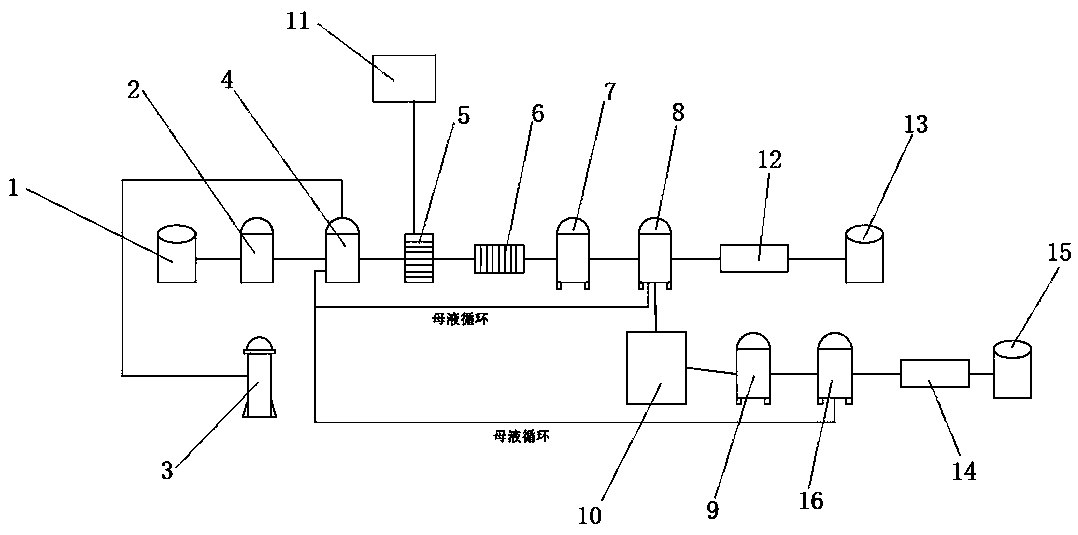
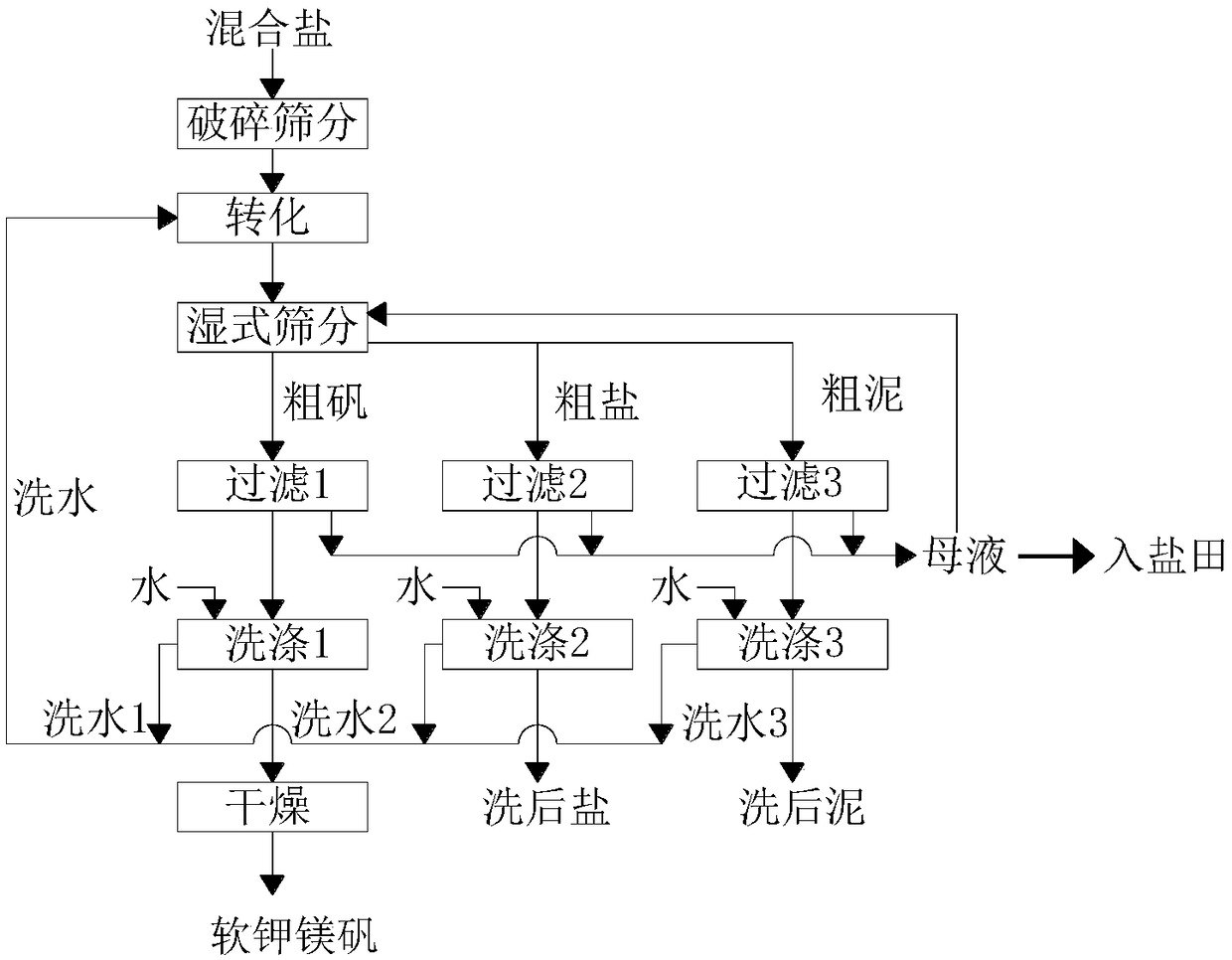
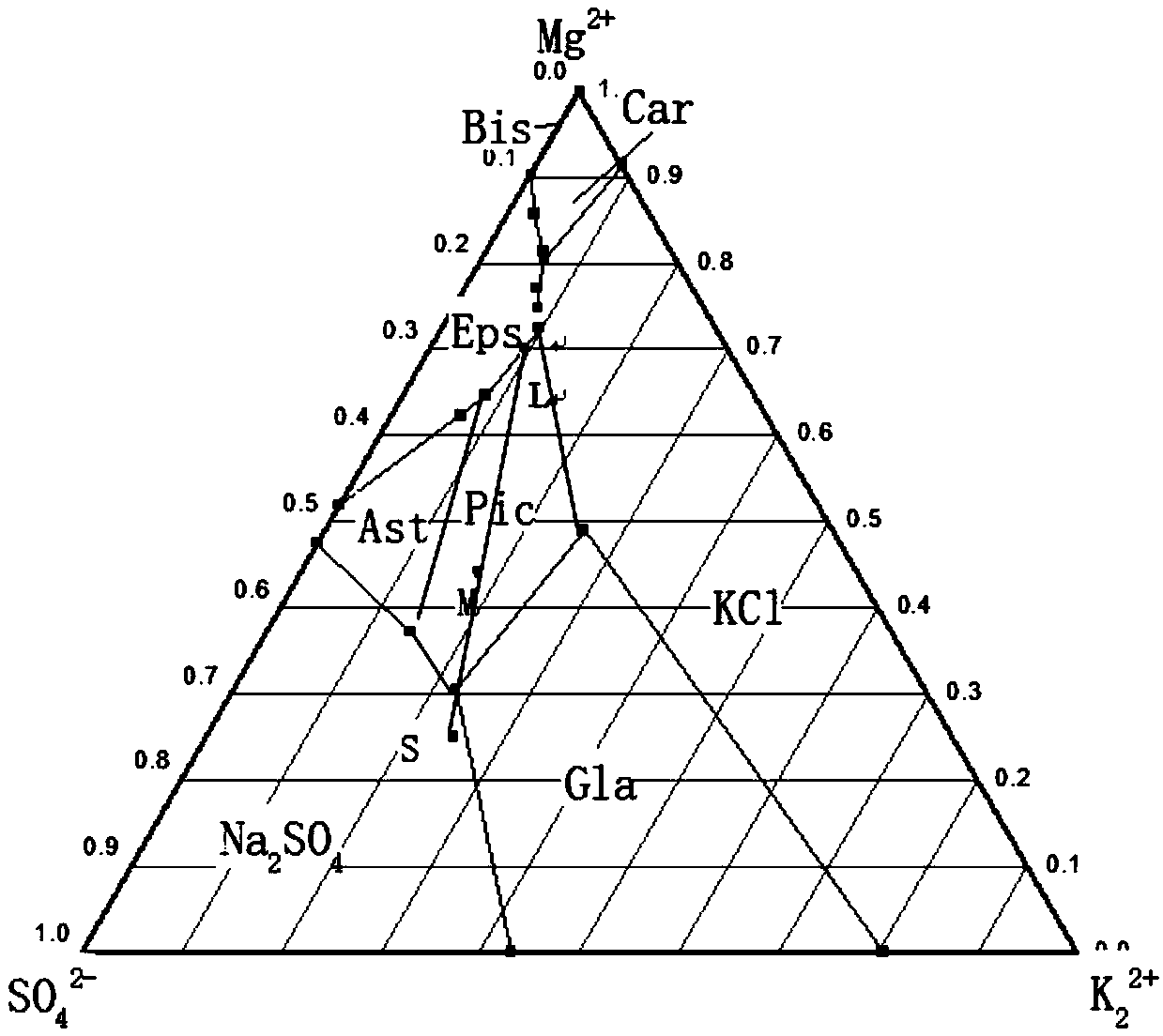
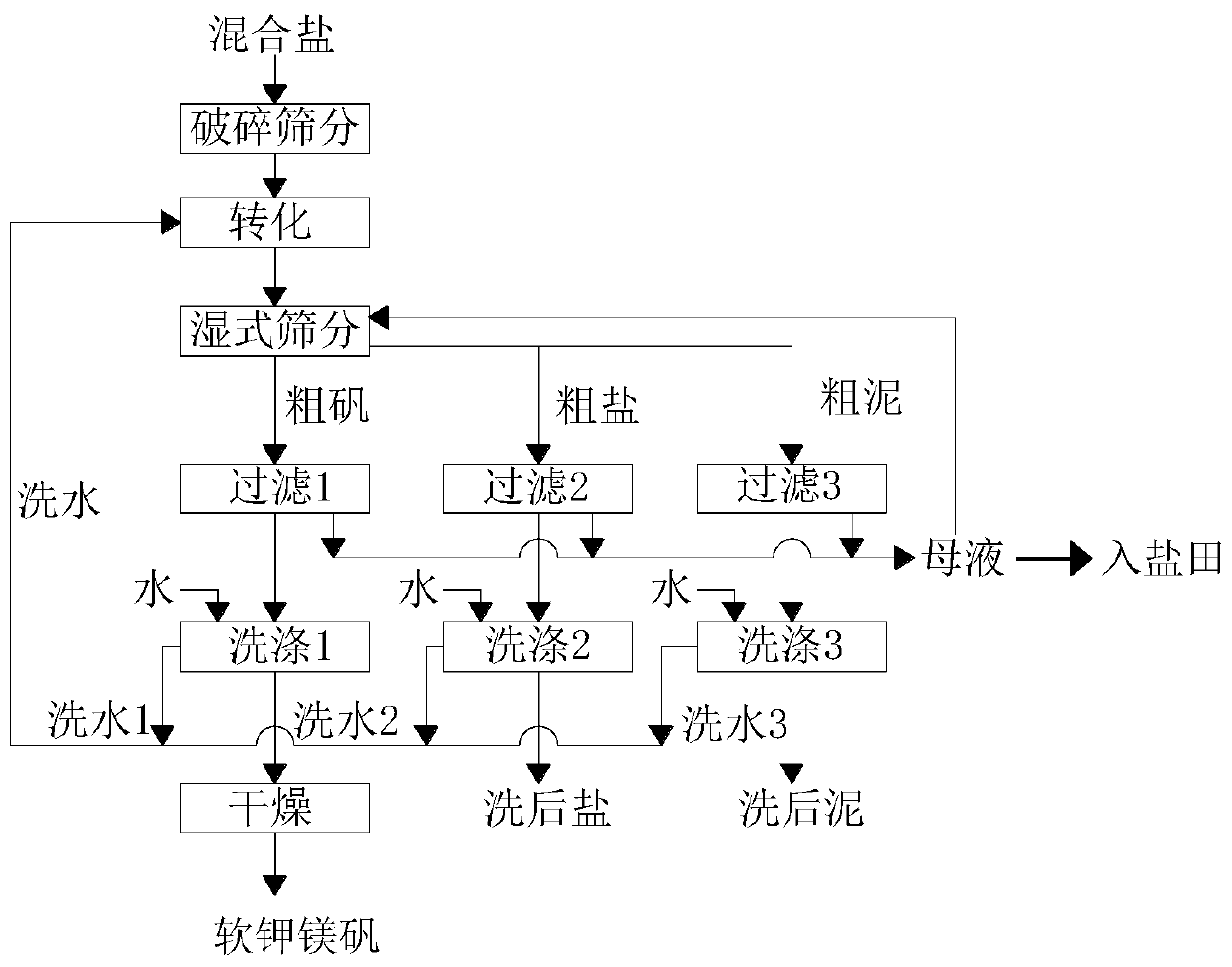
Patents
Literature
42results about "Double sulfate preparation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
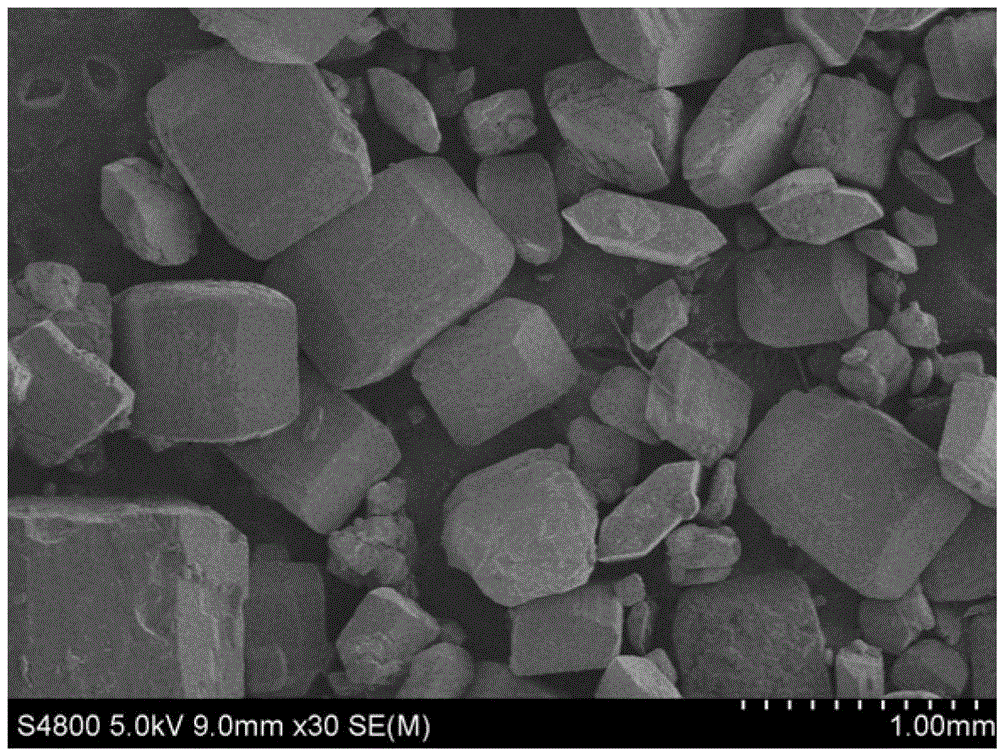
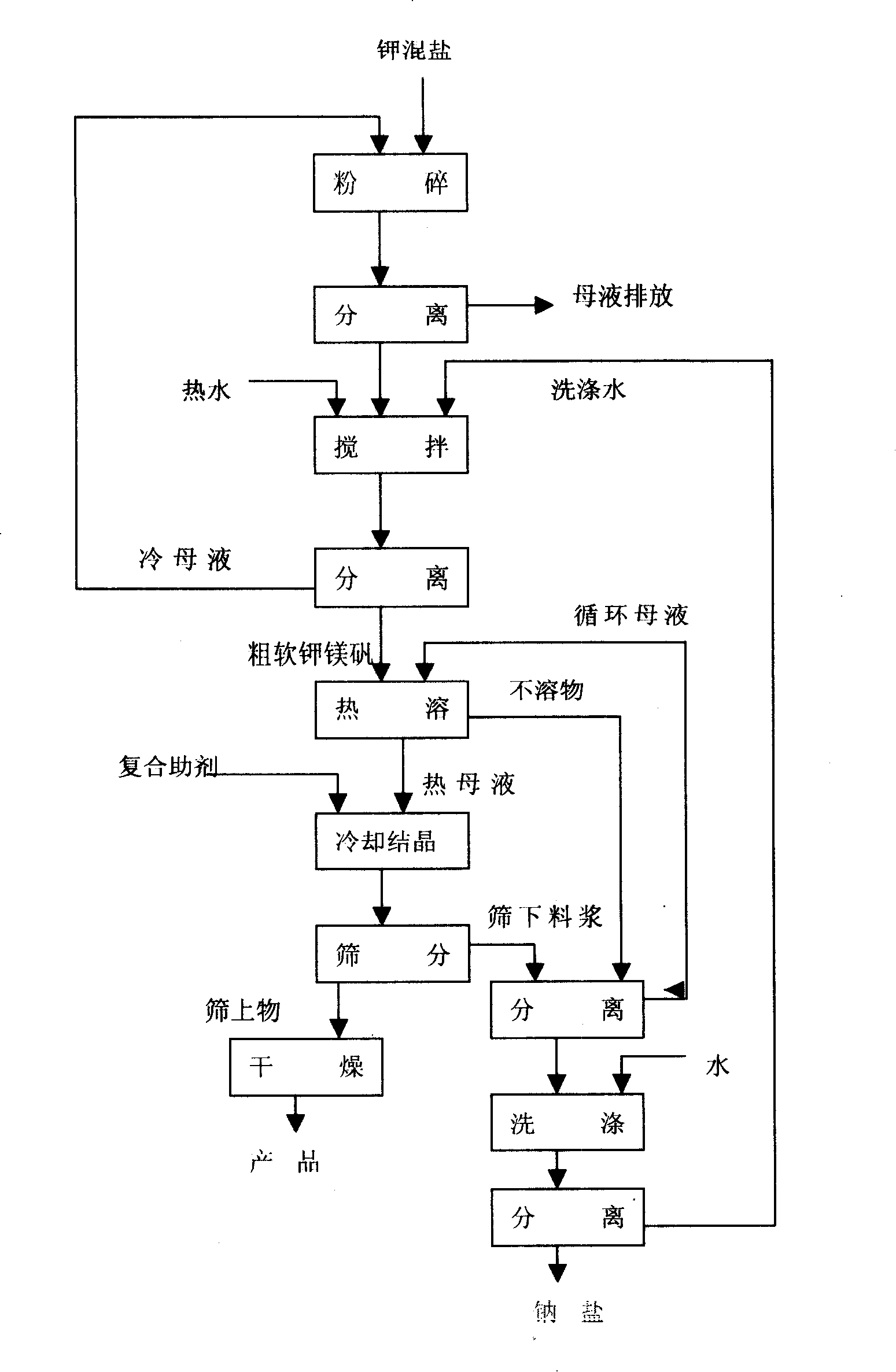
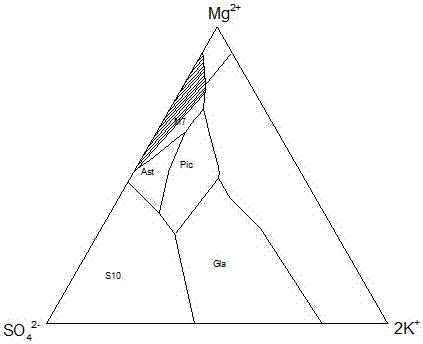
Novel technique for producing large-particle high-grade soft leonite from potassium mixed salt by hot crystallization
The invention relates to method for extracting schoenite of high purity from the raw material such as potassium magnesium sulfate subtype brine, sea salt bitter brine, lake salt, well salt brine, belonging to the salt chemistry industry, characterized in that potassium mixed with salt is wetly ground and crushed to remove the free magnesium chloride; potassium compound is discomposed by adding water; the magnesium chloride is dissolved and removed to obtain crude schoenite with sodium; the thermosol recrystallizing method is adopted to obtain large particle schoenite and at the same time separate sodium salt under the condition that compound growth substance and denaturant are added,. The novel process adopts the crystallization method to remove magnesium chloride in liquid phase and sieve the sodium salt in solid phase; developing a new conception for preparing the schoenite from the potassium mixed salt. Recycling rate of the potassium is higher than that of all kings of methods known at present and product grade can reach 99.5 percent with the best product quality in the world; the prepared large particle schoenite with high purity can be used as the raw material for producing potassium sulfate with high purity.
Owner:潘向东 +1
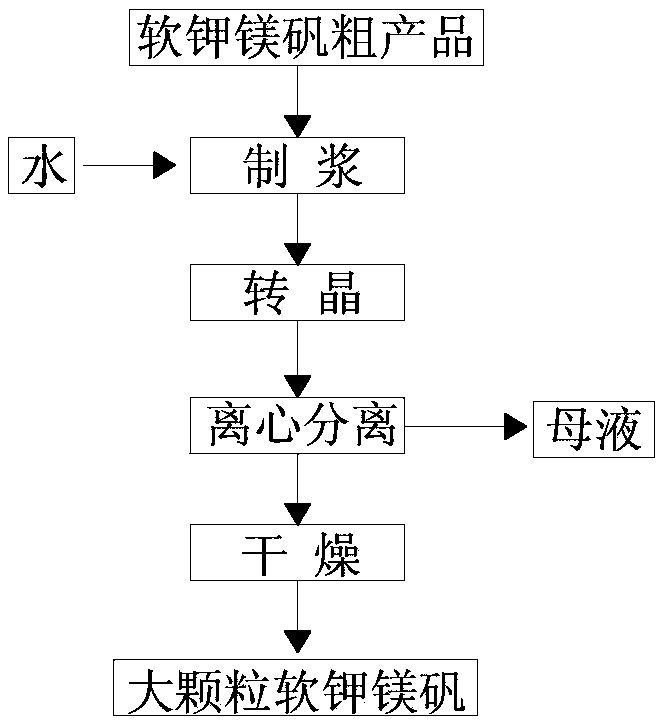
Method for preparing large-particle picromerite
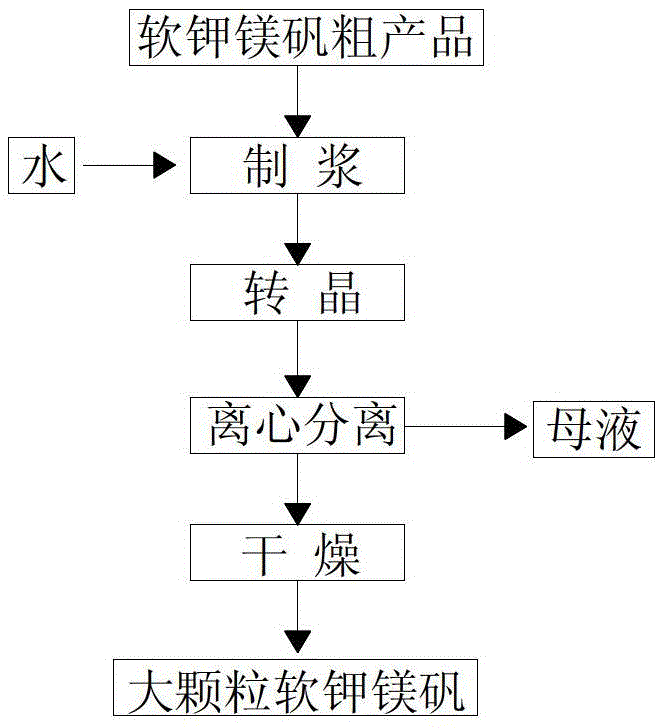
The invention relates to a method for preparing a large-particle picromerite from picromerite crude product. The method comprises the following steps: taking picromerite crude product gained through flotation as raw materials, and through a crystal transformation step of reducing the temperature from 50-70 DEG C to 20-30 DEG C, enabling compound leonite with four crystal water (or langbeinite without crystal water) to be changed into compound picromerite with six crystal water. The particle diameter of the prepared large particle picromerite can reach 620.5 micrometers to the maximal extent, the problem that fine particle picromerite is not easy to separate and dry and easy to agglomerate is solved, and meanwhile the potassium ion recovery ratio in the technology can reach above 80 %.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH +1
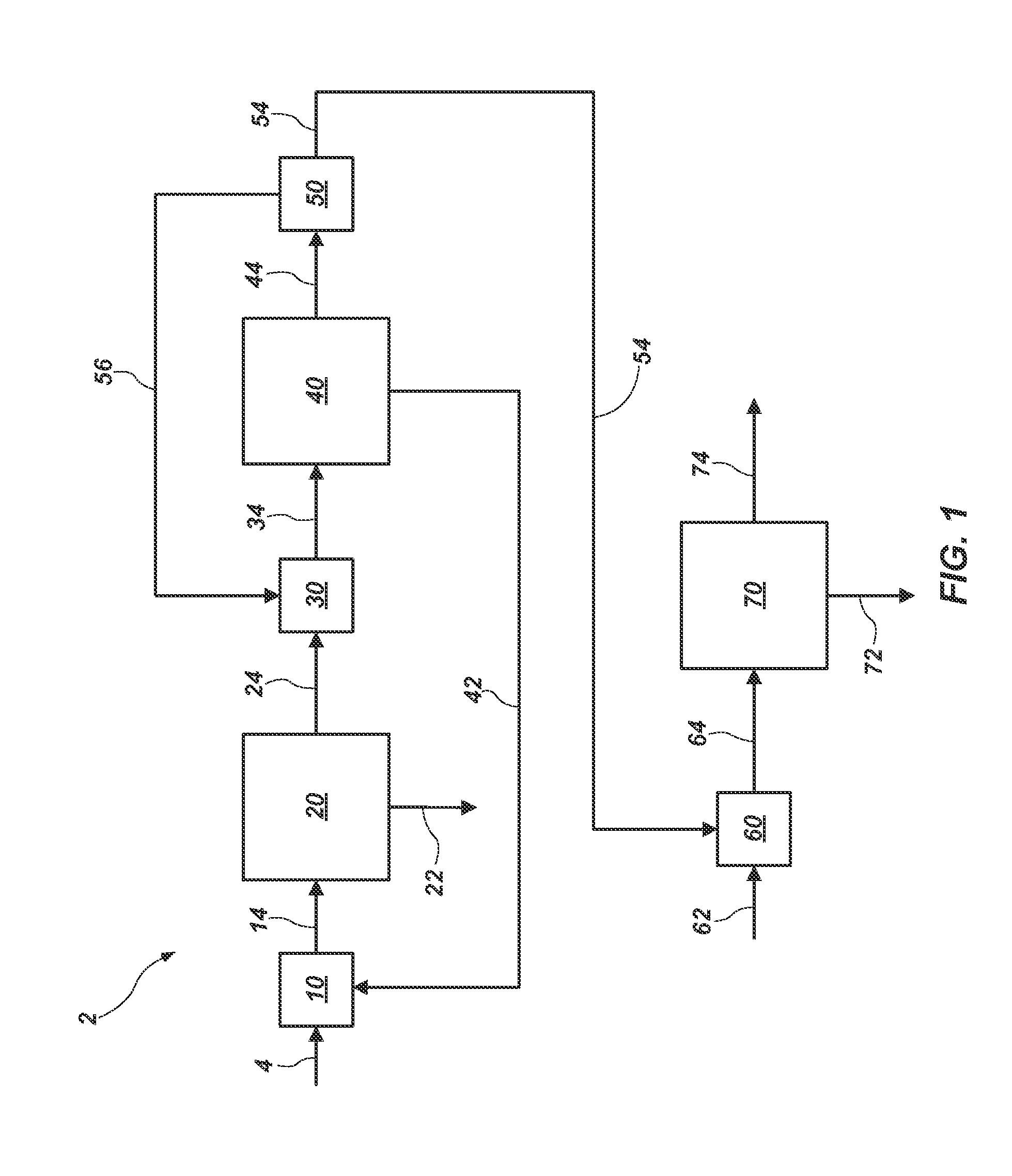
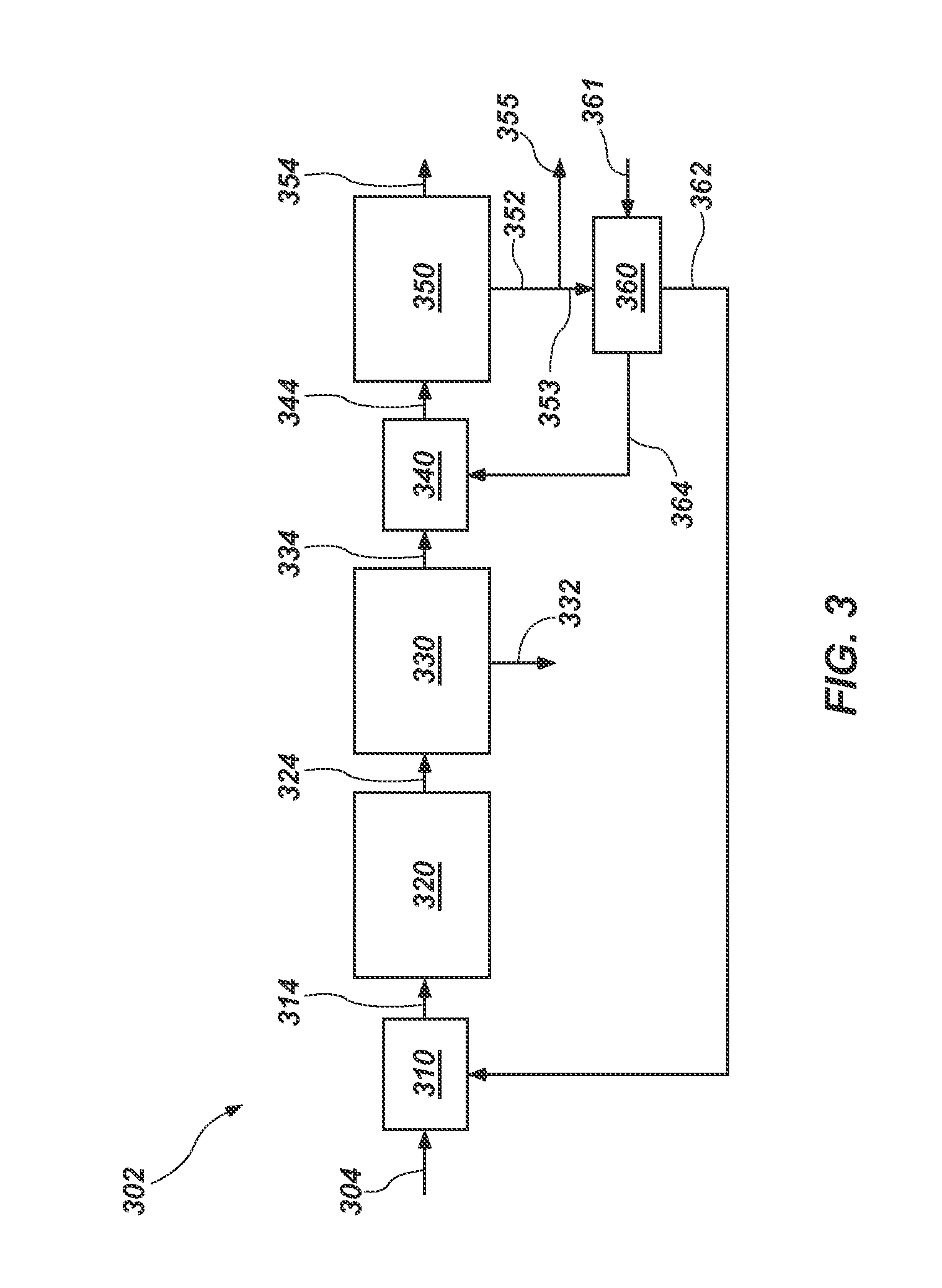
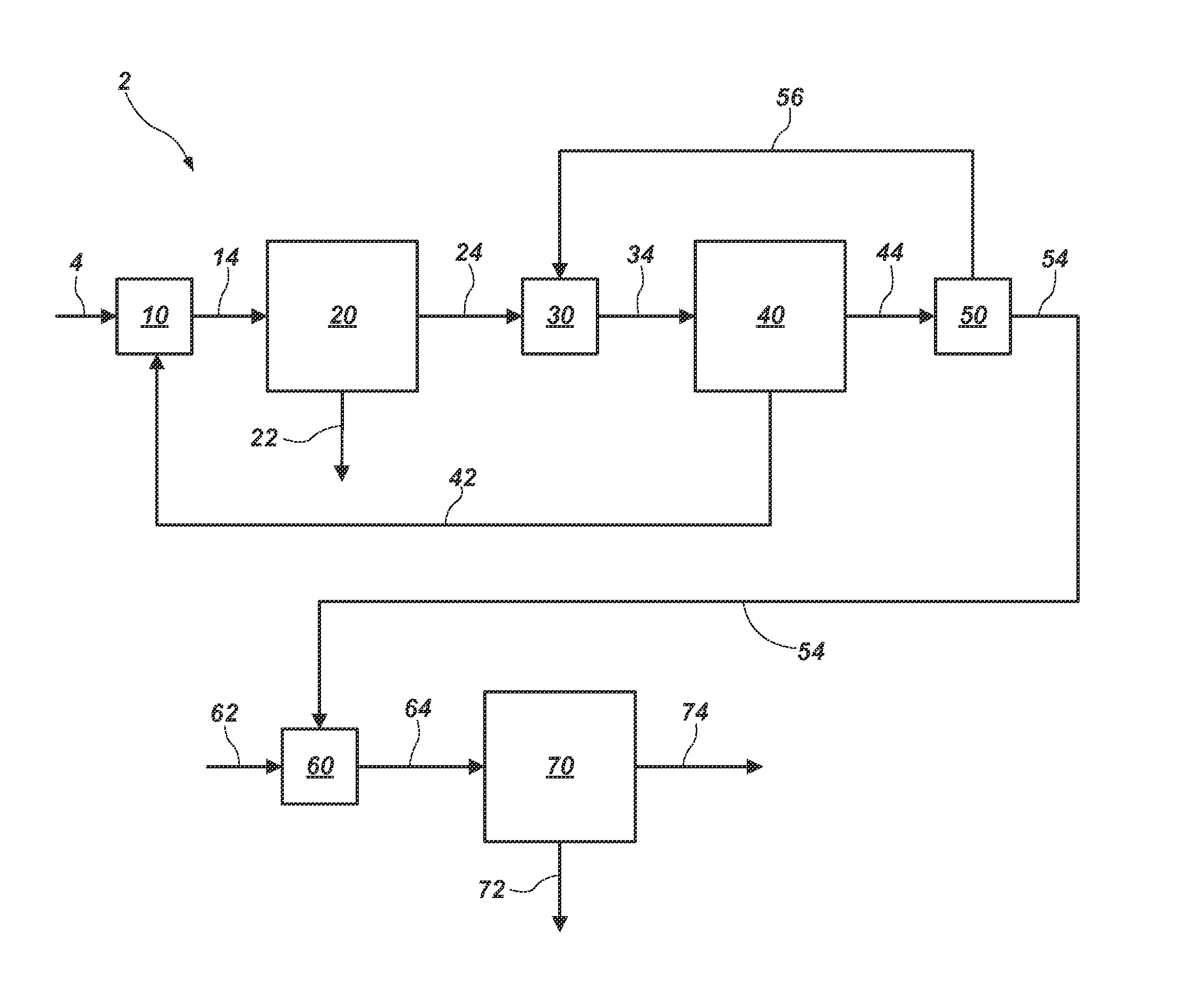
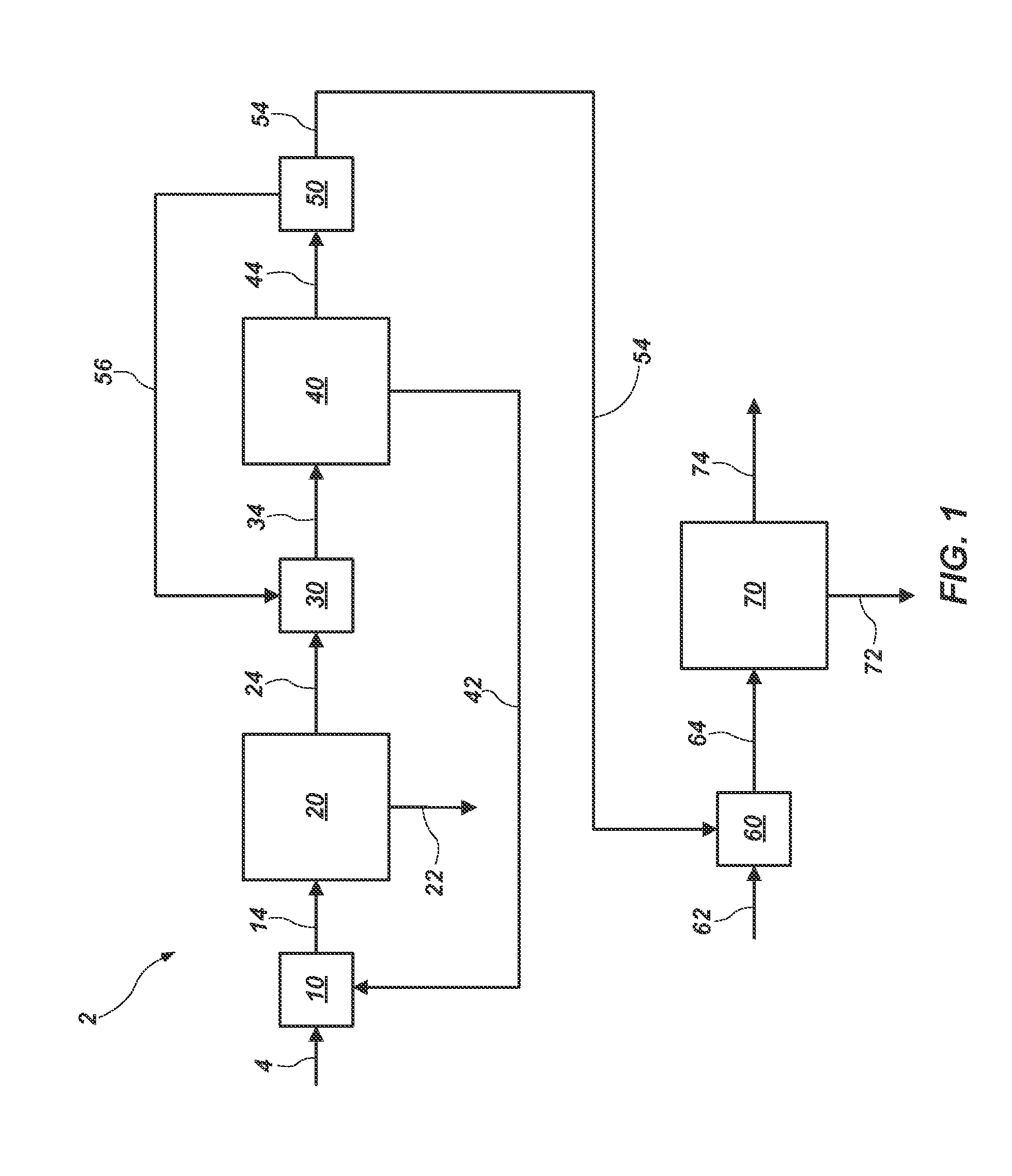
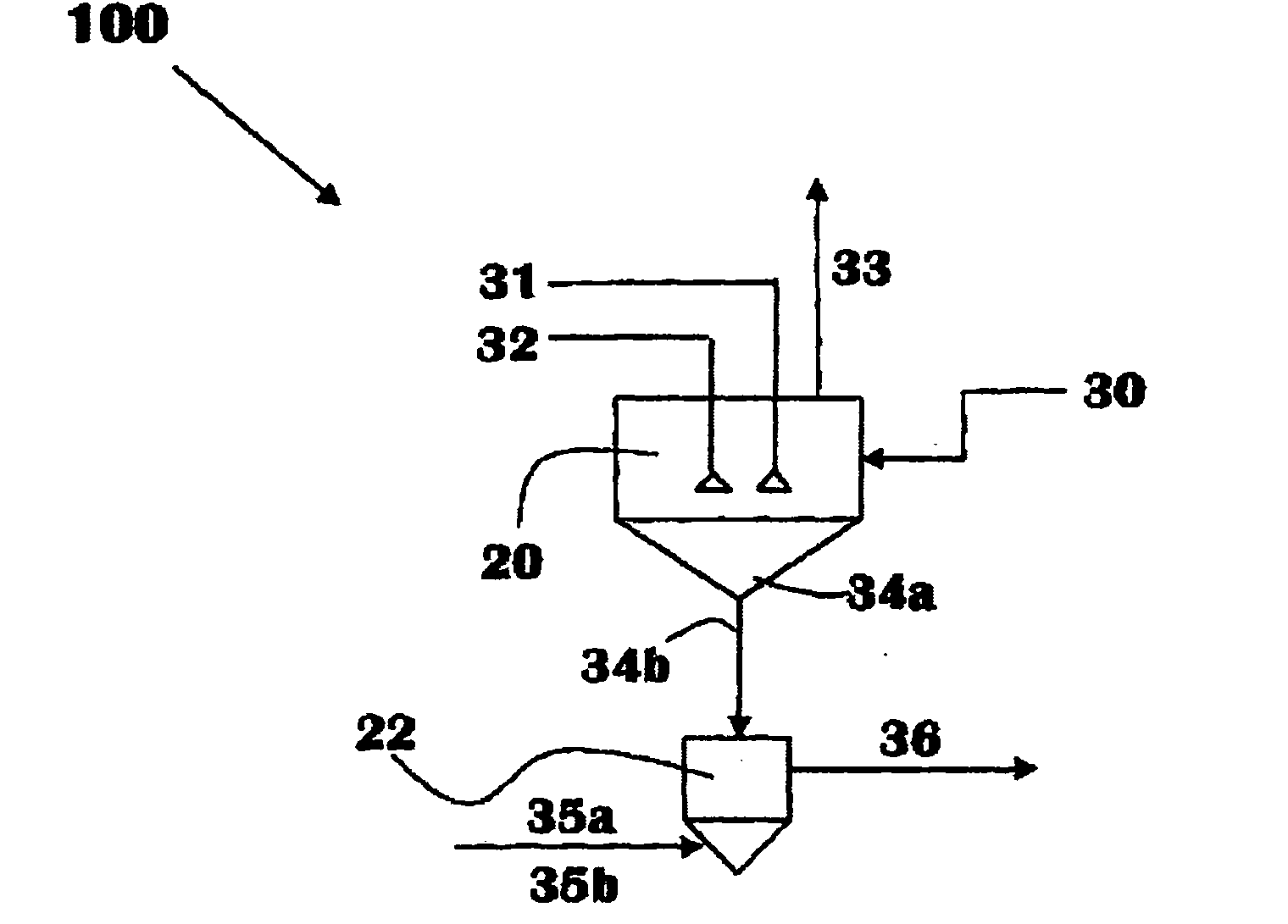
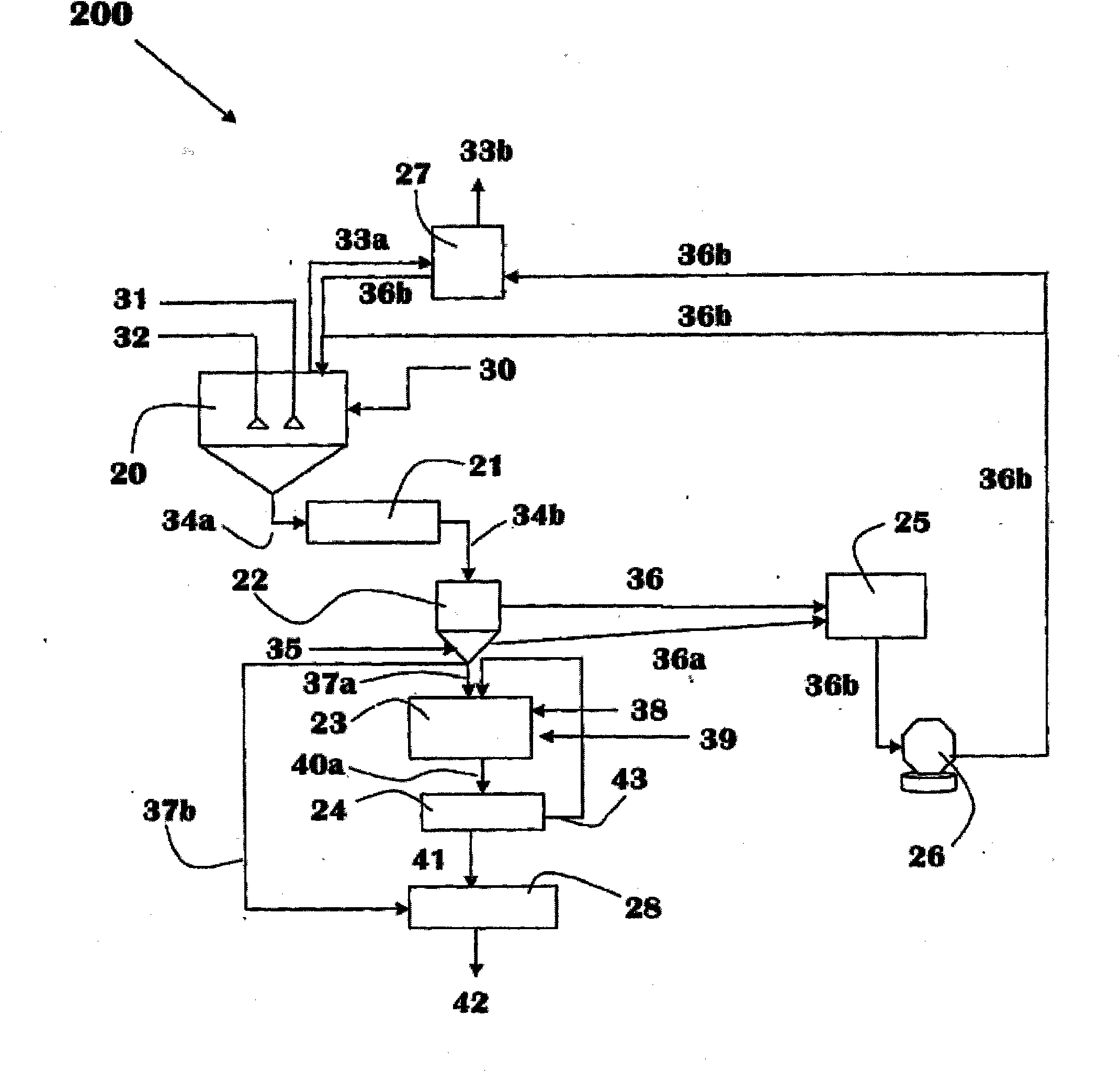
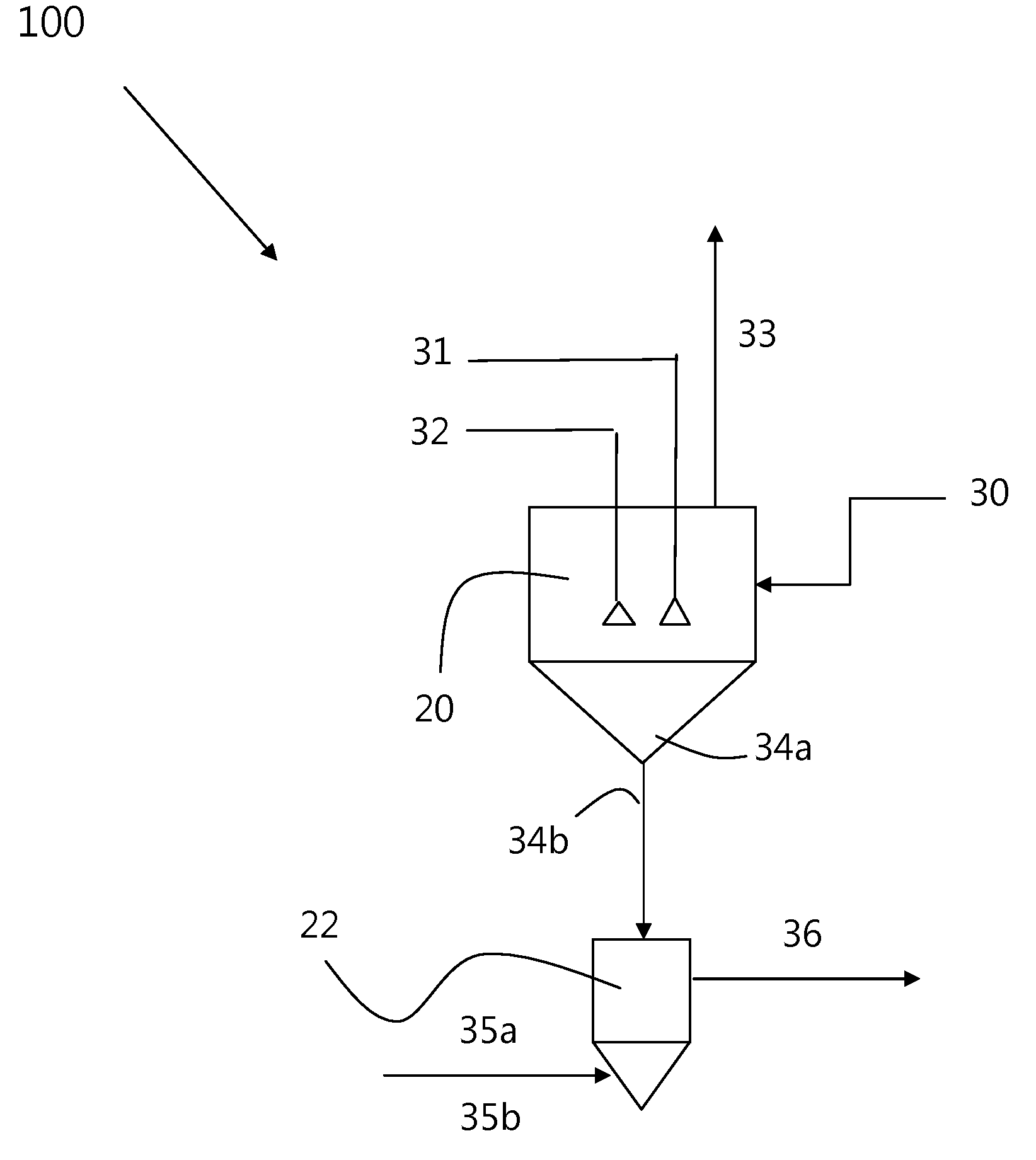
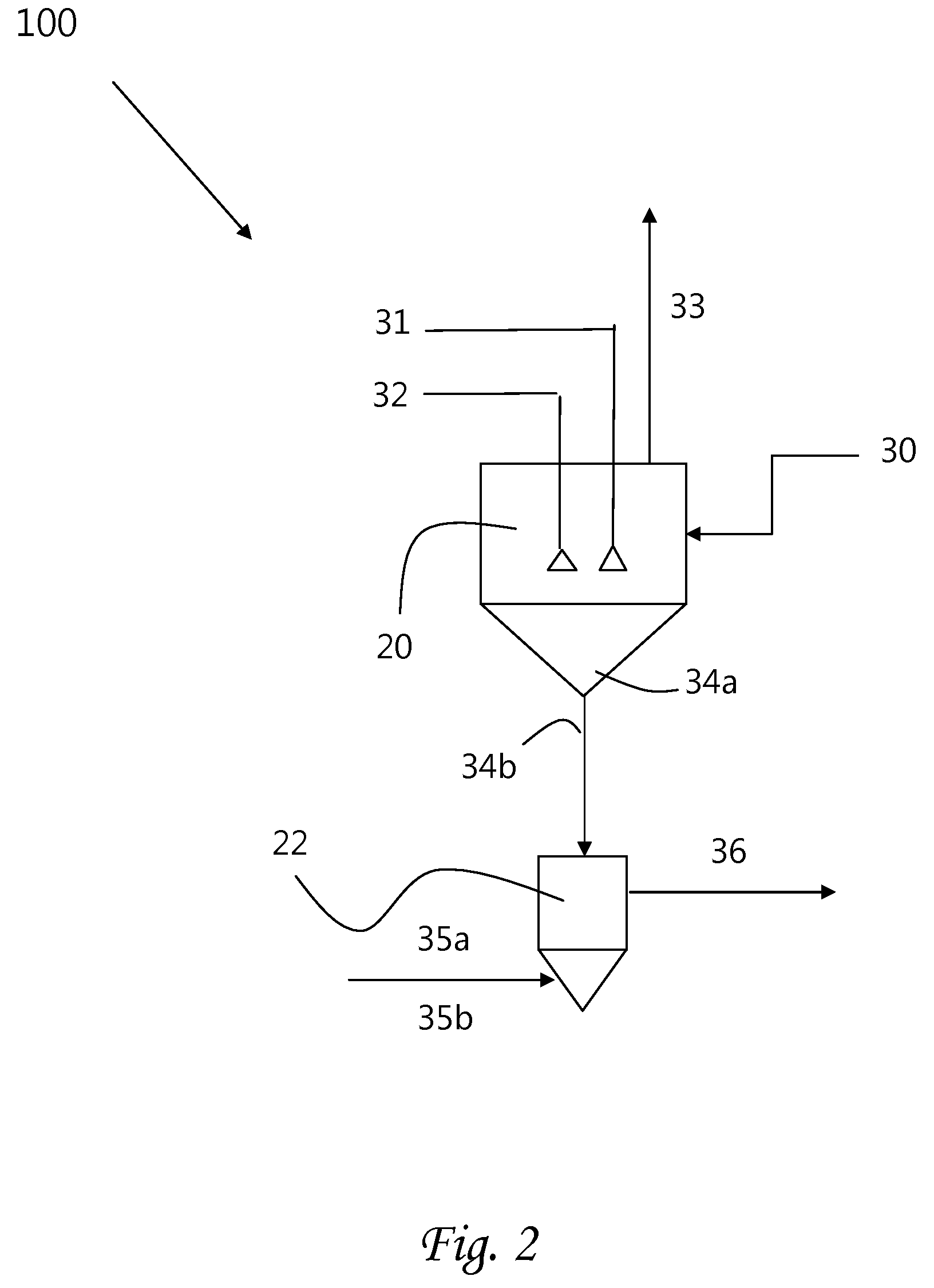
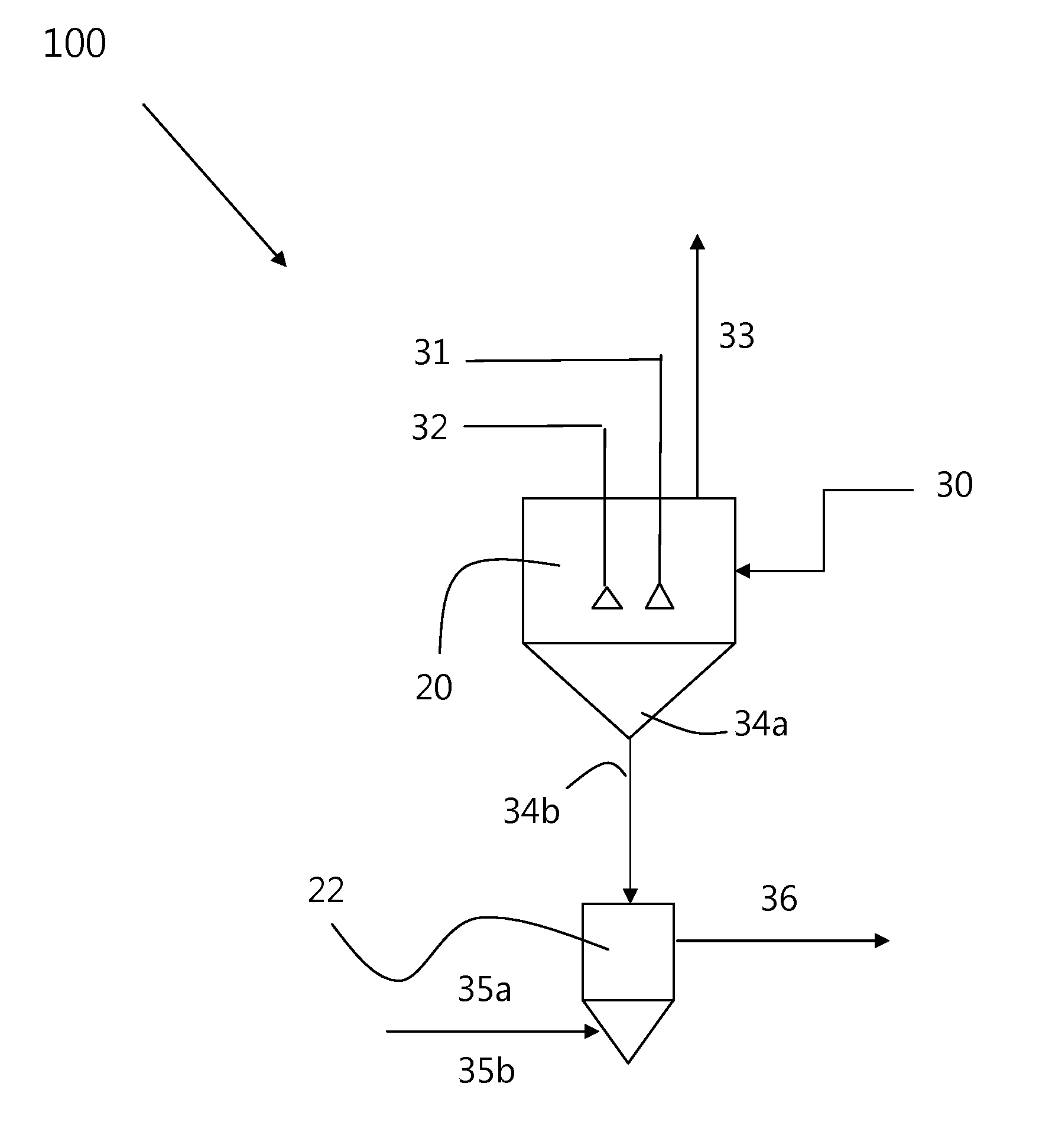
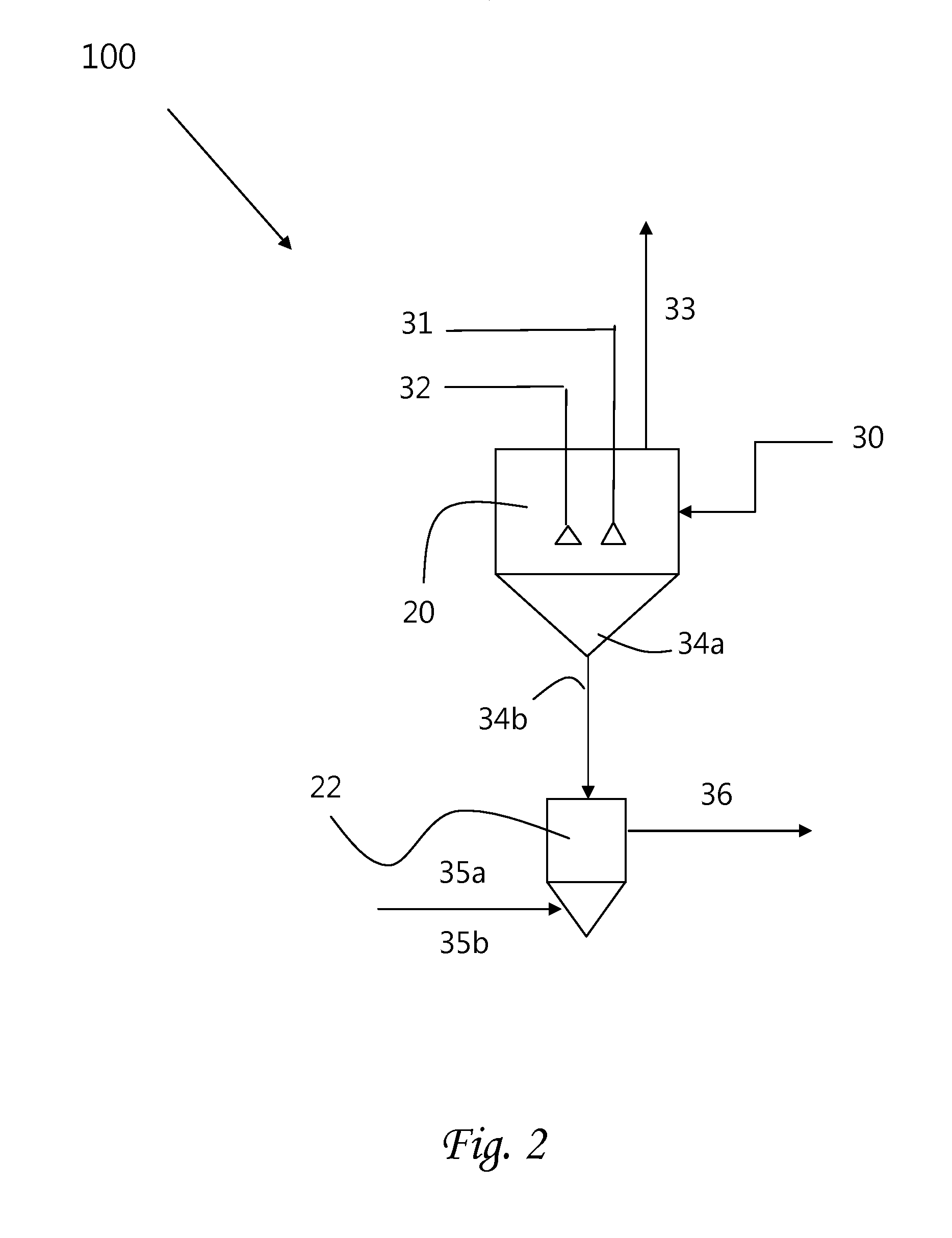
Methods of processing solutions of potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate, methods of producing potassium sulfate, and related systems
ActiveUS20140072507A1Economic value maximizationIncrease productionOther chemical processesDouble sulfate preparationPotassium sulfateAqueous solution
Methods of processing an aqueous solution comprising potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate include crystallizing K2SO4, crystallizing recycle crystals, and mixing at least a portion of the recycle crystals with the aqueous solution. Systems for processing potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate include a first crystallizer and a second crystallizer in fluid communication with the second mix tank. The second crystallizer is structured and adapted to precipitate recycle crystals from the concentrated liquor to form a potassium-depleted recycle brine. The recycle crystals precipitated in the second crystallizer have a composition suitable to be recycled to the first crystallizer to increase the production of SOP.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL POTASH CORP USA
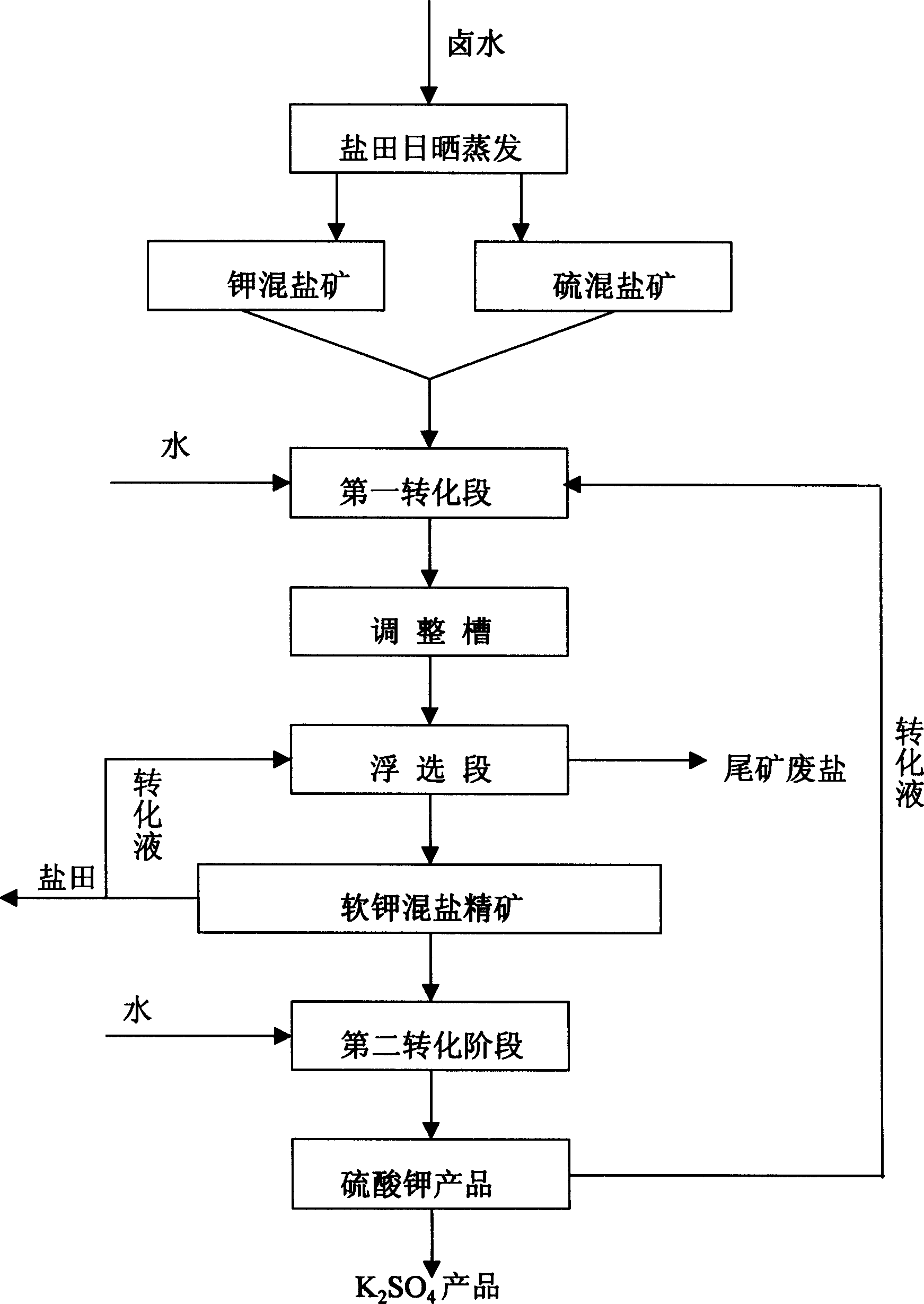
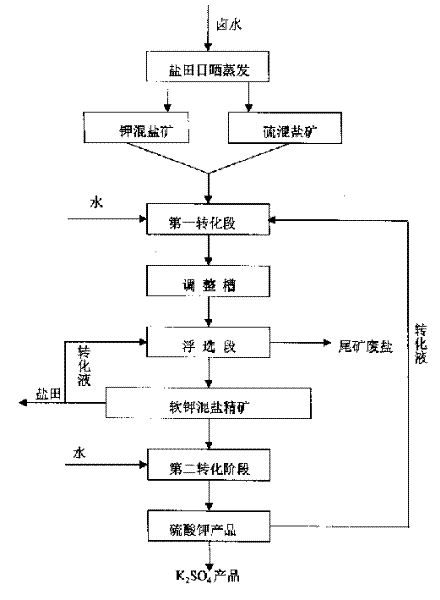
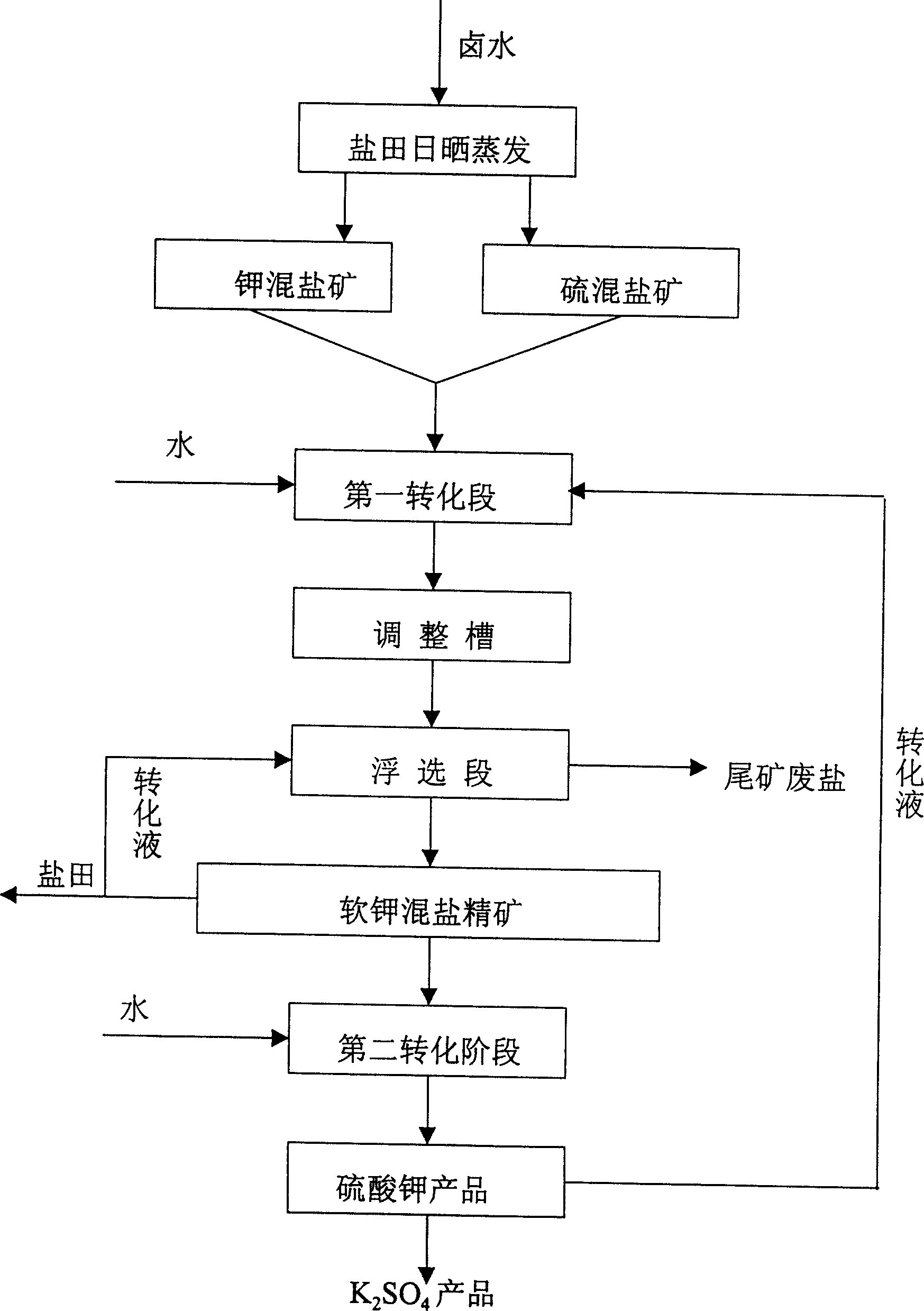
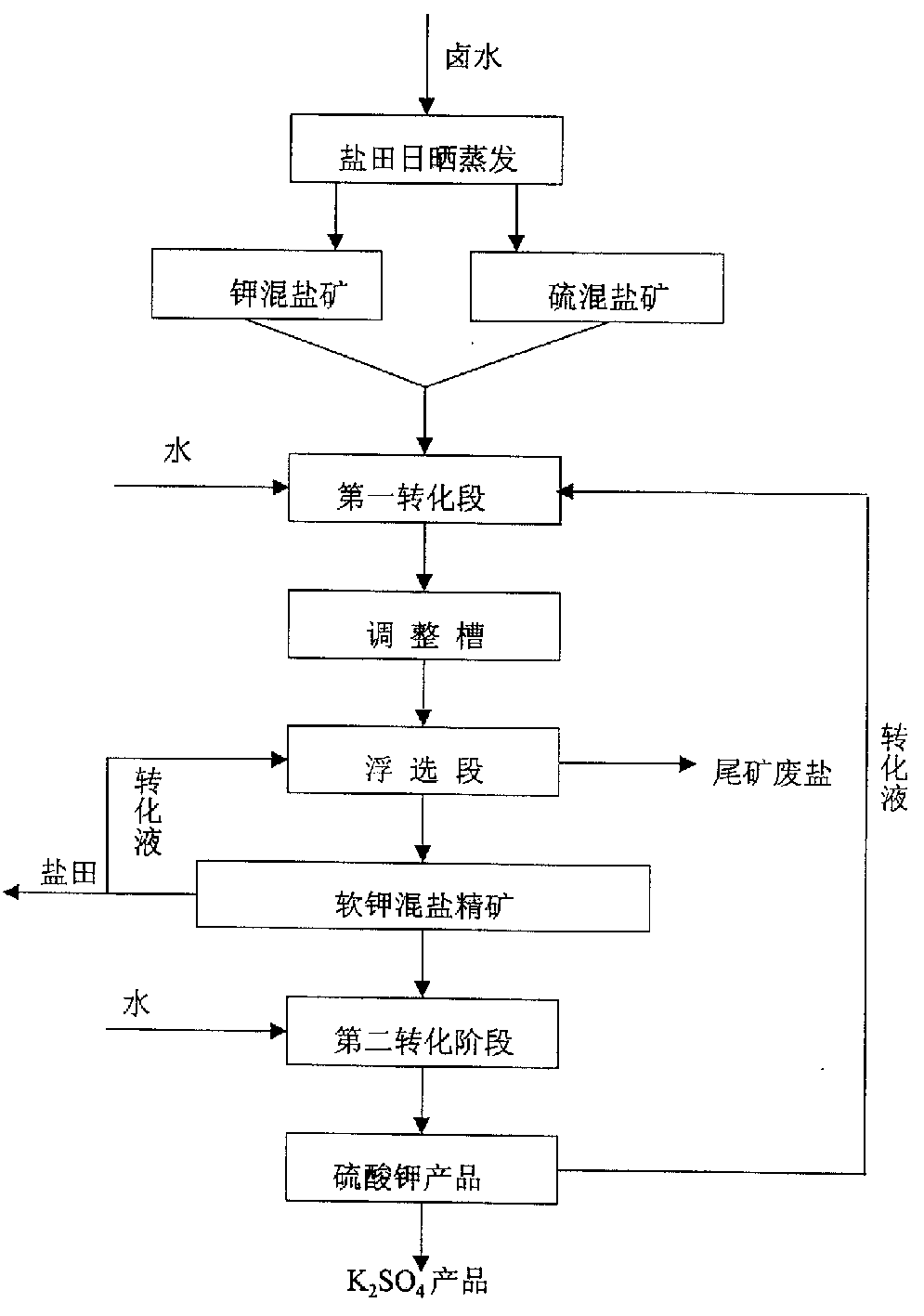
Potassium sulfate preparing process from sulfate-type salt lake bittern
InactiveCN1548372AAdaptable to changeWhite colorDouble sulfate preparationFlotationSalt lakeChloride
The present invention is one method of preparing potassium sulfate with sulfate type lake bittern resource. The preparation process includes the following steps: shining bittern to obtain mixed sulfate mineral with sodium chloride, schoenite, magnesium sulfate and potassium chloride as main components and mixed potassium salt mineral with sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium sulfate and carnallite as main components; mixing these two kinds of mineral and converting with water at normal temperature to obtain coarse mixed schoenite mineral; floating the mixed schoenite mineral to obtain concentrated mixed schoenite mineral; adding water to the high-grade concentrated mixed schoenite mineral and decomposing directly to obtain potassium sulfate product; water washing the tailing to obtain industrial salt. The technological process is power saving and low in cost, and has other advantages.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Process of preparing potassium sulfate with potassium containing bittern of magnesium sulfate subtype
The present invention provides process of preparing potassium sulfate with potassium containing subtype magnesium sulfate bittern. The process includes naturally evaporating potassium containing subtype magnesium sulfate bittern from salt lake to crystallize and separate out potassium containing sulfate and sulfate radical containing carnallite successively; grinding the potassium containing sulfate, decomposing to convert and floating to obtain picromerite; decomposing sulfate radical containing carnallite to convert and floating to obtain coarse potassium chloride; mixing picromerite, coarse potassium chloride and potassium sulfate mother liquid to obtain slurry, washing, filtering, decomposing to convert and filtering separation to obtain potassium sulfate. The present invention has low production cost, high yield and high product quality.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Phosphate-free scale inhibitor for water treatment
InactiveCN104192870AEasy to degradeNo pollutionDouble sulfate preparationSulfate/bisulfate preparationPhosphatePollution
The invention relates to the technical field of water treatment, in particular to a phosphate-free scale inhibitor for water treatment, which is good in effect, low in cost and high in scale inhibition capacity and cannot cause secondary pollution to the water body. The phosphate-free scale inhibitor is characterized by comprising the following components: polyacrylic acid, hydrogen peroxide, rubber tannin, mirabilite, sodium citrate, zinc chloride, sodium molybdate, polyaspartic acid, acrylic acid sulfonic acid, polyepoxysuccinic acid and triethanolamine. When the phosphate-free scale inhibitor is used, the components are taken in proportion, water is added, and after a solution is prepared, the solution is added to water treatment equipment; compared with the prior art, the phosphate-free scale inhibitor is non-toxic and non-phosphorus, main organic components are easily degraded, the environmental pollution cannot be caused, and thus the subsequent treatment cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:ANHUI GREEN TITAN ENVIRONMENTAL TECH
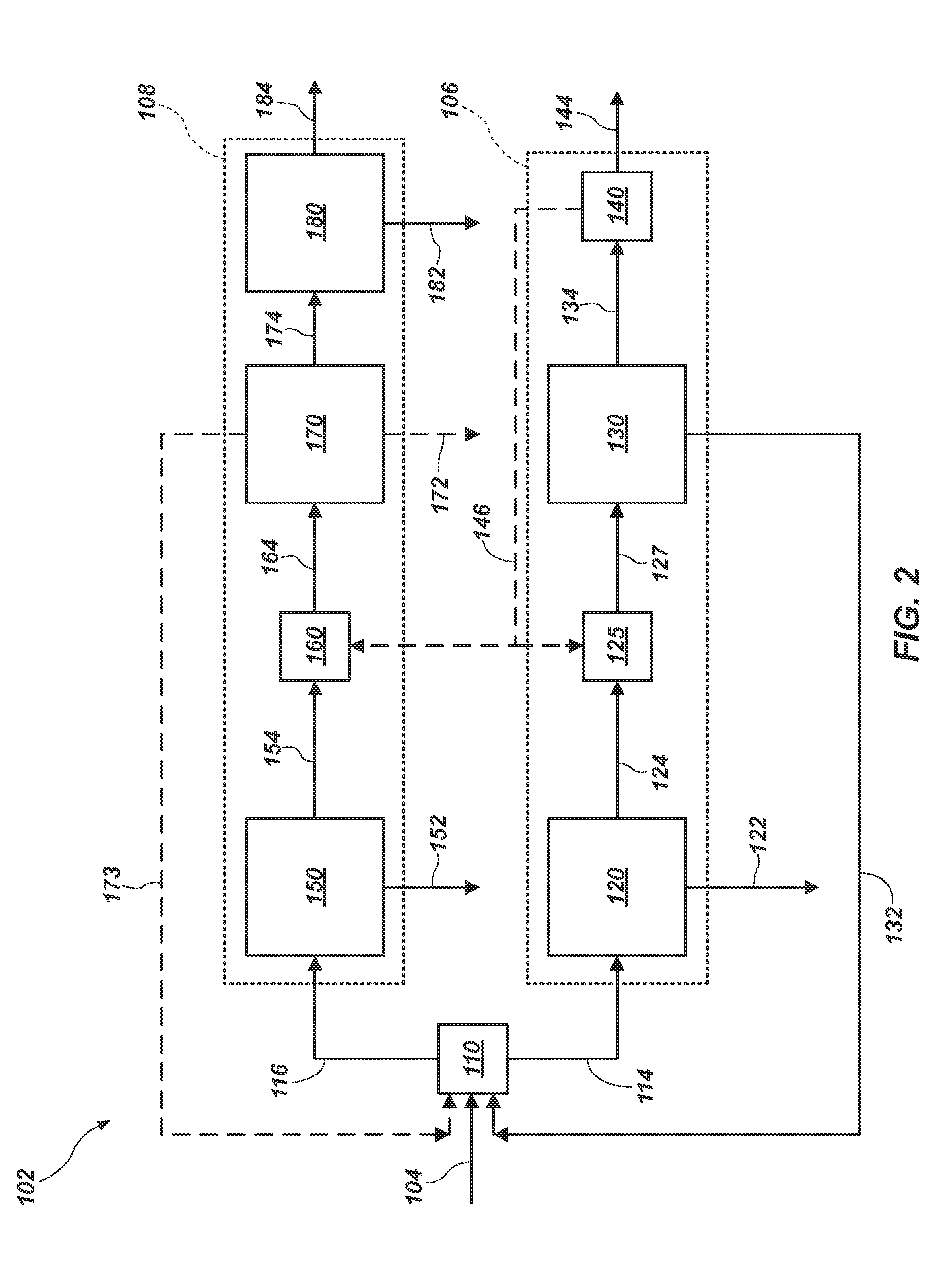
Methods of processing solutions of potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate, methods of producing potassium sulfate, and related systems
ActiveUS8802048B2Increase productionDouble sulfate preparationSulfate/bisulfate preparationPotassium sulfateAqueous solution
Methods of processing an aqueous solution comprising potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate include crystallizing K2SO4, crystallizing recycle crystals, and mixing at least a portion of the recycle crystals with the aqueous solution. Systems for processing potassium sulfate and magnesium sulfate include a first crystallizer and a second crystallizer in fluid communication with the second mix tank. The second crystallizer is structured and adapted to precipitate recycle crystals from the concentrated liquor to form a potassium-depleted recycle brine. The recycle crystals precipitated in the second crystallizer have a composition suitable to be recycled to the first crystallizer to increase the production of SOP.
Owner:INTERCONTINENTAL POTASH CORP USA
Potassium sulfate preparing process from sulfate-type salt lake bittern
InactiveCN1255320CAdaptable to changeWhite colorDouble sulfate preparationFlotationDecompositionEnergy analysis
The invention provides a method for producing potassium sulfate by using sulfate-type salt lake brine resources. The method comprises the following steps: drying the sulfate-type salt lake brine in a salt field to obtain sodium chloride, soft potassium and magnesium Sulfate mixed salt ore of vanadium, magnesium sulfate and potassium chloride and potassium salt mixed salt ore mainly containing sodium chloride, potassium chloride, magnesium sulfate and carnallite; after mixing these two kinds of ores, they are mixed with The water is converted to produce coarse langbeinite mixed ore. The mixed ore is selected through the flotation process to select the langbeinite mixed salt concentrate, and then add water to the high-grade langbeinite mixed salt concentrate to decompose directly. Potassium sulfate product can be obtained; its tailings can be used as industrial salt after being washed with water; compared with the existing similar process, the present invention removes the grinding process with large power consumption, and the whole process does not add potassium chloride, saving Energy saving, cost reduction, simple process, normal temperature and pressure operation, strong adaptability to different grades of raw material ores, and good product purity and whiteness.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
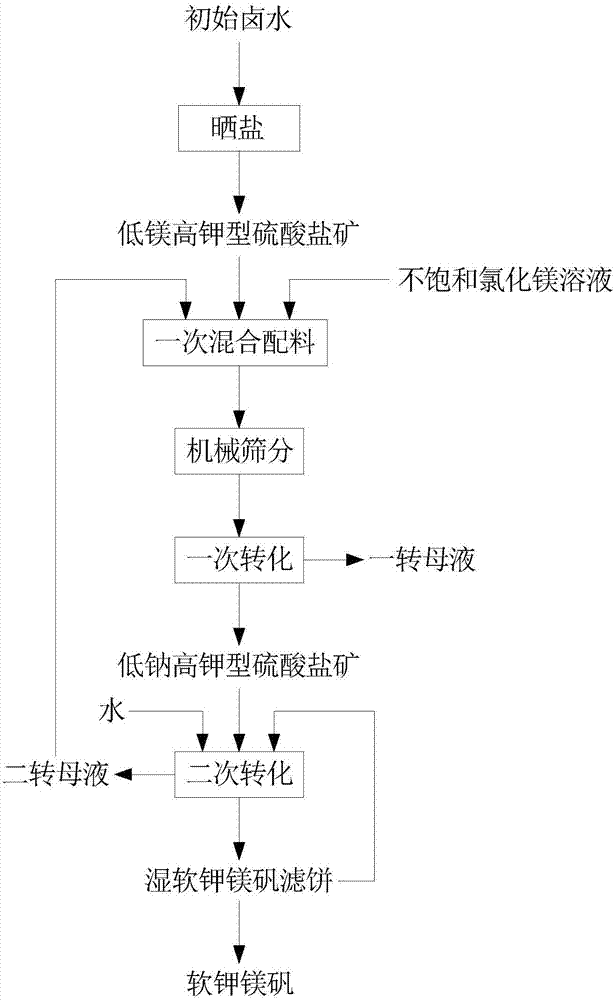
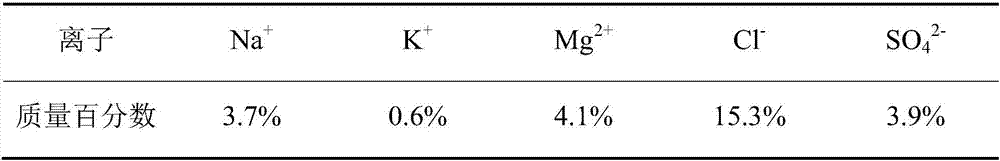
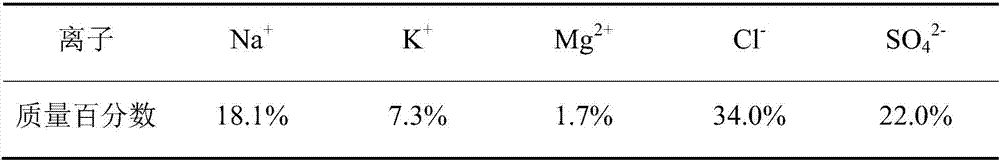
Picromerite preparation method based on brine mixing method
InactiveCN107381603ASolution areaSolve the pollution of the environmentDouble sulfate preparationPotassium fertilisersSulfateEvaporation
The invention discloses a picromerite preparation method based on a brine mixing method. The picromerite preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, evaporating initial brine in the sun for salt making to obtain low-magnesium and high-potassium sulfate ore; S2, performing primary mixing on the low-magnesium and high-potassium sulfate ore and an unsaturated magnesium chloride solution, performing primary transformation after removal of sodium chloride, and obtaining primary-transformation solid low-sodium and high-potassium sulfate ore after solid-liquid separation; S3, performing secondary mixing on the primary-transformation solid low-sodium and high-potassium sulfate ore and water, performing secondary transformation, and obtaining a wet picromerite filter cake after solid-liquid separation; S4, drying the wet picromerite filter cake to obtain picromerite. According to the method, waste brine or similar-composition brine produced after sodium chloride production based on HohYanhu is taken as the initial brine, the brine resource of complex points in a mirabilite phase area can be used for producing picromerite through one time of brine evaporation for salt making and two times of brine mixing, recycling of potassium and magnesium resources is realized, and salt lake resources are further used comprehensively.
Owner:QINGHAI INST OF SALT LAKES OF CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparing method of picromerite by adopting mother liquor of potassium sulfate production by conversion method and sodium sulfate as raw materials
InactiveCN104016381ALess process investmentReduce manufacturing costDouble sulfate preparationEvaporationSlurry
The invention discloses a preparing method of picromerite by adopting a mother liquor of potassium sulfate production by a conversion method and sodium sulfate as raw materials. The preparing method includes: mixing the potassium sulfate mother liquor and anhydrous sodium sulfate or a saturated sodium sulfate solution to obtain a mixed solution, or successively mixing the potassium sulfate mother liquor with magnesium-containing brine or magnesium-containing salts, anhydrous sodium sulfate or the saturated sodium sulfate solution to obtain the mixed solution; performing a replacement reaction at 0-67.5 DEG C; subjecting the reaction slurry after the reaction is finished to solid-liquid separation so as to obtain solid that is the picromerite; subjecting the separated liquid to evaporation or evaporation to dryness to precipitate a salt mixture of the picromerite and sodium chloride; and separating the picromerite from the sodium chloride by a direct flotation method or a reverse flotation method after the salt mixture is smashed. The preparing method plays a supporting role for the product quality of potassium sulphate production in the former section, and has characteristics of extremely low investment, production cost and energy consumption and high yield.
Owner:陈兆华
Salt pan tedding technology of high-magnesium and low-potassium sulfate brine
ActiveCN107352560ASolve the key technical problems that cannot directly produce potassium sulfateIncrease resourcesMagnesium chloridesDouble sulfate preparationHigh magnesiumSalt lake
A salt pan tedding technology of high-magnesium and low-potassium sulfate brine comprises the following steps: 1, introducing the high-magnesium and low-potassium sulfate brine into a sodium chloride salt pan, naturally tedding the brine, and introducing the brine into an epsomite salt pan when epsomite in the brine reaches saturation and epsomite precipitates; 2, evaporating the brine, and introducing the brine into first stage carnallite salt pan when the percentage of precipitated epsomite is 40-80 wt%; 3, evaporating the brine, and introducing the brine into a second stage carnallite salt pan when the percentage of precipitated carnallite is 40-60 wt%; 4, continuously evaporating the brine, continuously precipitating the carnallite, and introducing the brine into an old brine salt pan after the brine reaches an old brine point; and 5, crushing first stage carnallite ores, and decomposing and dehalogenating the crushed first stage carnallite ores. The method allows high-quality potassium sulfate to be produced from the high-magnesium and low-potassium sulfate brine which is only used to produce potassium chloride originally, and improves the resource exploitation rate of like salt lakes and underground brine resources and the added values of the product.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
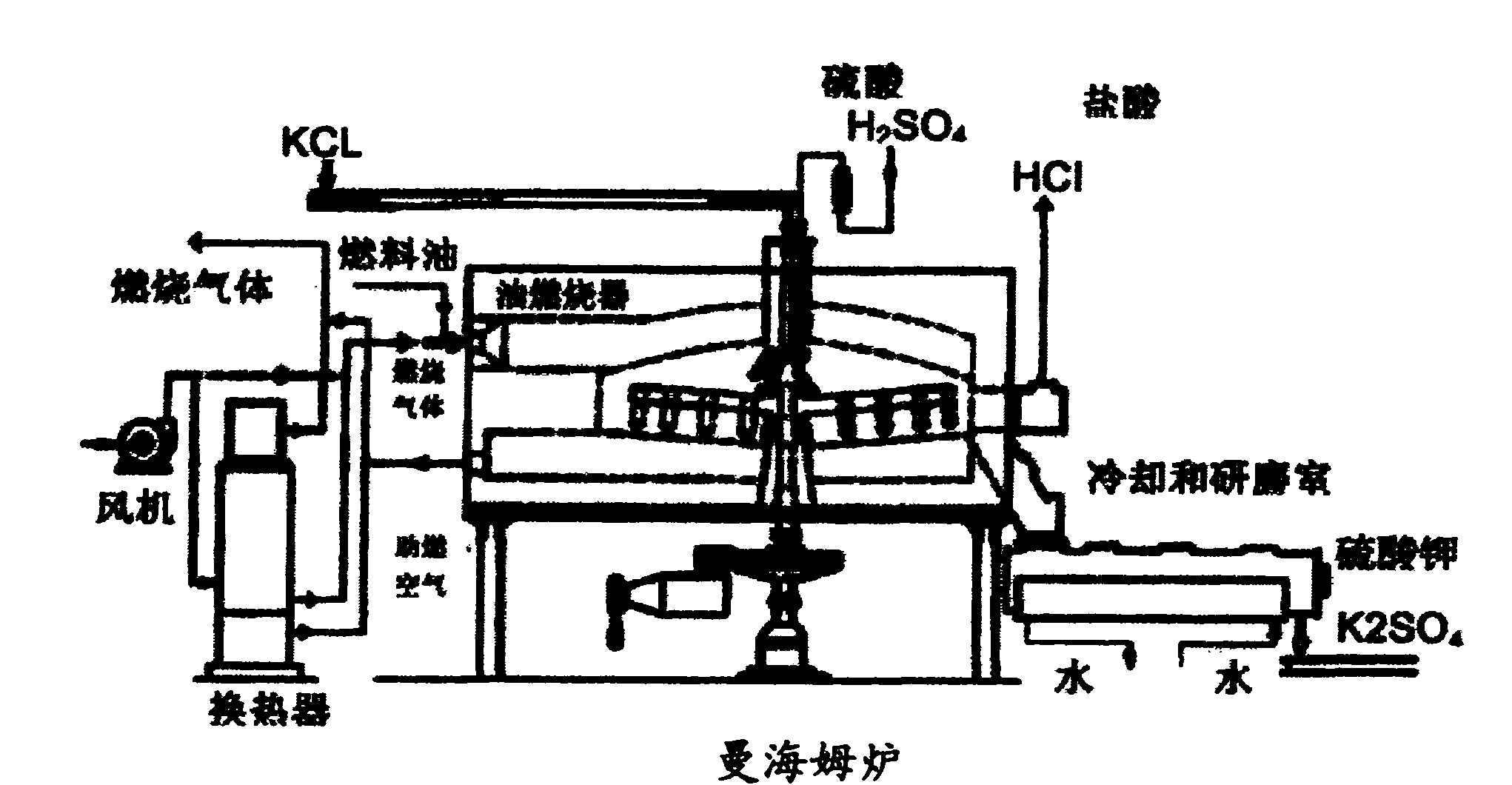
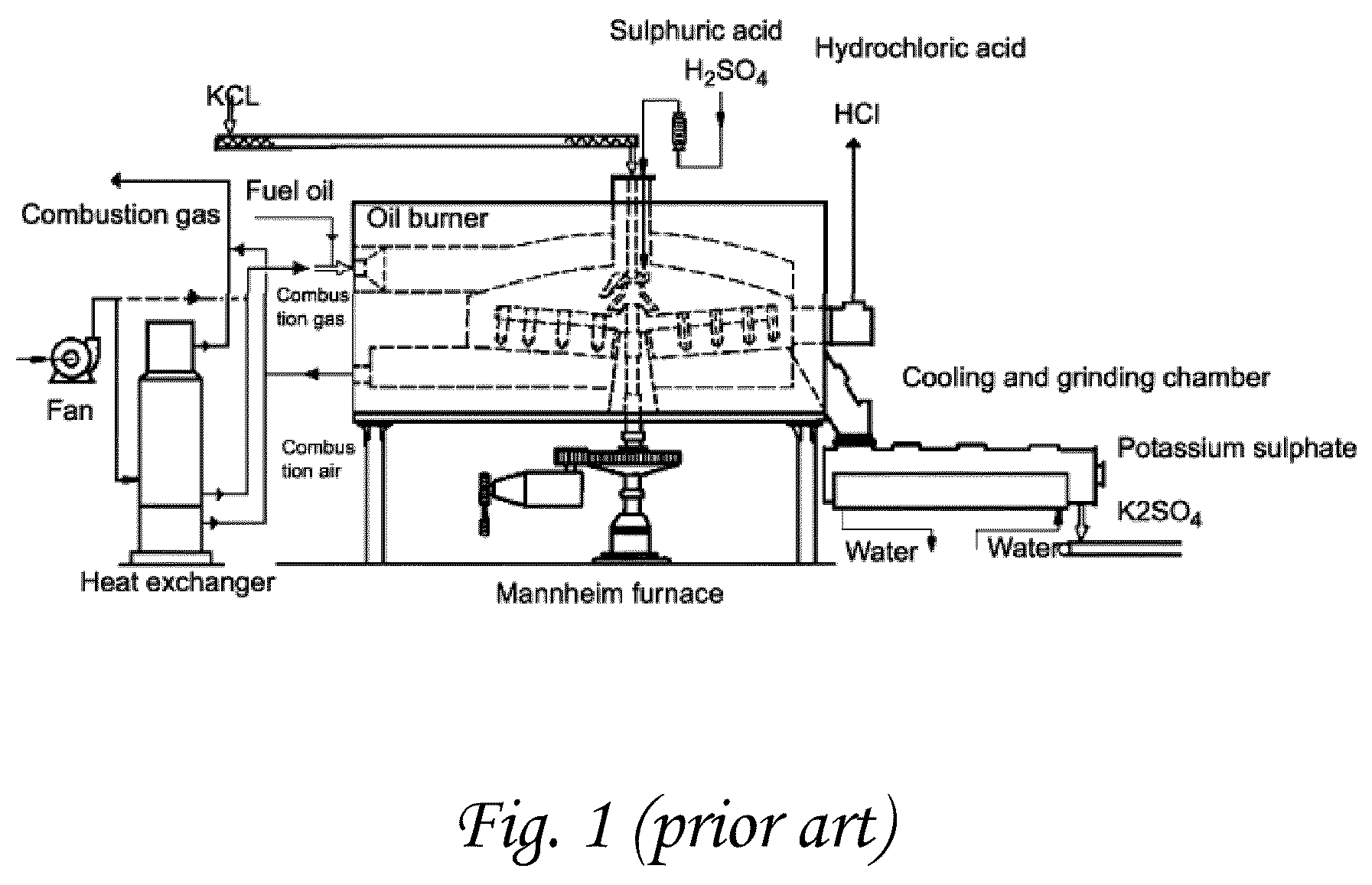
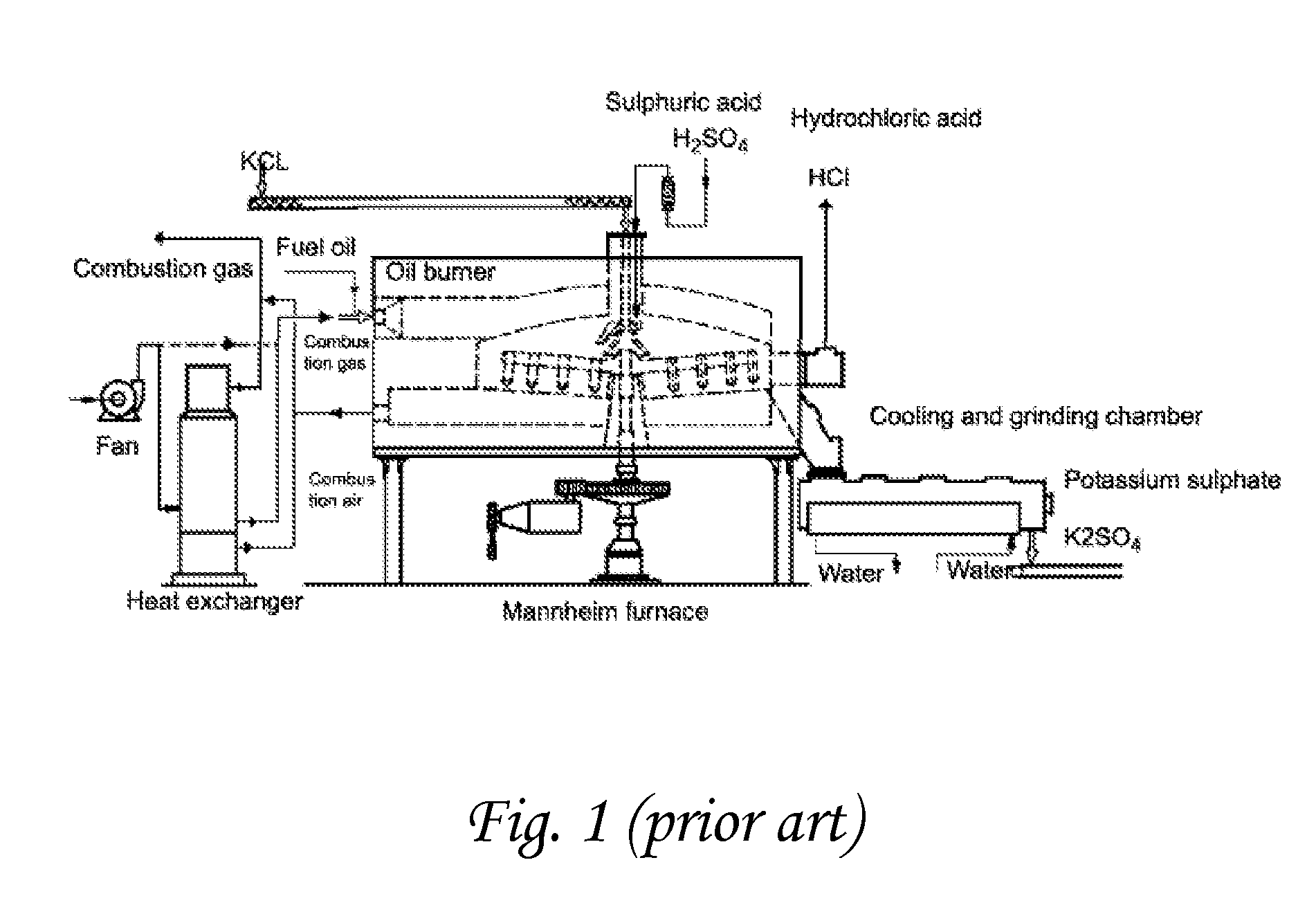
Chemical process to produce hydrogen chloride and chloride-free compound potassium sulfate fertilizers or other metal sulfates
A method is disclosed for production of a sulfate-containing salt and anhydrous gaseous HCl from a metal chloride (MClx) and oleum. MClx and oleum are mixed together with a water-containing liquid, forming gaseous HCl and a solution of a sulfate-containing salt or double salt. The salt is precipitated from the solution, and in a preferred embodiment, the supernatant liquid from the precipitation is recycled to the reaction mixture as the water-containing liquid in subsequent reaction cycles. In a preferred embodiment, HCl discharged from the reaction mixture is scrubbed to remove dust, water vapor and traces of H2SO4, yielding anhydrous HCl of >90% purity. The exothermicity of the reaction between the water-containing liquid and the oleum is sufficient that, unlike methods known in the prior art, the process proceeds quickly and efficiently without any necessity for additional heating of the reaction mixture. This method provides high-purity, low-chlorine sulfates, including the novel potassium sulfate double salts K3(NH4)(SO4)2, 3K2SO4*MgSO4 and 3K2SO4*CanMg2-nSO4.
Owner:F P C ENTERPRISE 2008
Chemical process to produce hydrogen chloride and chloride-free compound potassium sulfate fertilizers or other metal sulfates
InactiveUS7887776B2Chlorine/hydrogen-chlorideCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesMetal chloridePotassium sulfate
A method is disclosed for production of a sulfate-containing chlorine free salt and anhydrous gaseous HCl from a metal chloride (MClx), oleum and water. MClx and oleum are mixed together with a water-containing liquid, forming gaseous HCl and a solution of a sulfate-containing salt. The salt is precipitated from the solution, and in a preferred embodiment, the supernatant liquid from the precipitation is recycled to the reaction mixture as the water-containing liquid in subsequent reaction cycles. The exothermicity of the reaction between the water-containing liquid and the oleum is sufficient to remove chlorine in the form of substantially pure useful HCl and enables the process to proceed without additional heating of the reaction mixture. When the metal is potassium, this method produces high-purity novel sulfate salts with high potassium content K3(NH4)(SO4)2, 3K2SO4.MgSO4 and 3K2SO4.CanMg1-nSO4.
Owner:FINKELSHTEIN LEONID
Salt pan technology for separating ingredients by temperature differences
InactiveCN108217693AImprove work efficiencyReduce salt contentCalcium/strontium/barium chloridesMagnesium chloridesWater dischargeInorganic Chemical
The invention relates to the technical field of salt lake chemical engineering of inorganic chemical industry, and discloses a salt pan technology for separating ingredients by temperature differences. The salt pan technology comprises a temperature difference salt pan and a storage pool, wherein a system water inlet is formed in one side of the temperature difference salt pan; a water dischargingopening is formed in one side, far away from the system water inlet, of the temperature difference salt pan; the water discharging opening is communicated with the storage pool; a pump pool is arranged inside the storage pool; a water pump communicating with the temperature difference salt pan is arranged inside the pump pool; a system water outlet is formed in one side of the storage pool. The salt pan technology for separating ingredients by temperature differences and application have the advantages that for a hot solution after solid separation, pure solids are separated out in the cooling process by adding a proper amount of fresh water; the solids can be favorably and further purified; pure solids are beneficial for preparation of other salts (such as preparation of potassium sulphate from high-quality picromerite, preparation of potassium chloride and magnesium metal from high-purity salt pan carnallite, and preparation of potassium sulphate from high-purity magnesium sulfate heptahydrate).
Owner:地矿集团格尔木盐湖资源开发有限公司
Picromerite feed and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to picromerite feed and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes the steps of S1, preparing materials, to be specific, collecting solarized carnallite from asalt lake and tail salt discharged to a tailings dam during production to provide materials for preparation of picromerite; S2, converting, to be specific, mixing the carnallite and tail salt in a mass ratio of 1.86, and converting under the water addition of 49.8% and the temperature of 25 DEG C for 90 min to obtain a solid phase converted from the mixture, wherein the solid phase mainly includes sodium chloride and picromerite. Carnallite of a salt lake and tail salt from production process are used to prepare picromerite herein; picromerite with the potassium yield of 54.9% can be attained; the picromerite prepared with the carnallite of the salt lake and the tail salt from the production process can be applied to feeds, thereby preventing fed animals from lacking potassium and experiencing muscular weakness, heart failure and respiratory failure; the problem is solved that picromerite prepared in the prior art has poor quality and causes insufficient potassium content to feeds, and therefore, normal growth of animals is affected.
Owner:青海蓝湖善成生物技术有限公司
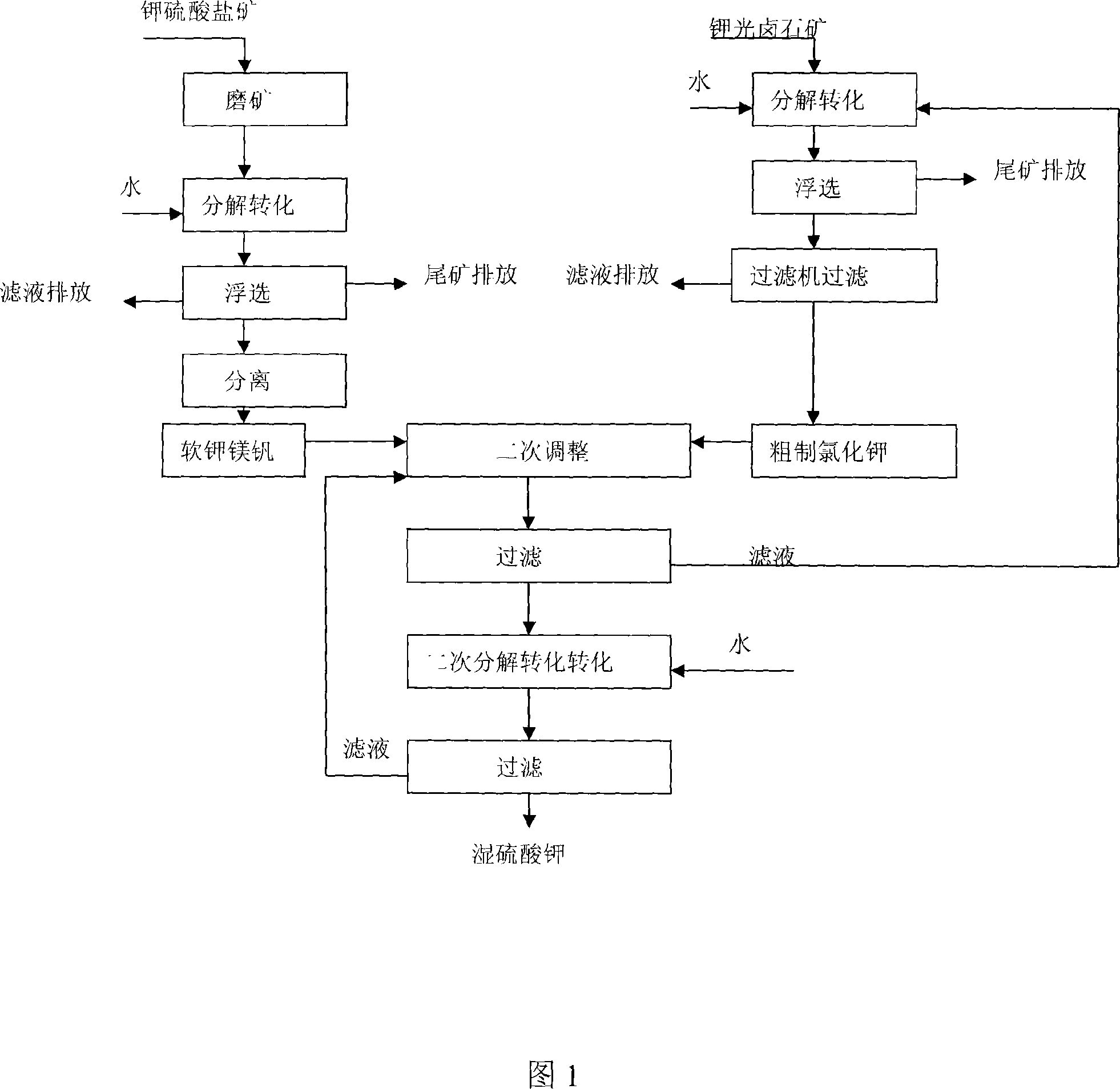
A process for the production of potassium sulphate and magnesium sulphate from carnallite and sodium sulphate
According to some embodiments there is provided a process for the recovery of SOP from Sulphate bearing mineral and Carnallite or Sylvenite, comprising: Dissolving Carnallite in water to obtain Sylvenite and high Magnesium Chloride brine; Adding Sodium Sulphate to said Carnallite to produce mixture of Kainte\Leonite, KCl and NaCl precipitant and brine containing Mg Cl2, KCl, NaCl; Separating the NaCl from the mixture; Obtaining a precipitant mixture of Leonite with KCl; Filtering said Leonite and washing with water to yield pure mixture of Leonite with KCl; Adding KCl to the Leonite with the KCl; and Decompose said Leonite with the KCl to SOP.
Owner:DEAD SEA WORKS
Technology for preparing kainite with potassium-containing heptahydrate epsomite raw product
ActiveCN103738983AHigh yieldSimple processDouble sulfate preparationAlkali metal chloridesMass ratioEconomic benefits
The invention relates to a technology for preparing kainite with a potassium-containing heptahydrate epsomite raw product. The technology comprises the following steps: (1) mixing brine according to the mass ratio of the potassium-containing heptahydrate epsomite raw product to magnesium sulfate saturated epsomite mother liquor or old brine being 1:(1-3), then adding in a heating fluid bowl for heating to 60-90 DEG C, preserving the heat for dissolution for 0.5-4 hours to obtain hot brine; (2) preserving the heat and filtering the hot brine obtained in the step (1), wherein the filter residue is crude kainite; (3) adding water with the amount of 1-4 times of the weight of the crude kainite equivalently to the crude kainite obtained in the step (2) and then washing with slurry to obtain high-quality kainite and potassium-containing repulping water; (4) returning the potassium-containing repulping water obtained in the step (3) to the step (1) to replace the epsomite mother liquor or old brine used in the step (1). According to the technology, the flow is simple, the solution temperature is low, the energy consumption is low, the production cost is low and economic benefits are good.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Preparation method of anhydrous magnesium chloride
PendingCN114014346AImprove qualityImprove product qualityMagnesium chloridesDouble sulfate preparationPhysical chemistryOrganosolv
The invention discloses a preparation method of anhydrous magnesium chloride, which comprises the following steps: reacting anhydrous magnesium formate powder with anhydrous hydrogen chloride gas in an anhydrous organic solvent to generate anhydrous magnesium chloride and formic acid, and removing the anhydrous organic solvent and formic acid to obtain anhydrous magnesium chloride, wherein the anhydrous magnesium formate powder is suspended in the anhydrous organic solvent, and the anhydrous hydrogen chloride gas is dissolved in the anhydrous organic solvent. The anhydrous magnesium chloride with extremely high quality can be obtained by the method disclosed by the invention.
Owner:SHENZHEN MAXCHEMTECH
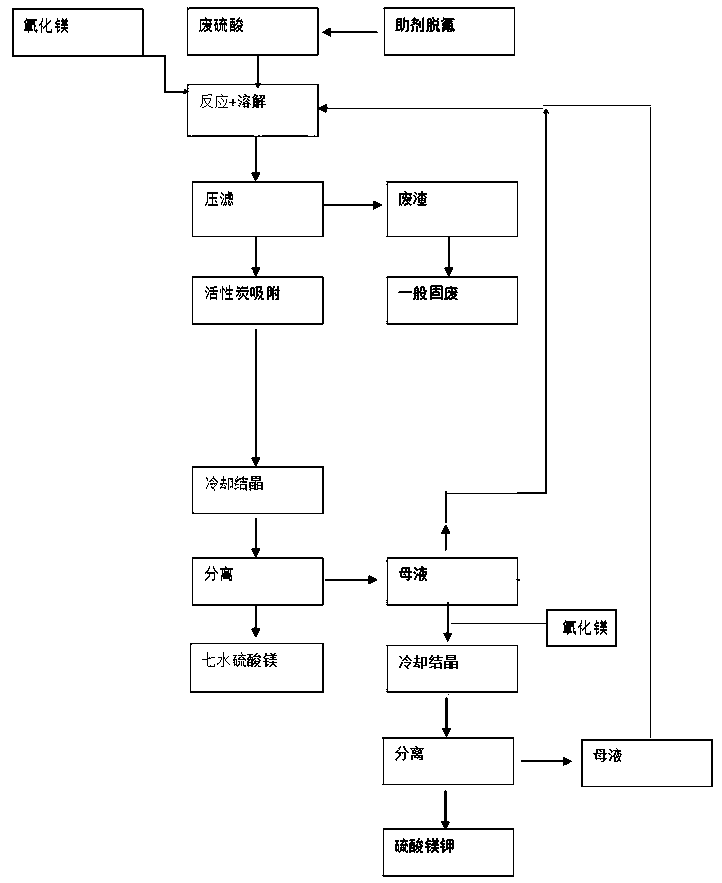
A waste sulfuric acid recycling device and process
ActiveCN110963510BAchieve recyclingIncrease concentrationDouble sulfate preparationSulfate/bisulfate preparationActivated carbon filtrationPotassium bisulfate
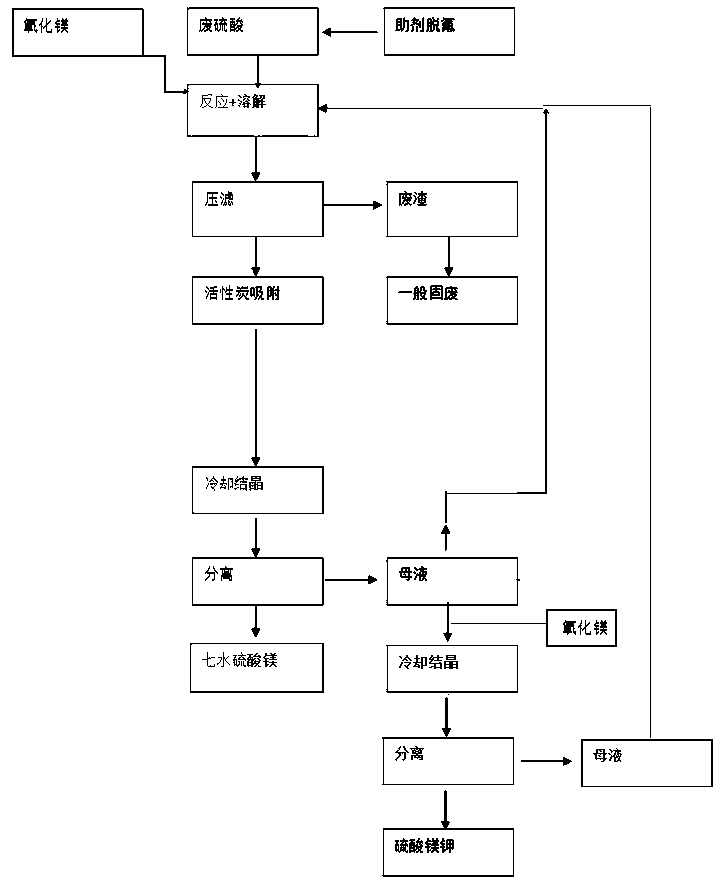
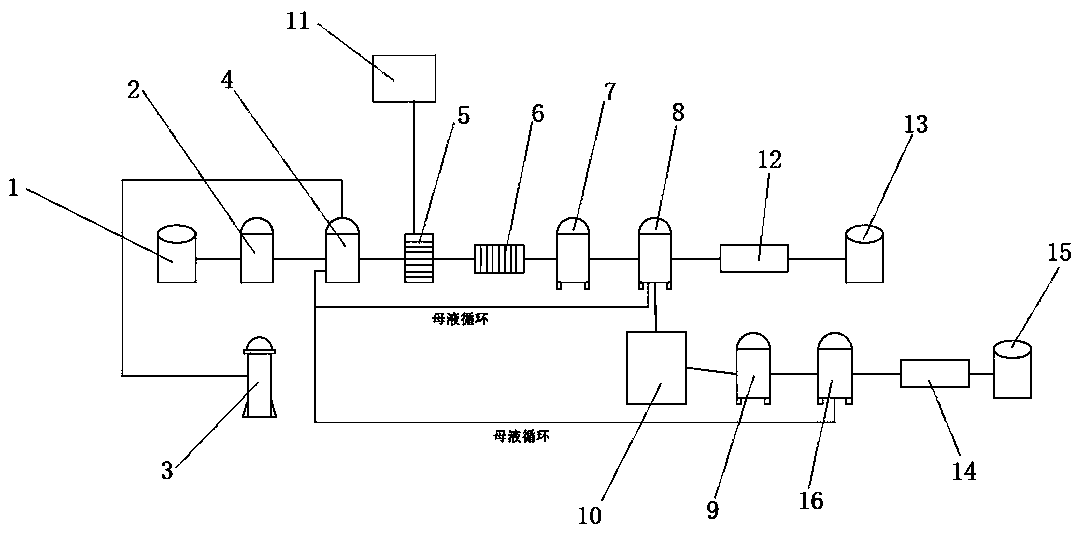
The invention relates to a recovery and treatment method of waste sulfuric acid, comprising S1: performing defluorination pretreatment on waste sulfuric acid; S2: transferring waste sulfuric acid to a reaction kettle, adding magnesium oxide for reaction; S3: performing pressure filtration on the reaction solution, and transferring the waste residue to Waste residue storage tank, the filtrate is transferred to activated carbon filtration equipment; S4: The mother liquor of magnesium sulfate is separated from the first crystallization tank to detect the content of potassium bisulfate. According to whether the content of potassium bisulfate in the mother liquor reaches the predetermined threshold, it is decided whether the mother liquor should continue to circulate or recover sulfuric acid Potassium hydrogen is recycled. The method and device of the present invention can realize the recovery of potassium hydrogensulfate in waste sulfuric acid, and through the circular purification of the mother liquor, when the concentration of potassium hydrogensulfate in the mother liquor does not reach the threshold value, the mother liquor is returned to the reactor to continue to increase the potassium hydrogensulfate of the mother liquor Concentration, when the concentration of potassium bisulfate in the mother liquor reaches the threshold, the mother liquor is transferred to the crystallization tank, magnesium oxide is added to generate potassium magnesium sulfate and the material is separated and discharged, realizing the low-cost recovery of potassium bisulfate in waste sulfuric acid.
Owner:山东齐创石化工程有限公司
Process for Production of Potassium Sulfate, Ammonium Sulfate, and Calcium Carbonate from Syngenite
PendingUS20220340437A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesDouble sulfate preparationPhysical chemistryProcess engineering
Described herein is a process for the production of potassium sulfate and ammonium sulfate from syngenite. Specifically, the syngenite is produced from waste liquors and low value minerals and is used to produce valuable secondary products. Specifically, instead of performing the decomposition reaction in one step at high temperature, this process performs the reaction in 2 steps at temperatures lower than the decomposition temperature of ammonium bicarbonate: a first step to reach the equilibrium and produce saturated potassium sulfate brine, and a second step to complete the syngenite decomposition reaction.
Owner:UPCYCLE MINERALS INC
Process for the production of potassium sulphate and magnesium sulphate from carnallite and sodium sulphate
According to some embodiments there is provided a process for the recovery of SOP from Sulphate bearing mineral and Carnallite or Sylvenite, comprising: Dissolving Carnallite in water to obtain Sylvenite and high Magnesium Chloride brine; Adding Sodium Sulphate to said Carnallite to produce mixture of Kainte\Leonite, KCl and NaCl precipitant and brine containing Mg Cl2, KCl, NaCl; Separating the NaCl from the mixture; Obtaining a precipitant mixture of Leonite with KCl; Filtering said Leonite and washing with water to yield pure mixture of Leonite with KCl; Adding KCl to the Leonite with the KCl; and Decompose said Leonite with the KCl to SOP.
Owner:DEAD SEA WORKS
Method for preparing large-particle picromerite
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH +1
Chemical process to produce hydrogen chloride and chloride-free compound potassium sulfate fertilizers or other metal sulfates
A method is disclosed for production of a sulfate-containing salt and anhydrous gaseous HCl from a metal chloride (MClx) and oleum. MClx and oleum are mixed together with a water-containing liquid, forming gaseous HCl and a solution of a sulfate-containing salt or double salt. The salt is precipitated from the solution, and in a preferred embodiment, the supernatant liquid from the precipitation is recycled to the reaction mixture as the water-containing liquid in subsequent reaction cycles. In a preferred embodiment, HCl discharged from the reaction mixture is scrubbed to remove dust, water vapor and traces of H2SO4, yielding anhydrous HCl of >90% purity. The exothermicity of the reaction between the water-containing liquid and the oleum is sufficient that, unlike methods known in the prior art, the process proceeds quickly and efficiently without any necessity for additional heating of the reaction mixture. This method provides high-purity, low-chlorine sulfates, including the novel potassium sulfate double salts K3(NH4)(SO4)2, 3K2SO4.MgSO4 and 3K2SO4.CanMg1-nSO4.
Owner:FINKELSHTEIN LEONID
Device and process for recycling waste sulfuric acid
ActiveCN110963510AAchieve recyclingIncrease concentrationDouble sulfate preparationSulfate/bisulfate preparationHydrogen SulfateActivated carbon filtration
The invention relates to a method for recycling waste sulfuric acid. The method comprises the following steps: S1, carrying out defluorination pretreatment on waste sulfuric acid; S2, transferring thewaste sulfuric acid into a reaction kettle, and adding magnesium oxide for reaction; S3, carrying out filter pressing on a reaction liquid, transferring waste residues to a waste residue storage tank, and transferring filtrate to activated carbon filtering equipment; and S4, separating a magnesium sulfate mother liquor through a first crystallization kettle, detecting the content of potassium hydrogen sulfate, and determining whether the mother liquor is continuously circulated or recycled after potassium hydrogen sulfate is recycled according to whether the content of potassium hydrogen sulfate in the mother liquor reaches a preset threshold value or not. According to the method and the device, the recovery of potassium hydrogen sulfate in the waste sulfuric acid can be realized; the mother liquor is circularly purified, when the concentration of potassium hydrogen sulfate in the mother liquor does not reach a threshold value, the mother liquor flows back to the reaction kettle to continue to increase the concentration of potassium hydrogen sulfate in the mother liquor, and when the concentration of potassium hydrogen sulfate in the mother liquor reaches the threshold value, themother liquor is transferred to the crystallization kettle, the magnesium oxide is added, potassium magnesium sulfate is generated, separated and discharged, and the low-cost recovery of potassium hydrogen sulfate in the waste sulfuric acid is achieved.
Owner:山东齐创石化工程有限公司
Comprehensive recycling process for potassium-containing tailings after extraction of potassium sulfate from salt lake brine
ActiveCN112110461ASolve the problem of introducing flotation mother liquorReduce manufacturing costSievingScreeningEnvironmental engineeringPotassium sulfate
The invention discloses a comprehensive recycling process for potassium-containing tailings after extraction of potassium sulfate from salt lake brine. The comprehensive recycling process comprises the following steps: (1) separating potassium chloride flotation tailings and picromerite flotation tailings through a vibrating screen; (2) mixing the potassium chloride flotation tailings obtained inthe step (1) and the picromerite flotation tailings screen underflow, adding water or brackish water or picromerite conversion mother liquor, then adding a reverse flotation reagent, and carrying outflotation-solid-liquid separation to obtain industrial salt; (3) adding fresh water or brackish water or potassium sulfate high-potassium mother liquor into the sodium chloride flotation tailings obtained in the step (2) to be mixed, and conducting conversion-solid-liquid separation; and (4) mixing potassium chloride with the picromerite concentrate obtained in the step (3) and water or brackish water, conducting converting to generate potassium sulfate and potassium sulfate high-potassium mother liquor, and after solid-liquid separation, washing and drying solid potassium sulfate to obtain apotassium sulfate product. The method does not need an ore grinding process, is low in energy consumption, mainly prepares potassium sulfate and industrial salt, and is good in product purity, high inyield and low in cost.
Owner:CHANGSHA DESIGN & RES INST OF CHEM IND MIN
Comprehensive treatment method of graphene oxide waste acid
PendingCN114162841ANo emissionsGuaranteed purityDouble sulfate preparationMagnesium sulfatesPotassium manganateChemical products
The invention relates to a comprehensive treatment method of graphene oxide waste acid and belongs to the field of wastewater treatment.The mode that magnesium oxide is added in two steps is adopted, magnesium oxide is added in the first batch to adjust the pH value of the waste acid to be proper, then potassium permanganate is added to convert manganese ions in the solution into manganese dioxide, filtration and separation are conducted, magnesium oxide is supplemented to react with sulfuric acid, and the waste acid is obtained; carrying out circulating concentration and crystallization until the molar mass ratio of Mg < 2 + > to K < + > in a separation solution is 1: 1, and separating to prepare a magnesium sulfate chemical product; according to the method, the purity of the obtained magnesium sulfate is guaranteed, the purity of the obtained magnesium sulfate can reach 99% or above, all-element recycling of the graphene waste acid is achieved, and no waste is discharged.
Owner:山东金利特新材料有限责任公司
Method for preparing picromerite from mixed salt
ActiveCN109052432AEfficient extractionEfficient removalDouble sulfate preparationPotassium ionsEnergy consumption
The invention provides a method for preparing picromerite from a mixed salt. According to the method for preparing the picromerite from the mixed salt, by using the mixed salt as a raw material and using appropriate ion composition in the mixed salt, the picromerite is prepared through transformation and screening processes; problems that the energy consumption is high, the floor space is large, the production efficiency is low, a flotation agent is easily mixed in a product and so on in the prior art are solved; and meanwhile, the potassium ion recovery rate of the process can reach 68% or above; and the production of each ton of picromerite only consumes 2.5-3.5 tons of mixed salts. The mixed salt comprises the components of 9.38-10.38% of K<+>, 7.62-8.62% of Mg<2+>, 6.16-7.16% of Na<+>,29.02-30.02% of SO4<2->, 21.00-31.00% of Cl<-> and 23.83-24.83% of H2O according to the weight percentage.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of large-particle potassium magnesium sulfate crystals and small-particle potassium magnesium sulfate crystals
InactiveCN107954453ALow costNo pollution in the processDouble sulfate preparationSulfate/bisulfate preparationHydrogen SulfateGranularity
The invention relates to a preparation method of large-particle potassium magnesium sulfate crystals and small-particle potassium magnesium sulfate crystals. The preparation method includes followingsteps: 1), preparing a hot potassium hydrogen sulfate solution of 25-65wt% in concentration; 2), slowly adding the potassium hydrogen sulfate solution in the step 1) into magnesia or magnesium hydroxide for neutralizing, and holding temperature to obtain hot mixed liquid, wherein the end point of neutralizing is when pH is 6-8; 3), performing solid-liquid separation on the mixed liquid to obtain small-particle potassium sulfate crystals and primary filtrate; 4), performing cooling crystallization and solid-liquid separation on the primary filtrate to obtain large-particle potassium magnesium sulfate crystals and secondary filtrate. Preparation of the large-particle potassium magnesium sulfate crystals is realized by controlling concentration of raw materials and determination of the end point of neutralizing, high-quality potassium magnesium sulfate with granularity reaching 2-4.75mm can be obtained directly, and cost for granulation is reduced.
Owner:LOMON LAND AGRI
Method for preparing langbeinite with mixed salt
ActiveCN109052432BEfficient extractionEfficient removalDouble sulfate preparationPotassium ionsIonic composition
The invention provides a method for preparing picromerite from a mixed salt. According to the method for preparing the picromerite from the mixed salt, by using the mixed salt as a raw material and using appropriate ion composition in the mixed salt, the picromerite is prepared through transformation and screening processes; problems that the energy consumption is high, the floor space is large, the production efficiency is low, a flotation agent is easily mixed in a product and so on in the prior art are solved; and meanwhile, the potassium ion recovery rate of the process can reach 68% or above; and the production of each ton of picromerite only consumes 2.5-3.5 tons of mixed salts. The mixed salt comprises the components of 9.38-10.38% of K<+>, 7.62-8.62% of Mg<2+>, 6.16-7.16% of Na<+>,29.02-30.02% of SO4<2->, 21.00-31.00% of Cl<-> and 23.83-24.83% of H2O according to the weight percentage.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF TECH
Method for preparing picromerite from magnesium sulfate subtype brine
PendingCN112047364AEasy to operateNo pollution in the processDouble sulfate preparationEnvironmental chemistryEngineering
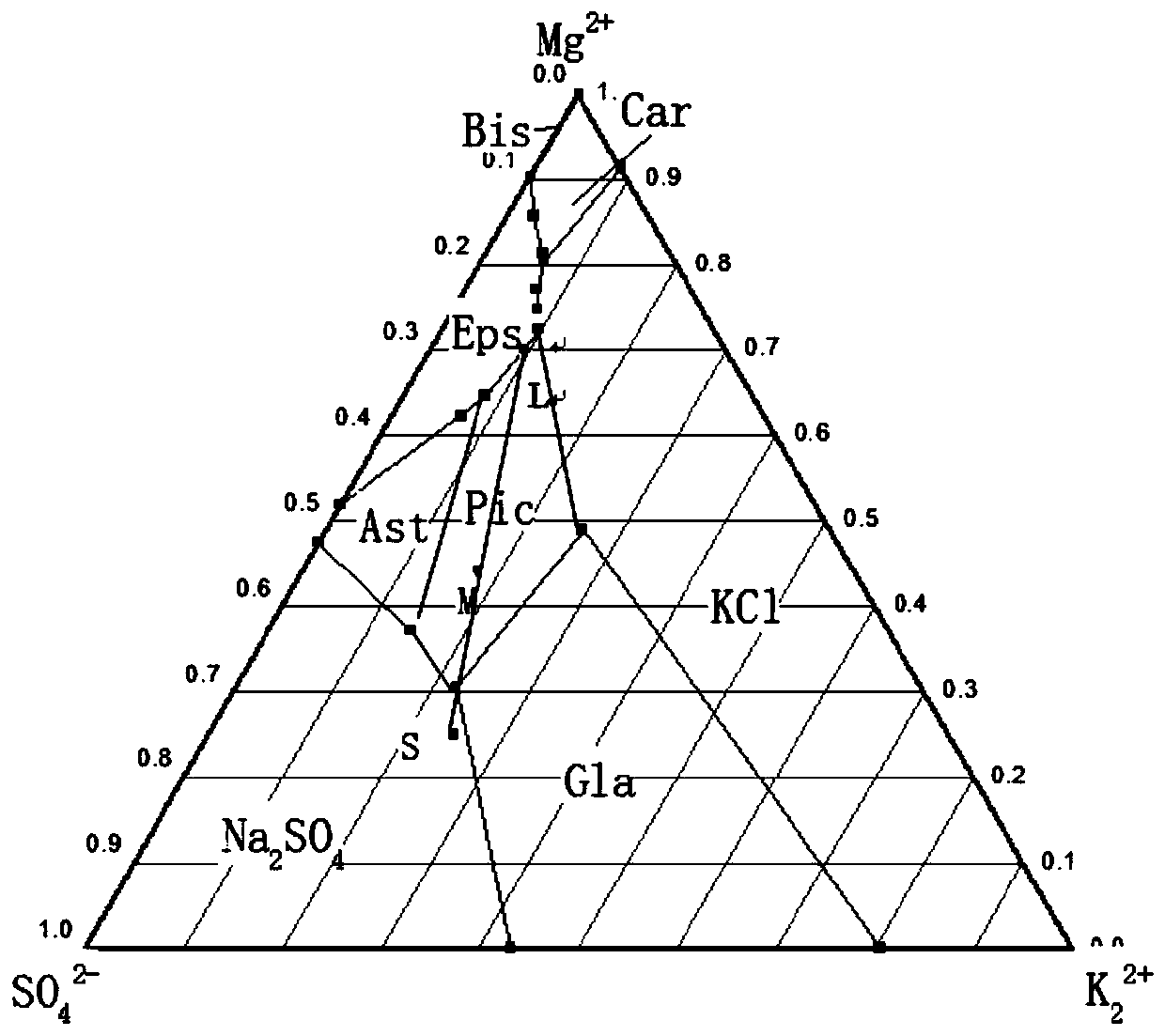
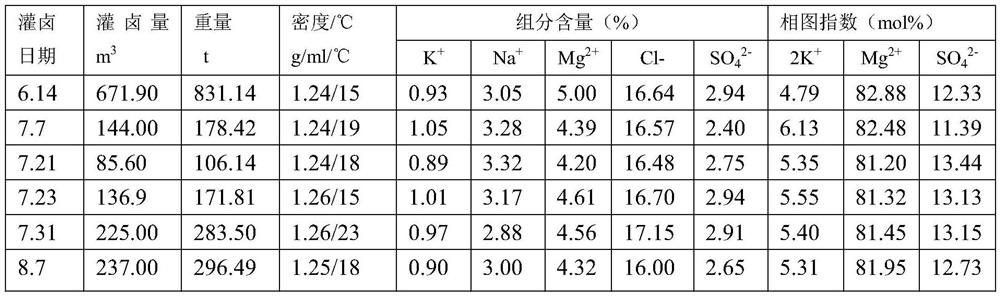
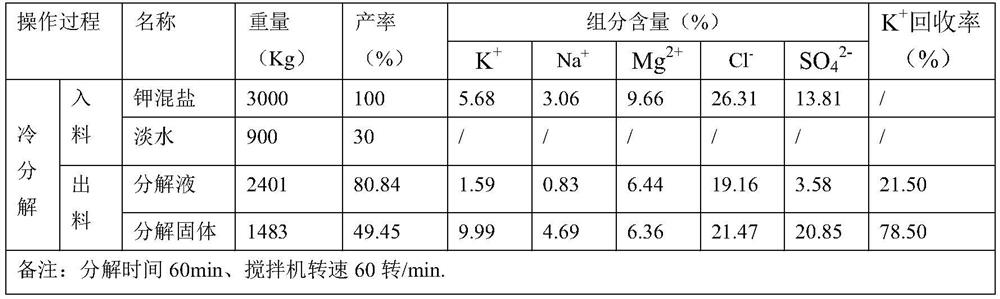
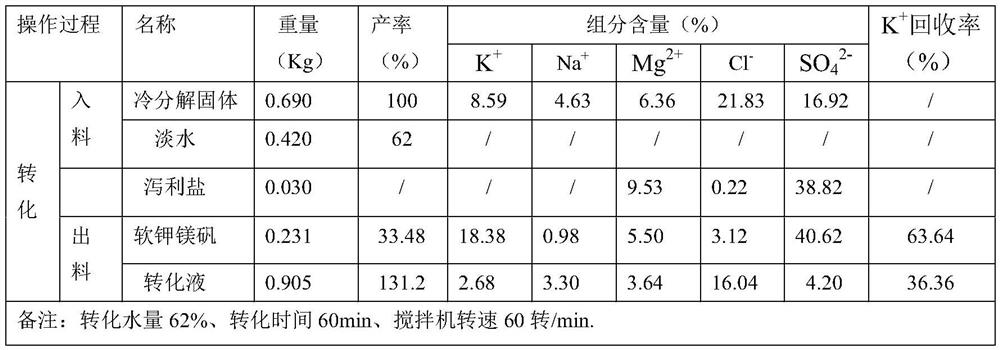
The invention discloses a method for preparing picromerite from magnesium sulfate subtype brine, and belongs to the technical field of chemical engineering. The method comprises the following steps: step 1, preparing potassium mixed salt by a salt pan natural expansion test: naturally evaporating a salt pan in summer, and filling brine and drying for six times in the sun; step 2, carrying out colddecomposition on the potassium mixed salt; step 3, adding epsomite for conversion; and through comparison tests of multiple conversion water quantity and conversion time tests, 0.690 Kg of solids after cold decomposition are selected by taking K<+> recovery rate maximization as an index, and the conversion water quantity is determined to be 62%, the conversion time is determined to be 60min, andthe addition amount of the epsomite is determined to be 130% of a theoretical calculation value, i.e., 30g for the test. The preparation process disclosed by the invention is simple to operate, pollution-free and low in economic cost.
Owner:QINGHAI QAIDAM COMPREHENSIVE GEOLOGICAL & MINERAL EXPLORATION INST
Popular searches
Alkali metal sulfite/sulfate purification Solution crystallization Rubidium/caesium/francium compounds Product crystals bed crystallization Lithium sulfates/sulfites Sulfate preparation Ammonium sulfates Preparation from chlorides Magnesium sulfites Magnesium/calcium/strontium/barium sulfides/polysulfides
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com