vanadium content. The technical proposal is as follows: a purifying agent with the concentration ranging from 0.6 to 10g / L is added into the low concentration water solution containing vanadium with the concentration of V2O5 of ranging from 2000 to 5000mg / L, the mixture is mixed evenly with a pH value ranging from 6 to 8; the low concentration water solution containing vanadium performs the ion exchange adsorption through the strongly basic anion ion exchange resin at a speed of 2.0 to 10mLh<-1>mL<-1> wet resin to the adsorption and saturation of the strongly basic anion ion exchange resin to obtain the resin containing vanadium and the adsorption under liquid; and then the mixing solution of 3 to 5wt percent of sodium hydroxide and 8 to 13wt percent of sodium chloride is prepared to be as a strippant, the use level of the strippant is three to five times of the volume of the resin containing vanadium, the strippant performs the desorption through the resin containing vanadium at a speed of 0.8 to 1.6 mLh<-1>mL<-1> wet resin to obtain the vanadium enriching fluid; finally, the purifying agent with the concentration ranging from 0.1 to 2.5g / L is added into the vanadium enriching fluid, the purified fluid is obtained after the solid-fluid separation. The method has the characteristics that the purifying time is shortened, the purifying agent consumption is reduced, the vanadium loss is reduced, the purifying effect is good and the technique is simple.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of battery-grade lithium carbonate
InactiveCN108285158AImprove overall recoveryFulfil requirementsLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium carbonateSulfate
The invention provides a preparation method of battery-grade lithium carbonate. The preparation method comprises the steps: roasting lithionite, sodium sulfate and limestone by using a sulfate method,evaporating and concentrating a leachate, adding sodium carbonate, carrying out primary lithium sedimentation, and then, carrying out cooling to separate out sodium; and then, carrying out secondarylithium sedimentation. After a purified liquid is subjected to the primary lithium sedimentation and the secondary lithium sedimentation, the total recovery rate of lithium is high, and the requirement of battery-grade lithium carbonate is met. The method provided by the invention is capable of not only increasing the lithium sedimentation efficiency, but also reducing the loss of lithium in a sodium separation process during lithium sedimentation and sodium separation, simple in operation and high in safety.
Owner:SHANDONG LUBEI ENTERPRISE GROUP
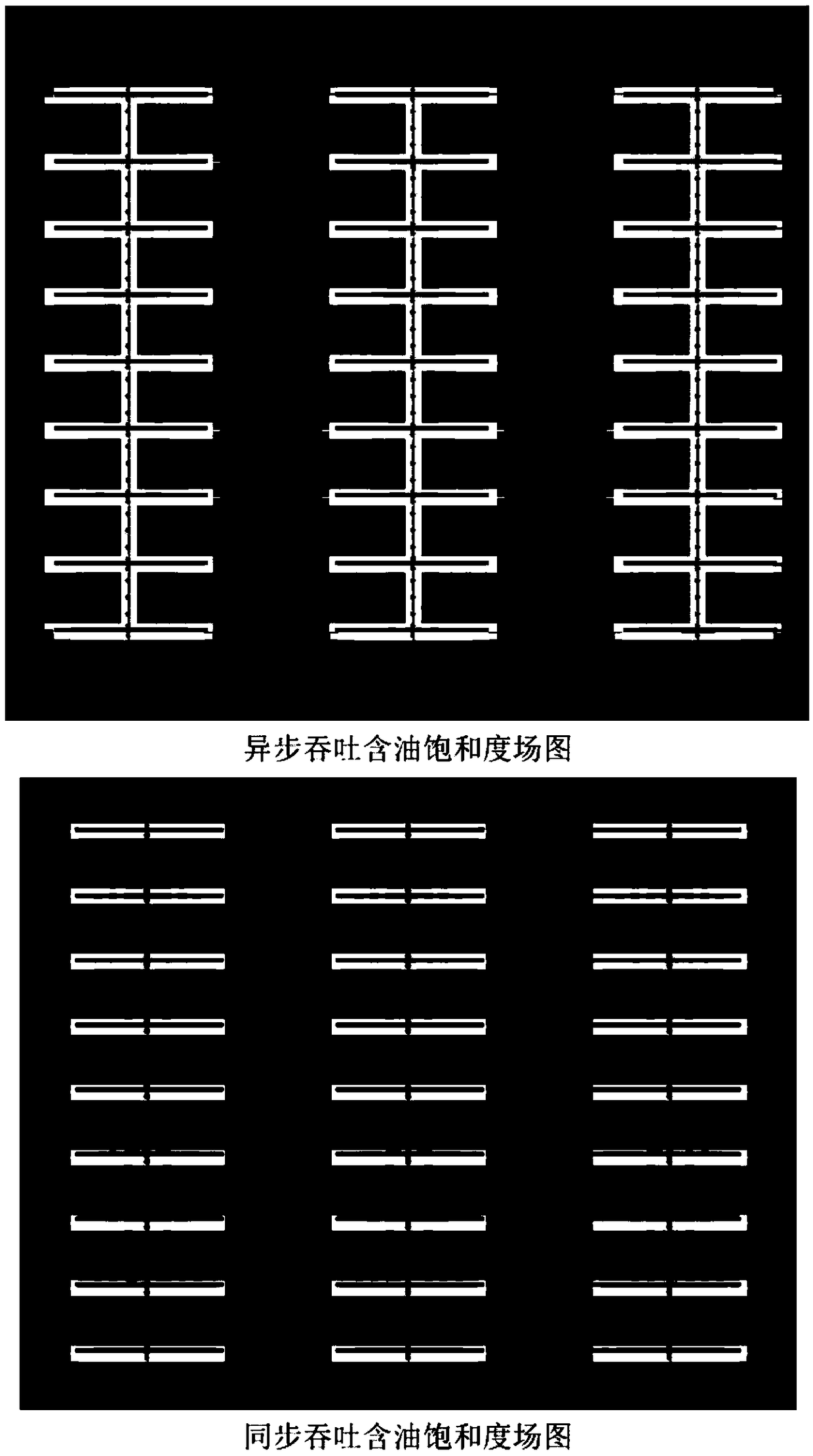
CO2-injection asynchronous-throughput energy supplement method of ultralow-permeability compact oil reservoir horizontal wells
The invention provides a CO2-injection asynchronous-throughput energy supplement method of ultralow-permeability compact oil reservoir horizontal wells. The method comprises that a horizontal well rowis arranged along the direction of the maximal principle stress, at least one local well and two adjacent wells are laid, and the reservoir stratum reconstruction by fracturing is carried out on thehorizontal wells; and a scheme that throughput of one well is asynchronous with that of the adjacent well but synchronous with that of the other well adjacent to the adjacent well is used, and the whole throughput period includes gas injection, soaking and oil extraction. CO2 can reduce the tension in a crude oil interface, the volume of crude oil is expanded, the density and viscosity of the crude oil are reduced, light components in the crude oil are extracted, and the permeability of regions near the wells are improved; stratum energy is supplemented, the problems that water injection exploitation of an unconventional stratum is low in spreading efficiency, easy to water channeling and hard to improve the final recovery efficiency are solved, and high and stable yield of an oil field isensured; and the asynchronous throughput method can alleviate the gas bypassing phenomenon of the local well, gas bypassing characteristic of the adjacent wells is used for displacement, and the total recovery degree is imporved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
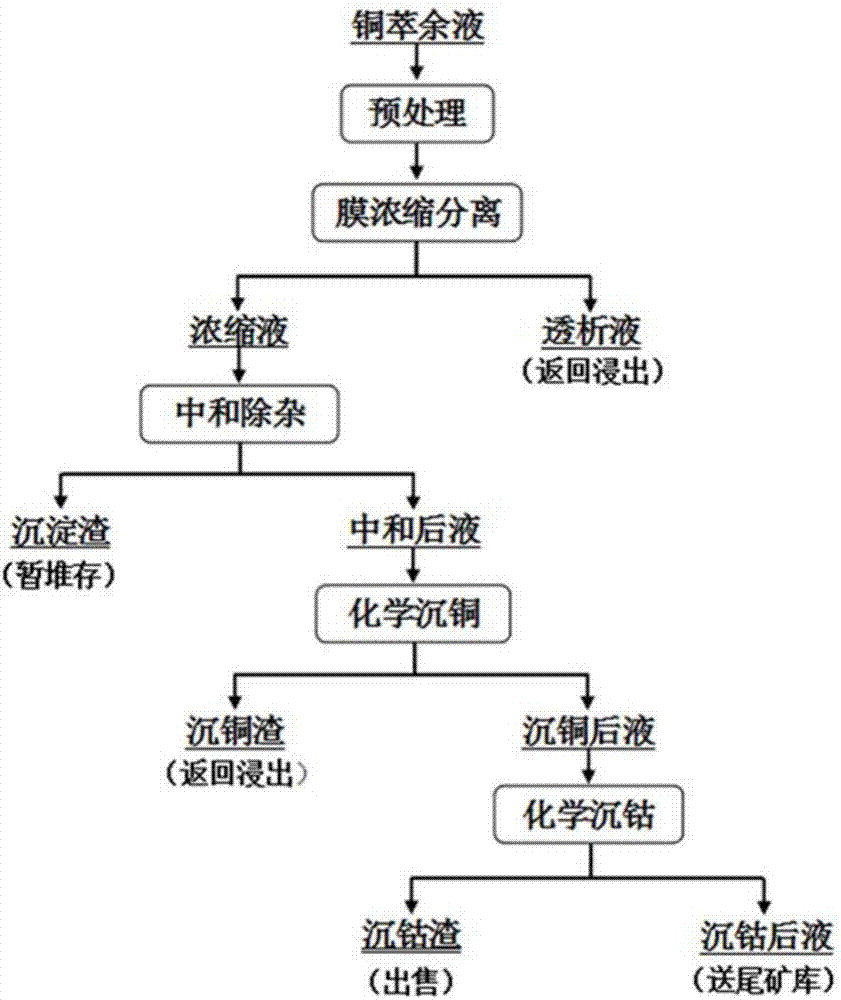
Method for recovering copper and cobalt in copper raffinate by adopting nanofiltration membrane concentration separation-neutralization and sedimentation
ActiveCN107460315AGood effectReduce waste water dischargeProcess efficiency improvementChemistryNanofiltration
The invention belongs to the technical field of wet metallurgy, particularly relates to a method for comprehensively recovering useful resources from a copper raffinate, and especially relates to a method for recovering copper, cobalt and sulfuric acid in the low-cobalt copper raffinate by adopting a nanofiltration membrane concentration separation-neutralization and sedimentation technology. Concretely, the nanofiltration membrane concentration separation technology is adopted for preventing copper, cobalt, iron, calcium, aluminum, arsenic and magnesium in the copper raffinate from entering a concentrated solution, the concentrated solution is treated by chemical precipitation so as to recover valuable metal cobalt and copper, and meanwhile, iron, aluminum, arsenic, calcium and magnesium impurities in the raffinate are open-circuit removed; and a dialysate (a sulfuric acid solution) returns to a leaching system of a copper hydrometallurgy process, so that the aims of recycling the useful resources in the raffinate, purifying and removing impurities are achieved, and meanwhile, the quality requirements of leaching and electrodeposition processes on the solution during copper hydrometallurgy production are met.
Owner:中国有色集团刚果矿业有限公司 +3
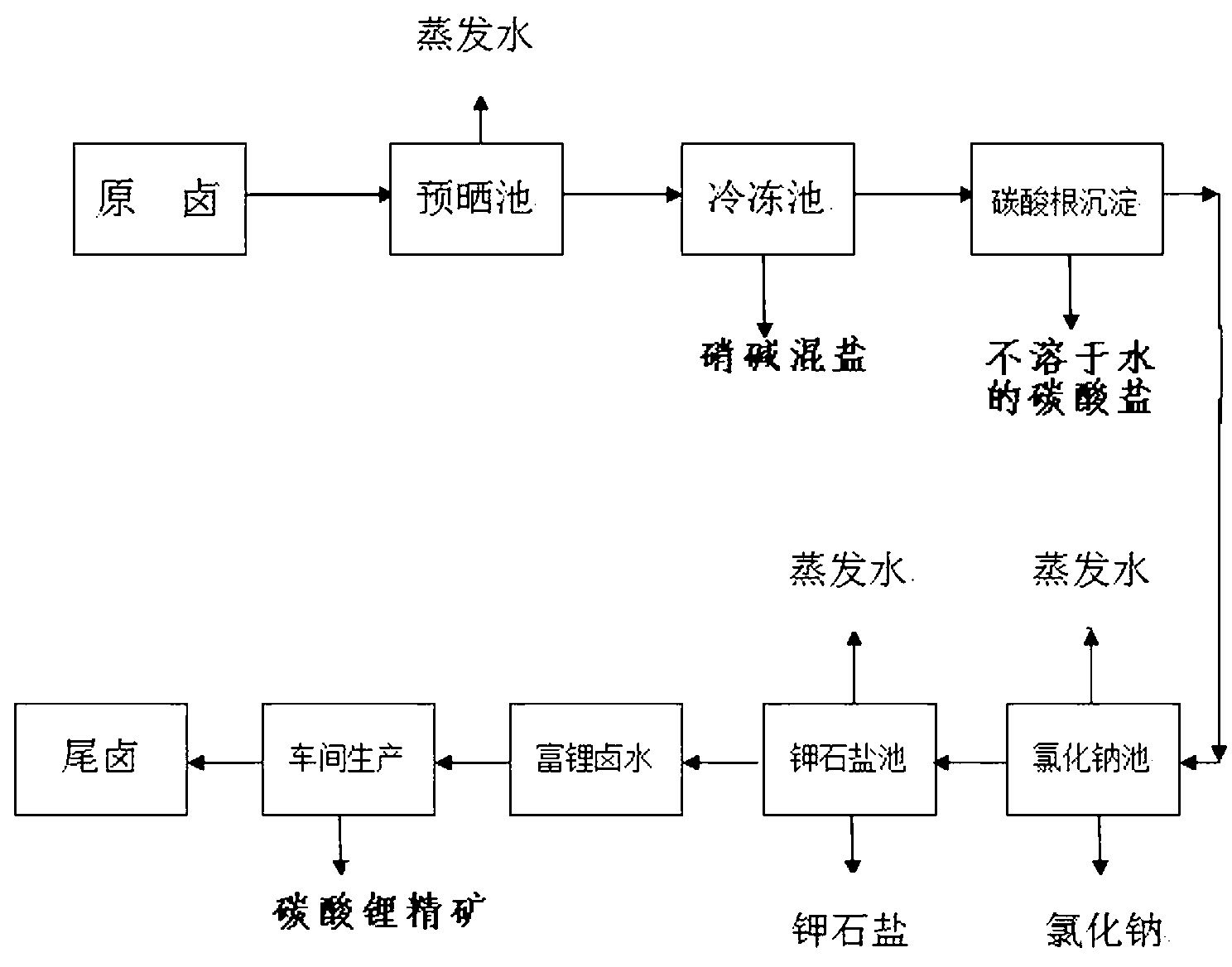
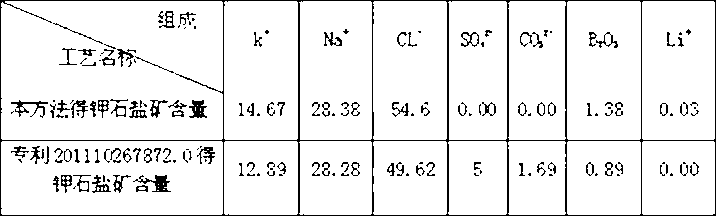
Method for separating carbonate from carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium to prepare sylvinite ore and lithium carbonate concentrate
InactiveCN103058232AEfficient use ofPrevent precipitationAlkali metal chloridesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesSylviniteLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a method for separating carbonate from carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium to prepare sylvinite ore and lithium carbonate concentrate, wherein the carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium is pre-concentrated, the carbonate is separated from the carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium by means of combination of frozen alkaline and a precipitant so as to prepare the concentrated bittern with the content of carbonate reduced, then the concentrated bittern is further concentrated, the sylvinite ore separated out by evaporative crystallization is separately collected and prepared after the content of the potassium ion in the bittern is up to 51.70g / L, the lithium enrichment bittern with the content of the lithium ion being 4-26g / L is prepared, and the lithium enrichment bittern is guided into a crystallizer, added with sodium carbonate, and separated in a centrifugal way to obtain the lithium carbonate concentrate. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the lithium enrichment concentration is increased because the carbonate in the bittern is removed; the purity of the obtained lithium carbonate and the overall recovery of the lithium ion are high; continuous industrialization and automated production of the preparation of the lithium carbonate concentrate can be implemented; high-grade sylvinite can be prepared from a salt pan, and the potassium ion recovery of the salt pan is increased; and the residual bittern of which the lithium is extracted can be comprehensively developed conveniently so as to further extract substances like boron, rubidium, cesium bromine.
Owner:TIBET XUSHENG MINING DEV
Process for extracting and separating nickel-phase form bone coal ore by high pressure oxygen-ammonia leaching
InactiveCN101177735AReduce pollutionImprove the operating environmentProcess efficiency improvementSal ammoniacChemistry
The invention relates to a technology of extracting and separating nickel-molybdenum from coal mines through high-pressure oxygen-ammonia immersion. Original ores are ground into powder and then immersed into hartshorn, and then oxygen is fed to cause reaction pressure to be between 1.5mPa-3.0mPa; after reaction and filtration, obtained base solution after ammonia distilling is dissolved by acid, and then organic phase containing molybdenum and water phase containing nickel acquired through extraction and separation are purified respectively. Compared with the prior art, the technology of the invention greatly reduces the environmental pollution, and improves the comprehensive utilization rate of mineral resources, with high recovery rate of valuable metals and high production purity. A semi-commercial experiment demonstrates that the recovery of the nickel-molybdenum all reaches above 90 percent.
Owner:李锋铎
Clean production process for vanadium oxide
ActiveCN101412539BSolve difficult environmental problemsSolve the technical problem of not being able to obtain high-quality vanadium productsVanadium oxidesProcess efficiency improvementSlagWastewater
The invention relates to a method for cleanly producing vanadium oxide, which belongs to the field of extraction of vanadium oxide. The technical problems to be solved by the invention is to provide the method for cleanly producing the vanadium oxide which not only can obtain a high-quality vanadium product, but also can ensure that vanadium waste water can be reclaimed. The method for producing the vanadium oxide comprises the following steps: preparing roasting raw materials, calcification roasting; infiltrating, separating solid and liquid, precipitating vanadium by ammonium salt, calcining for deaminating or reducing, and the like. Waste water after vanadium extraction can be returned to a system for recycling after the waste waster is subjected to neutralizing treatment by lime creamso as to realize zero drainage of the waste water. The method also improves the reclamation rate of vanadium to be superior to that of the prior process, and reduces production cost. Through combining with other technologies, the method can change extracted slag and other waste into secondary resource to be used once again, and realize clean production.
Owner:攀钢集团西昌钒制品科技有限公司
Method for preparing vanadium-and-iron enriched material by using vanadium enriched steel slags
InactiveCN109913660ASolve pollutionShort processProcess efficiency improvementOrganic acidPregnant leach solution
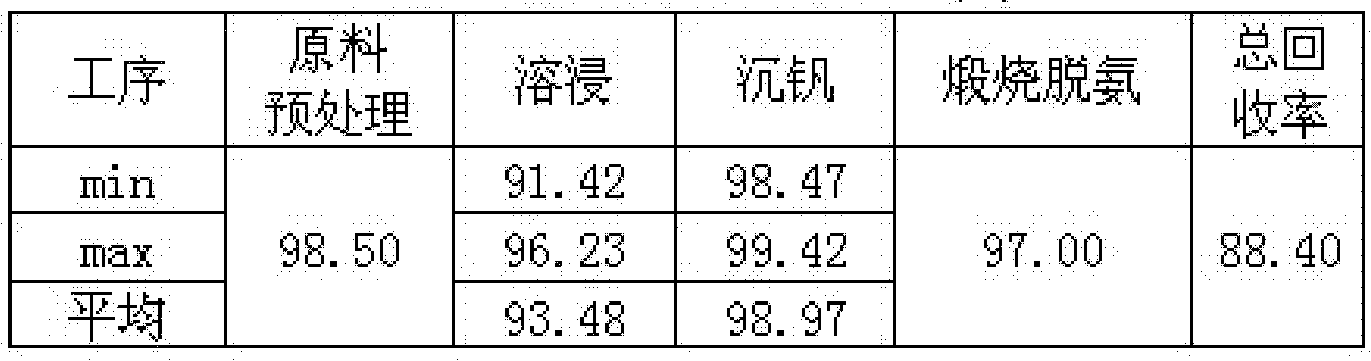
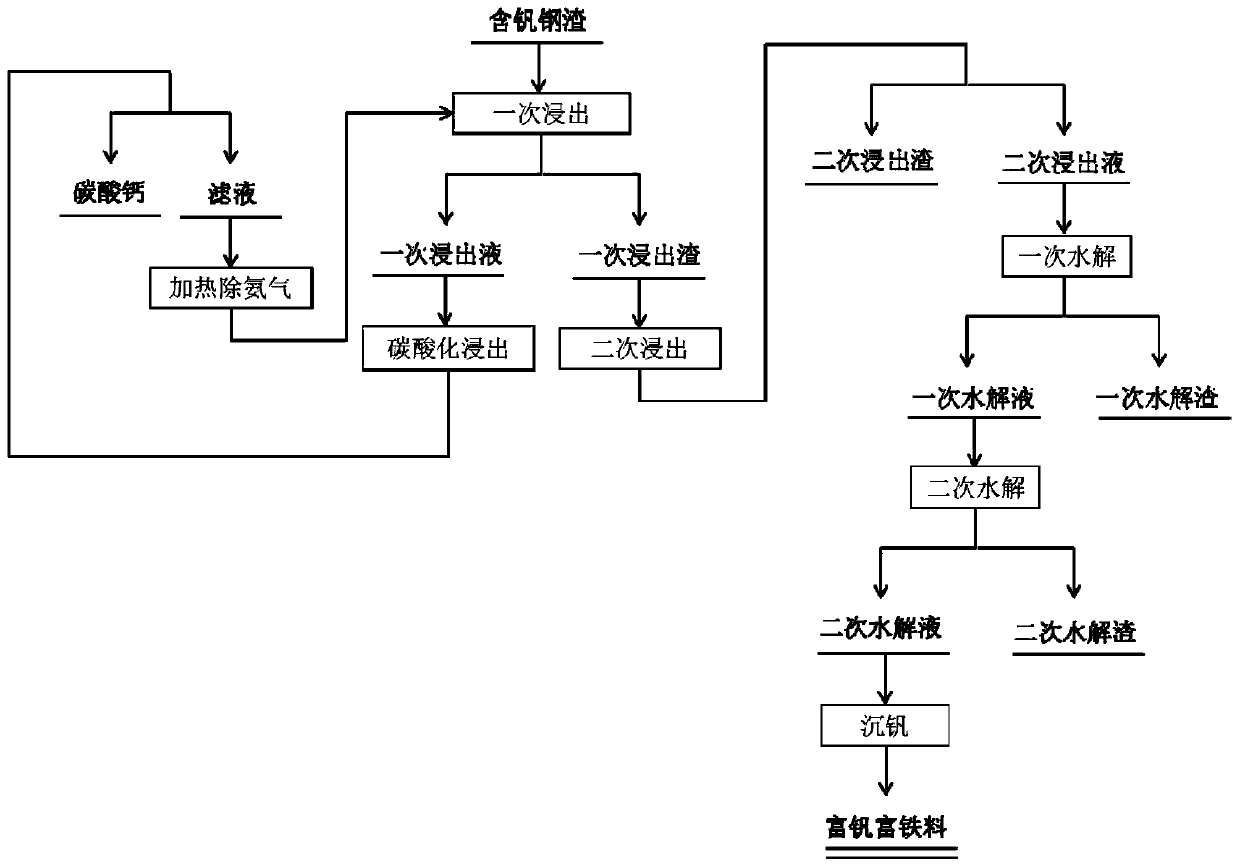
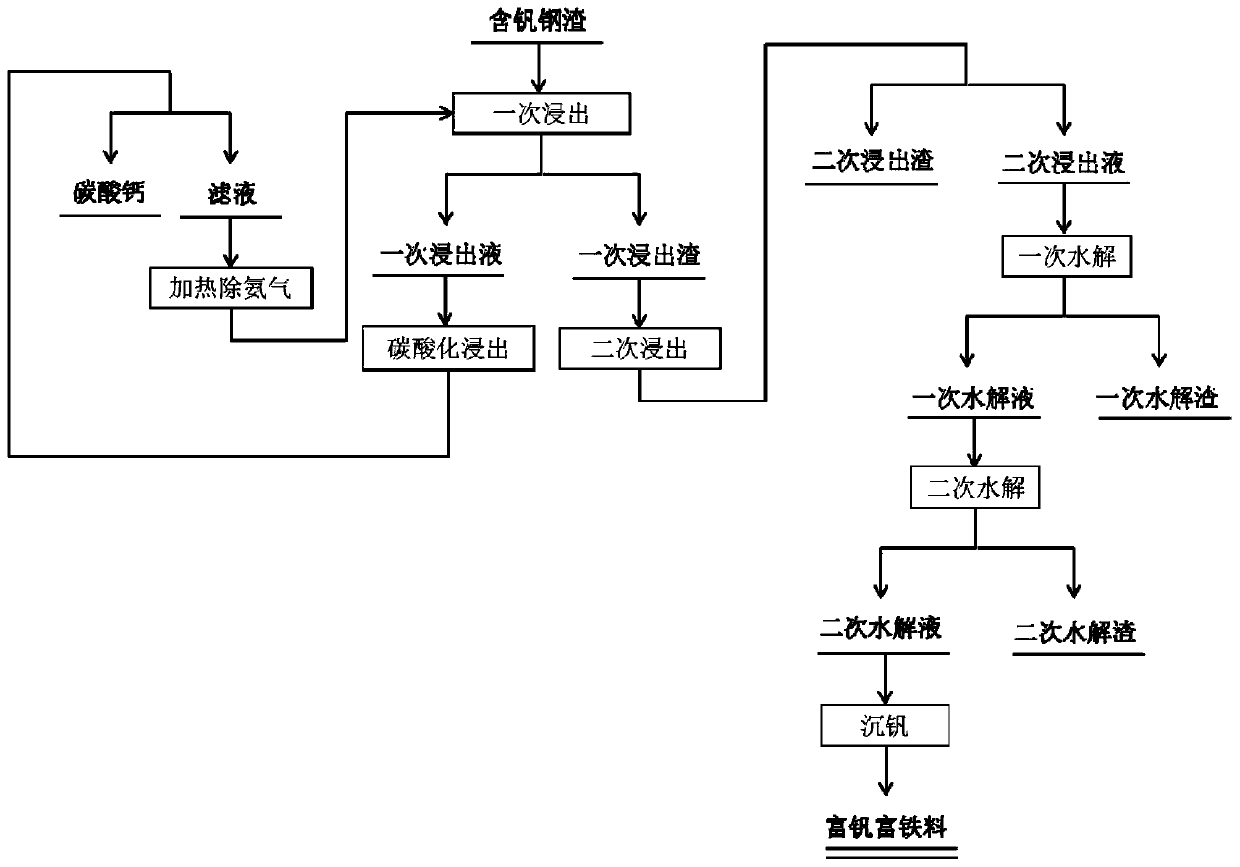
The invention relates to a method for preparing a vanadium-and-iron enriched material by using vanadium enriched steel slags. The method comprises the steps that (1), the vanadium enriched steel slagsare pulverized and leached by using an ammonium chloride solution to obtain primary leaching slags through filtering separation; (2), the primary leaching slags are washed and leached by using an organic acid solution, and secondary leaching solution is obtained through filtering separation; (3), the secondary leaching solution is mixed with a hydrogen peroxide solution, primary hydrolysis is conducted after the pH value is adjusted, and primary hydrolysate is obtained after filtering separation; (4), secondary hydrolysis is conducted on the primary hydrolysate after pH is adjusted, and secondary hydrolysate is obtained after filtering separation is conducted; (5), vanadium condensation is conducted after the pH value of the secondary hydrolysate is adjusted, and solid-phase drying is conducted after filtering; or the secondary hydrolysate is heated, evaporated and crystallized. The method has the advantages that the process is short, better effects of saving energy and environment protecting are achieved, the added value of the product is high, the economical benefit is high, and the recovery rate of the vanadium is greatly improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV LIAONING
Method for recovering scandium from zirconium oxychloride acid pickle, and extracting agent for method
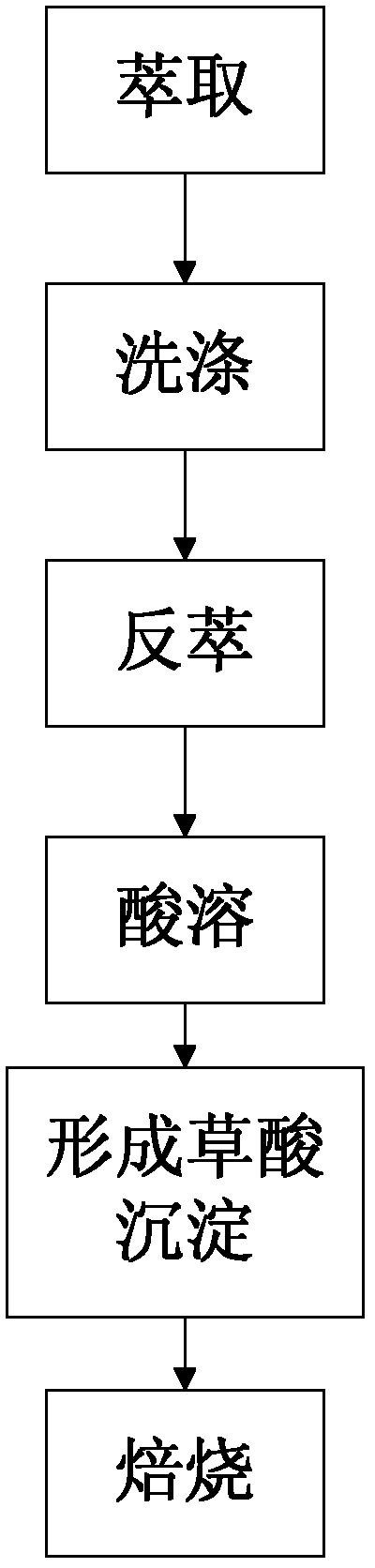
InactiveCN102605199ARealize processingImprove overall recoveryProcess efficiency improvementChemistryTitanium
The invention provides a method for recovering scandium from zirconium oxychloride acid pickle, and an extracting agent for the method; and the extracting agent is a mixture comprising 70-99% of P350 and 1-30% of P507 according to the volume ratio. The extracting agent is especially suitable for extracting the scandium from the acid pickle so as to effectively separate titanium, zirconium, thorium and other rare earth impurities in the acid pickle; the acid pickle can be treated only by the conventional scandium recovery method; furthermore, the total yield of the scandium is more than 80%, so that the treatment capacity is high, and industrialized continuous production can be realized.
Owner:HUNAN ORIENTAL SCANDIUM
Method for extracting indium and germanium from pyrometallurgical crucible residues by whole-wet method
The invention relates to a non-ferrous metal metallurgy and comprehensive recovery technology, in particular to a method for extracting indium and germanium from pyrometallurgical crucible residues by a whole-wet method, belonging to the technical field of non-ferrous metal metallurgy. The method comprises the following steps: grinding and sieving the crucible residues, and then leaching the indium by dilute sulphuric acid with the density of 0.5-1.0M according to the mass ratio of liquid to solid of 5-3:1; adding MnO2 the weight of which is 0.8-1.5 times of that of the dilute sulphuric acid to dilute sulphuric acid-leaching residues, and then leaching germanium by utilizing sulfuric acid with the density of 2-3M according to the ratio of liquid to solid of 5-3:1 in an oxidation manner; leaching the remaining indium and germanium from the oxidation-leaching residues by adopting a C1-1 solution with the density of 4-8wt% in a chlorination manner, keeping the ratio of liquid to solid be 5:1, meanwhile controlling the acidity be 60-80g / L with sulfuric acid; and recovering the leached indium in each segment by an extraction method, precipitating the leached germanium with tannin, and finally calcining to obtain germanium concentrate. The method has less environmental pollution; most part of germanium and indium can be respectively recovered in a leaching manner, wherein the indium can be recovered as well as the germanium; and higher recovery rate can be maintained.
Owner:云南天浩稀贵金属股份有限公司
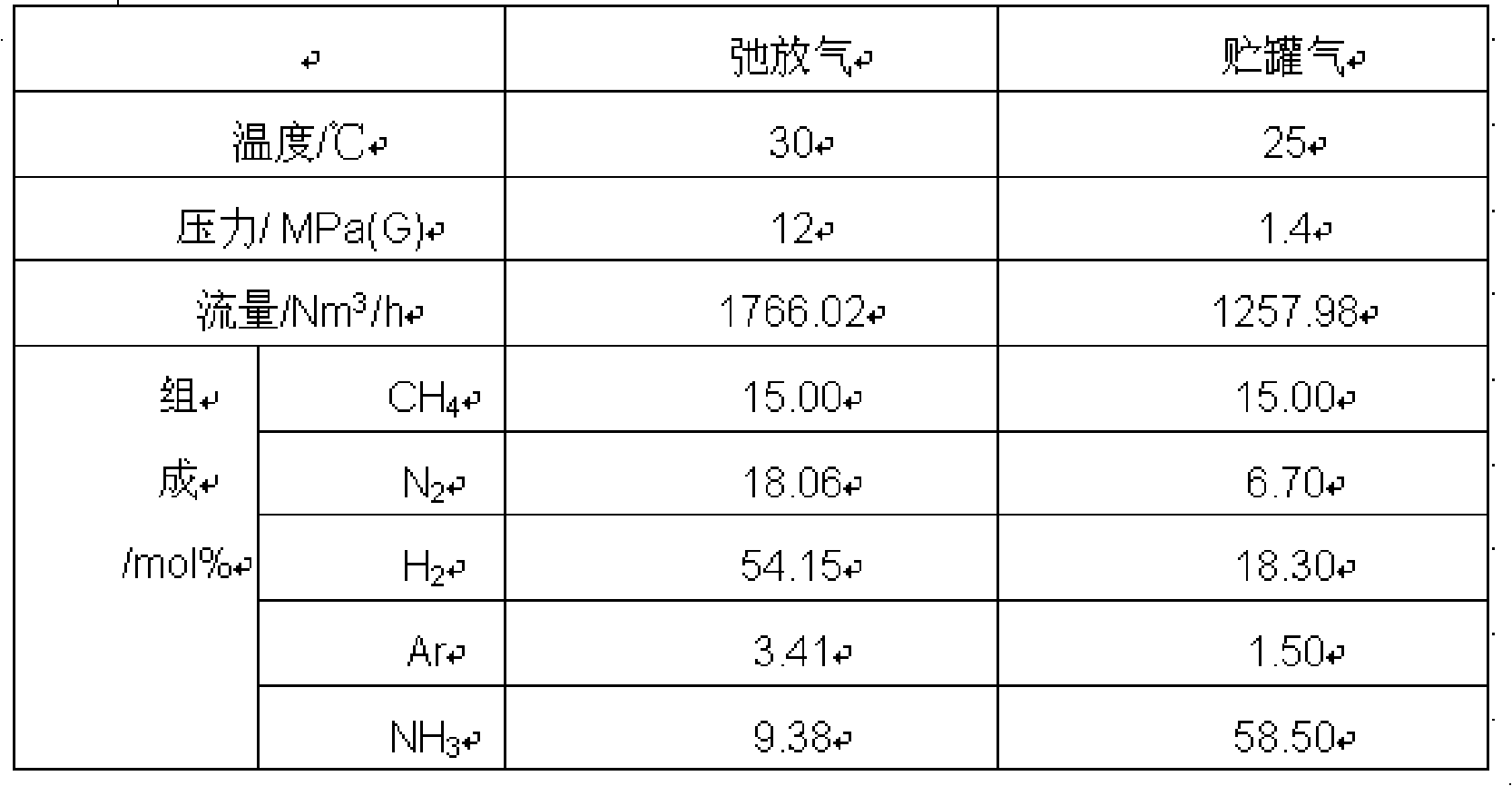
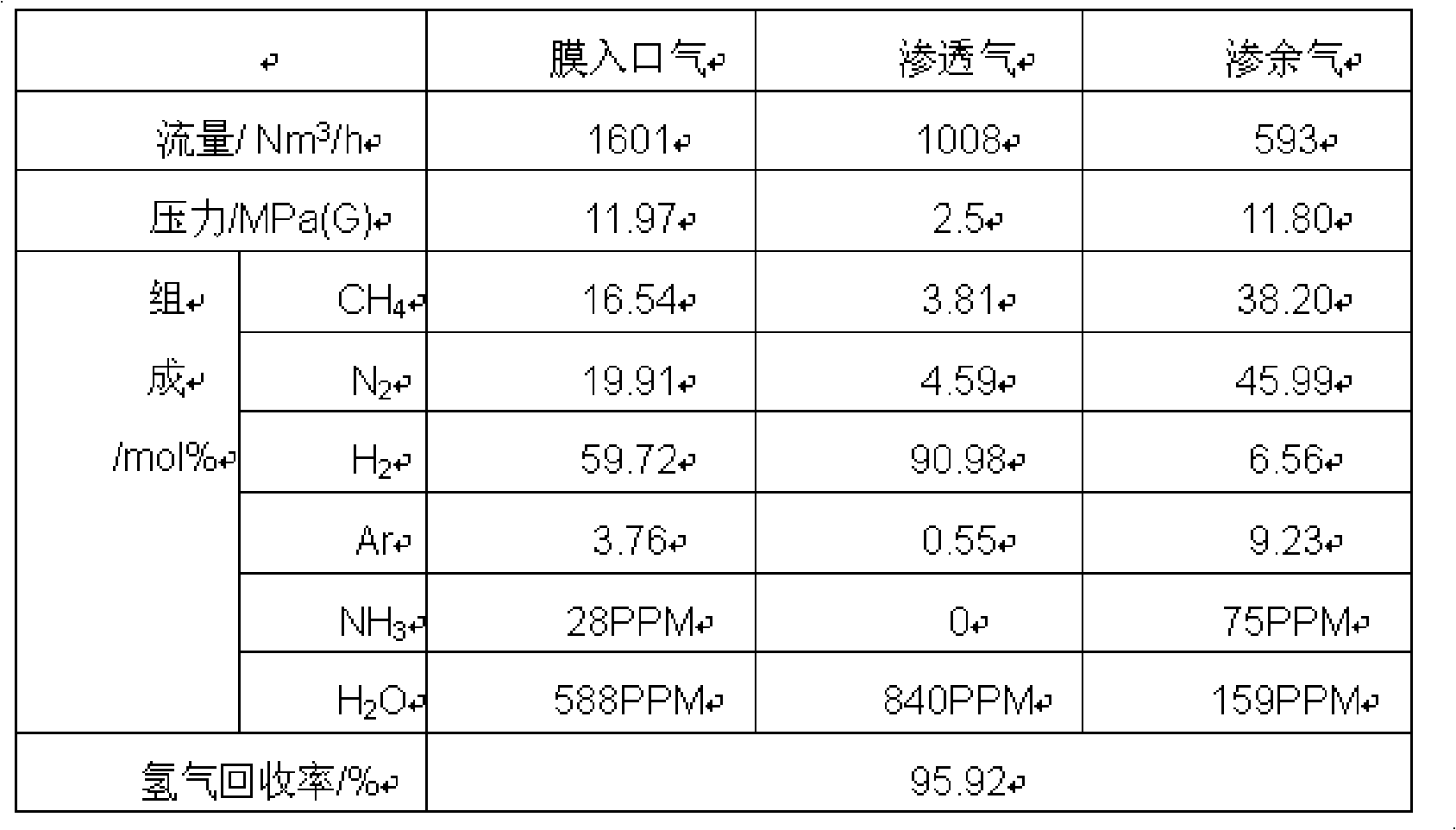
Method and device for recovering hydrogen on purge gas in synthetic ammonia and gas stored in tank
ActiveCN101590364AGuaranteed uptimeImprove overall recoveryDispersed particle separationMolecular sieveHydrogen
The invention discloses a method and a device for recovering hydrogen on purge gas in synthetic ammonia and gas stored in a tank. The method comprises the following steps that: firstly, the purge gas and the gas stored in the tank are subjected to ammonia washing treatment; the purge gas subjected to ammonia washing is sent to a precise filter for removing water fog, is subjected to temperature adjustment by a preheater and sent to a hydrogen film separator; hydrogen in the purge gas is returned by excess pressure to a synthesis compressor at the permeable side of the hydrogen film separator; gas at the permeable excess side of the hydrogen film separator is subjected to pressure reduction, and then is mixed with low-pressure gas stored in the tank subjected to ammonia washing; the gas stored in the tank is mixed and sent to a molecular sieve adsorber and a dust filter for removing residual ammonia and water, and then is sent to a cold box system; and gas exhausted from the cold box is used as a hydrogen product and fuel gas. The invention utilizes the self high pressure of the purge gas, reclaims the hydrogen by a film separation method, the hydrogen at the permeable side of the film is returned to the synthesis compressor by the excess pressure, and overcomes the defects of complicated equipment, high manufacturing and maintenance cost and low recovery rate of usable gas such as hydrogen and the like caused by independent recovery of hydrogen on the prior purge gas and the gas stored in the tank.
Owner:GUIZHOU CHITIANHUA +1
Method for extracting indium and tin from waste ITO targets through reduction and electrolysis
ActiveCN104711426AImprove conversion rateImprove overall recoveryPhotography auxillary processesIndiumElectrolysis
The invention provides a method for extracting indium and tin from waste ITO targets through reduction and electrolysis. According to the method, waste ITO targets having undergone crushing and ball milling are reduced in a reducing furnace through reducible substances, and indium oxide and tin oxide are respectively reduced into metallic indium and metallic tin; an indium tin alloy anode is casted under the protection of alkali; and electrolysis is carried out under alkaline conditions so as to realize electrodeposition of tin onto a cathode and recovery of refined tin, anode mud is indium hydroxide, and refined indium is extracted from indium hydroxide through leaching, purifying and electrodeposition. The method provided by the invention has simple process flow, a short cycling period and high recovery rates of indium and tin and overcomes the problem of difficult filtering of indium hydroxide at the same time, so the method has the obvious advantages of low recovery cost, energy conservation, environmental protection, etc. In industrial production, the recovery rate of tin reaches 98.5%, the recovery rate of indium is more than 99%, and the grades of refined indium and refined tin exceed 99.995%.
Owner:ZHUZHOU SMELTER GRP
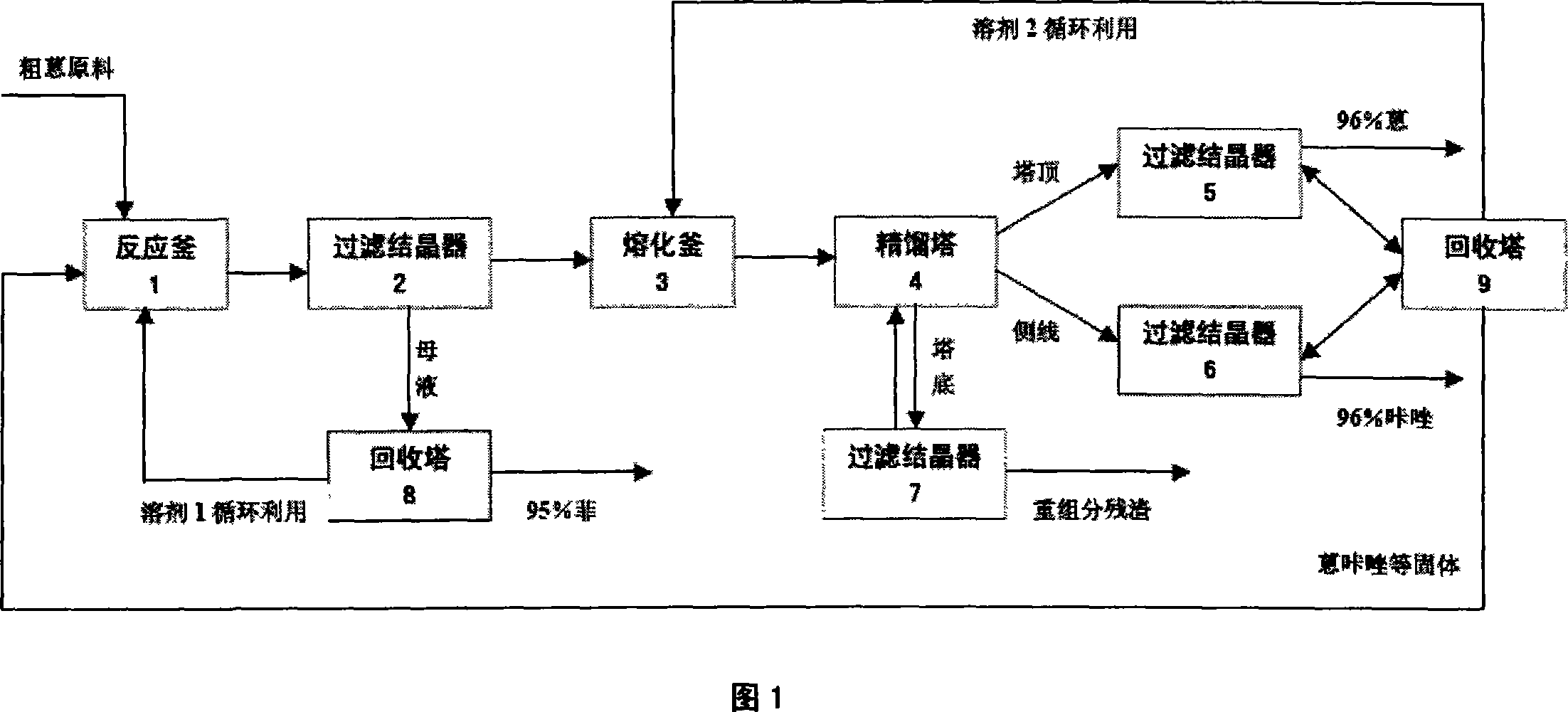
Method for refining high-purity anthracene and carbazole from crude anthracene
InactiveCN101229988AImprove product gradeImprove overall recoveryDistillation purification/separationCrystallisation purification/separationAnthraceneBenzene
The invention relates to a method for refining anthracene and carbazole with a high purity from the crude anthracene. The method mainly consists of four steps: crude benzene with a doffing phenanthrene, separation of the anthracene from the carbazole by a rectification, a crystal preparation of the anthracene and the carbazole as well as solvent recycle. Solvent 1 is firstly used for removing the phenanthrene from the crude anthracene. The obtained anthracene and carbazole solid is mixed with solvent 2 and is rectified. The obtained anthracene and carbazole is cooled, crystallized and washed, and the anthracene with the purity of more than 96 percent is obtained. The method completely solves the problem of easy blocking in the rectification system. The invention has a higher product grade and a high yield and continuous stable operation. The using solvent amount is low (only 1 / 2 to 2 / 3 of the original solvent amount is required); besides, the invention has the advantages of low energy consumption (saving 30 to 50 percent totally) and flexible operation. The invention is particularly applicable to the anthracene and carbazole production with a large production scale, high requirement for the quality and environment protection and energy saving.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
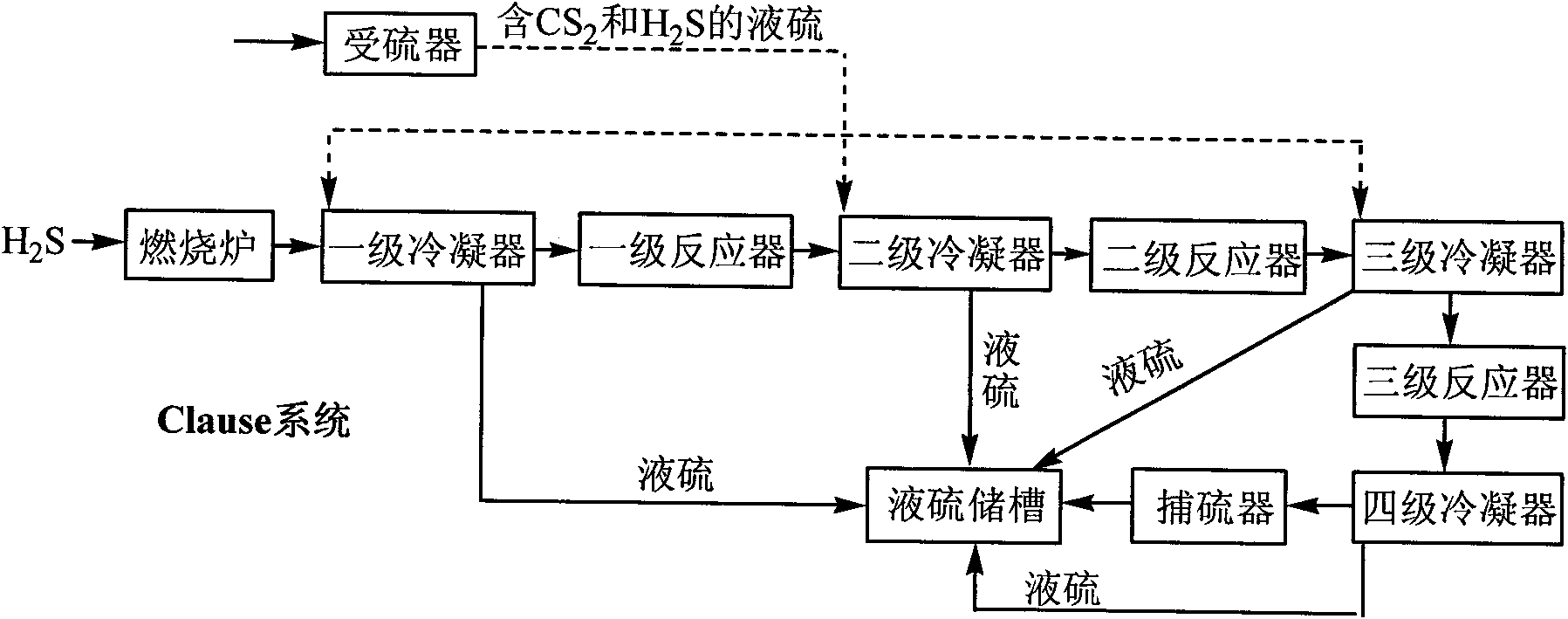
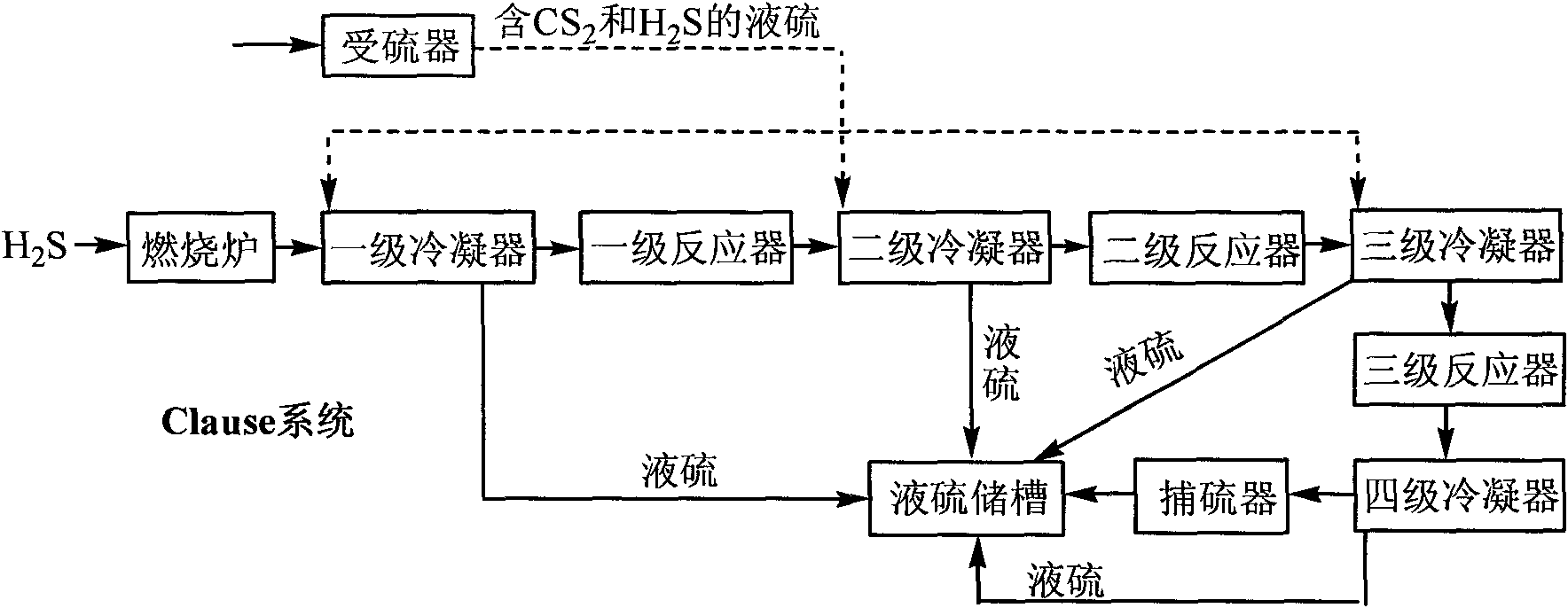
Method for recovering liquid sulfur containing carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide
InactiveCN101850950AAvoid recyclingLow costSulfur preparation/purificationTotal recoverySulfur containing
The invention relates to a method for recovering liquid sulfur containing carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide. The liquid sulfur is recovered after the liquid sulfur is introduced in a sulfur receptor. The invention is characterized in that the liquid sulfur from the sulfur receptor is directly introduced into a Clause system for further recovery; and the liquid sulfur in the sulfur receptor comprises the following components by mass percent: 93.5-96 percent of liquid sulfur, 0.5-4.0 percent of carbon disulfide and 1.0-3.5 percent of hydrogen sulfide. The invention adopts the Clause system to directly recover excessive liquid sulfur containing carbon disulfide and hydrogen sulfide and effectively improves the recovery efficiency and the operation safety of the liquid sulfur. The process flow of the method is simple, the equipment used in the method is less and the cost is effectively reduced. Moreover, by adopting the method of the invention, the total recovery rate of sulfur can reach 99.5 percent and the environmental pollution is hardly caused.
Owner:重庆化医紫光新材料有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com