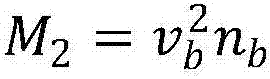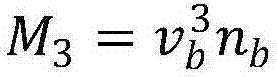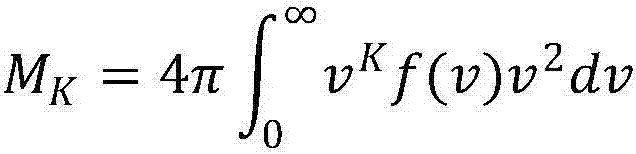Patents
Literature
48 results about "Electron spectroscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Electron spectroscopy is an analytical technique to study the electronic structure and its dynamics in atoms and molecules. In general an excitation source such as x-rays, electrons or synchrotron radiation will eject an electron from an inner-shell orbital of an atom. Detecting photoelectrons that are ejected by x-rays is called x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) or electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA). Detecting electrons that are ejected from higher orbitals to conserve energy during electron transitions is called Auger electron spectroscopy (AES).
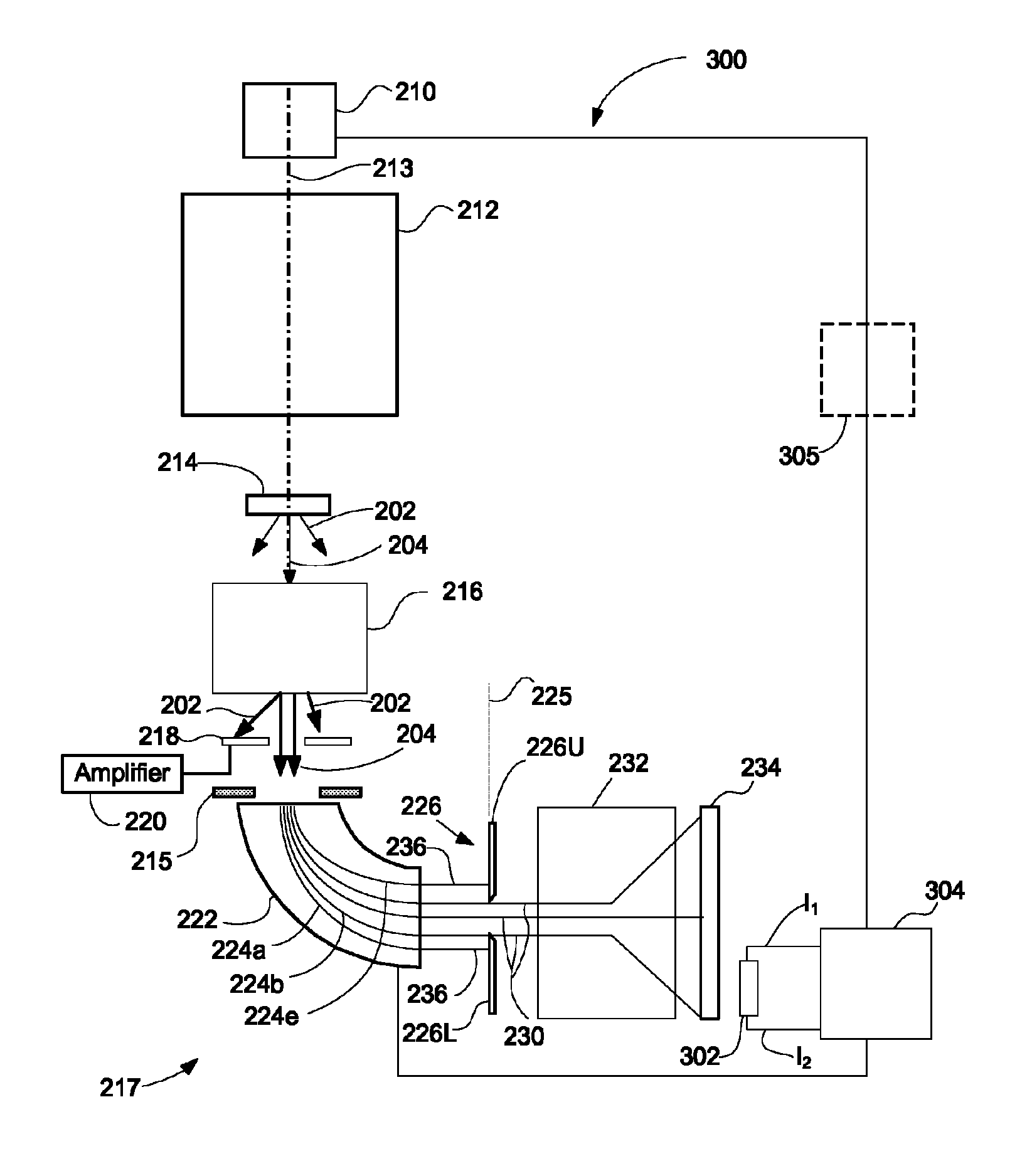
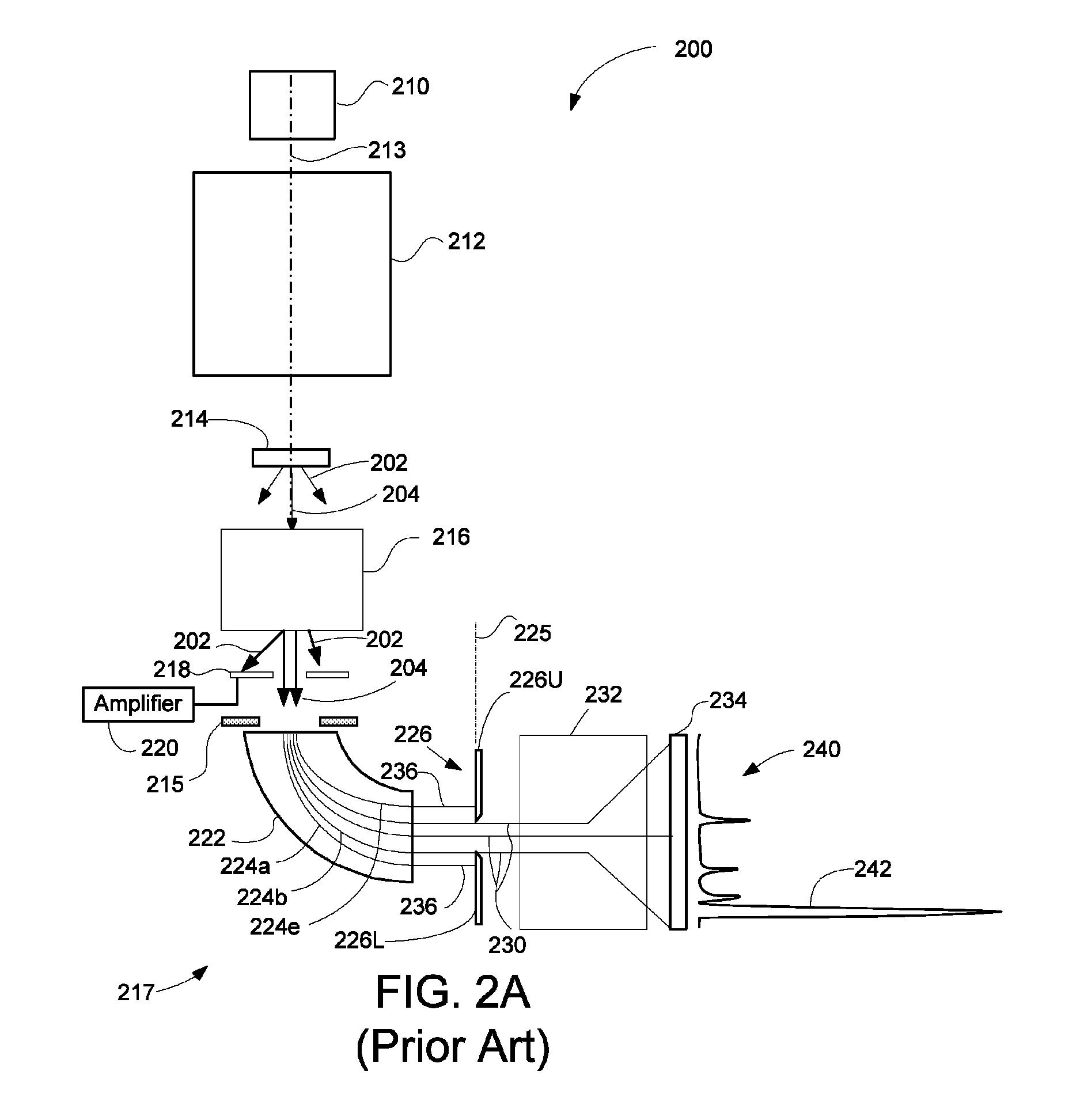
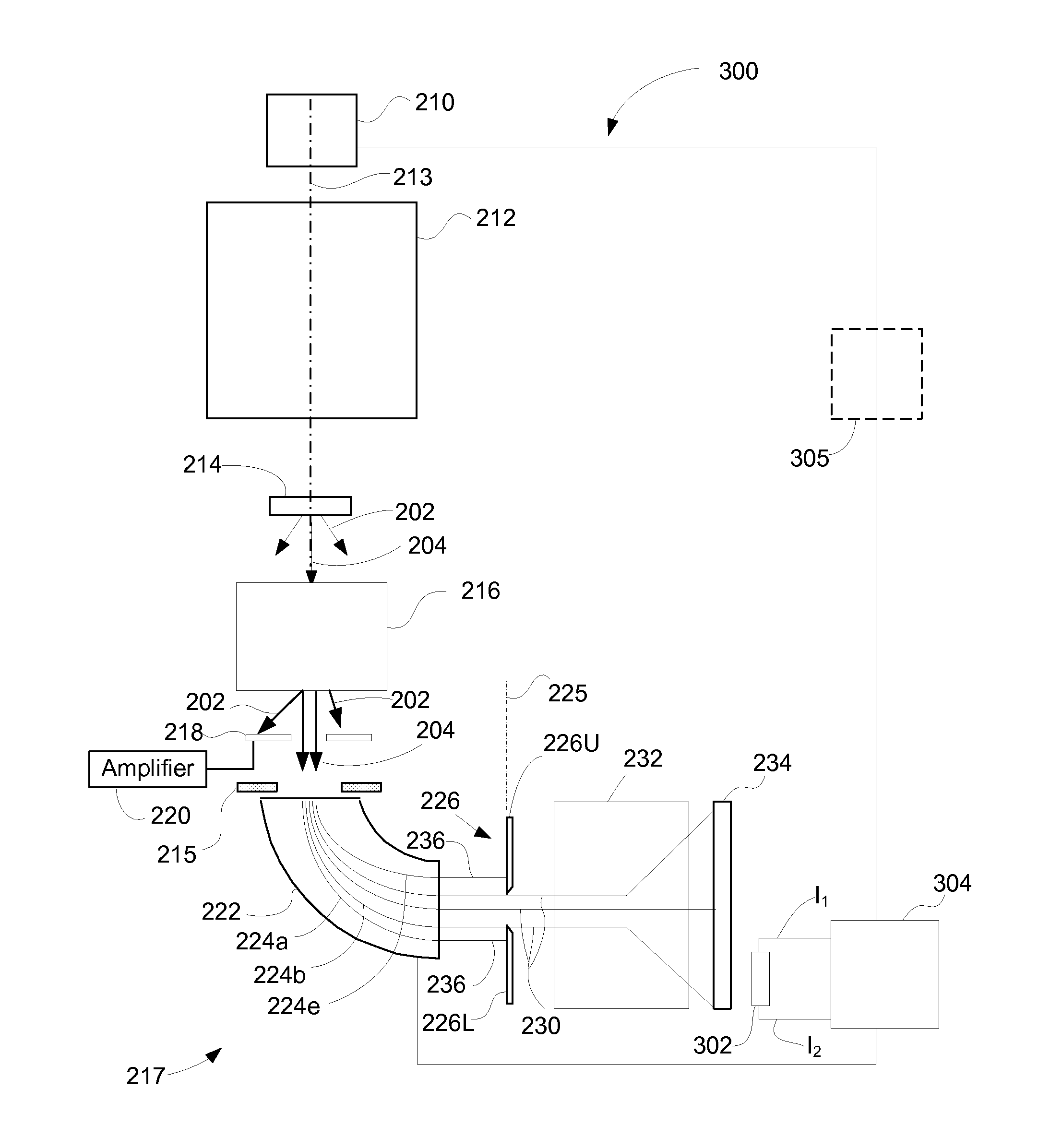
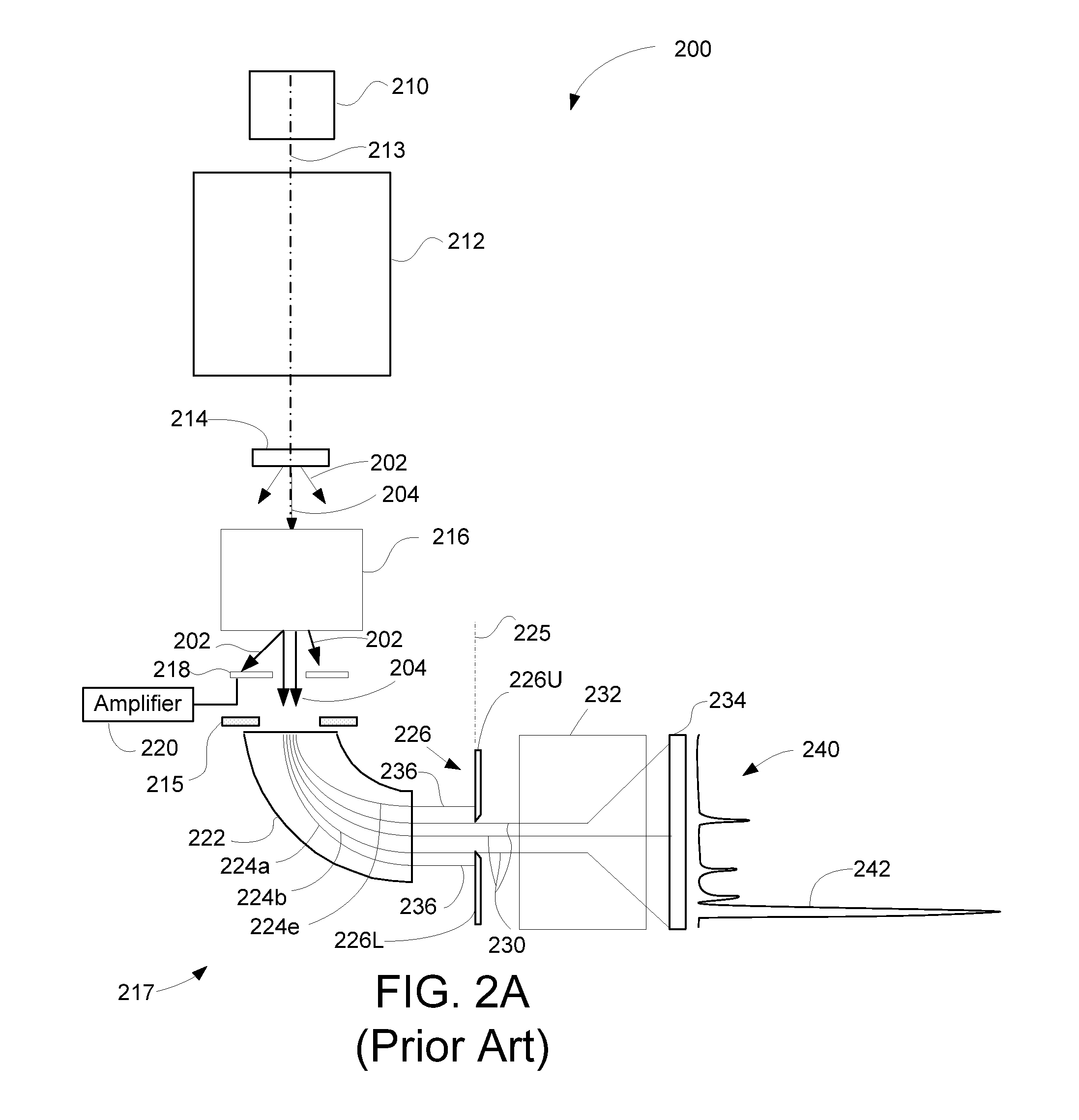
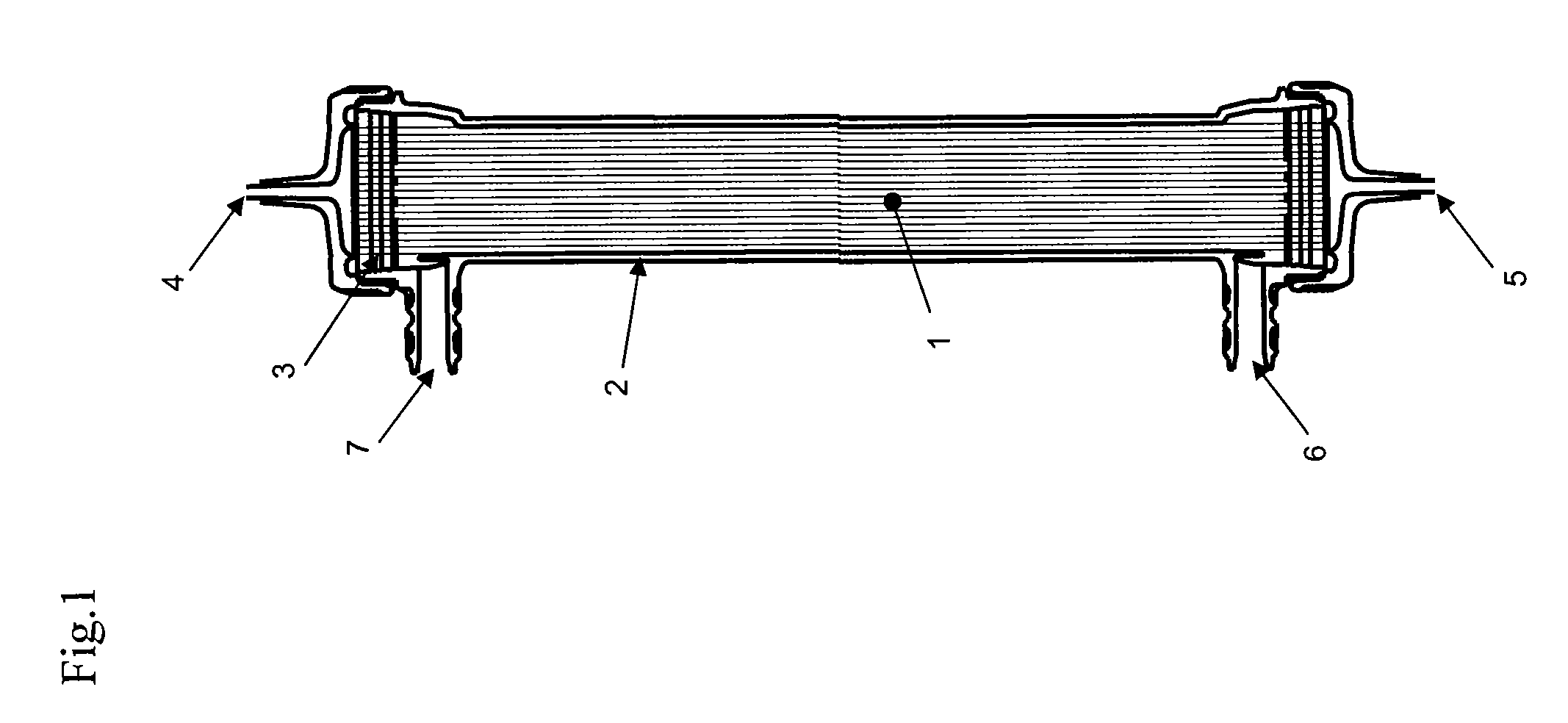
Detector system for use with transmission electron microscope spectroscopy
ActiveUS8334512B2Improve performanceRapid and accurate informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectron spectroscopyElectron microscope
A detector system for a transmission electron microscope includes a first detector for recording a pattern and a second detector for recording a position of a feature of the pattern. The second detector is preferably a position sensitive detector that provides accurate, rapid position information that can be used as feedback to stabilize the position of the pattern on the first detector. In one embodiment, the first detector detects an electron energy loss electron spectrum, and the second detector, positioned behind the first detector and detecting electrons that pass through the first detector, detects the position of the zero-loss peak and adjusts the electron path to stabilize the position of the spectrum on the first detector.
Owner:FEI CO
Separation membrane, method of producing the same and separation membrane module using the separation membrane
ActiveUS20110017654A1Decreasing performance of membraneImprove hydrophobicitySolvent extractionGlovesPhysical chemistryElectron spectroscopy
A separation membrane includes a membrane comprising a polymer, characterized in that a functional layer is formed on the surface in one side of the membrane, the peak area percentage of carbon derived from ester group measured by the electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) on the surface of the preceding functional layer is 0.1% (by atomic number) or more but not more than 10 (% by atomic number), and the peak area percentage of carbon derived from ester group measured by the electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) on the surface opposite to the functional layer is not more than 10 (% by atomic number). A separation membrane module suffering from little sticking of organic matters, proteins, platelets and so on is provided with the separation membrane as a built-in membrane.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
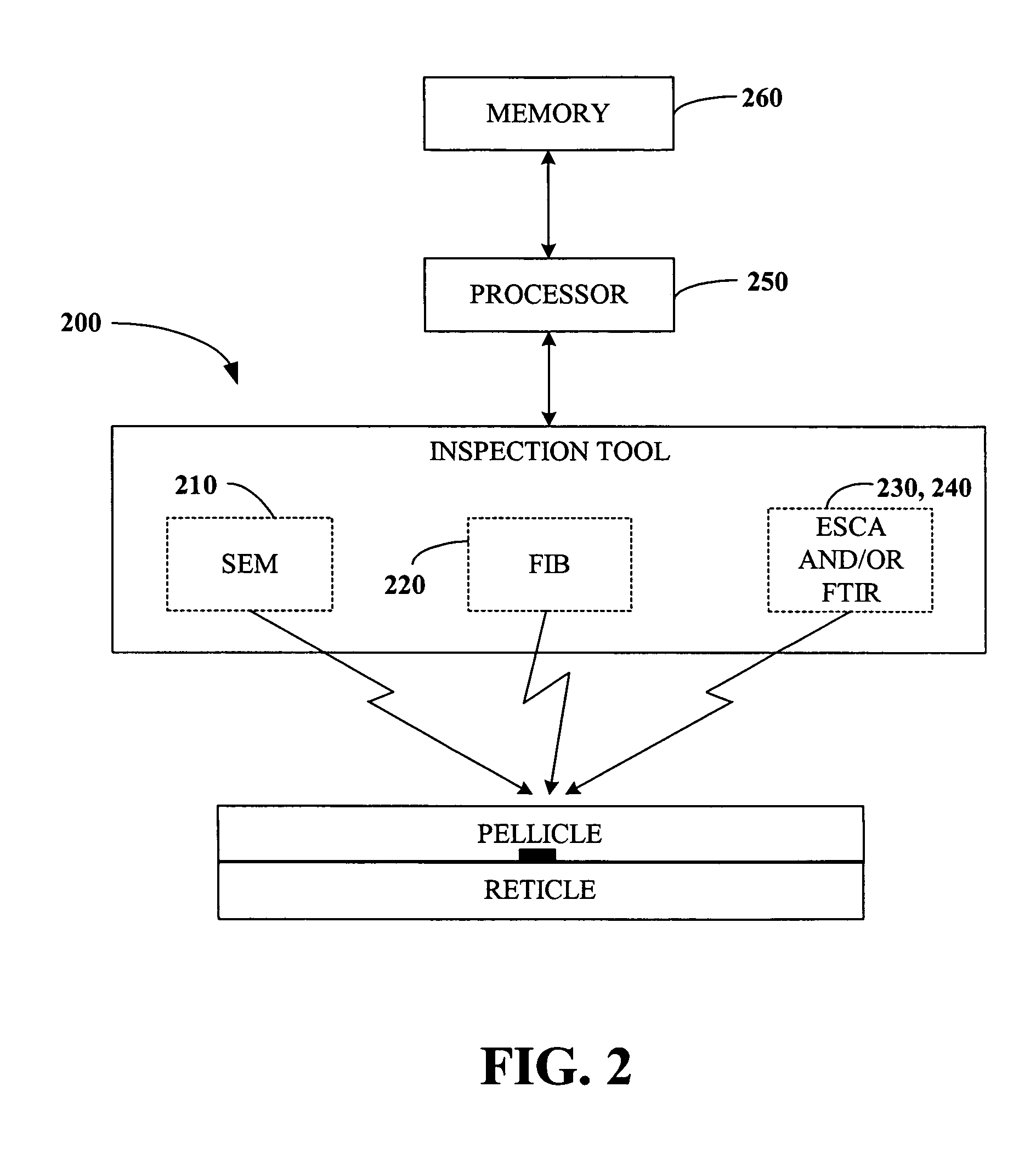
Real time analytical monitor for soft defects on reticle during reticle inspection
ActiveUS7069155B1Improve accuracyAccurate decisionImage enhancementImage analysisReal time analysisChemical signature
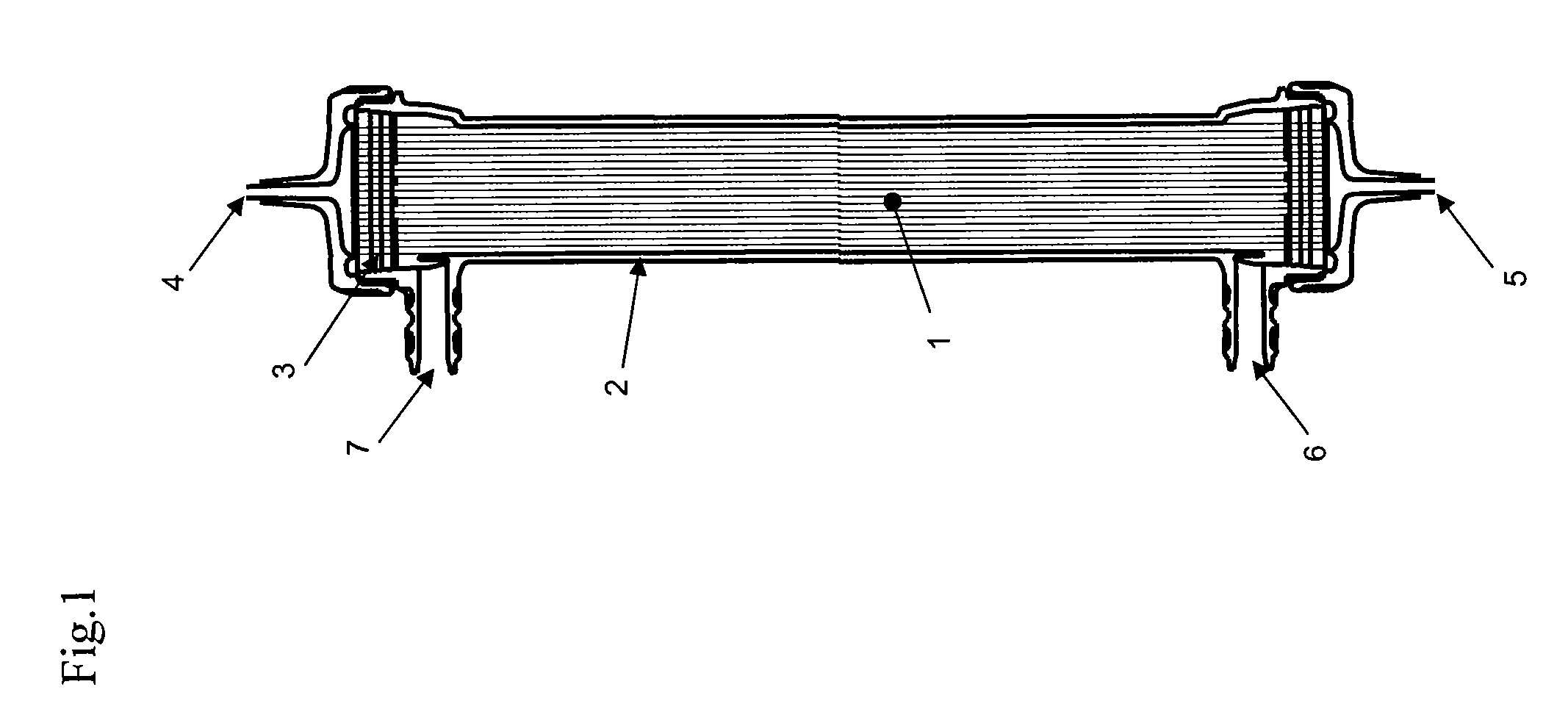
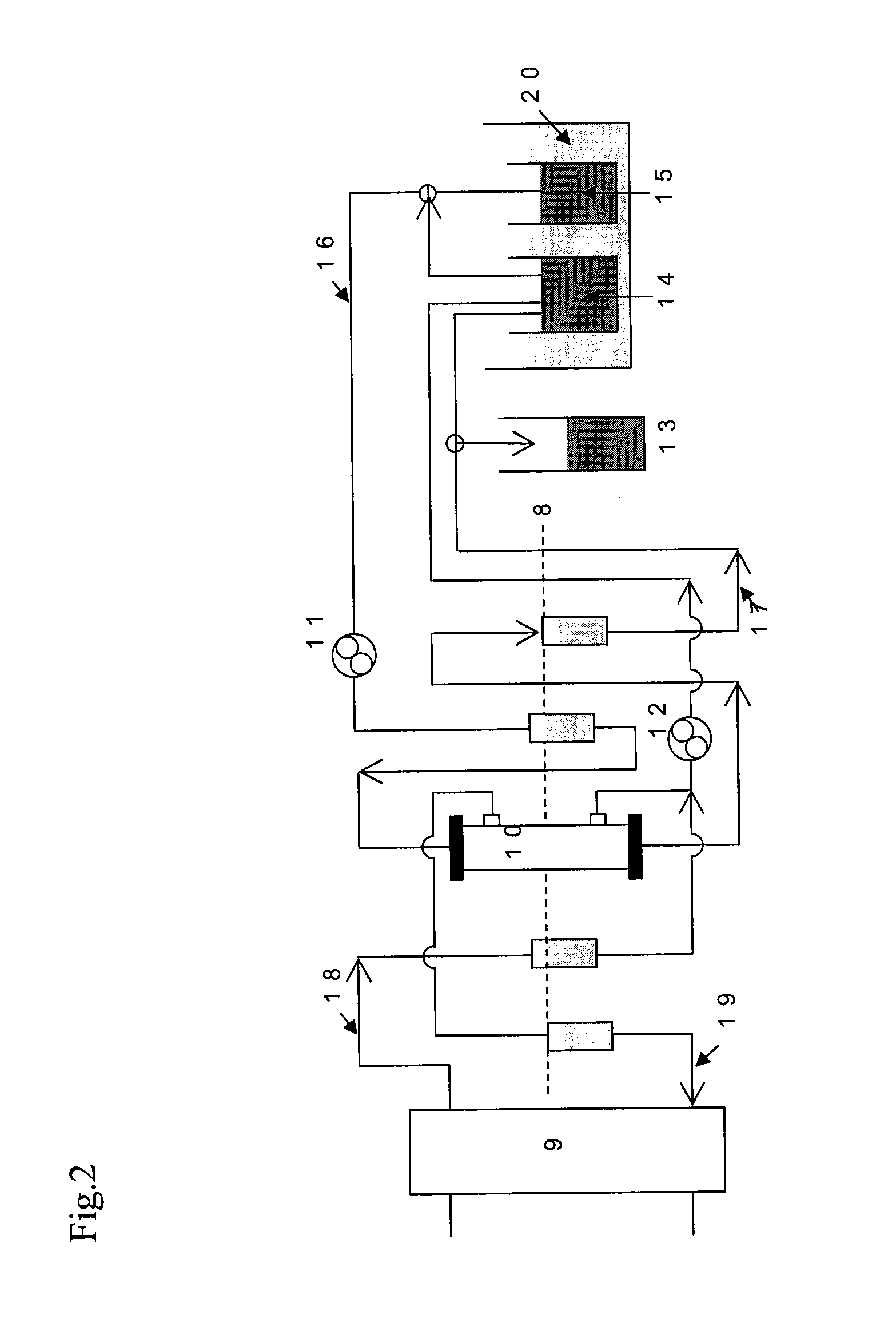
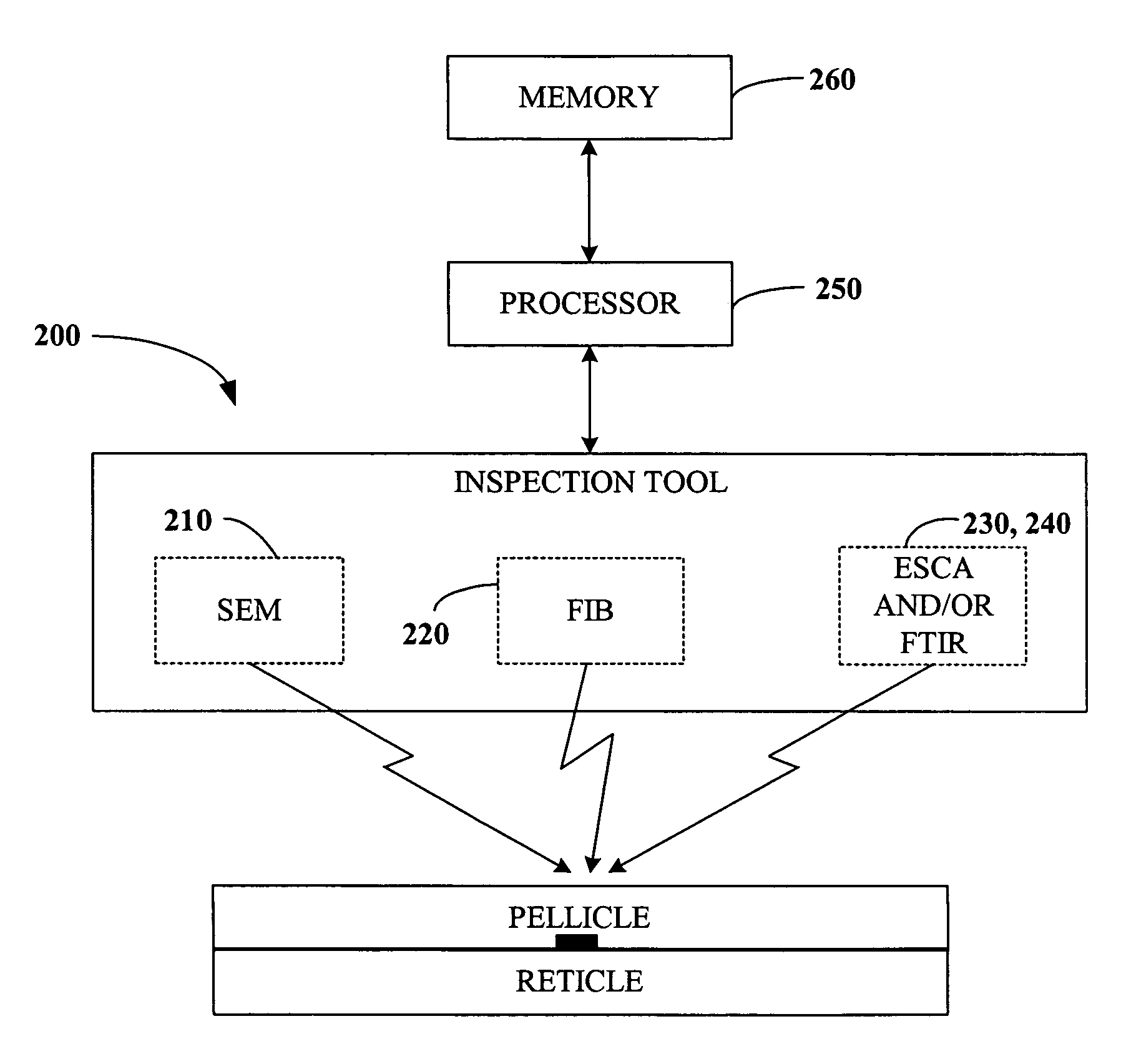
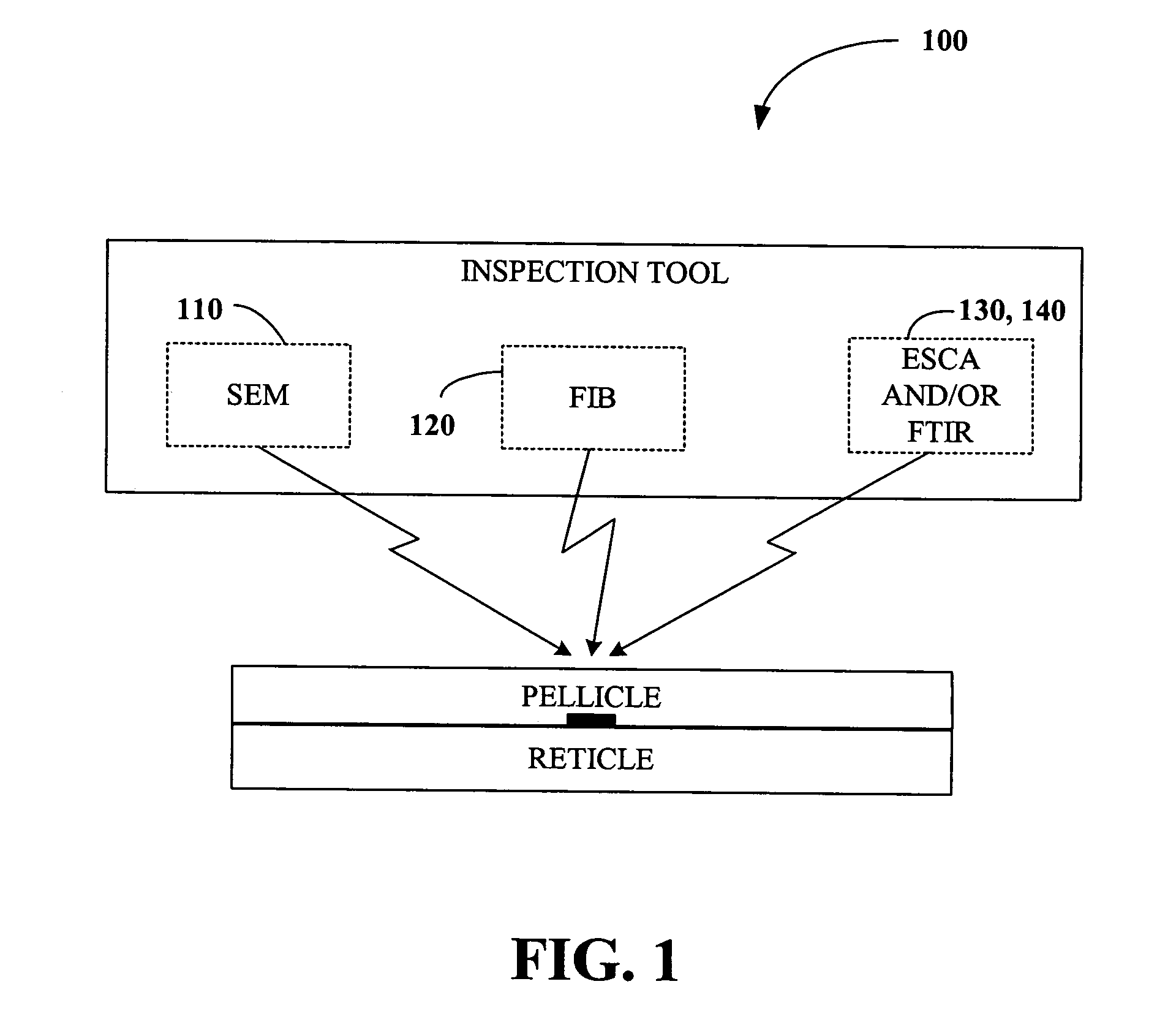
The present invention generally relates to semiconductor processing, and in particular to methods and systems for analyzing photolithographic reticle defects that include detecting soft defects on a reticle and analyzing the material composition of the defects for a particular chemical signature. Specifically, the present invention scans and images a soft defect via an optical inspection scan of a reticle, mills the defect using a Focused Ion Beam, and analyzes the defect for signatures using Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis and / or Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy. The present invention thus provides for real-time analysis of the chemical composition of a soft defect on a reticle without the need for a defect identification navigation system. According to an aspect of the present invention, reticle defects can be monitored without removal of a pellicle, thus facilitating increased throughput and decreased cost in reticle repair and / or cleaning. According to another aspect of the invention, signatures occurring in trace amounts can be removed via employing a Focused Ion Beam in a non-reactive gas environment.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Detector System for Use with Transmission Electron Microscope Spectroscopy
ActiveUS20120049060A1Improve performanceRapid and accurate informationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesElectron spectroscopyElectron microscope
A detector system for a transmission electron microscope includes a first detector for recording a pattern and a second detector for recording a position of a feature of the pattern. The second detector is preferably a position sensitive detector that provides accurate, rapid position information that can be used as feedback to stabilize the position of the pattern on the first detector. In one embodiment, the first detector detects an electron energy loss electron spectrum, and the second detector, positioned behind the first detector and detecting electrons that pass through the first detector, detects the position of the zero-loss peak and adjusts the electron path to stabilize the position of the spectrum on the first detector.
Owner:FEI CO
Separator material and method of producing the same, and alkali secondary battery separator
InactiveUS20060147804A1Improve the level ofAlkaline accumulatorsFinal product manufacturePolyolefinCombustion
A separator material of the present invention is a sulfonated nonwoven that comprises a polyolefin ultra-fine short fiber having a fineness of less than 0.5 dtex and other polyolefin short fiber(s). The other polyolefin short fibers include a polyolefin thermal bonding short fiber. At least a portion of the polyolefin thermal bonding short fiber is flattened to bond the component fibers together. The nonwoven has a specific surface area in a range of 0.6 m2 / g to 1.5 m2 / g and satisfies the following ranges. (1) A ratio (S / C)E of the number of sulfur atoms (S) to the number of carbon atoms (C) in the nonwoven, as measured by Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA), is in a range of 5×10−3 to 60×10−3. (2) A ratio (S / C)B of the number of sulfur atoms (S) to the number of carbon atoms (C) in the nonwoven, as measured by a flask combustion technique, is in a range of 2.5×10−3 to 7×10−3. (3) A ratio (S / C)E / (S / C)B (depth of sulfonation) of (S / C)E to (S / C)B is in a range of 1.5 to 12. Thus, a separator material that has a high level of self-discharging performance when charge and discharge are repeatedly performed, a high level of process performance when assembling a battery, and a high level of short-circuit withstand capability; a method of producing the same; and an alkali secondary battery separator, are provided.
Owner:DAIWABO HLDG
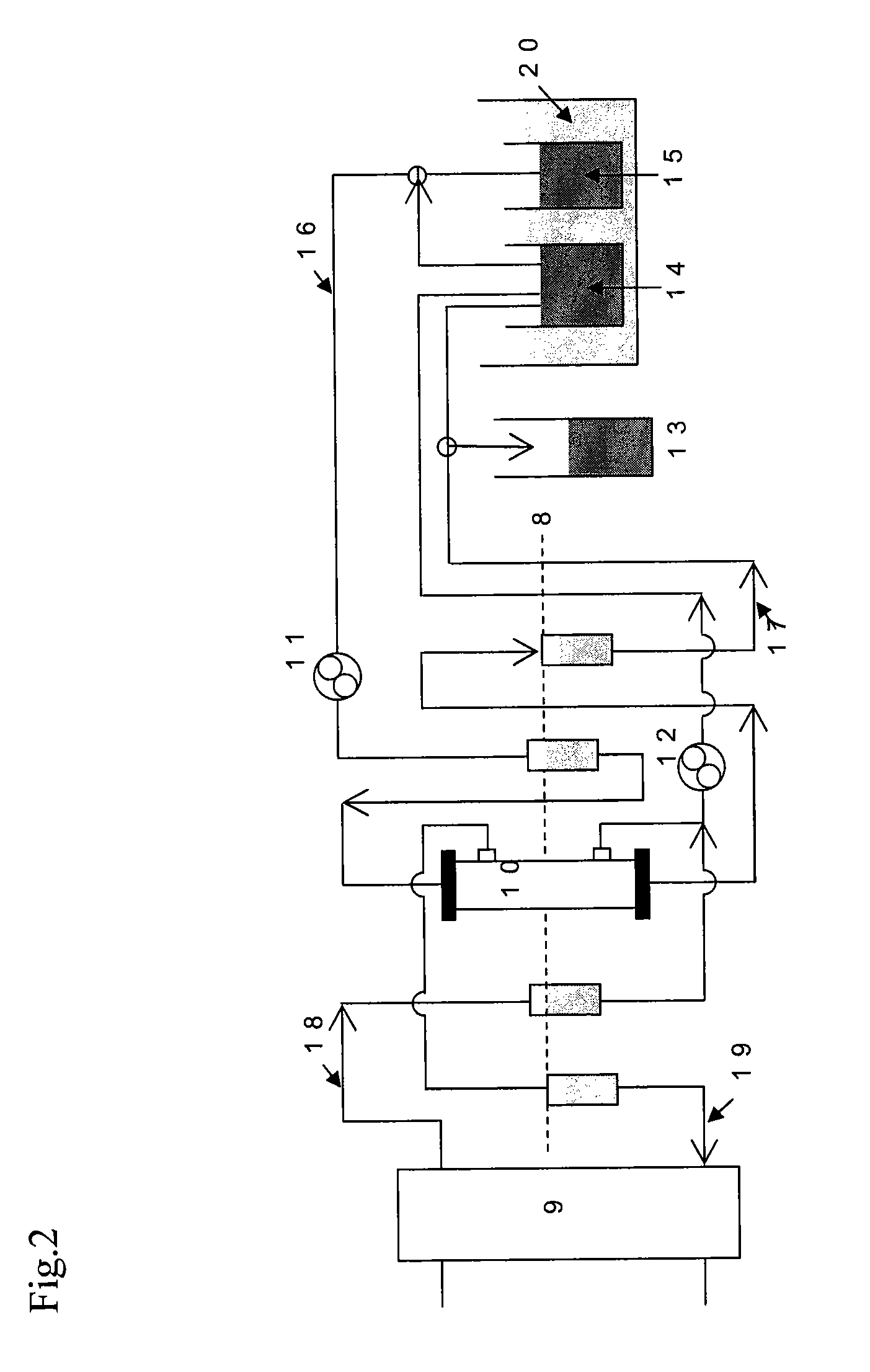
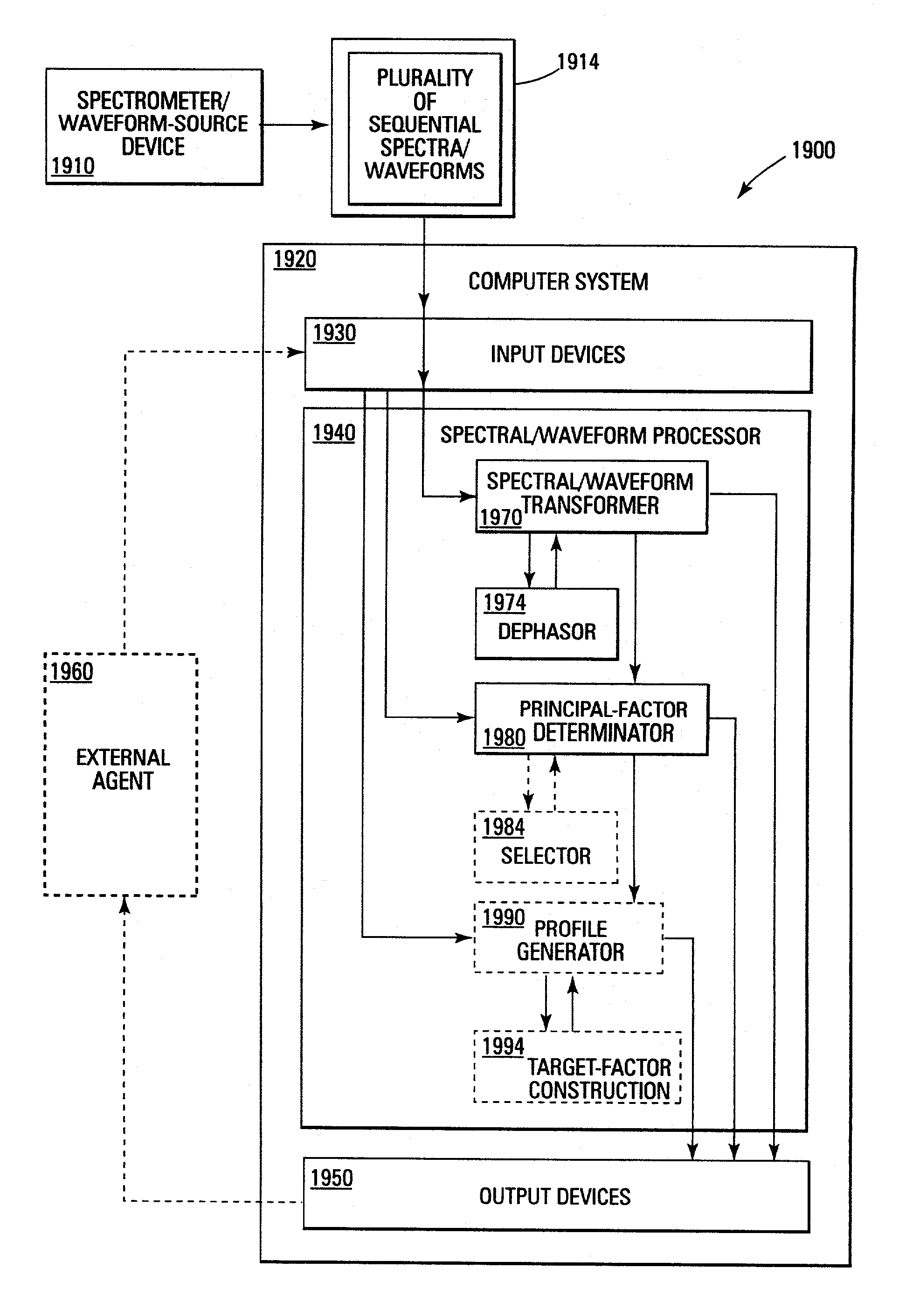
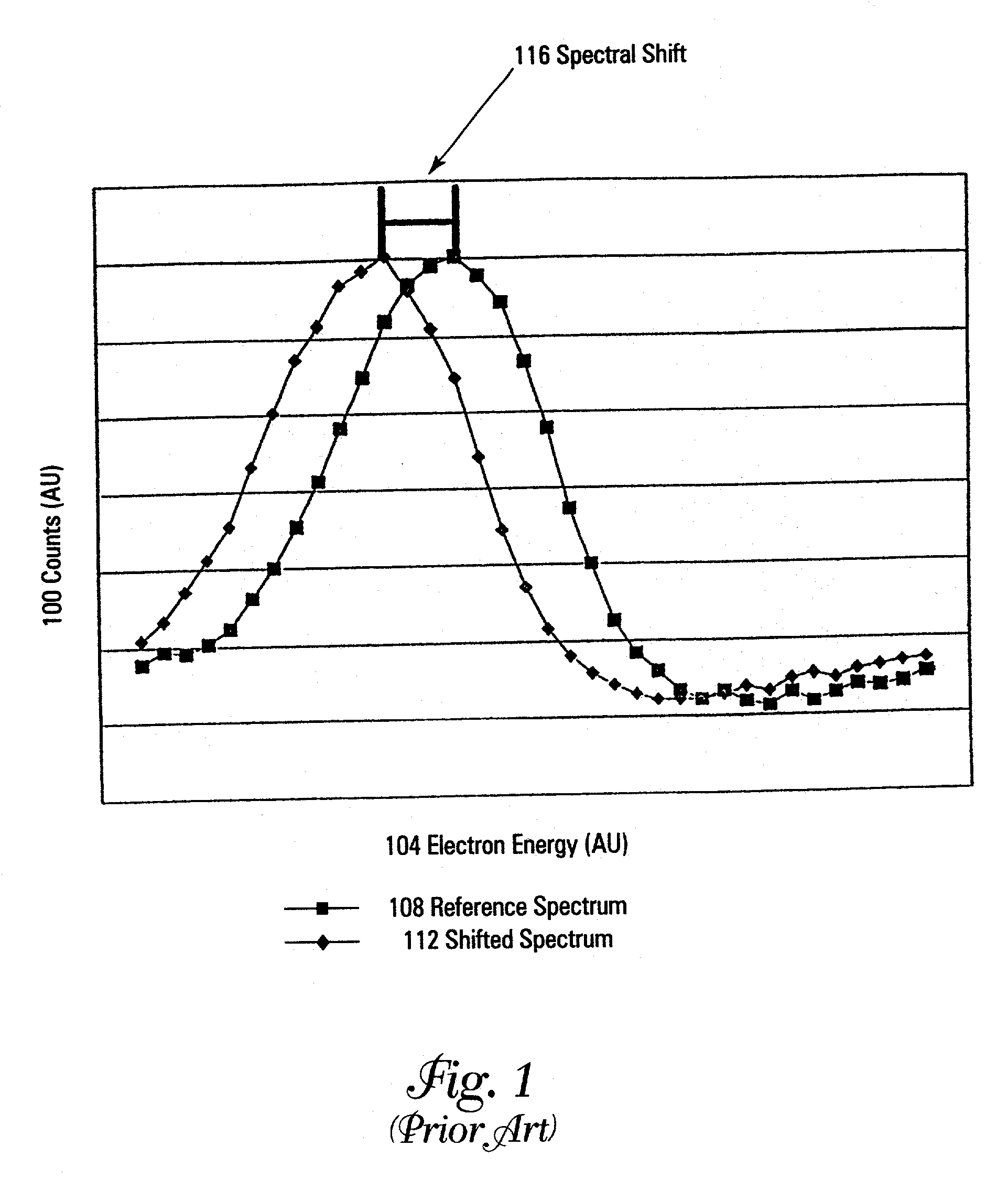
Method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift
InactiveUS7002143B2Reduce dimensionalityParticle separator tubesIsotope separationFrequency spectrumElectron spectroscopy
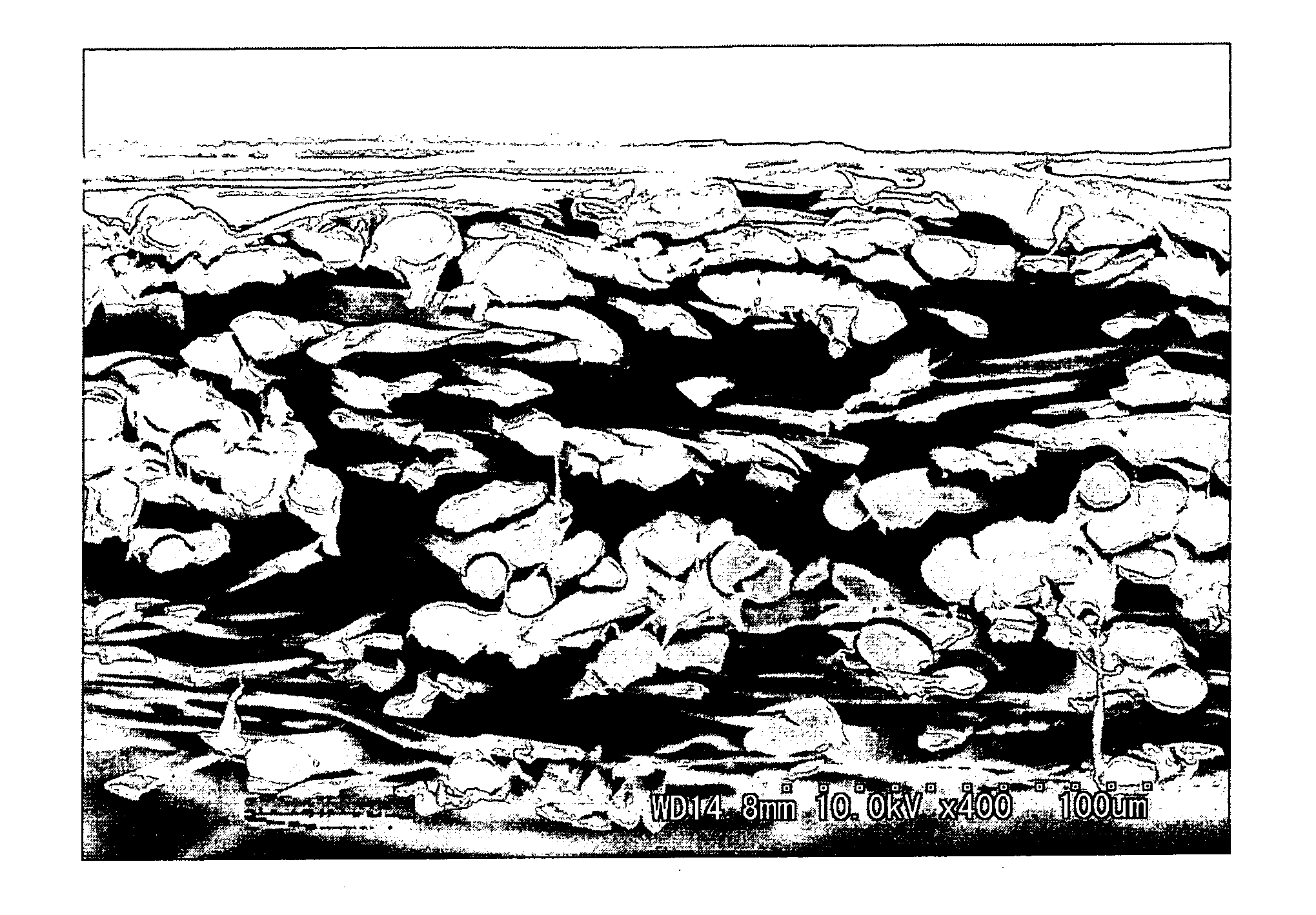
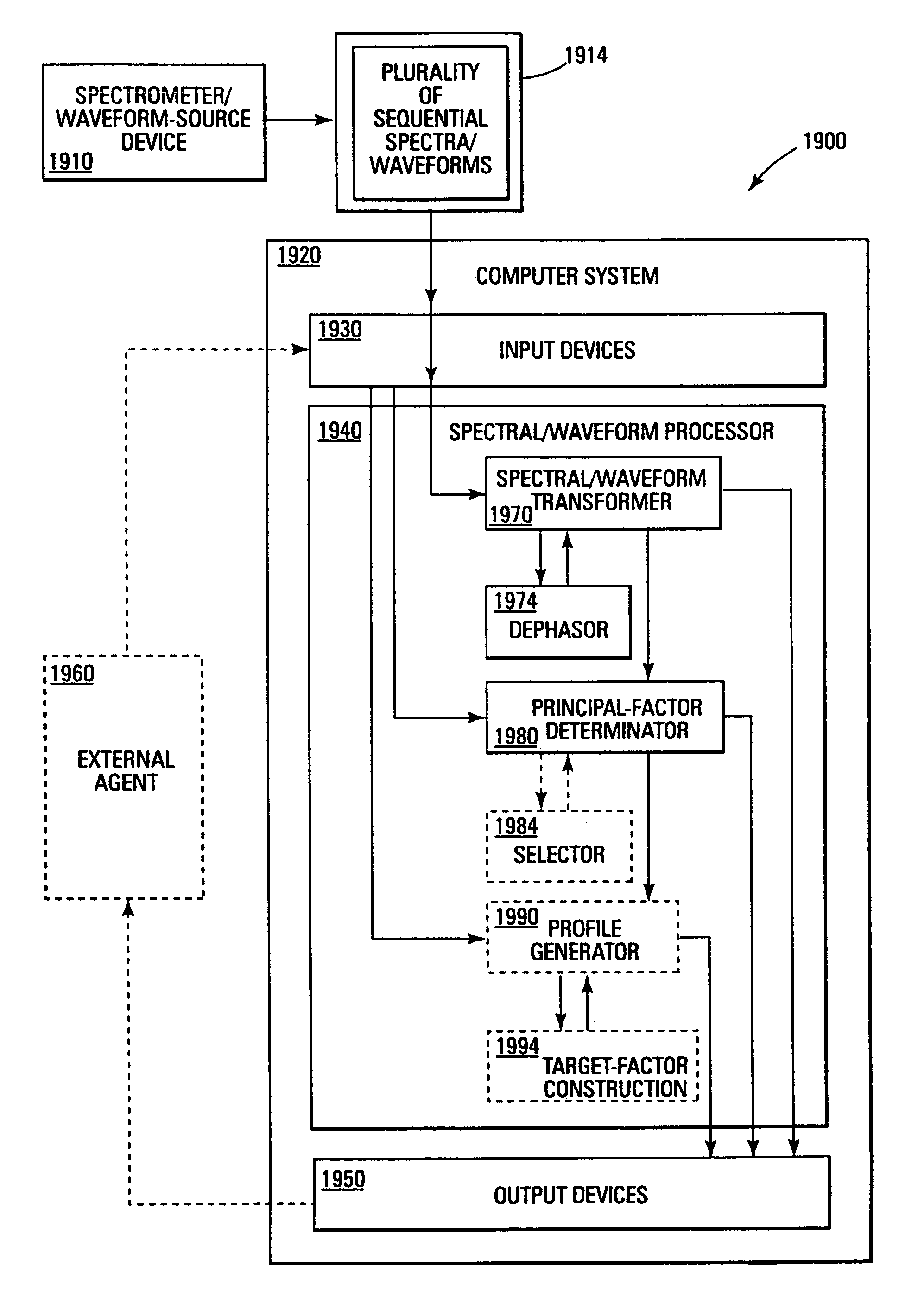
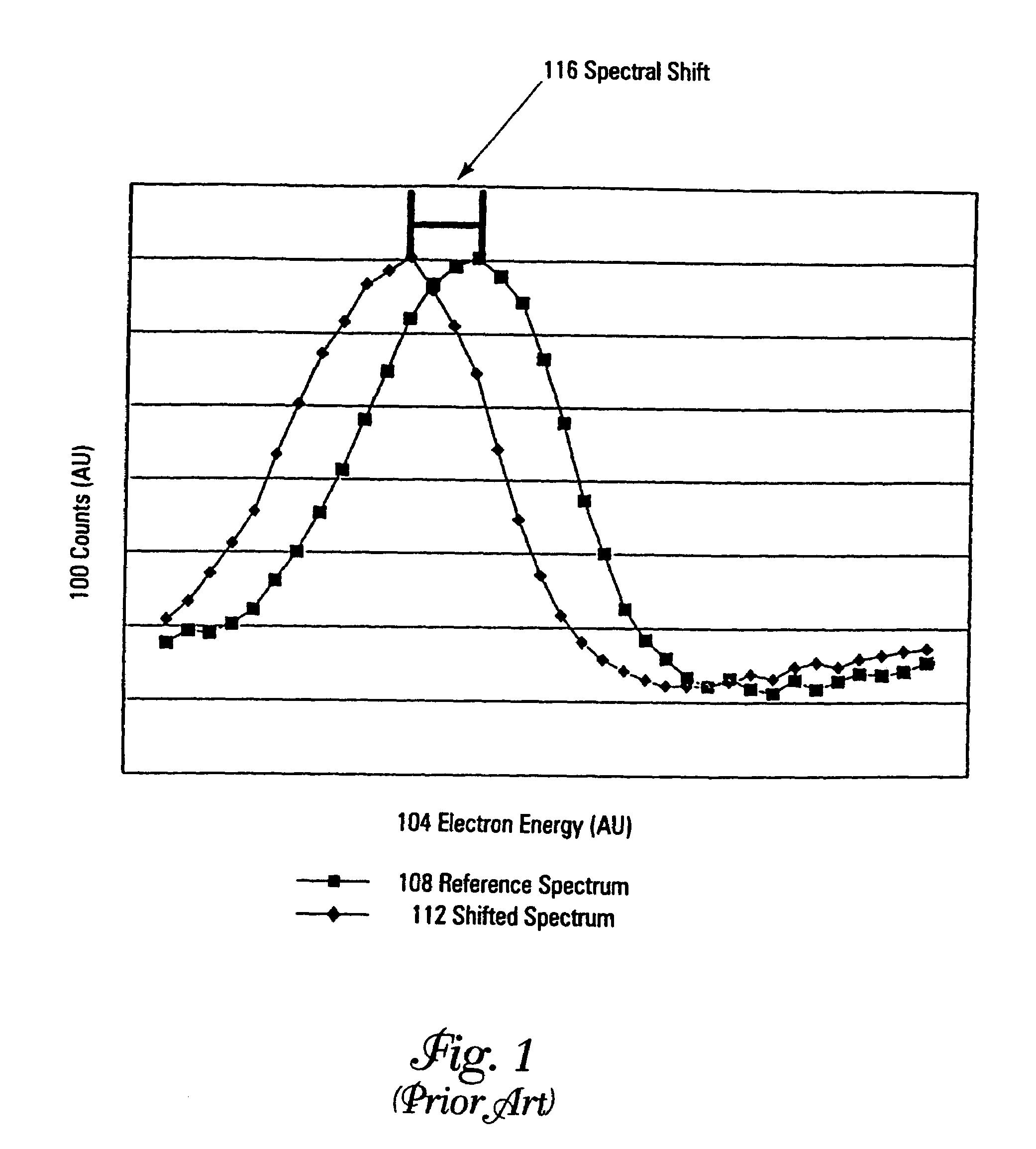
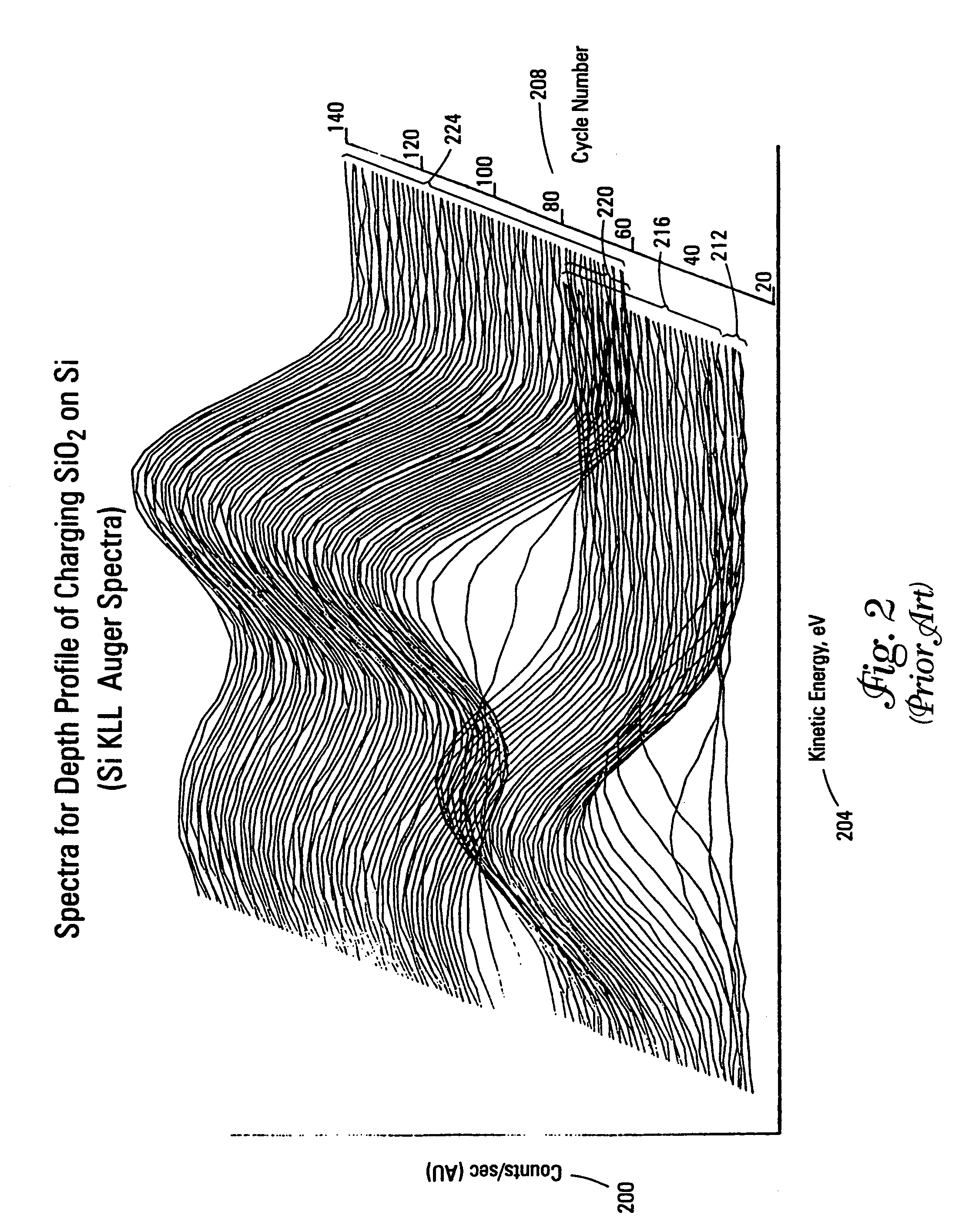
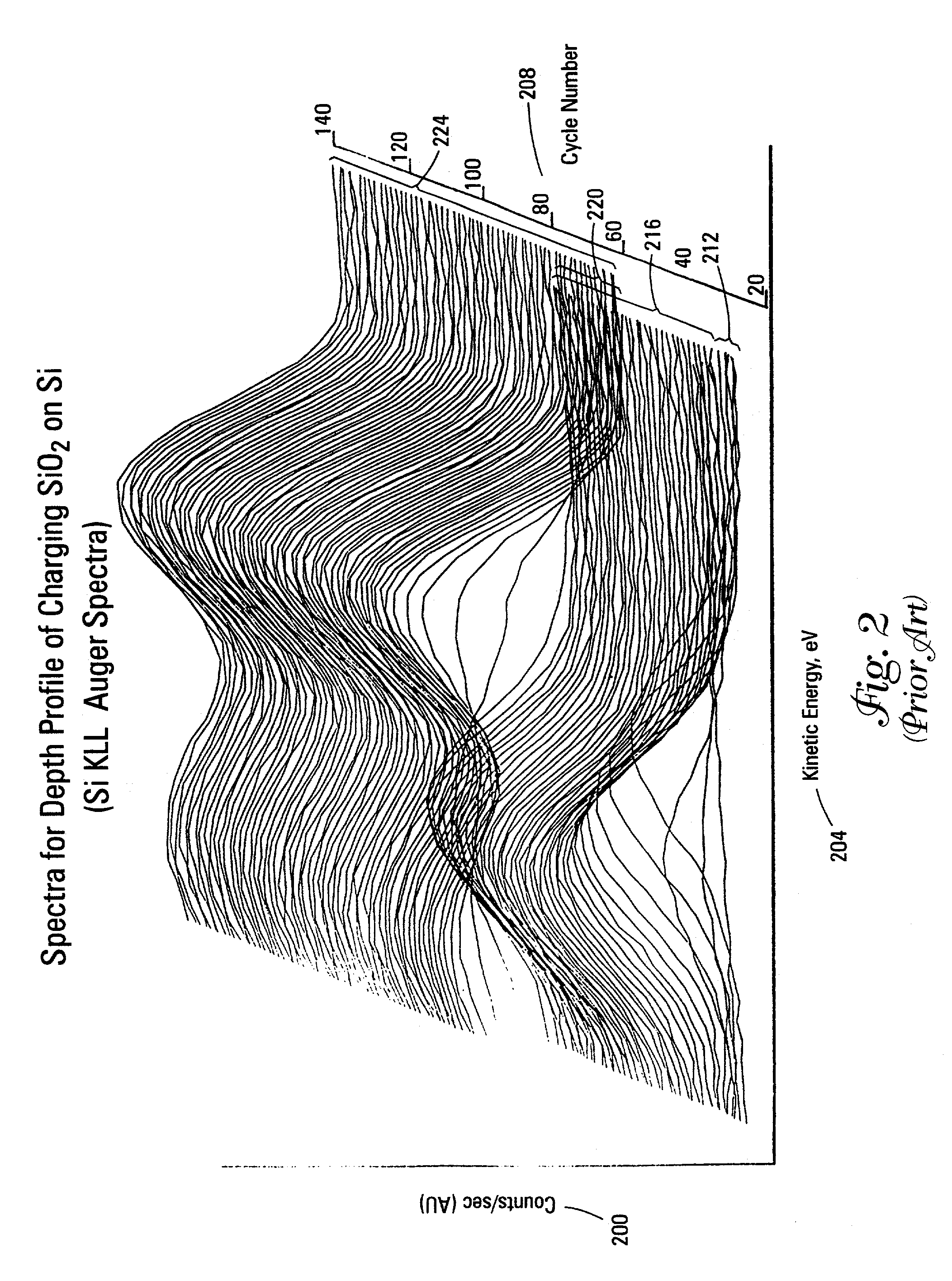
A method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift is disclosed. The present invention removes the effects of drift from a sequential series of waveforms obtained from a waveform-source device, or spectra, from a spectrometer, to produce for output a sequential series of drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra, respectively. In addition, the present invention performs a factor analysis, or alternatively a linear-least-squares analysis, on an array of the drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra to provide a set of drift-compensated principal factors; and, generates drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles from a profile trajectory lying within a space of the set of drift-compensated principal factors. In addition, in the case of spectra, the invention provides for conversion of the drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles to drift-compensated compositional profiles. The invention finds particular utility in the field of electron spectroscopy when the invention is applied to correcting sputter-depth-profile analyzes for the effects of spectral drift caused by charging in insulating samples. The invention, by extension, also, finds utility in waveform processing in situations where a sequential series of waveforms having similar features are offset by arbitrary phase shifts, and, even more generally, in time-series analysis, where a time-series is affected by leading or lagging data.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
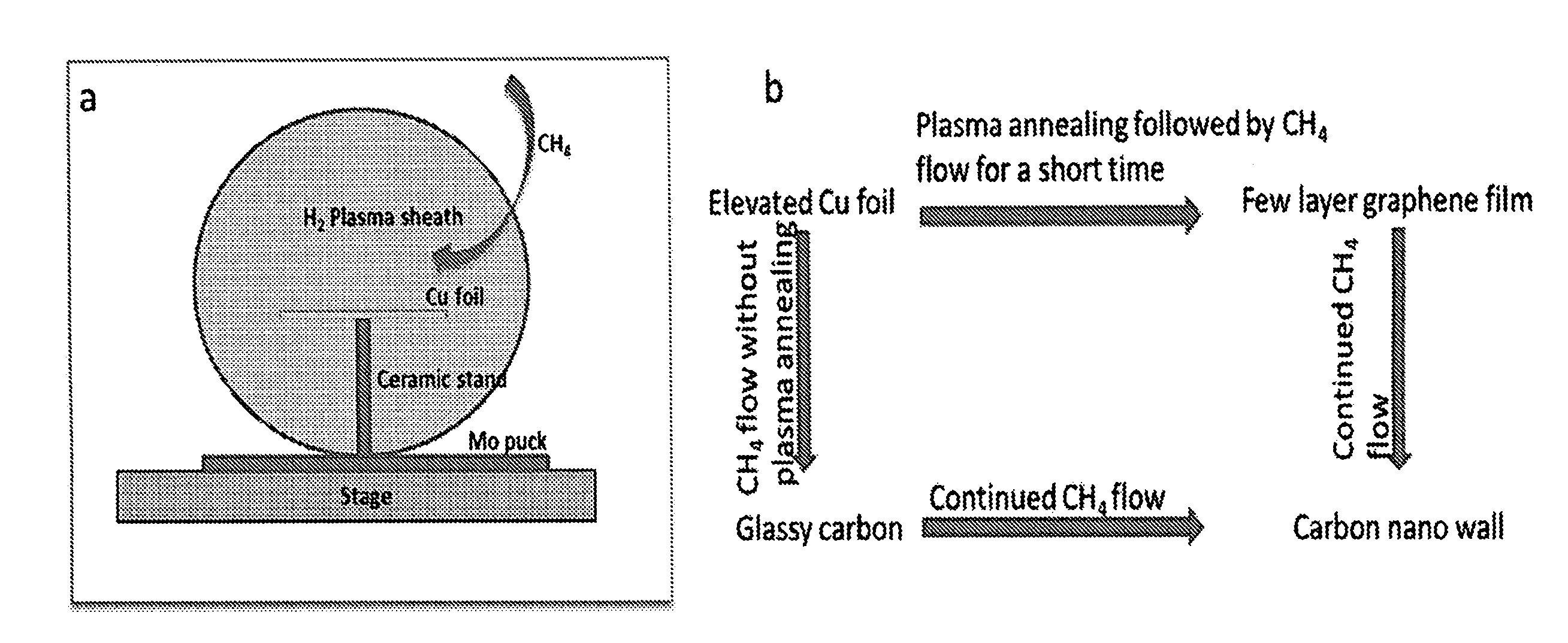
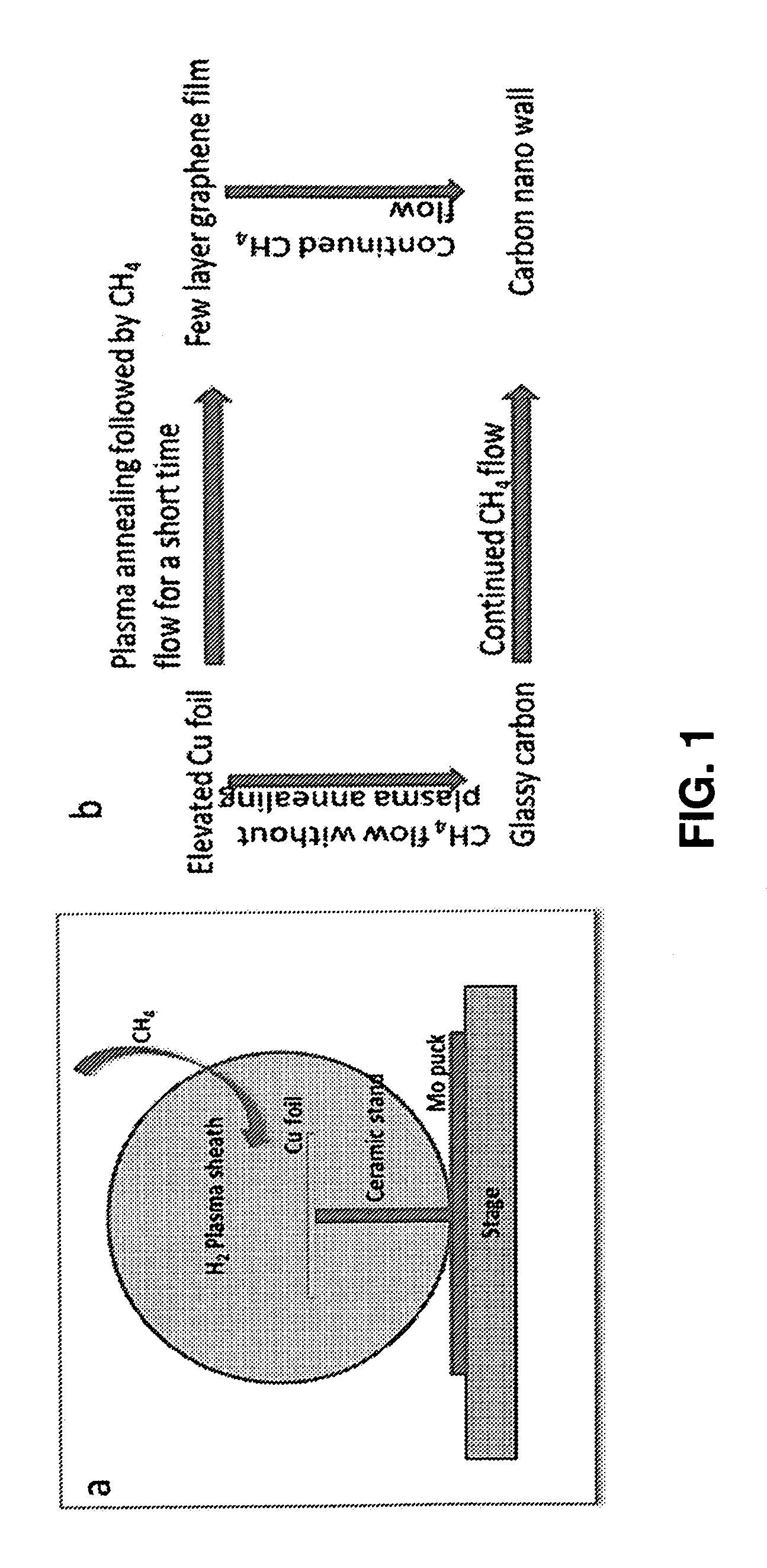
Rapid synthesis of graphene and formation of graphene structures
ActiveUS20150037515A1Shorten the timeReduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneDoped grapheneX-ray
A process for rapid synthesis of few-layer graphene films on Cu foil by microwave plasma chemical vapor deposition (MPCVD). The plasma / metal interaction can be useful for a rapid synthesis of such thin films. The process can produce films of controllable quality from amorphous to highly crystalline by adjusting plasma conditions during growth processes of ˜100 sec duration and with little or no supplemental substrate heating. Films have been characterized using Raman spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The results help to identify the stages involved in the MPCVD deposition of thin carbon films on Cu foil. In yet other embodiments, the films are doped during synthesis by introduction of nitrogen gas in the reactor. Raman spectroscopy, X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and scanning tunneling microscopy reveal crystal structure and chemical characteristics. Nitrogen concentrations up to approximately 2 atomic % are observed. The growth process requires only a few minutes without supplemental substrate heating and offers a promising path toward large-scale synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene films.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Electron Spectroscopy Analysis Method and Analytical Apparatus
InactiveUS20080042057A1Negligible damageLow costMaterial nanotechnologyPreparing sample for investigationX-rayElectron spectroscopy
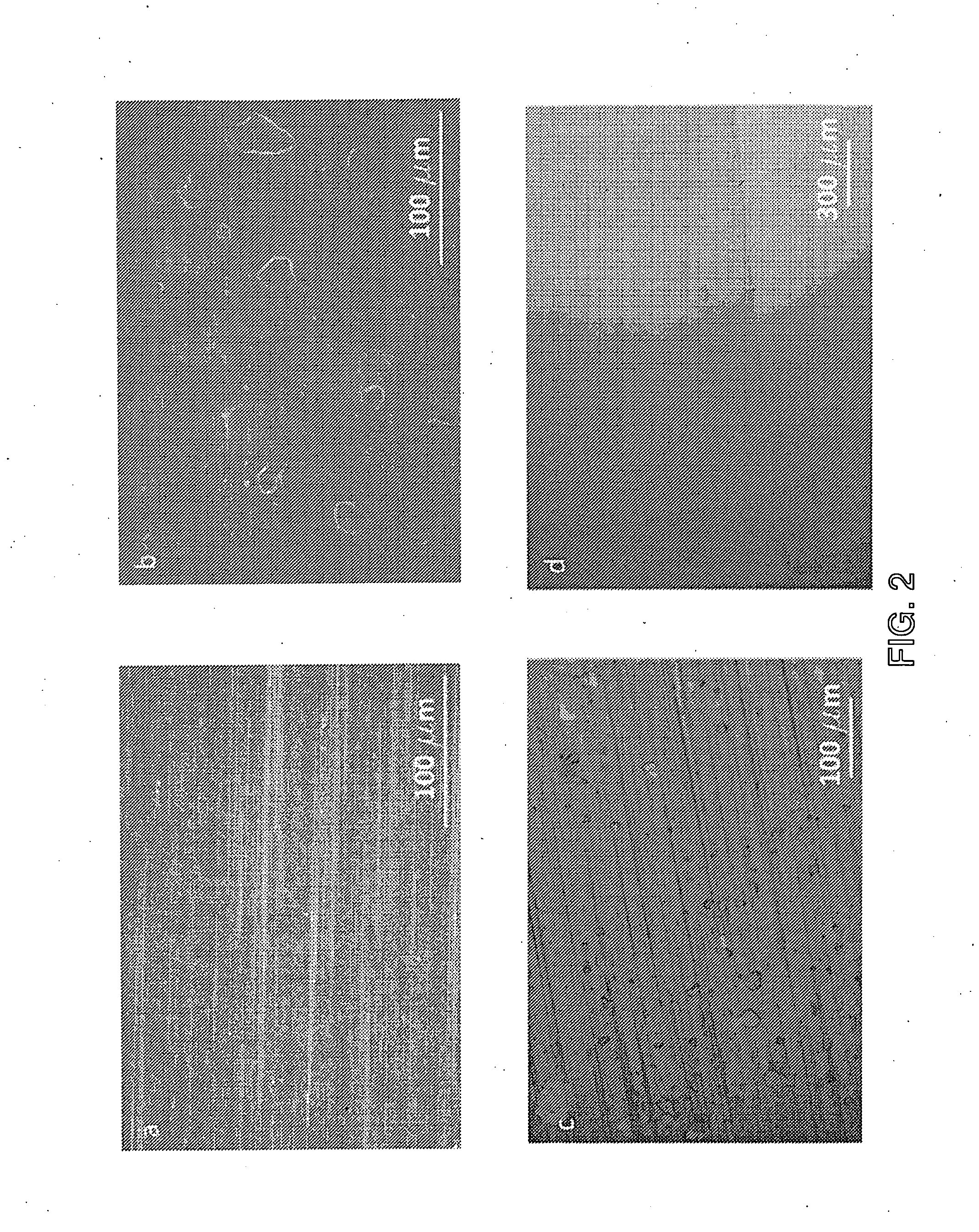
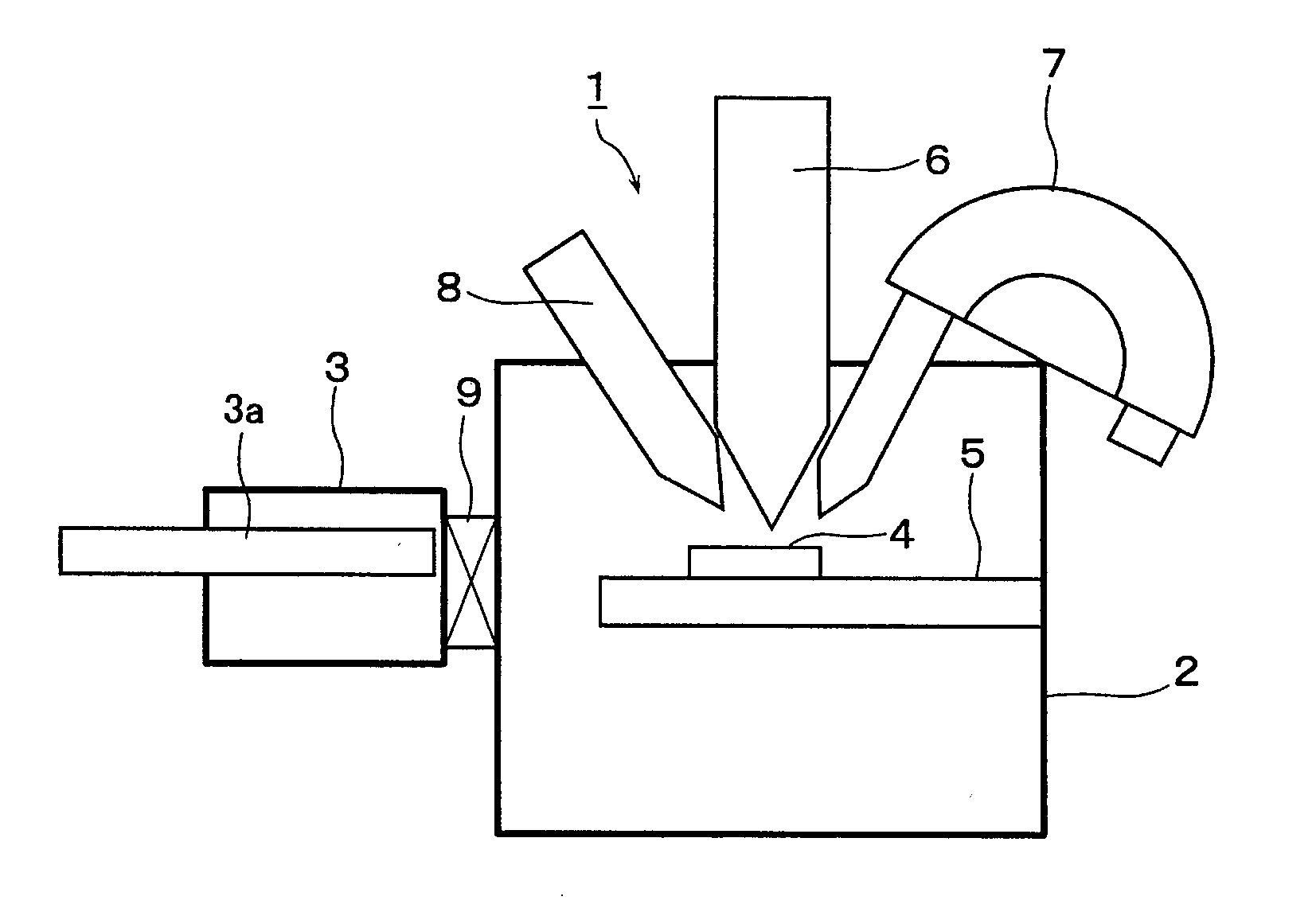
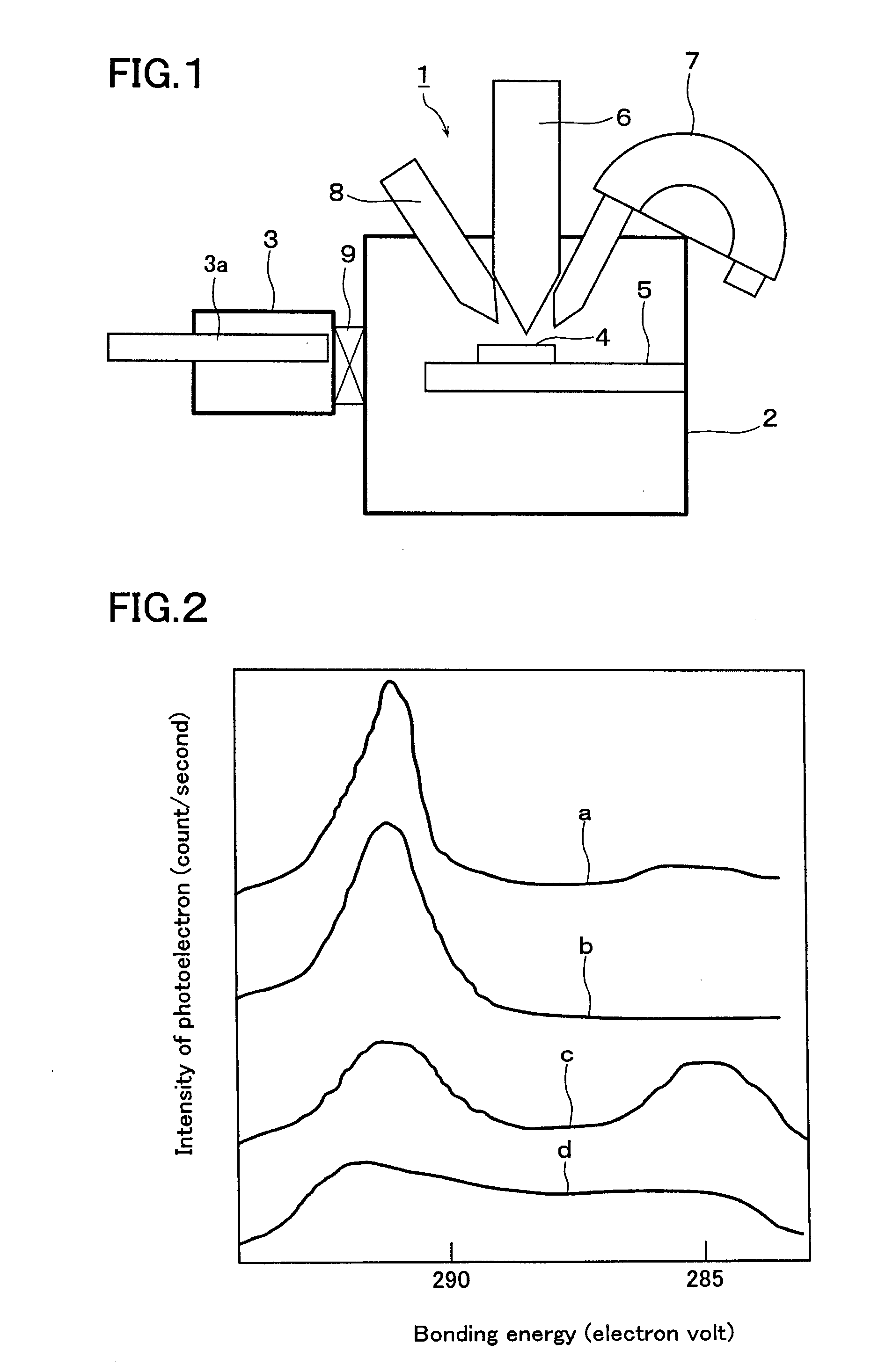
[Task] The invention enables uniformly etching a surface of a sample with an improved repeatability, and etching at a low cost without requiring any large-scale equipment.[Means for Solving the Problem] In an electron spectroscopy analytical apparatus (1) for executing an analysis of a composition, a chemical state and the like of a surface of a sample (4) or in a depth direction thereof by irradiating an X-ray to the sample (4) from a high-energy particle irradiating unit (6) within a vacuum chamber (2) under a vacuum atmosphere, and detecting a kinetic energy of electrons emitted from the sample (4) by an electric energy analyzer (7) on the basis of a photoelectric effect, the surface of the sample (4) is ion-etched by irradiating a fullerene ion beam to the surface of the sample (4) from an ion gun (8) before irradiating the high-energy particle to the sample (4).
Owner:ULVAC PHI
Synclastic dual-channel time-of-flight mass spectrometer
InactiveCN103094051ASimple structureImprove collection efficiencyTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron spectroscopyMass analyzer
Provided is a synclastic dual-channel time-of-flight mass spectrometer. The mass spectrometer comprises collateral dual-channel accelerators (1), a minitype vacuum chamber body (2), a laser sputtering ion source (3), an ion signal detector (4), an ion signal detector (5), and an ion collimator (6). When ions generated by the laser sputtering ion source (3) enter into the dual-channel accelerators (1), the front segment and the rear segment are respectively accelerated to the ion signal detector (4) and the ion signal detector (5) for detection in the same direction. Ion beams generated by the ion source are segmented to an upper part and a lower part through a dual-channel time-of-flight mass analyzer by the collimator, and are respectively transversely accelerated, deflected and focused to the upper detector and the lower detector to record ion time-of-flight mass spectrometry. If the upper detector is replaced by an electron energy analyzer, then a photoelectron spectroscopy experiment for selecting some ions can be carried out at the same time. The synclastic dual-channel time-of-flight mass spectrometer is combined with the electron energy analyzer, and can quickly and conveniently carry out a laser irradiation experiment for ions of all mass peaks. The measured electron spectroscopy of a certain ion and mass peak time-of-flight of the certain ion have a strict corresponding relation. The whole instrument is compact, small and exquisite, simple in structure, and convenient to operate. More importantly, acquired ion electron spectroscopy signal to noise ratio is high, and resolution ratio is high.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method for lithographic printing plate
InactiveUS20020039703A1Maintain good propertiesInhibition formationSurface reaction electrolytic coatingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhosphorous acidX-ray
The present invention relates to a preparation method for a lithographic printing plate, which comprises forming a presensitized plate by coating a photosensitive layer or thermosensitive layer on an aluminum substrate treated with an aqueous solution after optionally anodized and developing the presensitized plate with a developer comprising no silicate, wherein the aqueous solution comprises at least one compound selected from the group consisting of nitrite group-containing compound, fluorine atom-containing compound and phosphorous atom-containing compound, in the proviso that when the at least one compound is fluorine atom-containing compound, the treated aluminum substrate has a surface which satisfies the formula: 0.30.ltoreq.A / (A+B).ltoreq.0.90 (wherein, A represents peak area of fluorine atom (1S) (counts.multidot.eV / sec) determined by X ray Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA), and B represents peak area of aluminum atom (2P) (counts.multidot.eV / sec) determined by X ray ESCA), and when the at least one compound is phosphorous atom-containing compound, the treated aluminum substrate has a surface which satisfies the formula: 0.05.ltoreq.A / (A+B).ltoreq.0.70 (wherein, A represents peak area of phosphorous atom (2P) (counts.multidot.eV / sec) determined by X ray ESCA, and B represents peak area of aluminum atom (2P) (counts.multidot.eV / sec) determined by X ray ESCA).
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
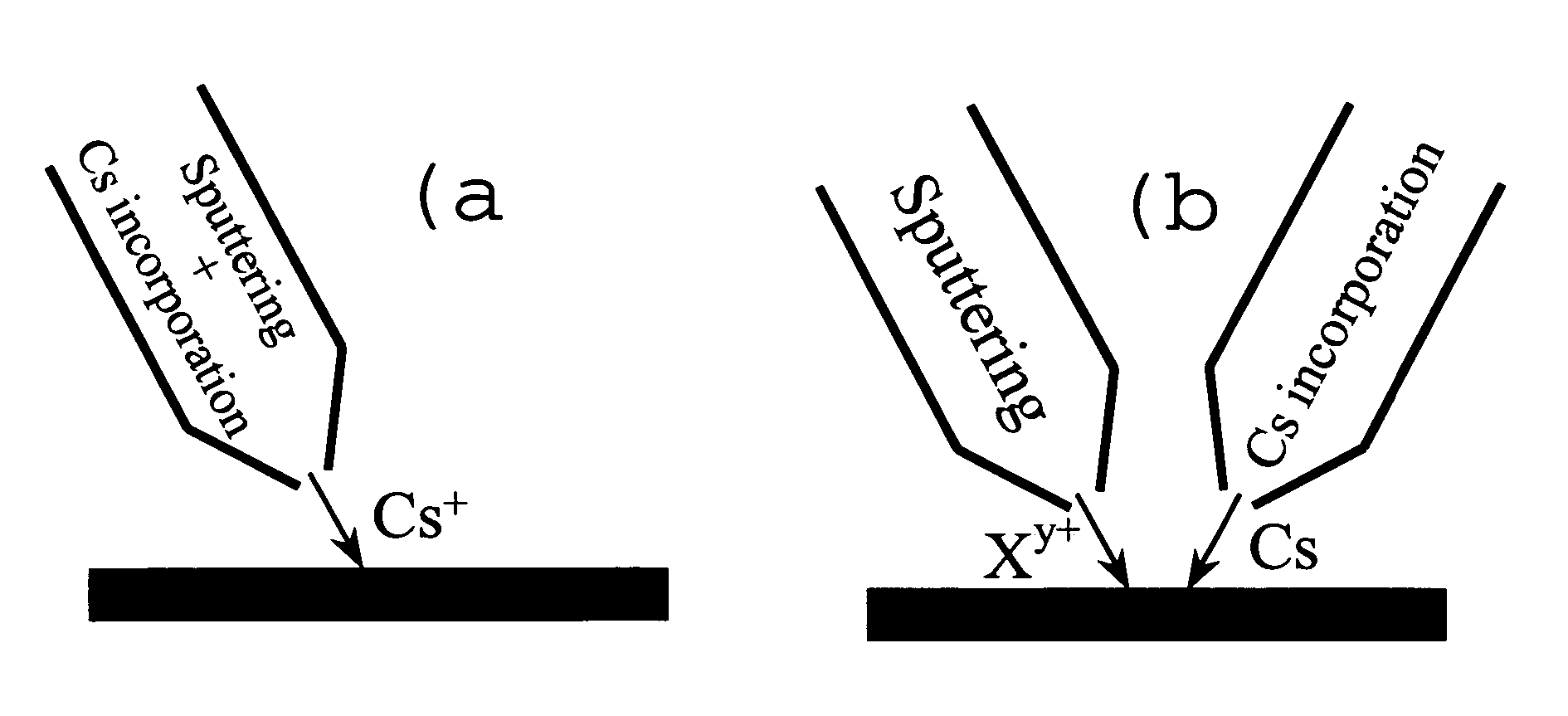
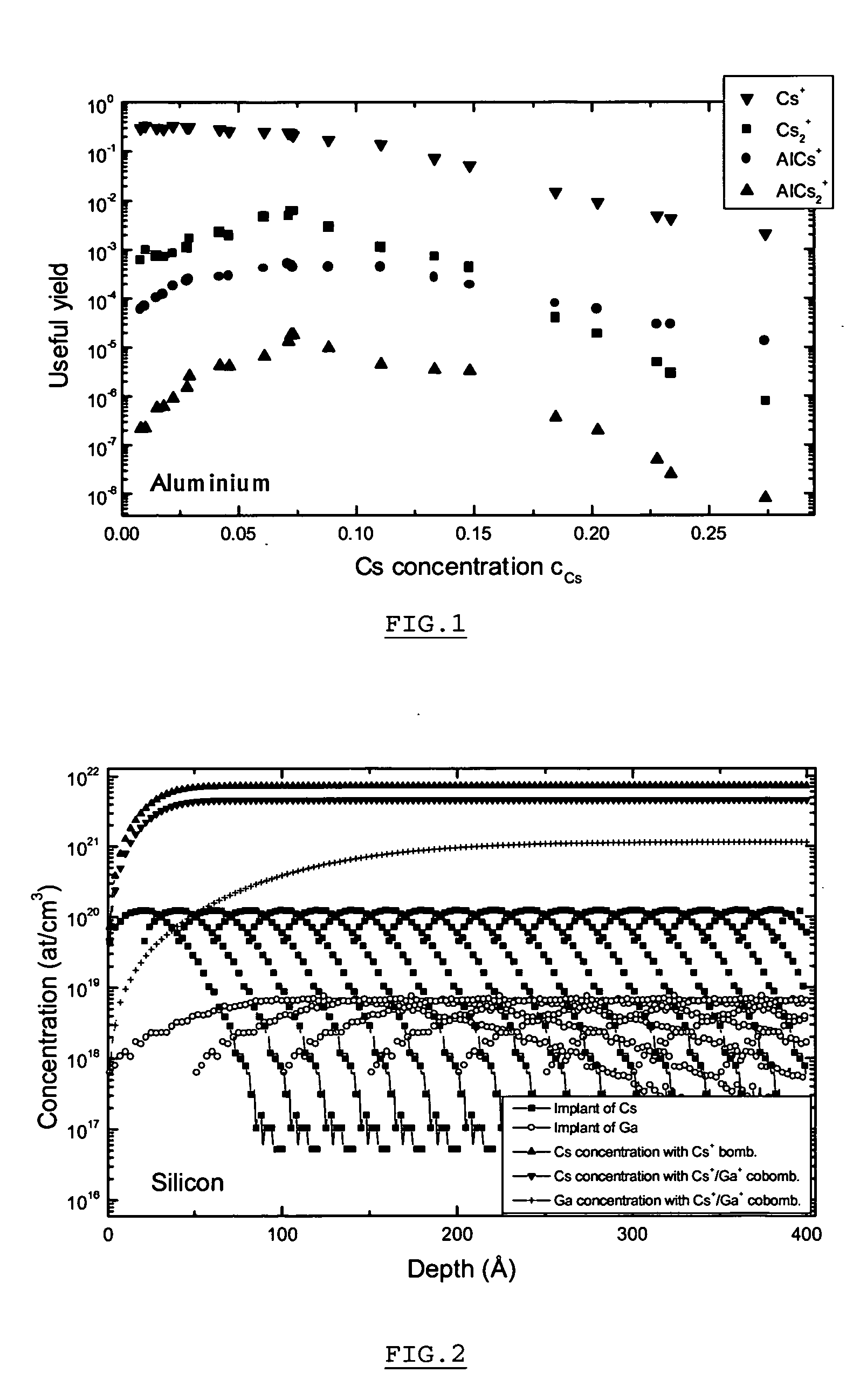
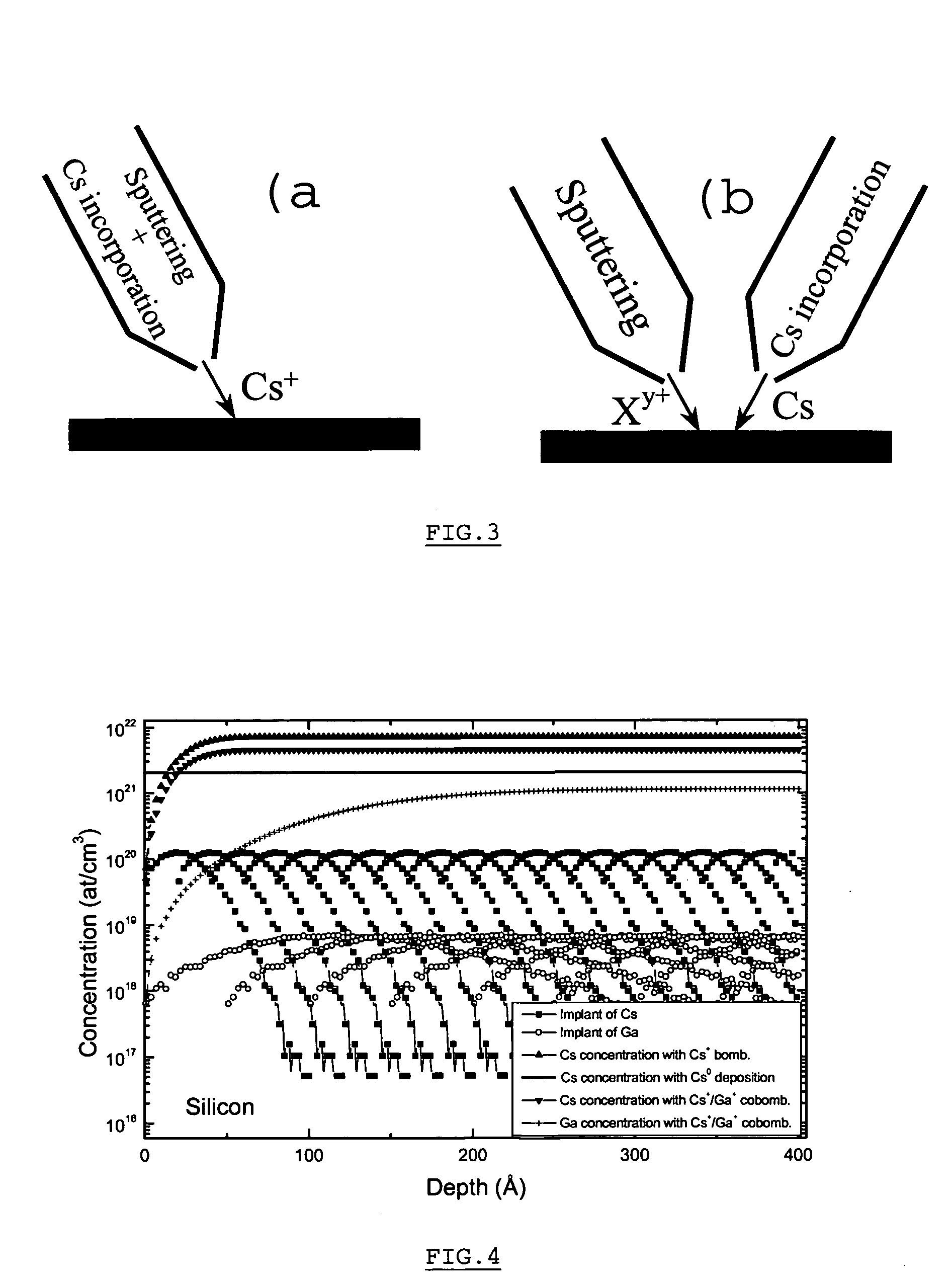
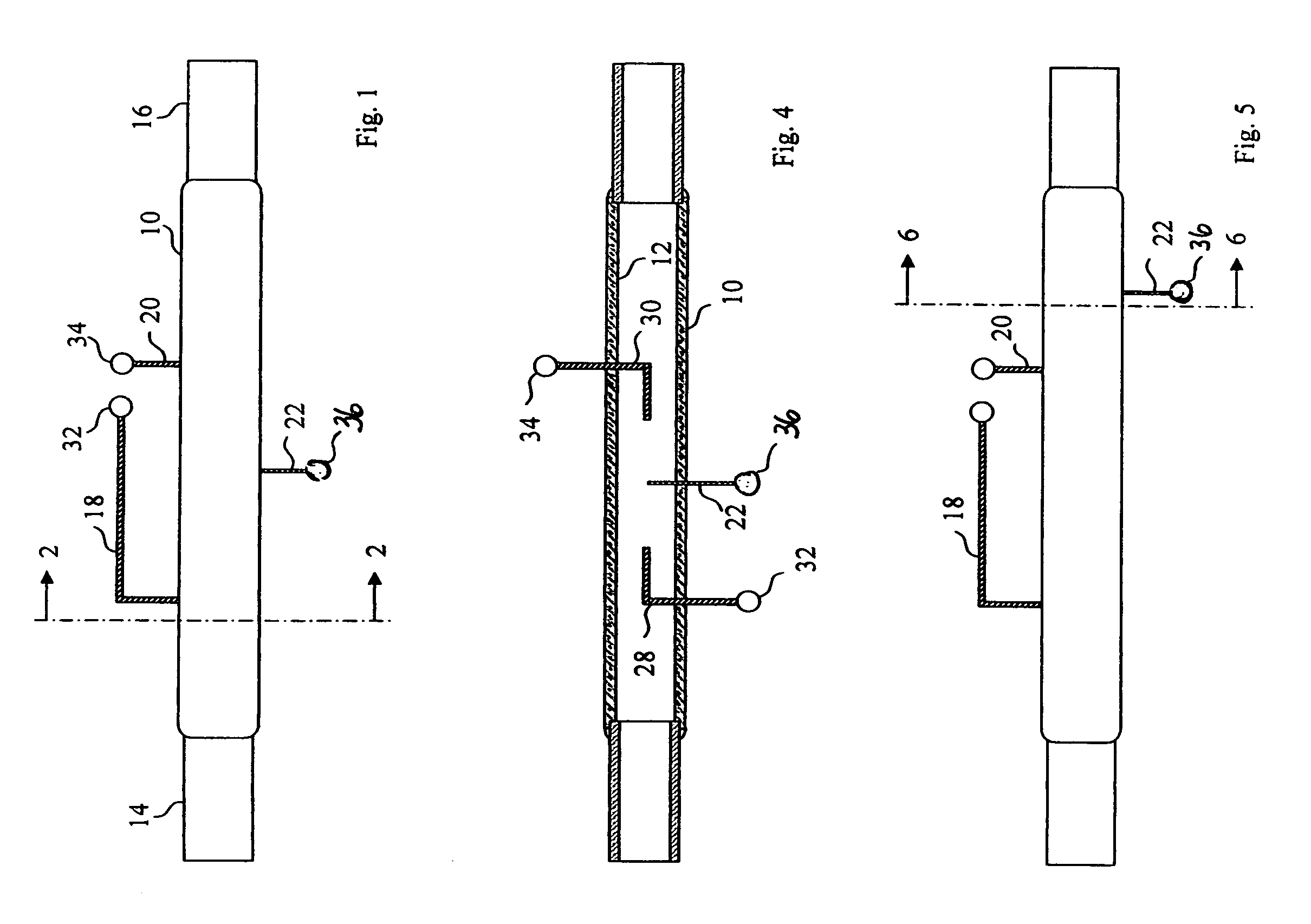
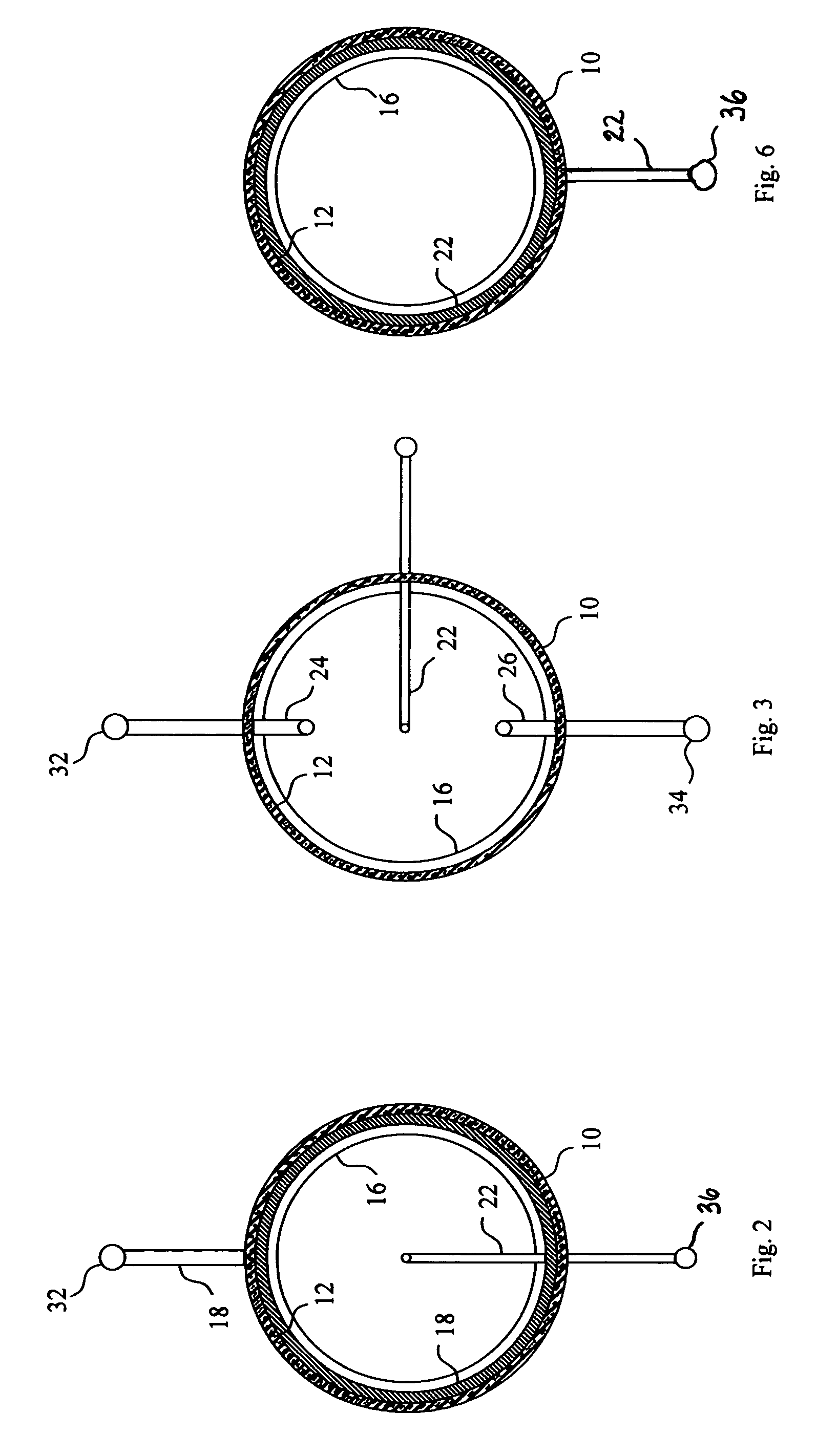
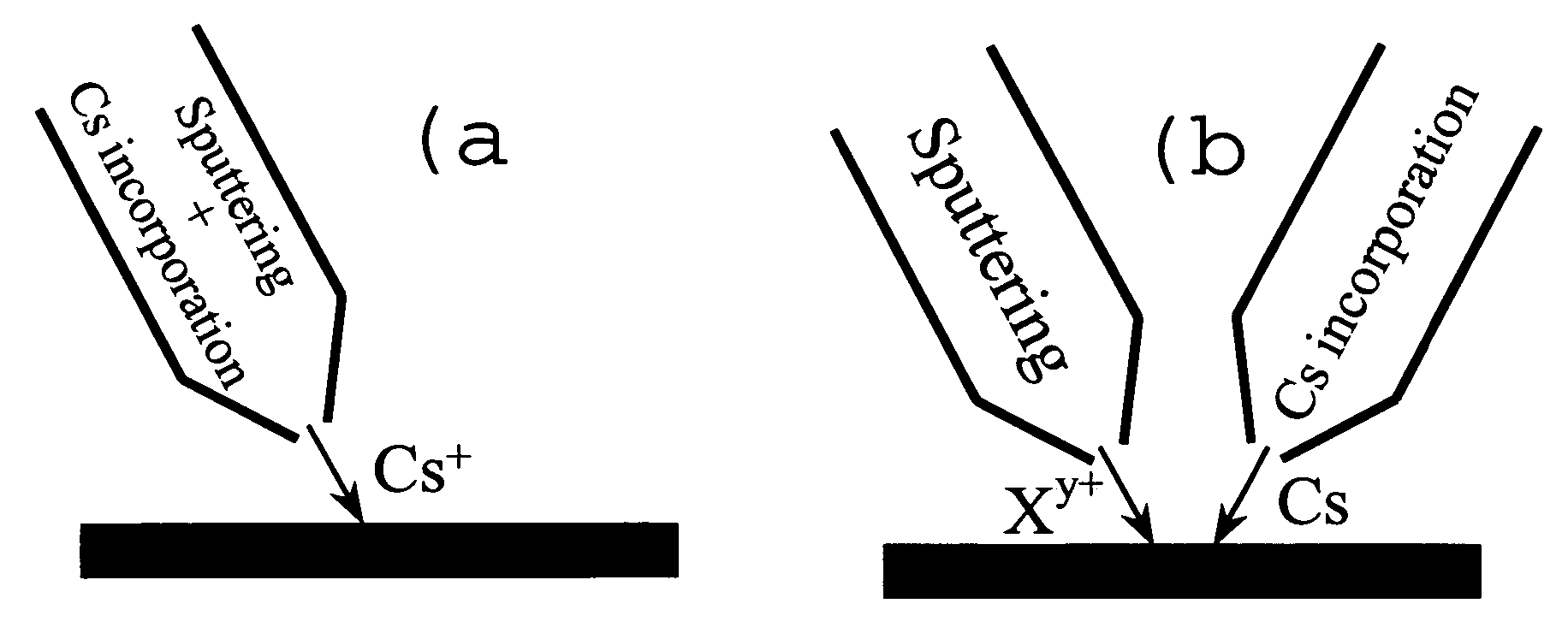
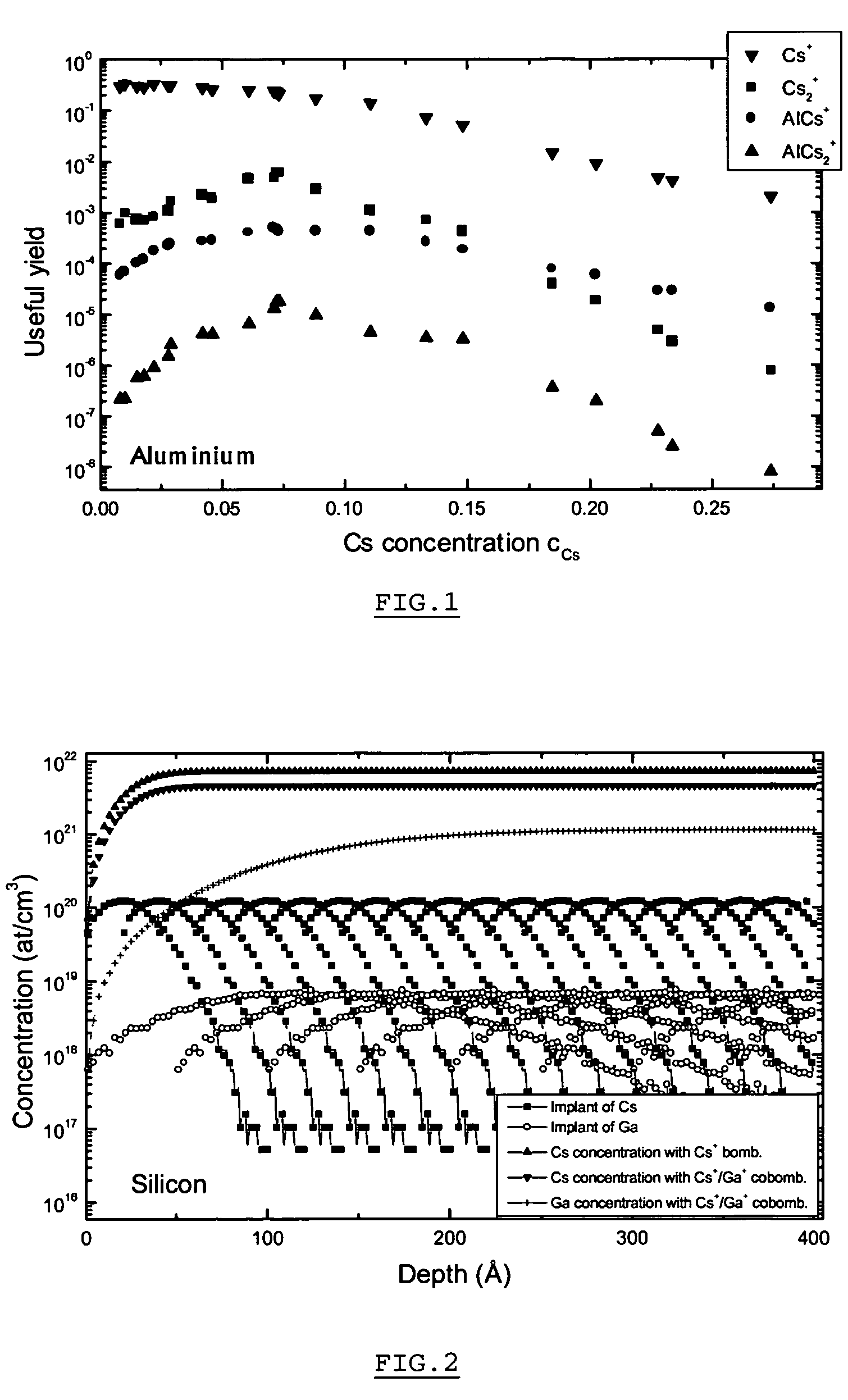
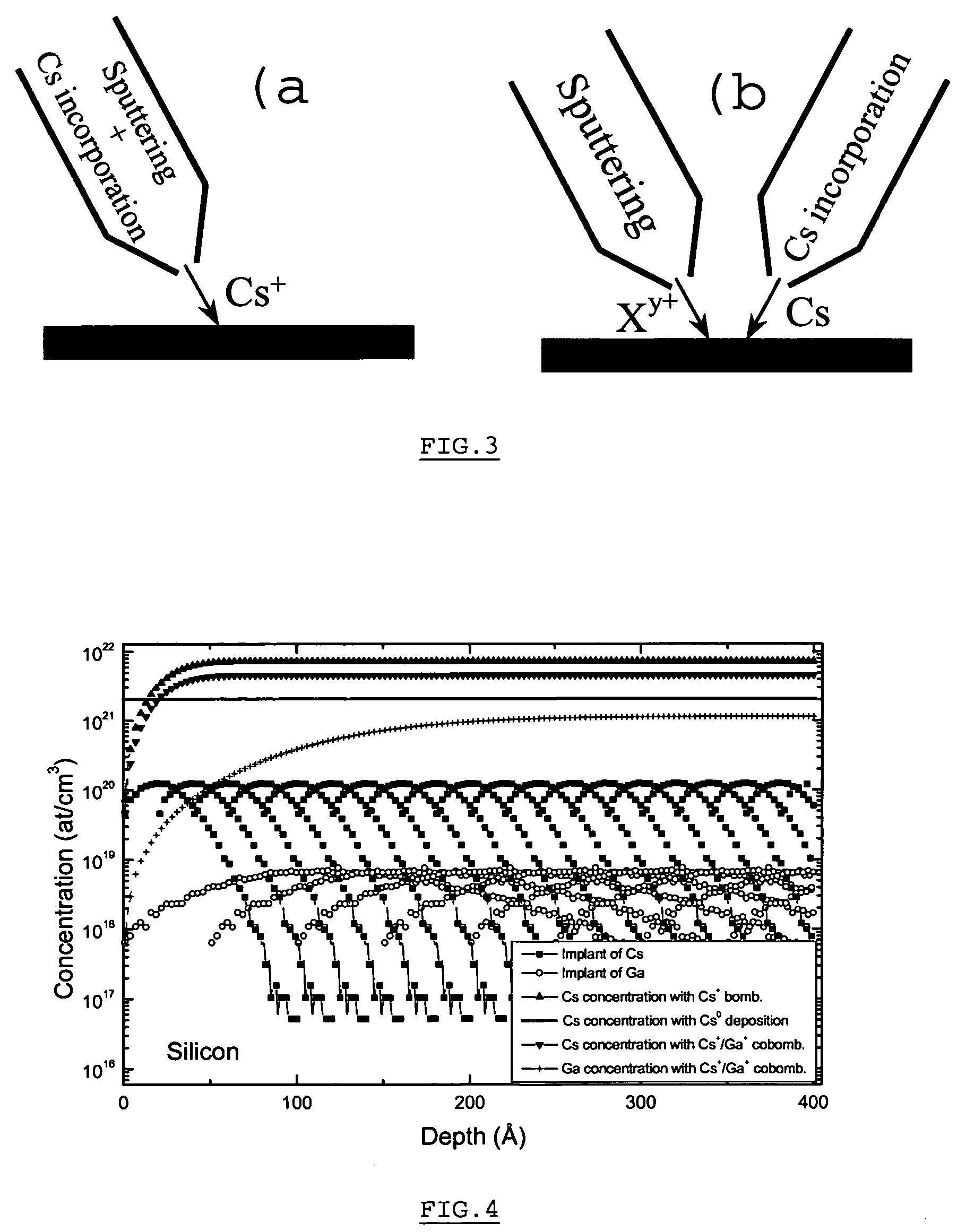
Method and apparatus for in situ depositing of neutral cs under ultra-high vacuum to analytical ends
ActiveUS20060011865A1Laser detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltra-high vacuumElectron spectroscopy
The present invention relates to a method for modifying the electronic properties of a surface to analytical ends, such as SIMS or electron spectroscopy, characterised in that it comprises in situ deposition of pure neutral cesium (Cs0), under ultra-high vacuum, said neutral cesium being enabled in the form of a collimated adjustable stream. The invention relates also to the special column designed for implementing the method and to the corresponding energy and / or mass analyser instrument.
Owner:CENT RECH PUBLIC GABRIEL LIPPMANN
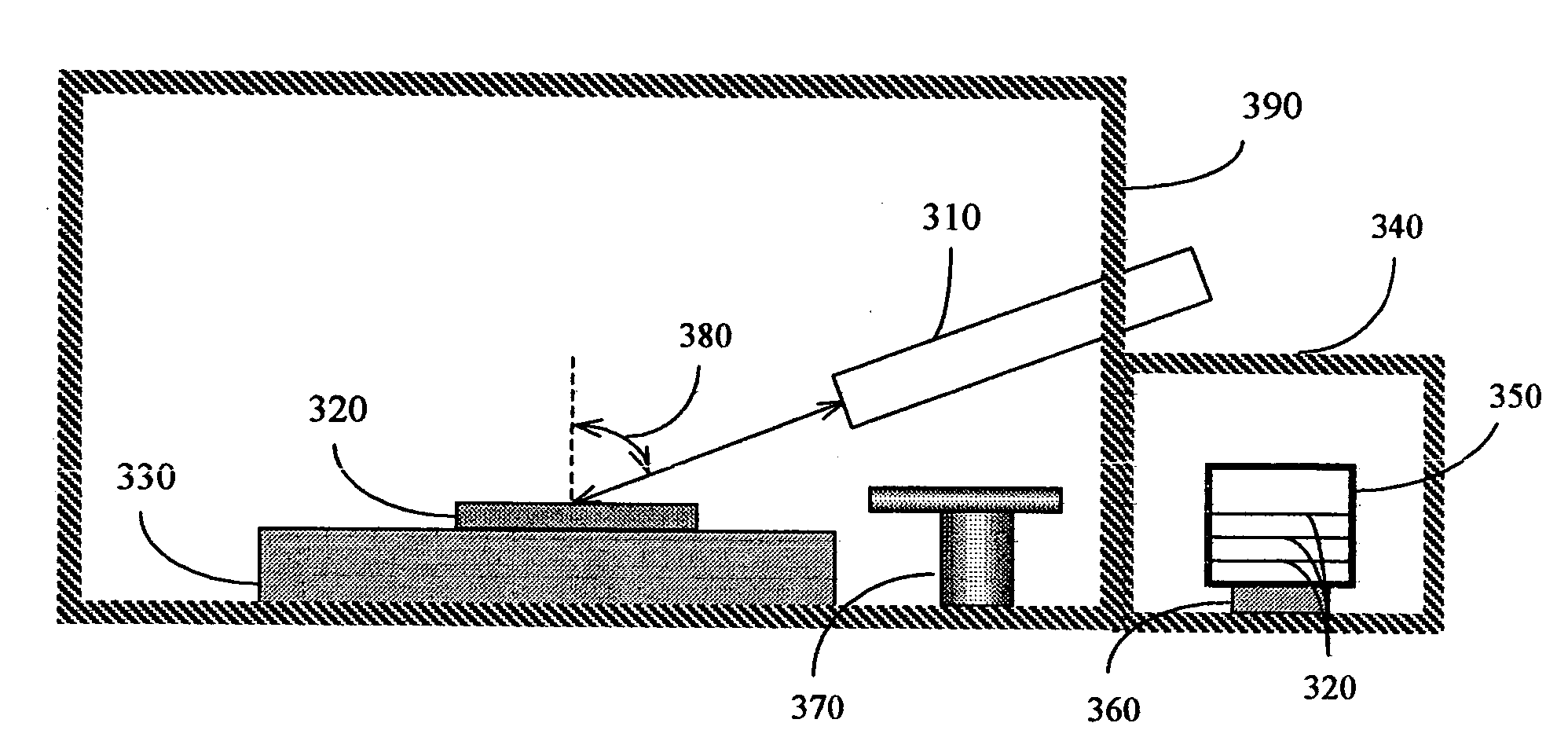
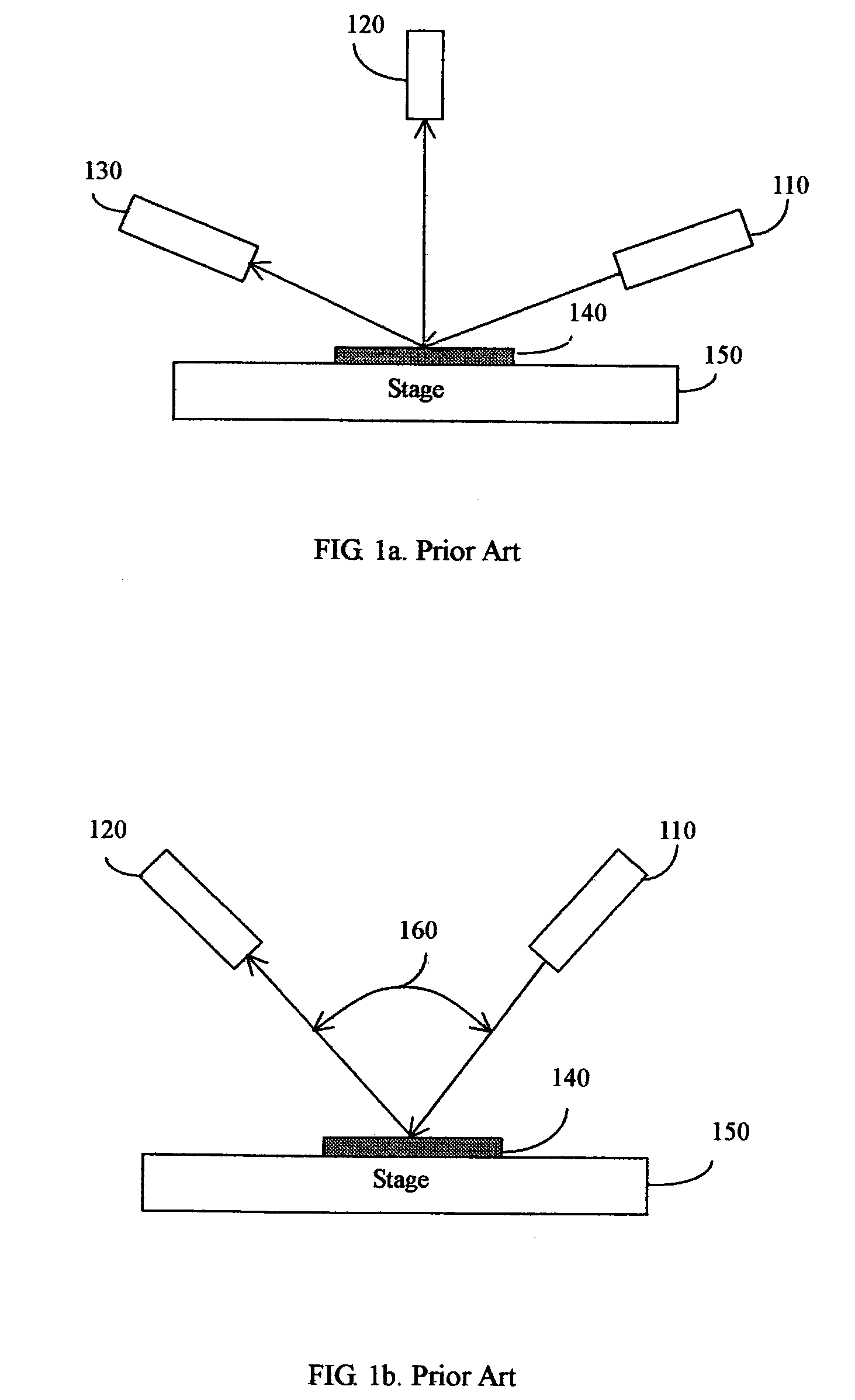
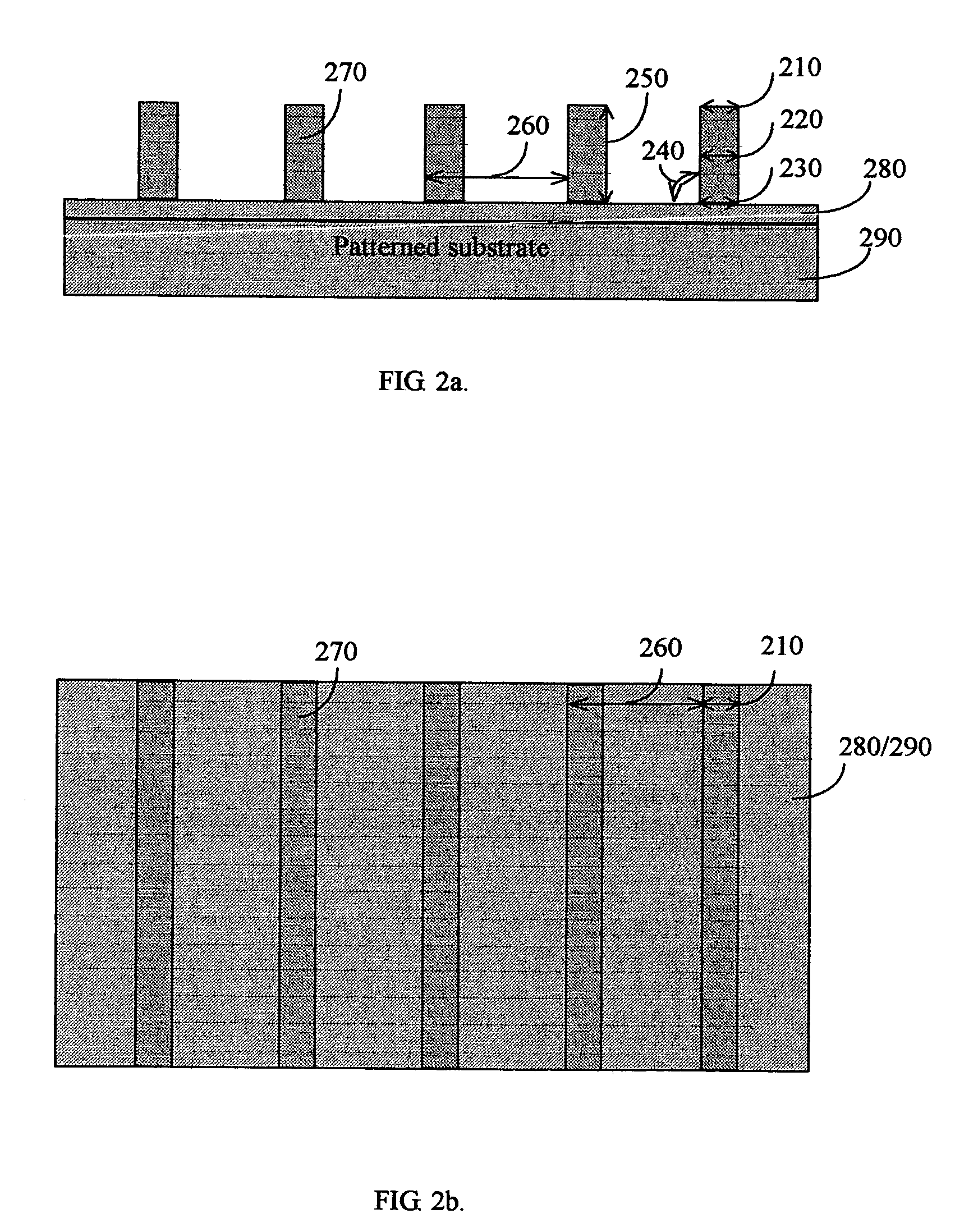
Electron spectroscopic metrology system
InactiveUS20060043291A1Electric discharge tubesMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionProduction rateMetrology
The present invention discloses a new electron spectroscopic metrology system using an electron beam to measure the periodic feature on a substrate. The present invention provides a measurement system for the geometry parameters of the periodic feature which is only a few repeating small elements in the measurement area. The present invention has the following advantages: (1) capable of measuring a small feature of an array of lines (line width less than a couple of ten nanometers); (2) capable of measuring a small feature of an array of via holes; (3) capable of measuring an isolated feature, with a line and patch ratio less than 1:10; (4) capable of measuring a small area, less than twenty five square micrometers; (5) no need to input detailed knowledge about the feature and its film stack; (6) simple theoretical model to derive the geometry parameters. The total simplicity of the present invention will enhance the electron spectroscopic metrology system's overall performance and productivity.
Owner:PENG GANG GRANT
Separation membrane, method of producing the same and separation membrane module using the separation membrane
ActiveUS8613361B2Lower performance requirementsImprove hydrophobicitySemi-permeable membranesMembranesPhysical chemistryElectron spectroscopy
A separation membrane includes a membrane comprising a polymer, characterized in that a functional layer is formed on the surface in one side of the membrane, the peak area percentage of carbon derived from ester group measured by the electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) on the surface of the preceding functional layer is 0.1% (by atomic number) or more but not more than 10 (% by atomic number), and the peak area percentage of carbon derived from ester group measured by the electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) on the surface opposite to the functional layer is not more than 10 (% by atomic number). A separation membrane module suffering from little sticking of organic matters, proteins, platelets and so on is provided with the separation membrane as a built-in membrane.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift
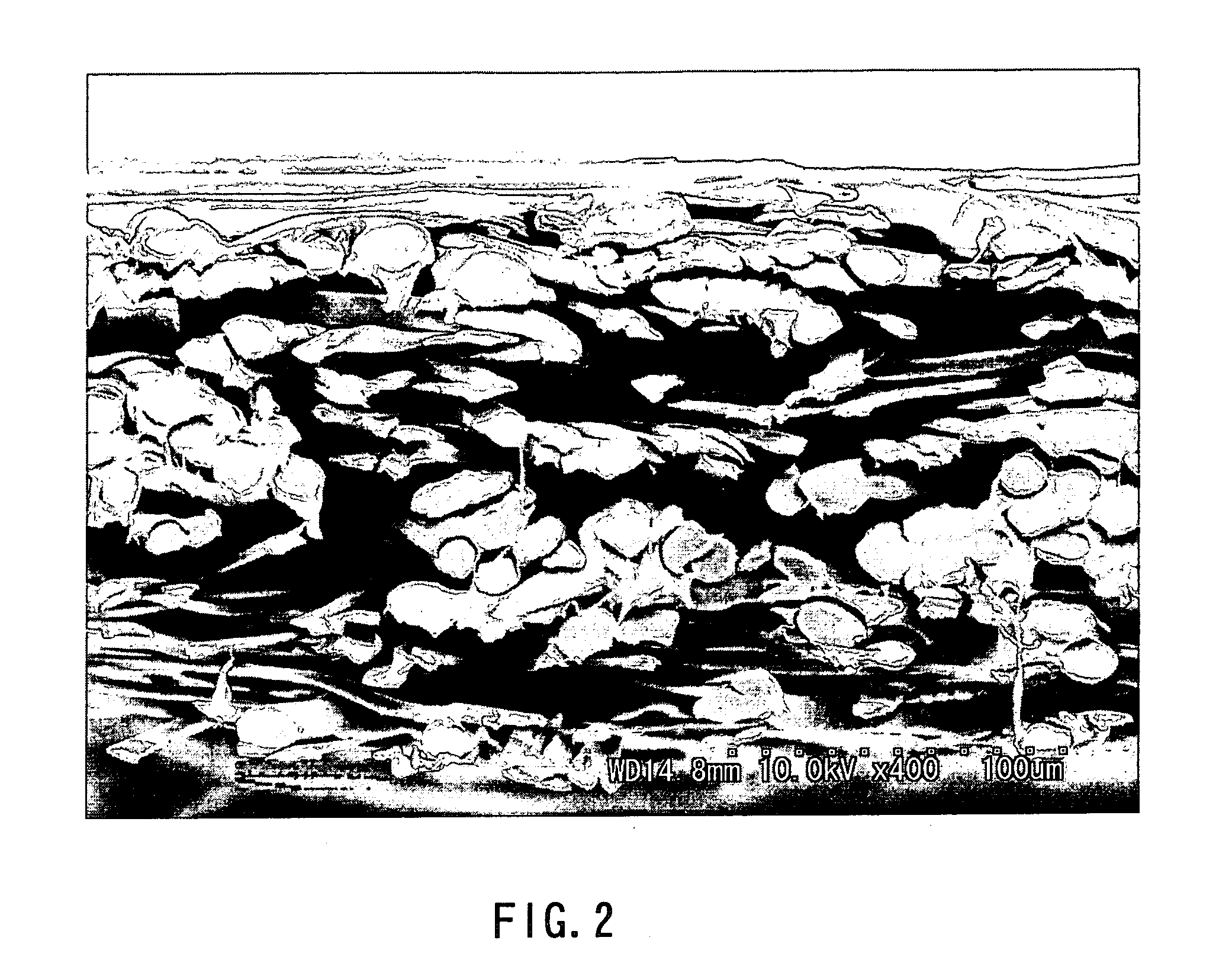
A method and apparatus for compensating waveforms, spectra, and profiles derived therefrom for effects of drift is disclosed. The present invention removes the effects of drift from a sequential series of waveforms obtained from a waveform-source device, or spectra, from a spectrometer, to produce for output a sequential series of drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra, respectively. In addition, the present invention performs a factor analysis, or alternatively a linear-least-squares analysis, on an array of the drift-compensated waveforms, or spectra to provide a set of drift-compensated principal factors; and, generates drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles from a profile trajectory lying within a space of the set of drift-compensated principal factors. In addition, in the case of spectra, the invention provides for conversion of the drift-compensated scaled target-factor profiles to drift-compensated compositional profiles. The invention finds particular utility in the field of electron spectroscopy when the invention is applied to correcting sputter-depth-profile analyses for the effects of spectral drift caused by charging in insulating samples. The invention, by extension, also, finds utility in waveform processing in situations where a sequential series of waveforms having similar features are offset by arbitrary phase shifts, and, even more generally, in time-series analysis, where a time-series is affected by leading or lagging data.
Owner:IBM CORP
Mn4CaO4 core structure-containing water cracking catalyst and preparation method and application thereof
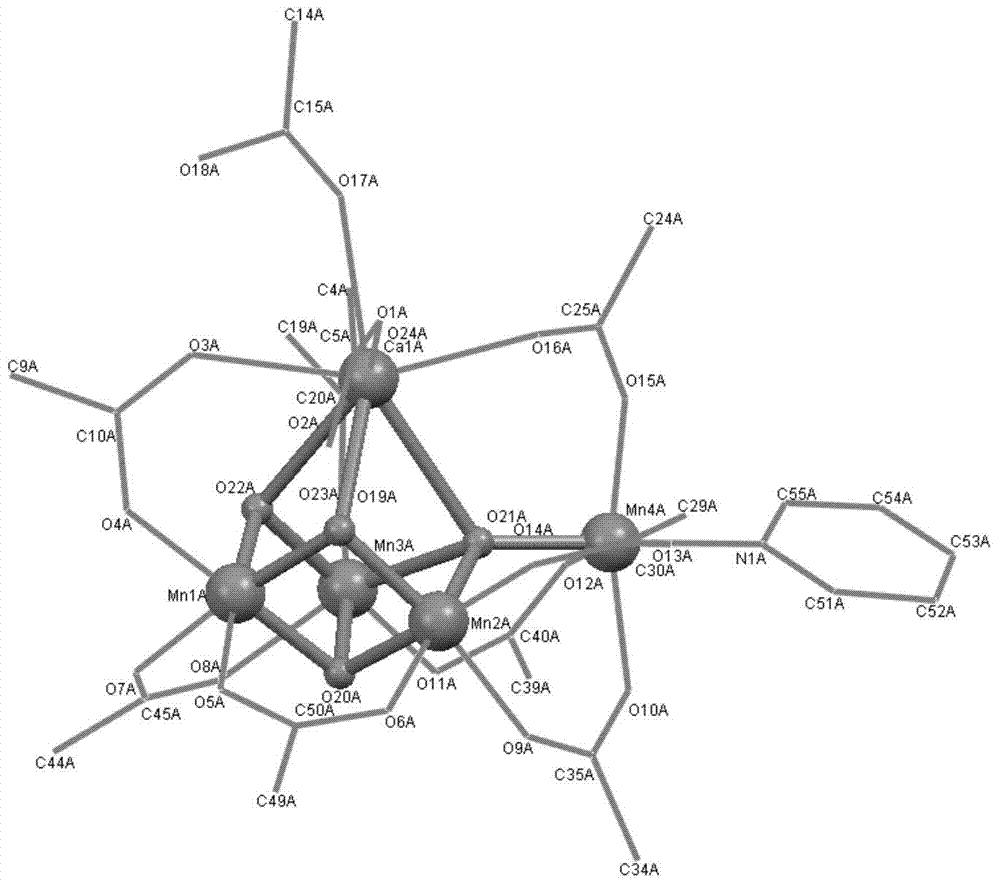
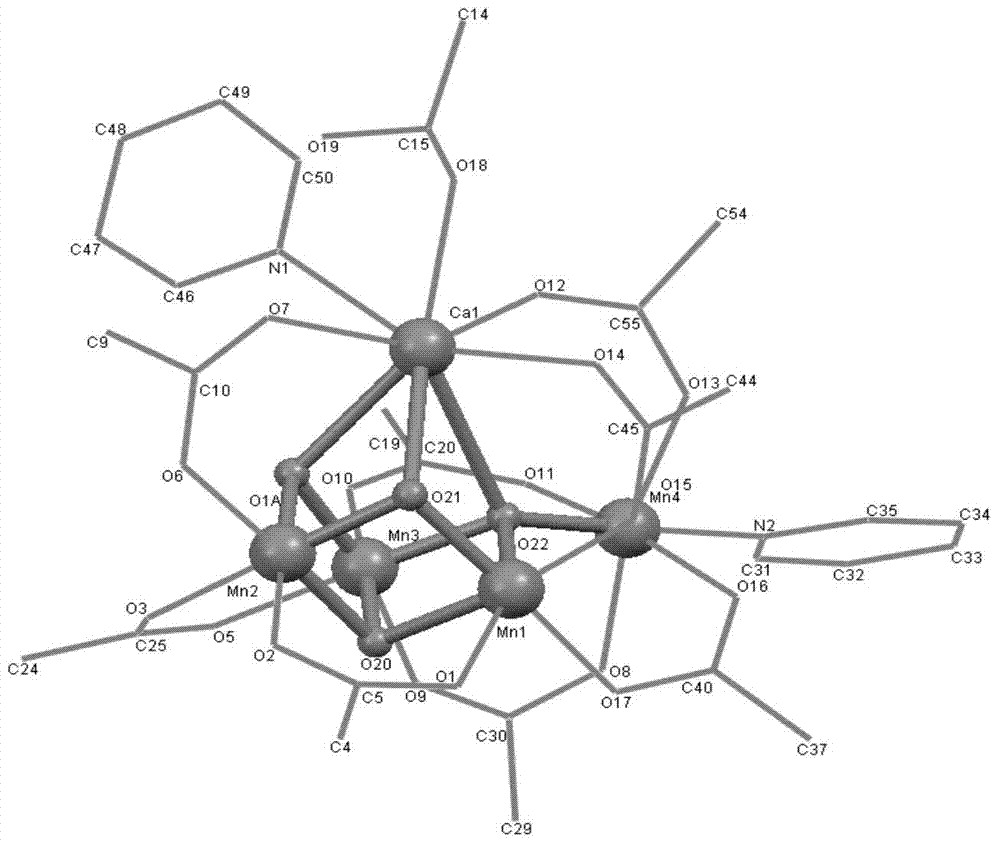
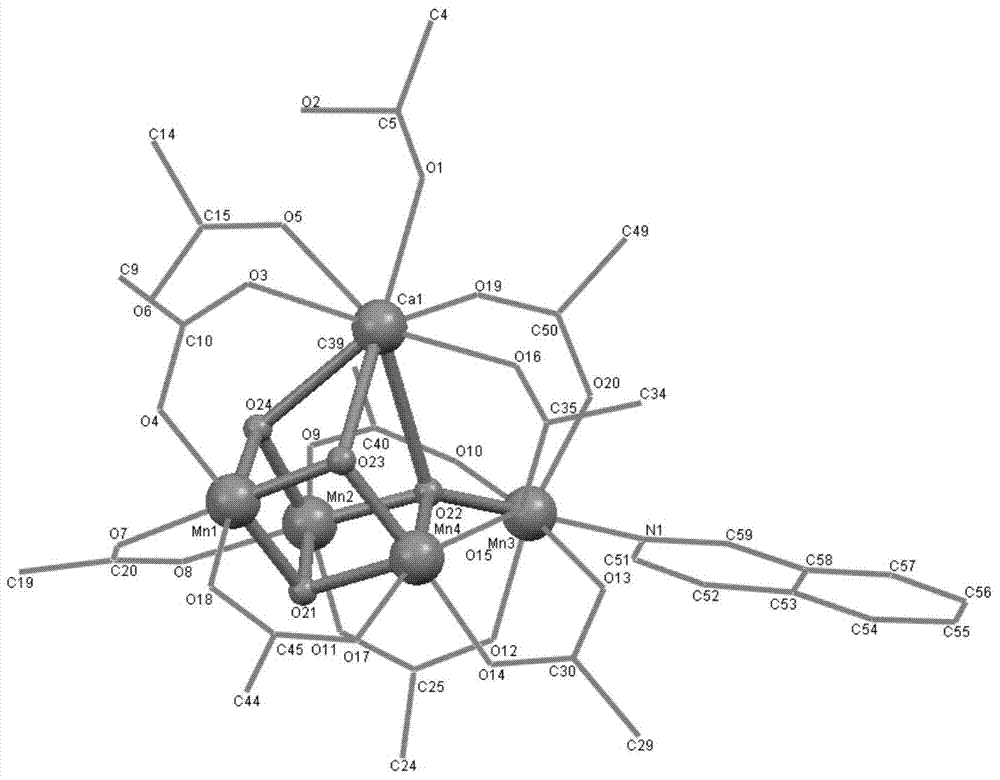
ActiveCN104761591ACatalytic crackingOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic reactionsX-rayElectron spectroscopy
The present invention provides a preparation method and application of a Mn4CaO4 core structure-containing water cracking catalyst, a Mn4CaO4 core structure-containing cluster compound is compounded by cheap metal ions (Mn<2 +> and Ca<2 +> ions), a simple carboxylic ligand and a permanganate, the spatial structure is detected by single crystal X-ray diffraction, and physicochemical properties are characterized by electron spectroscopy, electrochemistry and electron paramagnetic nuclear magnetic resonance technology and the like. The cluster compound can catalyze the water cracking in the presence of an oxidant for release of oxygen, and also can catalyze the water cracking on the electrode surface, and electrons are released to the electrode surface to form a current.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for making lithographic plate
InactiveCN1334492AFast heat conductionImprove conduction abilityPhotosensitive material processingPrinting pre-treatmentNitriteX-ray
The present invention relates to a preparation method for a lithographic printing plate, which comprises forming a presensitized plate by coating a photosensitive layer or thermosensitive layer on an aluminum substrate treated with an aqueous solution after optionally anodized and developing the presensitized plate with a developer comprising no silicate, wherein the aqueous solution comprises at least one compound selected from the group consisting of nitrite group-containing compound, fluorine atom-containing compound and phosphorous atom-containing compound, in the proviso that when the at least one compound is fluorine atom-containing compound, the treated aluminum substrate has a surface which satisfies the formula: 0.30 <= A / (A+B)<=0.90 (wherein, A represents peak area of fluorine atom (1S) (counts eV / sec) determined by X ray Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA), and B represents peak area of aluminum atom (2P) (counts eV / sec) determined by X ray ESCA, and when the at least one compound is phosphorous atom-containing compound, the treated aluminum substrate has a surface which satisfies the formula: 0.05 <= A / (A+B) <= 0.70 (wherein, A represents peak area of phosphorous atom (1P) (counts eV / sec) determined by X ray ESCA, and B represents peak area of aluminum atom (2P) (counts eV / sec) determined by X ray ESCA.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Nano Bi-material Electromagnetic Spectrum Shifter
ActiveUS20170090082A1Wider colorReduce absorptionMirrorsVacuum evaporation coatingFrequency spectrumFiltration
The present invention relates to a nano bi-material, electromagnetic spectrum shifter based on said nano bi-material and method to produce said electromagnetic spectrum shifter using said nano bi-material. In particular, the present invention provides nano bi-material based electromagnetic spectrum shifter, e.g. color filters, with a wide range of transmission and color tunability and methods to produce said color filters. The present invention has applications in color filtration and production of color filters; reflector and production of reflectors; and electromagnetic spectrum shifter and production of electromagnetic spectrum shifters.
Owner:HONG KONG BAPTIST UNIV
Toner for electrostatic image development, manufacturing method thereof, electrostatic image developer and image forming method
A toner for electrostatic image development comprising a binder resin and a colorant, the toner having a content of an aluminum element with respect to carbon of approximately 0.005 atm % to approximately 0.02 atm % as measured by X-ray photo-electron spectroscopy.
Owner:FUJIFILM BUSINESS INNOVATION CORP
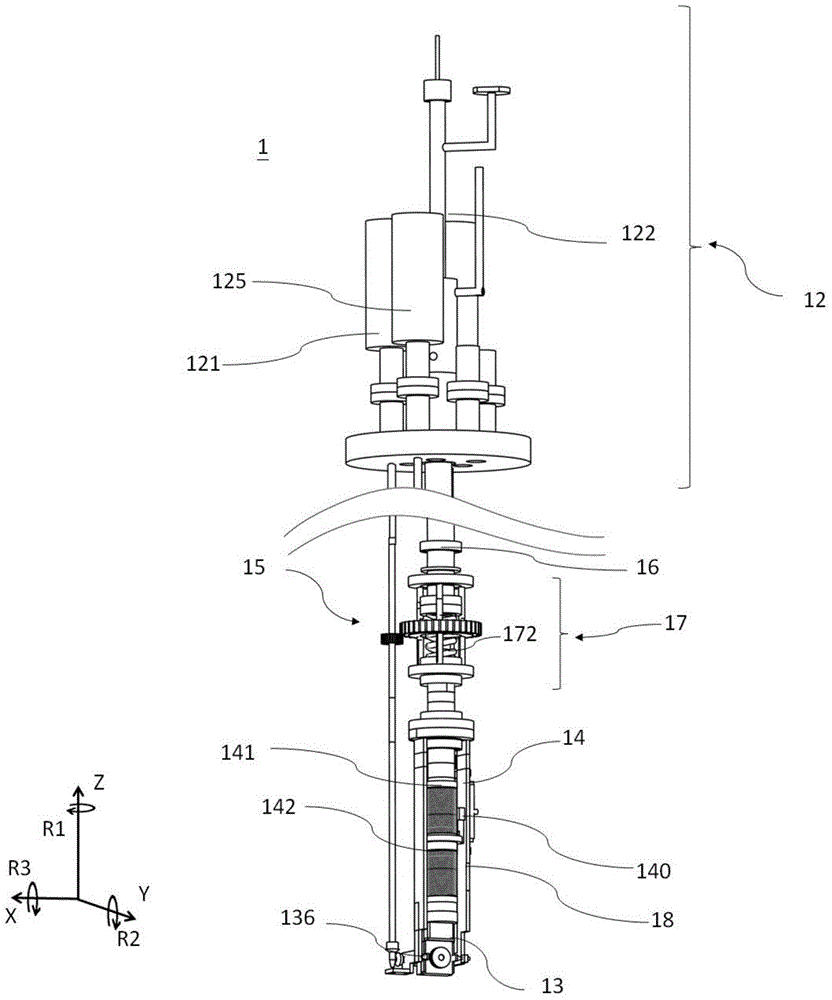
Electron spectroscopy system
ActiveUS20190096627A1Maintain throughputHigh momentum and energy resolutionStatic energy spectrometersElectron spectroscopyRadio frequency
An electron spectroscopy system and method are disclosed. In another aspect, an ultrabright and ultrafast angle-resolved electron spectroscopy system is provided. A further aspect of the present system employs an electron gun, a radio frequency cavity and multiple spectrometers. Yet another aspect uses spectrometers in an aligned manner to deflect and focus electrons emitted by the electron gun. Moreover, an ultrafast laser is coupled to an electron spectroscopy system. A bunch of monochromatic electrons have their energy compressed and reoriented in an additional aspect of the present system. A further aspect of the present electron spectroscopy system employs adaptive and / or adjustable optics to optimize both time and energy compression. Another aspect provides at least two RF lenses or cavities, one before a specimen and one after the specimen.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
Rapid synthesis of graphene and formation of graphene structures
ActiveUS9187824B2Shorten the timeReduce the temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneDoped grapheneX-ray
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Glass substrate, method for producing glass substrate and black matrix substrate
InactiveCN106458734AExcellent adhesionPrevent peelingNon-linear opticsGlass productionSilicate glassElectron spectroscopy
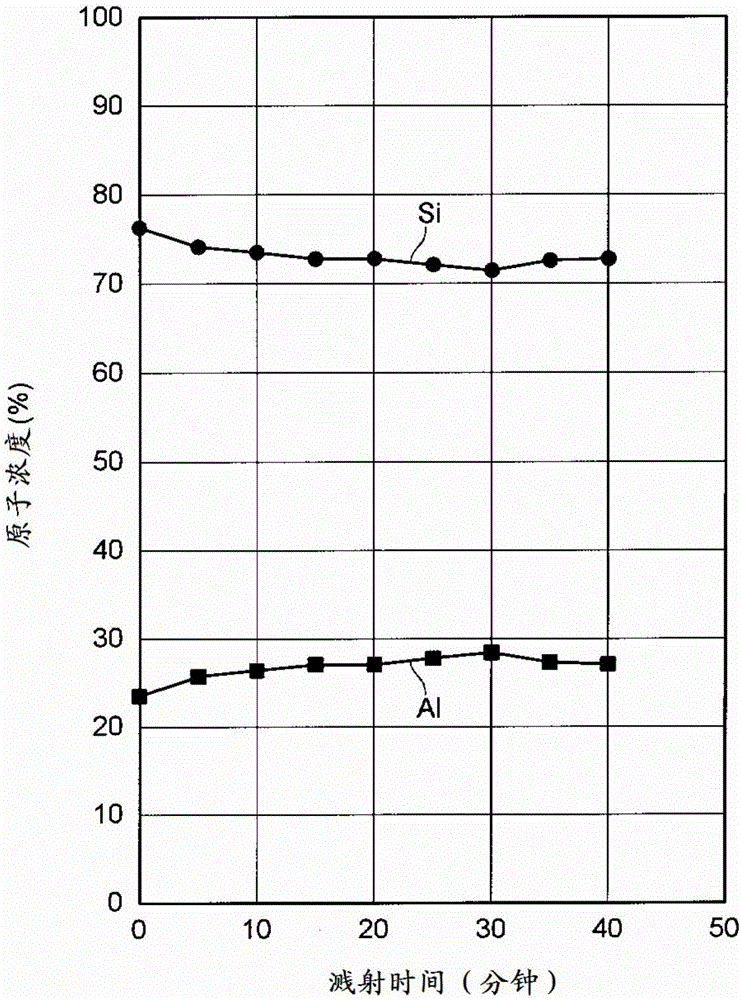
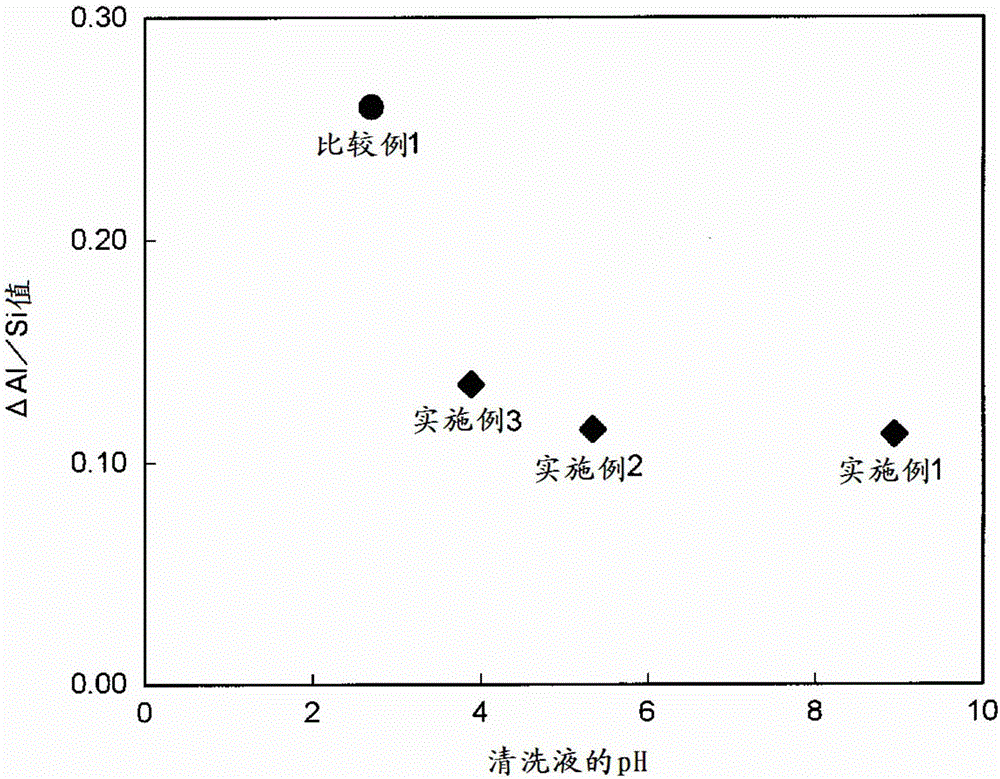
A glass substrate which is formed of silicate glass containing aluminum and which is configured so that the value obtained by subtracting the ratio of the atomic concentration of aluminum to the atomic concentration of silicon in the surface of the glass substrate as measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy from the ratio of the atomic concentration of aluminum to the atomic concentration of silicon in the inside of the glass substrate as measured by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy is 0.25 or less.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD
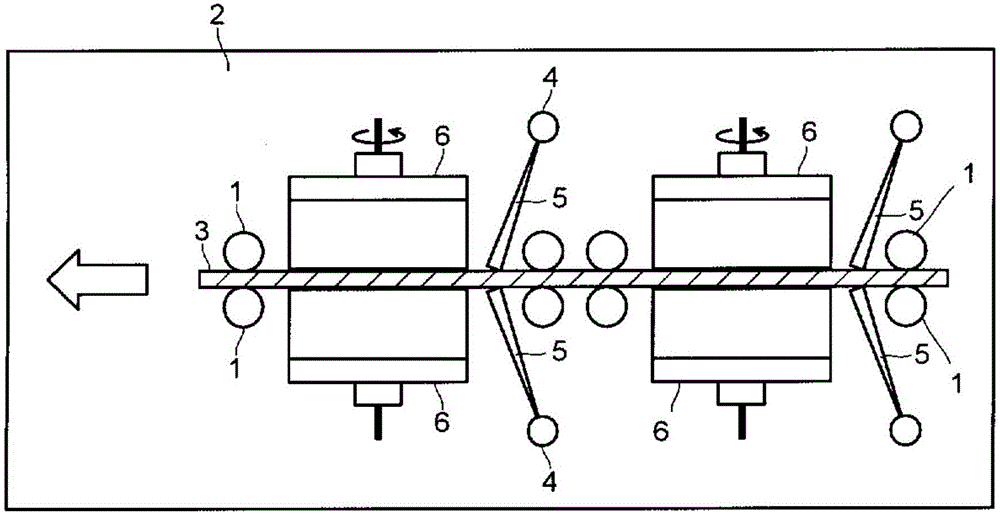
Photo electron spectroscopy equipment having sample adjustment controller
ActiveCN105466739AImprove convenienceImprove thermal conductivityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationEngineeringElectron spectroscopy
The invention relates to photo electron spectroscopy equipment having a sample adjustment controller, wherein the sample adjustment controller comprises a control portion, a joint portion, a sample portion and a transmission portion, one end of the control portion is connected to one end of the joint portion, the other end of the joint portion is connected to the sample portion, the transmission portion is respectively connected to the control portion, the joint portion and the sample portion, the joint portion comprises at least a corrugated pipe, and an operator can drive the transmission rod of the transmission portion by controlling the control handle of the control portion to make the joint portion be driven by the transmission rod so as to further change the position of the sample portion. According to the present invention, the sample adjustment apparatus is suitable for any degrees of vacuum environments.
Owner:GAINIA INTELLECTUAL ASSET SERVICES
Gas detection and identification apparatus and method
InactiveUS20070273384A1Easy to implementHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalytePenning ionization
Gas detection and identification apparatus that receives a flow of a mixture of a carrier gas and an analyte gas and detects and identifies the components of the flowing gas mixture by Penning Ionization Electron Spectroscopy (PIES).
Owner:SHEVEREV VALERY A
Metal oxide thin film, method of producing same, and coating solution for forming metal oxide thin film used in said method
ActiveUS20160118253A1Increase the amount addedLow production costTransistorConductive materialBinding energyNitrogen
A metal oxide thin film according to the present invention has a peak which is attributed to 1s electrons of nitrogen in a binding energy range of 402 eV to 405 eV in an XPS spectrum obtained by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy, in which peak areas, which are obtained by separation of peaks having a peak energy of a metal-oxygen bond attributed to 1s electrons of oxygen, satisfy the following expression.0.9<D / E (1)(D represents a peak area of a component having a peak position in a binding energy range of 529 eV or higher and lower than 531 eV, and E represents a peak area of a component having a peak position in a binding energy range of 531 eV to 532 eV)
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
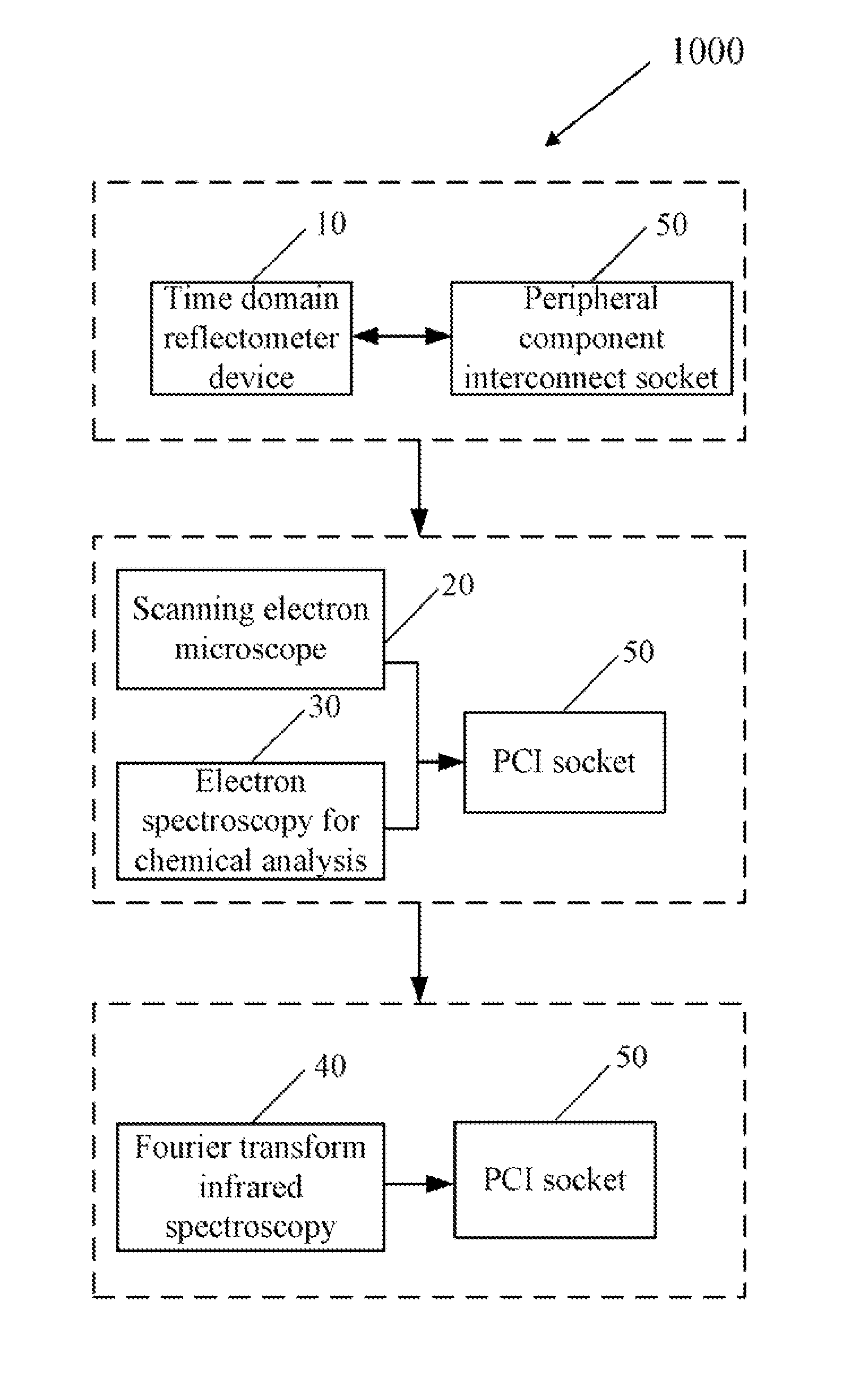
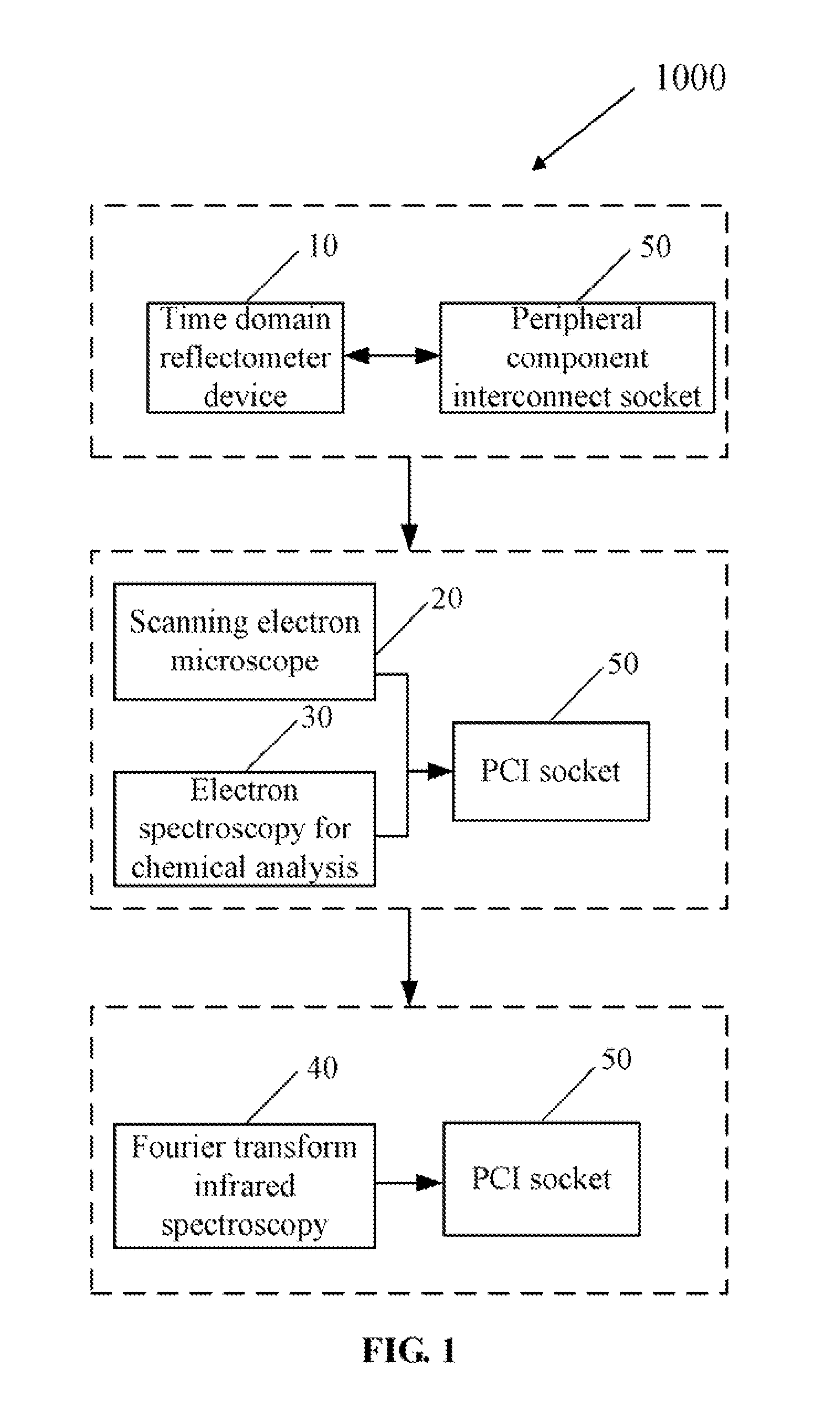
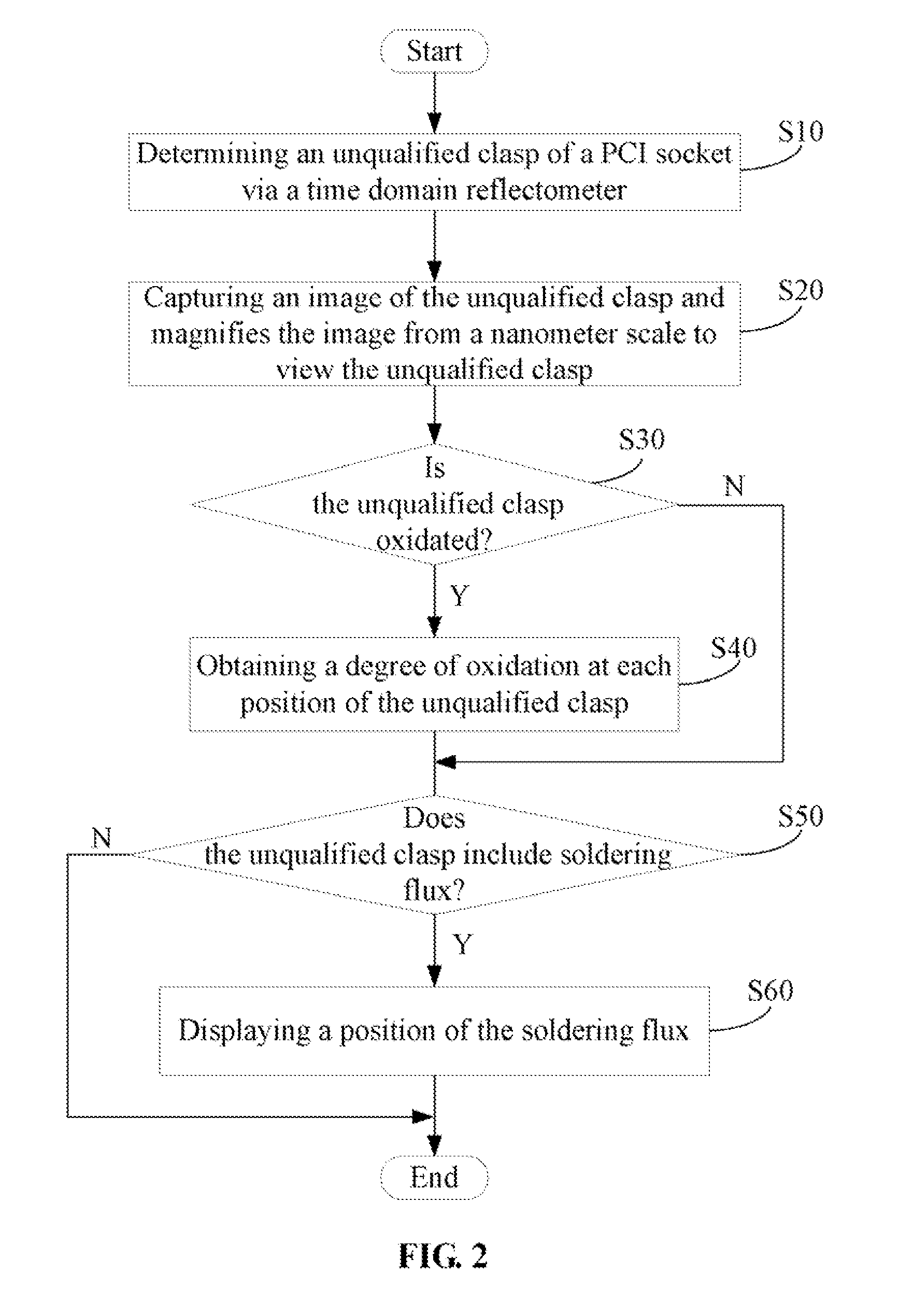
Method for analyzing peripheral component interconnect sockets
InactiveUS20120014589A1Electrical measurement instrument detailsElectric connection testingTime domainTime-domain reflectometer
A method uses a time domain reflectometer (TDR) to determine unqualified clasps of a peripheral component interconnect (PCI) socket. A scanning electron microscope (SEM) captures an image of an unqualified clasp and magnifies the image from a nanometer scale to view the unqualified clasp. An electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA) obtains a degree of oxidation at each position of the unqualified clasp in response to a determination that the unqualified clasp is oxidated. A Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) displays a position of the soldering flux using in response to the determination that the unqualified clasp comprises the soldering flux.
Owner:HON HAI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Gas detection and identification apparatus and method
InactiveUS7408360B2Easy to implementHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAnalytePenning ionization
Gas detection and identification apparatus that receives a flow of a mixture of a carrier gas and an analyte gas and detects and identifies the components of the flowing gas mixture by Penning Ionization Electron Spectroscopy (PIES).
Owner:SHEVEREV VALERY A
Method and apparatus for in situ depositing of neutral Cs under ultra-high vacuum to analytical ends
ActiveUS7205534B2Laser detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltra-high vacuumElectron spectroscopy
The present invention relates to a method for modifying the electronic properties of a surface to analytical ends, such as SIMS or electron spectroscopy, characterised in that it comprises in situ deposition of pure neutral cesium (Cs0), under ultra-high vacuum, said neutral cesium being enabled in the form of a collimated adjustable stream. The invention relates also to the special column designed for implementing the method and to the corresponding energy and / or mass analyser instrument.
Owner:CENT RECH PUBLIC GABRIEL LIPPMANN
Light modulation film and method for manufacturing same, and light modulation element
ActiveUS20180173076A1Excellent light modulation performanceLight modulation performanceVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingDehydrogenationX-ray
A light modulation film (1) includes a light modulation layer (30) whose state is reversibly changed between a transparent state by hydrogenation and a reflective state by dehydrogenation, and a catalyst layer (40) that promotes hydrogenation and dehydrogenation in the light modulation layer, in this order on a polymer film substrate (10). In a thickness-direction distribution of an element concentration as measured by X-ray electron spectroscopy, the light modulation layer (30) includes a light modulation region (32) with an oxygen content of 50 atom % or more and having a thickness of 10 nm or more on a catalyst layer (40)-side, and an oxidized region (31) with an oxygen content of less than 50 atom % on a polymer film substrate (10)-side.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method for simulating spatial energy spectrum environment by using single energy electron beam
InactiveCN107219414AImprove accuracyImplementation descriptionEnvironmental/reliability testsBeam matchingElectron spectroscopy
The invention discloses a method for simulating a spatial energy spectrum environment by using a single energy electron beam. The method comprises: a spatial plasma distribution function and a velocity element of the distribution function of a GEO orbit are determined; expression relationships between characterization parameters and the velocity element of a single energy electron beam and plasma are established respectively; a matching equation is established by using velocity element identity as a matching target according to a plasma characterization parameter value of a to-be-simulated spatial energy spectrum environment, the equation is solved to obtain the density and velocity of the single energy electron beam for simulating the spatial energy spectrum environment, and then the energy and beam current density of the single energy electron beam are obtained by transform. According to the invention, the velocity elements of the single energy electron beam and the spatial energy spectrum distribution plasma are matched and the energy and beam current density selection parameters of the single energy electron beam are obtained by calculation, so that description of spatial energy spectrum plasma environment characteristics is realized accurately and the support is provided for improving accuracy of the satellite charging-discharging effect ground simulation test.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF PHYSICS CHINESE ACADEMY OF SPACE TECH
Electrode film for electric double-layer capacitor and production method therefor
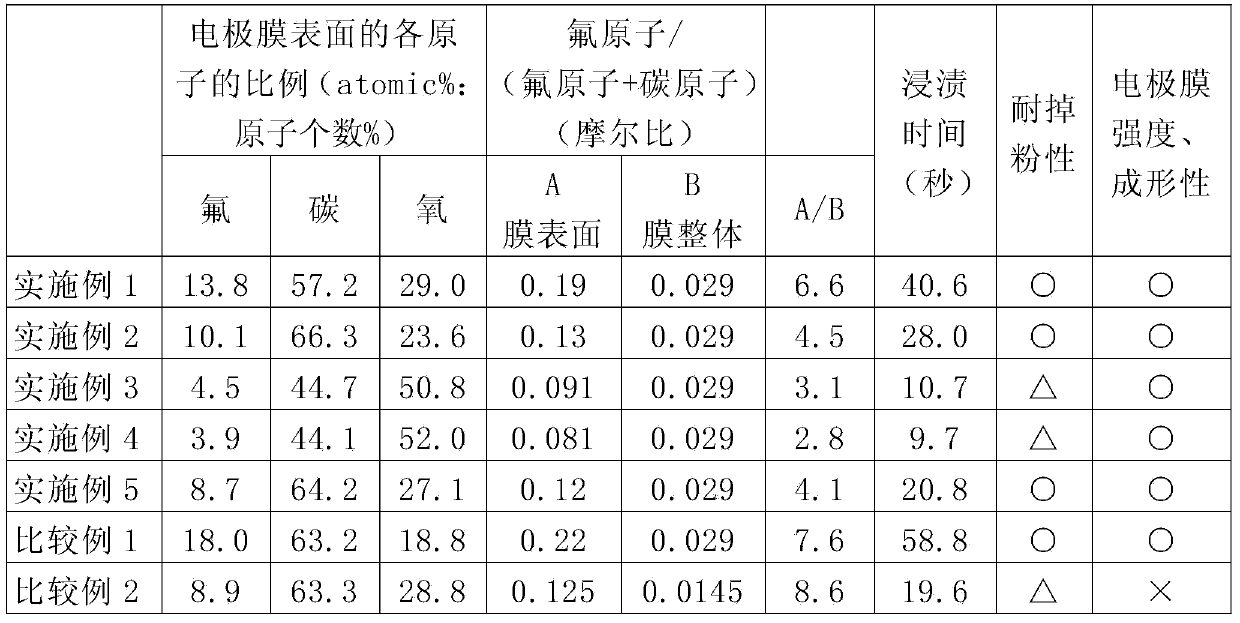
ActiveCN104272410AImprove impregnation effectHybrid capacitor electrodesHybrid/EDL manufactureActivated carbonElectron spectroscopy
[Problem] To provide an electrode film for an electric double-layer capacitor having high electrolyte impregnation while including a similar amount of fluororesin to conventional products. [Solution] An electrode film for an electric double-layer capacitor including activated carbon and a fluororesin binder, characterized by fulfilling A / B<=7.0 in at least one surface thereof (wherein A is the proportion of fluorine atoms to the total number of fluorine atoms and carbon atoms in the surface of the electrode film as measured using Electron Spectroscopy for Chemical Analysis (ESCA) and B is the proportion of fluorine atoms to the total number of fluorine atoms and carbon atoms contained in the electrode film.)
Owner:NIPPON VALQUA IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com