Green process for extracting fibers from plants
A green process and process technology, applied in fiber raw material processing, natural cellulose pulp/paper, non-woody plant/crop pulp, etc., can solve the problems of small scale, long time consumption, low efficiency, etc., and achieve good growth and improved Effect of fiber yield and noise reduction
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
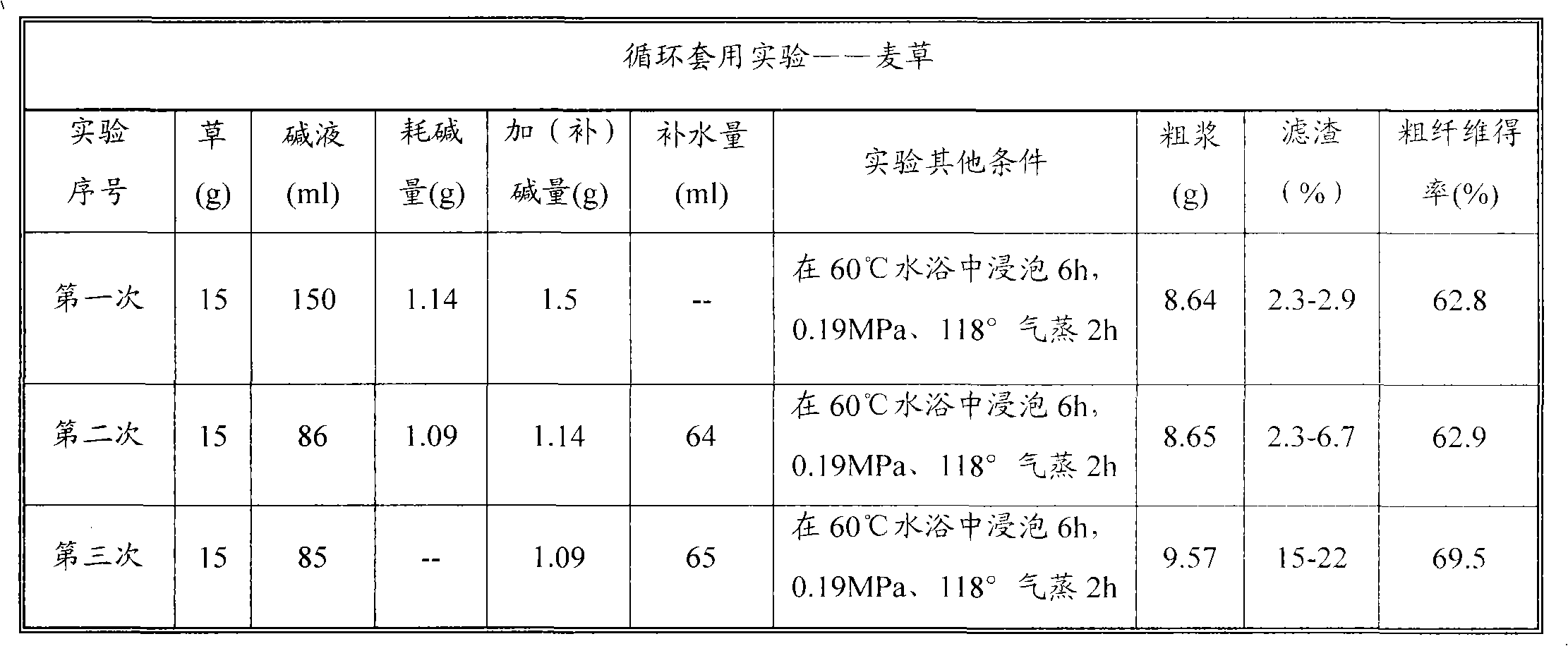
[0034] Embodiment 1 (wheat straw pulping)
[0035] Test one: Dissolve 0.378g of solid calcium oxide in 150 grams of water, add 5g of wheat straw (moisture content 8.3%), soak at room temperature for 0.5 hours, then add it into an autoclave and heat it up to boil. Raise the temperature from room temperature to 150°C for 1 hour; keep warm at 150°C for 2 hours; after cooking, cool down and release the pressure, discharge the cooking material, directly beat, wash, filter, and dry at 105°C to constant weight to obtain 3.42g crude Fiber, the crude fiber yield is 74.6%, after screening through a 40-mesh sieve, 0.60 g of sieve residue is obtained, the sieve residue rate is 17.5%, and the fine pulp yield is 61.5%.
[0036] Test 2: Dissolve 0.378g of solid calcium oxide in 150 grams of water, add 5g of wheat straw (moisture content 8.3%), soak at room temperature for 24 hours, add in an autoclave, seal it, and heat it up for cooking. Raise the temperature from room temperature to 150°C...
Embodiment 2
[0037] Embodiment 2 (bamboo pulping)
[0038] Test 1: Bamboo was pre-soaked in lime water for 40 hours, after proper grinding, it was soaked in NaOH solution for the second time, and then steamed, beaten and washed to obtain coarse pulp. The yield of brown stock was 70%, and the Kappa value was 50.51.
[0039] Test 2: Bamboo was pre-soaked in lime water for 40 hours, and then soaked in lime water for a second time for 40 hours after proper grinding, steamed in a pressure cooker, beaten and washed to obtain coarse pulp. The yield of coarse pulp was 71.9%, and the Kappa value was 58.15.
Embodiment 3
[0040] Embodiment 3 (wood pulping)
[0041] Pre-soak the wood with lime water at 60°C for 20 hours, soak it in lime water for 20 hours after proper grinding, then cook it in an autoclave (160°C) for 4 hours, and finally beat and wash to obtain crude fibers. The yield of crude fibers is 65.7%. The fiber extraction rate is above 95%.
[0042] Two, caustic soda pulping
[0043] Embodiment 1 (normal temperature stirring rice straw pulping)
[0044] 10g of rice straw (moisture content 9%) was stirred and soaked in 1.5% NaOH solution at 60°C for 12 hours, filtered out, beaten, washed, and filtered to obtain 6.2g of crude fibers with a crude fiber yield of 68.1%.
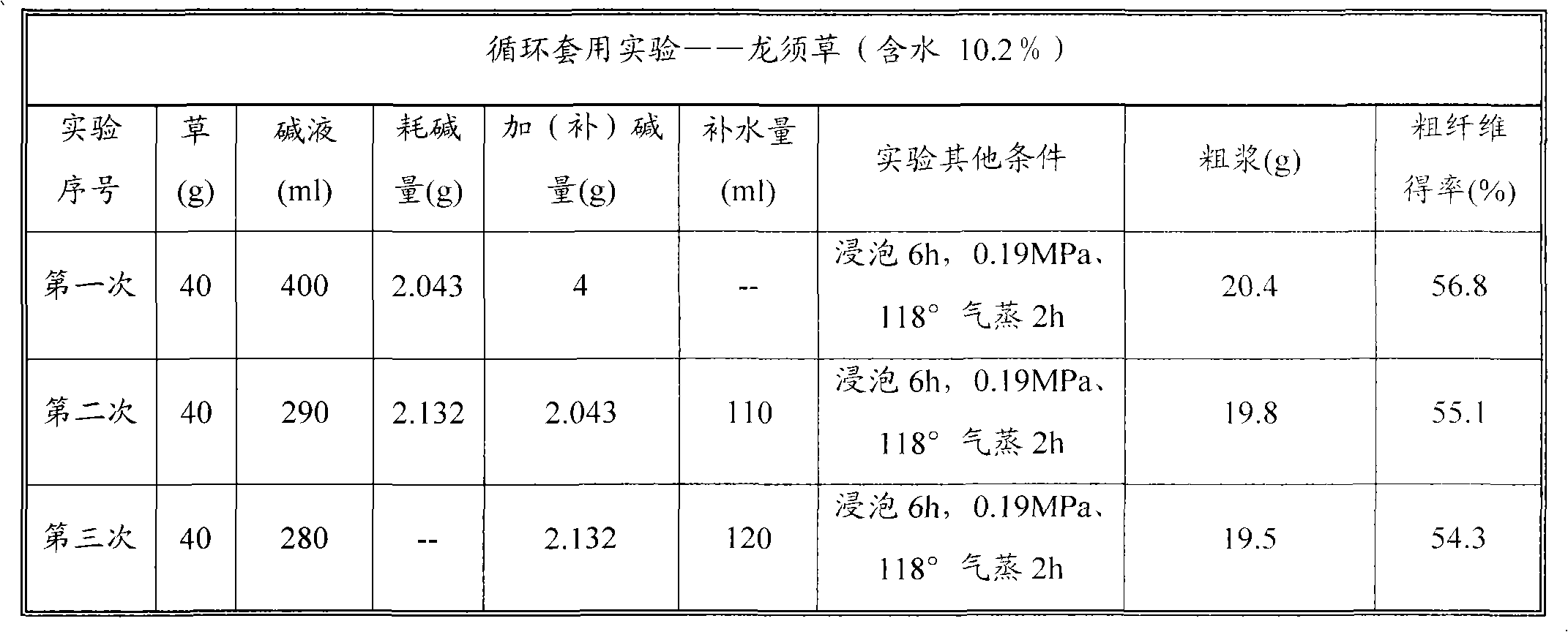
[0045] Embodiment 2 (Pulping with caustic soda method in circulation of Asparagus chinensis)
[0046] Test 1: Soak 300g of asparagus (moisture content 10.2%) in 3000ml of 1.0% NaOH solution at room temperature for 6 hours, then filter out, steam at 0.19MPa, 118°C for 2 hours, take out and polish, wash pulp, and filter o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tear index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Tensile index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com