Enhanced biogas production from nitrogen bearing feed stocks
A technology for raw materials and biogas, which is used in gas production bioreactors, waste fuels, biochemical instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of increased dehydration costs, slowness, and inability to fully operate raw materials.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
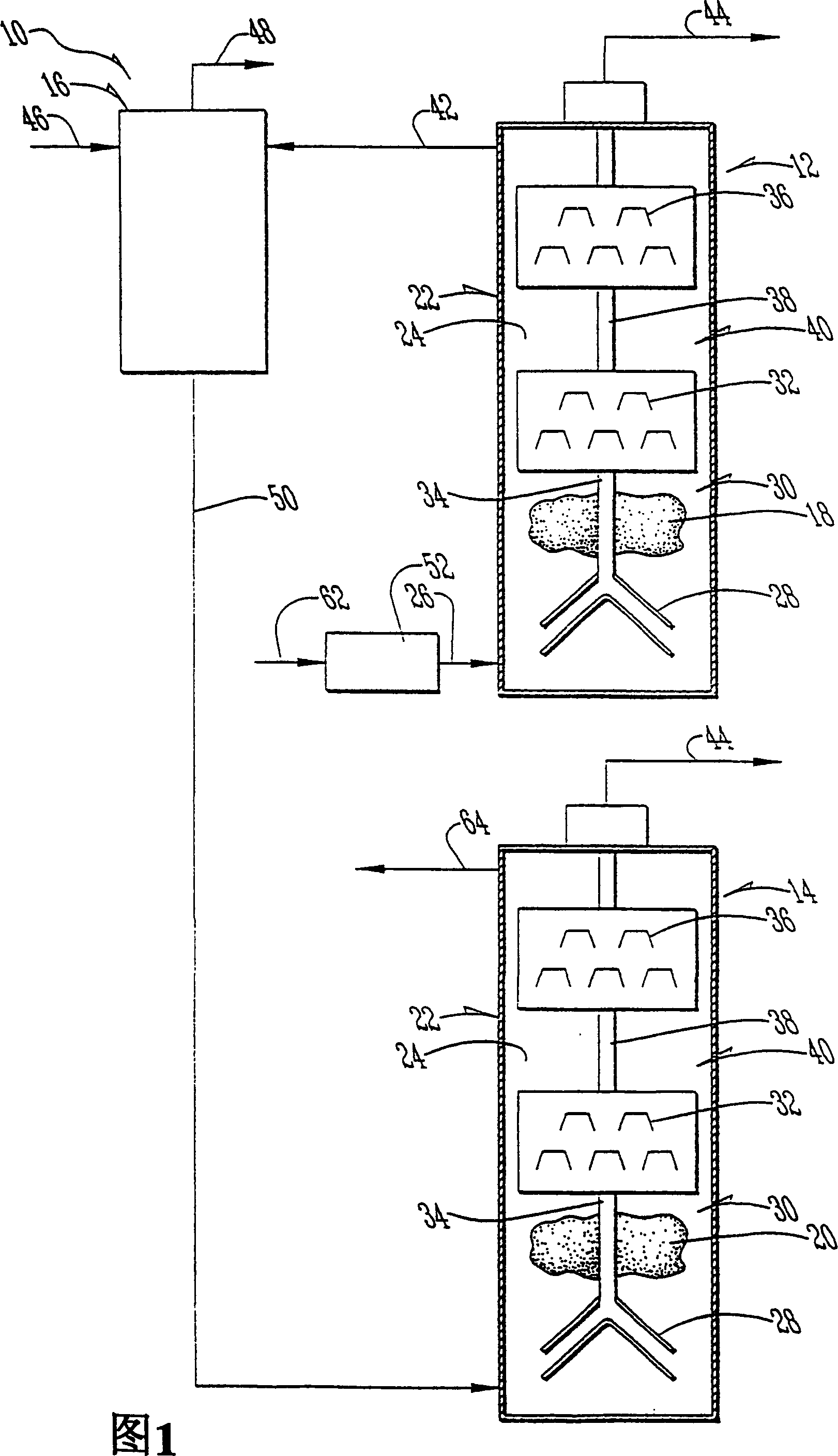
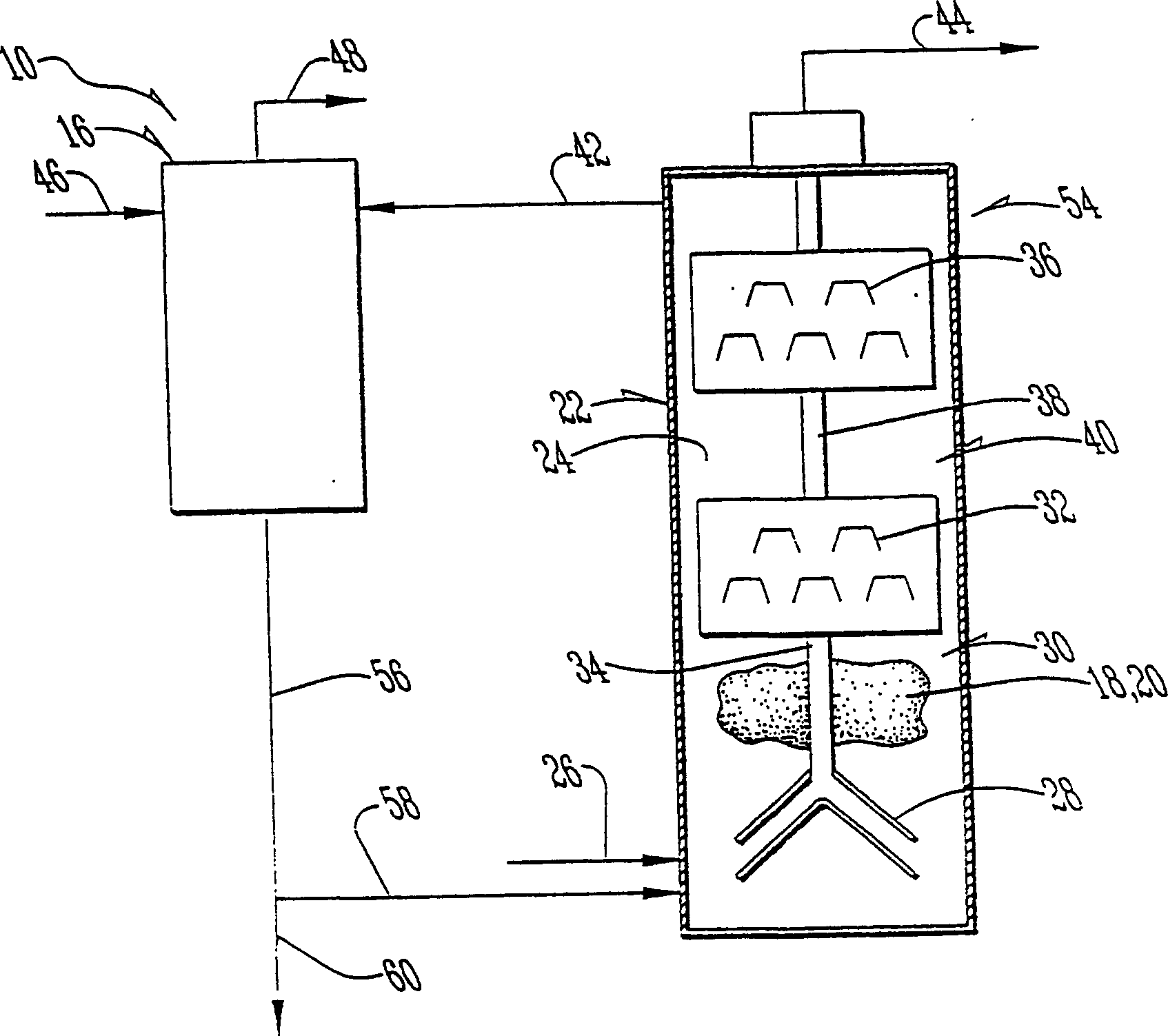
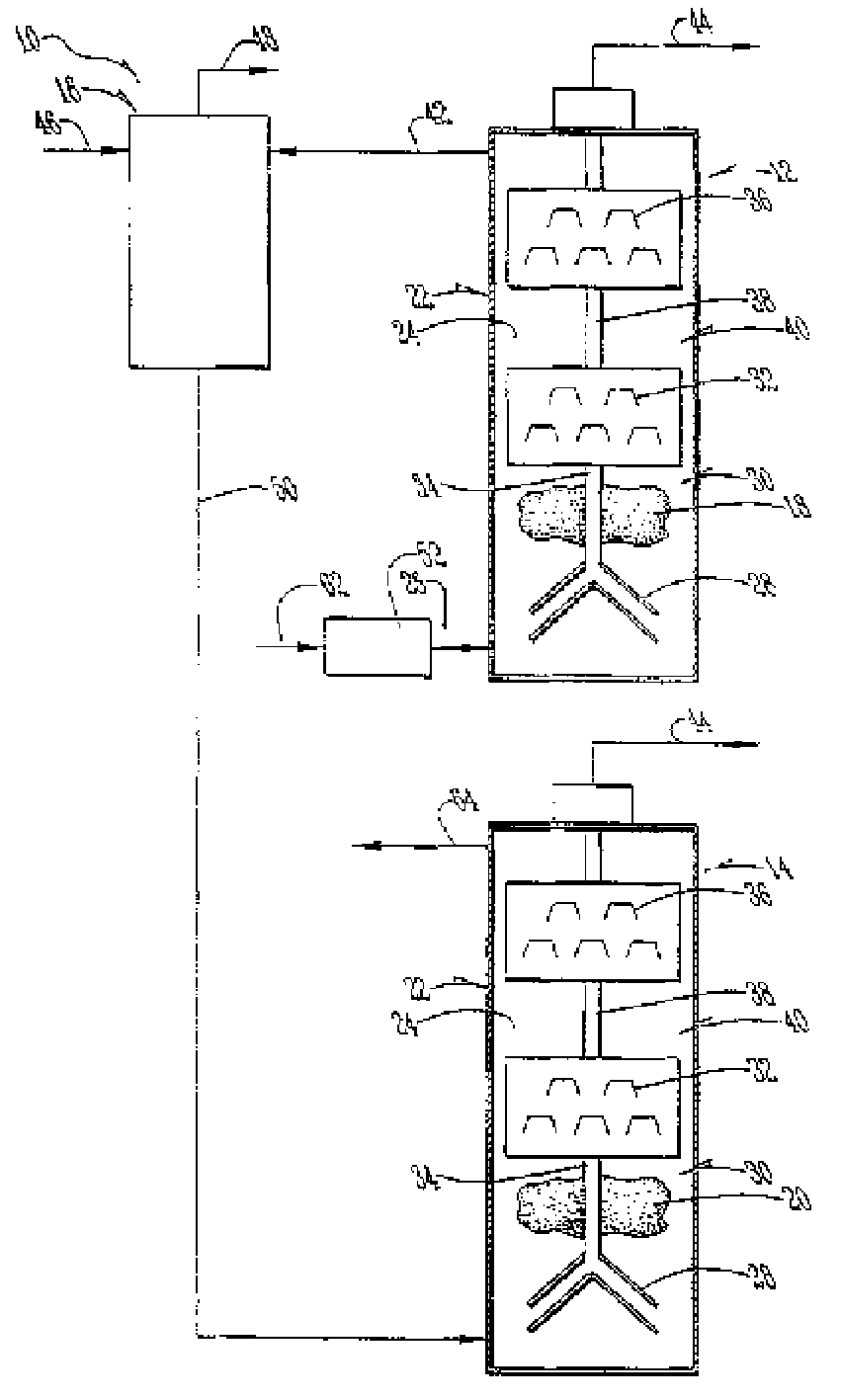
[0031] When the feedstock is highly concentrated or contains toxic materials, use the figure 2 in the structure. As detailed above, in this embodiment ammonia is continuously removed from the recycle stream, allowing reactor 54 to operate at sufficiently low ammonia concentrations that methanogens 20 or methane-producing bacteria can be inhibited. Like the first embodiment, ammonia may be removed by using an ammonia recovery process (ARP), adsorption, air stripping, steam stripping, or any of a variety of ammonia recovery or removal techniques and some combinations thereof.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com