Patents
Literature
44 results about "Ammonia levels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
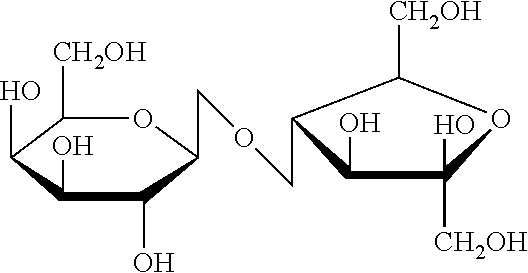
Use of lactulose in the treatment of autism
InactiveUS20080058282A1Avoid accumulationReverses effectBiocideNervous disorderNervous systemAntibiotic Y
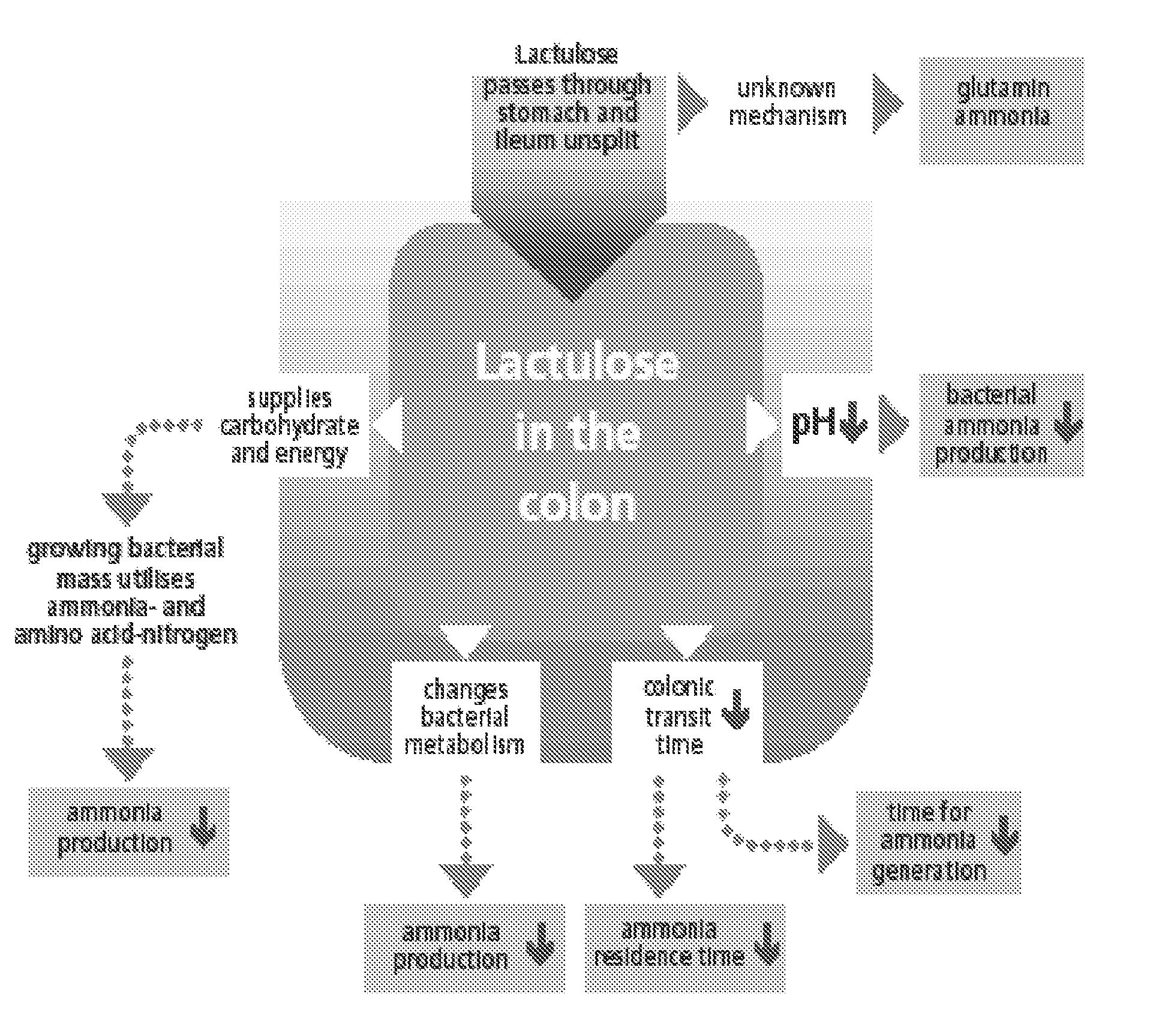
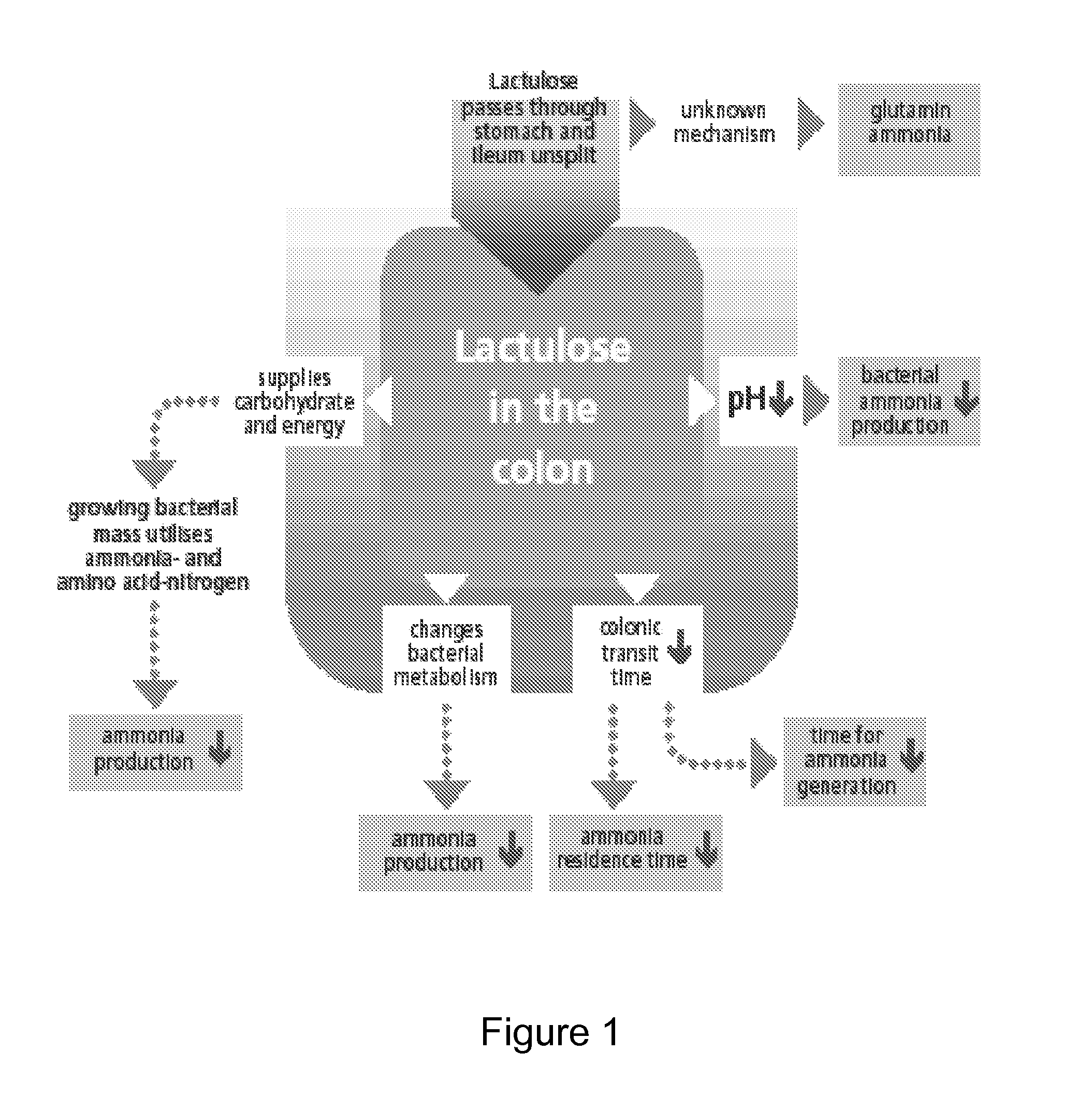
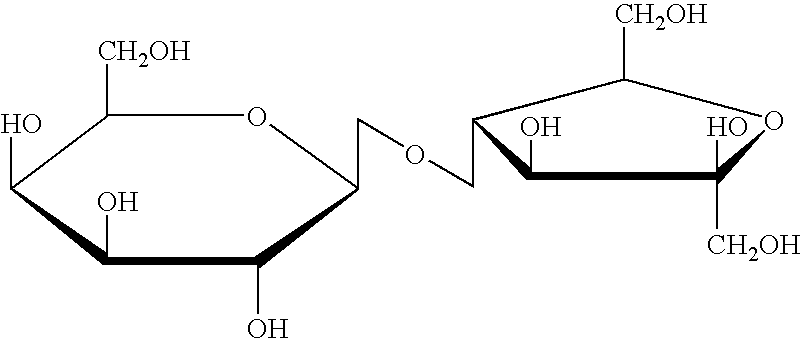
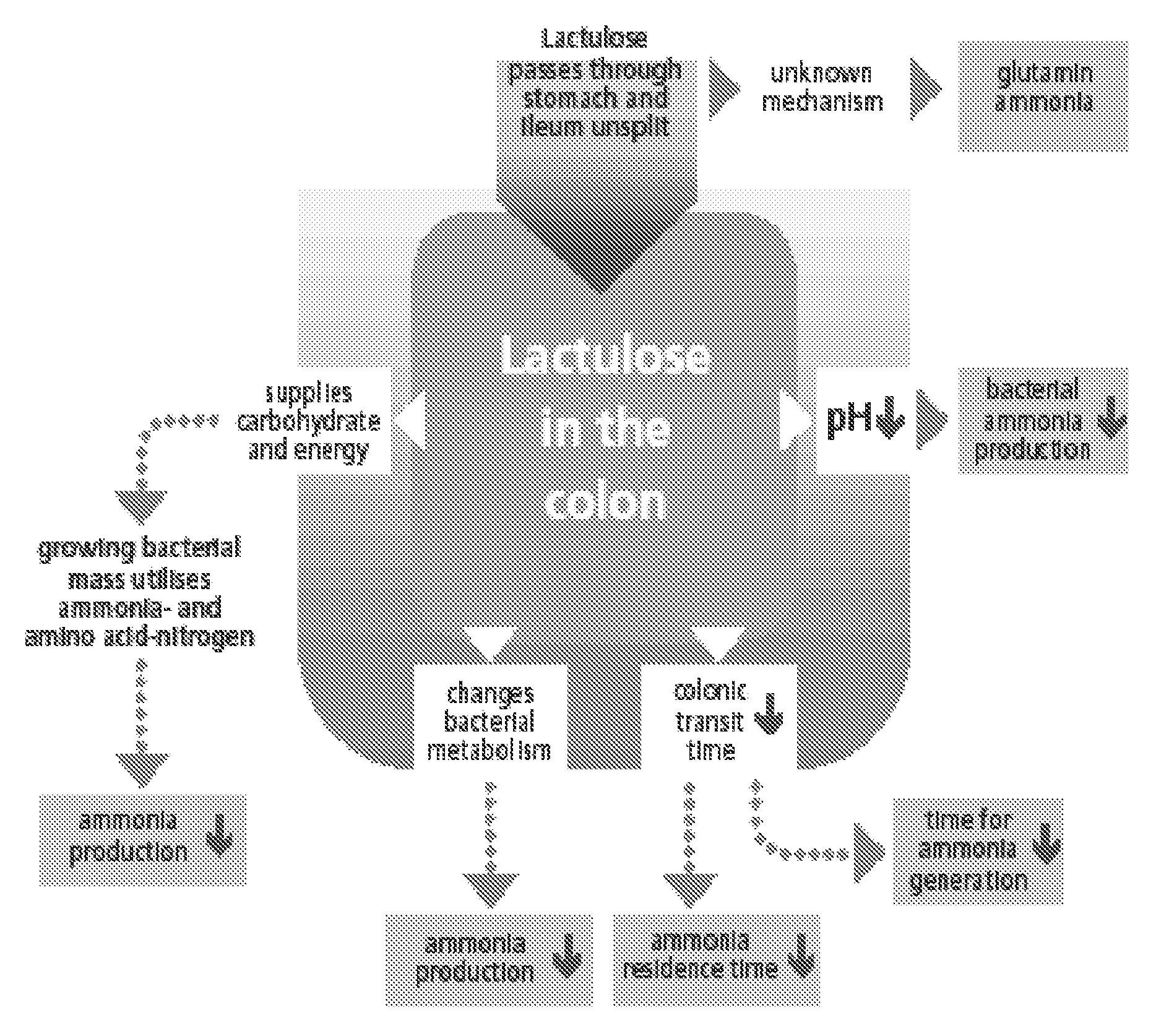
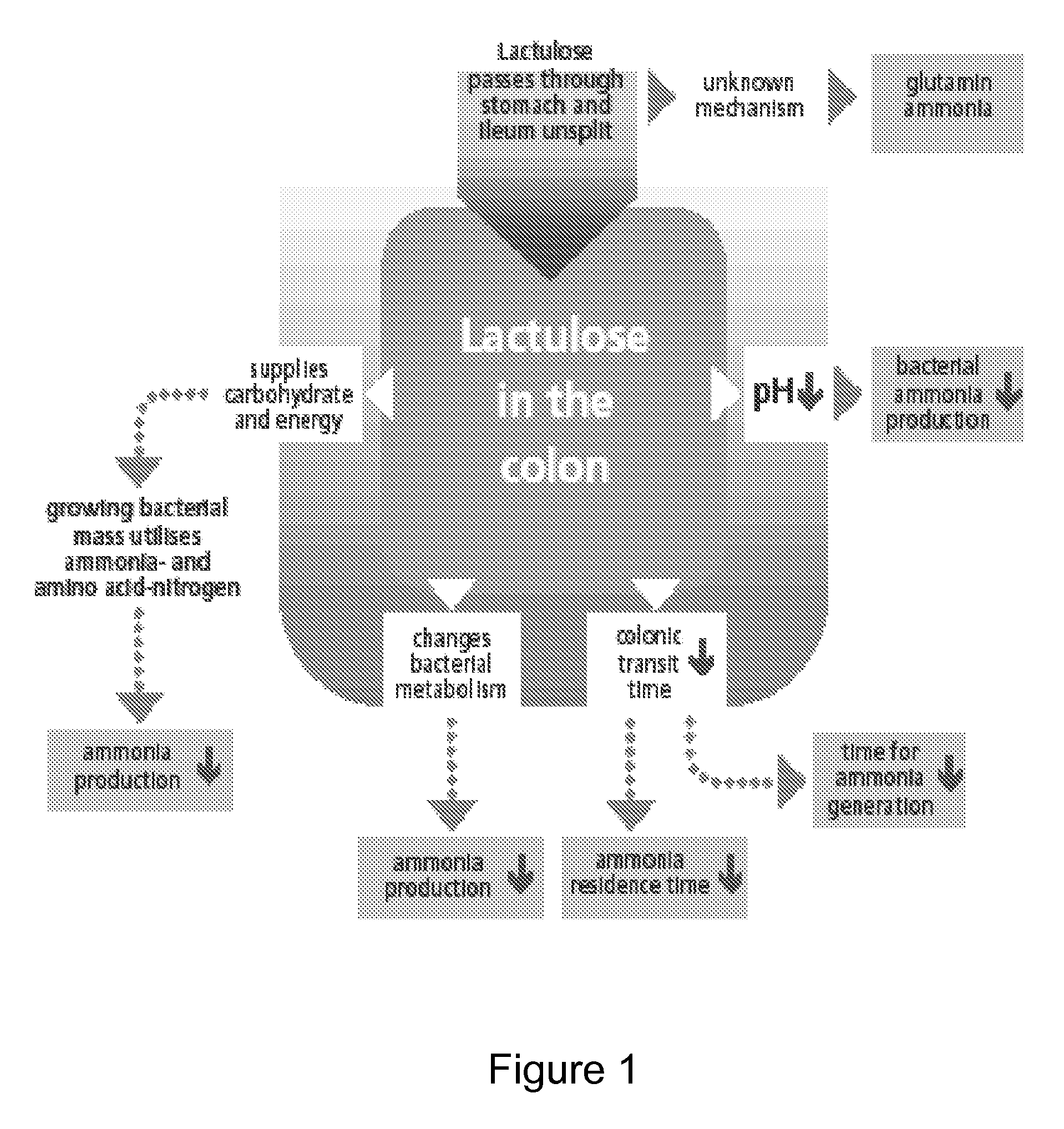
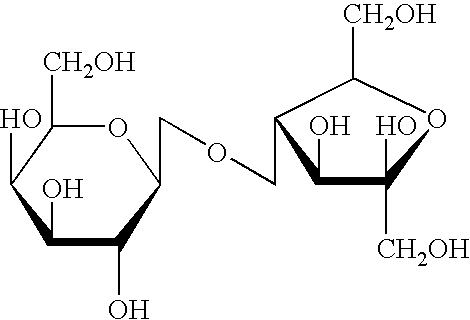
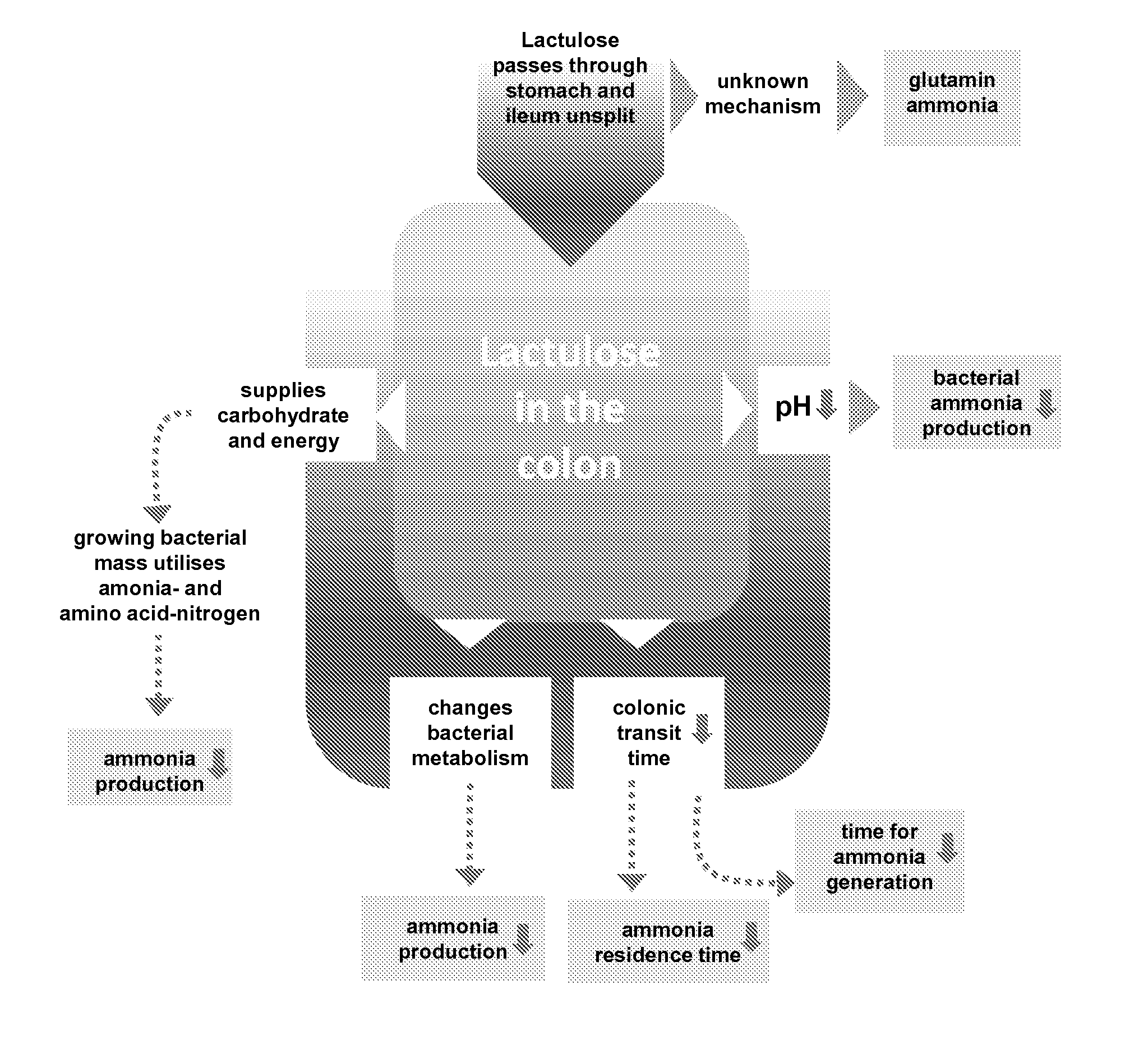
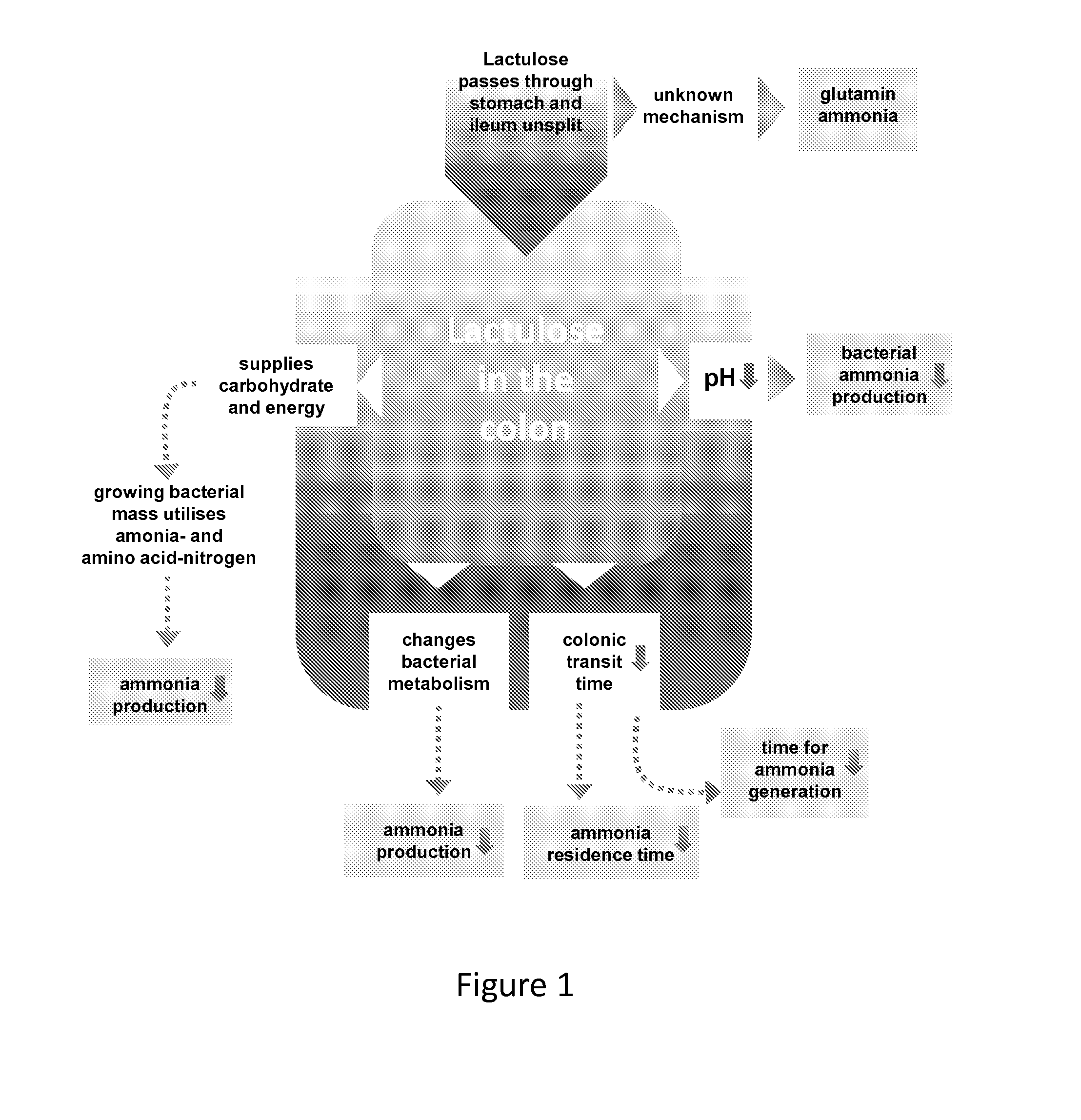
A treatment for autism in which an effective amount of lactulose is administered in order to bind excess ammonia in the gastrointestinal tract, the bloodstream, and the nervous system in order to prevent or reverse ammonia poisoning caused by the administration of certain antibiotics. Lactulose molecules in the colon are fermented by certain bacteria. The fermentation process lowers the colonic pH, and ammonia, in the form of ammonium ions, is used by the bacteria for amino acid and protein synthesis. This lowers the serum ammonia levels and reduces neurotoxicity.
Owner:CUREMARK
Use of lactulose in the treatment of autism
InactiveUS20080161265A1Avoid accumulationReverses effectBiocideNervous disorderBacteroidesNervous system
A treatment for autism in which an effective amount of lactulose is administered in order to bind excess ammonia in the gastrointestinal tract, the bloodstream, and the nervous system in order to prevent or reverse ammonia poisoning caused by the administration of certain antibiotics. Lactulose molecules in the colon are fermented by certain bacteria. The fermentation process lowers the colonic pH, and ammonia, in the form of ammonium ions, is used by the bacteria for amino acid and protein synthesis. This lowers the serum ammonia levels and reduces neurotoxicity.
Owner:CUREMARK
Use of lactulose in the treatment of autism
ActiveUS20120004192A1Avoid accumulationReverses effectBiocideNervous disorderBacteroidesNervous system
A treatment for autism in which an effective amount of lactulose is administered in order to bind excess ammonia in the gastrointestinal tract, the bloodstream, and the nervous system in order to prevent or reverse ammonia poisoning caused by the administration of certain antibiotics. Lactulose molecules in the colon are fermented by certain bacteria. The fermentation process lowers the colonic pH, and ammonia, in the form of ammonium ions, is used by the bacteria for amino acid and protein synthesis. This lowers the serum ammonia levels and reduces neurotoxicity.
Owner:CUREMARK
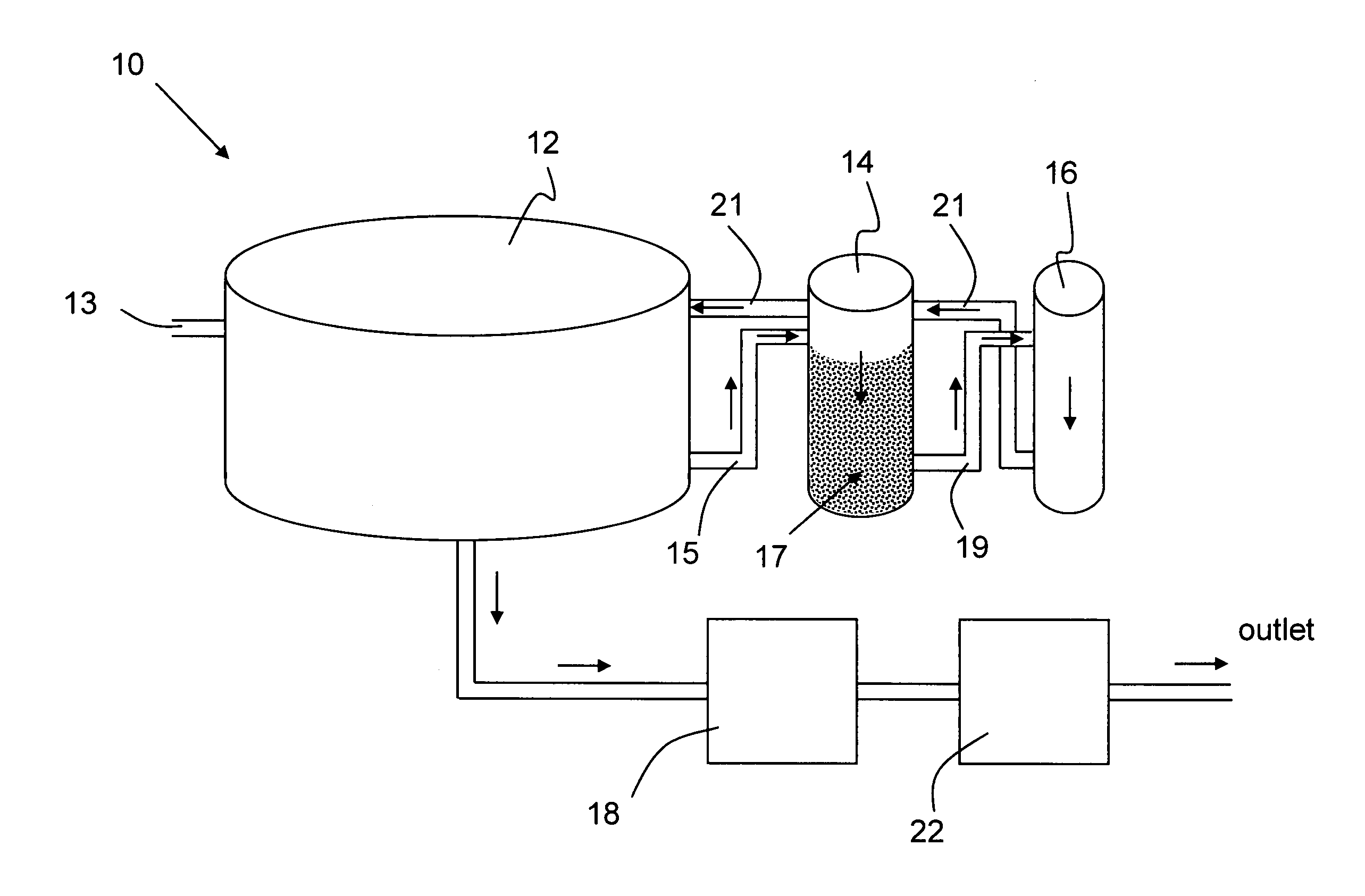
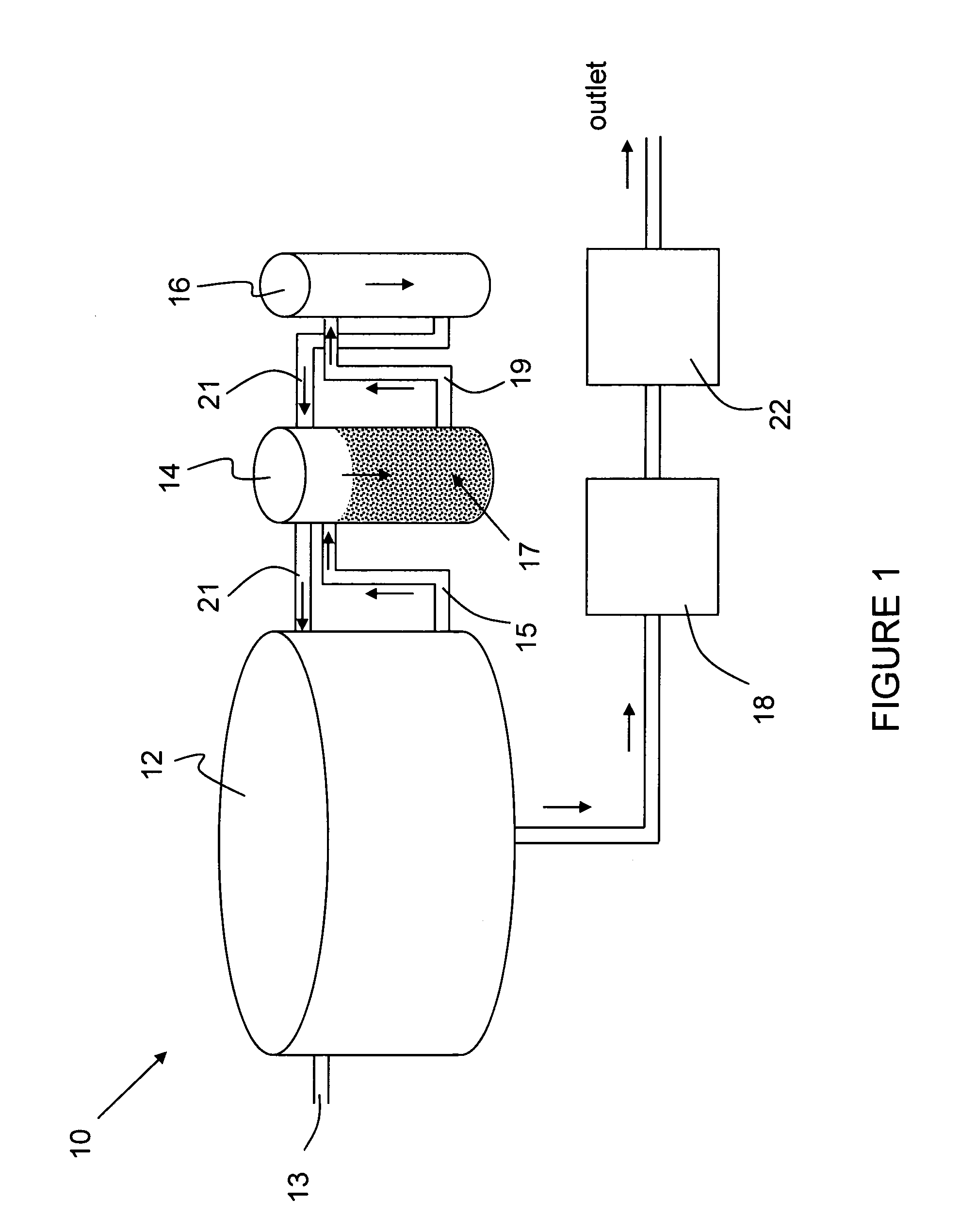
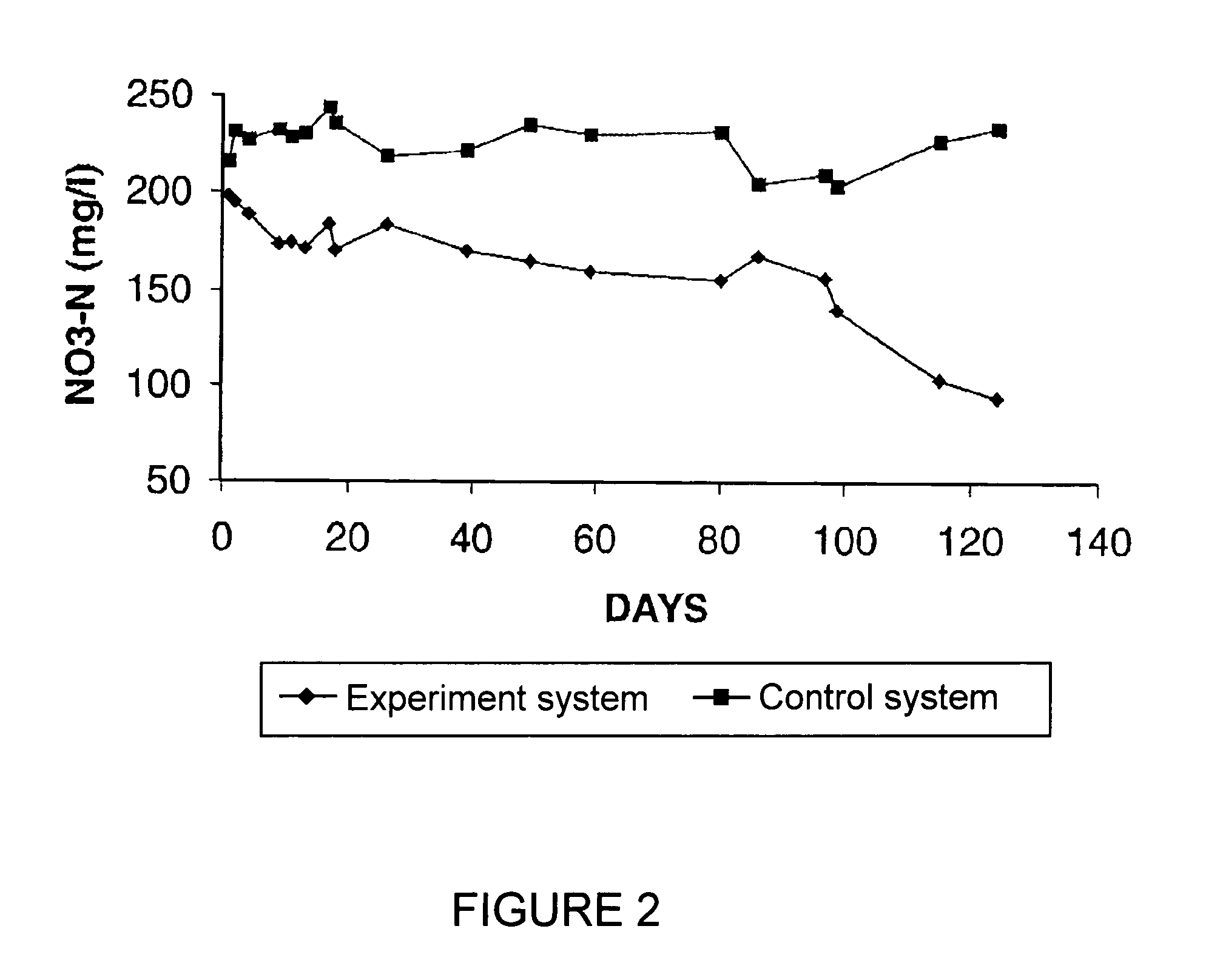
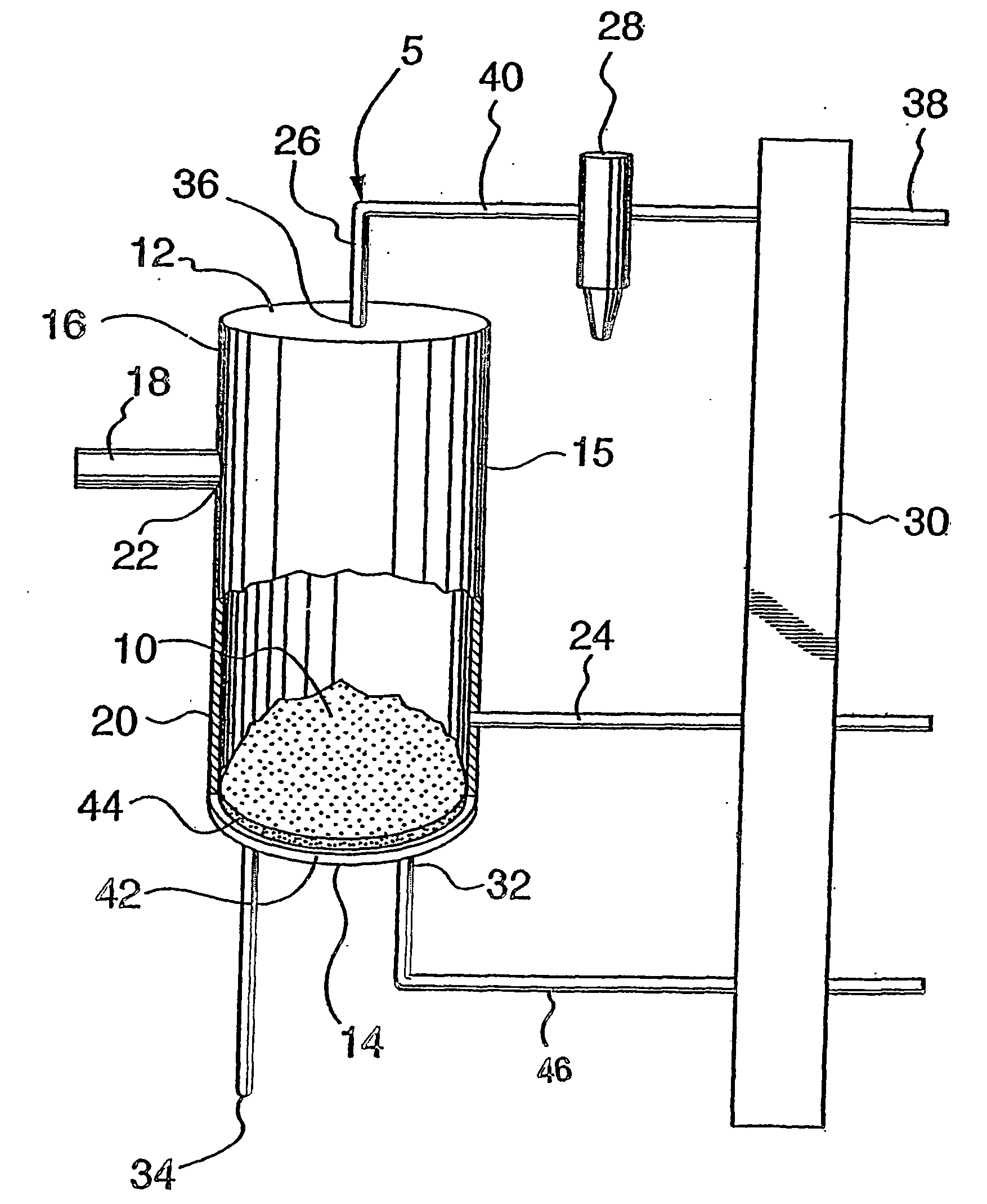
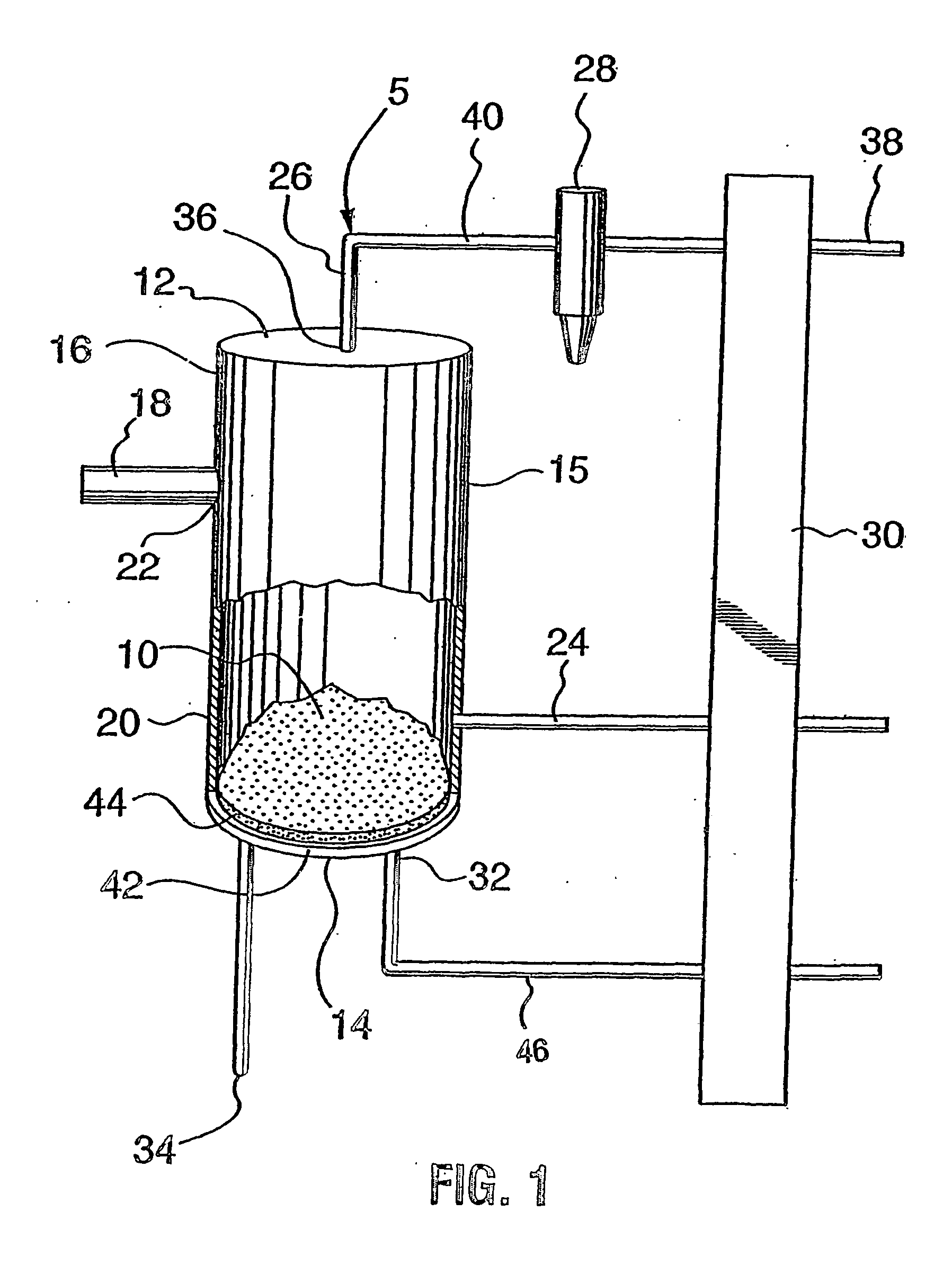
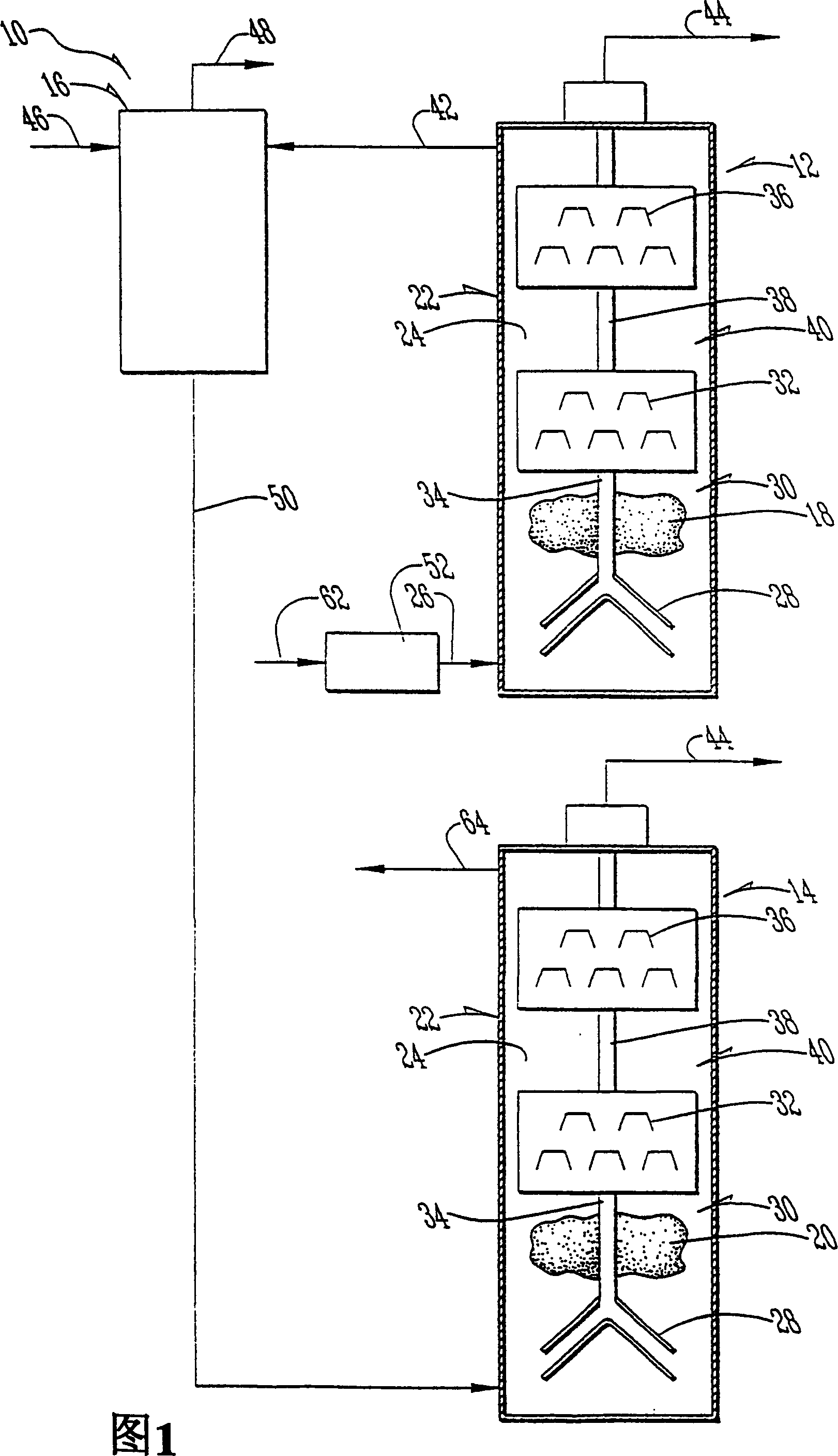
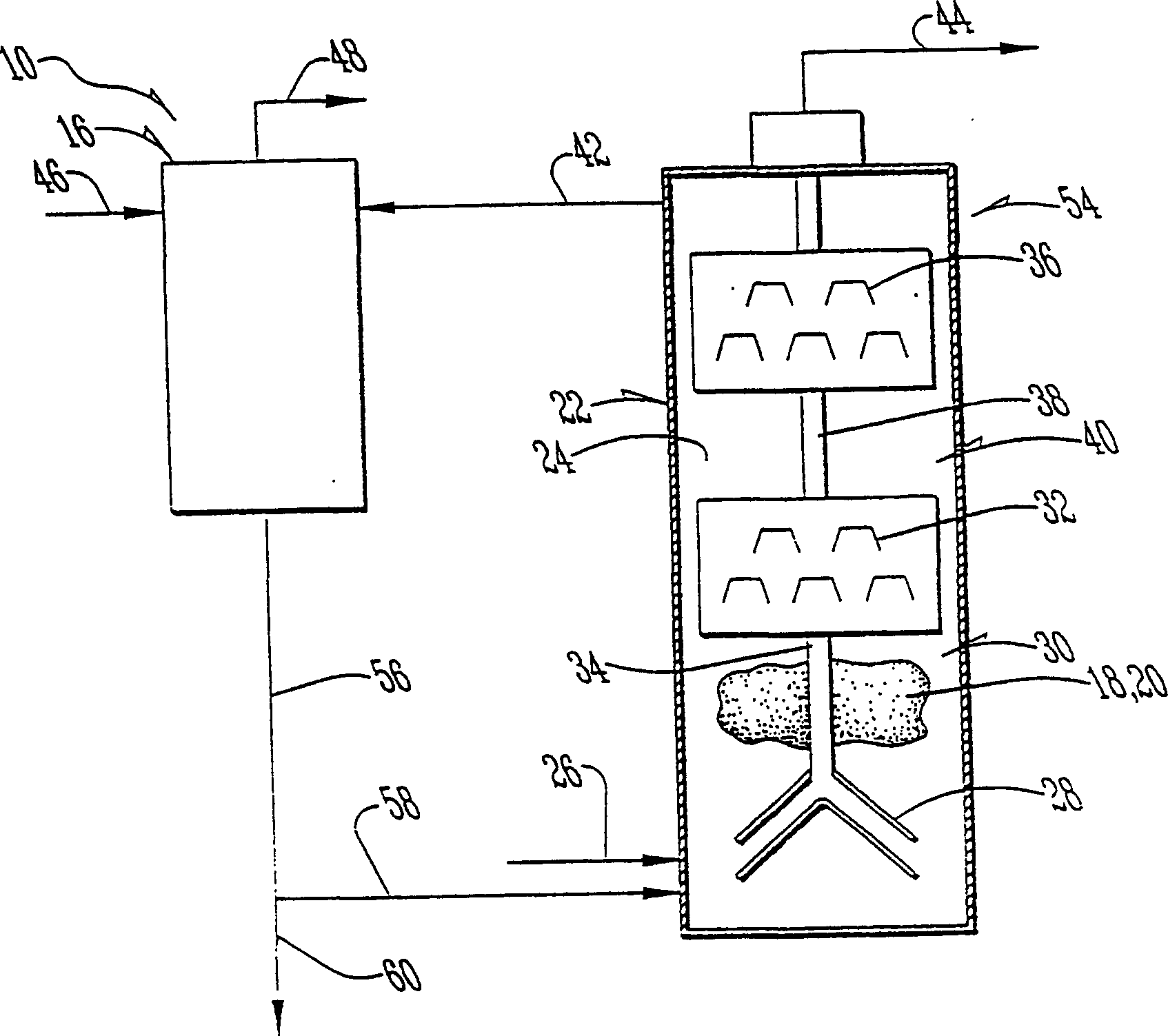
Aquaculture nitrogen waste removal
ActiveUS7082893B2Treatment with anaerobic digestion processesTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesNitrateReactor system
The present invention relates to a two-stage biofilter reactor system for removing nitrogenous compounds from a recirculating aquaculture system. The system includes a aerobic nitrification unit and a downstream anaerobic denitrification unit, wherein both units have a mobile bed of suspended media whereon bacteria can grow and reduce nitrate and / or ammonia levels in the recirculating aquaculture system. Use of the two-stage system has the advantage of reducing the water exchange rates and consumption of salt when maintaining a saline effluent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BALTIMORE COUNTY
Method for diagnosis of helicobacter pylori infection
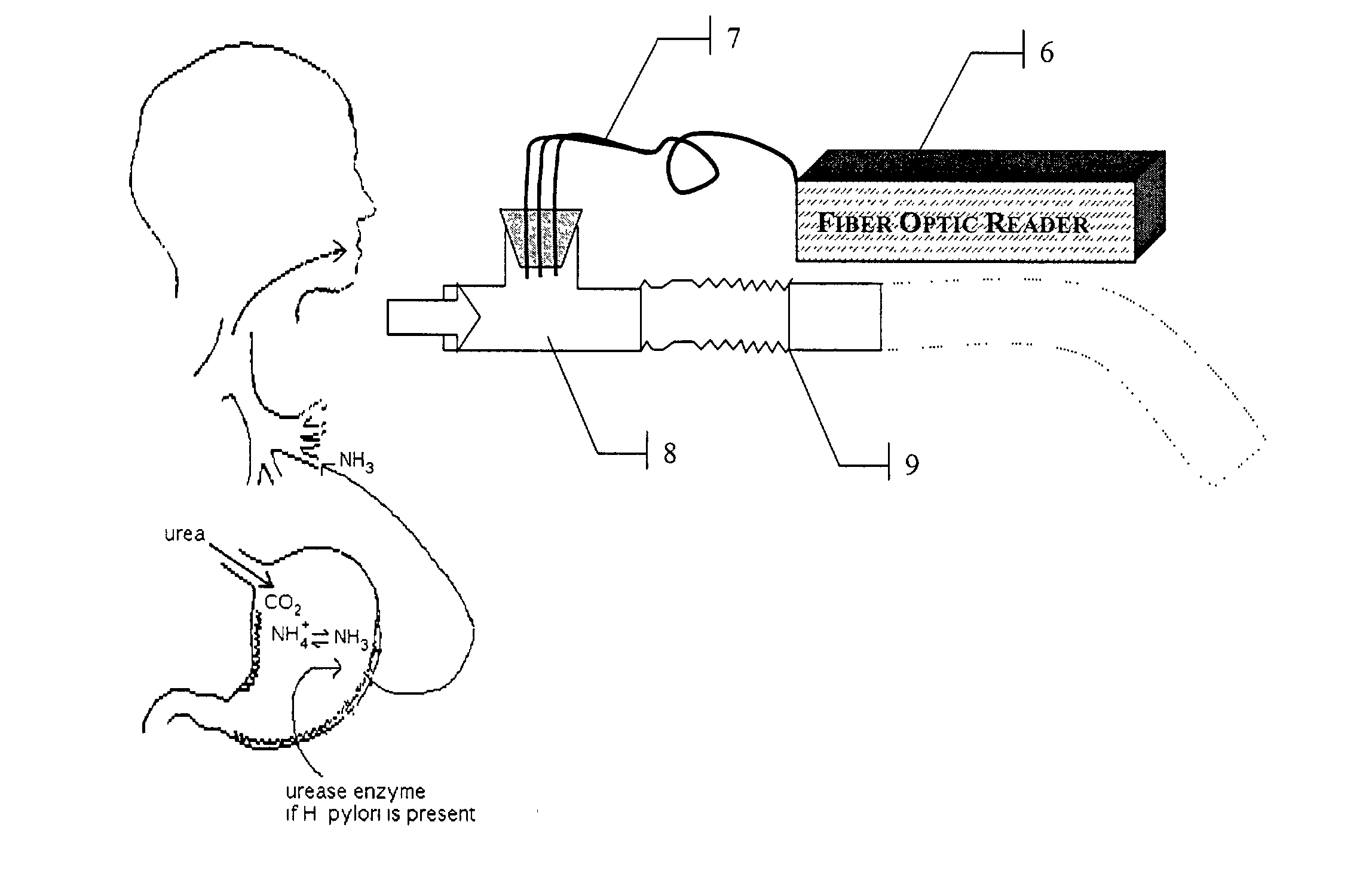
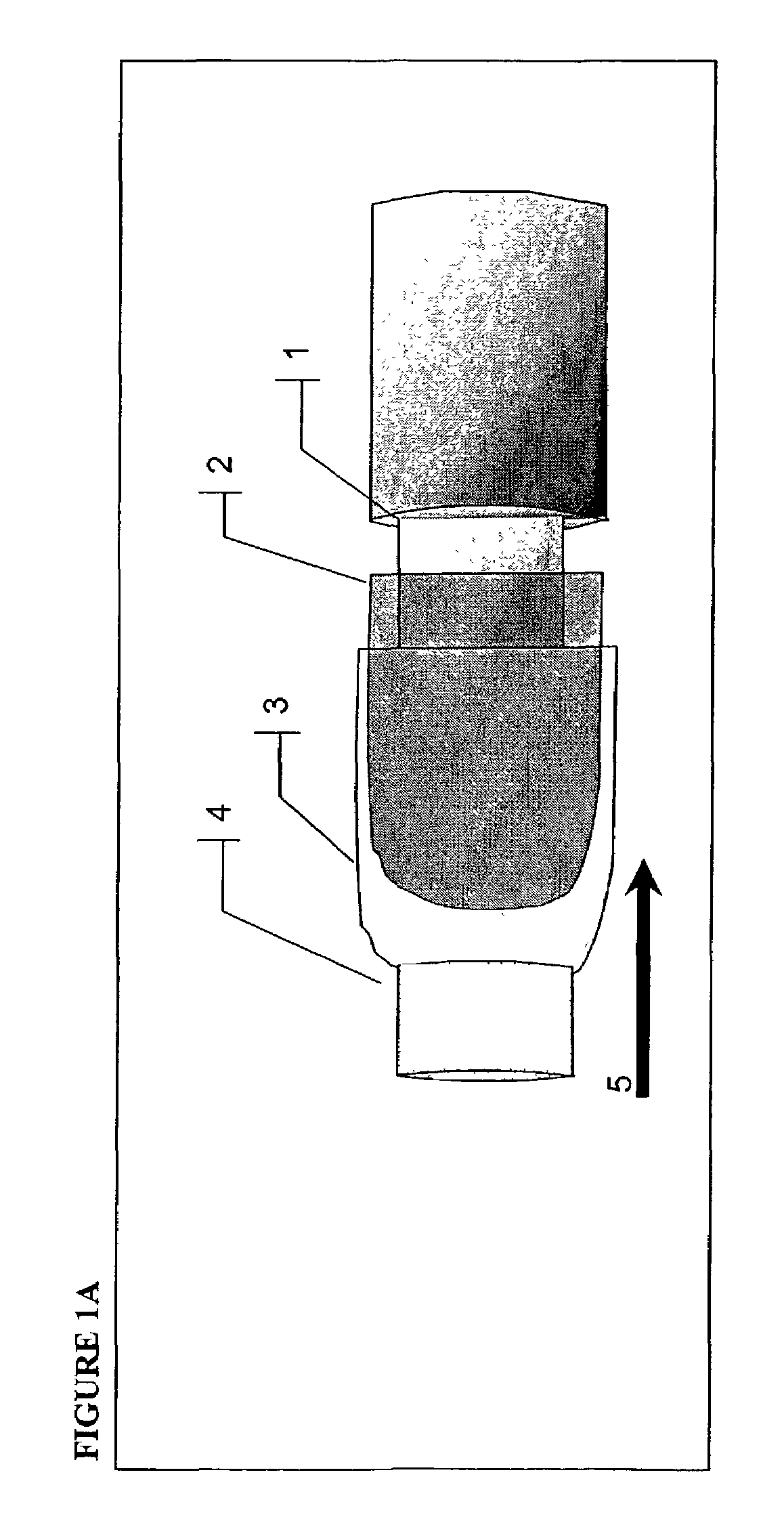
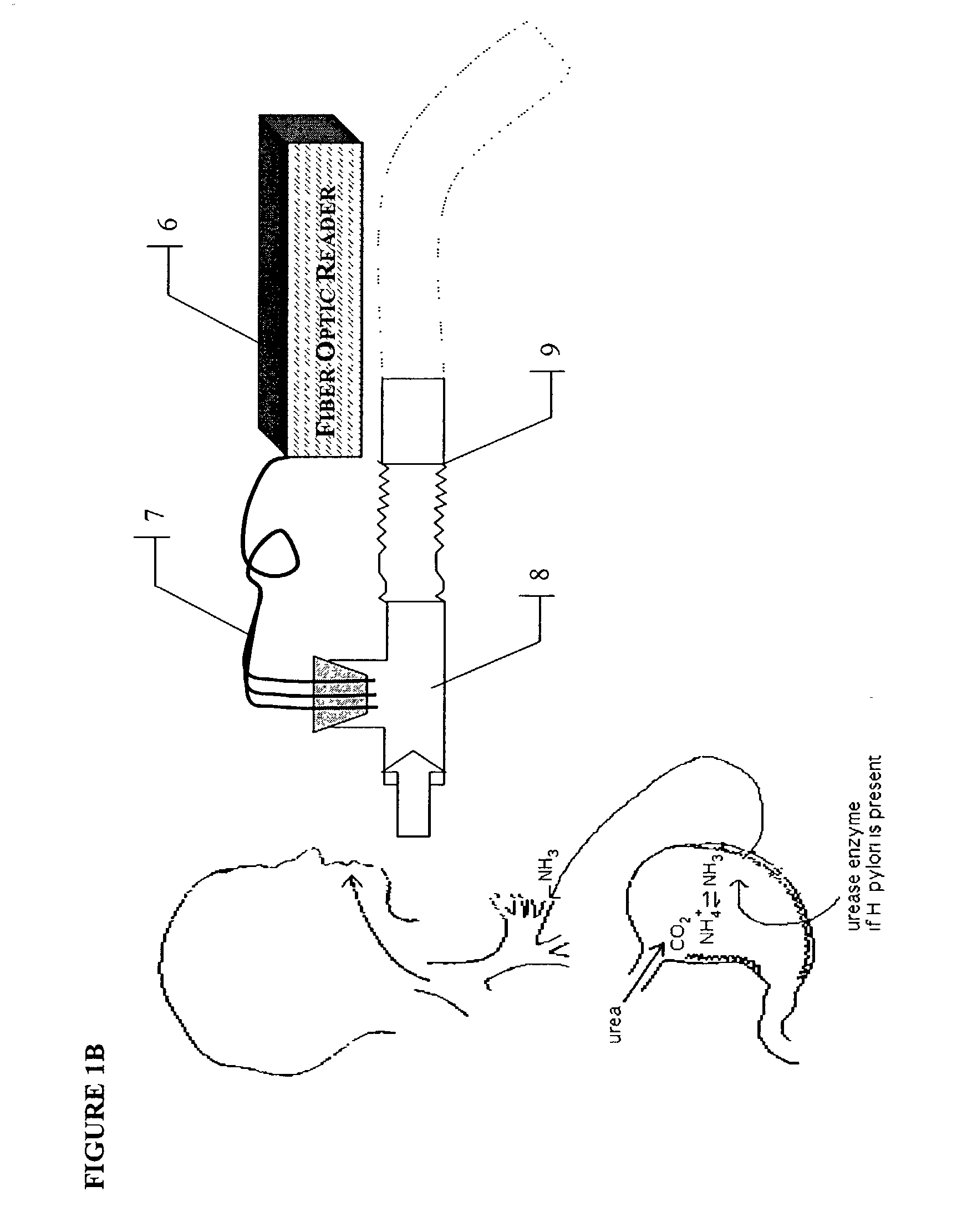
InactiveUS7014612B2Accurate identificationWithdrawing sample devicesRespiratory organ evaluationReflection spectroscopyIsotopic tracer
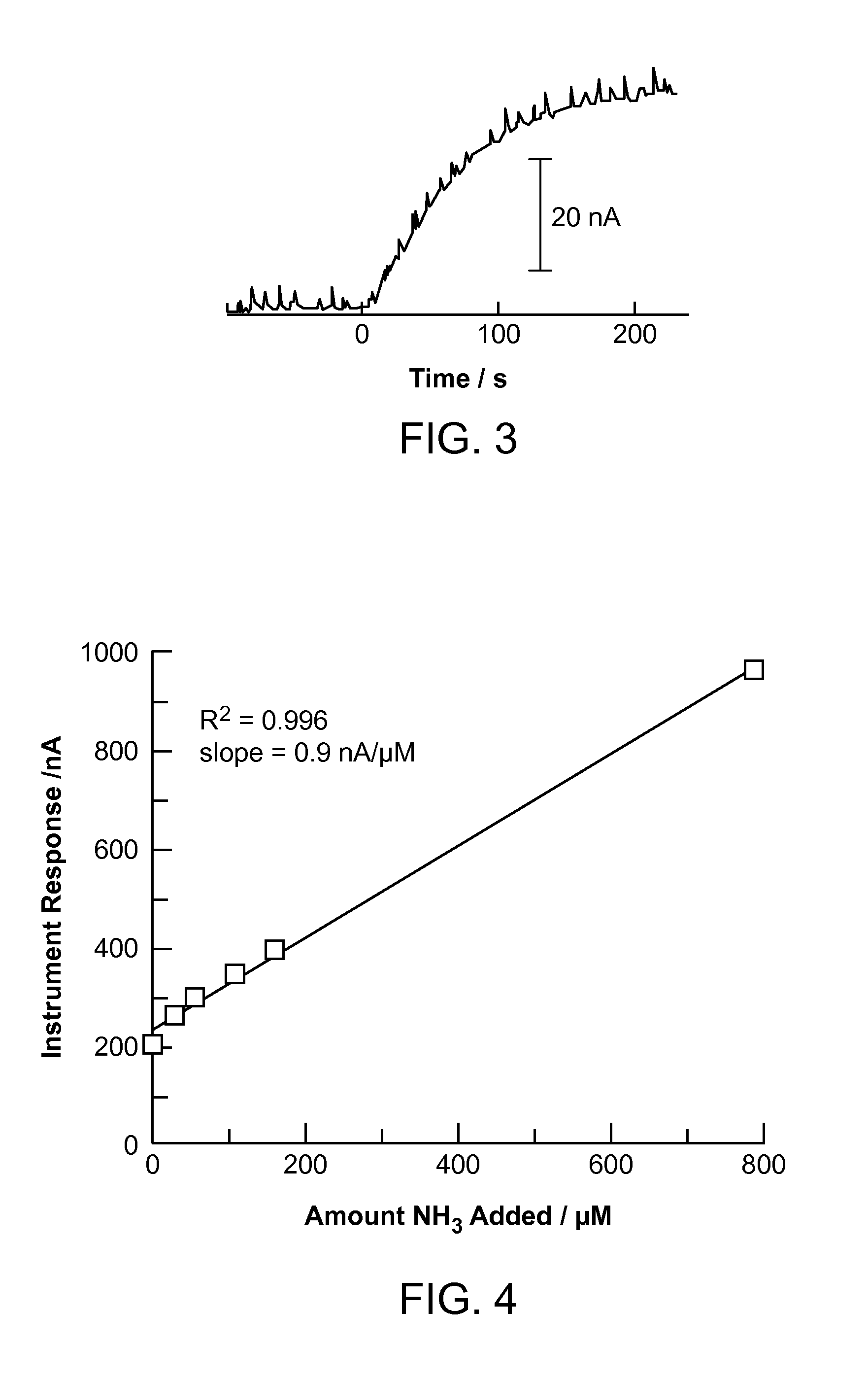
A rapid, non-invasive breath-test method and device for diagnosing the presence or absence of H. pylori in a subject without administration of isotopic tracers is described. The device consists of a highly sensitive colorimetric ammonia sensor placed in contact with sampled subject breath. The sensor is measured using appropriate reflection spectroscopy instrumentation. The breath-test method consists of measuring a basal ammonia level with the device, administering non-isotopic urea and continuing measurement of the ammonia content in a plurality of consecutive breaths. Diagnostic differences in breath ammonia are identified between H. pylori infected and uninfected individuals.
Owner:PHOTONIC BIOSYST
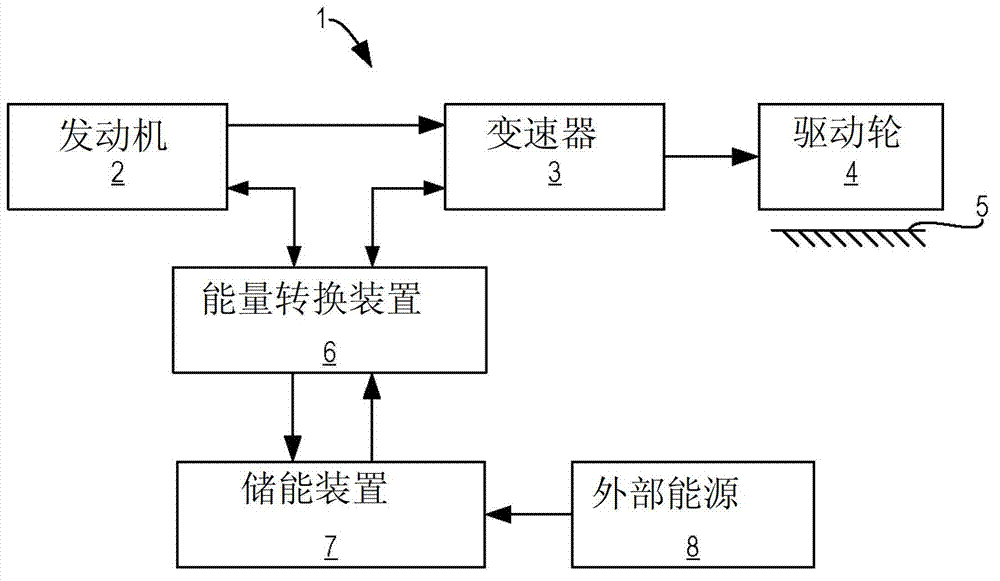
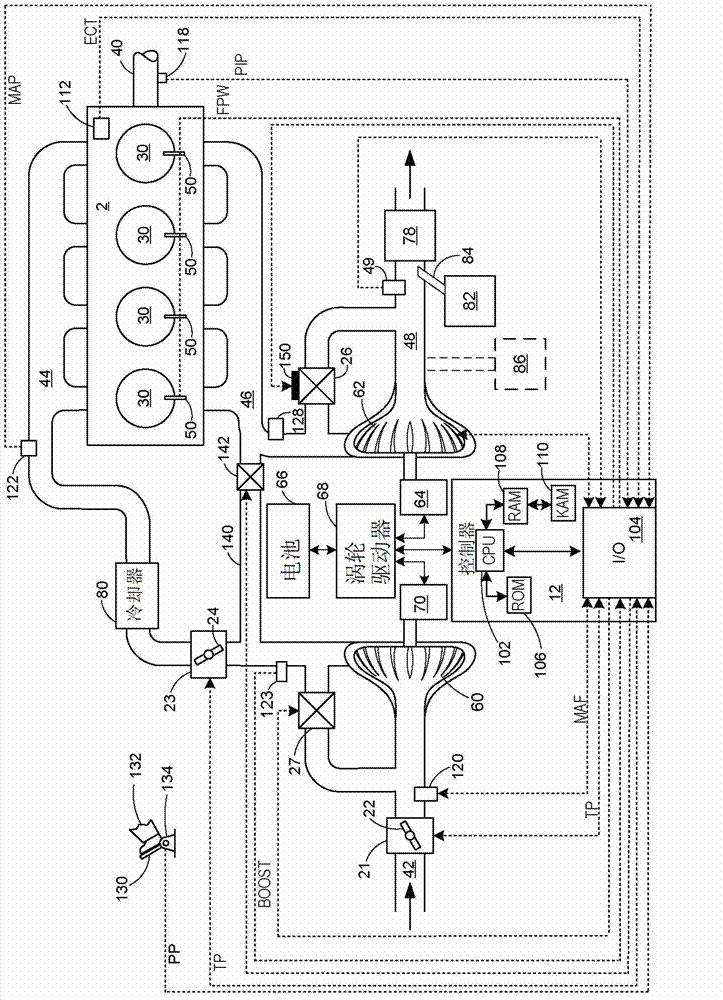
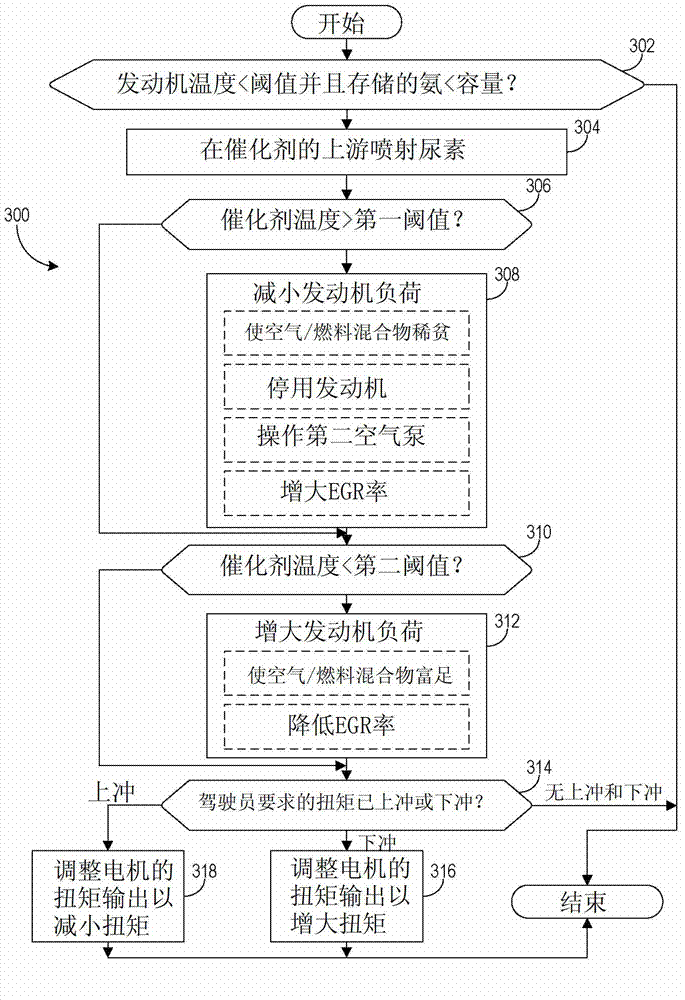
Ammonia storage control
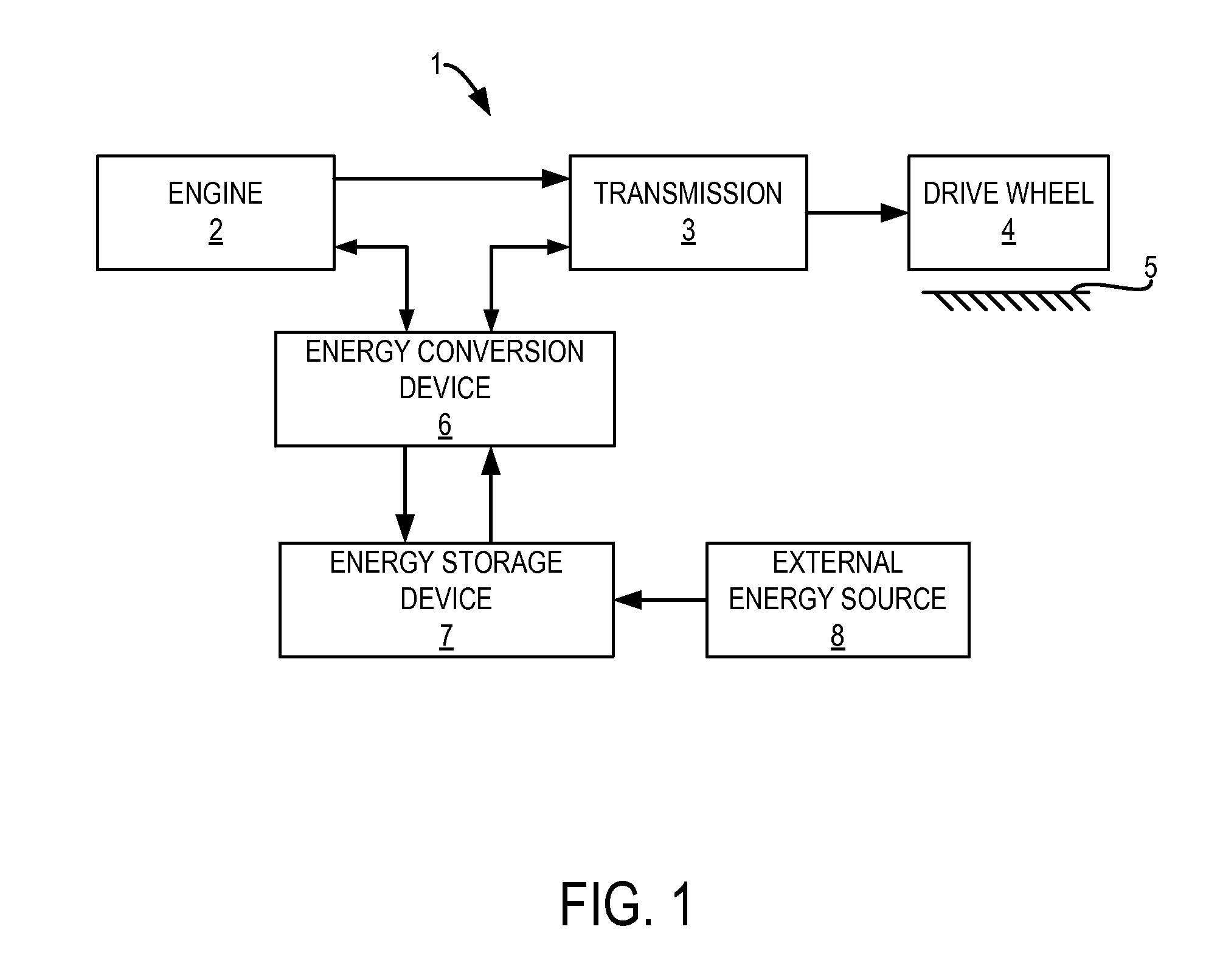
Various methods for controlling ammonia levels stored in a catalyst by controlling exhaust gas temperatures are provided. In one embodiment, a temperature of a catalyst in an internal combustion engine is determined. If the temperature of the catalyst exceeds a first threshold at which an ammonia capacity of the catalyst for the temperature is below a current stored ammonia level in the catalyst, a load of the engine is reduced including adjusting a torque output of a motor operatively coupled to the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
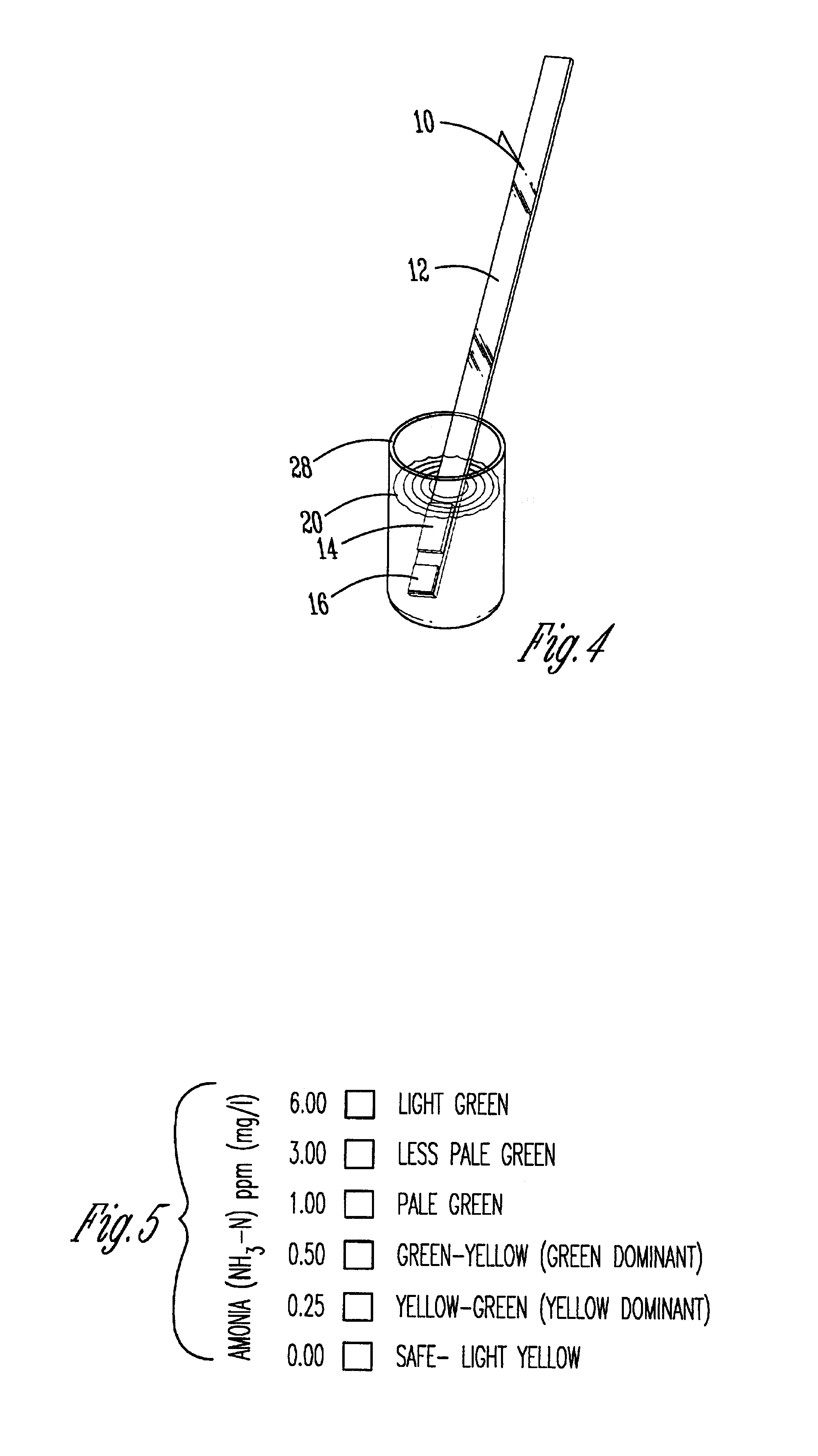
Quick acting toxic ammonia test for aqueous samples
InactiveUS7033839B1Material analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorWater/sewage treatmentAmmonia levelsColor response
A method, test reagent and device usable as a test strip for detecting toxic ammonia levels in water samples such as aquarium water. The volume of the water to be tested contacted with a soda lime reagent to raise the pH to at least 10, and simultaneously contacted with a hydrophobic barrier membrane capable of allowing only ammonia gas to pass through. The membrane is coated with a pH chromogenic indicator mixture which changes color if ammonia gas passes through. The color response of the sample is compared with standard color charts to determine the toxic ammonia potential.
Owner:HACH CO
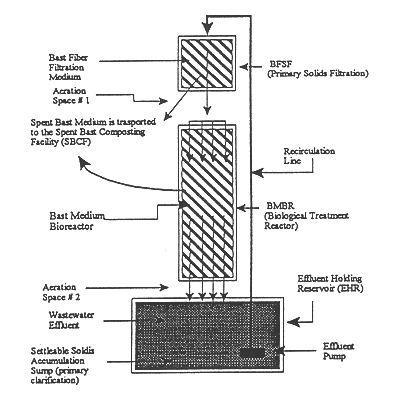
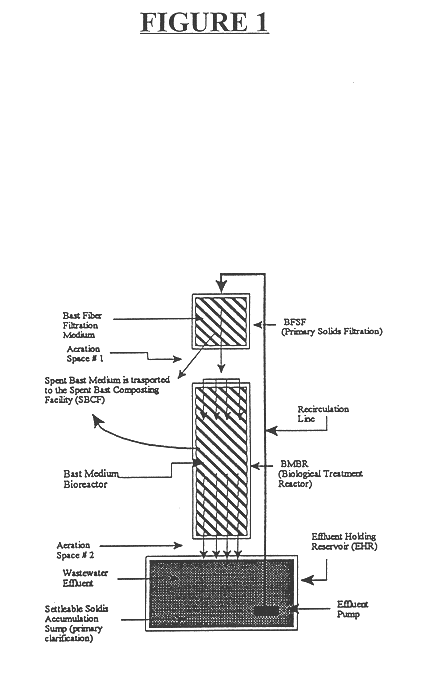
Bast medium biological reactor treatment system for remediation and odor suppression of organic waste streams
InactiveUS6436288B1Eliminate odorReduce odorTreatment using aerobic processesSeparation devicesMicroorganismWaste stream
The invention relates to a holistic sustainable wastewater treatment system that utilizes a bast medium as the attached growth medium. The wastewater treatment system of the present invention (Bast Medium Biological Reactor Treatment System) reduces odors and in-house ammonia levels and increases the overall water quality of organic waste streams. It uses naturally occurring microorganisms to process wastewater and remove odor without chemical augmentation. The Bast Medium Biological Reactor Treatment System is simple, with few moving parts and low maintenance requirements. The invention also relates to a method for treating wastewater using the wastewater treatment system according to the present invention.
Owner:MISSISSIPPI STATE UNIVERSITY
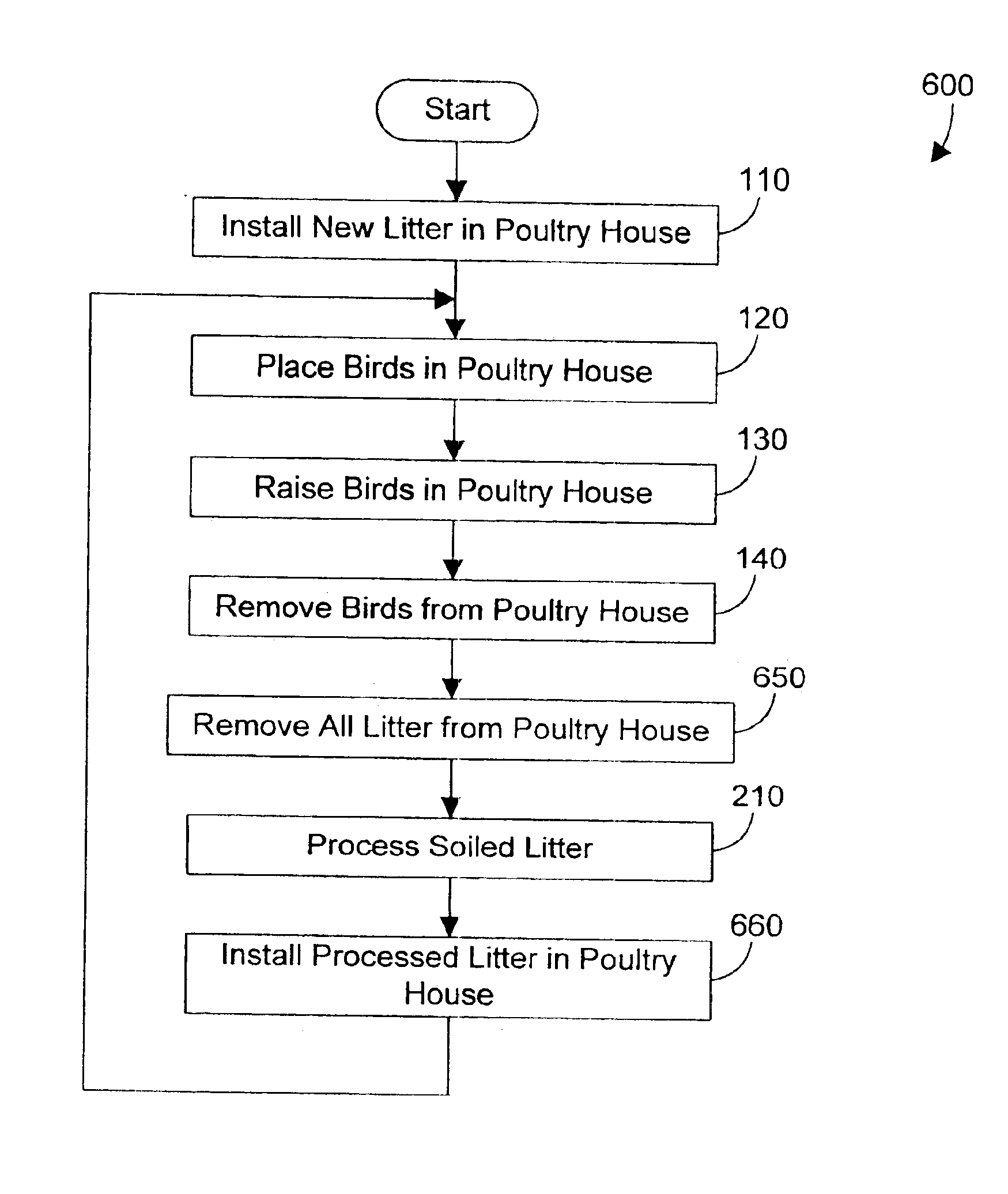
Method for processing and recycling animal waste and method for doing business using the same
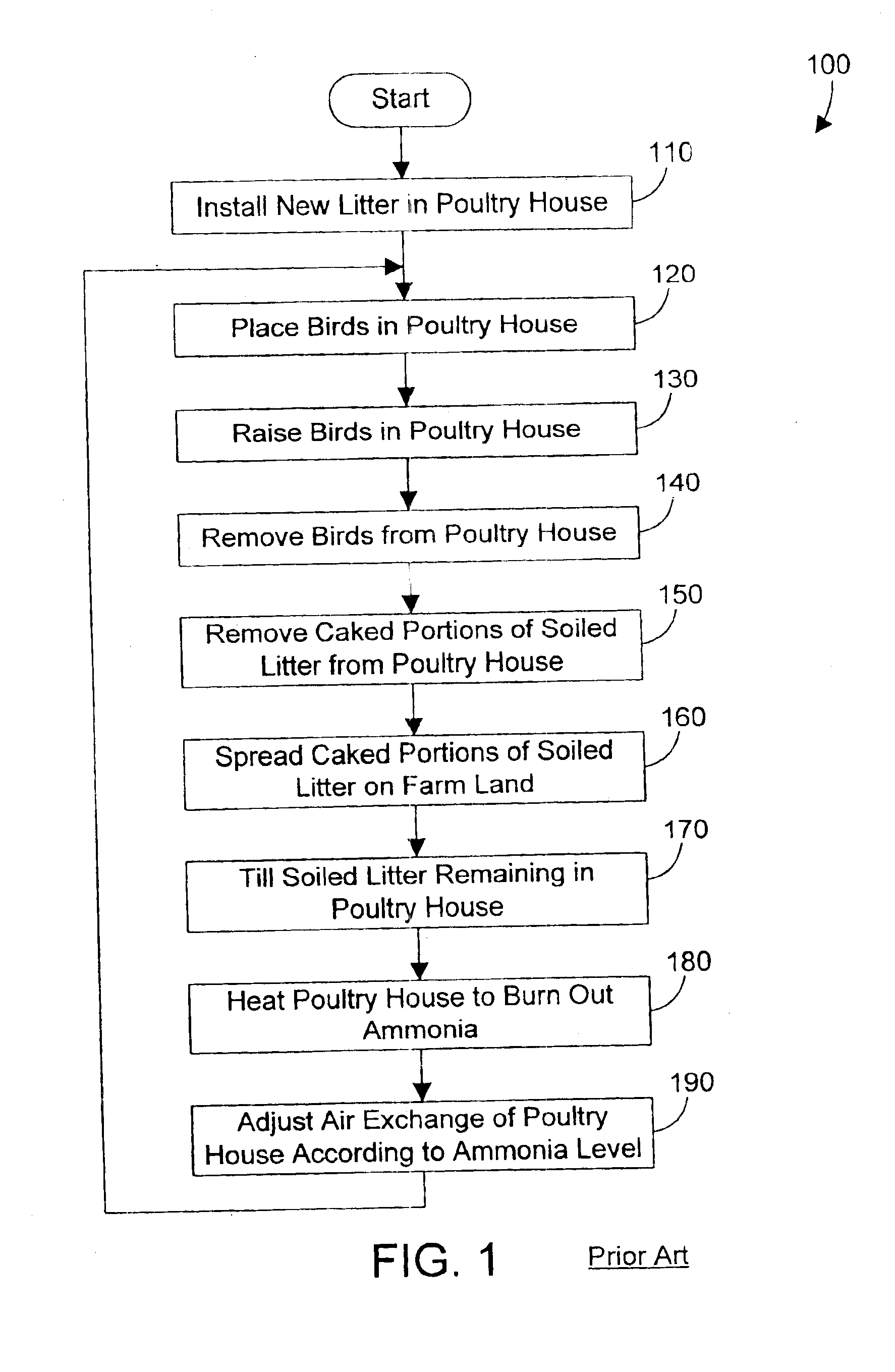
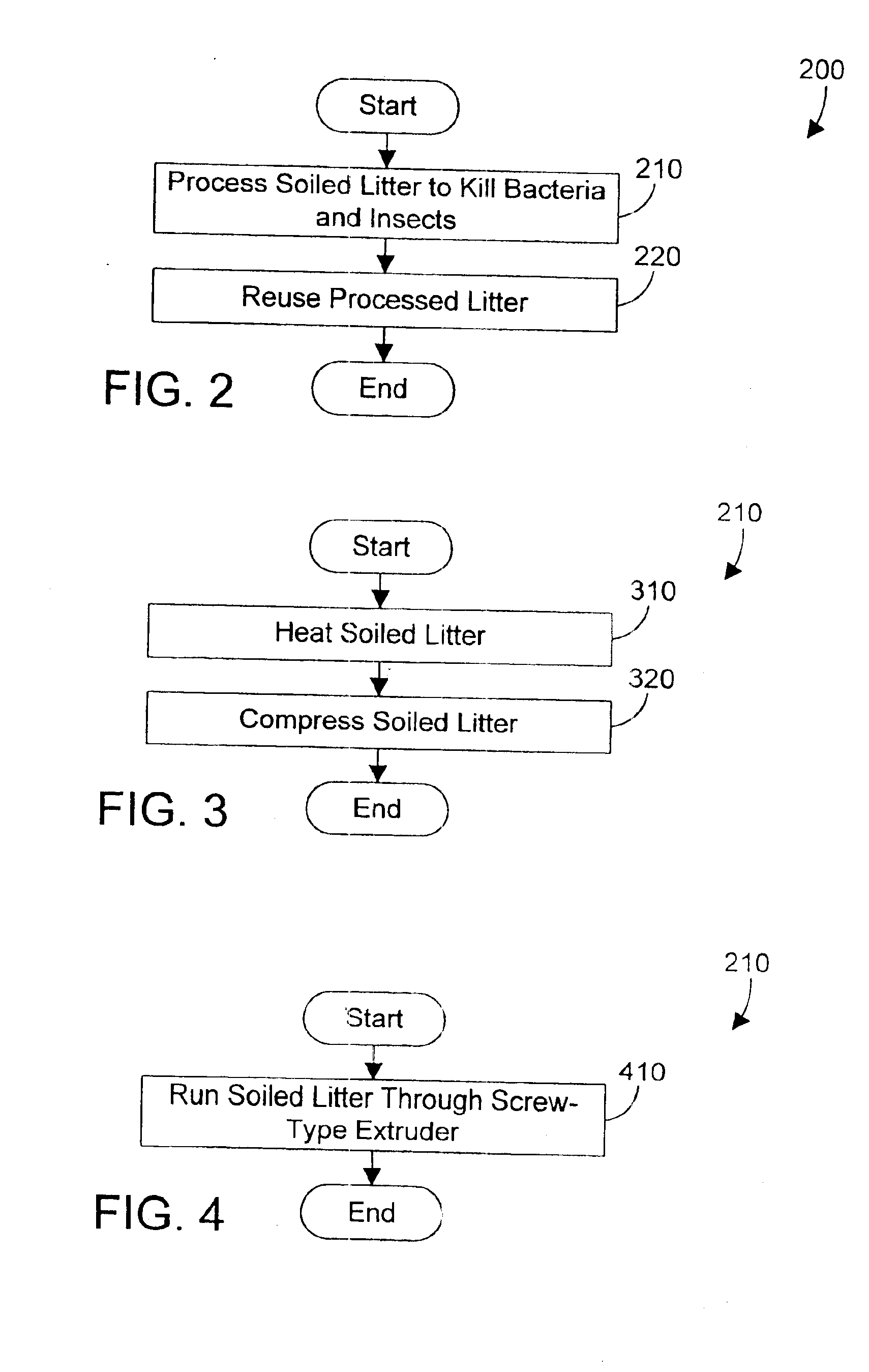
InactiveUS6860236B2Reduce ammonia levelsReduce moistureOther apparatusBird housingsAnimal foodLitter
A method for processing animal waste reduces ammonia levels and moisture and eliminates darkling beetles by heating and compressing the animal waste (such as soiled litter). In the preferred embodiments, the heating and compressing are done simultaneously using a screw-type extruder that is commercially available, but has only been used to date for producing animal food and feed products. By heating and compressing the animal waste, the volume of waste is reduced, bacteria in the waste is destroyed, and all darkling beetles in the waste are killed. In addition, the resulting processed waste may be recycled because it is free of bacteria and in a dry form. The preferred embodiments also include methods for doing business that include the processing of animal waste.
Owner:WOOD JAMES L
Rapid small volume detection of blood ammonia
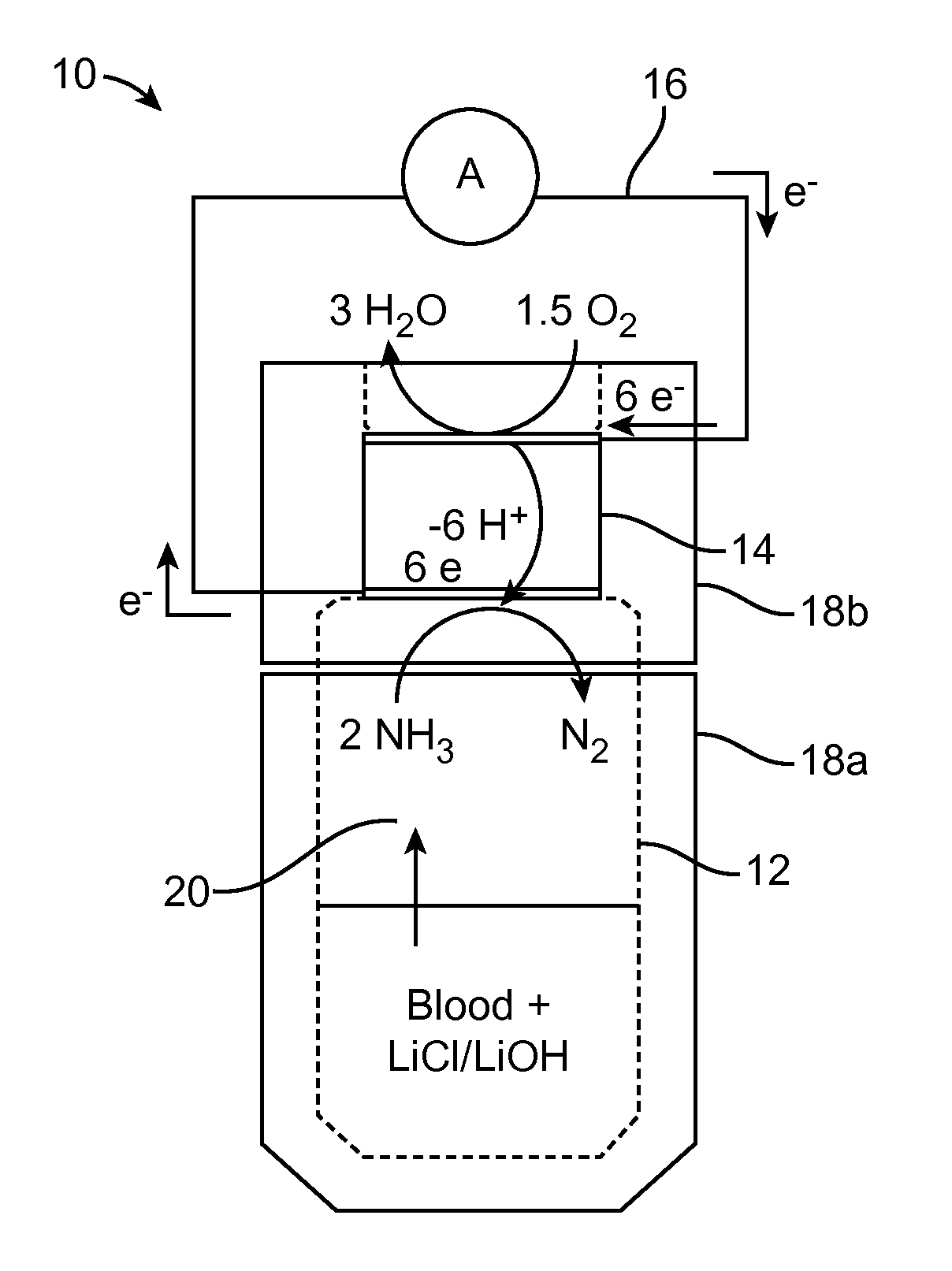
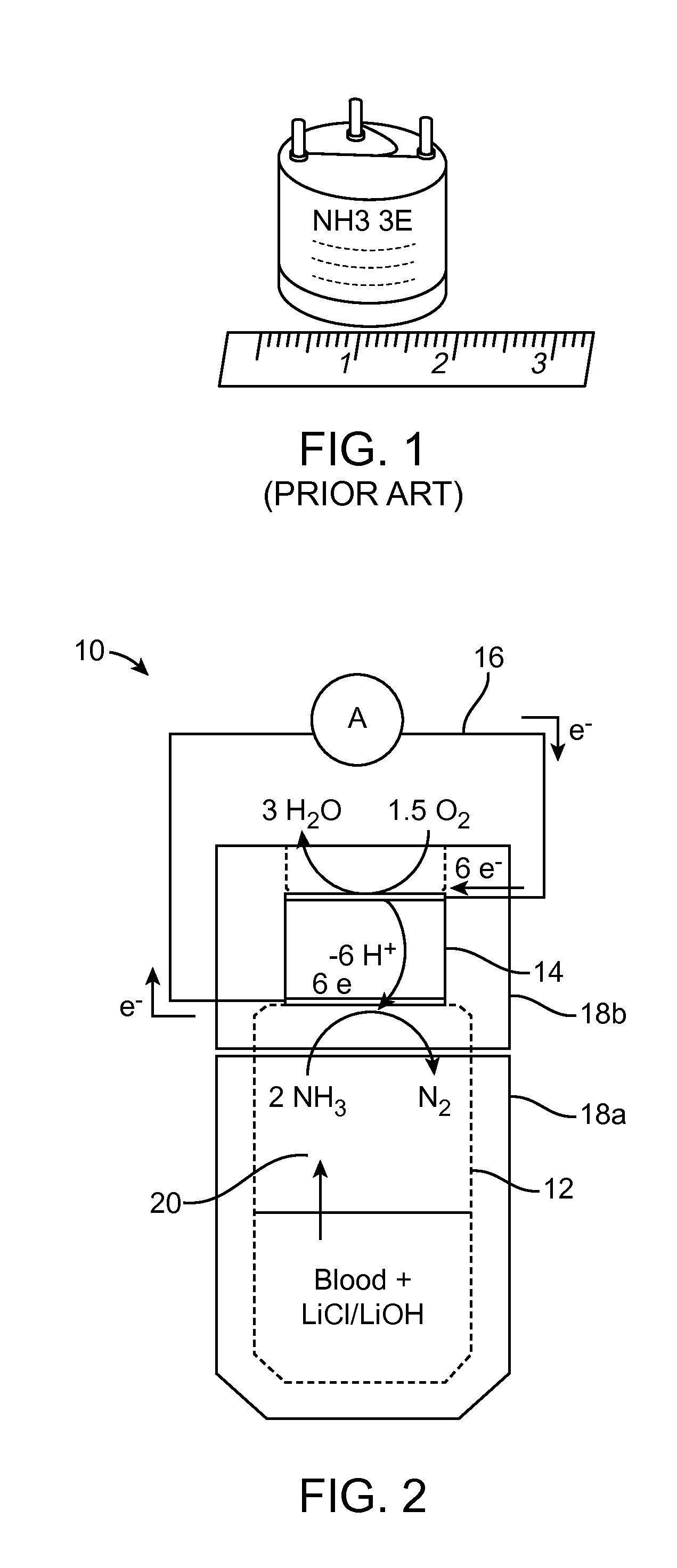
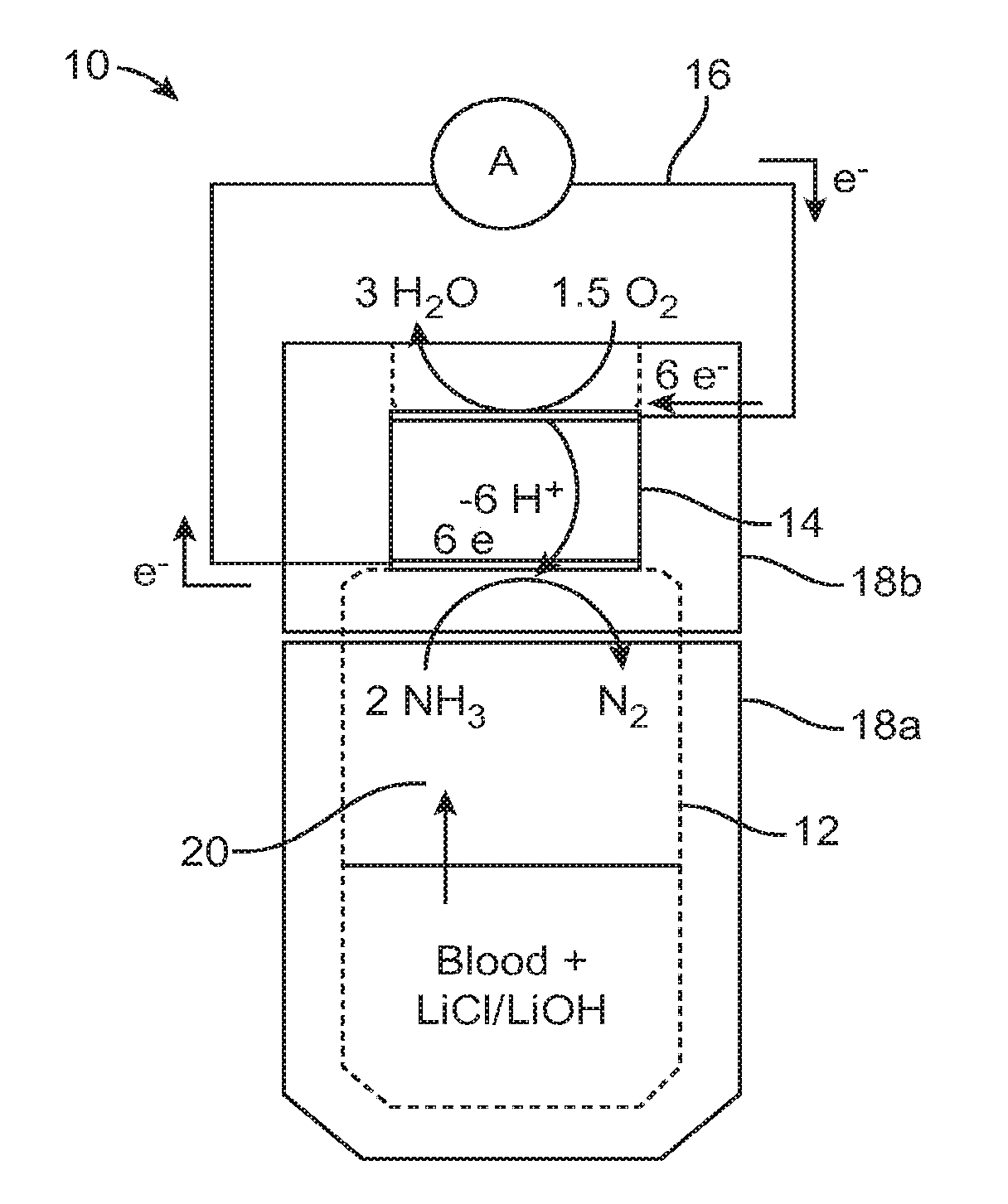
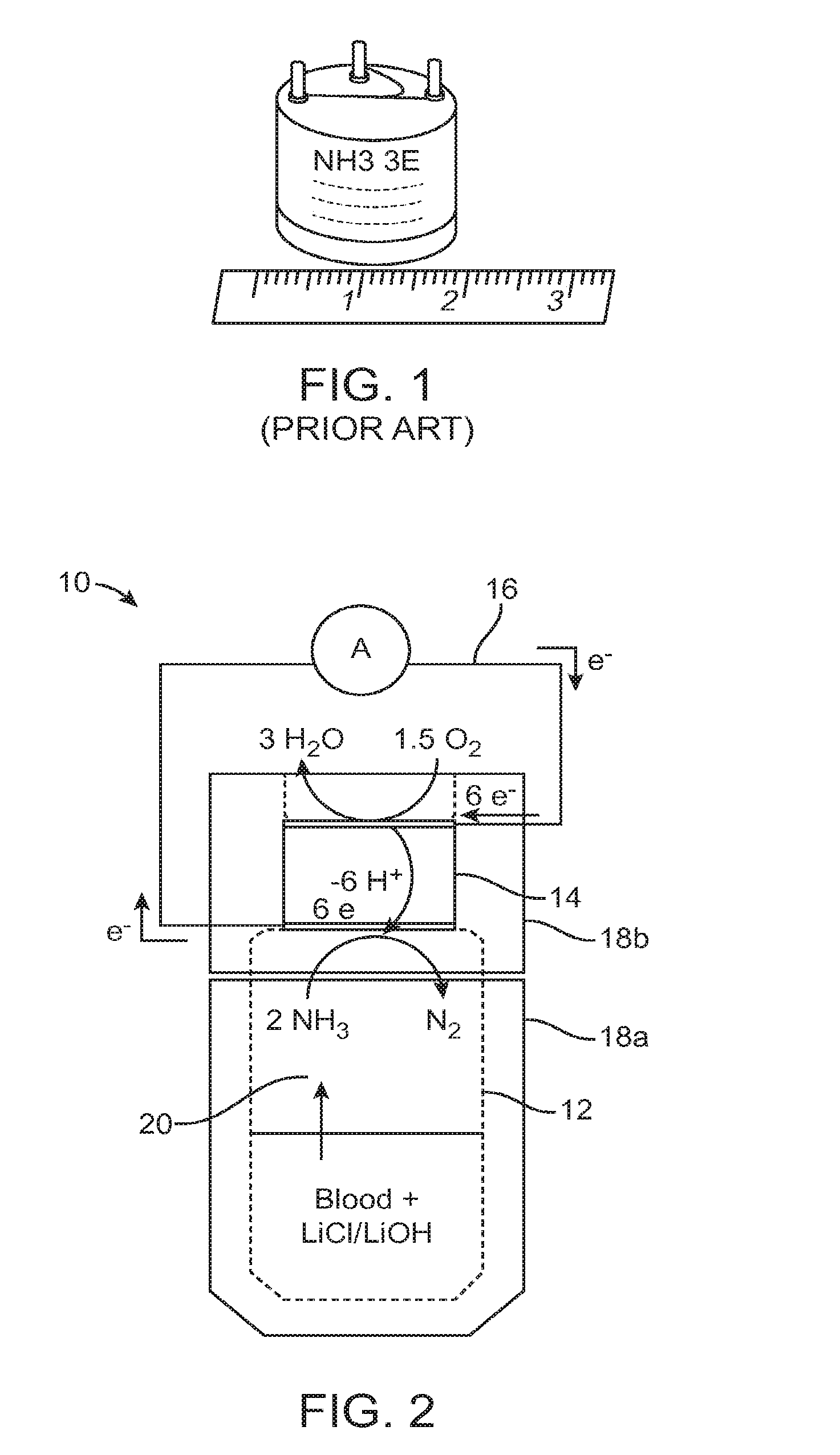
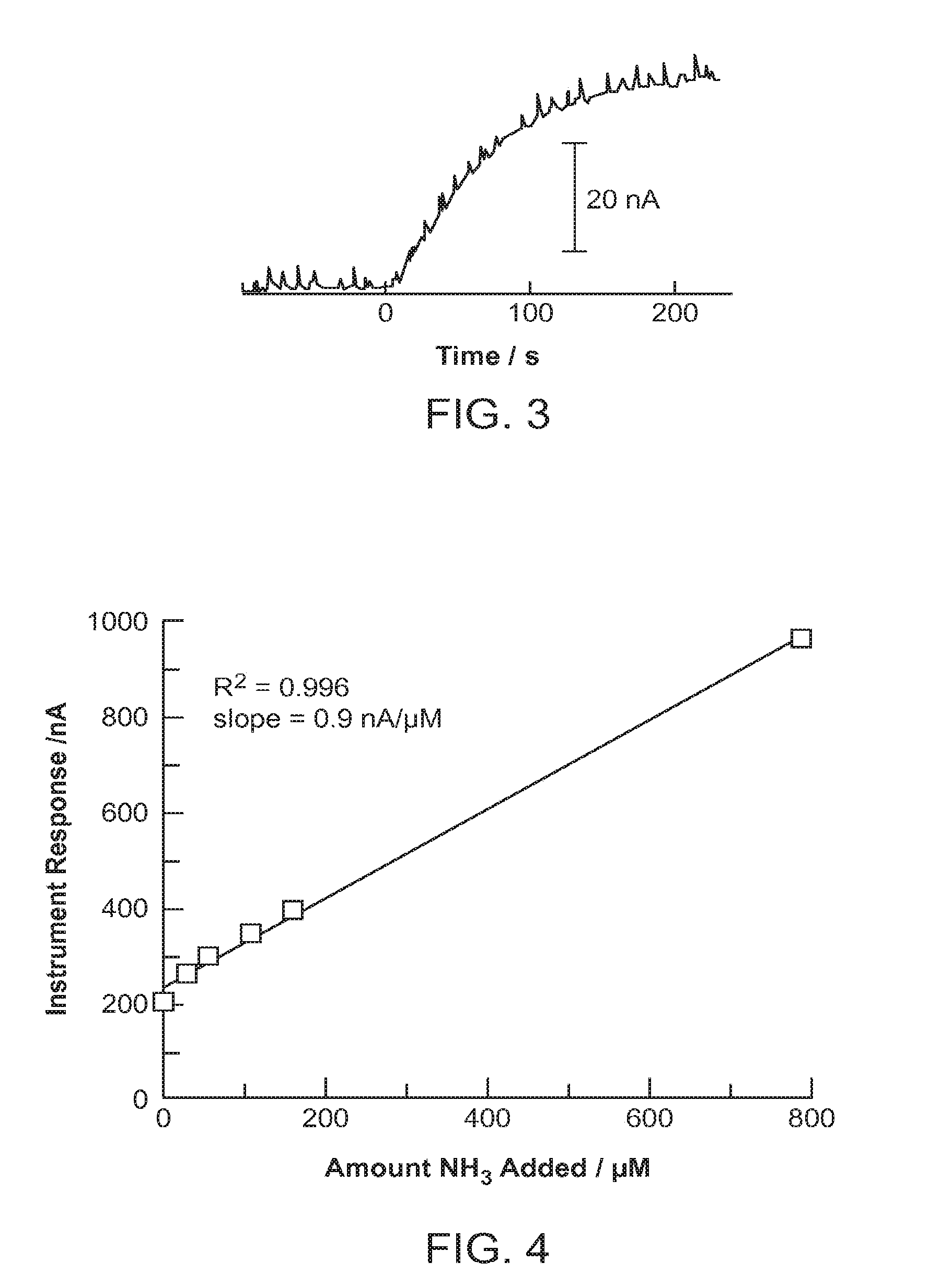
ActiveUS20150226702A1Facilitate and hasten leaving bloodSmall and convenient to useWeather/light/corrosion resistanceVolume/mass flow measurementPower flowBlood ammonia
A method for measuring ammonia in a blood sample may involve positioning the blood sample in proximity with an ammonia gas sensor, generating a current with the ammonia gas sensor in response to ammonia gas released from the blood sample, and measuring the current generated by the ammonia gas sensor, using a current measurement member coupled with the ammonia gas sensor. A device for measuring an ammonia level in a blood sample may include a blood sample containment member, an ammonia gas sensor coupled with the blood sample containment member, and a current measurement member coupled with the ammonia gas sensor. The method and device may be used to measure an ammonia level in a blood sample as small as one drop of blood, or approximately 0.05 mL of blood.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method of reducing unburned carbon levels in coal ash
InactiveUS20070045299A1Reducing carbon levelLower Level RequirementsSolid waste managementLighting and heating apparatusPulverized fuel ashOxygen
There is disclosed a method of reducing carbon levels in fly ash. The method comprises the steps of: (a) placing the fly ash in a microwave reactor; (b) exposing said fly ash to microwave radiation in the presence of carbon-free material so as to raise its temperature to at least 600° C. while agitating the fly ash in the presence of oxygen; and; (c) terminating exposure of said fly ash to said microwave radiation when the carbon content of the fly ash falls below a predetermined value. The method is also used to reduce ammonia levels in fly ash.
Owner:HENDRIX HLDG +1
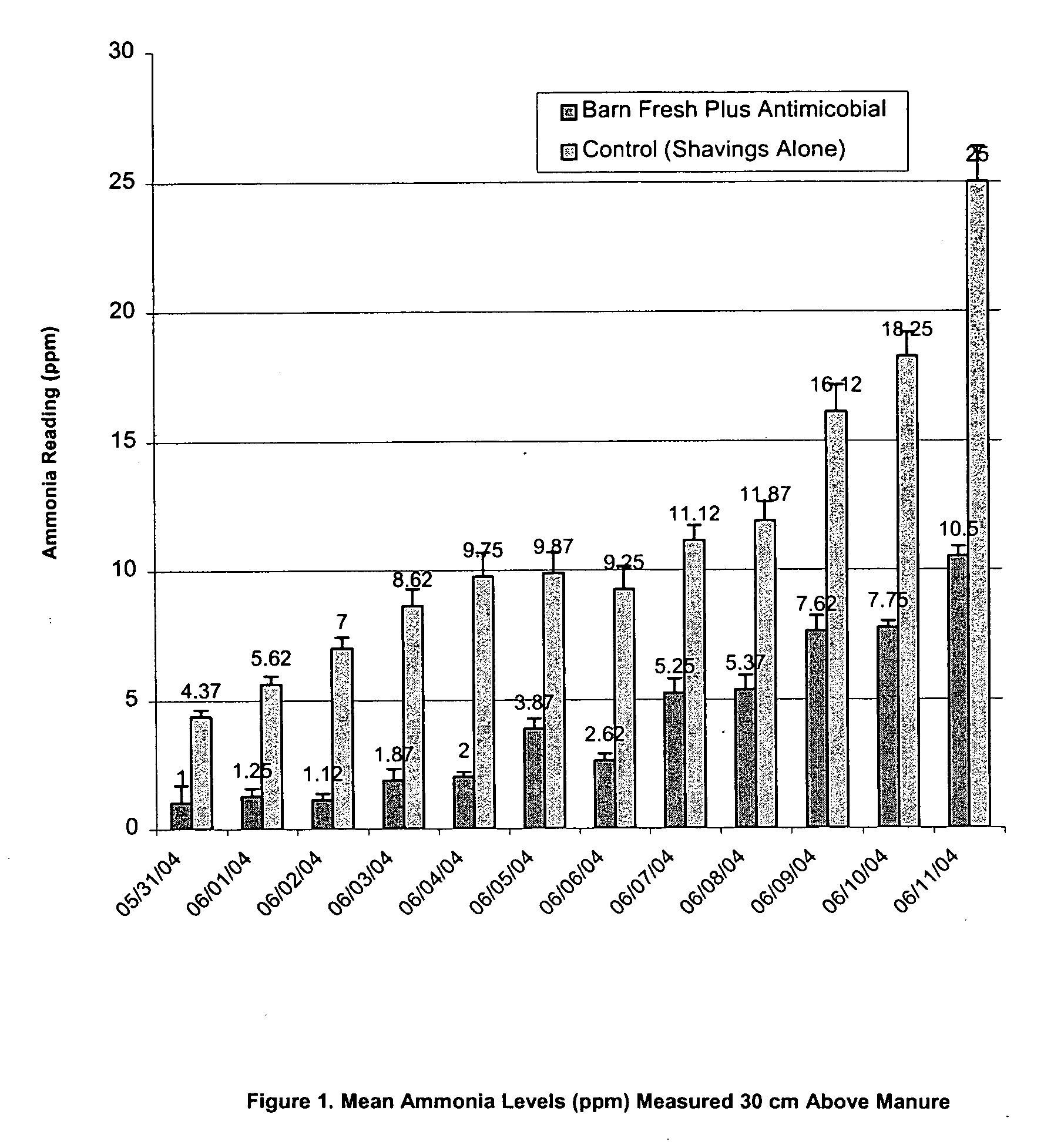
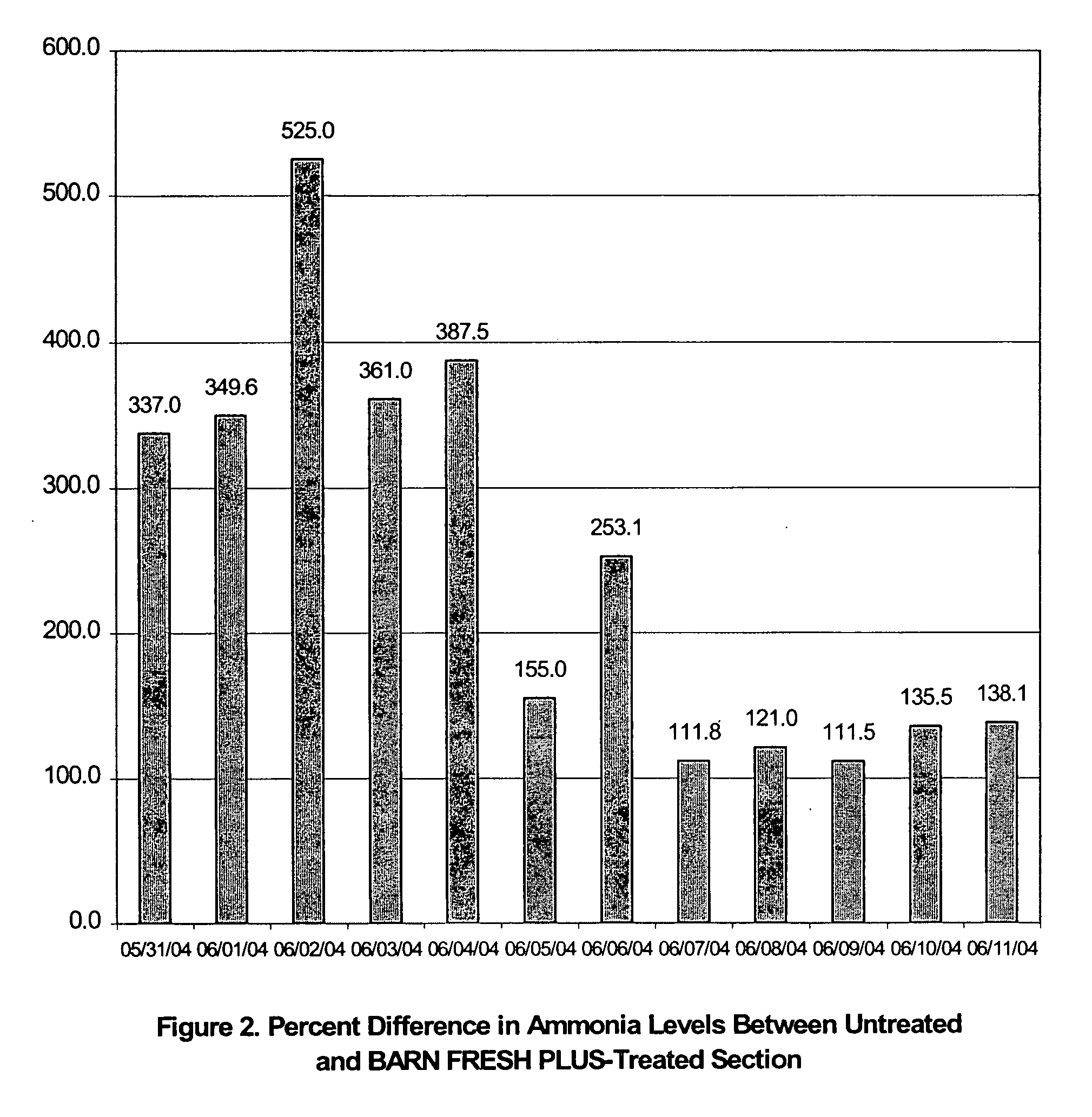
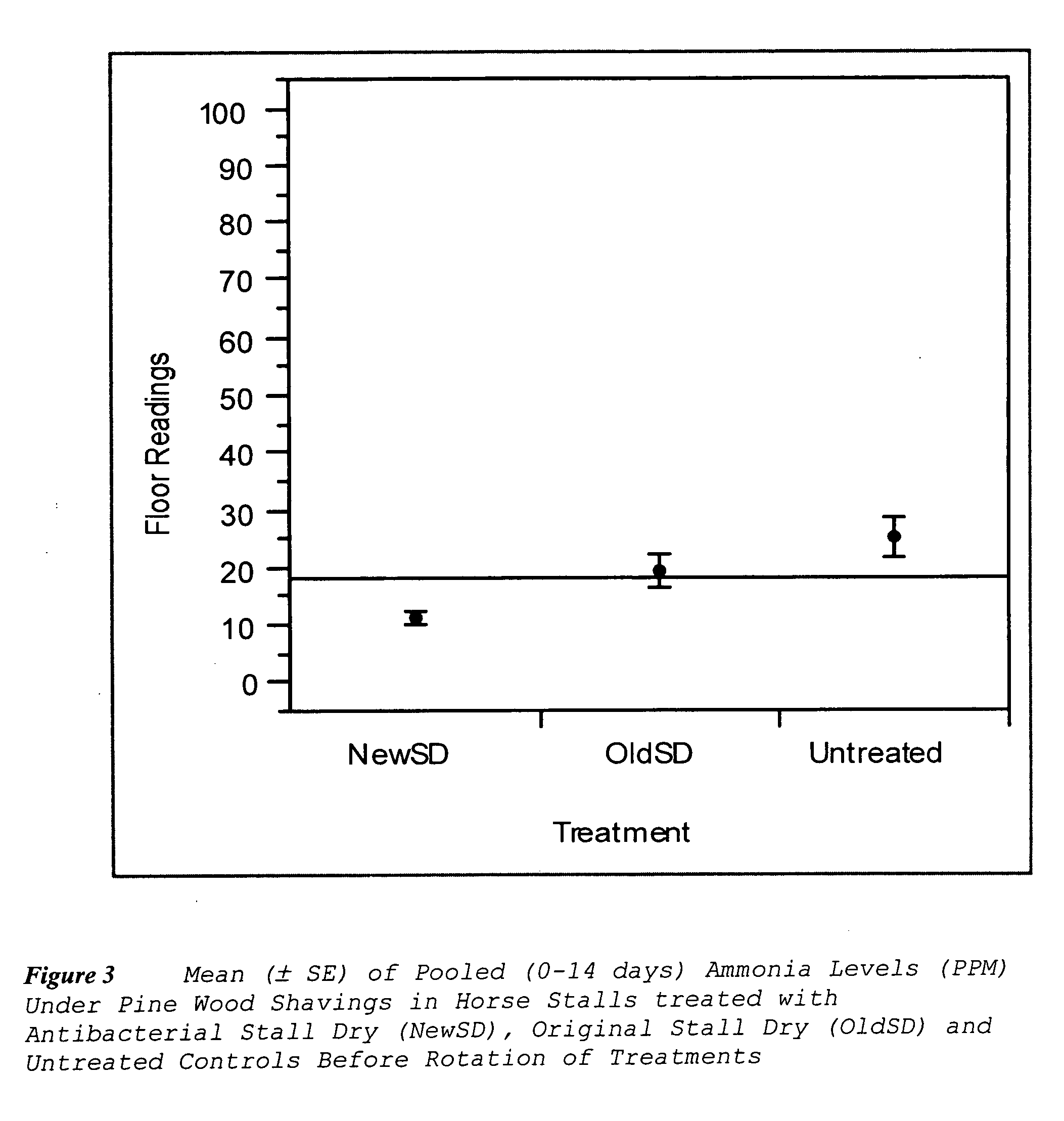
Antimicrobial additive for large animal or poultry beddings
The present invention provides a method for reducing ammonia levels, odour, microorganisms and insects in large animal stalls using a bedding material additive comprising a clay-based particulate absorbent material and an aliphatic bromo-nitro-bactericide.
Owner:ABSORBENT PROD INC
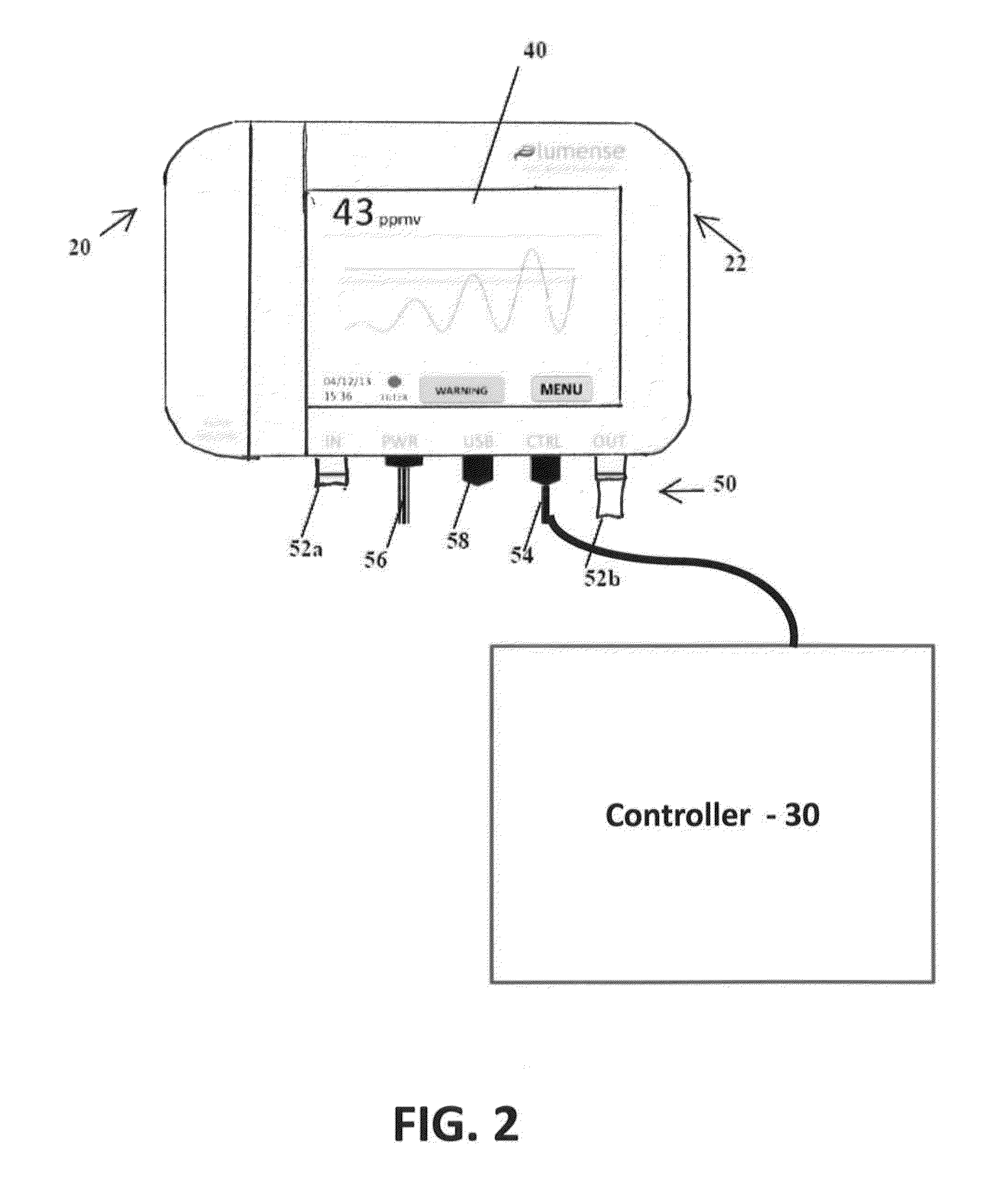
System and Method for Sensing Ammonia
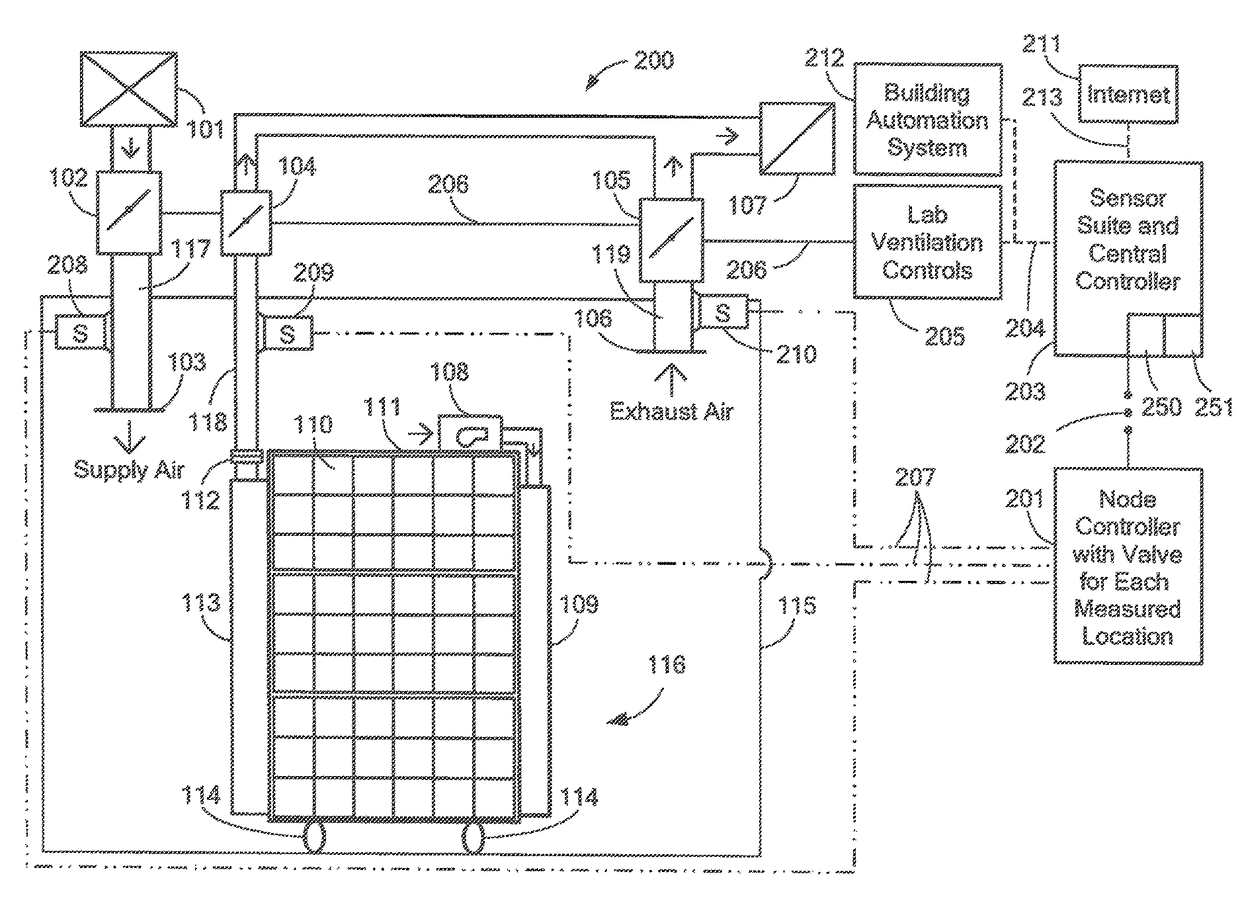
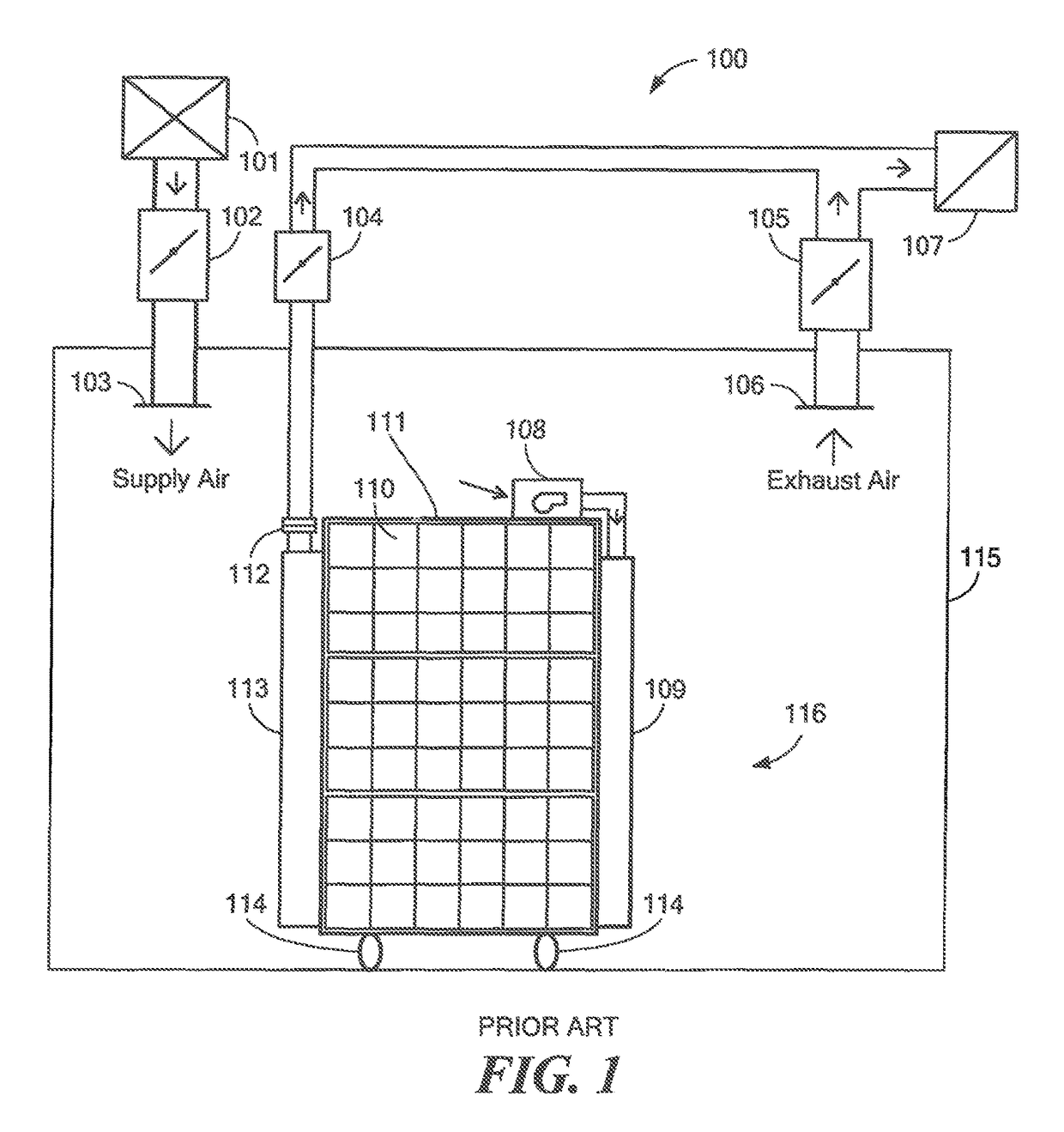
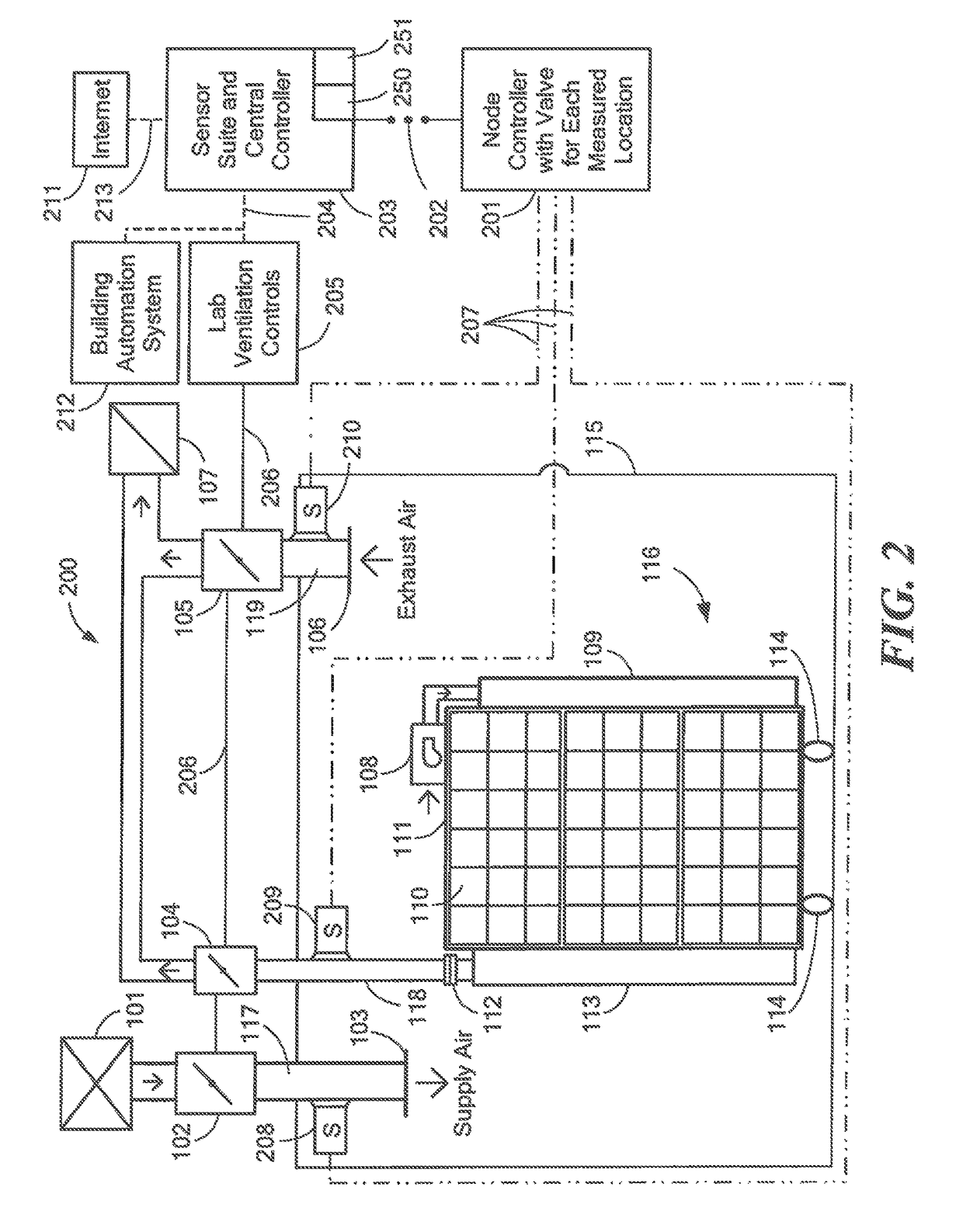
A system and method for the monitoring of ammonia in a fluid. The ammonia monitoring system includes an ammonia sensor that is configured to detect trace amounts of ammonia (NH3) in a fluid (i.e., gas or liquid) that is pumped through it in real time. The real time ammonia sensor includes an interferometer configured to track the amount of ammonia that is pumped into the real time ammonia sensor. The ammonia monitoring system, via the real time ammonia sensor, is further configured to detect ammonia levels in industrial poultry houses and provide electronic feedback to the building's ventilation control system.
Owner:LUMENSE
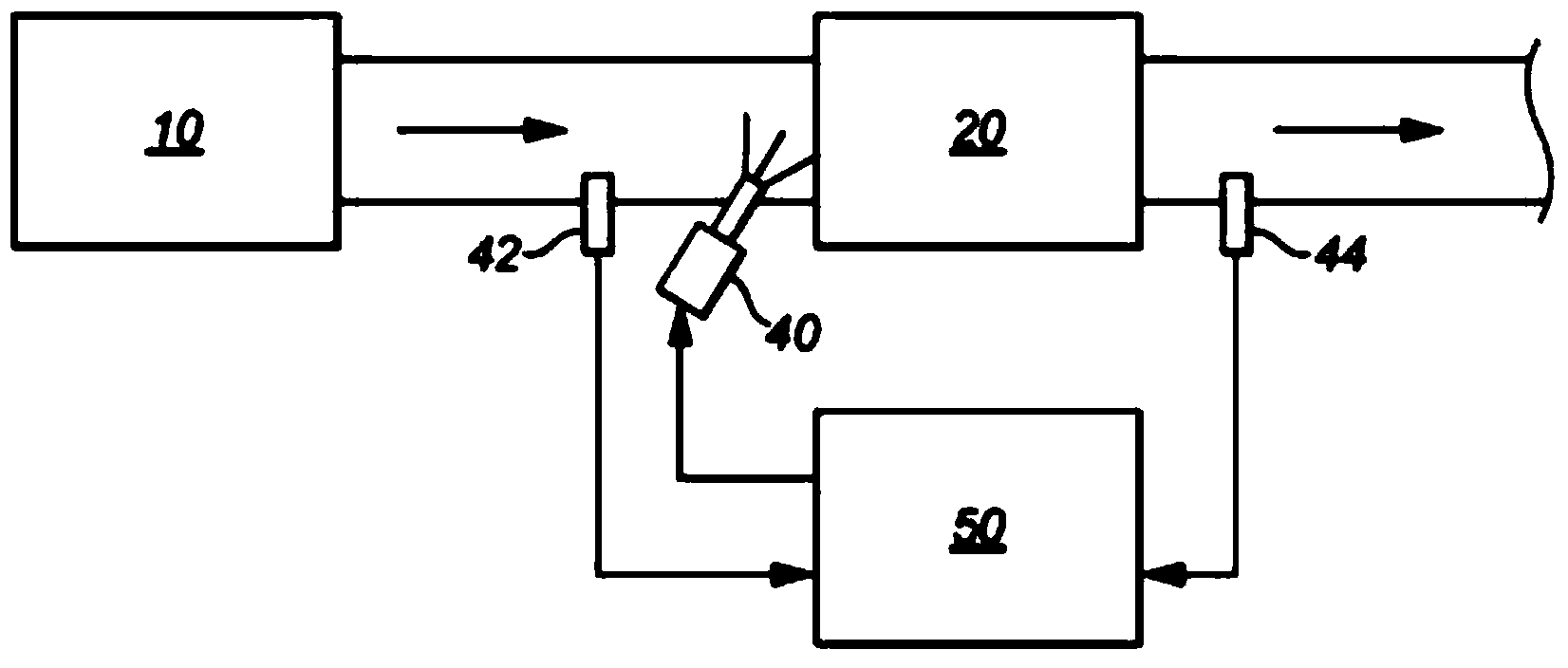
Method and apparatus for estimating the amount of reductant slip in a selective catalytic reduction device
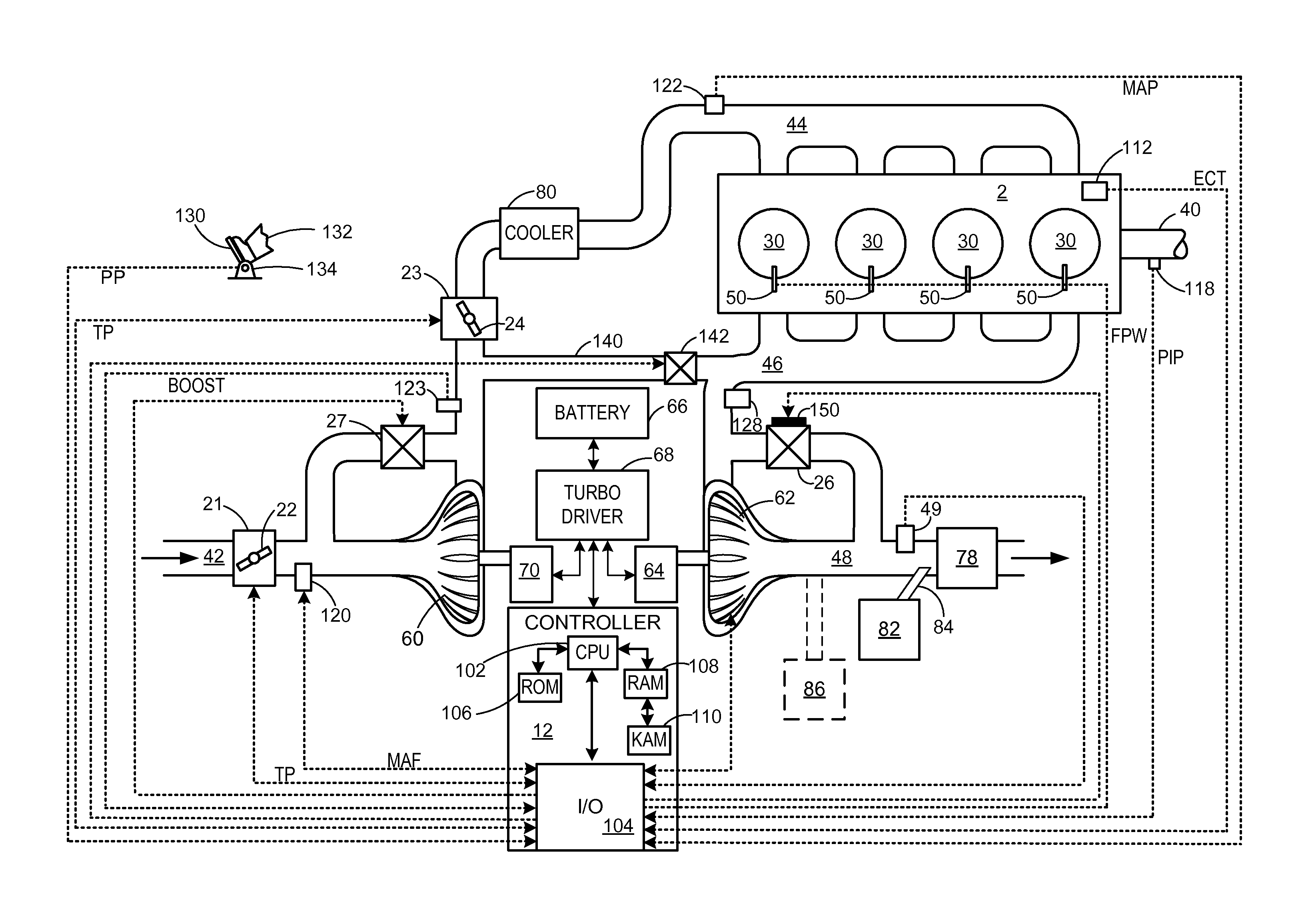
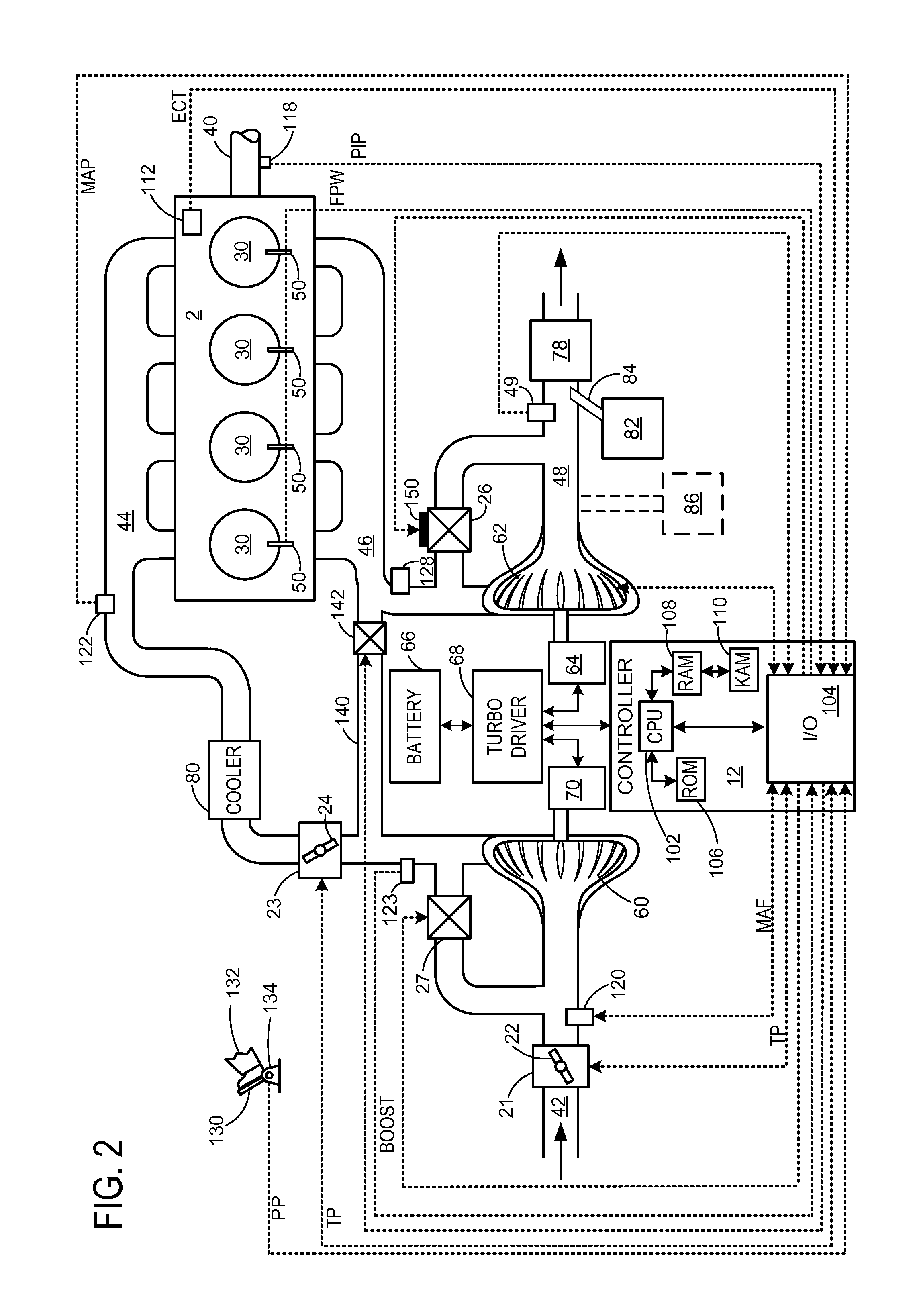
InactiveCN104411936AGas treatmentInternal combustion piston enginesProcess engineeringInternal combustion engine
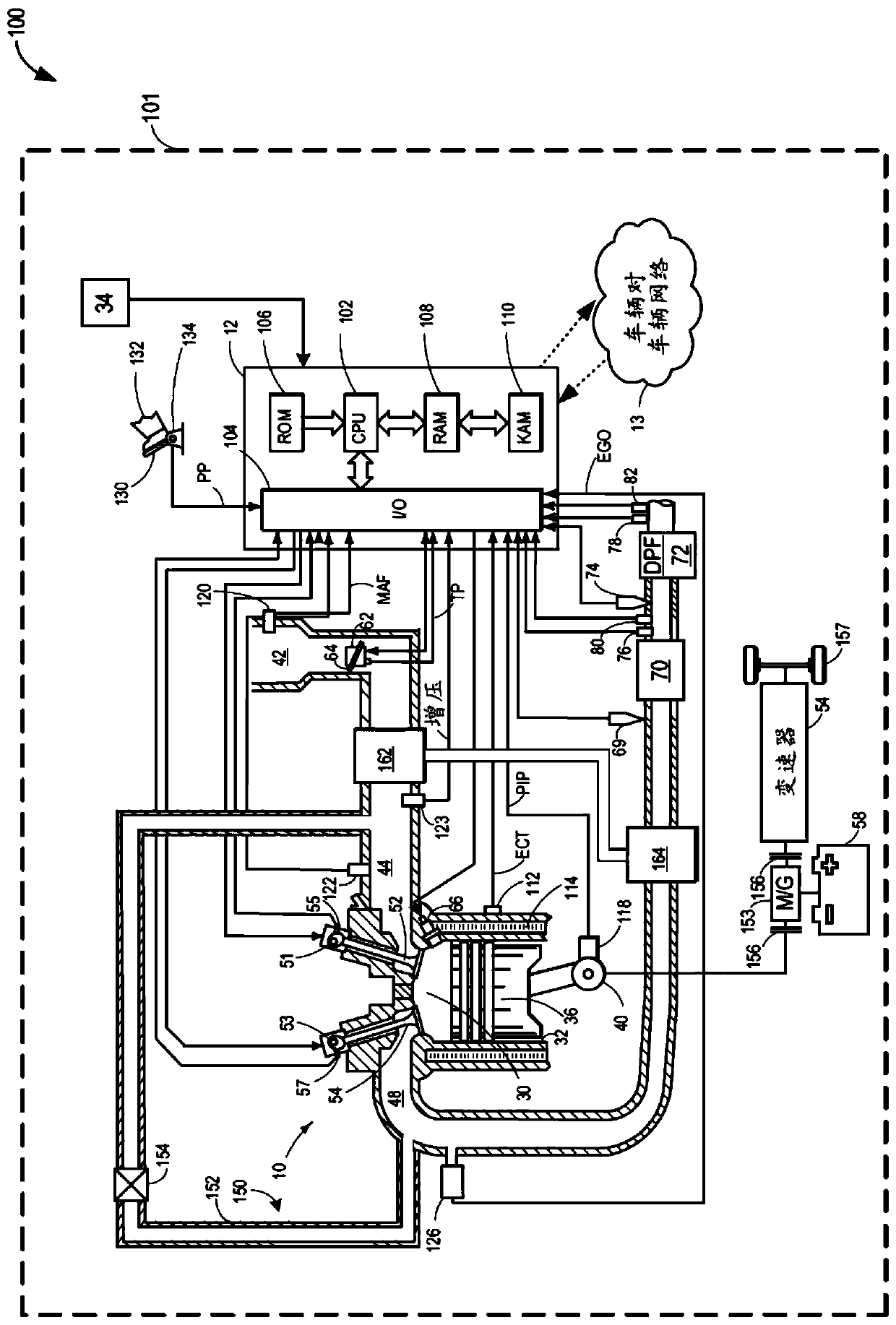
Disclosed is a method and apparatus for estimating the amount of ammonia output from a Selective Catalytic Reduction (SCR) device 20 located in the exhaust system of a vehicle powered by an internal combustion engine. A NOx sensor 44 is located downstream of the SCR to monitor the output of the SCR device and provide data for controlling the dosage of a reductant supplied to the SCR. The NOx sensor is sensitive to NOx which may be output from the SCR when it is under-dosed but is also sensitive to ammonia which may be present when the SCR is over-dosed. Consequently the signal from the NOx sensor is a combination of the NOx and / or ammonia levels in the exhaust. The method and apparatus for estimating the amount of ammonia output from the SCR determine a NOx conversion efficiency of the SCR using a variance of a NOx input measurement from a NOx sensor 42 located upstream of the SCR and a variance of a NOx output measurement from the NOx sensor 44 located downstream of the SCR. An estimate of the actual NOx output from the SCR is then determined using the measured NOx input value and the NOx conversion efficiency of the SCR. The resulting estimate of NOx output is used in conjunction with the measured NOx output to determine the ammonia output by subtracting the estimated NOx output from the measured NOx output to provide an estimate of the ammonia output.
Owner:PERKINS ENGINES
Air sampling system providing compound discrimination via comparative PID approach
ActiveUS9651531B2Mechanical apparatusSpace heating and ventilation safety systemsAir sampleEngineering
Owner:AIRCUITY
Live water compositions for bio-cycling of aquariums
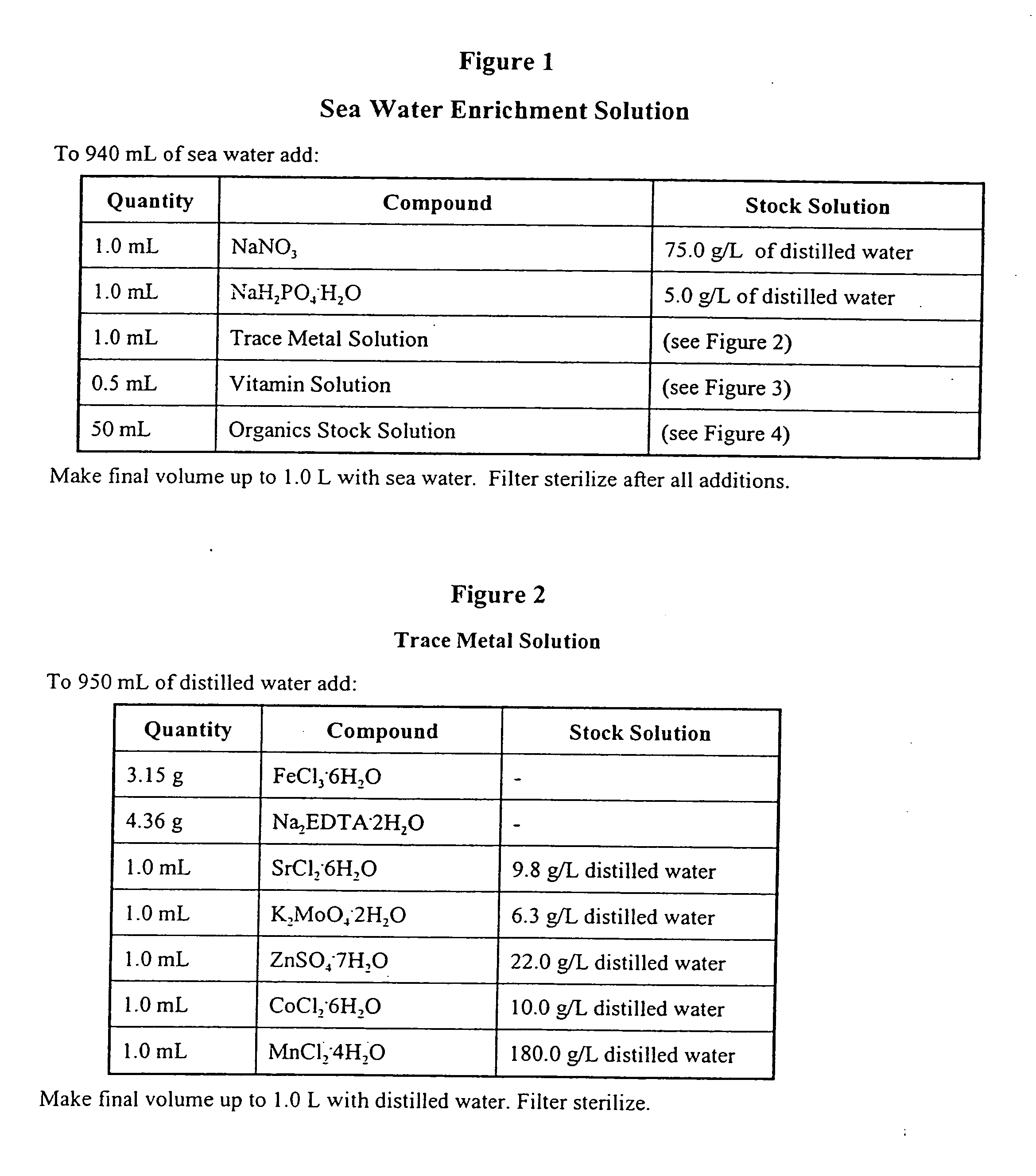
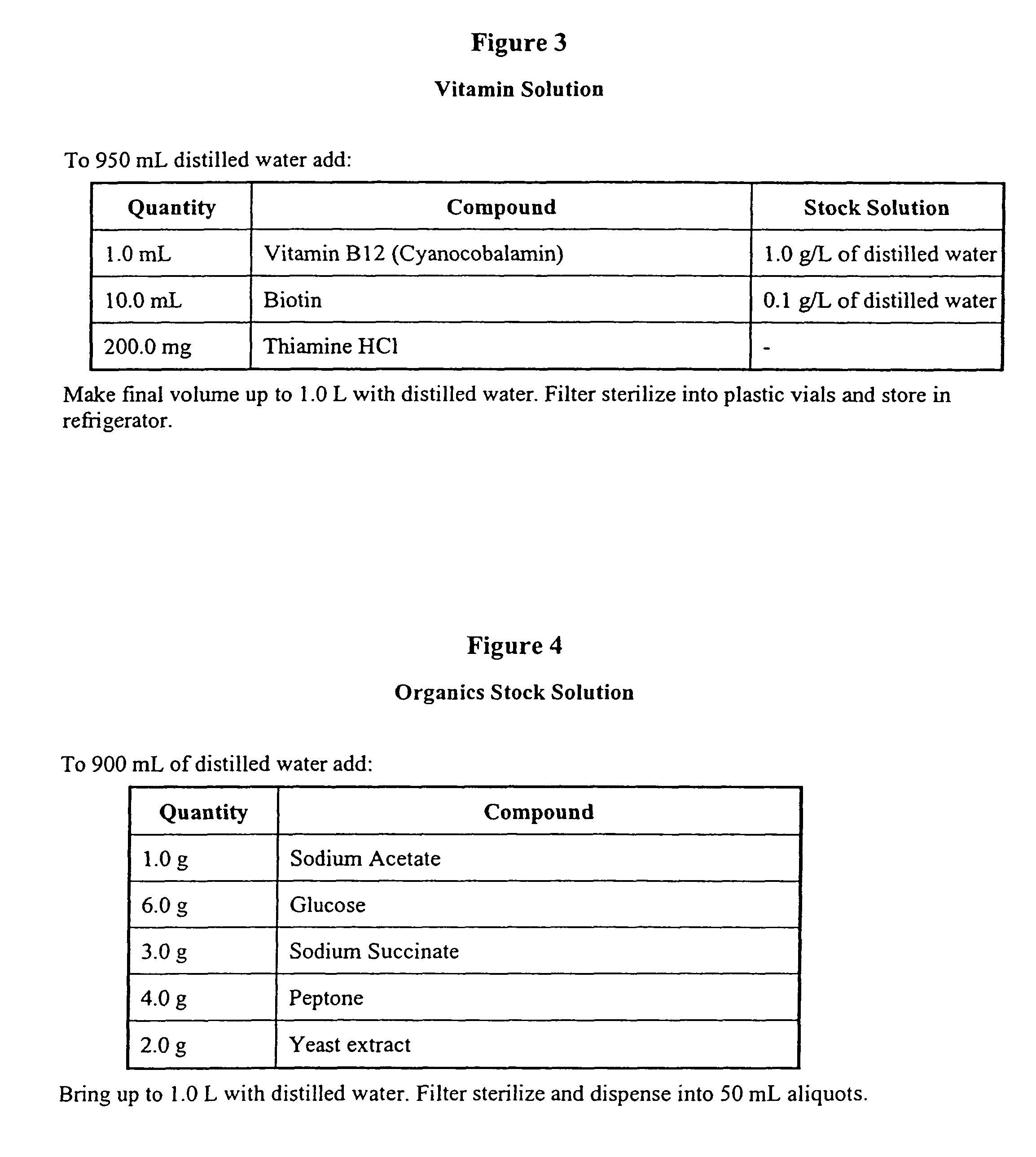
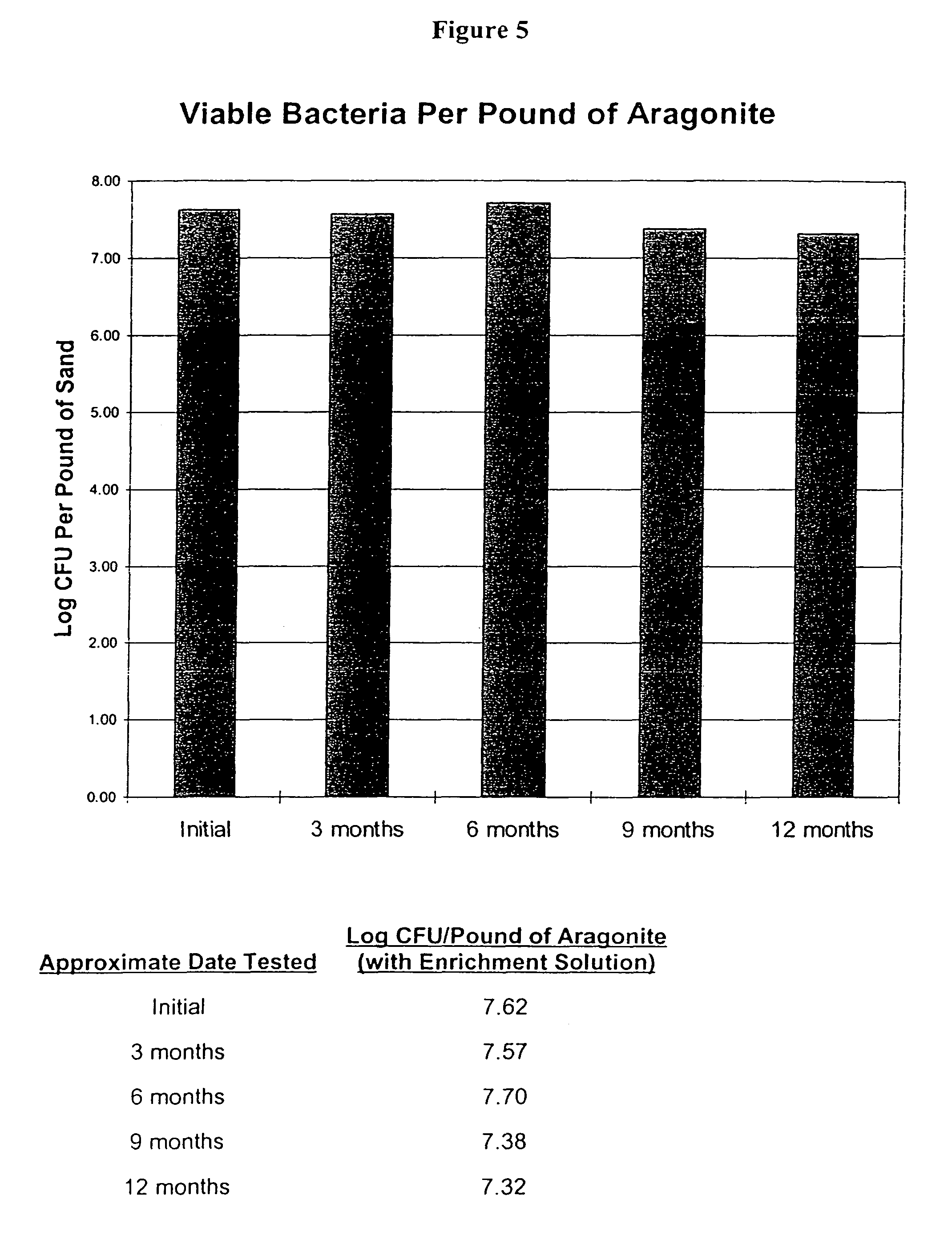
InactiveUS20050076850A1Rapid bio-cycling of marine aquariumsBacteriaUnicellular algaeEvaporationAmmonia levels
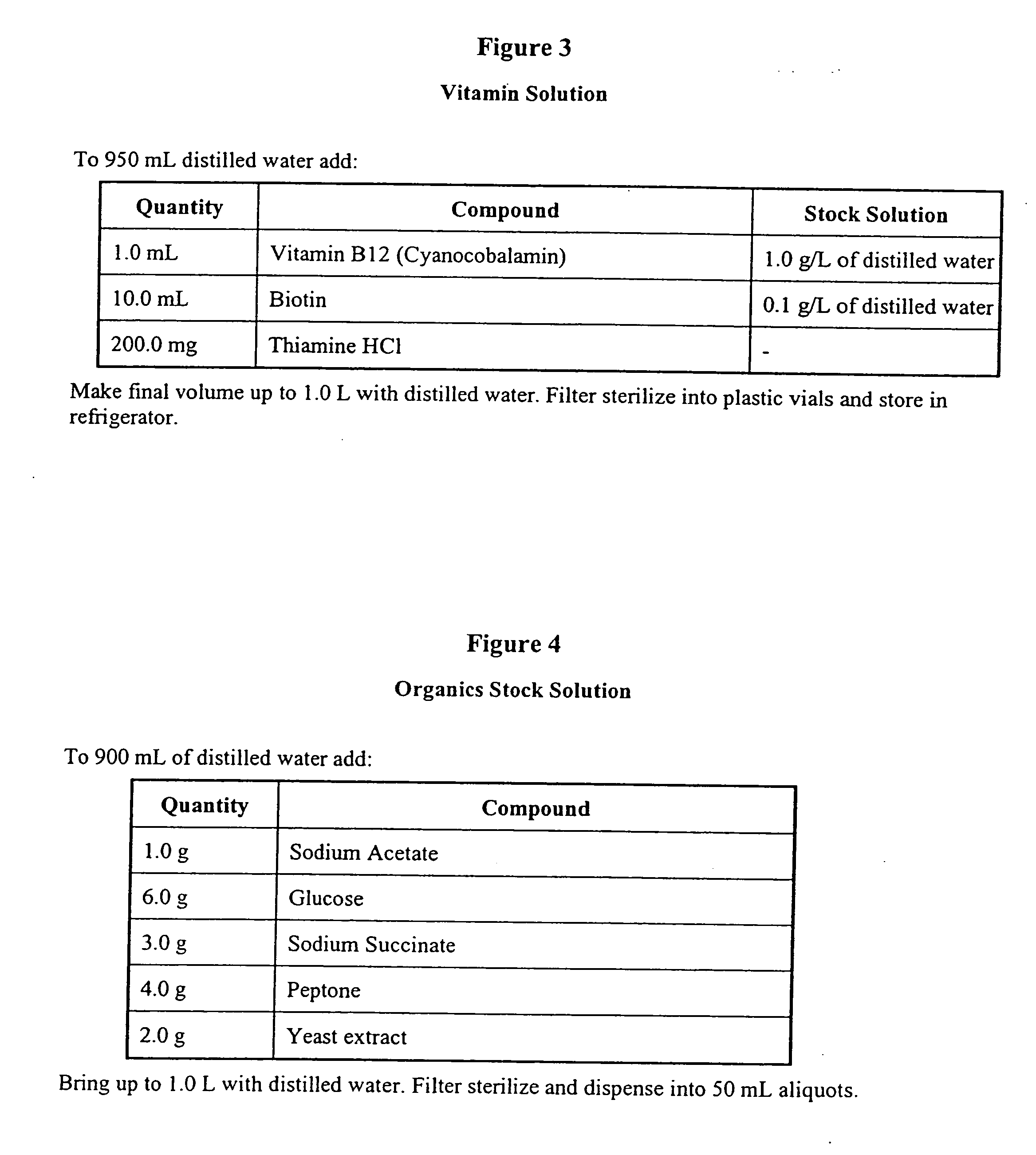
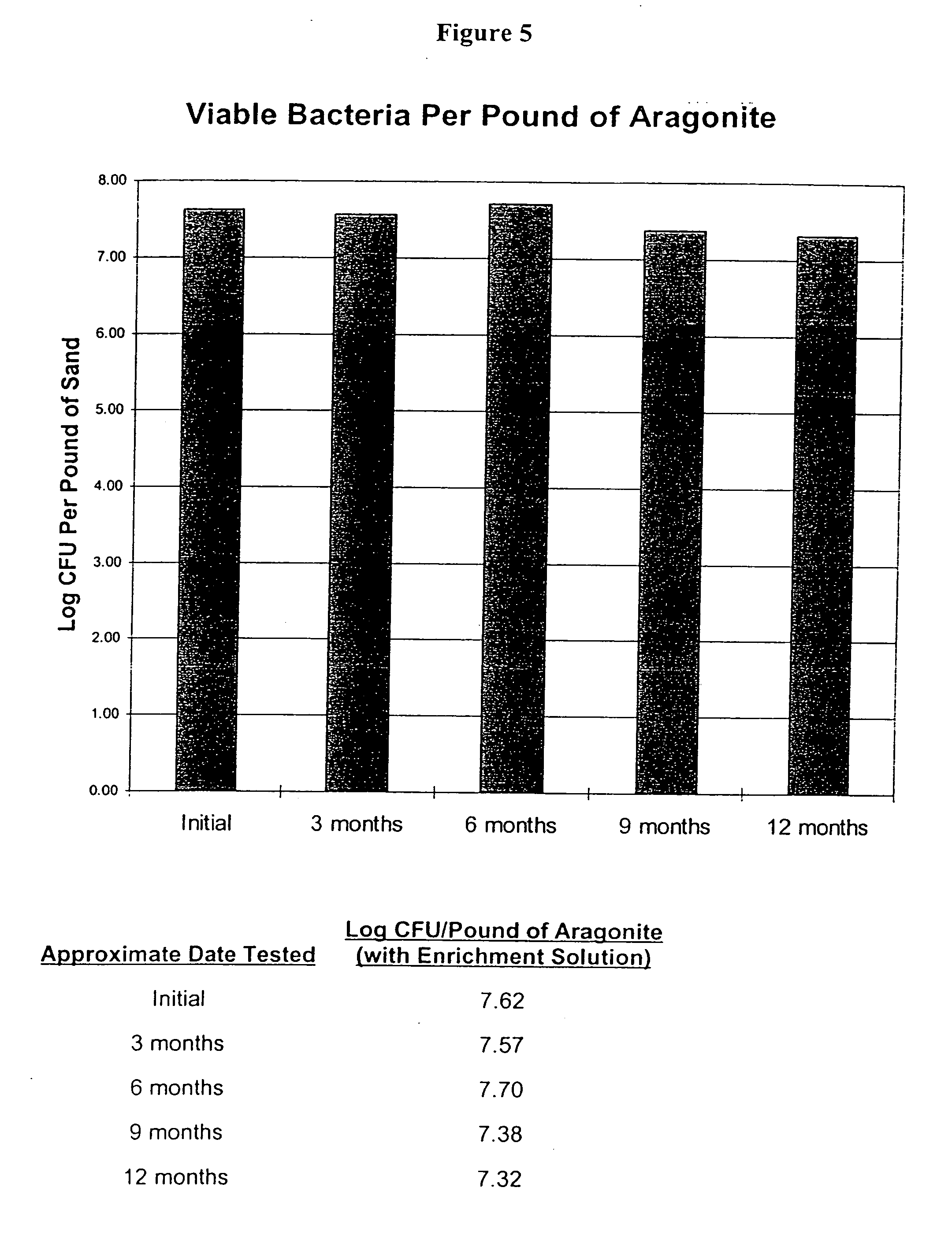
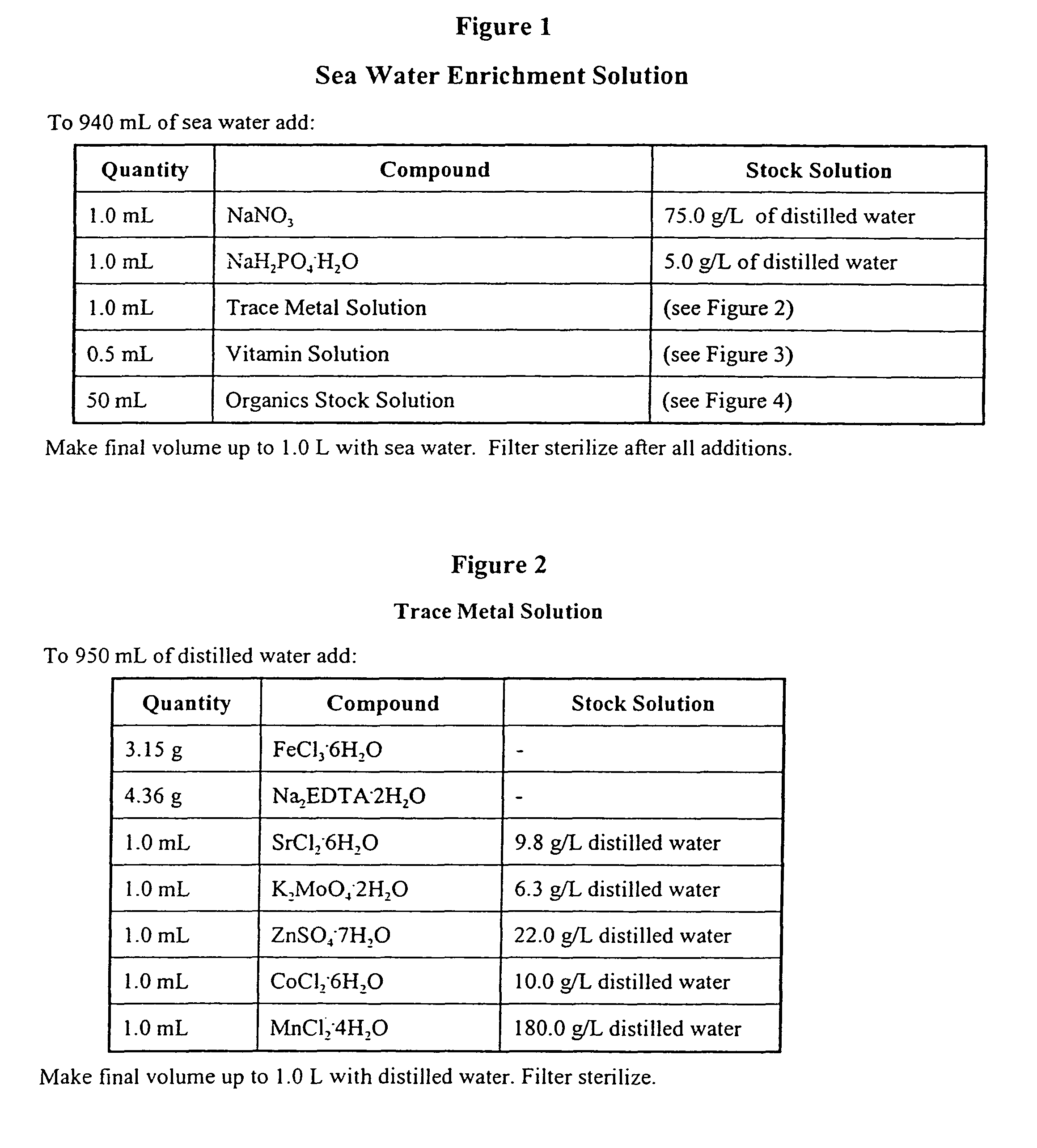
Live water solutions containing natural fresh water or saltwater microorganisms, is used in the bio-cycling of aquariums and to provide a healthy aquatic environment. Live water obtained from natural bodies of water, such as an ocean, sea, lake, river, or stream is filtered through filter media having a pore size between 5 and 20 microns to remove contaminants and debris while allowing microorganisms to remain in suspension. The live water is packaged in containers for retail sale thereby providing consumers with a source of live aquarium water for use in an aquarium during initial set-up, to replace water lost to evaporation, and for effecting quick water changes. An enrichment solution is disclosed to aid in maintaining the microorganisms metabolically and physiologically viable for extended periods. In an alternate embodiment, the live water is concentrated to a salinity level not less than 0.8 aw thereby reducing volume while maintaining microorganism viablility. Rapid biochemical cycling of an aquarium is achieved by introducing the live water into an aquarium whereby marine microorganisms instantly contribute to establishing a healthy aquatic environment by reducing harmful ammonia levels and through denitrification.
Owner:MORRIS BARRINGTON A +1
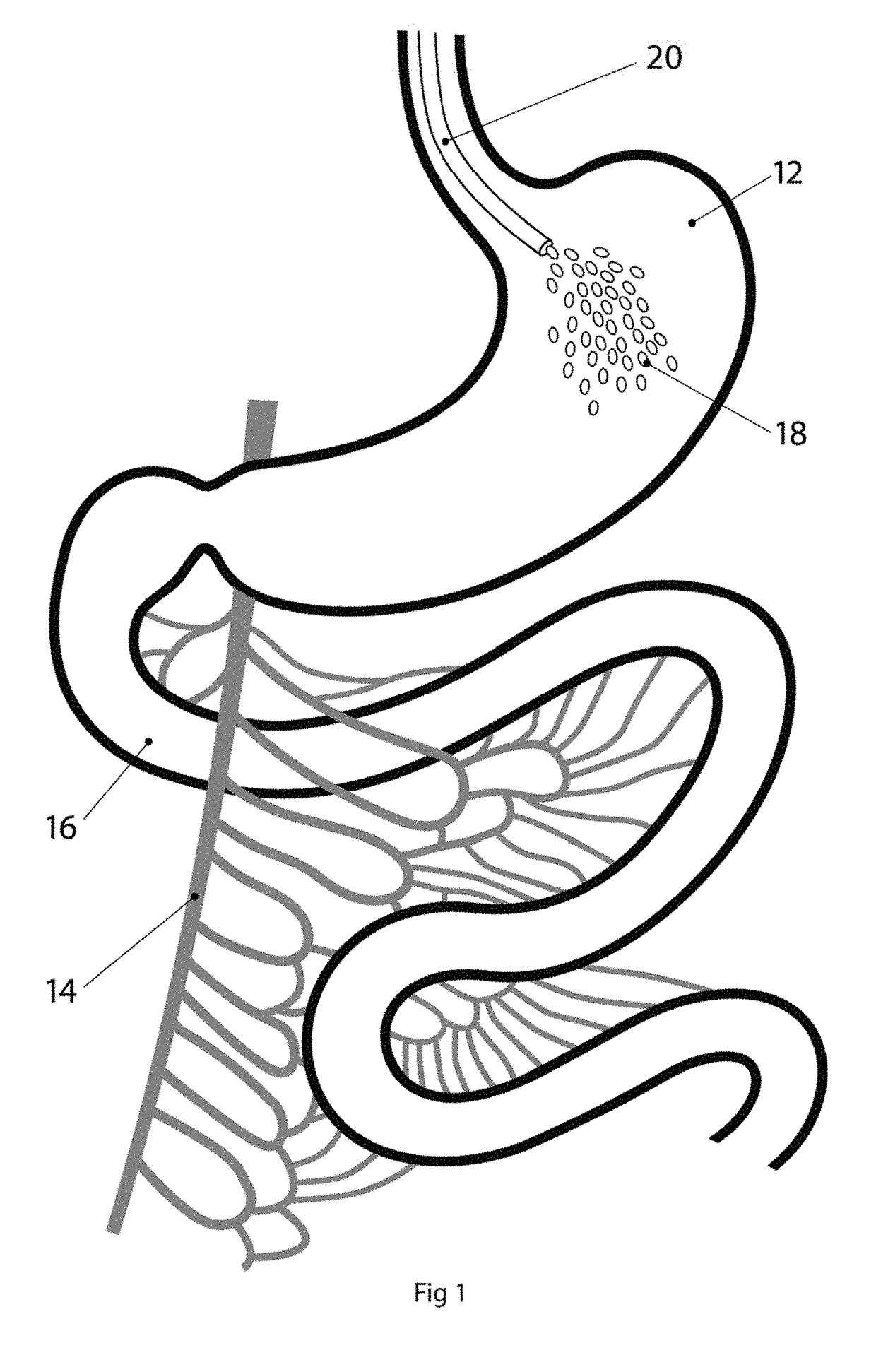
Enhanced biogas production from nitrogen bearing feed stocks
InactiveCN1511114AAvoid inhibitionWater contaminantsGas production bioreactorsMicroorganismAcetogenesis
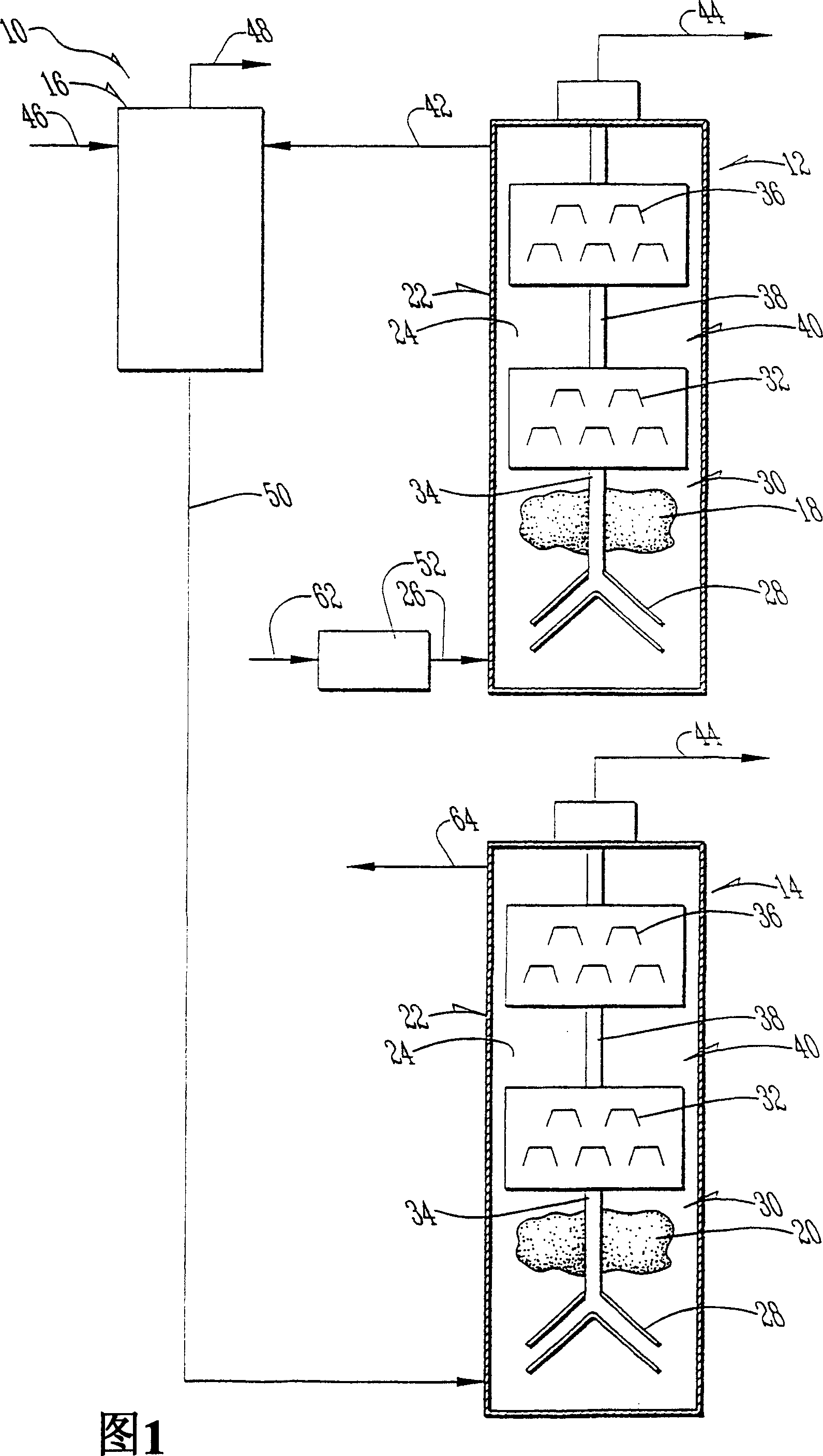
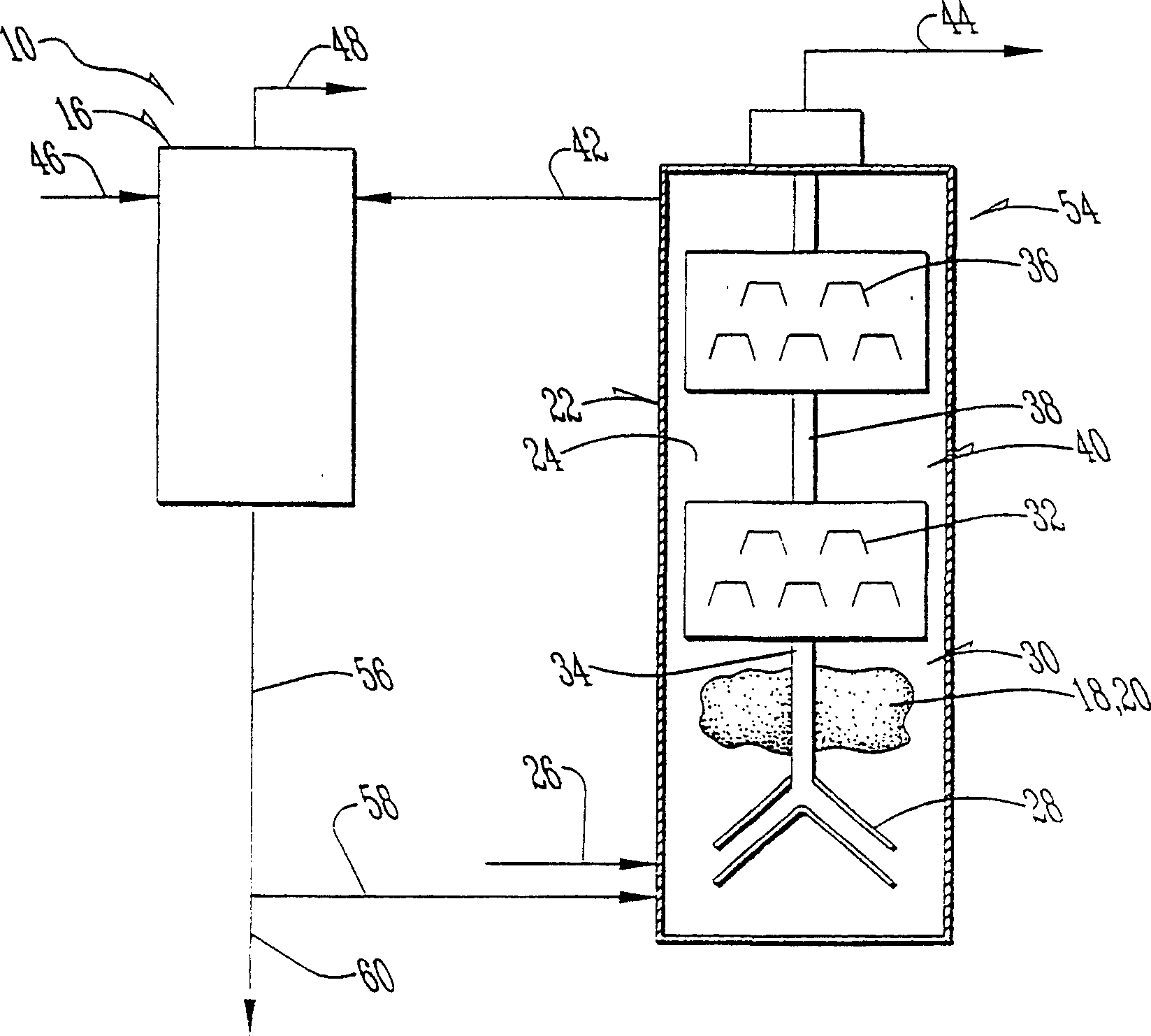
A system comprising a first anaerobic digester (12), an ammonia recovery vessel (16) and a second anaerobic digester (14). Microorganisms in the first digester are primarily hydrolyzers and acetogens, while those in the second digester are primarily methanogens. A nitrogen containing feed stock undegoes hydrolysis ans acetogenesis in the first digester. The effluent is passed to the ammonia recovery vessel in which ammonia is removed. The low ammonia effluent stream is passed to the second digester to undergo methanogenesis, generating a biogas. In an alternate embodiment, a single anaerobic digester is used. The effluent is treated for ammonia removal and recycled to the digester to keep the ammonia levels sufficiently low to avoid ammonia inhibition.
Owner:亚历山大·G·法斯本德
Antimicrobial additive for large animal or poultry beddings
The present invention provides a method for reducing ammonia levels, odor, microorganisms and insects in large animal stalls using a bedding material additive comprising a clay-based particulate absorbent material and an aliphatic bromo-nitro-bactericide.
Owner:ABSORBENT PROD INC
Ammonia storage control
Various methods for controlling ammonia levels stored in a catalyst by controlling exhaust gas temperatures are provided. In one embodiment, a temperature of a catalyst in an internal combustion engine is determined. If the temperature of the catalyst exceeds a first threshold at which an ammonia capacity of the catalyst for the temperature is below a current stored ammonia level in the catalyst, a load of the engine is reduced including adjusting a torque output of a motor operatively coupled to the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hyperammonemia therapy for children suffering from urea cycle disorders
A method and composition for treating or preventing the progression of hyperammonemia caused by a Urea Cycle Disorder, the method comprising administration of an effective amount of porous activated carbon particles, wherein the porous activated carbon particles are enteric-coated in order to control their release and adsorption properties. The porous activated carbon particles or microspheres can initially be coated with lactulose, followed by enterically coating the lactulose-covered carbon particles. The inventive method and composition provides a safe and uncomplicated reduction of ammonia levels in affected children.
Owner:CT DEV ONE LLC
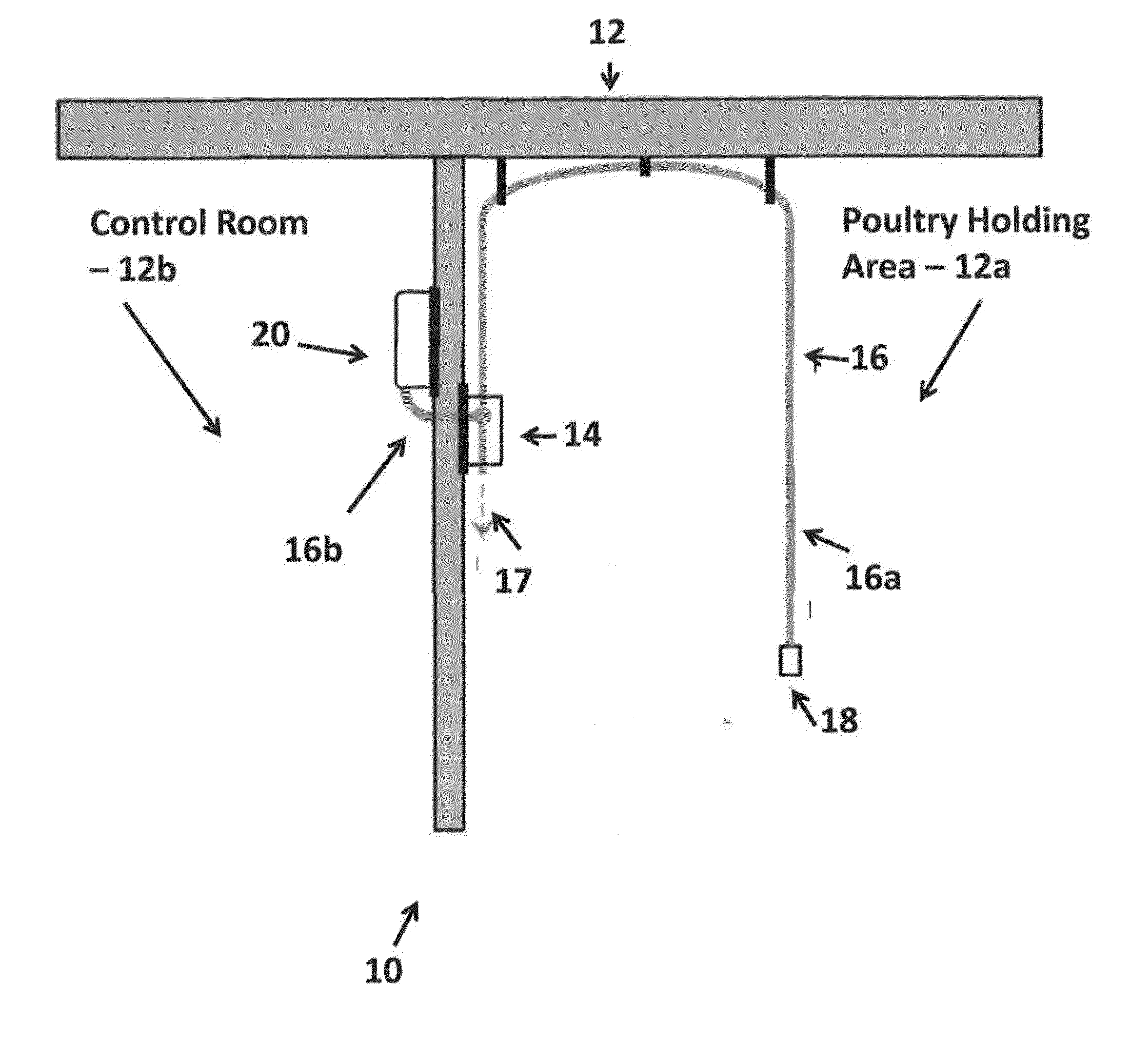
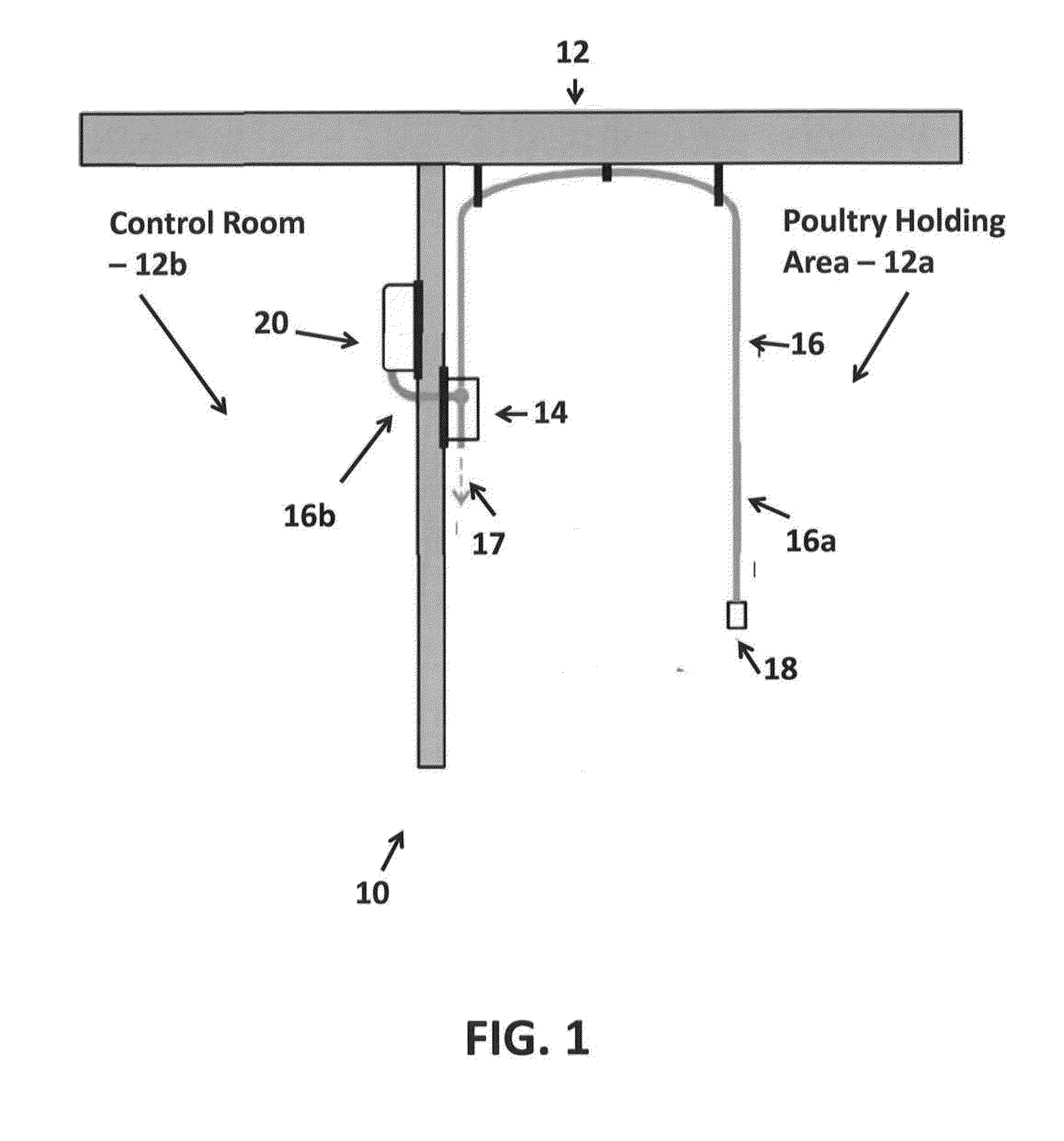
Monitoring and alert system for ventilated rack systems
The present invention is directed to monitoring / alert systems, devices, and methods useable with animal housing units. Embodiments include a primary component, such as a system controller device, for monitoring maintenance and operational events in a housing unit and a secondary component, such as a environmental monitoring device for analyzing environmental conditions. For example, the system controller device monitors unit functions (e.g., relating to power, pre-filter(s), filter(s), fan(s), air pressure, air temperature, electrical connections, etc.) and causes alert(s) to be sent (e.g., via email or text message) if there is a malfunction or abnormal operational data. The environmental monitoring device collects environmental data (e.g., time, temperature, humidity, light, sound, carbon dioxide levels, or ammonia levels) and causes alert(s) to be sent if an abnormal environmental condition is detected. The primary and secondary components may function in connection with one another, other devices, a network, or as stand-alone devices.
Owner:LAB PROD INC
System and method for particulate filter regeneration
PendingCN110857651AAdjust the spray limitImprove emission qualityInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusPtru catalystAmmonia storage
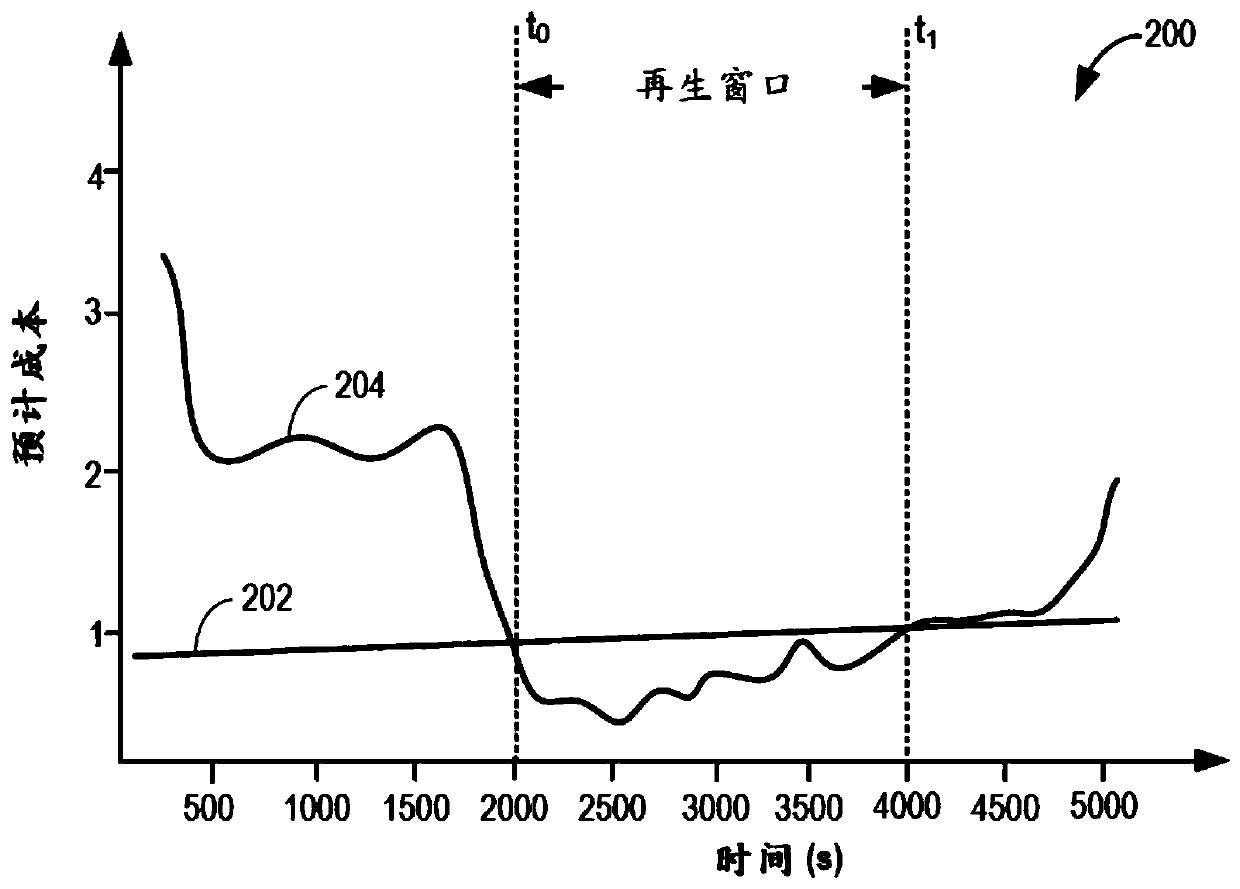
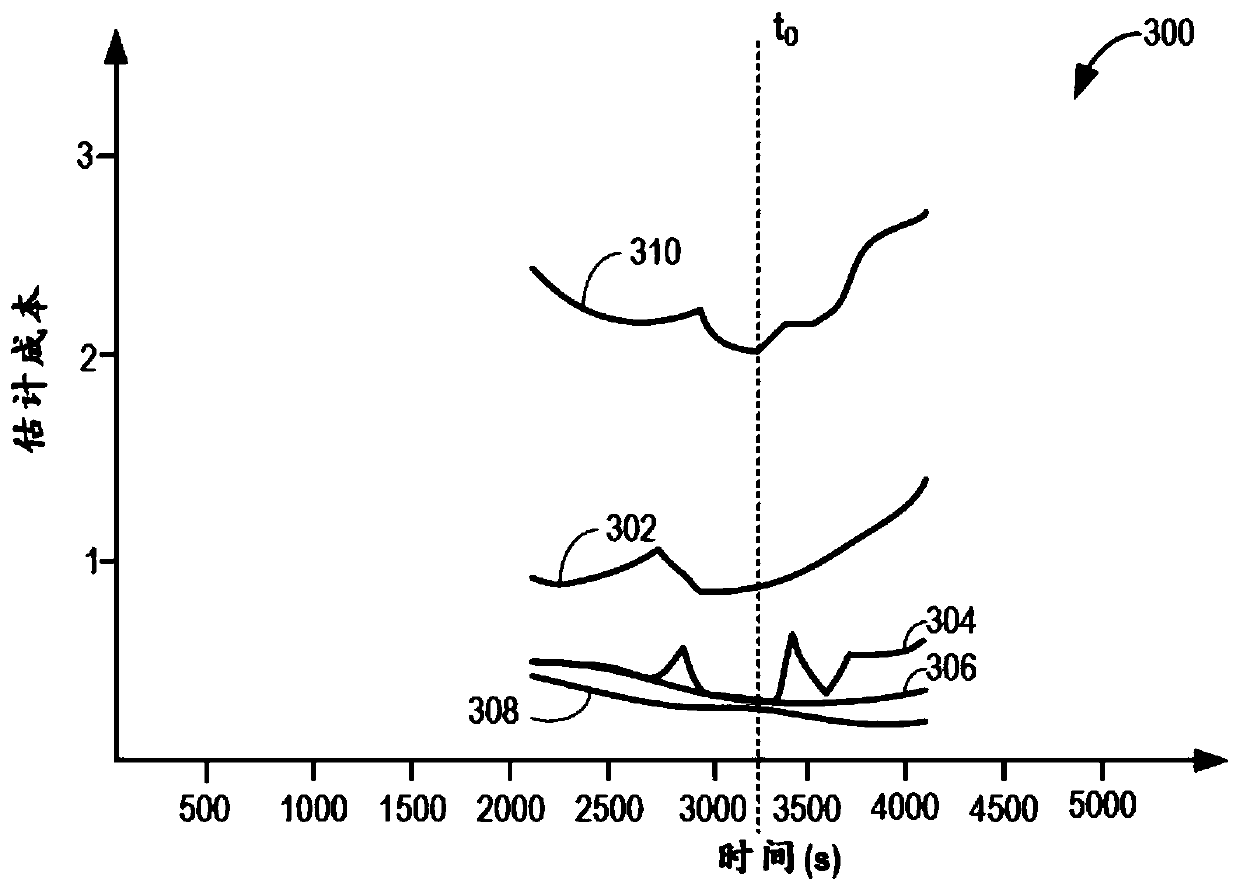
The invention provides a system and method for particulate filter regeneration. Methods and systems are provided for regenerating an exhaust particulate filter based on a projected vehicle drive cycleand catalyst ammonia storage level. In one example, a method may include scheduling a PF regeneration during a regeneration window to maintain a threshold ammonia level in an exhaust catalyst, at theend of the drive cycle.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Object location device and system
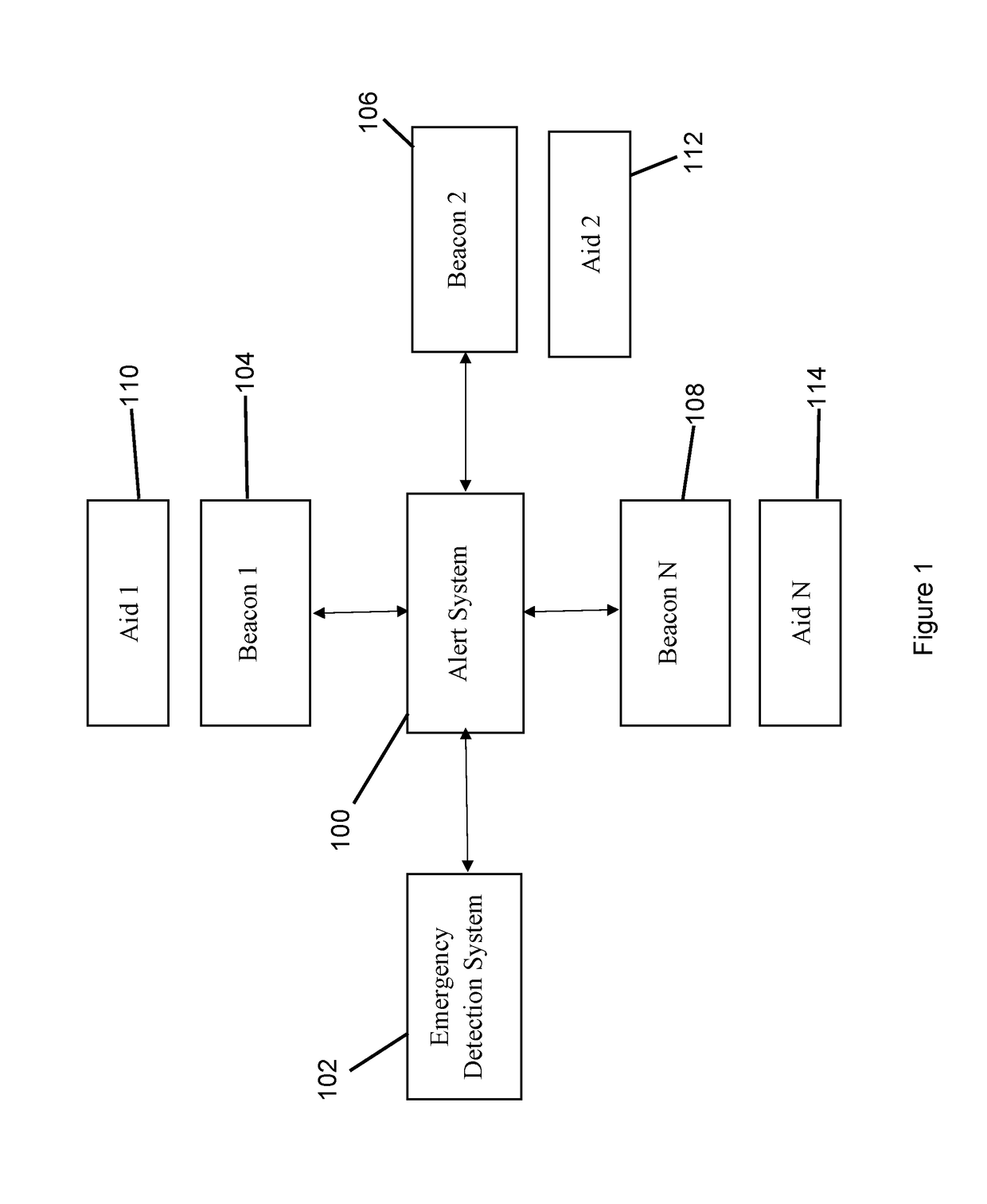
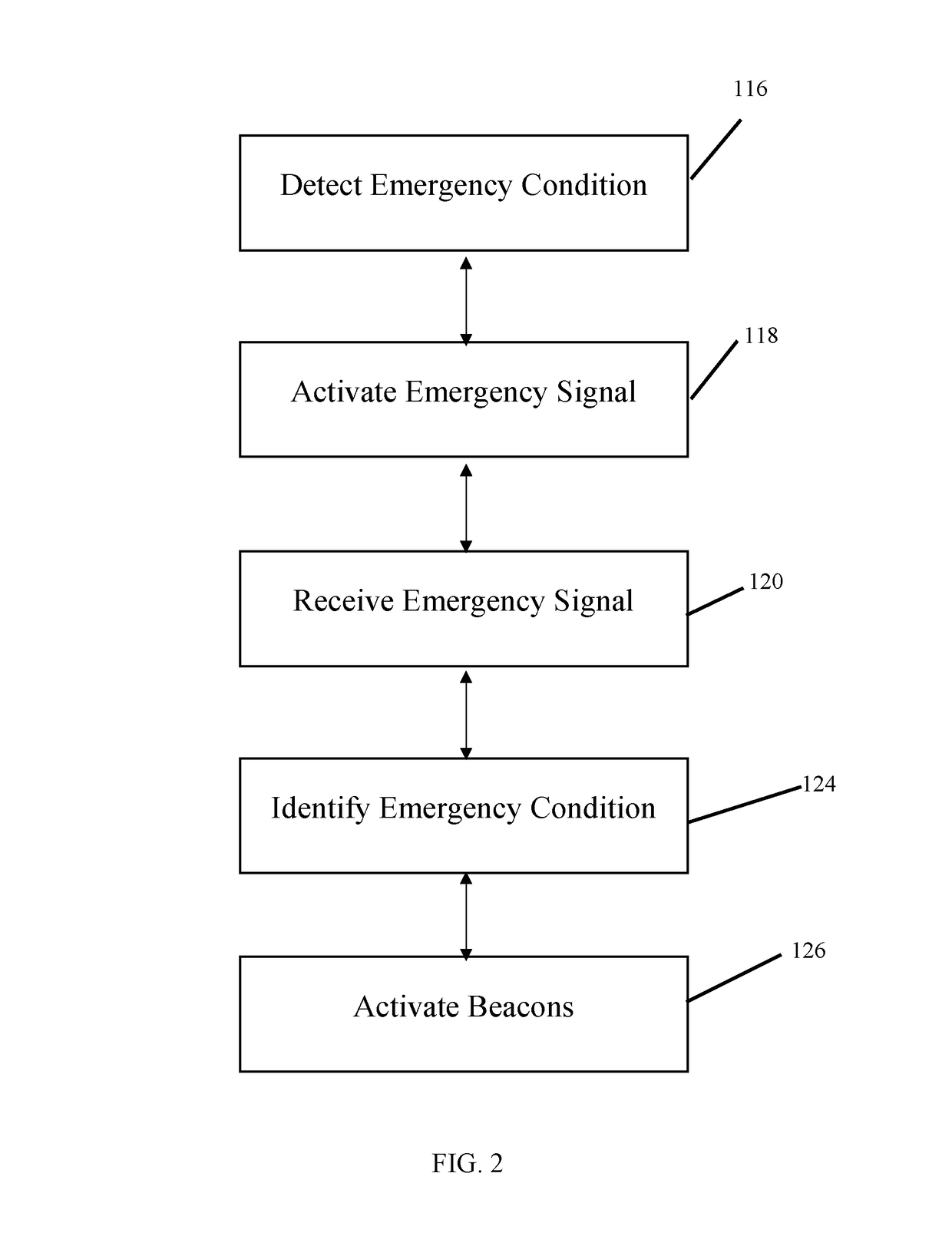
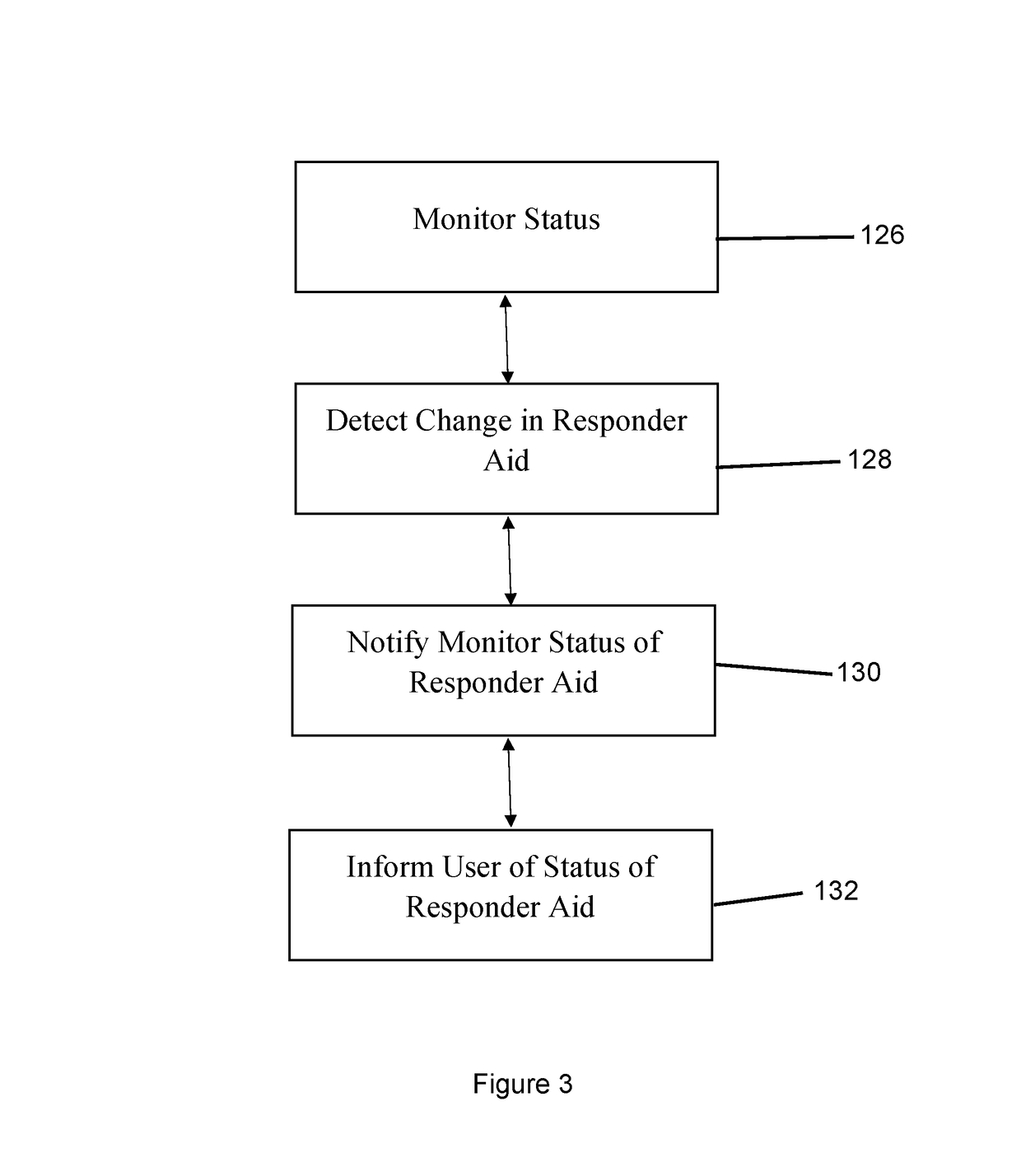
The alert system notifies the user, such as a first responder, to a response location at which a responder aid device is located. Such a responder aid device aids the user in responding to an emergency or alarm condition. The alert system communicates with the emergency detection system of a building. The emergency detection system detects emergency conditions, such as fire, carbon monoxide, ammonia levels, and other emergency conditions. The alert system receives the emergency signal from the emergency detection system. The alert system activates at least one beacon or multiple beacons. These beacons show the location of the responder aid device through an alert, such as a visual alert and / or an audible alert. A monitor device alerts the users as to which responder aid devices have been used, applied, or otherwise employed in response to the alarm or emergency conditions.
Owner:WALKER MARION KELLY +1
Live water compositions for bio-cycling of aquariums
InactiveUS8076118B2Rapid biochemical cyclingRapid cycling of a marine aquariumBacteriaUnicellular algaeFresh water organismWater source
Live water solutions containing natural fresh water or saltwater microorganisms, is used in the bio-cycling of aquariums and to provide a healthy aquatic environment. Live water obtained from natural bodies of water, such as an ocean, sea, lake, river, or stream is filtered through filter media having a pore size between 5 and 20 microns to remove contaminants and debris while allowing microorganisms to remain in suspension. The live water is packaged in containers for retail sale thereby providing consumers with a source of live aquarium water for use in an aquarium during initial set-up, to replace water lost to evaporation, and for effecting quick water changes. An enrichment solution is disclosed to aid in maintaining the microorganisms metabolically and physiologically viable for extended periods. In an alternate embodiment, the live water is concentrated to a salinity level not less than 0.8 aw thereby reducing volume while maintaining microorganism viability. Rapid biochemical cycling of an aquarium is achieved by introducing the live water into an aquarium whereby marine microorganisms instantly contribute to establishing a healthy aquatic environment by reducing harmful ammonia levels and through denitrification.
Owner:MORRIS BARRINGTON A +1
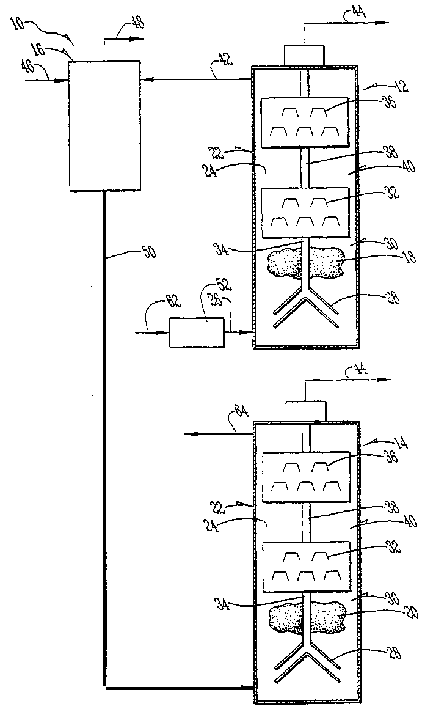
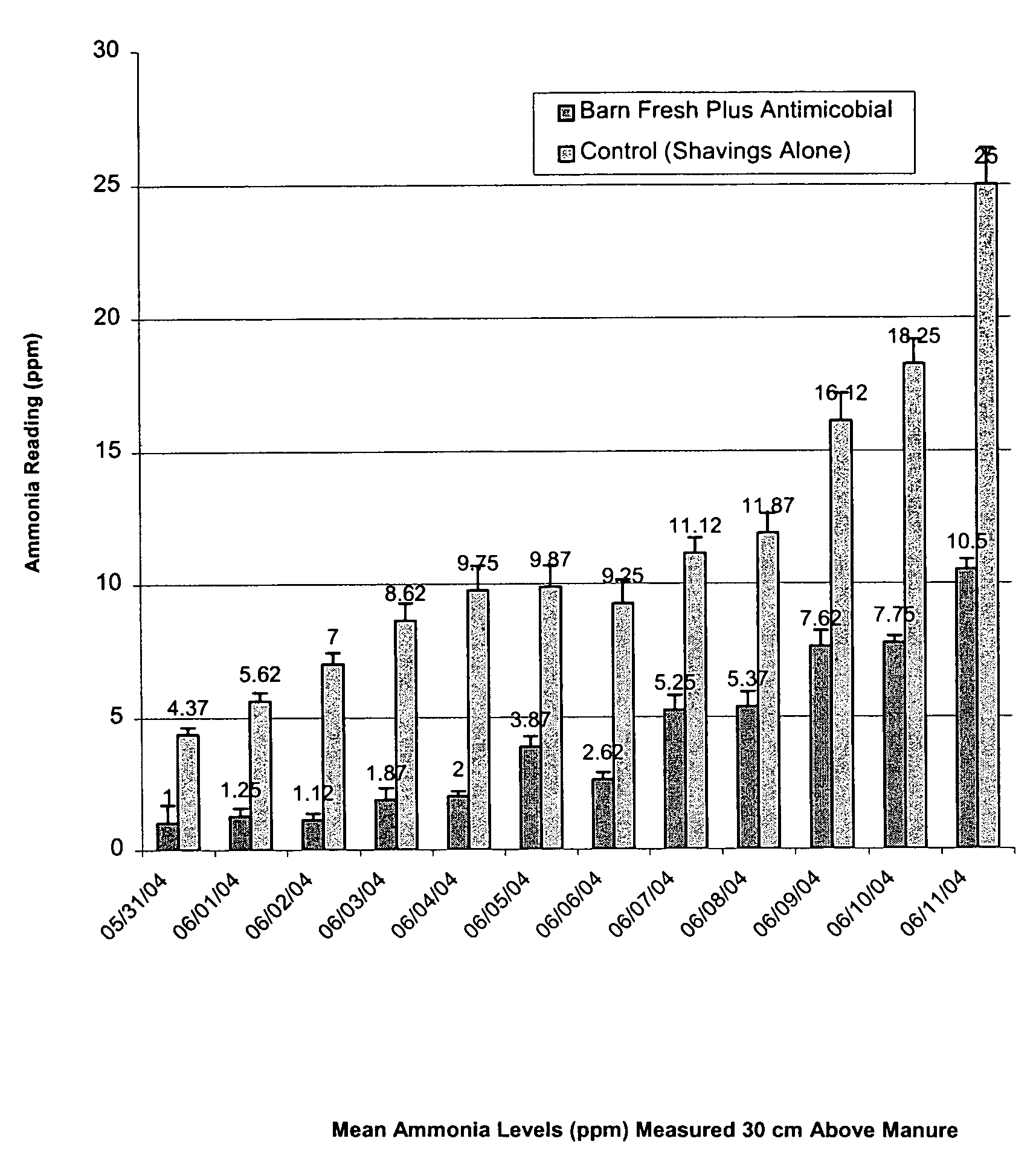
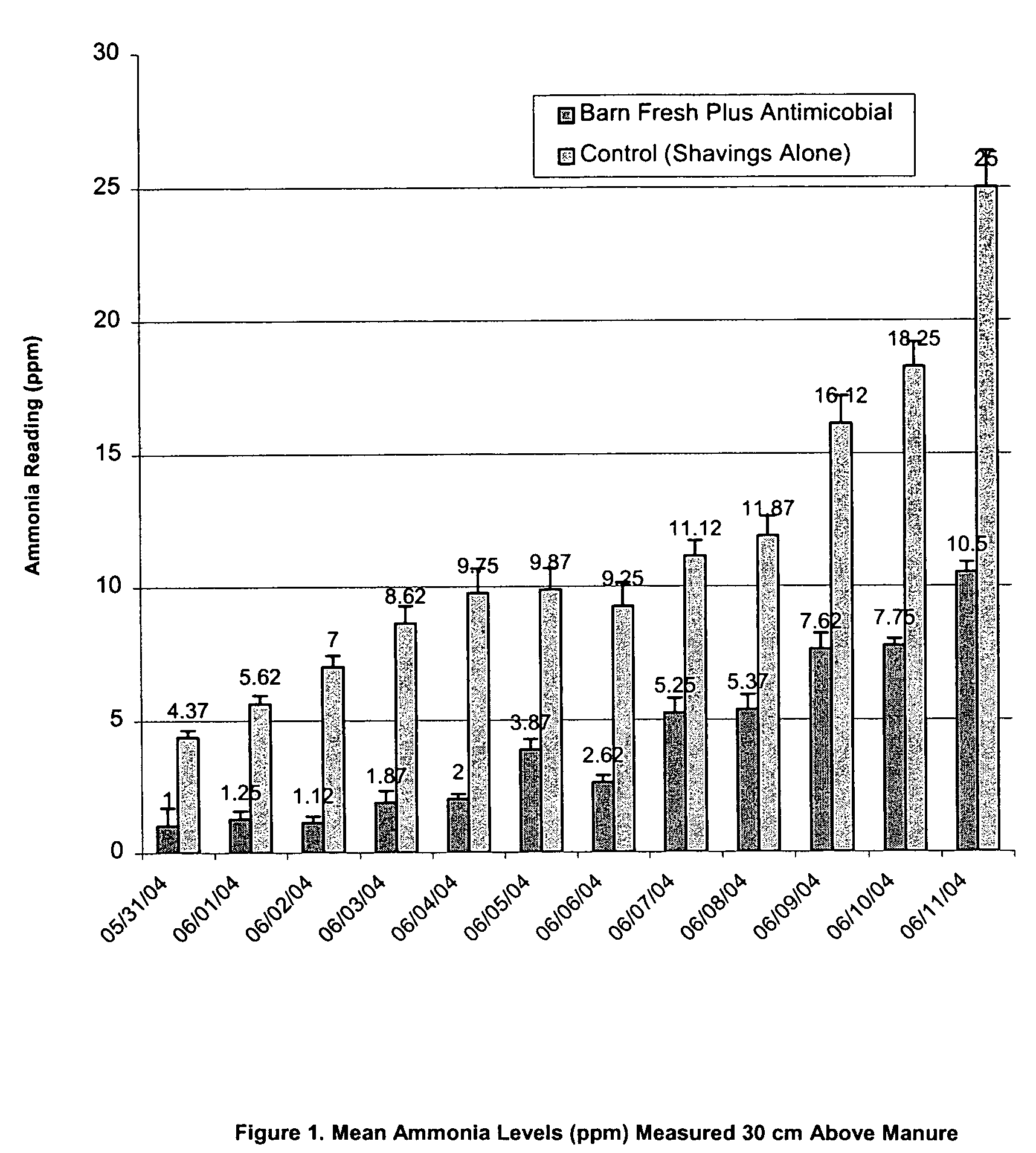
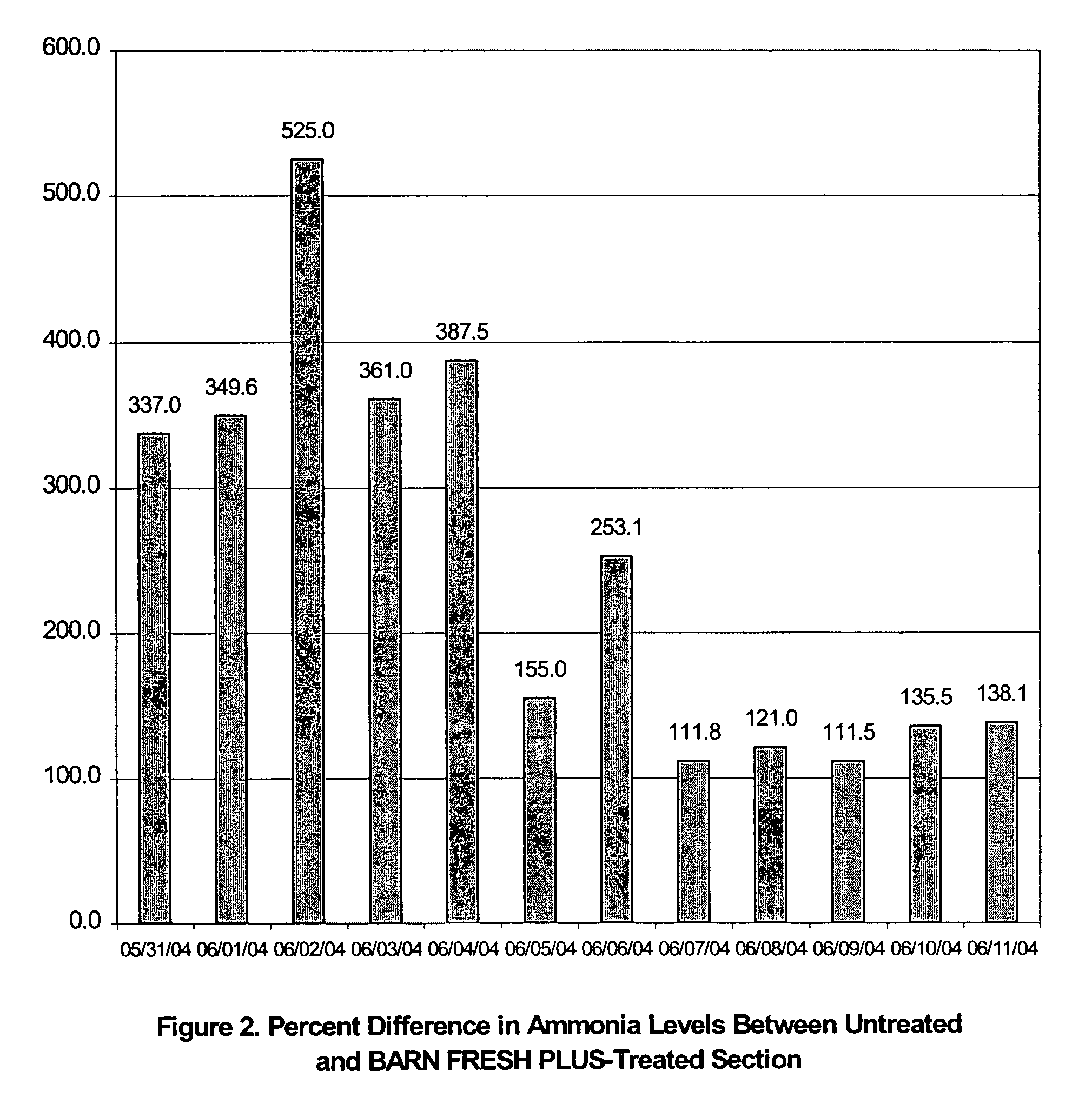
Methods for Reducing Ammonia Levels in Manure
InactiveUS20120269923A1Lower Level RequirementsReduced pHCalcareous fertilisersProductsCation-exchange capacityFeces
Owner:ROSE ACRE FARMS +1
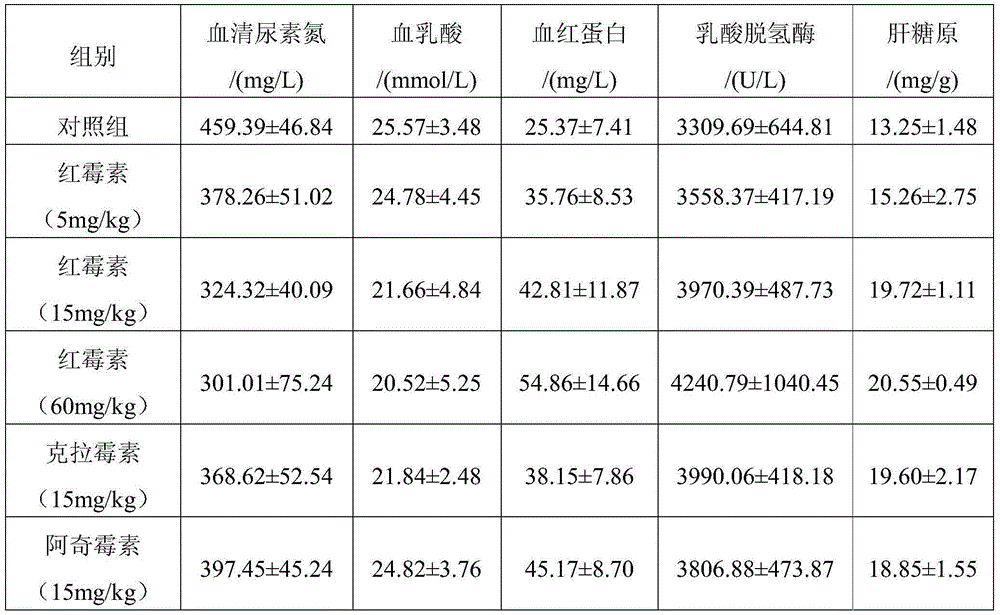
Applications of macrolide antibiotics and Erythromycin in preparation of anti-fatigue disease medicines
InactiveCN105106229AExtended swim timeAvoid elevationOrganic active ingredientsAntinoxious agentsDiseaseLactate dehydrogenase
The invention relates to applications of macrolide antibiotics, especially Erythromycin, in preparation of anti-fatigue disease medicines. The anti-fatigue function of macrolide antibiotics, especially Erythromycin is discovered firstly, animal test results show that macrolide antibiotics can prolong swimming time of mice bearing load greatly, lower the serum urea ammonia level after strenuous exercise, inhibit rise of blood lactic acid, keep or increase the content of ferrohemoglobin, raise lactate dehydrogenase activity, raise liver starch reserve, reduce liver starch consumption during exercise, and have functions of alleviating fatigue and increasing exercise endurance greatly.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
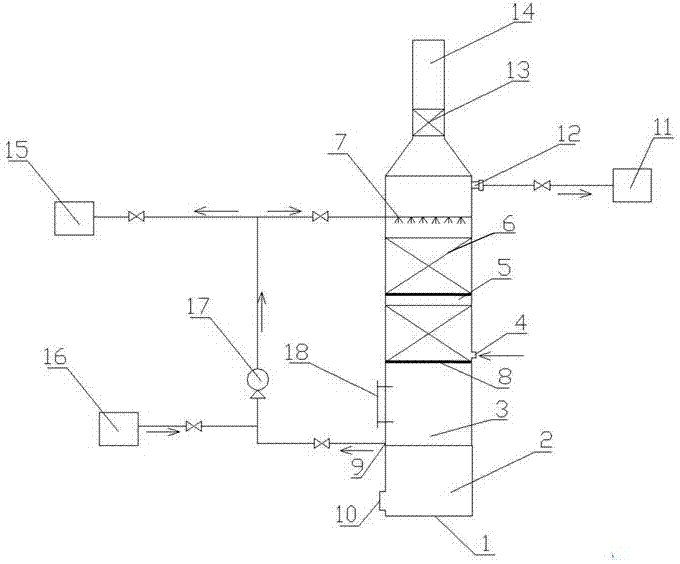
Method for recycling ammonia gas in exhaust gas
InactiveCN107252618AHigh recovery rateSimple structureGas treatmentDispersed particle separationWater sourceSoft water
The invention discloses an ammonia recovery device in waste gas, which comprises an ammonia washing tower, the bottom of the ammonia washing tower is a base, a manhole is arranged on the base, a storage area is arranged above the base, an absorption area is arranged above the storage area, and an absorption area is arranged above the storage area. A spraying device is provided above the spraying device, and the first flue gas outlet is provided on the wall of the ammonia washing tower above the spraying device, and a chimney is provided on the top of the ammonia washing tower. Packing support plates are provided, and each packing support plate is provided with a plurality of holes, the bottom of the absorption area is provided with a flue gas inlet, and a liquid level gauge is provided on the wall of the ammonia washing tower outside the absorption area. An ammonia water outlet is provided at the bottom of the area, and the ammonia water outlet is connected to the soft water source, the ammonia water storage device and the spray device of the ammonia washing tower, and a pump is arranged between the ammonia water outlet and the spray device. The invention has reasonable design, the ammonia-containing waste gas passes through the ammonia washing tower to recycle the ammonia gas, can improve the ammonia recovery rate, and has the advantages of no pollution and zero discharge to the waste gas.
Owner:HENAN ZHONGHONG GRP COAL
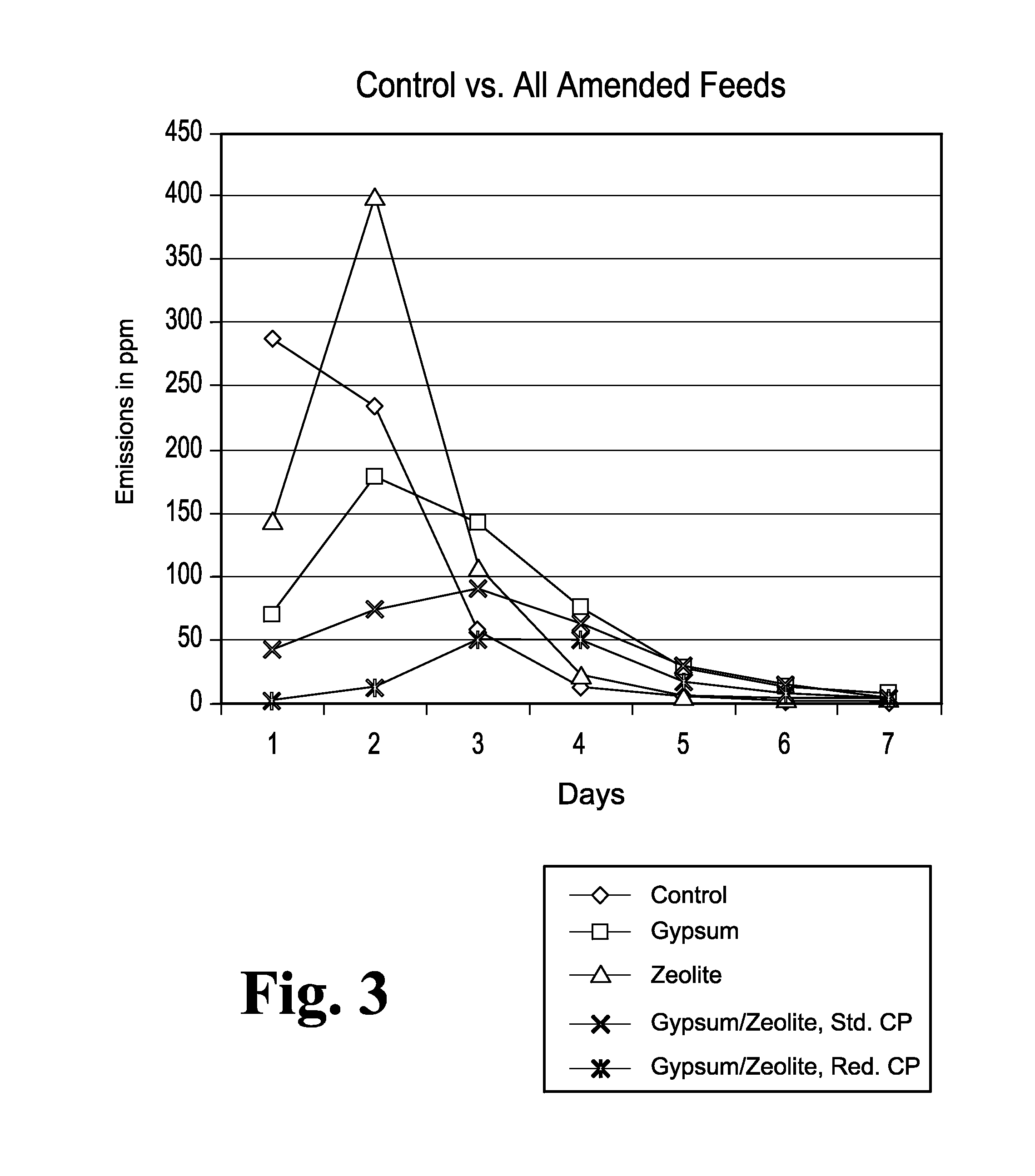
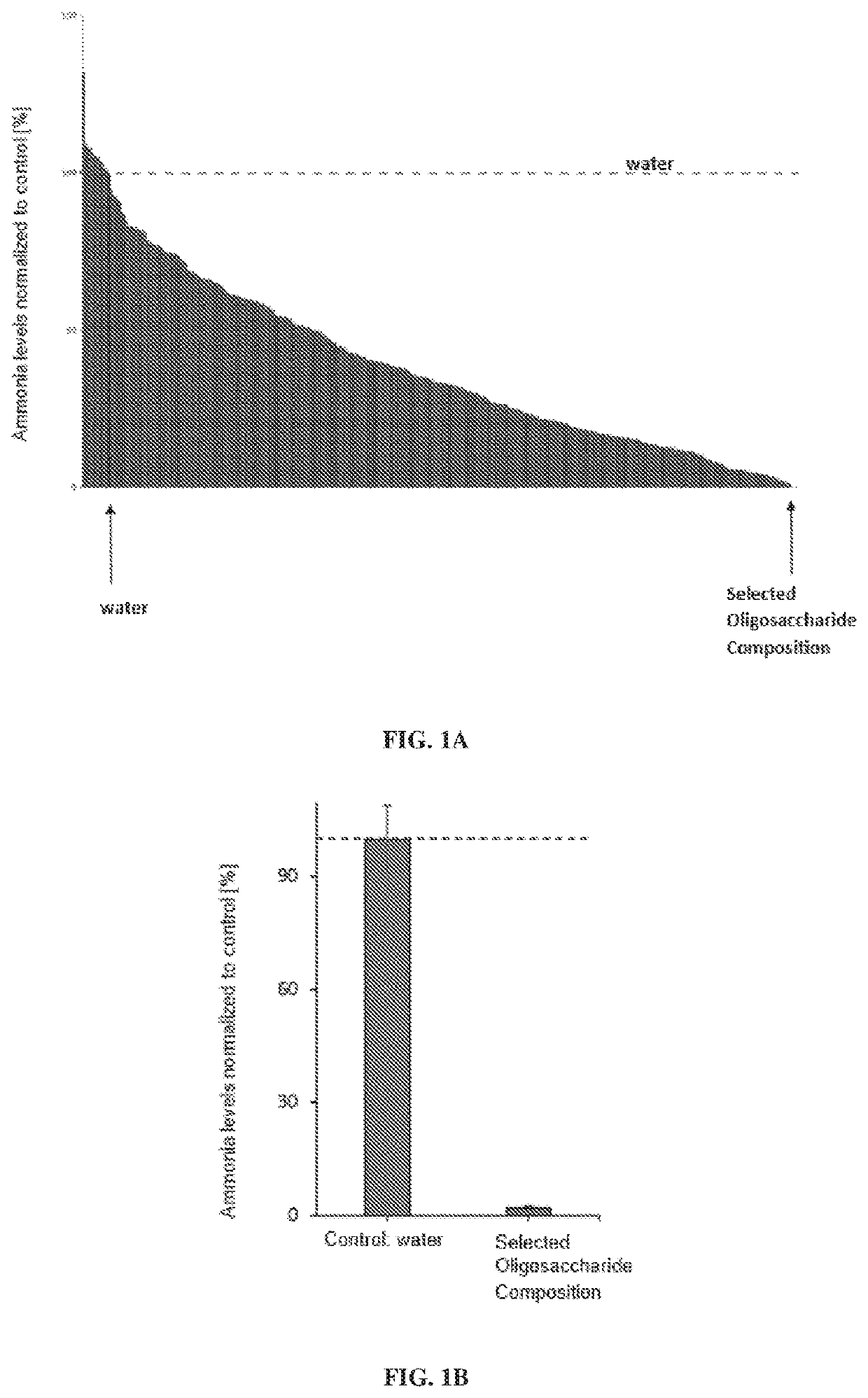
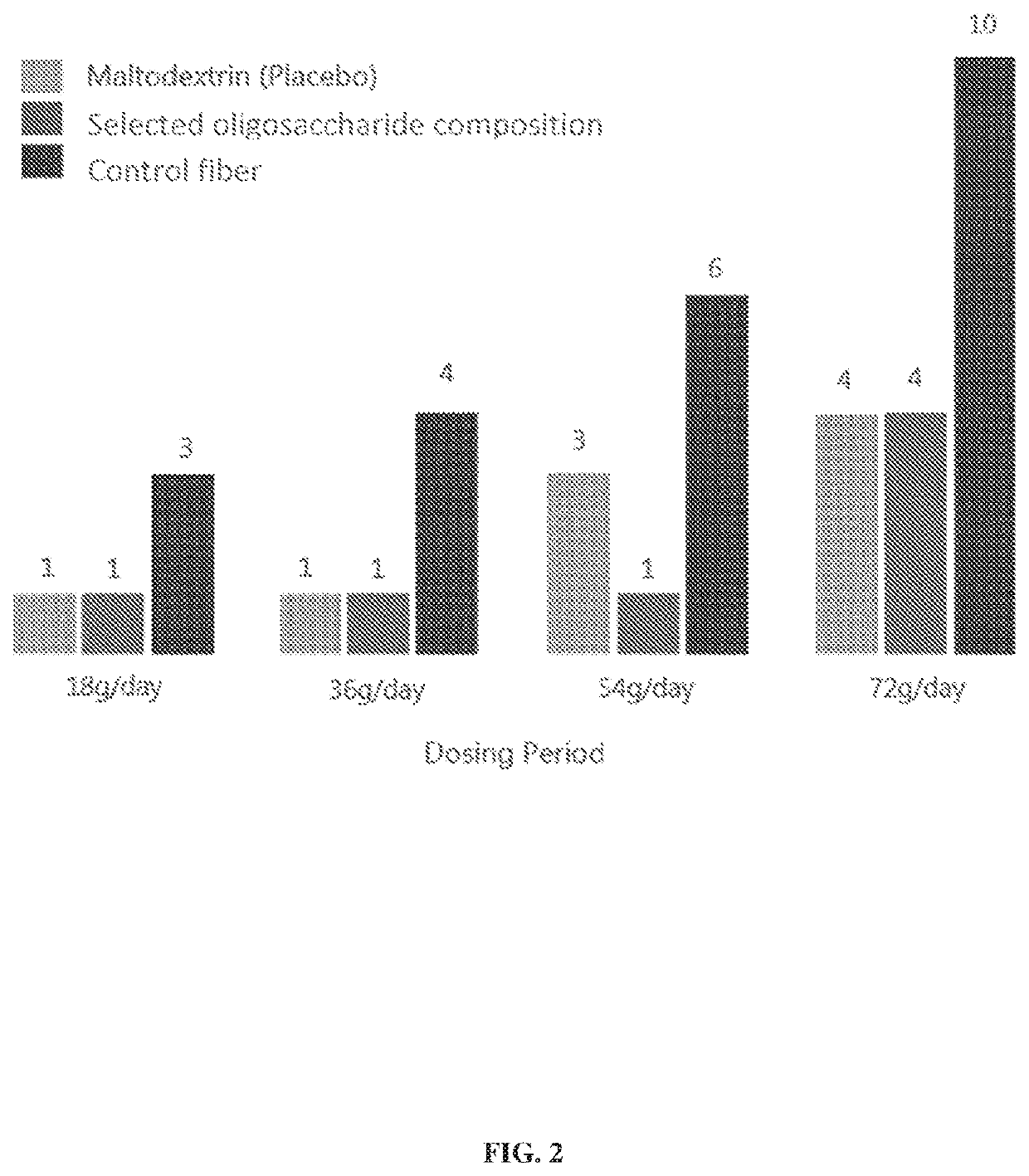
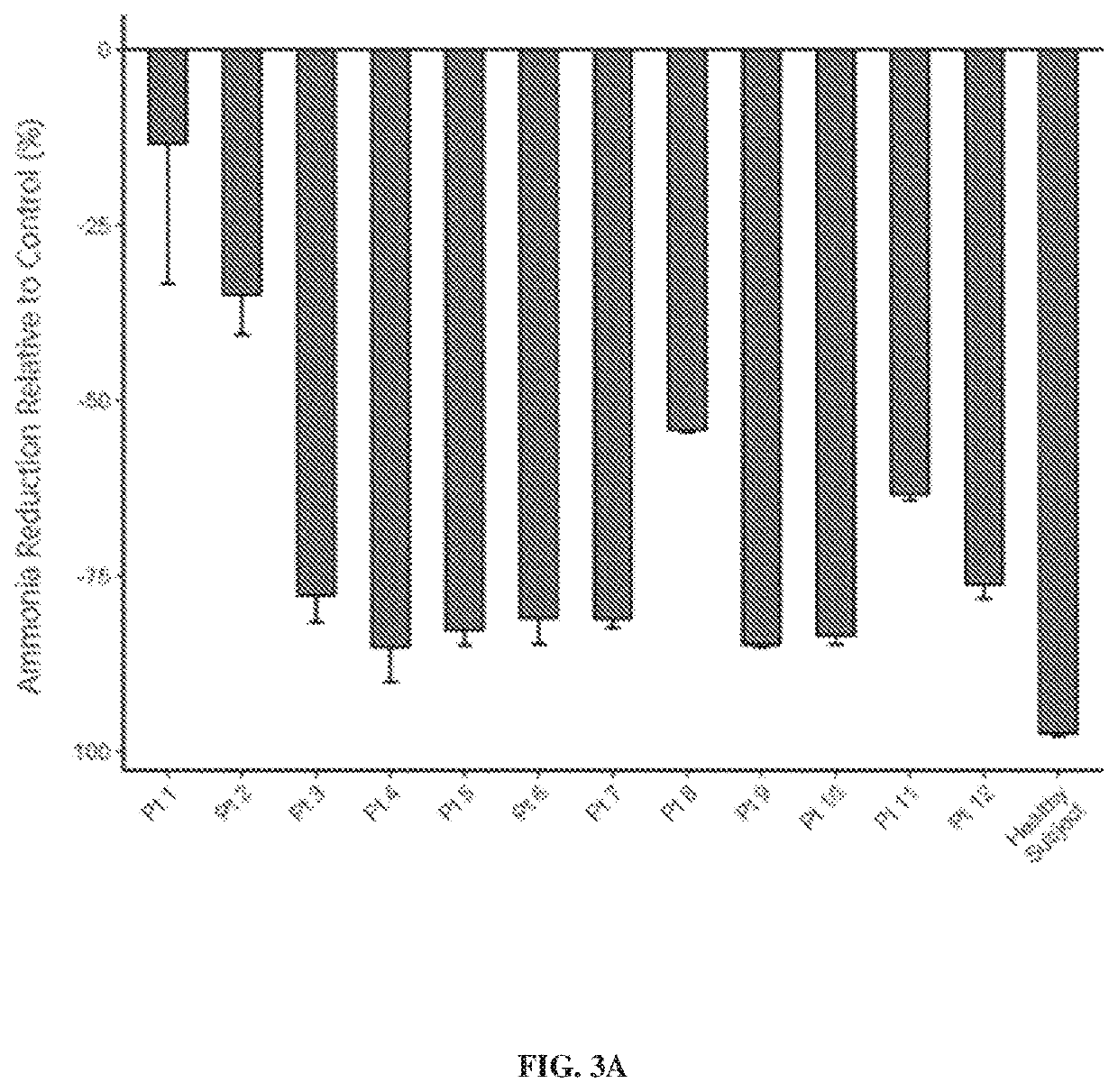
Oligosaccharide compositions and methods of use thereof for reducing ammonia levels
PendingUS20210198302A1Reduce ammonia levelsGood for healthSugar derivativesMetabolism disorderDiseaseMicroorganism
Aspects of the disclosure relate to oligosaccharide compositions and methods of making the same. Also provided are methods of using oligosaccharide compositions as microbiome metabolic therapies for reducing ammonia levels and for the treatment of hyperammonemia-related diseases (e.g., urea cycle disorders and hepatic encephalopathy).
Owner:DSM NUTRITIONAL PROD
Enhanced biogas production from nitrogen bearing feed stocks
InactiveCN1239412CAvoid inhibitionWater contaminantsGas production bioreactorsMicroorganismAcetogenesis
A system comprising a first anaerobic digester (12), an ammonia recovery vessel (16) and a second anaerobic digester (14). Microorganisms in the first digester are primarily hydrolyzers and acetogens, while those in the second digester are primarily methanogens. A nitrogen containing feed stock undegoes hydrolysis ans acetogenesis in the first digester. The effluent is passed to the ammonia recovery vessel in which ammonia is removed. The low ammonia effluent stream is passed to the second digester to undergo methanogenesis, generating a biogas. In an alternate embodiment, a single anaerobic digester is used. The effluent is treated for ammonia removal and recycled to the digester to keep the ammonia levels sufficiently low to avoid ammonia inhibition.
Owner:亚历山大·G·法斯本德
Rapid small volume detection of blood ammonia
ActiveUS20170030893A1Facilitate and hasten leaving bloodSmall and convenient to useMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDisease diagnosisPower flowBlood ammonia
A method for measuring ammonia in a blood sample may involve positioning the blood sample in proximity with an ammonia gas sensor, generating a current with the ammonia gas sensor in response to ammonia gas released from the blood sample, and measuring the current generated by the ammonia gas sensor, using a current measurement member coupled with the ammonia gas sensor. A device for measuring an ammonia level in a blood sample may include a blood sample containment member, an ammonia gas sensor coupled with the blood sample containment member, and a current measurement member coupled with the ammonia gas sensor. The method and device may be used to measure an ammonia level in a blood sample as small as one drop of blood, or approximately 0.05 mL of blood.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com