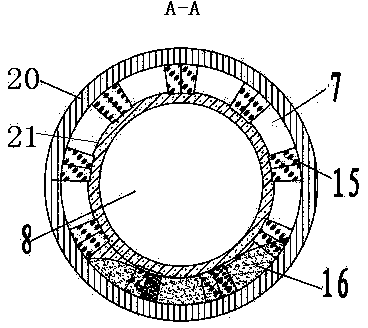
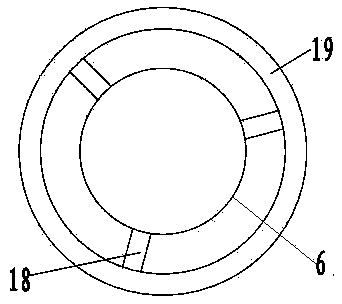
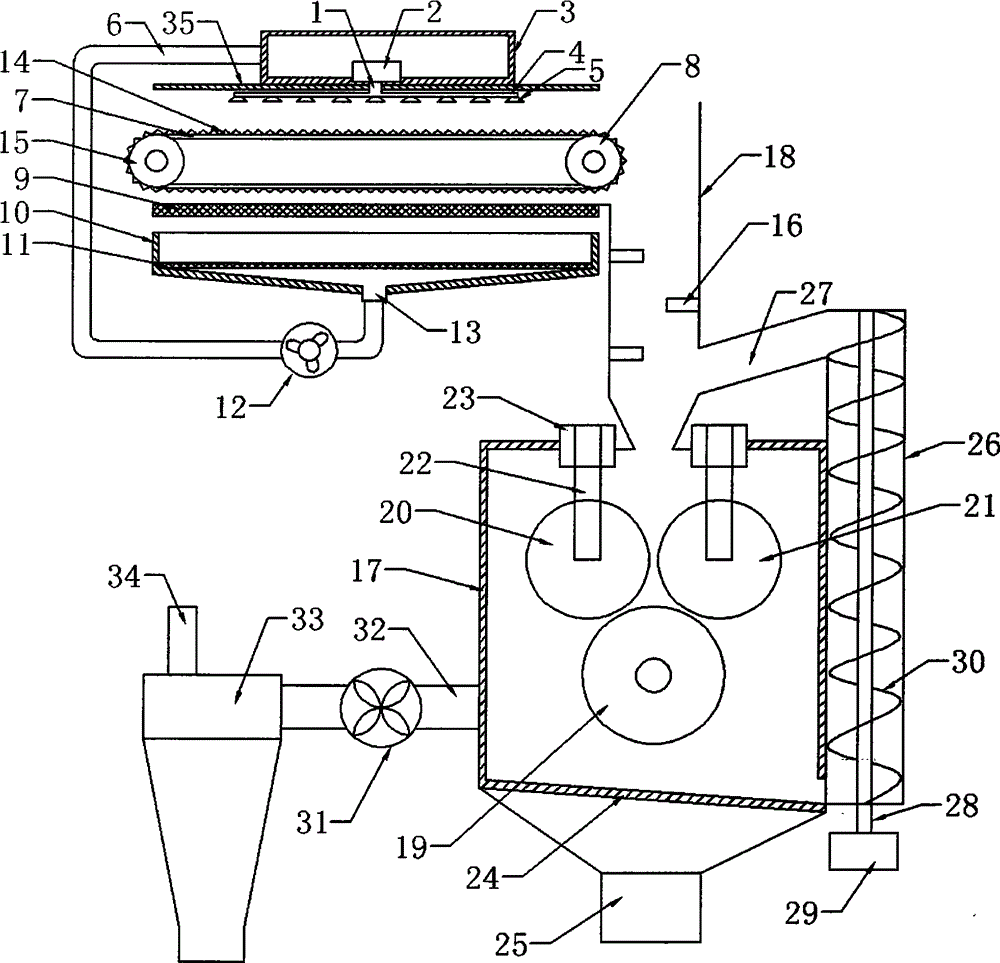
Patents
Literature
846results about "Lime production" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Polymer nanocomposite implants with enhanced transparency and mechanical properties for administration within humans or animals
Polymer nanocomposite implants with nanofillers and additives are described. The nanofillers described can be any composition with the preferred composition being those composing barium, bismuth, cerium, dysprosium, europium, gadolinium, hafnium, indium, lanthanum, neodymium, niobium, praseodymium, strontium, tantalum, tin, tungsten, ytterbium, yttrium, zinc, and zirconium. The additives can be of any composition with the preferred form being inorganic nanopowders comprising aluminum, calcium, gallium, iron, lithium, magnesium, silicon, sodium, strontium, titanium. Such nanocomposites are particularly useful as materials for biological use in applications such as drug delivery, biomed devices, bone or dental implants.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Nanotechnology for drug delivery, contrast agents and biomedical implants
A nanocomposite structure comprising a nanostructured filler or carrier intimately mixed with a matrix, and methods of making such a structure. The nanostructured filler has a domain size sufficiently small to alter an electrical, magnetic, optical, electrochemical, chemical, thermal, biomedical, or tribological property of either filler or composite by at least 20%.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Sorbent for separation of carbon dioxide (CO2) from gas mixtures
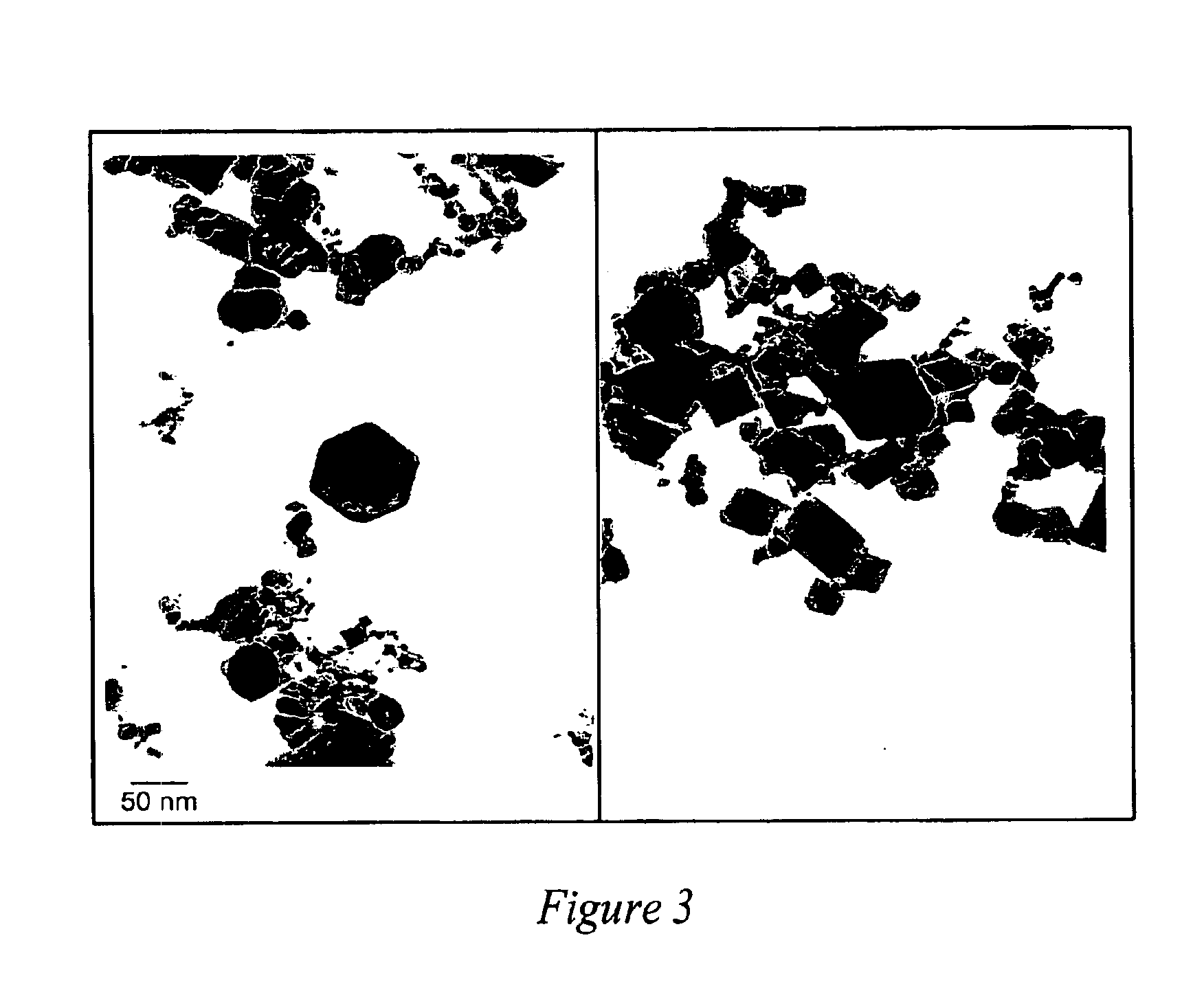
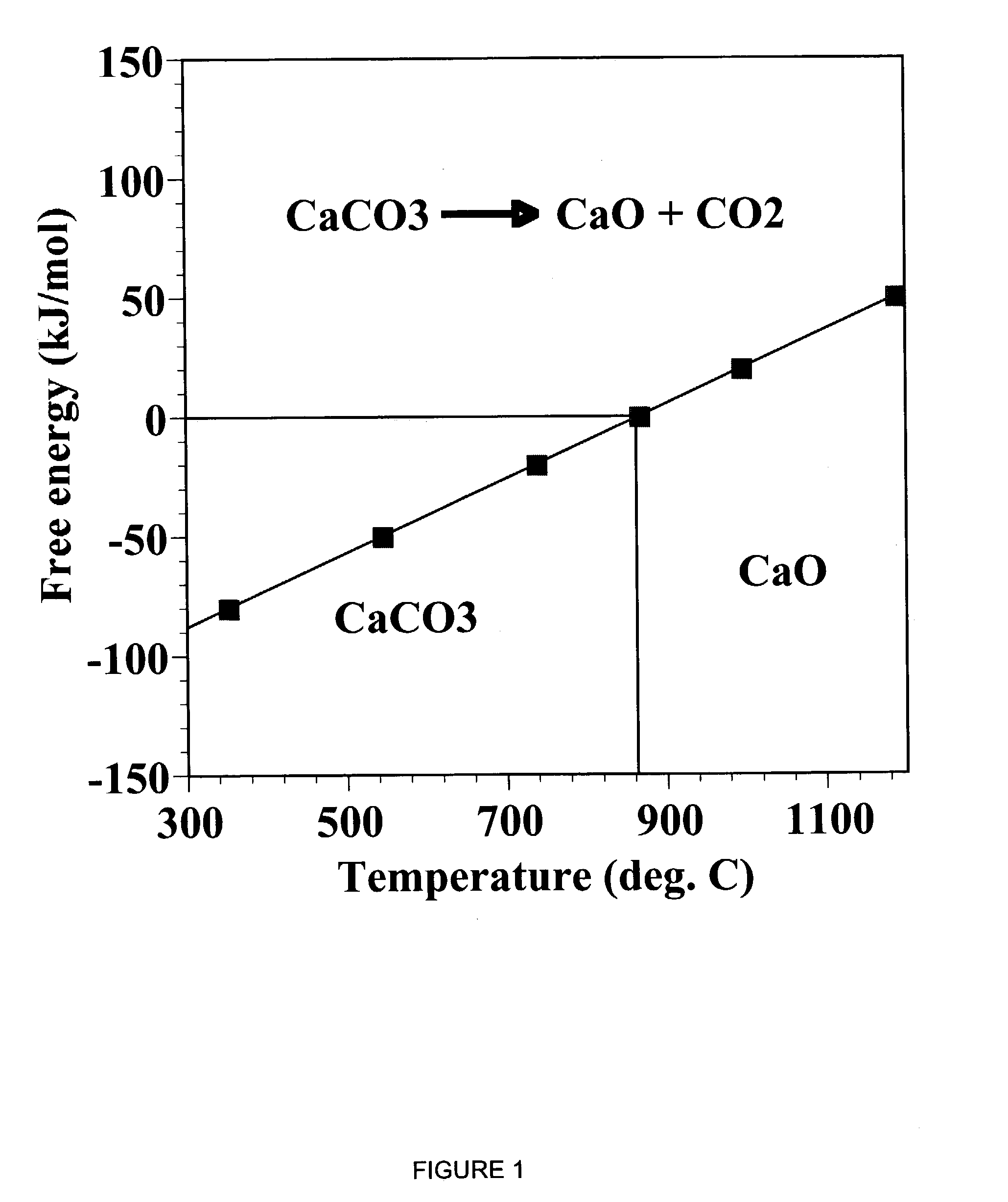
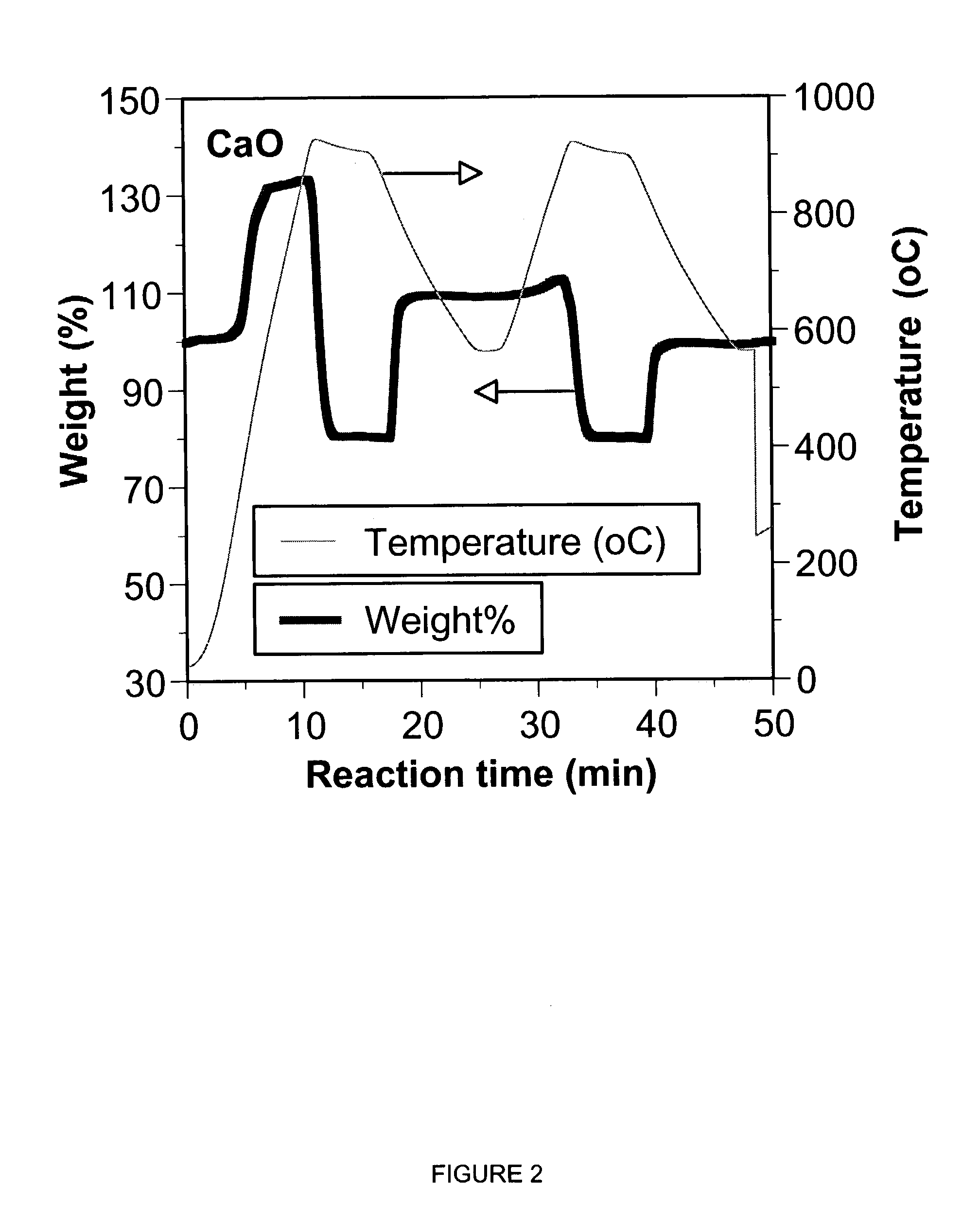
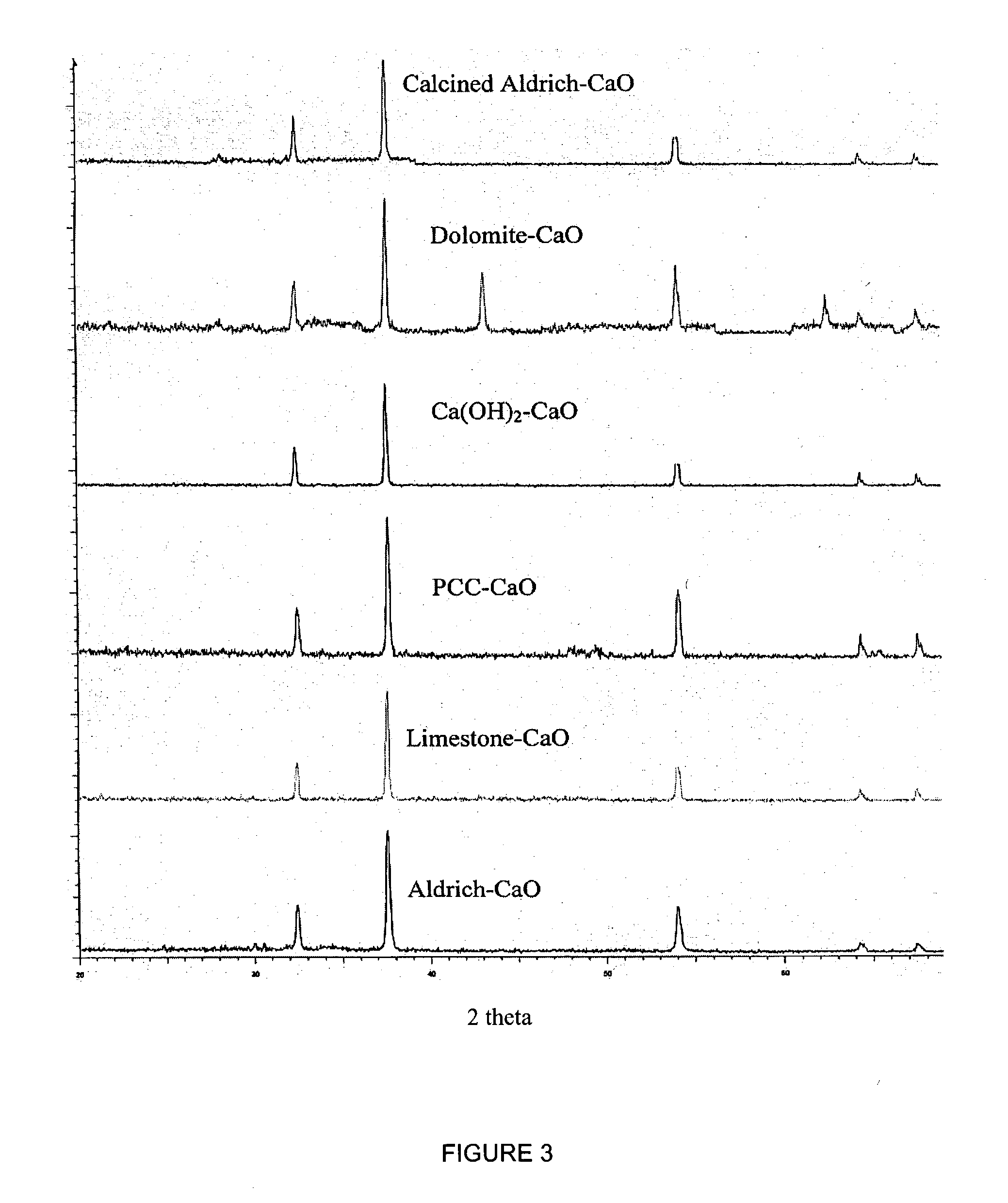
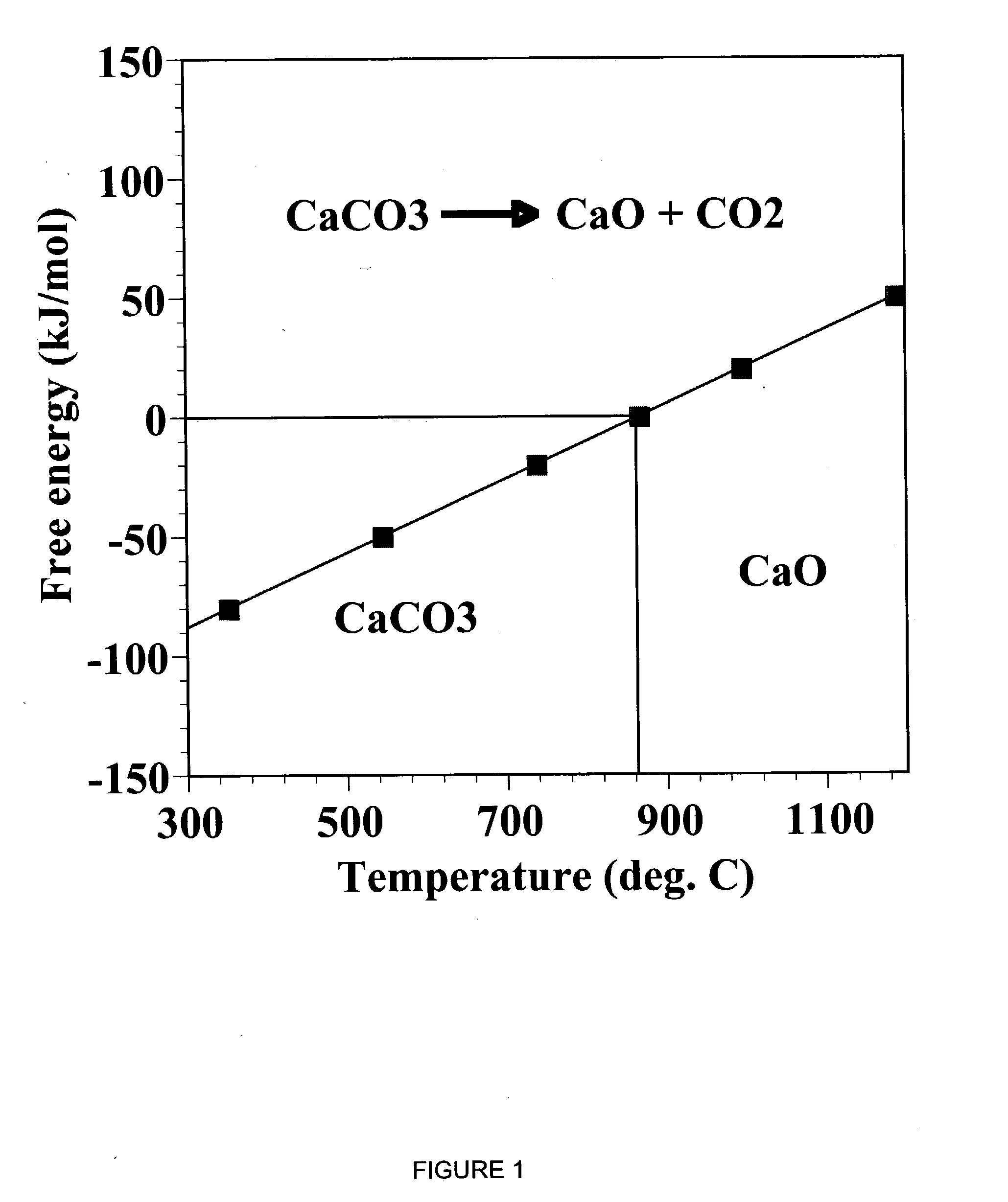
A reaction-based process has been developed for the selective removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from a multicomponent gas mixture to provide a gaseous stream depleted in CO2 compared to the inlet CO2 concentration in the stream. The proposed process effects the separation of CO2 from a mixture of gases (such as flue gas / fuel gas) by its reaction with metal oxides (such as calcium oxide). The Calcium based Reaction Separation for CO2 (CaRS-CO2) process consists of contacting a CO2 laden gas with calcium oxide (CaO) in a reactor such that CaO captures the CO2 by the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Once “spent”, CaCO3 is regenerated by its calcination leading to the formation of fresh CaO sorbent and the evolution of a concentrated stream of CO2. The “regenerated” CaO is then recycled for the further capture of more CO2. This carbonation-calcination cycle forms the basis of the CaRS-CO2 process. This process also identifies the application of a mesoporous CaCO3 structure, developed by a process detailed elsewhere, that attains >90% conversion over multiple carbonation and calcination cycles. Lastly, thermal regeneration (calcination) under vacuum provided a better sorbent structure that maintained reproducible reactivity levels over multiple cycles.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
Nanostructured powders and related nanotechnology
InactiveUS7081267B2Low costReduce operating costsNitrogen compoundsSelenium/tellurium compundsThermal energyOxygen
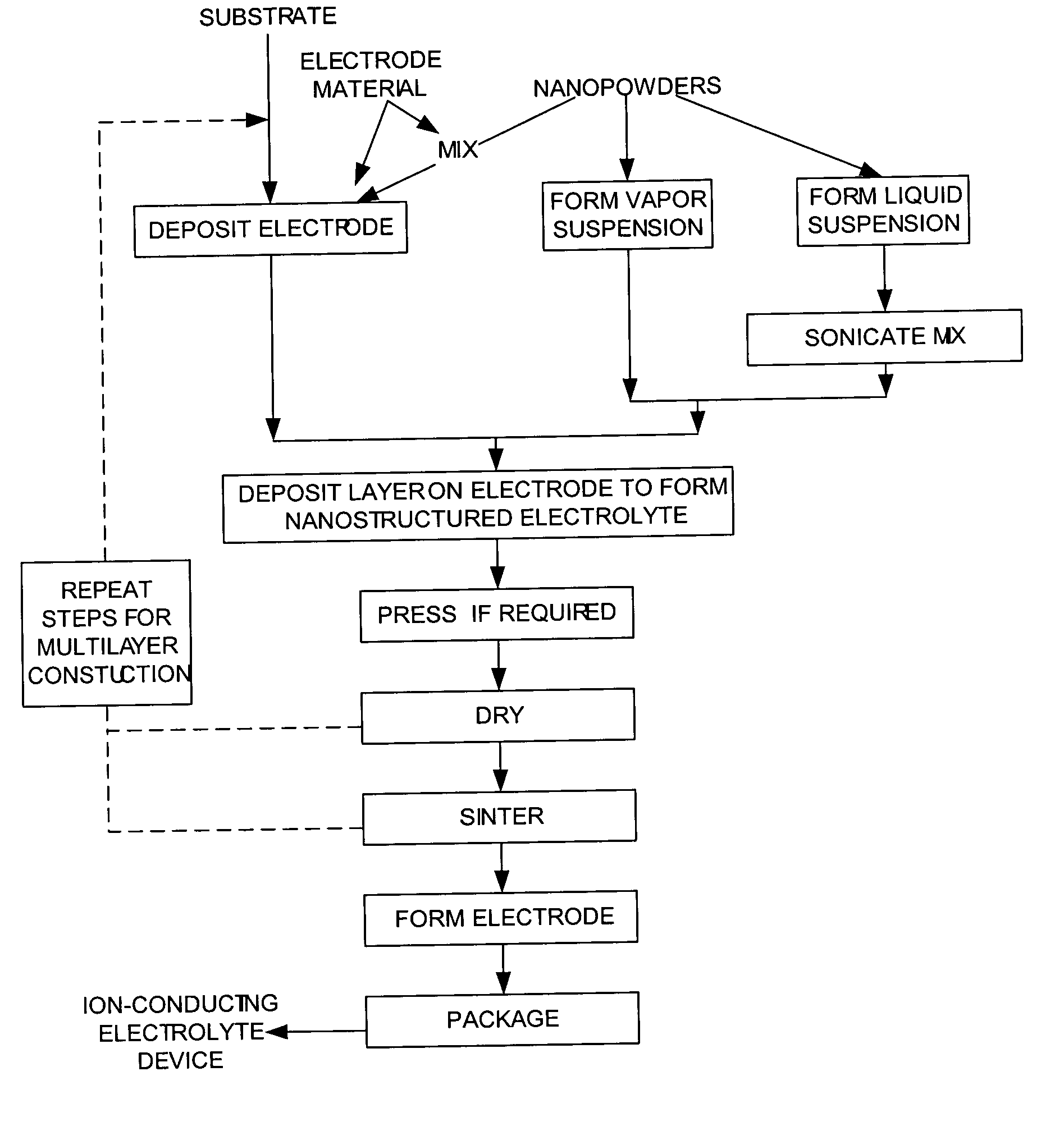
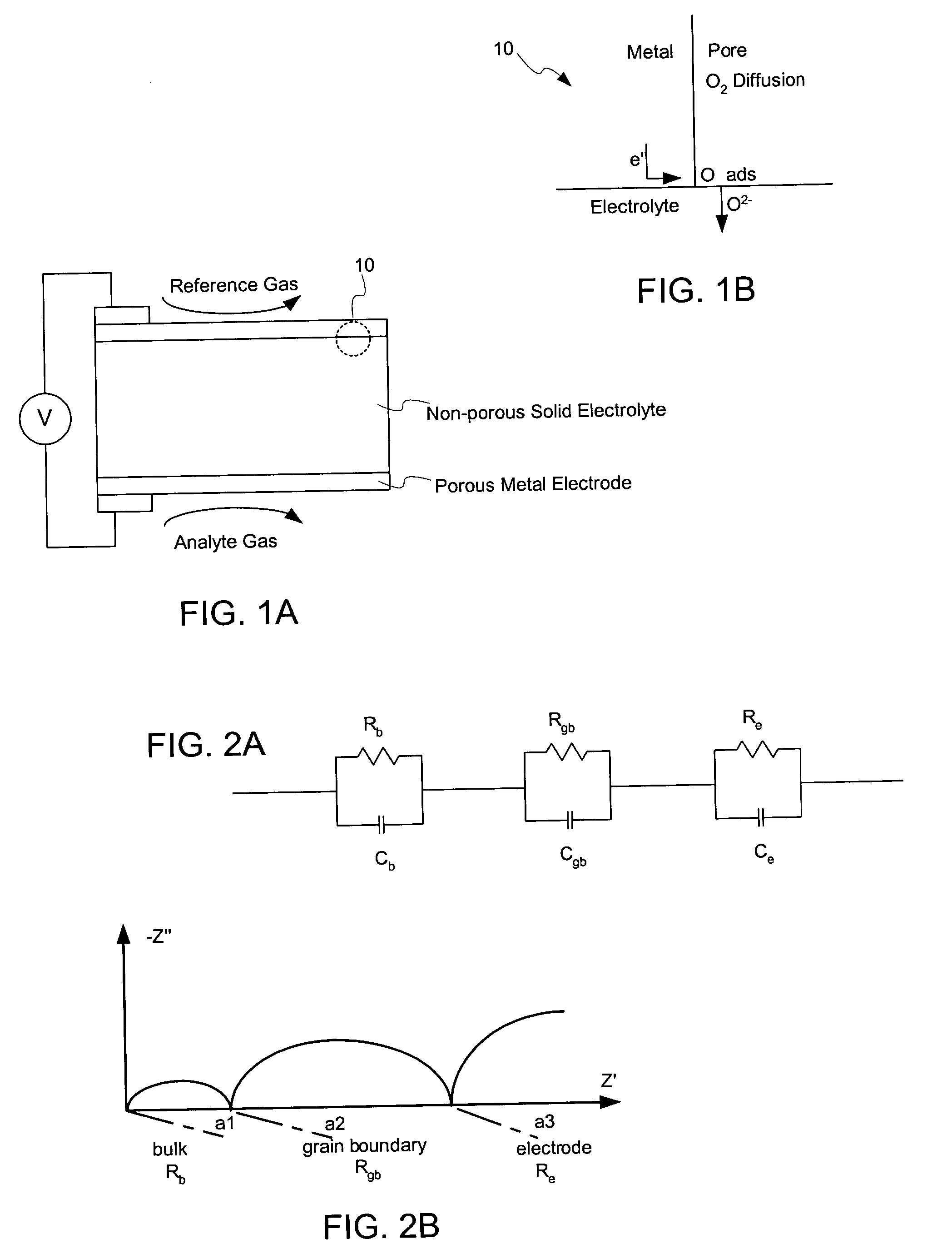
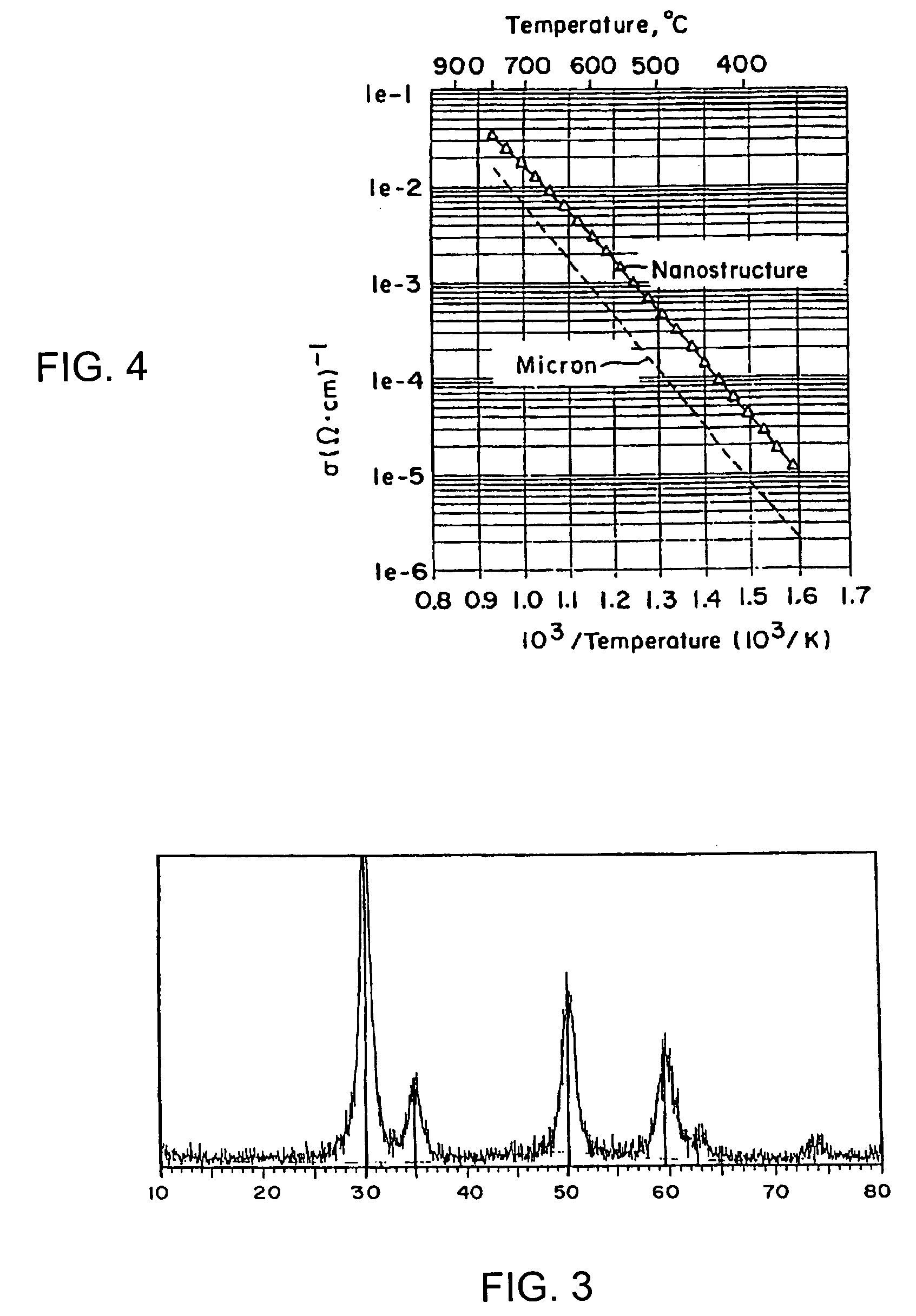
Methods to manufacture nanoscale particles comprising metals, alloys, intermetallics, ceramics are disclosed. The thermal energy is provided by plasma, internal energy, heat of reaction, microwave, electromagnetic, direct electric arc, pulsed electric arc and / or nuclear. The process is operated at some stage above 3000K and at high velocities. The invention can be utilized to prepare nanopowders for nanostructured products and devices such as ion conducting solid electrolytes for a wide range of applications, including sensors, oxygen pumps, fuel cells, batteries, electrosynthesis reactors and catalytic membranes.
Owner:PPG IND OHIO INC
Separation of carbon dioxide (CO2) from gas mixtures by calcium based reaction separation (CaRS-CO2) process
A reaction-based process has been developed for the selective removal of carbon dioxide (CO2) from a multicomponent gas mixture to provide a gaseous stream depleted in CO2 compared to the inlet CO2 concentration in the stream. The proposed process effects the separation of CO2 from a mixture of gases (such as flue gas / fuel gas) by its reaction with metal oxides (such as calcium oxide). The Calcium based Reaction Separation for CO2 (CaRS-CO2) process consists of contacting a CO2 laden gas with calcium oxide (CaO) in a reactor such that CaO captures the CO2 by the formation of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). Once “spent”, CaCO3 is regenerated by its calcination leading to the formation of fresh CaO sorbent and the evolution of a concentrated stream of CO2. The “regenerated” CaO is then recycled for the further capture of more CO2. This carbonation-calcination cycle forms the basis of the CaRS-CO2 process. This process also identifies the application of a mesoporous CaCO3 structure, developed by a process detailed elsewhere, that attains >90% conversion over multiple carbonation and calcination cycles. Lastly, thermal regeneration (calcination) under vacuum provided a better sorbent structure that maintained reproducible reactivity levels over multiple cycles.
Owner:THE OHIO STATES UNIV
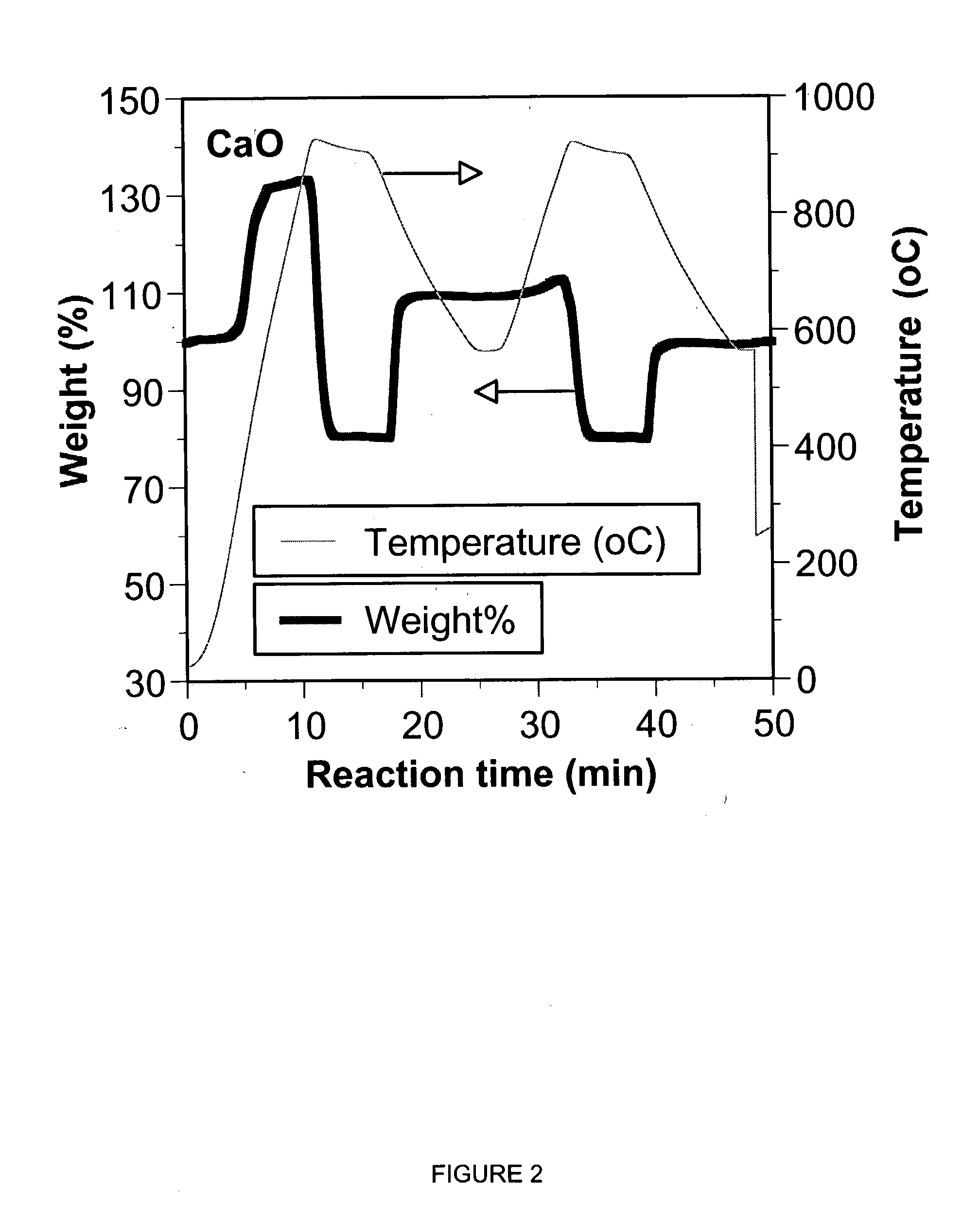
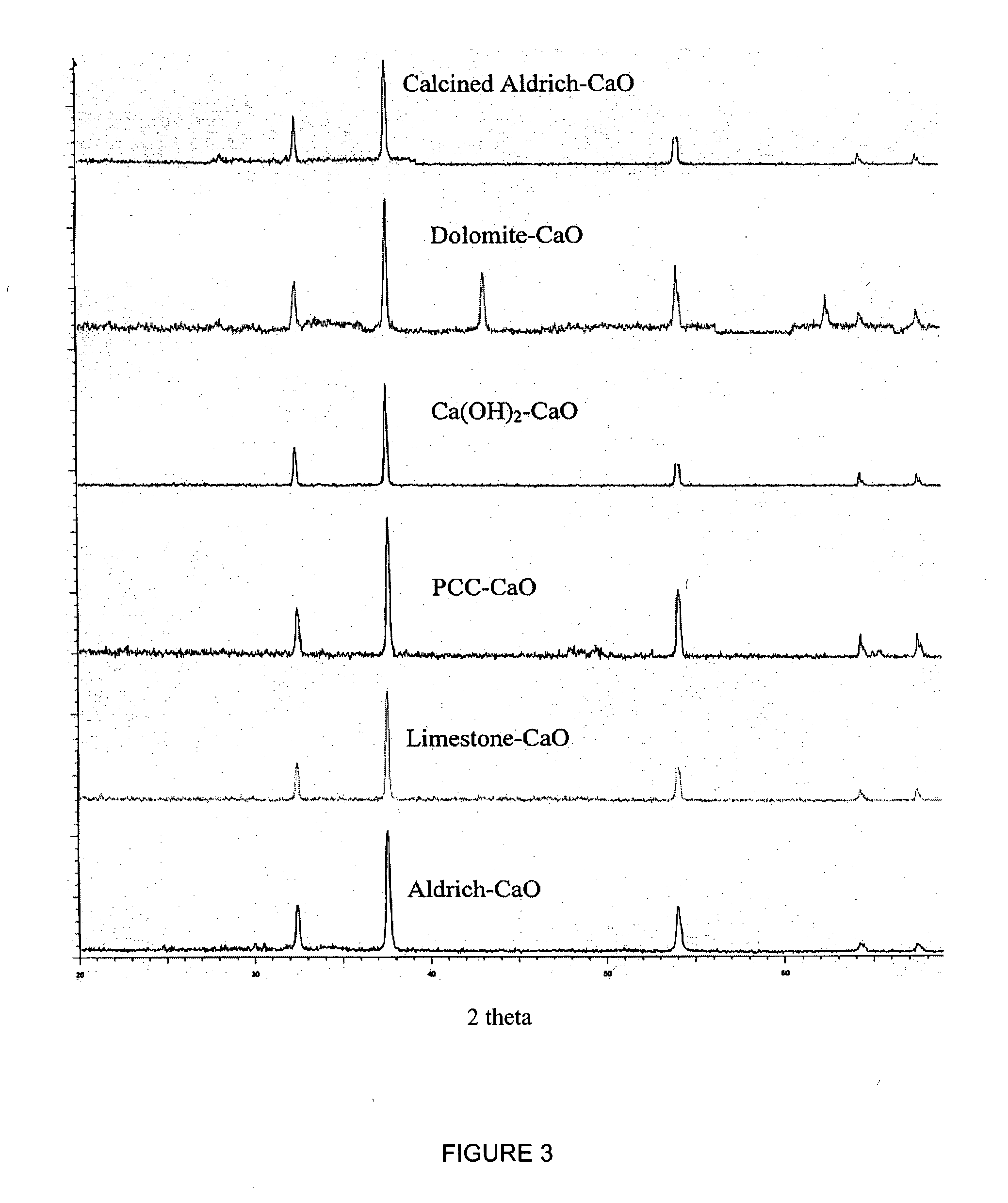
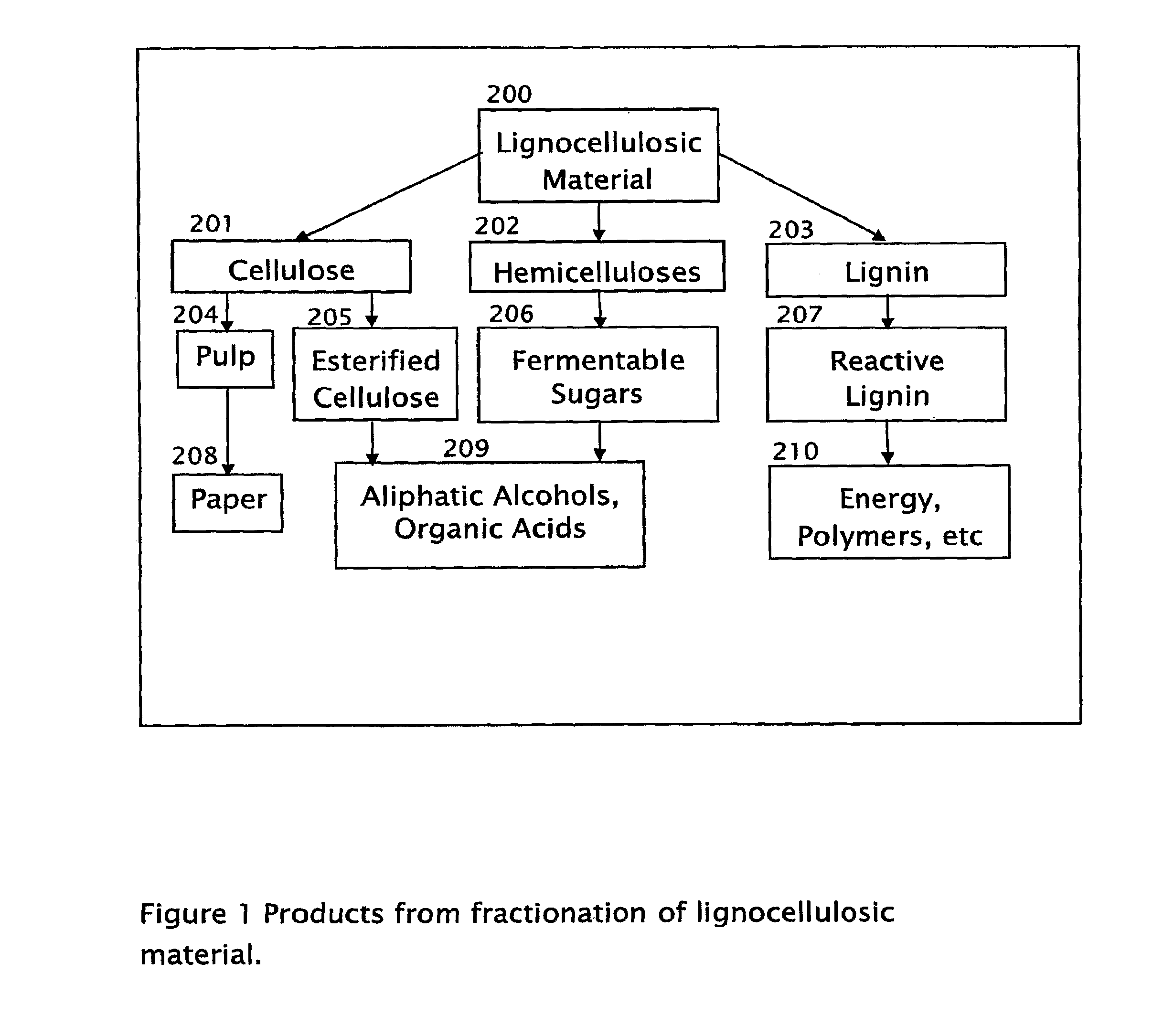
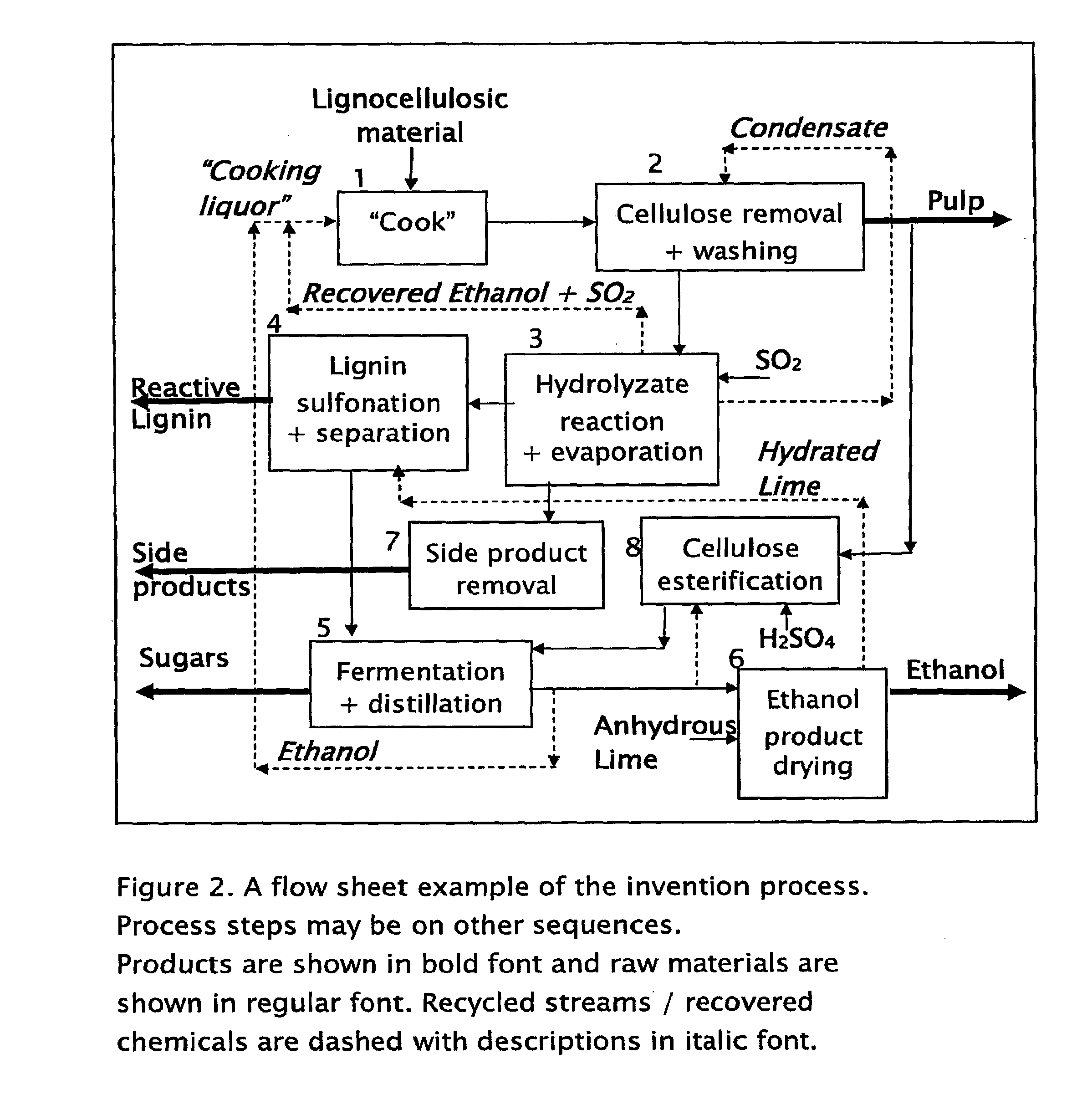
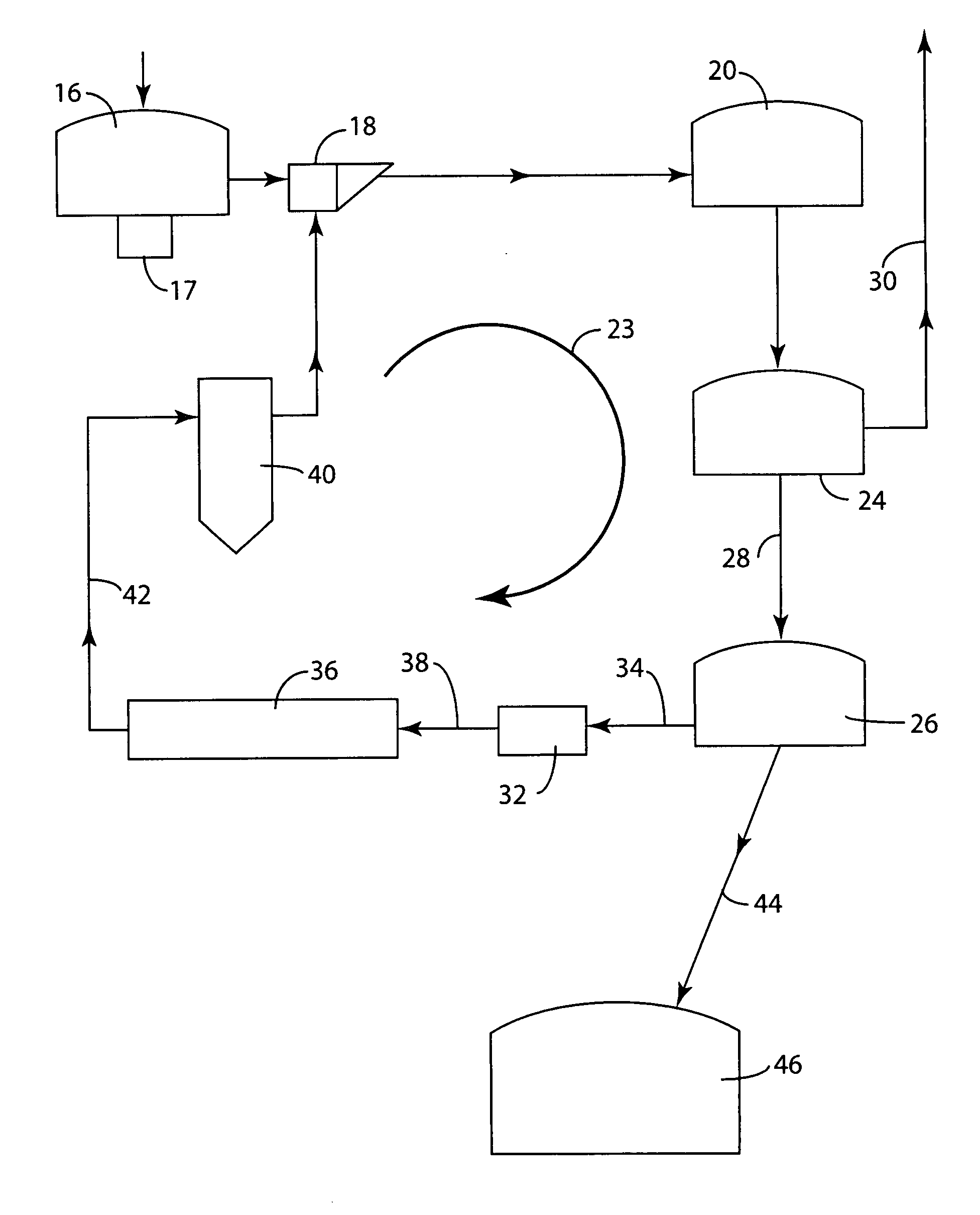
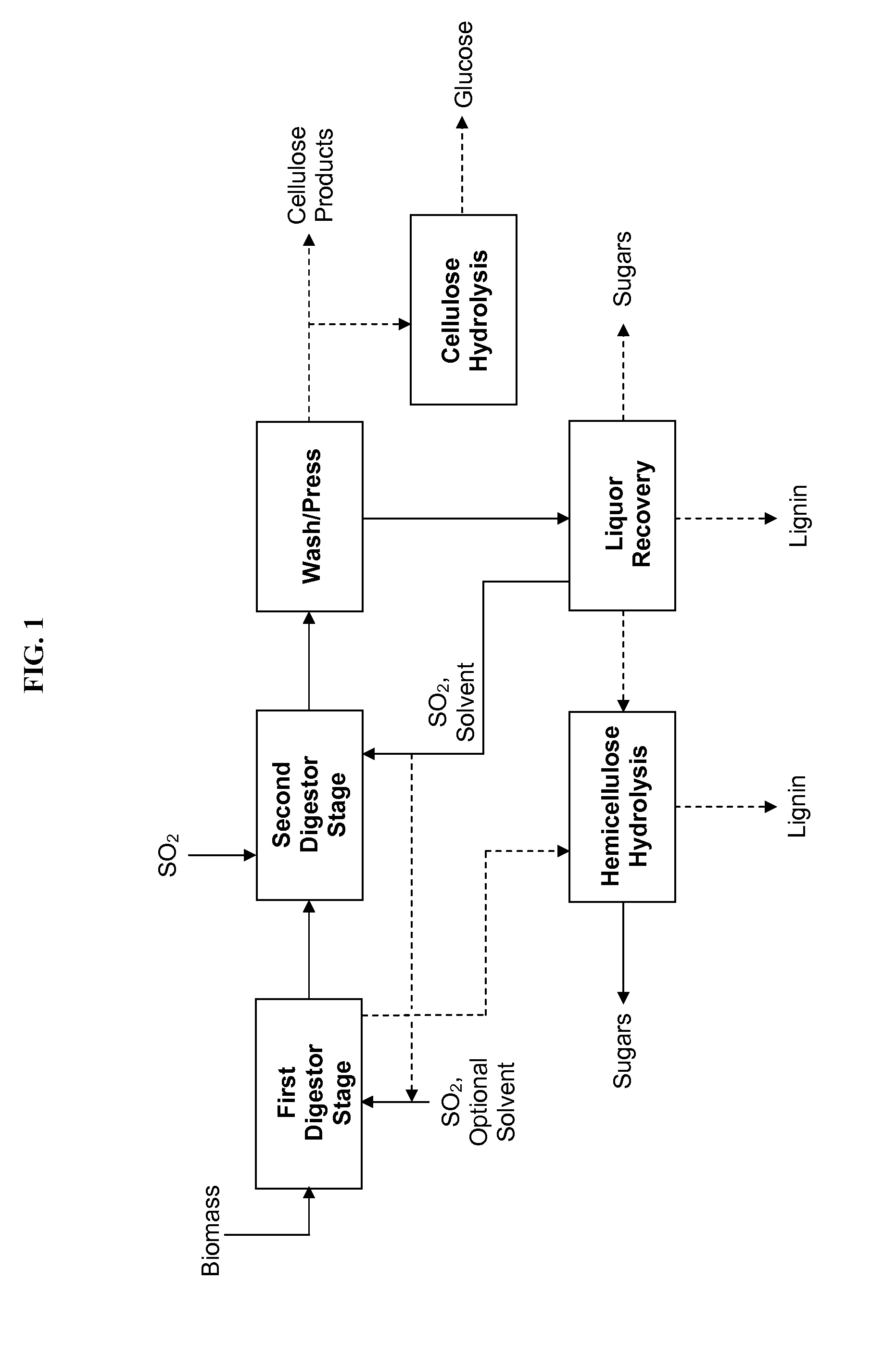
Process for the stepwise treatment of lignocellulosic material to produce reactive chemical feedstocks
InactiveUS20110003352A1Using liquid separation agentCalcium/strontium/barium sulfatesSulfonateLignosulfonates
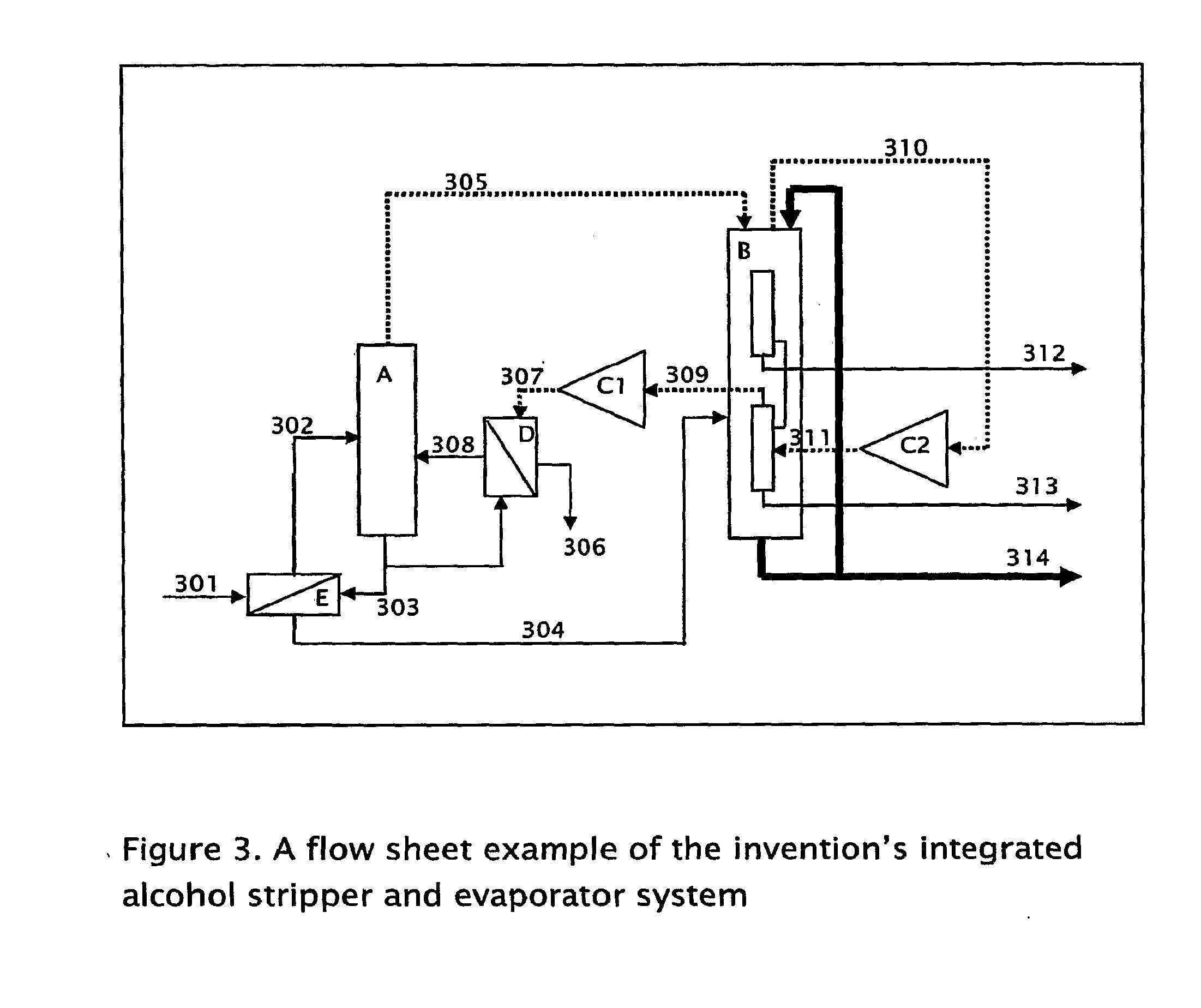
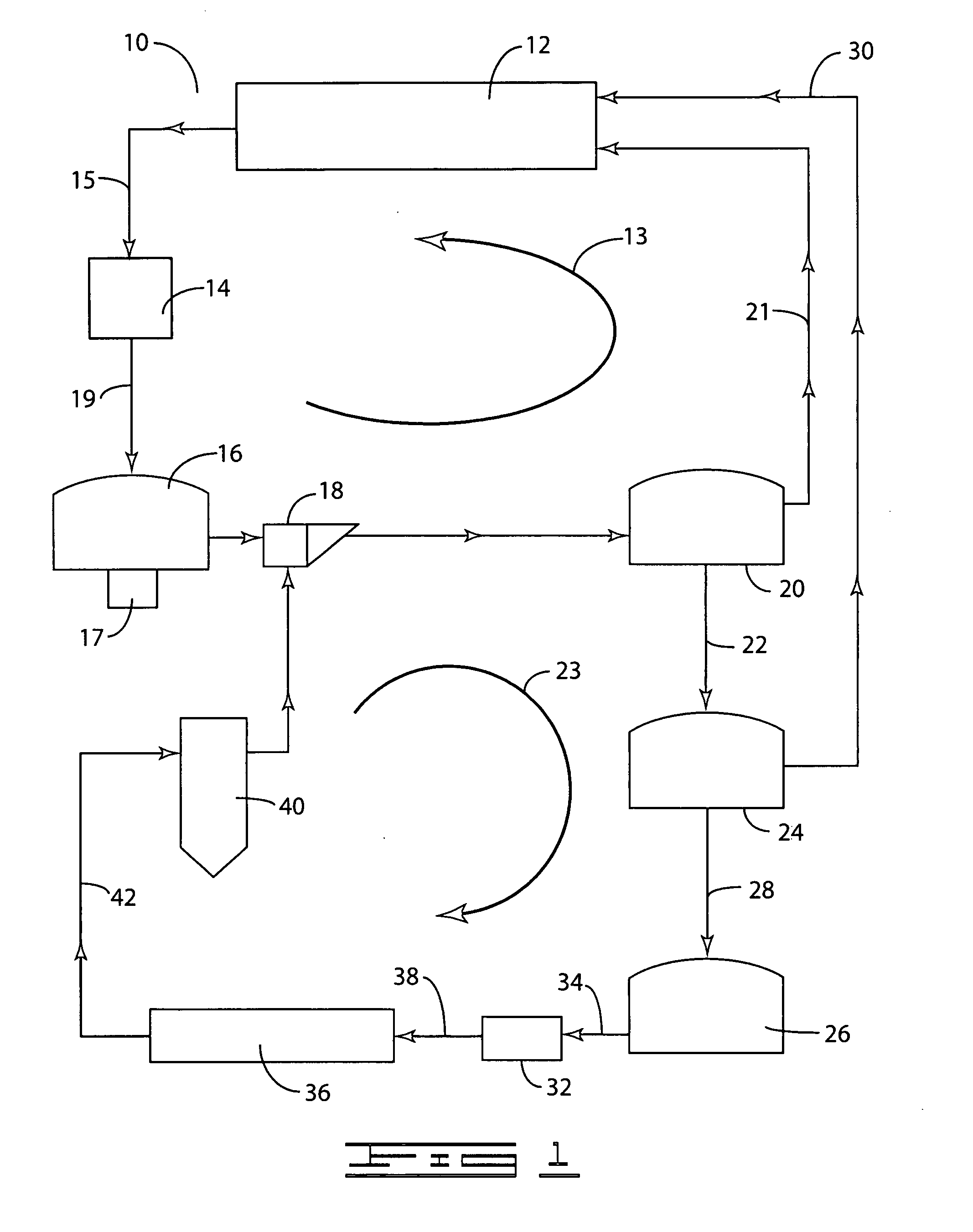
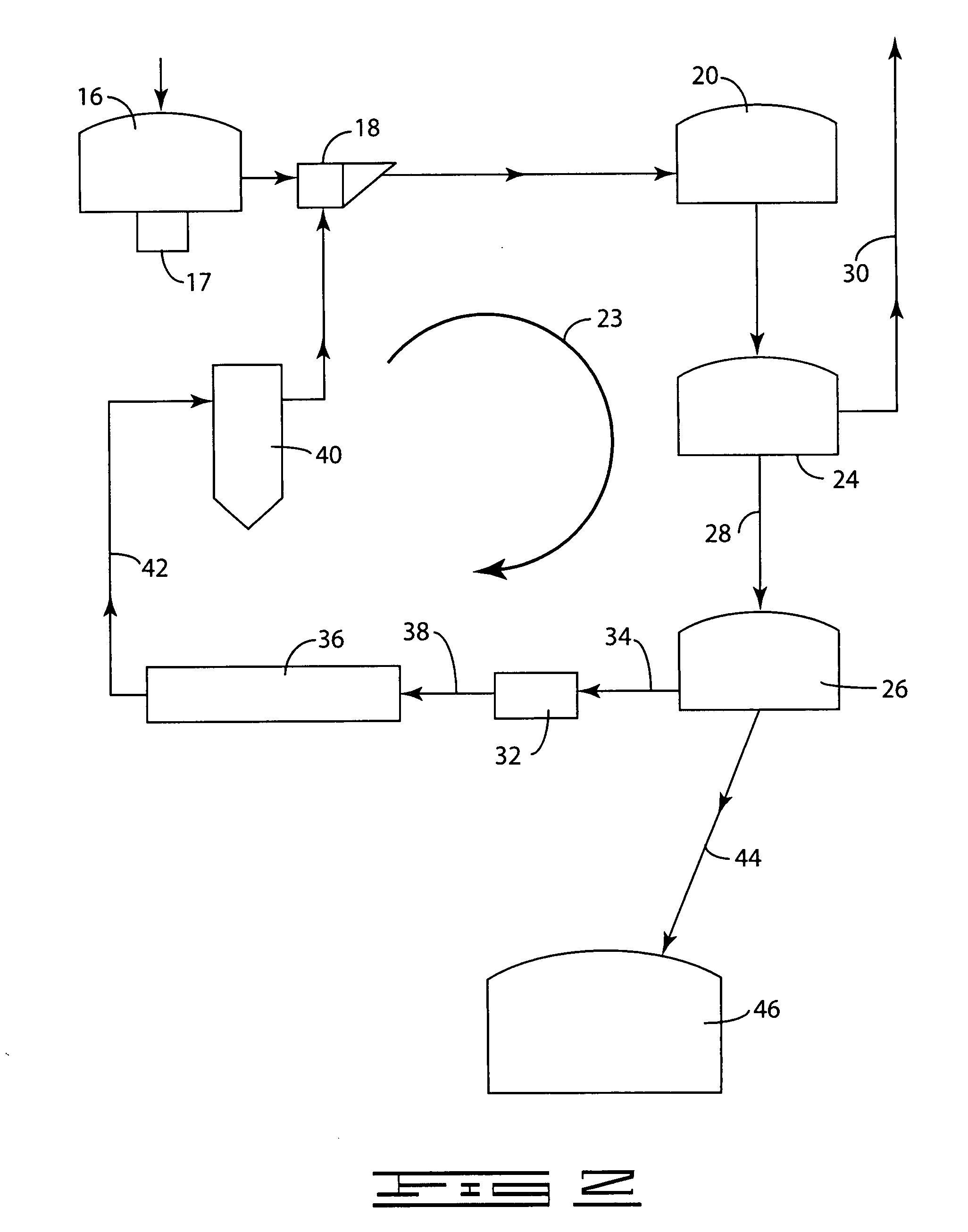
A method for the fractionation of lignocellulosic materials into reactive chemical feedstock in a batch or semi continuous process by the stepwise treatment with aqueous aliphatic alcohols in the presence of sulfur dioxide or acid. Lignocellulosic material is fractionated in a fashion that cellulose is removed as pulp, or converted to esterified cellulose, cooking chemicals are reused, lignin is separated in the forms of reactive native lignin and reactive lignosulfonates and hemicelluloses are converted into fermentable sugars, while fermentation inhibitors are removed. In an integrated vapor compression stripper and evaporator system, aliphatic alcohol is removed from a liquid stream and the resulting stream is concentrated for further processing.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC +1
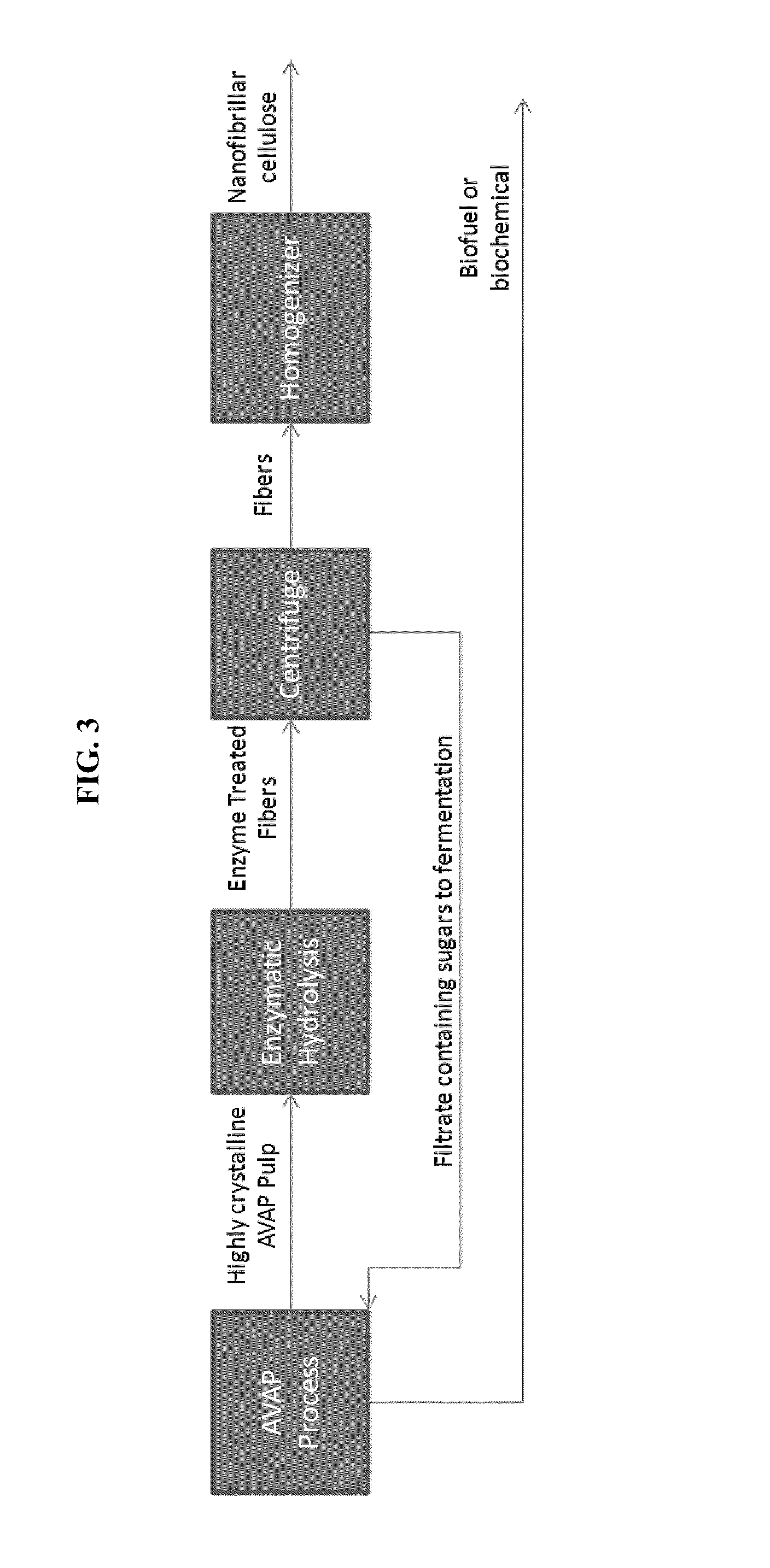
Processes and apparatus for producing nanocellulose, and compositions and products produced therefrom
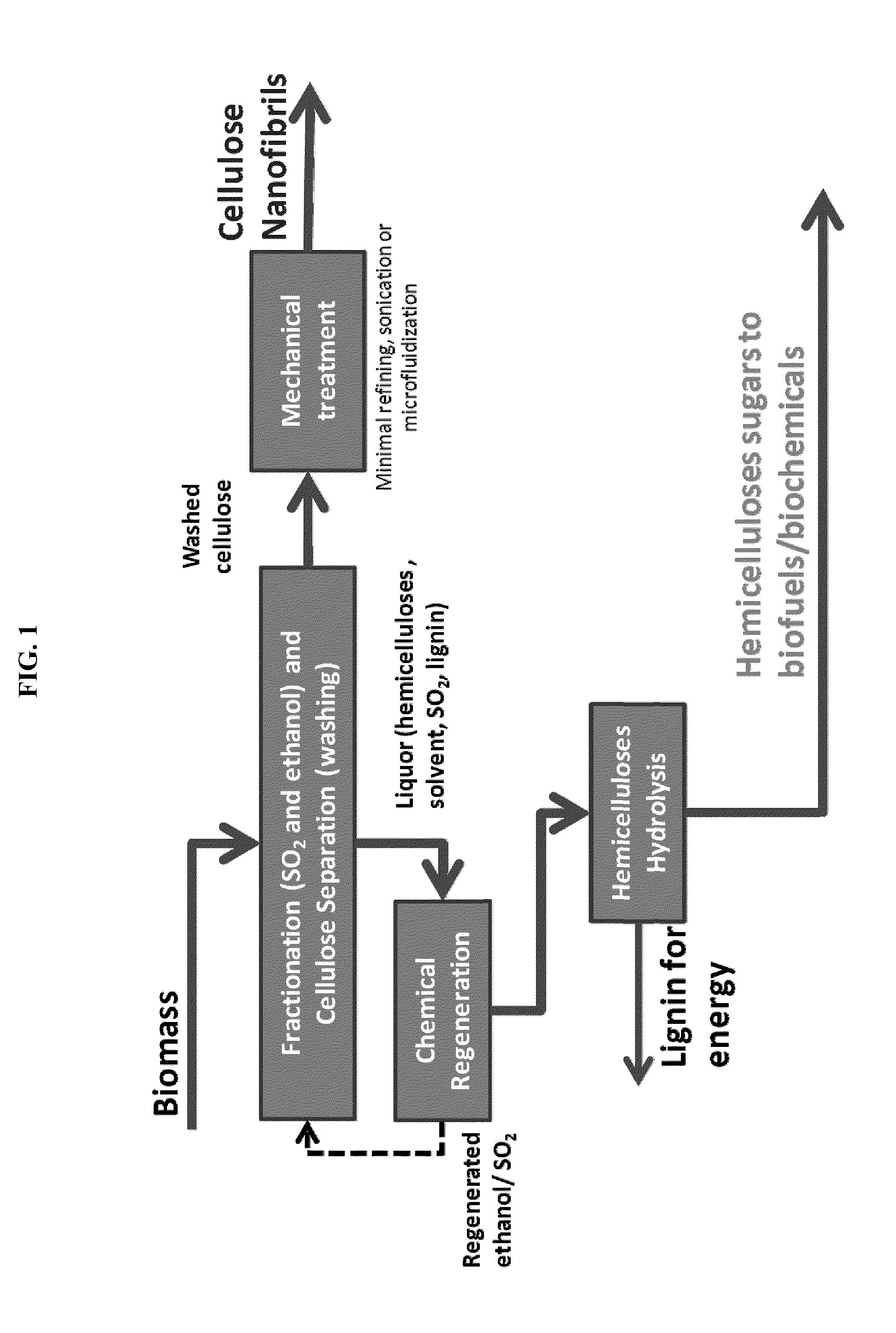
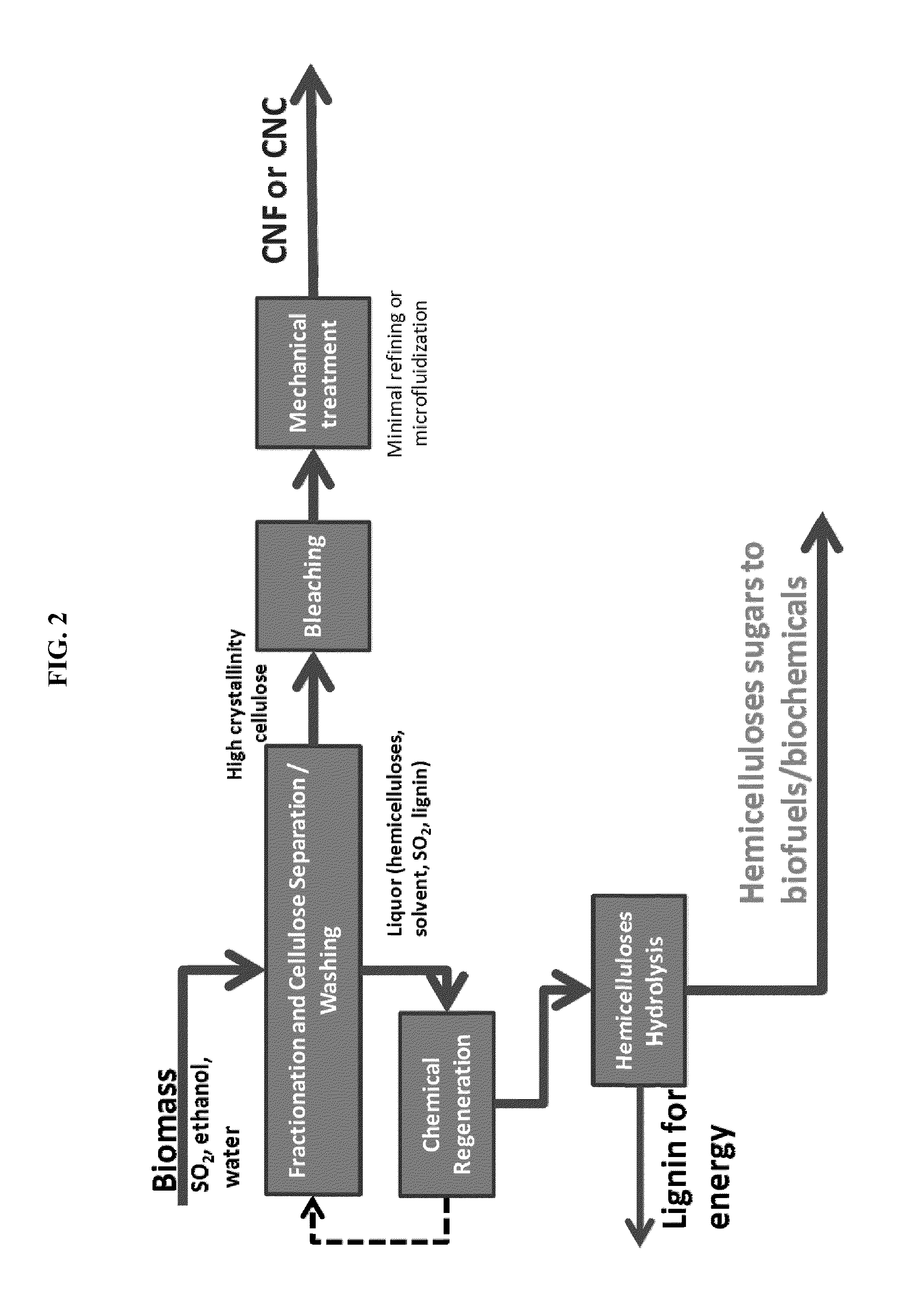
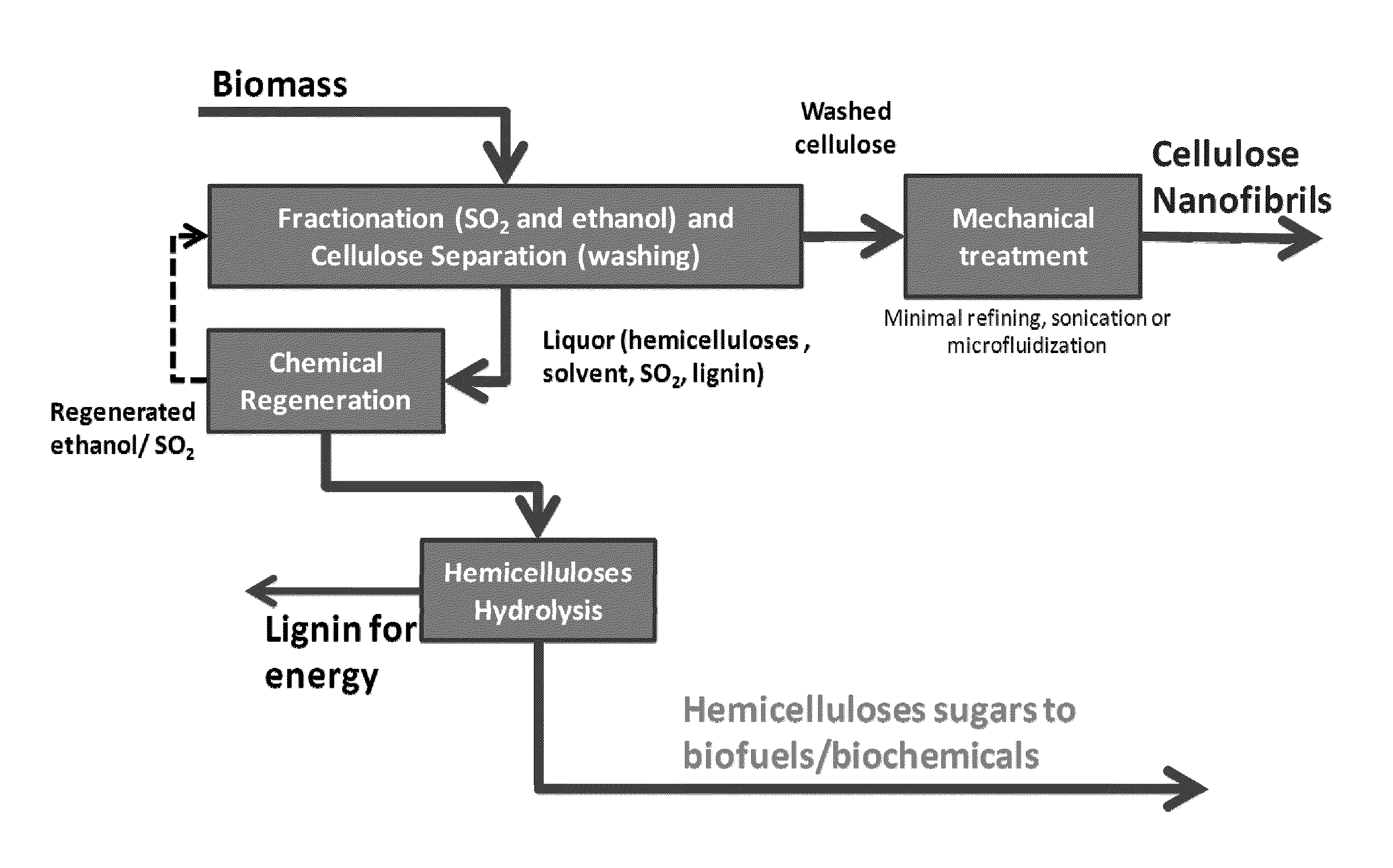
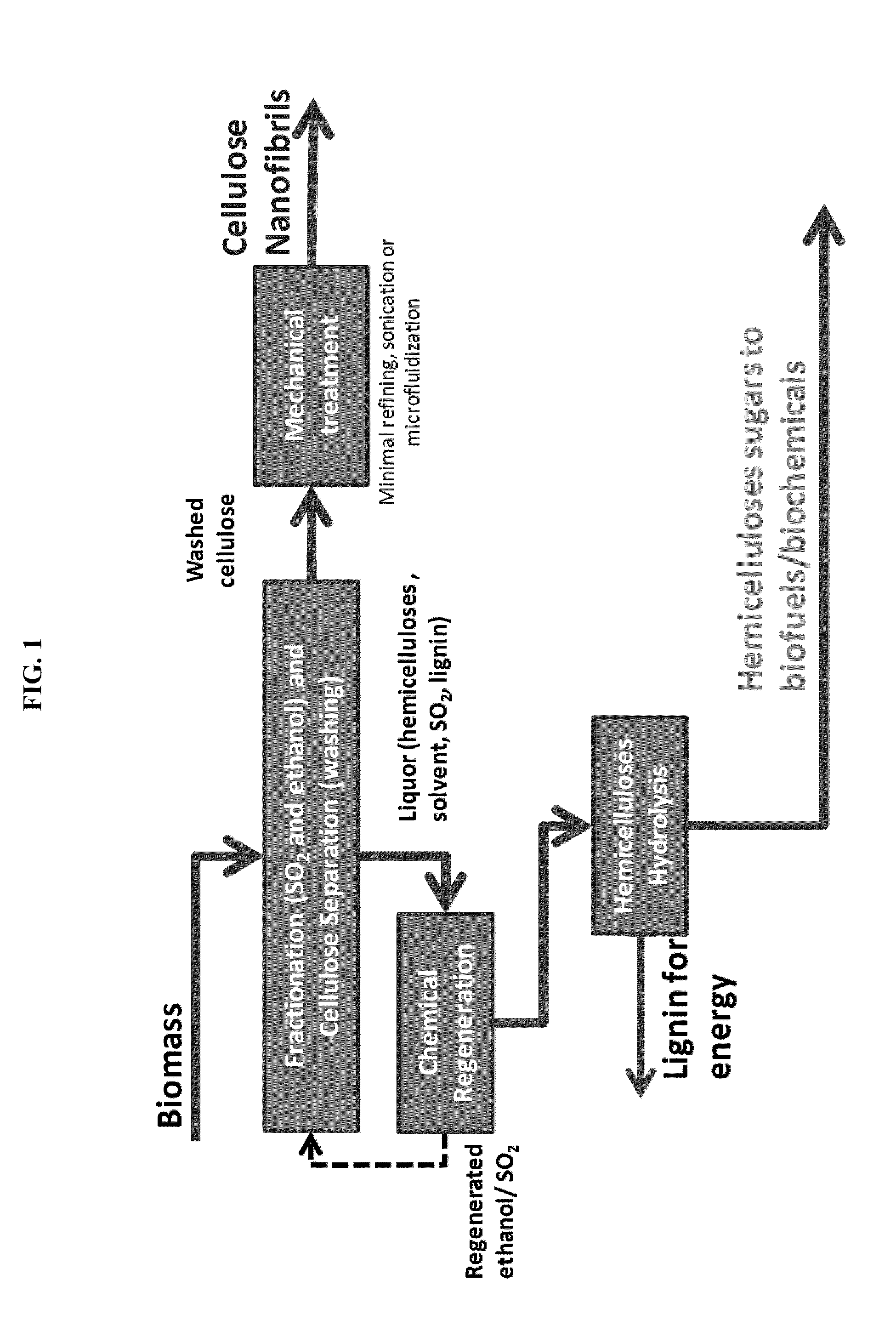
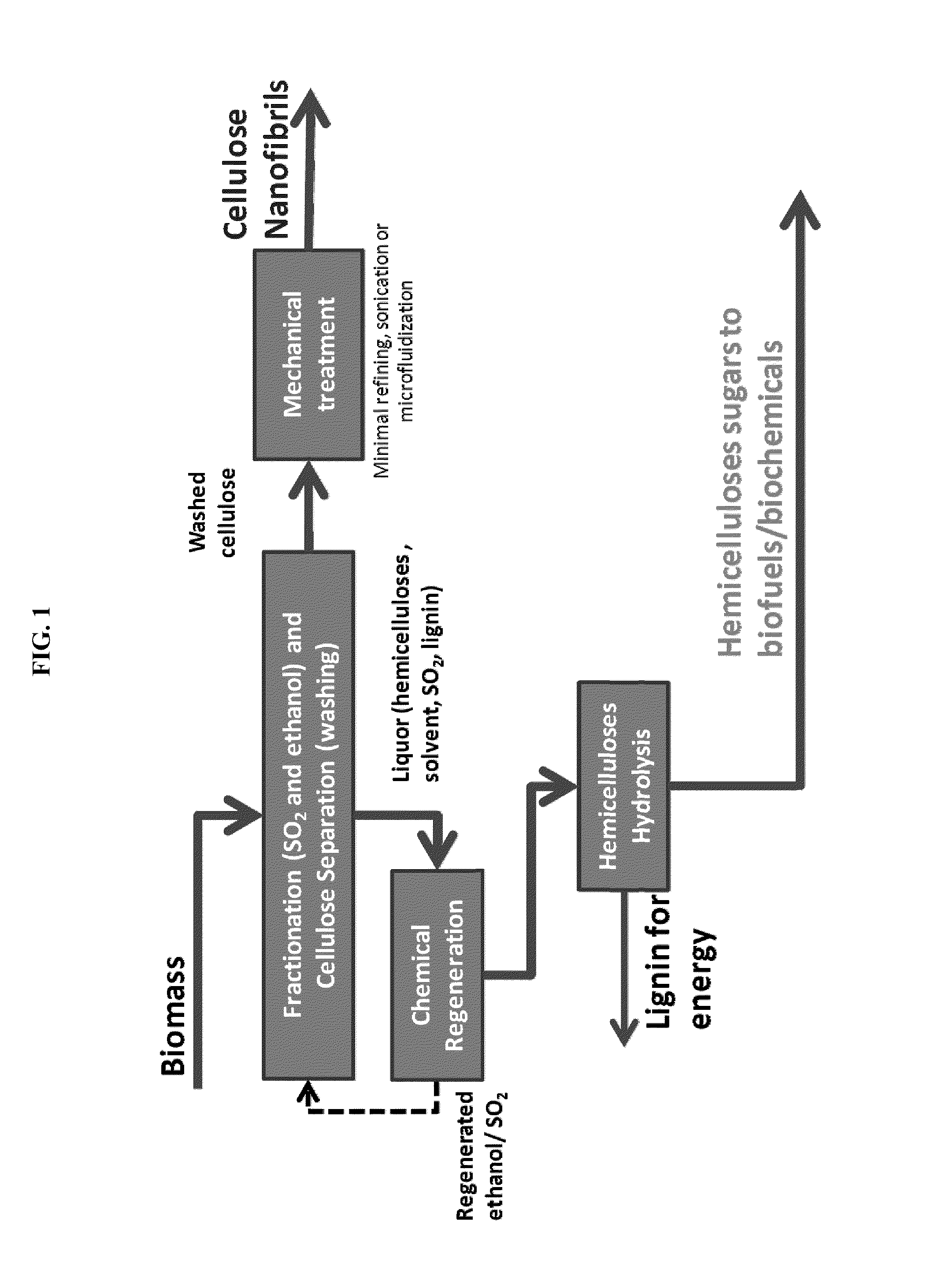
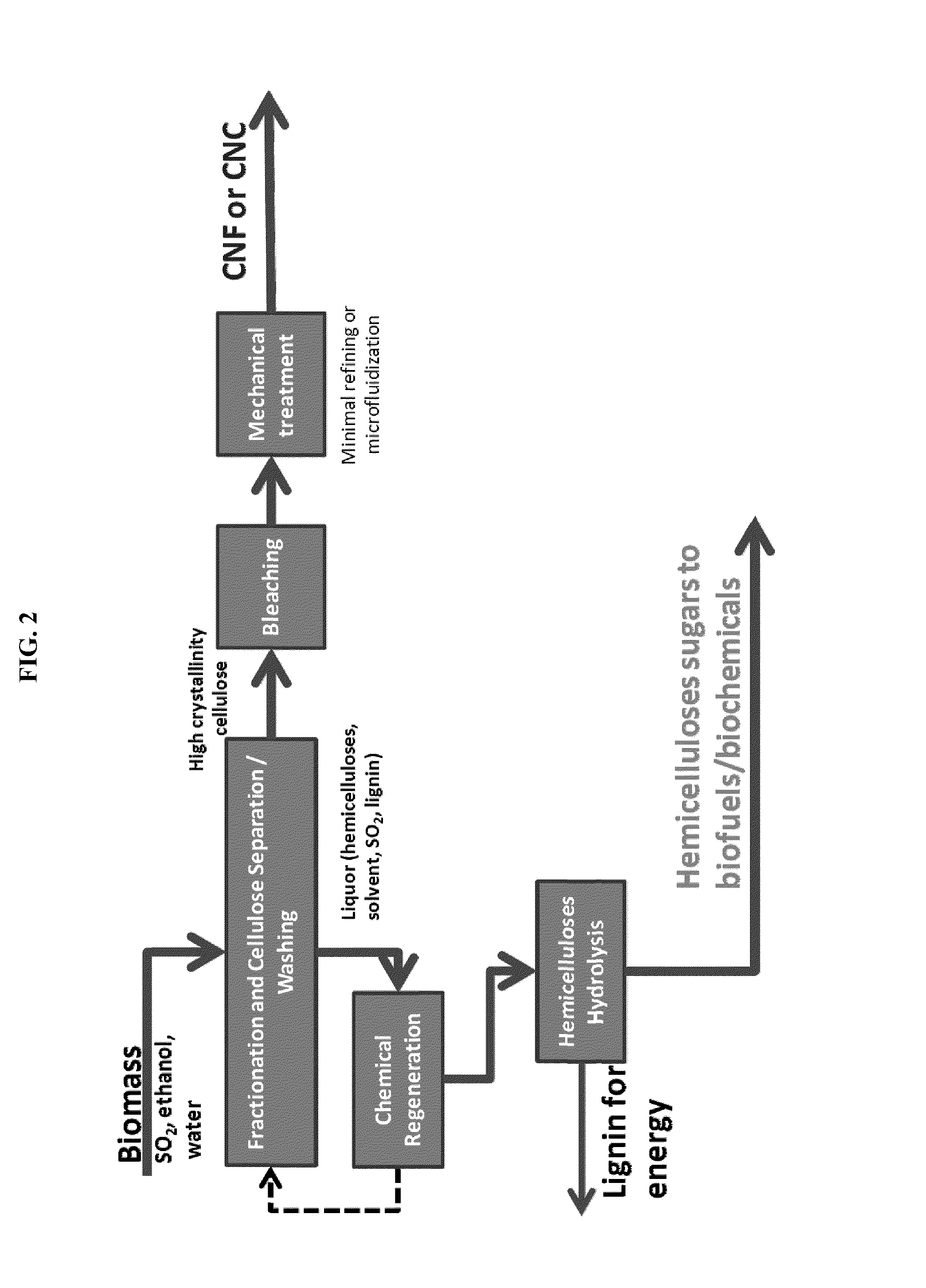
Processes disclosed are capable of converting biomass into high-crystallinity nanocellulose with surprisingly low mechanical energy input. In some variations, the process includes fractionating biomass with an acid (such as sulfur dioxide), a solvent (such as ethanol), and water, to generate cellulose-rich solids and a liquid containing hemicellulose and lignin; and mechanically treating the cellulose-rich solids to form nanofibrils and / or nanocrystals. The total mechanical energy may be less than 500 kilowatt-hours per ton. The crystallinity of the nanocellulose material may be 80% or higher, translating into good reinforcing properties for composites. The nanocellulose material may include nanofibrillated cellulose, nanocrystalline cellulose, or both. In some embodiments, the nanocellulose material is hydrophobic via deposition of some lignin onto the cellulose surface. Optionally, sugars derived from amorphous cellulose and hemicellulose may be separately fermented, such as to monomers for various polymers. These polymers may be combined with the nanocellulose to form completely renewable composites.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Methods for producing pulp and treating black liquor
InactiveUS20060201641A1Maintaining output qualityRaise the reaction temperaturePretreatment with water/steamPulp liquors combustionCalcium silicateOrganic content
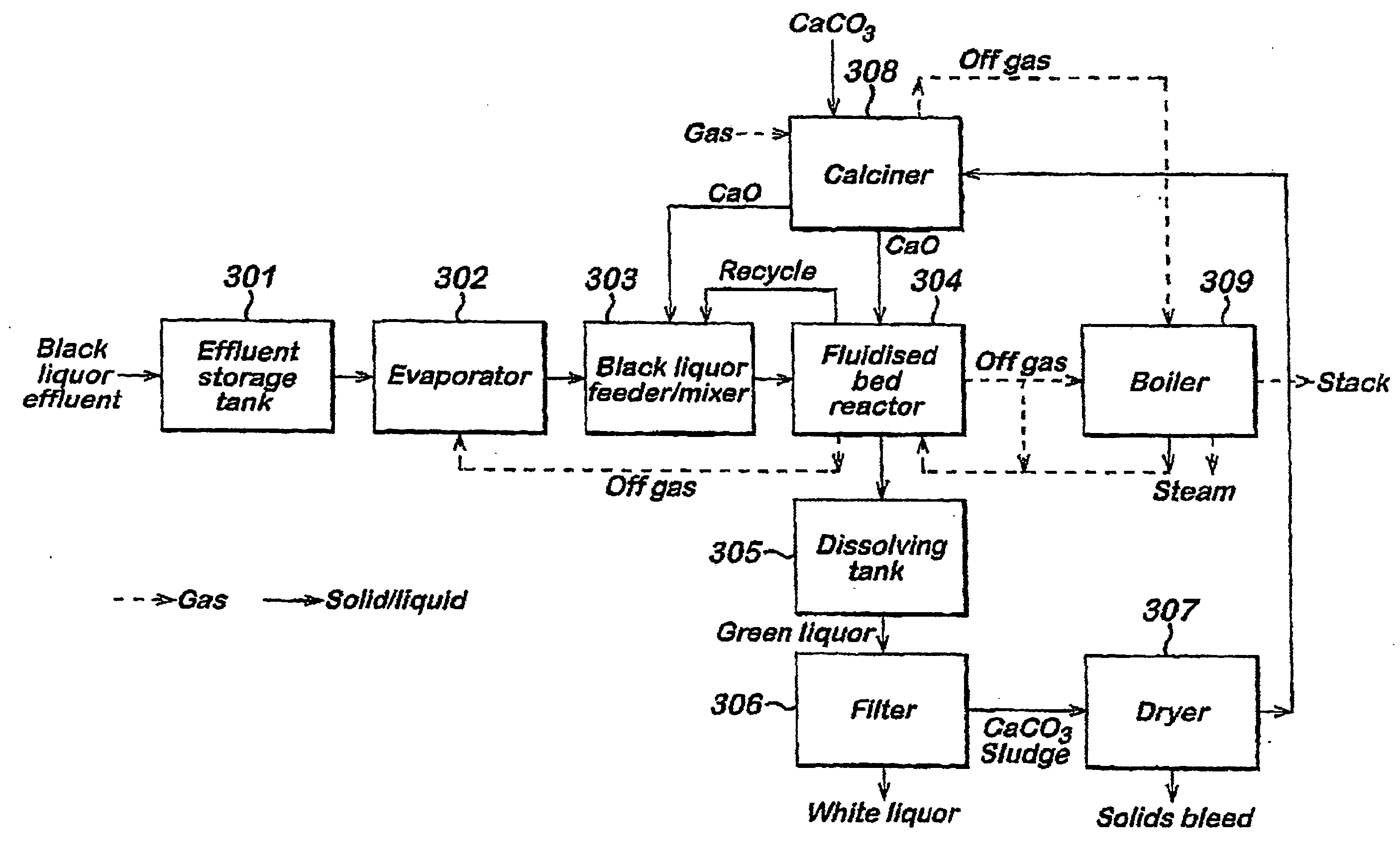
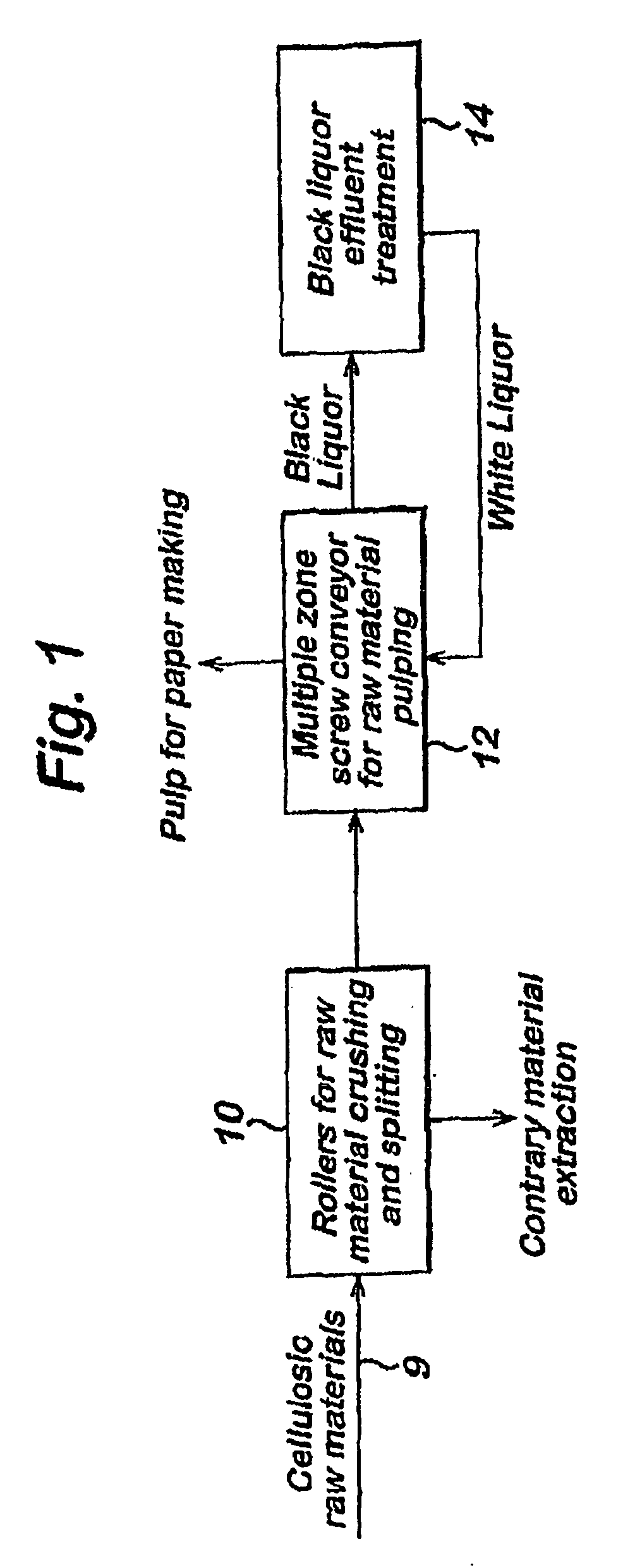
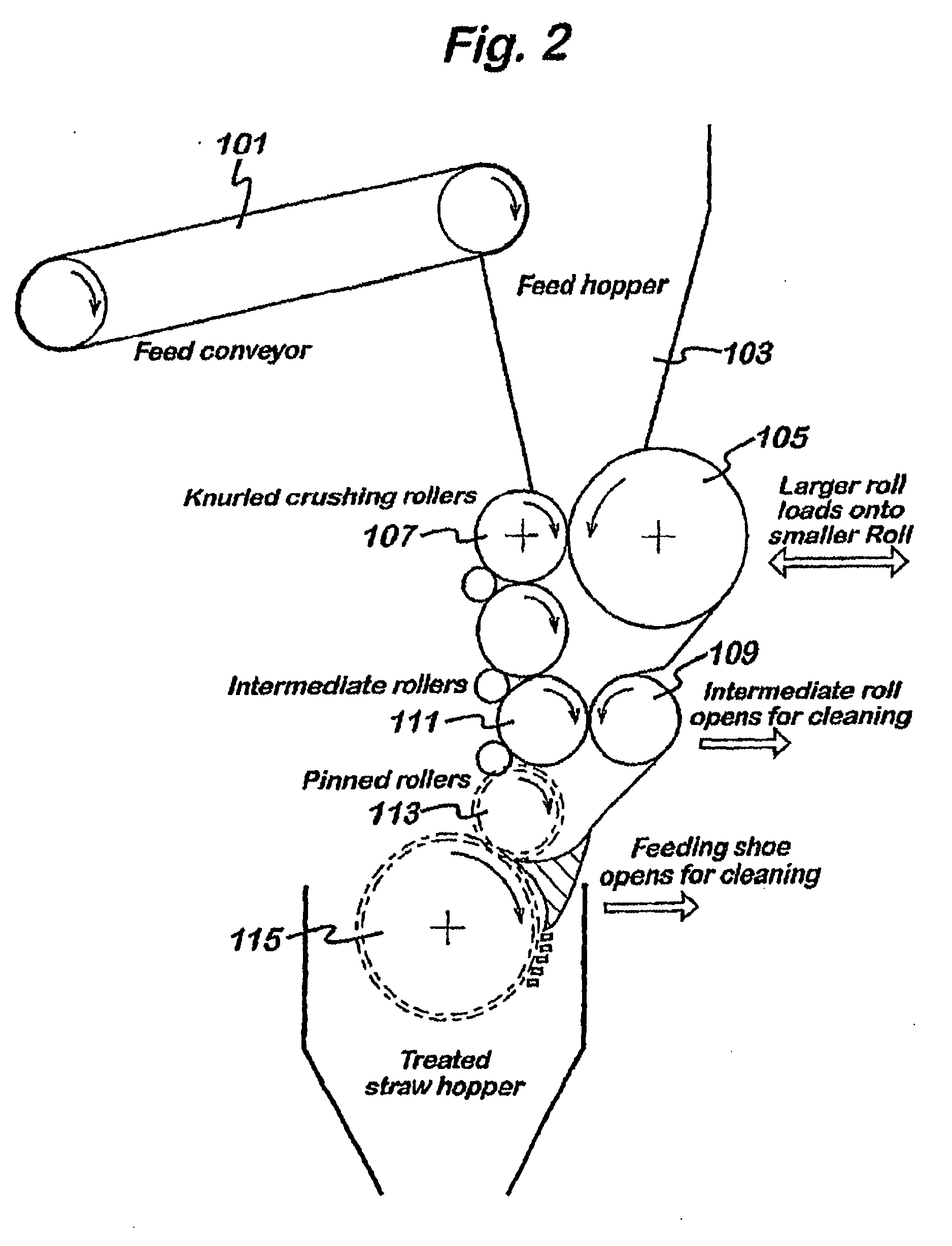
A method is provided for treating black liquor particularly derived from non-wood pulp, by heating with an alkaline earth metal oxide in a toroidal fluidised bed reactor at a temperature of above 650° C. The method may be used alone or as part of a method of converting graminaceous raw material to pulp for paper or board, said method comprising (a) digesting said raw material with a white liquor based on sodium hydroxide and further comprising calcium hydroxide in an amount effective to substantially convert silica of said raw material to calcium silicate; (b) recovering pulp and black liquor substantially free of uncombined silica; (c) heating the black liquor in a fluidized bed reactor containing calcium oxide for catalysing conversion of organic content of said black liquor to gas and for providing recovered solids including sodium values of said white liquor and calcium oxide; and regenerating said white liquor using said recovered solids. The use of the above mentioned white liquor permits treatment of wheat straw, rice straw and other high-silica materials without resulting in a black liquor that is difficult to treat.
Owner:BIOREGIONAL MINIMILLS UK
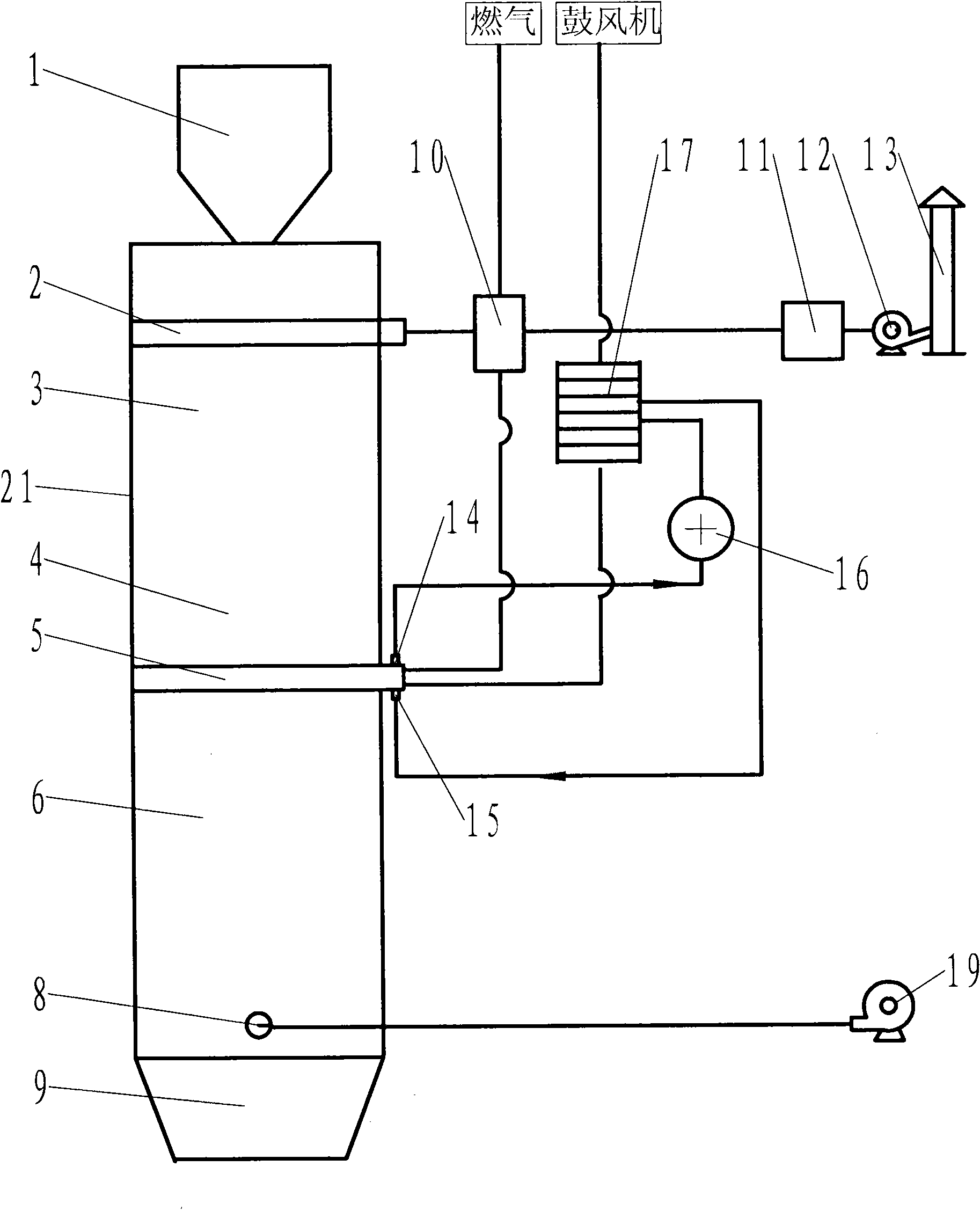
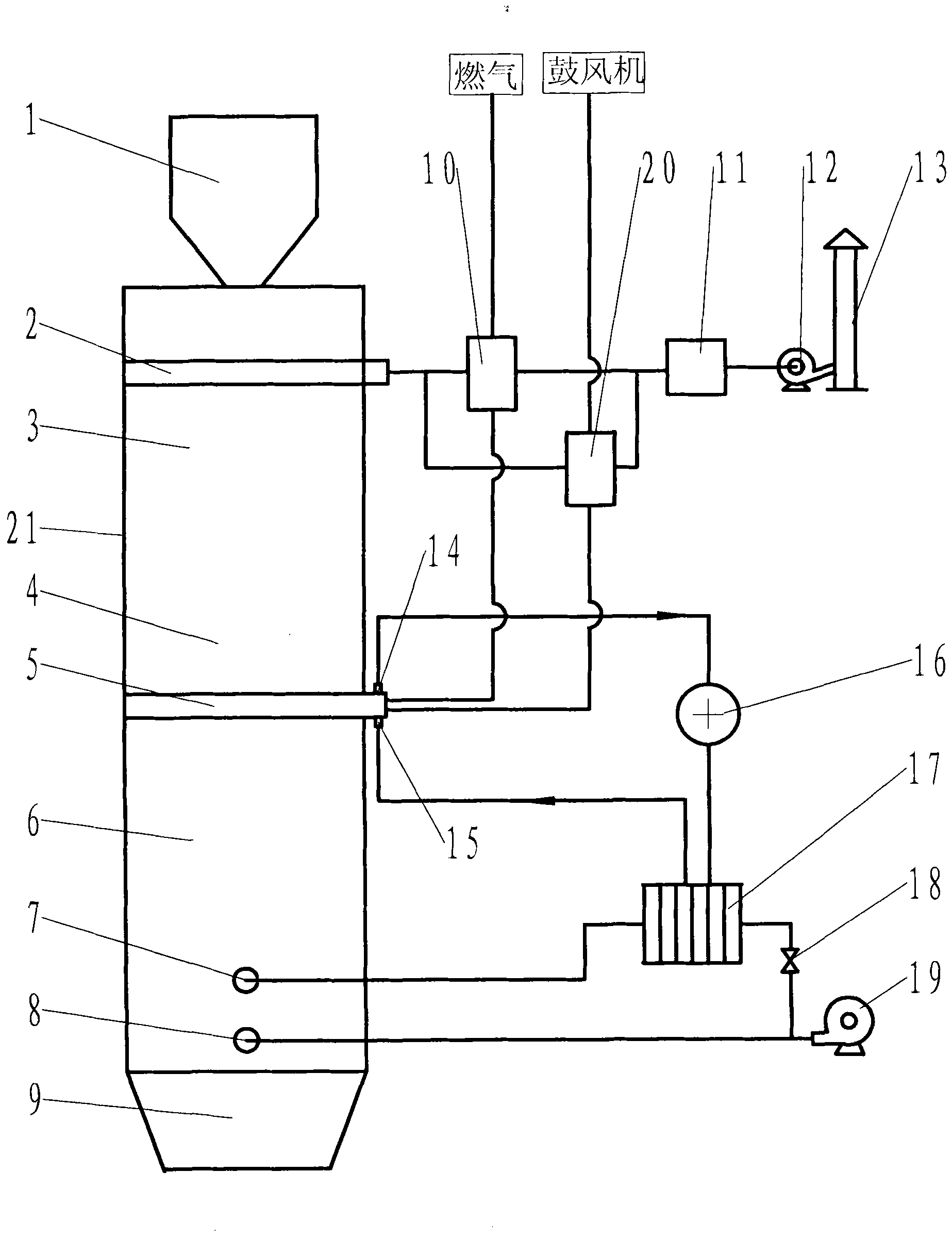
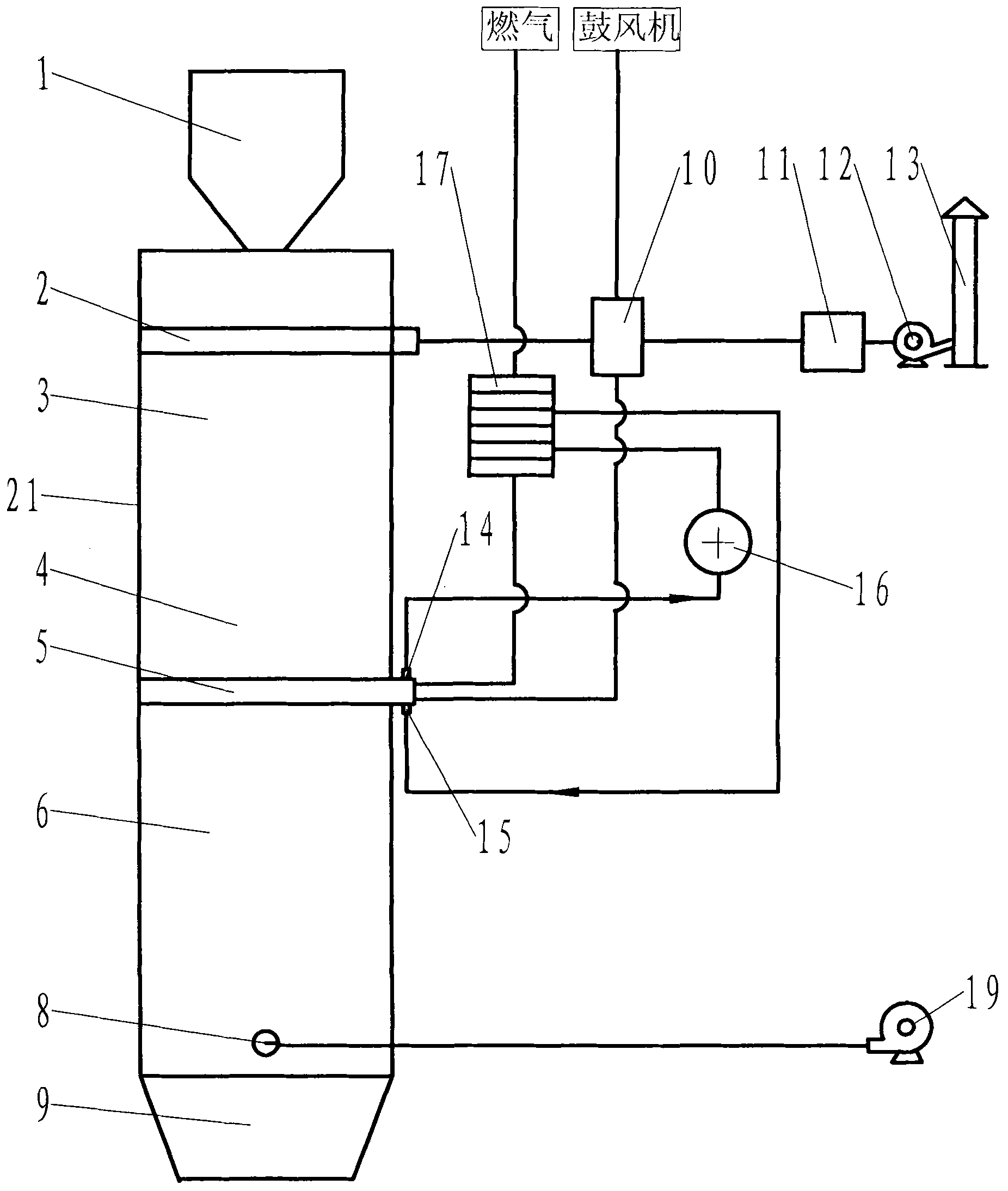
Vertical continuous calcination lime burner
InactiveCN101195520AHigh activityCalcination process is reasonableLime productionInterior spaceLime kiln
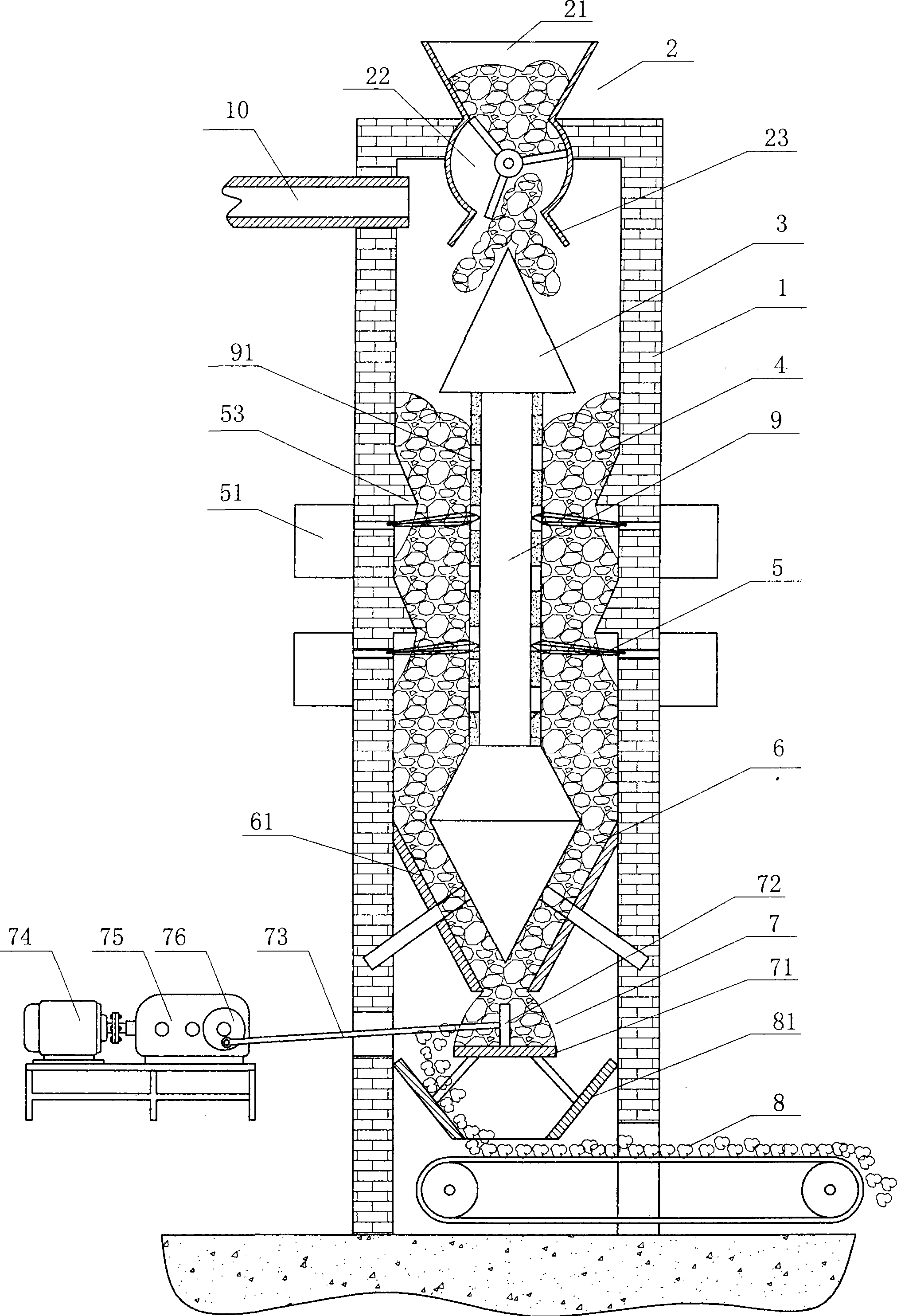
The invention discloses a vertical and continuously calcining lime kiln, including a cylindrical kiln body. From the top down, the kiln body is successively provided with an air-lock feeding device, a distributing device, a preheating zone, calcining zone, cooling zone and a continuously discharging device. The air-lock feeding device is located on the top of the kiln body, the distributing device is located on the upper of the inner chamber of the kiln body, the preheating zone is located below the distributing device, the calcining zone is located below the preheating zone, the cooling zone is located below the calcining zone and the continuously discharging device is located below the discharge port but at the cooling zone. The top of the kiln body is equipped with air discharge pipe, heat wind exhaust passage which is devised axially along the kiln body and can extend to the preheating zone is equipped in the inner space of the kiln body, and a plurality of air outlets and inlets are equipped on the copper wall of the heat wind exhaust passage. The invention enables to continuously manufacture, can control the lime in the kiln to drop with a uniform speed, has no sintering phenomenon, can control the lime to fall with constant speed on every level surface in the kiln and completely put an end to undersintering and oversintering.
Owner:黄官禹
Calcination process of active lime
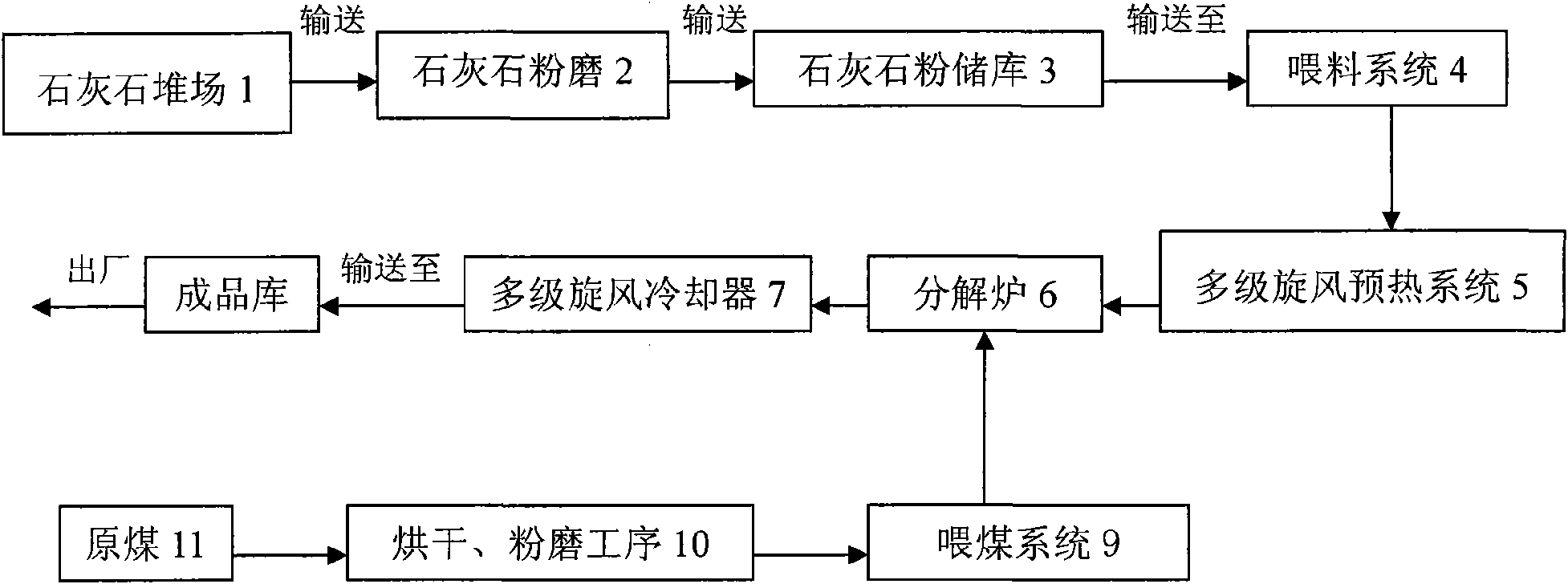
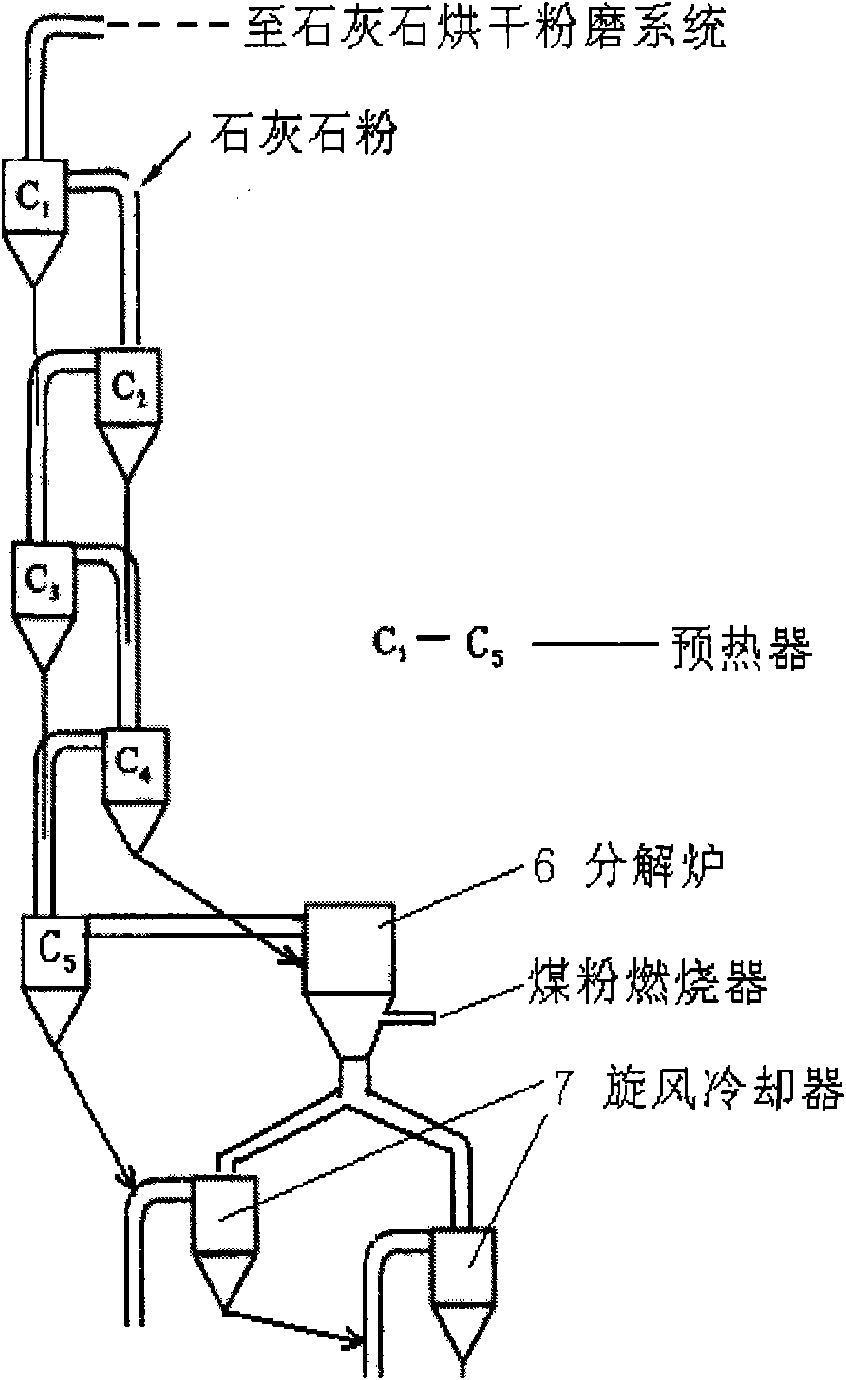
The invention discloses a calcination process of active lime. The calcination process adopts a preheating-suspension calcination device comprising a multi-stage cyclone preheating system, a decomposing furnace and a multi-stage cyclone cooler. The calcination process is characterized in that limestone powder which is broken and homogenized into blocks is ground into fine powder, the fine powder is placed in a storage tank for homogenization, then preheated by the multi-stage cyclone preheating system and sent to the decomposing furnace for calcination, thereby preparing the active lime, and the active lime is further cooled by the multi-stage cyclone cooler for obtaining the active lime; wherein the main control temperature of the decomposing furnace is 850-950 DEG C; and the calcination time is 3-5 seconds. The calcination process utilizes the preheating-suspension calcination reaction method for calcining the active lime, and fuel can use low-grade fuel-biluminous coal. Compared with the traditional process, the calcination time is short, the effective utilization rate of the lime product is high, the product quality is stable, the energy consumption is low, and a production region has no environmental pollution; meanwhile, the calcined active lime is the fine powder, the use is very convenient, and the range of applications is broader in comparison with the active lime calcined by the traditional process, thereby being conductive to promotion and implementation.
Owner:BEIJING LIULIHE CEMENT
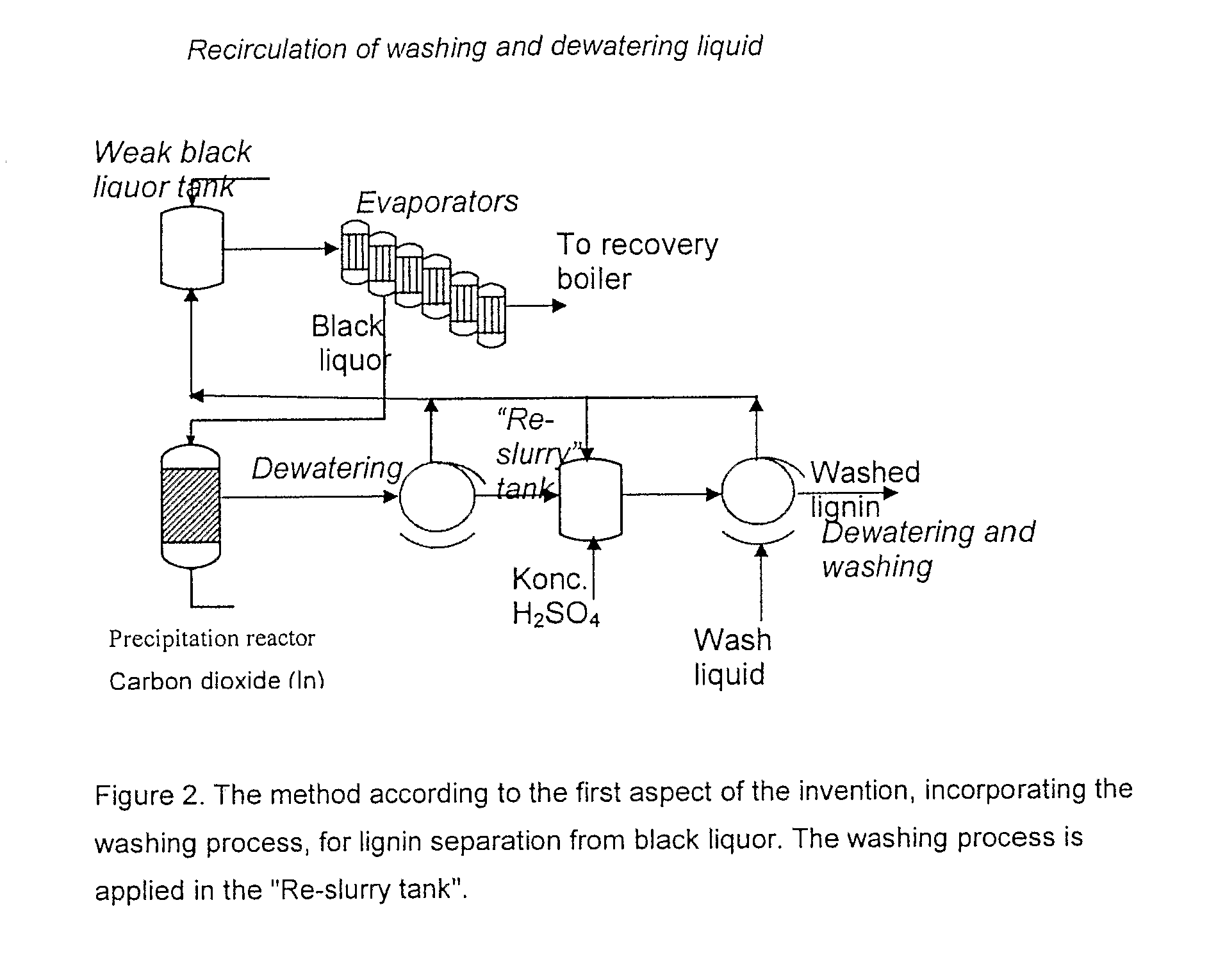
Method for Separating Lignin from Black Liquor
ActiveUS20080047674A1Smoother resultAvoid cloggingLignin derivativesPulp by-products recoveryLignin degradationBlack liquor
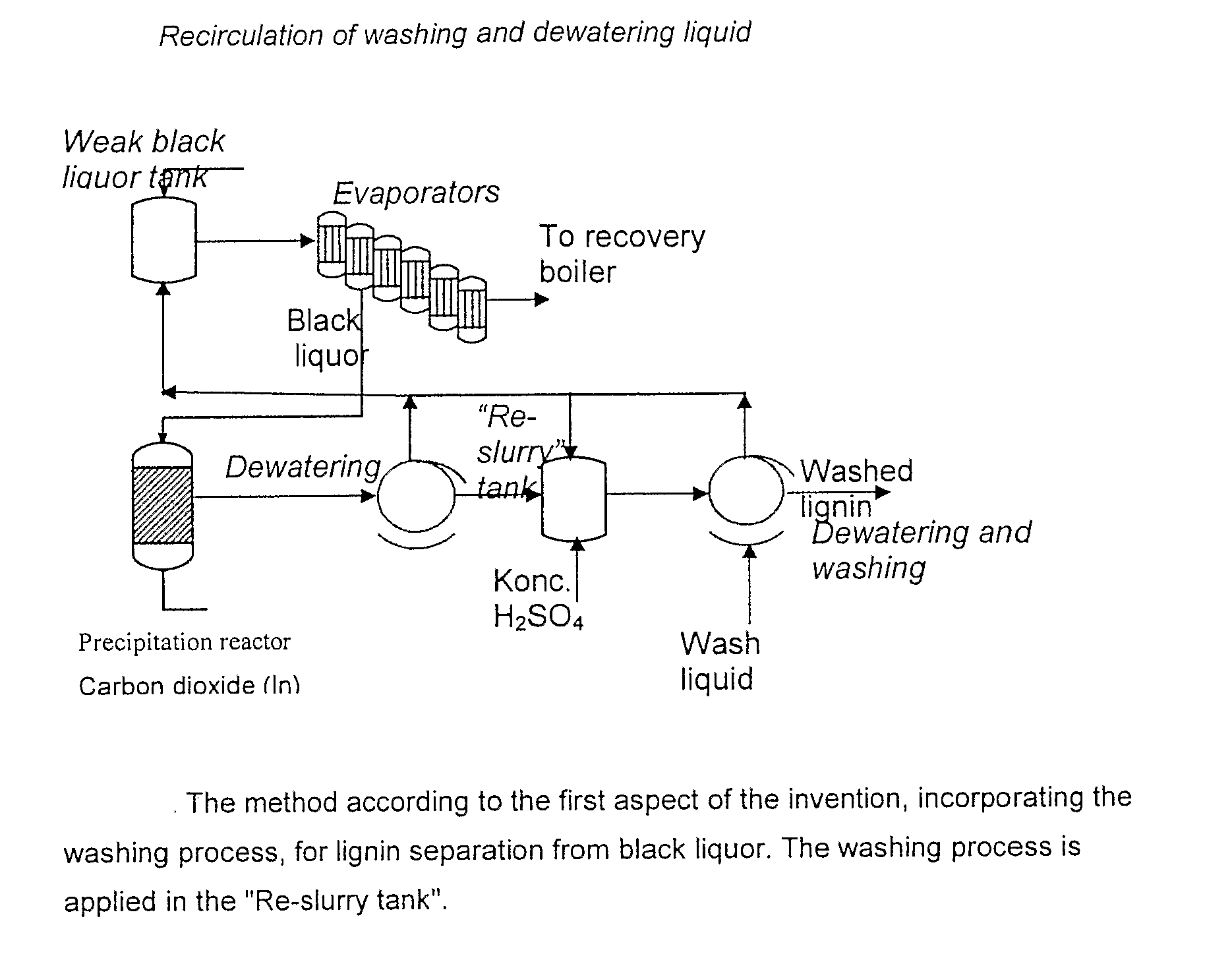
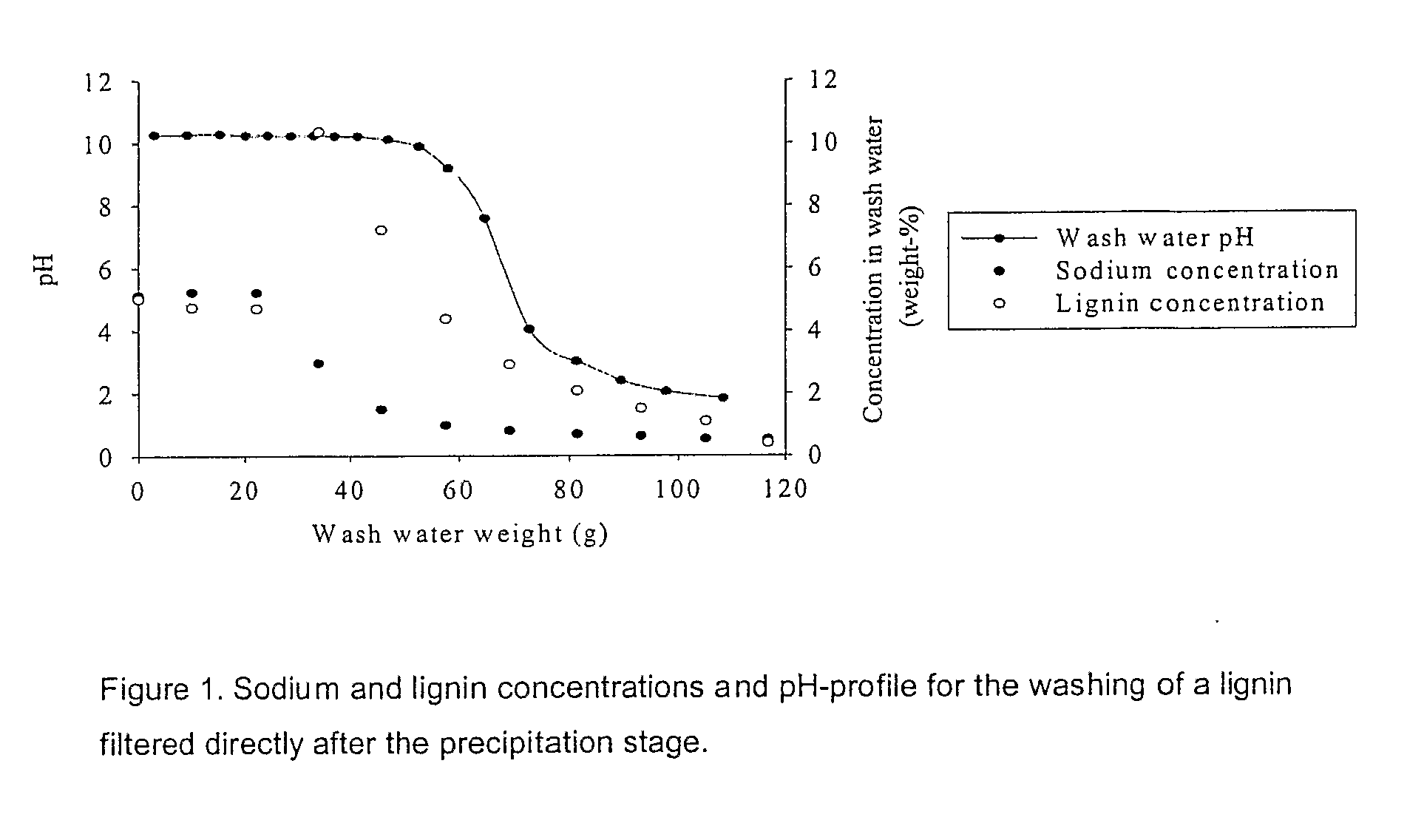
Method for separating lignin from black liquor includes the following steps: a) precipitating lignin by acidifying black liquor and thereupon dewatering, b) suspending the lignin filter cake obtained in step a) to obtain a second lignin suspension and adjusting the pH level to approximately that of the washing water of step d) below, c) dewatering of the second lignin suspension, d) adding washing water and performing a displacement washing at substantially constant conditions without any dramatic gradients in the pH, and e) dewatering the lignin cake produced in step d) into a high dryness and displacing the remaining washing liquid in the filter cake, whereby a lignin product is obtained which has an even higher dryness after the displacement washing of step d). The lignin product or an intermediate lignin product obtained by the method, and its use, preferably for the production of heat or chemicals is also disclosed.
Owner:LIGNOBOOST
Converter less-slag smelting process
The invention relates to a converter less-slag smelting process, belonging to the converter steelmaking field. The invention has the following main process characteristics: decarburization slag and dephosphorization slag with high dephosphorization rate in the dephosphorization period and decarburization period and high poured phosphorus content are recycled in the converter blowing process and the aims of reducing the consumption of converter lime and reducing the consumption of the steel material can be achieved. The converter smelting process is divided to a dephosphorization period and a decarburization period. In the dephosphorization period, lower flow is adopted for blowing, slag is poured after the dephosphorization period, the slag-removing rate is more than 30%; slag is conserved after the decarburization period, the decarburization slag is recycled, the dephosphorization efficiency is increased to reduce the additive amount of lime; the lime of the dephosphorization period is reduced gradually and the lime of the decarburization period is increased gradually, with the increase of heats; the balance can be achieved after 3-5 heats; and compared with the normal smelting method, the total consumption of lime of the method is reduced by 30%-60% when the balance is achieved.
Owner:SHOUGANG CORPORATION
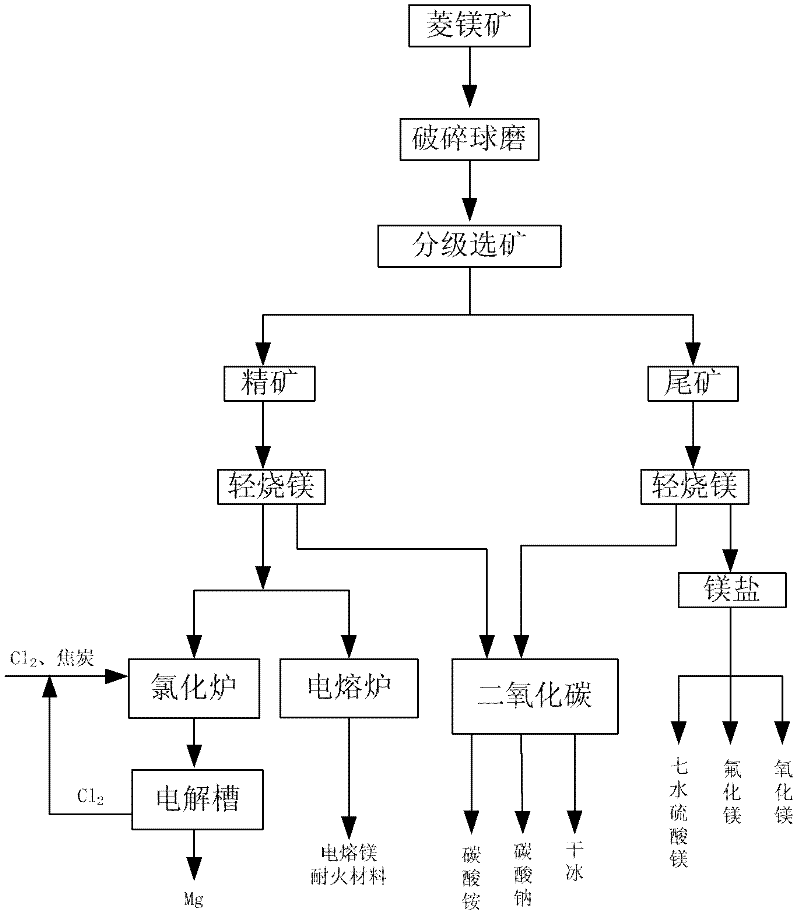
Integrated utilization method of low grade magnesite
InactiveCN102515213ASave raw materialsSimple processCarbon compoundsAmmonium carbonates/bicarbonatesElectrolysisMagnesium salt
The invention belongs to the fields of integrated utilization technology of magnesite and environmental protection, and relates to an integrated utilization method of low grade magnesite. The method comprises steps of: magnesite fragmentation; ore grinding; ore dressing; ore dressing product calcining; conversion of calcined useful components into magnesium salt to prepare high purity magnesium oxide or direct electrolysis of the calcined useful components into magnesium metal or preparation of refractory material; and recovery utilization of gas generated by calcination. The invention comprehensively utilizes useful ingredients in the magnesite, realizes zero discharge of magnesite mine tailing, increases utilization rate of low grade magnesite and efficiently utilizes ore resource; and especially, fluidized roasting by a horizontal fluidized bed saves energy consumption and maximize economic benefit.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Processes and apparatus for producing nanocellulose, and compositions and products produced therefrom
Processes disclosed are capable of converting biomass into high-crystallinity nanocellulose with surprisingly low mechanical energy input. In some variations, the process includes fractionating biomass with an acid (such as sulfur dioxide), a solvent (such as ethanol), and water, to generate cellulose-rich solids and a liquid containing hemicellulose and lignin; and mechanically treating the cellulose-rich solids to form nanofibrils and / or nanocrystals. The total mechanical energy may be less than 500 kilowatt-hours per ton. The crystallinity of the nanocellulose material may be 80% or higher, translating into good reinforcing properties for composites. The nanocellulose material may include nanofibrillated cellulose, nanocrystalline cellulose, or both. In some embodiments, the nanocellulose material is hydrophobic via deposition of some lignin onto the cellulose surface. Optionally, sugars derived from amorphous cellulose and hemicellulose may be separately fermented, such as to monomers for various polymers. These polymers may be combined with the nanocellulose to form completely renewable composites.
Owner:API INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Method for producing active pulverized lime by utilizing coal gas to calcine limestone through suspended state pre-heating decomposing furnace
The invention relates to a method for producing active pulverized lime by utilizing coal gas to calcine limestone through a suspended state pre-heating decomposing furnace, which belongs to the field of environment protection production of building materials. The method comprises the voltage stabilizing and conveying process of coal gas, the combustion heating process of the coal gas in a decomposing furnace for sufficiently combusting the coal gas in the suspended state pre-heating decomposing furnace to obtain the active quicklime powder as staflux in the lime calcining production, and the process for cooling the lime by a grate type cooler. Coke-oven coal gas, blast furnace coal gas, converter coal gas and mixed coal gas in the metallurgy production process are respectively adopted as fuel for replacing the coal powder in the traditional process for calcining and decomposing the lime powder. The method solves the problem of environment pollution caused by coal firing, improves the utilization rate of the excessive coal gas generated during steel making, reduces the outwards discharge of the coal gas, simultaneously improves the production efficiency and the heat efficiency of the lime calcination, and improves the activity of the lime.
Owner:SHANDONG IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Method for preparing light magnesium carbonate and magnesium oxide from dolomite sea water bittern
InactiveCN101327942AReduce energy consumptionReduce manufacturing costMagnesium carbonatesMagnesiaHigh concentrationFiltration
The invention relates to a method for preparing light magnesium carbonate and magnesia using dolomite and sea water brine as materials. The dolomite is calcined to light fired dolomite and kiln gas, wherein the light fired dolomite reacts with the sea water brine to obtain magnesium hydroxide, the magnesium hydroxide is added into the magnesium-precipitation mother liquor to obtain a slurry of magnesium hydroxide, the kiln gas containing carbon dioxide of higher concentration is used for carbonizing the slurry of magnesium hydroxide. The magnesium bicarbonate solution is obtained by reacting the magnesium hydroxide slurry with compressed kiln gas which is cooled and purified in a carbonization tower. The basic magnesium carbonate is precipitated at room temperature by adding alkaline matters into the magnesium bicarbonate solution after pressure filtration and refine. The mixture solution is filtered or centrifugal separated to obtain wet basic magnesium carbonate and magnesium-precipitation mother liquor, the wet basic magnesium carbonate is dried to obtain light magnesium carbonate, the light magnesium carbonate is calcined to obtain light magnesium hydroxide. The method of the invention has advantages of low energy consumption, high resource utilization and obvious economic benefit without by product of calcium carbonate with low added value.
Owner:TIANJIN SEA WATER DESALINATION & COMPLEX UTILIZATION INST STATE OCEANOGRAPHI
Method for treating cement kiln dust
InactiveUS8043426B2Reduce releaseHighly effectiveSolid waste managementCinker content reductionCalcium hydroxideFluidized bed
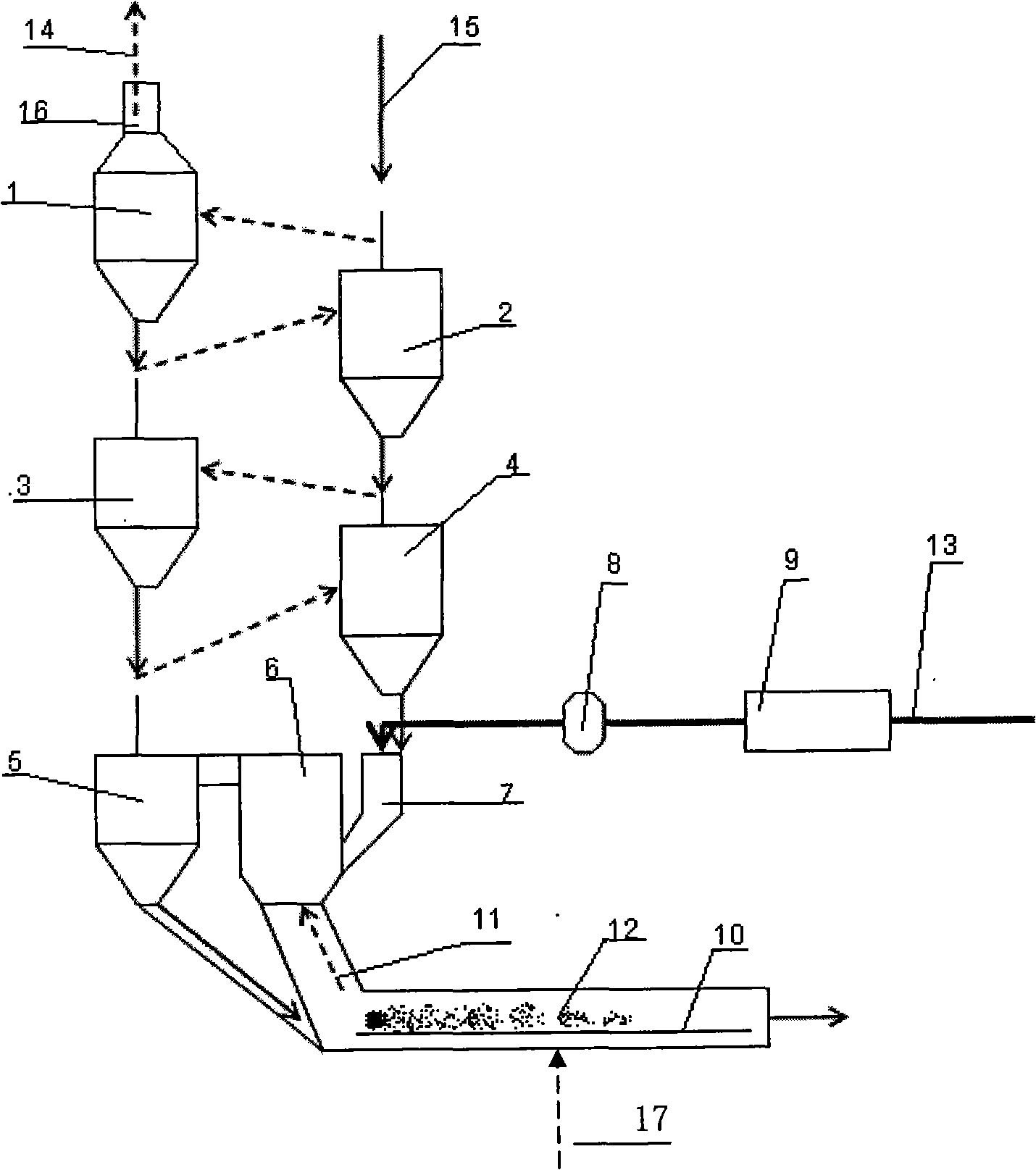
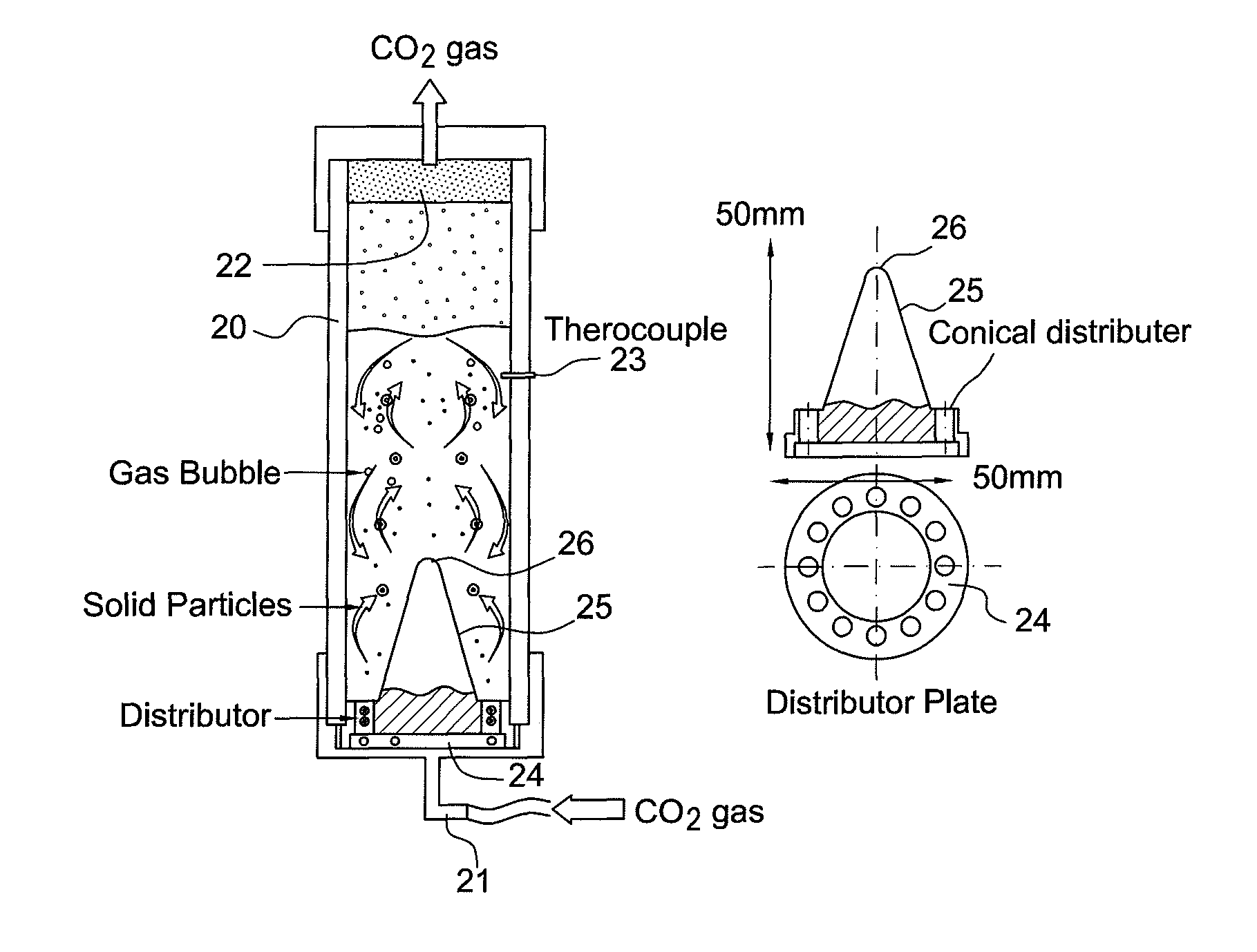
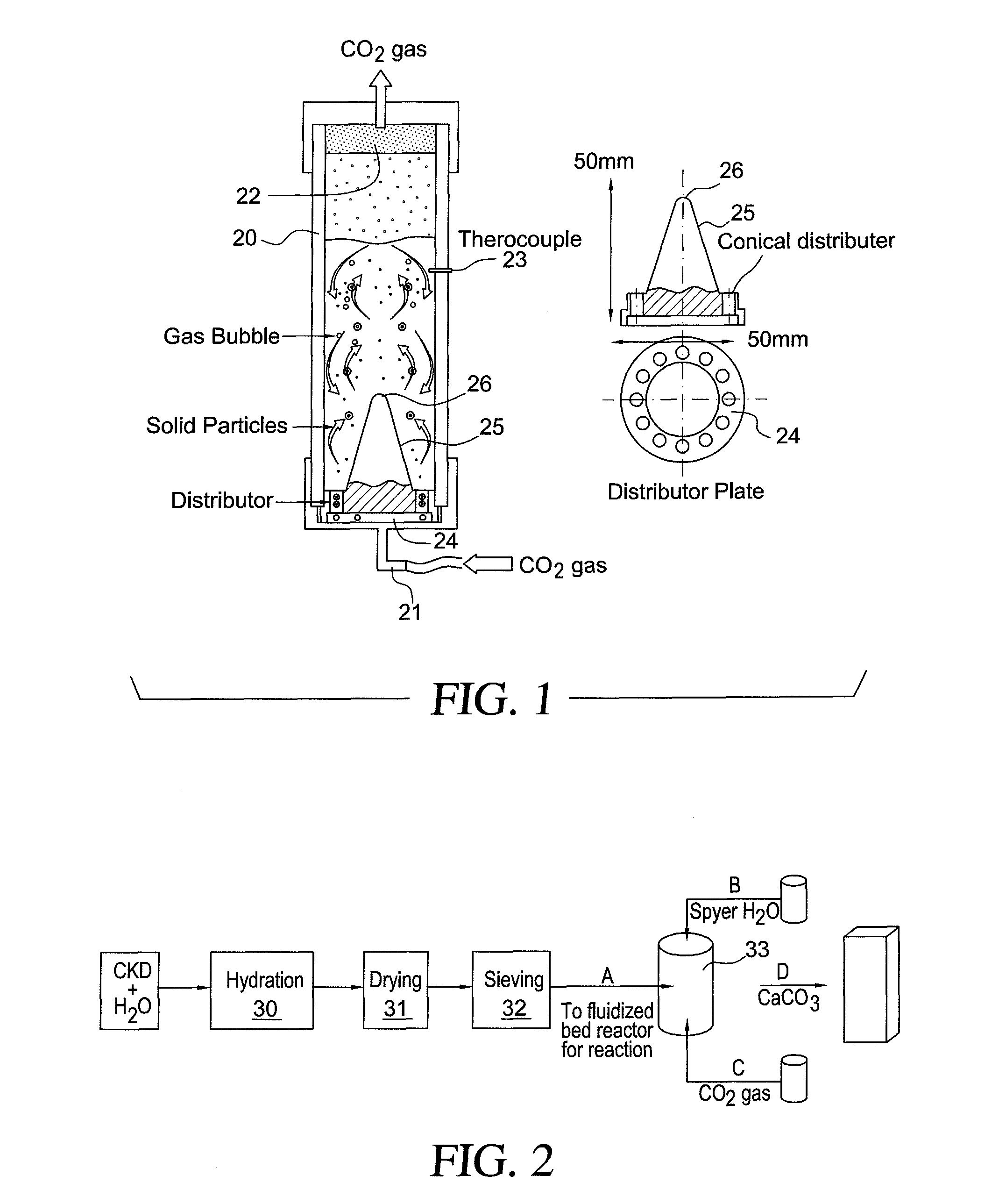
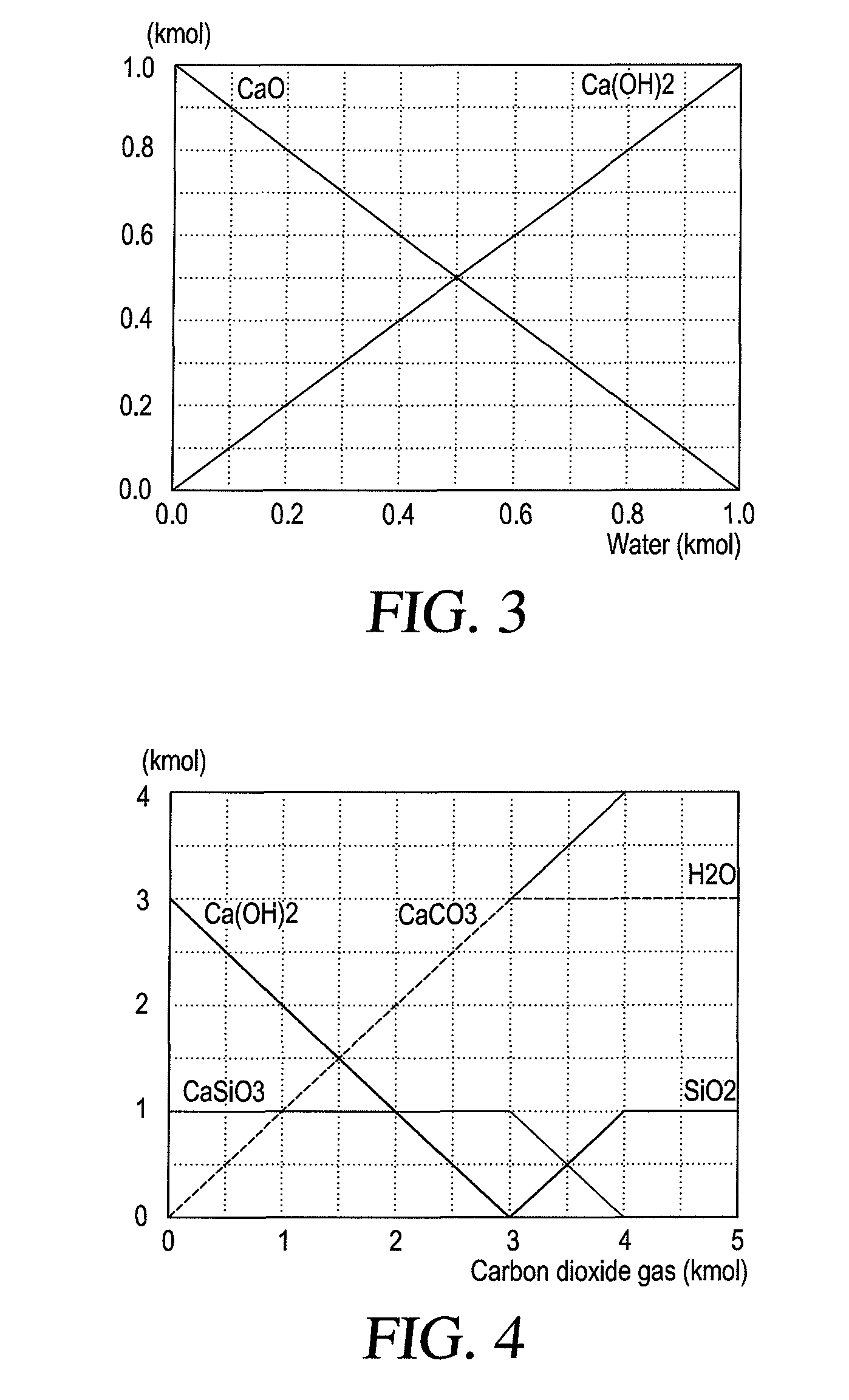
A method for treating cement kiln dust containing alkaline metal salts includes the steps of hydration (formation of calcium hydroxide), dehydration i.e. drying, fractionation by sieving and carbonation (reaction of the fractionated moistened cement kiln dust) with CO2 gas in a fluidized bed reactor.
Owner:UNITED ARAB EMIRATES UNIVERSITY
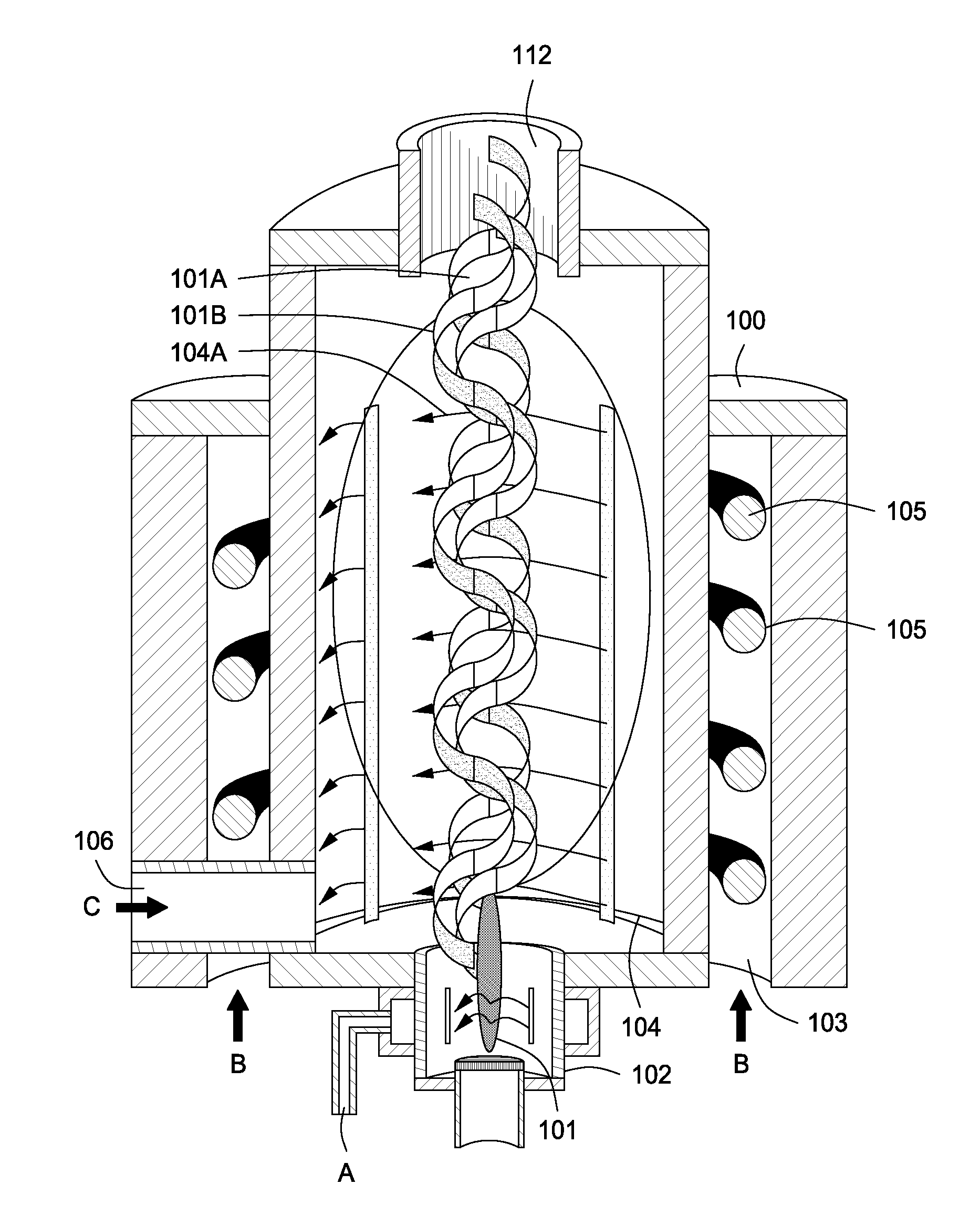
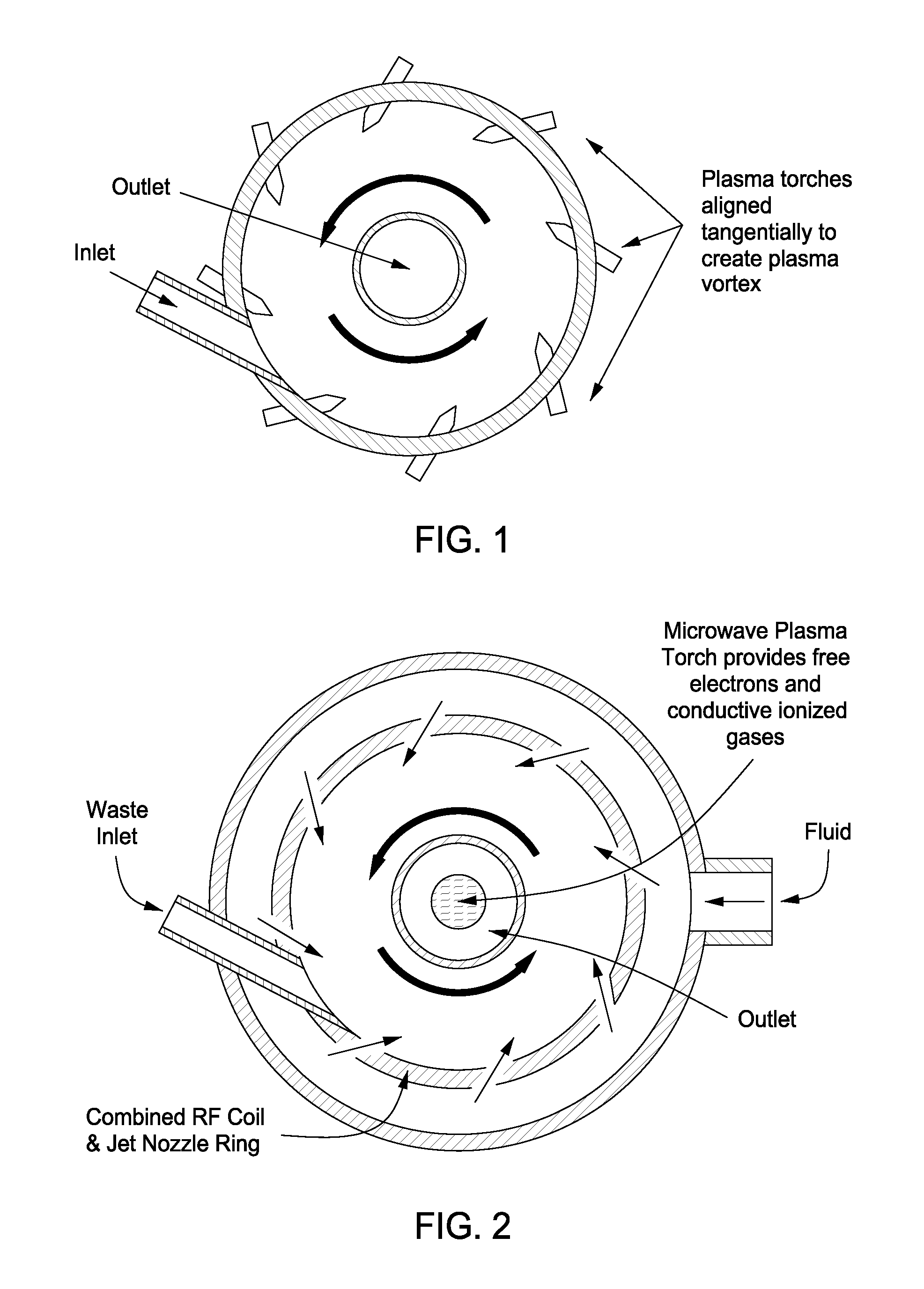
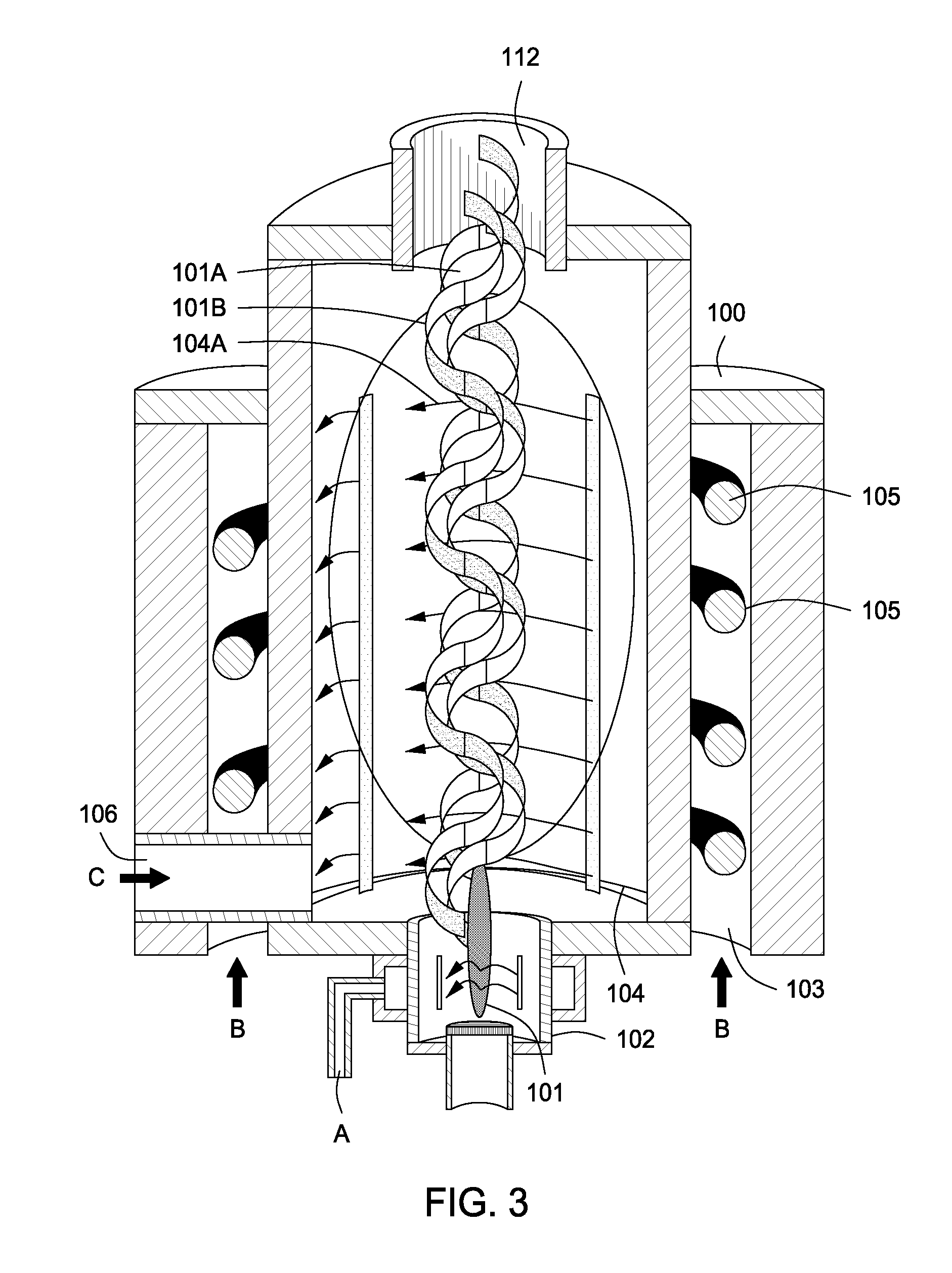
Plasma whirl reactor apparatus and methods of use
InactiveUS20100044483A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesAluminium compoundsSingle processAngular momentum
An apparatus for synergistically combining a plasma with a comminution means such as a fluid kinetic energy mill (jet mill), preferably in a single reactor and / or in a single process step is provided by the present invention. Within the apparatus of the invention potential energy is converted into kinetic energy and subsequently into angular momentum by means of wave energy, for comminuting, reacting and separation of feed materials. Methods of use of the apparatus in the practice of various processes are also provided by the present invention.
Owner:FORET PLASMA LABS
Green process for extracting fibers from plants
ActiveCN101899794ATime consuming to overcomeOvercome efficiencyDigestersPulping with inorganic basesFiberSlag
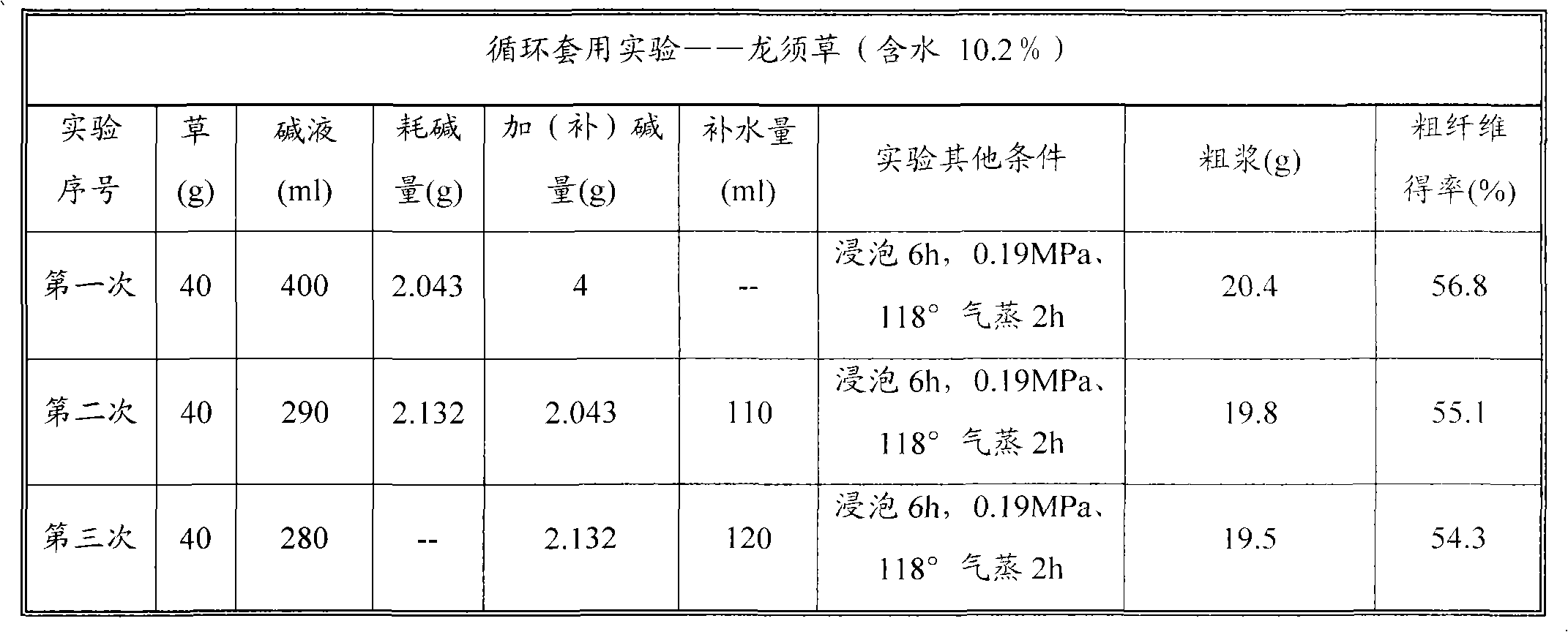
The invention relates to a sectional green process for extracting fibers from plant raw materials with high efficiency and high yield, which comprises the steps of: firstly, infiltrating or / and soaking plant raw materials with lime water (or carbide slag water solution) or dilute alkali; then steaming or boiling the raw materials; and finally, beating or steaming discharge and pulp washing to prepare fibers. The green process can also be comprehensively used for exploiting the utilization of lignin and extract, so as to realize the full-rate development of plants. The extract in the process can be recycled as a nutrient source for organisms such as plants, microbes, alga and the like, which breaks through the key technical bottleneck of the green and ecological industry, has significant theoretic and application values on the recycling economy, the sustainable development strategy and acquisition of energy sources, advanced materials and biological nutrient source from biomasses, and has extremely profound social benefits, economic benefits and ecological benefits.
Owner:BEIJING INSIGHT BIOMASS
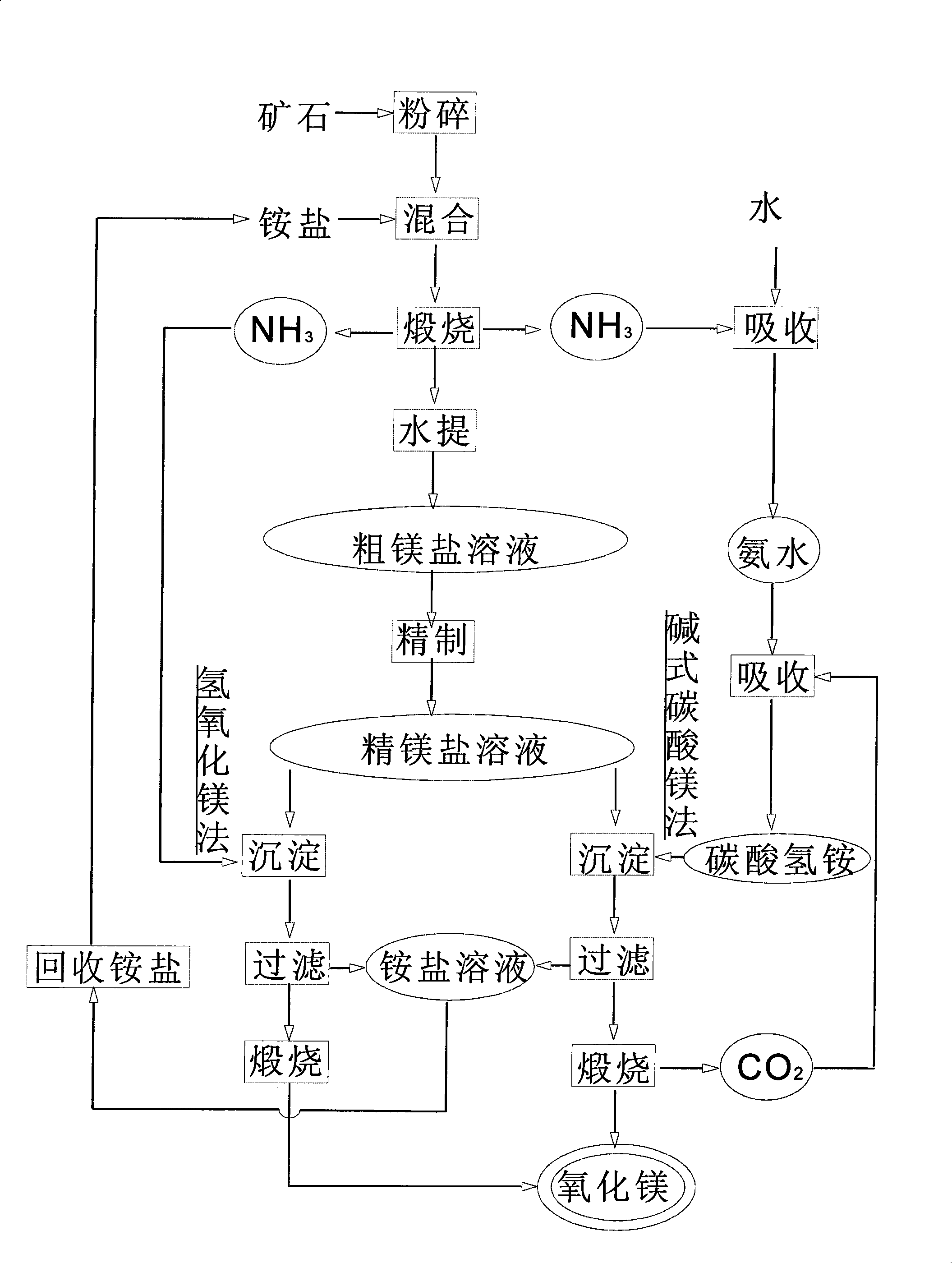
Method for preparing magnesian by calcining ammonium salt and magnesium-containing ore
InactiveCN101372402AReduce energy consumptionReduce consumptionLime productionMagnesium saltHigh energy
A method for preparing magnesium oxide by the mixed calcination of aminium salts and magniferous ores solves the problems existing in the existing method, such as high material cost, large project investment, high energy consumption and inconvenient use of side products. The method comprises the following steps: (1) magniferous ores are mixed with aminium salts; after calcination and aqueous extract, crude magnesium salt solution is obtained, and ammonia generated by the calcination is recovered, or ammonia generated by calcination is dissolved by water to obtain ammonia water; (2) after the crude magnesium salt solution is refined, the refined magnesium salt solution reacts with the restored ammonia to obtain magnesium hydroxide precipitate; or after ammonia water reacts with carbon dioxide generated by calcining basic magnesium carbonate precipitate to obtain ammonium acid carbonate solution, the ammonia water reacts with the magnesium salt solution to obtain basic magnesium carbonate precipitate once again; (3) the precipitates are separated and washed, magnesium oxide is obtained by drying and calcining, and the carbon dioxide generated by calcining basic magnesium carbonate precipitate is collected; (4) aminium salt solution, the precipitates of which are separated, is evaporated, concentrated and crystallized, and then is recovered to obtain aminium salts. In the invention, acid and precipitating agents used in the traditional technology are omitted. Therefore, the investment is reduced, and the material cost is lowered. In addition, the side product (aminium salts) can be circularly used, thus reducing the pollution.
Owner:王央贡
Method and device for producing active lime powder from calcined limestone
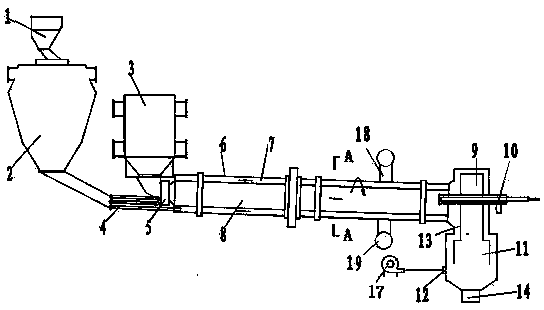
The invention discloses a method for producing active lime powder from calcined limestone. The method comprises the following steps: (1) by taking limestone as a raw material, crushing and grinding the limestone to obtain limestone powder; (2) preheating the limestone powder by a suspension preheating system, and heating the limestone powder after preheating by a combustion decomposition furnace, so that the limestone powder is subjected to further heat absorption and decomposition; and (3) cooling the material subjected to heat decomposition in the step (2) to obtain the active lime powder through a suspension cooling system. The invention discloses a device for employing the method. The preheated limestone powder can be fed from the lower and middle parts of the combustion decomposition furnace, the temperature of the combustion decomposition furnace can be flexibly regulated, and the generated lime powder has high activity; caloric content in primary cyclone waste gas in the suspension preheating system and temperature rise air in the suspension cooling system is fully utilized, and the aim of saving energy in the system is fulfilled; moreover, the degree of automation is high, the production efficiency is high, and the production scale is conveniently enlarged.
Owner:TIANJIN CEMENT IND DESIGN & RES INST
Particulate matter and methods of obtaining same from a kraft waste reclamation
InactiveUS20080219912A1Calcium/strontium/barium carbonatesGas treatmentParticulatesChemical composition
A method for obtaining particulate calcium carbonate having an average particle size less than about 12 microns is provided. The method includes the steps of (1) withdrawing from a pulp mill a mixture containing calcium carbonate; (2) treating the mixture to remove contaminants contained in the mixture to produce a treated mixture containing calcium carbonate and further having a chemical composition and / or purity which substantially inhibits the fusing together of calcium carbonate particulates; (3) recovering from the treated mixture particulate calcium carbonate having an average particle size less than about 12 microns. The calcium carbonate produced has a high surface area to volume ratio and is therefore highly reactive and suitable for numerous applications such as in the treatment of soil, filler paper production, paint production, and contaminant containment in coal stack emission assemblies.
Owner:S&S LIME
Processes and apparatus for producing nanocellulose, and compositions and products produced therefrom
Processes disclosed are capable of converting biomass into high-crystallinity nanocellulose with surprisingly low mechanical energy input. In some variations, the process includes fractionating biomass with an acid (such as sulfur dioxide), a solvent (such as ethanol), and water, to generate cellulose-rich solids and a liquid containing hemicellulose and lignin; and mechanically treating the cellulose-rich solids to form nanofibrils and / or nanocrystals. The total mechanical energy may be less than 500 kilowatt-hours per ton. The crystallinity of the nanocellulose material may be 80% or higher, translating into good reinforcing properties for composites. The nanocellulose material may include nanofibrillated cellulose, nanocrystalline cellulose, or both. In some embodiments, the nanocellulose material is hydrophobic via deposition of some lignin onto the cellulose surface. Optionally, sugars derived from amorphous cellulose and hemicellulose may be separately fermented, such as to monomers for various polymers. These polymers may be combined with the nanocellulose to form completely renewable composites.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Beam limekiln
ActiveCN101857383AReduce consumption costReduce manufacturing costLime productionGas pipelineChiller
The invention provides a beam limekiln, which mainly comprises a kiln body, a burning system, a discharging system, an air supply system and a control system, wherein a cooling belt of the kiln body is provided with an upper layer of burning beams and a lower layer of burning beams, and the burning beam is provided with a cooling system; and the cooling system comprises a cavity between a beam body and an outer wall, a connecting pipeline, a conducting oil circulating pump and a conducting oil cooler, and the conducting oil cooler comprises an oil way and an air pipeline. The conducting oil cooler is connected with a preheating air pipeline or a fuel gas pipeline or a cooling air pipeline of the cooling belt, and exchanges heat with hot combustion air or fuel gas or cooling air so as to recover heat discharged by cooling the conducting oil of the burning beam, thereby saving energy, reducing energy consumption and production cost and improving economic efficiency. The invention has reasonable flow and more optimized production operation.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG XINHUA IND FURNACE CO LTD
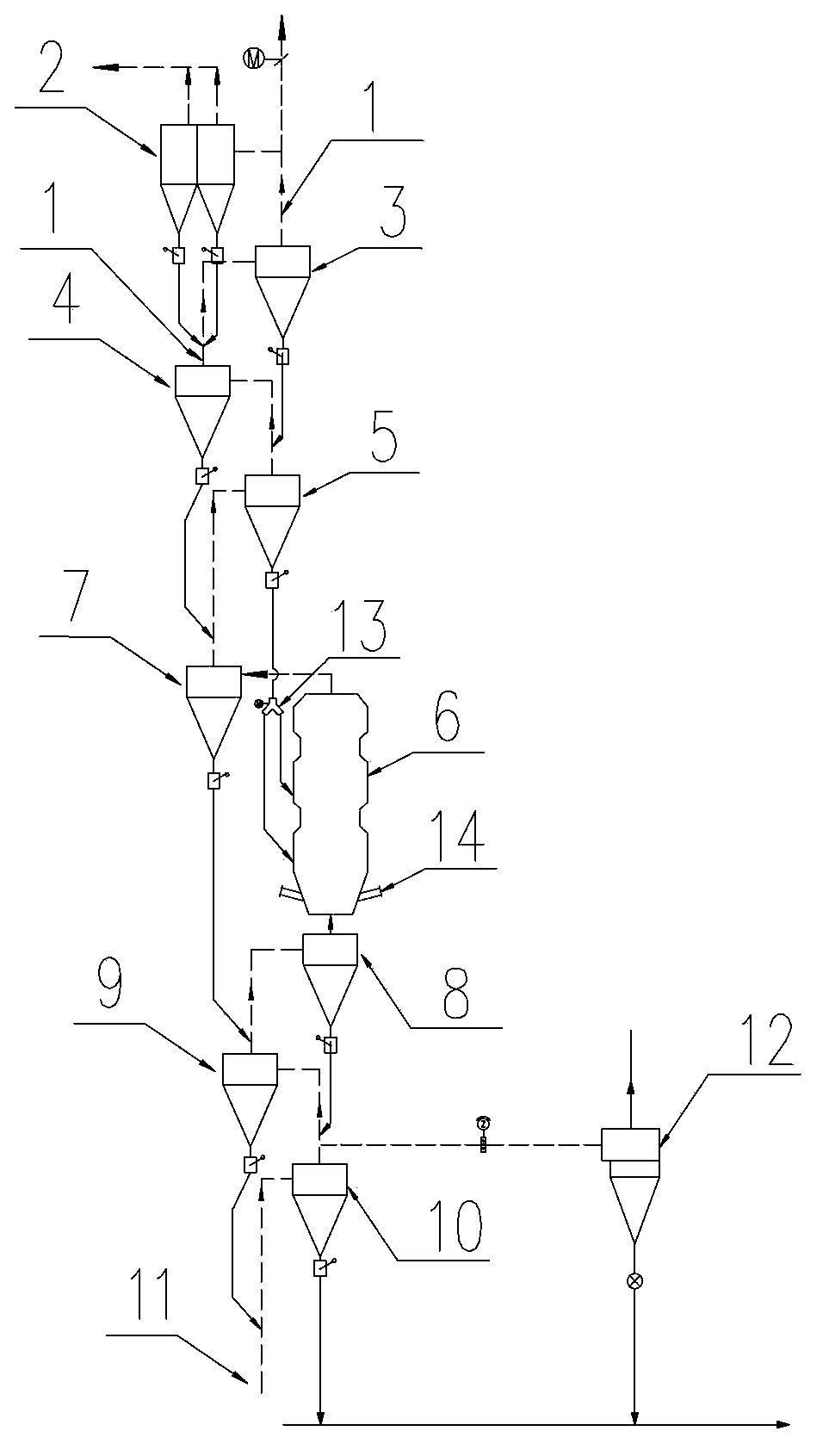
Energy-conservation and emission-reduction type active lime calcination method and apparatus
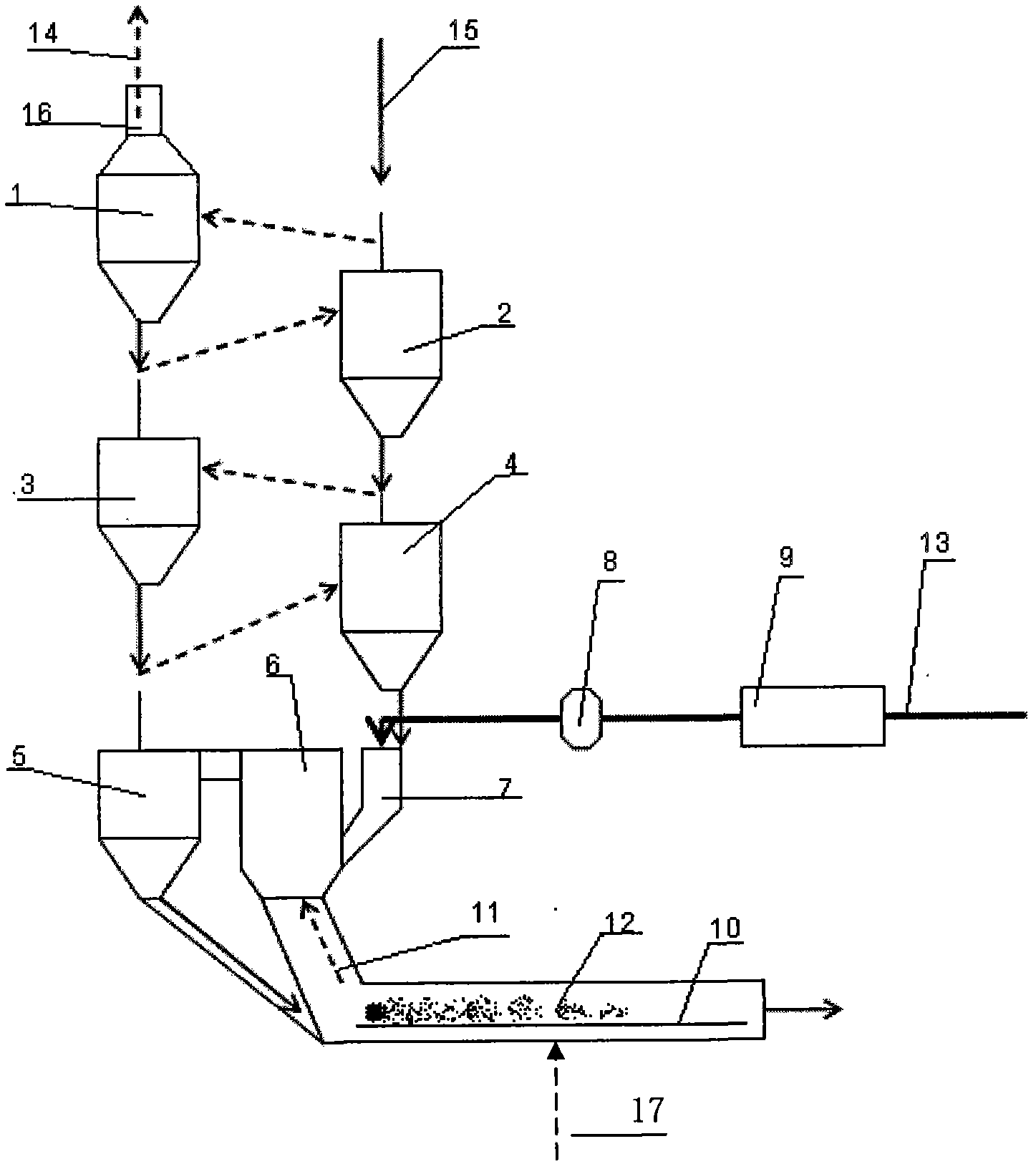
ActiveCN103304157AGranularity Requirements RelaxedImprove resource utilizationLime productionExhaust gas emissionsExhaust fumes
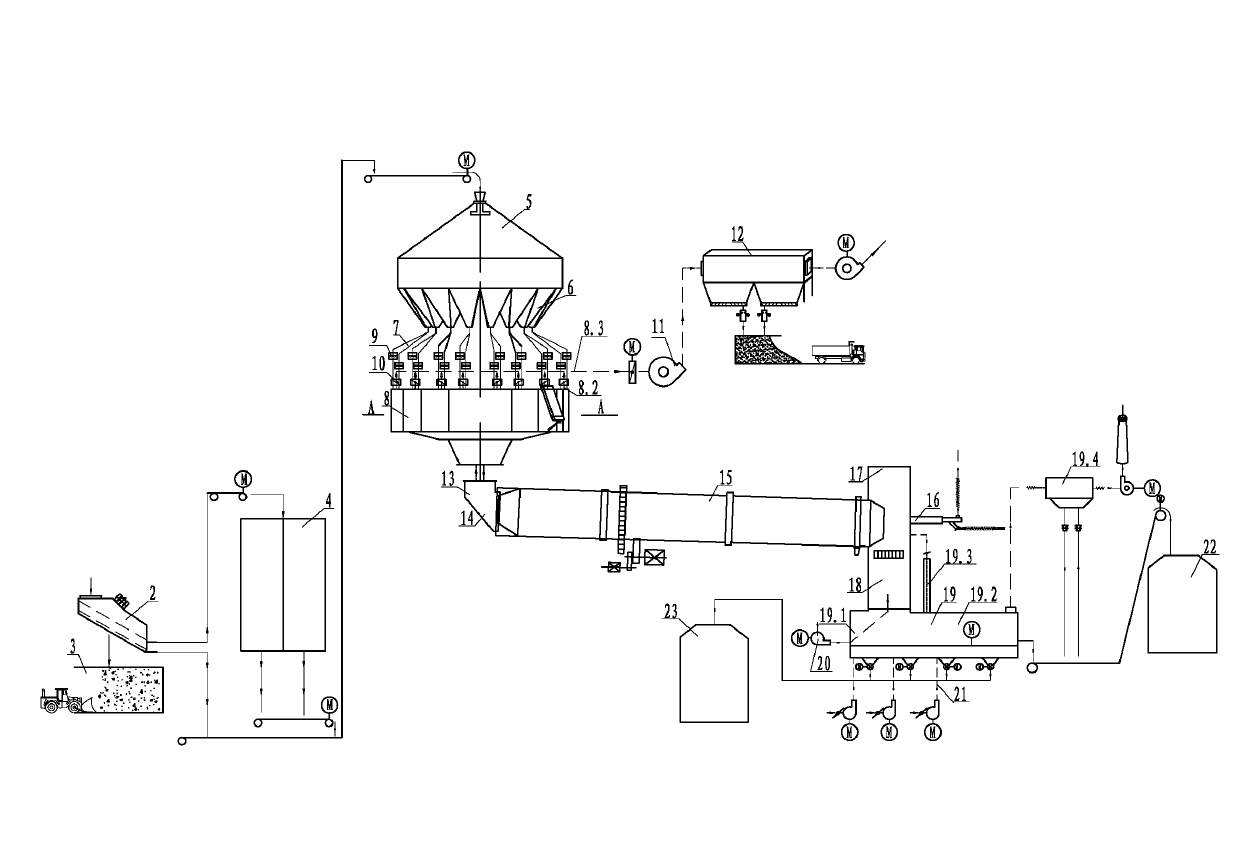
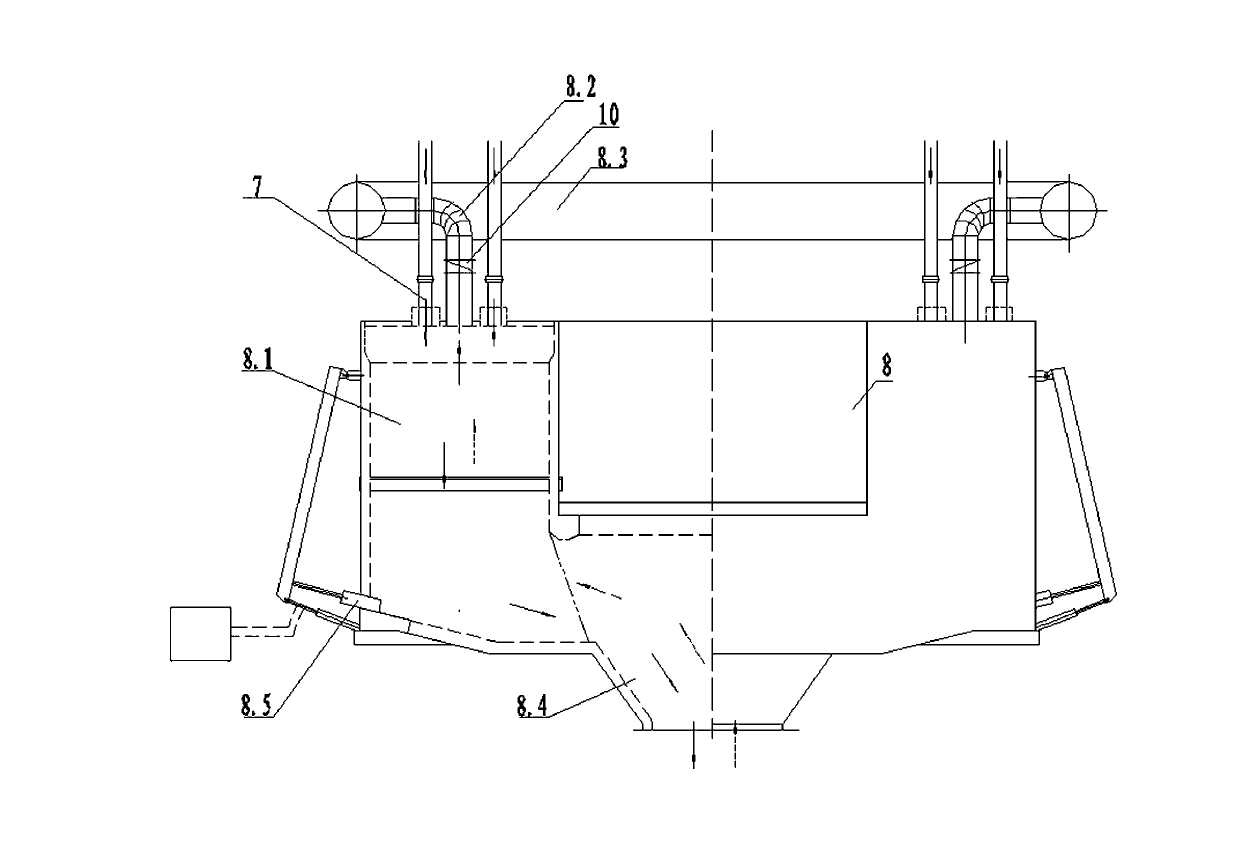
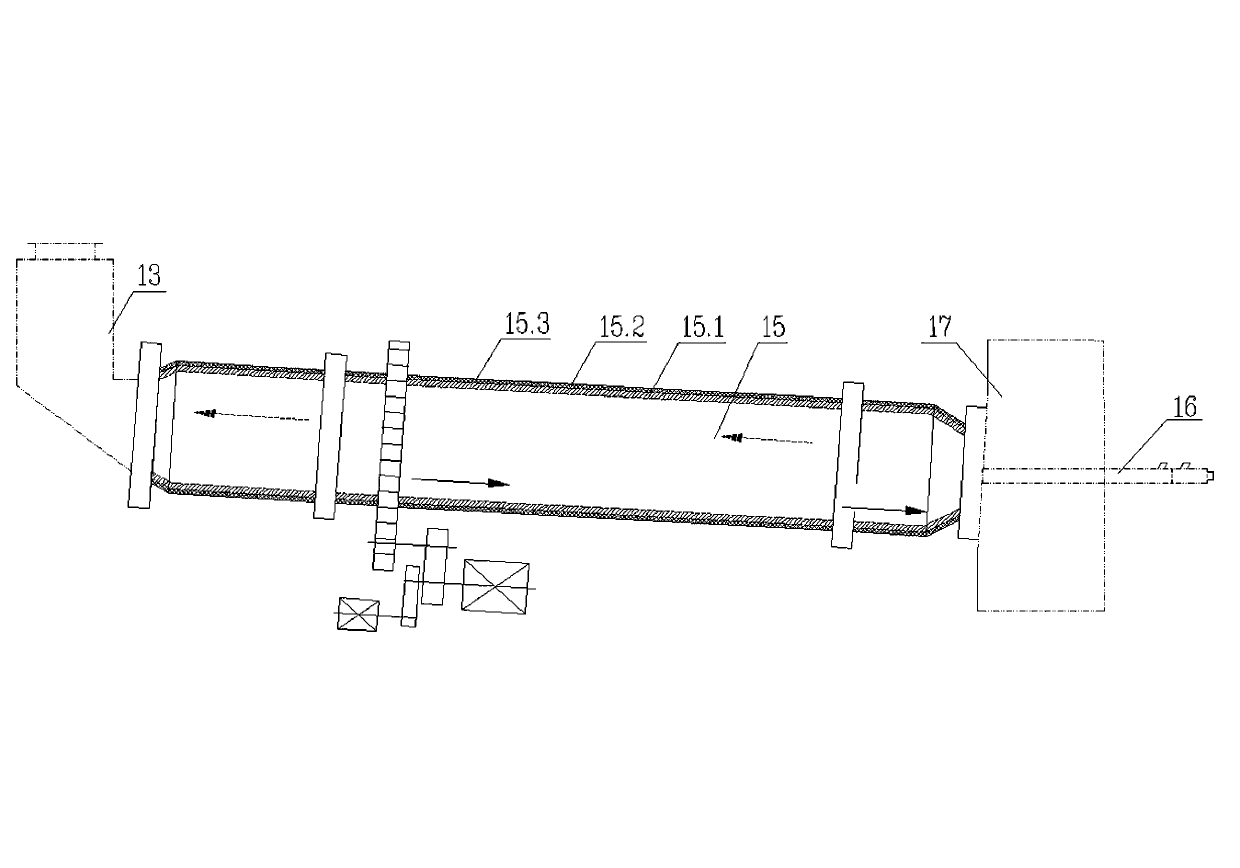
The invention provides a burning method for preparing an energy-conservation and emission-reduction type active lime. The method comprises the following steps: subjecting the raw material (1) limestone to size grading; respectively and evenly distributing the limestone of different grades into each preheating chamber (8.1) of a novel vertical preheater (8), preheating and partially decomposing the limestone with high temperature exhaust gas and introducing the limestone into a rotary kiln (15); calcining and decomposing the limestone under the action of a temperature field to allow CO2 to be produced and the limestone to become lime; and allowing the lime to enter into a shaft well device (18) for annealing and heat exchange, then introducing the lime into a cooling machine (19) for cooling and carrying out screening to separate blocky lime from powdery lime, thereby obtaining finished products, i.e., blocky lime and powdery lime. The invention further provides an apparatus composed of a size grading device (2), a distributor (5), a distribution warehouse (6), the novel vertical preheater (8), the rotary kiln (15), a kiln hood (17), a combustor (16), the shaft well device (18) and the cooling machine (19) for the method. The method and the apparatus provided by the invention has the characteristics of an expandable range of the size of the raw material limestone, low heat consumption, high production efficiency, a high activity degree of the products, low discharge of SO2 and exhaust gas, low cost, simple and convenient operation and capacity of meeting needs of larger-scale industrial production.
Owner:泰安中意重型工业设备有限公司
Rotary kiln with power generation device
ActiveCN104016596AReduce energy consumptionAvoid direct contactLime productionGas collecting tubeFlue gas
The invention relates to a rotary kiln with a power generation device. The rotary kiln comprises a power generation device, a material loading device, a material bin, a kiln body, a kiln end cover, a cooler and a cooling fan. A kiln head is provided with a burner; the kiln body is composed of an inner cylinder and an outer cylinder structure, a kiln chamber is in the middle of the inner cylinder, an annular space formed between the inner cylinder and the outer cylinder is a material chamber, and the annular space is provided with a support column; the rotary kiln is provided with a screw conveyor, a discharge passage and a gas collecting tube; the material loading device is connected with the material bin, the material bin is connected with the annular space through the screw conveyor, and the annular space through the discharge passage is connected with the cooler; and the lower part of the cooler is connected with a discharge hatch, the upper part of the cooler through the kiln head is connected with the kiln chamber, and the kiln chamber is connected with the power device. Through the kiln body with the inner cylinder and outer cylinder structure, limestone in the annular space is heated through flue gas dividing wall, so as to avoid direct contact of the flue gas with the material and benefit utilization and recovery of decomposed carbon dioxide gas; and at the same time, and waste heat of flue gas is utilized for power generation, so as to reduce the energy consumption of the rotary kiln.
Owner:SHIJIAZHUANG XINHUA IND FURNACE CO LTD
Heavy-calcium powder cleaning and smashing integrated equipment
InactiveCN104888887AExtended service lifeImprove crushing effectCleaning using liquidsGrain treatmentsEngineeringWater pipe
The invention discloses heavy-calcium powder cleaning and smashing integrated equipment. The equipment comprises a cleaning device and a smashing device. The cleaning device comprises a water pipe and an upper baffle; a water tank is arranged on the upper baffle, and a cleaning water pump is arranged in the water tank; the water pipe is arranged at the lower end of the cleaning water pump, and a cleaning frame is arranged at the lower end of the water pipe; a feeding hopper of the smashing device is arranged on the lower portion of the right side of a conveying belt, and is arranged on the upper portion of a smashing device body, and a check block is arranged in the feeding hopper; a driving gear is arranged in the smashing device body, and a first driven gear is arranged above the left side of the driving gear; the cleaning device and the smashing device are arranged, and conveyed aggregated rocks are washed out by clean water sprayed out of cleaning nozzles through the cleaning device, so that dust on the aggregated rocks is removed; and when the smashing device works, a hydraulic air cylinder drives a piston rod to vertically move, and the distance between the driving gear and the driven gear is adjusted, so that according to needs, the size of limestone particles obtained after smashing is adjusted, and the smashing effect of limestone is better.
Owner:刘海明
Biomass fractionation processes employing sulfur dioxide
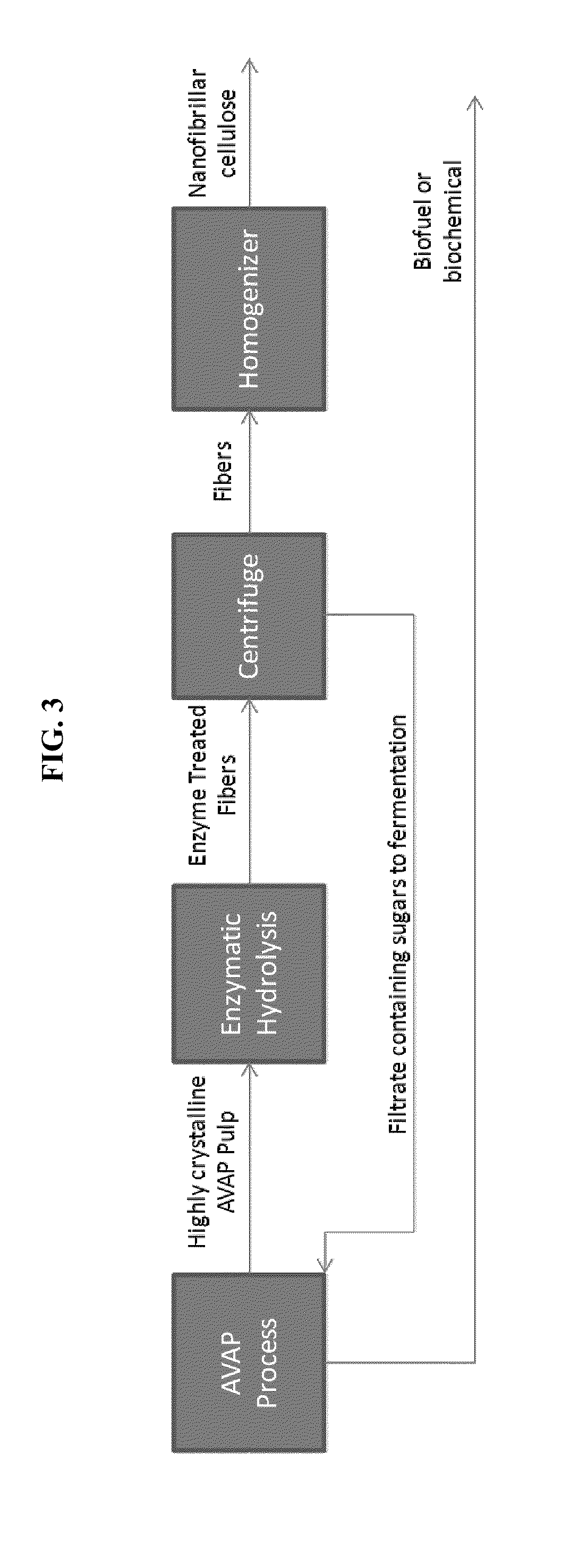
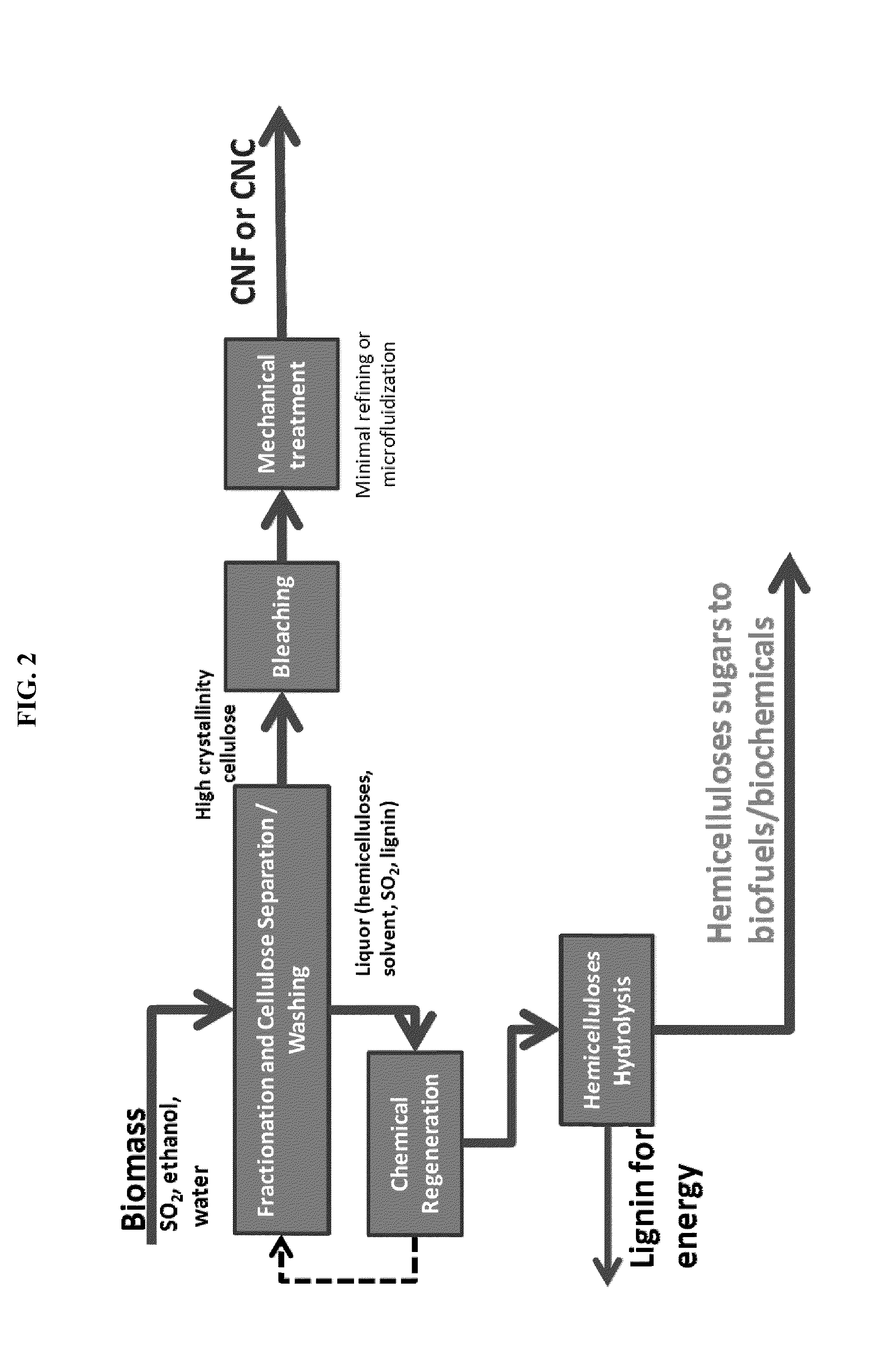
ActiveUS20140186899A1Good removal effectIncreased processing flexibilityPulping with acid salts/anhydridesPulp by-products recoveryFractionationD-Glucose
The present invention provides a process for fractionating lignocellulosic biomass, comprising: contacting biomass with SO2, water, and optionally a first solvent, to produce intermediate solids; then contacting the intermediate solids with SO2, water, and a second solvent, to produce cellulose-rich solids and a liquid phase comprising hemicelluloses and lignin. The first concentration of SO2 may be lower or higher than the second concentration of SO2. It is desirable to vary the SO2 and solvent concentrations in different stages to optimize the removal of hemicellulose versus lignin. The resulting cellulose-rich material can contain very low hemicellulose, very low lignin, or both low hemicellulose and low lignin. High-purity cellulose is useful both for producing glucose as well as for cellulose products or derivatives. The hemicelluloses may be hydrolyzed to produce monomeric sugars, and the lignin may be recovered as a co-product.
Owner:GRANBIO INTELLECTUAL PROPERTY HOLDINGS LLC
Method for smelting high-phosphorus steel by low-temperature low-silicon molten iron in converter
InactiveCN102776313AReduce usageReduce the burden onManufacturing convertersProcess efficiency improvementAlloyOxygen
The invention discloses a method for smelting high-phosphorus steel by low-temperature low-silicon molten iron in a converter. The method comprises the following steps that: scrap steel is added into the converter; active lime is added in the converter for the first time, and an oxygen lance, the position of which is lower than the normal position for 10-20 centimeters, blows oxygen; after the oxygen blowing is performed for 50-60 seconds, dolomite is added into the converter at one time; when the oxygen blowing is performed for 90-110 seconds, the oxygen lance is lifted to the normal oxygen blowing position, and active lime is added into the converter again; and tapping is carried out. The method fully utilizes the conditions of the low-temperature low-silicon molten iron in reducing a phosphorus removal rate to smelt the high-phosphorus steel, the phosphorus removal rate can be reduced to 40%-50% from the above 85% of the current conventional smelting, and thus the phosphorus content of the smelting at the end point is effectively improved; the lime addition amount is reduced to be not over 25Kg / ton of steel from 40Kg-60Kg / ton of steel, and the usage amount of phosphorus alloy can also be reduced; the waste residue discharge can be reduced; and moreover, a fluorite slagging agent is not used, and thus the environmental burden can be relieved.
Owner:武汉钢铁有限公司
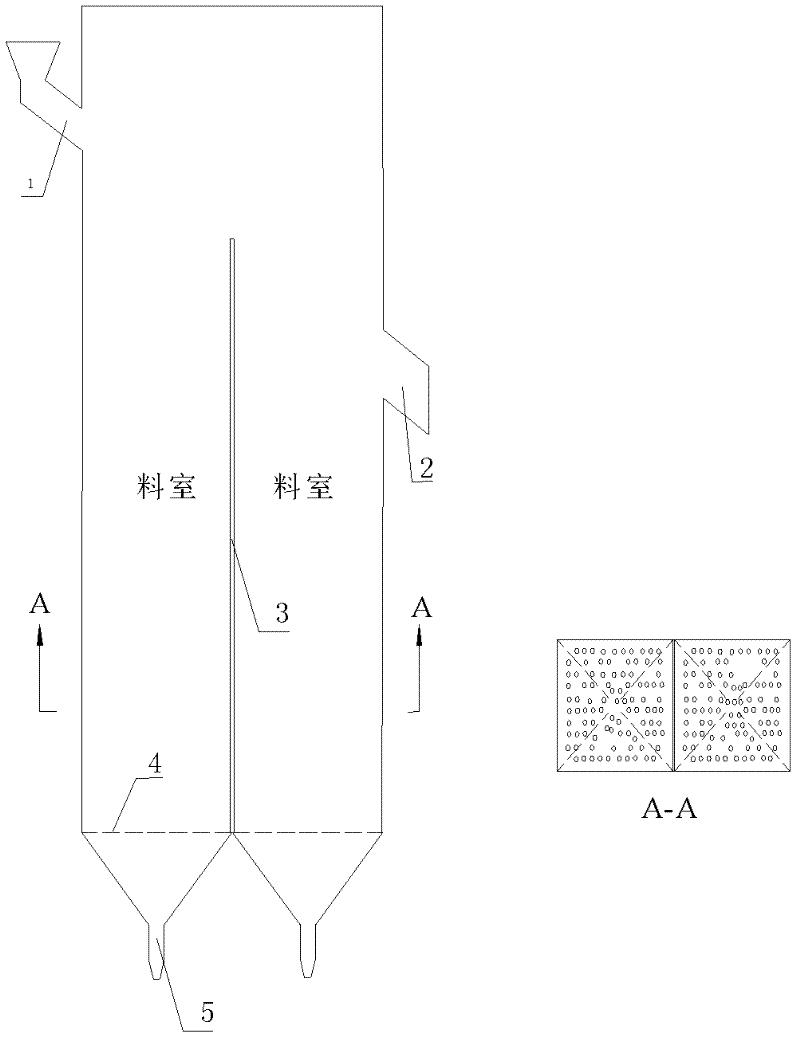
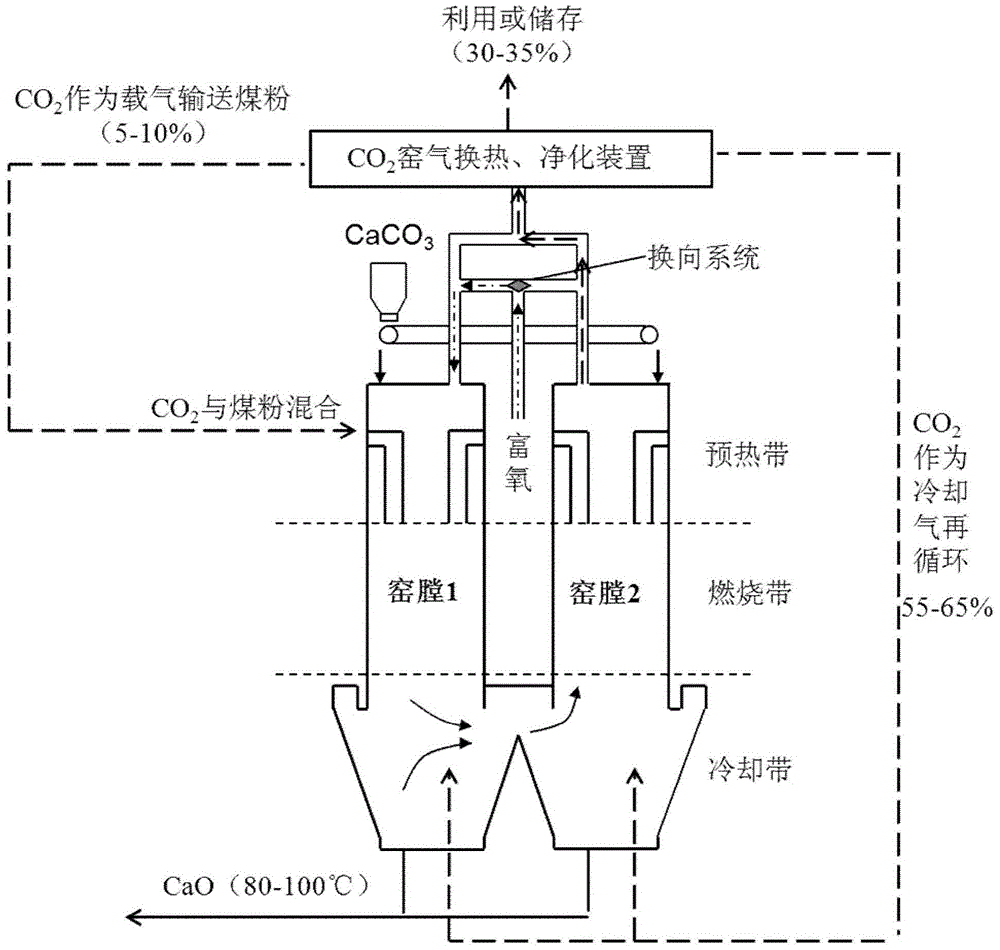
Parallel flow heat accumulating type lime kiln production technology based on CO2 accumulation
The invention discloses a parallel flow heat accumulating type lime kiln production technology based on CO2 accumulation. The parallel flow heat accumulating type lime kiln production technology includes the steps that limestone raw materials are fed into two kiln chambers of a parallel flow heat accumulating type lime kiln; carrier gas is sprayed into the kiln chambers; combustion supporting gas is fed; in a combustion zone of the current kiln chamber, limestone absorbs the heat generated by fuel combustion to be decomposed to generate quick lime and CO2 gas; the quick lime is discharged after being cooled to 80 DEG C to 100 DEG C; cooling gas, the CO2 gas generated by decomposing the limestone and CO2 gas generated by fuel combustion are mixed to enter the other kiln chamber to preheat limestone; flue gas generated by preheating releases heat to the limestone, then the temperature of the flue gas is reduced, the flue gas is exhausted, and CO2 gas with the volume concentration larger than 95% is generated; the parallel flow heat accumulating type lime kiln starts reversing work. By means of the parallel flow heat accumulating type lime kiln production technology, the high-purity CO2 gas is obtained while the high-quality lime is prepared. Compared with an existing technology, circulation of N2 in a system is avoided, the energy used for heating the N2 is saved, and the flue gas is recycled to achieve the aims of increasing the product added value, saving energy and reducing consumption.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com