Method for preparing vanadium-and-iron enriched material by using vanadium enriched steel slags
A steel slag and iron-rich technology, applied in the field of vanadium chemical metallurgy, can solve the problems of reducing sinter grade, loss of valuable element vanadium, and high impurities in steel slag, so as to avoid environmental pollution, reduce purification work, and achieve great economic benefits
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
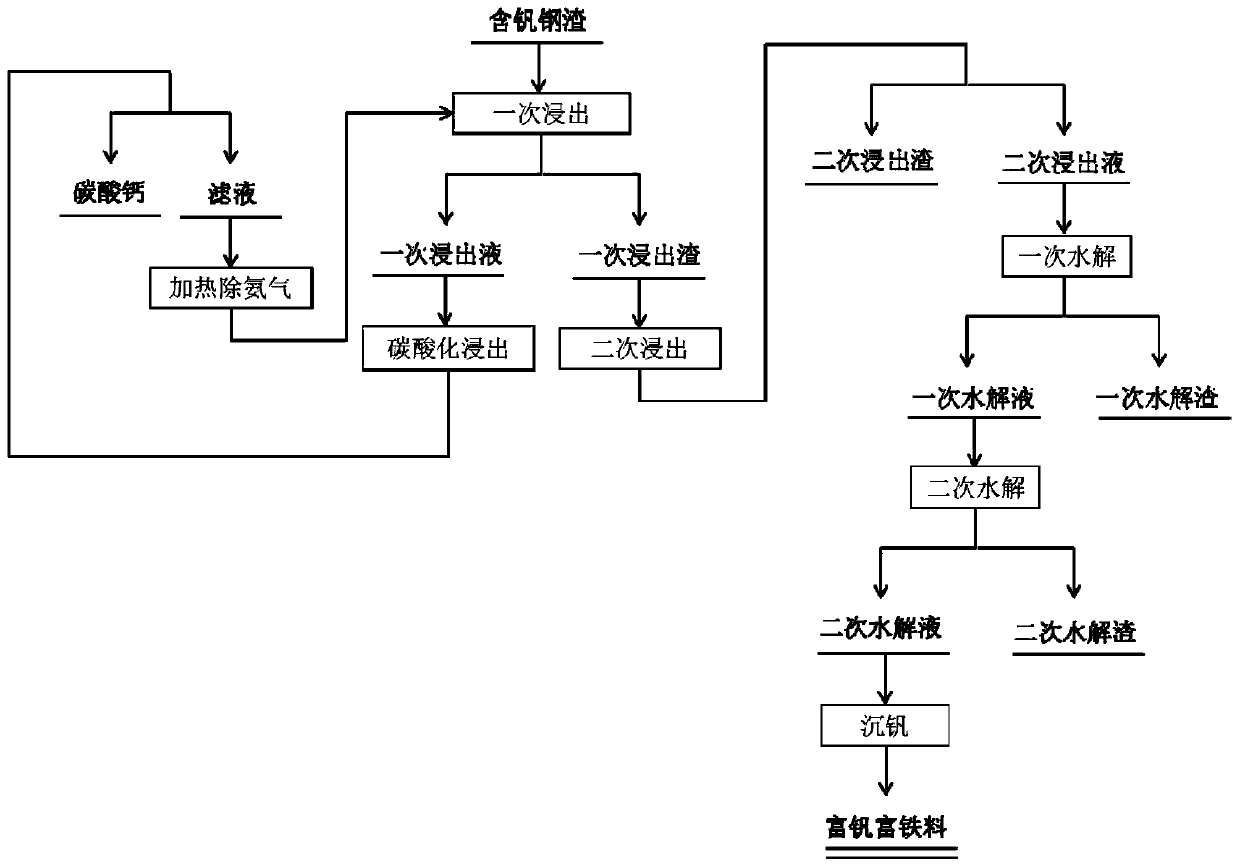
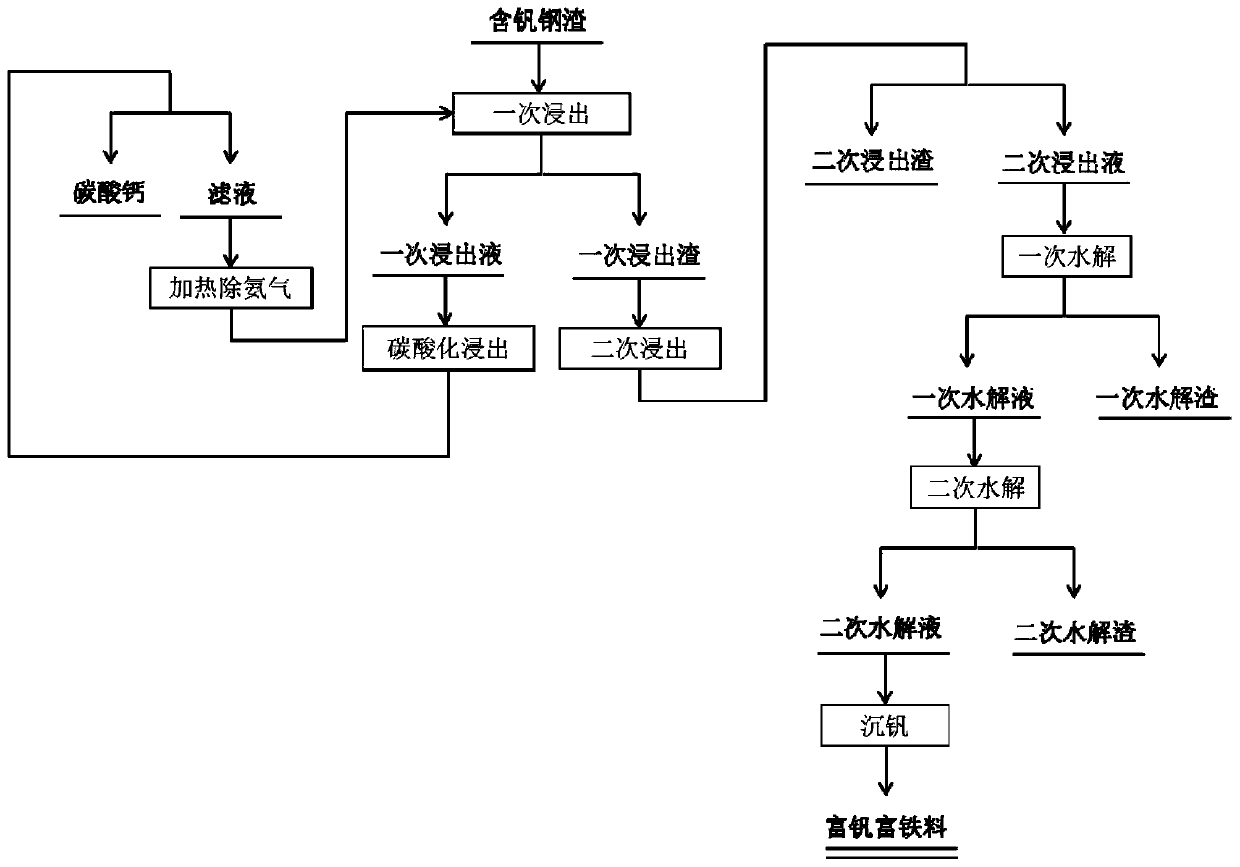
[0044] The vanadium-containing steel slag is crushed into powder, the particle size of the powder is 48-70 μm, and then leached with ammonium chloride solution under stirring conditions, the leaching temperature is 55 ° C, and the leaching time is 4 hours; the material after the primary leaching is filtered Separate to obtain primary leaching slag and primary leaching solution; the mass concentration of ammonium chloride solution is 32%, and the liquid-solid ratio of ammonium chloride solution and powder during primary leaching is 6L / kg;
[0045] Wash the primary leaching residue with water until the washing liquid is neutral, and carry out secondary leaching with an organic acid solution under stirring conditions. The organic acid is oxalic acid, the pH value of the organic acid solution is 2.0, the leaching temperature is 45°C, and the time is 90 minutes; The material after the secondary leaching is filtered and separated to obtain the secondary leaching residue and the secon...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0051] (1) The particle size of the powder is 60-100 μm, the temperature of the primary leaching is 65°C, and the time is 3 hours; the mass concentration of the ammonium chloride solution is 30%, and the liquid-solid ratio of the ammonium chloride solution to the powder during the primary leaching is 2L / kg;
[0052] (2) The organic acid of the organic acid solution is acetic acid, the pH value is 2.2, the secondary leaching temperature is 55° C., and the time is 80 minutes; the liquid-solid ratio of the organic acid solution to the primary leaching residue after washing is 2 L / kg during the secondary leaching;
[0053] (3) The primary mixed solution is adjusted to a pH value of 3.7 with sodium hydroxide, then heated to 65° C. under stirring conditions, and kept for 55 minutes for primary hydrolysis;
[0054] (4) The pH value of the primary hydrolyzate is adjusted to 4.6 with sodium hydroxide, and then under stirring co...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Method is with embodiment 1, and difference is:
[0058] (1) The particle size of the powder is 48-150 μm, the temperature of the primary leaching is 75° C., and the time is 2 hours; the mass concentration of the ammonium chloride solution is 28%, and the liquid-solid ratio of the ammonium chloride solution to the powder during the primary leaching is 3L / kg;
[0059] (2) The organic acid of the organic acid solution is citric acid, the pH value is 2.4, the secondary leaching temperature is 65° C., and the time is 60 minutes; the liquid-solid ratio of the organic acid solution to the primary leaching residue after washing is 3 L / kg during the secondary leaching;
[0060] (3) The primary mixed solution is adjusted to a pH value of 3.8 with sodium hydroxide, then heated to 75° C. under stirring conditions, and kept for 50 minutes for primary hydrolysis;
[0061] (4) The pH value of the primary hydrolyzate is adjusted to 4.7 with sodium hydroxide, and then under stirring ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com