Patents
Literature
58 results about "Sylvinite" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
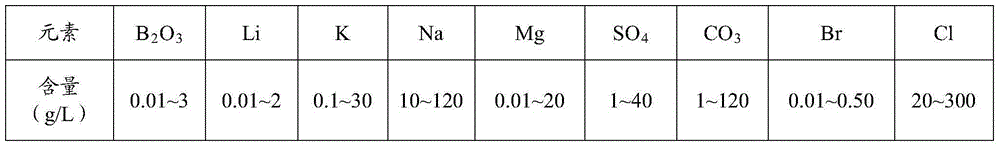
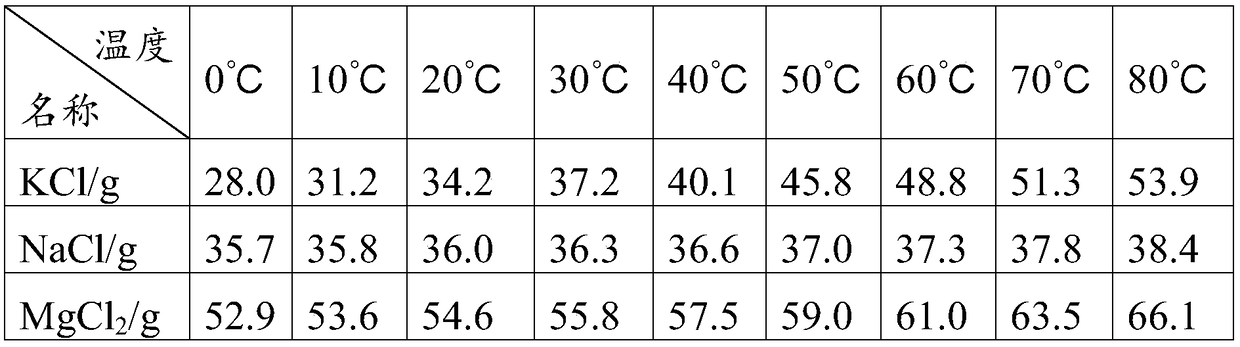
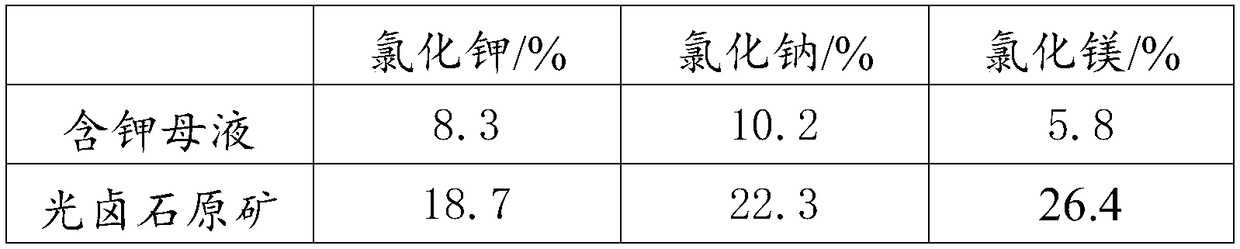
Sylvinite is a sedimentary rock made of a mechanical mixture of the minerals sylvite (KCl, or potassium chloride) and halite (NaCl, or sodium chloride). Sylvinite is the most important source for the production of potash in North America, Russia and the UK. Most Canadian operations mine sylvinite with proportions of about 31% KCl and 66% NaCl with the balance being insoluble clays, anhydrite and in some locations carnallite. Other deposits of sylvinite are in Belarus, Brazil, France, Germany, Kazakhstan, Slovakia and Spain.
Clean production process of plateau sulfate type boron-lithium salt lake brine
InactiveCN102910652AHigh purityReduce the ratio of magnesium to lithiumChemical industryAlkali metal halide purificationHydration reactionSylvinite
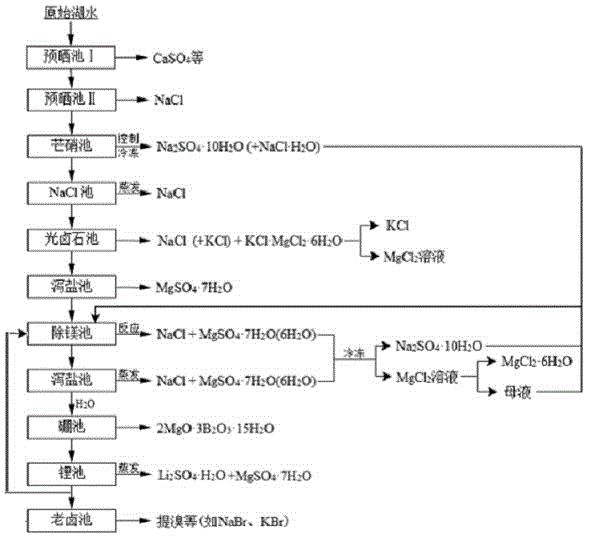
The invention relates to a clean production process of plateau sulfate type boron-lithium salt lake brine. The process comprises the following steps of: (1) arranging a pre-airing pond, a mirabilite pond, a NaCl pond, a carnallite pond, an epsom salt pond I, a magnesium removing pond, an epsom salt pond II, a boron pond, a lithium pond and an old brine pond; (2) controlling the sodium ion concentration in plateau sulfate type boron-lithium salt lake brine, precipitating mirabilite out in winter to obtain brine A, naturally evaporating the brine A, and salting out to obtain brine B; (3) naturally evaporating the brine B, and precipitating sylvine and carnallite out in sequence to obtain brine C; (4) naturally evaporating the brine C, precipitating an epsom salt out, and performing solid-liquid separation to obtain brine D and a solid A; (5) blending the brine D with mirabilite, removing magnesium to obtain brine E, and naturally evaporating brine E to obtain brine F and a solid B; (6) performing a hydration reaction on brine F, naturally evaporating, and precipitating reservoir water / inderite and brine G out; and (7) evaporating brine G or refrigerating for precipitating lithium sulfate, and processing the lithium sulfate into a corresponding product. The process has the advantages of comprehensive utilization of natural energy, saving in energy and environment friendliness.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
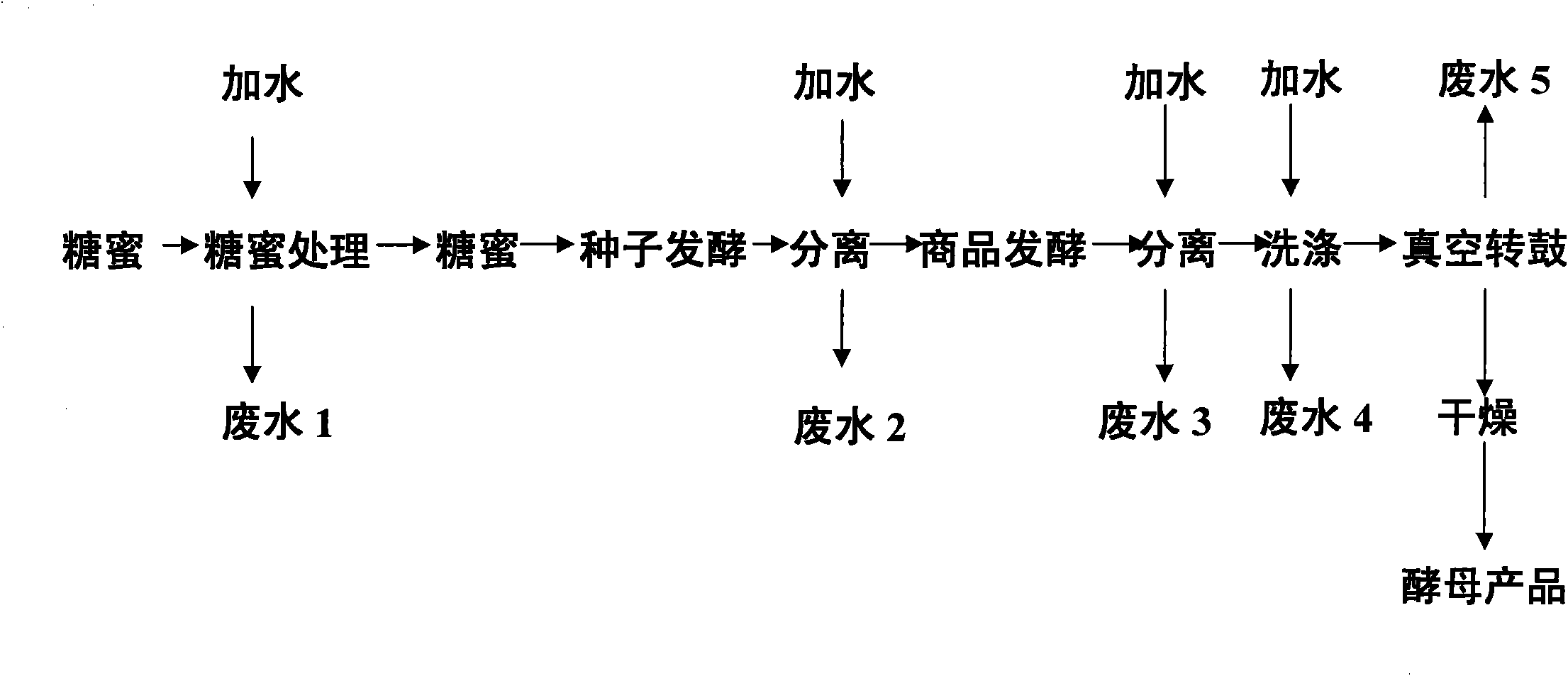
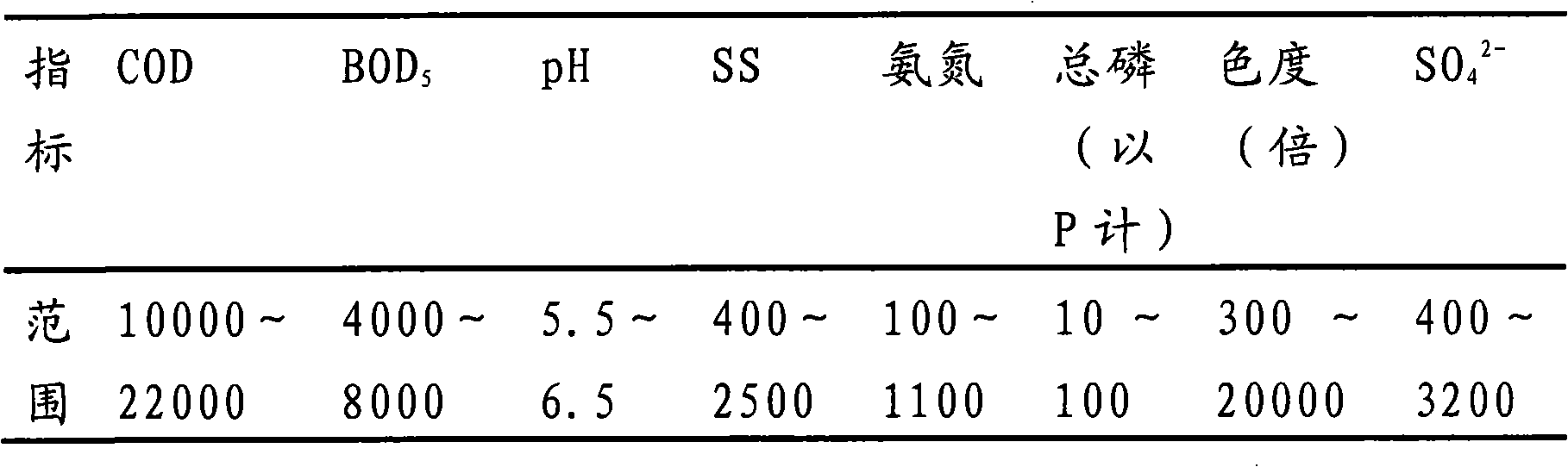
Yeast wastewater treatment method, feed additive obtained by same and feed product
ActiveCN102060341AMaintain acid-base balanceGuaranteed ion balanceGeneral water supply conservationBioloigcal waste fertilisersSylviniteAgricultural engineering
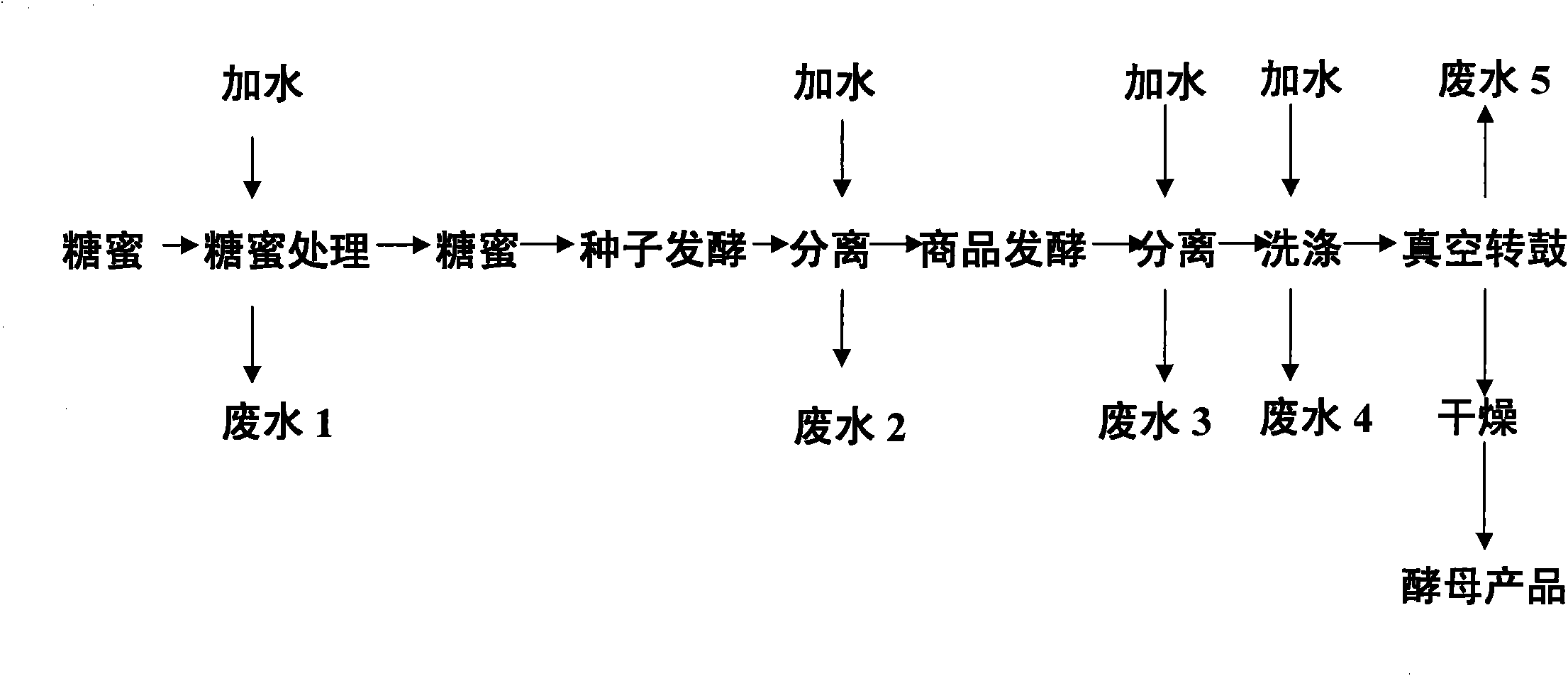
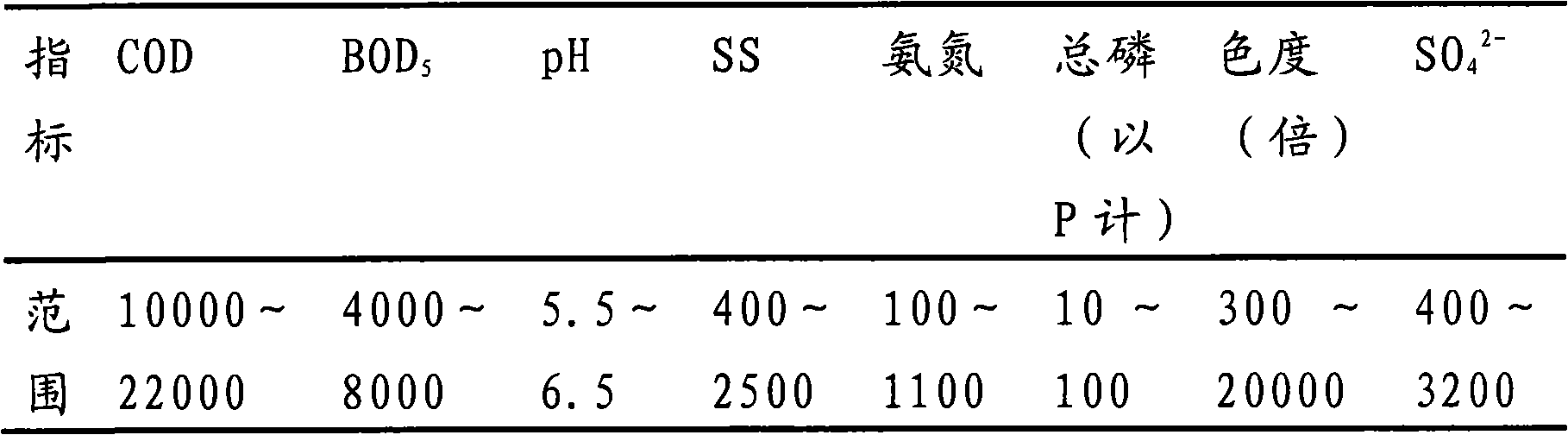
The invention provides a high-concentration organic yeast wastewater treatment method, a feed additive obtained by the method and a feed additive-containing feed product. High-concentration organic yeast wastewater can be treated and simultaneously converted into a fertilizer and the feed additive for utilization, so the high-concentration organic yeast wastewater treatment method provided by the invention improves the economic benefits of the yeast wastewater, greatly reduces the treatment cost of the yeast wastewater so as to realize the optimal comprehensive utilization of resources, and in addition, increases the potassium content of the fertilizers so as to obtain high-grade sylvinite fertilizers.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
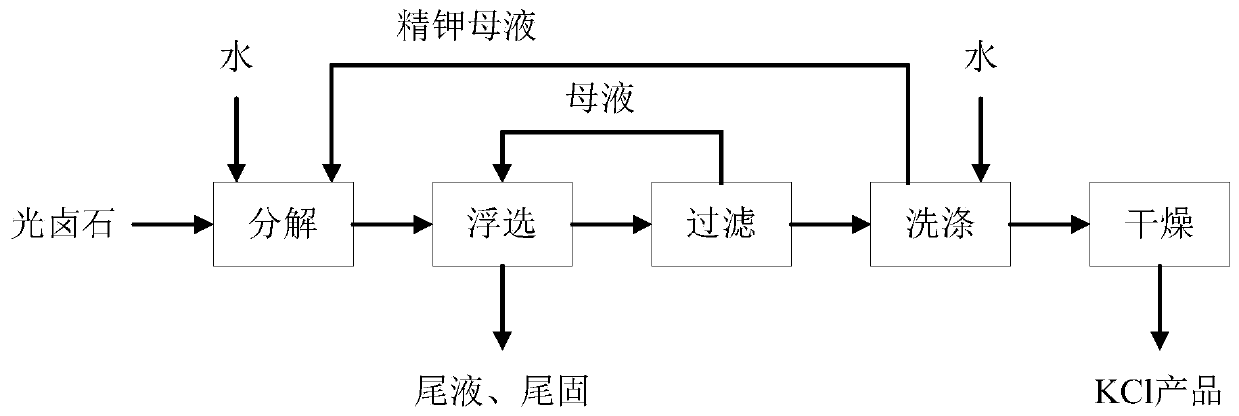
Process for extracting KCl coarse grains by carrying out flotation on solid sylvinite primary ores
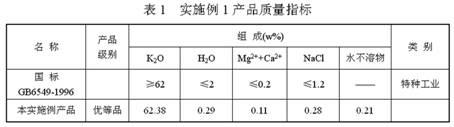
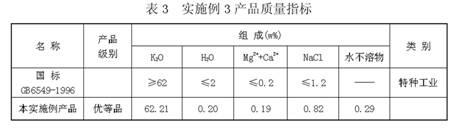
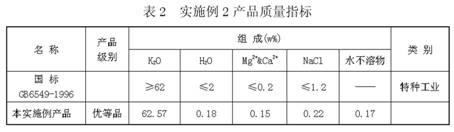
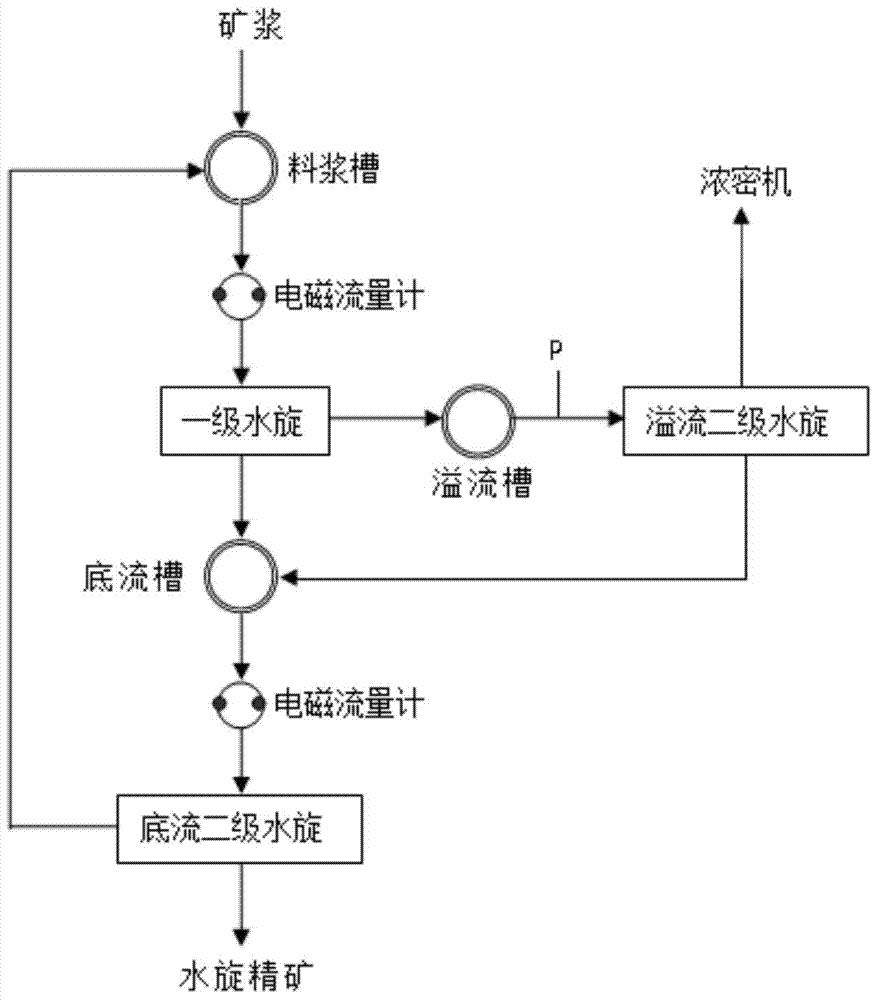
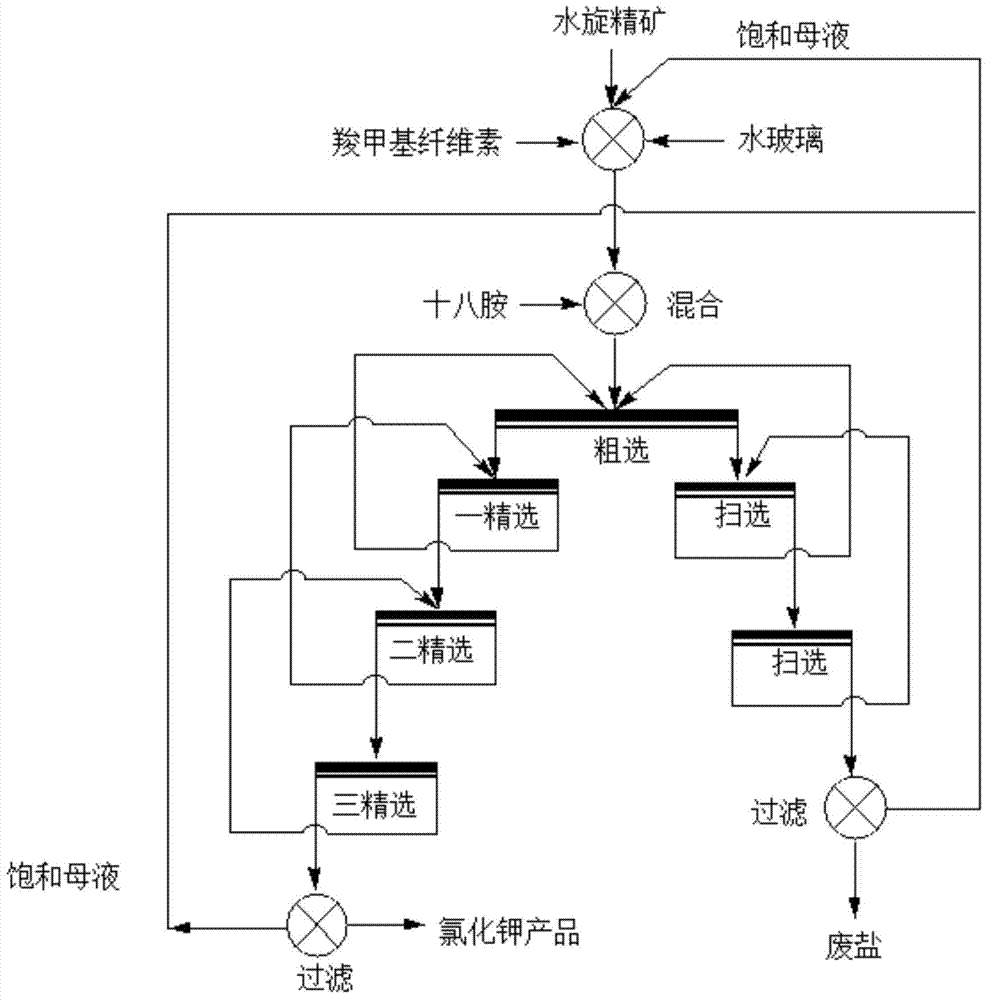
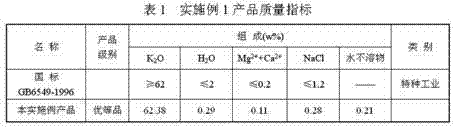
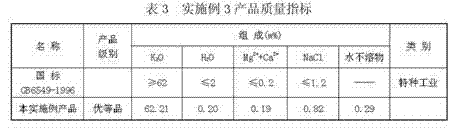
The invention discloses a process for extracting KCl coarse grains by carrying out flotation on solid sylvinite primary ores, comprising the following steps; (1) crushing the solid sylvinite primary ores; (2) carrying out coarse grinding on the crushed sylvinite; (3) feeding the sylvinite material subject to coarse grinding into a flotation machine for primary rougher flotation and secondary refined flotation; and (4) filtering and drying concentrates obtained by the secondary refined flotation, thus obtaining the high-quality KCl bulky grain product. The product is purely white and transparent; the average grain size is 1mm-2mm; and the KCl grade is not less than 90% (by weight), thus exceeding the common industrial and agricultural high-class KCl product standards of class-II and class-III and reaching the special industrial KCl standard of national standard GB6549-1996I.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Method for extracting potassium chloride from high-silt-content high-grade feldspar salt mine
InactiveCN103787372AImprove concentrate qualityHigh yieldAlkali metal chloridesSolventEnvironmental resistance
The invention discloses a method for extracting potassium chloride from a high-silt-content high-grade feldspar salt mine. The method comprises the following steps: (1) crushing and grinding the feldspar salt mine to obtain ore particles; (2) mixing the ore particles and a solvent to prepare slurry with the mass concentration of 25-40 percent, and desliming to obtain deslimed concentrate; and (3) preparing 20-30% ore pulp from the deslimed concentrate by using potassium chloride and sodium chloride co-saturated mother liquor, simultaneously adding a slurry inhibitor and a collecting agent, carrying out rough concentration on the ore pulp to obtain rough ore concentrate and concentrate to be swept, and carrying out more than two stages of selection on the rough ore concentrate to obtain selected foams, and dewatering the selected foams to obtain a potassium chloride product. According to the method disclosed by the invention, not only is the problem of waste ore accumulation solved, but also the environment-friendly problem is solved, resources are sufficiently utilized, wastes are turned into treasures, and the economic and social benefits are relatively remarkable.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for separating carbonate from carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium to prepare sylvinite ore and lithium carbonate concentrate
InactiveCN103058232AEfficient use ofPrevent precipitationAlkali metal chloridesLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesSylviniteLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a method for separating carbonate from carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium to prepare sylvinite ore and lithium carbonate concentrate, wherein the carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium is pre-concentrated, the carbonate is separated from the carbonate bittern containing lithium and potassium by means of combination of frozen alkaline and a precipitant so as to prepare the concentrated bittern with the content of carbonate reduced, then the concentrated bittern is further concentrated, the sylvinite ore separated out by evaporative crystallization is separately collected and prepared after the content of the potassium ion in the bittern is up to 51.70g / L, the lithium enrichment bittern with the content of the lithium ion being 4-26g / L is prepared, and the lithium enrichment bittern is guided into a crystallizer, added with sodium carbonate, and separated in a centrifugal way to obtain the lithium carbonate concentrate. Compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the following advantages: the lithium enrichment concentration is increased because the carbonate in the bittern is removed; the purity of the obtained lithium carbonate and the overall recovery of the lithium ion are high; continuous industrialization and automated production of the preparation of the lithium carbonate concentrate can be implemented; high-grade sylvinite can be prepared from a salt pan, and the potassium ion recovery of the salt pan is increased; and the residual bittern of which the lithium is extracted can be comprehensively developed conveniently so as to further extract substances like boron, rubidium, cesium bromine.
Owner:TIBET XUSHENG MINING DEV
Preparation method of potassium sulfate
InactiveCN104016379AImprove adaptabilityHigh yieldAlkali metal sulfites/sulfatesSylvinitePhysical chemistry
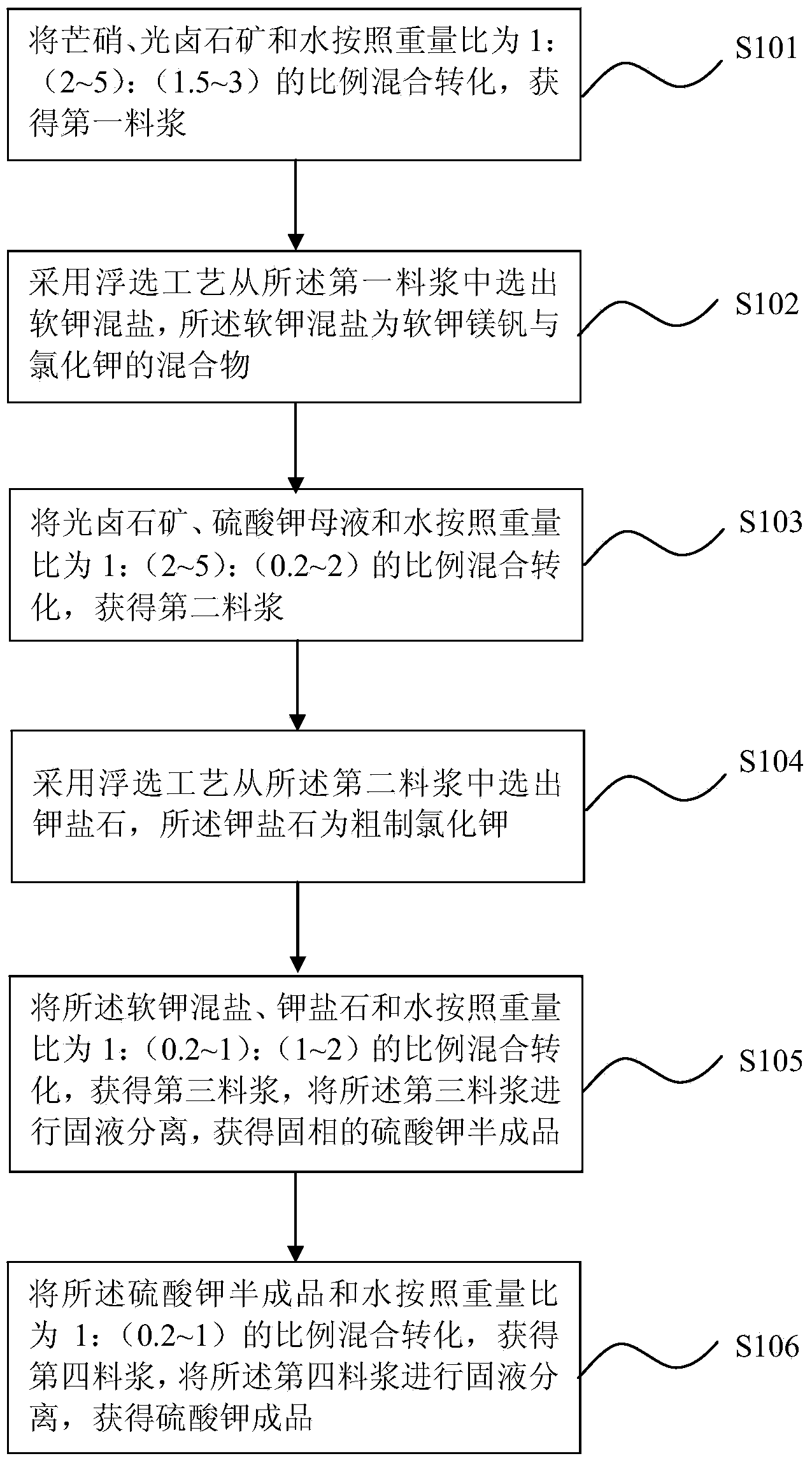
The invention discloses a preparation method of potassium sulfate. The method comprises the steps of S101, performing hybrid conversion on mirabilite, carnallite ore and water to obtain first slurry; S102, selecting soft potassium mixed salt from the first slurry by adopting a flotation process, wherein soft potassium mixed salt is a mixture of picromerite and potassium chloride; S103, performing hybrid conversion on carnallite ore, potassium sulfate mother liquor and water to obtain second slurry; S104, selecting sylvinite which is crude potassium chloride from the second slurry by using the flotation process; S105, performing hybrid conversion on soft potassium mixed salt, sylvinite and water to obtain third slurry, and performing solid-liquid separation on the third slurry to obtain a solid-phase potassium sulfate semi-finished product; S106, performing hybrid conversion on the potassium sulfate semi-finished product and water to obtain fourth slurry, and performing solid-liquid separation on the fourth slurry to obtain a potassium sulfate finished product. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention can be used for shortening the technological process and increasing the adaptability of the technology to raw materials.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nutrient for promoting growth of full herbal medical plant
ActiveCN102079667AReduce manufacturing costReduce dosageFertilizer mixturesSylviniteTrace element composition
Disclosed is a nutrient for promoting growth of full herbal medical plants, which is composed of the following main ingredients in percentage by weight: 10-30% of nucleotide sylvinite, 20-70% of grape sugar, 10-20% of amino acid and 10-30% of trace elements. The weight ratio of trace elements, such as Mn to B to Fe to Zn to Cu to Mo is 5:2:3:3:2:2. The nutrient is low in production cost, less in amount, easy to produce and promote massively and reasonable in interaction, is targeted strongly, non-toxic, harmless, non-residual, and no adverse side effect, has the advantages of increasing production, income and benefits, strengthening resistance, and promoting the growth of full herbal medical plants. The nutrient can increase the yield by 40%-100%.
Owner:新疆鸿悦现代农业科技有限公司
Method for extracting Mg, K, B and Li from mixed brine by utilizing natural energy
ActiveCN103553090AEnvironmental conditions unchangedMagnesium carbonatesBoron-oxygen compoundsSulfate radicalsSalt lake
The invention provides a method for extracting Mg, K, B and Li from mixed brine by utilizing natural energy. The method comprises the following steps: evaporating, freezing and evaporating carbonate salt lake brine and obtaining brine A when the content of Li in the brine is smaller than or equal to 2.5g / L or the content of lithium carbonate in precipitated solid ores is smaller than or equal to 0.5%; evaporating, freezing and evaporating sulfate salt lake brine and obtaining brine B when the content of Mg in the brine is more than or equal to 10g / L; obtaining brine C after mixing and reaction between the brine A and the brine B; obtaining brine D when naturally evaporating the brine C until the content of sulfate radicals is 5-40g / L; obtaining brine E after freezing the brine D to precipitate mirabilite; evaporating the brine E to a certain degree to obtain brine F; evaporating the brine F to precipitate sylvite and then obtaining brine G; obtaining brine H after freezing the brine G to precipitate mirabilite; mixing the brine H with mixed alkali obtained in the first step to react and then obtaining brine I when the concentration of Li in the solution is 0.5-1.5g / L; leading the brine I to a cooling tank and naturally evaporating the brine to precipitate borax.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for processing sylvite salt mine with high mud content
InactiveCN102976364AResolve separabilitySolve process problemsAlkali metal chloridesSylviniteDesalination
Owner:王定坤
Method for extraction of potassium chloride crude product from sylvine ore by triboelectric separation
ActiveCN105271309AChange the charging propertiesAchieve separationAlkali metal chloridesSylviniteElectrostatic separation
A method for extraction of a potassium chloride crude product from sylvine ore by triboelectric separation comprises the following steps: (1) crushing, to be more specific, solid sylvine ore is crushed, the material particle size is controlled in the range of 1-2mm; (2) ore grinding, to be more specific, the material crushed in the step (1) is ground until the mass content of the material less than or equal to 200 mesh is greater than or equal to 90%; (3) surface pretreatment, to be more specific, the material ground in the step (1) is sent into a preprocessor, and is added with a surface modifier for uniform mixing; and (4) electrostatic separation, to be more specific, the material added with the surface modifier in the step (3) is sent into an electrostatic separator for triboelectric separation of potassium chloride to obtain the potassium chloride crude product. The method does not require the use of saturated liquor, is not affected by factors such as temperature, pressure, and the like, ultimately does not produce sewage, and is simple in process, easy to operate, free of pollution, and good in separation efficiency, the yield is up to 90%; the resulting chloride potassium crude product has good quality, the chloride potassium content is up to 90%, and the economic benefit is obvious.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
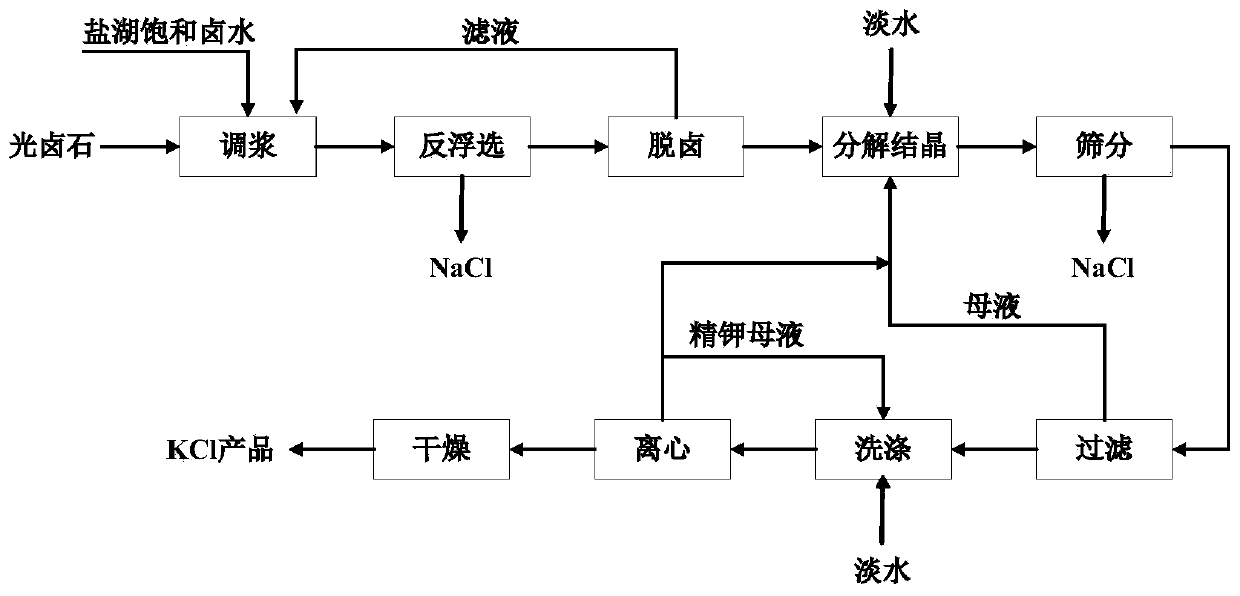
Production technology for recycling potassium chloride from saturated glaserite mother liquor
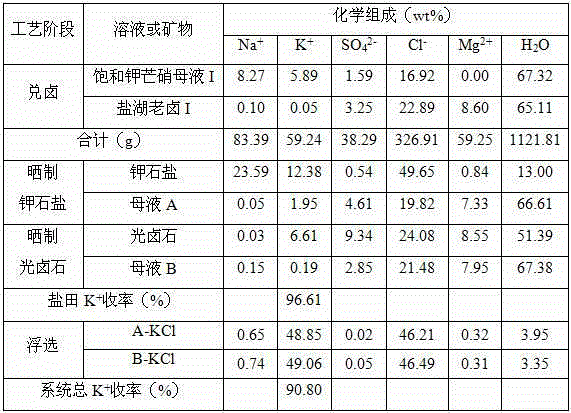
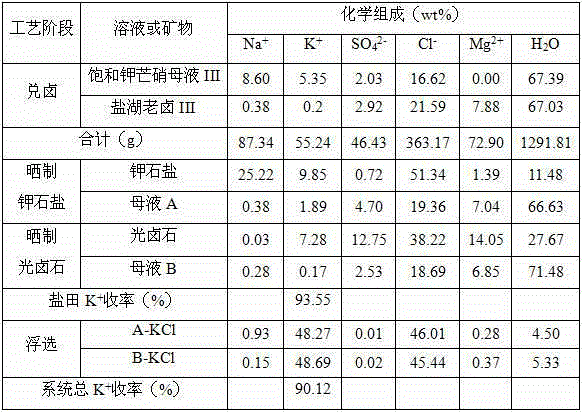
The invention provides a production technology for recycling potassium chloride from saturated glaserite mother liquor. The production technology comprises the following steps of 1, conducting brine mixing, wherein the saturated glaserite mother liquor and old brine in a salt lake are mixed according to the mass ratio of 1:0.6-1.5, and mother liquor mixed with the brine is obtained; 2, sun-curing sylvine, wherein after 20 wt%-35 wt% of water in the mother liquor mixed with the brine is naturally evaporated, solid-liquor separation is conduced, and then the sylvine and mother liquor A are obtained; 3, sun-curing carnallite, wherein after 10 wt%-30 wt% of water in the mother liquor A is naturally evaporated, solid-liquor separation is conduced, and carnallite and mother liquor B are obtained; 4, extracting potassium chloride, wherein floatation is conducted on the sylvine and the carnallite, and then the potassium chloride product is obtained. By the adoption of the production technology, the recovery rate of K+ in a technological salt field reaches up to 96.61%, the total yield of the K+ of a system reaches up to 91.95%, the purity of the potassium chloride product reaches up to 98.06%, and the potassium chloride product meets the agricultural potassium chloride superior product standard. The production technology is simple, low in energy consumption and cost, avoids co-separation of potassium-containing sulfate minerals, part of old brine in the salt field can be digested, and the environmental-protection problem is effectively relieved.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Process for extracting KCl coarse grains by carrying out flotation on solid sylvinite primary ores
The invention discloses a process for extracting KCl coarse grains by carrying out flotation on solid sylvinite primary ores, comprising the following steps; (1) crushing the solid sylvinite primary ores; (2) carrying out coarse grinding on the crushed sylvinite; (3) feeding the sylvinite material subject to coarse grinding into a flotation machine for primary rougher flotation and secondary refined flotation; and (4) filtering and drying concentrates obtained by the secondary refined flotation, thus obtaining the high-quality KCl bulky grain product. The product is purely white and transparent; the average grain size is 1mm-2mm; and the KCl grade is not less than 90% (by weight), thus exceeding the common industrial and agricultural high-class KCl product standards of class-II and class-III and reaching the special industrial KCl standard of national standard GB6549-1996I.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Method for recycling sylvinite by using carnallite decomposition mother liquor
ActiveCN108892156ASave waterIncrease profitAlkali metal chloridesAlkali metal halide formation shapeSylviniteFiltration
A method for recycling sylvinite by using carnallite decomposition mother liquor comprises the following steps that 1, the carnallite decomposition mother liquor is heated to 70-80 DEG C, and the preheated carnallite decomposition mother liquor is divided into carnallite decomposition mother liquor I and carnallite decomposition mother liquor II; 2, the carnallite decomposition mother liquor II continues to be heated to be boiled and evaporated, then cooling, crystallizing and filtering are carried out, the obtained solid phase is artificial carnallite, and the liquid phase is old brine; 3, anhydrous thermal decomposition is carried out to obtain high-temperature solid-liquid mixed ore pulp; 4, dehalogenation is carried out, wherein the high-temperature solid-liquid mixed ore pulp obtainedin step 3 is subjected to heat preservation and filtration, solid-liquid separation is realized, and solid sylvinite and high-temperature mother liquor are obtained. The method is simple in technological process, easy to operate and high in heat energy utilization rate, energy waste is avoided, good economic value and appreciation space are achieved, and a new process route and idea are providedfor utilization of a large amount of carnallite decomposition mother liquid generated by producing potassium chloride from carnallite in rainy and humid regions.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Method for extracting Mg, K, B and Li from mixed brine by utilizing natural energy
ActiveCN103553091AEnvironmental conditions unchangedMagnesium carbonatesMagnesium chloridesLithium carbonateMirabilite
The invention provides a method for extracting Mg, K, B and Li from mixed brine by utilizing natural energy. The method comprises the following steps: obtaining brine A through evaporating, freezing and evaporating carbonate brine until the Li content is smaller than or equal to 2.5g / L or the lithium carbonate content in precipitated solid ores is smaller than or equal to 0.5%; obtaining brine B through evaporating, freezing and evaporating sulfate brine until the Mg content is more than or equal to 10g / L; obtaining brine C after reaction between the brine A and the brine B; obtaining brine D after evaporating the brine C until the content of sulfate radicals is 5-40g / L; obtaining brine E after freezing the brine D to precipitate mirabilite; evaporating the brine E to precipitate sodium chloride and brine F; evaporating the brine F to precipitate sylvite ores and brine G; carrying out mixing and reaction on the brine G and high magnesium brine to obtain sylvite ores and brine H; mixing the brine H with mirabilite to react to obtain brine I; mixing the brine I with fresh water or sulfate original brine and evaporating the brine to precipitate boron ores and brine J; evaporating the brine J to obtain lithium ores and brine K; blending the brine K to recover Li and B.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
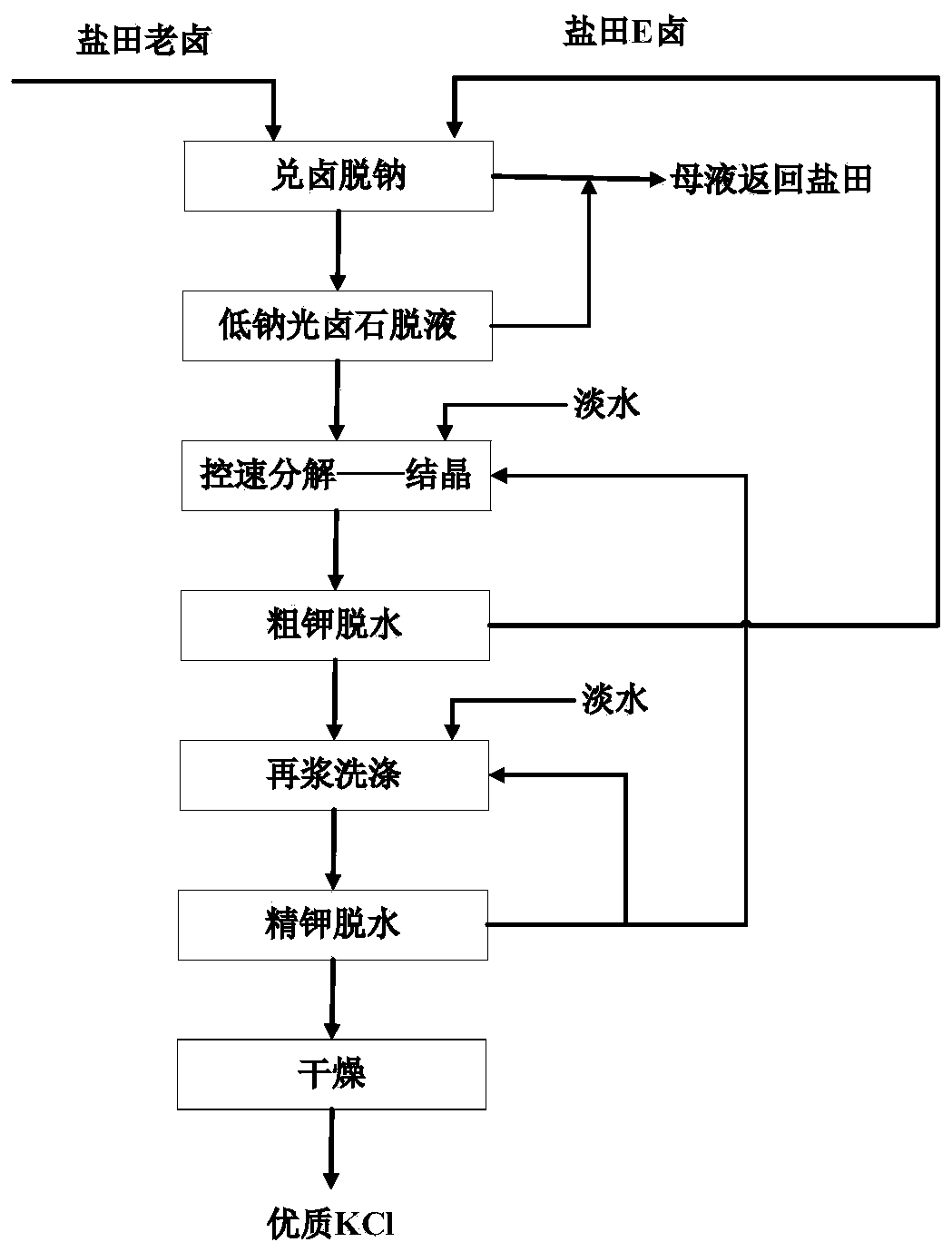
Production method of sylvinite
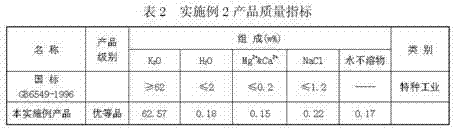
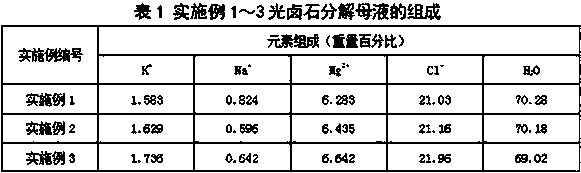
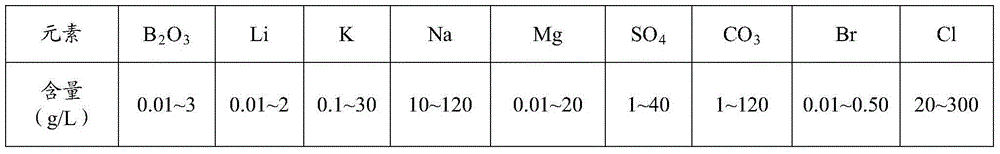
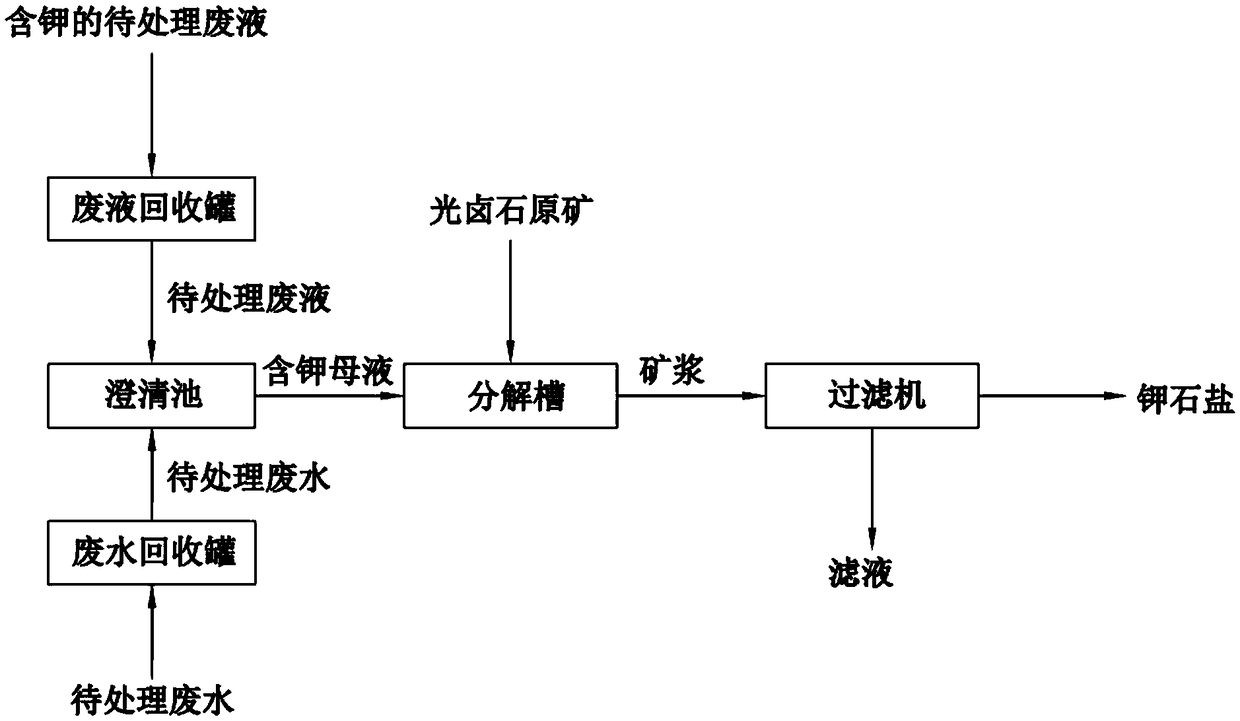
The invention discloses a production method of sylvinite. The production method of sylvinite comprises the following steps: proportioning potassium-containing to-be-treated waste liquor and to-be-treated wastewater to obtain a potassium-containing mother liquor; dissolving carnallite raw ores by the potassium-containing mother liquor to obtain ore pulp; and filtering the ore pulp to obtain the sylvinite. By proportioning the waste liquor and the wastewater to obtain the potassium-containing mother liquor and dissolving the carnallite raw ores by the potassium-containing mother liquor, magnesium chloride is dissolved massively and magnesium chloride is separated out in a saturated manner by means of a common ion effect, so that the sylvinite containing relatively high potassium quantity andmeeting the demands of refining potassium chloride is obtained, and water resources are saved. Influences on control 0f a follow-up production process and energy conservation and emission reduction are reduced as far as possible. Moreover, the carnallite raw ores are dissolved by the potassium-containing mother liquor, so that the baume degree of the ore pulp is increased, and the load of equipment is alleviated, therefore, the energy consumption and the loss of the equipment are further reduced to achieve the purpose of recycling resources, and the economical benefit is improved.
Owner:QINGHAI SALT LAKE IND
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107008414AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater treatment compoundsUltrasound - actionPtru catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst, belonging to the technical field of an environment-friendly and chemical catalyst. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking attapulgite, diopside, montmorillonite, sylvite, amazonite and lithium limestone porous materials as carriers, performing pore expansion and modification to the carriers through lithium hypochlorite and beryllium bis(acetylacetonate), adding a surfactant dioctadecyl-2-methyl hydroxyethyl ammonium chloride and performing surface activation treatment under ultrasonic wave effect, then leading the ultrasonically surface-activated carriers to have hydrothermal reaction with a complex mineralizer (borax and potassium sulfate), catalytic activity assistant precursors, namely praseodymium(III) tris[3-(trifluoromethylhydroxymethylene)-D-camphorate], 1,1,1-neodymium trifluoroacetylacetonate, tris(6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptafluoro-2,2-dimethyloctane-3,5-dionato-O,O')dysprosium (III) and holmium oxalate rare earth metal organic compound, and catalytic active site component precursors, namely common transitional metal organic compound ferrous fumarate, nickel citrate and copper glutamate and precious metal compound gold potassium tetrachloride in a hydrothermal reactor under the action of an emulsifier dimethylaminoacrylate palmitate ammonium chloroacetate, drying reactive products to remove moisture, and firing in a muffle furnace at certain temperature, to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing potassium chloride from carnallite
ActiveCN111533138AMining fastReduce contentMagnesium chloridesClimate change adaptationSylvinitePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a method for preparing potassium chloride from carnallite. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out high-temperature water-soluble mining treatment on carnallite ore by using fresh water to obtain potassium-rich saturated brine, mixing the potassium-rich saturated brine, sylvine saturated liquid and old brine, performing brine mixing, evaporation anddecomposition treatment to obtain artificial sylvine, and finally, carrying out low-temperature selective dissolution treatment on the artificial sylvine by using fresh water to prepare potassium chloride. The carnallite ore is exploited by adopting hot water, so that the content of sodium chloride in the potassium-rich saturated brine is reduced, the artificial sylvine is prepared into potassiumchloride only by one-time low-temperature selective dissolution, so that high yield and high quality of potassium chloride are guaranteed, and unnecessary energy consumption and impurity accumulationcaused by multiple times of cyclic hot-melting crystallization treatment of sylvine are avoided, meanwhile, the method provided by the invention is suitable for carnallite ores of different grades, extremely high in adaptability, loose in technical condition and convenient for technical promotion and implementation.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A process for the production of potassium sulphate and magnesium sulphate from carnallite and sodium sulphate
According to some embodiments there is provided a process for the recovery of SOP from Sulphate bearing mineral and Carnallite or Sylvenite, comprising: Dissolving Carnallite in water to obtain Sylvenite and high Magnesium Chloride brine; Adding Sodium Sulphate to said Carnallite to produce mixture of Kainte\Leonite, KCl and NaCl precipitant and brine containing Mg Cl2, KCl, NaCl; Separating the NaCl from the mixture; Obtaining a precipitant mixture of Leonite with KCl; Filtering said Leonite and washing with water to yield pure mixture of Leonite with KCl; Adding KCl to the Leonite with the KCl; and Decompose said Leonite with the KCl to SOP.
Owner:DEAD SEA WORKS
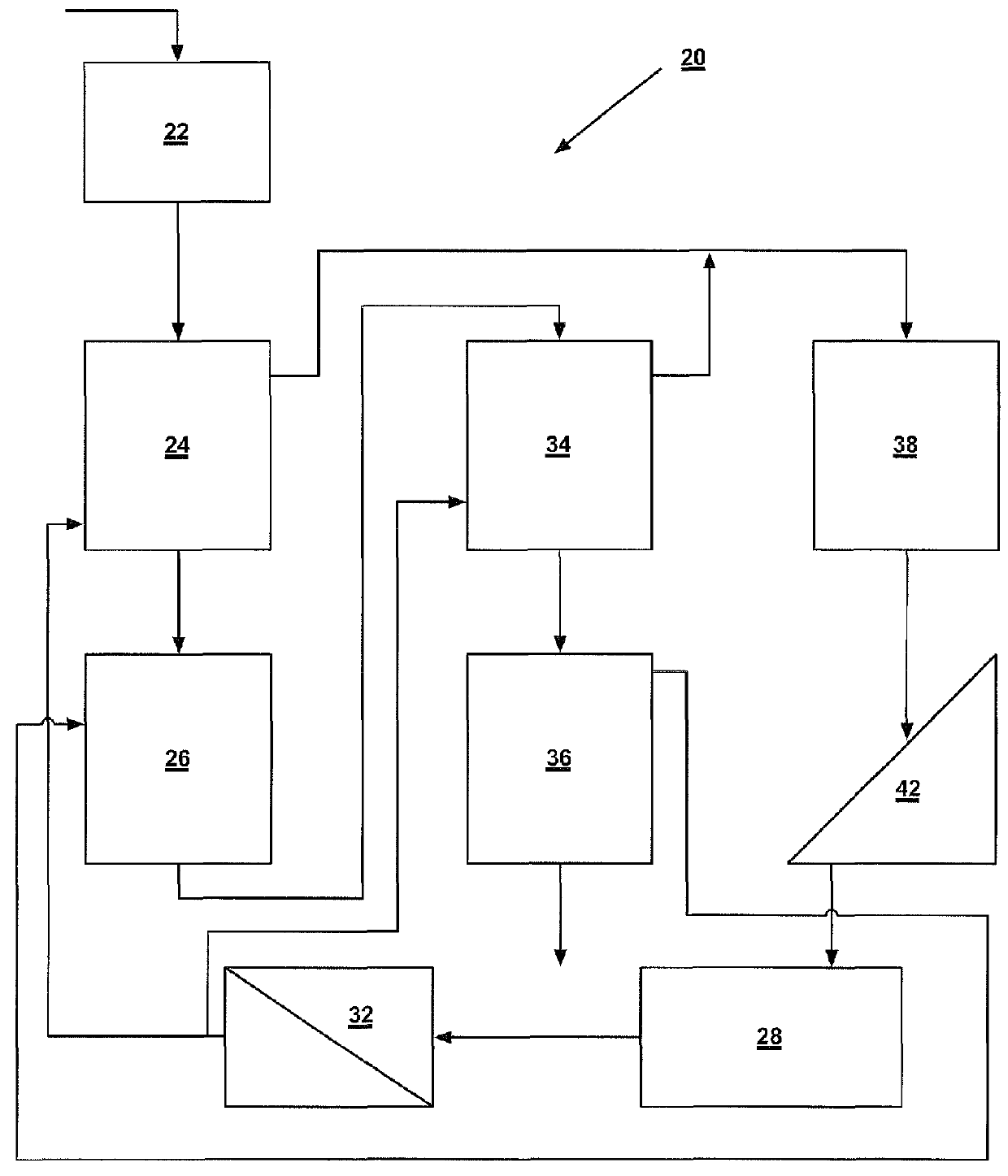
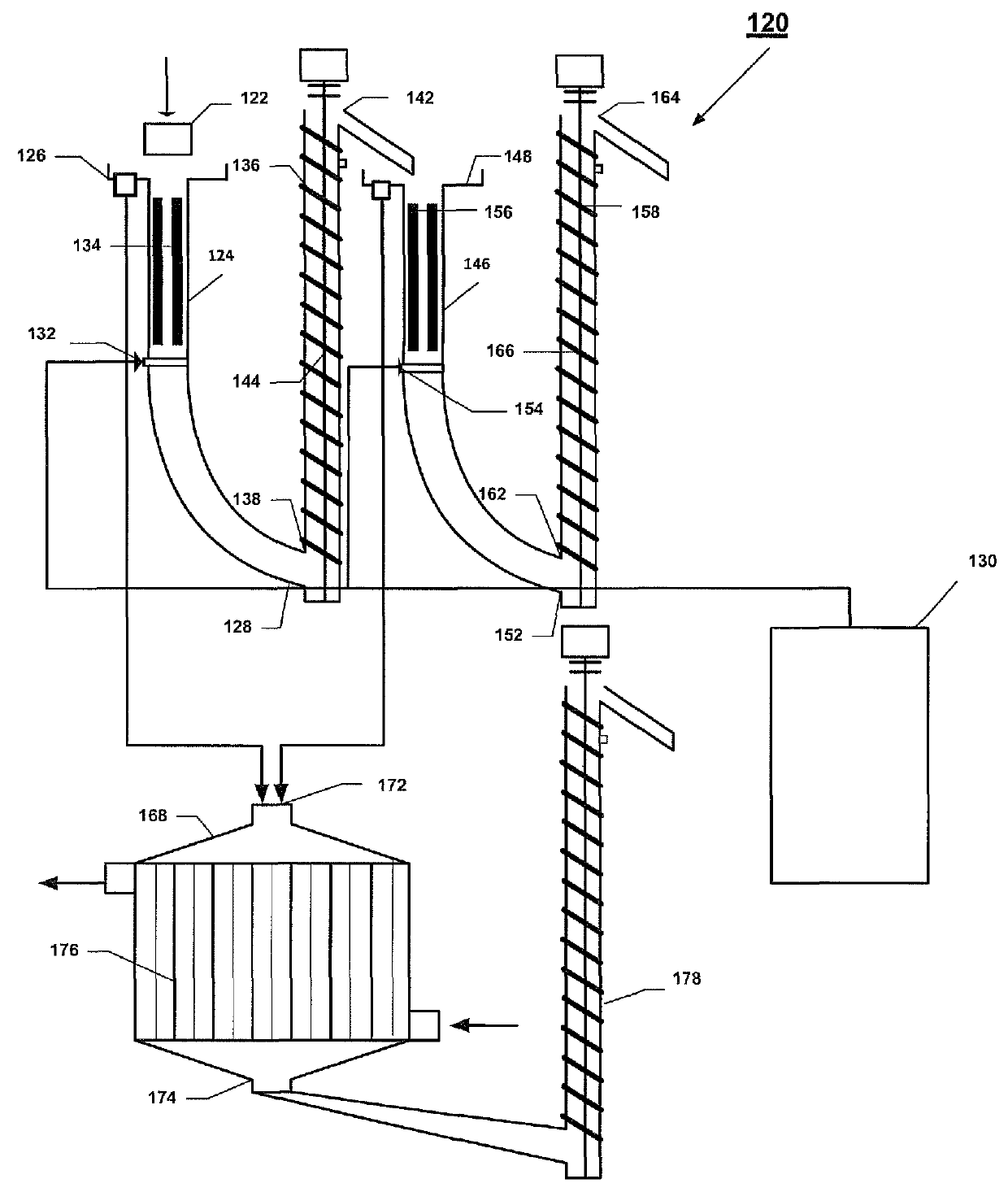
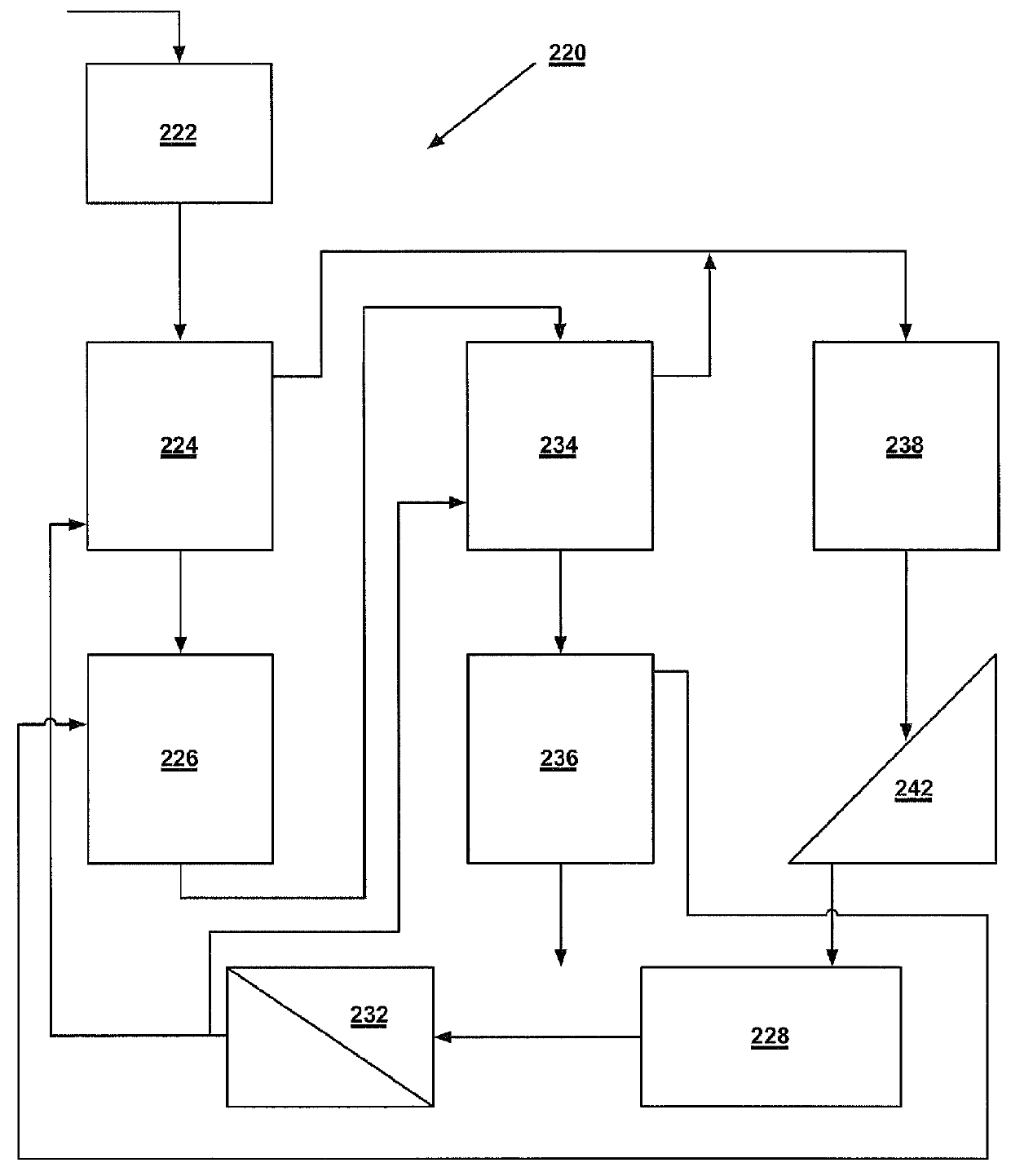
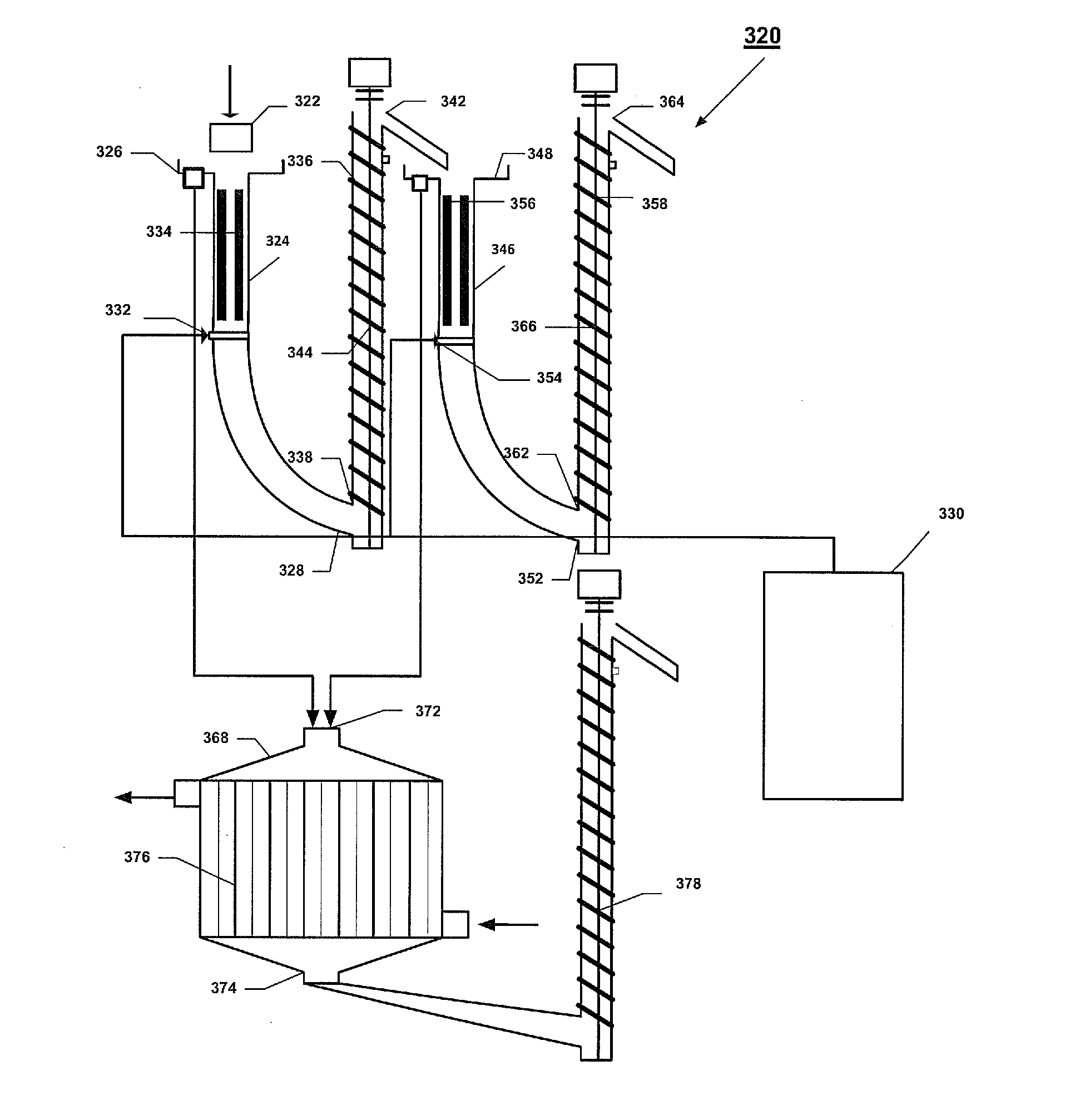
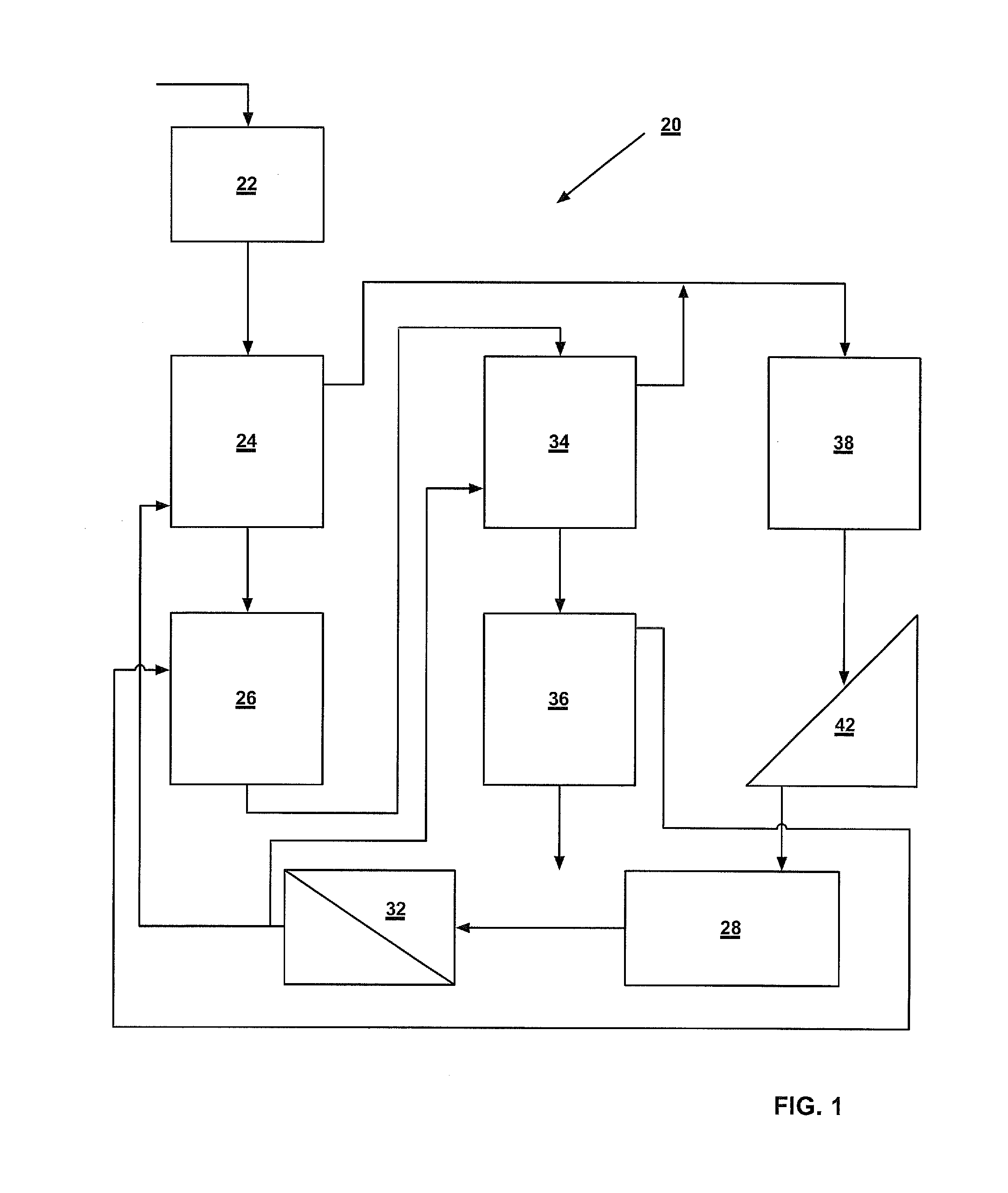
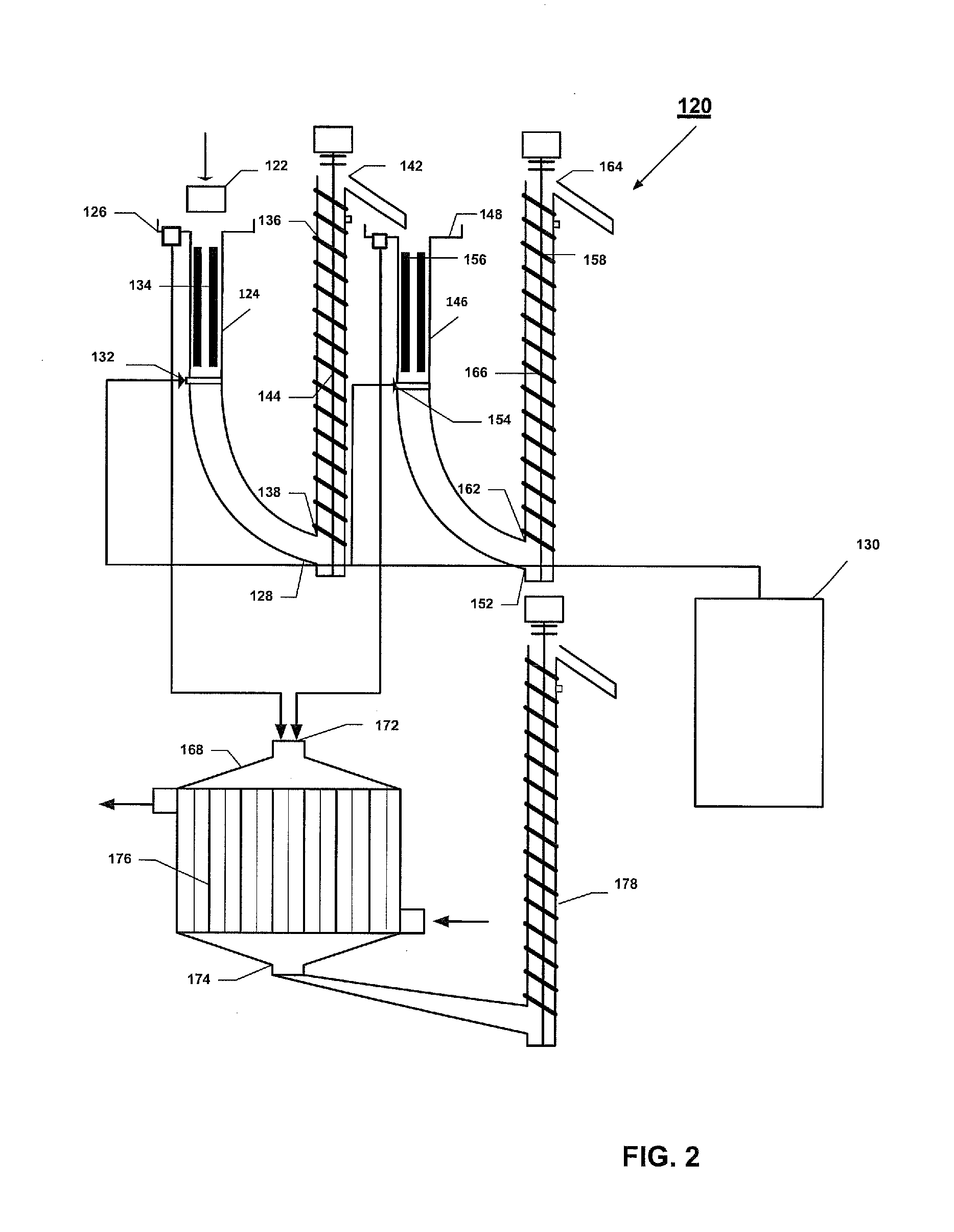
Systems and methods for processing sylvinite and carnallite ores
InactiveUS9227849B2Increase production and purity of productReduce material costsMagnesium chloridesHeat exchange cooling cystallizationSylviniteEngineering
Disclosed are systems and methods for processing carnallite or sylvinite ores. The system includes a measuring hopper, a lye clarifier, two vertical ore dissolving apparatuses, two ore dehydrators and one wet product dehydrator, a crystallizer, and a dryer. Each dissolving apparatus has alternating supply and grounding electrodes arranged in axial alignment with the apparatus. The ore is run through both dissolving apparatuses in succession and dehydrated after each dissolving apparatus. A dissolving lye is fed to each dissolving apparatus in countercurrent flow to the solid phase ore. The saturated lye from the dissolving apparatuses is transported to a crystallizer to be cooled. Cooling the lye forms crystalline potassium chloride or artificial carnallite, which then goes for dehydration and drying.
Owner:BIO TECHNO TERRA
Method for producing potassium chloride by using direct flotation process of third solid sylvinite
InactiveCN101774612BMeet environmental protection requirementsHigh yieldAlkali metal chloridesSylviniteFiltration
The invention relates to a method for producing potassium chloride by using the direct flotation process of third solid sylvinite. The method comprises the following steps: third solid sylvinite materials are crushed into particles with the diameter smaller than 10 millimeters, water is added into the crushed materials for decomposition to obtain slurry, and the weight ratio of the materials to water is 3:1 to 3.3:1; a flotation agent and a restraining agent are respectively added into the slurry, after the mixture is mixed evenly, a closed process including one-stage rough flotation, one-stage of scavenging flotation and two-stage fine flotation is carried out to perform flotation, and coarse potassium chloride, fine potassium chloride, tailing potassium chloride and decomposition motherliquid are respectively obtained after filtration; the decomposition mother liquid is evaporated and cooled for two times to fully change into magnesium chloride products; after coarse potassium chloride is washed, filtered and dried, a potassium chloride product the purity of which is more than 90% is obtained. The method can realize the decomposition process under the condition of large granularity, and effectively saves investment and running cost of grinding devices and raises the productivity of potassium chloride.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Preparation method of slow-release fertilizer with high fertilizer utilization rate for lotus root
InactiveCN107759373AReasonable ratioNutritional diversityCalcareous fertilisersBio-organic fraction processingFreeze-dryingChelated zinc
The invention discloses a preparation method of a slow-release fertilizer with a high fertilizer utilization rate for lotus root. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly mixingSpan and Tween, adding olive oil to be stirred, adding egg white, glutaraldehyde and berberine hydrochloride, raising the temperature and stirring, demulsifying, performing water-oil phase separation, washing, performing freeze drying, adding talcum powder and cyclodextrin, and uniformly mixing to obtain a first material; adding fermented compound bacteria into water to be uniformly mixed, addingchicken manure, oil-tea-cake, straw powder, shrimp shell meal, coal gangue, rice chaff and protein paste to be uniformly mixed, and performing stacking fermentation to obtain a second material; adding ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, defluorinated phosphate fertilizer, sylvinite, flue ash potash fertilizer, EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) chelated calcium, EDTA chelated zinc, EDTA chelated manganese and EDTA chelated copper into the second material to be uniformly mixed, pelletizing, spraying the first material for coating, and drying, thereby obtaining the slow-release fertilizerwith the high fertilizer utilization rate for lotus root.
Owner:定远县英华种植家庭农场
Special fertilizer for increasing survival rate of rice
InactiveCN107759418APromote growthIncrease productionAnimal corpse fertilisersExcrement fertilisersRice plantsNutrition
The invention discloses a special fertilizer for increasing the survival rate of rice. The special fertilizer comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 40-60 parts of ammonium chloride, 15-25 parts of defluorinated phosphate, 15-35 parts of sylvinite, 15-25 parts of carnallite, 2-6 parts of borax, 1-2 parts of zinc sulfate, 0.2-1 part of cupric nitrate, 1-2 parts of calcium nitrate, 1-2 parts of coal ash, 1-2 parts of expanded perlite, 1-3 parts of quartz sand, 1-2 parts of montmorillonoid, 30-50 parts of composted chicken manure, 20-30 parts of bamboo sawdust, 1-3 parts of activated carbon, 4-8 parts of olive cakes, 9-13 parts of fish bone powder, 20-30 parts of palm bran, 0.2-0.6 part of EM (Effective Microorganism) agents and 1-3 parts of a film agent. The special fertilizer is rich in nutrition, the yield of rice is greatly increased, the rice planted with the special fertilizer is full in grain and very low in disease rate, in addition, soil granule structures canbe reformed, soil can be relatively loosened, meanwhile the rice needs no pesticide in the growth process, and the special fertilizer is free of environment pollution and is ecological and environmentally friendly.
Owner:安徽耘泰农业发展有限公司
Method for improving chloride type salt pan production efficiency and chloride type salt pan product
InactiveCN110713195AImprove production efficiency is lowMagnesium sulfatesAlkali metal chloridesSylviniteSulfate radicals
The invention relates to the field of salt pans, in particular to a method for improving the production efficiency of a chloride type salt pan and a chloride type salt pan product. According to the method, a mirabilite solution is firstly added into brine, so that magnesium ions in the brine are combined with sulfate radicals in mirabilite, the magnesium ions are separated out of the brine in theform of magnesium sulfate crystals, and the content of the magnesium ions in the brine is reduced; and then the residual brine with the reduced content of the magnesium ions is subjected to evaporation and sun treatment to obtain a salt pan product. According to the method, the magnesium ions in the brine are firstly reduced, and the magnesium salt does not need to be dried in the sun in the subsequent evaporation and salifying process, so that the salifying time is greatly shortened, and the production efficiency of the salt pan is improved. After magnesium ions are reduced, a potash fertilizer production route is changed from a bischofite route to a more energy-saving and simpler sylvine route, so that the process difficulty is greatly reduced.
Owner:QINGHAI UNIV FOR NATITIES
Systems And Methods For Processing Sylvinite And Carnallite Ores
InactiveUS20140030164A1Increase production and purity of productReduce material costsMagnesium chloridesHeat exchange cooling cystallizationSylviniteEngineering
Disclosed are systems and methods for processing carnallite or sylvinite ores. The system includes a measuring hopper, a lye clarifier, two vertical ore dissolving apparatuses, two ore dehydrators and one wet product dehydrator, a crystallizer, and a dryer. Each dissolving apparatus has alternating supply and grounding electrodes arranged in axial alignment with the apparatus. The ore is run through both dissolving apparatuses in succession and dehydrated after each dissolving apparatus. A dissolving lye is fed to each dissolving apparatus in countercurrent flow to the solid phase ore. The saturated lye from the dissolving apparatuses is transported to a crystallizer to be cooled. Cooling the lye forms crystalline potassium chloride or artificial carnallite, which then goes for dehydration and drying.
Owner:BIO TECHNO TERRA
Yeast wastewater treatment method, feed additive obtained by same and feed product
ActiveCN102060341BMaintain acid-base balanceGuaranteed ion balanceGeneral water supply conservationBioloigcal waste fertilisersYeastHigh concentration
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Desliming agent for slime-bearing sylvinite and processing method for slime-bearing sylvinite
ActiveCN106587107AReduce dosageSimple processAlkali metal chloridesAlkali metal halide purificationCarboxymethyl celluloseSylvinite
The invention specifically relates to a desliming agent for slime-bearing sylvinite, belonging to the field of the chemical industry. The desliming agent for the slime-bearing sylvinite is carboxymethyl cellulose with an etherification degree of 0.75 to 0.9. The invention also discloses a processing method for the slime-bearing sylvinite. As the desliming agent is added in the process of processing of the slime-bearing sylvinite, slime in the slime-bearing sylvinite can be substantially removed. Compared with desliming methods / reagents in the prior art, the desliming agent provided by the invention is less in usage amount and is added once in the whole processing process; so treating process is substantially simplified, desliming efficiency is improved, and treating cost is reduced. Results of production and trial application show that the desliming agent and the processing method with high desliming rate are especially applicable to large Kunteyi salt flat potassium ore deposits in Lenghu Town, Qinghai Province, China.
Owner:曲保伦
Method for treating potassium mixed salt ore by adopting dense media and cold crystallization direct flotation
The invention relates to a method for treating potassium mixed salt ore by adopting dense media and cold crystallization direct flotation, and belongs to the technical field of mineral processing. Themethod comprises the following steps of crushing the potassium mixed salt type ore to below 10-30mm, dividing the crushed potassium mixed salt type ore into a coarse fraction and a fine fraction, andsorting the coarse fraction ore by adopting a dense medium cyclone to obtain three products, namely carnallite rough concentrate, potassium mixed salt ore and sylvine ore; carrying out cold decomposition crystallization or reverse flotation-cold decomposition crystallization on the carnallite rough concentrate, and refining to obtain KCl concentrate; and adopting the cold decomposition crystallization-direct flotation process in the potassium mixed salt ore and the fine-grained materials, adopting a direct flotation process in the sylvine ore, and then refining to obtain KCl concentrate. According to the method, the potassium mixed salt raw ore is divided into the low-sodium carnallite ore, the carnallite and sylvine mixed ore and the sylvine ore through three-product dense medium separation in advance, then different treatment processes are adopted for the three different ores, and the method has the advantages of being high in process adaptability, low in energy consumption, large in final KCl product granularity, high in recovery rate and the like.
Owner:BLUESTAR LEHIGH ENG INST CO LTD
Preparation method of low-sodium salt
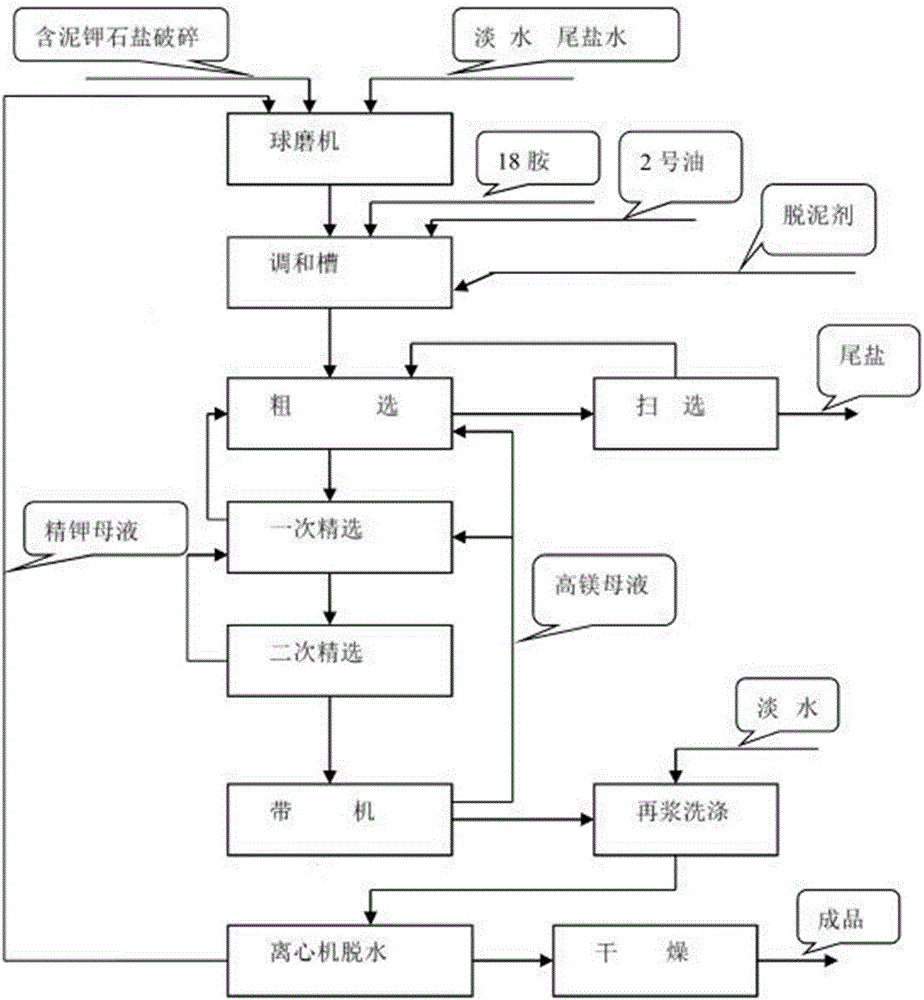
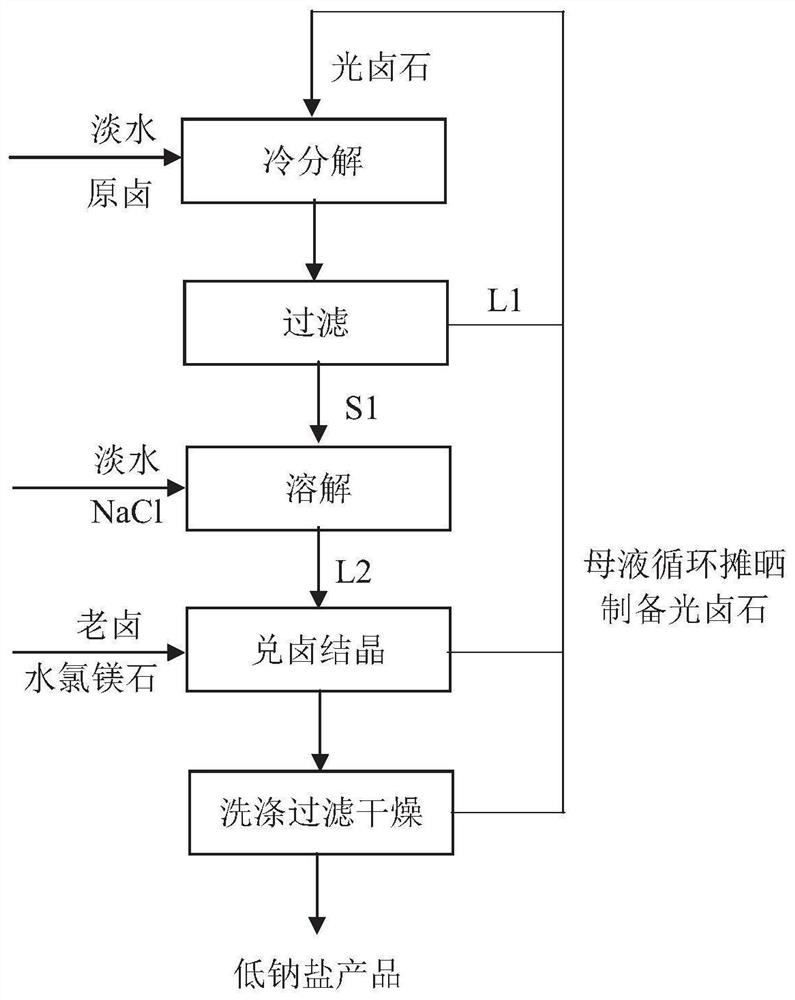
ActiveCN113753920AGood removal effectSimple processAlkali metal chloridesAlkali metal halide formation shapeSylviniteProcess engineering
The invention discloses a preparation method of low-sodium salt. The preparation method comprises the steps of decomposing carnallite to obtain first mother liquor and sylvinite solid; mixing the sylvinite solid with fresh water to form second mother liquor; and mixing the second mother liquor and old brine, reacting and crystallizing to obtain the low-sodium salt. The preparation method provided by the invention is simple in process flow, low in energy consumption, low in cost, green and environment-friendly; and the prepared low-sodium salt product meets the requirements of the low-sodium salt QB / T2019-2020 standard, is high in purity and controllable in particle size, and has relatively strong market competitiveness.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of extracting potassium chloride raw products in sylvinite ore through air jigging
A method of extracting potassium chloride raw products in sylvinite ore through air jigging comprises the following steps of (1) crashing: crashing solid sylvinite ore; (2) jigging separation: feeding crashed materials into an air jigging separator, taking gas-solid suspensoid of pressurized air plus magnetite powder or ferrosilicon powder as a medium to separate sodium chloride from potassium chloride, so as to obtain potassium chloride concentrate and sodium chloride tailings; or when the sylvinite ore contains carnallite, performing a first section of jigging separation to obtain potassium chloride and carnallite bulk concentrate and sodium chloride tailings, and then performing a second section of jigging separation to obtain potassium chloride concentrate and carnallite tailings; (3) magnetic separation: feeding the potassium chloride concentrate into a magnetic separator, and recycling the magnetite powder or the ferrosilicon powder, so as to obtain a potassium chloride product. According to the method, the cyclic utilization rate of the medium is high, the technological process is simple, the operability is high, the separation result is good, the yield coefficient can reach up to 90 percent, the content of KCL in the obtained potassium chloride product is larger than or equal to 72 percent, and the method is specially suitable for water-deficient areas.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Preparation method of ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst
InactiveCN107008415AEvenly dopedImprove adsorption capacityOther chemical processesWater treatment compoundsOcteneLithium hypochlorite
The invention relates to a preparation method of an ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst, belonging to the technical field of environment-friendly and chemical catalysts. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by taking attapulgite, diopside, montmorillonite, sylvite, pulverized fuel ash and coal gangue porous materials as carriers, performing pore expansion and modification to the carriers through lithium hypochlorite and beryllium bis(acetylacetonate), adding a surfactant dioctadecyl-2-methyl hydroxyethyl ammonium chloride and performing surface activation treatment under ultrasonic wave effect, then leading the ultrasonically surface-activated carriers to have hydrothermal reaction with a complex mineralizer (borax and potassium sulfate), catalytic activity assistant precursors, namely praseodymium(III) tris[3-(trifluoromethylhydroxymethylene)-D-camphorate], 1,1,1-neodymium trifluoroacetylacetonate, tris(6,6,7,7,8,8,8-heptafluoro-2,2-dimethyloctane-3,5-dionato-O,O')dysprosium (III), tris[N,N-bis(trimethylsilyl)amide] erbium rare earth metal organic compound, and catalytic active site component precursors, namely common transitional metal organic compound ferrous fumarate, nickel citrate and copper glutamate and precious metal compound tris(bipyridine)ruthenium(ii)chloride hexahydrate in a hydrothermal reactor under the action of an emulsifier dimethylaminoacrylate laurate ammonium chloroacetate, drying reactive products to remove moisture, and firing in a muffle furnace at certain temperature, to obtain the ozone heterogeneous oxidation solid catalyst.
Owner:SICHUAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com