Method for recycling metal palladium from waste palladium-aluminum oxide catalysts
A catalyst and alumina technology, applied in the field of recovering precious metals, can solve the problems of long static roasting time, low palladium recovery rate and high processing cost, and achieve the effects of reasonable reagent matching, high recovery rate and stable process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
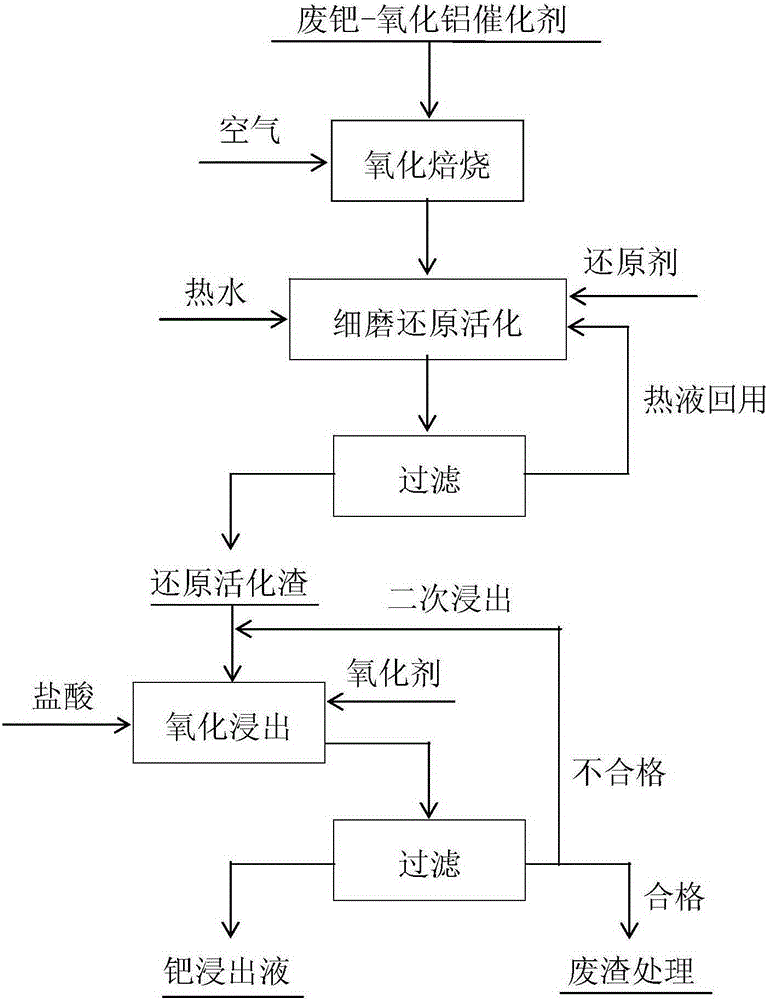
[0027] Use belt machine, grate machine or tunnel kiln for roasting, the material layer height is 120mm, the roasting temperature is 560°C, the exhaust air speed is 1.9m / min, the exhaust negative pressure is 2200Pa, the roasting time is 10-12min, the decarbonization The removal rate reaches 100%.
[0028] Pour calcined sand into a ball mill, the ball mill is an anti-corrosion ball mill, the mass ratio of grinding liquid to solid is 3:1, and the time is 20 minutes; the temperature of hot water is 80°C; the reducing agent is a mixture of formic acid and sodium formate, and the mass ratio of the two is 2: 1. The dosage is 1.5 times the molar ratio of the palladium content. After grinding-reduction, the particle size of the reduced slag is finely ground and the specific surface area is greater than 2500cm 2 g -1 , the reduced palladium content in the slag reaches over 95%.
[0029] Pour the reduction slag into the stirring extractor, then directly add hydrochloric acid, hydrogen...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Use belt machine, grate machine or tunnel kiln for roasting, the material layer height is 200mm, the roasting temperature is 600°C, the exhaust air speed is 2.2m / min, the exhaust negative pressure is 3500Pa, the roasting time is 10-12min, the decarbonization The removal rate reaches 100%.
[0032] Pour calcined sand into a ball mill, the ball mill is an anti-corrosion ball mill, the mass ratio of grinding liquid to solid is 3:1, and the time is 30 minutes; the temperature of hot water is 90°C; the reducing agent is a mixture of formic acid and sodium formate, and the mass ratio of the two is 1: 1. The dosage is 1.8 times the molar ratio of the palladium content. After grinding-reduction, the particle size of the reduced slag is finely ground and the specific surface area is greater than 2500cm 2 g -1 , the reduced palladium content in the slag reaches over 95%.
[0033] Pour the reducing residue into the stirring leaching device, then directly add hydrochloric acid, ...
Embodiment 3
[0035] Use belt machine, grate machine or tunnel kiln for roasting, the material layer height is 250mm, the roasting temperature is 650°C, the exhaust air speed is 2.5m / min, the exhaust negative pressure is 4500Pa, the roasting time is 10-12min, the decarbonization The removal rate reaches 100%.
[0036] Pour calcined sand into a ball mill, the ball mill is an anti-corrosion ball mill, the mass ratio of grinding liquid to solid is 3:1, and the time is 45 minutes; the temperature of hot water is 95°C; the reducing agent is a mixture of formic acid and sodium formate, and the mass ratio of the two is 1: 2. The dosage is twice the molar ratio of the palladium content. After grinding-reduction, the particle size of the reduced slag is finely ground and the specific surface area is greater than 2500cm 2 g -1 , the reduced palladium content in the slag reaches over 95%.
[0037] Pour the reduction residue into the stirring leaching device, then directly add hydrochloric acid, hyd...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com