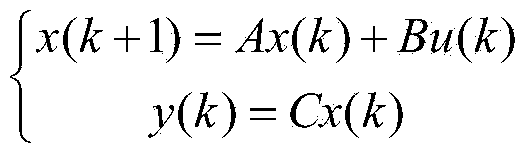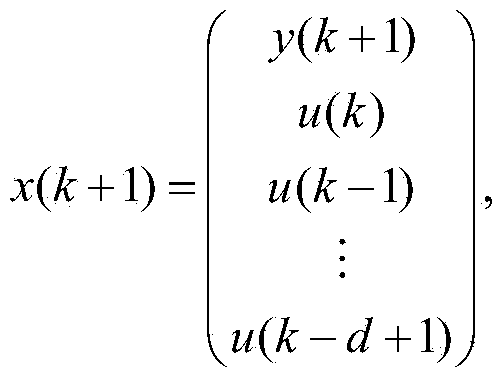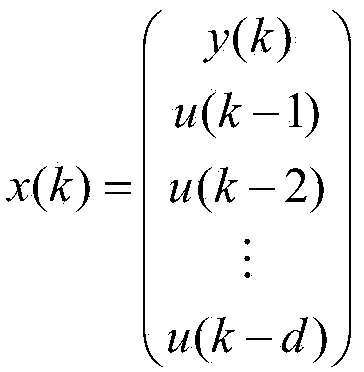Patents
Literature
83 results about "Batch distillation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
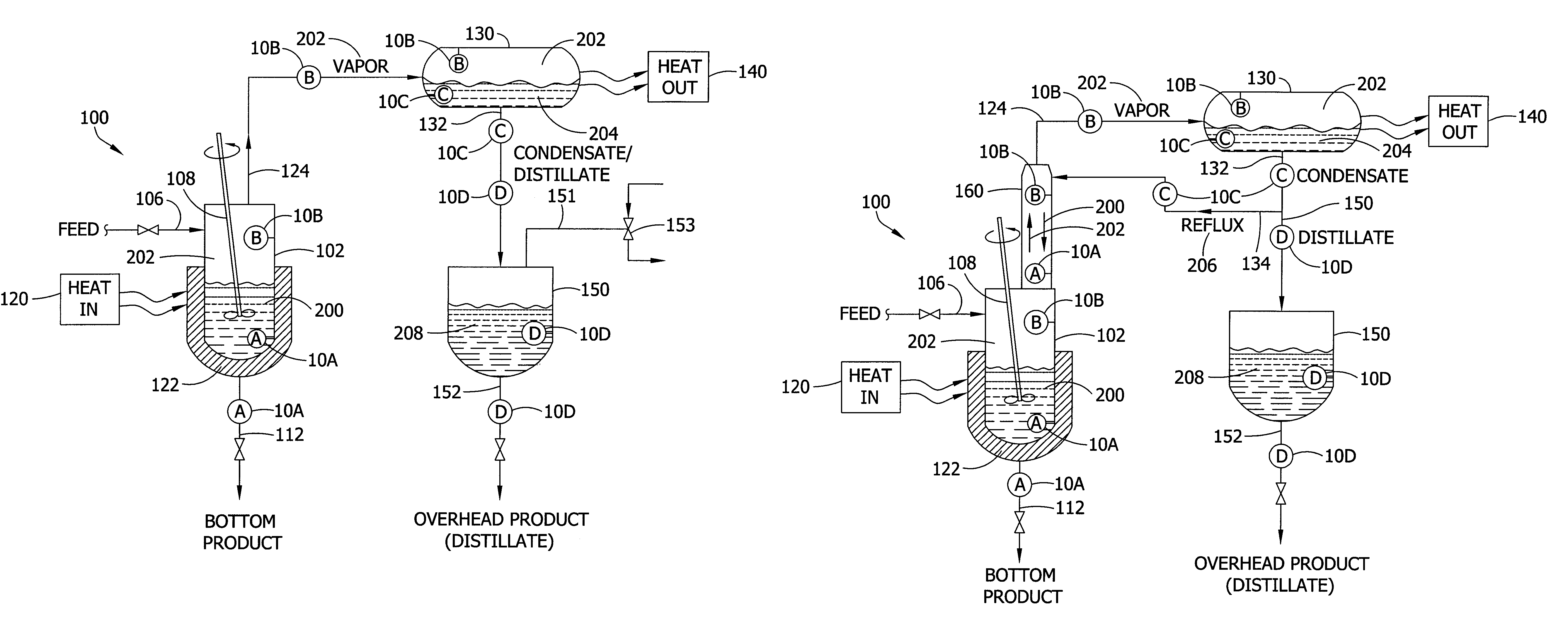
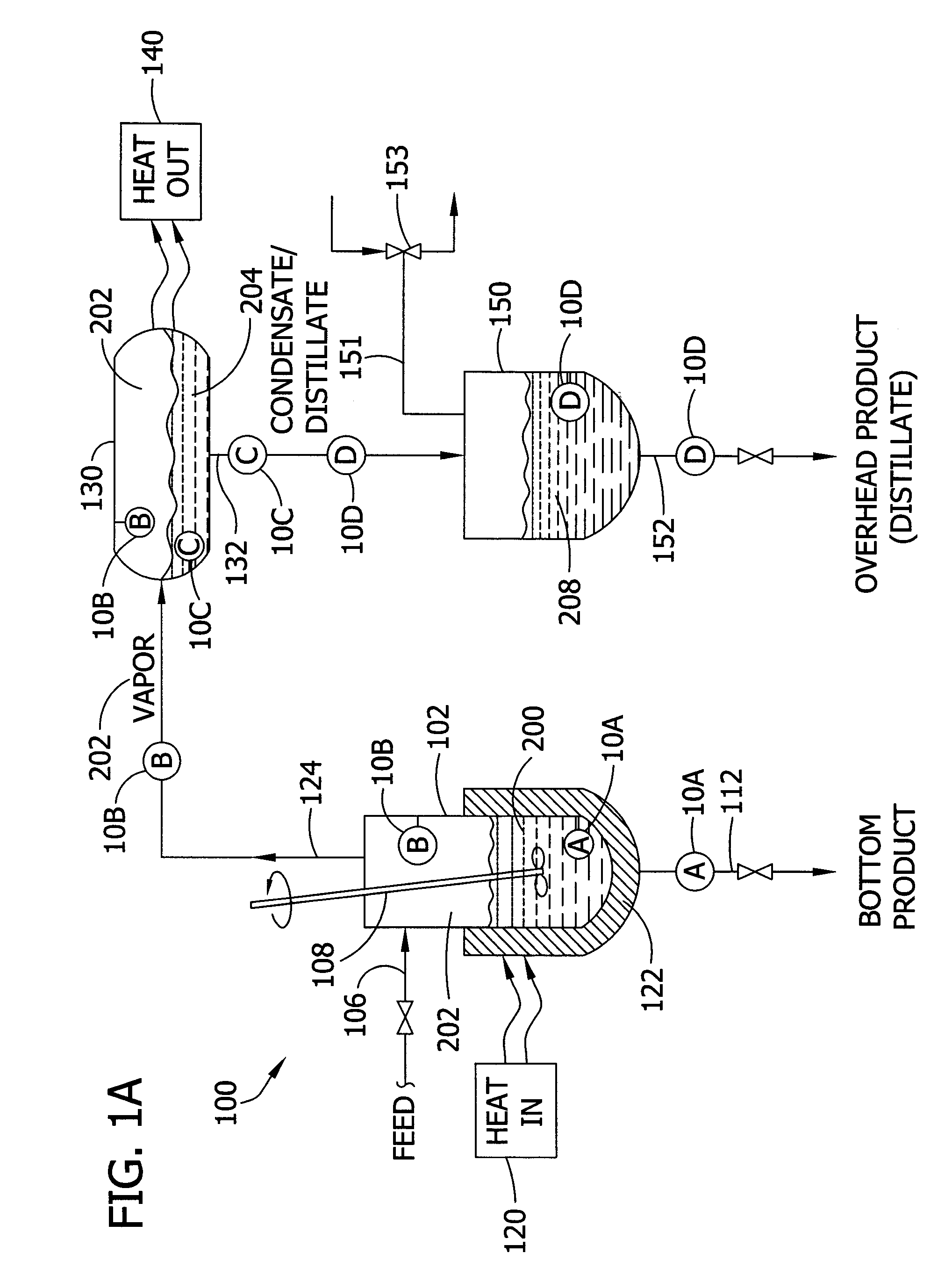
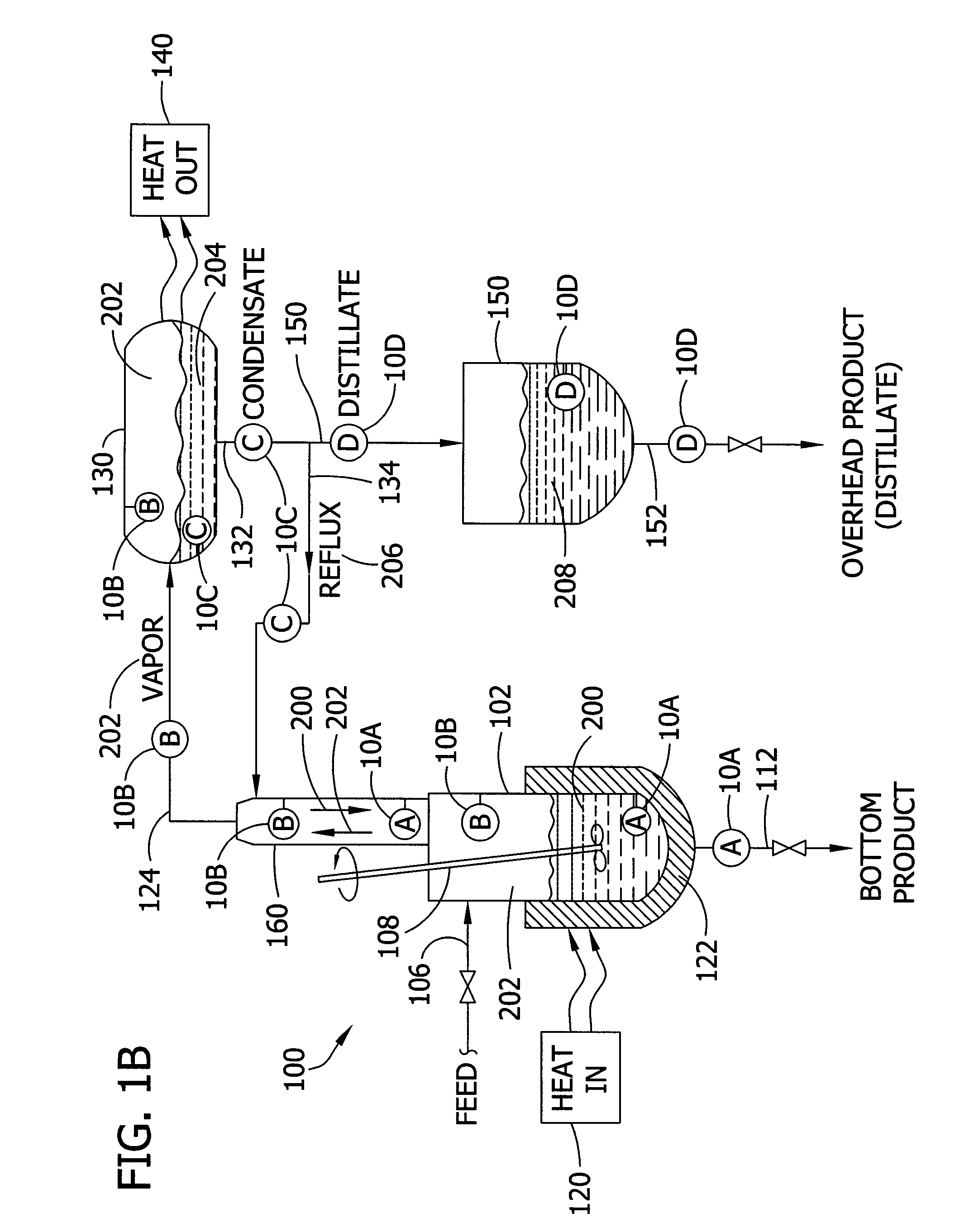
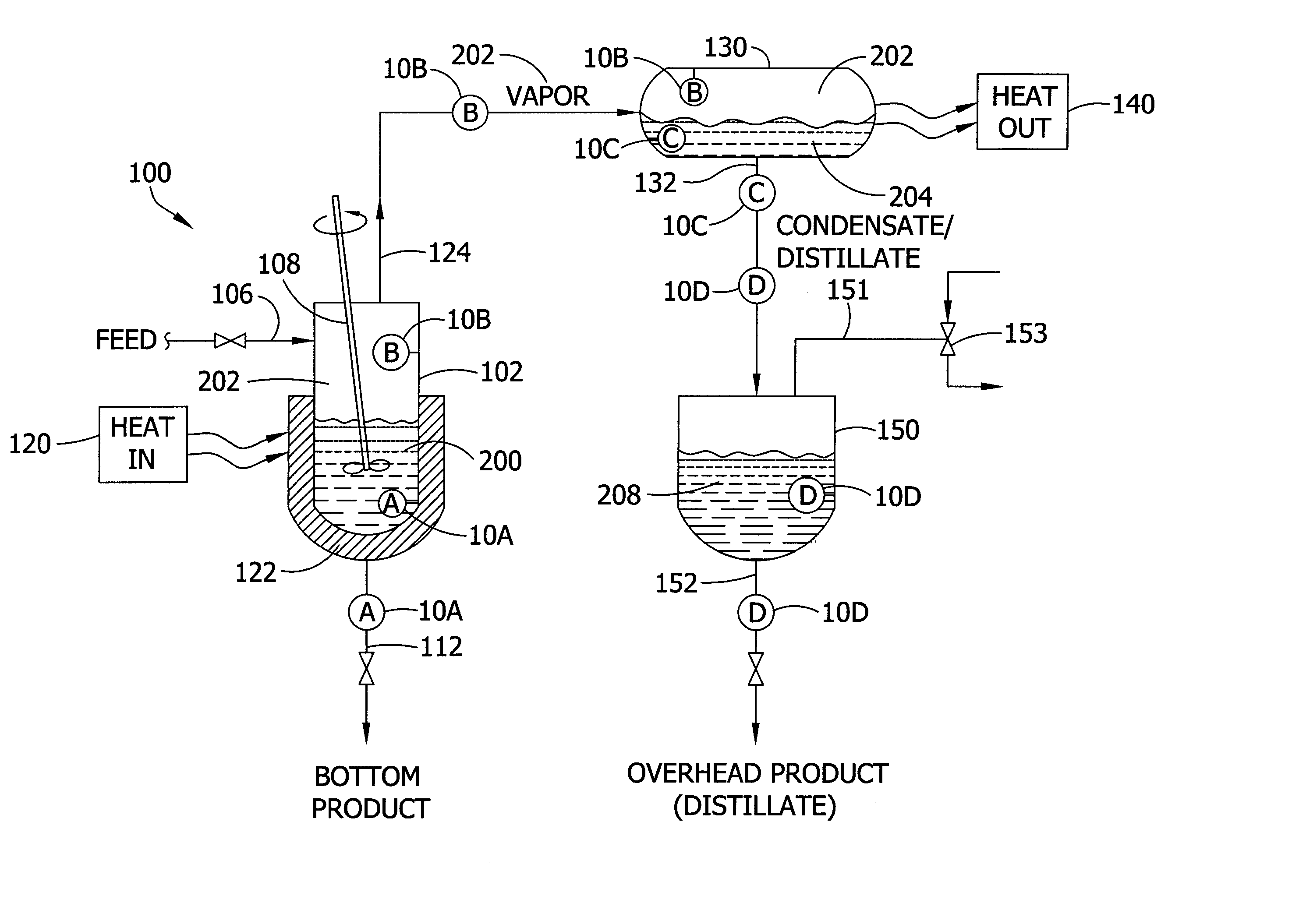
Batch distillation refers to the use of distillation in batches, meaning that a mixture is distilled to separate it into its component fractions before the distillation still is again charged with more mixture and the process is repeated. This is in contrast with continuous distillation where the feedstock is added and the distillate drawn off without interruption. Batch distillation has always been an important part of the production of seasonal, or low capacity and high-purity chemicals. It is a very frequent separation process in the pharmaceutical industry.
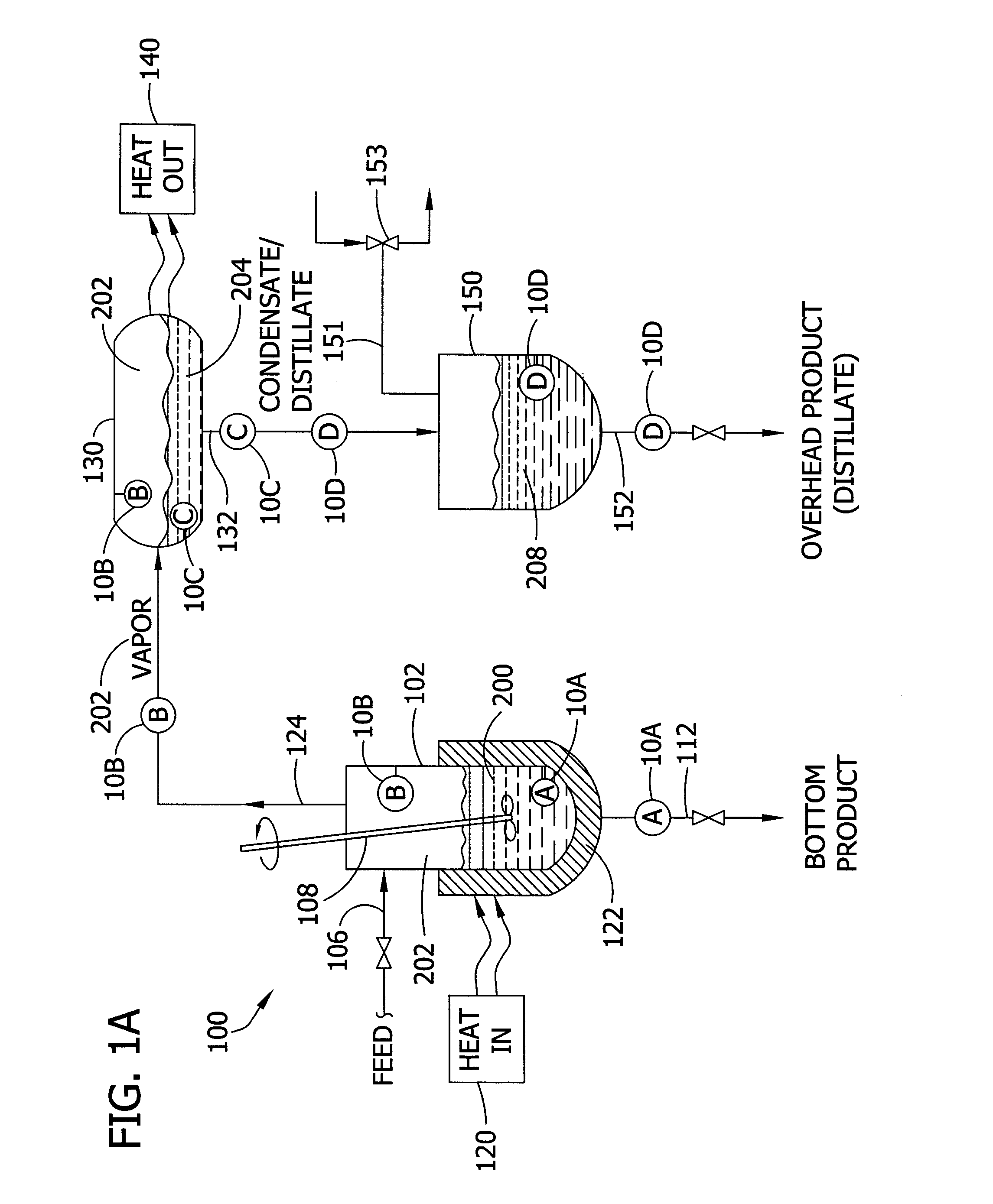
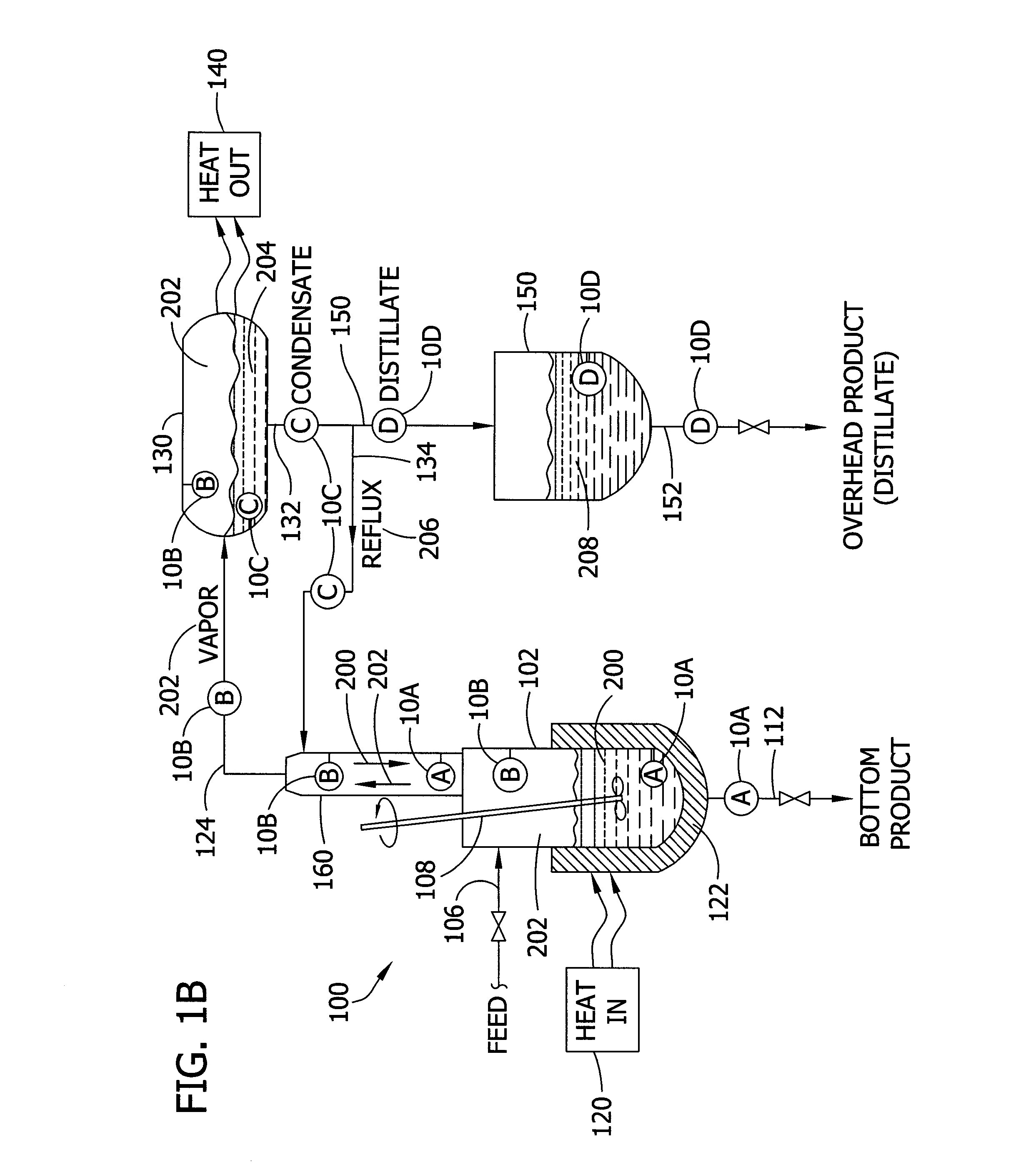
Systems for monitoring and controlling unit operations that include distillation
InactiveUS7603889B2High sensitivityHigh dielectric constantProcess control/regulationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDistillationUnit operation
Fluid sensor methods and systems adapted for monitoring and / or controlling distillation operations in fluidic systems, such as batch distillation operations or continuous distillation operations, are disclosed. Preferred embodiments are directed to process monitoring and / or process control for unit operations involving endpoint determination of a distillation, for example, as applied to a liquid-component-switching operation (e.g., a solvent switching operation), a liquid-liquid separation operation, a solute concentration operation, a dispersed-phase concentration operation, among others.
Owner:MEAS FRANCE
Monitoring and controlling unit operations
InactiveUS20070017291A1Efficiently sensingEffective monitoringProcess control/regulationAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDistillationUnit operation
Fluid sensor methods and systems adapted for monitoring and / or controlling distillation operations in fluidic systems, such as batch distillation operations or continuous distillation operations, are disclosed. Preferred embodiments are directed to process monitoring and / or process control for unit operations involving endpoint determination of a distillation, for example, as applied to a liquid-component-switching operation (e.g., a solvent switching operation), a liquid-liquid separation operation, a solute concentration operation, a dispersed-phase concentration operation, among others.
Owner:MEAS FRANCE
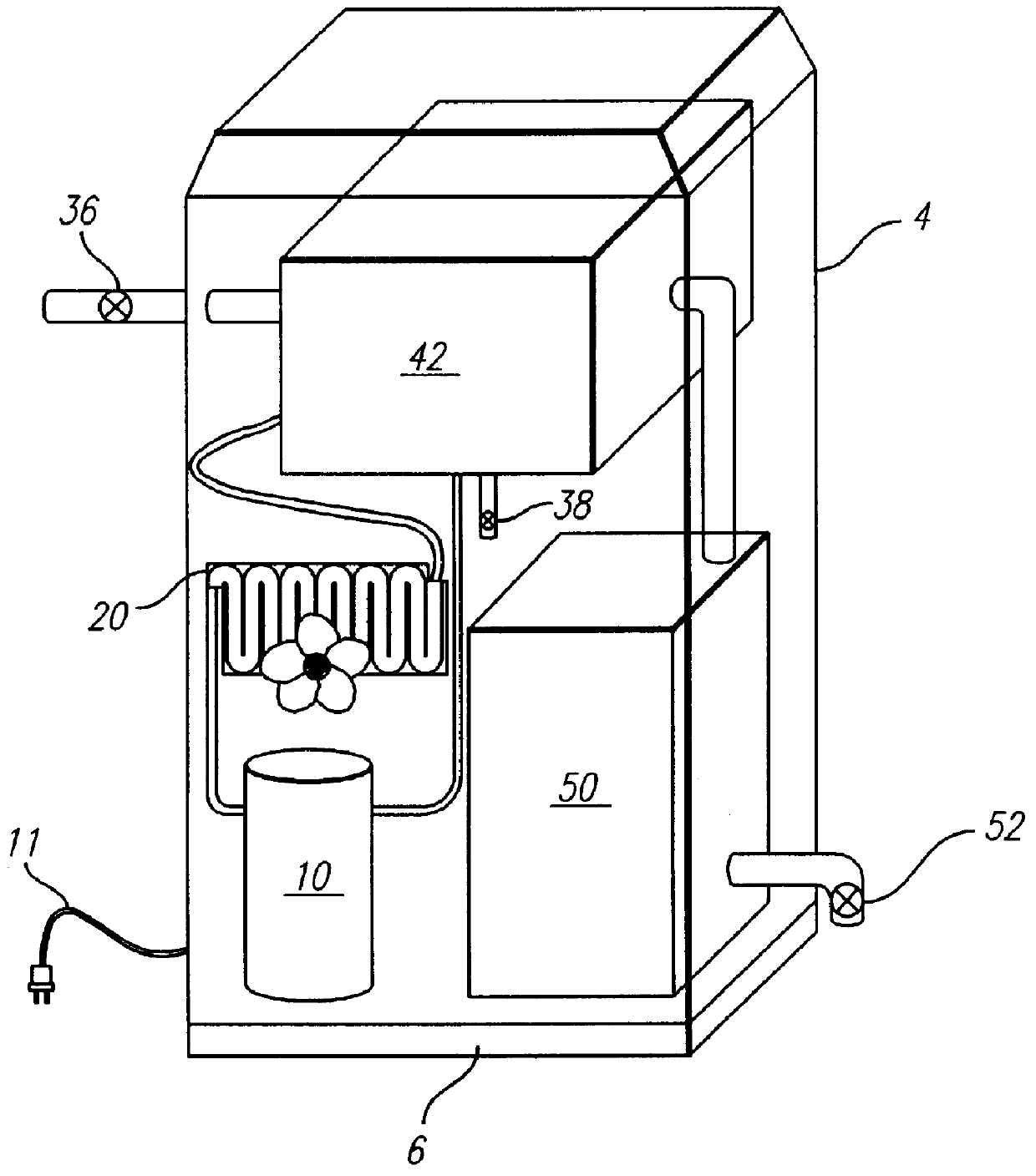
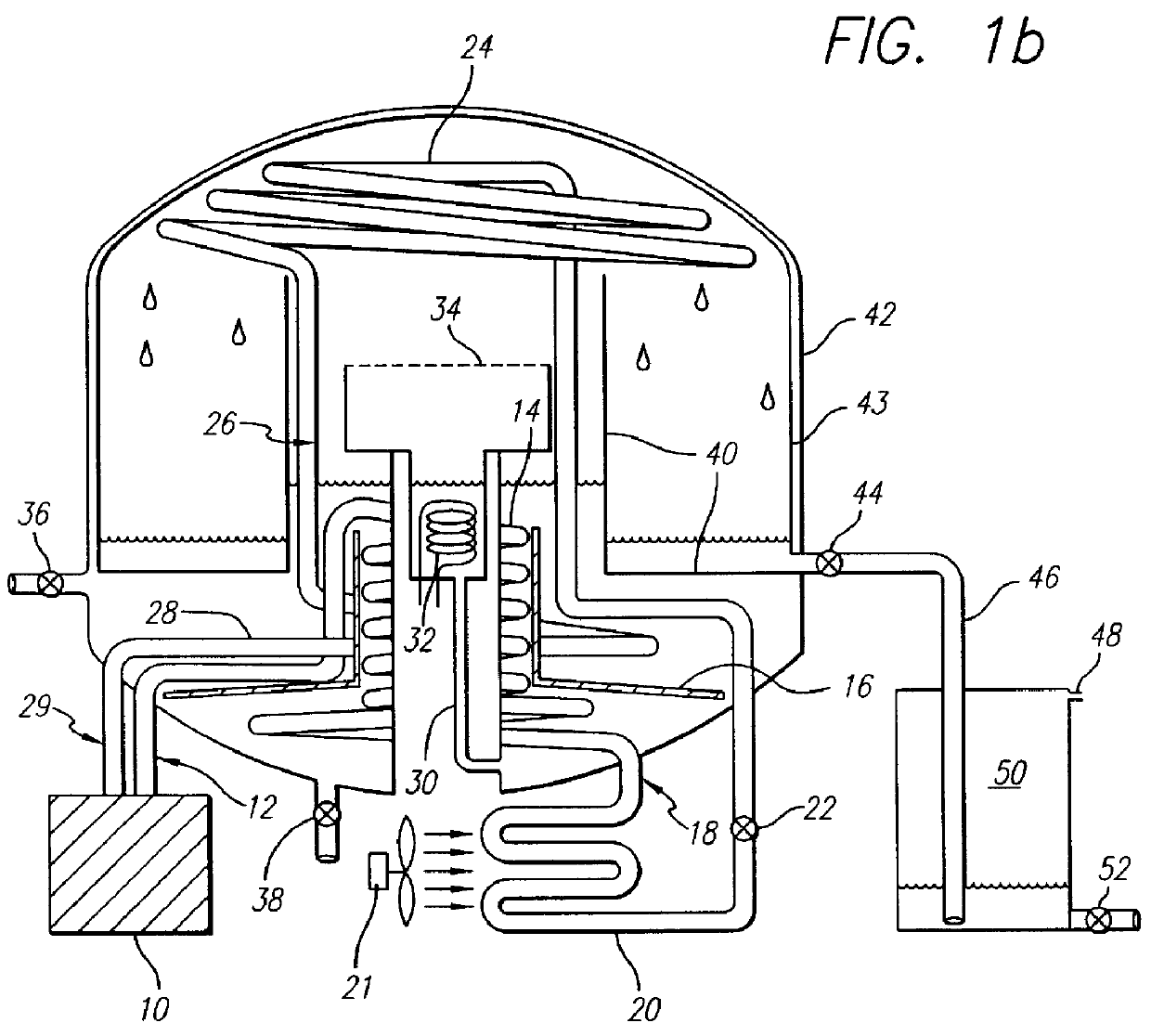
Compact vacuum distillation device
InactiveUS6010599AReduce problem sizeBoiling pointUsing liquid separation agentDistillation in boilers/stillsAtmospheric airEngineering
An apparatus for batch distilling a liquid at sub-atmospheric pressure, without the aid of a vacuum pump. The apparatus includes an evaporator section having a valved entry port through which a batch of liquid in a first atmospheric condition is added to the evaporator section. A condenser section receives distillate and is in communication with the evaporator section. A valved vent is provided for sealing said apparatus from the outside atmosphere to form a second atmospheric condition which is sealed from the atmosphere after a heating element vaporizes said liquid into an initial sufficient amount of a first vapor to purge the first atmospheric condition from the apparatus through the valved vent. A condenser is disposed for condensing a sufficient amount of the first vapor to form a third atmospheric condition at a pressure below the first atmospheric condition, and for condensing a second vapor to produce distillate.
Owner:AMERICAN TECH GROUP
Production technology for cracking butyl octanol residual liquid into C4 and C8 by means of alkaline liquid cracking agent
ActiveCN101892066AReasonable useEmission reductionThermal non-catalytic crackingFractionationPotassium hydroxide
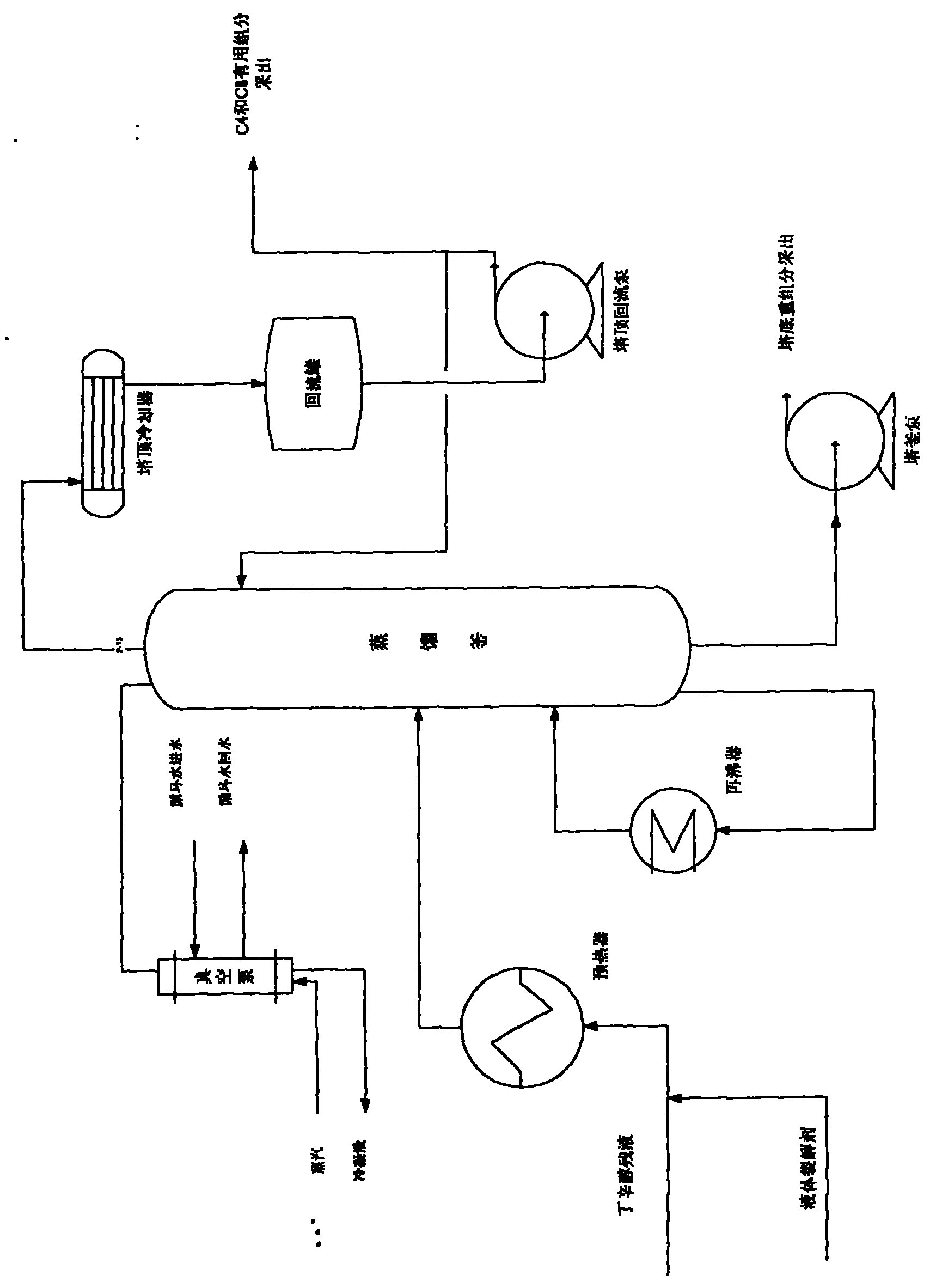
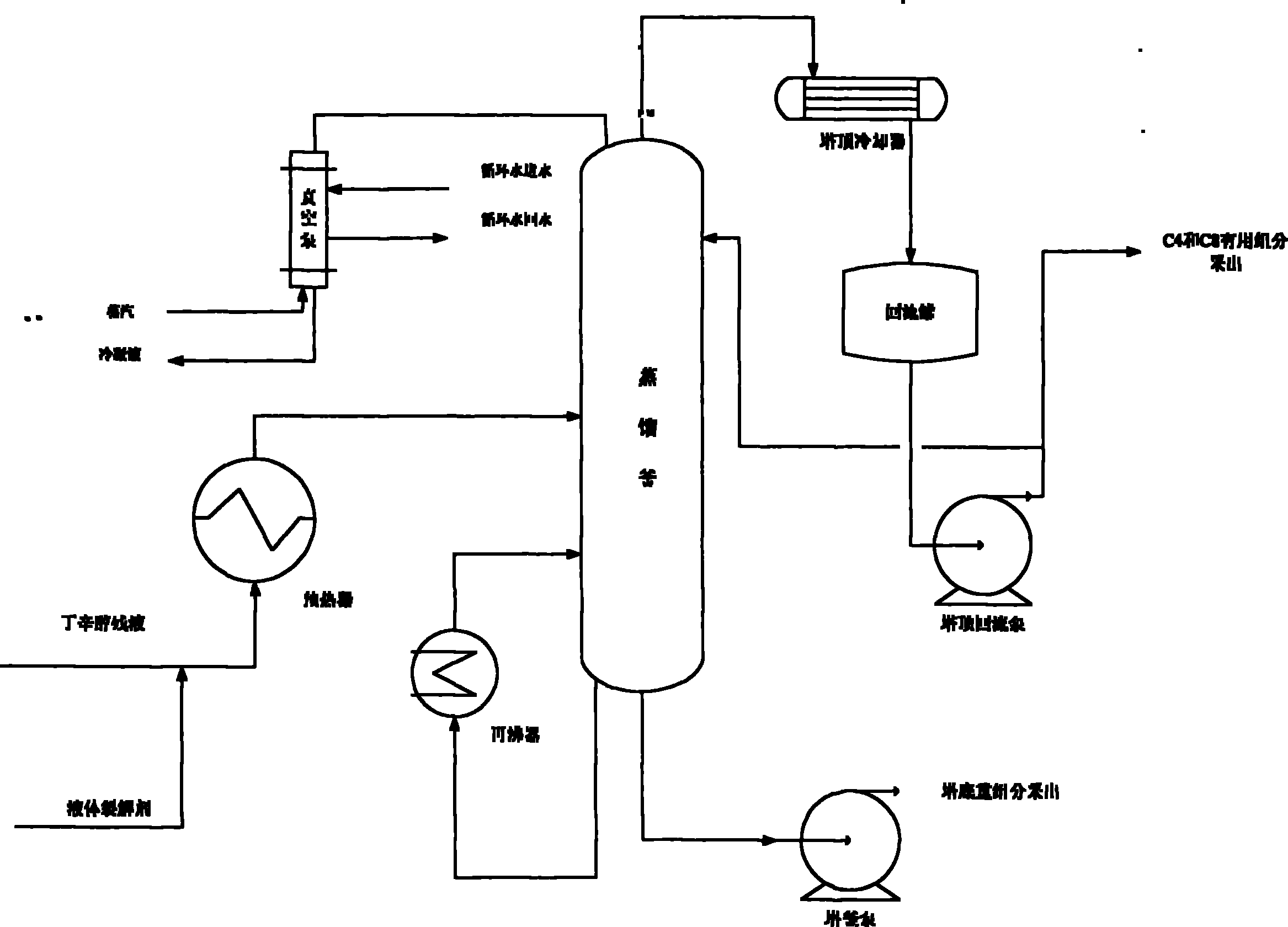
The invention relates to production technology for cracking butyl octanol residual liquid into C4 and C8 by means of an alkaline liquid cracking agent. The technology is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing the alkaline liquid cracking agent, wherein the alkaline liquid cracking agent consists of sodium hydroxide, potassium hydroxide, water, isopropanol, ethylene glycol, potassium permanganate, ethanol, barium nitrate and diboron trioxide; preheating the alkaline liquid cracking agent and the butyl octanol residual liquid through a preheater and adding into a distilling still, wherein the tower bottom temperature of the distilling still is between 200 and 280 DEG C, the tower top temperature is between 130 and 190 DEG C, and the tower top pressure is between 0.08 and 0.1Mpa below zero; and extracting the C4 and C8 generated by cracking from the tower top of the distilling still, pumping the C4 and C8 into a fractionating column at the downstream for fractionation, and extracting a small amount of uncracked heavy components from a tower bottom pump. The production technology has the advantages of high production capacity, high cracking selectivity, high content of the cracked useful components, low cost, simple process, and batch distillation or continuous distillation.
Owner:山东瑞利尔石油装备有限责任公司
Application of distillation and multi-stage molecular distillation technique in regeneration process for waste lubricant oil
InactiveCN101319166ANot easy to stickShort stayHydrocarbon distillationLubricant compositionDistillationPre treatment
The invention discloses a novel process of regenerating base oil from waste lubricating oil. The process which applies an advanced molecular distillation technology to regenerate base oil from waste lubricating oil can not only regenerate better base oil, but also carry out effluent fraction through multilevel series connections. The waste lubricating oil is deprived of light diesel oil in a rectification tower through pretreatment and deprivation of light components, and then the waste lubricating oil is pumped into a first-level molecular still through a first-level feed pump to distill off a relatively lighter base oil component as a product. Heavier components which are left by the first-level distillation and serves as the raw material of a second-level molecular still are pumped into the second-level molecular still through a second-level feed pump to distill off a component heavier than the first-level molecular distillation product to serve as a product, and the distillation residuals are taken as the raw material of a third-level distillation. The process is repeated in the manner until a required n level is reached, wherein n is more than or equal to 2 and is less than or equal to 5, and the recommended optimal level number is 3 or 2. The process has the advantages that: the obtained product only contains the base oil component, while other impurities including additives are discharged in the form of residuals; the process also can produce a plurality of products with good quality and varied viscosities, thereby bringing about great convenience for the preparation of product lubricating oil.
Owner:尹英遂 +2
Process for recovering distillation waste liquid generated by producing 1,4-butanediol
InactiveCN103274898AHigh recovery rateImprove overall recoveryOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationDistillationButanediol
The invention relates to a process for recovering distillation waste liquid generated by producing 1,4-butanediol and belongs to the technical field of recycling of organic waste liquid in the industrial production. According to the invention, the distillation waste liquid generated in the process of producing 1,4-butanediol by a Reppe method is used as a raw material; drained wastewater is used as an extracting agent; sodium sulfate is used as a salting-out agent; sulfuric acid is used as a catalyst for depolymerizing reaction; and by a circulating process of salting-out-extraction, reduced pressure batch distillation separation and depolymerizing reaction, various products in the distillation waste liquid, such as 1,4-butanediol, butanol and 3-tetrahydrofurfuryl alcohol are recovered. The process disclosed by the invention has the characteristics that various products can be recovered, the recovery rate of the products is high and the recovery economic benefits are good; the process sufficiently utilizes waste liquid resources and is beneficial to environment protection; the process is simple, reaction conditions are mild, equipment is conventional and recovery cost is low; and the process has a wide application range and is convenient to popularize and apply. The process can be widely applied to recycling of the organic waste liquid in the industrial production and is particularly suitable for recycling the waste liquid generated in the process of producing 1,4-butanediol by the Reppe method.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method and apparatus for removing and recycling organic phase in wastewater with distillation-free complete-molecular sieve
InactiveCN101318717AReduce consumptionImprove separation efficiencyDispersed particle separationWater/sewage treatment by heatingRecovery methodHigh concentration
The invention belongs to the environmental protection technical field, in particular relating to a recovery method and a recovery device for an organic solvent in wastewater. The recovery method has the following operation steps that: organic phase / water mixed steam above the wastewater containing the organic solvent is directly extracted, is heated, and then is passed through to a hydrophobic silicone zeolite adsorbent bed layer , an organic phase is absorbed by a hydrophobic adsorbent, and water is drained. Then a reduced pressure desorption or a carrier gas desorption mode is adopted to desorb the organic phase with high concentration absorbed by the hydrophobic silicone zeolite adsorbent to produce organic phase steam with a concentration more than 95 percent, and the steam is dried and dehydrated by a 3A molecular sieve or other drying agents to produce the organic phase with a concentration more than 99 percent. Compared with the prior batch distillation or extraction method, the method can realize the continuous production, and has simple equipment, small occupied area, high efficiency, low energy consumption, and wide application prospect on green environmental protection processes.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
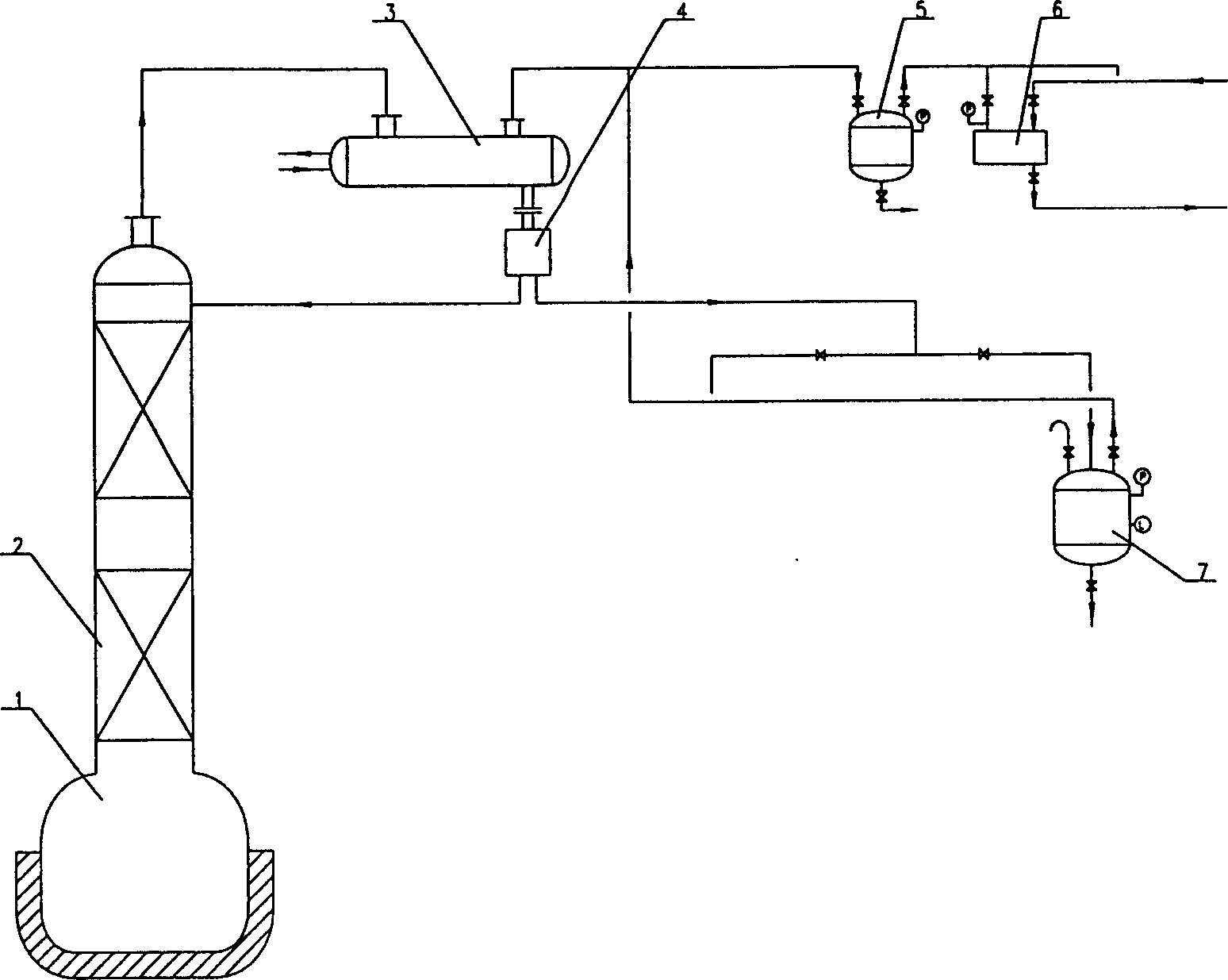
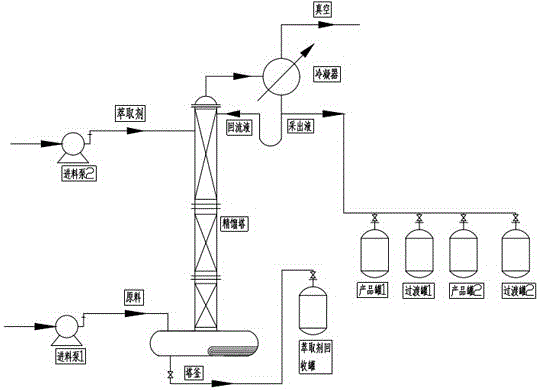
Device and method for separating diisopropylbenzene isomeride by virtue of reduced pressure batch distillation
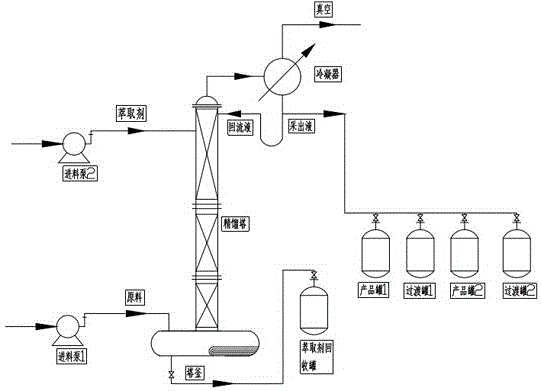
InactiveCN102219634AHigh purityShort operating timeDistillation purification/separationRefluxDistillation
The invention relates to a device and method for separating diisopropylbenzene isomeride by virtue of reduced pressure batch distillation. The device is a batch distillation tower consisting of a tower kettle, a material inlet, a distillation tower, a liquid distributor, a condenser, a catcher and a reflux tank, wherein one end of the reflux pipeline of the reflux tank is connected with the top of the distillation tower, and the other end of the reflux pipeline of the reflux tank is connected with a tower top product transition fraction tank and a tower top product tank; and simultaneously, avacuum tank is respectively connected with the catcher and the tower top product transition fraction tank as well as the tower top product tank through a buffer tank. When the pressure of the tower top is 132.0Pa-1320.0Pa, the temperature of the tower top is 80.0-82.0 DEG C and the temperature of the tower kettle is 90.0-95 DEG C, the variable reflux ratio operation is carried out: the operation reflux ratio when m-diisopropylbenzene with the purity above 99.0wt% is extracted is 7 / 1-9 / 1, and the operation reflux ratio when p-diisopropylbenzene with the purity of 99.0wt% is extracted is 15 / 1-20 / 1. The process has the characteristics of short operation time, low tower kettle temperature, less energy consumption and no thermosensitive reaction, and ensures that the purity of the separated product is high.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for treating wastewater produced by methylation reaction in metribuzin synthesis
InactiveCN101445304AReduce processingReduce pollutionMultistage water/sewage treatmentNature of treatment waterRefluxBromine
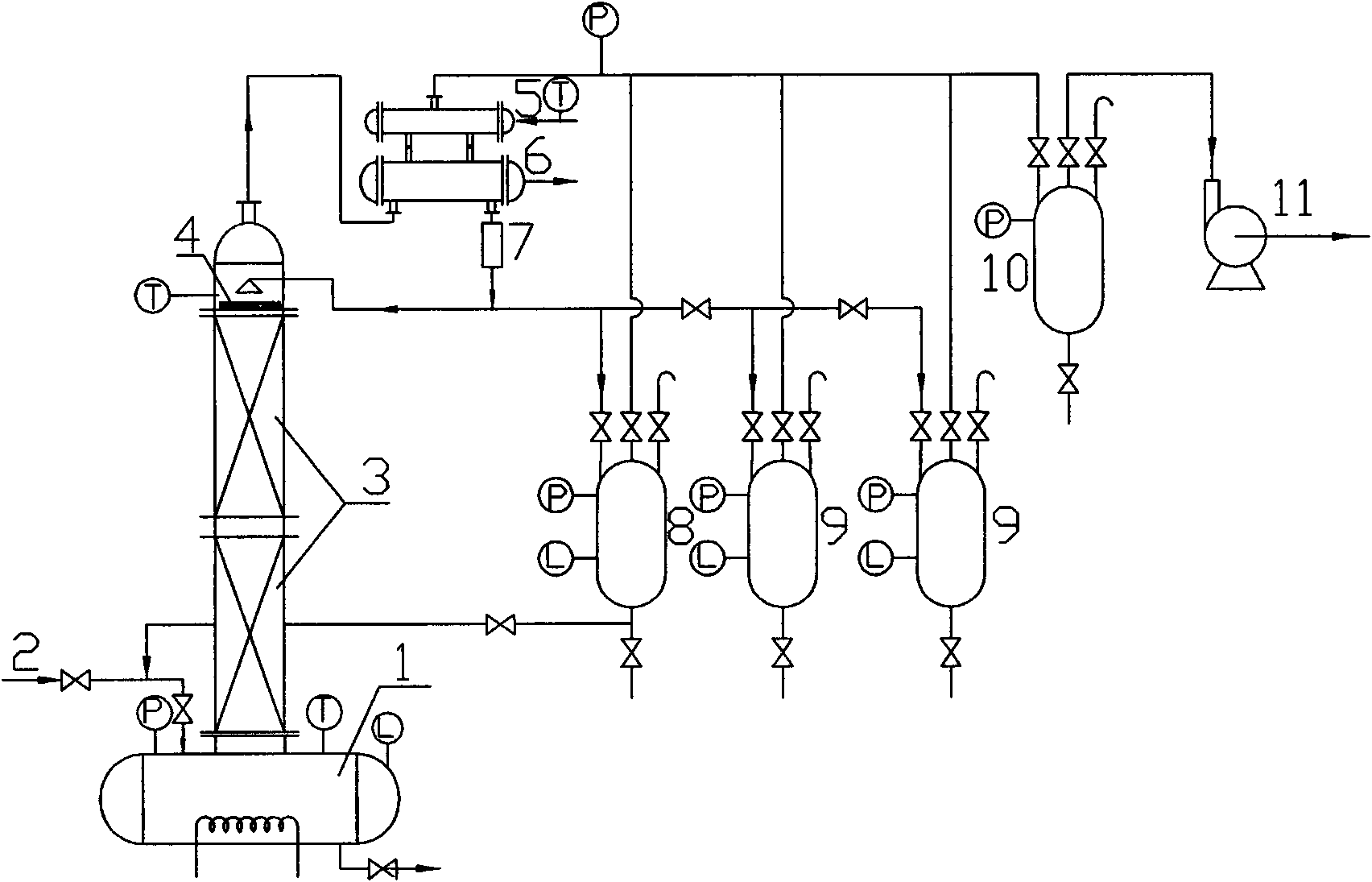
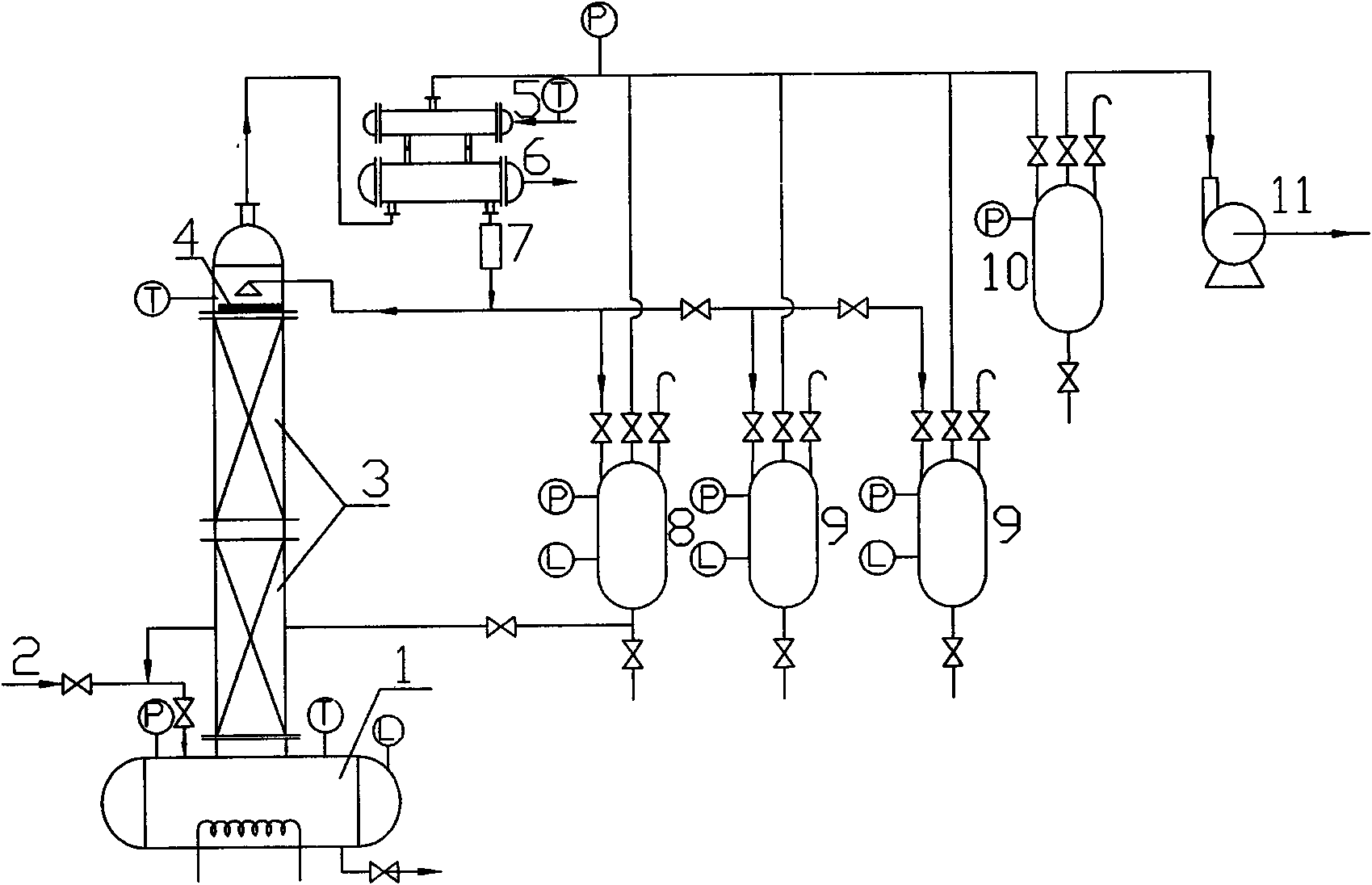
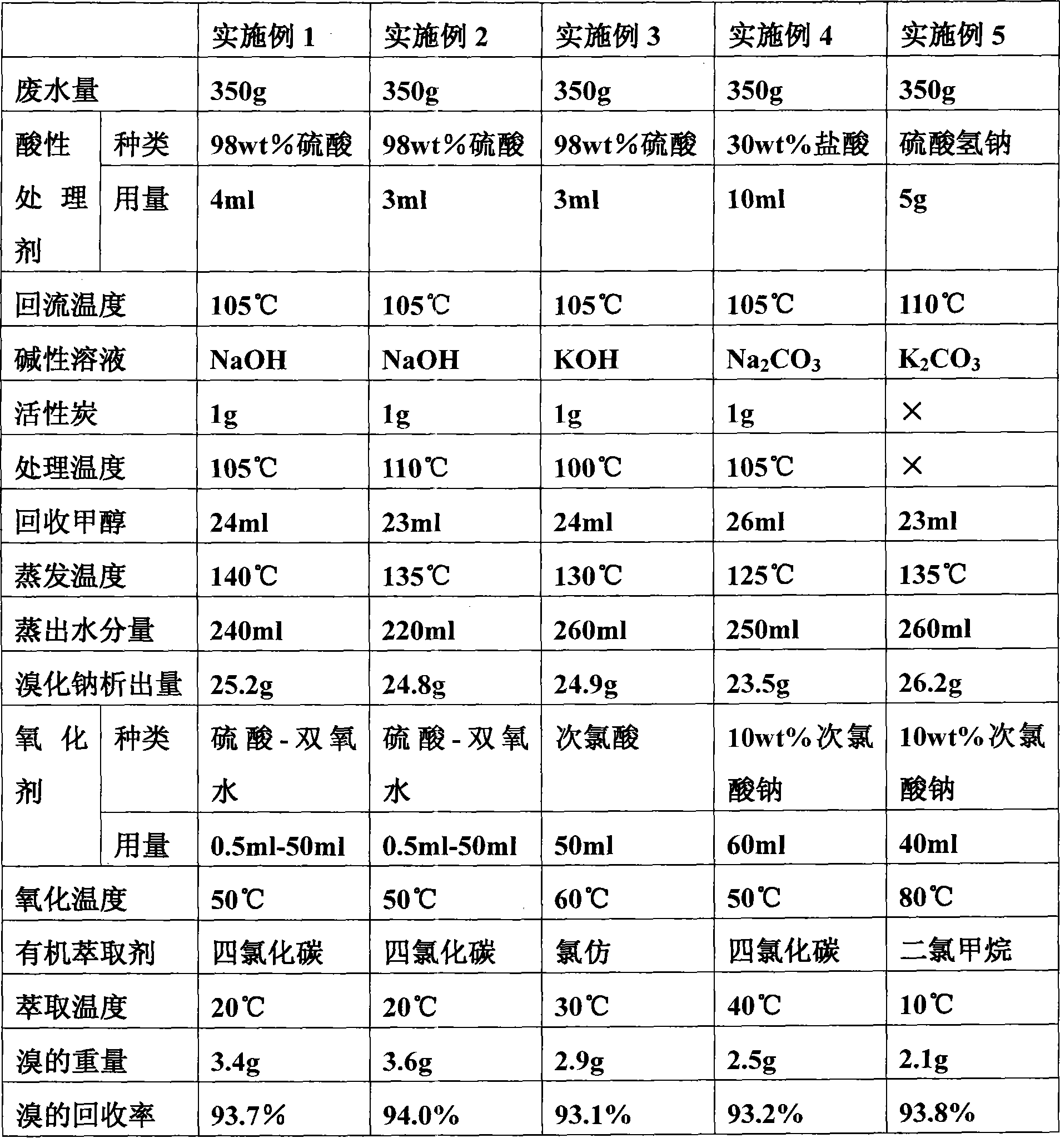
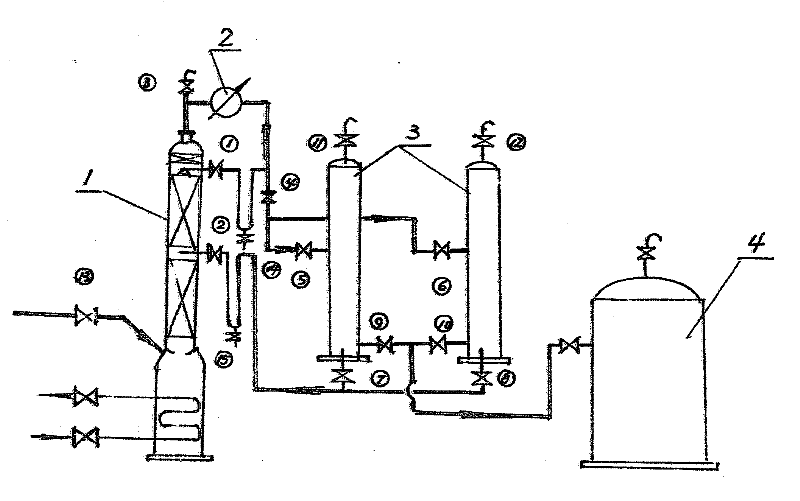
The invention discloses a method for treating wastewater produced by methylation reaction in metribuzin synthesis. In the method, the wastewater produced by the methylation reaction in the metribuzin synthesis is added with an acidic treating agent, and the obtained mixture is heated to 90 DEG C-120 DEG C and refluxed for deodorization and decolorization; and volatile gas in the wastewater and gas produced in the reflux are absorbed by alkaline solution for deodorization. Methanol in the wastewater is recovered by a batch distillation method. Residual liquid is heated to 100 DEG C-150 DEG C for evaporation, and then the residual liquid is naturally cooled by stirring until sodium bromide crystal is separated out. Filtrate is oxidized by an oxidant at the oxidation temperature of 50 DEG C-80 DEG C. A system is cooled to 10 DEG C-40 DEG C, and bromine in the system is extracted by an organic extractant, thus obtaining organic phase extracting solution with the bromine. The method helps solve the problem of treating methylated wastewater in metribuzin production, and reduce environmental pollution and production cost, the recovery rate of the bromine reaches more than 93%, and the method has good use value, and is simple and feasible.
Owner:JIANGSU HUAYI GARMENT CO LTD +1
Method for enriching and purifying icariin in epimedium herb
InactiveCN102070688AHigh adsorption selectivityParsing fastSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationEpimediumCoupling
The invention belongs to the field of natural organic chemistry and relates to a method for enriching and purifying icariin in epimedium herb by a batch distillation-macro absorption resin coupling method. The method is characterized in that: icariin is separated and purified by the batch distillation-macro absorption resin coupling method, the adsorption selectivity to icariin is high, adsorption and resolution are quick and adsorption volume is large; and extraction is convenient and quick, raw materials are readily available, production cost is low, separation effect is remarkable, extraction purity is high, an icariin semi-finished product with the icariin content of over 35 percent and an icariin finished product with the icariin content of over 95 percent can be obtained, and the defects of low extraction rate and low extraction purity by the conventional method are overcome. Macro absorption resin with stable physicochemical property, a large surface area, high exchange speed, high mechanical strength, high contamination resistance and high thermal stability is used, so that icariin is selectively adsorbed from solution by physical adsorption, adsorption and resolution are quick, and adsorption volume is large.
Owner:DAXINGANLING LINGOBERRY BOREAL BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for enriching and purifying common phellinus fungus general flavone in common phellinus fungus
ActiveCN102078339AHigh adsorption selectivityParsing fastFungi medical ingredientsImmunological disordersBiotechnologyCoupling
The invention belongs to the field of natural organic chemistry and relates to a method for enriching and purifying common phellinus fungus general flavone in common phellinus fungus by using a batch distillation-macroporous absorption resin coupling method. The method is characterized in that the common phellinus fungus general flavone is separated and purified by applying a macropore adsorption technology, the adsorption selectivity to the common phellinus fungus general flavone is better, the separation effect is remarkable, the extraction purity is high, the semi-finished product with more than 35 percent of the common phellinus fungus general flavone and the final product with above 90 percent of the common phellinus fungus general flavone can be obtained, and the defects of relatively lower conventional extraction rate and low extraction purity are overcome. Macroporous absorption resin with stable physicochemical property, large surface area, higher switching speed, high mechanical strength, strong contamination resistance and good thermal stability is selected, and the common phellinus fungus general flavone is selectively absorbed from a solution through physical adsorption, thus the method has the advantages of high adsorption, high deabsorption speed and larger adsorption capacity.
Owner:DAXINGANLING LINGOBERRY BOREAL BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for adopting melting crystallization technology to separate and purify succinonitrile
InactiveCN107721878AHigh purityShort operating timeCarboxylic acid nitrile purification/separationDissolutionSolvent
The invention relates to a method for adopting a melting crystallization technology to separate and purify succinonitrile. According to the method, succinonitrile coarse products are added into a melting crystallizer and heated to 59 DEG C for complete dissolution, then programmed heating is started to raise the temperature to 45-52 DEG C, after the temperature is stabilized for 10-180 min, crystallization mother liquor is released, and succinonitrile coarse crystals are obtained; then programmed heating is started, sweating is conducted, the temperature is stabilized for 10-180 min after reaching final sweating temperature, and high-purity succinonitrilee crystals with the purity of 99.95% or above are obtained. According to the method, a separation method of melting crystallization is adopted, no solvents or vacuum drying is needed, and the operation time is short; the operation is simple, the method is environmentally friendly, the product purity is high, and the crystallization mother liquor and sweating liquid can be recycled and purified again through melting crystallization; compared with an existing decompression batch distillation method, the energy consumption, operatingtemperature and cost are low, no polymerization coking phenomena occur in the operating process, and the yield and quality are not affected.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Production method of triethylamine extracted from waste liquid by batch distillation method
InactiveCN102442913AReduce manufacturing costAmino compound purification/separationLiquid wasteDistillation
The invention relates to a production method of triethylamine extracted from a waste liquid by a batch distillation method. After a water-bearing waste liquid generated when an aluminum silicate zeolite is produced by taking the triethylamine as a template agent is separated and extracted by the method provided by the invention, the triethylamine can be reused, the batch distillation method is adopted, the cohobation ratio and the tower bottom temperature are controlled, the extracted liquid is cooled and layered, a lower liquid is carried out reflux operationes, and an upper liquid is recycled into a finished product storage tank, so that the water content of the finished product is less than 1.5%, and the product is measureddetermined by a trace water analyzer. The main equipment comprises a distillation column, a condenser, a demixer and the like.
Owner:阎成华
Method for enriching and purifying betulin in birch barks
ActiveCN102093458AHigh adsorption selectivityParsing fastSteroidsHeat stabilityUltimate tensile strength
The invention belongs to the field of natural organic chemistry and relates to a method for enriching and purifying betulin in birch barks by utilizing a batch distillation-macroporous absorption resin method. The method has the advantages of good adsorption selectivity to betulin, quickness of adsorption and resolution, larger adsorption capacity, convenience and quickness of extraction, rich raw material source, low production cost, obvious separation effect and high extraction purity, can be used for obtaining a semi-finished betulin product with a content higher than 35 percent and a finished betulin product with a content higher than 98 percent and overcomes the defects of relatively lower conventional extraction ratio and low extraction purity. In the invention, macroporous absorption resin having stable physical and chemical properties, larger surface area, higher exchange speed, higher mechanical strength, strong antipollution capacity and good heat stability is used, which can selectively adsorb the betulin from the solution through physical adsorption, thus the invention has the advantages of quickness of adsorption and resolution and larger adsorption capacity.
Owner:DAXINGANLING LINGOBERRY BOREAL BIOTECH CO LTD
Device and method for extracting pyrene
ActiveCN102911004AHigh purityImprove processing stabilityDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsGeneral Packet Radio ServiceAnthracene
The invention relates to the field of organic compound extraction, in particular to a device and method for extracting pyrene. The invention is characterized in that anthracene oil is used as a raw material, and a high-purity pyrene product with purity more than 98% is obtained by using the boiling point difference among anthracene type compounds through the vacuum batch distillation and solvent washing processes. Compared with the prior art, the invention has the advantages that the process for extracting pyrene from anthracene oil is simple and easy to operate, and the price of equipment is low; the purity of extracted pyrene is high and reaches more than n98%, and the process has good stability; multi-component products can be simultaneously extracted; Profius-DP and Modbus field buses are simultaneously adopted in a flow measurement and control system, and network intelligent control is realized; and the device has GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) wireless and remote monitoring capability.
Owner:辽宁源宇化工有限公司
Batch distillation process for separating tert-butyl alcohol-methyl propionate azeotrope by mixed extractant
InactiveCN105037155AQuality improvementHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationExtractive distillationMethyl propionate
The present invention discloses a batch distillation process for separating tert-butyl alcohol-methyl propionate azeotrope by a mixed extractant. The process is characterized by using a mixture of ethylene glycol and an ionic liquid as an extractant, which is added from the upper end of an extractive distillation column; a tert-butyl alcohol-methyl propionate azeotrope is added to the kettle; by adjusting the reflux ratio, the quality of the product is controlled; and the product of methyl propionate, a methyl propionate-tert-butyl alcohol transition fraction, a tert-butyl alcohol products, and a tert-butyl alcohol-glycol transition fraction can be obtained from the top of the tower. The contents of products methyl propionate and tert-butyl alcohol are both higher than 99.5%; and the two transition fractions and bottom extractant can be recycled and treated in the next batch of materials. The process uses a batch vacuum distillation, has the advantages of simple equipment, less investment, flexible operation, low power consumption and high product quality, and is applicable to small and medium-scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Technology for separating tetrahydrofuran-methanol-water through three-tower batch distillation
ActiveCN111517920AGuaranteed separation effectEfficient separationOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationFluid phaseProcess engineering
The invention relates to a process for separating tetrahydrofuran-methanol-water through three-tower batch distillation. According to the characteristic that a tetrahydrofuran-methanol-water ternary mixture forms two binary azeotrope systems and the azeotropic composition changes under different pressures, separation of complex ternary systems in small-batch production is realized by adopting a mode that three rectifying towers are matched for operation. The mass fraction of the separated tetrahydrofuran liquid is greater than 99.9%, the mass fraction of the methanol liquid is greater than 99.9%, and the mass fraction of water is greater than 99.9%. The invention provides a novel batch distillation process, a third component does not need to be introduced, the process load is low, the costis saved, the liquid-phase component extracted from the bottom of the tower is subjected to effective component segmentation, high-purity tetrahydrofuran is separated, meanwhile, efficient recovery of methanol and water is realized, and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for refining 4-amino diphenylamine
InactiveCN1470499AHigh yieldIncrease contentAmino compound purification/separationDistillationAniline
The present invention relates to a method for refining 4-aminodiphenylamine by adopting three-column continuous rectification and intermittent distillation. The crude product of 4-aminodiphenylamine can be obtained by rectification in the column No.1, and the substances of phenylamine, phenazine and azobenzene can be obtained at the top of column, said crude product can be purified in column No.2, in the column No.3 the phenylamine is separated, and the intermittent column can be used for making batch distillation of 4-aminophenylamine made up by using column bottoms of column No.2 and returning it into column No.2 for refining it. The yield rate of its whole process can be raised to 99% from 94%, and the content of 4-aminodiphenylamine in the finished product is greater than 99 wt%, at the same time the phenylamine can be recovered, and can be used.
Owner:JIANGSU SINORGCHEM TECH CO LTD
Method for producing white spirit base by recycling ethanol from waste yeast dried steam
InactiveCN101245306AReduce pollutionResolve flavorAlcoholic beverage preparationSlurryFood resources
The invention provides a method for recycling alcohol from dried steam of waste yeast to prepare base of liquor, belonging to the technical field of brewing, which comprises surface air cooler condensation, tubular heat exchanger condensation, the absorption of absorption tower, crude process of alcohol, refining of alcohol, and post treatment of alcohol. Beer yeast slurry produces large amount of steam containing alcohol by the drying of a roller dryer, the steam enters a surface air cooler to condense most of water, the uncondensed steam enters a tubular heat exchanger to condense most of alcohol, and the rest uncondensed steam enters an absorption tower to be absorbed by water. After mixing the recycled alcohol-water blend, continuous distillation by a topping still is adopted to remove impurity and improve alcohol concentration, and batch distillation by the hog still is adopted for further refining, thereby acquiring high-quality liquor base used for blending liquor. The method recycles alcohol by three steps, and the recovery rate is up to 100 percent; by using the recycled alcohol to prepare liquor base, food resources are fully used, environmental pollution is reduced and economic benefits of enterprises are increased.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for separating diisopropylbenzene isomeride by virtue of reduced pressure batch distillation
InactiveCN102219634BHigh purityShort operating timeDistillation purification/separationDistillationBuffer tank
The invention relates to a device and method for separating diisopropylbenzene isomeride by virtue of reduced pressure batch distillation. The device is a batch distillation tower consisting of a tower kettle, a material inlet, a distillation tower, a liquid distributor, a condenser, a catcher and a reflux tank, wherein one end of the reflux pipeline of the reflux tank is connected with the top of the distillation tower, and the other end of the reflux pipeline of the reflux tank is connected with a tower top product transition fraction tank and a tower top product tank; and simultaneously, avacuum tank is respectively connected with the catcher and the tower top product transition fraction tank as well as the tower top product tank through a buffer tank. When the pressure of the tower top is 132.0Pa-1320.0Pa, the temperature of the tower top is 80.0-82.0 DEG C and the temperature of the tower kettle is 90.0-95 DEG C, the variable reflux ratio operation is carried out: the operation reflux ratio when m-diisopropylbenzene with the purity above 99.0wt% is extracted is 7 / 1-9 / 1, and the operation reflux ratio when p-diisopropylbenzene with the purity of 99.0wt% is extracted is 15 / 1-20 / 1. The process has the characteristics of short operation time, low tower kettle temperature, less energy consumption and no thermosensitive reaction, and ensures that the purity of the separated product is high.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Vacuum batch distillation process and device for purifying peach aldehyde from side discharge material
InactiveCN104592176AHigh yieldShorten distillation timeOrganic chemistryDistillation regulation/controlRefluxAlcohol
The invention relates to a vacuum batch distillation process and device for purifying peach aldehyde from a side discharge material. The vacuum batch distillation process comprises the following steps: adding a crude peach aldehyde product into a distilling column bottom at one time; vacuuming a distilling column; heating the column bottom to be 140-160 DEG C; keeping the column body at 50-80 DEG C; opening the column top to condense circulation water; when the column top has a reflux liquid, slowly enriching light components on the column top; when the temperature of the column top is stabilized to be 86-95 DEG C, acquiring 8-12wt% of capryl alcohol and transition fraction according to a variable reflux ratio; continuously implementing total reflux, and acquiring a peach aldehyde product from a low-level side discharge point when keeping the temperature of the column top at 85-95 DEG C and the temperature of a side at 120-140 DEG C; continuously implementing total reflux, rising the side acquiring position, and acquiring a residual peach aldehyde product from a high-level side discharge point. Compared with the prior art, on the basis of vacuum distillation, the vacuum batch distillation process adopts a vacuum side material discharge method, so that the yield of peach aldehyde is greatly increased, the distillation time is shortened, the energy consumption is reduced, the distillation efficiency is improved, and the purity of the product is greater than that of a column top discharge material.
Owner:SHANGHAI RES INST OF CHEM IND
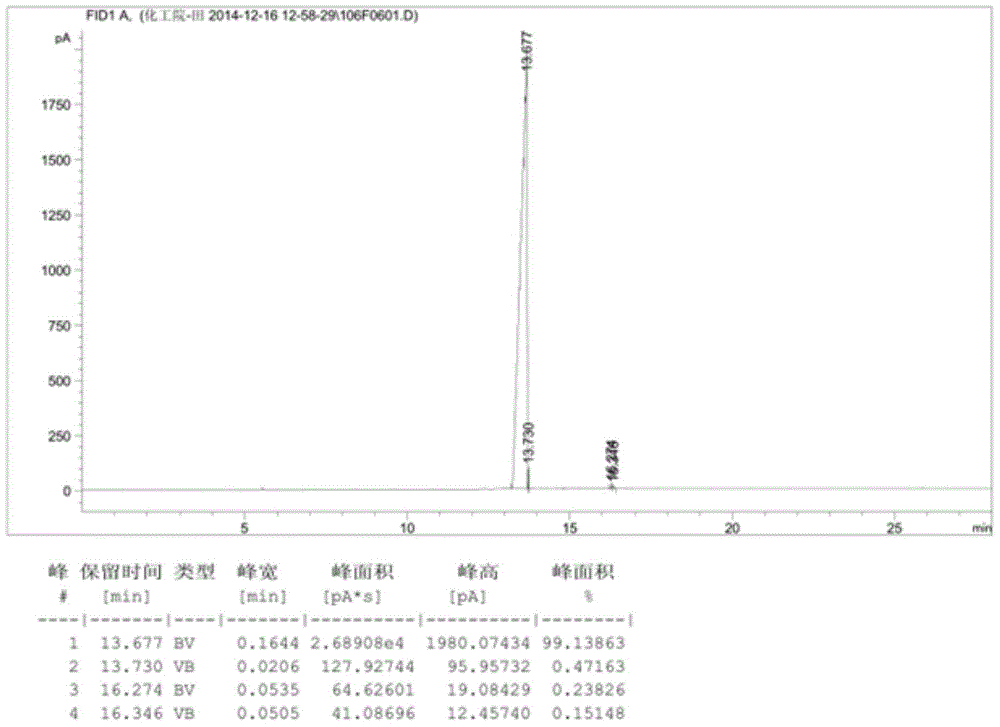
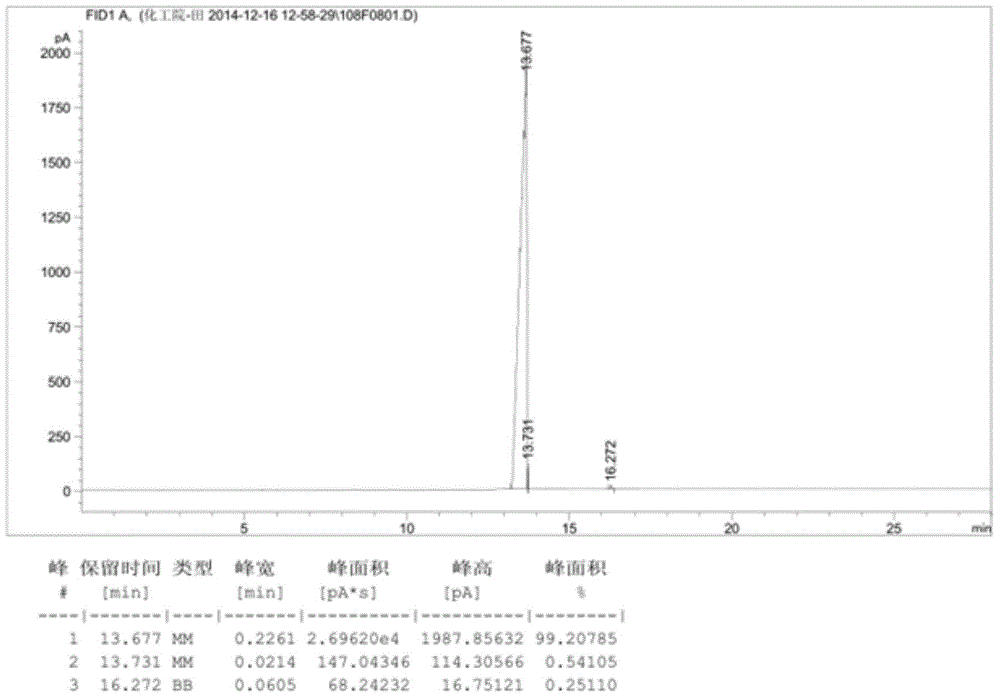
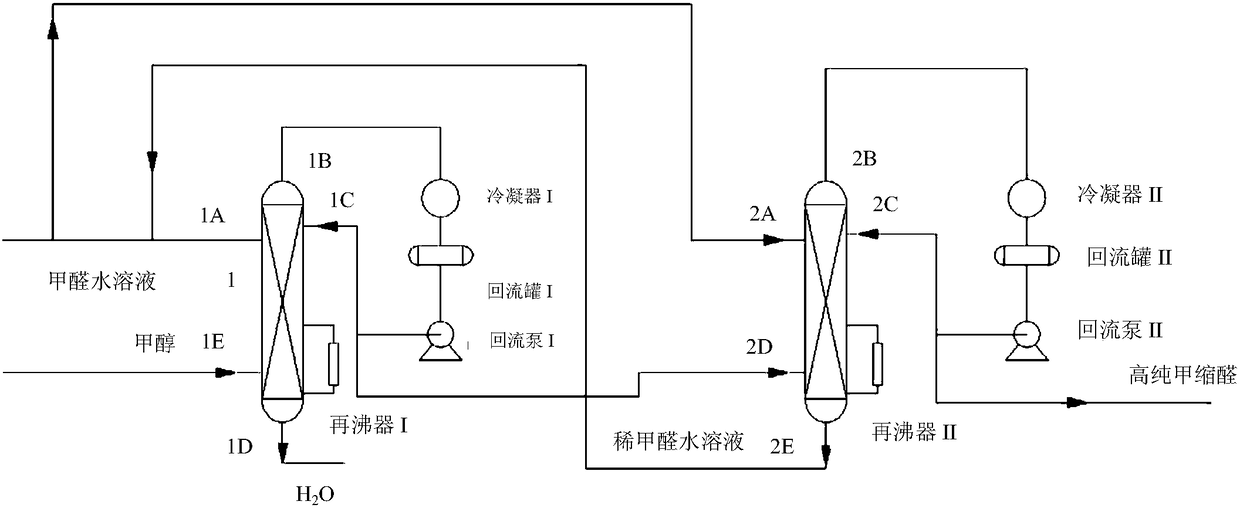
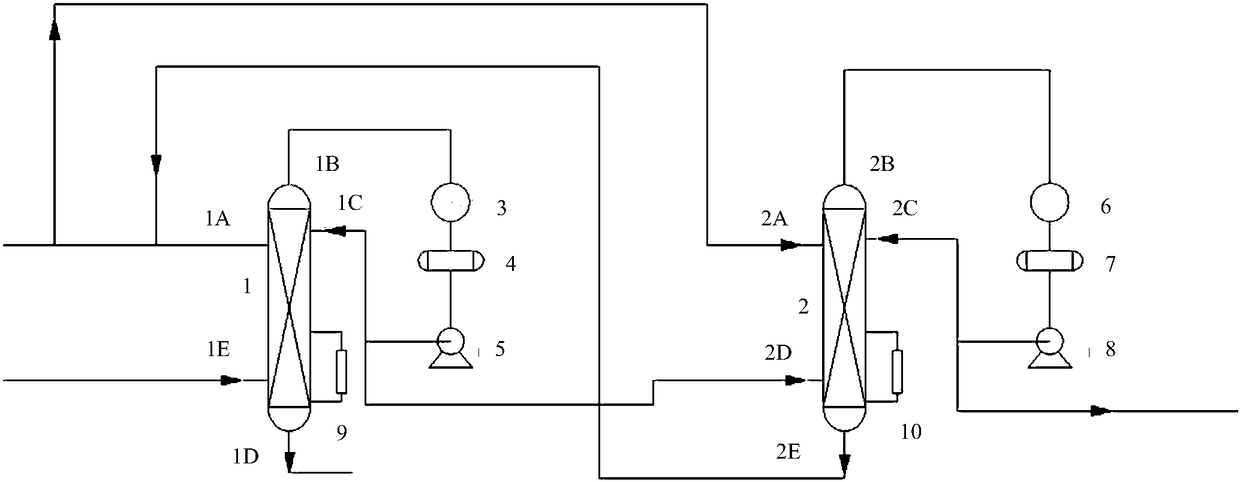
Device and method of utilizing catalytic distillation coupling technology to produce high-purity methylal
PendingCN108424358AMild process conditionsShort processOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationCouplingCatalytic distillation
The invention discloses a device and a method of utilizing catalytic distillation coupling technology to produce high-purity methylal. The device comprises a catalytic distillation tower I and a catalytic distillation tower II which are completely identical in inside structure and connected with each other. The catalytic distillation towers completely identical in structure are used, a method of enabling methanol and formaldehyde to be excessive alternately is used under action of a solid acid catalyst, both chemical balance and a co-boiling principle of methylal and methanol are broken, and the objective of refining high-purity methylal is achieved in one step. A high-purity methylal product is produced by adopting the catalytic distillation coupling method, so that the defects of other technologies like pressurization technology and extraction technology are overcome, and a new production technique having the advantages of mild process condition, short technical process, little investment, high efficiency, low consumption and environment-friendly production condition is created.
Owner:KAIRUI ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Apparatus and process for purifying peach aldehyde by decompressing batch rectifying
InactiveCN1255395CSimple operation processReduce thicknessOrganic chemistryEssential-oils/perfumesRefluxSurge tank
The invention discloses a device and process for purifying peach aldehyde by intermittent rectification under reduced pressure, which belongs to the separation and purification technology for synthesizing peach aldehyde. The device consists of a rectification tower, a condenser, a reflux tank, a surge tank, a vacuum pump, and a storage tank. The tower is equipped with high-efficiency packing. It is characterized in that the still of the rectification tower is a jacket column with a height-to-diameter ratio of 0.6 to 0.3. tube heater. The device is used to carry out the process of purifying peach aldehyde by intermittent distillation under reduced pressure. The pressure at the top of the tower is 133.3Pa ~ 1333Pa, and the temperature of the bottom of the tower is 150 ~ 180°C. Peach aldehyde with light components and qualified purity. The invention has the advantages that the tower kettle has the characteristics of small liquid film thickness, high evaporation efficiency, large heat transfer coefficient and short material residence time, the operation process of the tower is simple, and the product purity can reach more than 99 wt%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
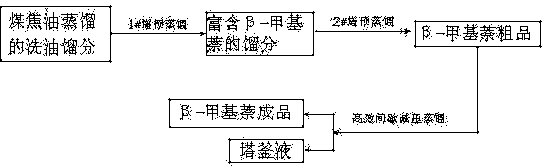
Method for extracting highly pure beta-methylnaphthalene from coal tar wash oil
InactiveCN103992199ALower requirementReduce pollutionDistillation purification/separationDistillationPhysical chemistry
The invention belongs to the field of coal fine chemical industry, and relates to a method for extracting highly pure beta-methylnaphthalene from coal tar wash oil of. The method adopts a continuous pre-distillation and efficient batch distillation combining method. Continuous distillation adopts atmospheric distillation, and is carried out in two stages. Efficient batch distillation is characterized in that crude beta-methylnaphthalene obtained through the continuous pre-distillation undergoes batch vacuum rectification in a rectification tower. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, low equipment requirements, mild technological conditions, low energy consumption, low requirements of raw materials, low equipment corrosion, and reduction the pollution of the environment. The chemical purity of beta-methylnaphthalene obtained in the invention can reach above 97.5%.
Owner:HUANGHUA XINNUOLIXING FINE CHEM
Method for preparing high-purity m-xylylene diisocyanate
InactiveCN113321599ASolve the problem of difficult separation of heavy phase componentsPrevent self-aggregationIsocyanic acid derivatives purification/separationFlash distillationXylyleneMethylene diisocyanate
The invention relates to a method for preparing high-purity m-xylylene diisocyanate (m-XDI). The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: feeding a crude product reaction liquid containing m-xylylene diisocyanate, a solvent and reaction byproducts into a light-phase flash evaporator operated at negative pressure for flash evaporation, and then feeding the above materials into a high-vacuum batch distillation tower for batch distillation, conducting refluxing with different reflux ratios for different fractions so as to finally obtain a qualified product. According to the method, the problem that heavy-phase components of the m-XDI reaction liquid are difficult to separate in a conventional rectification process is solved; and meanwhile, the self-agglutination phenomenon of the m-XDI reaction liquid containing the heavy-phase components in the rectification process is avoided, and the rectification yield of m-XDI can be improved.
Owner:甘肃银光聚银化工有限公司
Batch process PI-PD control method for state space prediction function control optimization
The invention discloses a batch process PI-PD control method for state space prediction function control optimization. The method includes the steps that firstly, a state space model of a temperature object in a reboiler is established on the basis of real-time operation data of the temperature object in the reboiler in a batch distillation column, and basic object features are extracted; secondly, parameters of a corresponding PI-PD controller are set according to state space prediction function control features; finally, PI-PD control is performed on the temperature object in the reboiler. According to the method, the state space prediction function control performance is assigned to PI-PD control, and therefore the performance of a traditional control method is effectively improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
Deep drying water removing method used for bipentene
ActiveCN109534940AHigh affinityAdaptableDistillation purification/separationHydrocarbonsMolecular sieveBatch distillation
The invention relates to a deep drying water removing method used for bipentene. The method includes adding to-be-dried bipentene and an entrainer into a batch distillation device, performing azeotrope water carrying, and collecting dipentene fraction through vacuum distillation; and adding the dipentene fraction into an adsorption column carrying activated molecular sieves to perform adsorption so that dried bipentene can be obtained. The method is mainly to meet the using requirements for the water content of a polymerization inhibitor during a production process of tetrafluoroethene; and the drying method is simple in technology and equipment, high in drying efficiency and fast in effect, so that the method is an ideal choice for industrialization, and has good application prospects.
Owner:ZHONGHAO CHENGUANG RES INST OF CHEMICALINDUSTRY CO LTD
Recycling and separating process of heavy component residual liquid in carbonylation production process of acetic acid
ActiveCN102126943AEfficient recyclingSimple processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationAcetic acidEthynodiol Diacetate
The invention discloses a recycling and separating process of heavy component residual liquid in the carbonylation production process of acetic acid, belonging to the separation technical field of the organic chemical engineering. The process comprises the following steps: firstly, the residual liquid is sent to a wiped film evaporator to perform reduced pressure operation and remove high polymer heavy component; and secondly, light component enters a batch distillation device to obtain the products such as acetic acid, acetoxyacetic acid and ethylene glycol diacetate through separation and purification. The invention adopts the recycling and separating process of the acetic acid heavy component residual liquid; the flow is simple, the process is easy to operate; after the high polymer heavy component is removed, the residual liquid meets the requirements of environmental protection treatment; and the products with high added value can be effectively recycled, the recovery rate is more than 90% and the process is an efficient and environmentally friendly recycling and separating process.
Owner:NANJING CHANGJIANG JIANGYU PETROCHEM CO LTD
Method for separating tertiary butanol and water
InactiveCN101607870AHigh purityHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound separation/purificationHigh concentrationDistillation
The invention relates to an azeotrope separation method, in particular to a method for separating tertiary butanol and water. The tertiary butanol is separated from the water through a coupling method of total reflux batch distillation and pervaporation. A device comprising a batch distillation tower, a pervaporation membrane component and a water injection pump is used. The method for separating tertiary butanol and water is characterized in that a separation process comprises the following steps: a tertiary butanol water solution is dropped into the batch distillation tower, the total reflux operation is firstly carried out in the batch distillation tower, the azeotrope of the tertiary butanol-water enters a membrane separator through a condenser to further carry out dehydration separation after being converged at the tower top, permeation side pressure keeps absolute pressure of 700-7500Pa through the injection of the water injection pump, a tertiary butanol water solution separates the tertiary butanol from the water through the membrane separator, the tertiary butanol product with high concentration can be obtained in a tower kettle of a distillation tower, the water permeates in a vapor phase chamber at the downstream of the membrane separator, and the water is separated from the tertiary butanol through vaporization and condensation in vacuum low pressure. The invention has the advantages of convenient production process operation, no introduction of other solvents, and high yield of the tertiary butanol and certain promotion value.
Owner:烟台只楚天大精馏设备工程技术有限公司
Batch distillation process for separating isopropanol-isopropyl acetate azeotrope through mixed extraction agent
InactiveCN105061147AQuality improvementHigh purityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationRefluxDistillation
The invention discloses a batch distillation process for separating isopropanol-isopropyl acetate azeotrope through a mixed extraction agent. The batch distillation process is characterized in that a mixture of ethylene glycol and an ionic liquid is selected to serve as the extraction agent and is added from the upper end of an extraction distillation tower, isopropanol-isopropyl acetate azeotrope is added to a kettle, the quality of a product is controlled by regulating the reflux ratio, and an isopropanol product, an isopropanol-isopropyl acetate interim fraction, an isopropyl acetate product and an isopropyl acetate-ethylene glycol interim fraction are sequentially obtained from the top of the tower. The content of isopropyl acetate and the content of the isopropanol product are both higher than 99.5%, and the two interim fractions and the extraction agent at the bottom of the tower can be recovered and used for processing of the next batch of materials. Batch pressure-reduction distillation is adopted, and the batch distillation process has the advantages of simple equipment, few investment, flexible operation, low energy consumption, high product quality and the like and is suitable for medium-scale and small-scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com