Production technology for recycling potassium chloride from saturated glaserite mother liquor
A production process, the technology of potassium mirabilite, applied in the direction of alkali metal chloride and the like, can solve the problems of difficult separation, complex potassium salt recovery process, etc., and achieve the effects of simple composition, simple process, and simplified precipitation form.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
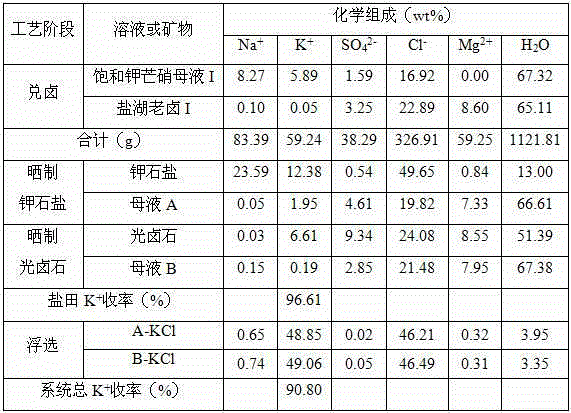
[0034] (1) Mixing with brine: 1000g saturated potassium mirabilite mother liquor (See Table 1 for chemical composition) and 689g salt lake brine (Refer to Table 1 for chemical composition) Mix with halogen at 20℃ and mix well to obtain 1689g of mother liquor with halogen;
[0035] (2) Sun-dried potash salt: Transfer 1689g of the brine-mixing mother liquor obtained in step (1) to the potash-salt field, and naturally evaporate 570g (equivalent to 33.75wt% of the brine-mixing mother liquor) water at 23°C to precipitate potash Solid-liquid separation after salting, to obtain 347 g of potash salt and 772 g of mother liquor A;
[0036] (3) Sun-dried carnallite: transfer 772g mother liquor A obtained in step (2) to carnallite salt field, and naturally evaporate 98g (equivalent to 12.69wt% of mother liquor A) water at 22°C to precipitate carnallite After solid-liquid separation, 216g carnallite and 458g mother liquor B are obtained;
[0037] (4) Extraction of potassium chloride: the 347g ...
Embodiment 2
[0042] (1) Mixing with brine: 1000g saturated potassium mirabilite mother liquor (See Table 2 for chemical composition) and 1177g salt lake brine (Refer to Table 2 for chemical composition) Mix with halogen at 25℃ and mix well to obtain 2177g of mother liquor with halogen;
[0043] (2) Sun-dried potash salt: Transfer 2177g of the brined mother liquor obtained in step (1) to the potash salt field, and evaporate 496g (equivalent to 22.78wt% of the brined mother liquor) of water at 23°C to precipitate potash After the salt is solid-liquid separated, 313g potash salt and 1368g mother liquor A are obtained;
[0044] (3) Sun-dried carnallite: transfer 1368g of mother liquor A obtained in step (2) to carnallite salt field, and naturally evaporate 232g (equivalent to 16.96wt% of mother liquor A) water at 26°C to precipitate carnallite After solid-liquid separation, 400g carnallite and 736g mother liquor B are obtained;
[0045] (4) Extraction of potassium chloride: the 313g of potash salt...
Embodiment 3
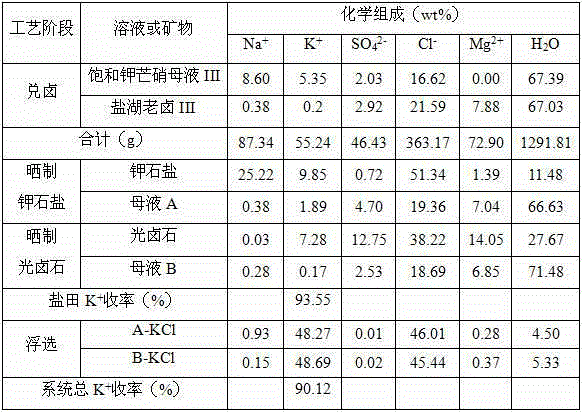
[0050] (1) Mixing with brine: 1000g saturated potassium mirabilite mother liquor (See Table 3 for chemical composition) and 917g salt lake brine (See Table 3 for chemical composition). Mix with halogen at 30°C and mix well to obtain 2917g of mother liquor with halogen;
[0051] (2) Sun-dried potash salt: transfer 1917g of the brine-mixing mother liquor obtained in step (1) to the potash-salt field. At 28°C, 562g (equivalent to 29.32wt% of the brine-mixing mother liquor) of water is naturally evaporated to precipitate potash Solid-liquid separation after salting to obtain 340g potash salt and 1015g mother liquor A;
[0052] (3) Sun-dried carnallite: Transfer 1015g of mother liquor A obtained in step (2) to carnallite salt field, and naturally evaporate 242g (equivalent to 23.84wt% of mother liquor A) water at 27℃ to precipitate carnallite After solid-liquid separation, 251g carnallite and 522g mother liquor B are obtained;
[0053] (4) Extraction of potassium chloride: the 340g of ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com