Method for removing and recovering arsenic from lead anode slime
A technology for recovering arsenic from lead anode slime, which is applied in the direction of improving process efficiency, etc., to achieve high removal rate, low processing cost, and prevent secondary pollution
Active Publication Date: 2010-12-29
YONGZHOU FUJIA NON FERROUS METALS
View PDF3 Cites 30 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
In order to overcome the deficiencies of the existing lead anode slime dearsenic pretreatment method, the purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for effectively removing and reclaiming arsenic in lead anode slime in sodium hydroxide solution
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
Embodiment 2
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
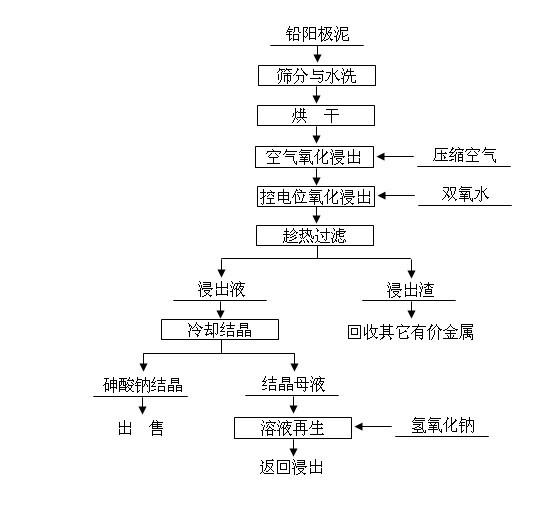
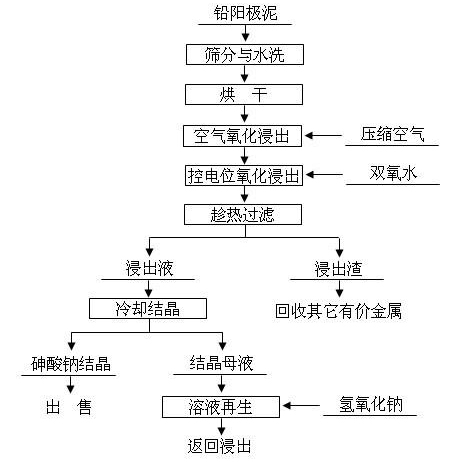
The invention discloses a method for removing and recovering arsenic from lead anode slime, which comprises the following steps of: performing screening, hot water washing and baking on the lead anode slime, performing oxidation leaching by controlling potential in sodium hydroxide solution, oxidizing the arsenic by using compressed air and hydrogen peroxide as oxidants respectively, adding the oxidized arsenic into alkaline leachate, and ensuring metals such as bismuth, lead, stibium and copper are oxidized and then enter alkaline leaching residue together with noble metals; and after alkaline oxidization leaching process is finished, filtering while hot, performing cooling crystallization on the leachate to generate sodium arsenate crystals, supplementing certain sodium hydroxide to crystallization mother liquor, returning the crystallization mother liquor to the leaching process, and separating and recovering the arsenic and other valuable metals from the lead anode slime. The arsenic leaching rate is over 98.0 percent and the secondary arsenic pollution is free; and the method has the advantages of low requirement on equipment materials, safe operation, low labor intensity, short treatment time and good operating environment.
Description
technical field The invention relates to a hydrometallurgical process in the field of metallurgy, in particular to a hydrometallurgical method for effectively removing and recovering arsenic from lead anode slime. Background technique Lead anode slime is composed of various components that are insoluble in the electrolyte during the electrolytic refining process of crude lead. Its composition and yield mainly depend on factors such as anode composition, casting quality and electrolysis technical conditions. The yield of lead electrolytic anode slime fluctuates 0.9~1.8%, moisture content about 35~40%, anode slime mainly contains arsenic, lead, antimony, bismuth, copper, gold, silver and scattered metals, etc. Therefore, lead anode slime is used to extract antimony, bismuth and rare precious metals, etc. important raw materials. Due to the depletion of mineral resources, high-arsenic lead ores are widely used in the smelting process of lead, which makes the content of arsenic...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C22B9/00C22B3/12C22B30/04
CPCY02P10/20
Inventor 杨天足王安刘伟锋蔡练兵文剑锋张杜超窦爱春李家元杨际幸
Owner YONGZHOU FUJIA NON FERROUS METALS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com