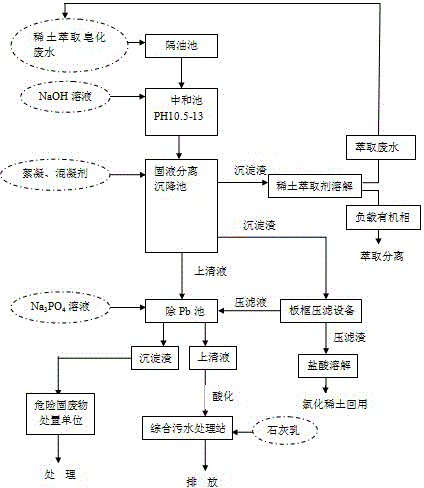
Technology of removing lead and recycling rare earth from saponified wastewater generated during process of rare earth extraction
A technology for saponifying wastewater and rare earths, applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, can solve the problems of reducing the recovery rate of rare earths, substandard discharge, inability to completely precipitate and remove heavy metal elements, etc., and achieve the effect of good comprehensive utilization of resources and improvement of governance level.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] A process for removing lead and recovering rare earths from rare earth extraction saponification wastewater, comprising the following steps: clarifying and removing rare earth extraction saponification wastewater with a pH of 3.5, a rare earth content of 459 mg / L, and a Pb content of 38 mg / L through a grease trap. Oil, to obtain the rare earth extraction saponification wastewater that removes organic oily substances such as extractants; add 5mol / L NaOH solution under stirring, adjust the pH value to 9, obtain rare earth hydroxide precipitation and lead hydroxide precipitation, continue to add 5mol / L NaOH solution NaOH solution, because the lead hydroxide precipitate will dissolve after the excessive addition of alkali, adjust the pH value to 12, the lead hydroxide precipitate will be completely dissolved, and the dissolved lead ion will be obtained; add 50g / L polyaluminum chloride solution 50ppm, and then add 5g / L polyacrylamide 5ppm, after stirring for coagulation and f...
Embodiment 2
[0023] A process for removing lead and recovering rare earths from rare earth extraction saponification wastewater, comprising the following steps: clarifying and removing rare earth extraction saponification wastewater with a pH=4.0, a rare earth content of 500 mg / L, and a Pb content of 56 mg / L through a grease trap. Oil, to obtain the rare earth extraction saponification wastewater that removes organic oily substances such as extractants; add 5mol / L NaOH solution under stirring, adjust the pH value to 9, obtain rare earth hydroxide precipitation and lead hydroxide precipitation, continue to add 5mol / L NaOH solution NaOH solution, because the lead hydroxide precipitate will dissolve after the excessive addition of alkali, adjust the pH value to 12, the lead hydroxide precipitate will be completely dissolved, and the dissolved lead ion will be obtained; add 50g / L polyaluminum chloride solution 50ppm, and then add 5g / L polyacrylamide 5ppm, after stirring for coagulation and floc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com