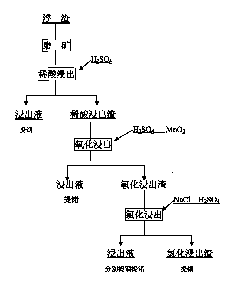
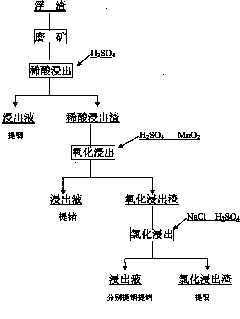
Method for extracting indium and germanium from pyrometallurgical crucible residues by whole-wet method
An all-wet, crucible technology, applied in the field of comprehensive recovery of germanium and non-ferrous metal smelting and extraction of indium, can solve the problems of lower recovery rate, unfavorable leaching and separation of indium and germanium, unfavorable germanium recovery, etc., and achieves low environmental pollution and high recovery. rate effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0013] Take crucible scum as raw material, its composition is Pb 28.30%, Zn 8.12%, Ge 1.36%, In 0.96%, Ag 4267g / T, Fe 28.19%, the raw material is ground, all sieved 120 mesh, and stirred at room temperature , leached with 1.0M dilute sulfuric acid for 12 hours, the liquid-solid ratio was 5:1, and the terminal acidity was 11g / L. The leaching solution contains In860mg / L, Zn18.68g / L, and Ge 0mg / L. The dilute sulfuric acid leaching residue is oxidized and leached with sulfuric acid with a concentration of 5%, the liquid-solid ratio is 5:1, the reaction temperature is 70°C, and MnO with 1 times the feeding amount is evenly added 2 , Reaction time 6h, terminal acidity pH=3.0. The leaching solution contains germanium 2.48g / L and indium 2mg / L. The leaching rate of indium in dilute acid leaching is 40.31%, germanium is 0%; the leaching rate of germanium in oxide leaching is 80.24%, and indium is 0%. The first two stages of leaching can leach indium and germanium respectively. Oxida...
Embodiment 2
[0015] Take 674 kg of sieved 120-mesh material, and the grades of each element are Pb31.76%, Zn8.55%, Ge1.85%, In9481g / T, Ag3592.8g / T, Fe31.82%. Dilute sulfuric acid leaching: final acid (calculated as sulfuric acid) 11g / L, add 300 kg of sulfuric acid, stir and leaching at room temperature for 12 hours, and obtain a leaching solution of 3.85m 3 , containing indium 690mg / L, containing germanium 3mg / L; oxidation leaching: stirring and leaching at a temperature of 80°C for 6 hours, adding 700 kg of manganese powder, and the final acidity pH=2.5, and the volume of the leachate was 3.93m 3 , the leach solution contains germanium 2.49g / L, and indium content=5mg / L; chlorination salt leaching: add 240 kg of sodium chloride, add 220 kg of sulfuric acid, and the reaction temperature is >90°C to obtain a leach solution of 3.91m 3 , the acidity (sulfuric acid) of the leach solution is 67g / L, and the solution contains In882mg / L and Ge568mg / L. Dilute acid leaching and oxidation leaching ca...
Embodiment 3
[0017] Take 864 kg of sieved 120-mesh material, and the grades of each element are Pb 28.70%, Zn12.23%, Ge0.82%, In1.49%, Ag4367g / T, Fe33.81%. Dilute sulfuric acid leaching: final acid (calculated as sulfuric acid) 13g / L, 400 kg of sulfuric acid was added, stirred and leached at room temperature for 12 hours, and the leachate was 4.86m 3 , containing indium 1.02g / L, containing germanium 5mg / L; oxidation leaching: stirring and leaching at a temperature of 75°C for 6 hours, adding 900 kg of manganese powder, and the final acidity pH=3.0, resulting in a leachate volume of 4.70m 3 , the leaching solution contains germanium 1.18g / L, and indium=0mg / L; chlorination salt leaching: add 310 kg of NaCl, add H 2 SO 4 300 kg, reaction temperature > 90°C, leaching solution 4.56m 3 , the acidity of the leaching solution (sulfuric acid meter) 62g / L, In1.64g / L, Ge303mg / L. Three-stage leaching, leaching rate of In96.65%, Ge97.88%, dilute acid leaching, oxidation leaching, indium and germaniu...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com