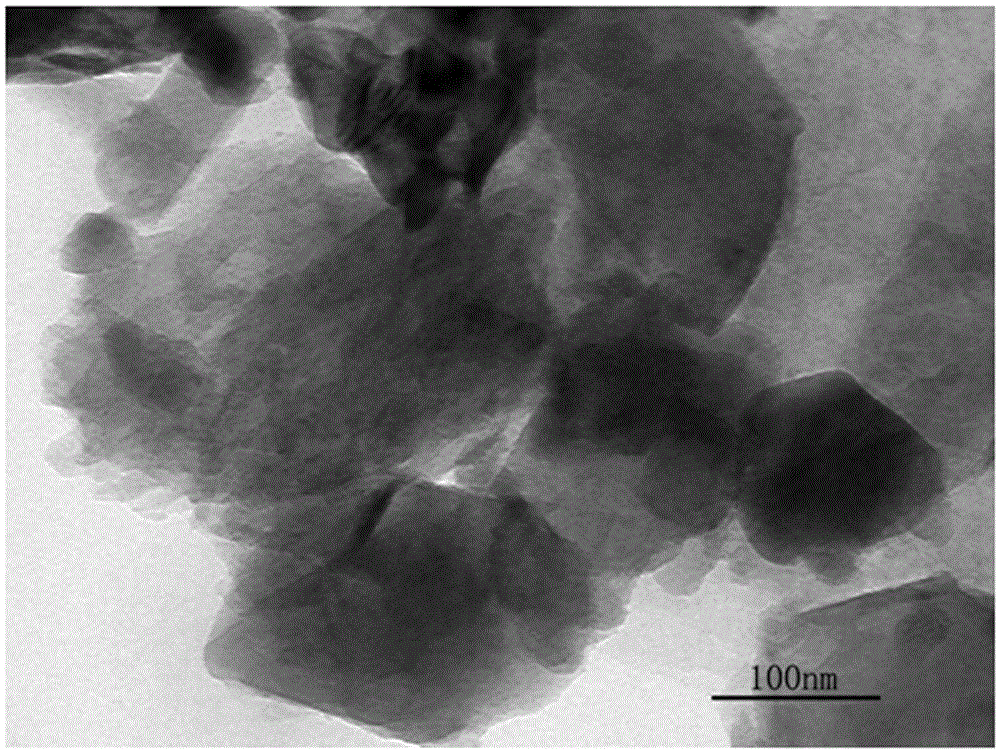
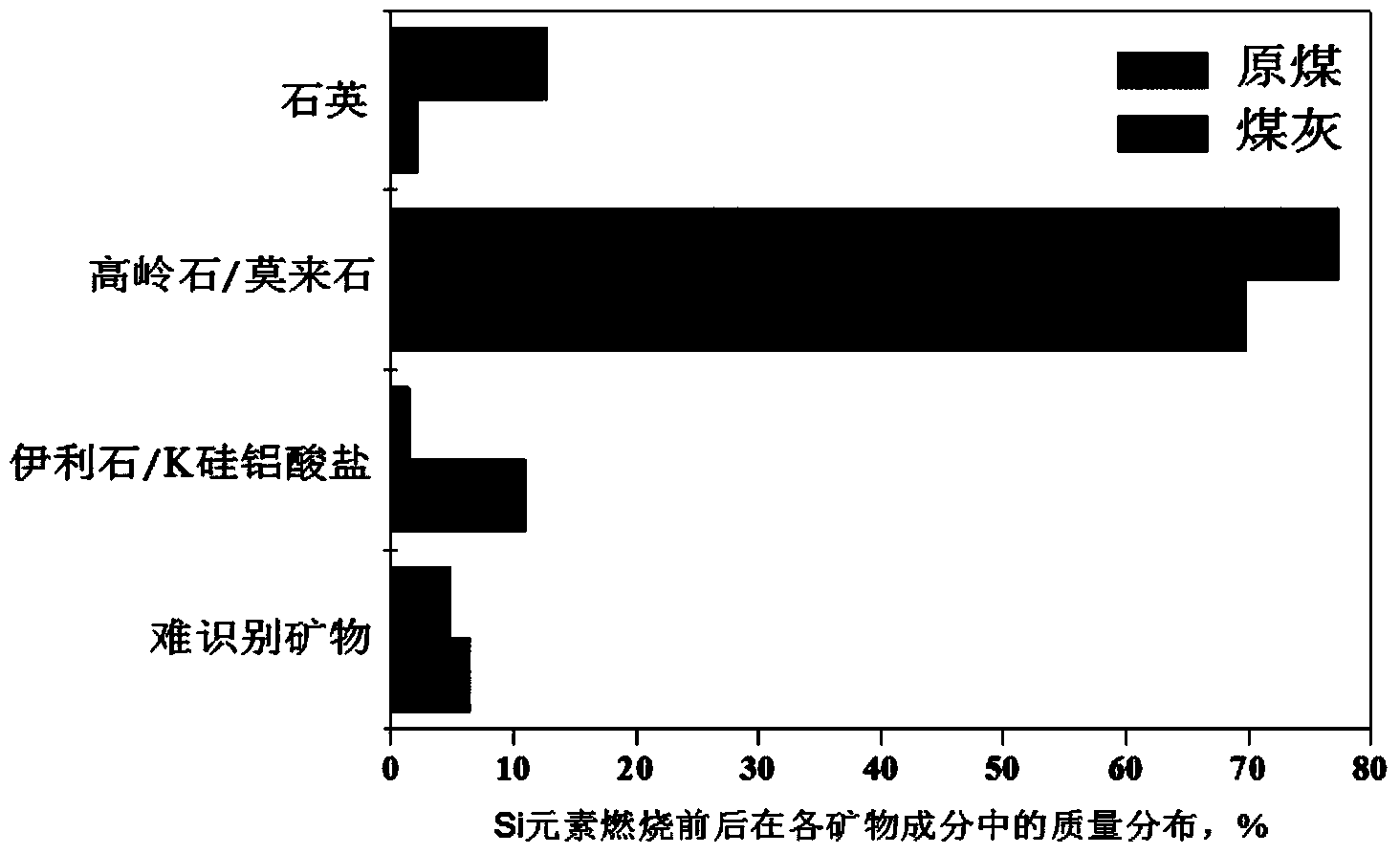
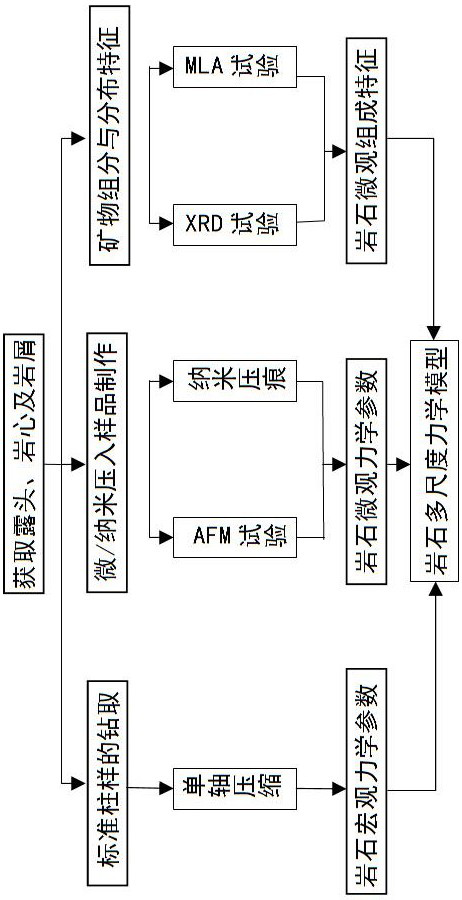
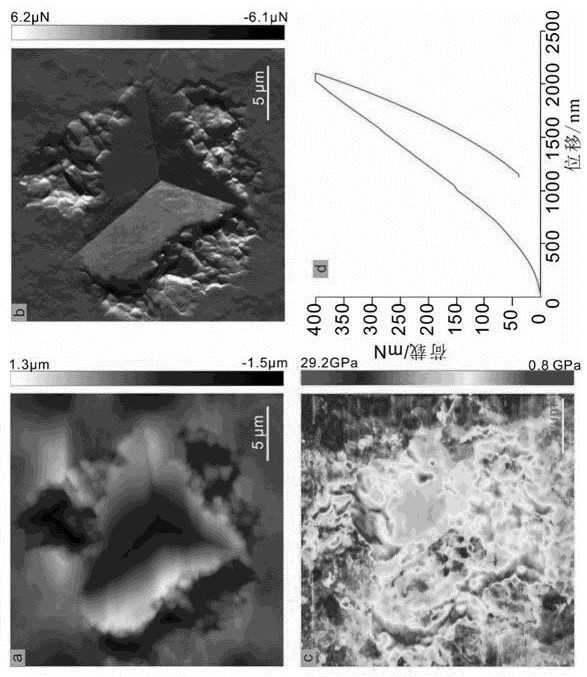
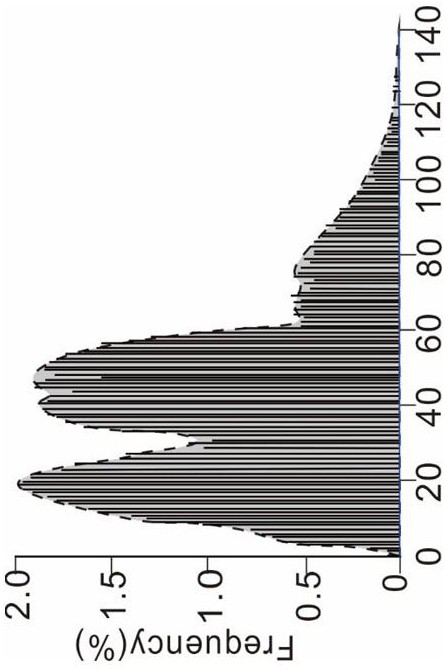
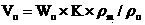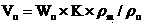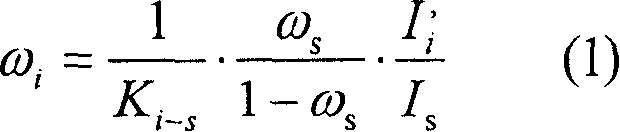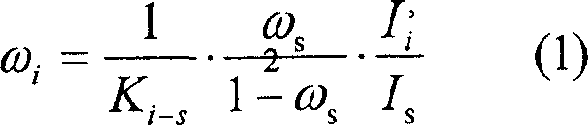Patents
Literature
119 results about "Mineralogical composition" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Mineralogy is the study of minerals . Rocks in the earth's crust are composed of one or more minerals. A mineral in the geologic sense is a naturally occurring, inorganic, crystalline solid. A particular mineral has a specific chemical composition.
Method For Simulating And Estimating Sandstone Properties
InactiveUS20070203677A1Computation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsPorosityMaceral
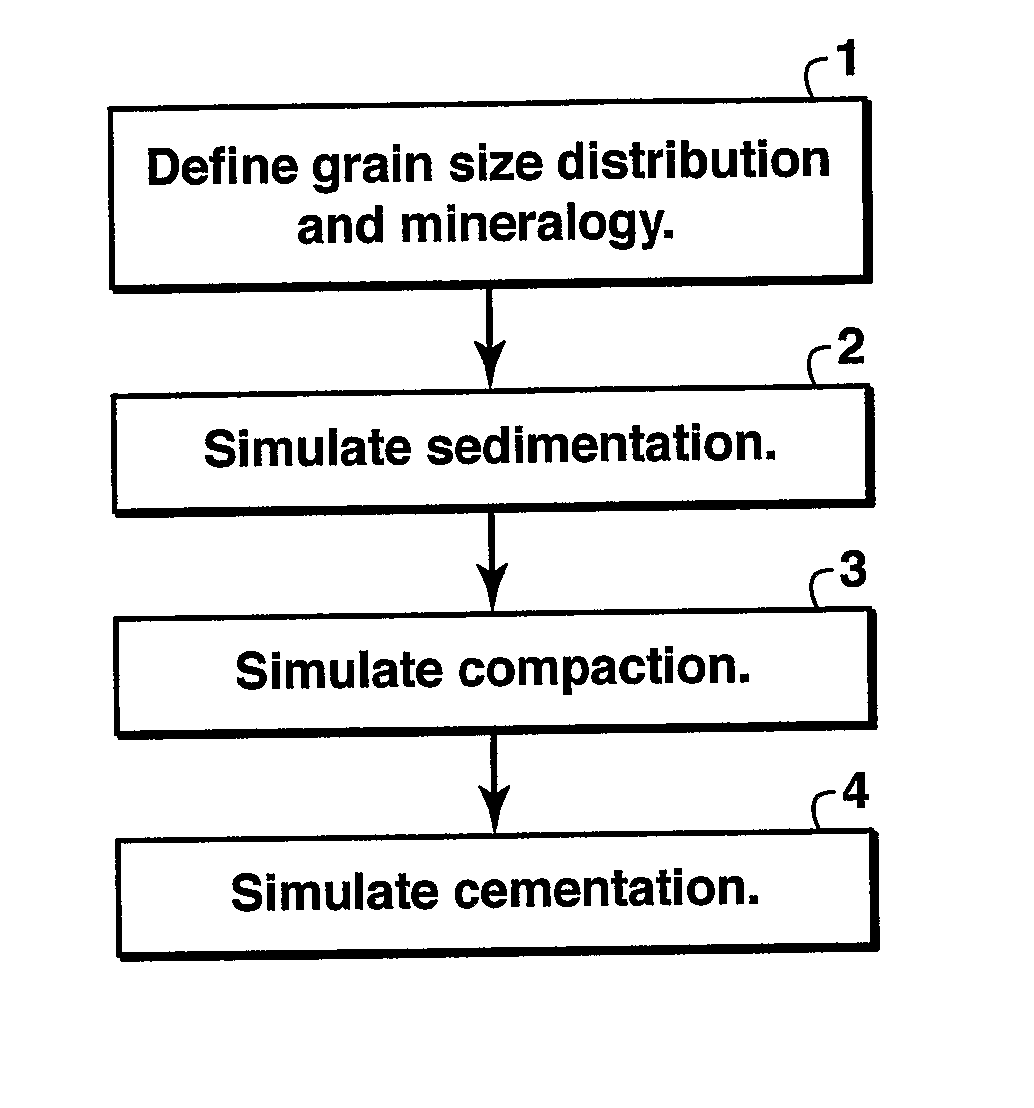
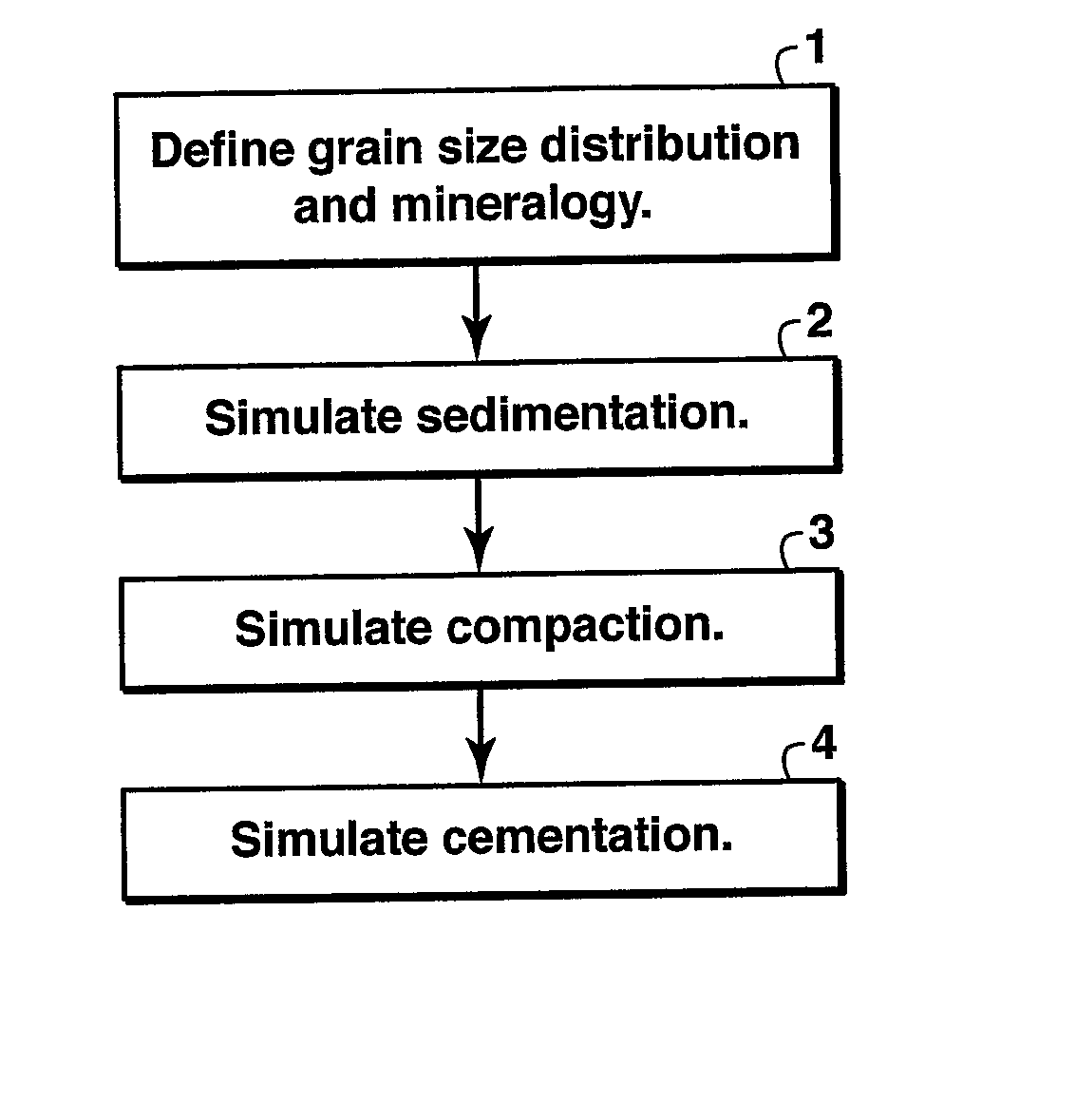
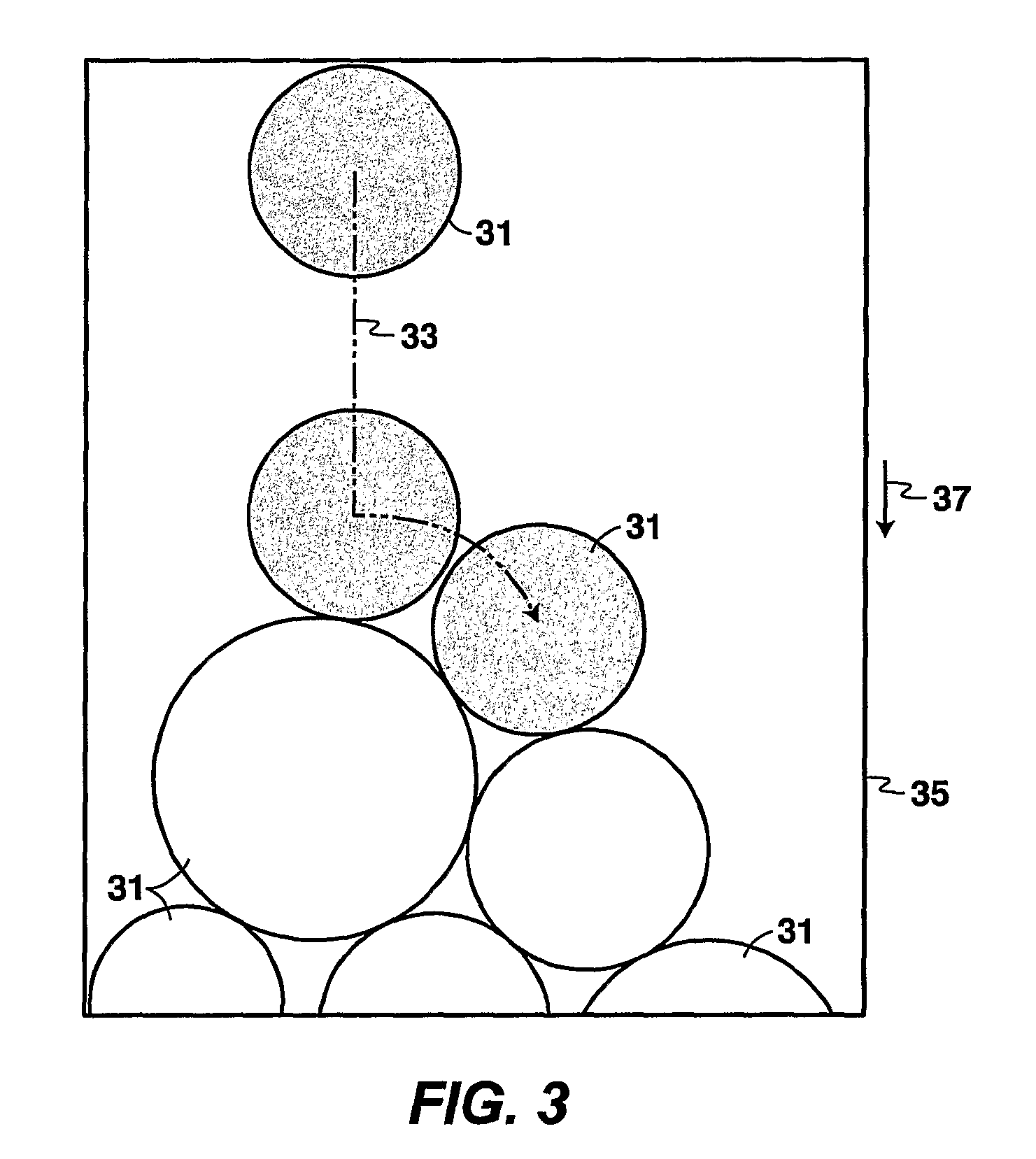
The invention is a method for simulating sandstone deposition. The sandstone is simulated by estimating the grain size distribution and mineral composition of grains in the sandstone, simulating sedimentation of grains from the grain size distribution and mineral composition of the grains, simulating compaction of the grains, and simulating cementation of the grains. Properties of the sandstone such as porosity and permeability may be estimated from the simulated sandstone. The method permits multiple mineralogies to be simulated during the burial history of sedimentation, compaction and cementation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
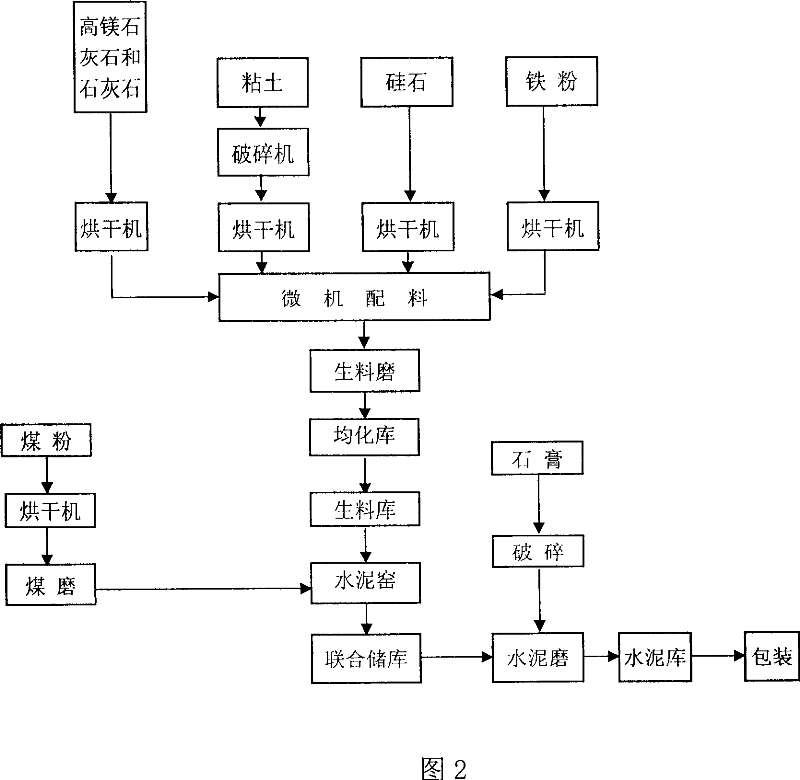
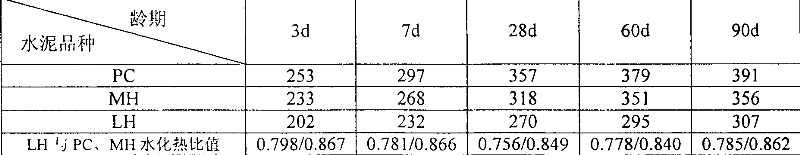
High-magnesium low-heat portland cement clinker aggregate and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101041560AImprove crack resistanceLow heat of hydrationClinker productionHigh magnesiumPortland cement
The invention discloses a high-magnesium lower thermal silicate cement clinker, making mineralogical composition at (mass percent): 40 -65% C2S, 15-40% C3S, 1-8% C3A, 10-25% C4AF and content of MgO at 2.0-6.0%. The invention also discloses a preparing method of high-magnesium lower thermal silicate cement clinker, including indispensable steps of producing cement clinker with raw materials and controlling content of MgO of cement clinker at 2.0-6.0%.
Owner:CHINA BUILDING MATERIALS ACAD
Preparation method for red mud-based iron-series catalyst and application of red mud-based iron-series catalyst in hydrogen production through cracking of methane
InactiveCN105478120AWell-developed pore structureIncrease contentHydrogenHeterogenous catalyst chemical elementsDispersityRed mud
Owner:HENAN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Microscomic numerical model generation method considering rock structure characteristics and mineral composition
ActiveCN110069844ASimulation is accurateImprove computing efficiencyDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsFree interfaceMineral particles
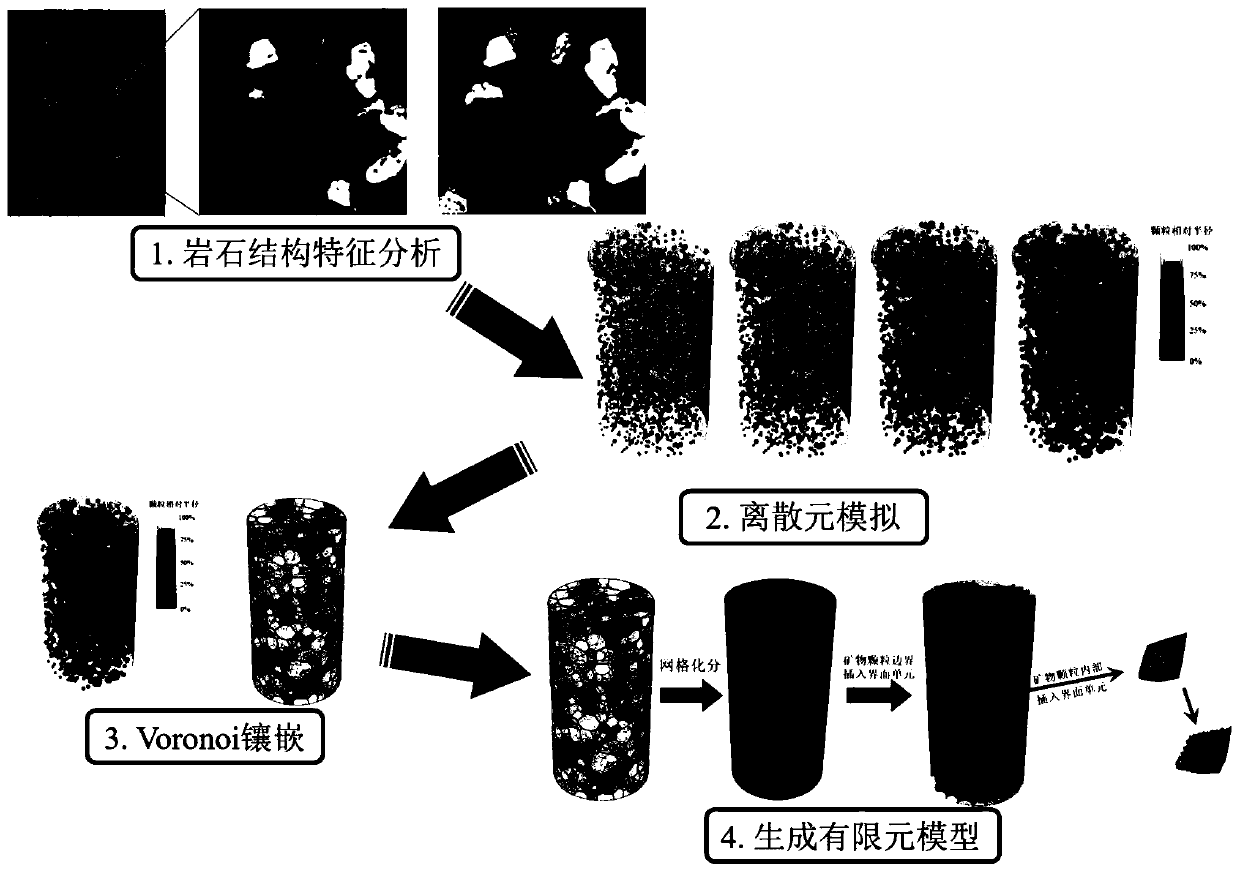
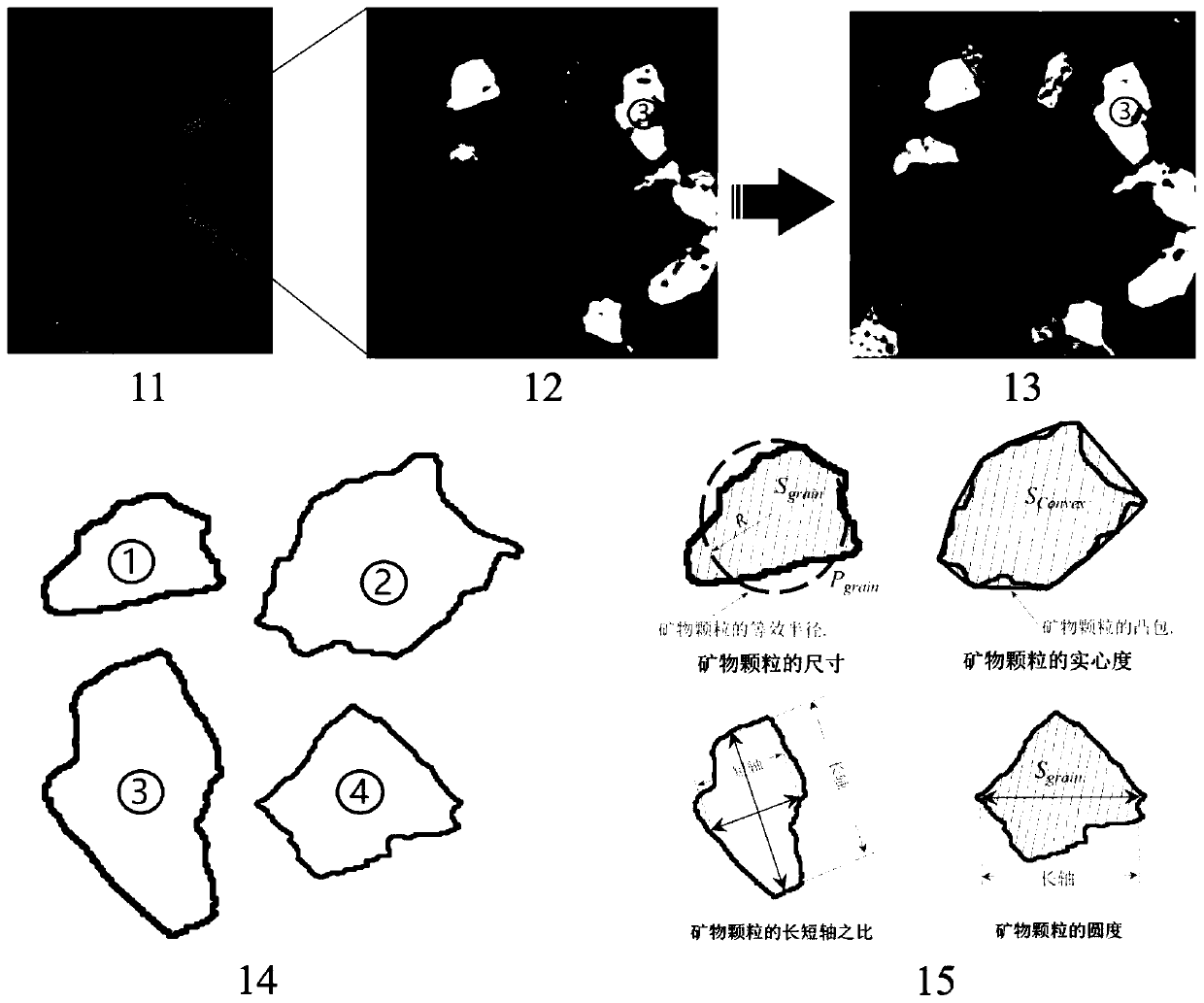
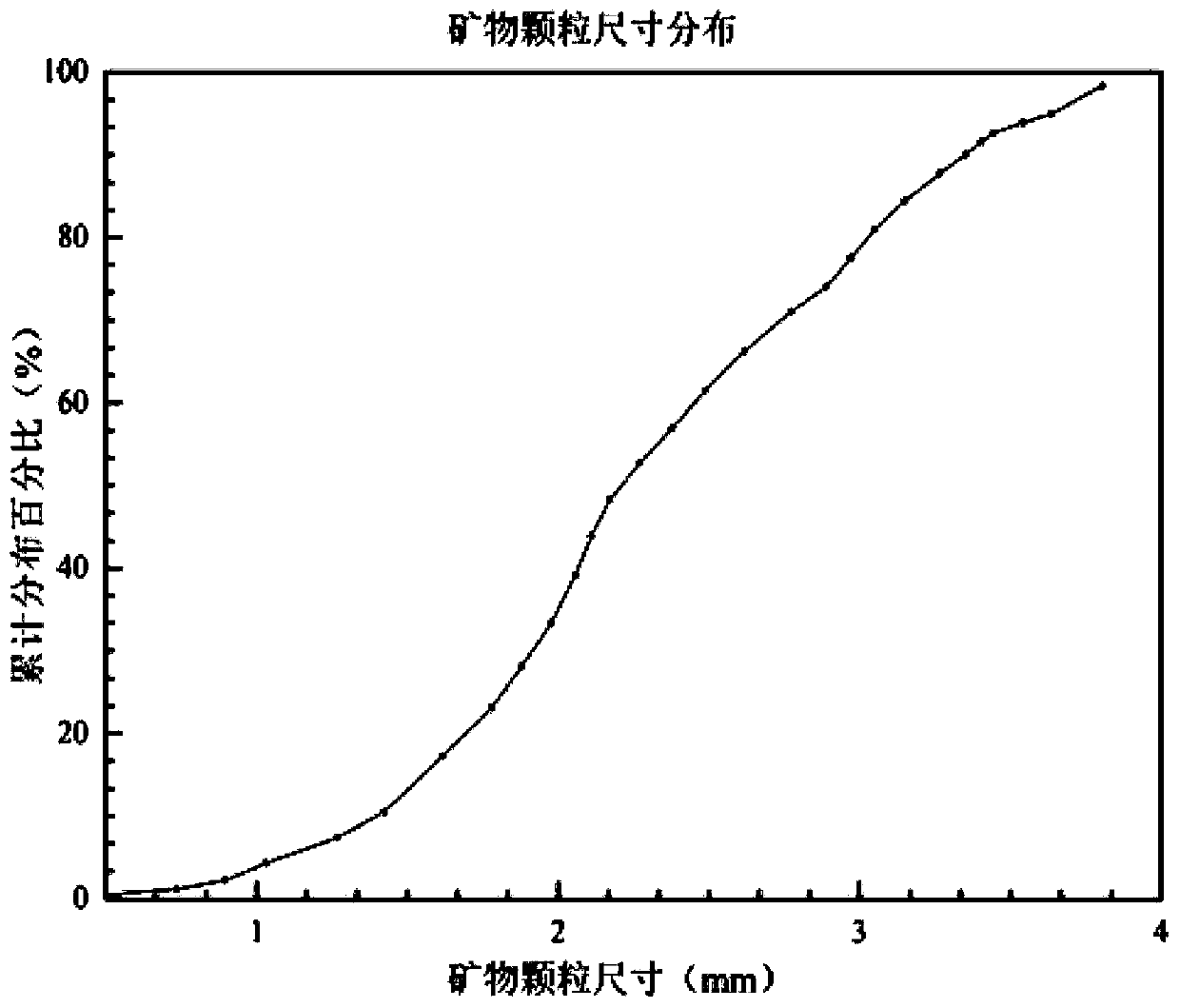
The invention discloses a microscomic numerical model generation method considering rock structure characteristics and mineral composition. Microscopic structure characteristics and mineral composition of rock can be considered, a microscopic numerical model reflecting the rock structure characteristics and the mineral composition is established, and rock mechanics numerical simulation can be carried out more truly. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out rock structure characteristic analysis on a rock sample to obtain the size, form, mineral type and other information of mineral particles; simplifying the mineral particles with irregular shapes into balls with reduced sizes, and rearranging the particles by adopting a particle size expansion method, and obtaining a compact structure; secondly, extracting information such as spatial positions and sizes of particles, and performing Voronoi graph-based spatial region division on the particle assembly; and finally, performing finite element mesh division on the obtained Voronoi polycrystal structure, and inserting thickness-free interface units into mineral particle boundaries and the interiors of particles to generate a finite element numerical model capable of reflecting a rock structure and a lithofacies structure.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Shale classification method
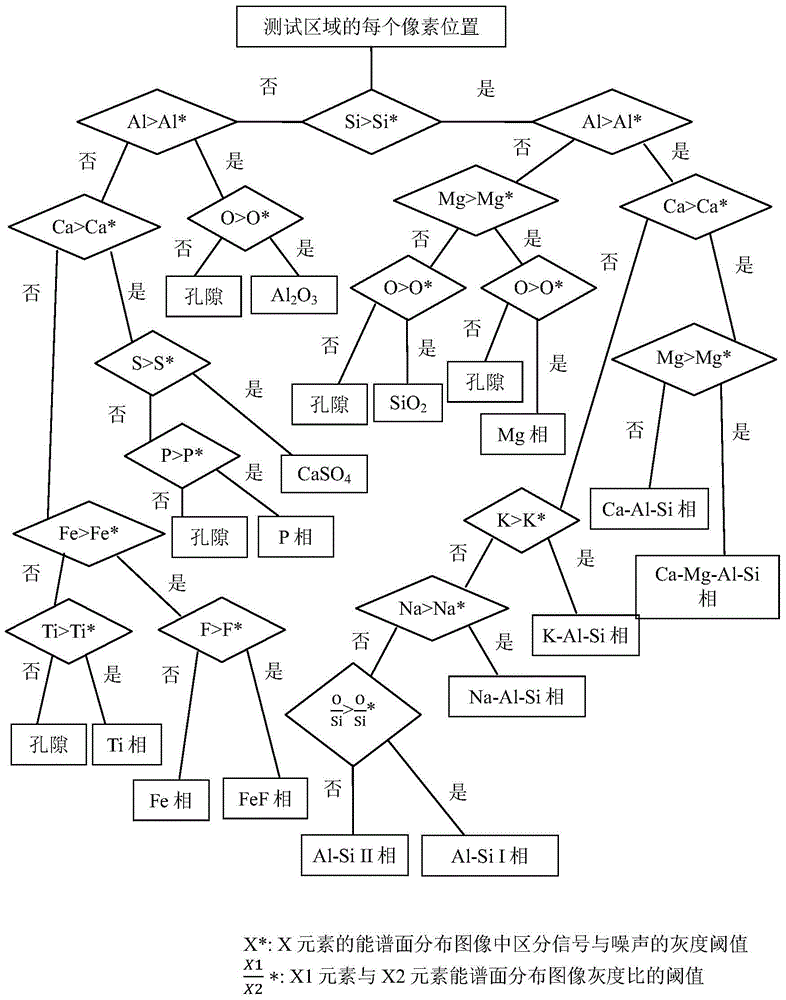
The invention discloses a shale classification method. The method includes the first step of determining the types of macroscopic structures of shales by observing shale cores, the second step of determining organic matter types and total content of organic carbon through kerogen and organic carbon analysis and obtaining the volume fraction of organic matter components through the total content of organic carbon, a conversion coefficient, the organic matter density and the rock density, the third step of determining mineral composition of the shales and obtaining the volume fraction of calcareous mineral components, the volume fraction of felsic mineral components and the volume fraction of clay mineral components through thin section authentication and total rock mineral analysis, the fourth step of classifying the shales according to the four-component three-end-member principle, and the last step of classifying the shales and conducting reasonable simplification through a core macroscopic structure and rock type combined method. The shale classification method is applicable to laboratory studies and outside work, is a method with reasonable logic and high operability for classification of the shales, solves the problems that the shale classification methods are varied and the organic matter components are ignored, and can be used for studying formation causes of the shales conveniently and guiding field logging and fracturing transformation.
Owner:董春梅
Enhanced recovery response prediction
ActiveUS20170017011A1Easy to explainImprove aspectEarth material testingPermeability/surface area analysisLaboratory Test ResultRock sample
Owner:CONOCOPHILLIPS CO
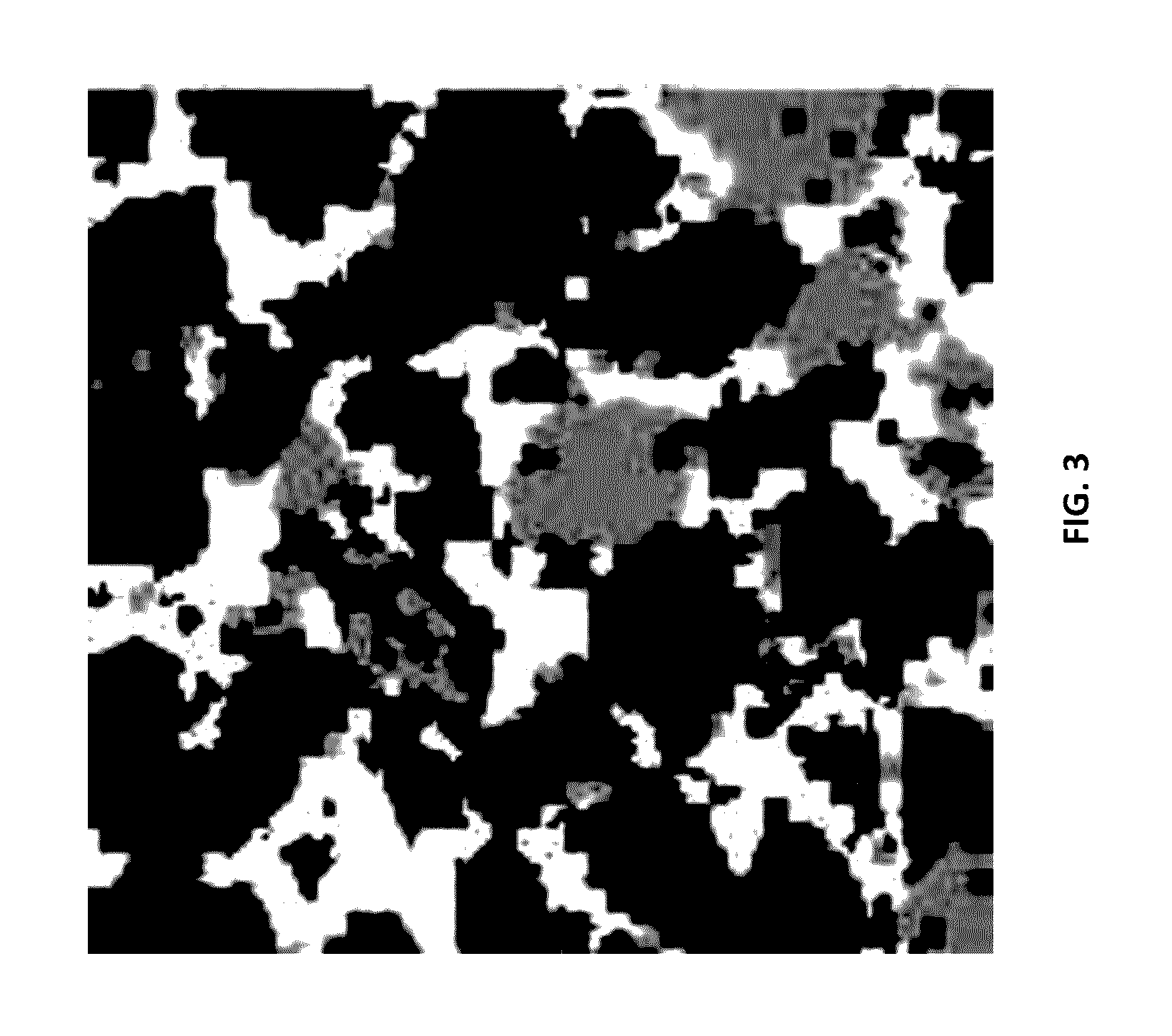
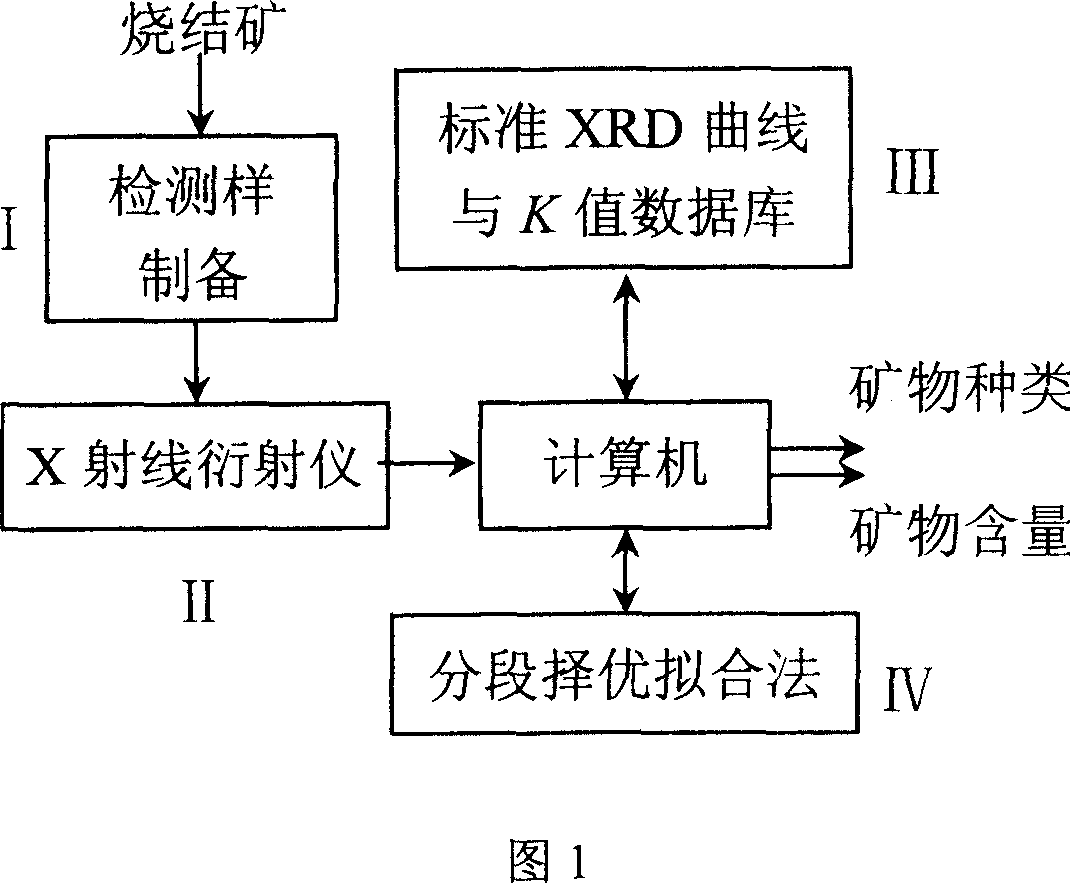
Automatically identifying and quantitatively detecting method for high alkalinity sintered ore main minerals
InactiveCN1945298AQuantitative speedSolve the problem of structural parameter uncertaintySpecial data processing applicationsMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionAlkalinityX-ray
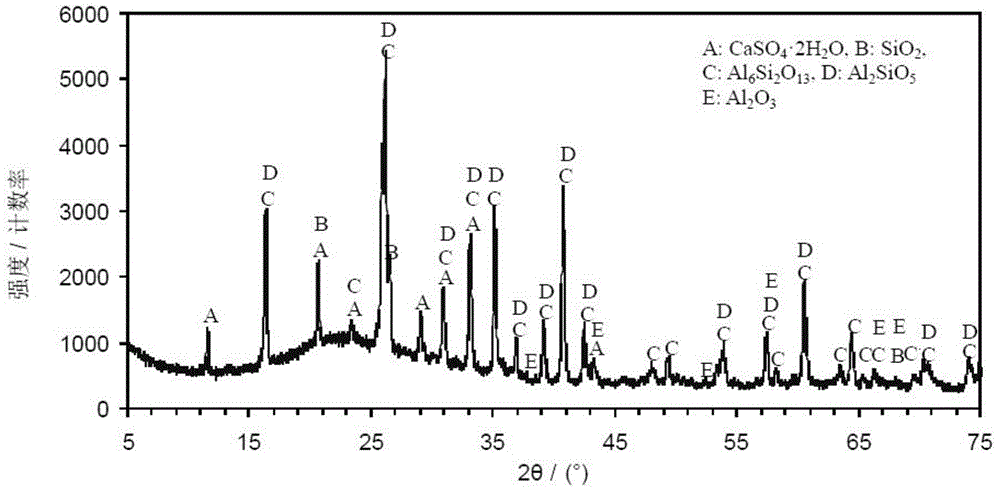
The automatic main mineral identifying and quantitatively detecting method for high alkalinity sintered ore belongs to the field of metallurgical technology. The method includes four parts of preparing sintered ore sample, X ray diffraction condition for quantitative analysis, standard diffraction curve database of high alkalinity sintered ore minerals, and sectional optimizing fitting and computer software. The method of the present invention makes it possible to identify the minerals in high alkalinity sintered ore and measure the content fast automatically. In addition, the present invention has less sampling error and no visual error.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
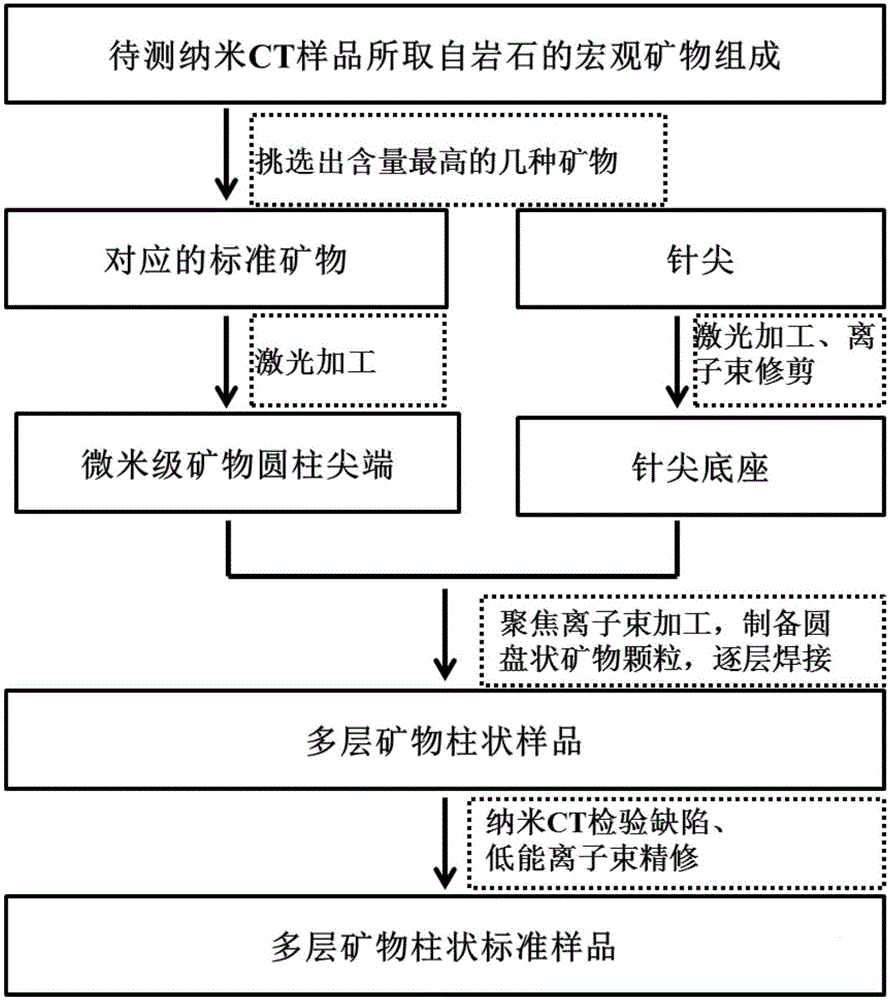
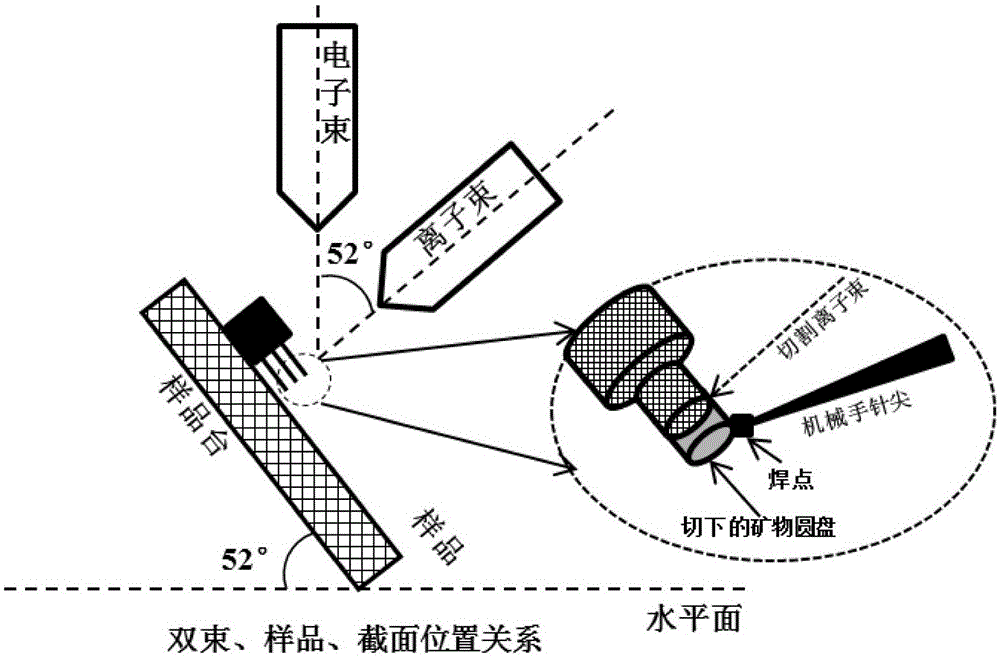
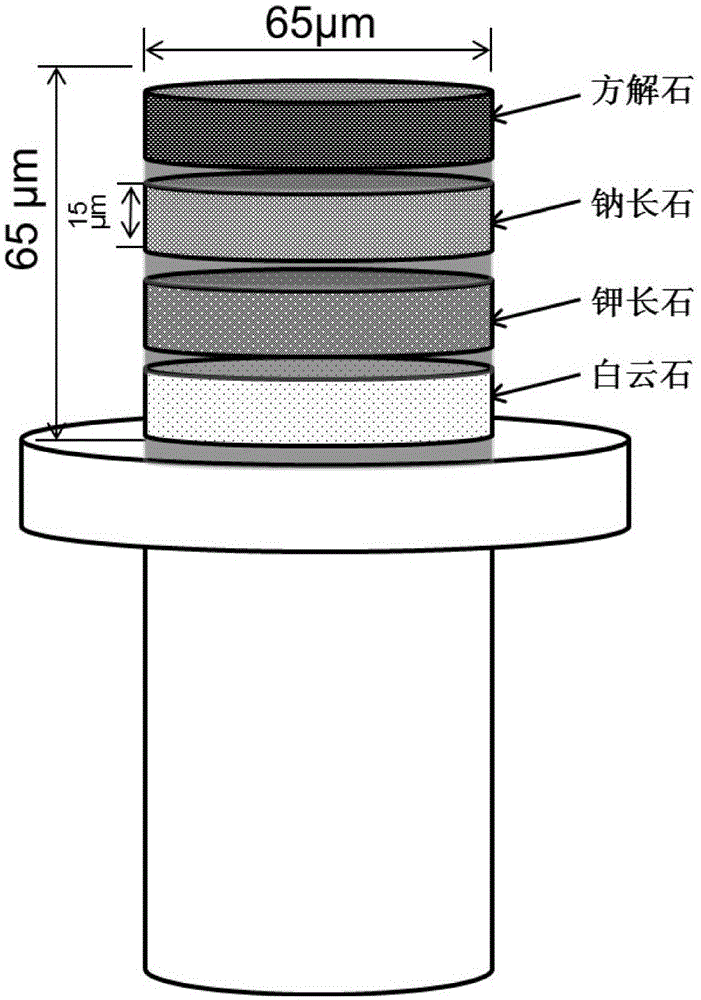
Mineral standard sample used for nanometer CT, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105067395AFill vacancyRealize one-time calibrationPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationMineral particlesMineral identification
The invention provides a mineral standard sample used for nanometer CT, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method of the mineral standard sample comprises the following steps: selecting standard mineral particles according to the mineral composition of a rock to be measured; respectively processing at least one of the selected standard mineral particles to form mineral sample discs; and welding one of the mineral sample discs to a pedestal, and stacking and welding all the mineral sample discs to form the mineral standard sample. When the mineral standard sample is used in mineral analysis, mineral identification is carried out by using the gray scale information of the standard mineral sample and a rock sample to make unknown mineral particles in the rock sample identified and calibrated, so the three dimensional distribution, the volume proportions and the mineral particle dimension distribution of corresponding mineral components in the rock sample are obtained. The method effectively fills up the gap in preparation methods of like standard samples, and meets urgent demands of microscopic three dimensional mineral analysis in the petroleum geology field.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Additives for cement
The invention provides a belite-calcium sulphoaluminate-ferrite (BCSAF) cement composition comprising: a BCSAF clinker which clinker has the following mineralogical composition, based on the total weight of the clinker: 5 to 25%, preferably 10 to 20%, of a calcium aluminoferrite phase having the general formula C2AxF(1-X), wherein X is from 0.2 to 0.8; 15 to 35% of a calcium sulphoaluminate phase; 40 to 75% of belite (C2S); from 0.01 to 10% in total of one or more minor phases selected from calcium sulphates, alkali metal sulphates, perovskite, calcium aluminates, gehlenite, free lime and periclase and / or a vitreous phase; and an alkanolamine.
Owner:HOLCIM
Method of making pozzolands and cementitious materials from coal combustion by-products
InactiveUS20060032408A1Permanently eliminating damageSpace is requiredSolid waste managementMaterials sciencePozzolan
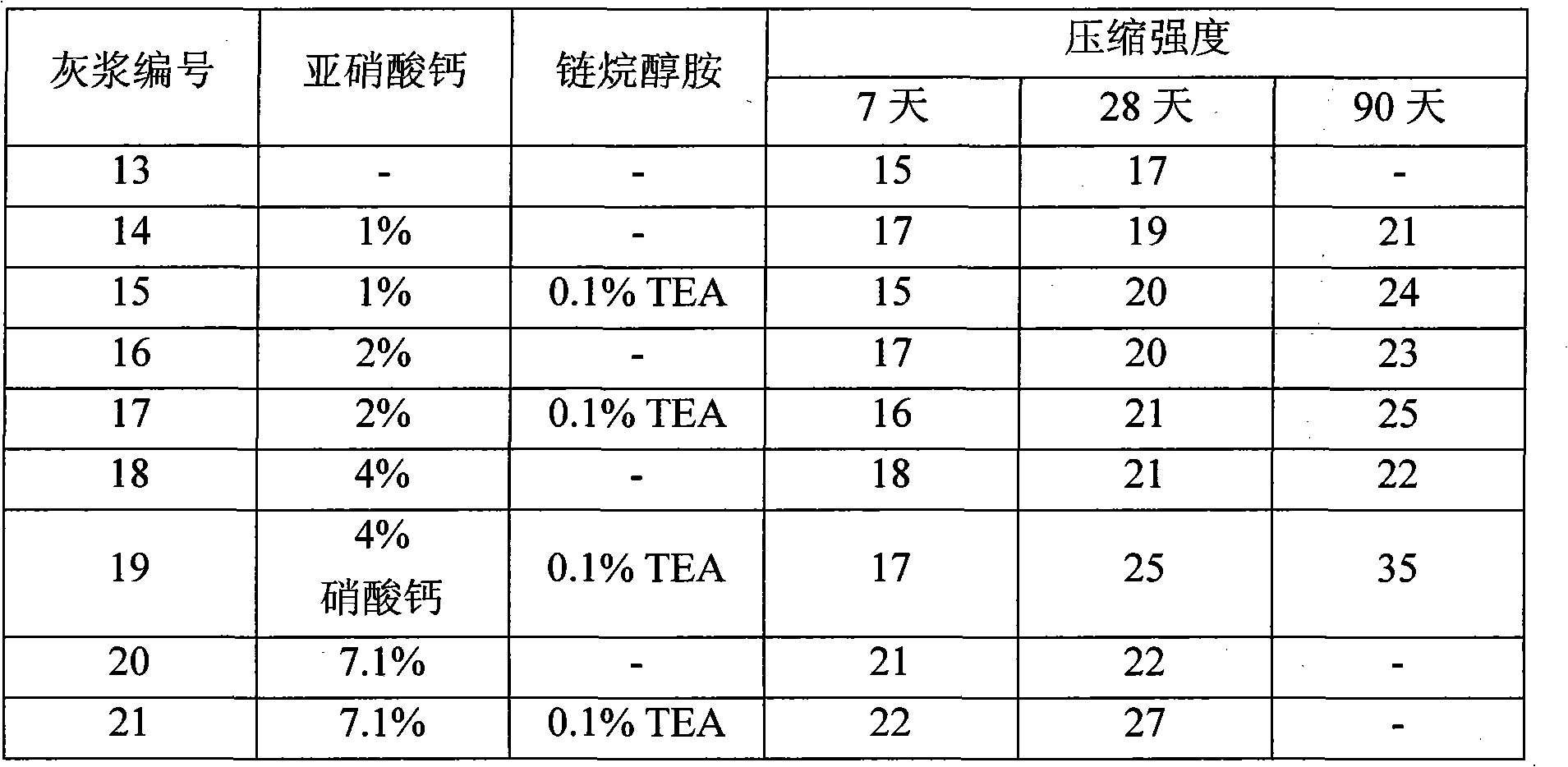
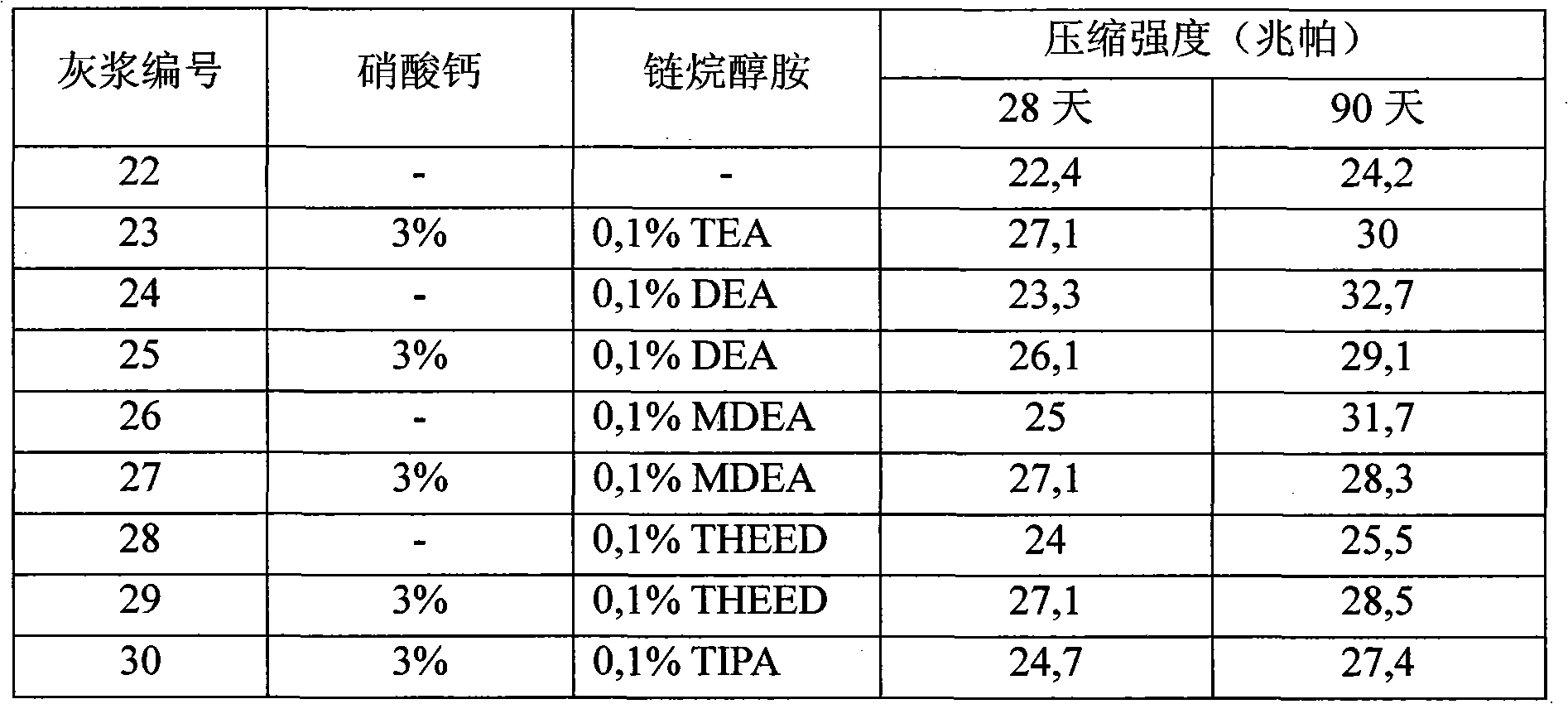
Ash produced by many coal-fired utilities has little or no commercial value as a cement additive or as a component in building materials because of its chemical or mineralogical composition. This condition is especially common with ash materials produced by Fluidized Bed Combustion boilers (FBC) or Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion boilers (CFBC) fired with bituminous coal or waste coals (gob) reclaimed from inactive coal mine sites. The present invention describes a novel process that converts otherwise low-value materials such as bottom and fly ashes produced by a FBC or CFBC boilers, for example, into materials that have desirable physical, chemical and mineralogical compositions that can be used as a valuable cement additive or component in building materials. The novel process closely integrates the boiler (steam generator) that produces the ash with a new high-temperature process, such as a kiln. The ash is mixed with limestone or other bulk materials to provide a feed for the kiln of the desired chemical composition. The mixture is treated at elevated temperatures in the kiln to produce a product, that in combination with further processing, exhibits desirable pozzolanic properties. Integrating boiler and kiln operations provides economic and environmental benefits. Waste heat produced by the kiln that would otherwise be released into the atmosphere is made available to the steam or turbine cycle, thus improving the overall boiler heat rate. Effluents and gases produced by the kiln may be efficiently treated by the boiler environmental control systems or independent environmental control systems. Novel production methods and feed materials will be claimed.
Owner:STRABALA WILLIAM M
Method for simulating and estimating sandstone properties
InactiveUS7933757B2Computation using non-denominational number representationGeological measurementsPorosityMineralogical composition
The invention is a method for simulating sandstone deposition. The sandstone is simulated by estimating the grain size distribution and mineral composition of grains in the sandstone, simulating sedimentation of grains from the grain size distribution and mineral composition of the grains, simulating compaction of the grains, and simulating cementation of the grains. Properties of the sandstone such as porosity and permeability may be estimated from the simulated sandstone. The method permits multiple mineralogies to be simulated during the burial history of sedimentation, compaction and cementation.
Owner:EXXONMOBIL UPSTREAM RES CO
Formula for producing sintered bricks from iron tailings and application of formula
InactiveCN105645917AReduce occupancyCompliance with Resource Utilization PolicySolid waste disposalBrickMaceral
The invention relates to a formula of for producing sintered bricks from iron tailings. The formula is applicable to the production of sintered bricks by taking fine-grain iron tailings as a main raw material. According to the formula, the iron tailings (or other metallic and nonmetallic tailings) which are subjected to concentrating and dewatering are mixed with a certain ratio of coal slurry so as to form raw materials, the content of SiO2 in the mixture is enabled to be higher than 50%, the content of Al2O3 in the mixture is enabled to be higher than 6%, the content of CaO in the mixture is enabled to be lower than 6%, the content of MgO in the mixture is enabled to be lower than 6%, the calorific value is controlled to be 1.465MJ / Kg to 1.780 MJ / Kg, and thus the requirements on green brick sintering are met. The formula has the effects that the mixture overcomes the defects of the iron tailings and the coal slurry separately served as raw materials of the sintered bricks, the mineral composition and physical properties of the raw materials are optimized, the comprehensive utilization of fine-grain tailings of mines is realized, and the reduction of the cost of the sintered bricks is facilitated.
Owner:范庆霞
Sepiolite-containing curing agent for treating heavy metal pollution soil
InactiveCN101962551AChange natureGood restorativeAgriculture tools and machinesSolid waste managementAgricultural landMaceral
The invention relates to the technical field of the treatment of polluted soil, in particular to a sepiolite-containing curing agent for treating heavy metal pollution soil. The curing agent comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 25 to 40 percent of cement, 40 to 65 percent of sepiolite and 10 to 20 percent of quicklime. The curing agent has the advantages that: the risk of secondary pollution is not caused and the property of the original soil is not changed remarkably when heavy metal ions are fixed by the sepiolite; and the mineral composition of the sepiolite is very close to that of the original powder clay, so that the cement and the quicklime are prevented from damaging a soil structure greatly. Due to the advantage, the curing agent remarkably recovers an agricultural land polluted by a heavy metal areal source and has good social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparing zirconium oxide/mullite crystal whisker multiple phase material
A method for preparing a zirconia / mullite whisker composite material by crushing, batching, co-grinding with high-energy ball milling, compacting and heat treatment using natural bauxite and zircon minerals as raw materials; the method prepares In the composite material structure, the average diameter of the mullite whiskers is 1.5-3 μm, the aspect ratio is 8-10, and the zirconia is evenly distributed in the network structure formed by the mullite whiskers in an irregular granular shape. The invention fully utilizes the chemical and mineral composition characteristics of natural bauxite and zircon minerals, and has the characteristics of low raw material cost, simple preparation process and environmental friendliness.
Owner:PUYANG REFRACTORIES GRP CO LTD
Method for measuring reflectivity of mineral and composition of mineral phase
InactiveCN101034059AReduce labor intensityReduce labor timeScattering properties measurementsComplex mathematical operationsPhase compositionImage acquisition
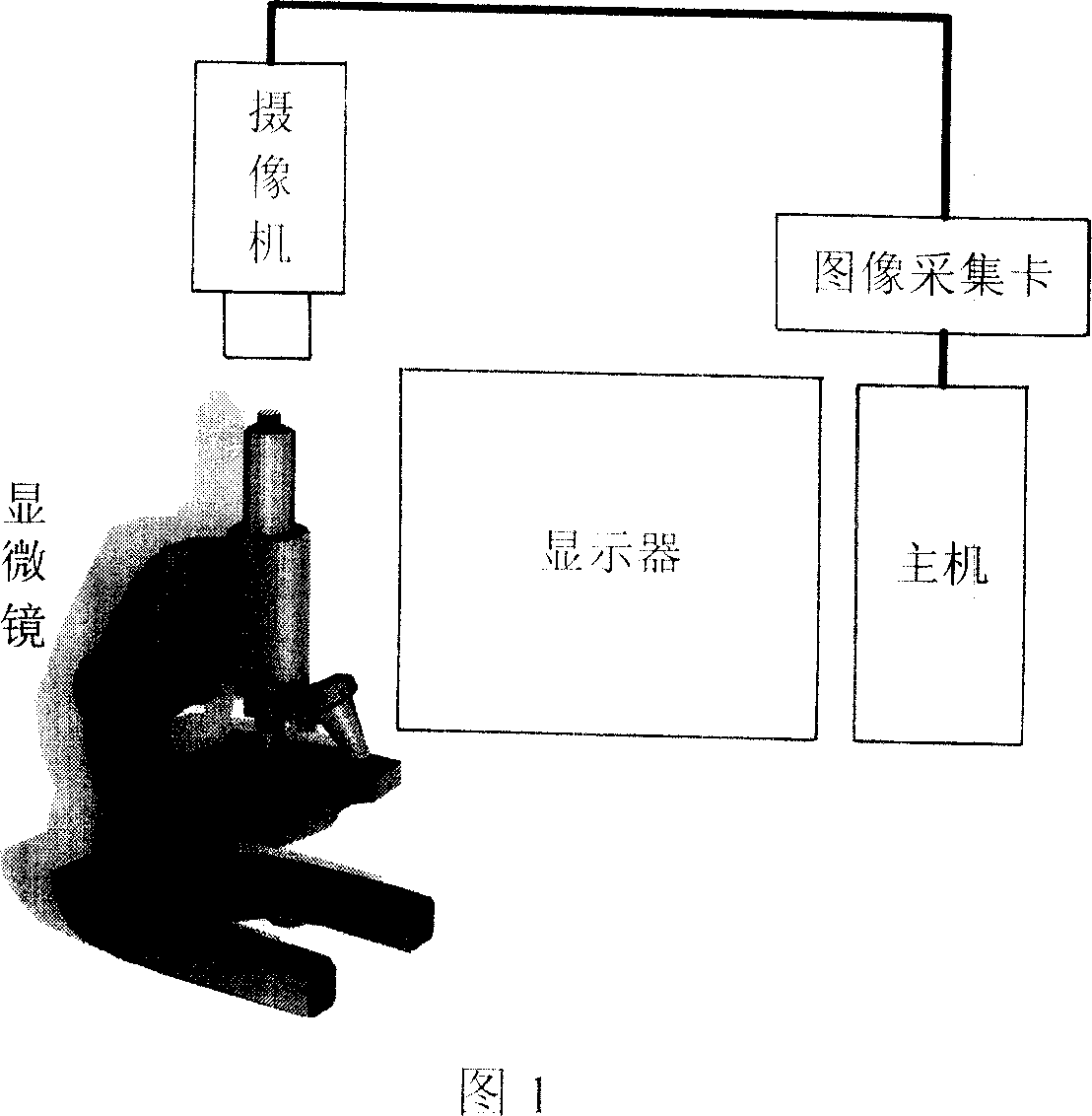
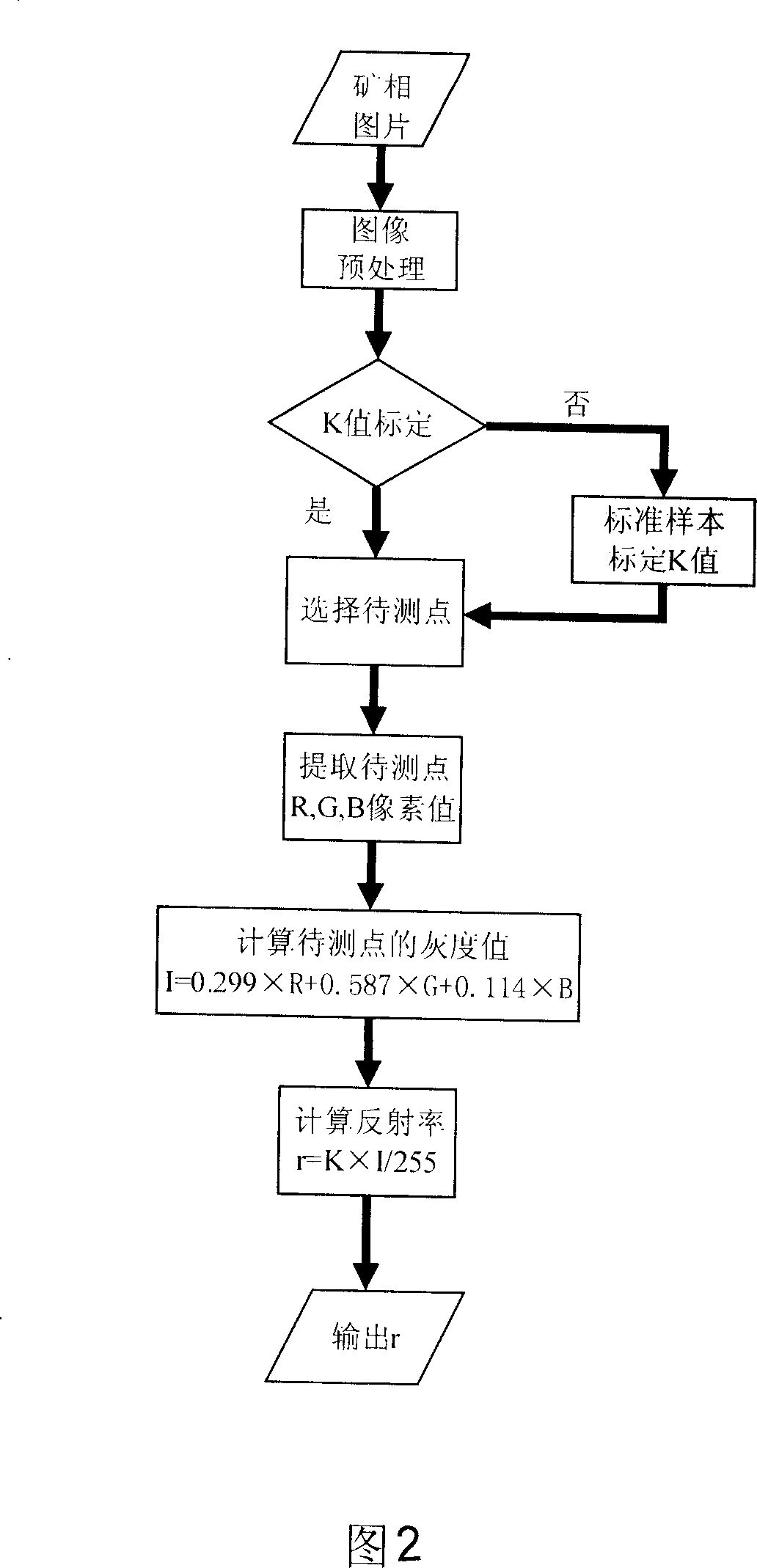
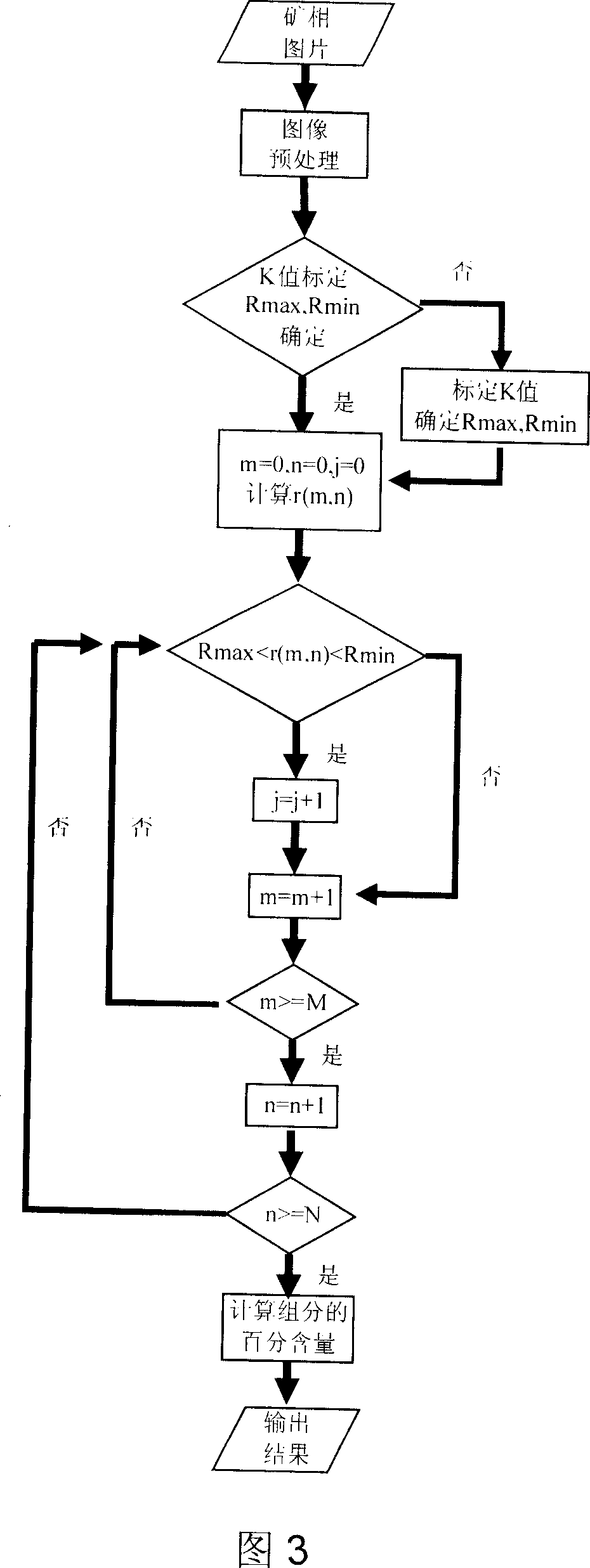
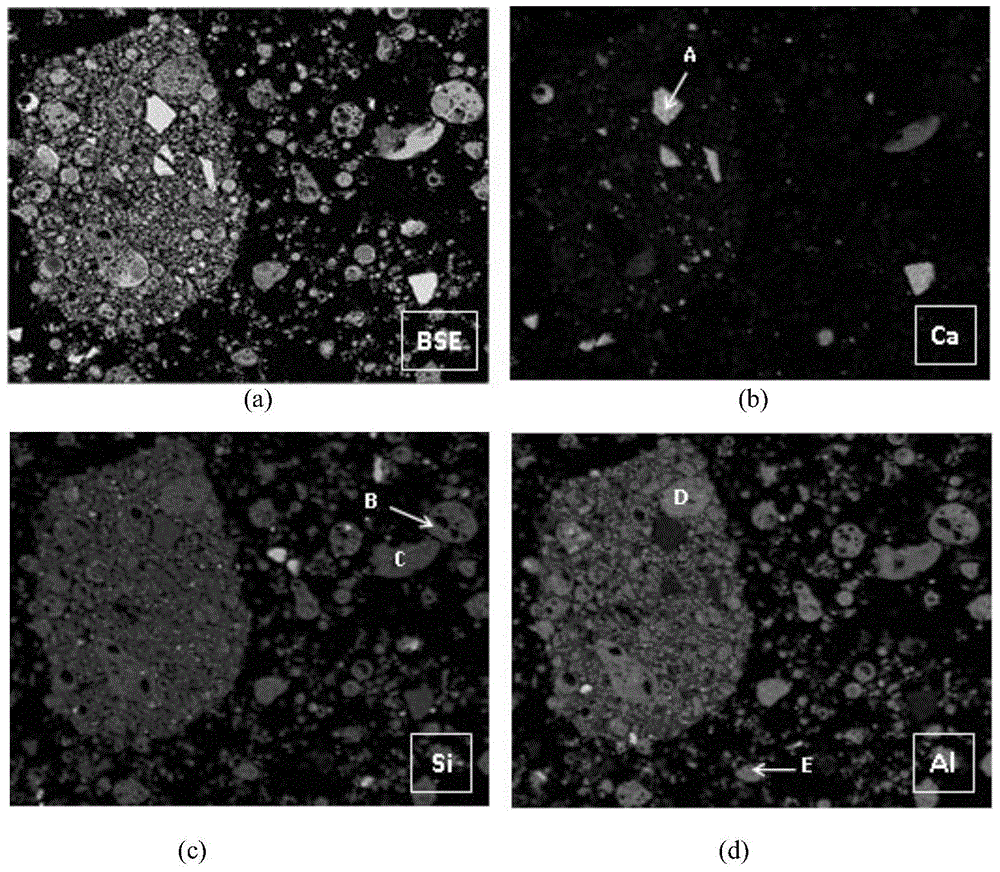
This invention supplies a method of measuring mineral reflectivity and mine phase composition. First put mineral polished section on reflected light microscope for observation, by camera and image collecting card to obtain mineral picture to input computer;then utilize given reflectivity core sample to carry out k value standardization of image acquisition system at certain intensity of irradiance; finally by computer calculating reflectivity and mineral composition content, calculator execute as follows step;image preprocessing;abstract measuring point's R, G, B pixel value; Calculate reflectivity base on this invention supplied model, and count pixel point size in whole picture belong to mineral reflectivity interval; thereby calculate reflectivity and mineral composition content. This invention not only accuracy, quickly, large depress detecting personnel labor intensity and working hours;Furthermore has no need of external equipment, just need fixing corresponding software, to realize mineral image reflectivity's two-dimension visualization.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
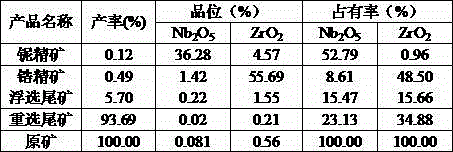
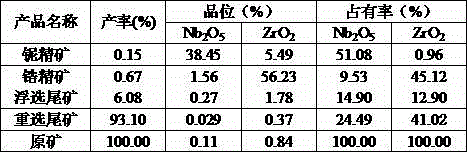
Niobium-zirconium ore mineral separation method
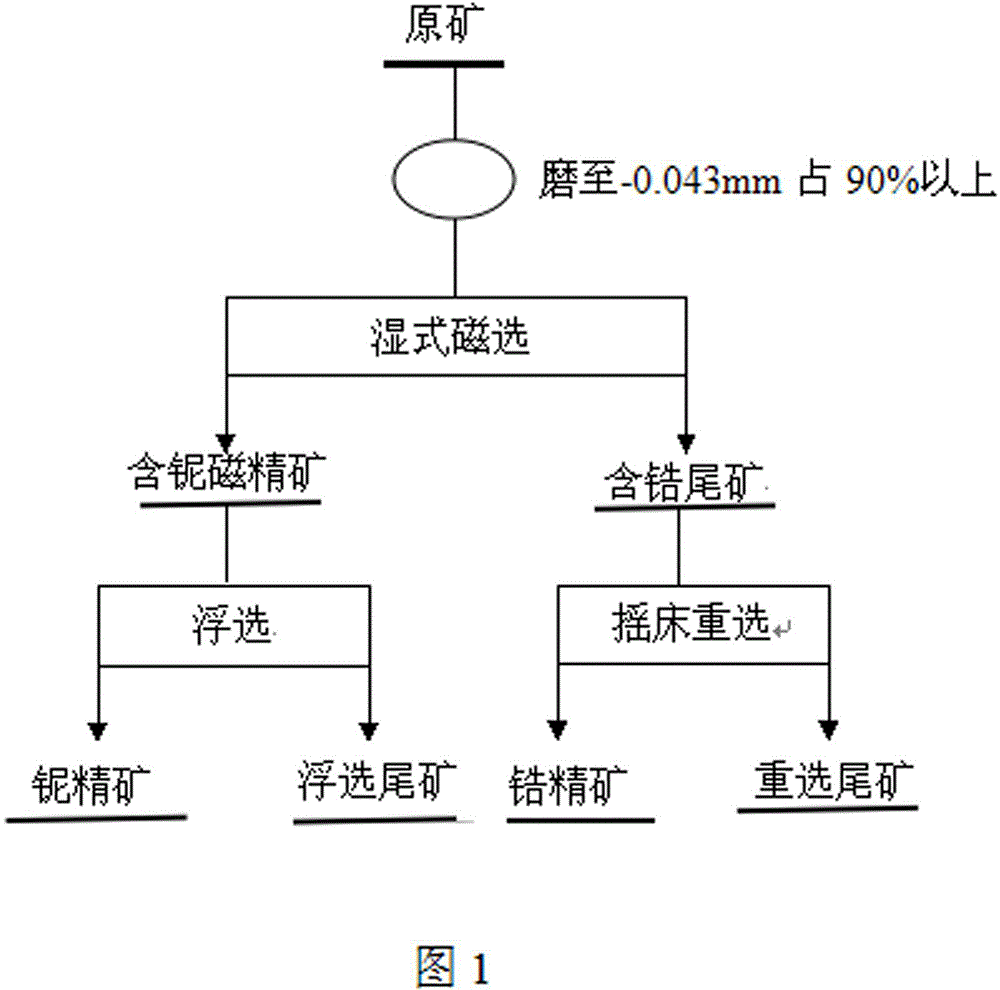
A niobium-zirconium ore mineral separation method is characterized by including the following steps of conducting wet magnetic separation to obtain zirconium-contained magnetic concentrates and niobium-contained tailings after grinding raw ore, conducting flotation on the zirconium-contained magnetic concentrates to obtain zirconium concentrates and flotation tailings with water glass as regulators and hydroximic acid granules as collectors, and conducting gravity separation by shaking tables on the niobium-contained tailings to obtain niobium concentrates and gravity separation tailings. The niobium-zirconium ore mineral separation method is simple in process; compared with the prior art, the Nb2O5 recovery rate is increased by about 20% and the ZrO2 recovery rate is increased by about 15%. The method is suitable for niobium-zirconium ore mines complex in mineral composition and fine in insetting grain size.
Owner:广东省工业技术研究院(广州有色金属研究院)
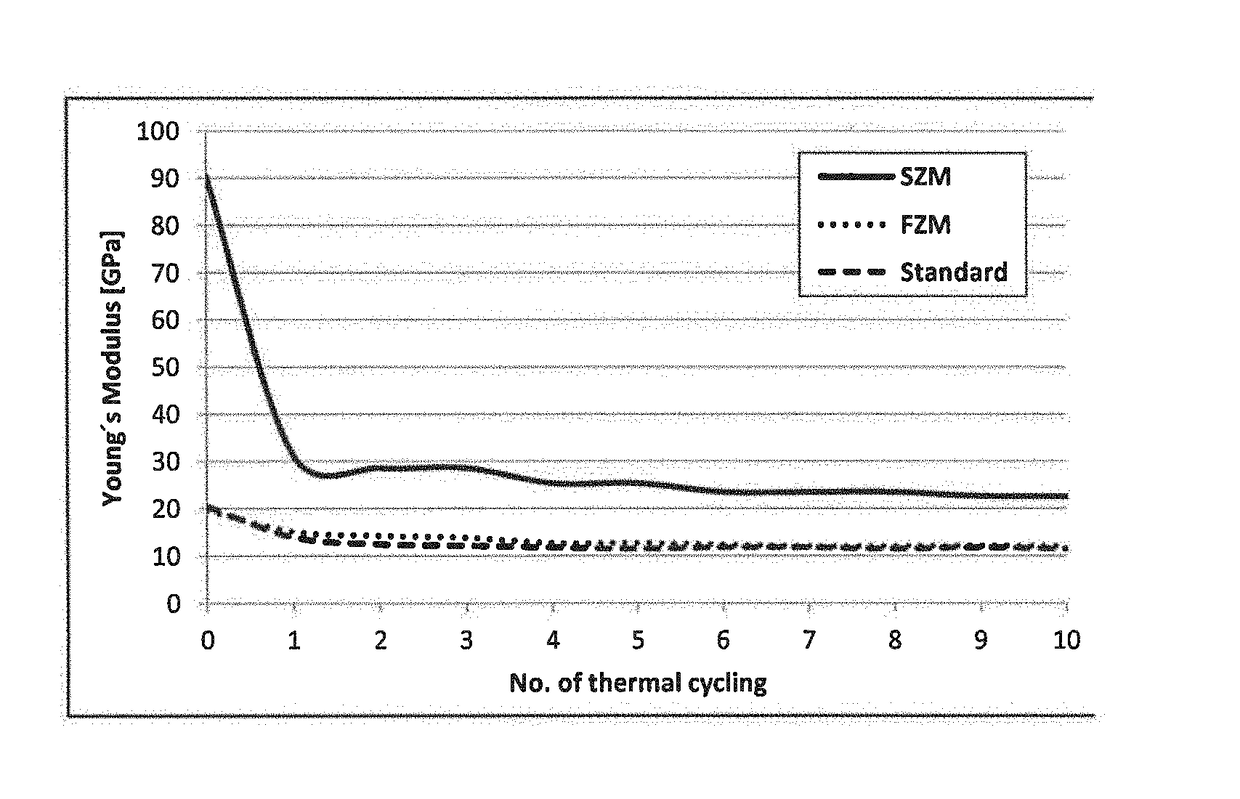
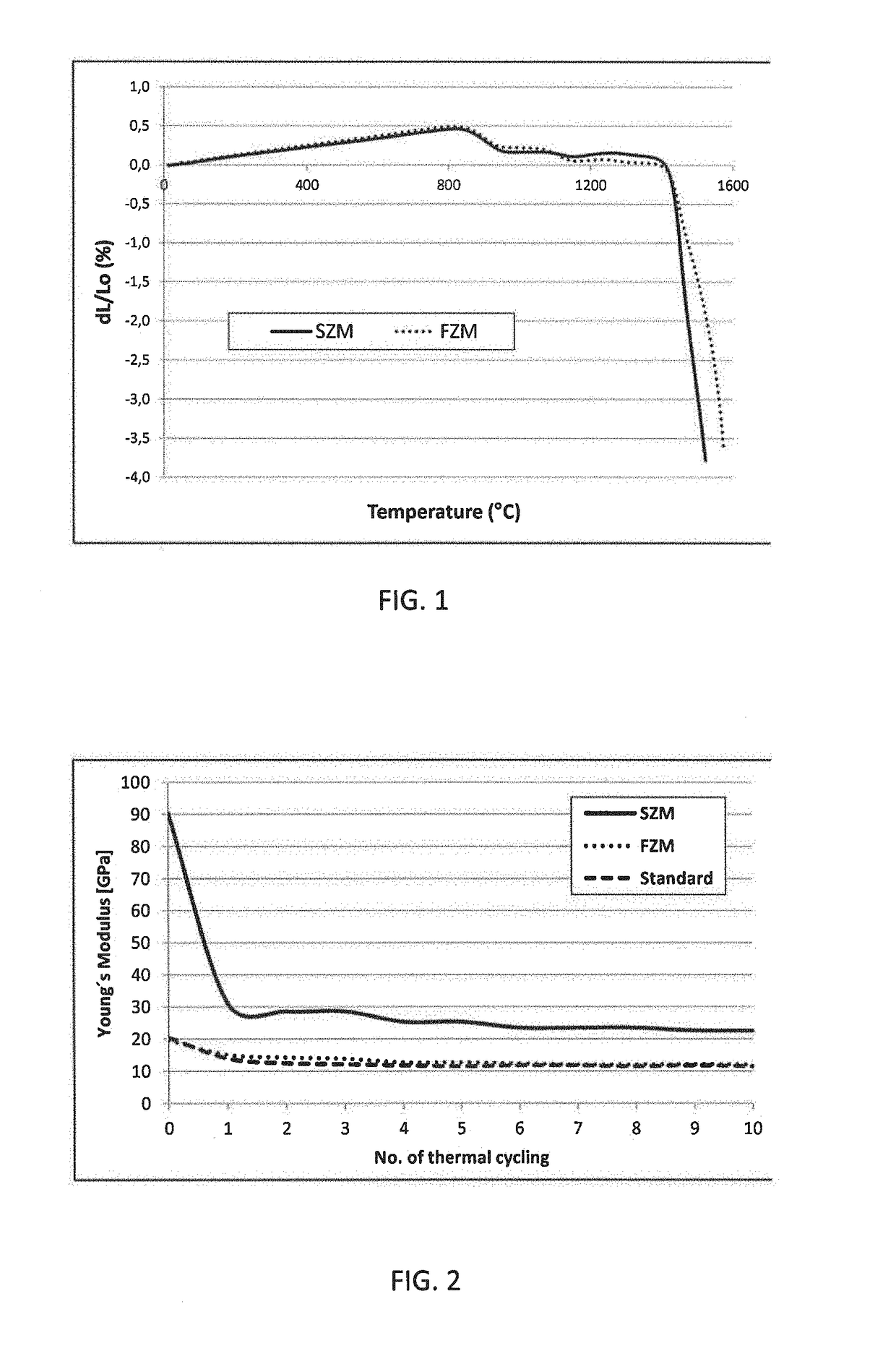
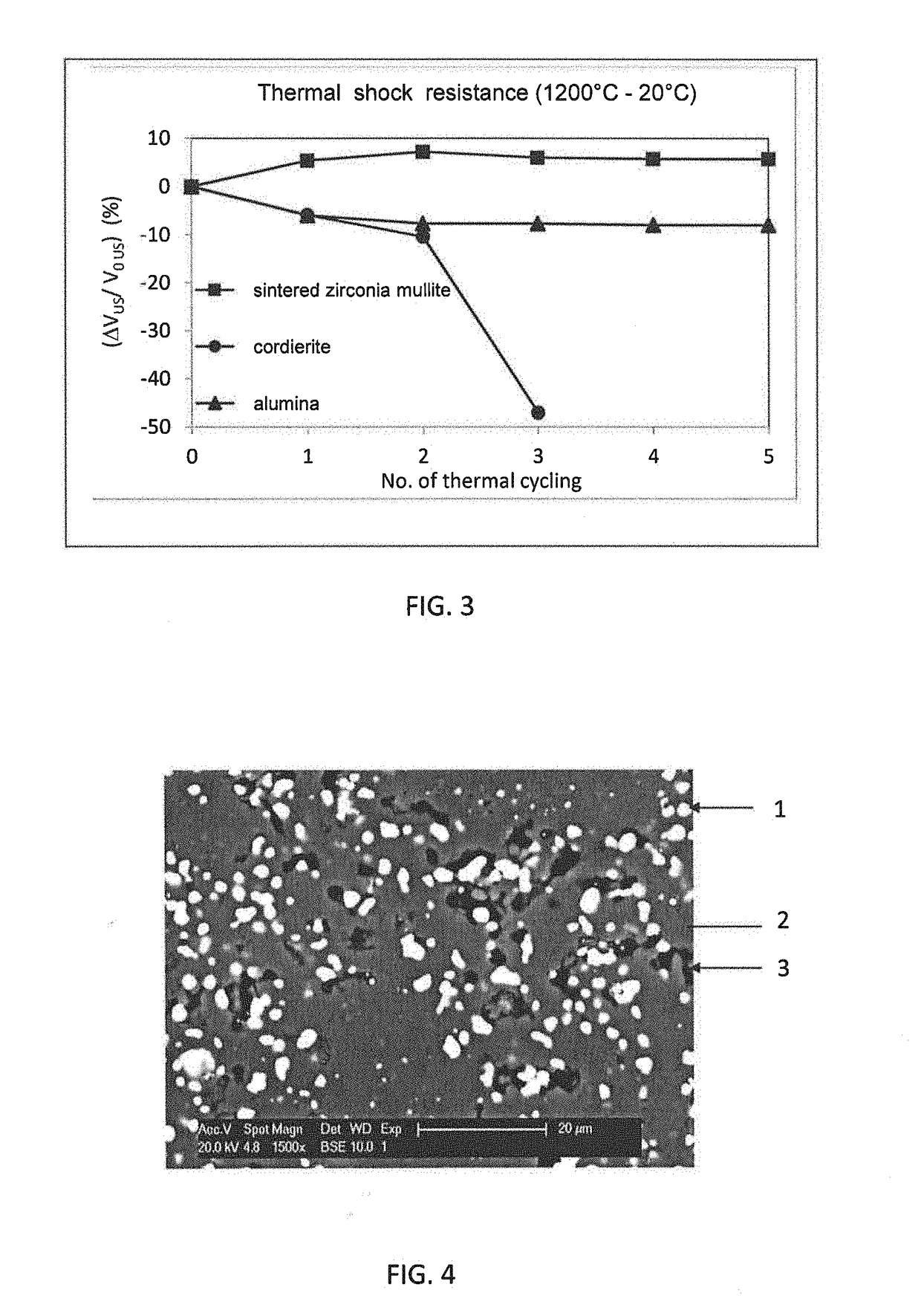
Sintered zirconia mullite refractory composite, methods for its production and use thereof
The present invention relates to a zirconia mullite refractory composite comprising 55 wt.-% to 65 wt.-% Al2O3, 15 wt.-% to 25 wt.-% SiO2, 15 wt.-% to 25 wt.-% ZrO2 and less than 3 wt.-% raw material based impurities, whereby the mineralogical composition of the composite comprises 65 wt.-% to 85 wt.-% mullite and 15 wt.-% to 35 wt.-% zirconia.
Owner:IMERTECH SAS
Diatomite-containing curing agent for controlling heavy-metal-contaminated soil
InactiveCN101962552AChange natureGood restorativeAgriculture tools and machinesSolid waste managementAgricultural landMaceral
The invention relates to the technical field of control of contaminated soil, in particular to a diatomite-containing curing agent for controlling heavy-metal-contaminated soil. The curing agent has the following materials by weight percent: 25-40 percent of cement, 40-65 percent of diatomite and 10-20 percent of calcined lime. The invention has the advantages of having no risk of secondary pollution while the diatomite fixes the heavy metal ions and having no obvious change for the properties of natural soil. The composition of minerals of the diatomite is very close to that of undisturbed silty clay, so that larger damage caused by the cement and the calcined lime to a soil body structure is avoided. Due to the advantage, the curing agent has very obvious effect for restoring agricultural lands contaminated by heavy metal surface sources, and has good social, economic and environmental benefits.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for oxidizing treatment of steel plant slag to obtain cement-based materials
InactiveUS6946014B2Improve propertiesImprove hydration kineticsManufacturing convertersCement productionSlagPortland cement
A method for treating a raw steel plant slag to transform it into a hydraulic binder at least equivalent to a Portland cement clinker, comprises the following steps: oxidizing treatment with input of oxygen, air or a mixture thereof at a pressure ranging between 1 to 15 bars, at a temperature ranging between 1650 and 1400° C., of raw steel slag containing, relative to the raw slag total weight, at least 45 wt. % of CaO and less than 30 wt. % of Fe2O3; and adding to the slag a lime source optionally with silica and / or alumina, so that the slag, after tranformation and at room temperature, has a propotion of Fe2O3 of less than 13 wt. % and a mineralogical composition comprising at least 40 wt. % in C3S mineralogical phase and more than 10 wt. %, of calcium ferrite, relative to the final slag total weight.
Owner:SA CIMENTS LAFARGE
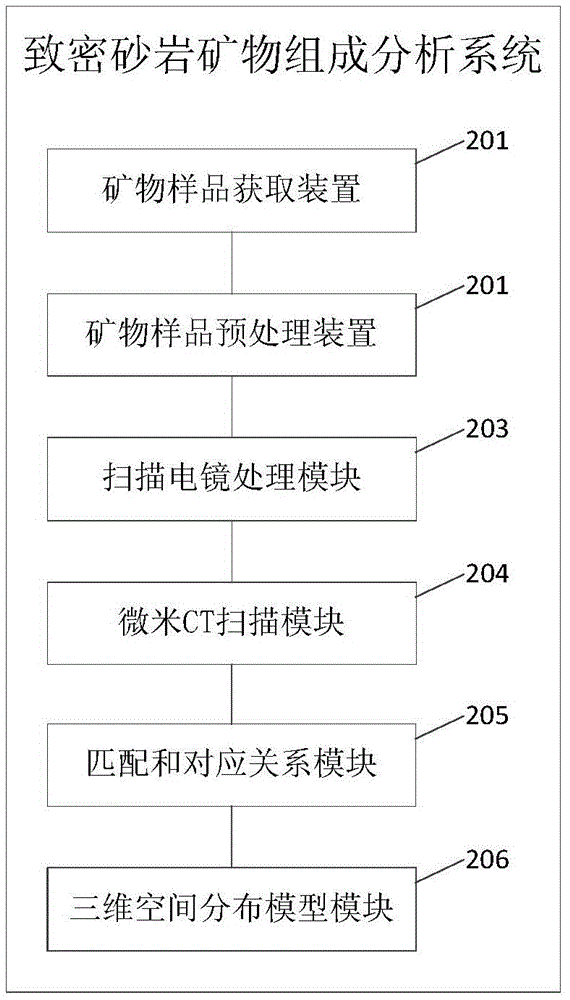
Method and system for analyzing mineral composition of dense sandstone
ActiveCN105628726AForm an intuitive imageThe composition is visually displayedCharacter and pattern recognitionMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationComputed tomographyDistribution characteristic
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method and a system for analyzing mineral composition of dense sandstone. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a mineral sample; pretreating the mineral sample; performing point-by-point energy spectrum analysis on the pretreated mineral sample by using a scanning electron microscope to obtain a scanning electron microscope gray image and a corresponding energy spectrum data volume, comparing the energy spectrum data volume with a standard mineral database, and determining mineral plane distribution characteristics of the gray image; performing micron CT scanning on the pretreated mineral sample, and acquiring a gray slice of a scanning result; comparing gray image with the gray slice, determining the gray image and a matching image in the gray slice, and according to the matching image and the gray image, determining a corresponding relation between a mineral in the gray slice and a gray value; and according to the corresponding relation, establishing a three-dimensional spatial distribution model of the mineral, and determining occurrence and spatial distribution characteristics of the mineral. Through the method and the system for analyzing the mineral composition of the dense sandstone, provided by the invention, accuracy and intuition of mineral composition analysis can be improved.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Energy dispersion X-ray spectrum-based analysis method for phases of fly ash
ActiveCN105241904AHigh resolutionThe number of particles is sufficientMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionColor imageFluorescence
The invention relates to an energy dispersion X-ray spectrum-based analysis method for phases of fly ash. The method comprises the following concrete steps: (1) analyzing chemical composition of the fly ash through a chemical process or X-ray spectrofluorimetry; (2) analyzing mineral composition of the fly ash through X-ray diffraction; (3) determining the kinds of elements requiring acquisition of images of power spectrum surface distribution; (4) acquiring backscattered electron images and element power spectrum surface distribution images of the fly ash and carrying out power spectrum point analysis on main phases; and (5) designing a phase analysis method, comprehensively processing the power spectrum surface distribution images of every elements in a same area and then removing noise in analysis results so as to obtain phase-split pseudo-color images and phase analysis results of the fly ash. The phase analysis method provided by the invention is effective to both crystalline and amorphous phases and sensitive to low-content phases. The method can be used for analyzing the kinds of phases composing the fly ash, calculating the volume percentage contents of the phases and observing spatial distribution of the phases.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
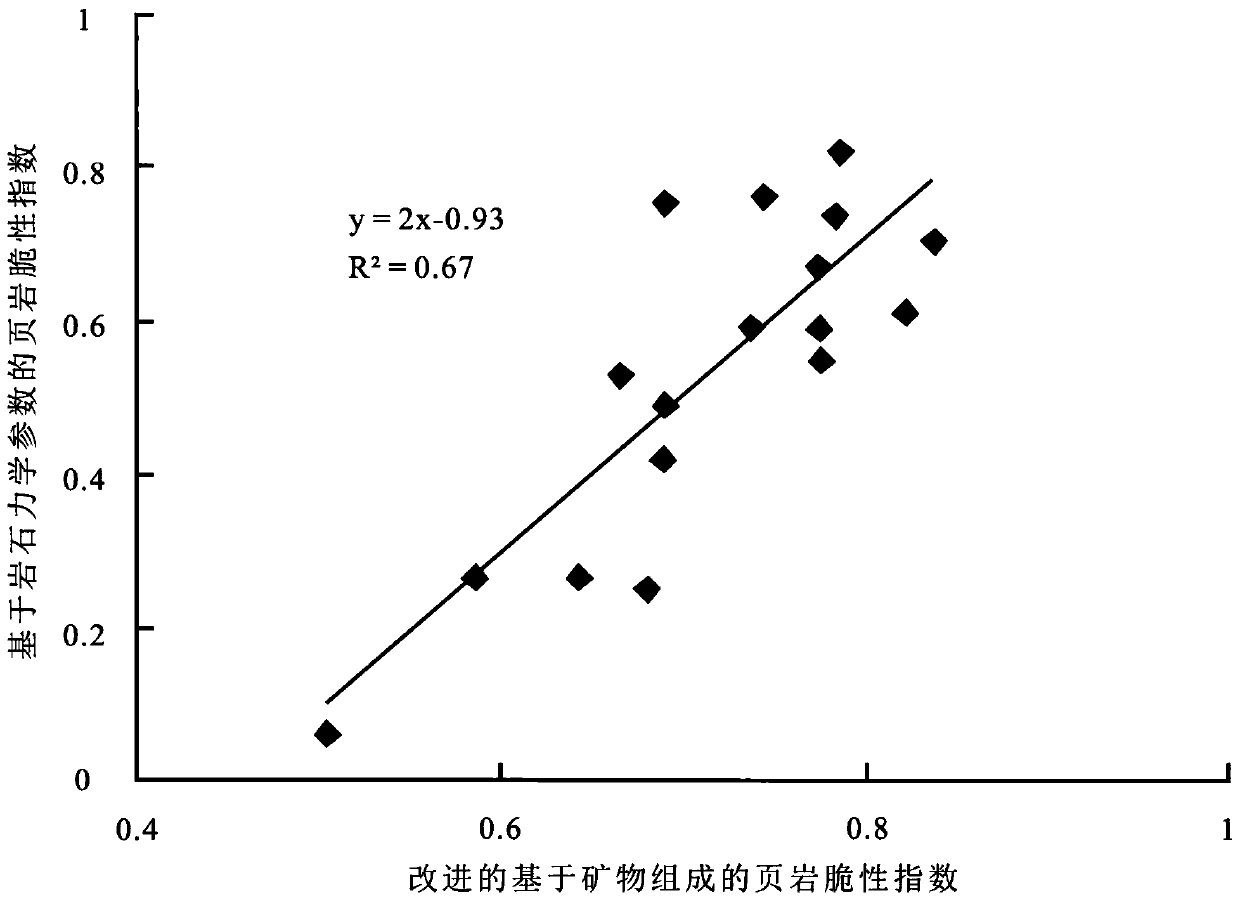
Method for determining improved shale brittleness index based on mineral composition
InactiveCN110596165AHigh precisionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial analysis by optical meansClay mineralsX-ray
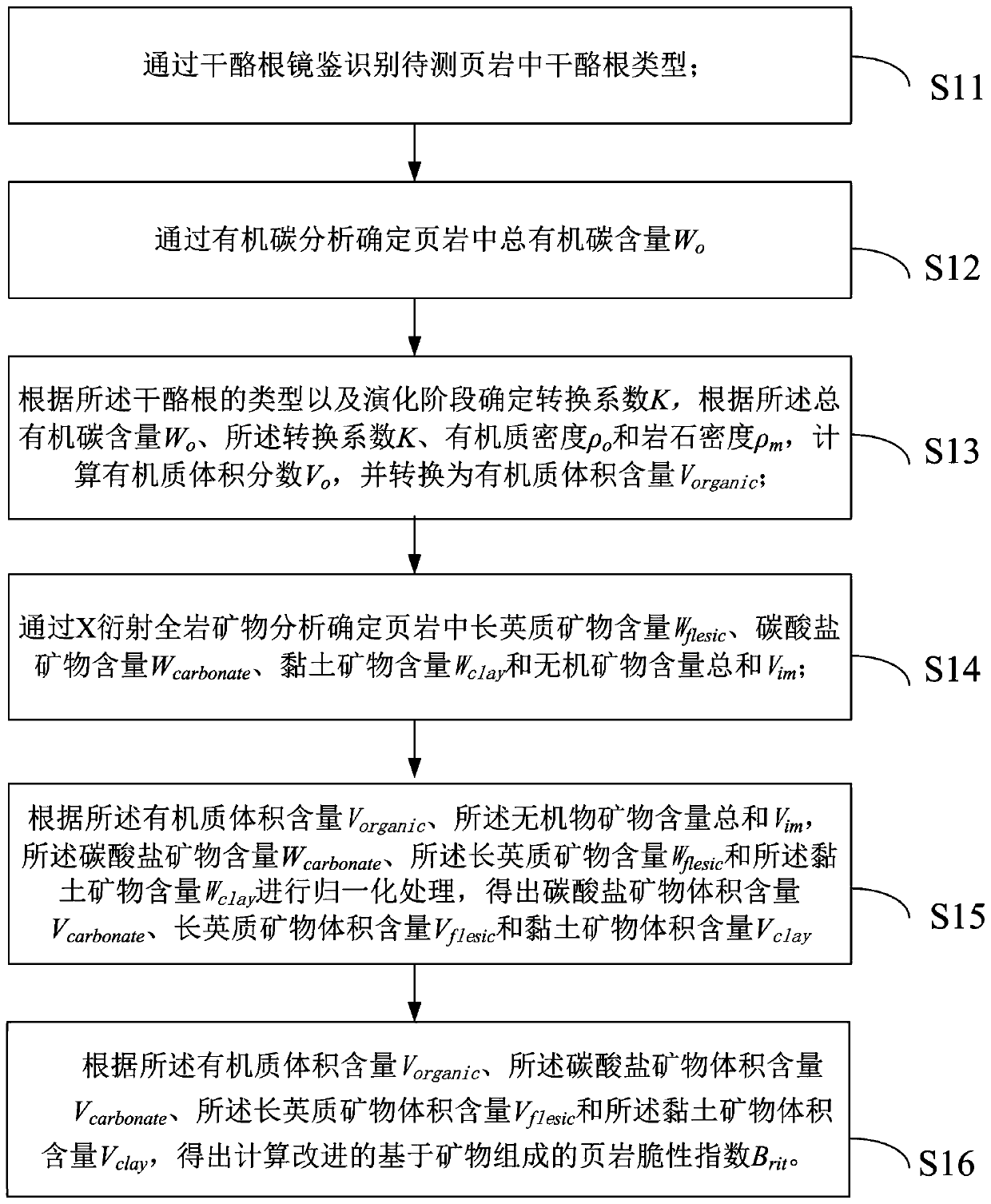
The invention discloses a method for determining an improved shale brittleness index based on mineral composition. The method comprises the steps of: identifying a kerogen type in to-be-tested shale through a kerogen mirror, and determining a total content Wo of organic carbon in the shale by organic carbon analysis; calculating a volume fraction Vo of an organic matter, and then figuring out a volume content Voganic of the organic matter; and determining the content Wflesic of femic minerals, the content Wcarbanate of carbonate minerals, the content Wclay of clay minerals and a total sum Vimof inorganic minerals in the shale through X-ray diffraction total rock mineral analysis, performing normalization processing to obtain the volume content Vcarbonate of the carbonate minerals, the volume content Vflicec of the femic minerals and the volume content Vcarbonate of the clay minerals, and calculating the improved shale brittleness index Brit based on mineral composition. By adopting the method, the dual effect of the carbonate minerals on the compressibility of the shale can not only reflected, and the accuracy of the shale brittleness index is also improved.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
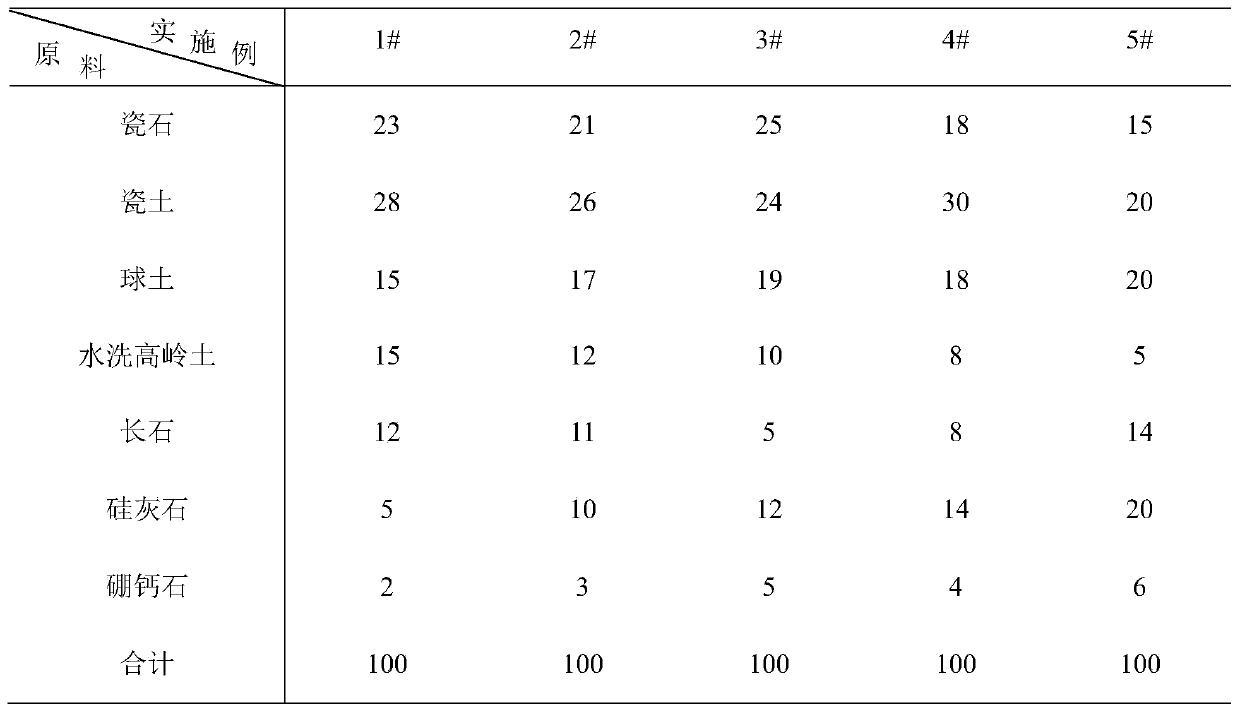
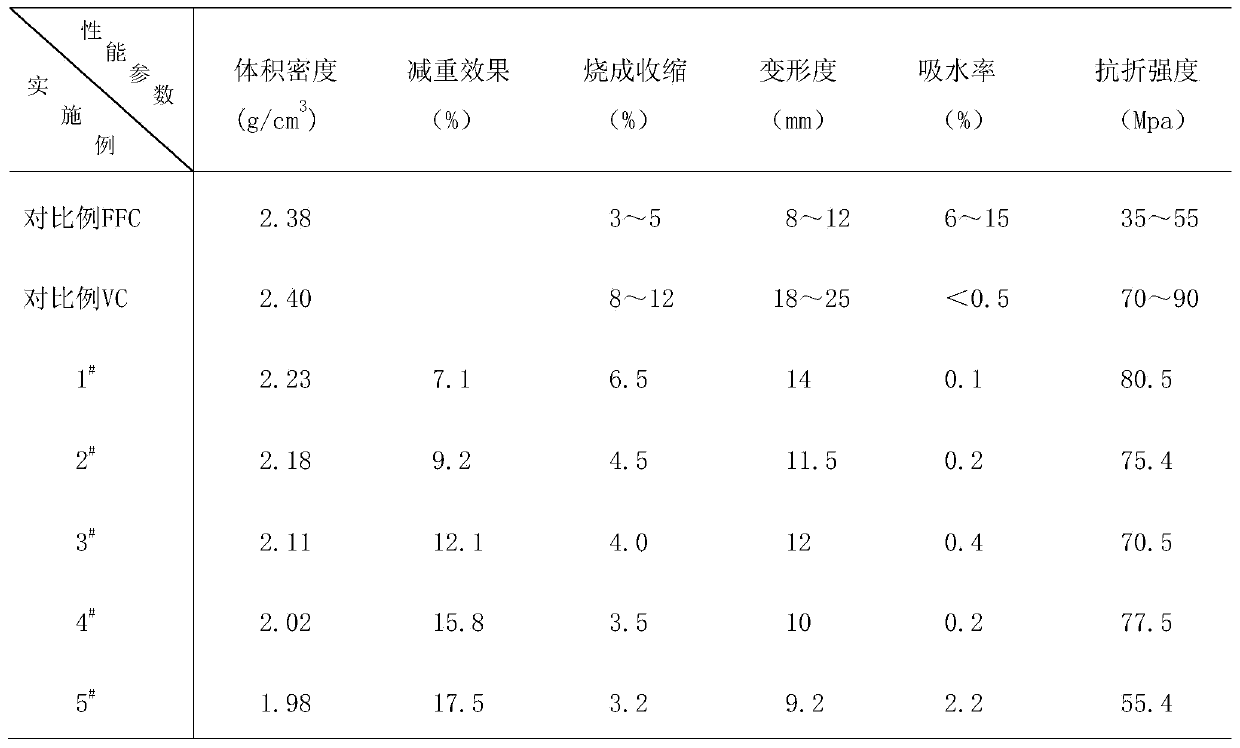
Sanitary ceramic formula and preparation method
ActiveCN111533530AHigh refractorinessSmall degree of deformationCeramic materials productionClaywaresChemical compositionMullite
The invention relates to the field of preparation processes of sanitary ceramics, in particular to a formula and a preparation method of sanitary ceramics, which improve the refractoriness of a greenbody and reduce the deformation degree of the green body by adjusting the raw material composition of the formula and optimizing the chemical composition. In the mineral composition of a common feldspar porcelain body, a proper amount of wollastonite raw material is introduced, the content of an anorthite crystalline phase is increased on the basis of original mullite and quartz crystalline phases, and a proper amount of closed independent pores are formed, so that the shrinkage rate and the volume density are reduced; by introducing a proper amount of the borocalcite flux, an (O = B-O-B = O)structure can be provided, the integrity and compactness of a network structure around the pores of the borocalcite flux are ensured, and the sizes of the independent pores are controlled within a certain range so as to avoid reduction of the firing strength.
Owner:HUIDA SANITARY WARE
Evaluation method for brittleness of shale
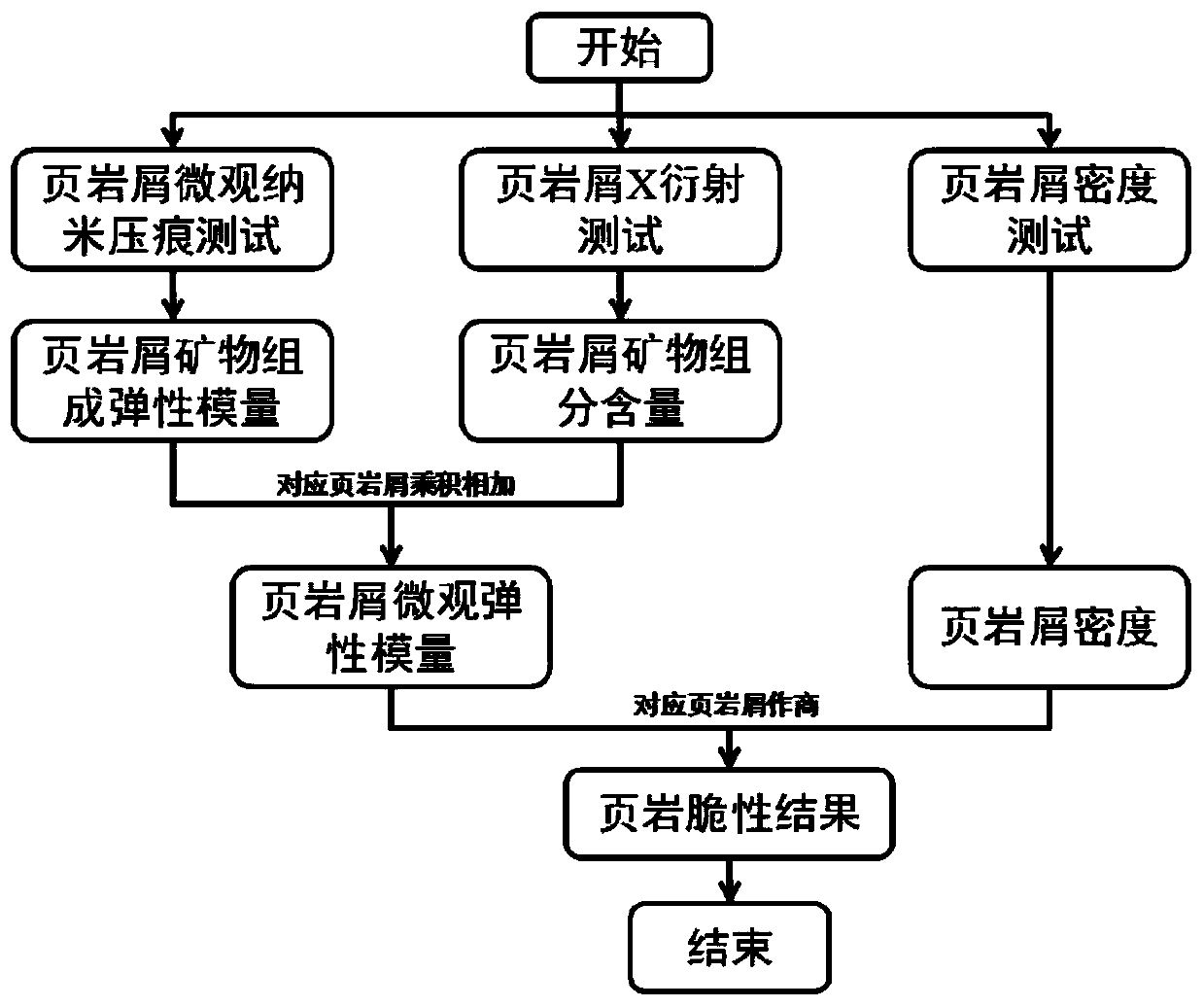
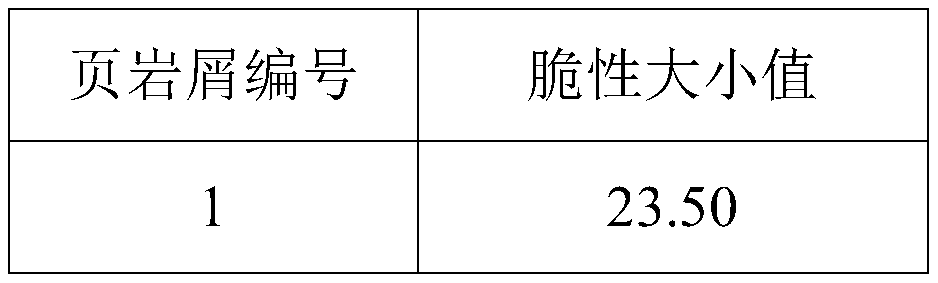
InactiveCN110186755AStrong real-time evaluationSimple samplingPreparing sample for investigationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesX-rayVolumetric Mass Density
An evaluation method for brittleness of shale includes the following steps: (1) obtaining shale cuttings returned from a target shale gas well bottom, and separately performing microscopic nanoindentation, X-ray diffraction and density tests; (2) based on obtained data of the microscopic nanoindentation, X-ray diffraction and density tests, separately calculating an elastic modulus, a component content and rock debris sample density constituted by various types of mineral substances of each of the shale cuttings; and (3) substituting the elastic modulus, mineral component content and a shale cuttings density value constituted by the various types of mineral substances of each of the shale cuttings into a brittleness evaluation model formula, wherein Wi represents a content of an i mineralcomponent in the shale; Ei represents the elastic modulus of i mineral composition in the shale, GPa; [rho] represents shale density, g / cm3, and a B value obtained by the model reflects a brittlenesscharacteristic of a shale reservoir where the shale is located. The method can perform real-time evaluation on the brittleness of the shale simply, quickly and at low cost.
Owner:SHAANXI TECHN INST OF DEFENSE IND
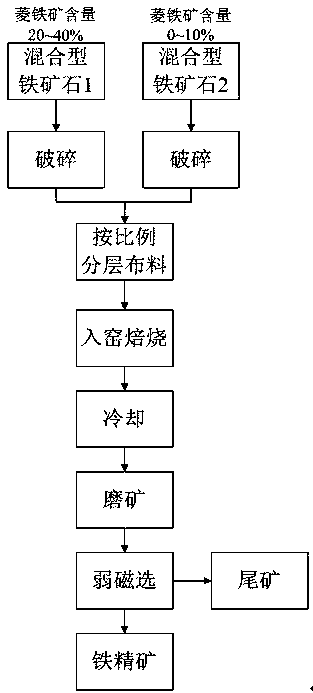
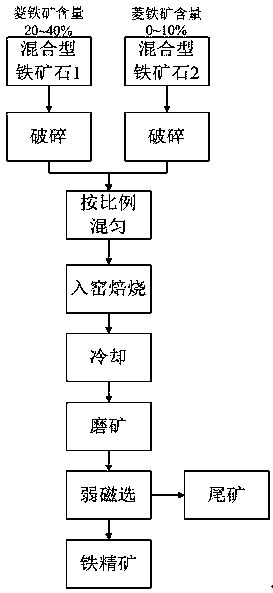
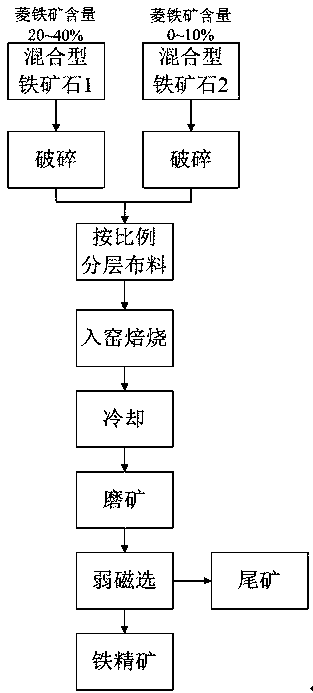
Magnetizing roasting method for complex refractory mixed type iron ore
The invention relates to a magnetizing roasting method for complex refractory mixed type iron ore. By means of the method, according to the mineral composition of the mixed type iron ore, weakly magnetic iron ore in the mixed type iron ore is converted into strong magnetic iron ore in the manner of mixing the mixed type iron ore high in siderite content with the mixed type iron ore low in siderite content or containing no siderite according to a certain ratio for compound magnetizing roasting, and iron ore concentrate high in iron grade and iron recycling index can be obtained from roasted ore through a conventional weakly magnetic separation process. The magnetizing roasting method can be suitable for coal-based reduction processes of tunnel kilns, rotary kilns and the like, no or a small quantity of reducing agent can be prepared in a roasted object in the magnetizing roasting technological process, and therefore the energy consumption of the roasting process is lowered.
Owner:GANSU JIU STEEL GRP HONGXING IRON & STEEL CO LTD
Fracability measurement method and system
A method for estimating a fracability index for a geological location includes determining a fabric metric and a mineralogical composition metric for a geological sample extracted from a geological location and estimating a fracability index for the geological location from the fabric metric and the mineralogical composition metric. The fabric metric may be a grain related measurement such as grain size or angularity, or a pore-space related measurement such as pore area, diameter, aspect ratio, and circumference, or statistics associated with such measurements. In certain embodiments, determining the mineralogical composition metric includes detecting a prevalence of at least one organic proxy within the geological sample such as vanadium, iron, uranium, thorium, copper, sulfur, zinc, chromium, nickel, cobalt, lead and molybdenum. Determining the mineralogical composition metric may also include detecting a prevalence of one, two, or all of siliciclastics, carbonate and clay.
Owner:CGG SERVICES SA
Shale brittleness evaluation method based on mechanical heterogeneity
The invention discloses a shale brittleness evaluation method based on mechanical heterogeneity. The shale brittleness evaluation method comprises the steps: the mineral constituent deviation factor is determined according to shale mineral compositions; the dynamic Young modulus and the dynamic Poisson ratio of various minerals are determined; according to the dynamic Young modulus and the dynamicPoisson ratio of the various minerals, the estimation Young modulus and the estimation Poisson ratio of a reservoir are determined through a constituent model, and through linear fitting, a linear fitting formula for calculating the corresponding fitting Young modulus and fitting Poisson ratio through the dynamic Young modulus and the dynamic Poisson ratio is obtained; through linear fitting dataand actually-measured data, the corresponding multiple lower limit and multiple upper limit are calculated, the estimation Young modulus multiple, the estimation Poisson ratio multiple, the estimation Young modulus and the estimation Poisson ratio are determined; and the brittleness factor is calculated. The shale brittleness evaluation method considers the influence of the shale mechanical heterogeneity on brittleness evaluation, the magnitude of brittleness of all intervals of a located stratum can be determined through the method, and the theoretical guidance is provided for fracturing.
Owner:SOUTHWEST PETROLEUM UNIV
Recognition method of supracrustal rock pore filler
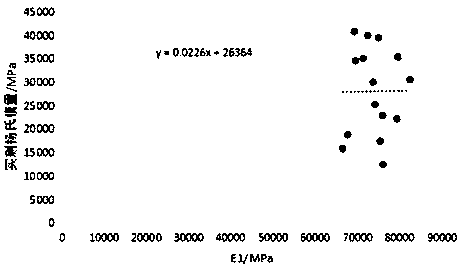
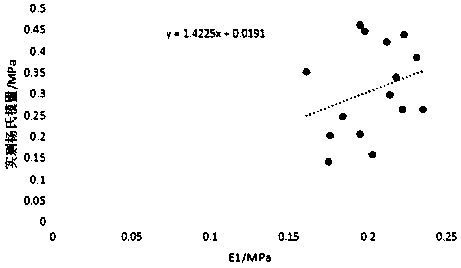
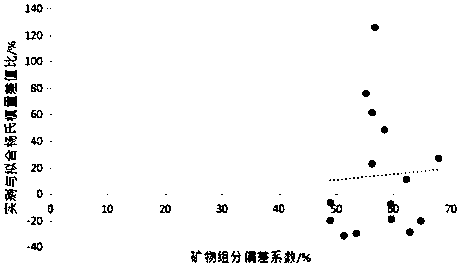
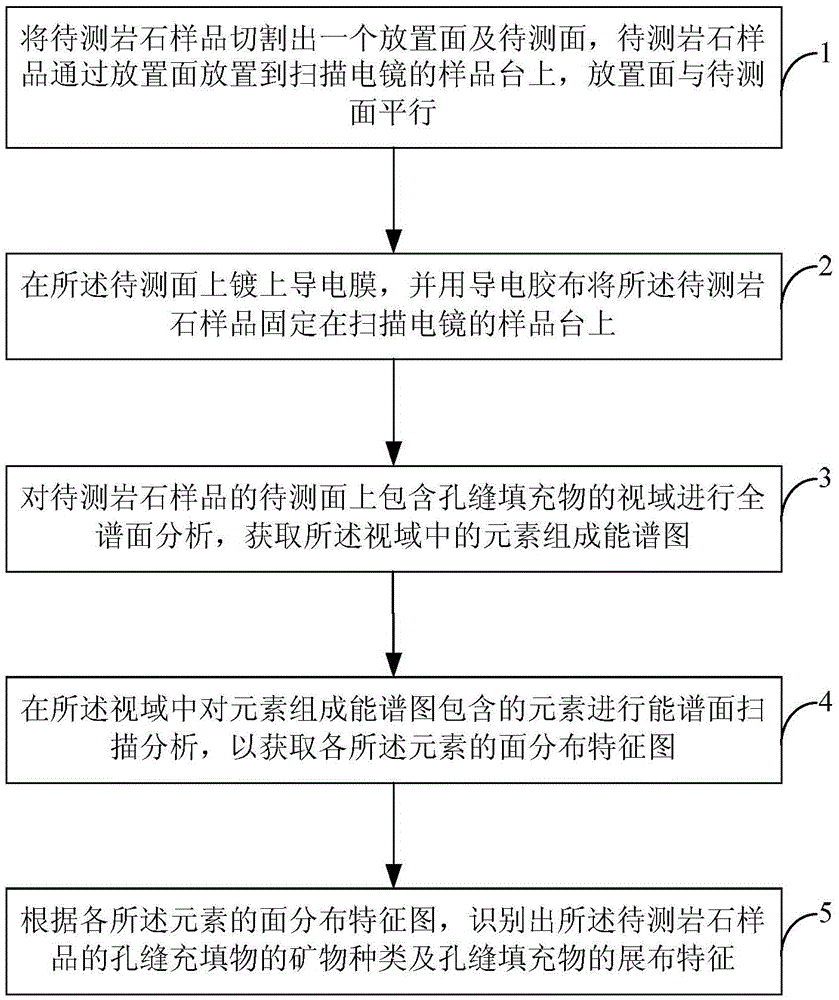
The invention provides a recognition method of supracrustal rock pore filler. The recognition method of the supracrustal rock pore filler includes the steps that full-spectrum-plane analysis is performed on a field of vision, comprising the pore filler, on a surface to be measured of a rock sample to be measured, and an element composition energy spectrum diagram in the field of vision is obtained; energy-spectrum-plane scanning analysis is performed on elements contained in the element composition energy spectrum diagram in the field of vision so that plane distribution characteristic diagrams of all the elements can be obtained; according to the plane distribution characteristic diagrams of all the elements, the mineral species and distribution characteristics of the pore filler of the rock sample to be measured are recognized. By means of the recognition method, the mineral composition and distribution characteristics of the supracrustal rock pore filler can be accurately recognized.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
Method for identifying slagging trend of different mineral components in coal ash
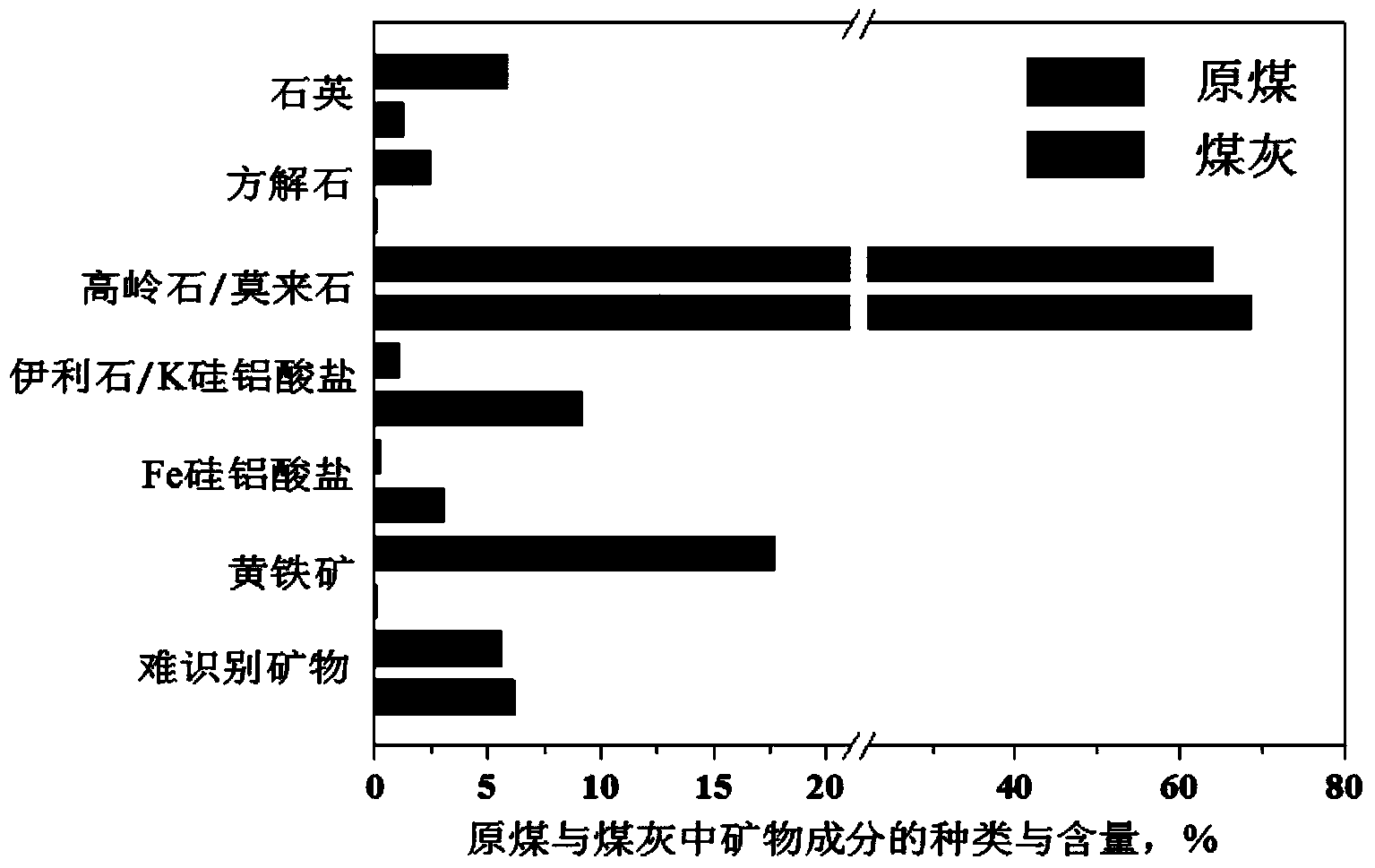
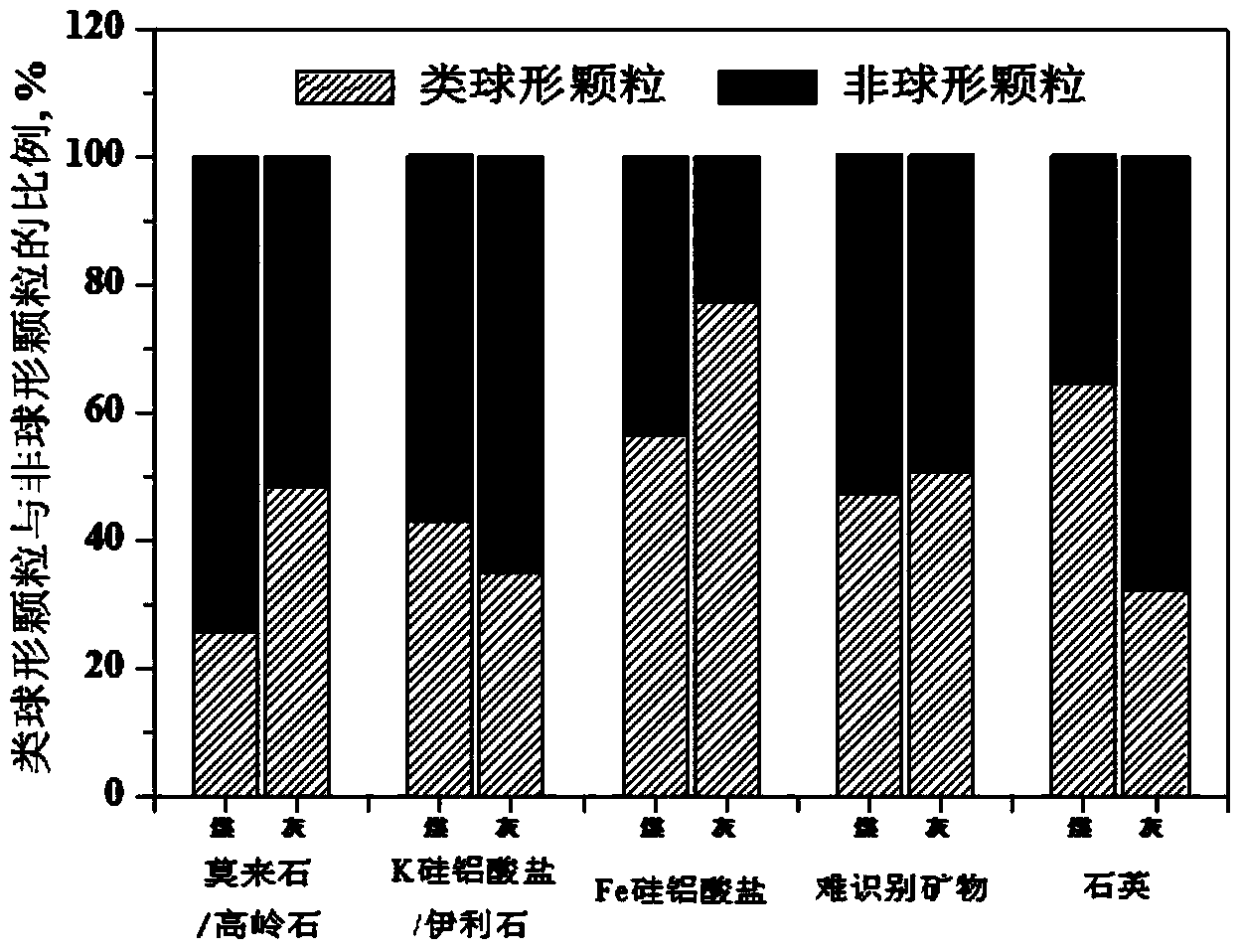
The invention discloses a method for identifying the slagging trend of different mineral components in coal ash by using the computer controlled scanning electron microscope (CCSEM) technology. The CCSEM is used for analyzing the type of minerals in the coal ash and raw coals, the contents of all mineral components, the sphericity of mineral particles and the number ratio of similar spherical particles; a sphericity distribution pattern of the minerals with the same chemical compositions in the coal ash and the raw coals is drawn; the possibility of fusing the mineral components is judged according to the increment of the similar spherical particle ratio of the minerals with the same chemical compositions before and after combustion; source minerals of all mineral components in the coal ash are determined to analyze the factor of changing the similar spherical particle ratio of each component to identify the fusing and slagging trend of the coal ash particles of all the mineral compositions. The fusing behavior of the coal ash particles of all the mineral compositions is clearly identified through analyzing the variation of the coal ash particle sphericity of different mineral compositions; the theoretic and technical guidance is provided for identifying the slagging trend of each mineral component in the coal ash and searching the solution from the coal mineral source for the easily slagged mineral components.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for determining macroscopic modulus of shale through fine/micro mechanical test
PendingCN113029746AFast Prediction of Elastic ModulusTo overcome the poor timeliness of preparationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesMacroscopic scaleYoung's modulus
A method for determining the macroscopic modulus of shale through a fine / micro mechanical test comprises the following steps: obtaining a macroscopic test result through a uniaxial compression test, and sequentially carrying out nanoindentation test and atomic force microscope test on a rock slice to obtain the Young modulus of a sample under the microscopic scale and the microscopic scale, and carrying out coupling analysis on the obtained data and carrying out macro-scale upgrading. Herein, results of the nanoindentation and the atomic force microscope are first analyzed to determine the fine / microscale modulus of the shale; and then, based on MLA result, the mineral compositions is classified according to modulus difference, and t mechanihecal parameters under a microscopic scale and a microscopic scale are updated by adopting a Mori-Tanaka homogenization method so as to determine the macroscopic modulus of the shale. The method can be used for rapidly predicting the mechanical parameters such as the elastic modulus and the hardness of the material, the rock debris can be used for performing MLA, AFM and nanoindentation tests in the drilling process to obtain macroscopic mechanical parameters, the test cost is reduced, and the test period is greatly shortened.
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF MINING & TECH (BEIJING)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com