Method for extracting Mg, K, B and Li from mixed brine by utilizing natural energy
A technology of mixing brine and natural energy, applied in chemical instruments and methods, magnesium halides, boron oxides, etc., can solve problems such as difficult to determine processing methods, large processing capacity, and long distances
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0029] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention.
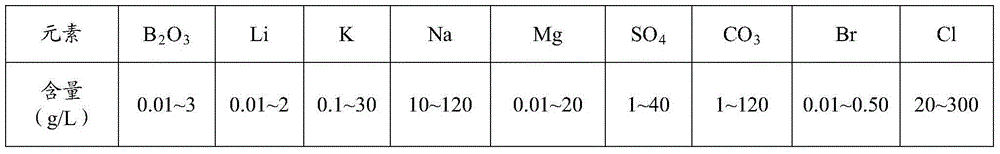
[0030] The invention provides a method for extracting beneficial elements such as Li, B, K, Mg, etc. by mixing carbonate-type salt lake brine and sulfate-type salt lake brine. The temperature difference and the temperature difference between day and night are large, drought, little rain, strong wind, etc., through thorough cleaning of salt lake brine, the enrichment and separation of beneficial elements in it can be realized.
[0031] The specific steps of this method are described as follows:
[0032] In the first step, the carbonate-type salt lake brine undergoes evaporation, freezing, and evaporation treatment in sequence....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com