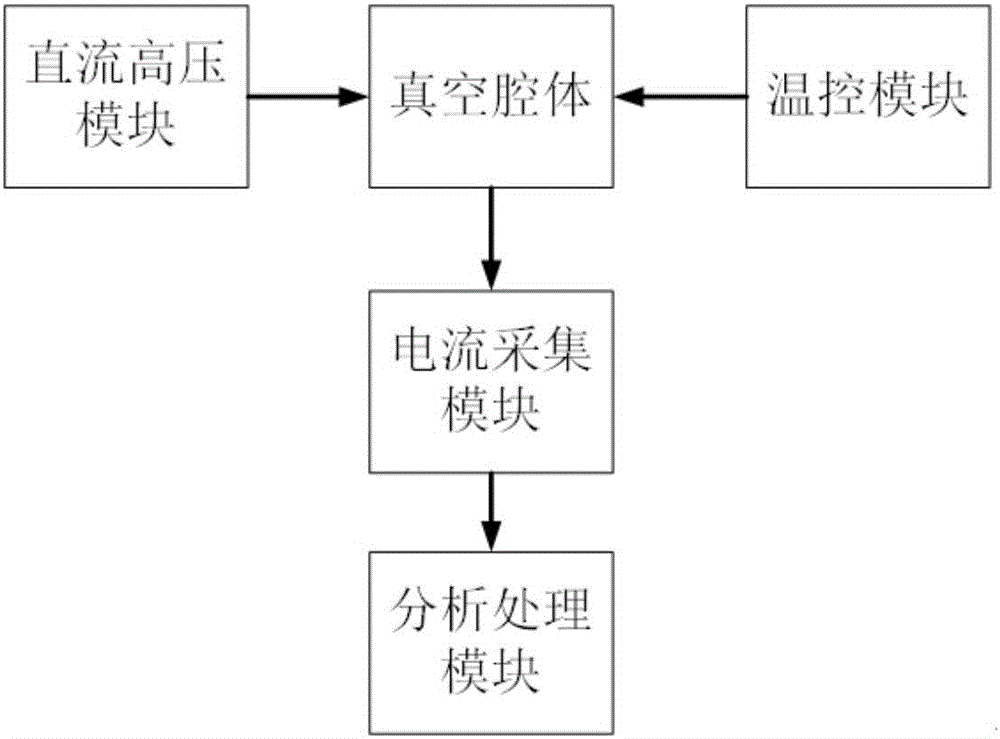
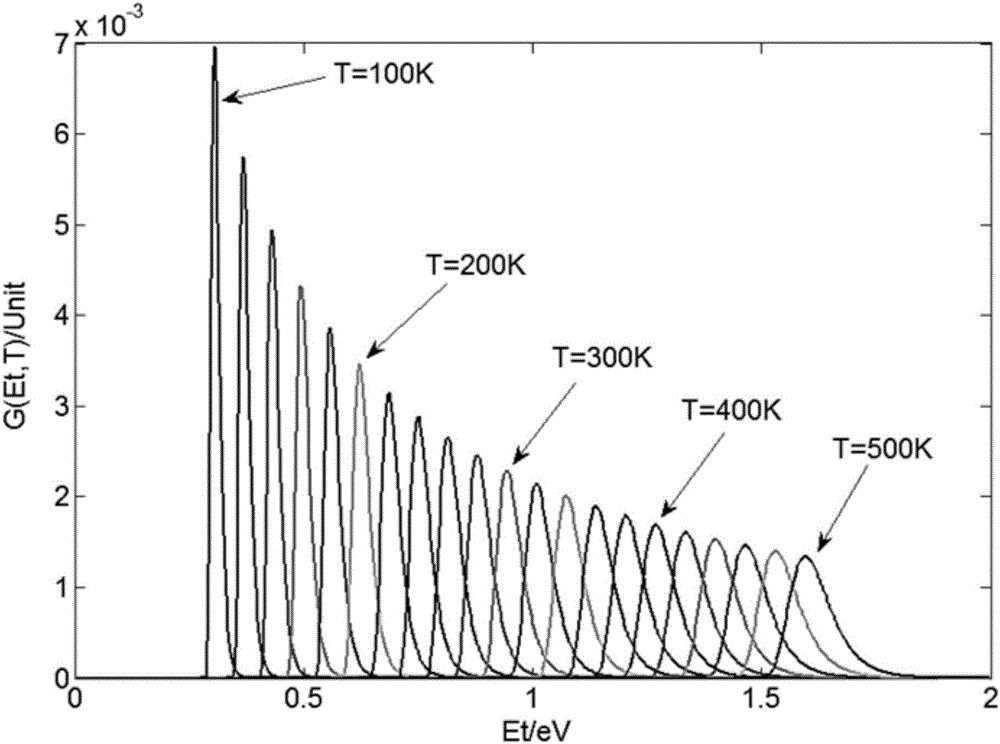
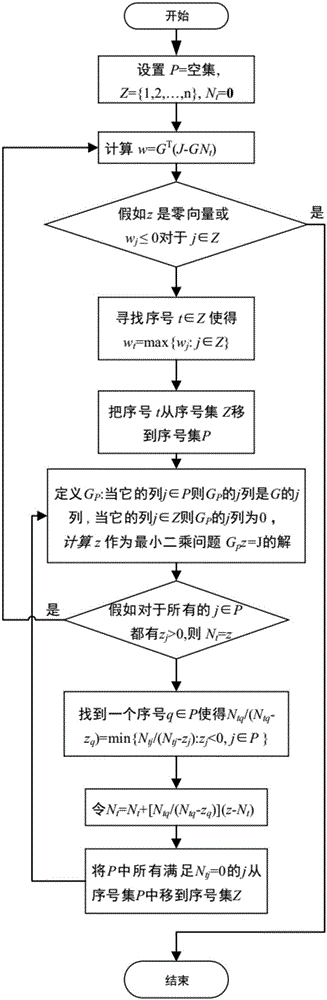
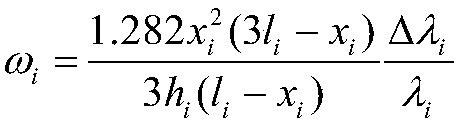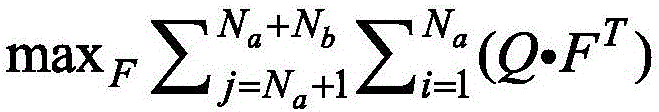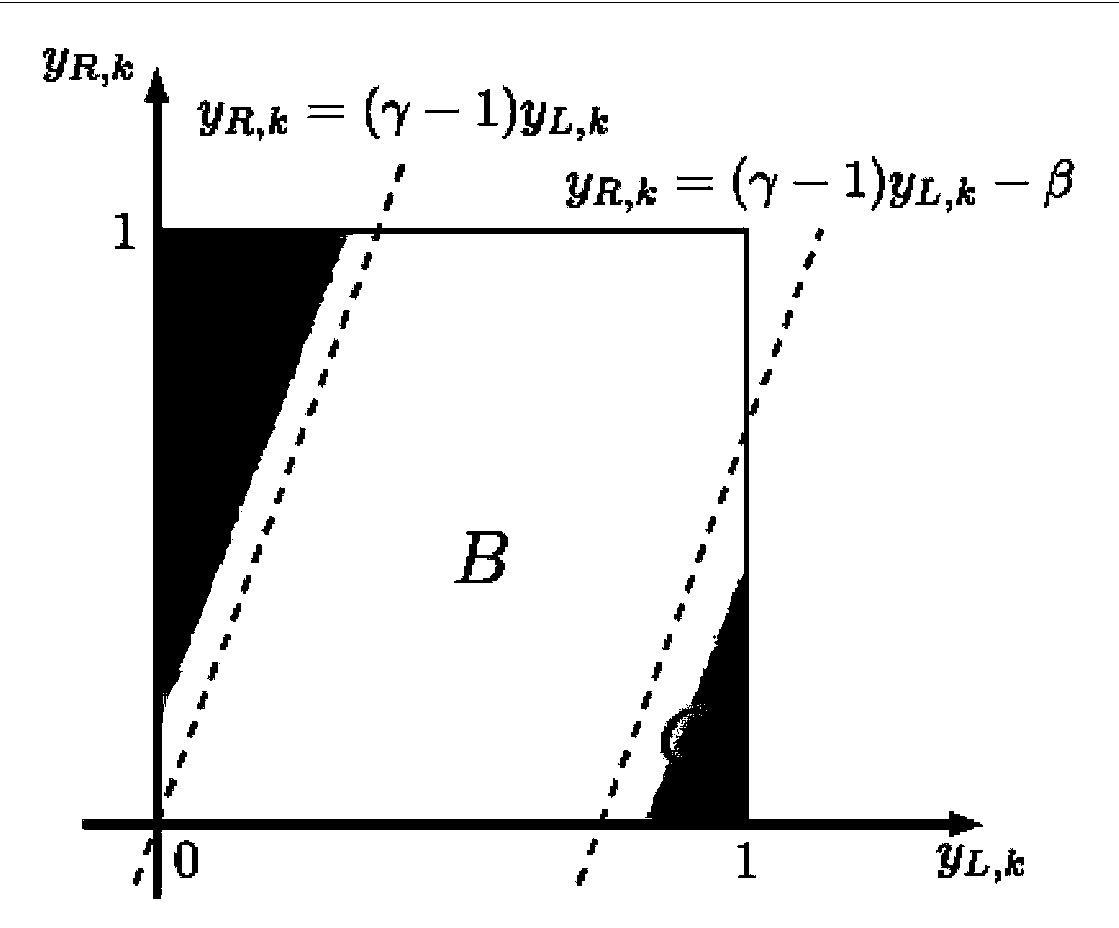Patents
Literature
91 results about "Linear least squares" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
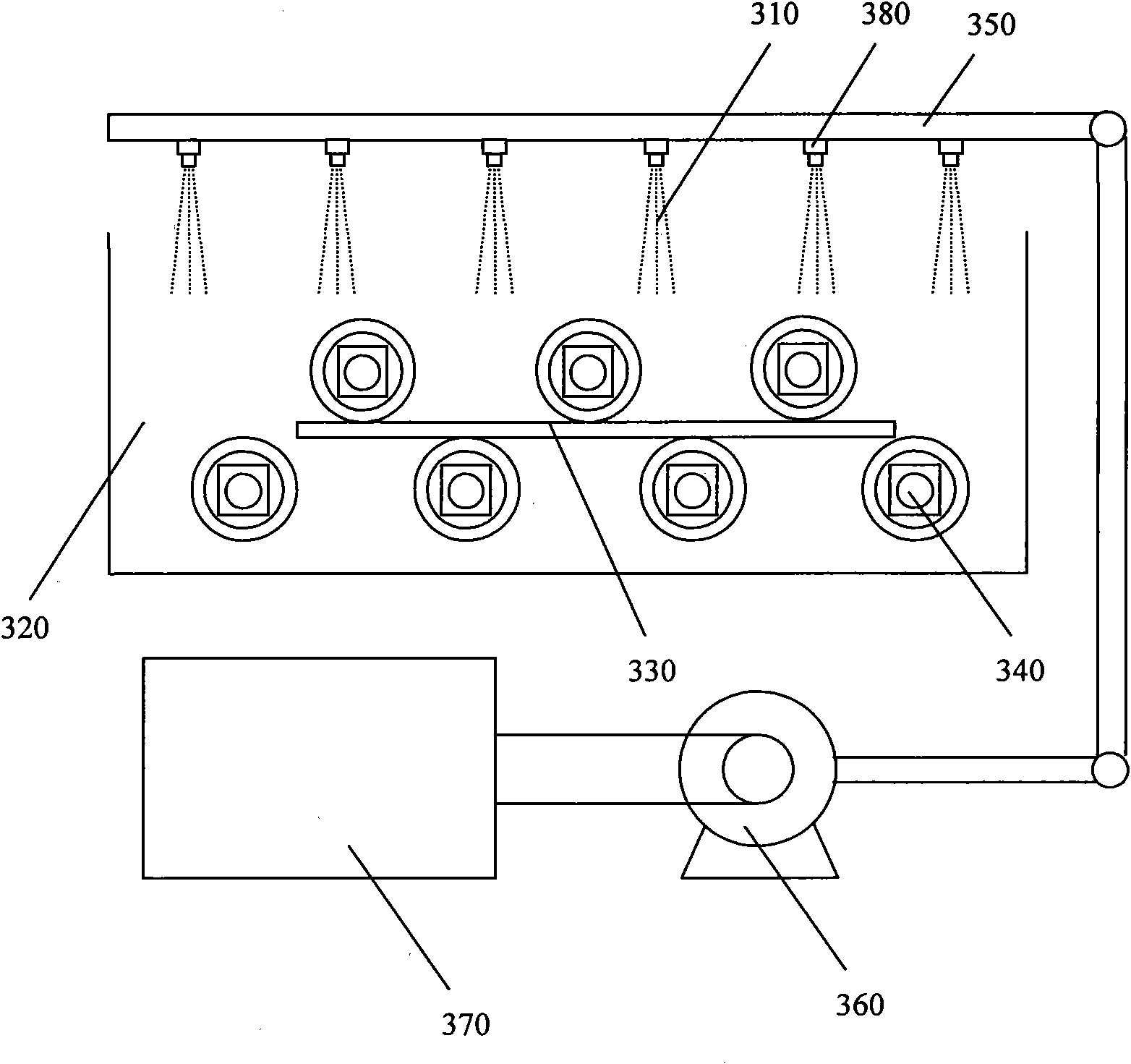
Method for inverting effective leaf area index by utilizing geometric projection and laser radar
InactiveCN102997871AImprove estimation accuracyImprove estimation efficiencyUsing optical meansPorosityKnowledge Field
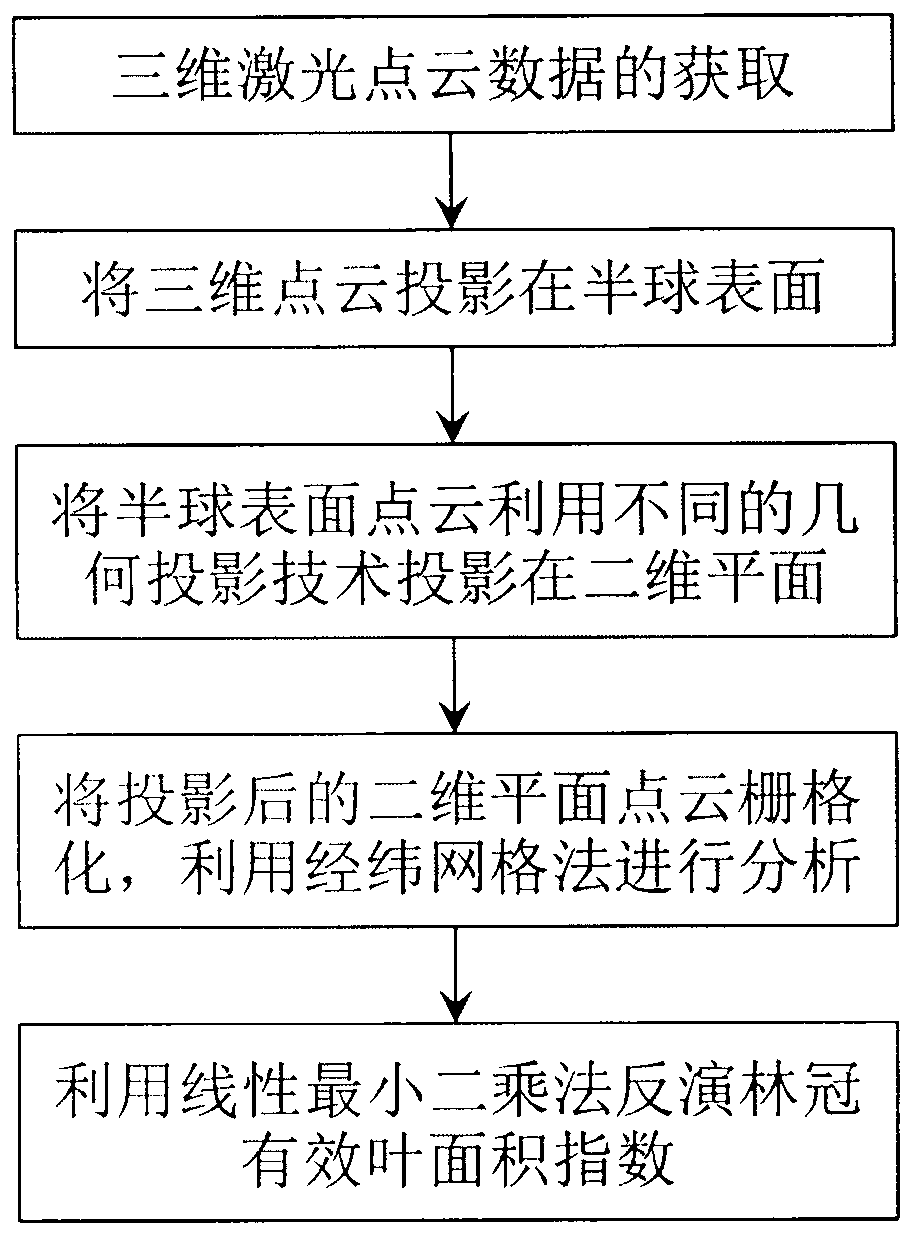
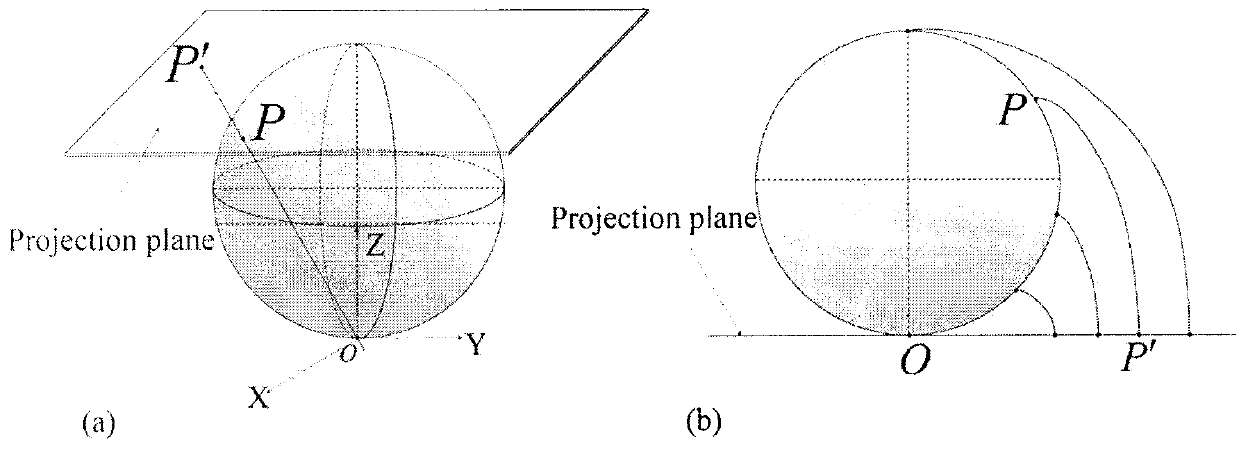
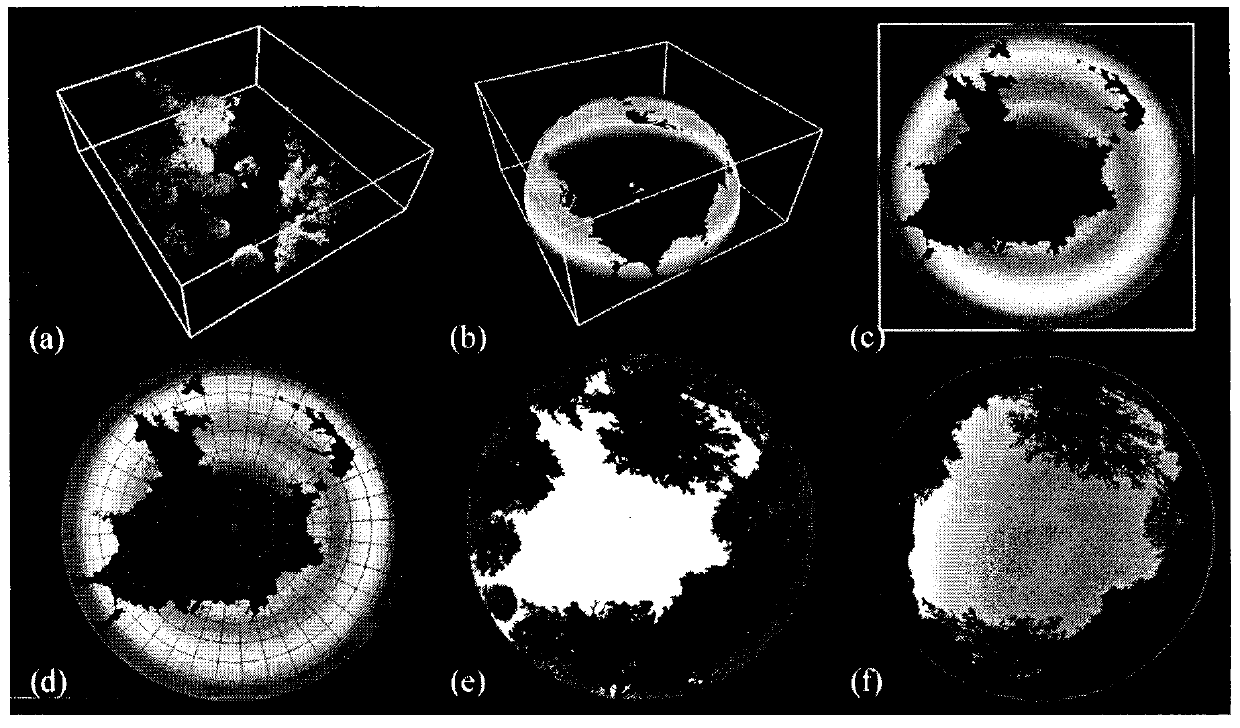
The invention provides a method for inverting effective leaf area index by utilizing geometric projection and laser radar and belongs to the field of research on methods for acquiring forest canopy structure parameter. The method includes the following steps: acquiring and preprocessing three-dimensional laser point cloud data of a plant canopy layer, converting a coordinate system of point cloud data, utilizing different geometric projections to project the three-dimensional point cloud data into a two-dimensional plane space and convert the data into a grid image and further utilizing the linear least square inversion algorithm to conduct estimation of porosity and effective leaf area index. Compared with a traditional observation method, the method is small in work amount and free of contact type observation and damage to the canopy structure and radiative characteristics, has the advantages of being objective, high in efficiency and accurate. A method for extracting three-dimensional structure and biological physical diversity information from laser radar data is developed, and characterization is conducted on the horizontal and vertical distribution change rule of leaves.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
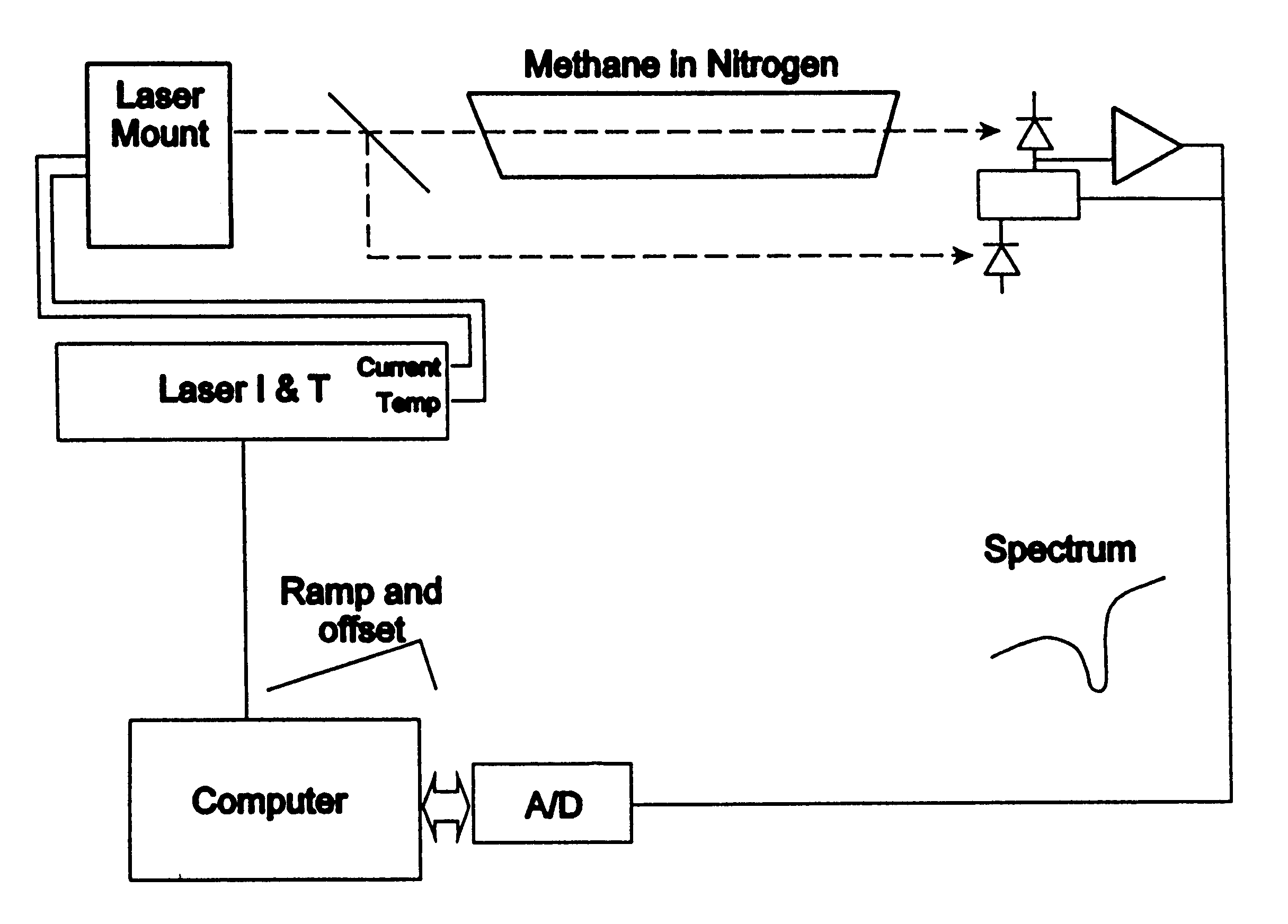
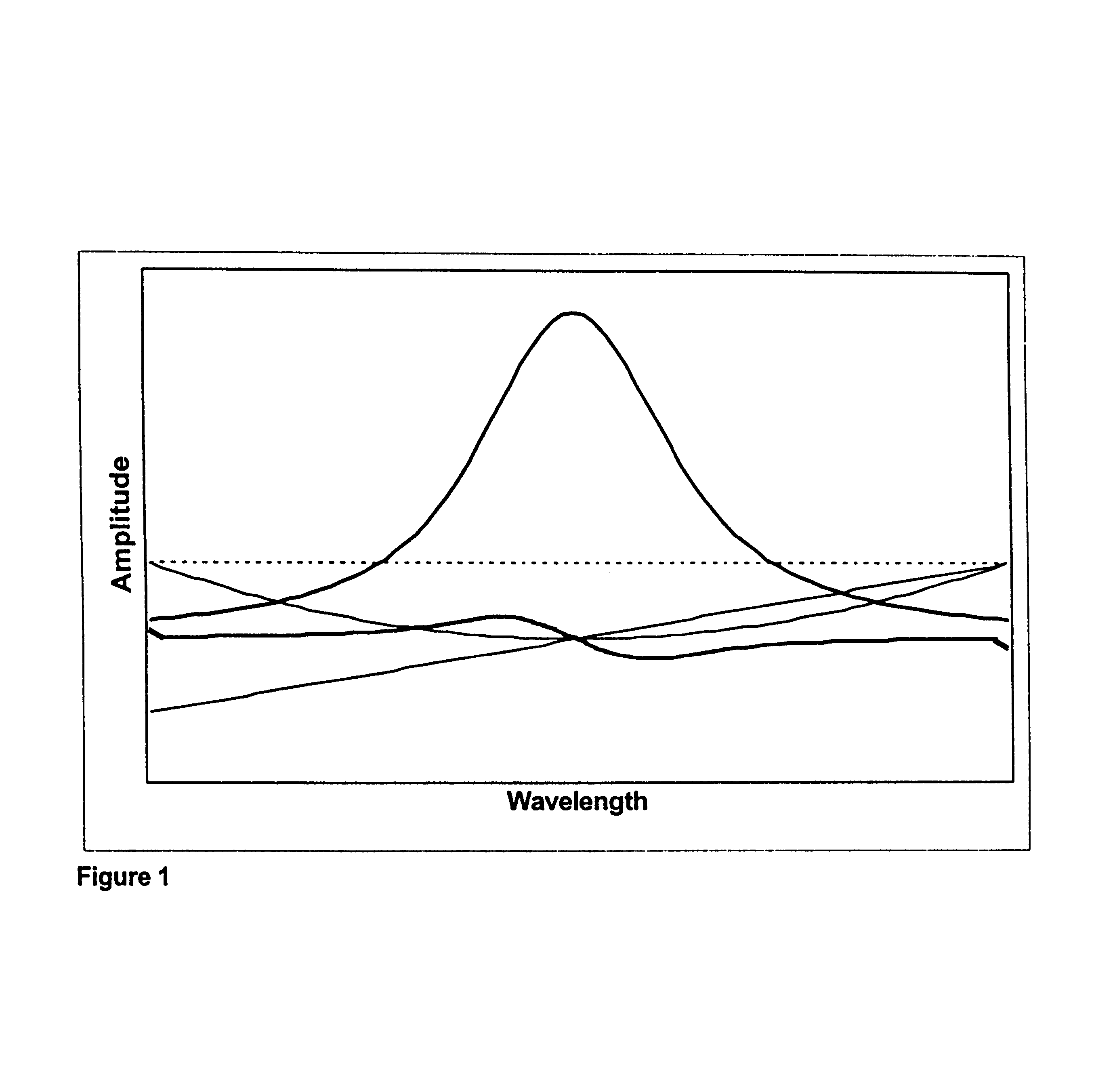
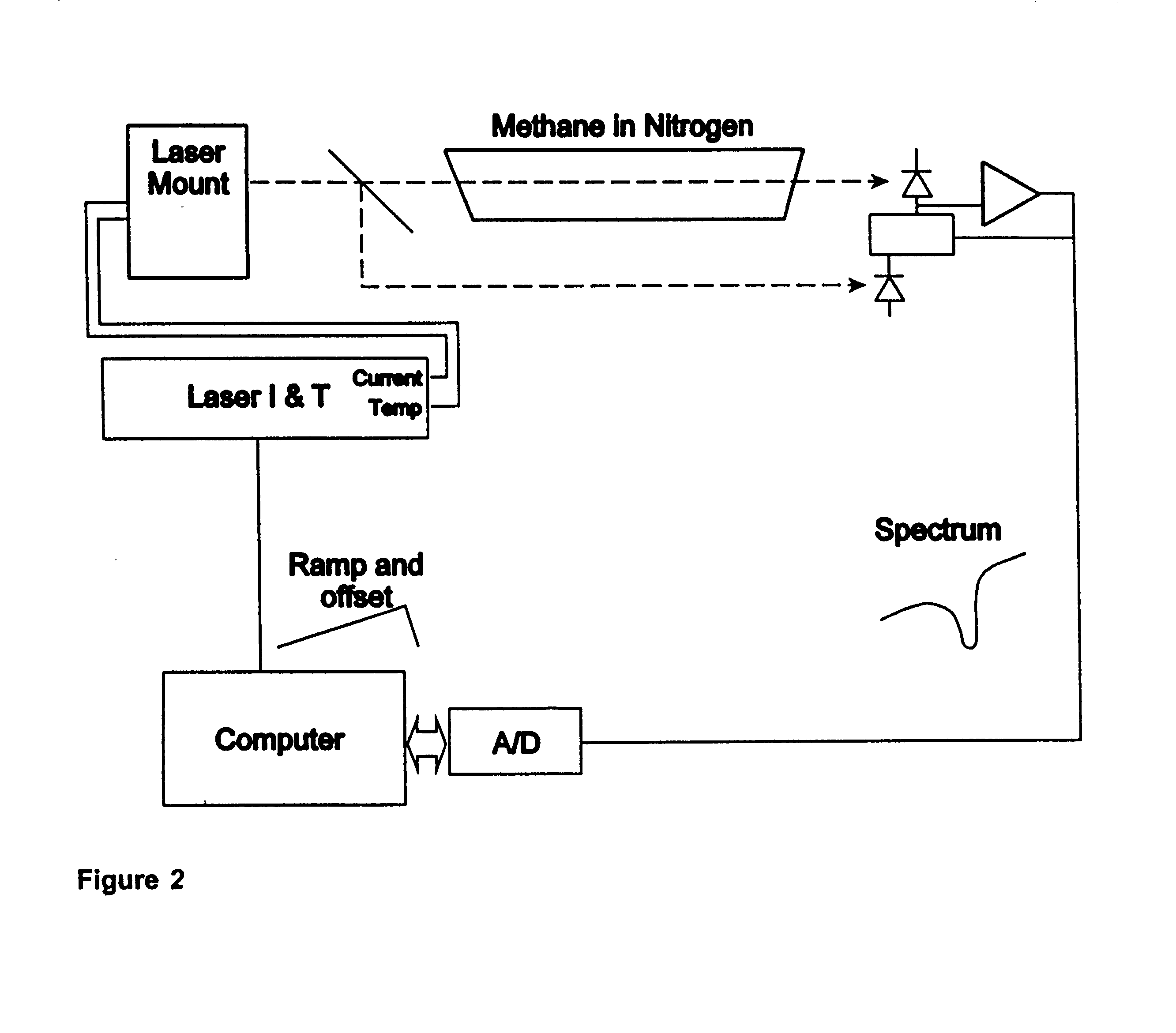
Filtering to measure gas concentrations from spectral features
InactiveUS6615142B1Absorption/flicker/reflection spectroscopyChemical methods analysisAnalyteGas concentration
A spectrographic apparatus and method comprising providing a spectrometer, digitizing a sample spectrum in a spectral range that includes at least one feature of an analyte, and comparing, via a linear least squares computation, the sample spectrum to a spectrum known to closely approximate the sample spectrum at a reference condition and to one or more derivatives of the known spectrum taken with respect to one or more parameters of the reference condition.
Owner:SOUTHWEST SCI
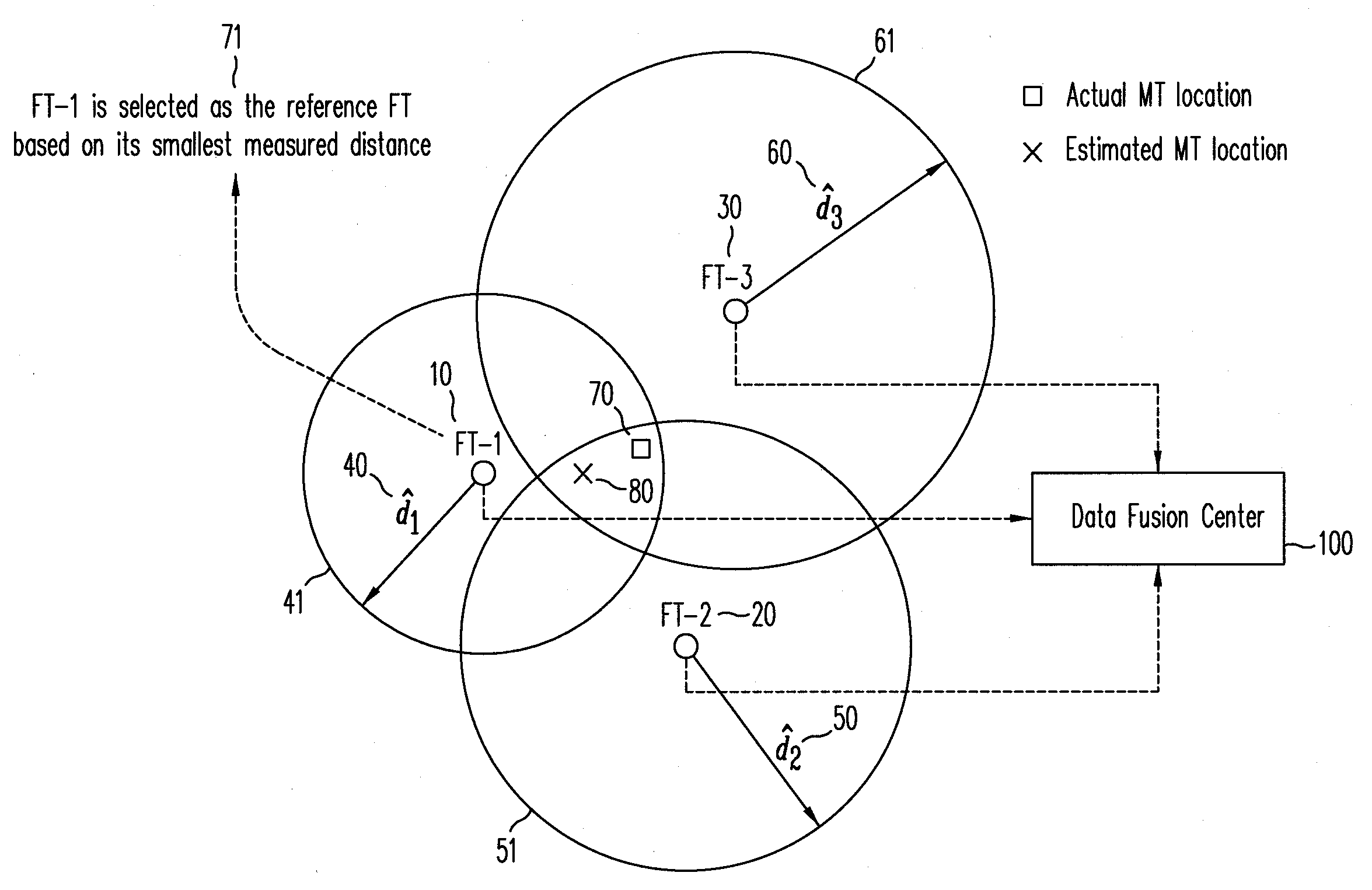
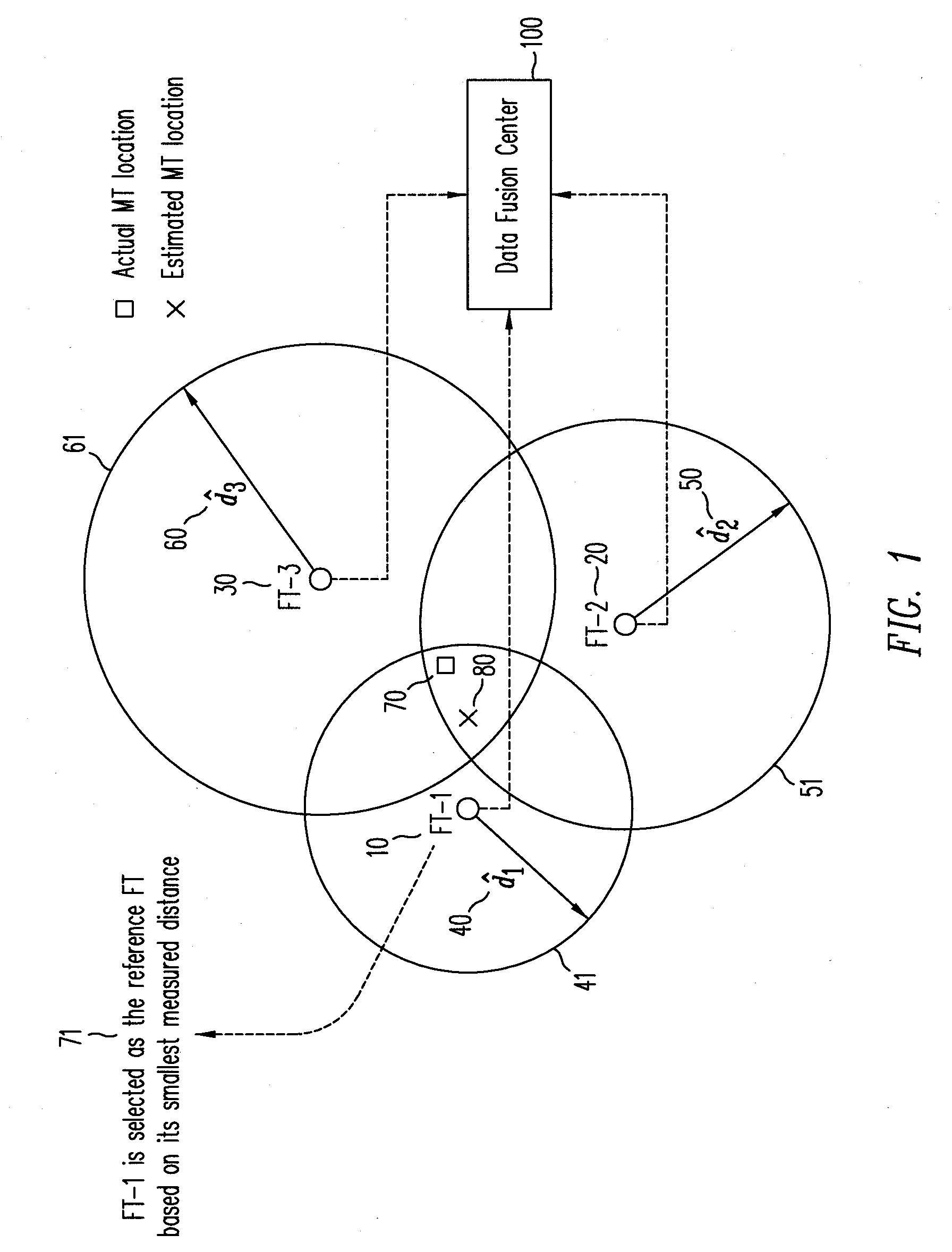
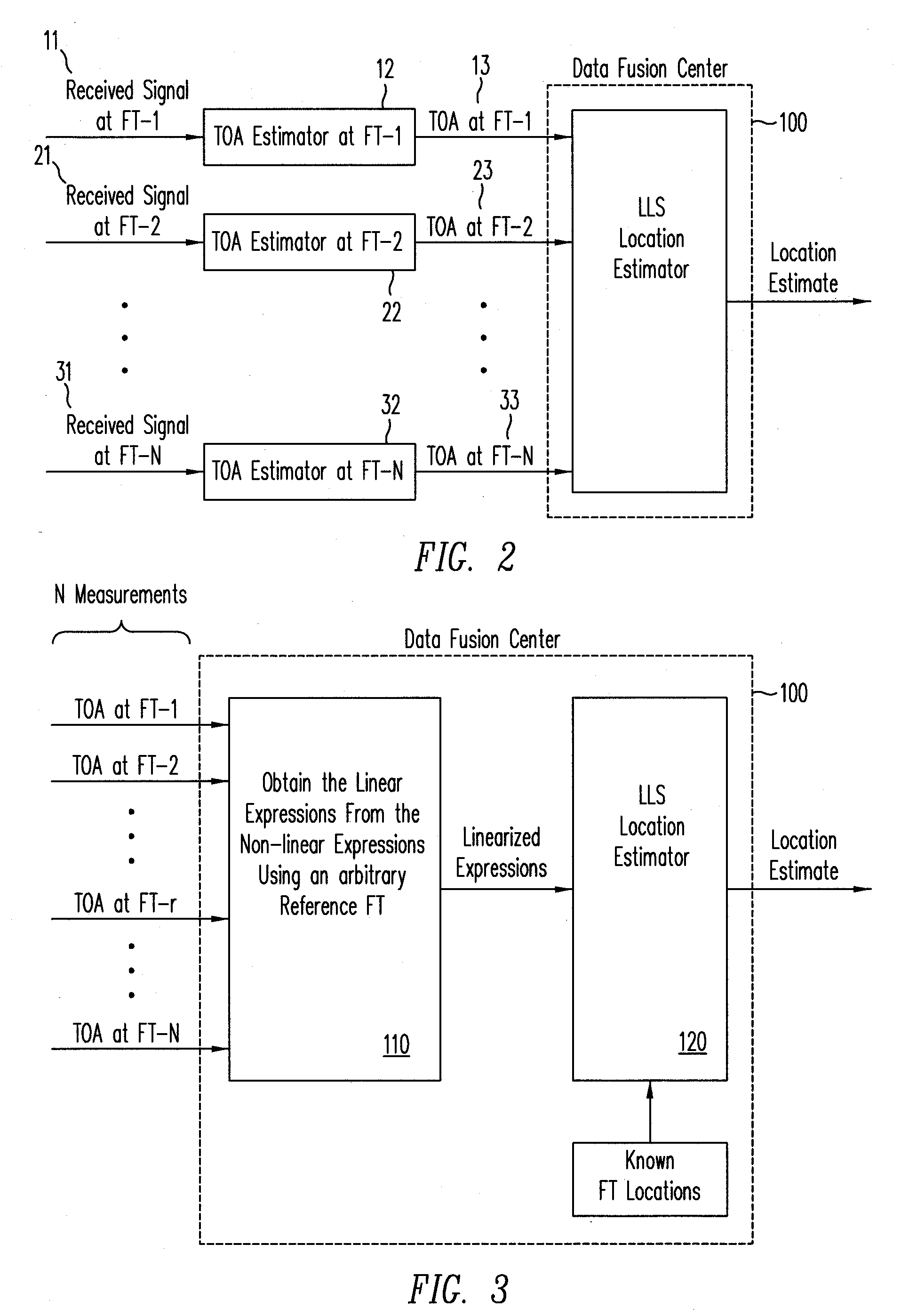
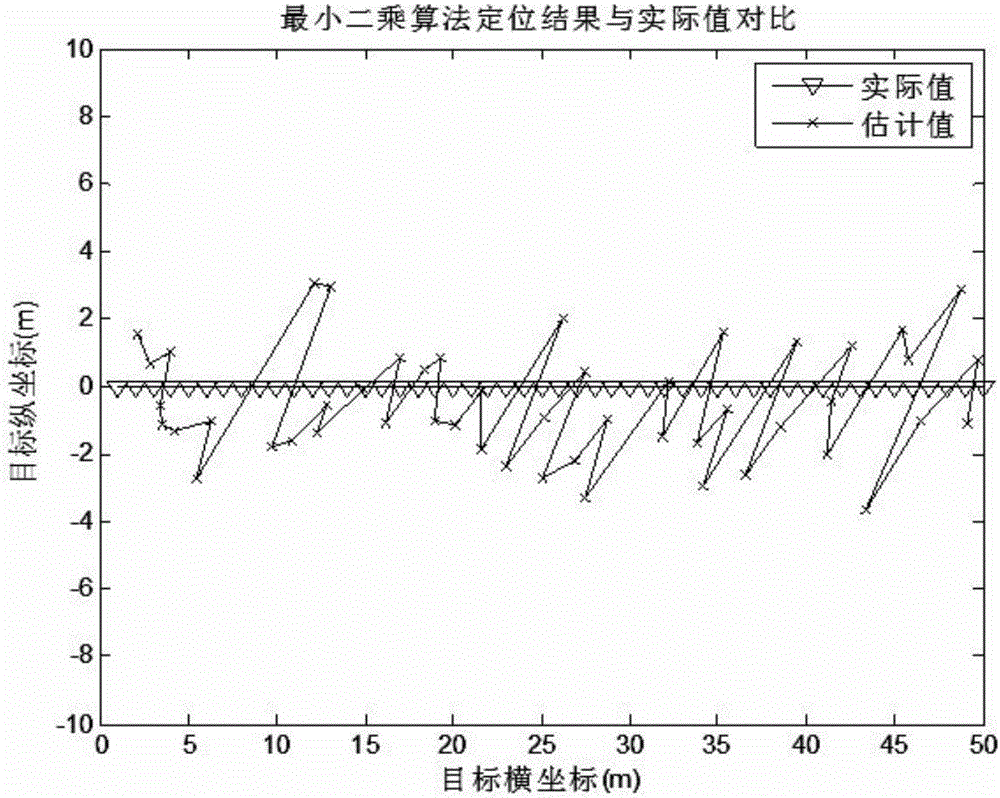
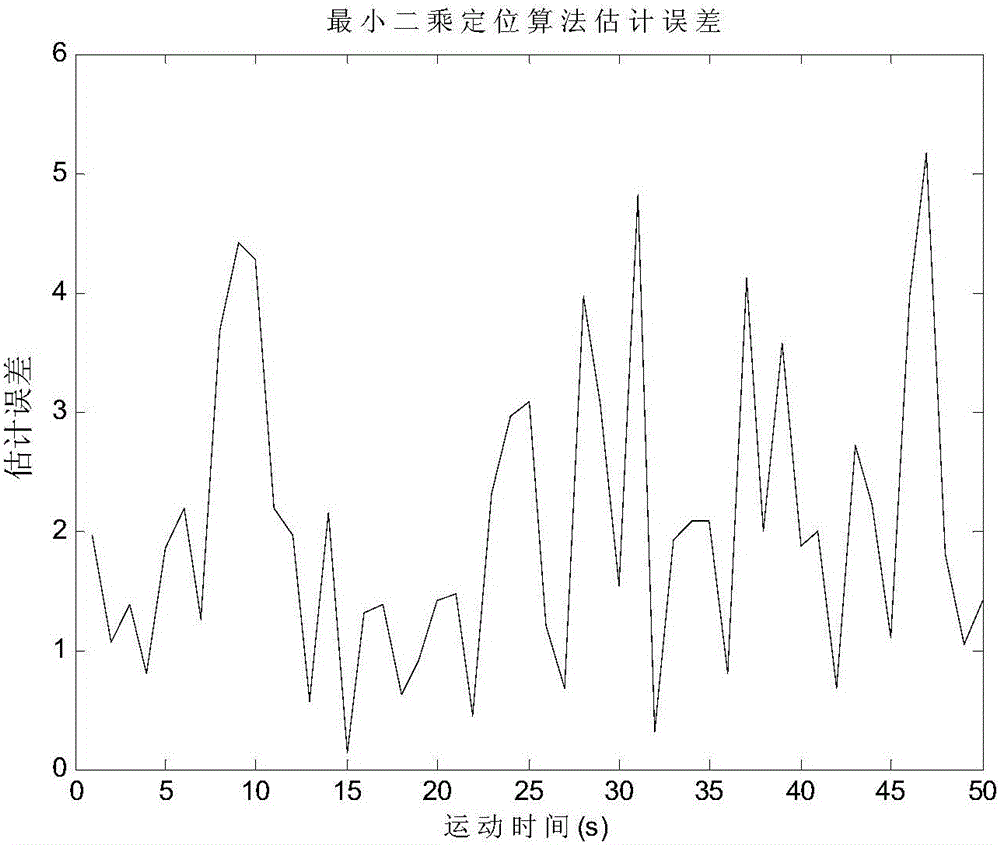
Method for an improved linear least squares estimation of a mobile terminal's location under los and nlos conditions and using map information
ActiveUS20090069029A1Reduce complexityHigh positioning accuracyDirection finders using radio wavesTelephonic communicationLinear modelCovariance matrix
A linear least squares (LLS) estimator provides a low complexity estimation of the location of a mobile terminal (MT), using one of the fixed terminals (FTs) as a reference FT to derive a linear model. A method for selecting a reference FT is disclosed, which improves the location accuracy relative to an arbitrary approach to selecting the reference FT. In addition, a covariance-matrix based LLS estimator is proposed in line-of-sight (LOS) and non-LOS (NLOS) environments to further provide accuracy, taking advantage of the correlation of the observations. Different techniques for selecting the reference FT under non-LOS (NLOS) conditions are disclosed. A map-based two-stage LLS estimator assists in selecting the reference FT under NLOS conditions.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Curved path approximation in vehicle guidance systems and methods
ActiveUS9804603B1Prevent overfittingAutonomous decision making processPosition/course control in two dimensionsGuidance systemIn vehicle
Improved vehicle guidance systems and methods are provided. A generated guidance curve approximates a vehicle trajectory path comprising a set of two-dimensional reference points. The guidance curve is based on a summed and weighted radial basis functions. Weighting is associated with coefficients calculated using linear least-squares regression to minimize approximation error between the guidance curve and the vehicle trajectory path. Guidance instructions are based, at least in part, on a nearest location point, and a tangent direction and curvature of the guidance curve at the nearest location point. The controller autonomously guides the vehicle along the guidance curve. The basis functions can have a cardinality less than a cardinality of the reference points. A distorting effect at the path ends can be minimized by augmenting the path ends of the vehicle trajectory path. Irregular reference point spacing can be mitigated using regularization techniques.
Owner:LEADER TECH
Method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift
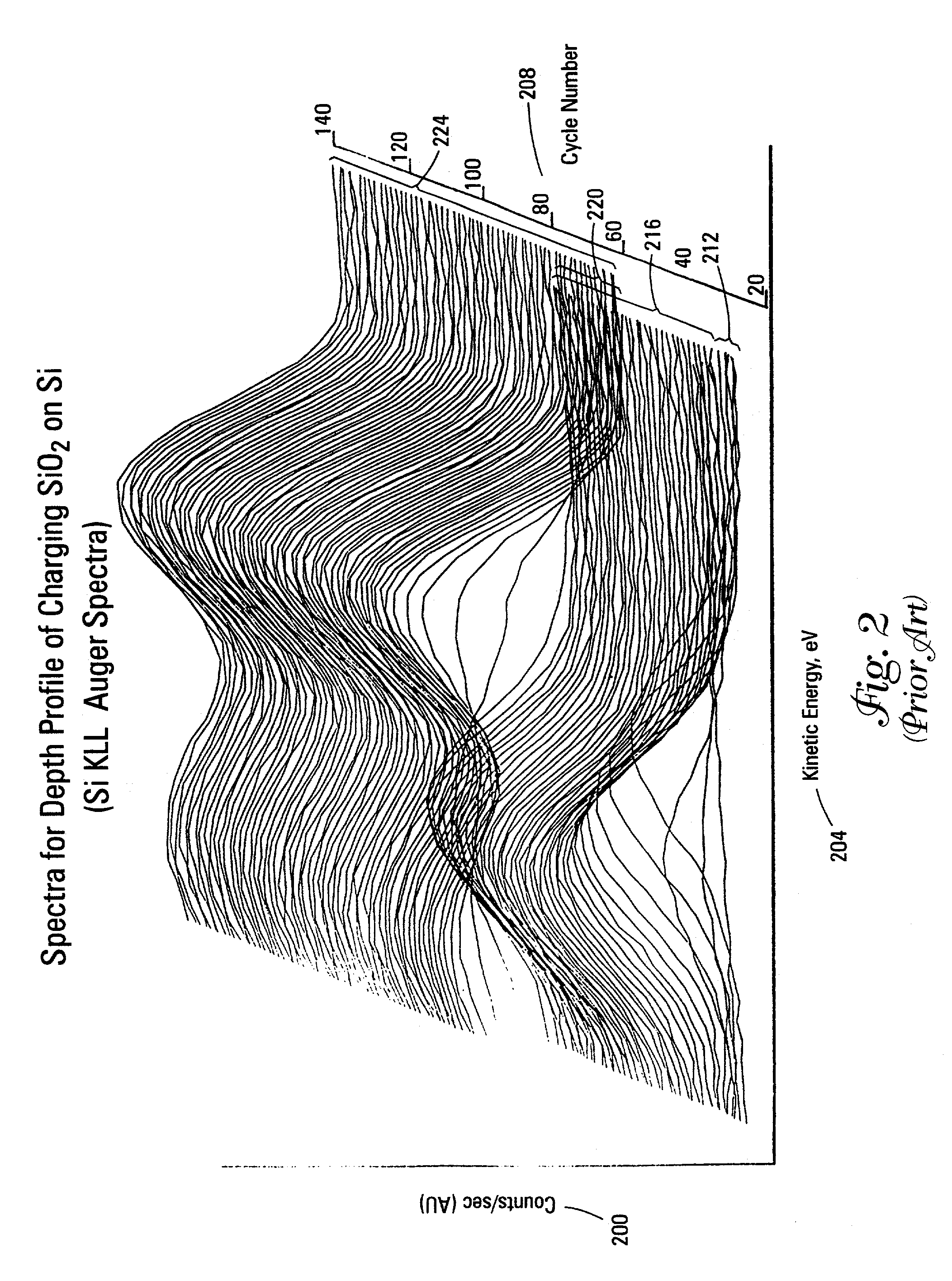
InactiveUS7002143B2Reduce dimensionalityParticle separator tubesIsotope separationFrequency spectrumElectron spectroscopy
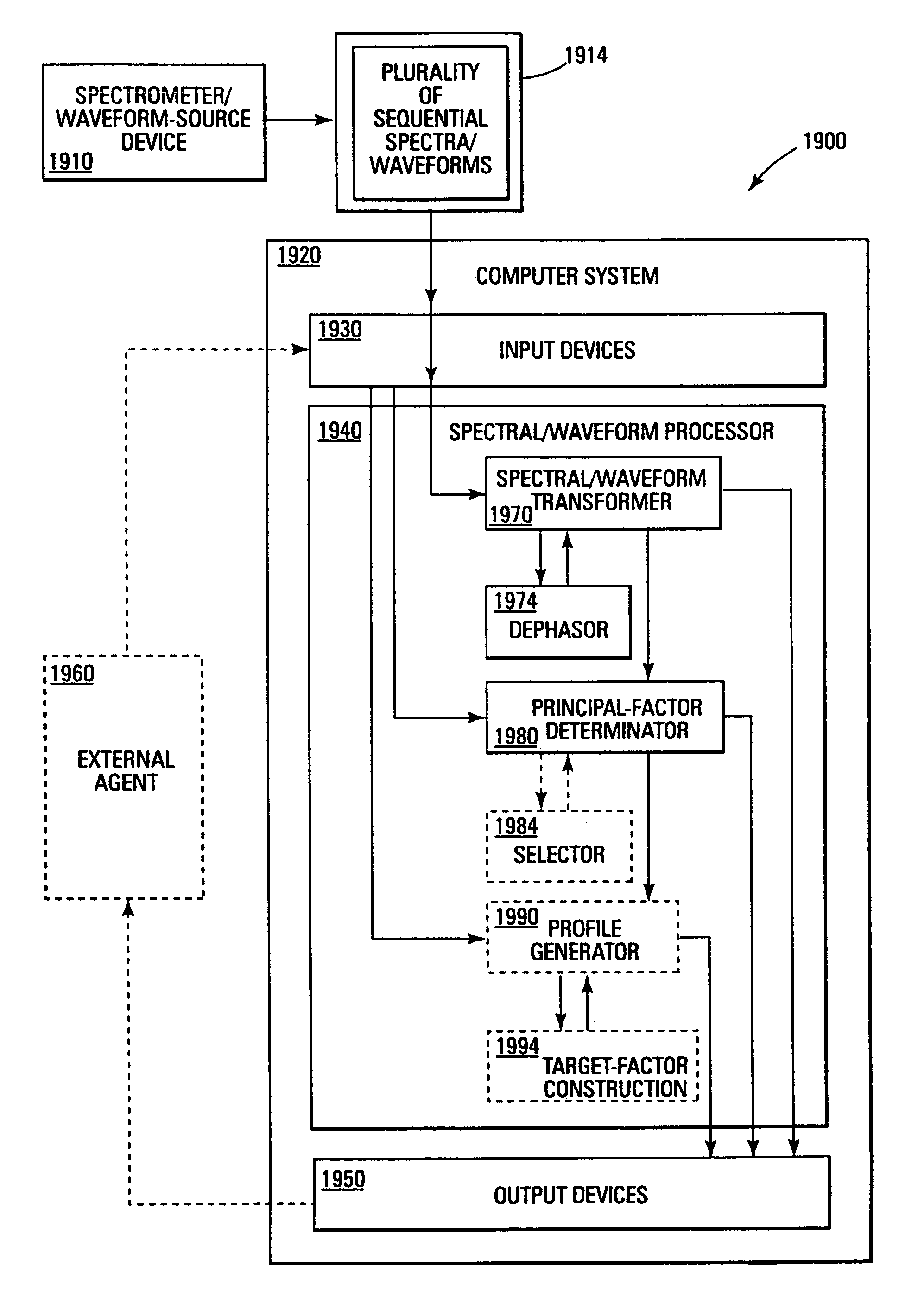
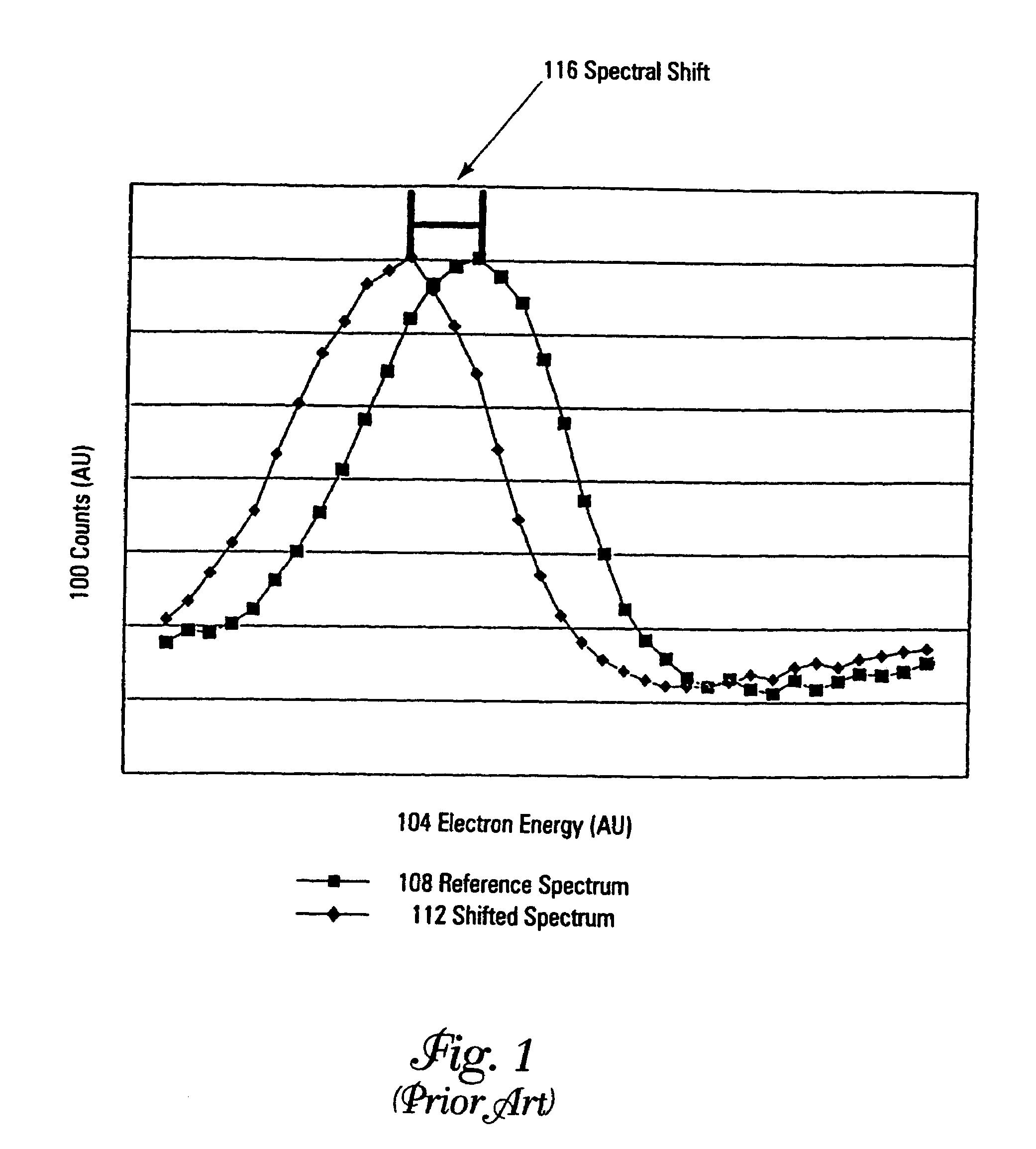
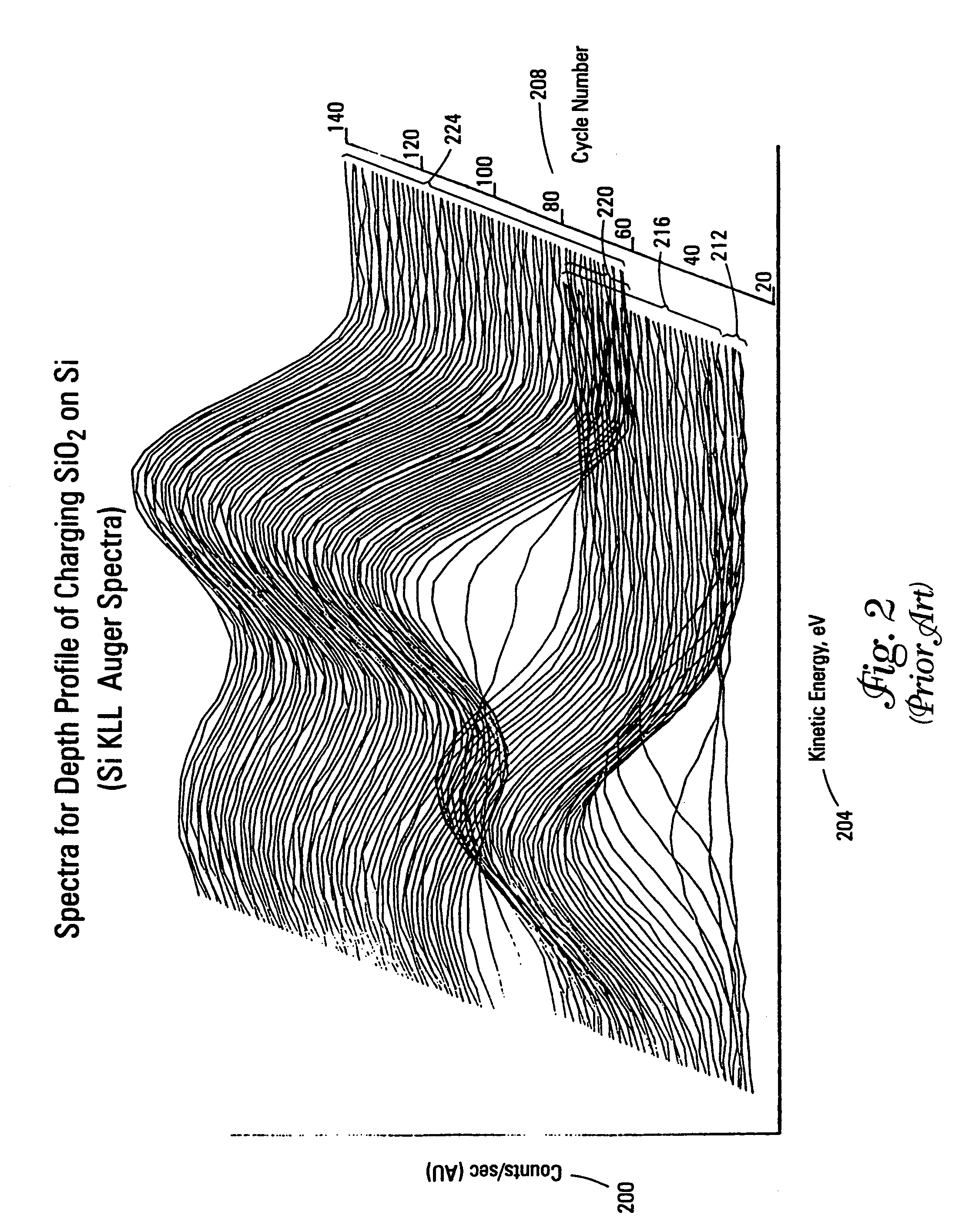
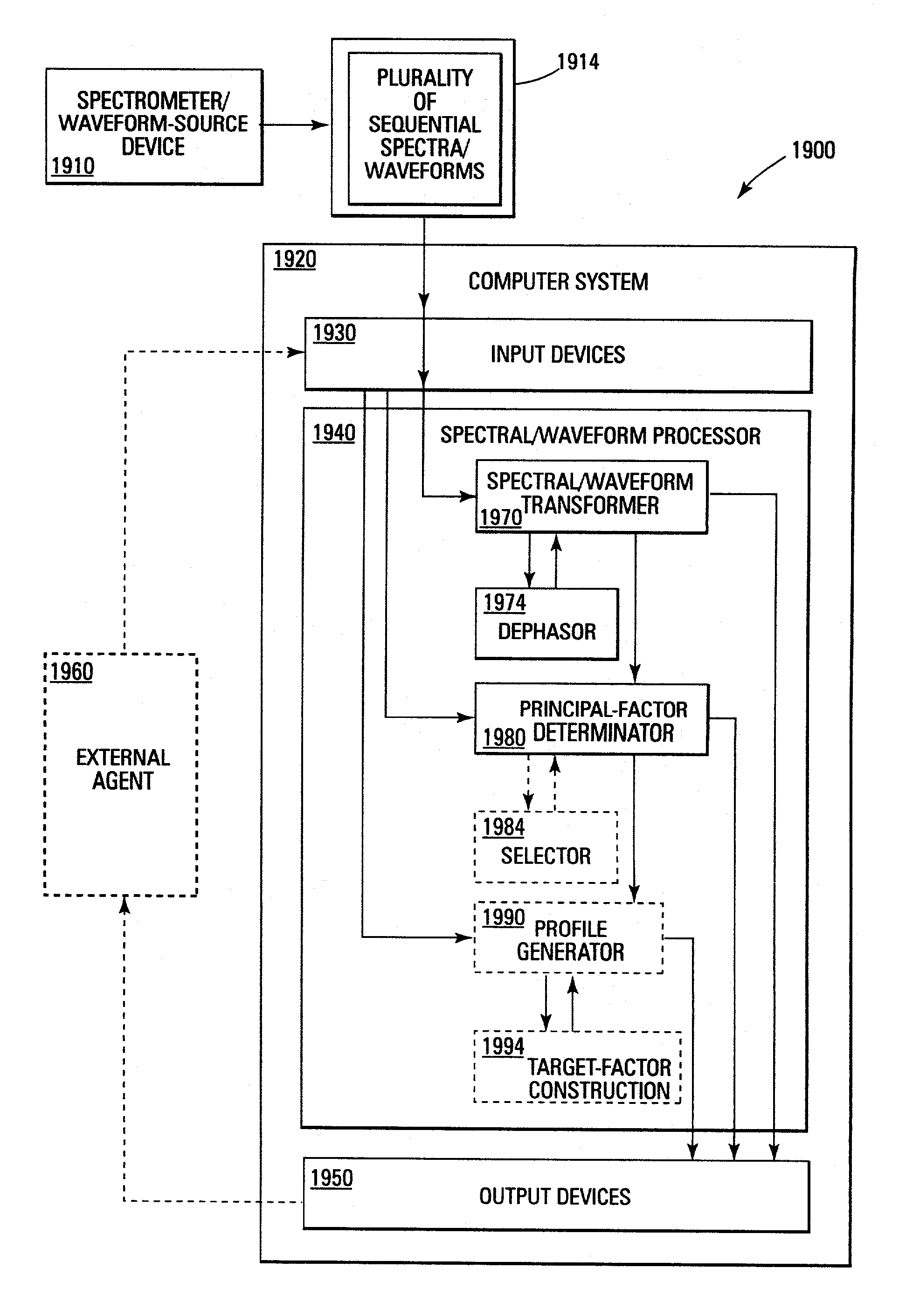
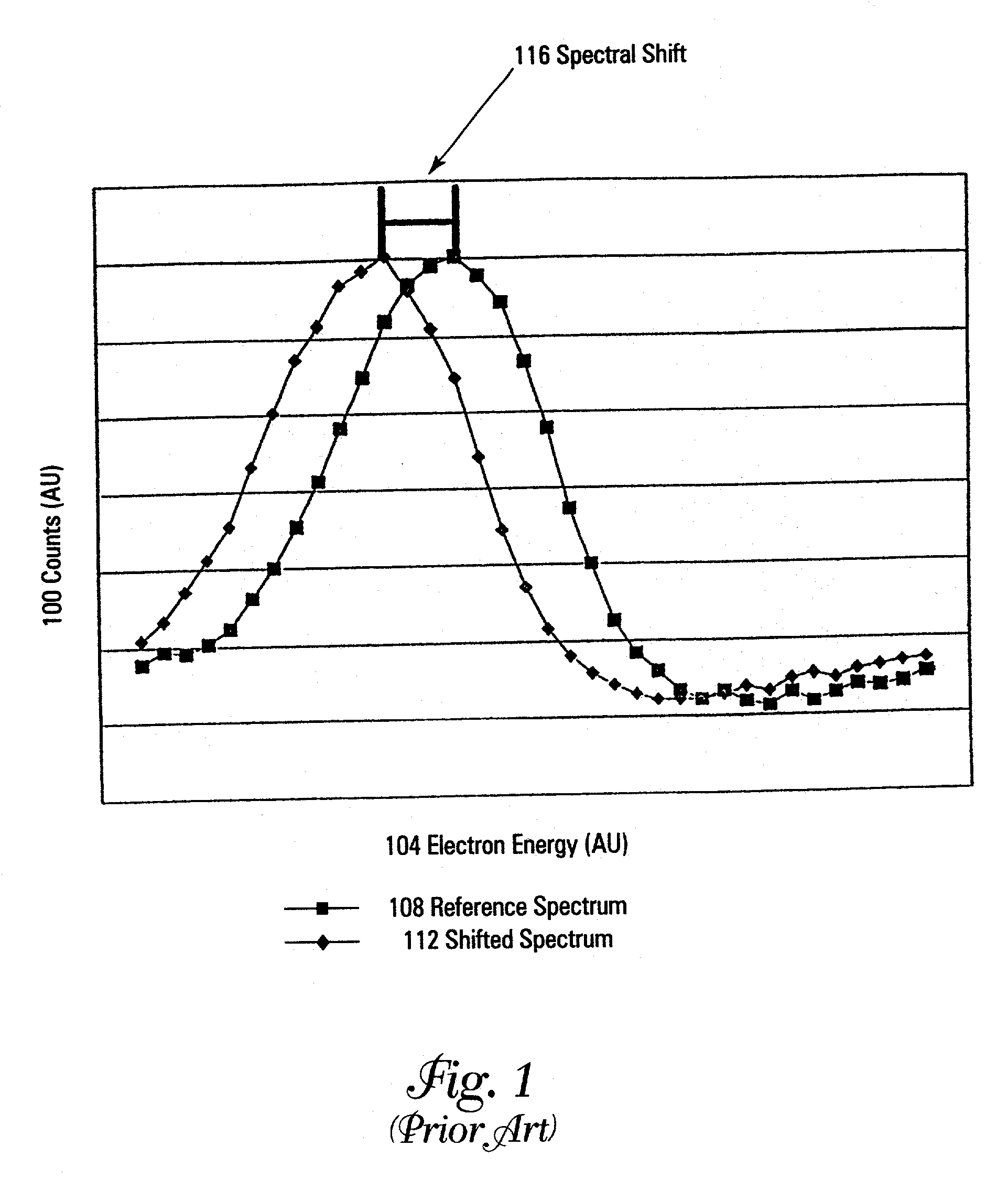
A method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift is disclosed. The present invention removes the effects of drift from a sequential series of waveforms obtained from a waveform-source device, or spectra, from a spectrometer, to produce for output a sequential series of drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra, respectively. In addition, the present invention performs a factor analysis, or alternatively a linear-least-squares analysis, on an array of the drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra to provide a set of drift-compensated principal factors; and, generates drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles from a profile trajectory lying within a space of the set of drift-compensated principal factors. In addition, in the case of spectra, the invention provides for conversion of the drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles to drift-compensated compositional profiles. The invention finds particular utility in the field of electron spectroscopy when the invention is applied to correcting sputter-depth-profile analyzes for the effects of spectral drift caused by charging in insulating samples. The invention, by extension, also, finds utility in waveform processing in situations where a sequential series of waveforms having similar features are offset by arbitrary phase shifts, and, even more generally, in time-series analysis, where a time-series is affected by leading or lagging data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for estimation of computer resource usage by transaction types
InactiveUS20060248529A1Reduce in quantityQuantity minimizationError detection/correctionMultiprogramming arrangementsComputer resourcesAlgorithm
The present invention provides a system (10) and method (30) for estimating computing resource usage (14) for each transaction type comprising the steps of obtaining utilisation data and transaction count data, applying a linear least squares algorithm (32) to the input data (22), wherein the linear least squares algorithm (32) comprises further steps arranged to reduce the time required to perform the aforementioned linear least squares algorithm computation.
Owner:LOBOZ CHARLES ZDZISLAW +2
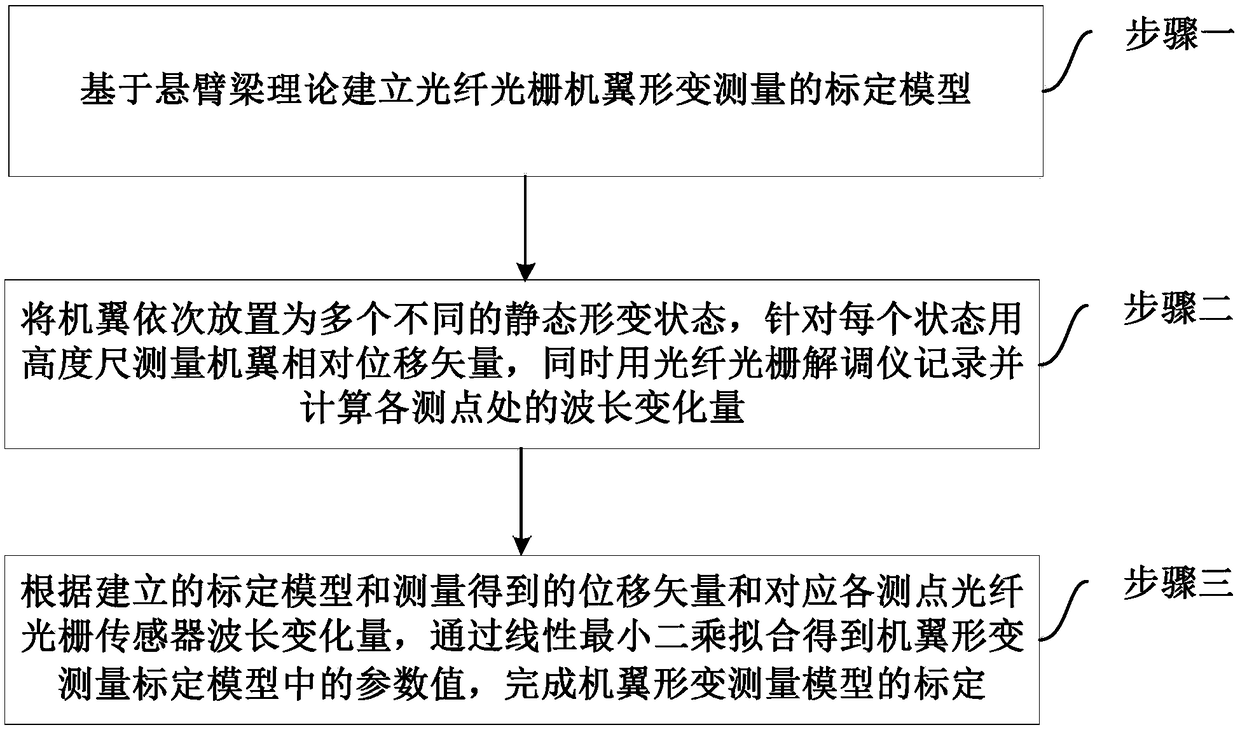
Cantilever beam theory-based fiber bragg grating wing deformation measurement modeling and calibration method
ActiveCN108801166AOvercoming the difficult problem of precise description of flexible changesUsing optical meansRadio wave reradiation/reflectionFiberLinear least squares
The invention discloses a cantilever beam theory-based fiber bragg grating wing deformation measurement modeling and calibration method. The method includes the following steps that: a fiber bragg grating wing deformation measurement calibration model is established based on the cantilever beam theory; a wing is arranged into a plurality of different static deformation states sequentially, the relative displacement vector of the wing is measured with a height gauge for each state, and at the same time, a fiber bragg grating demodulator is adopted to record and calculate a wavelength variationquantity at each measuring point; and parameter values in the wing deformation measurement calibration model can be obtained through linear least squares fitting, and the calibration of a wing deformation measurement model can be completed. With the method of the invention adopted, difficulty in accurately describing flexibility change of a baseline between the phase centers of a primary IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit) and a secondary IMU which is caused by the dynamic change of the baseline of the elastic deformation of the body structure of an aircraft can be eliminated; and a dynamic modelof the change of the flexible baseline with the time is not required to be established, after the wing deformation measurement model is calculated, and a wing deformation displacement vector can be obtained.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Product dimension sub-pixel measurement method under industrial microscale motion blurred imaging condition
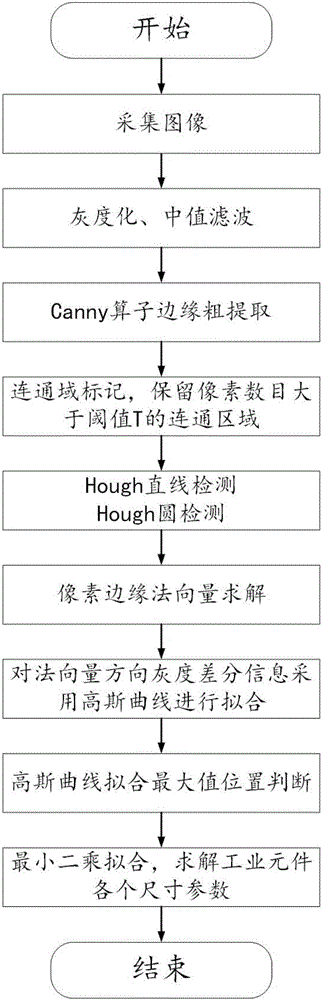
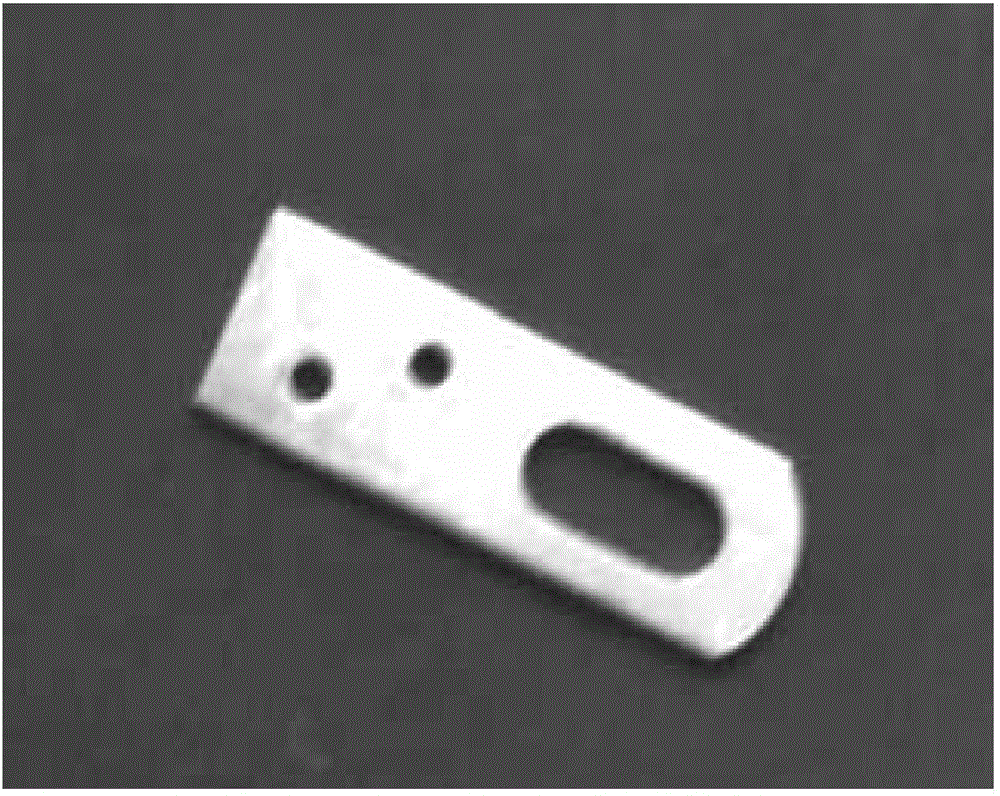
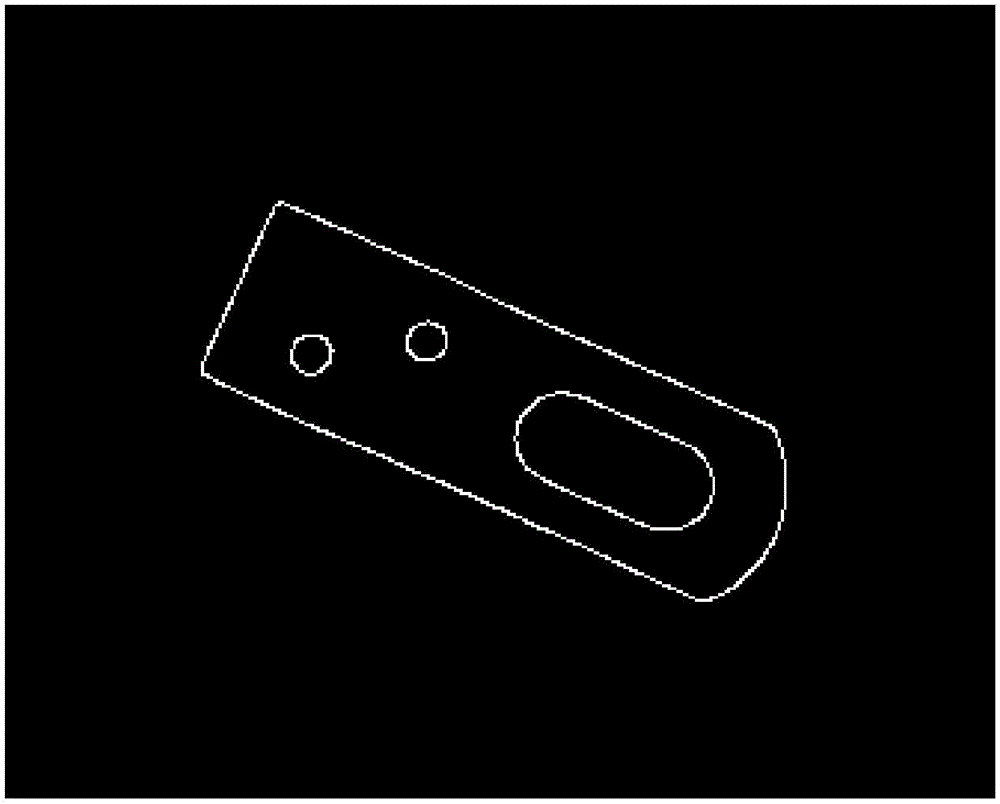
ActiveCN106651828ASolve the accuracy problemSolve technical problems with poor robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisLinear least squaresSize parameter
The invention provides a product dimension sub-pixel measurement method under an industrial microscale motion blurred imaging condition and relates to an industrial product dimension high precision measurement method based on machine visual sense. In order to solve the problem that the conventional mainstream sub-pixel measurement algorithm is low in precision when the industrial collection image has microscale motion blur, the method provided by the invention firstly carries out graying and median filtering processing to an industrial element image, and adopts a Canny operator to perform edge crude extraction and local connected domain processing; then the linear edge and the arc edge in the image are subjected to detection and recognition, the normal vector of the pixel contained in each edge in an original gray image is calculated, and the gray value difference of the edge pixel in the normal vector direction is calculated, and the position of the quadratic fit curve maximum is solved and determined; and finally, the position of the effective sub-pixel of the linear edge is subjected to linear least square fitting, and the each dimensional parameter of the industrial element is solved. The method is suitable for the sub-pixel measurement of the product dimension.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Oriented electromagnetic steel sheet and manufacturing method therefor
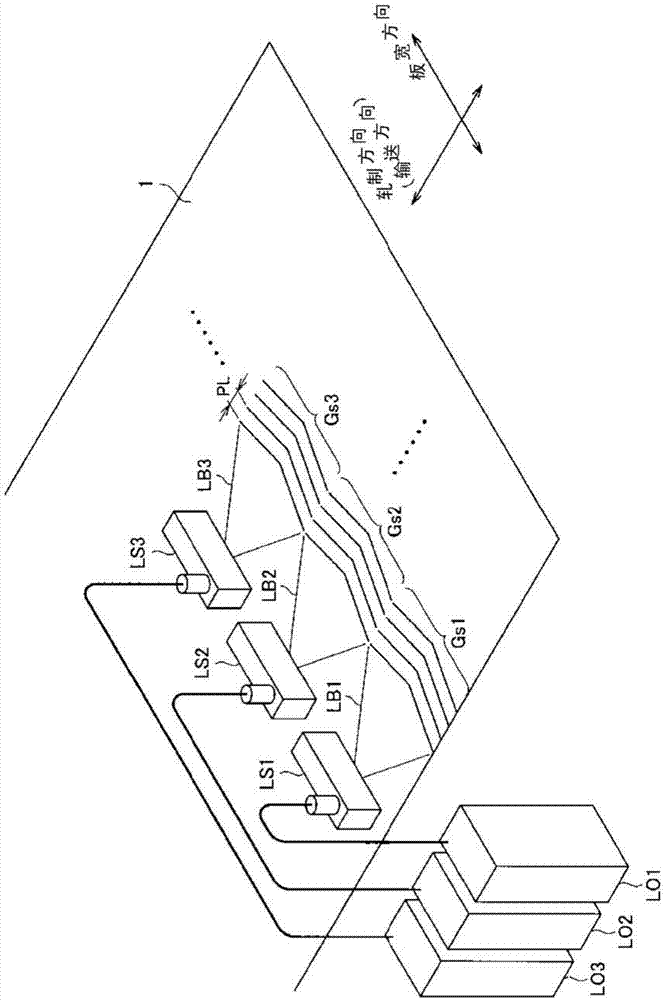
ActiveCN104203486AWarpage suppressionInorganic material magnetismInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureGroove widthElectrical steel
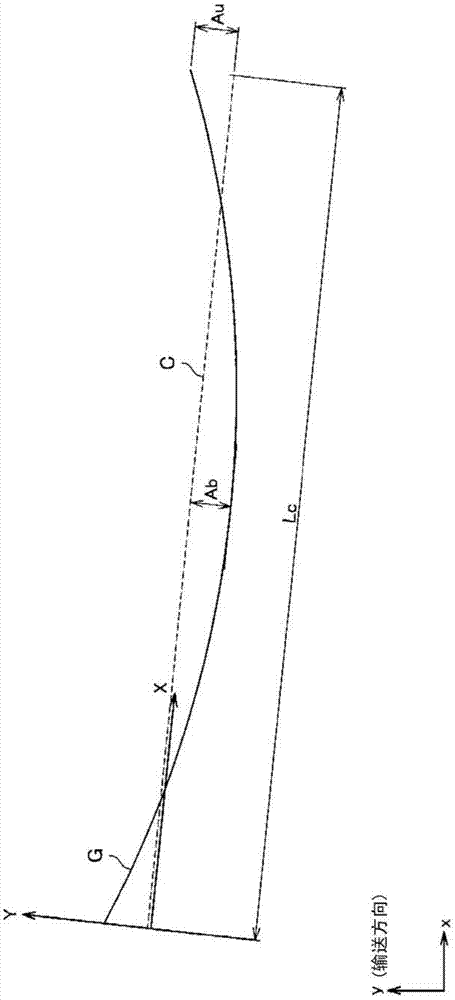
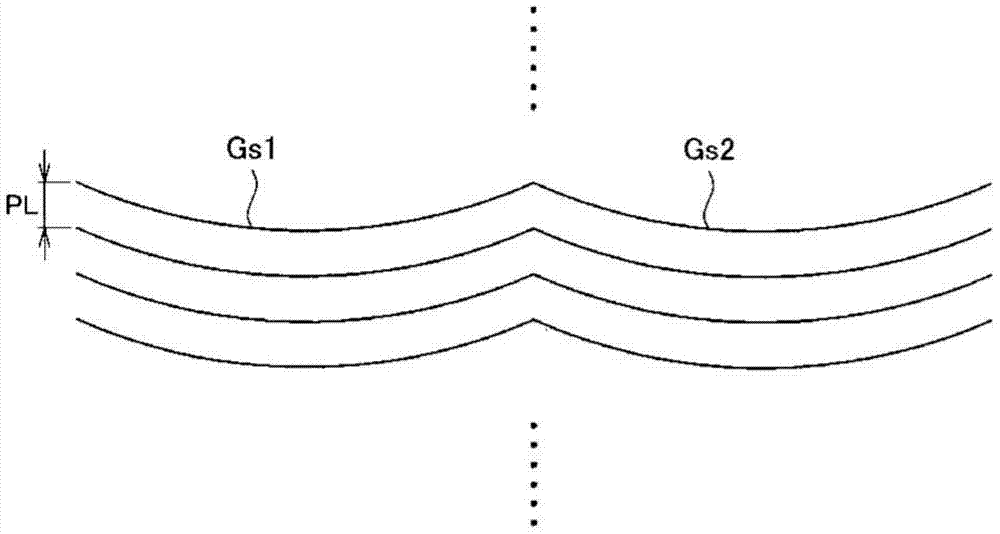
For this grain-oriented electrical steel sheet in which grooves extending in the direction intersecting with the conveyance direction are formed at a specified pitch (PL) in the conveyance direction by irradiation of a laser beam: the relationship between the standard deviation (D) of the distance from the linear least squares approximation line for the center line of the grooves in the groove width direction to each position on the center line and the pitch (PL) satisfies formula (1); and the mean angle formed between the tangent at each position on the center line and the direction orthogonal to the conveyance direction is greater than 0° and equal to or less than 30°. 0.02 <= (D / PL) ...(1)
Owner:NIPPON STEEL CORP
Nonlinear frequency modulation component decomposition-based time-frequency domain modal parameter identification method
ActiveCN107329932AEasy to identifyEasy to useComplex mathematical operationsDecompositionFrequency modulation
The invention discloses a nonlinear frequency modulation component decomposition-based time-frequency domain modal parameter identification method comprising steps of (1) acquiring a dynamic response signal of a to-be-identified structure and setting sampling time and frequency, (2) building a redundancy Fourier model including the response signal, instantaneous frequency and instantaneous amplitude via Fourier series, (3) extracting instantaneous frequency information of the response signal according to generalized parameterization time-frequency transform, (4) extracting instantaneous amplitude information of the response signal according to a regularized least square method according to the acquired instantaneous frequency information, (5) conducting structure modal parameter identification via a linear least square fitting algorithm based on the instantaneous frequency information and slope information of the instantaneous amplitude logarithm and (6) analyzing errors of an identification result. Signal analysis and modal parameter identification are conducted according to a structure vibration response signal, so simple and easy use can be achieved; modal parameter identification precision for high-compact modal structures can be effectively improved; and strong adaptability and interference resistance capacity can be provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for measuring brightness range influencing comfort degree of stereoscopic image
ActiveCN102497565AVerification of universalityImprove comfortTelevision systemsSteroscopic systemsDifference-map algorithmBrightness perception
The invention discloses a method for measuring a brightness range influencing the comfort degree of a stereoscopic image. The method comprises the following steps of: performing brightness processing on unqualified views on the boundary of a stereoscopic grayscale image with a first qualified comfort degree according to a secondary step length to obtain a plurality of secondary stereoscopic grayscale images; performing the brightness processing on unqualified views on the boundary of the stereoscopic grayscale image with a second qualified comfort degree according to a tertiary step length to obtain a plurality of tertiary stereoscopic grayscale images; processing the tertiary stereoscopic grayscale images according to a preset rule to obtain tertiary stereoscopic grayscale views of which a statistical average value is more than or equal to 4, and defining the tertiary stereoscopic grayscale views as stereoscopic grayscale images with a third qualified comfort degree; performing fitting by using a piecewise linear least squares fitting method to obtain a stereoscopic image comfortable brightness matching map and a stereoscopic image comfortable brightness difference map; and computing an average value of the two maps to obtain a brightness comprehensive piecewise linear and brightness difference comprehensive piecewise linear fitting straight line. Researches on the influence of a brightness factor on the comfort degree of a binocular stereoscopic image are made quantitatively.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Underwater moving target extended Kalman filtering tracking method based on distributed sensor energy ratios
The invention discloses an underwater moving target extended Kalman filtering tracking method based on distributed sensor energy ratios. First logarithms of energy ratios of every two sensors are introduced as observation values, thereby obtaining an observation sequence of different moments; then based on the state of motion of a target, a nonlinear observation equation is converted into an approximately linear observation equation in an error-controllable range, and a linear state-space model is built; then an extended Kalman filtering sequential iterative solution algorithm of the state-space model is derived; a linear least squares (ER-LS) positioning algorithm is utilized to position the moving target which enters an underwater sensor network range, thereby obtaining an initial value of extended Kalman filtering; and finally, an underwater target motion trail with improved performance is obtained through sequential filtering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
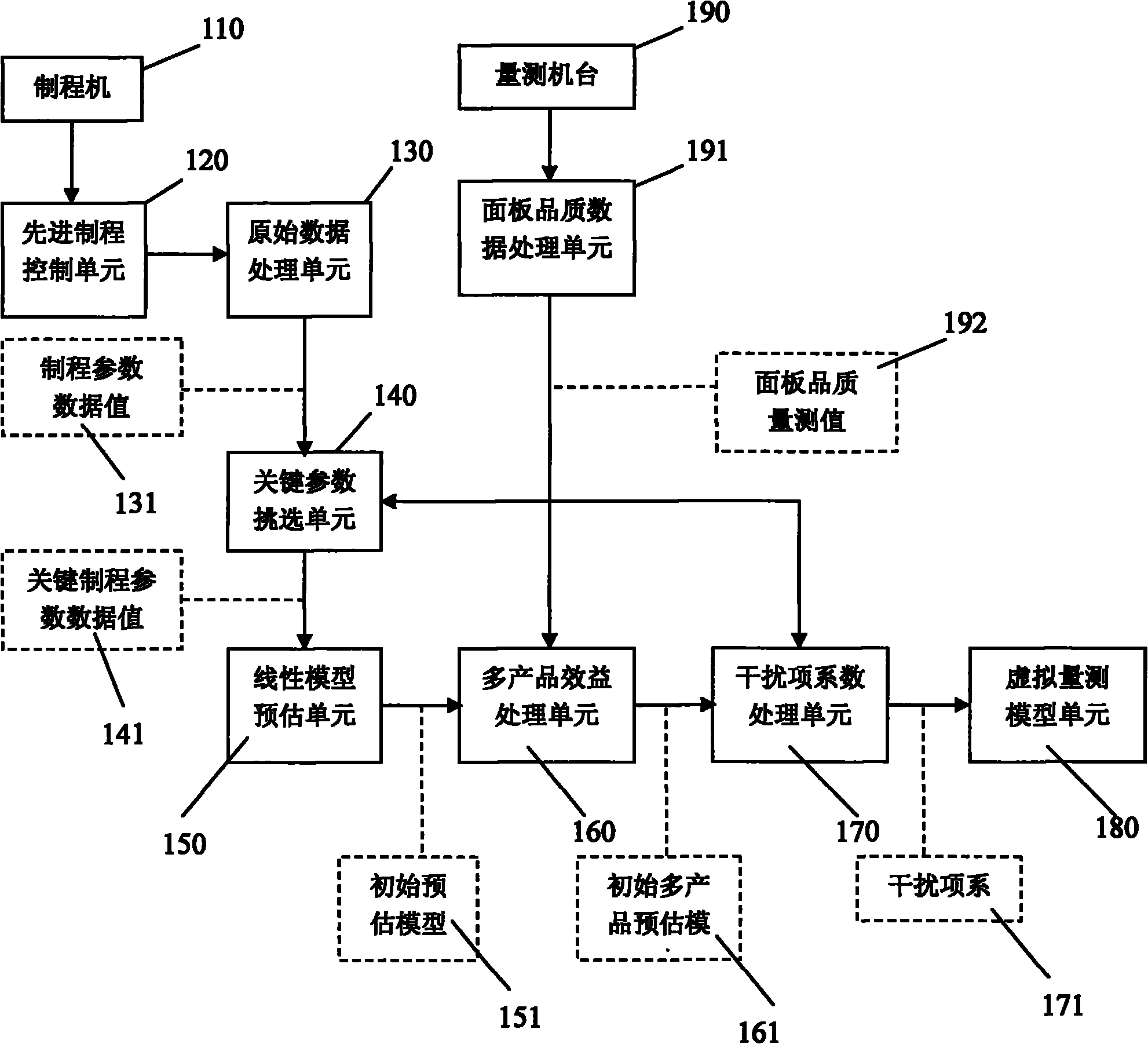
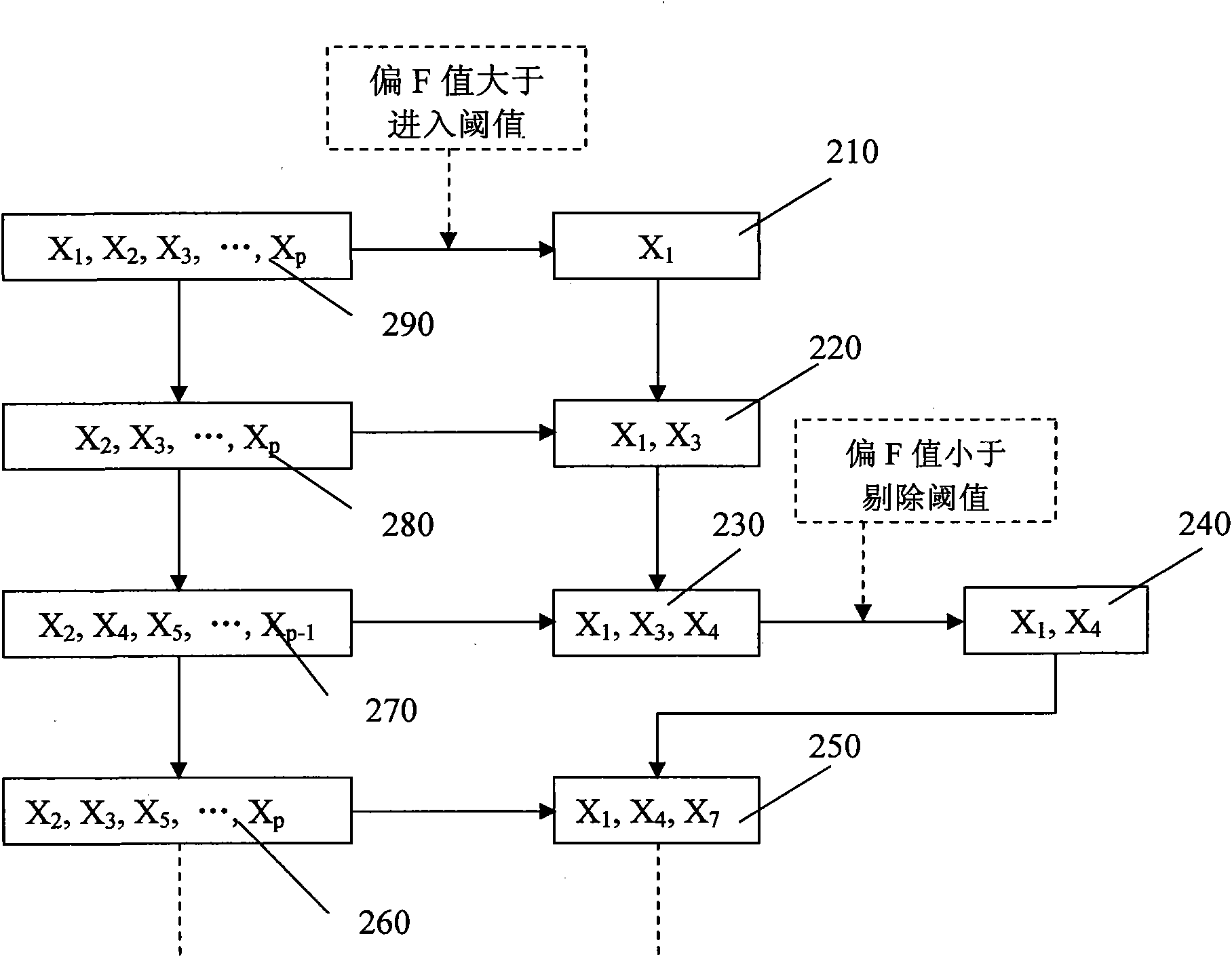
Panel quality virtual measurement method and system for TFT-LCD etching process
InactiveCN101976045AImprove understandingReduce complexitySemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementAdaptive controlQuality dataThin-film-transistor liquid-crystal display
The invention discloses a panel quality virtual measurement method and a panel quality virtual measurement system for a thin film transistor-liquid crystal display (TFT-LCD) etching process. The method comprises the following steps that: an advanced process control unit acquires the process parameter data value of at least one process machine; a measurement machine acquires panel quality measurement values; a panel quality data processing unit subtracts the average value of the panel quality measurement values from a sampled panel quality measurement value and then divides the difference by standard deviation of the panel quality measurement value; a key parameter selection unit selects a key process parameter data value; a linear model pre-estimation unit establishes an initial pre-estimation model by a linear least square algorithm; a multi-product benefit processing unit generates an initial multi-product pre-estimation model; and a distracter coefficient processing unit acquires an estimation value and processes the estimation value by a time sequence recursive algorithm to generate a distracter coefficient and then establish a virtual measurement model unit. Through the method and the system, the quality of various panels with the same process formula and different specifications can be forecast, the frequency of sampling measurement is reduced and the complexity of the pre-estimation model is reduced.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Linear real-time estimation method of conductivity resistance-capacitance network parameter
InactiveCN102087317AEliminate the effects of uncertaintyAvoid uncertaintyFluid resistance measurementsCapacitanceAnti jamming
The invention relates to a linear real-time estimation method of a conductivity resistance-capacitance network parameter, belonging to the technical field of solution conductivity soft measurement. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: converting the measurement of solution conductivity into the parameter estimation of an equivalent resistance-capacitance network: on the basis of a mathematical model between a square wave excitation signal, a response direct-current voltage signal and two resistance and capacitance parameters of the equivalent resistance-capacitance network, carrying out multi-element polynomial fitting on the non-linear model off line; adopting an alternating-current square wave excitation resistance-capacitance network of various frequencies by taking the existence of various uncertainties into account during on-line measurement; meanwhile, establishing an over-determined equation set by utilizing the off line fitted multi-element polynomial model; and obtaining the real-time estimation of a resistance-capacitance parameter through a Gauss elimination finite step arithmetic operation and a radical operation of quartic equation solving on the basis of linear least square principle. The method has the advantages of higher estimation speed and stronger anti-jamming capability and is suitable for the on-line real-time accurate measurement of the conductivity industry.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Low-coherence interference demodulation method based on monochrome frequency absolute phase
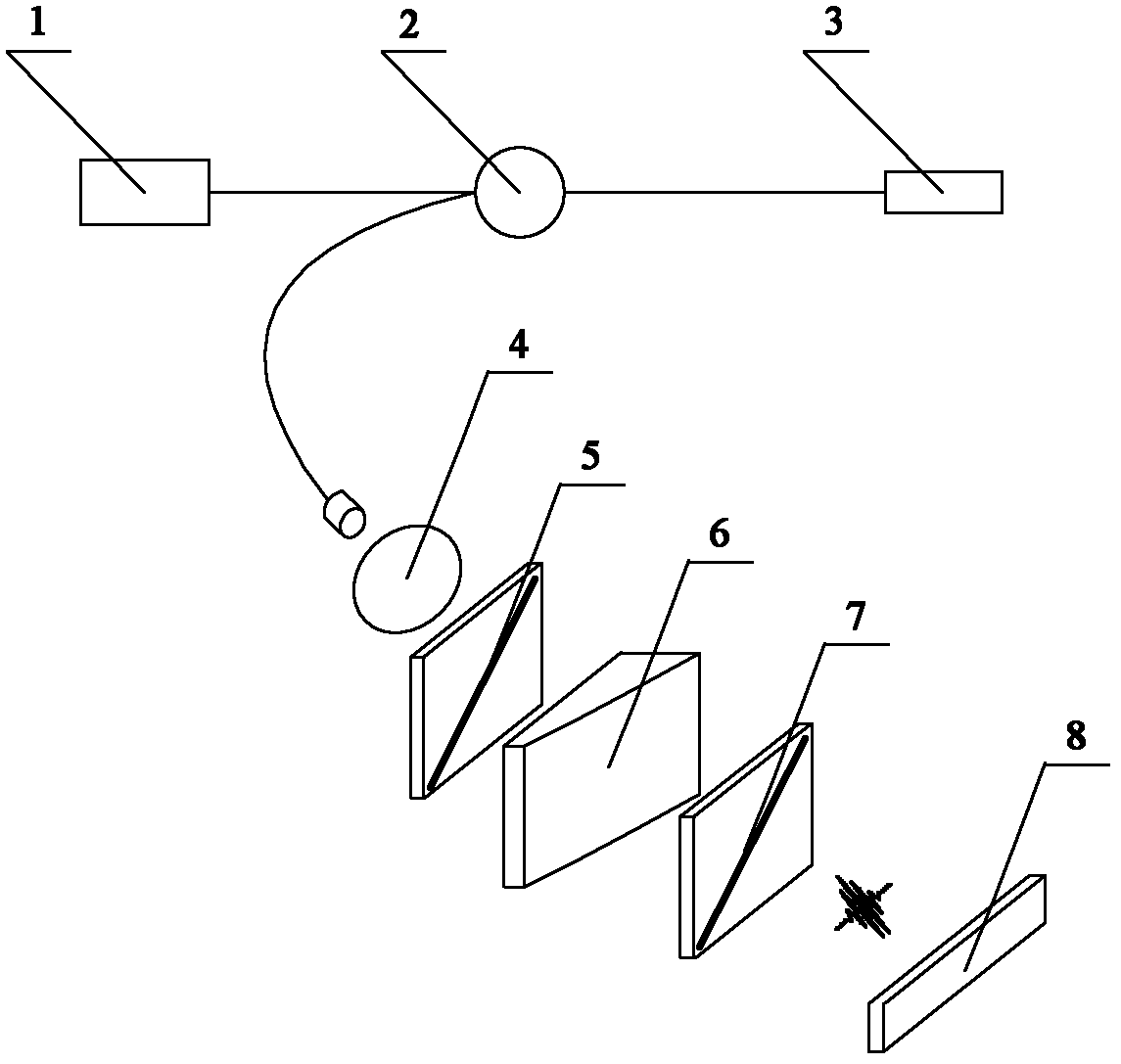
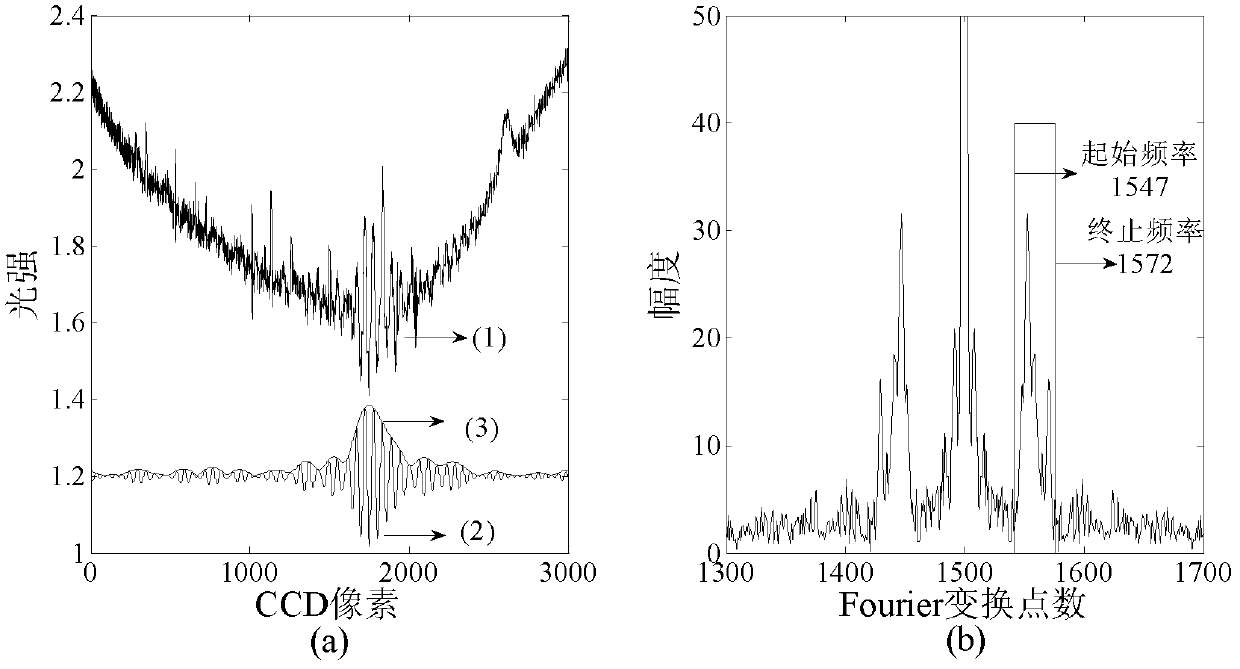
ActiveCN102607612ASmall amount of calculationSuitable for high-speed demodulation occasionsLight demodulationConverting sensor output opticallyRefractive indexOptical pathlength
The invention provides a low-coherence interference demodulation method based on a monochrome frequency absolute phase, belonging to the field of optical fiber sensing. The low-coherence interference demodulation method based on the monochrome frequency absolute phase is widely applied to measurements of various static physical quantities, such as temperature, pressure, displacement and refractive index, and detection of object three-dimensional feature. According to the method, a Fabry-Perot sensor is selected as a sensing element for sensing external air pressure intensity variation, an optical wedge is used as an optical path difference space scanning element, and interference strips are formed in a partial area with an optical path difference of zero. The low-coherence interference demodulation method comprises the following steps of: firstly, carrying out Fourier conversion on an interference signal to obtain phase information which is aliased within a section of (-pi, pi); then selecting a phase with a standard frequency as a reference phase, carrying out phase unwrapping according to frequency-phase monotonous properties, and carrying out linear least-squares regression on the unwrapped phase so as to obtain a fitting straight intercept; and finally, dividing the intercept by an integer part of 2*pi, so as to obtain an interference order of a reference frequency; and finally, obtaining the absolute phase of the reference frequency by combining a relative phase obtained through the Fourier conversion. Therefore, the demodulation is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Video softcast method based on channel characteristic
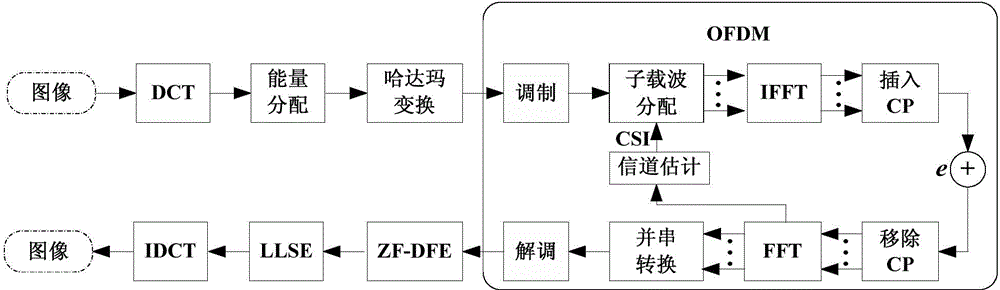
ActiveCN104994103AImprove performanceMulti-frequency code systemsError prevention/detection by transmission repeatHadamard transformCyclic prefix
The invention relates to a video softcast method based on a channel characteristic. According to the method, subcarriers of the highest quality of a video data allocation channel are transmitted in a physical layer, and a decoding terminal uses a linear least square estimator (LLSE) to denoise and uses zero forcing decision feedback equalization (ZF-DFE) to decode, so that the video recovery quality is improved finally. The video softcast method comprises following steps that a coding terminal reads in a video sequence and partitions images, removes intra-frame redundancy through discrete cosine transformation (DCT), performs power distribution so as to minimize reconstruction errors, and finally generates data of the same significance through hadamard transform; acquired data packages are sent into orthogonal frequency division multiplexing (OFDM), data of each package is simply modulated firstly so as to form a series of symbols, subcarriers are allocated according to CSI transmitted by a feedback channel, serial-parallel conversion, inverse fast fourier transform (IFFT), cyclic prefix insertion and parallel-serial conversion are performed on the symbols so as to obtain OFDM transmission symbols, and the transmission symbols are transmitted into additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) to be sent to a receiving terminal; the process of the receiving terminal is opposite to the process of a transmitting terminal; and the decoding terminal uses the LLSE to denoise, and uses ZF-DFE to decode, and inverse discrete cosine transformation (IDCT) is performed finally, so as to acquire the recovered video.
Owner:TAIYUAN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift
A method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift is disclosed. The present invention removes the effects of drift from a sequential series of waveforms obtained from a waveform-source device, or spectra, from a spectrometer, to produce for output a sequential series of drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra, respectively. In addition, the present invention performs a factor analysis, or alternatively a linear-least-squares analysis, on an array of the drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra to provide a set of drift-compensated principal factors; and, generates drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles from a profile trajectory lying within a space of the set of drift-compensated principal factors. In addition, in the case of spectra, the invention provides for conversion of the drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles to drift-compensated compositional profiles. The invention finds particular utility in the field of electron spectroscopy when the invention is applied to correcting sputter-depth-profile analyses for the effects of spectral drift caused by charging in insulating samples. The invention, by extension, also, finds utility in waveform processing in situations where a sequential series of waveforms having similar features are offset by arbitrary phase shifts, and, even more generally, in time-series analysis, where a time-series is affected by leading or lagging data.
Owner:IBM CORP
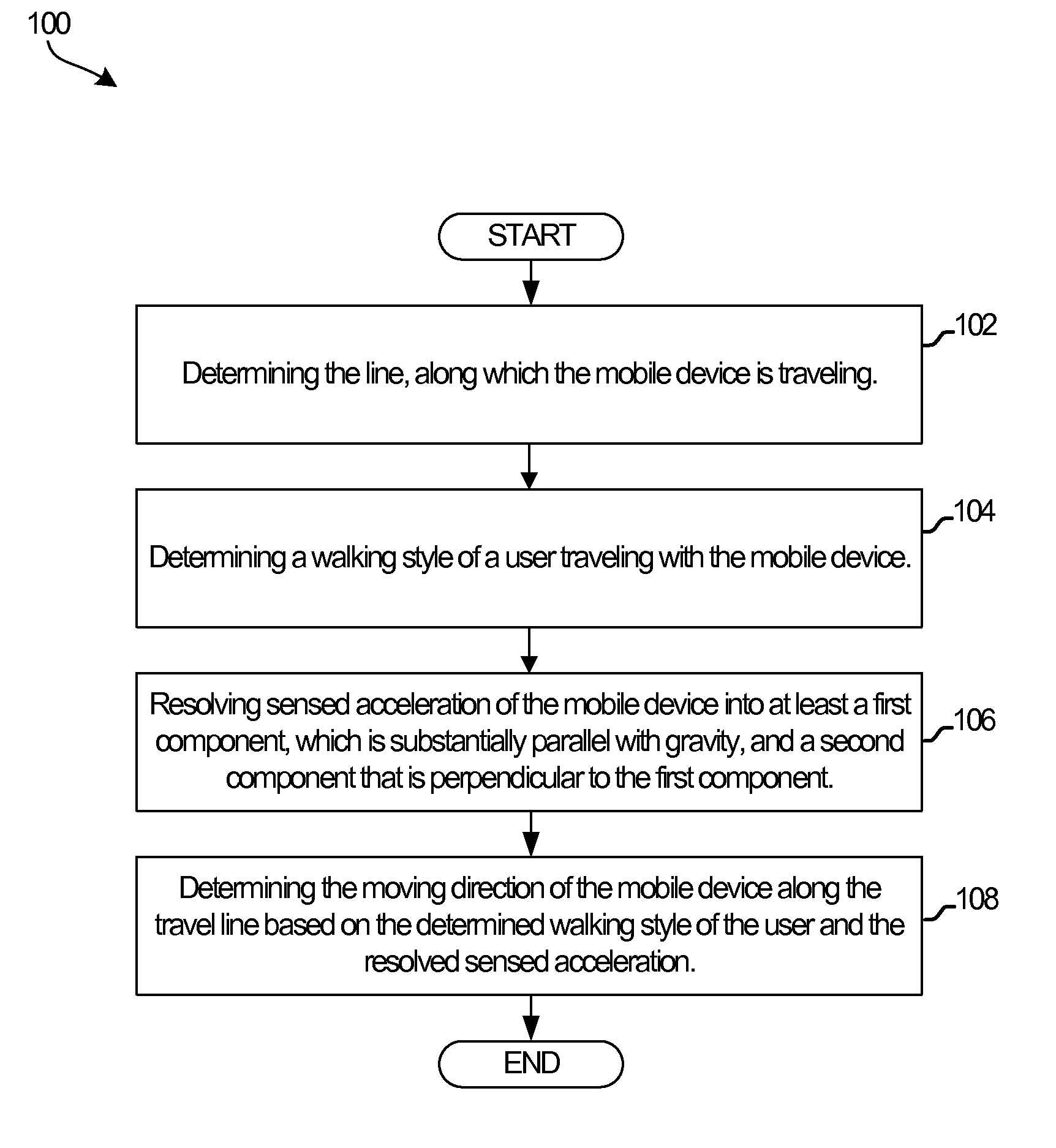
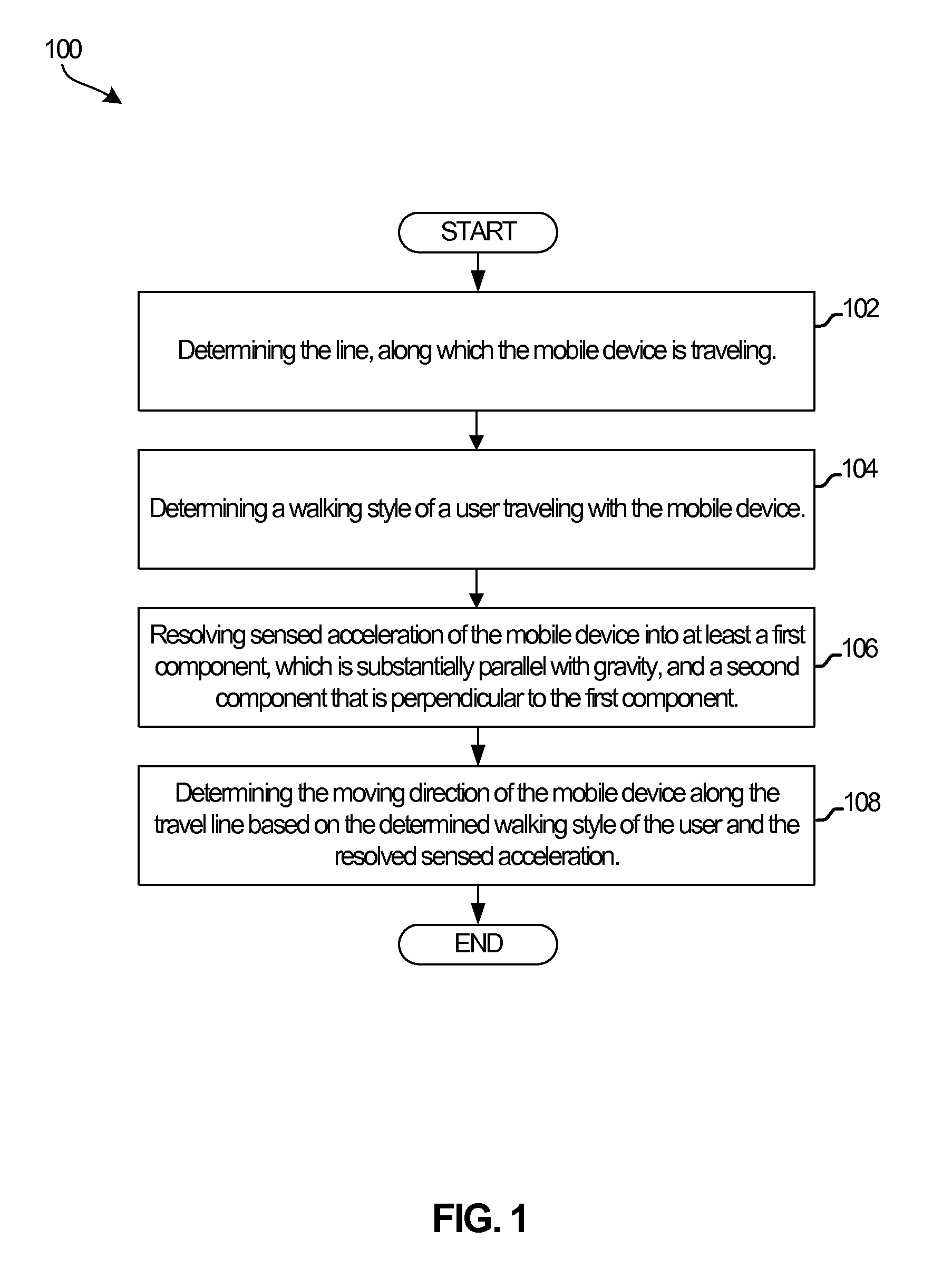
Travel direction detection
InactiveUS8578773B1Navigation by speed/acceleration measurementsAcceleration measurementDirection detectionMobile device
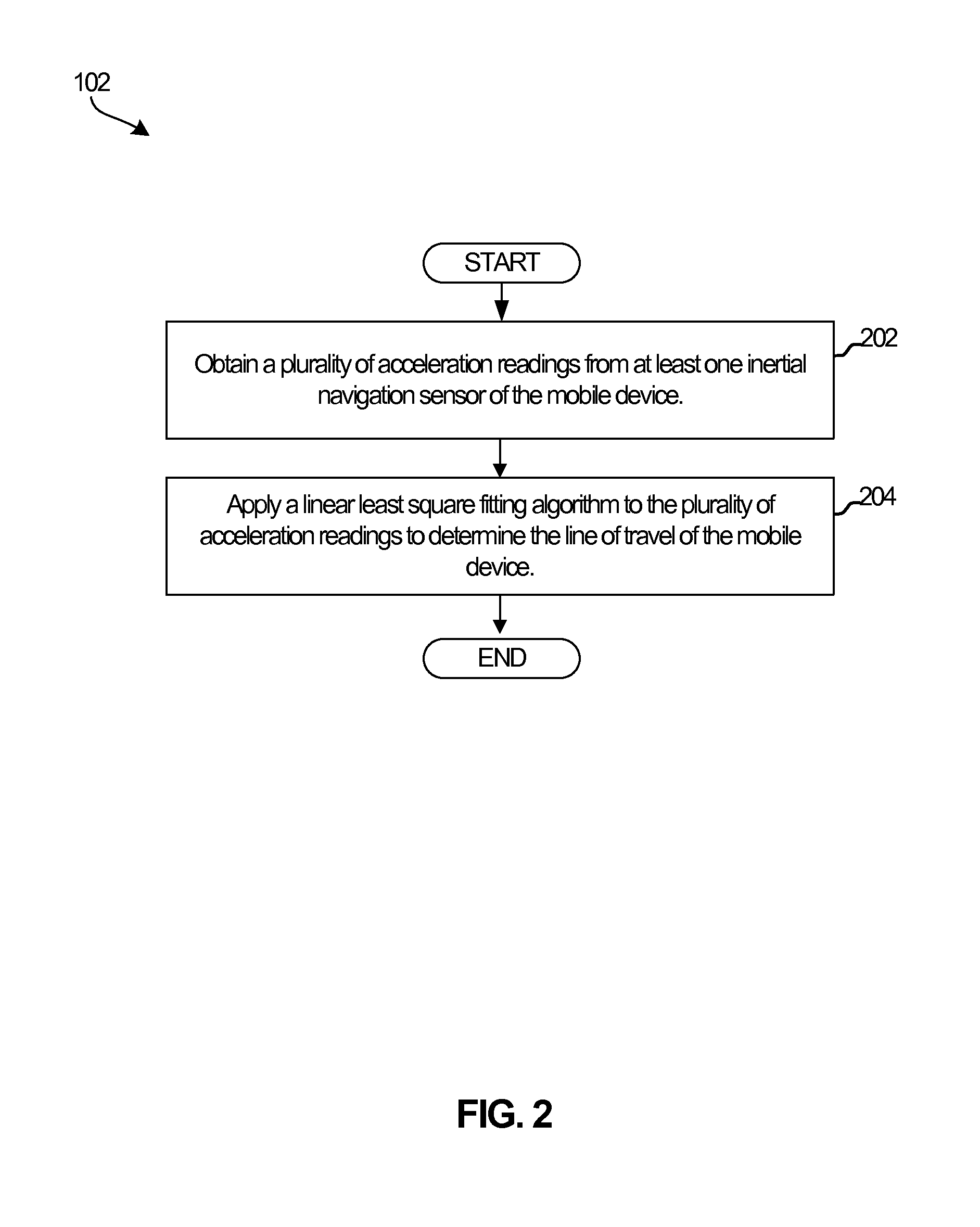
A device and method of determining a travel direction of a mobile device carried by a user are disclosed. The method includes determining a line along which the mobile device is traveling, where the determining may be based on sensed acceleration of the mobile device. A walking style of the user traveling with the mobile device may be determined. The sensed acceleration may be resolved into at least two mutually perpendicular components. A first component may be substantially parallel with gravity, and a second component may be orthogonal to the first component. The travel direction of the mobile device along the travel line may be determined based on a user's walking style and the resolved sensed acceleration. The determining of the line may include applying a linear least square fitting method to a plurality of acceleration readings obtained from at least one inertial navigation sensor.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
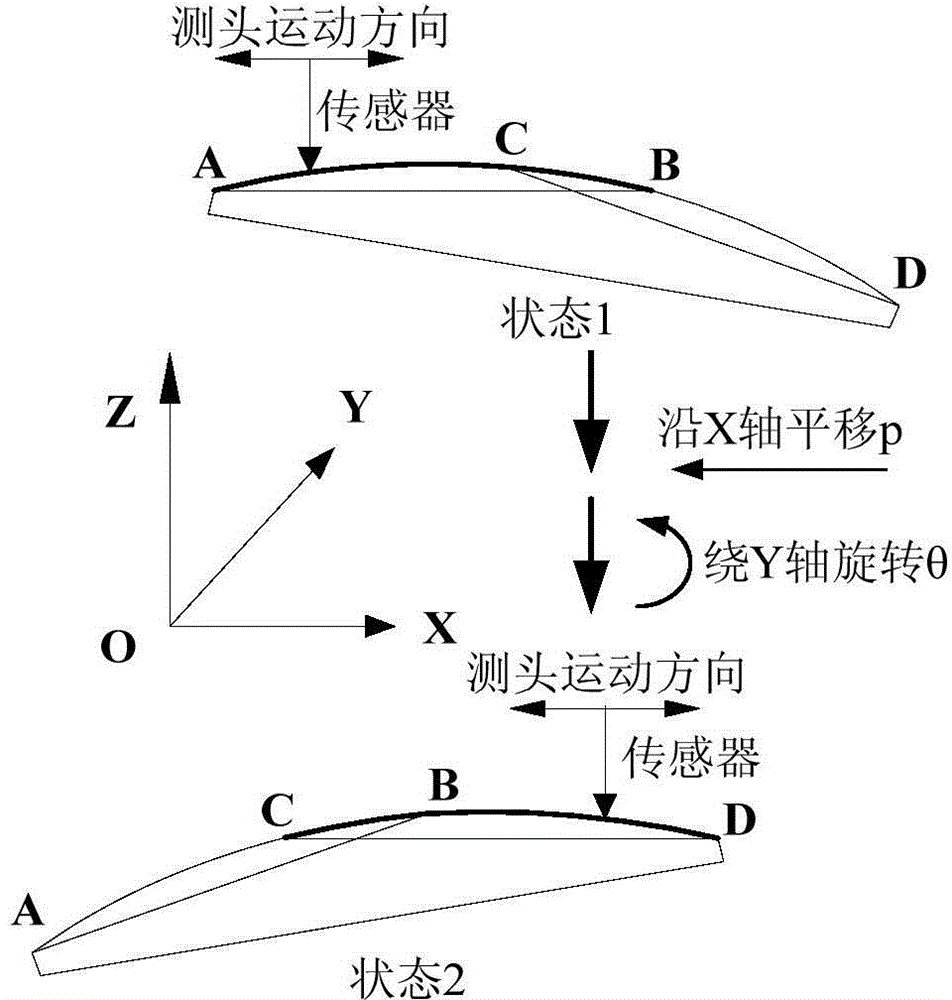
Splicing measurement method for two sections of profiles of large-caliber optical aspheric element
The invention relates to non-optical spherical elements, in particular to a splicing measurement method for two sections of profiles of a large-caliber optical aspheric element. The splicing measurement method includes providing a method of aligning data points of an overlapped area on the basis of a principle that radius of curvature is unchanged; building a preliminary optimized mathematic model for twp-section surface figure profile splicing according to a multibody system kinetic theory, a slope difference value and an inversion method; according to a simulation result of the preliminary splicing mathematic model, performing linear least square fitting on preliminary splicing errors, removing accumulated errors, and providing a final two-section splicing optimized algorithm. Experiments in which a Taylor Hobson contourgraph and an auxiliary measuring clamp are utilized to measure planar optical elements of 150mm and data processing by using the splicing optimized algorithm are performed, and results of the experiments show that maximum standard deviation of the splicing errors is 0.868 micrometer, and high-accuracy surface figure detection needs of optical elements at a grinding stage can be met.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Least square direction finding method based on time difference of arrival of sound signals
InactiveCN107861096AGood precisionImprove estimation accuracyDirection/deviation determination systemsSound sourcesEstimation methods
The invention provides a least square direction finding method based on the time difference of arrival of sound signals. The basic idea is that an absolute value type cost function is adopted when a Lagrange multiplier is solved so as to enable the Lagrange multiplier to have a clear expression; the standard sound velocity is adopted to replace the measured sound velocity when the Lagrange multiplier is calculated, so that the whole direction finding process is independent of the sound velocity; and rough direction estimation for a sound source is acquired by adopting a linear least square direction finding technology to serve as a judgment basis when the Lagrange multiplier is calculated. Compared with the prior art, the beneficial effects lie in that the direction finding method providedby the invention is better than the traditional estimation method in terms of the accuracy of azimuth angle and pitch angle estimation and is more excellent in accuracy of pitch angle estimation.
Owner:中国人民解放军陆军炮兵防空兵学院
Convex optimization-based high-precision positioning method
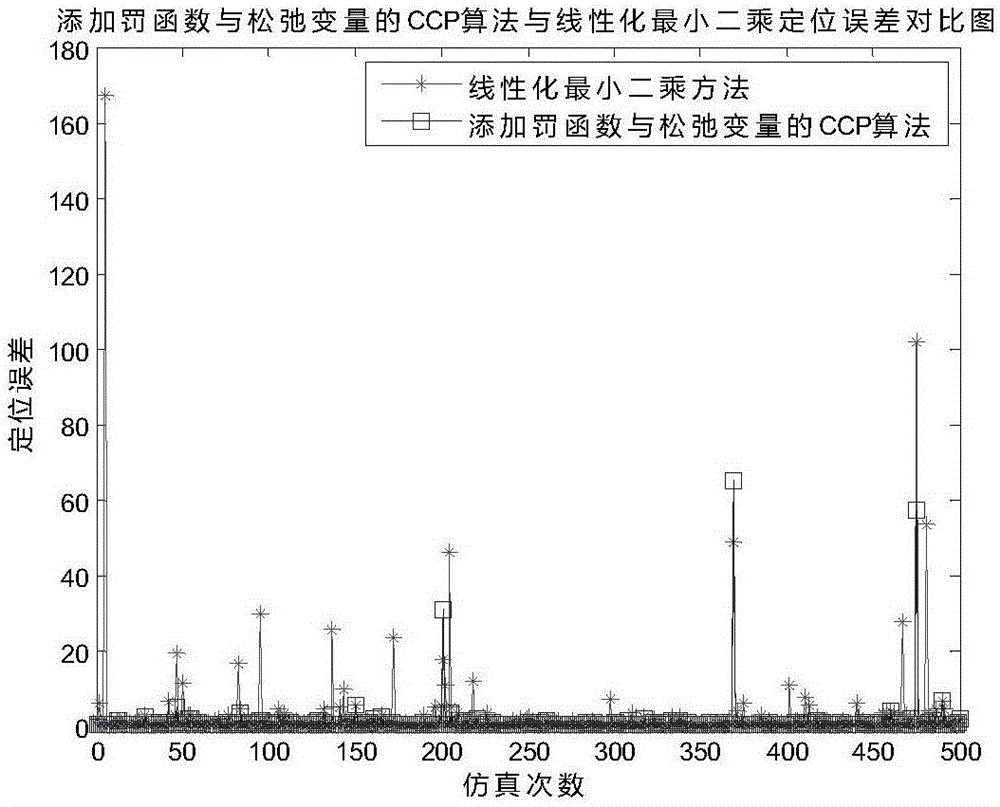
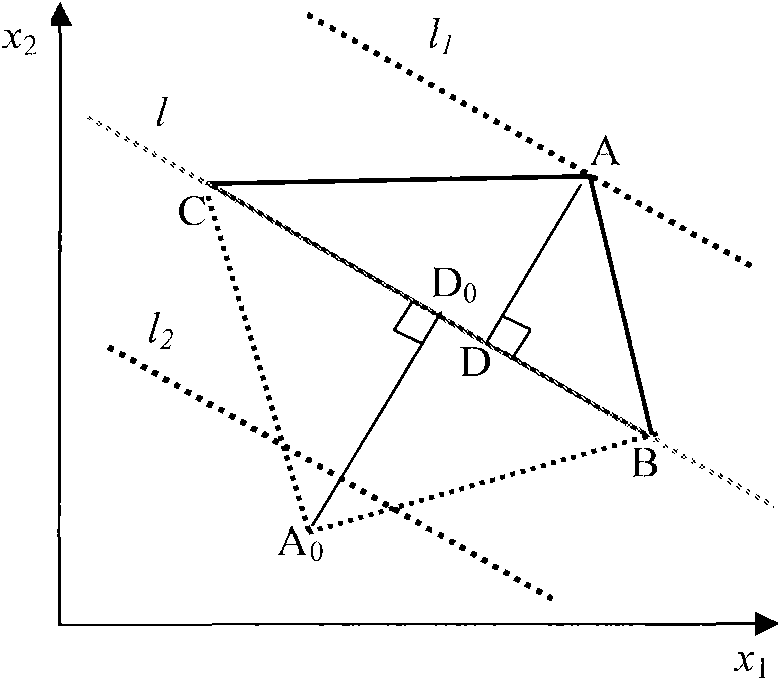
ActiveCN106556828ARelax restrictionsExpand the feasible areaWave based measurement systemsSlack variableUnderwater
The present invention relates to a convex optimization-based high-precision positioning method in an underwater target positioning problem. The method of the present invention comprises a step of setting the to-be-calculated coordinate of a target as x=[x0,y0,z0]<T>, wherein the step comprises firstly measuring the distances ri between the target to several surrounding beacons and the coordinates ai=[xi, yi, zi]<T> corresponding to the beacons, setting the range finding errors to each beacon as Epsilon i which follow the Gaussian distribution of which the expected value is 0 and the variance is sigma i<2>, and obtaining a range finding equation of the target, etc. By carrying out the formal transformation and adding the limitation conditions on a least-square structure of an underwater target spherical intersecting positioning equation, the least-square structure is transformed into a DC structural form in a convex optimization theory, and further a convex-concave process (CCP) method can be utilized to solve, and aiming at the disadvantage that a direct CCP algorithm need to iterate an initial value in a feasible domain, a slack variable and a penalty function are added in an original optimization equation, thereby expanding the feasible domain, and broadening the limitation to the initial value. Compared with a linear least-square positioning calculation method, the convex optimization-based high-precision positioning method enables the positioning precision to be improved, and realizes the high-precision underwater target positioning.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
High-spectrum image end member selection method based on linear least-squares support vector machine
InactiveCN101794443AGood effectImprove efficiencyWave based measurement systemsImage analysisLeast squares support vector machineComputer science
The invention provides a high-spectrum image end member selection method based on an LLSSVM (Linear Least-Squares Support Vector Machine), comprising the following steps of: 1. selecting N pixel points as initial end members; 2. using the end element in the i position of the present selected end members as '1' class and the rest of N-1 end members as '0' class, executing i=1 for the first time, and establishing corresponding LLSSVM discrimination functions, namely distance measuring and calculating functions; 3. sequentially calculating the distance of each pixel, if the absolute distance of one pixel is greater than 1, substituting the end member in the i position for the pixel, setting the i to be equal to 1 and then switching to the step 2; 4. i=i+1, if i is greater than N, switching to step 5, and otherwise, switching to the step 2; and 5. finishing when the current end member is the final selected end member. The high-spectrum image end member selection method is accomplished by adopting the LLSSVM as a main tool and has the advantages of no need of dimension-reduction pretreatment and low complexity.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
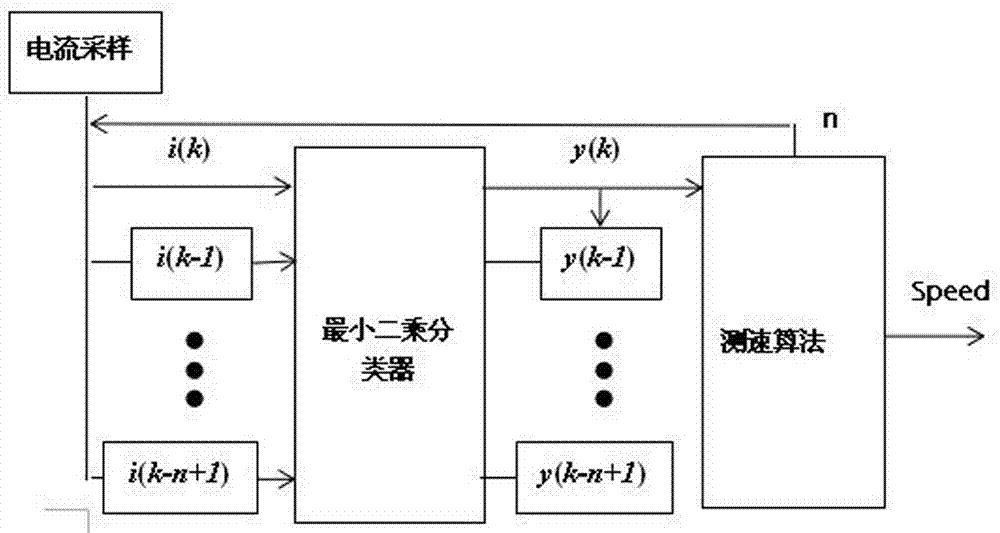
Brush DC motor speed regulation method based on least square classified velocity measurement
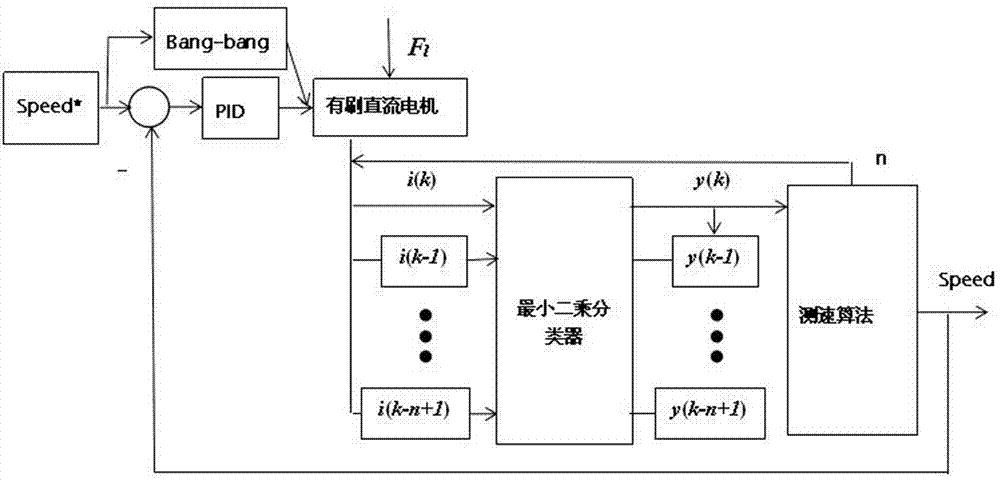
ActiveCN106953561ASmall amount of calculationAvoid learningField or armature current controlMotor speedComputer module
The invention relates to a brush DC motor speed regulation method based on least square classified velocity measurement. A least square classified velocity measurement module and PID speed regulation are adopted. The least square classified velocity measurement comprises that a linear least square classifier divides current sequences into a peak sequence and a non-peak sequence, the number of current peaks per revolution is fixed, and the motor speed is calculated. The PID speed regulation is a PID controller adopting speed feedback of the least square classified velocity measurement. The brush DC motor speed regulation method based on the least square classified velocity measurement adopts the least square classifier to identify the current peak, realizes the sensorless PID speed regulation based on the current ripple and the high tracking precision without sensor speed regulation of the brush DC motor, has the characteristics of simplified structure and capability of adapting to the complex environment. The least square classified calculation of offline training is simple.
Owner:FUZHOU UNIV
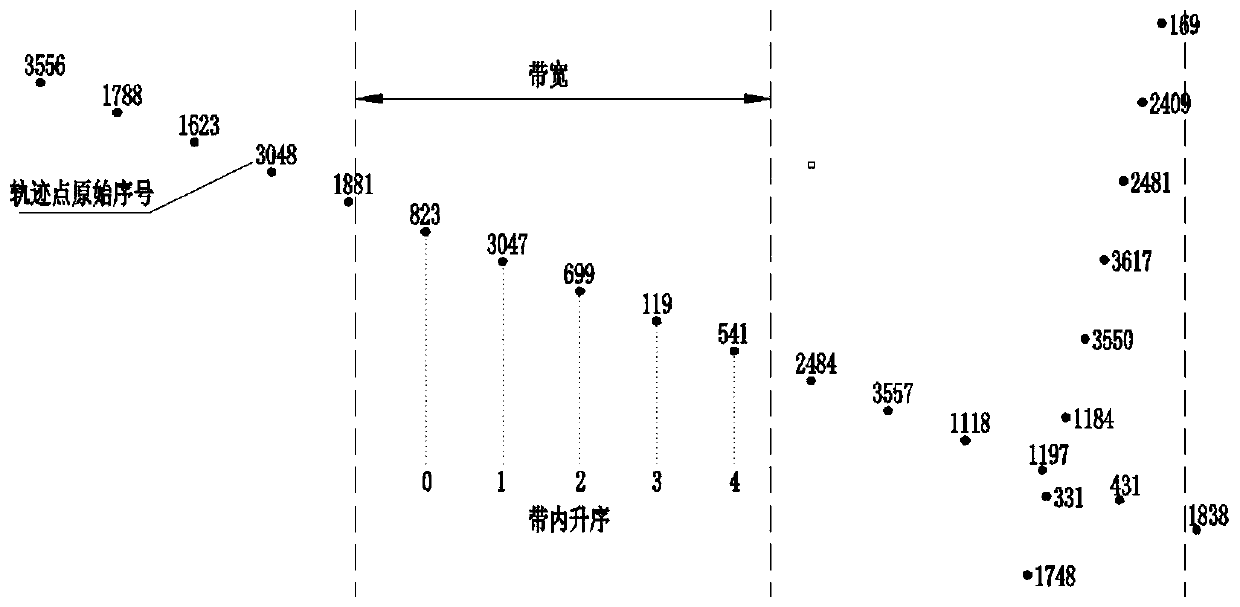
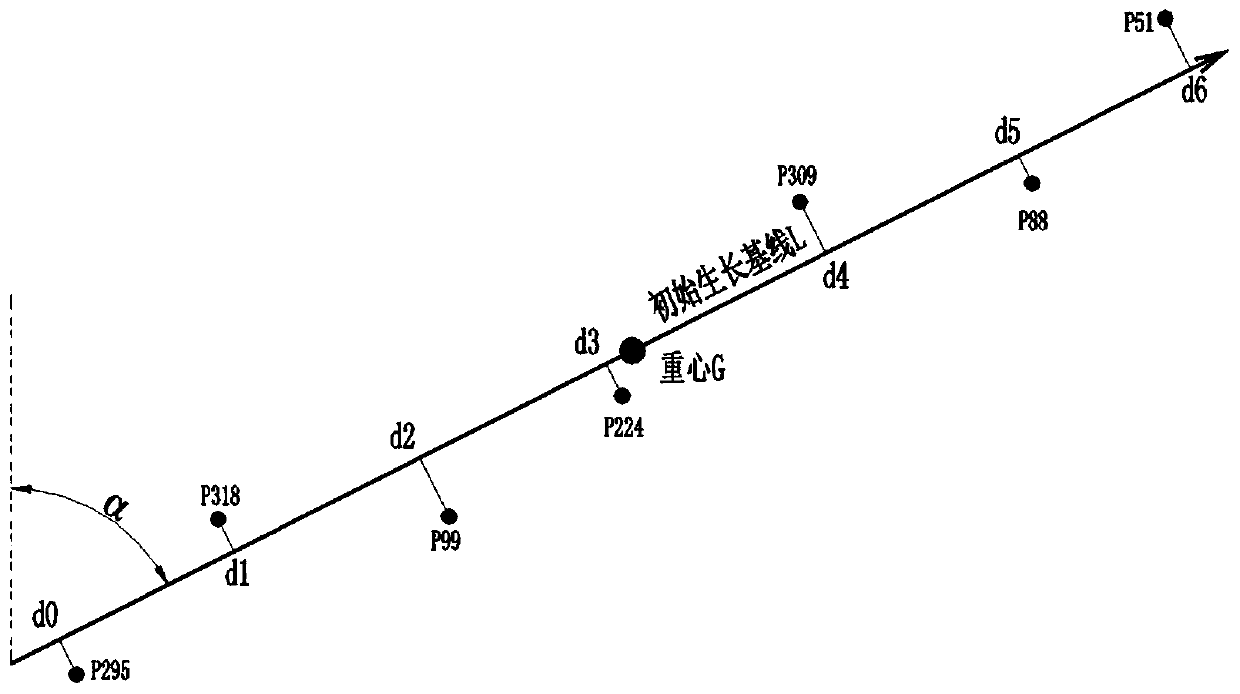
A road center line determination method based on linear sorting
ActiveCN109934889AAccurately track topological orientationAccurate trackingDrawing from basic elementsLinear least squaresGravitation
The invention discloses a road center line determination method based on linear sorting, which comprises the following steps: S1, randomly selecting a discrete track point as a reference point, and selecting track points of which the distances from the track points to the reference point are smaller than a preset distance to form a point set {P}; S2, performing linear least square fitting on the point set {P} to construct a growth baseline; S3, projecting the point set {P} to a growth baseline, and performing one-dimensional linear sorting on the track points according to the longitudinal displacement of projection points relative to the center of gravity to form an initial ordered queue {A}; S4, searching the track points to be sorted point by point, inserting the track points to be sorted into the ordered queue {A} and the point set {P} according to the projection positions of the track points to be sorted on the growth baseline, and updating the growth baseline of the point set {P}.According to the method, accurate and rapid linear sorting of disordered track points of the road center line is realized based on spatial zoning and a sliding growth baseline, and the sorted discrete track points are connected to obtain the road center line.
Owner:CHINA RAILWAY SIYUAN SURVEY & DESIGN GRP
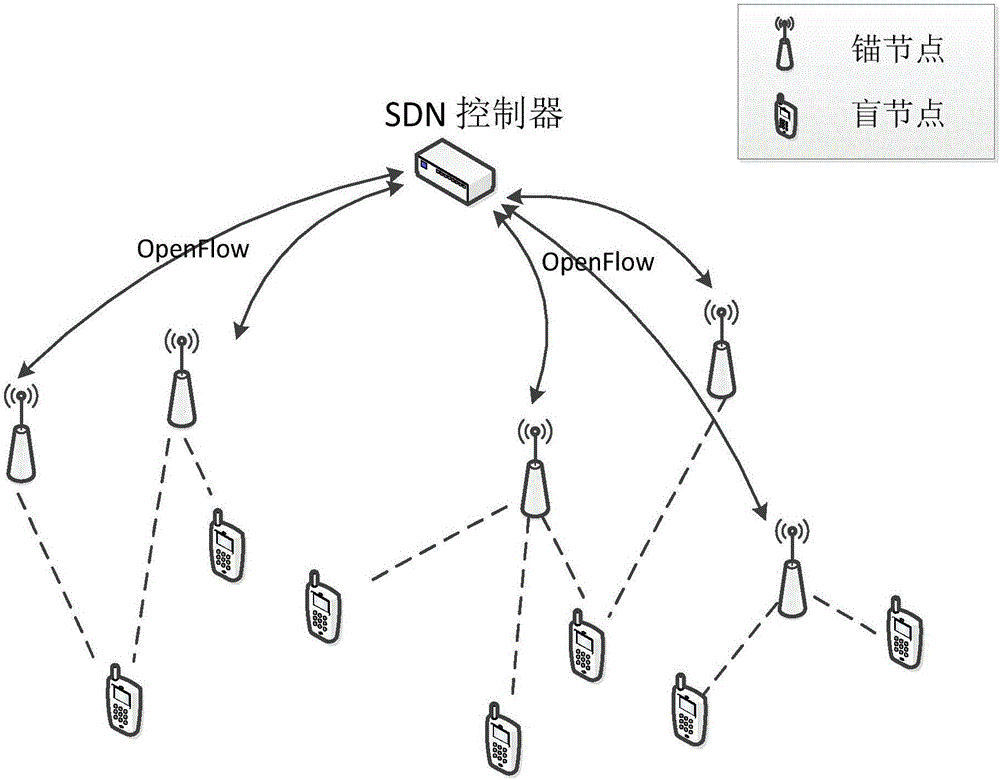
Positioning method in software defined wireless sensor network
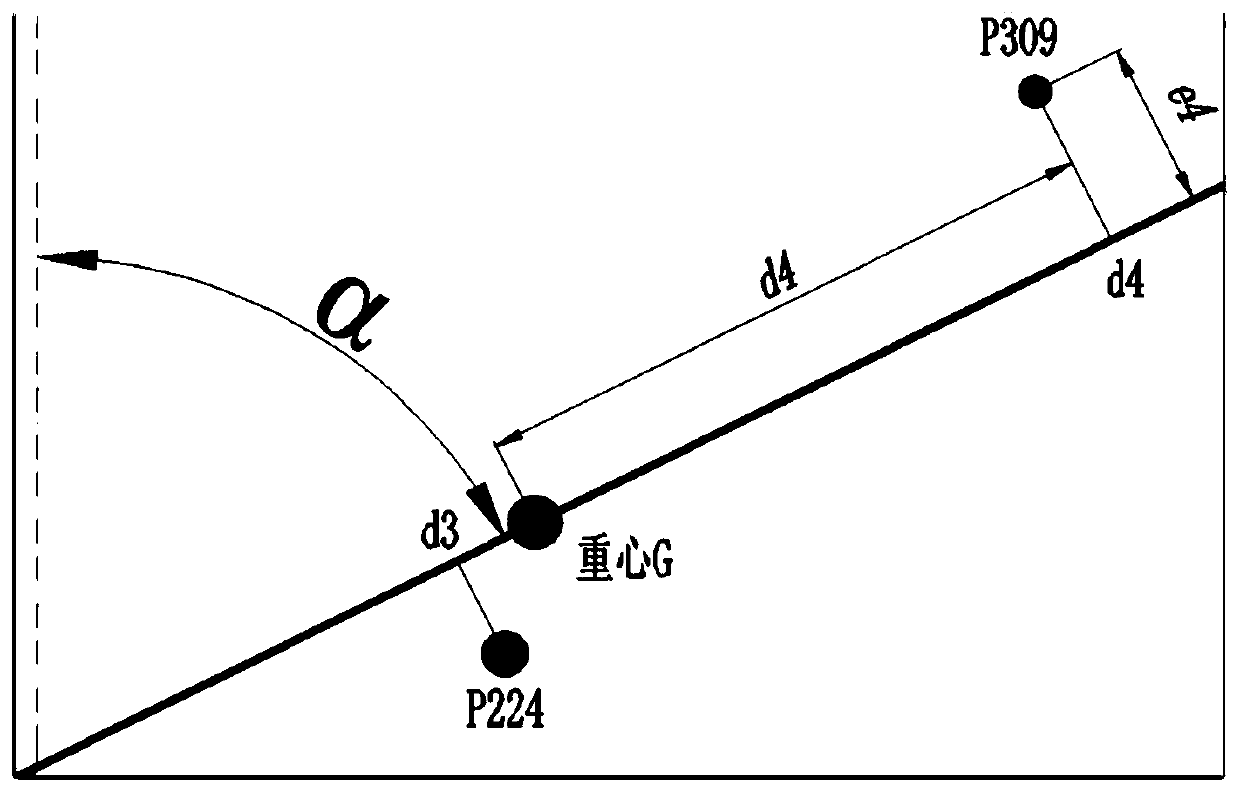
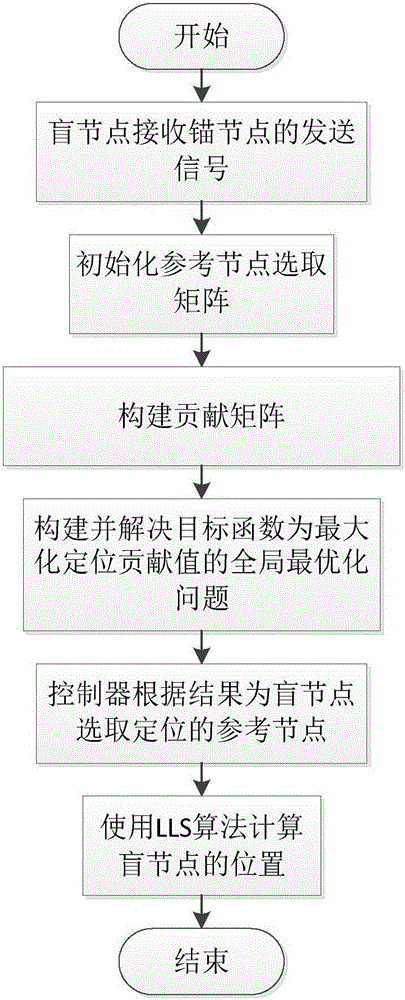
ActiveCN105960009ABig contributionHigh positioning accuracyNetwork topologiesMobile wireless sensor networkWireless sensor networking
The invention provides a positioning method in a software defined wireless sensor network. The method comprises the steps of setting a contribution matrix for nodes in a network, wherein a certain element in the matrix is the contribution value of an anchor node in the row which corresponds with the element to a blind node positioning result in the line that corresponds with the element; according to the set matrix, constructing an optimization problem by means of knowability of a controller in the software defined network to global network information, selecting a positioning node from all anchor nodes for the blind node through a 0-1 programming method, wherein a requirement that the sum of powers of selected links is not larger than the total power of the wireless sensor network is satisfied, and maximizing the contribution value of the selected links in the network on condition that the requirement is satisfied; and calculating the position of the blind node by means of a linear least square algorithm by means of the known position information of the selected positioning node. The positioning method can be used for selecting a node which most facilitates positioning on condition that the power of the wireless sensor network is limited and furthermore improves positioning precision.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Solid dielectric trap depth and density detection method based on thermally stimulated current
ActiveCN106596640AAvoid influenceImprove fault toleranceMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansFault tolerancePower flow
The invention discloses a solid dielectric trap depth and density detection method based on thermally stimulated current. The method is characterized in that thermoelectric stimulation is conducted on a solid dielectric film, a thermally stimulated current curve of the solid dielectric film is detected, current components caused by charge release of traps with different depths in the solid dielectric film are analyzed through a numerical integration method, a two-dimensional matrix formed by a characteristic function is obtained, the measured thermally stimulated current curve serves as input based on the nonnegative linear least-squares algorithm, and finally density distribution of the traps with different depths in the solid dielectric film is obtained. According to the method, it is not needed to assume the energy level distribution of the traps in the calculation process, the whole curve is automatically analyzed, and the probability of personal errors is eliminated; besides, the influence of wrong data like negative current data can be effectively avoided, and thus the method is more accordant with actual conditions and has better fault tolerance.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
High fidelity three-dimensional display method compatible with two-dimensional display based on LED backlight modulation
InactiveCN103926703AQuality assuranceReduce power consumptionOptical elementsTime domainIntensity coefficient
The invention provides a high fidelity three-dimensional display method compatible with two-dimensional display based on LED backlight modulation. A linear least square problem is obtained for a calculation error by establishing a backward compensation module of time domain psychological visual modulation display; a backlight intensity coefficient is introduced, and an optimization problem is obtained through the linear least square problem; the optimization problem is simplified and converted into a geological problem to be solved, and an optimal and improved scheme of the time domain psychological visual modulation display is obtained. The existing 3-D technology is improved, so that the three-dimensional display technology can be compatible backwards, a user can see the three-dimensional display with switch glasses, and meanwhile a 2-D image can be clearly provided without wearing the glasses. According to the scheme of the high fidelity three-dimensional display method compatible with two-dimensional display based on LED backlight modulation, power consumption is low, complexity is low, a 3-D image with high quality is provided with priority, and meanwhile the quality of the 2-D image can be ensured.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
Linear real-time estimation method of conductivity resistance-capacitance network parameter
InactiveCN102087317BEliminate the effects of uncertaintyAvoid uncertaintyFluid resistance measurementsCapacitanceAnti jamming
The invention relates to a linear real-time estimation method of a conductivity resistance-capacitance network parameter, belonging to the technical field of solution conductivity soft measurement. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: converting the measurement of solution conductivity into the parameter estimation of an equivalent resistance-capacitance network: on the basis of a mathematical model between a square wave excitation signal, a response direct-current voltage signal and two resistance and capacitance parameters of the equivalent resistance-capacitance network, carrying out multi-element polynomial fitting on the non-linear model off line; adopting an alternating-current square wave excitation resistance-capacitance network of various frequencies by taking the existence of various uncertainties into account during on-line measurement; meanwhile, establishing an over-determined equation set by utilizing the off line fitted multi-element polynomial model; and obtaining the real-time estimation of a resistance-capacitance parameter through a Gauss elimination finite step arithmetic operation and a radical operation of quartic equation solvingon the basis of linear least square principle. The method has the advantages of higher estimation speed and stronger anti-jamming capability and is suitable for the on-line real-time accurate measurement of the conductivity industry.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
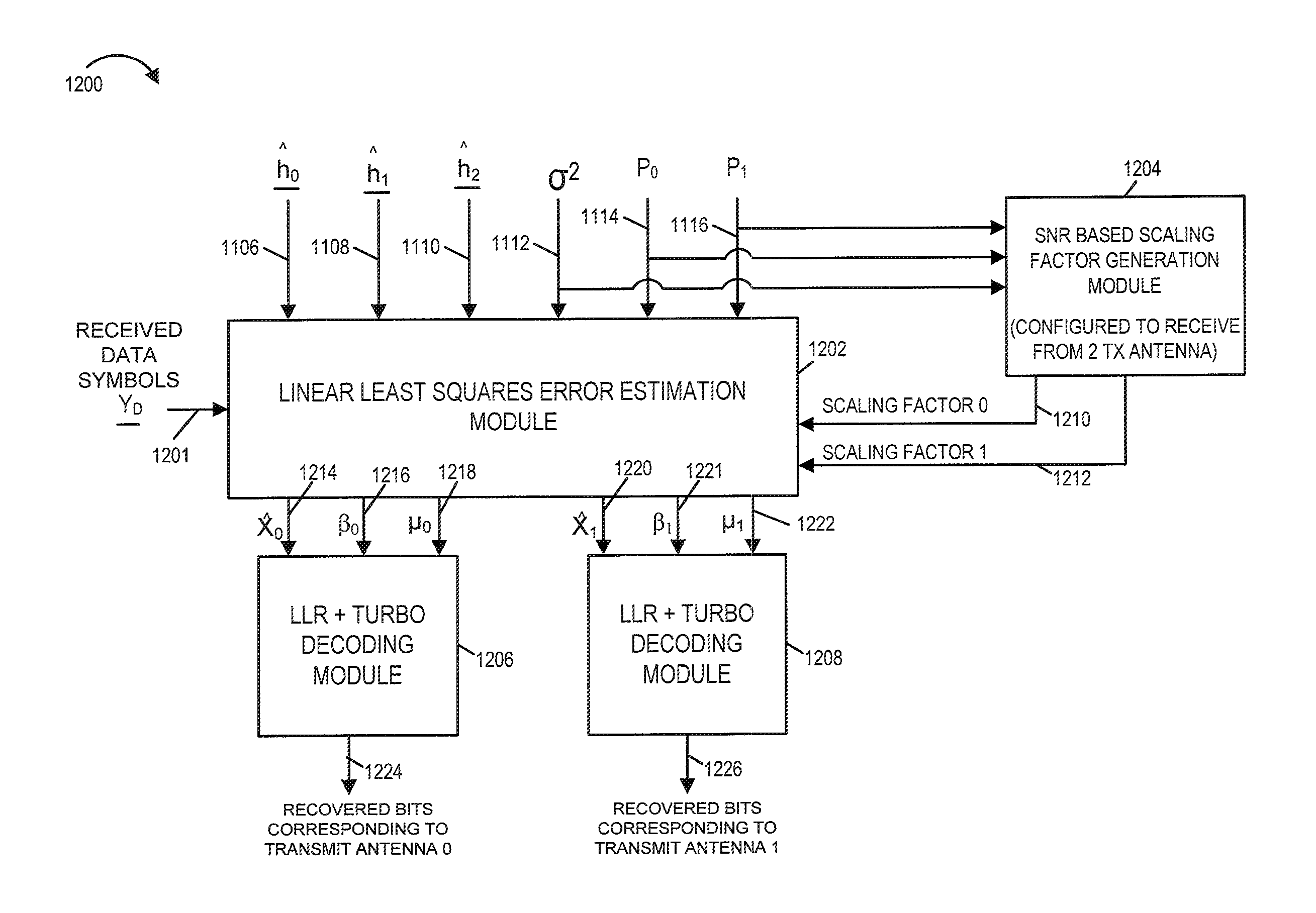
Scaling methods and apparatus using SNR estimate to avoid overflow
InactiveUS8311143B2Efficient implementationSpatial transmit diversityError detection/prevention using signal quality detectorLinear least squaresElectrical and Electronics engineering
Methods and apparatus for avoiding overflow and underflow conditions through the determination of appropriate scaling factors in signal estimation processing in a receiver are described. The receiver estimates transmitted symbols from one or more transmitter device antennas, while avoiding underflow and overflow conditions. A pilot based noise estimate and an estimated expected received signal power, corresponding to a transmit antenna, are used to generate an SNR corresponding to the transmit antenna. The generated SNR is used to determine, e.g., select from a fixed size set of predetermined scale factor values, a scale factor to be used for estimation processing associated with the transmit antenna. In some embodiments, the generated scaling factors are used by a fixed point processing linear least squares error estimation module. Scaling factor determination is performed at a rate which is slower than the rate at which symbols are received from a transmit antenna.
Owner:QUALCOMM INC
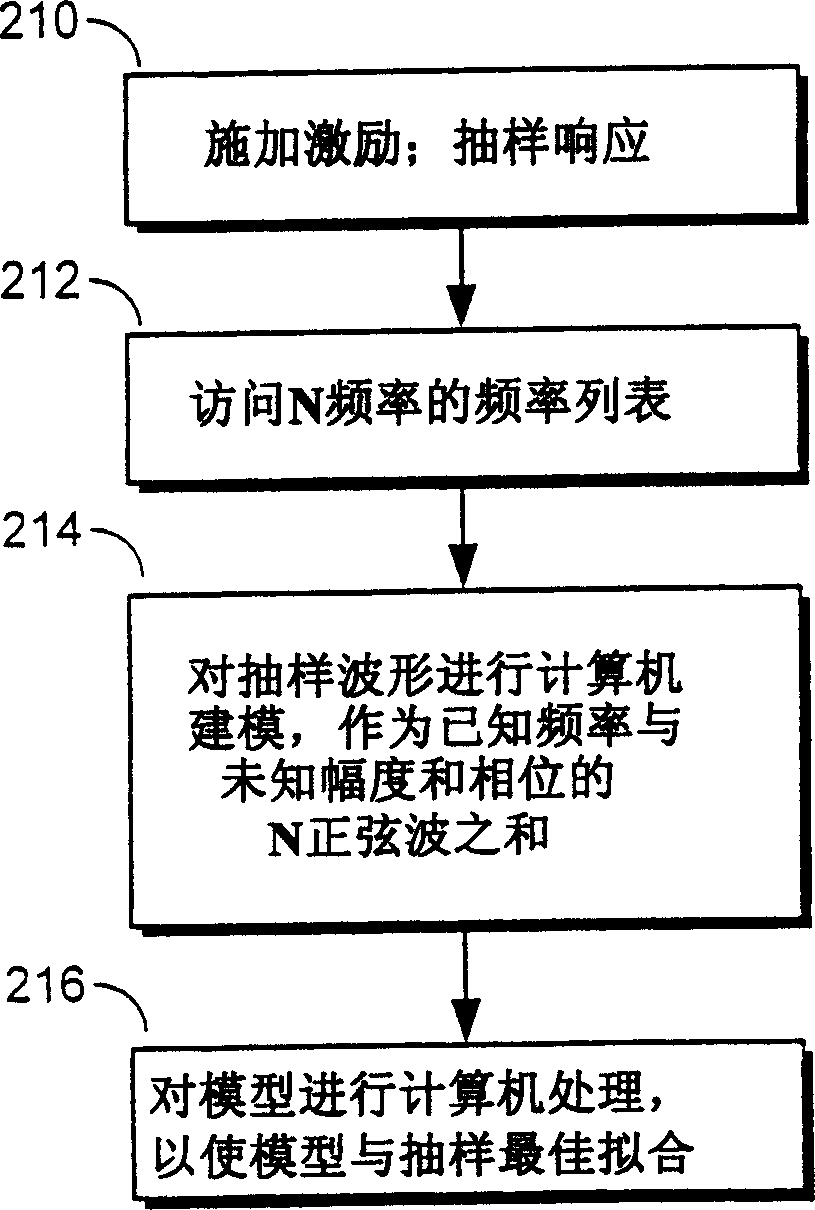
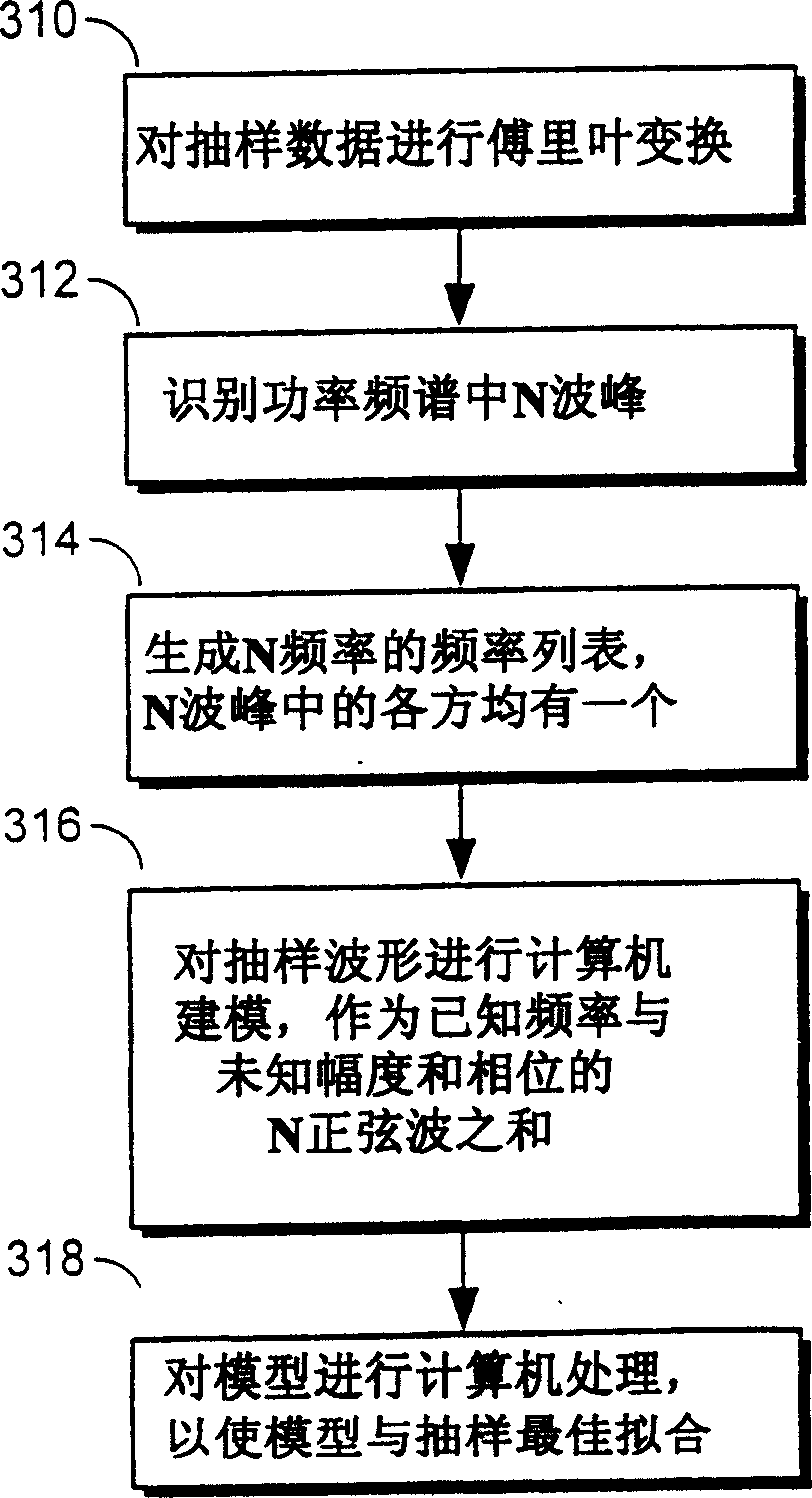
Low leakage technique for determining power spectra of non-coherently sampled data
The present invention provides a technique for determining the amplitudes of frequency components of a waveform sampled from an automatic test system, which includes assembling a list of N frequencies expected to be found in the sampled waveform. A test program running on the tester generally supplies the list of frequencies. The technique assumes that the sampled waveform conforms to an idealized waveform model that mathematically corresponds to a sum of N sinusoids. Each of the N sinusoids that make up the model has unknown amplitude and a frequency that equals one of the N frequencies in the list of frequencies. The technique attempts to solve for the unknown amplitude of each of the N frequencies by mathematically minimizing, via a linear least-squares algorithm, the difference between the model and the actual, sampled waveform.
Owner:TERADYNE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com