Method for refining lithium from salt lake brine with high magnesium-lithium ratio
A technology of salt lake brine and high magnesium-to-lithium ratio, applied in the field of refined lithium, can solve the problems of not considering the influence of membrane performance of magnesium-lithium separation effect, not considering the applicability of equipment, and increasing the number of nanofiltration membrane systems, etc. The effect of easy promotion and application, improving quality and competitiveness, and reducing energy consumption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064] The technical solutions of the present invention are explained below in conjunction with the drawings and embodiments, which are only used as explanations of the application rather than limitations.
[0065] The composition of the old brine used in the present invention and the composition of the brine at each stage are shown in Table 1. The present invention stipulates that fresh water is the water on the permeation side of the reverse osmosis membrane.
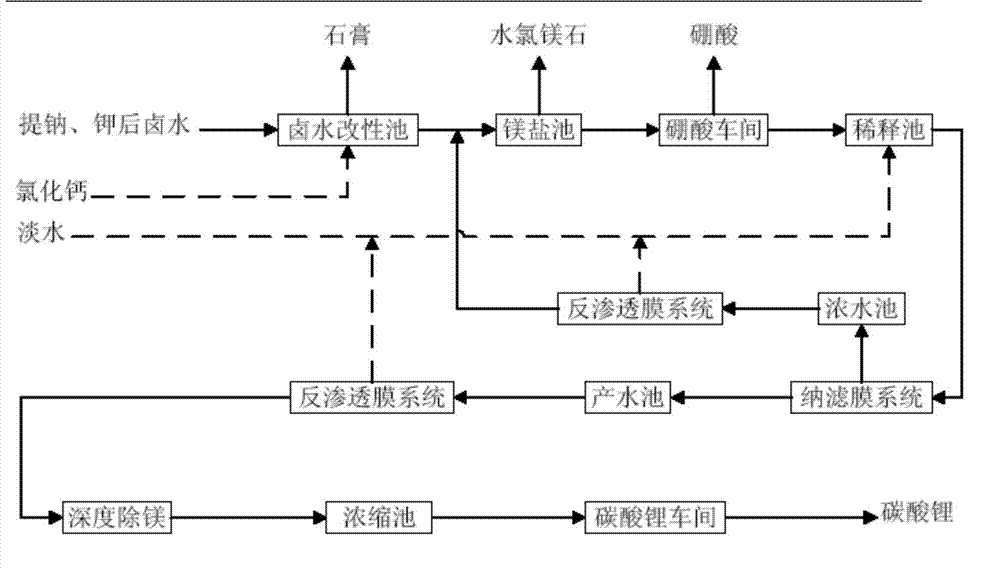
[0066] Such as figure 1 As shown, the method for refining lithium from high-magnesium-lithium ratio salt lake brine comprises the following steps:
[0067] 1) Remove the sulfate radicals of the brine (old brine) after extracting sodium and potassium, and then evaporate to obtain boron-lithium-rich brine.
[0068] This step includes first adding calcium chloride or its saturated solution to the brine after removing sodium and potassium, and the sulfate radical is precipitated in the form of gypsum. The brine after re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com