Patents
Literature
48results about How to "Reduce TFe content" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blast-furnace smelting method for vanadium titano-magnetite
InactiveCN101775451ARaise the gradeReduce tons of iron slagBlast furnace detailsMagnetiteBlast furnace smelting
The invention discloses a blast-furnace smelting method for vanadium titano-magnetite. The method is realized in a way that: vanadium titano-magnetite accounts for 30-60% of ferrous burden which is fed into a blast furnace, and the burden comprises 40-65% of agglomerate, 30-50% of pellet and 5-10% of lump ore; the diacidic basicities CaO / SiO2 of agglomerate, pellet and blast-furnace slag are respectively controlled at 1.6-2.5, 0.6-1.0 and 1.05-1.20; the content of MgO in blast-furnace slag is controlled at 7.5-9.0%; by adding two batches of ore and three batches of coke and using the charging operation of the development center, manganese oxide ore or sintered manganese ore powder, and fluorite are incorporated into injection coal and injected into the blast furnace along with the coal powder; and thus, the content of MnO in the slag and the content of CaF2 in the slag are respectively controlled at 1.0-4.5% and 0.50-2.0%, and the oxygen-enrichment percentage of the blast furnace is controlled at 2.0-4.0%. Compared with the smelting blast furnace using the same quality and structure of the burden, the comprehensive coke ratio of the invention is reduced by 20-50kg per ton of iron, the content of TFe in the slag is reduced by 50%, and the comprehensive cost per ton of iron is reduced by 30-50 yuan. The invention has wide prospects for popularization and application.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Method for synchronously dephosphorization and vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing molten iron
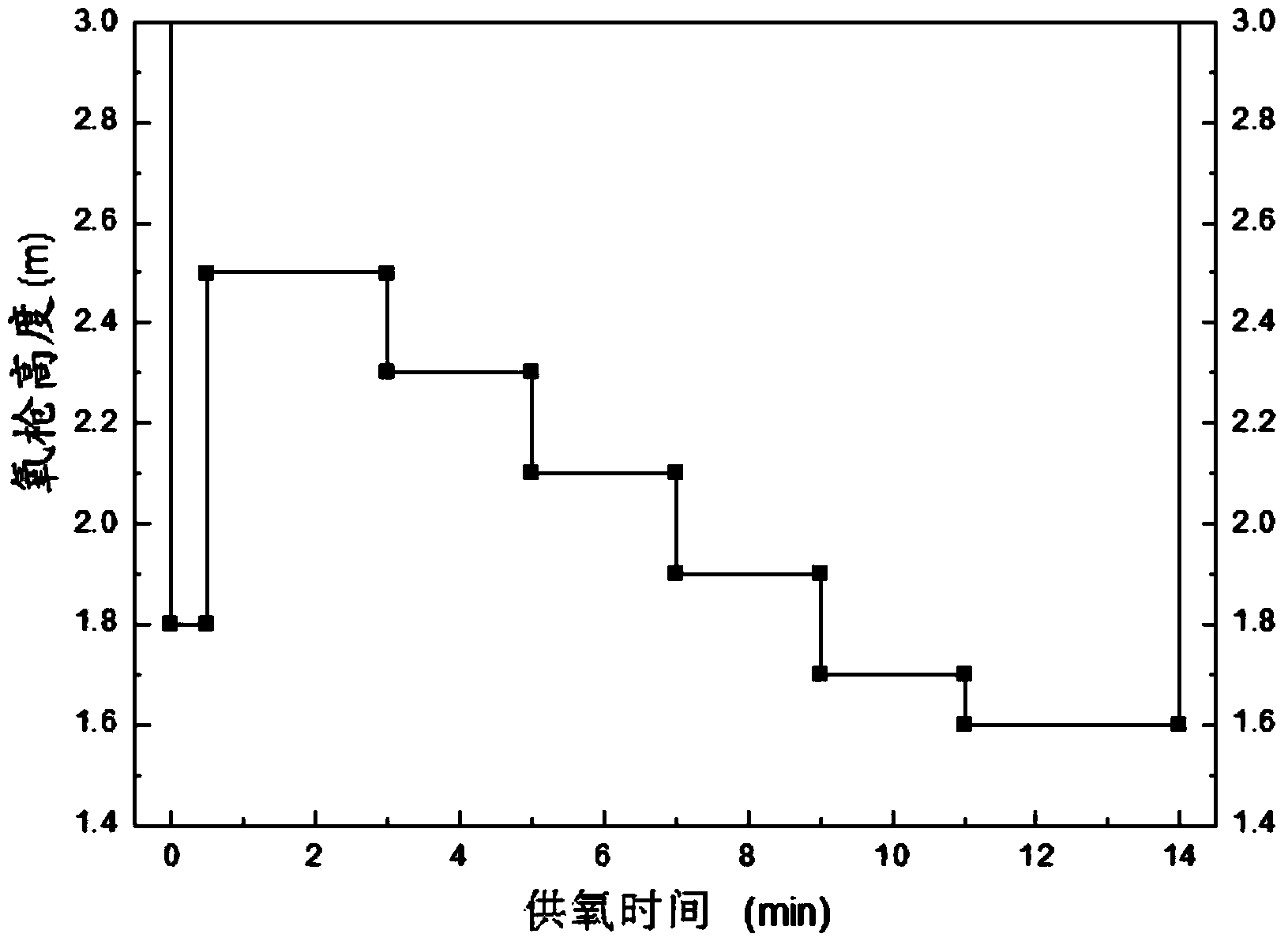
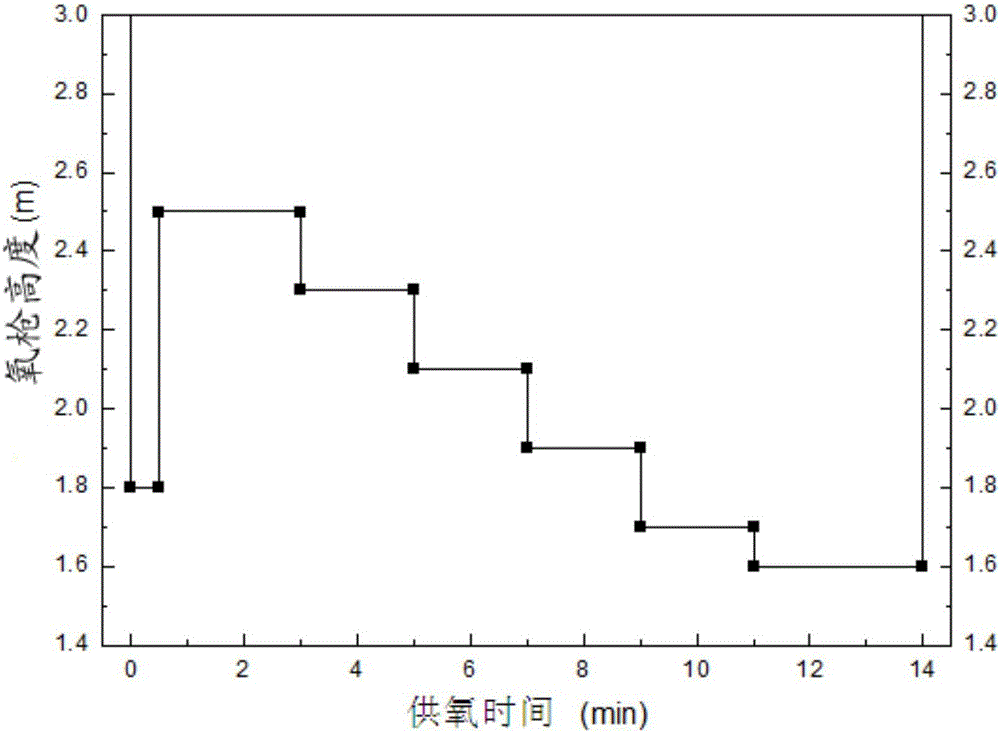
The invention discloses a method for synchronously dephosphorization and vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing molten iron. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling temperature of vanadium-containing molten iron at 1230-1250 DEG C; carrying out oxygen-injection blowing, wherein oxygen flow is constantly controlled at 17000-25000Nm<3> / h, and the blowing process sequentially comprises three stages; the first stage starts from blowing to 1-2min of blowing, gun position is 1.6-1.8m, and lime for controlling alkalinity of slag to be 2-4 lime and 15-20kg / tFe of iron scale are added simultaneously; the second stage starts after 1-2min of blowing, gun position is 1.8-2.1m, and 5-18kg / tFe of iron scale is added in the process that oxygen-injection time is not greater than 3min; and the third stage starts from blowing to 2min of the end, 0.5-2kg / tFe of high-magnesium lime is added, and gun position is reduced to 1.6-1.8m; and blowing to end, and discharging semi-steel and vanadium slag. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that corrosion to lining of a vanadium extraction converter is effectively avoided, and dephosphorization and vanadium extraction are synchronously implemented; and TFe content in the vanadium slag is reduced.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Method for simultaneously conducting dephosphorization and vanadium extraction on vanadium-contained molten iron through converter
ActiveCN105349728ALighten the task of dephosphorizationAvoid erosionManufacturing convertersNitrogen gasOxygen
The invention belongs to the field of iron and steel smelting and particularly relates to a method for simultaneously conducting dephosphorization and vanadium extraction on vanadium-contained molten iron through a converter. The method aims to solve the problem that a furnace lining of a converter is corroded by a conventional dephosphorization and vanadium extraction agent, part of phosphorus in the molten iron is removed while vanadium extraction is conducted, and the content of TFe in vanadium slag is reduced, so that the steel material consumption is reduced, and low-phosphorus semisteel is provided for a steel converter. The method for simultaneously conducting dephosphorization and vanadium extraction on the vanadium-contained molten iron through the converter comprises the following steps that A, after the molten iron is poured into the vanadium extraction converter, blowing is conducted through a deoxygenation lance, the oxygen flow is controlled to be 20000-35000 Nm<3> / min in the whole process, and the nitrogen bottom blowing intensity is 0.1-0.3 Nm<3> / t.min; B, after nitrogen bottom blowing is conducted for 1-2 min, the lance position is controlled according to 1.9-2.0 m, and meanwhile steel slag, ferric oxide and lime are added in sequence for slagging; C, the lance position of the deoxygenation lance is controlled to 2.0-2.2 m two minutes before blowing is finished; and D, the semisteel and the vanadium slag are discharged after blowing is finished.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Fluoride-free slagging medium for use in converter and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102827990AReduce ton consumption costIncreased Metal YieldManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingMetallic aluminum
The invention relates to a fluoride-free slagging medium for use in a converter and a preparation method thereof. The fluoride-free slagging medium comprises metal aluminum, aluminum sesquioxide, iron and oxides thereof, silicon dioxide, calcium oxide, magnesium oxide and other inevitable impurities, and is suitable for slagging during steelmaking in the converter. Used raw materials are ordinary, a pelletizing process is advanced and reliable, and the fluoride-free slagging medium is convenient to use. The fluoride-free slagging medium has the advantages that: the reaction dynamics condition of a melting bath can be improved remarkably, a good slagging effect is achieved, and the problems of steel adhesion to an oxygen lance, melting spraying and poor capability of removing S and P from slag caused by 'return to dryness' of slag are solved; the TFe content of slag is lowered, the metal yield of molten steel is increased, and the tonnage consumption cost of molten steel is lowered; furnace lining erosion is reduced, and a good slag splashing effect is achieved; and F<-> is not contained, so that environmental protection is facilitated, fluoride-free steelmaking is realized, and the slagging medium is suitable for the requirement of cleanliness in a steelmaking production process of the converter.
Owner:西峡县恒基冶材有限公司
Method for smelting weather resistant steel through high-phosphorus-content steel discharging by converter
ActiveCN103773916AReduced dephosphorization capacityReduce TFe contentManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSlagMaterial consumption
The invention relates to a method for smelting weather resistant steel through high-phosphorus-content steel discharging by a converter. The method comprises the steps of adding waste steel liquor which is treated by KR desulfuration into the converter in a blending manner; performing slag retaining and slag making operations in the converter: retaining 3-5 tons of furnace slag of the last converter, and making slag only through light-roasted dolomite; in a converter blowing process, lifting an oxygen gun to a high position after the oxygen gun is ignited, quickly reducing the position of the oxygen gun step by step after a gas mixing stage, adding roasted dolomite and ores for cooling in the later stage of oxygen blowing, and quickly pulling carbons at the low gun position in the later stage of blowing; controlling an end point of the converter to discharge the steel. According to the method, auxiliary material consumption of the converter can be reduced, the phosphorus content of the end point of the converter is increased, the phosphorus iron consumption is alleviated, the final slag TFe content of the converter is reduced, and the iron loss in the converter blowing process is relieved.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Converter slag fluoride-free fusing agents and method for producing the same
ActiveCN102839252AHigh activityReduce ton consumption costManufacturing convertersSteelmakingMetallic aluminum
The invention relates to converter slag fluoride-free fusing agents and a method for producing the converter slag fluoride-free fusing agents. The converter slag fluoride-free fusing agents comprise metallic aluminum, manganese oxide, aluminum oxide, iron and iron oxide, silica, calcium oxide, magnesium oxide and other unavoidable impurities, and are suitable for slagging in the process of converter steelmaking. Used raw materials are common, balling process is advanced and reliable, and the fluoride-free fusing agents are convenient to use. The converter slag fluoride-free fusing agents and the method for producing the converter slag fluoride-free fusing agents have the advantages of obviously improving reaction kinetics conditions of a molten pool, being high in slag activity, well resolving the problems of steel-bonding of an oxygen lance, metal splashing and poor capacity of sulphur (S)-removing and phosphorus (P)-removing of slag due to re-drying of the slag, lowering tetrafluoroethylene (TFe) content of the slag, increasing yield of ferrum (Fe) in liquid steel, reducing cost of the liquid steel per ton, shortening smelting time, improving content and yield of manganese in the liquid steel, reducing corrosion to a furnace lining, having good slag-splashing and furnace-protection effects, being favorable for environment protection and achieving fluoride-free steel-making due to the fact that fluoride (F-) does not exist, and meeting the requirements for cleaning in the converter steel-making production process.
Owner:西峡县恒基冶材有限公司
Converter vanadium extraction process of low silicon low temperature vanadium-containing molten iron
The invention discloses a converter vanadium extraction process of low silicon low temperature vanadium-containing molten iron, and the process comprises blowing of the low silicon low temperature vanadium-containing molten iron in a converter and addition of a coolant in the blowing process, the blowing end point temperature is controlled to be 1340 to 1370 DEG C; the coolant use amount is 5-24kg / t low silicon low temperature vanadium-containing molten iron; the blowing process comprises the following three stages: a first stage from the beginning of the oxygen blowing to the oxygen blowing amount reaching 9-12% of the total oxygen blowing amount, a second stage from the end of the first stage to the oxygen blowing amount reaching 85-90% of the total oxygen blowing amount, and a third stage from the end of the second stage to the end of the oxygen; in the first stage, the gun height of the blowing process is controlled to be 1.6-1.8m; in the second stage, the gun height of the blowing process is controlled to be 1.9-2.1m; and in the third stage, the gun height of the blowing process is controlled to be 1.6-1.8m. Through the converter vanadium extraction process, the obtained vanadium slag is high in grade, obtained semi steel is high in C content and the goal of ''removing vanadium and holding carbon'' can be better realized.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for reducing semisteel steel-making final slag total iron content
The invention relates to a method for reducing semisteel steel-making final slag total iron content and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. The invention aims at providing the method for reducing the semisteel steel-making final slag total iron content. The method comprises the following steps: adding a magnesium carbon ball after finishing semisteel converter smelting, performing top-blowing nitrogen for 20-50s, standing for 60-120s after finishing nitrogen blowing, and tapping. By adopting the method, the semisteel steel-making converter final slag TFe content is controlled within 18%, the final slag TFe is obviously reduced and the effect is obvious, additionally the method is simple in operation, few in magnesium carbon ball dosage and low in cost.
Owner:PANGANG GROUP RESEARCH INSTITUTE CO LTD
Converter vanadium extraction process of high silicon vanadium-containing molten iron
The invention discloses a converter vanadium extraction process of high silicon vanadium-containing molten iron, and the converter vanadium extraction process is as follows: blowing the high silicon vanadium-containing molten iron in a converter, and adding a coolant in the blowing process; the blowing end point temperature is controlled to be 1380 to 1420 DEG C; the coolant use amount is 30-37kg / t high silicon vanadium-containing molten iron; the gun height of the blowing process is controlled to be 1.5-2m. Through the technical proposal, the obtained vanadium slag is high in grade, namely high in vanadium content and low in TFe content, semi steel obtained by the converter vanadium extraction process is high in C content (in the range of 3.7-4.1 weight%), the goal of ''removing vanadium and holding carbon'' can be better realized, the semi steel temperature can meet the follow-up steelmaking demand.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
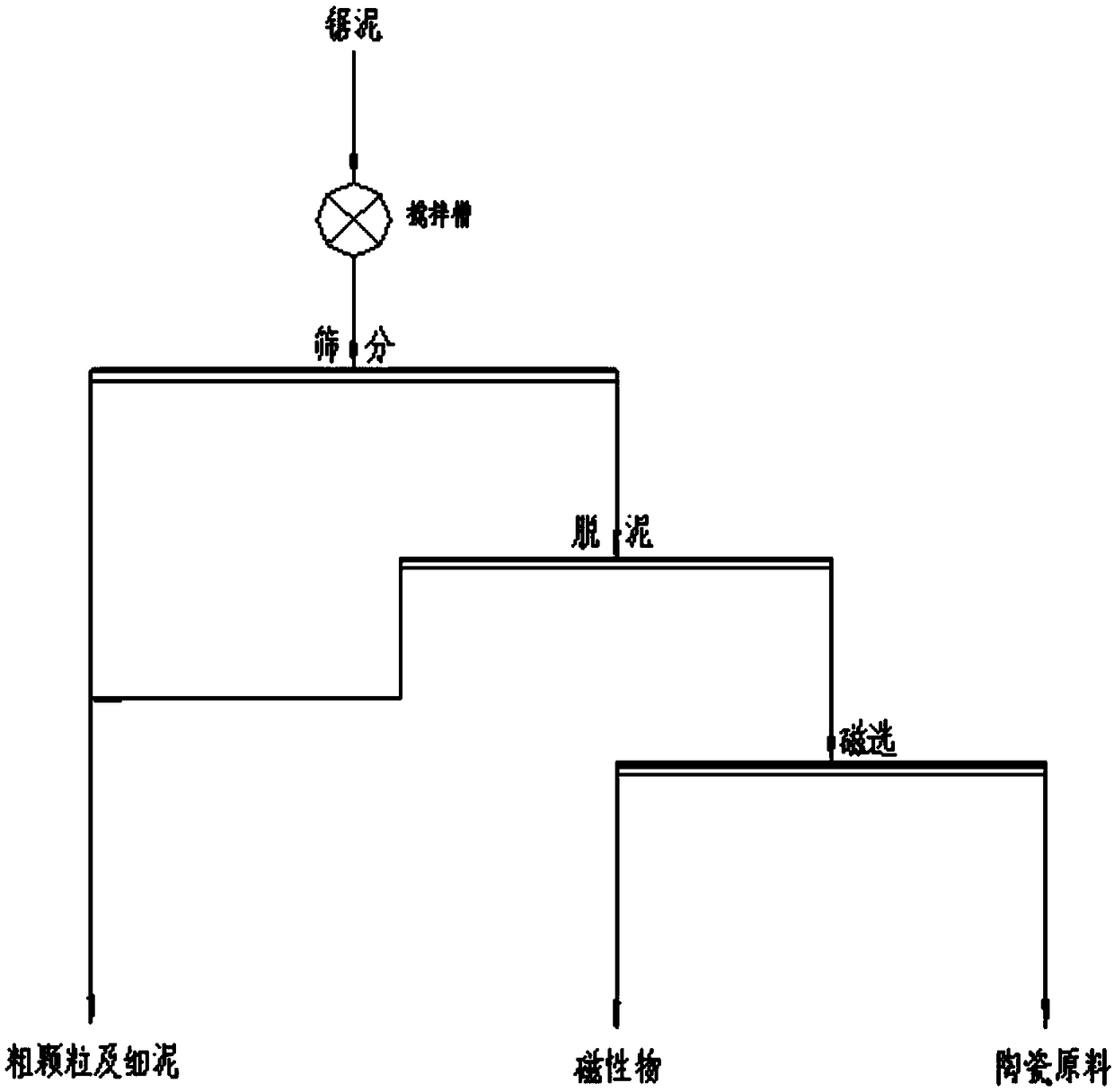
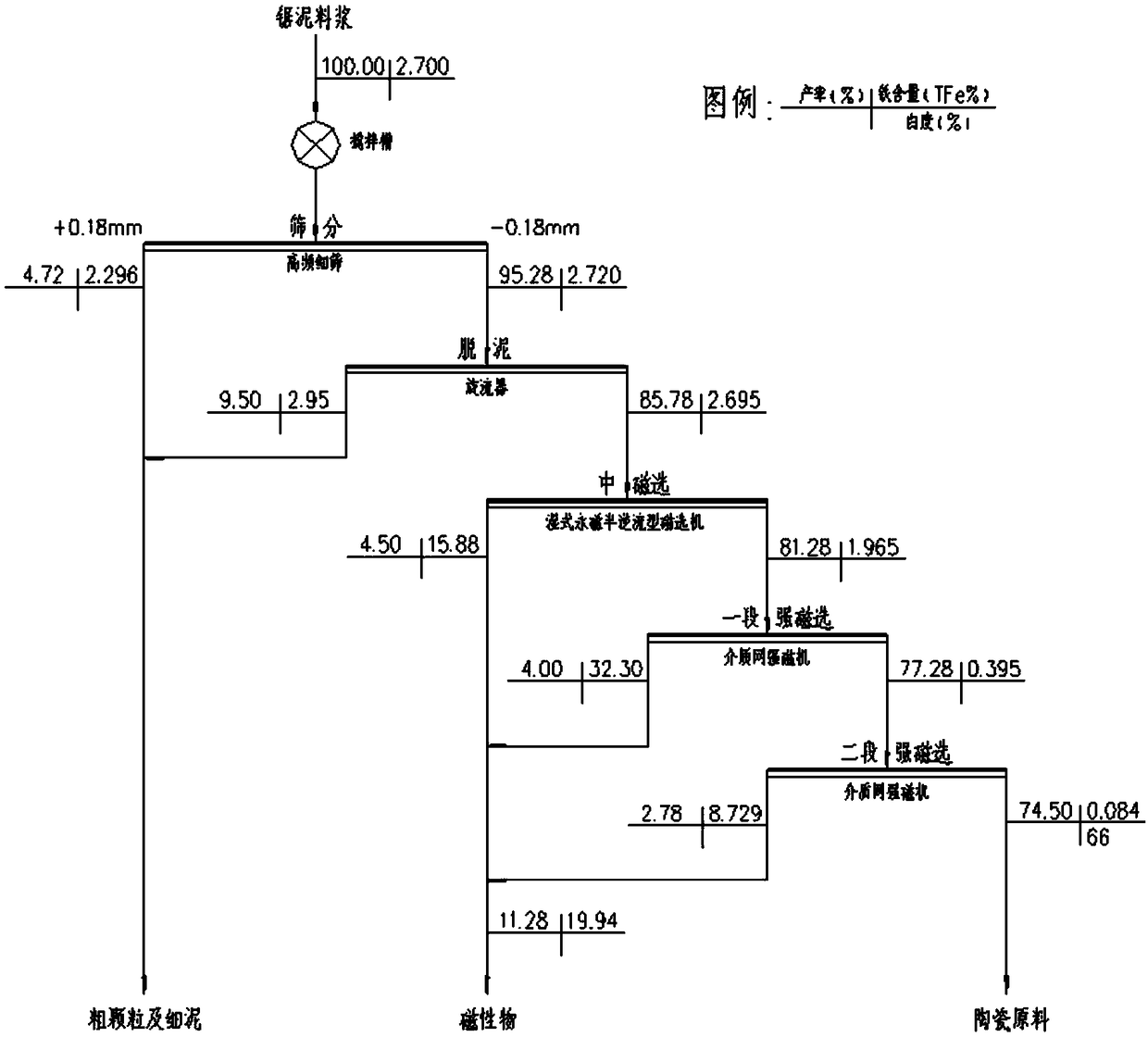
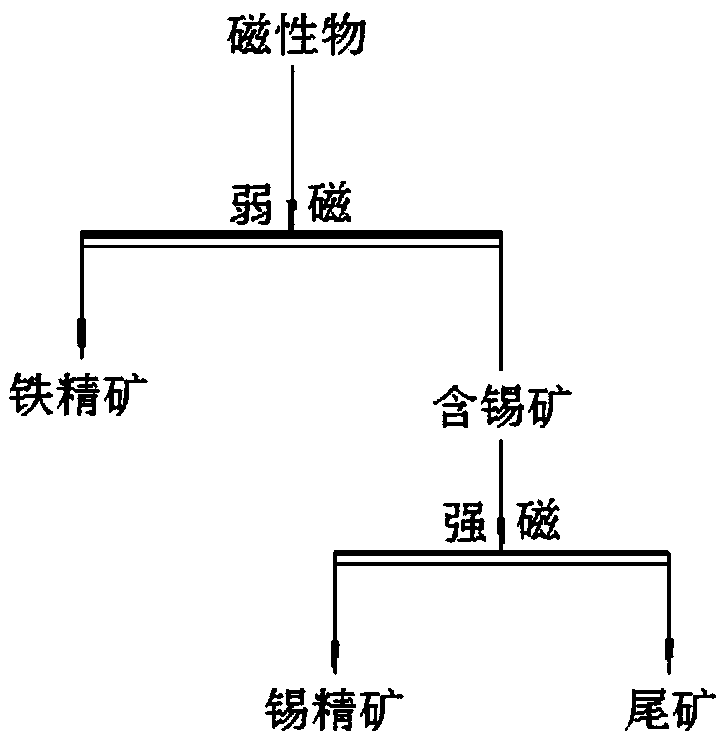
Method of using tin-and-iron-containing stone sawing mud with high efficient
ActiveCN109453892AHigh yieldHigh whitenessSolid separationMechanical material recoverySlurryCoarse particle
The invention discloses a method of using tin-and-iron-containing stone sawing mud with high efficient. The method comprises the following steps that 1 ) screening is carried out, stone sawing mud powder slurry is uniformly stirred and then screening is carried out, and screened coarse particles and screened fine particles are obtained; desliming is carried out, the obtained screened fine particles in the step 1 ) are subjected to the desliming treatment so as to obtain coarse particles and fine mud after the desliming; and 3 ) magnetic separation is carried out, the deslimed coarse particlesobtained in the step 2 ) are subjected to the magnetic separation, and magnetic materials and ceramic raw materials are obtained. According to the method, the stone sawing mud is processed through processes such as the screening, the desliming, the magnetic separation and the like, a high-whiteness ceramic raw material is recycled, the valuable metal tin and iron in the high-whiteness ceramic rawmaterial can further be recycled, so that effective utilization of waste resources and comprehensive recovery of metal resources are realized, waste of the resources is reduced, emission is reduced, and the environment is protected.
Owner:ZHONGYE-CHANGTIAN INT ENG CO LTD
Method for improving furnace age of converter
InactiveCN108251590AReduce TFe contentReduce erosion rateManufacturing convertersAlkalinityMolten steel
The invention discloses a method for improving the furnace age of a converter and belongs to the technical field of metallurgy. In order to improve the furnace age of the converter, the invention provides the method for improving the furnace age of the converter; the method comprises the following steps: adding dolomite into the converter; after blending semi-steel into the converter; blowing andadding active lime, dolomitic lime, an acidic composite slag forming agent and converter waste residues into the converter; controlling a lance position and oxygen blowing strength of an oxygen lanceand controlling the alkalinity of terminal-point furnace slag to 3 to 4, so as to obtain terminal-point molten steel and terminal-point slag. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the dolomite is used for producing the slag and the converter waste residues are added to replace part of metallurgy auxiliary materials, so that the content of TFe in the terminal-point slag is reduced, the tapping temperature is reduced and the terminal-point carbon content is improved; the furnace age of the converter is remarkably improved and the smelting effect is not influenced.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Converter steelmaking technology
InactiveCN102382930AReduce TFe contentReduce consumptionManufacturing convertersLime productionSteelmakingMaterials science
The invention discloses a converter steelmaking technology, and belongs to the technical field of converter steelmaking. In smelting, the technology is mainly characterized in that: the blowing process is divided into two processes, namely the front period of blowing is a dephosphorization period, and the later period of blowing is a decarburization period. Different from a conventional smelting technology, the technology is mainly characterized in that: slag is poured when the dephosphorization period is finished, and slag is not poured when the decarburization period is finished. According to the poured dephosphorization slag, the quantity of the poured dephosphorization slag is more than 30 percent, and the TFe content of the slag is less than 14 percent. Therefore, the technology brings the biggest benefits of saving lime, reducing the consumption of steel and iron and remarkably reducing the phosphorus content together with the increment of the number of smelting furnaces after the decarburization period is finished. The technology has the other characteristic that the smelting period is not increased and is basically as same as the conventional technology.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
Semi-steel smelting constant-pressure constant lance steelmaking method
ActiveCN106011362AReduce process dry-outReduce splashManufacturing convertersSteelmakingSmelting process
The invention relates to a semi-steel smelting constant-pressure constant lance steelmaking method, and belongs to the technical field of semi-steel smelting. The semi-steel smelting constant-pressure constant lance steelmaking method is provided to reduce the process lance position fluctuation in order to fundamentally reduce the TFe content of final slag. A slagging system is optimized, and corundum slag is used to carry out early slagging and process slag adjustment in order to reach semi-steel smelting rapid slagging and reduce process drying. The TFe content and splash are fundamentally reduced through constant-pressure constant lance operation without special slag modifying treatment. The method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low cost, reduction of the drying and splashing probability in the semi-steel smelting process, stationary process, and realization of control of the TFe content of the final slag within 17%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Dephosphorization converter blowing control method
The invention discloses a dephosphorization converter blowing control method and belongs to the technical field of steelmaking. The method comprises top-blown oxygen supply flow control and gun position control during blowing, wherein in early blowing, controlled oxygen supply flow is 30000-35000 Nm<3> / h, the oxygen supply flow is adjusted to 20000-25000 Nm<3> / h 2-3 min after blowing and is adjusted to 12000-15000 Nm<3> / h 2-3 min before the end; in early stage, gun position is controlled to 2 meters and is adjusted to 1.4 meters 2-3 minutes after the early stage until blowing is ended. Through oxygen supply flow and gun position controlling during blowing, it is possible to guarantee full melting of waste steel, dephosphorization smelting final slag is 1.8-2.2 in alkalinity, element P content at the end of dephosphorization smelting is averagely up to 0.025%, dephosphorization rate is increased, TFe content of the final slag is lowered, low-cost dephosphorization converter smelting is achieved, the production target high efficiency is achieved, and the temperature requirement of semi-steel is unaffected.
Owner:SHOUGANG JINGTANG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for producing low-phosphorus semisteel by vanadium-contained molten iron converter
ActiveCN106222357AImplement extractionAchieving extraction and partial removal of phosphorusManufacturing convertersSlagNitrogen
The invention belongs to the field of steel and iron smelting, and in particular, relates to a method for producing low-phosphorus semisteel by a vanadium-contained molten iron converter. The method for producing the low-phosphorus semisteel by the vanadium-contained molten iron converter comprises the following steps: (A) after iron is mixed by a vanadium extracting converter, an oxygen reducing gun performs blowing; the oxygen flow is controlled within 1.5-3.0 Nm3 / t.min in the whole process; and the bottom blowing nitrogen strength is 0.2-0.4 Nm3 / t.min; (B) a gun position is controlled by above 10-30 mm according to a reference gun position before blowing by 2 min; steel making converter final slag is added at the beginning of blowing; iron-contained oxides are added after blowing by 1-2 min; the reference gun position is reduced to during blowing by 2-5 min; and the gun position is controlled by above 30-50 mm according to the reference gun position before blowing by 2 min; and (C) the semisteel and 50% of vanadium slag are discharged after blowing; in a second furnace, the oxygen supply system is the same with the first furnace; the basicity of the slag is controlled within 1.5-1.8 by the added lime quantity; the semisteel and 50% of vanadium slag are discharged after blowing; and the subsequent furnace operation is the same with the second furnace.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Method for dephosphorizing vanadium-containing molten iron in vanadium extraction converter
ActiveCN106244760ALighten the task of dephosphorizationReduce TFe contentManufacturing convertersNitrogenMaterial consumption
The invention belongs to the steel smelting field, and particularly relates to a method for dephosphorizing vanadium-containing molten iron in a vanadium extraction converter. The method aims to solve the problem that vanadium-extraction and dephosphorization efficiency is relatively low in the conventional method, and reduce TFe content in vanadium slag, so that steel material consumption is reduced, and low-phosphor semisteel is provided for a steel-making converter. The method for dephosphorizing vanadium-containing molten iron in the vanadium extraction converter comprises the following steps of: A, after iron is completely converted in the vanadium extraction converter, a deoxygenation lance is used for blowing, wherein oxygen gas flow is controlled to be 1.5-3.0Nm<3> / t.min throughout the whole process, and bottom-blowing nitrogen strength is 0.2-0.4 Nm<3> / t.min; B, lime is added when blowing starts, a lance position is controlled 10-30mm above a standard lance position 2 minutes before blowing; iron oxide scale or other oxides with high iron content are added 1-2 minutes after blowing; the lance position is controlled according to the standard lance position 2 minutes after blowing; and the lance position is controlled 30-50mm above the standard lance position 2 minutes before blowing is ended; and C, discharging semisteel and vanadium slag after blowing is ended.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Vanadium extracting converter slag adjusting method
The invention relates to a vanadium extracting converter slag adjusting method, and belongs to the technical field of converter vanadium extraction. The technical problem to be solved by the invention is to provide the vanadium extracting converter slag adjusting method capable of further reducing the iron loss. The method comprises the following steps: molten vanadium-titanium contained iron is mixed into a converter; a sodium salt modifying agent is added within one minute before ending of blowing; and after the blowing is finished, the tapping is performed to obtain semisteel and vanadium slag. Before the blowing is finished, the sodium salt modifying agent is adopted to adjust the slag; and the converter vanadium slag components can be controlled within a proper range before tapping of the converter, so that the purposes of reducing the vanadium slag melting point, optimizing the vanadium slag slag-iron separation effect and reducing the steel-iron consumption are achieved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for making steel by using dephosphorized steel slag
The invention provides a method for making steel by using dephosphorized steel slag. The method comprises the following steps: dephosphorizing steel slag to obtain the dephosphorized steel slag; and making steel by using the dephosphorized steel slag. The invention provides the method for making steel by dephosphorizing and recycling the converter steel slag in order to solve the problems that the converter dephosphorizing efficiency is reduced and the consumption of auxiliary materials is increased due to continuous accumulation of phosphorus in the steel slag caused by slag remaining operation of a converter. On the basis of existing slag remaining operation, the consumption of the auxiliary materials is further reduced, the converter dephosphorization efficiency is improved, meanwhile, the problem that a semisteel smelting heat source is insufficient can be relieved, the TFe content of final slag is reduced, and the remarkable cost reduction and emission reduction effects are achieved.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
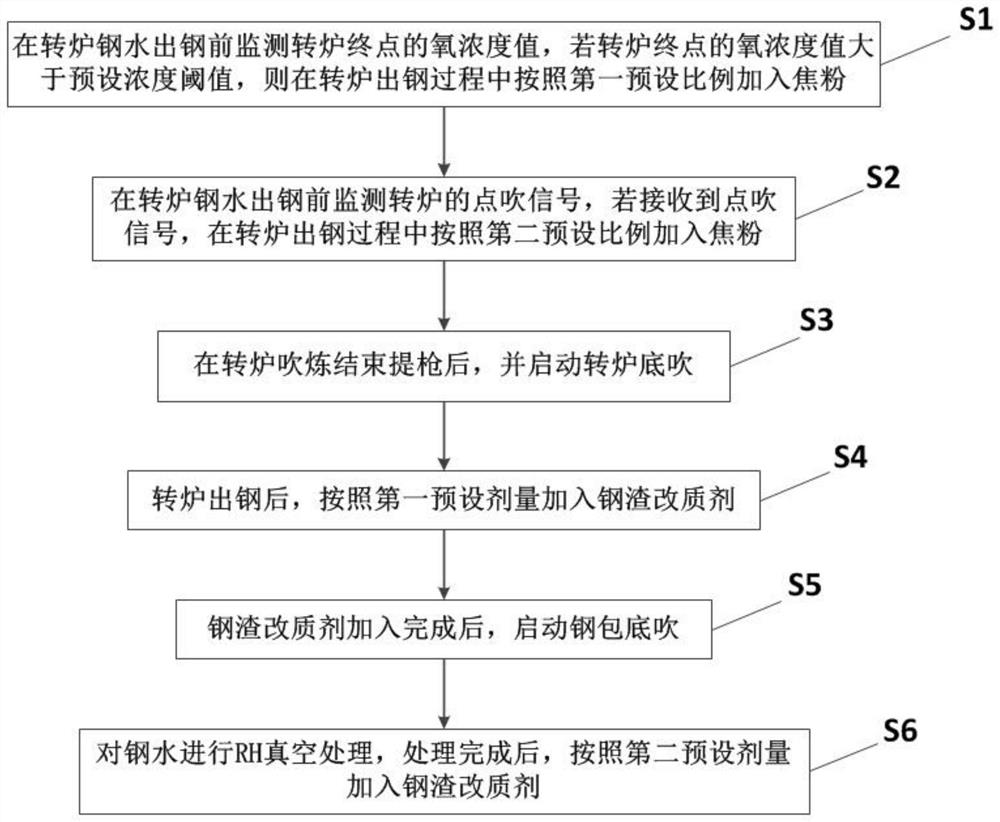
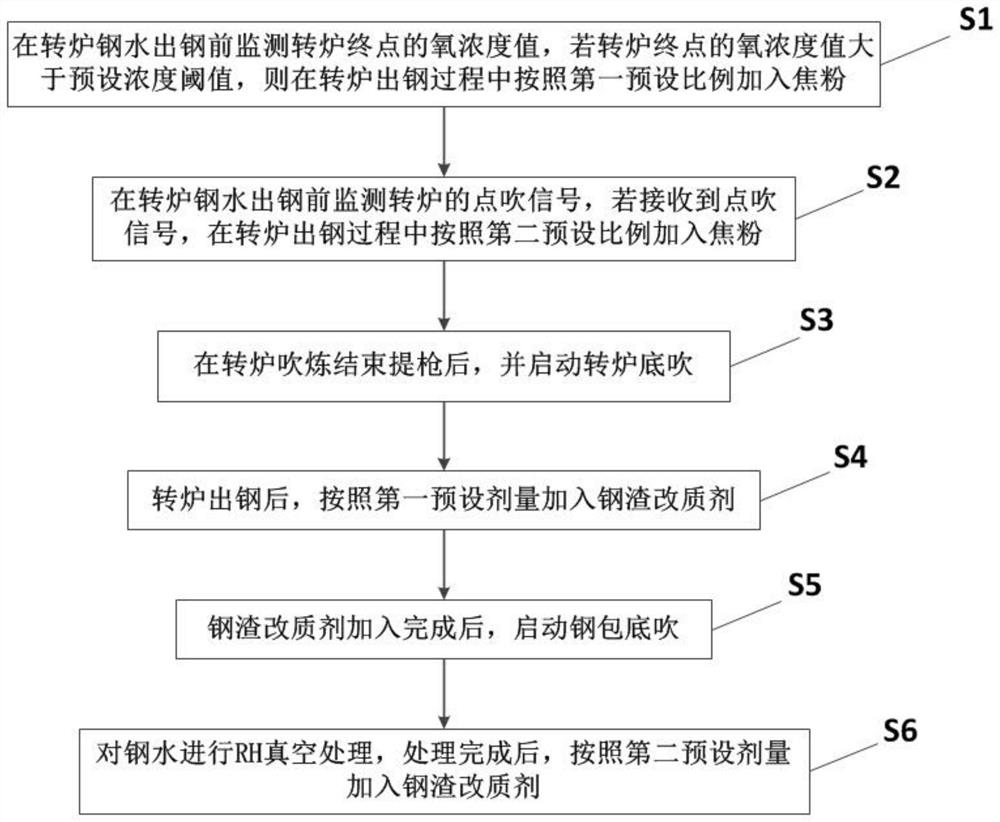
Ultra-low carbon IF molten steel peroxidation treatment method
PendingCN113957199AReduce oxygen contentReduce peroxidationManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSlagCoke
The invention relates to an ultra-low carbon IF molten steel peroxidation treatment method. The ultra-low carbon IF molten steel peroxidation treatment method comprises the following steps: monitoring an oxygen concentration value of a converter terminal point before converter molten steel tapping, and adding a coke powder according to a first preset proportion in the converter tapping process if the oxygen concentration value of the converter terminal point is greater than a preset concentration threshold value; monitoring a point blowing signal of the converter before converter molten steel tapping, and adding the coke powder according to a second preset proportion in the converter tapping process if the point blowing signal is received; starting the converter bottom blowing after the converter blowing is finished and a gun is lifted; adding a steel slag modifier according to a first preset dosage after converter tapping; starting steel ladle bottom blowing after the steel slag modifier is added; and performing RH vacuum treatment on the molten steel, and adding the steel slag modifier according to a second preset dosage after the treatment is completed. According to the invention, the oxygen content of the molten steel after converter tapping can be effectively reduced, and the degree of peroxidation of the molten steel is reduced.
Owner:SD STEEL RIZHAO CO LTD
Bottom-blown air brick of top and bottom repeatedly blown converter and installing structure thereof
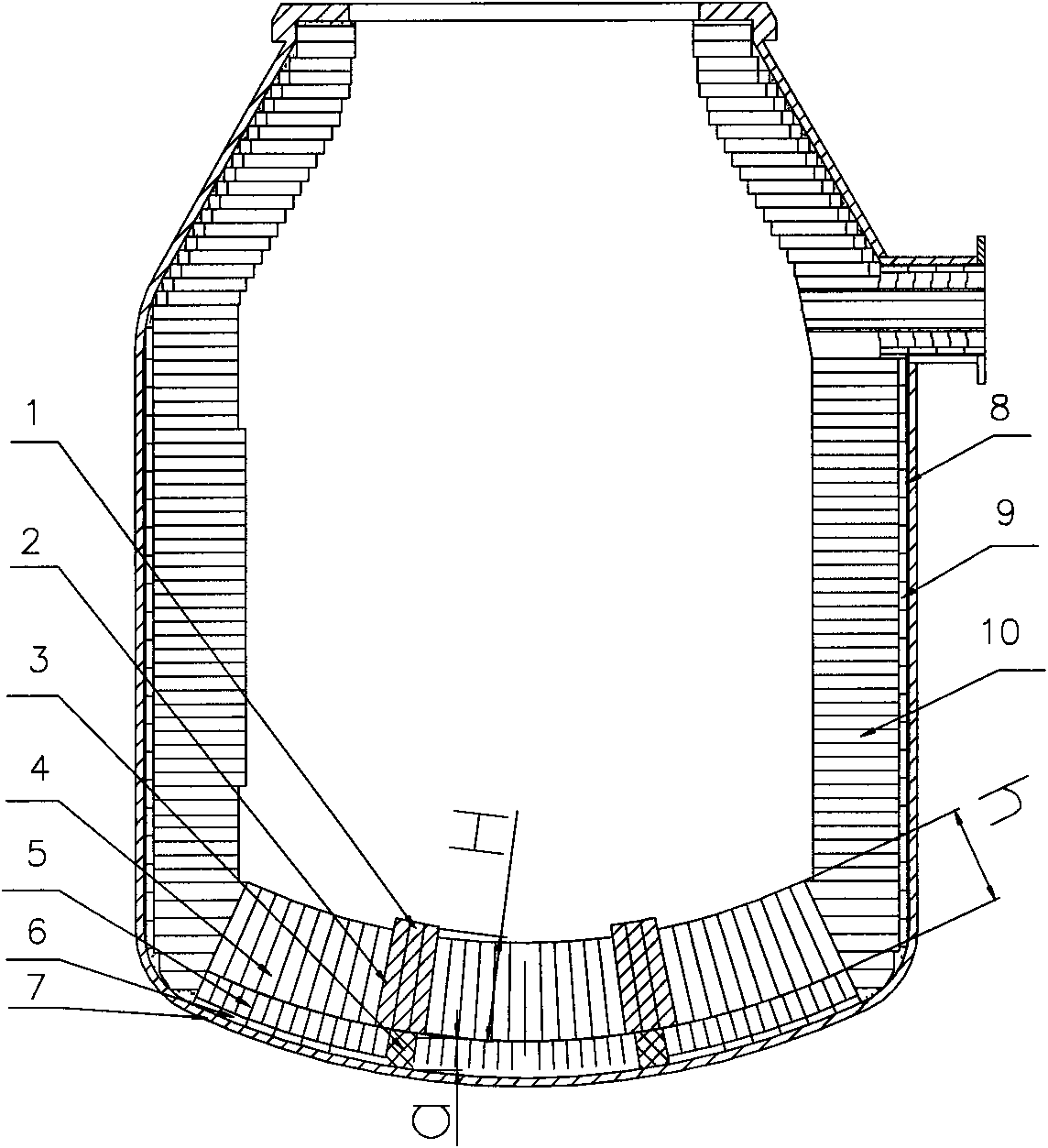
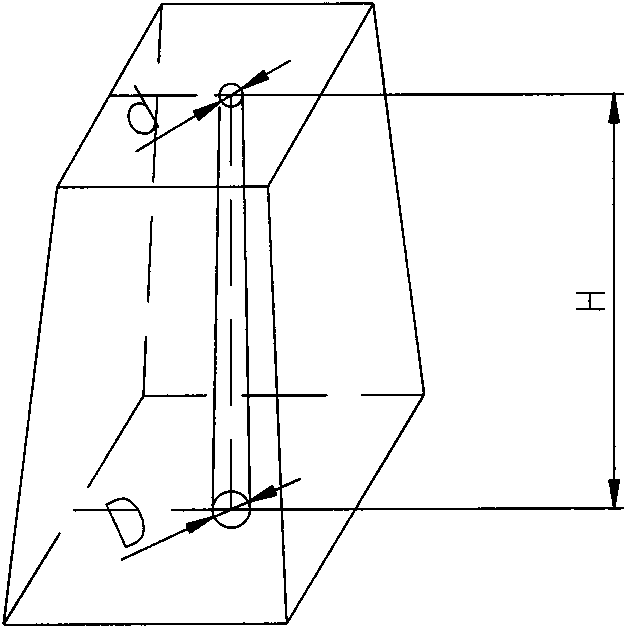
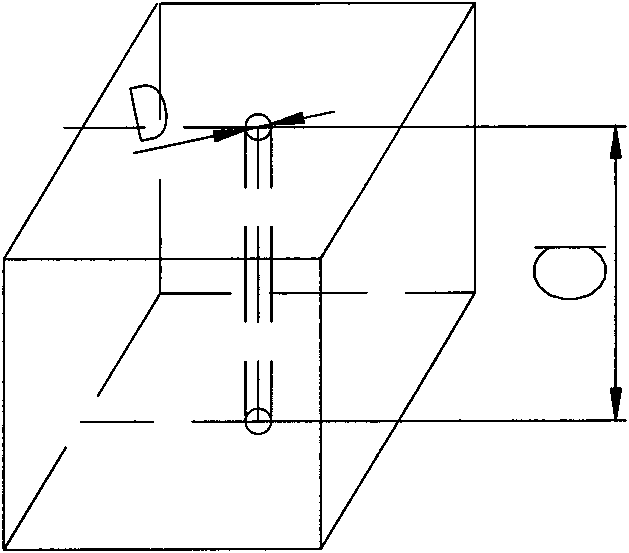
InactiveCN101613781BSolve the blockageExtend your lifeManufacturing convertersBrickChemical reaction
The invention relates to a bottom-blown air brick of top and bottom repeatedly blown converter and an installing structure thereof, which are mainly characterized in that two sides of the bottom-blown air brick are respectively laid with a protective brick, the height H of the bottom-blown air brick and the protective brick is more 80-120 mm than that h of a bottom working liner magnesia carbon brick, the shape size of the bottom-blown air brick is the same with the shape size of the protective bricks at two sides of the bottom-blown air brick, and the protective bricks and the bottom-blown air brick are tread gauged bricks. The invention can promote slag-metal cupping at the top of the bottom-blown air brick during the production primary period of a new converter to be rapidly produced, thereby solving the problem of blockage or burning-out of the bottom-blown air brick, ensuring the air permeability, and greatly prolonging the service life of the bottom-blown air brick, wherein the service life of the bottom-blown air brick reaches more than 20,000 furnaces. The layout structure of the air brick strengthens the mixing of molten steel in a molten pool, quickens elements in the molten pool to mutually generate the chemical reaction, and remarkably reduces the content of TFe in the slag, wherein the content of the TFe averagely reaches below 15 percent.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
A method for synchronous oxidation and separation of phosphorus and vanadium in vanadium-containing molten iron in a converter
The invention belongs to the field of steel smelting and particularly relates to a method of separating phosphorus and vanadium by simultaneous oxidation of vanadium-bearing molten iron in a converter. The method provided by the invention aims to solve the problem that the efficiency of vanadium extraction and phosphorus removal for molten iron by a conventional method is relatively low, and reduces the content TFe in vanadium slag, so that the consumption of an iron and steel material is reduce and low-phosphorous semi-steel is provided for the steel-making converter. The method of separating phosphorus and vanadium by simultaneous oxidation of vanadium-bearing molten iron in the converter provided by the invention comprises the steps of: A, after iron is blended in the vanadium-extracting converter, descending an oxygen lance to blow, wherein the oxygen flow in the full course is controlled at 1.5-3.0Nm3 / t.min, and the intensity of bottom blowing nitrogen is 0.2-0.4N3 / t.min; B, adding lime after blowing is started, and controlling the lance position 10-30mm over a standard lance position 2min before blowing; after blowing in 1-2min, adding iron oxide scales or other high iron-bearing oxides; controlling the lance position according to the standard lance position 2min after blowing; and controlling the lance position 30-50mm over the standard lance position 2min before blowing is finished; and C, after blowing is finished, discharging semi-steel and vanadium slag.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
A kind of method for producing low phosphorus semi-steel by vanadium-containing molten iron converter
ActiveCN106222357BImplement extractionAchieve partial removalManufacturing convertersNitrogenNitrogen gas
The invention belongs to the field of steel and iron smelting, and in particular, relates to a method for producing low-phosphorus semisteel by a vanadium-contained molten iron converter. The method for producing the low-phosphorus semisteel by the vanadium-contained molten iron converter comprises the following steps: (A) after iron is mixed by a vanadium extracting converter, an oxygen reducing gun performs blowing; the oxygen flow is controlled within 1.5-3.0 Nm3 / t.min in the whole process; and the bottom blowing nitrogen strength is 0.2-0.4 Nm3 / t.min; (B) a gun position is controlled by above 10-30 mm according to a reference gun position before blowing by 2 min; steel making converter final slag is added at the beginning of blowing; iron-contained oxides are added after blowing by 1-2 min; the reference gun position is reduced to during blowing by 2-5 min; and the gun position is controlled by above 30-50 mm according to the reference gun position before blowing by 2 min; and (C) the semisteel and 50% of vanadium slag are discharged after blowing; in a second furnace, the oxygen supply system is the same with the first furnace; the basicity of the slag is controlled within 1.5-1.8 by the added lime quantity; the semisteel and 50% of vanadium slag are discharged after blowing; and the subsequent furnace operation is the same with the second furnace.
Owner:CHENGDU ADVANCED METAL MATERIALS IND TECH RES INST CO LTD
Recovery method of high calcium vanadium slag
ActiveCN104911367BEasy to recyclePrevent overflowRecycling and recovery technologiesProcess efficiency improvementRecovery methodChemical composition
Owner:PANGANG GROUP CHENGDU STEEL & VANADIUM
Steel making final slag adjustment and preparation method and application method thereof
InactiveCN104060023AWide variety of sourcesReduce manufacturing costManufacturing convertersSteelmakingMolten steel
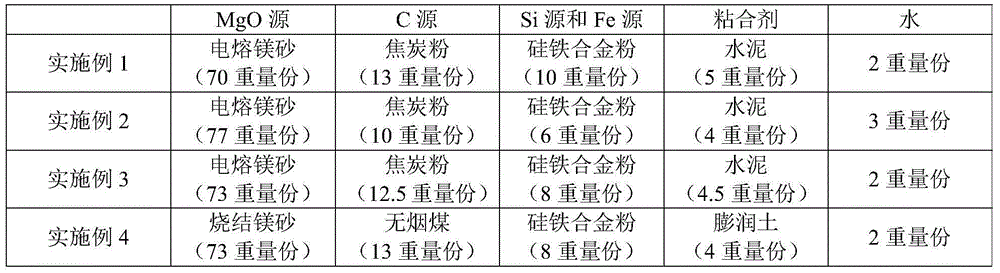
The invention discloses a steel making final slag adjustment agent and a preparation method and an application method thereof, and wherein the steel making final slag adjustment agent comprises 73 to 85 wt% of MgO, 8 to 14 wt% of C, 4 to 8 weight% Si and 1 to 5 weight% of Fe on the basis of taking the total weight of the steel making final slag adjustment agent as a reference. When the steel making final slag adjustment agent is used, molten steel temperature drop is small, the steel making final slag adjustment agent is used after blowing of converter steelmaking is completed and before steel tapping, and the steel making final slag adjustment agent can reduce the content of TFe in final slag, and can reduce the production cost.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
A kind of method for reducing tfe content in converter final slag
ActiveCN114317871BReduce TFe contentReduce consumptionManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingSmelting process
This application provides a method to reduce the tFE content in the final residue of the turntable. The oxygen supply and slag manufacturing system adopts the combination and complement of the intelligent steelmaking push mode and experience operation.The effect of peak operations, full -process residue stability, and final residue effect during the sensitive period of the sensitive period to ensure that the smelting process is controlled; the high -strength operation of the furnace blowing at the bottom of the stove, high -efficiency nitrogen slag operation before the furnace, steel out of steel, and steel out of steelAdd the slag ball to achieve the use of auxiliary means to further reduce the final slag TFE content on the basis of the conventional blowing process operation.%, Limestone consumption is reduced by no less than 5kg / T. The content of the remaining steel water manganese is increased by 0.03WT%, the content of the end steel water C content increases by 0.02WT%, and the cost of tons of steel is reduced by 18.76 yuan / t.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL GRP YONGFENG LINGANG CO LTD
A method for smelting weather-resistant steel by tapping high-phosphorus steel in a converter
ActiveCN103773916BReduced dephosphorization capacityReduce TFe contentManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementSlagMaterial consumption
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
A method for simultaneously dephosphorizing and extracting vanadium in a vanadium-containing molten iron converter
ActiveCN105349728BLighten the task of dephosphorizationAvoid erosionManufacturing convertersNitrogen gasOxygen
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Semi-steel smelting steelmaking method with constant pressure and constant gun
ActiveCN106011362BReduce process dry-outReduce splashManufacturing convertersSteelmakingSmelting process
The invention relates to a semi-steel smelting constant-pressure constant lance steelmaking method, and belongs to the technical field of semi-steel smelting. The semi-steel smelting constant-pressure constant lance steelmaking method is provided to reduce the process lance position fluctuation in order to fundamentally reduce the TFe content of final slag. A slagging system is optimized, and corundum slag is used to carry out early slagging and process slag adjustment in order to reach semi-steel smelting rapid slagging and reduce process drying. The TFe content and splash are fundamentally reduced through constant-pressure constant lance operation without special slag modifying treatment. The method has the advantages of simplicity in operation, low cost, reduction of the drying and splashing probability in the semi-steel smelting process, stationary process, and realization of control of the TFe content of the final slag within 17%.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
A kind of production method of low phosphorus steel
ActiveCN106244898BStir wellReduce contentProcess efficiency improvementSteelmakingProcess engineering
The invention belongs to the field of steel smelting, and particularly relates to a production method of low-phosphorous steel in order to solve the problem that the efficiency of vanadium extraction and dephosphorization from molten iron is low by using the conventional method and to reduce the content of TFe in vanadium slag. The production method of the low-phosphorous steel comprises the following steps: A, after iron is added to a vanadium extraction converter, an oxygen reducing lance carries out converting, the flow of oxygen is controlled at 1.5-3.0Nm<3> / t.min throughout, and the strength of bottom blowing nitrogen is 0.2-0.4N<3> / t.min; B, the converting begins, final slag of a steel-making converter is added, 2min before the converting, a lance position is controlled at 10-30mm above a reference lance position, 1-2min after the converting, scale or other high-iron oxides are added, 2min after the converting, the lance position is controlled according to the reference lance position, and 2min before the converting is finished, the lance position is controlled at 30-50mm above the reference lance position; C, after the converting is finished, semisteel and vanadium slag are discharged; and D, the semisteel is added to a steelmaking furnace, the alkalinity of pre-slag is controlled at 2.0-3.0, the alkalinity of secondary slag is controlled at 3.0-4.5, and the tapping temperature is controlled according to the requirement of the steel type.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP
Method for synchronously dephosphorization and vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing molten iron
The invention discloses a method for synchronously dephosphorization and vanadium extraction of vanadium-containing molten iron. The method comprises the following steps of: controlling temperature of vanadium-containing molten iron at 1230-1250 DEG C; carrying out oxygen-injection blowing, wherein oxygen flow is constantly controlled at 17000-25000Nm<3> / min, and the blowing process sequentially comprises three stages; the first stage starts from blowing to 1-2min of blowing, gun position is 1.6-1.8m, and lime for controlling alkalinity of slag to be 2-4 lime and 15-20kg / tFe of iron scale are added simultaneously; the second stage starts after 1-2min of blowing, gun position is 1.8-2.1m, and 5-18kg / tFe of iron scale is added in the process that oxygen-injection time is not greater than 3min; and the third stage starts from blowing to 2min of the end, 0.5-2kg / tFe of high-magnesium lime is added, and gun position is reduced to 1.6-1.8m; and blowing to end, and discharging semi-steel and vanadium slag. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that corrosion to lining of a vanadium extraction converter is effectively avoided, and dephosphorization and vanadium extraction are synchronously implemented; and TFe content in the vanadium slag is reduced.
Owner:PANZHIHUA IRON & STEEL RES INST OF PANGANG GROUP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com