Patents
Literature
78results about "Static energy spectrometers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
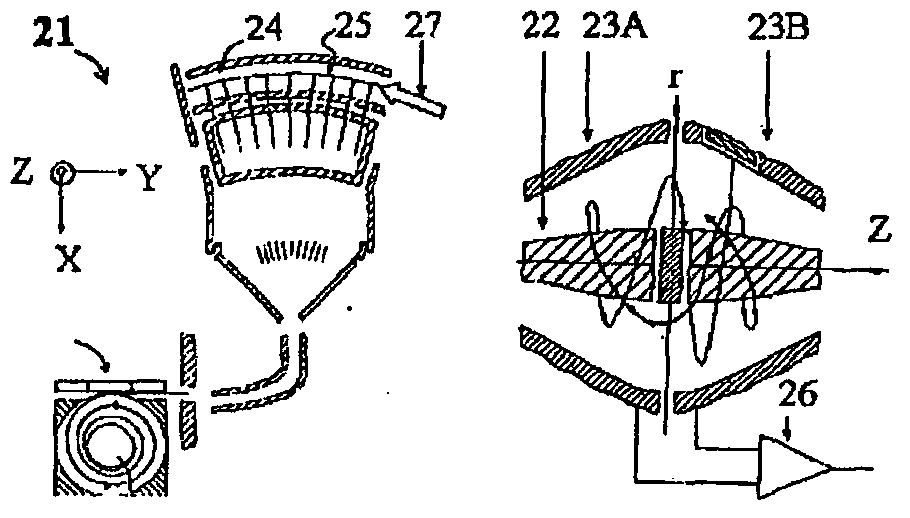
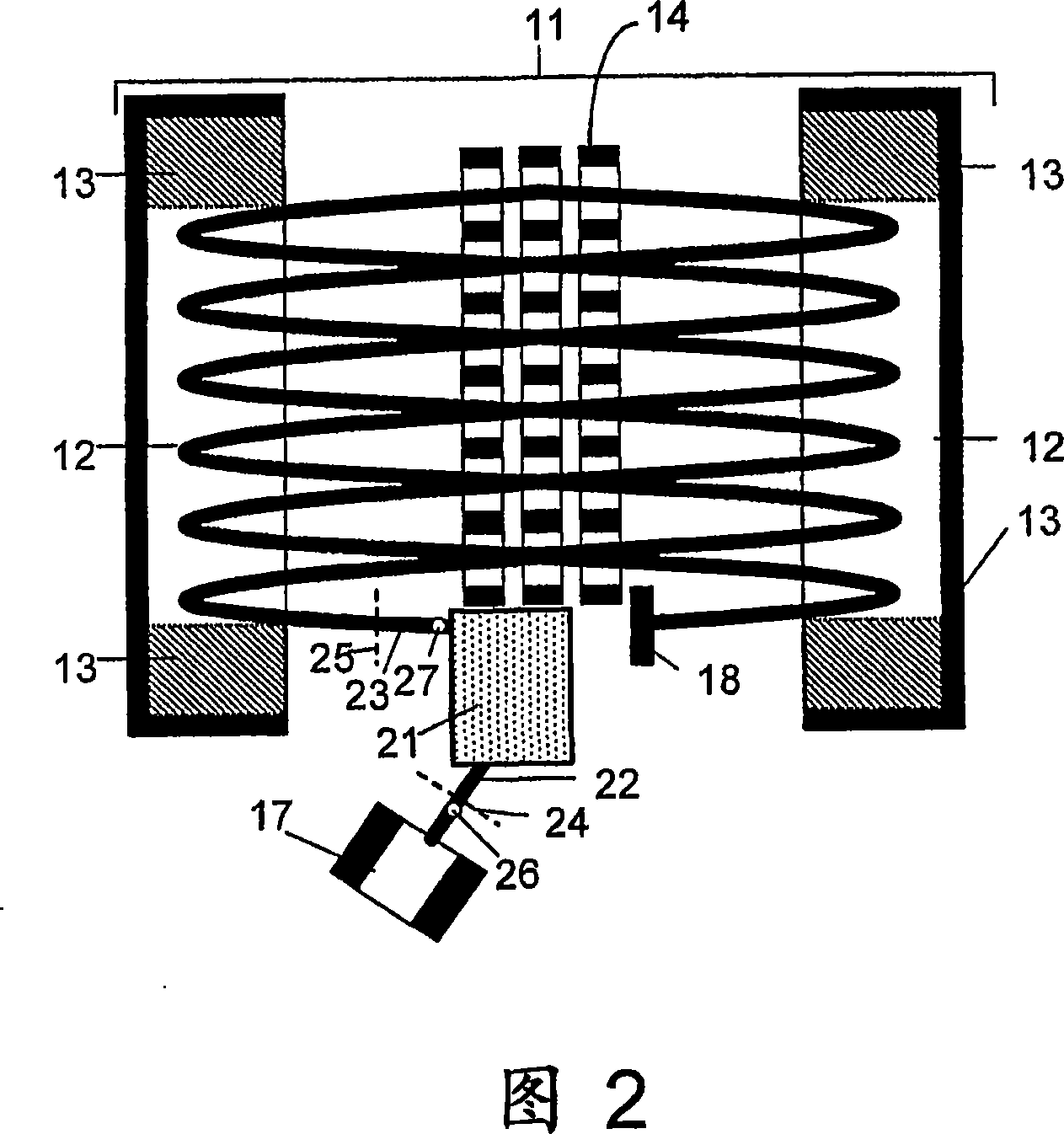
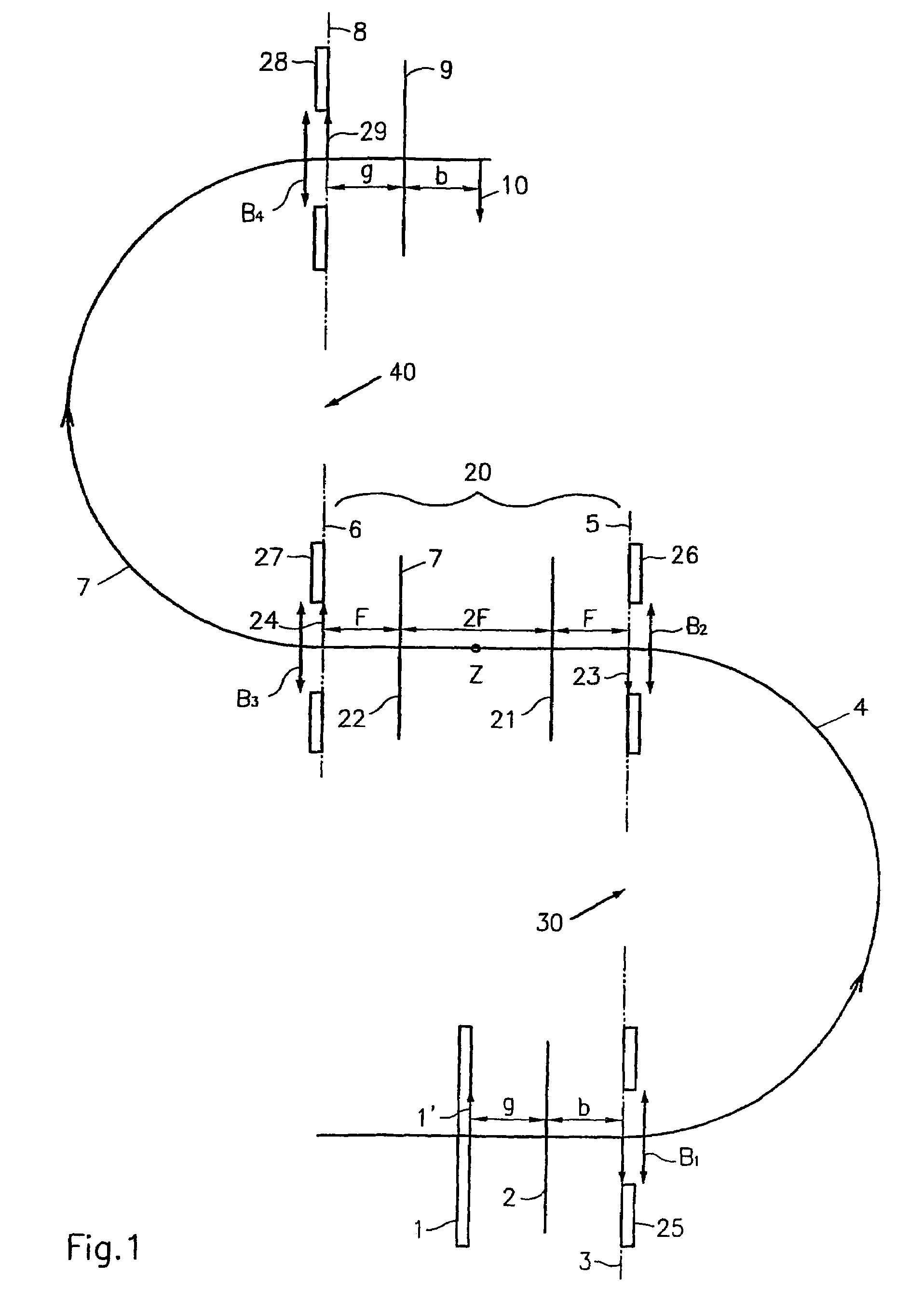
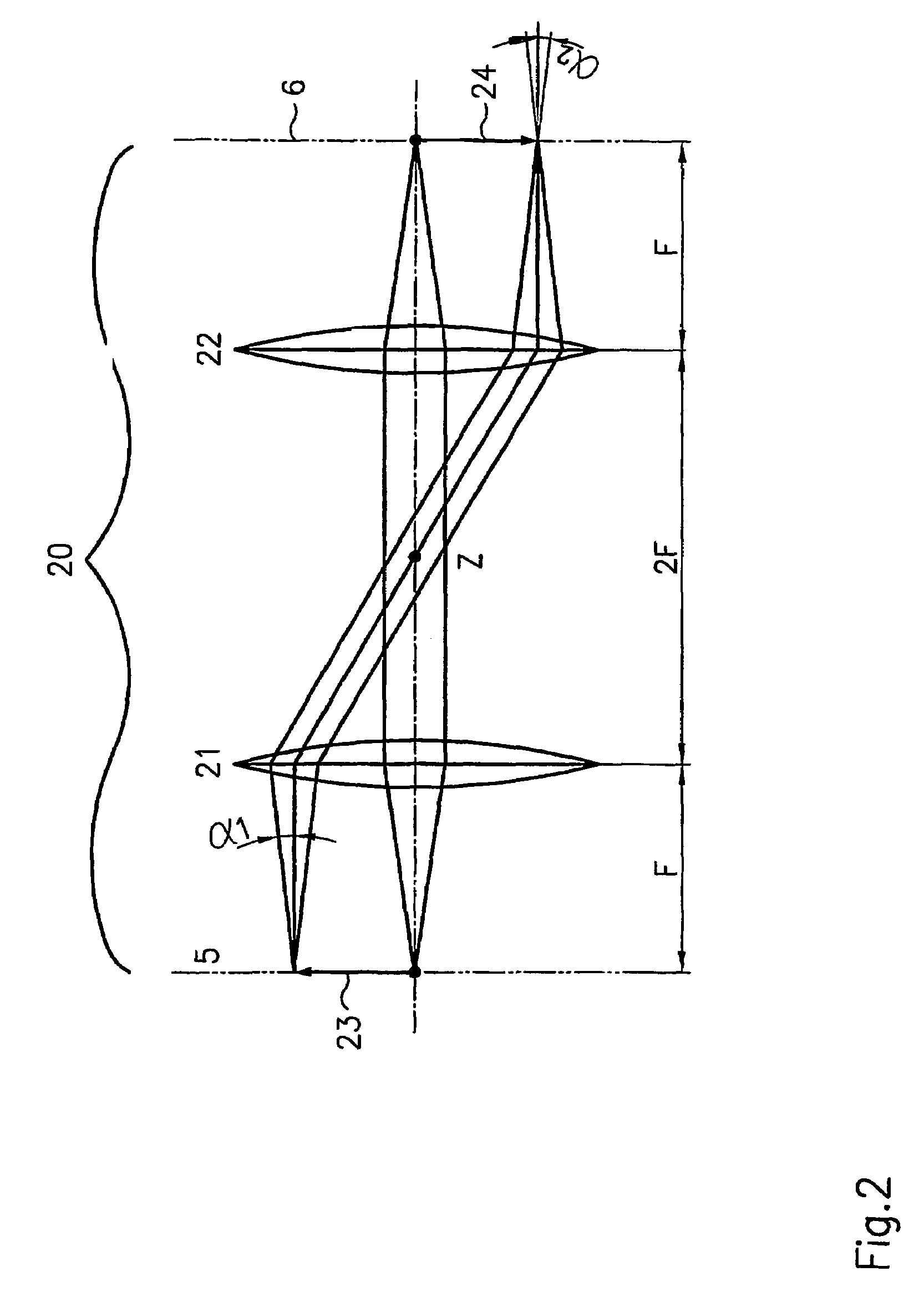
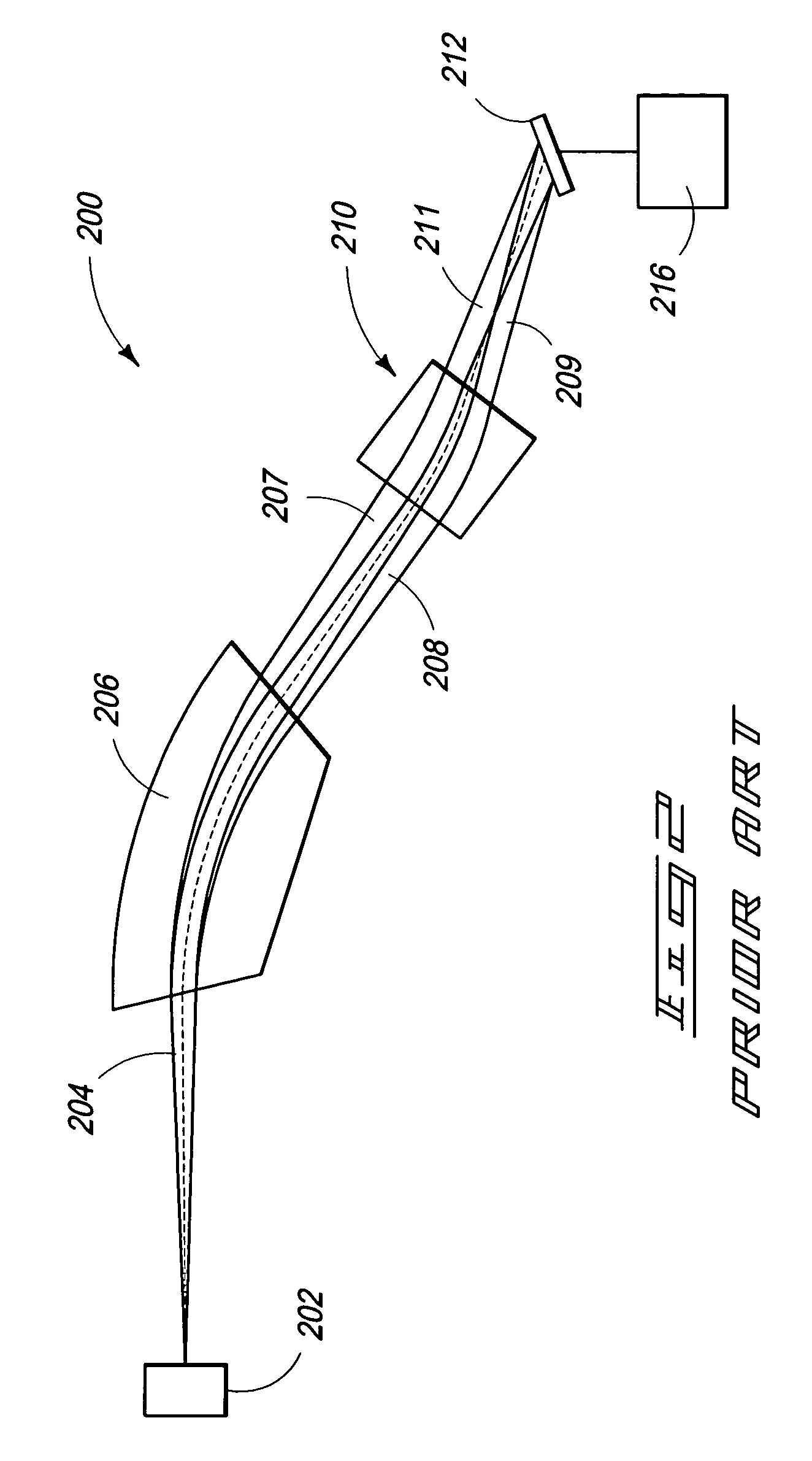
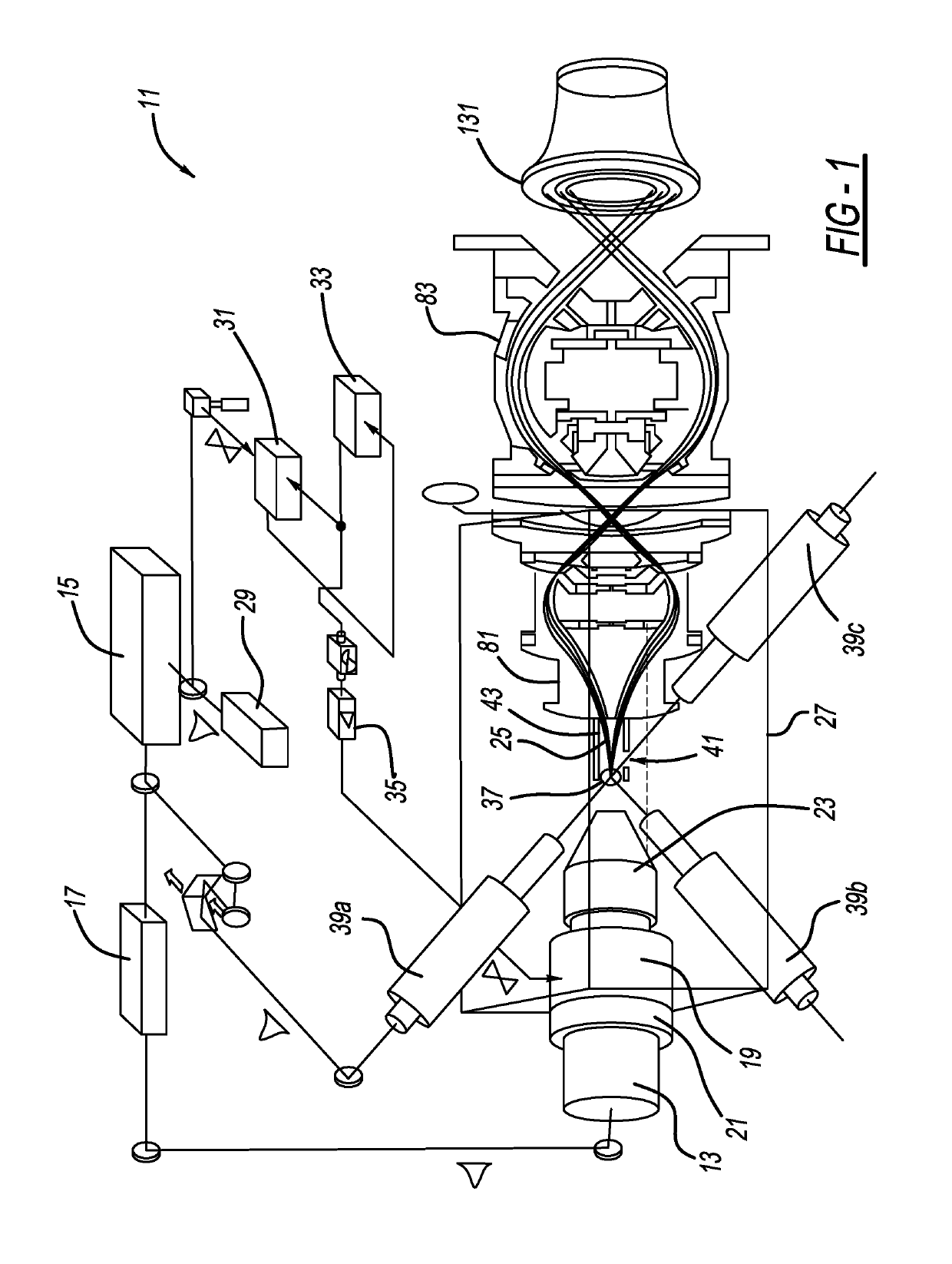
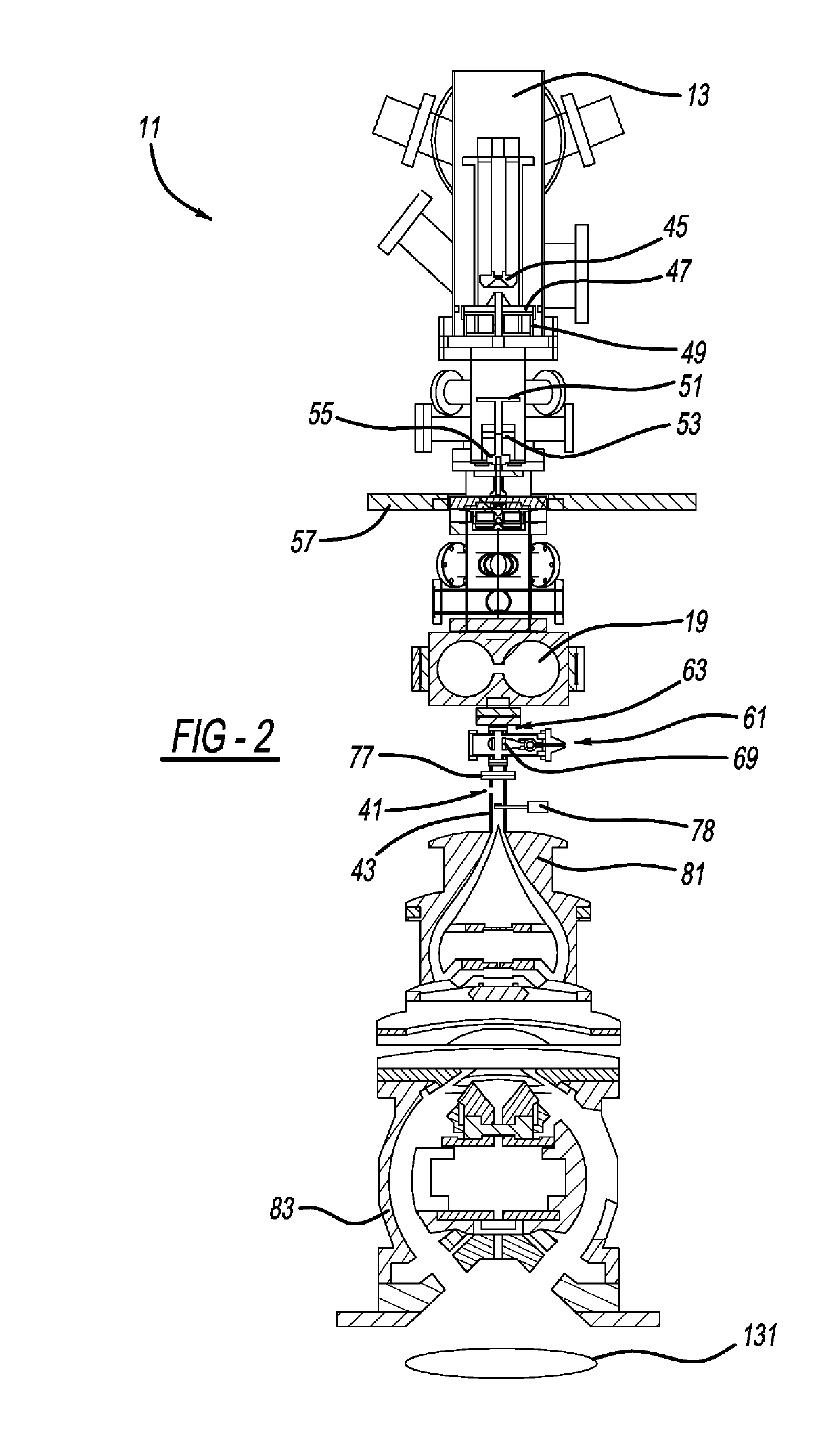
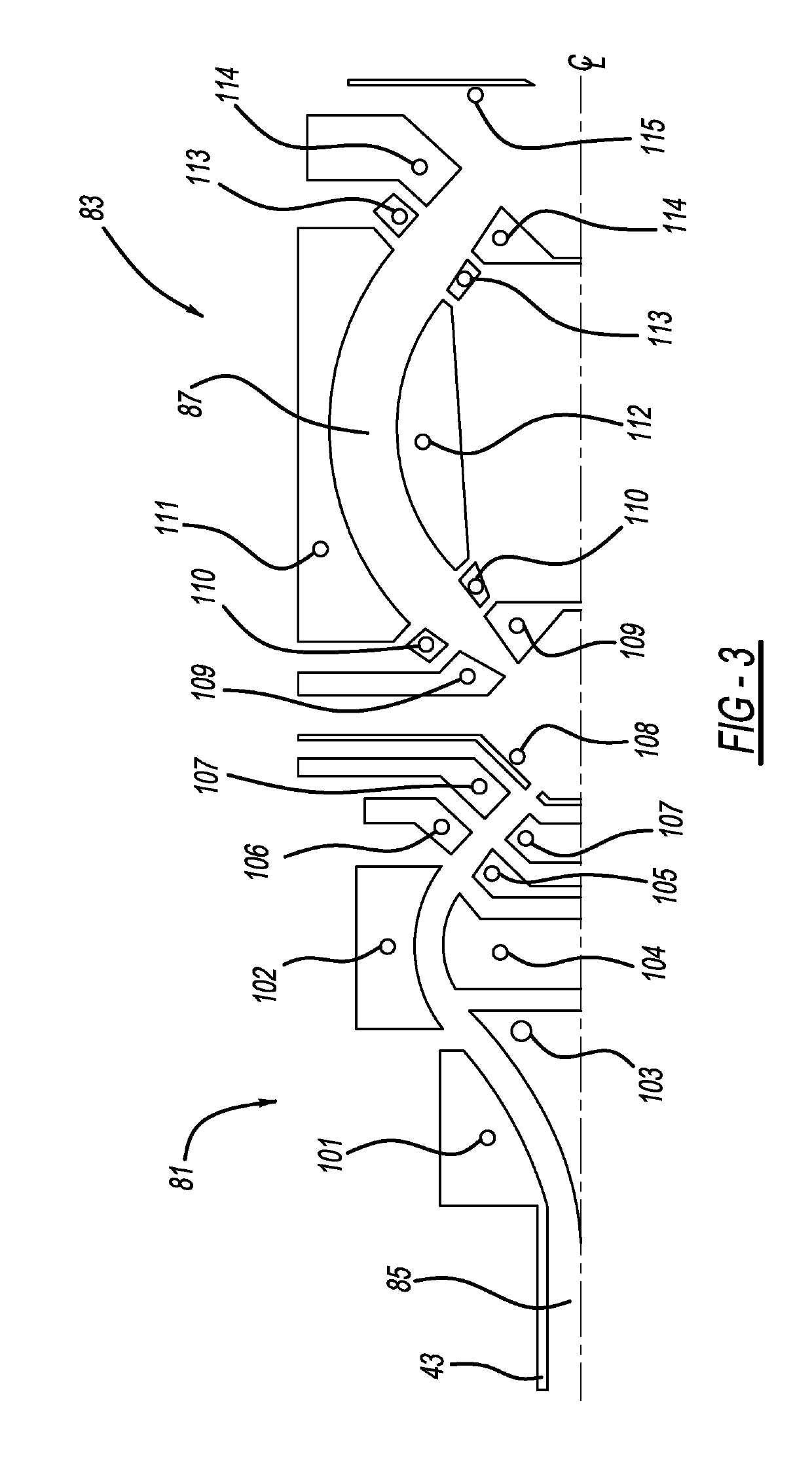
Multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer with isochronous curved ion interface
ActiveUS20060214100A1Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryIon transfer
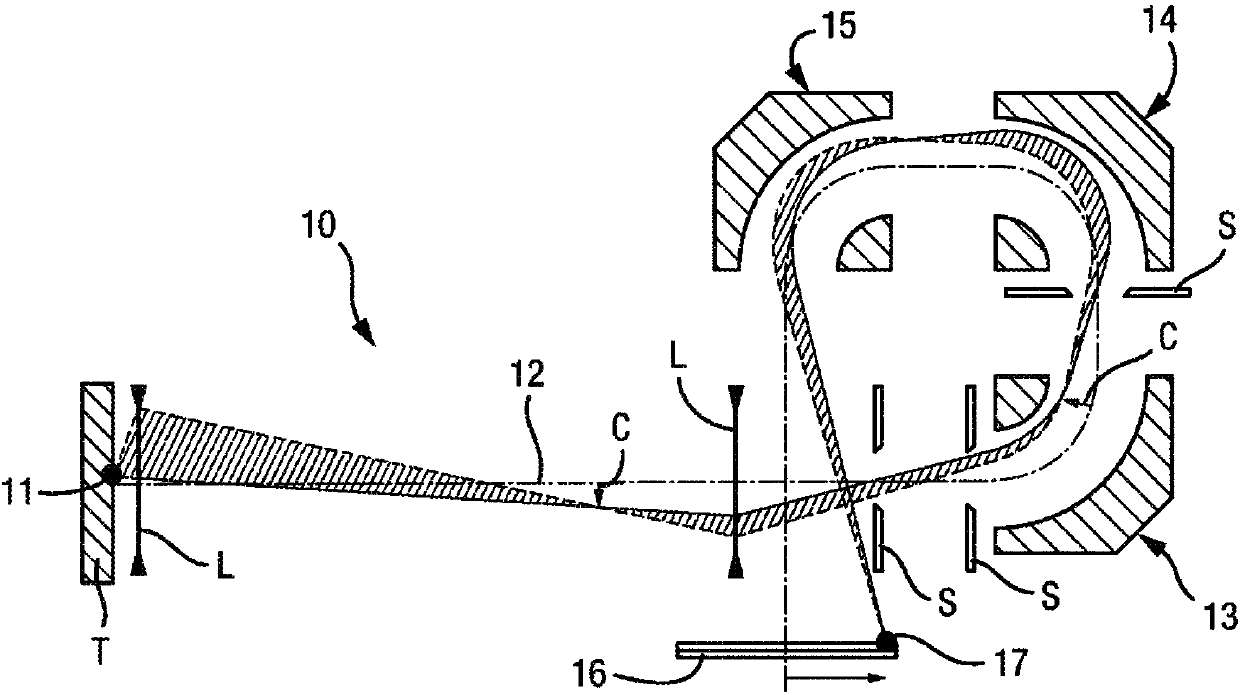
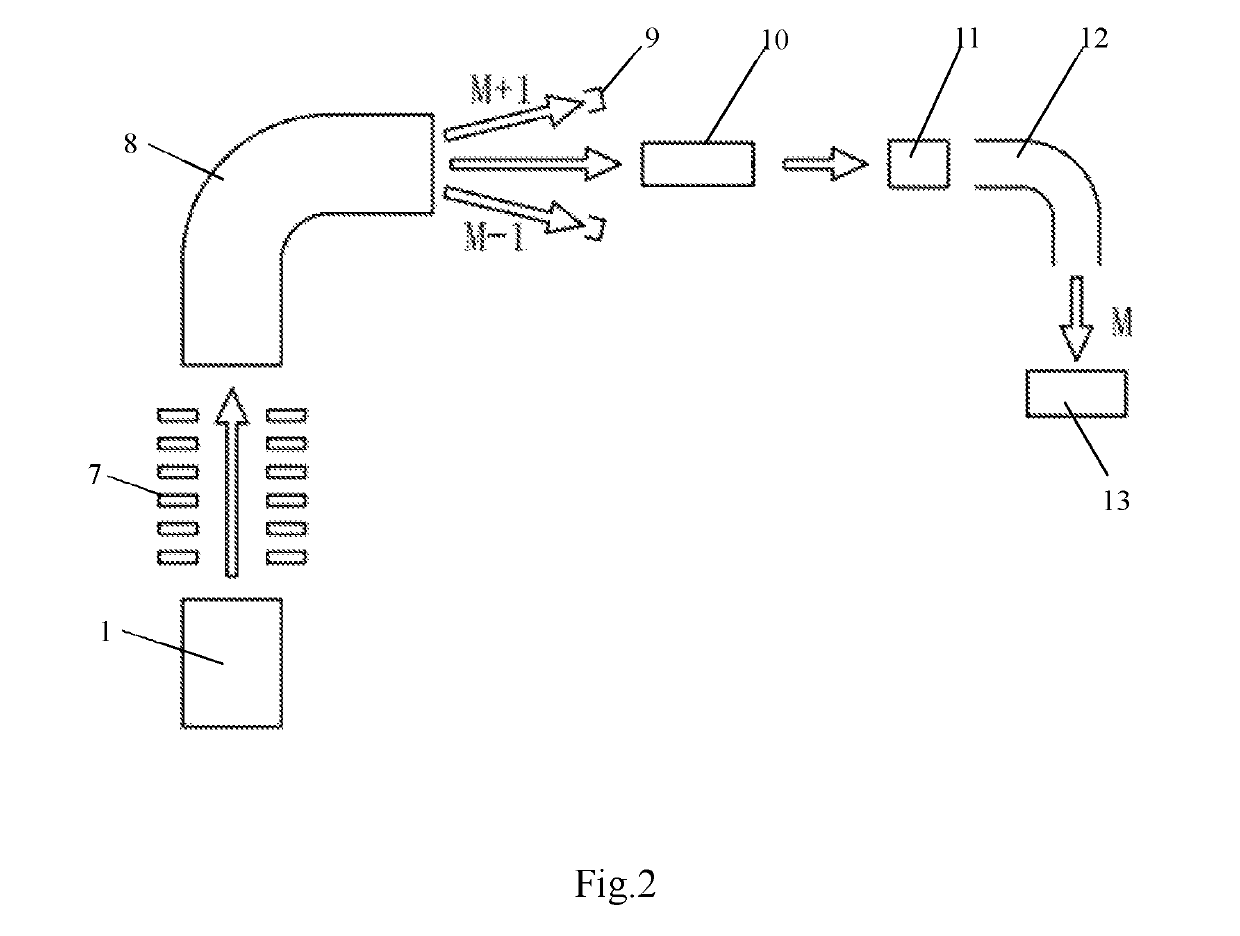
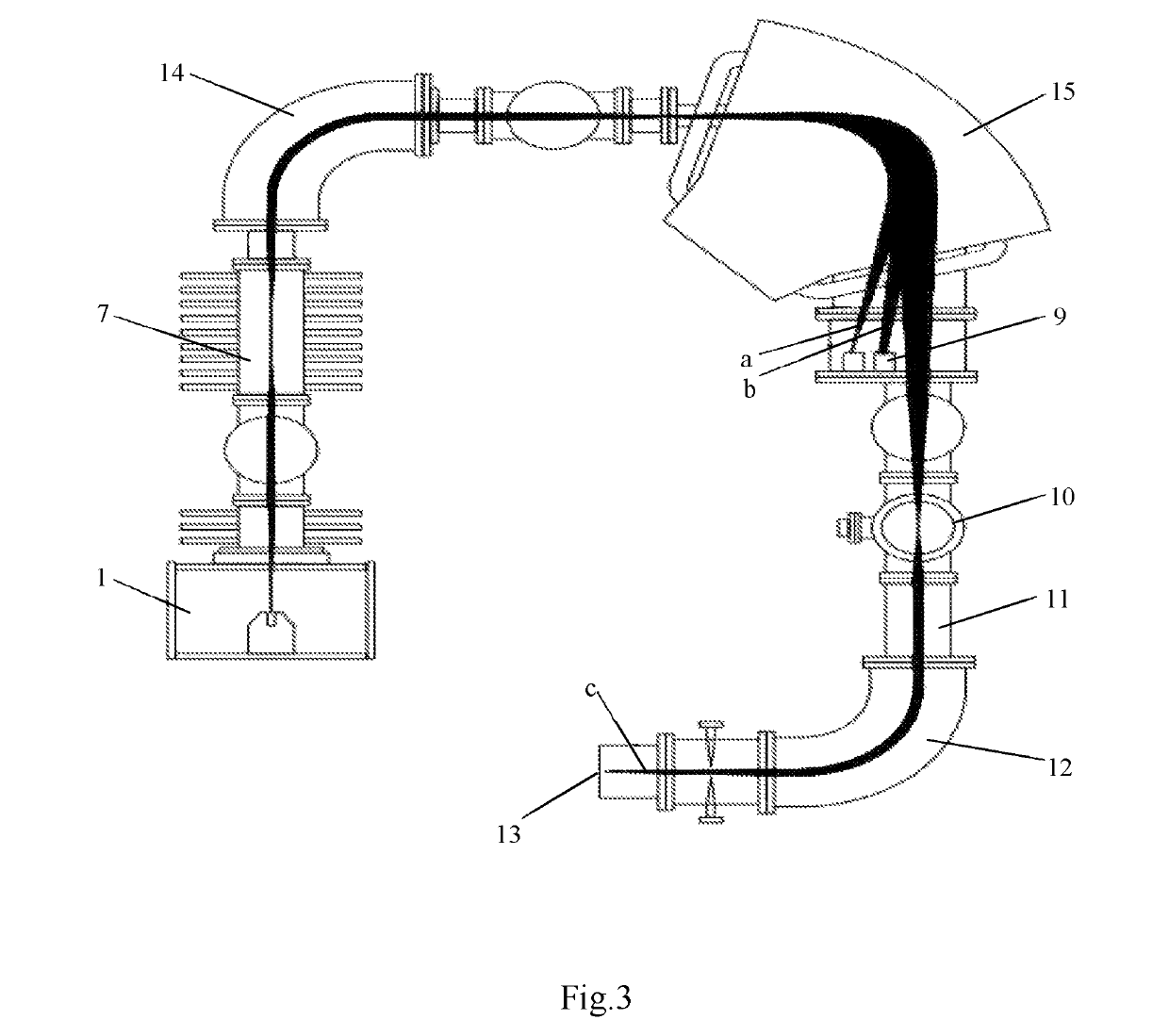
The present invention relates generally to a multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MR TOF MS). To improve mass resolving power of a planar MR TOF MS, a spatially isochronous and curved interface may be used for ion transfer in and out of the MR TOF analyzer. One embodiment comprises a planar grid-free MR TOF MS with periodic lenses in the field-free space, a linear ion trap for converting ion flow into pulses and a C-shaped isochronous interface made of electrostatic sectors. The interface allows transferring ions around the edges and fringing fields of the ion mirrors without introducing significant time spread. The interface may also provide energy filtering of ion packets. The non-correlated turn-around time of ion trap converter may be reduced by using a delayed ion extraction from the ion trap and excessive ion energy is filtered in the curved interface.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer with isochronous curved ion interface
ActiveUS7326925B2Time-of-flight spectrometersIsotope separationIon trap mass spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometry
The present invention relates generally to a multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer (MR TOF MS). To improve mass resolving power of a planar MR TOF MS, a spatially isochronous and curved interface may be used for ion transfer in and out of the MR TOF analyzer. One embodiment comprises a planar grid-free MR TOF MS with periodic lenses in the field-free space, a linear ion trap for converting ion flow into pulses and a C-shaped isochronous interface made of electrostatic sectors. The interface allows transferring ions around the edges and fringing fields of the ion mirrors without introducing significant time spread. The interface may also provide energy filtering of ion packets. The non-correlated turn-around time of ion trap converter may be reduced by using a delayed ion extraction from the ion trap and excessive ion energy is filtered in the curved interface.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Spectrometer and method of spectroscopy
InactiveUS6104029AStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersOptical spectrometerEnergy analyser
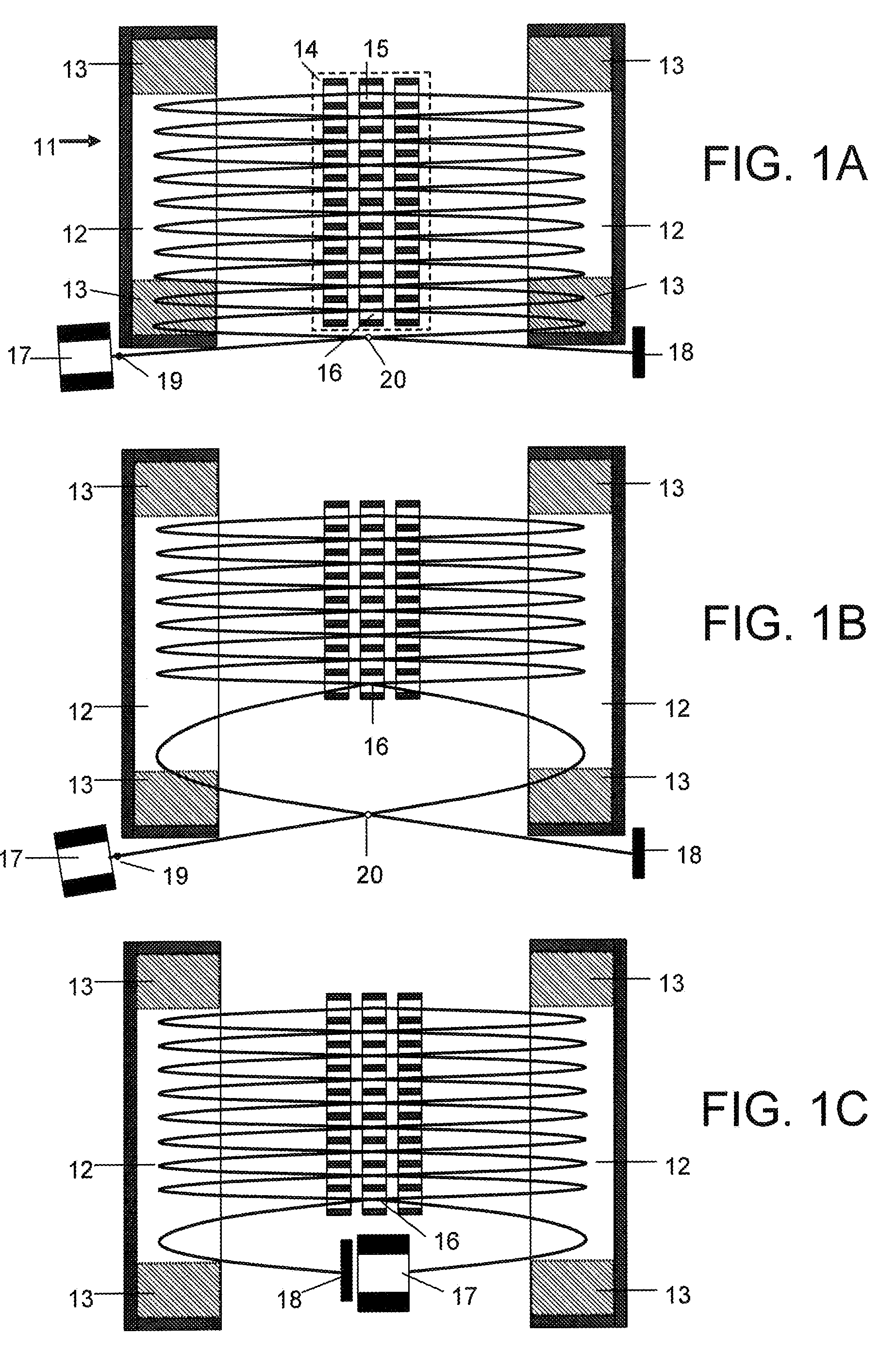
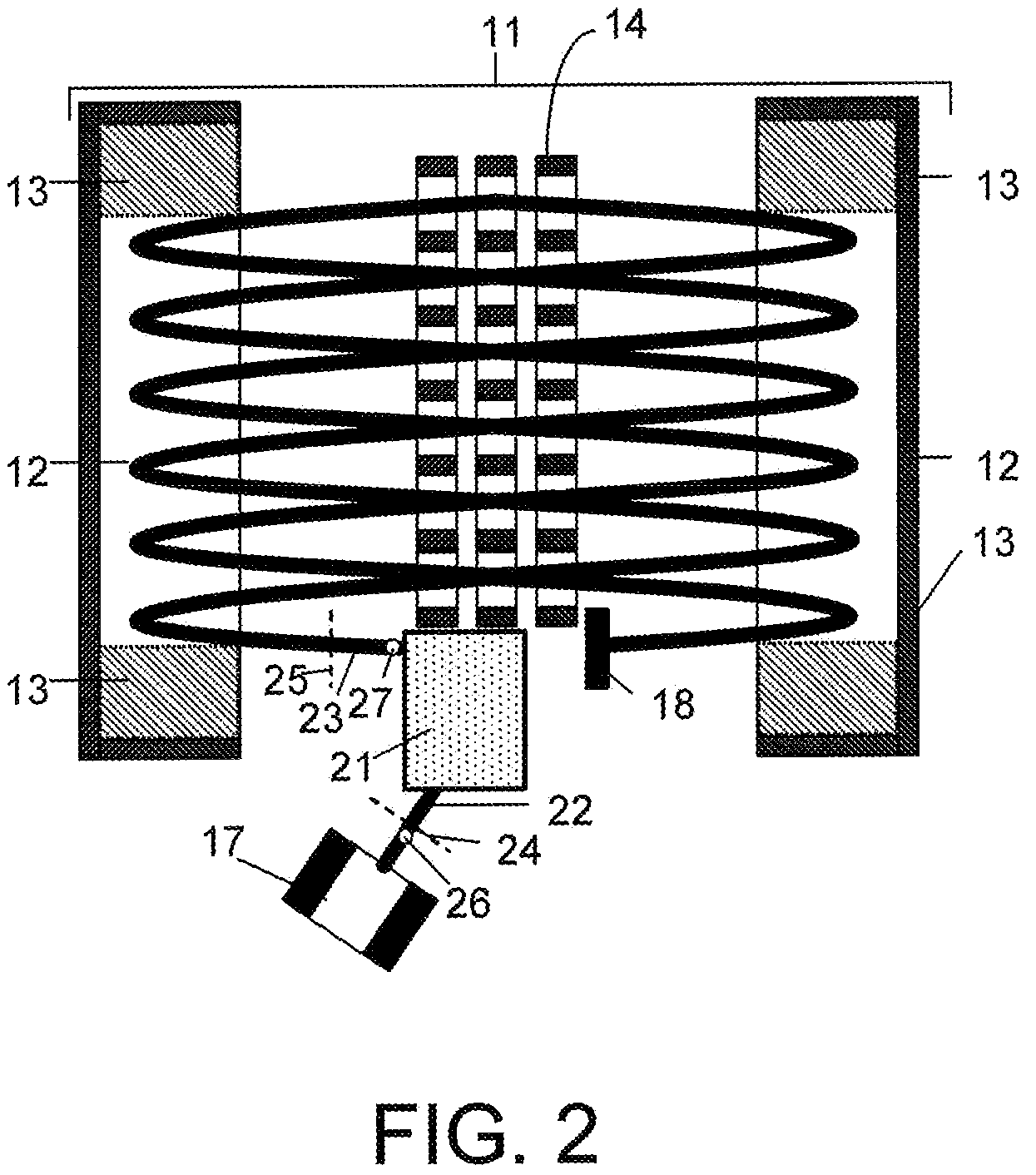
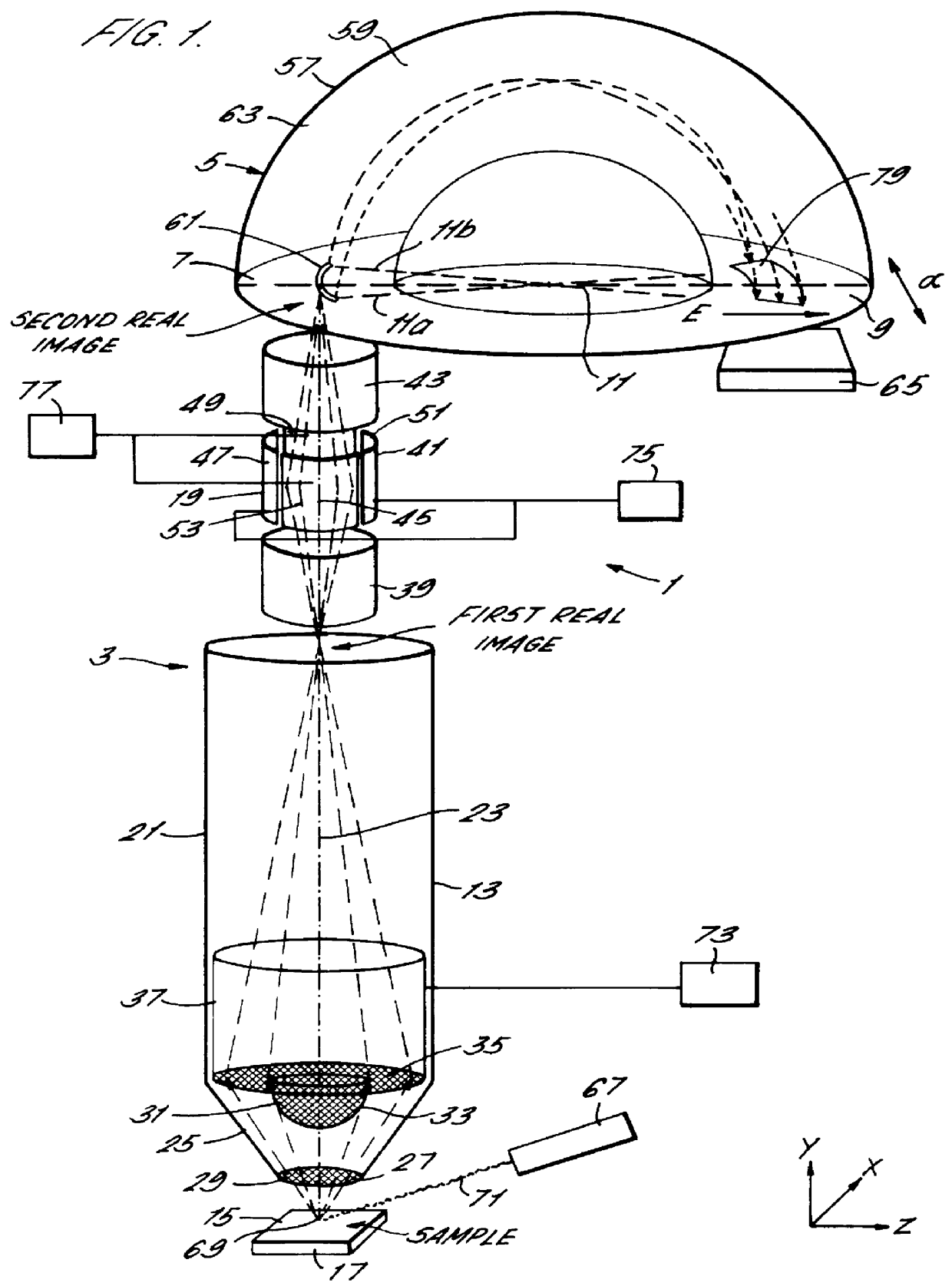
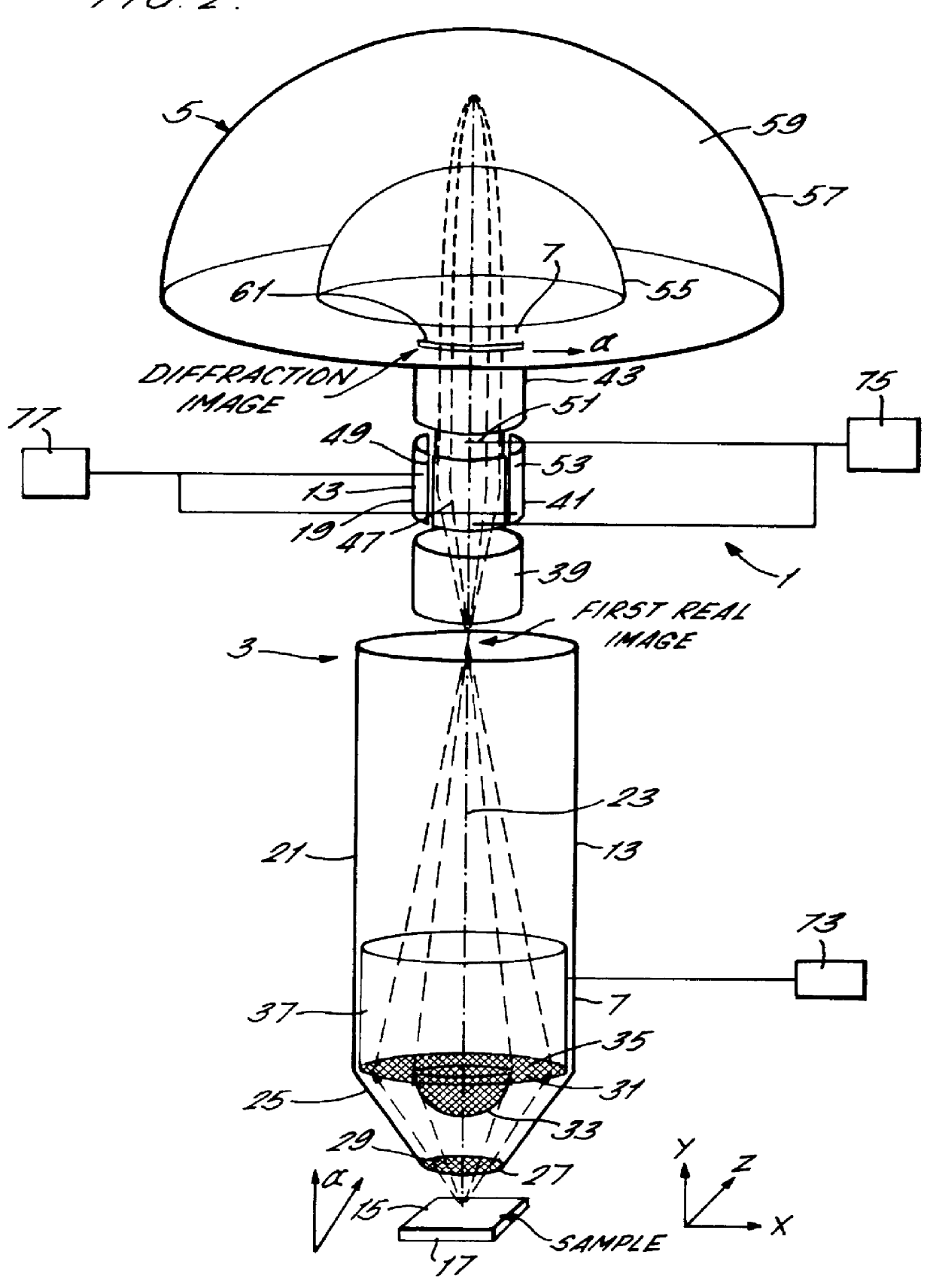
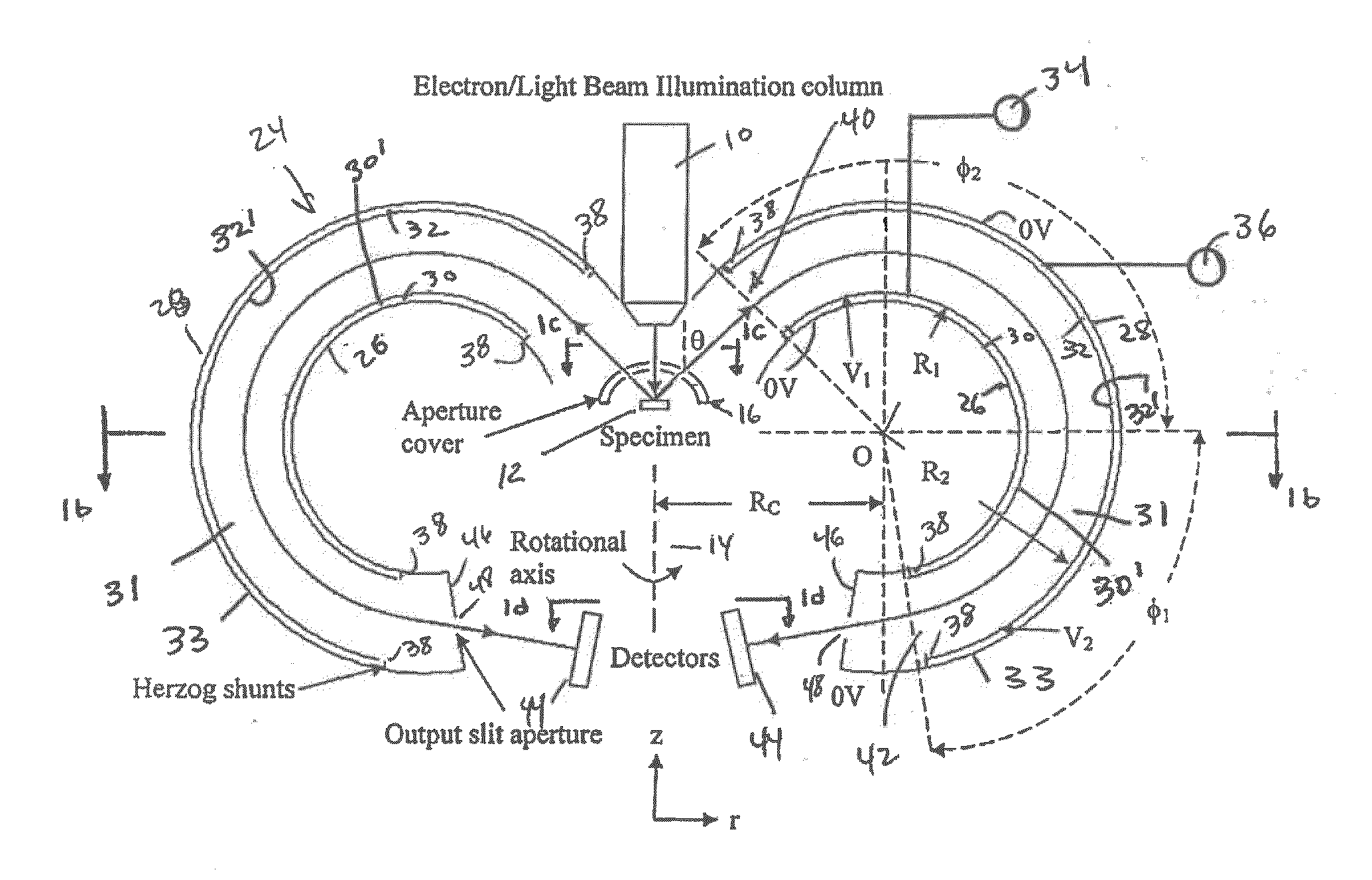
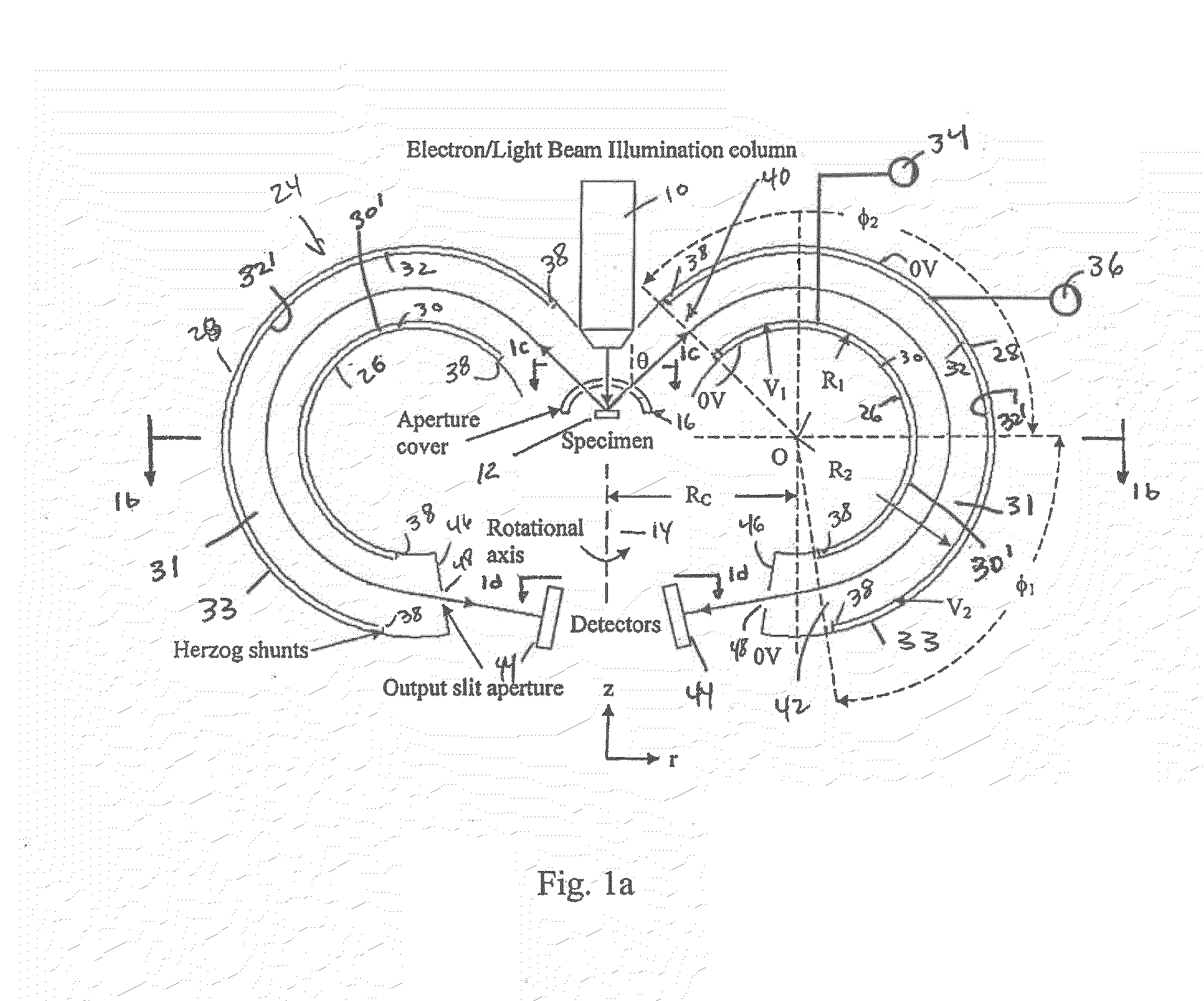
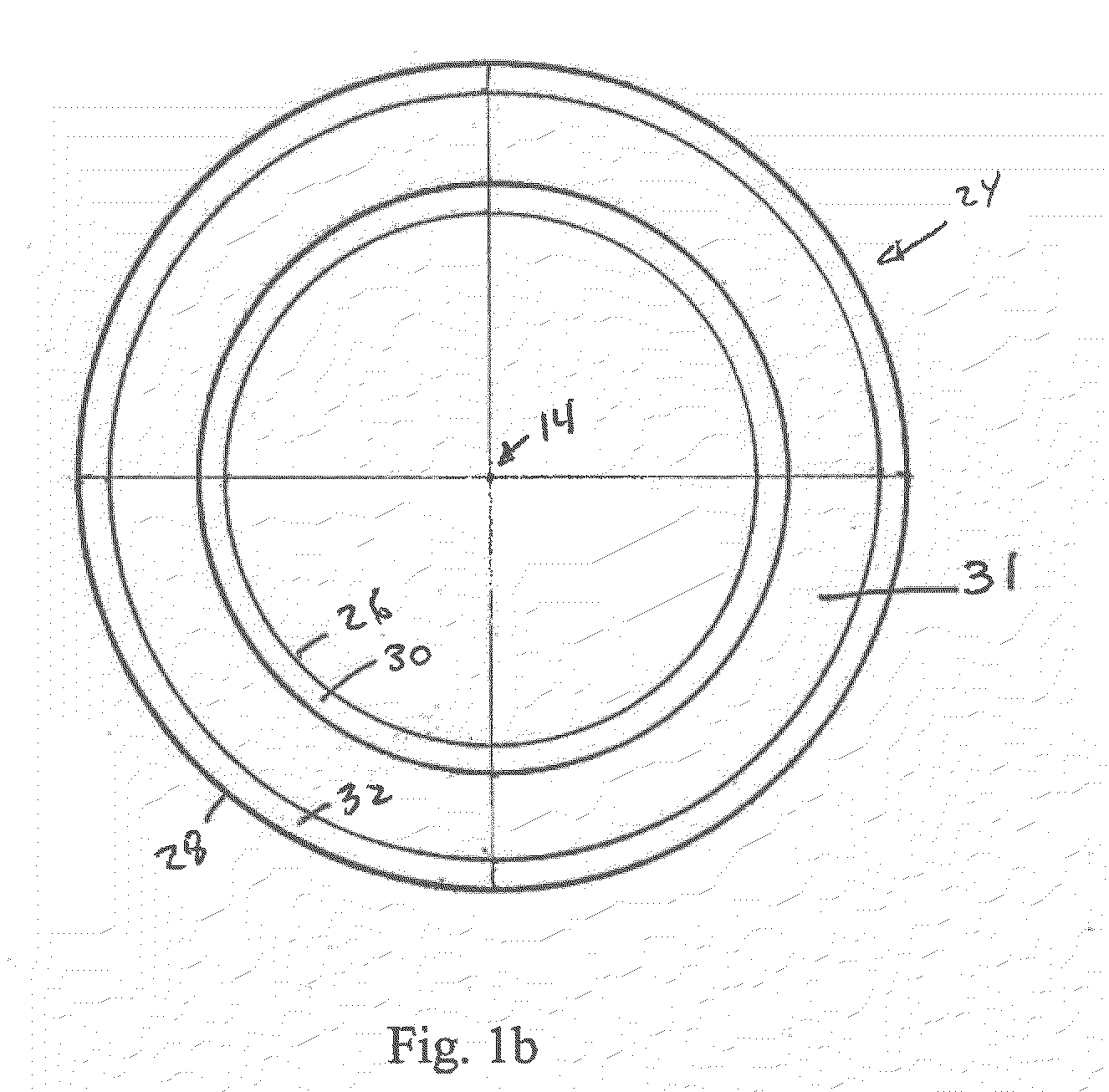
A spectrometer and method of spectroscopy are provided for surface analysis. The spectrometer comprises an energy analyser for analysing the energies of charged particles liberated from a sample, a lens arranged to project a diffraction image of the analysis area at the image plane of the lens and a detector for detecting the charged particles. The analyser and lens are arranged to generate an image at the detector in which the charged particles are distributed along a first direction according to their emission angles and are distributed along another direction according to their energies. The detector is arranged to detect the distribution of charged particles in the image along the first direction to provide angle resolved energy spectra.
Owner:VG SYST
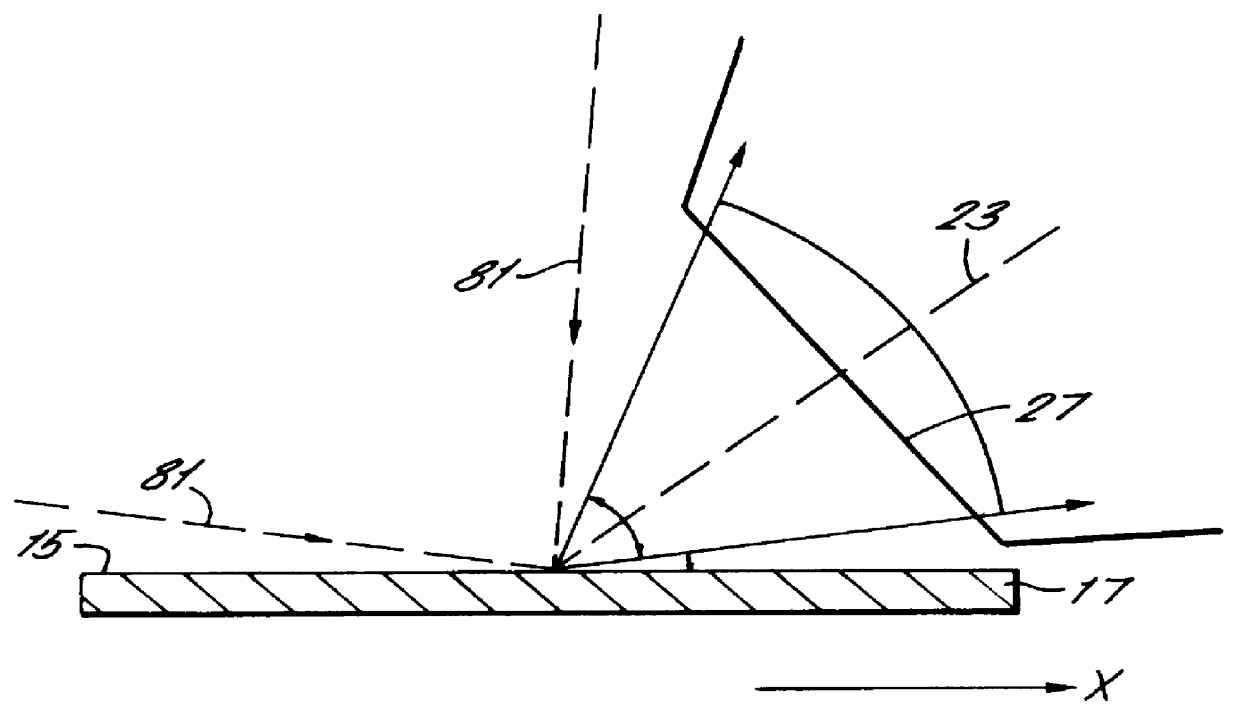
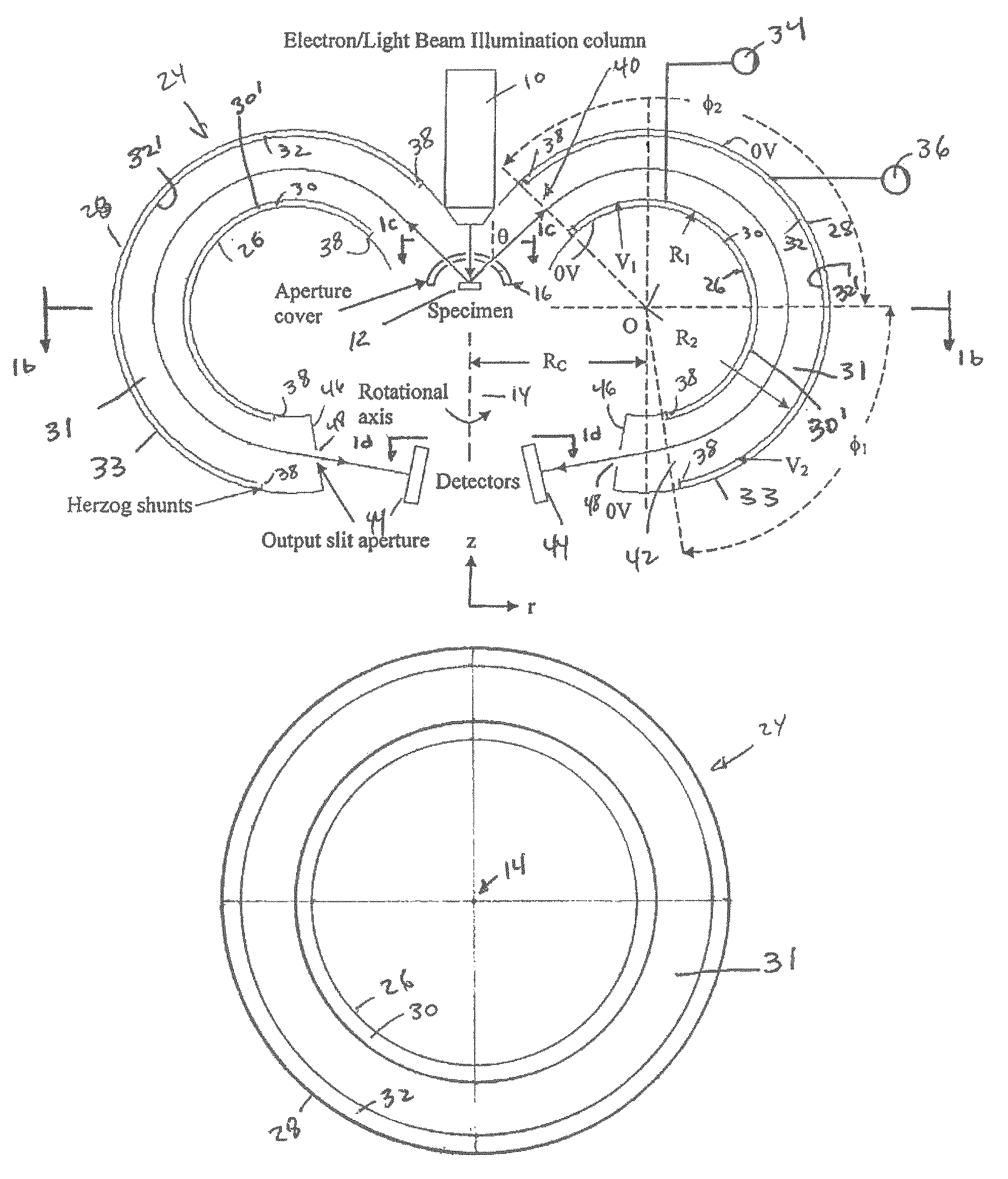
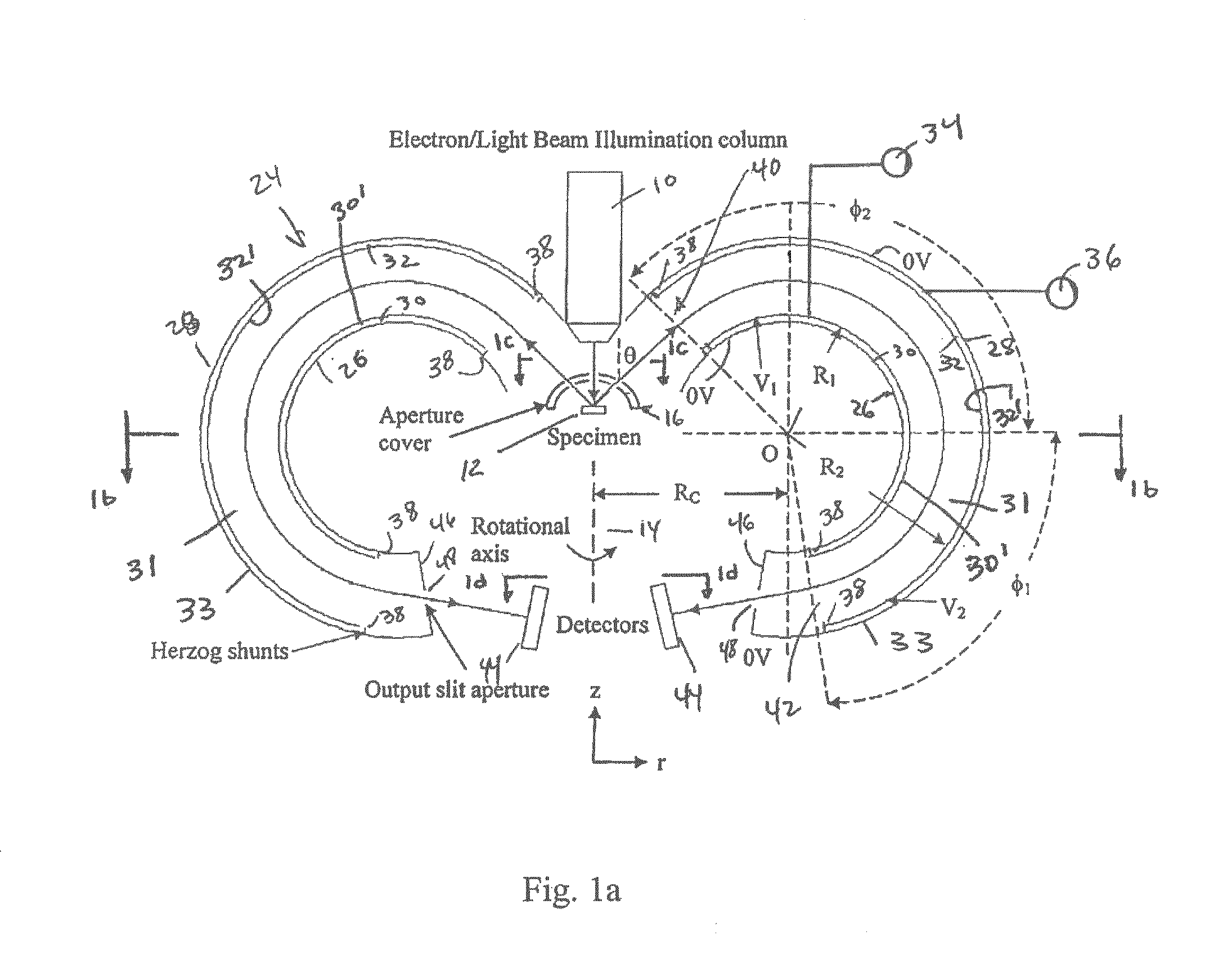
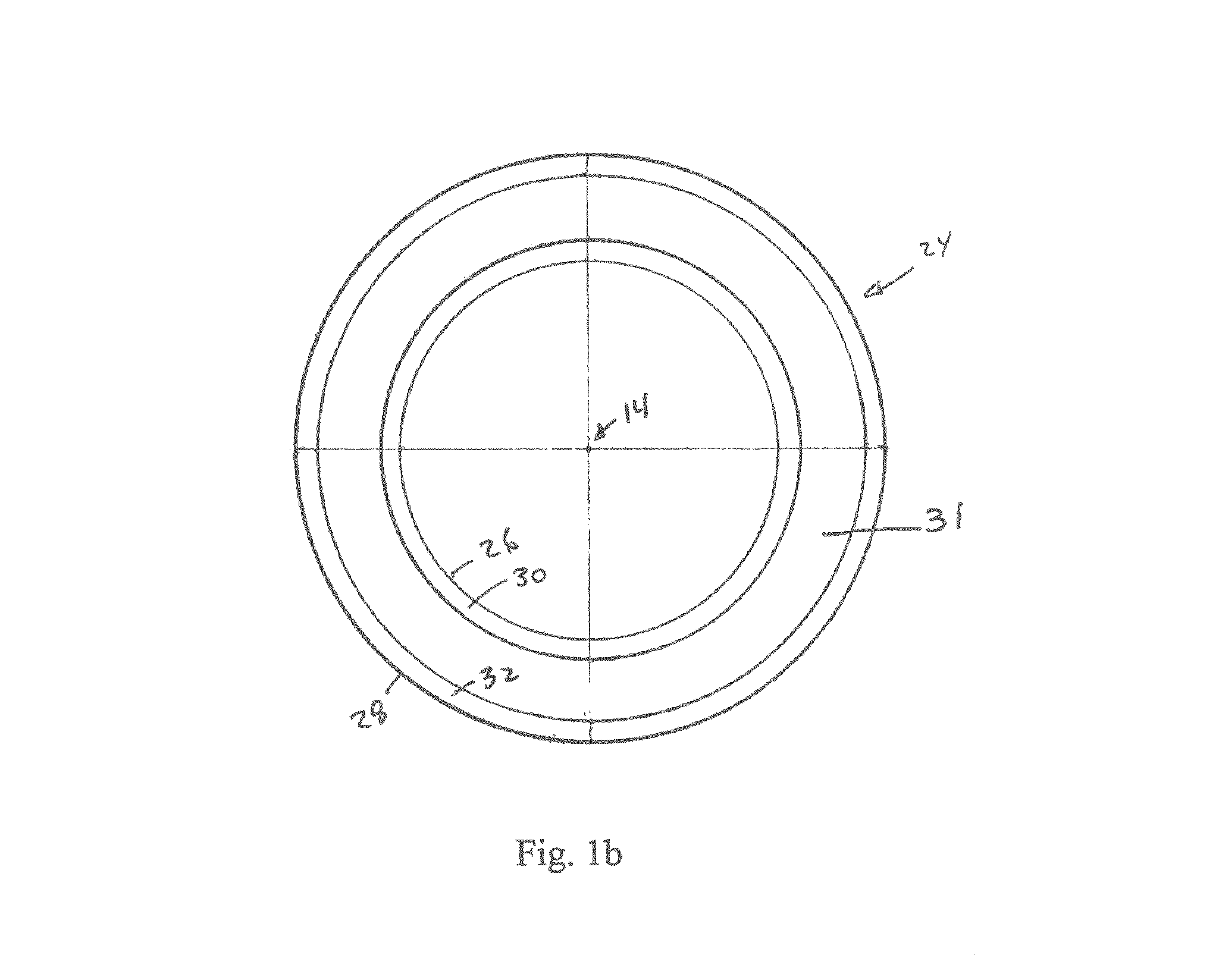
Electrostatic electron spectrometry apparatus
ActiveUS8013298B2Improved energy resolutionHigh simulationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesSpectrometerElectron
An apparatus for spectrometry that includes a spectrometer configured for second order focusing and capable of 2π azimuthal collection.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
Electrostatic electron spectrometry apparatus
ActiveUS20100127168A1Improved energy resolutionShortening of trajectory run timeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesFtir spectraSpectrometer
An apparatus for spectrometry that includes a spectrometer configured for second order focusing and capable of 2π azimuthal collection.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
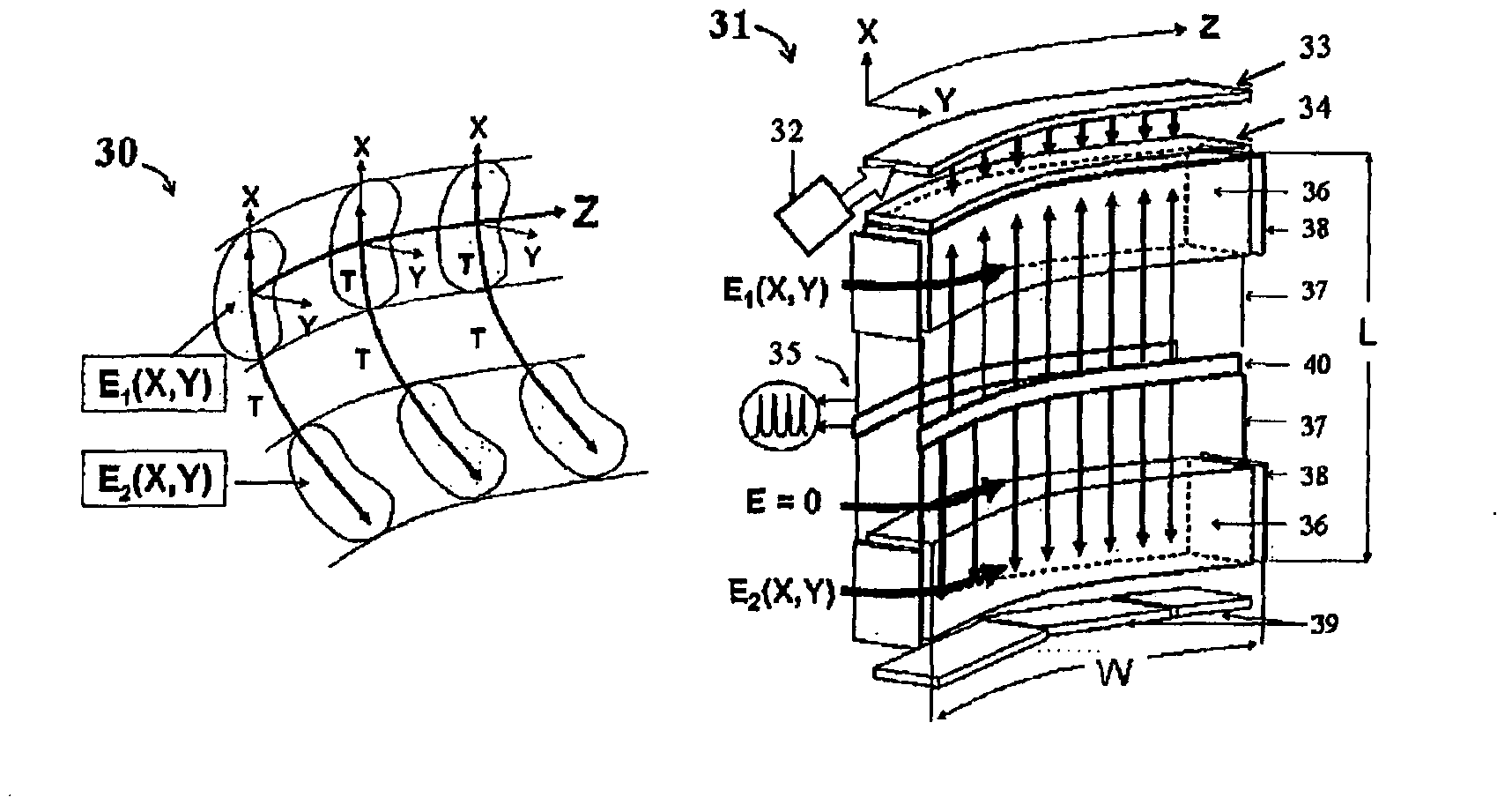
Ion trap mass spectrometer
ActiveCN102884608AImprove acquisitionPerfectly compatibleStability-of-path spectrometersTime-of-flight spectrometersTime–frequency analysisMass analyzer
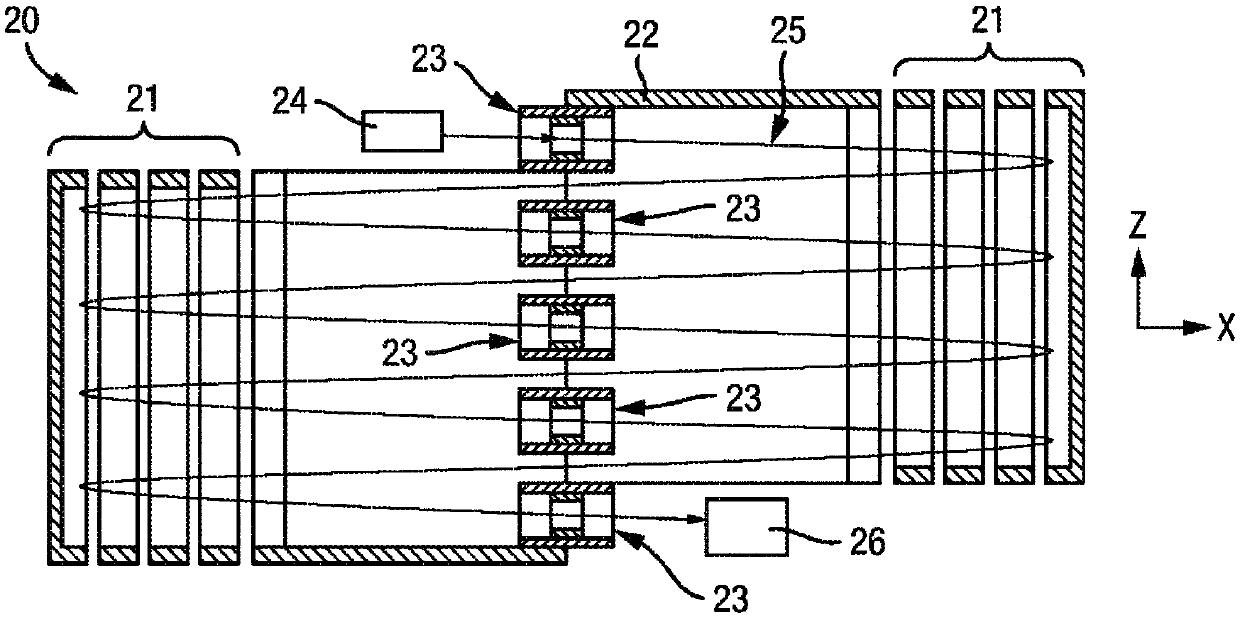
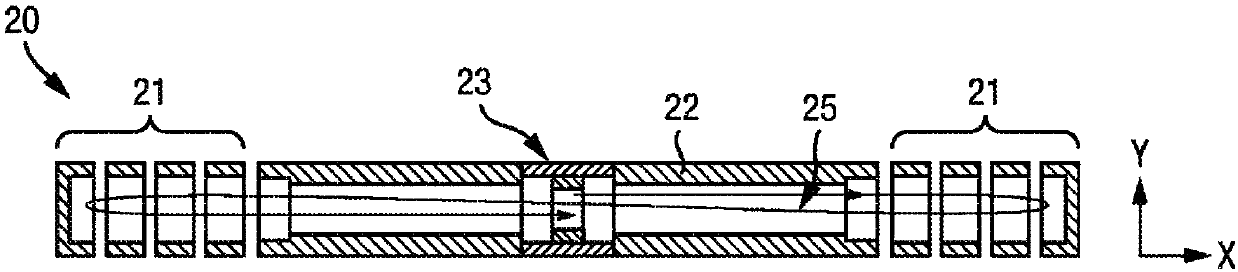
The application relates to an ion trap mass spectrometer. An apparatus 41 and operation method are provided for an electrostatic trap mass spectrometer with measuring frequency of multiple isochronous ionic oscillations. For improving throughput and space charge capacity, the trap is substantially extended in one Z-direction forming a reproduced two-dimensional field. Multiple geometries are provided for trap Z-extension. The throughput of the analysis is improved by multiplexing electrostatic traps. The frequency analysis is accelerated by the shortening of ion packets and either by Wavelet-fit analysis of the image current signal or by using a time- of-flight detector for sampling a small portion of ions per oscillation. Multiple pulsed converters are suggested for optimal ion injection into electrostatic traps.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Multi-reflecting time-of-flight mass spectrometer with isochronous curved ion interface
ActiveCN101171660ATime-of-flight spectrometersImaging particle spectrometryTime-of-flight mass spectrometryImage resolution
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Aberration-correcting cathode lens microscopy instrument
ActiveUS20070200070A1Stability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationExit planeElectron diffraction pattern
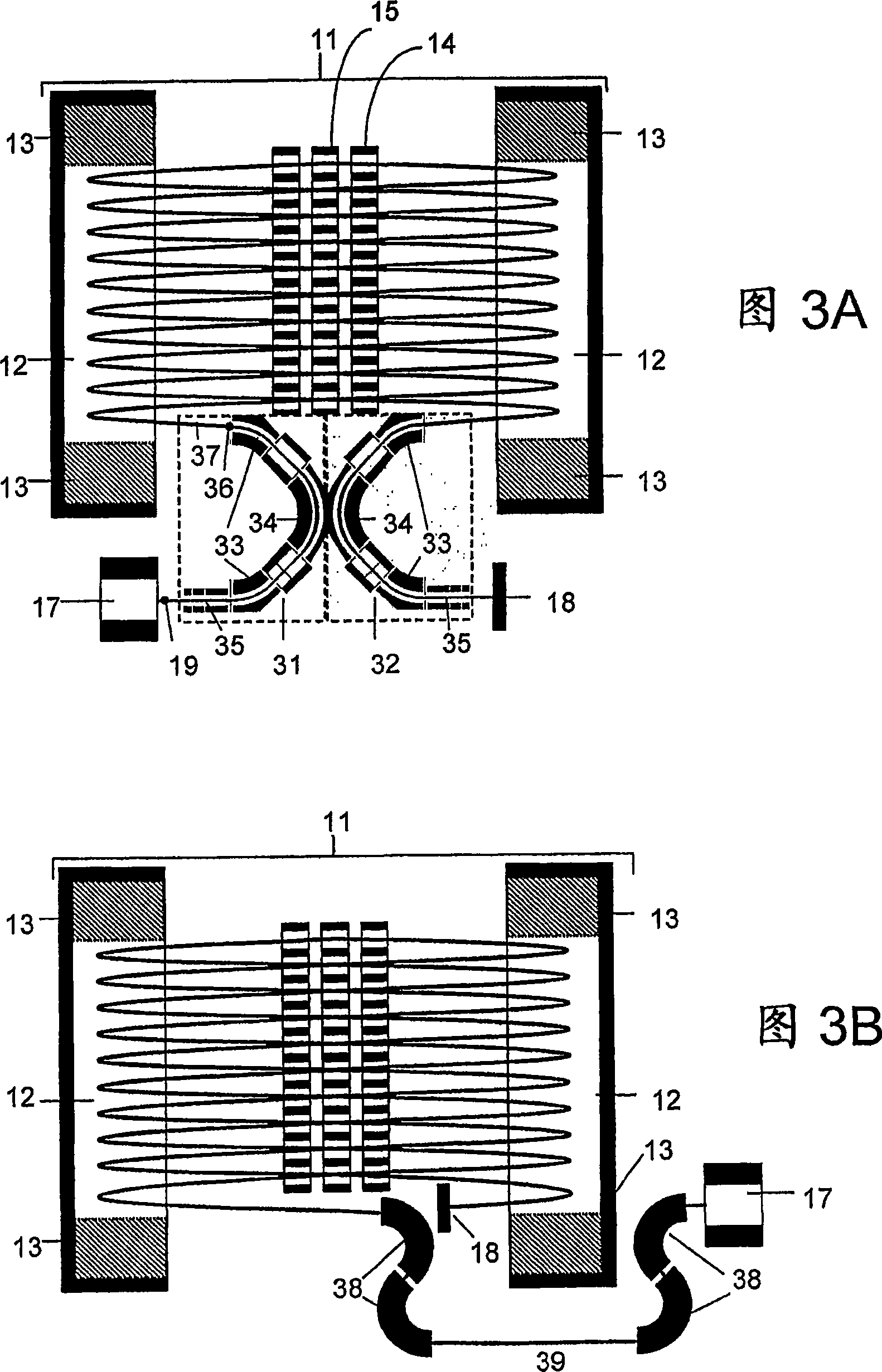
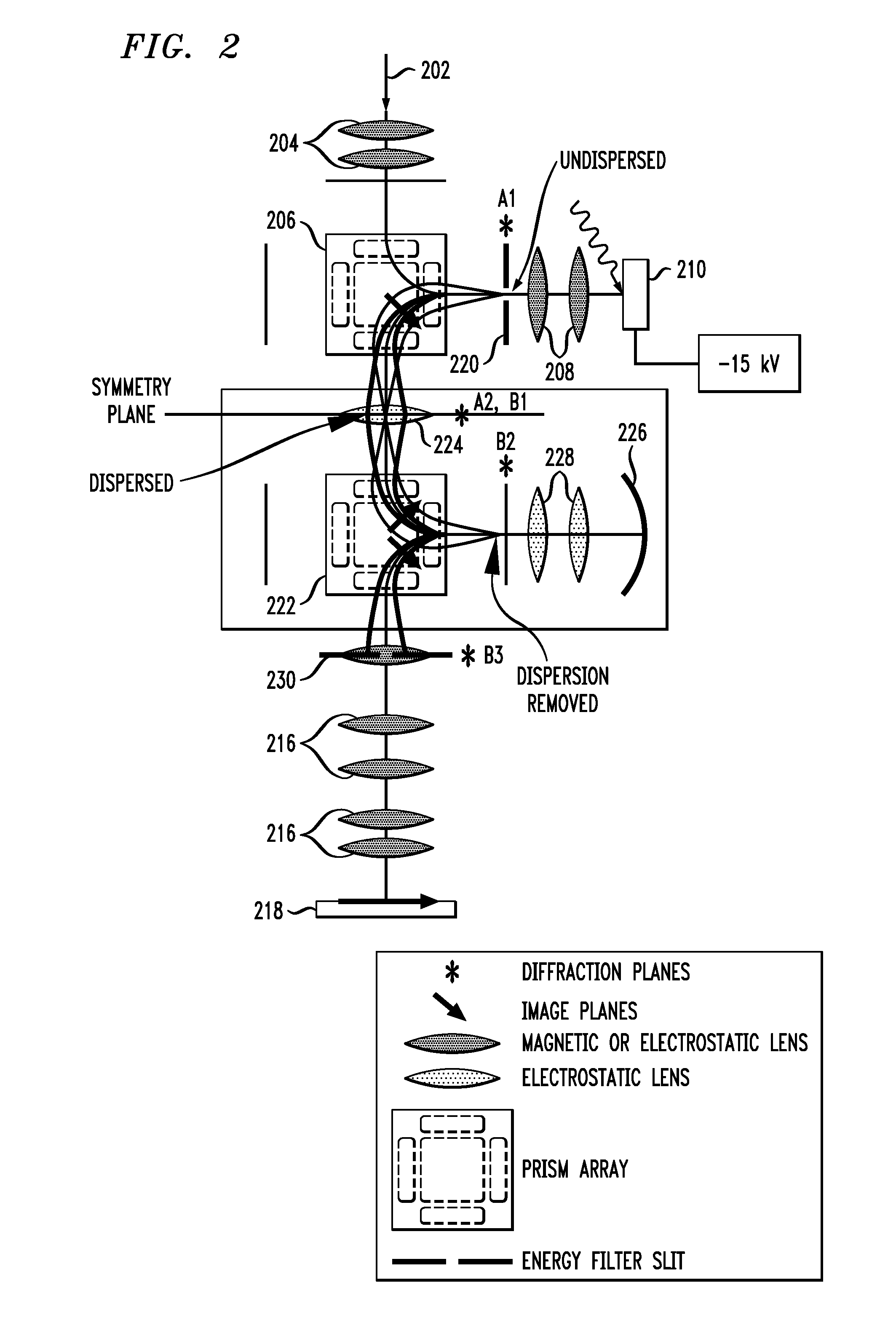
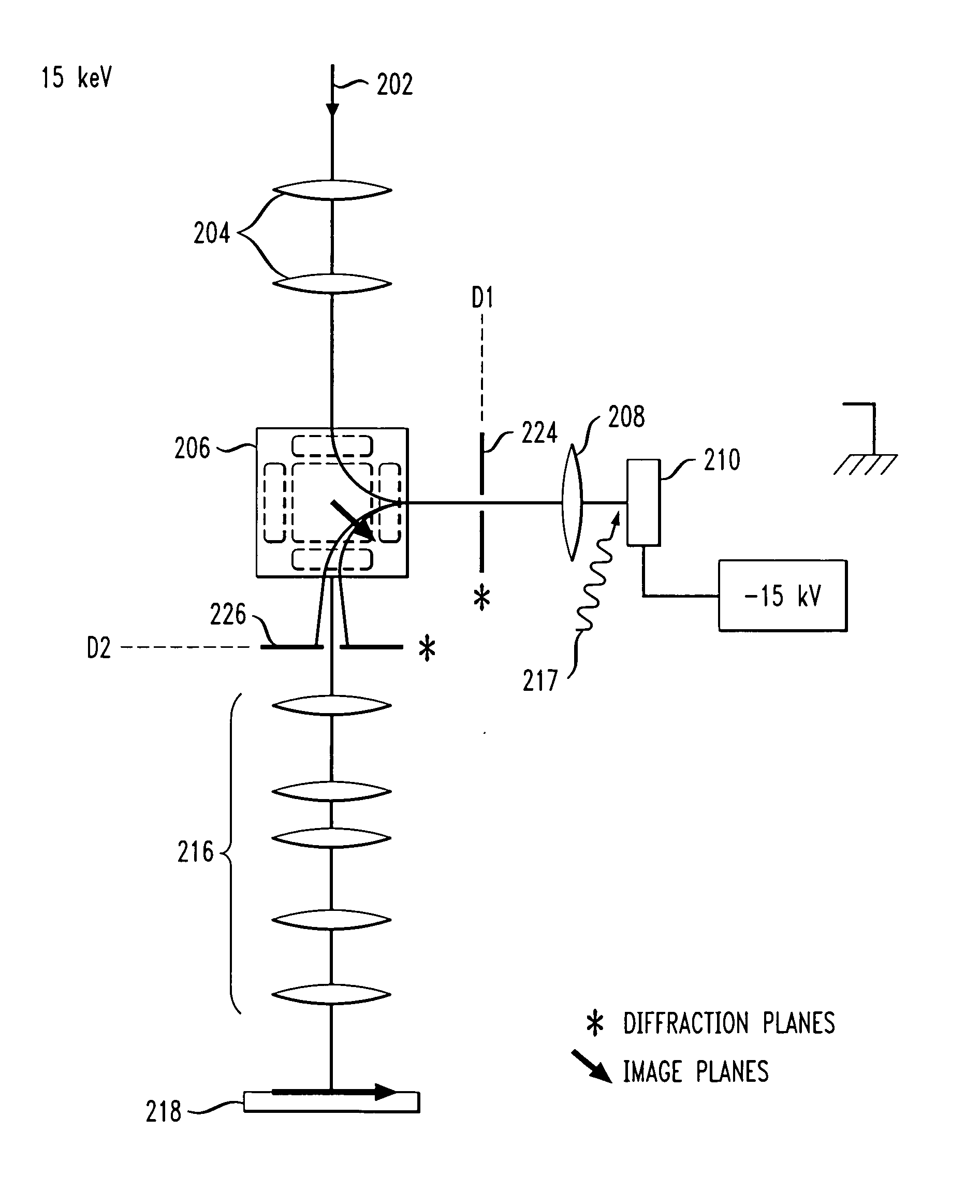
An aberration-correcting microscopy instrument is provided. The instrument has a first magnetic deflector disposed for reception of a first non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern. The first magnetic deflector is also configured for projection of a first energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern in an exit plane of the first magnetic deflector. The instrument also has an electrostatic lens disposed in the exit plane of a first magnetic deflector, as well as a second magnetic deflector substantially identical to the first magnetic deflector. The second magnetic deflector is disposed for reception of the first energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern from the electrostatic lens. The second magnetic deflector is also configured for projection of a second non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern in a first exit plane of the second magnetic deflector. The instrument also has an electron mirror configured for correction of one or more aberrations in the second non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern. The electron mirror is disposed for reflection of the second non-dispersed electron diffraction pattern to the second magnetic deflector for projection of a second energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern in a second exit plane of the second magnetic deflector.
Owner:IBM CORP
Electrostatic ion mirrors
ActiveUS9396922B2Evenly distributedHigh isochronicityTime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsImage resolutionParticle physics
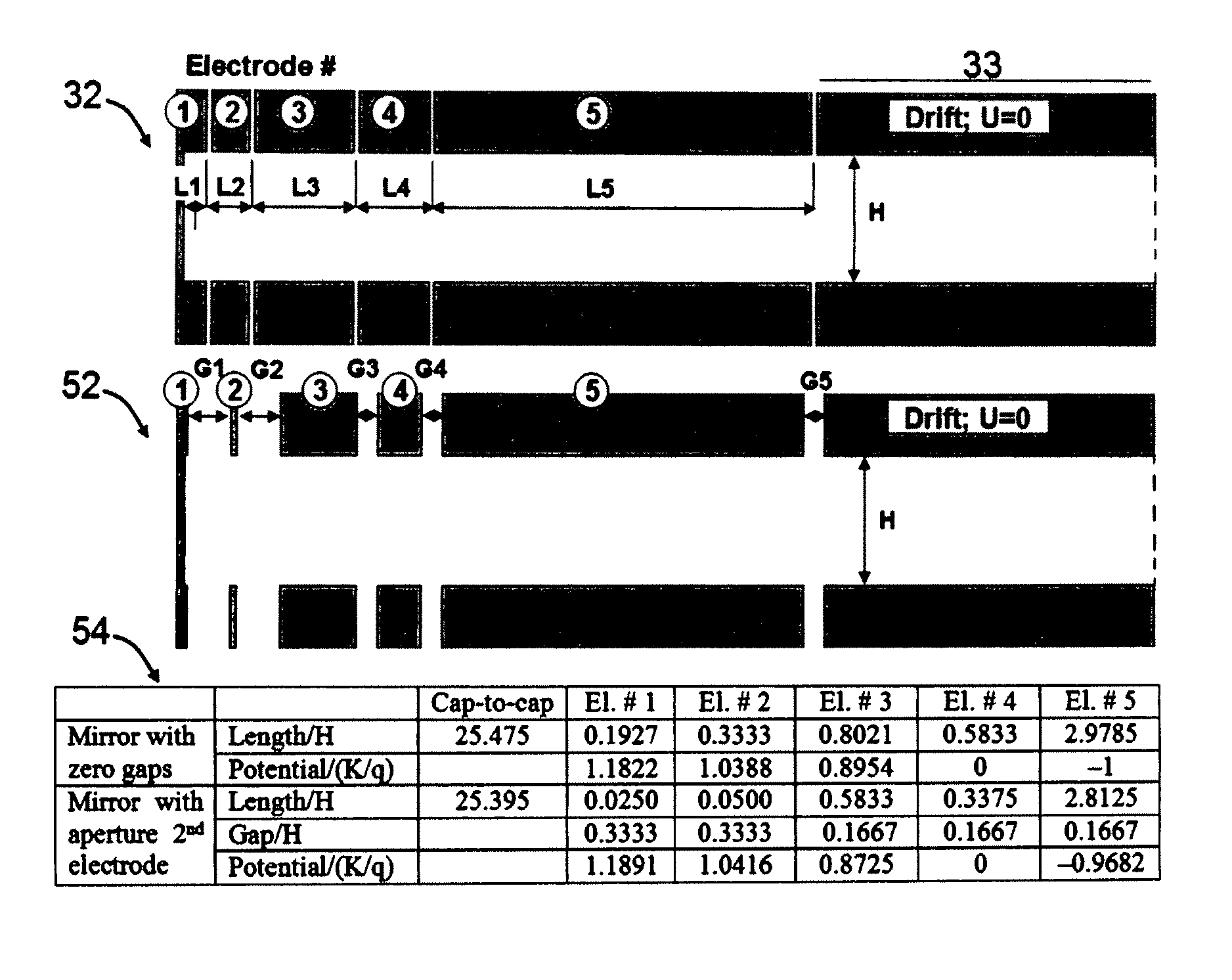
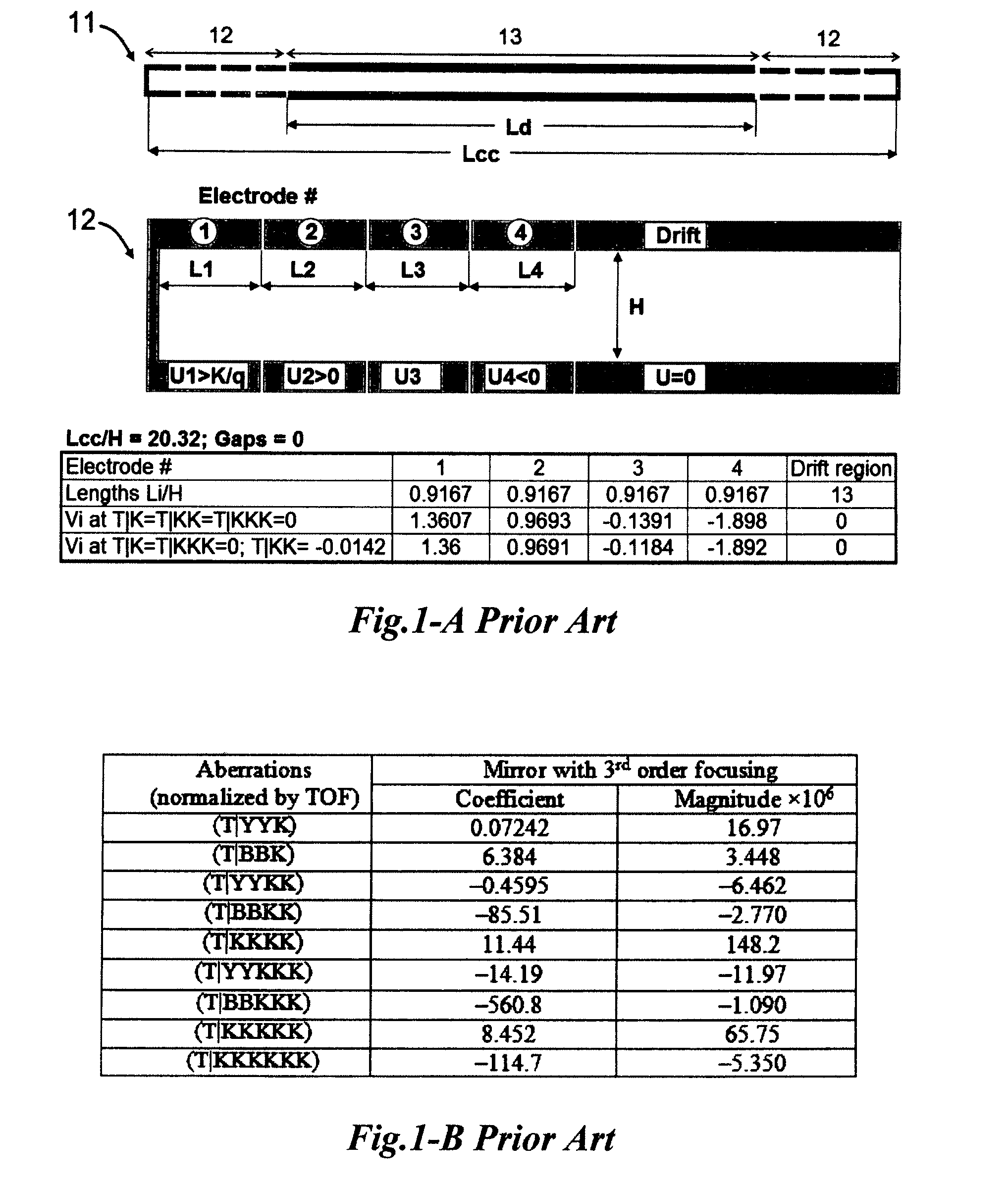
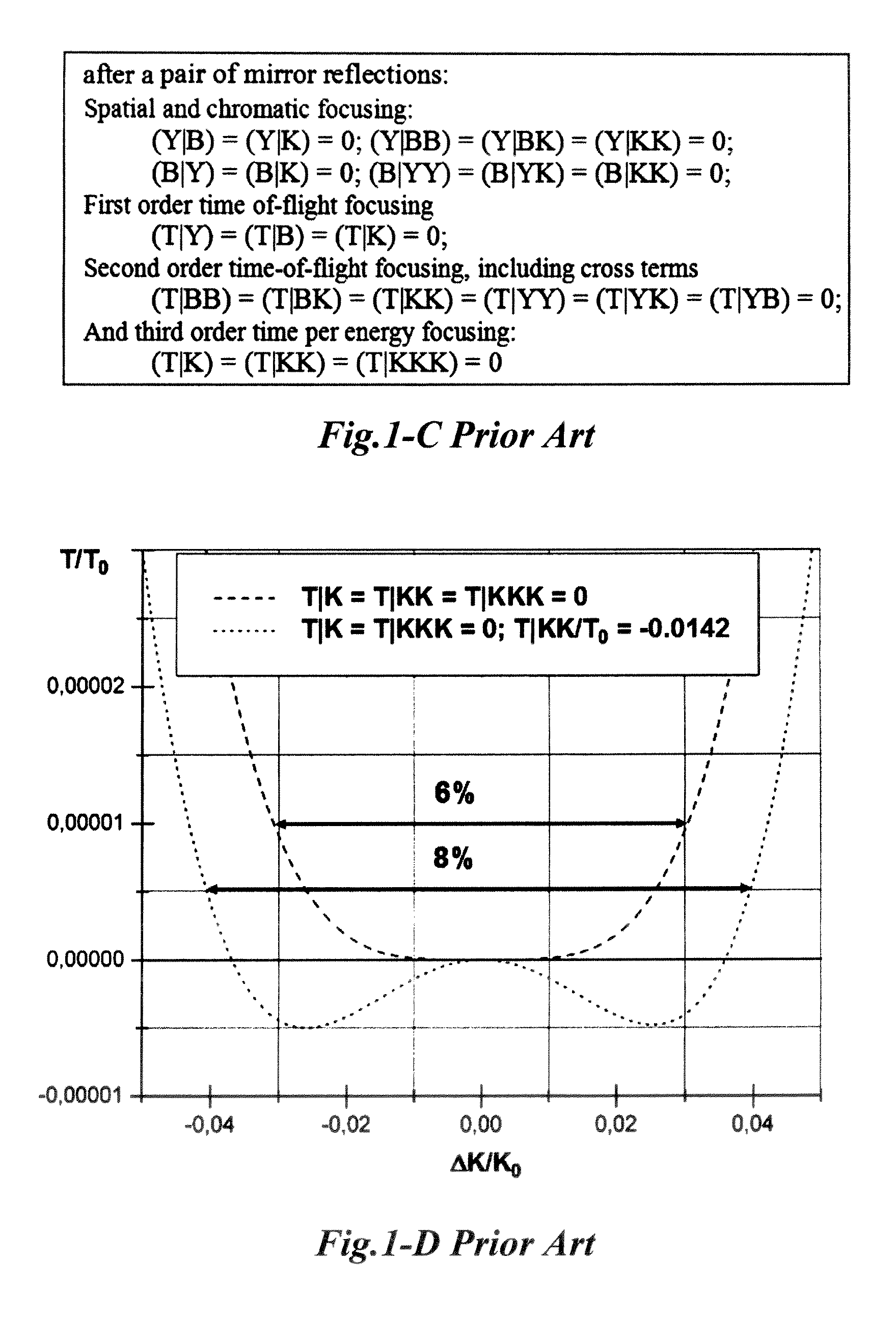
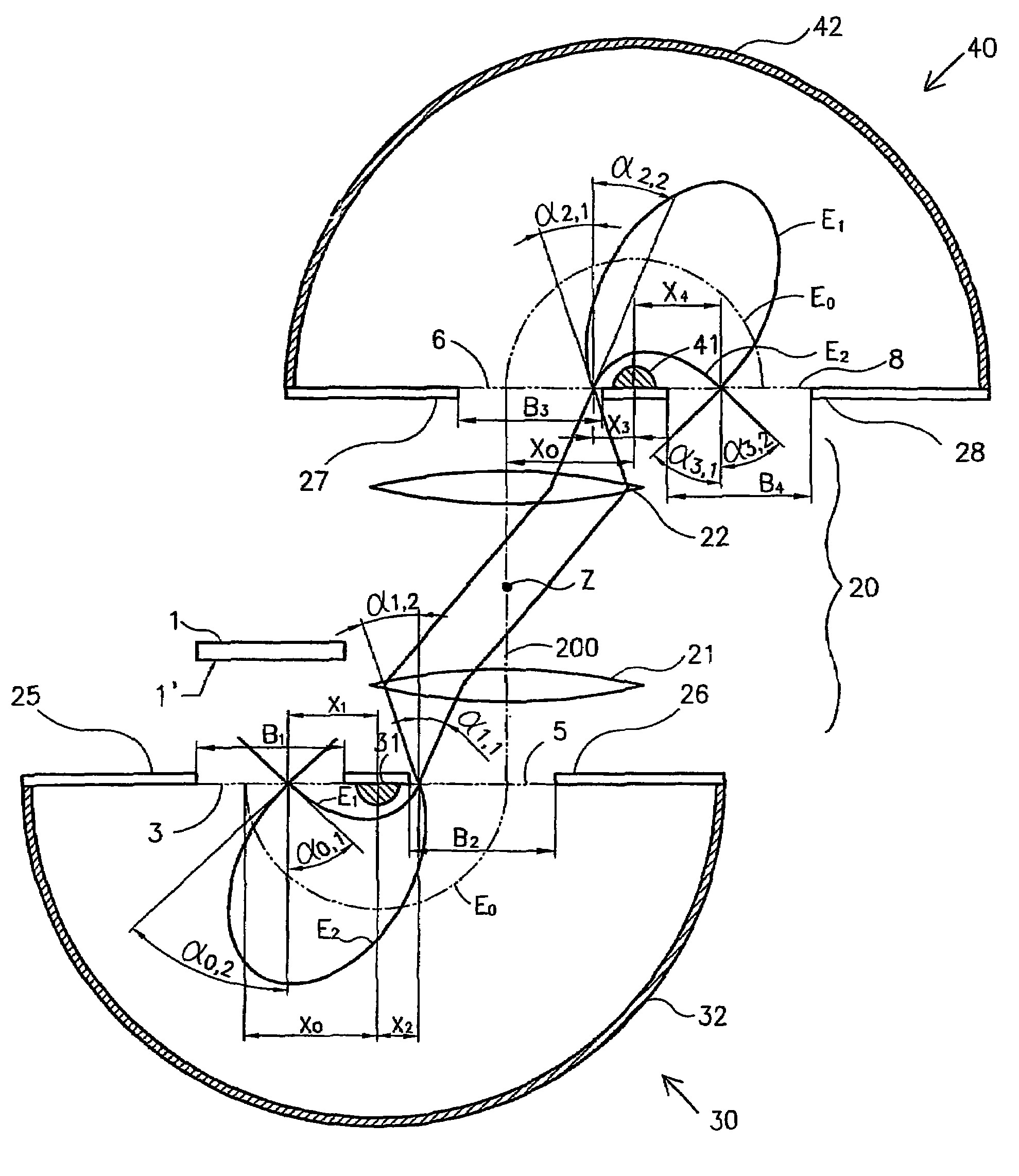
An electrostatic ion mirror is disclosed providing fifth order time-per-energy focusing. The improved ion mirror has up to 18% energy acceptance at resolving power above 100,000. Multiple sets of ion mirror parameters (shape, length, and voltage of electrodes) are disclosed. Highly isochronous fields are formed with improved (above 10%) potential penetration from at least three electrodes into a region of ion turning. Cross-term spatial-energy time-of-flight aberrations of such mirrors are further improved by elongation of electrode with attracting potential or by adding a second electrode with an attracting potential.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
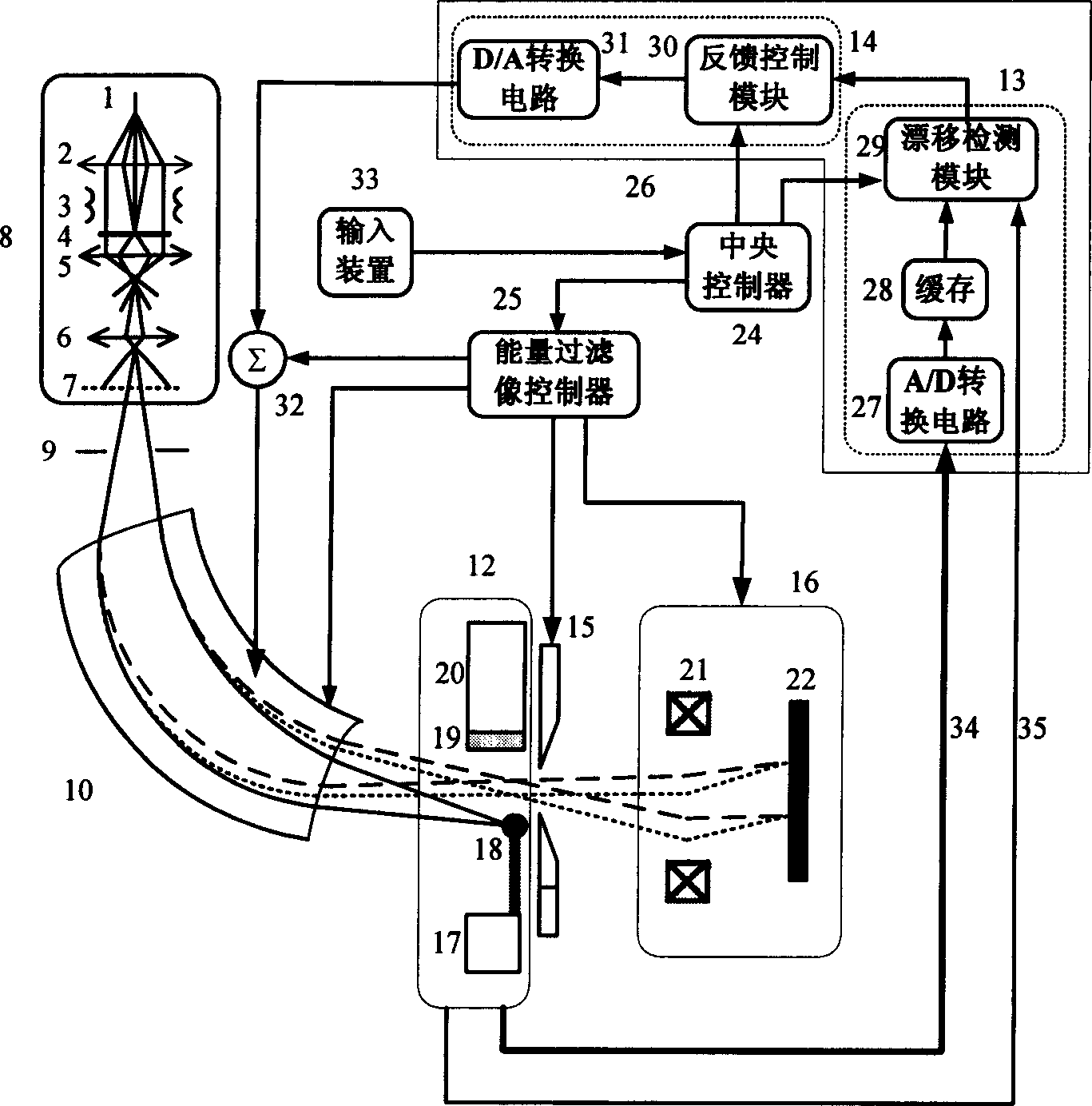
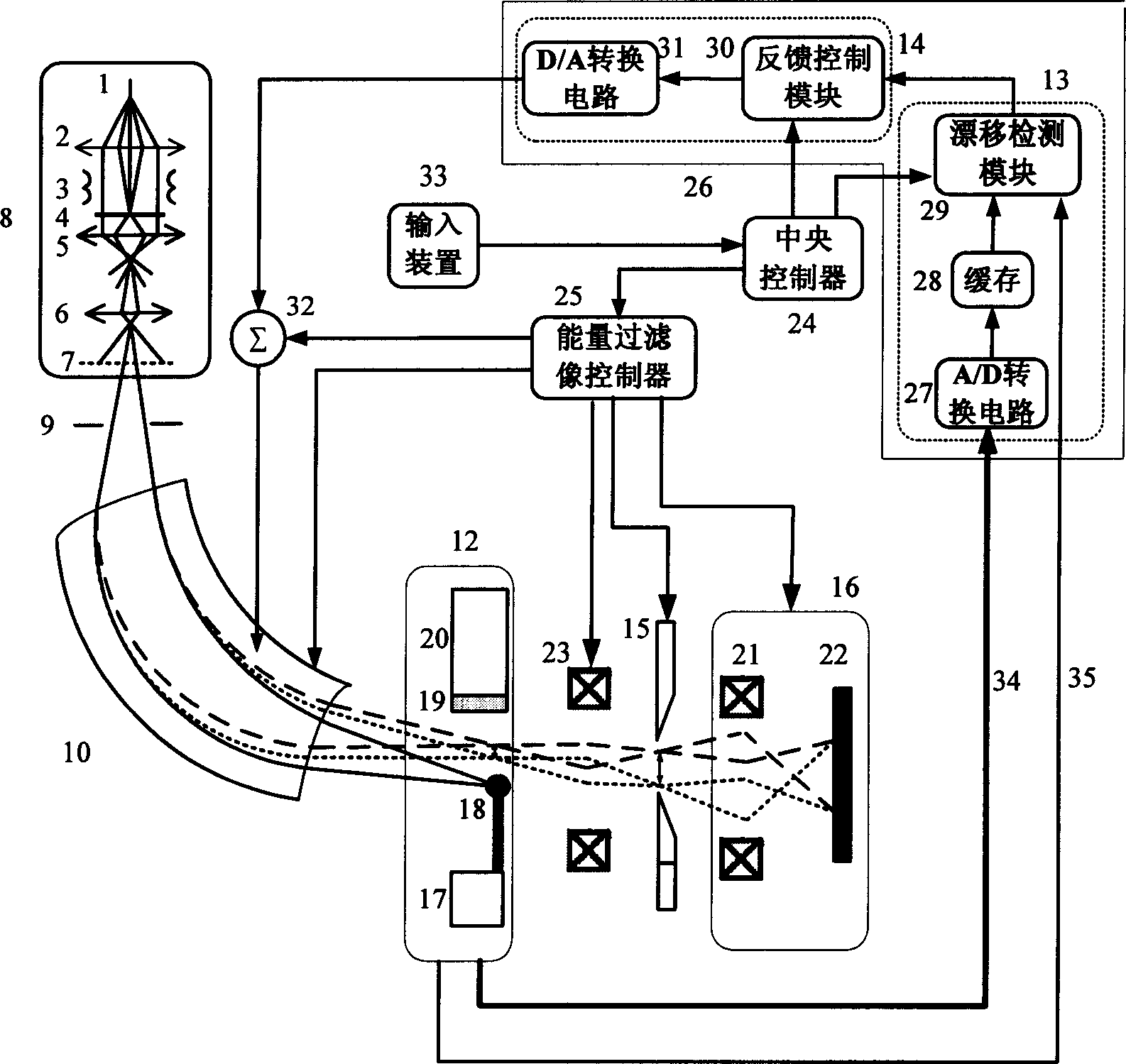
Method and apparatus for receiving high stable energy filtering electronic microscopic image
InactiveCN1862761AImprove spatial resolutionGood monochromaticityStatic energy spectrometersDrift detectionIt equipment
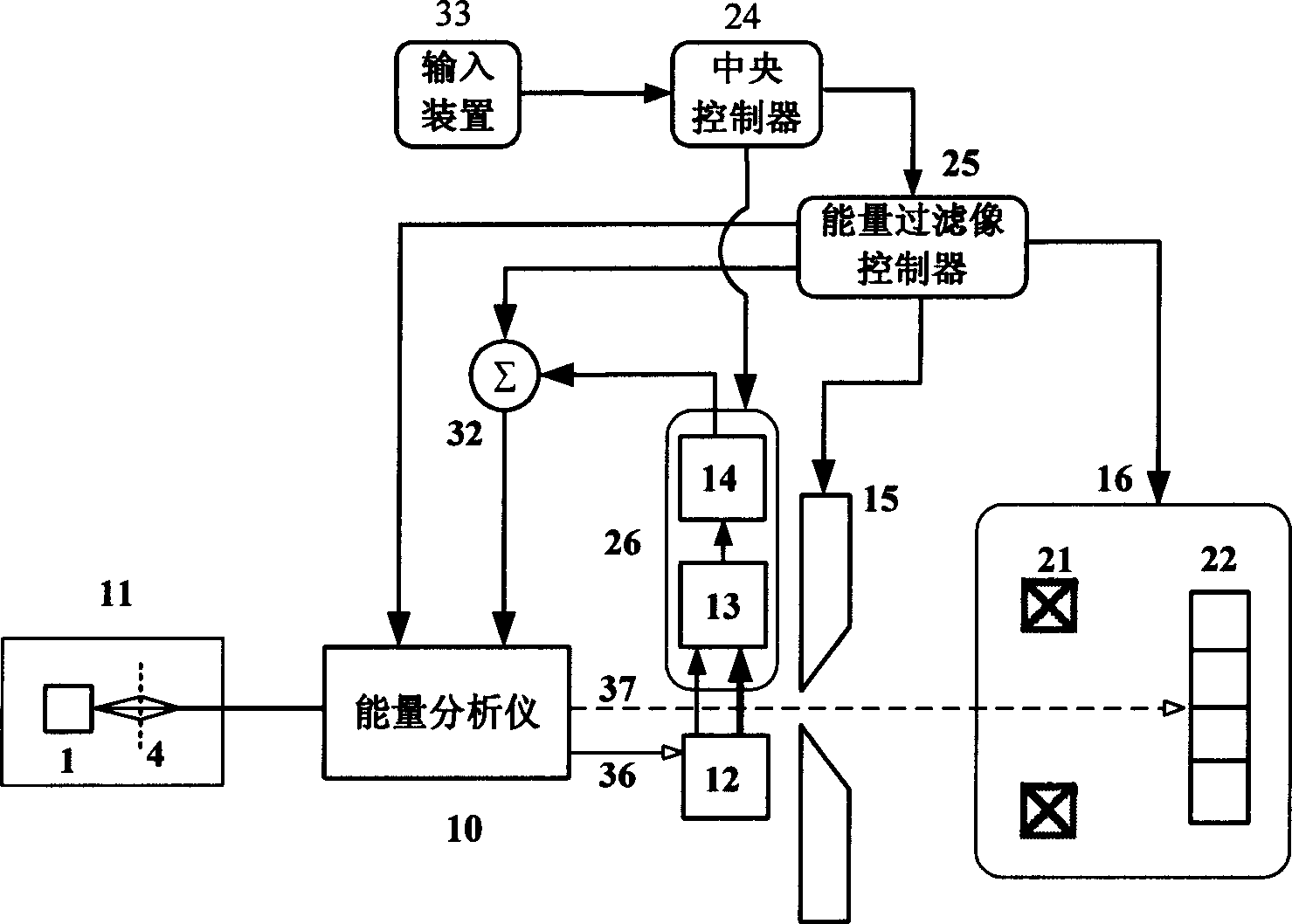
This invention relates to high stable energy filtration digital microscopic imaging receives method and its equipment. It belongs to energy filtration digital microscopic imaging technique field. Drift detection feedback method is used to eliminate the drift of different energy digital space distribution to energy selecting crack caused by high voltage fluctuation or interference of electromagnetic wave. So the energy filtration receive device can keep the filtrated electron energy stable all the time during signal acquisition process. Then energy selecting crack width is adjusted to make energy segment that contain sample excitatory feature spectrum information. So the high space distinguishing and high energy distinguishing energy filtration image can be got after accumulation.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
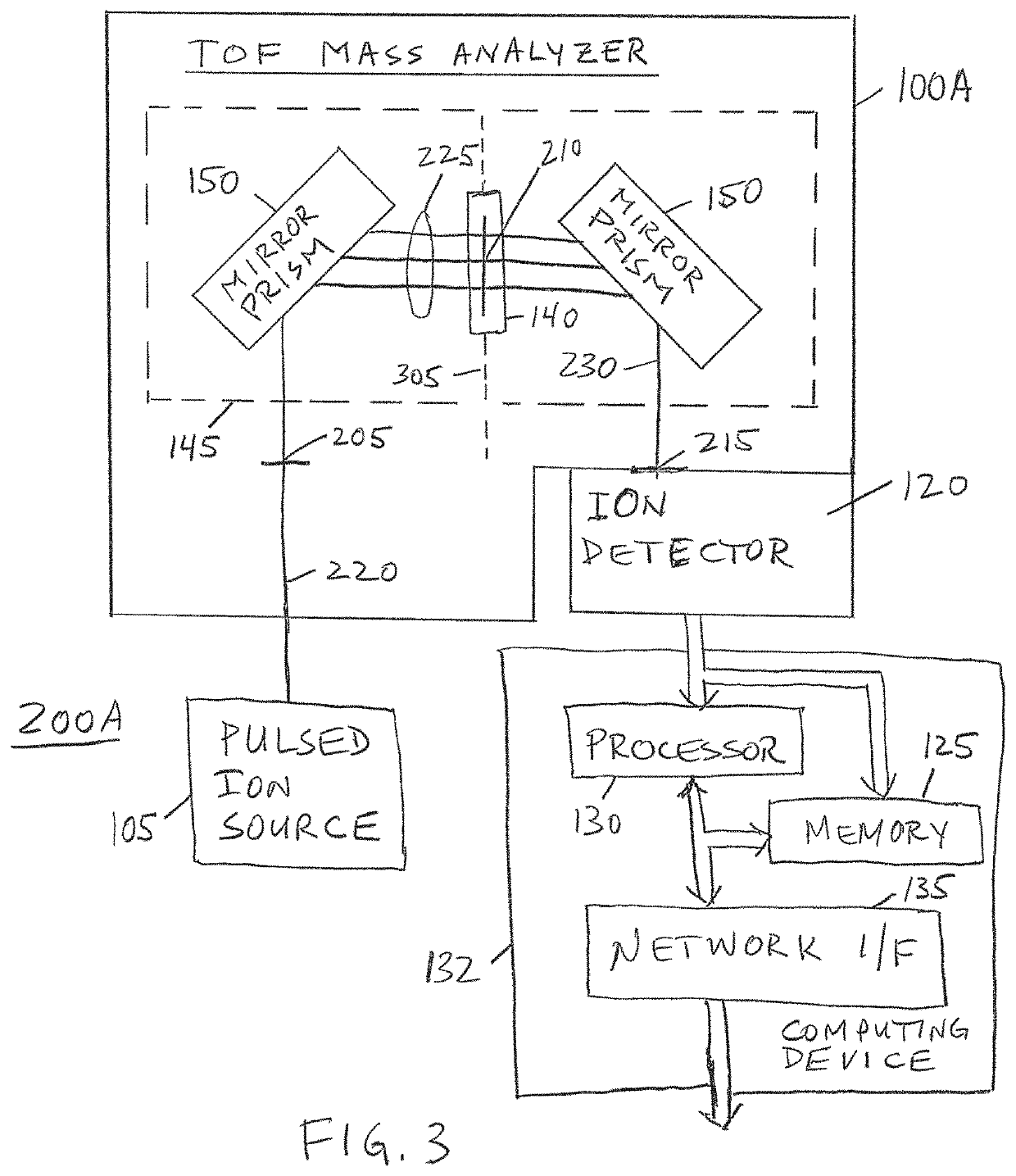
Multimode ion mirror prism and energy filtering apparatus and system for time-of-flight mass spectrometry
ActiveUS10622203B2Mass resolvingImprove accuracyTime-of-flight spectrometersIon sources/gunsBandpass filteringMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
A mass analyzing apparatus and system are disclosed for time-of-flight (“TOF”) mass spectrometry analysis. A representative system includes a first electrostatic mirror prism to reflect a first ion beam and provide an intermediate ion beam having an intermediate TOF focus and having a spatial dispersion of ions proportional to ion kinetic energies; and a second electrostatic mirror prism to reflect the second ion beam and converge the spatial dispersion of ions to provide a third, recombined ion beam having an output TOF focus; and an ion detector arranged at the output TOF focus to receive and detect the ions of the third ion beam. A bandpass filter may be arranged at the intermediate TOF focus to selectively allow propagation of ions of the second ion beam having a selected range of ion kinetic energies. Configurations having additional electrostatic mirror prisms are disclosed, including for tandem MS-MS and selectable time-of-flight.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
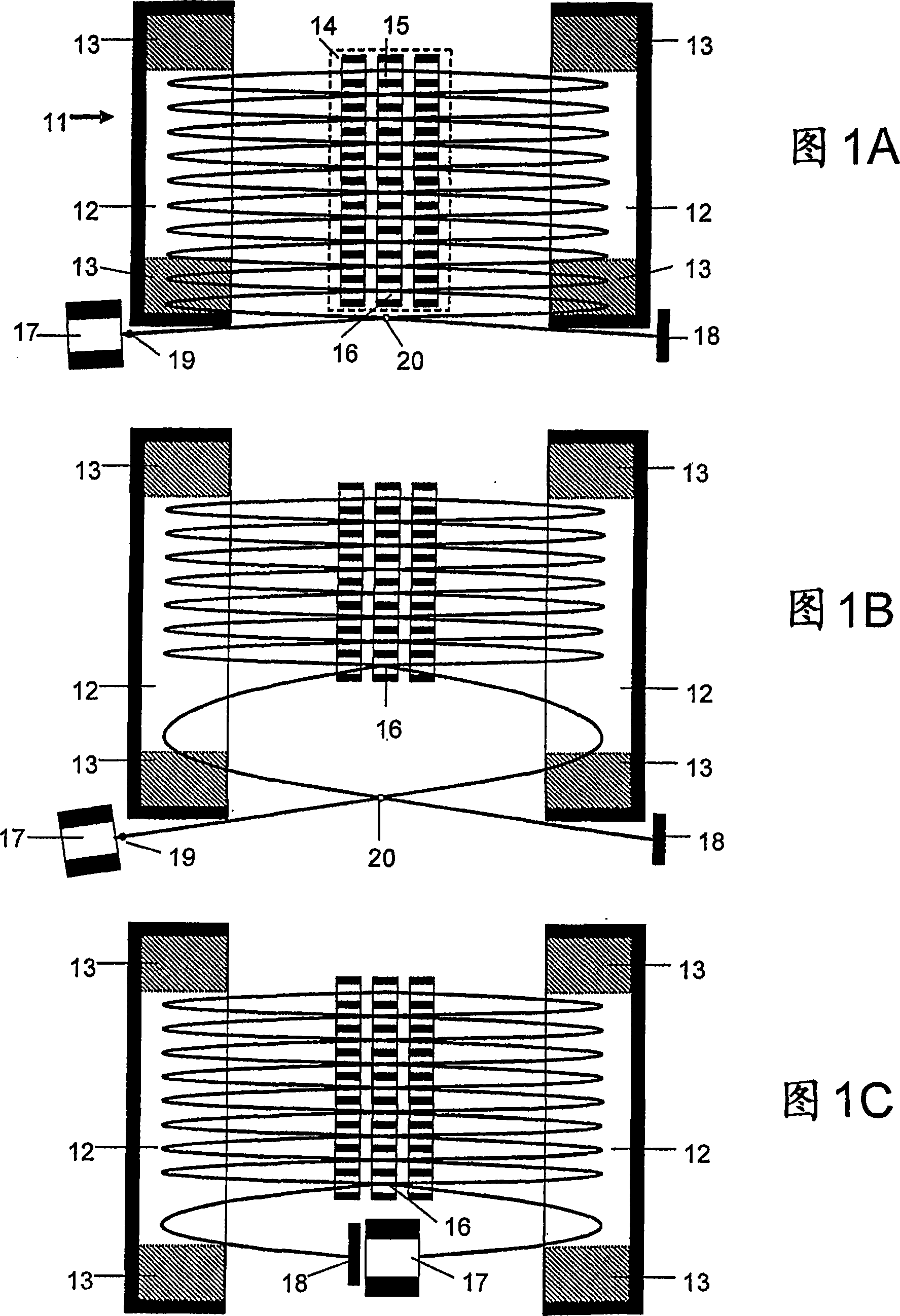
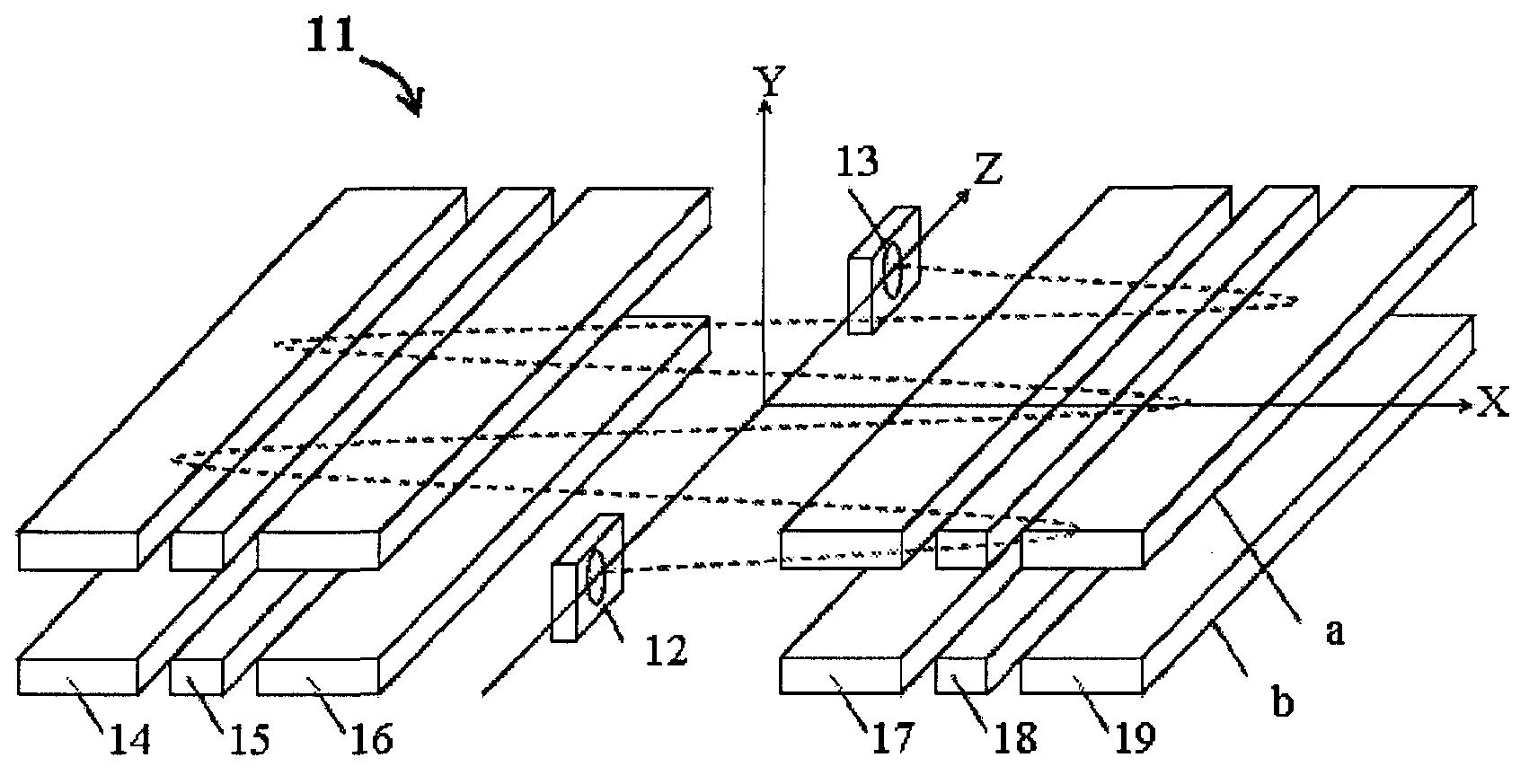
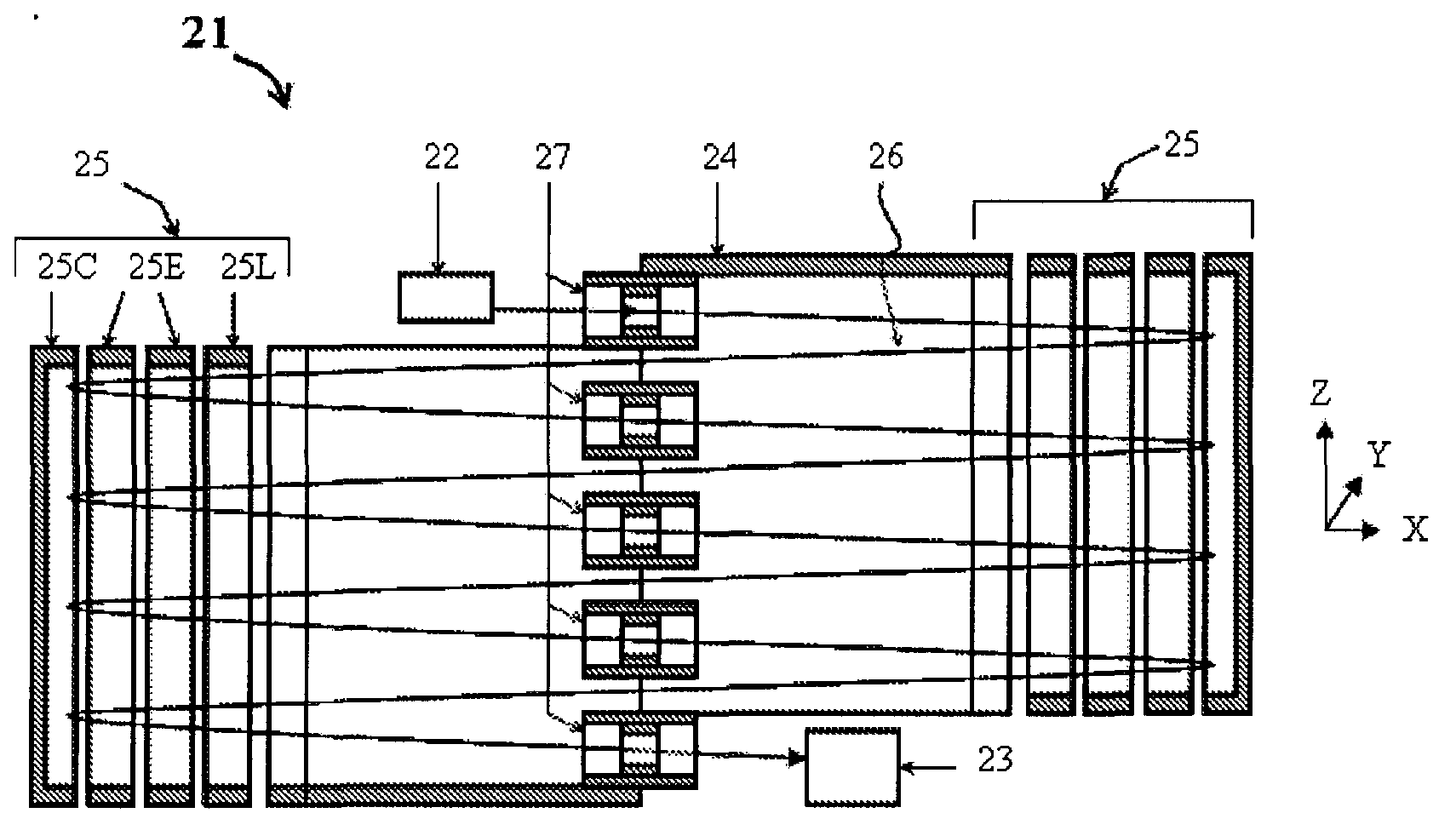
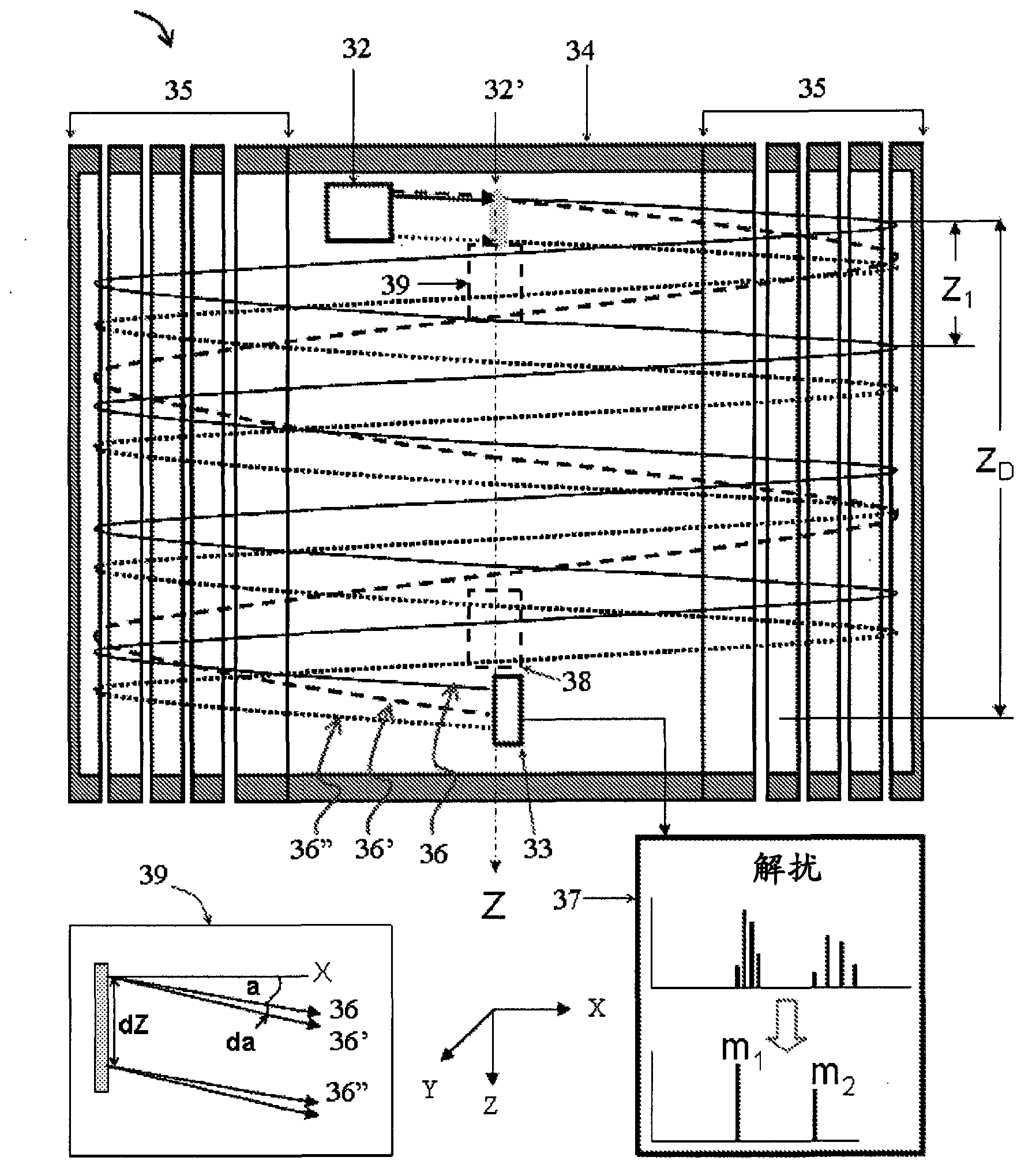
Open trap mass spectrometer
ActiveCN102939638ATime-of-flight spectrometersElectron/ion optical arrangementsIon trap mass spectrometrySignal on
An open electrostatic trap mass spectrometer is disclosed for operation with wide and diverging ion packets. Signal on detector is composed of signals corresponding to multiplicity of ion cycles, called multiplets. Using reproducible distribution of relative intensity within multiplets, the signal can be unscrambled for relatively sparse spectra, such as spectra past fragmentation cell of tandem mass spectrometer, past ion mobility and differential ion mobility separators. Various embodiments are provided for particular pulsed ion sources and pulsed converters such as orthogonal accelerators, ion guides, and ion traps. The method and apparatus enhance the duty cycle of pulsed converters, improve space charge tolerance of the open trap analyzer and extends the dynamic range of time-of-flight detectors.
Owner:LECO CORPORATION
Multi-Turn Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometer
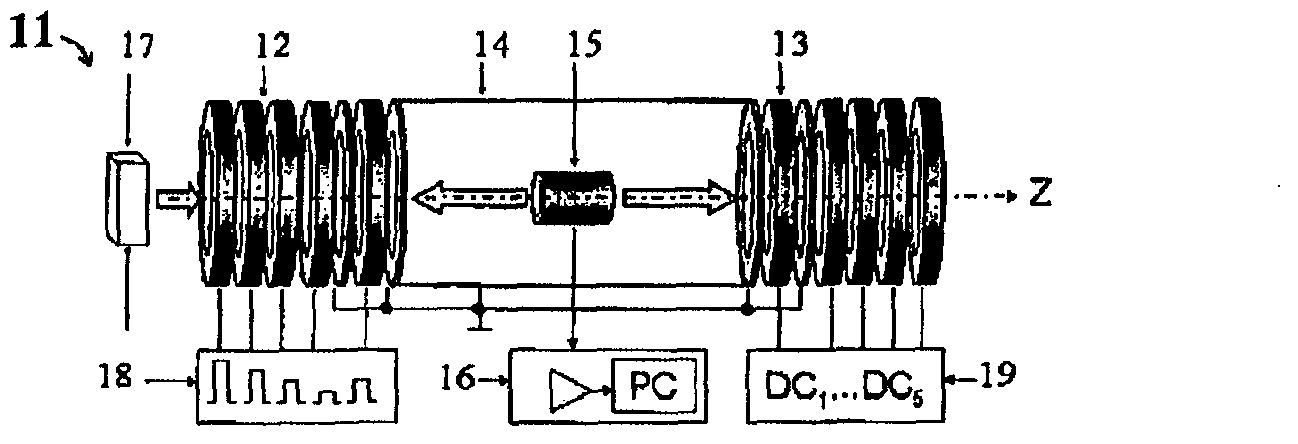
InactiveUS20110248161A1Improve quality resolutionEasy to operateIsotope separationStatic energy spectrometersOvertakingImage resolution
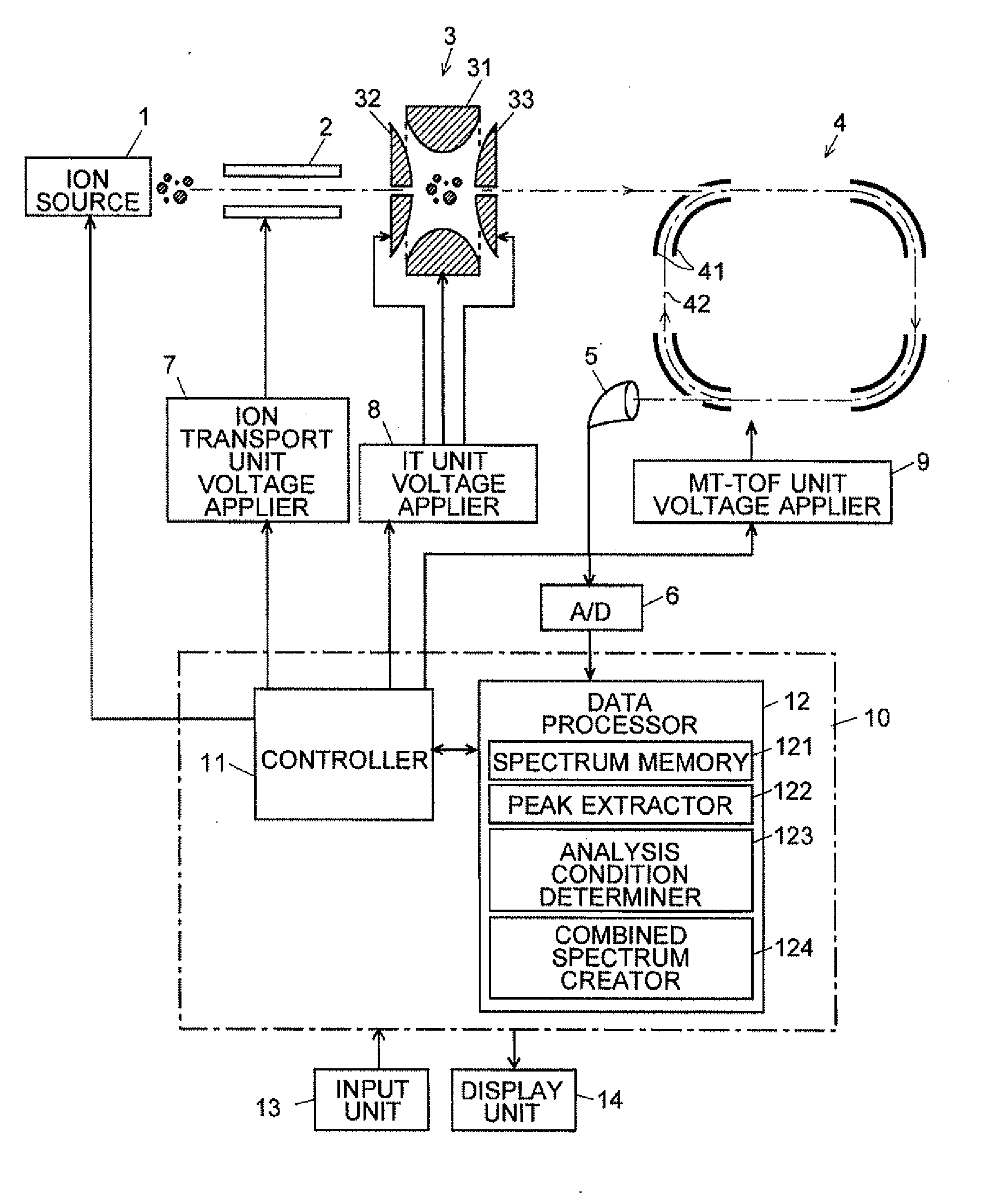
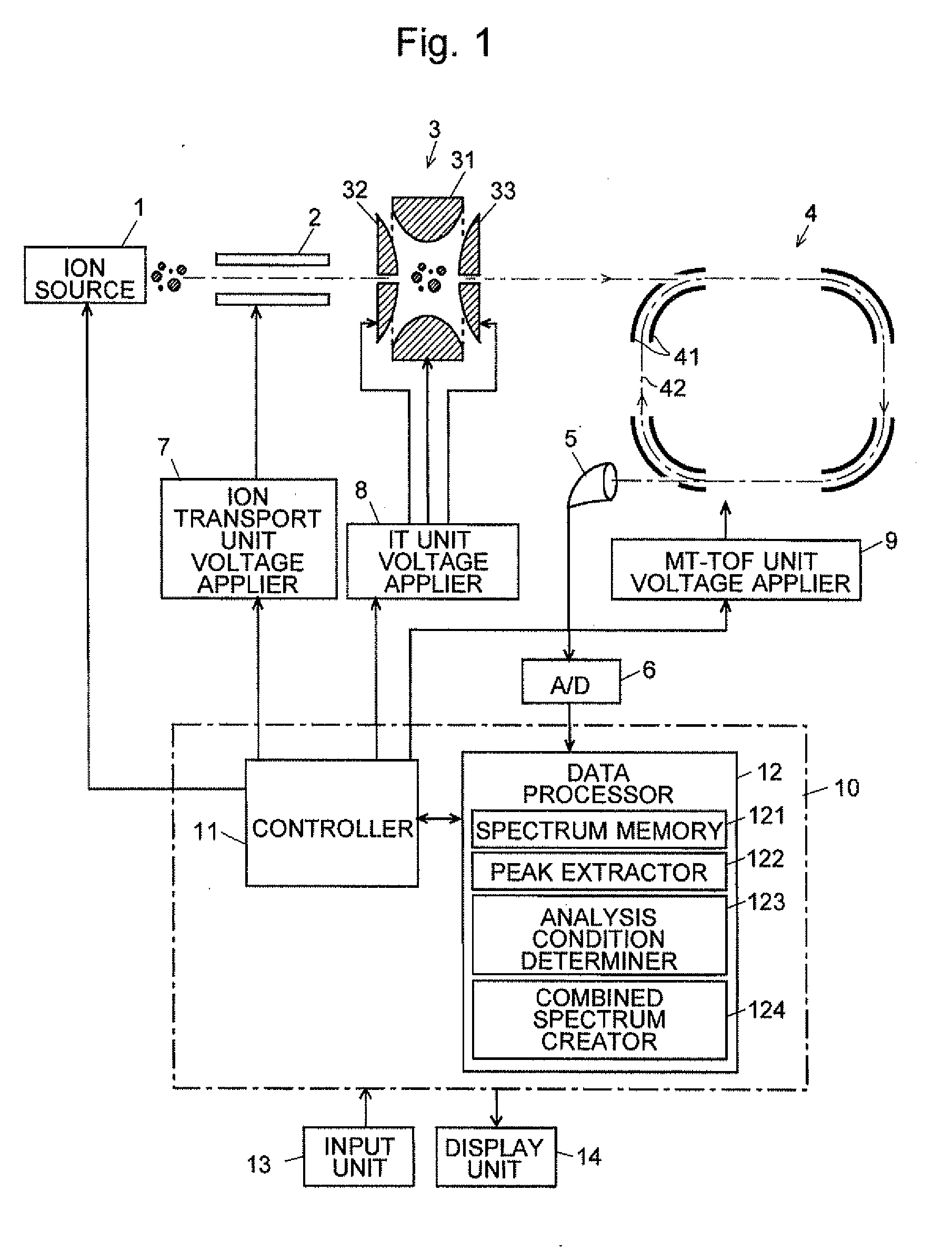
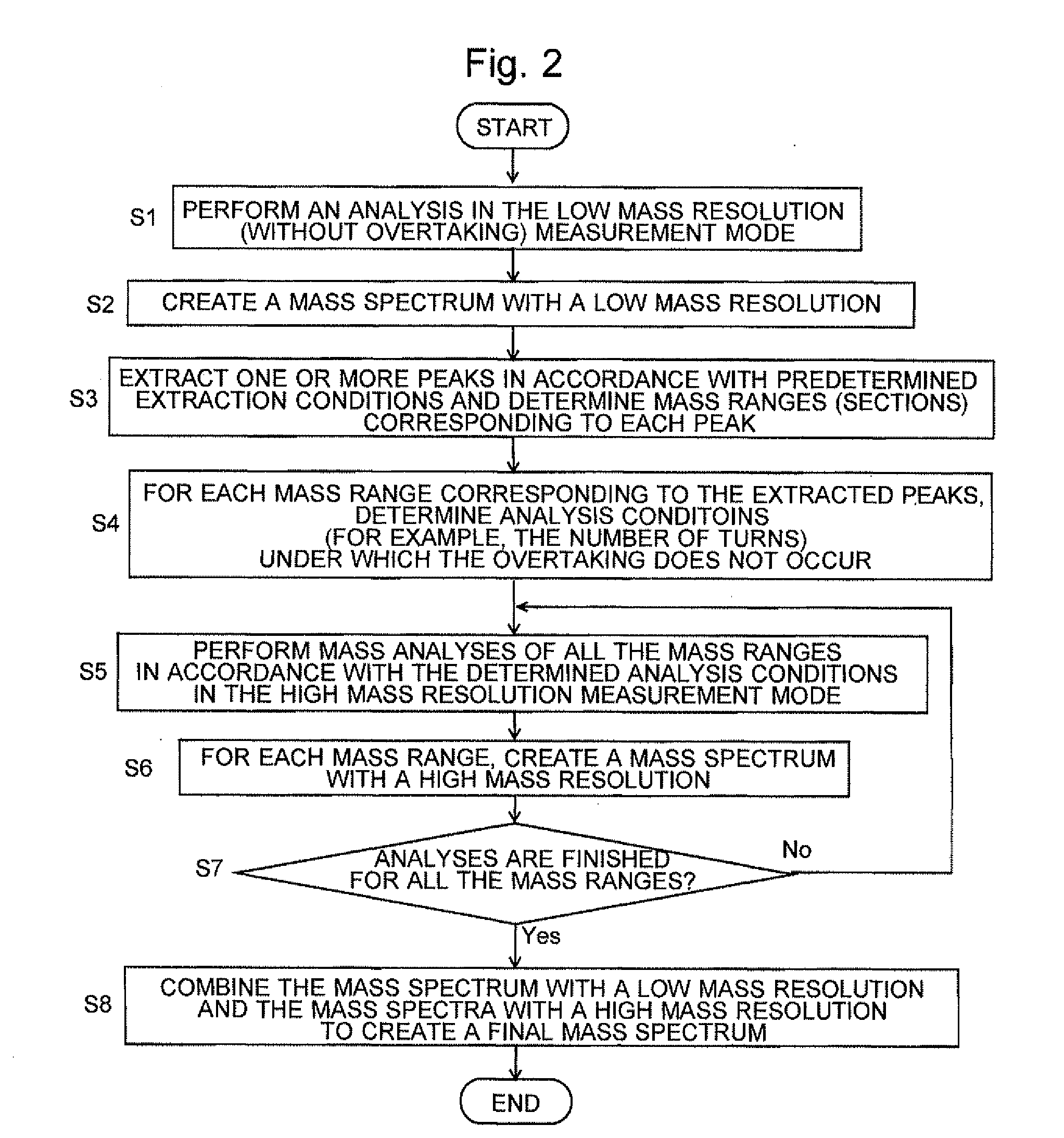
The present invention aims at automatically obtaining a mass spectrum over a wide mass range with a high mass resolution, without the need of the complicated determination of the number of turns or other troublesome computations due to the overtaking of ions on a loop orbit. First, a mass analysis of a target sample is performed under conditions which ensure that the overtaking of ions does not occur, to obtain a mass spectrum with a low mass resolution (S1 and S2). One or more peaks appearing on the mass spectrum are extracted based on predetermined conditions, the mass ranges corresponding to the extracted peaks are determined, and the analysis conditions which ensure that the overtaking of ions does not occur are determined for each of the mass ranges (S3 and S4). Then, in accordance with the analysis conditions, ions within a restricted mass range are selected and ejected from the ion trap to be made to fly along the loop orbit, and mass spectra with a high mass resolution are obtained (S5 and S6). The mass spectrum with a low mass spectrum and the mass spectra with a high mass resolution are eventually combined to create a mass spectrum over a wide mass range (S8).
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP
Energy-filtering cathode lens microscopy instrument
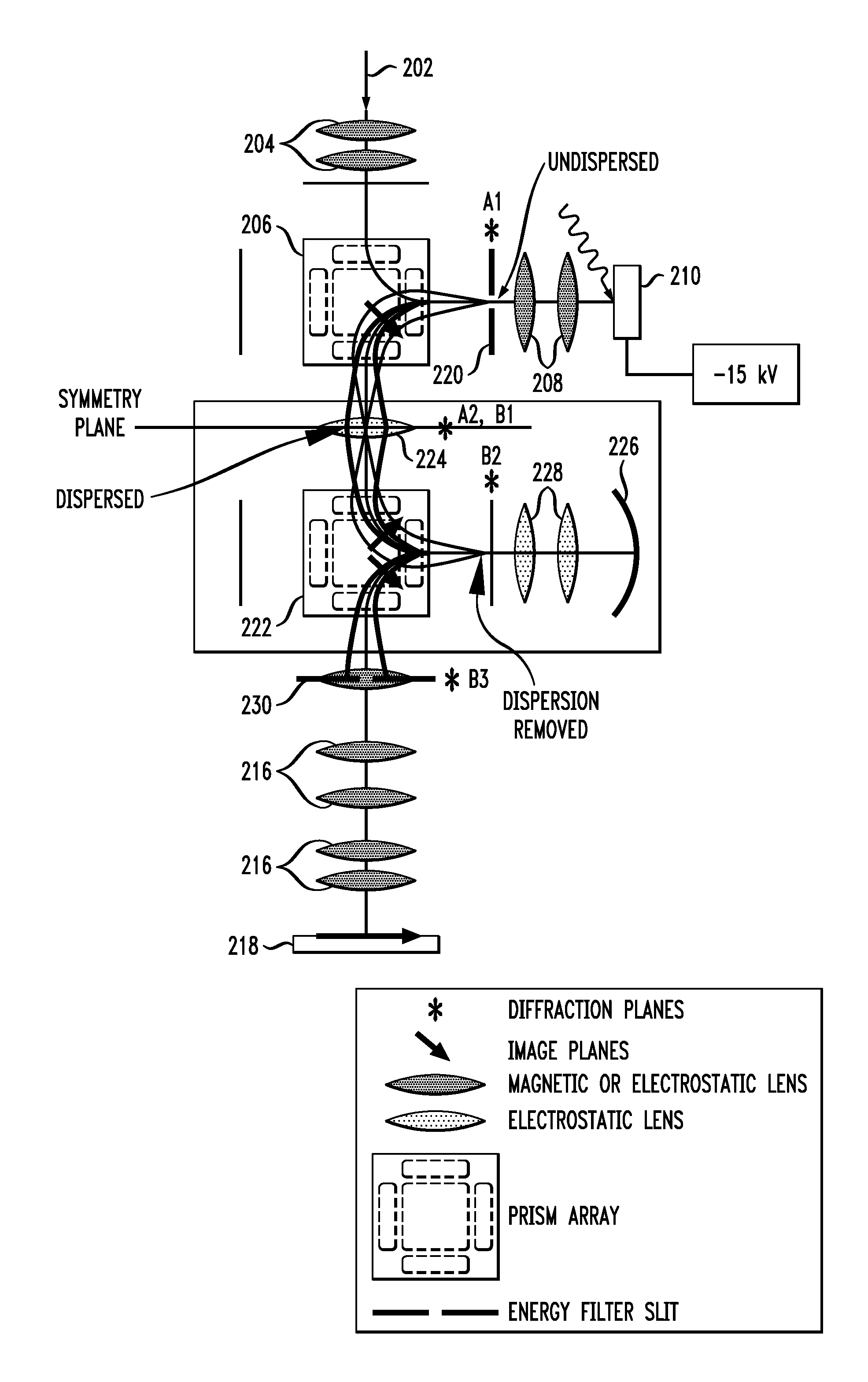
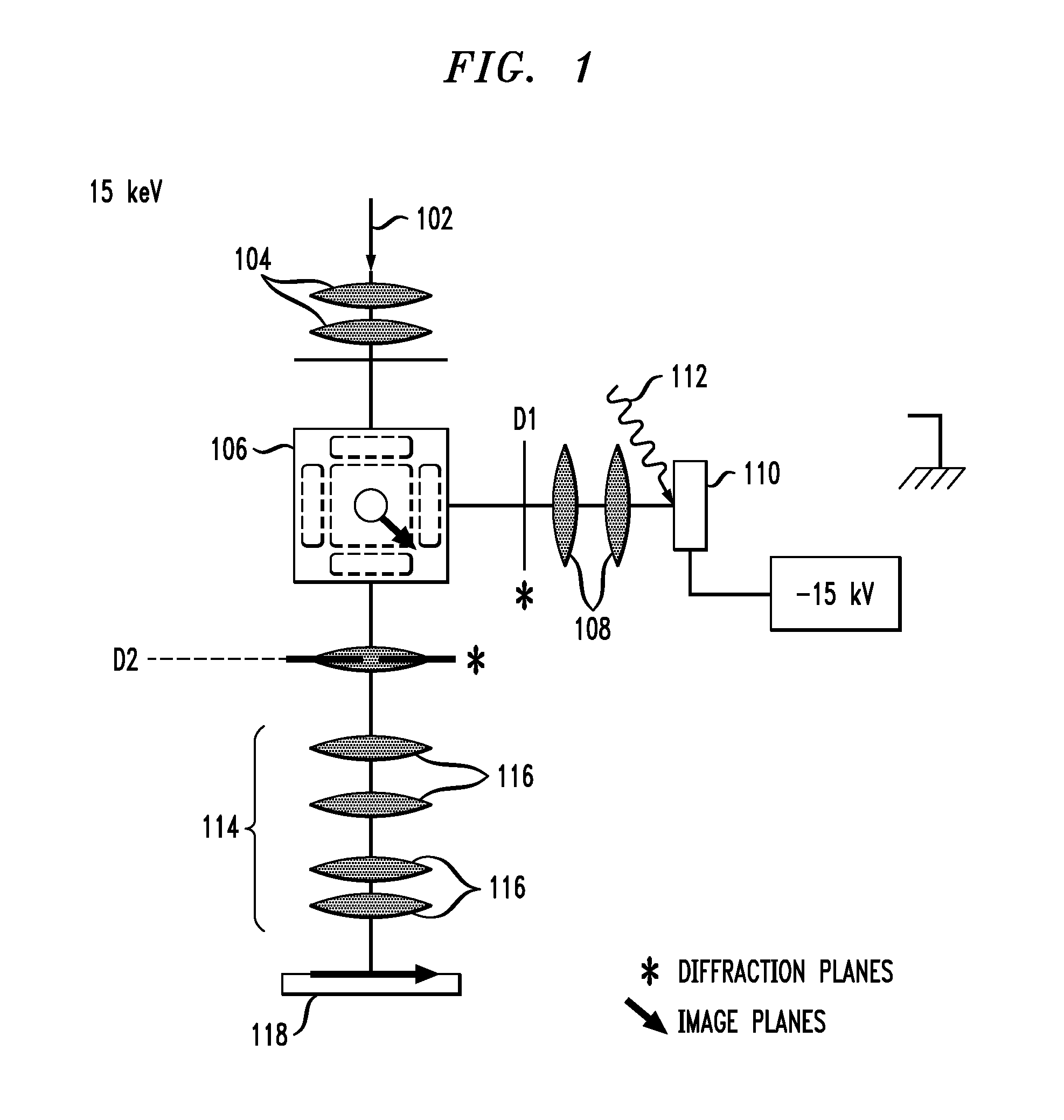
InactiveUS20070200062A1Eliminate the problemLow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesExit planeElectron diffraction pattern
An energy filtering microscopy instrument is provided. An objective lens is disposed for reception of electrons in order to form an electron diffraction pattern in a backfocal plane of the objective lens. An entrance aperture disposed in the backfocal plane of the objective lens for filtering a slice of the electron diffraction pattern. A magnetic deflector has an entrance plane and an exit plane. The entrance aperture is disposed in the entrance plane. The magnetic deflector is disposed to receive the slice of the electron diffraction pattern and project an energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern to the exit plane. An exit aperture is disposed in the exit plane of the magnetic deflector for selection of desired electron energy of the energy dispersed electron diffraction pattern.
Owner:IBM CORP
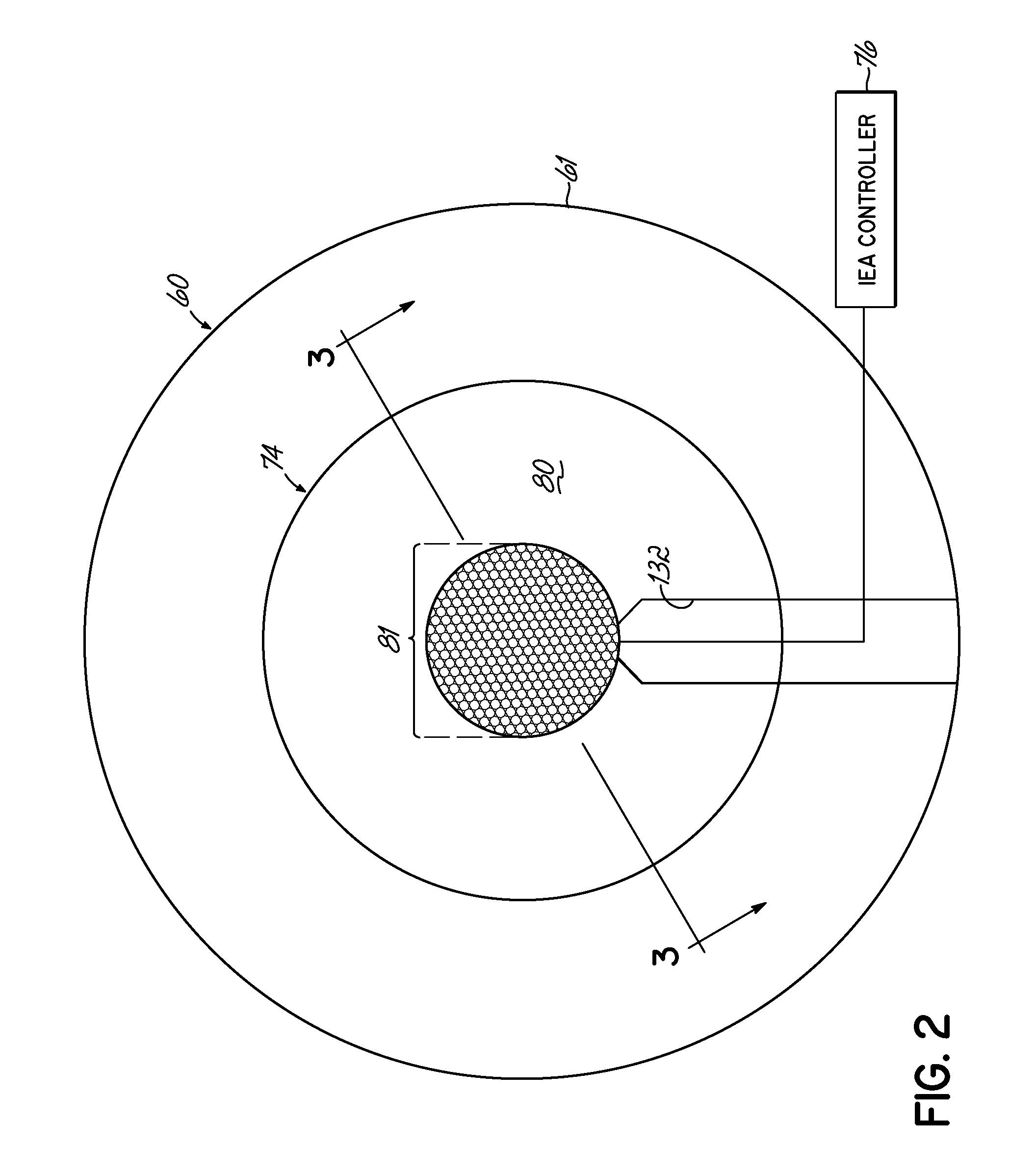
Ion energy analyzer and methods of manufacturing the same
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
Ion optics systems
InactiveUS20060163473A1Avoid spreadingHigh resolutionElectron/ion optical arrangementsIsotope separationMirror imageOptic system
In various embodiments, provided are ion optics systems comprising two or more pairs of ion condensers arranged where the first member and second member of each pair are disposed on opposite sides of a first plane such that the first member of the pair has a position that is substantially mirror-symmetric about the first plane relative to the position of the second member of the pair and wherein the deflection angle of each of the ion condensers is less than or equal to about π radians.
Owner:MDS CO LTD
Spherical Aberration Corrected Electrostatic Lens, Input Lens, Electron Spectrometer, Photoemission Electron Microscope And Measuring System
InactiveUS20080135748A1Wide acceptance angleImprove performanceThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron microscopePhotoelectron microscopy
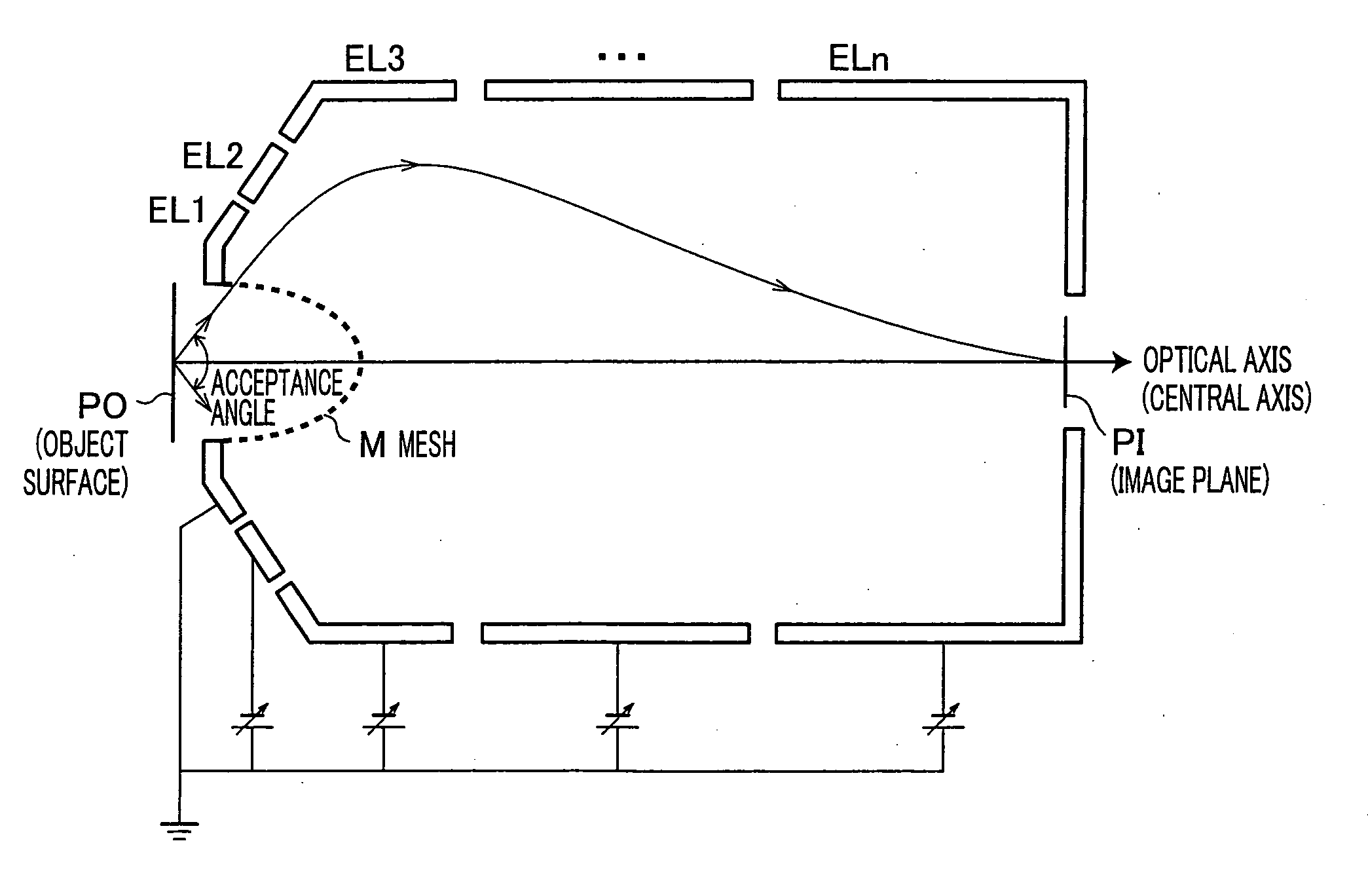
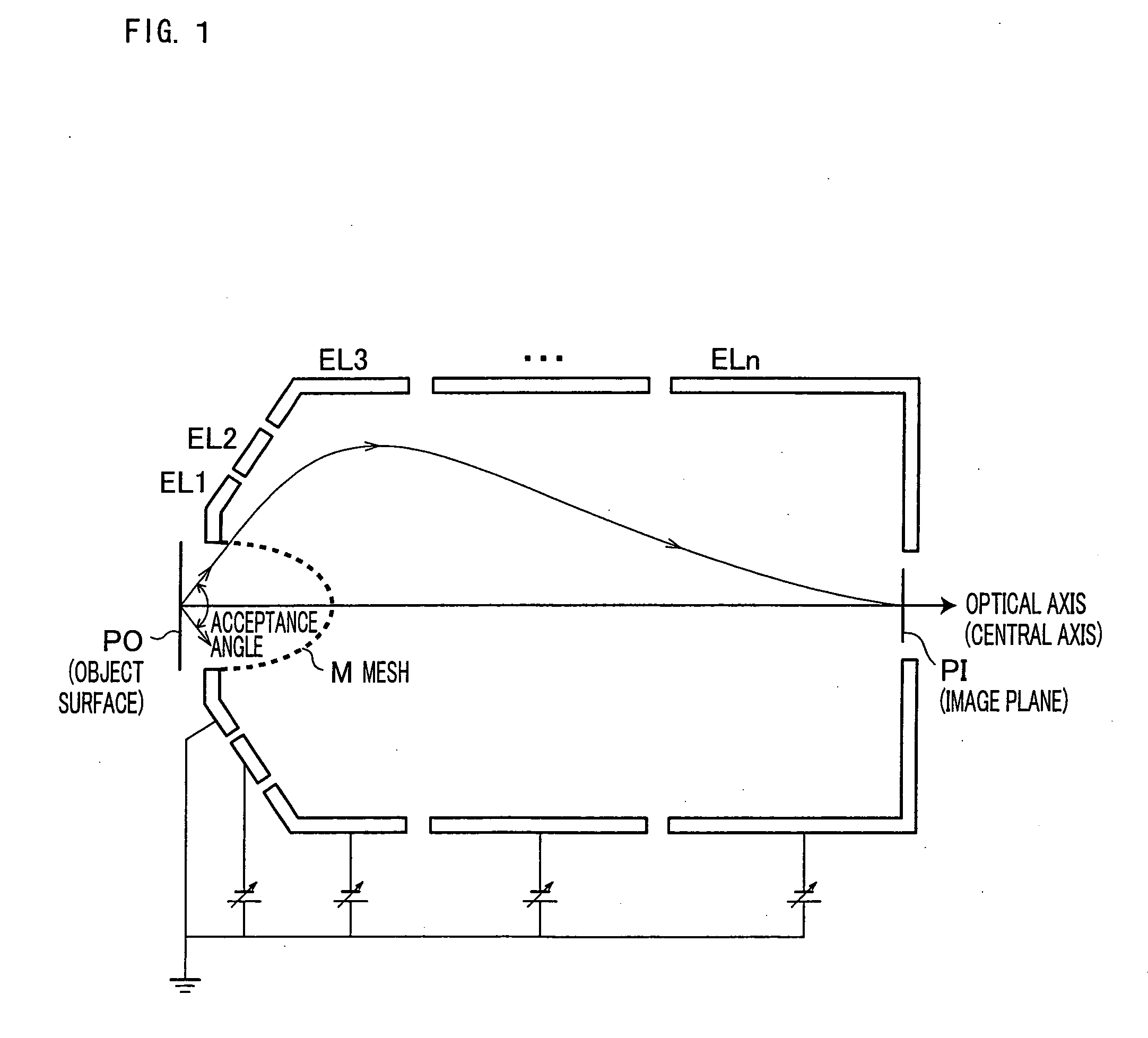
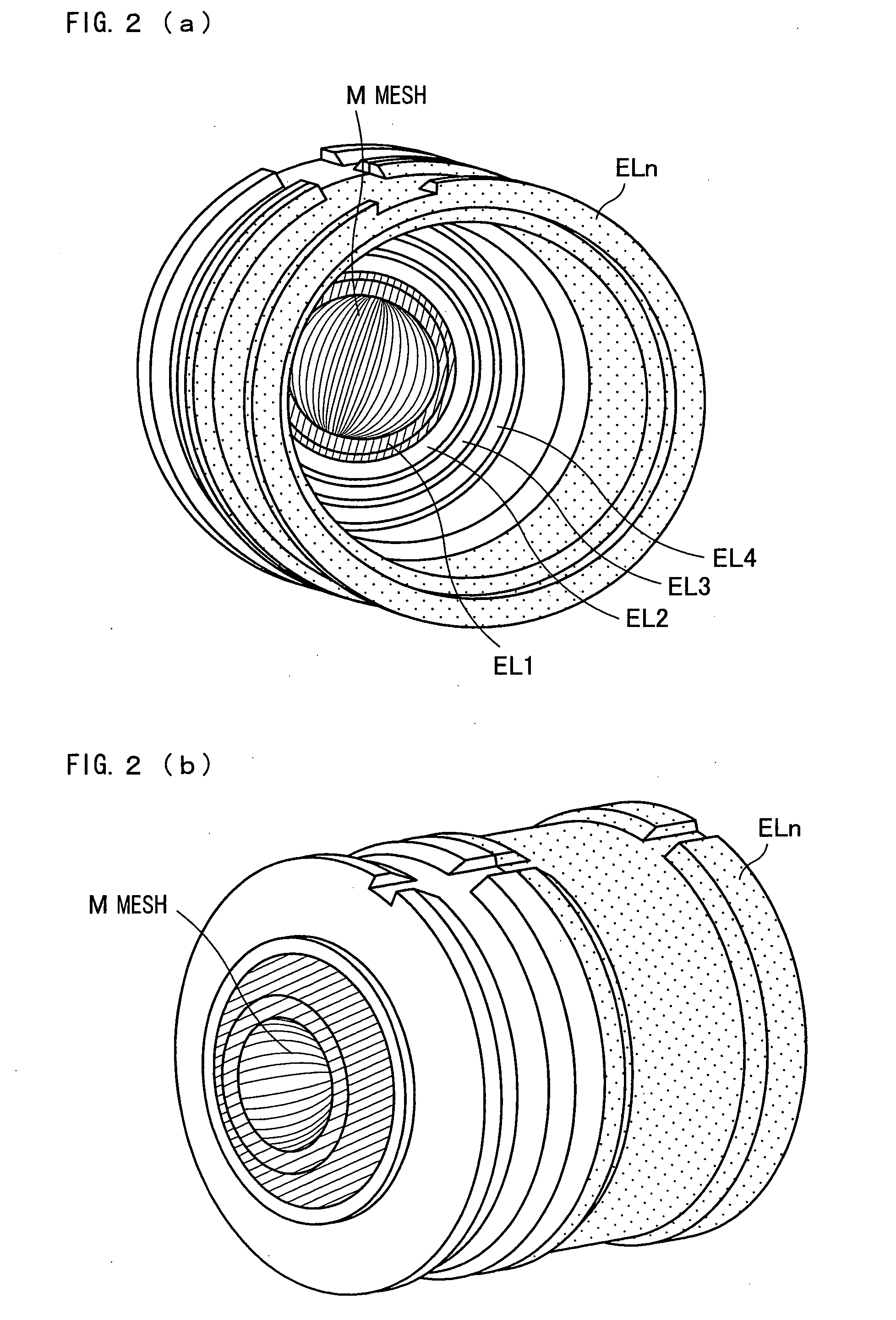
A mesh (M) having an ellipsoid shape or a shape close to the ellipsoid shape is attached to an electrode (EL1) among electrodes (EL1 to ELn). Voltages of the later-stage electrodes (EL2 to ELn) are appropriately set. With this arrangement, a local negative spherical aberration generated by the mesh (M) is cancelled out with a positive spherical aberration. This optimizes an electric field distribution. As a result, this realizes an electrostatic lens whose acceptance angle is extended to about±60°.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Ion optics systems
InactiveUS7439520B2High resolutionLimited resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsOptic systemMirror image
In various embodiments, provided are ion optics systems comprising two or more pairs of ion condensers arranged where the first member and second member of each pair are disposed on opposite sides of a first plane such that the first member of the pair has a position that is substantially mirror-symmetric about the first plane relative to the position of the second member of the pair and wherein the deflection angle of each of the ion condensers is less than or equal to about π radians.
Owner:MDS CO LTD
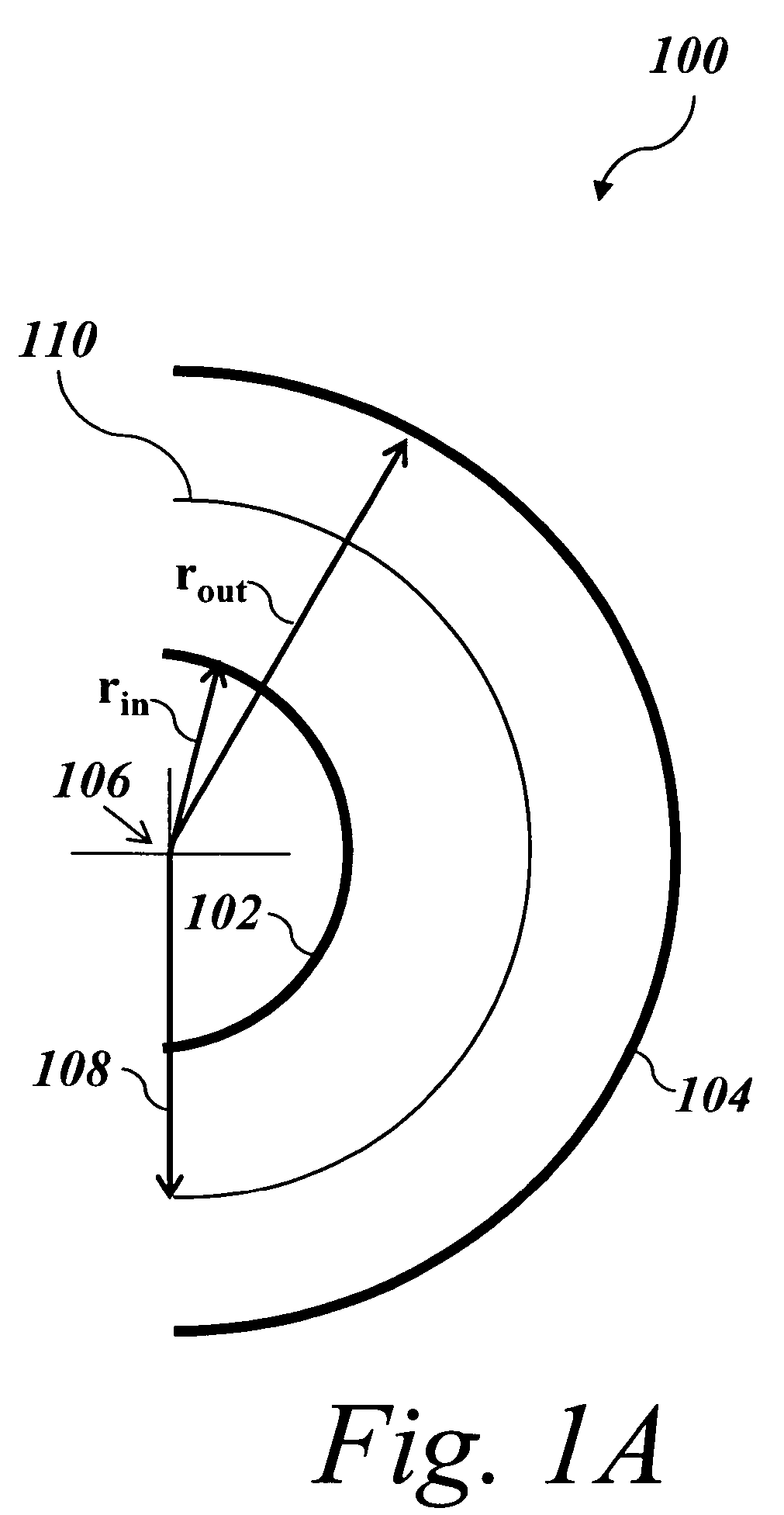
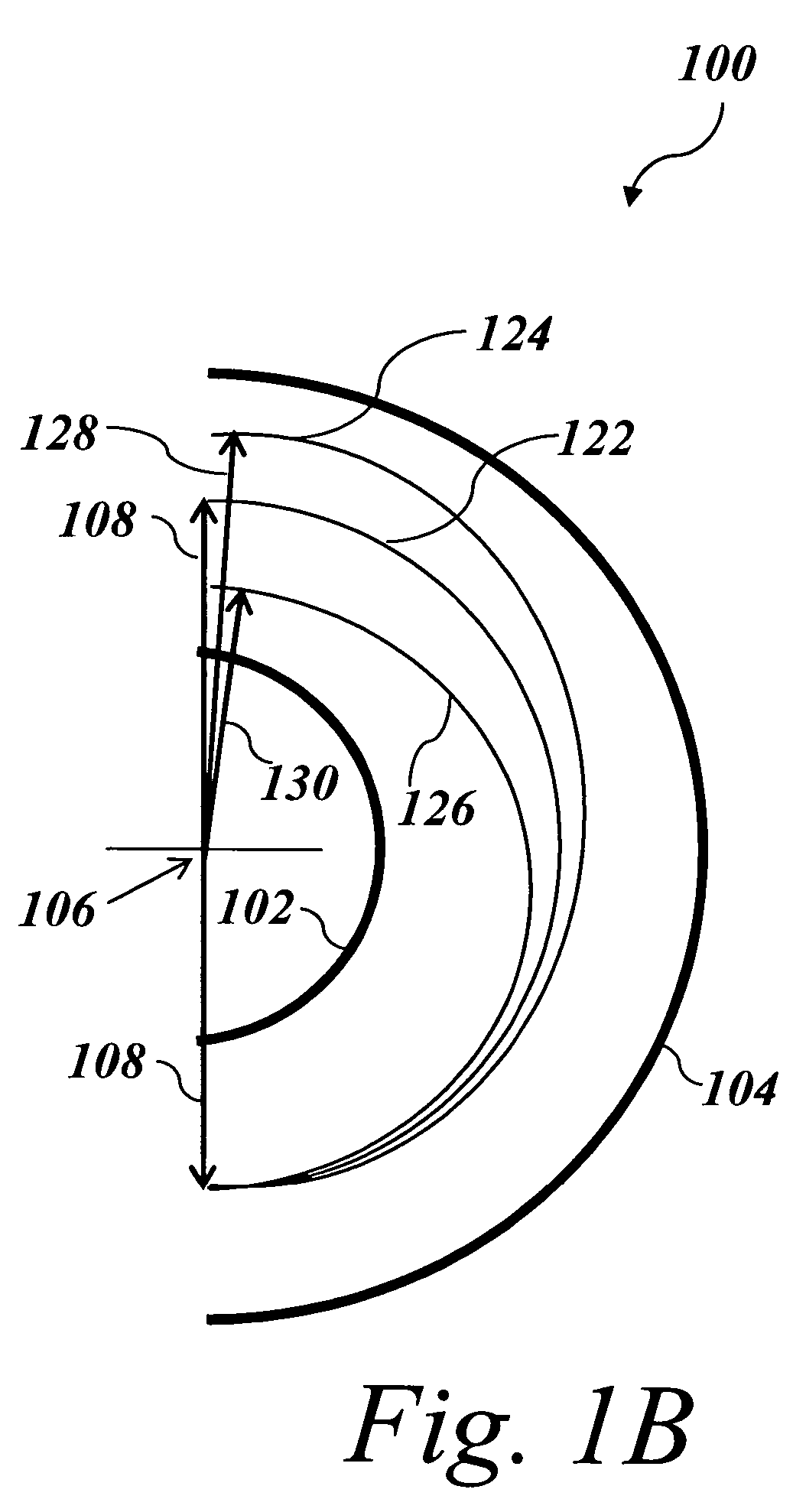
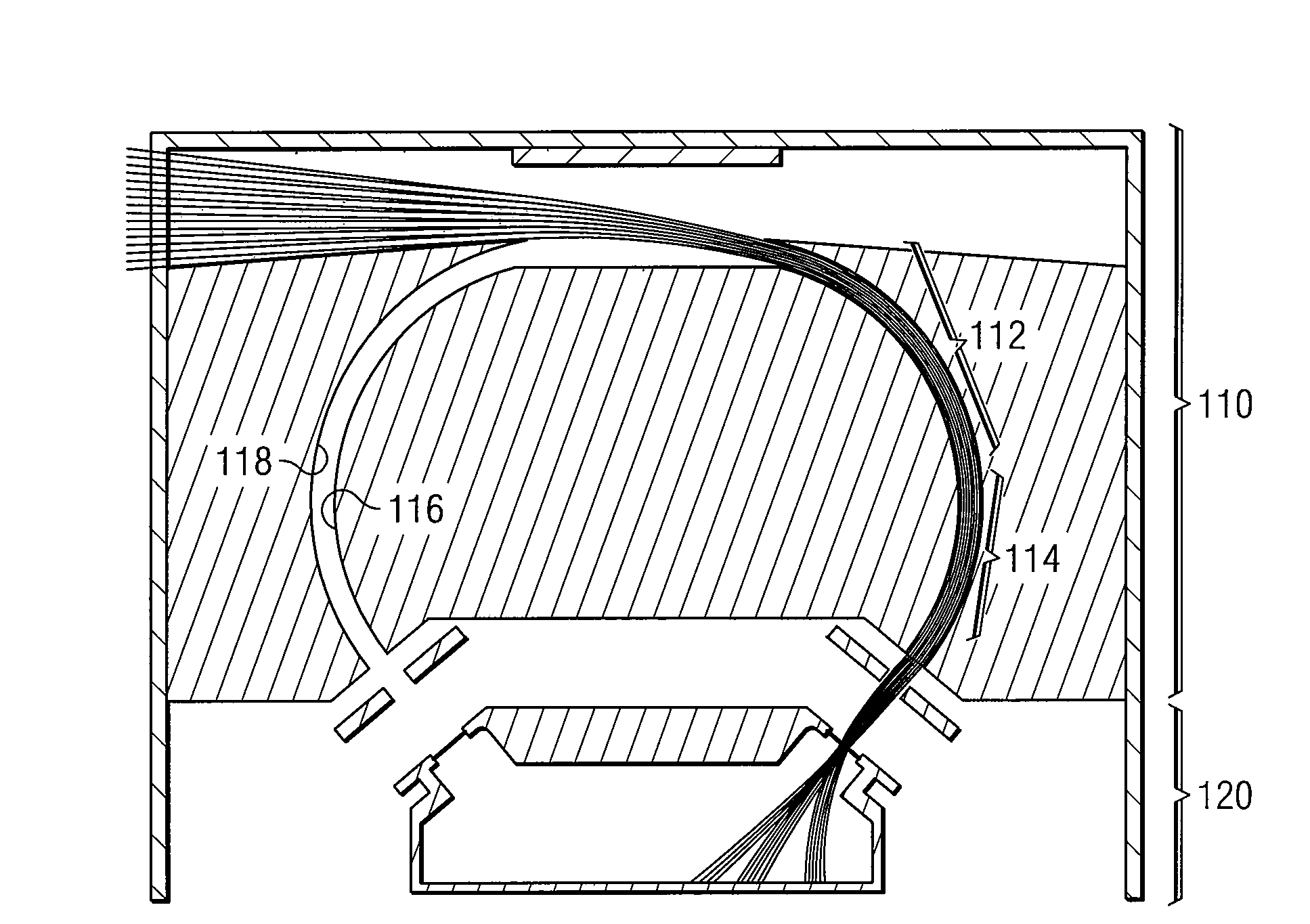
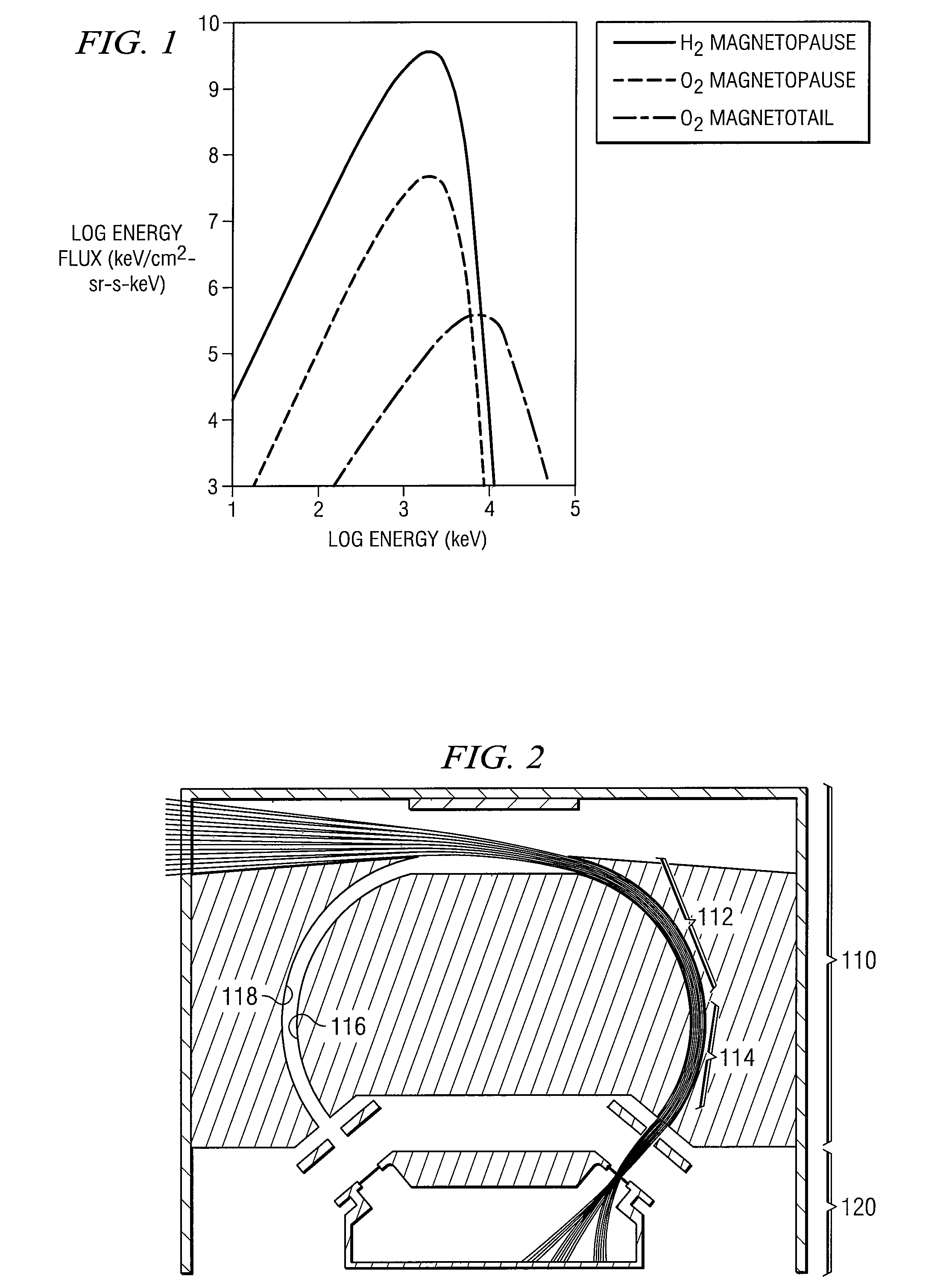
Ion Composition Analyzer with Increased Dynamic Range
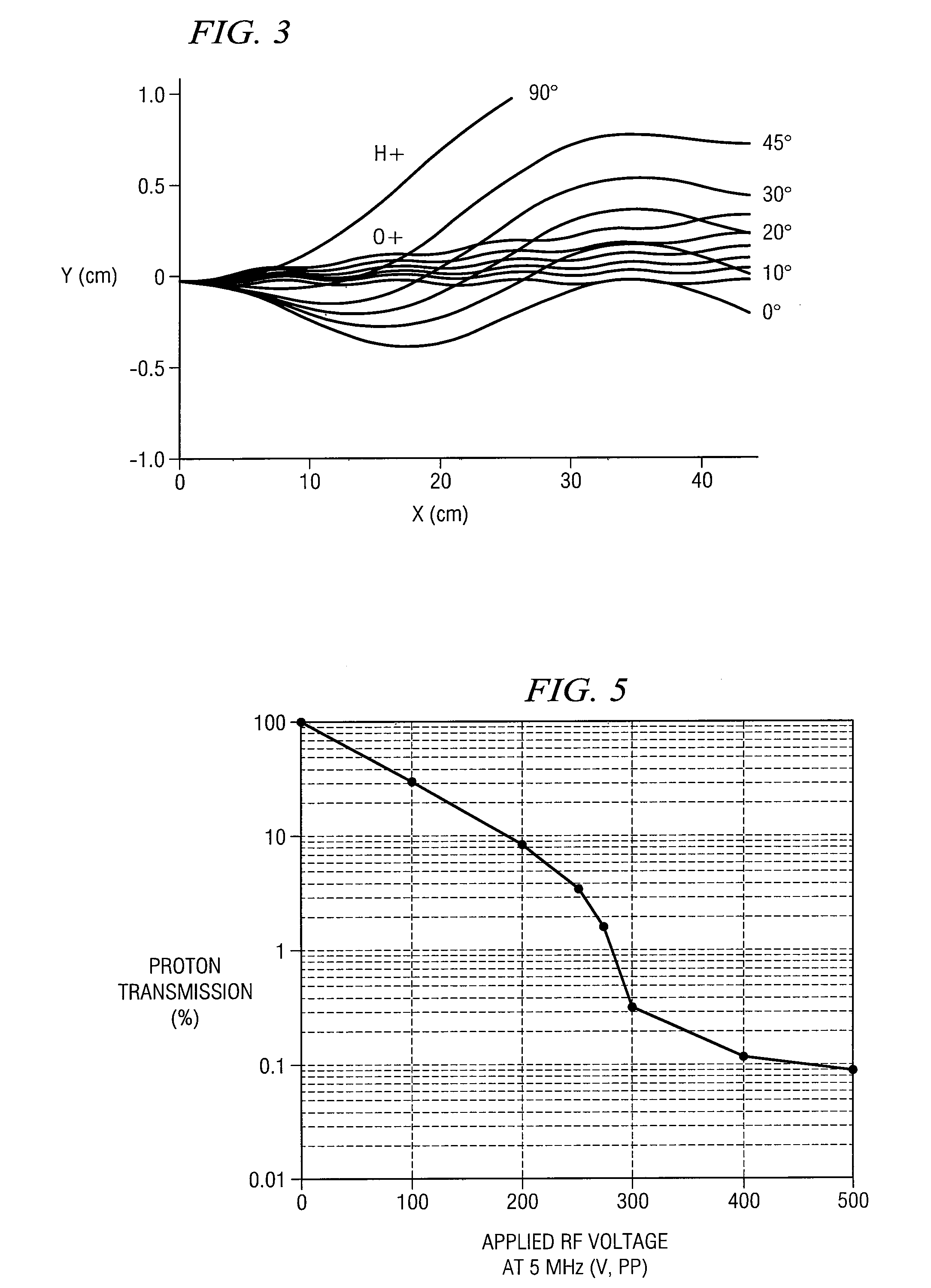
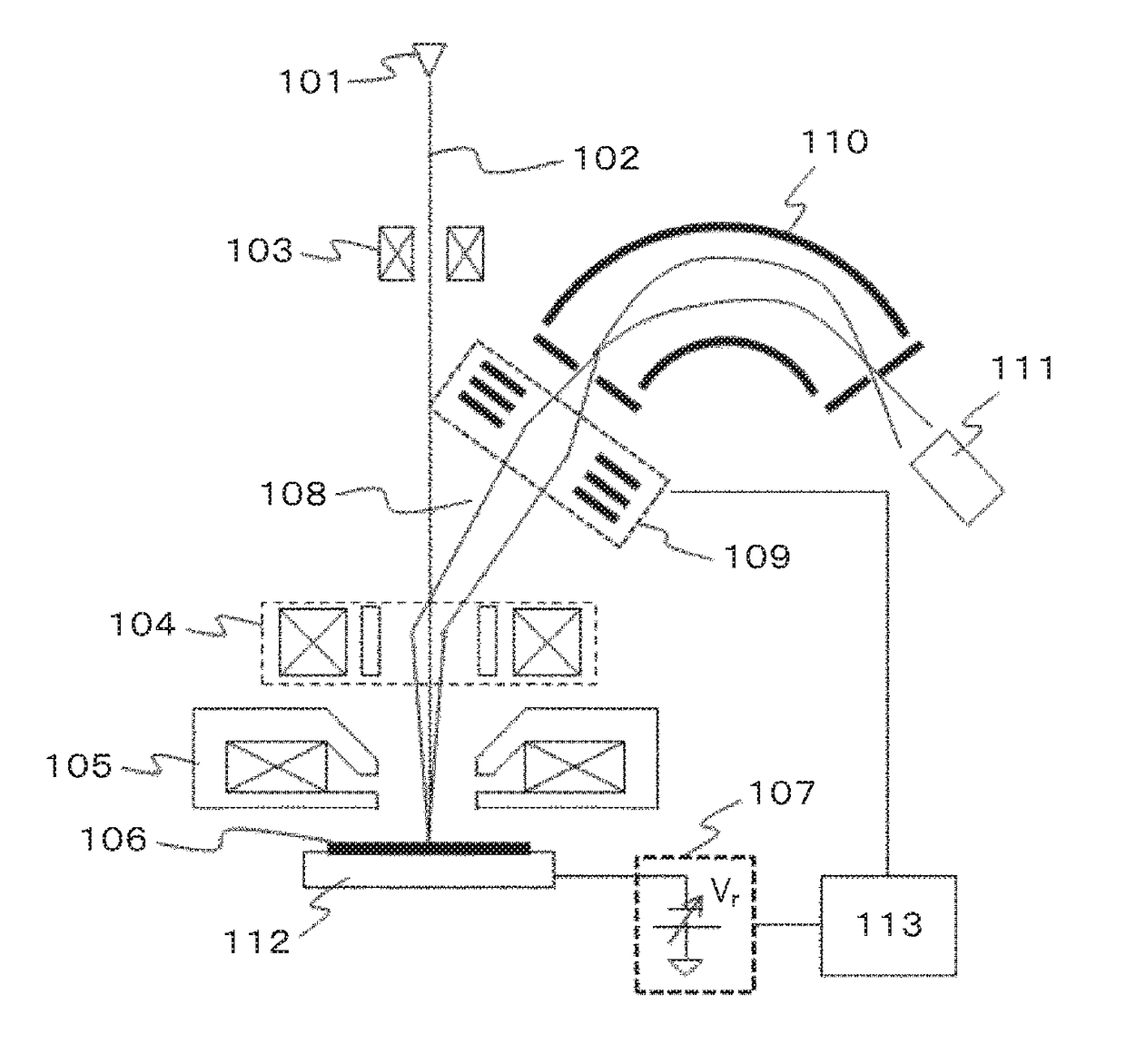
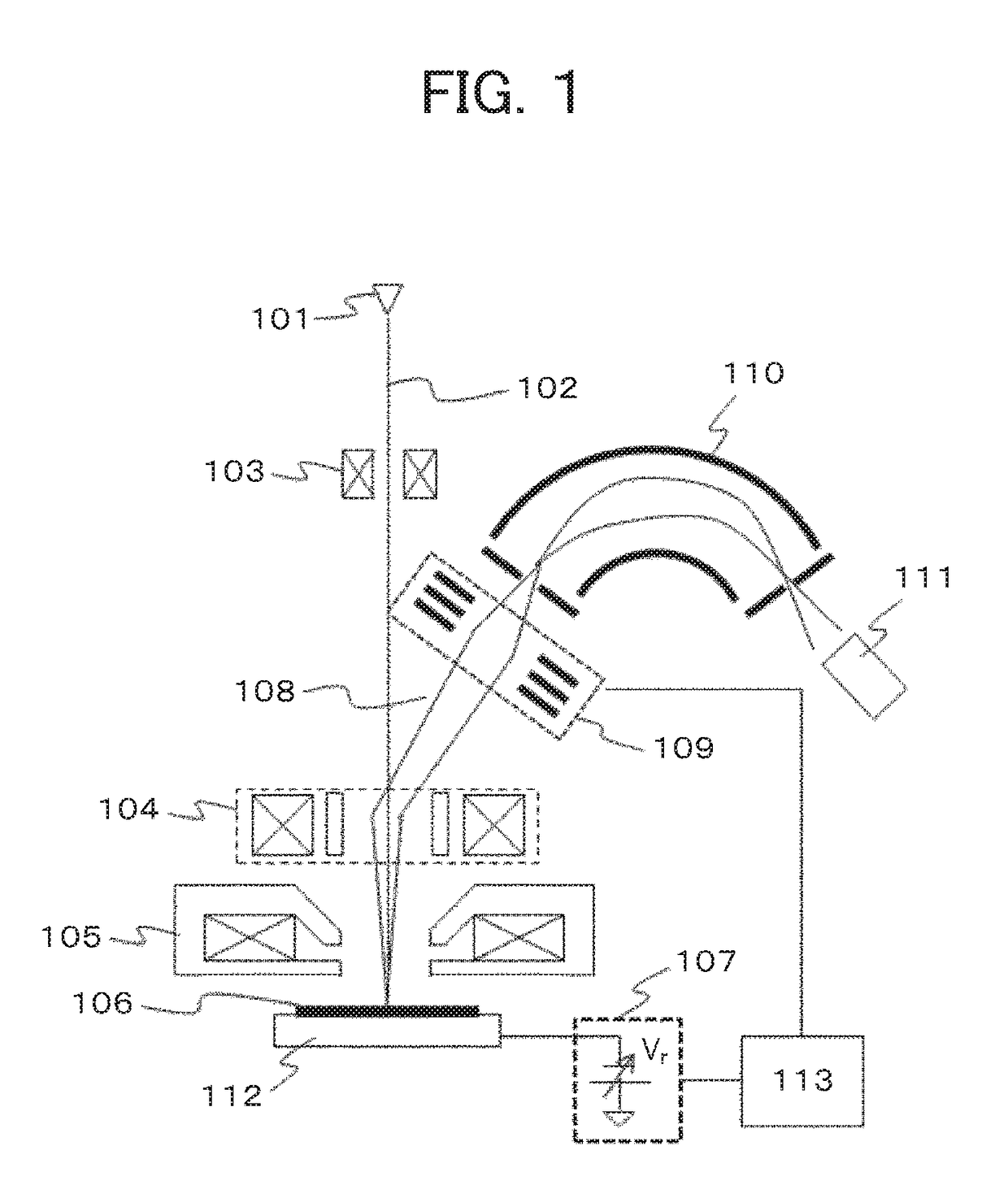
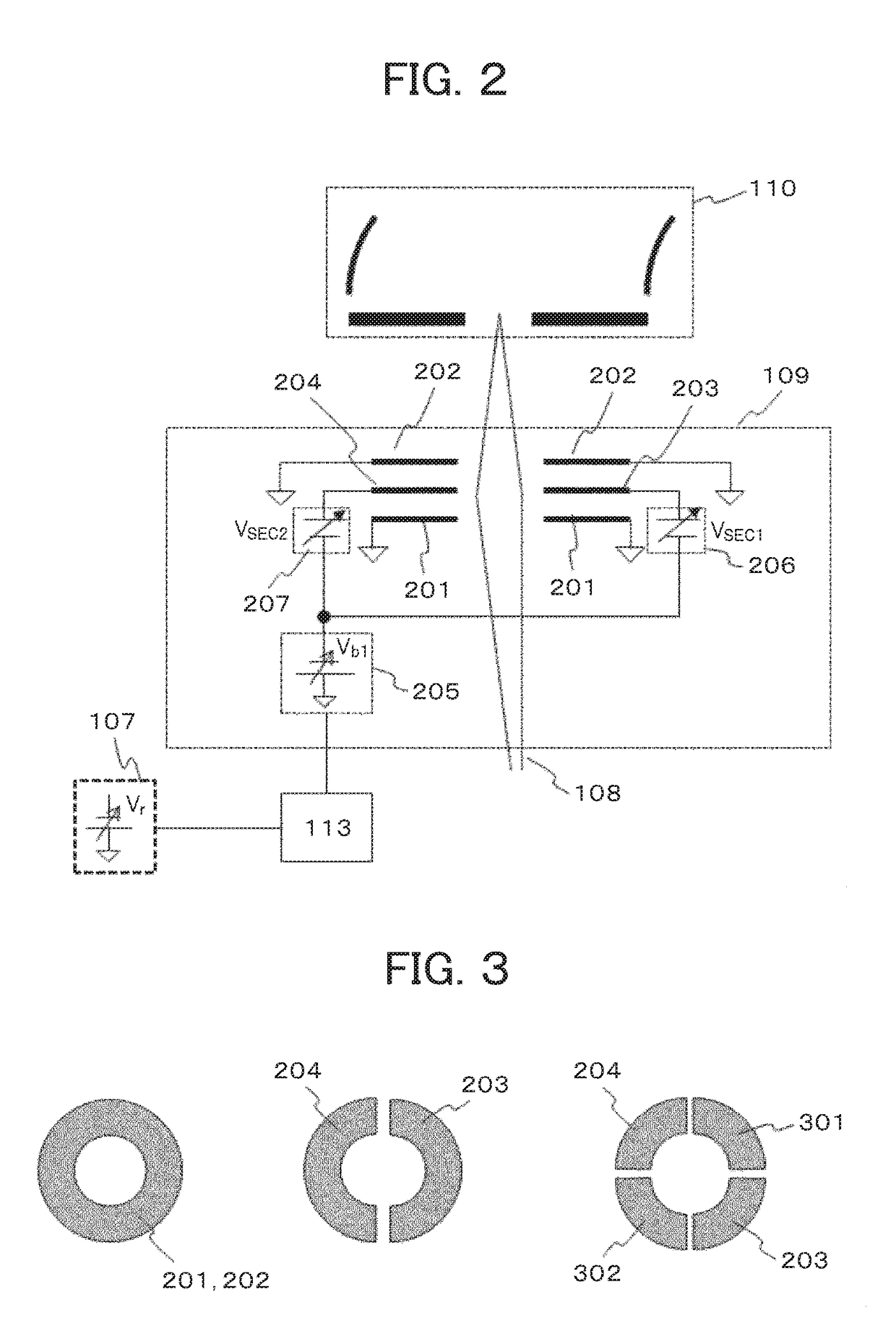
A system and method for separating ions in an ion mixture, such as a plasma in space. The ion mixture enters an electrostatic analyzer, whose ion path has at least two sections. A first section applies a DC voltage to the ions, and a next section applies an RF frequency voltage to the ions. Appropriate DC and RF voltages are applied, such that at least a portion of the lower mass ions are absorbed into the RF section of the analyzer. The heaver ions are transmitted out of the ion path and are readily available for further analysis.
Owner:SOUTHWEST RES INST
Scanning electron microscope and method for controlling same
ActiveUS20170186583A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationStatic energy spectrometersElectron sourceScanning tunneling microscope
The scanning electron microscope includes: an electron source; a first deflector for deflecting a primary electron beam emitted from the electron source; a second deflector for focusing the primary electron beam deflected by the first deflector and deflecting a second electron from a sample, which is generated the focused primary electron beam, to the outside of the optical axis; a voltage applying unit for applying a negative voltage to the sample to decelerate the primary electron beam; a spectrometer for dispersing the secondary electron; a detector for detecting the secondary electron passing through the spectrometer; an electrostatic lens provided between the second deflector and the spectrometer; and a voltage control unit that controls the voltage applied to the electrostatic lens based on the negative voltage applied to the sample. The electrostatic lens allows the deflecting action to be overlapped with the converging action.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Imaging mass spectrometer
ActiveCN108292586AHigh resolutionImprove spatial resolutionTime-of-flight spectrometersSpectrometer detectorsImage resolutionMass analyzer
A time-of-flight mass spectrometer is disclosed and comprises ion optics that map an array of ions at an ion source array (71) to a corresponding array of positions on a position sensitive ion detector (79). The ion optics include at least one gridless ion mirror (76) for reflecting ions, which may compensate for various aberrations and allows the spectrometer to have relatively high mass and spatial resolutions.
Owner:MICROMASS UK LTD +1
Energy filter image generator for electrically charged particles and the use thereof
ActiveUS7250599B2Eliminate differencesMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationIsotope separationEnergy analyserPlane of incidence
Owner:OMICRON NANO TECH +1
Mass spectrometer and methods of increasing dispersion between ion beams
A mass spectrometer includes a magnetic sector configured to separate a plurality of ion beams, and an electrostatic sector configured to receive the plurality of ion beams from the magnetic sector and increase separation between the ion beams, the electrostatic sector being used as a dispersive element following magnetic separation of the plurality of ion beams. Other apparatus and methods are provided.
Owner:BATTELLE ENERGY ALLIANCE LLC
Electron spectroscopy system
ActiveUS20190096627A1Maintain throughputHigh momentum and energy resolutionStatic energy spectrometersElectron spectroscopyRadio frequency
An electron spectroscopy system and method are disclosed. In another aspect, an ultrabright and ultrafast angle-resolved electron spectroscopy system is provided. A further aspect of the present system employs an electron gun, a radio frequency cavity and multiple spectrometers. Yet another aspect uses spectrometers in an aligned manner to deflect and focus electrons emitted by the electron gun. Moreover, an ultrafast laser is coupled to an electron spectroscopy system. A bunch of monochromatic electrons have their energy compressed and reoriented in an additional aspect of the present system. A further aspect of the present electron spectroscopy system employs adaptive and / or adjustable optics to optimize both time and energy compression. Another aspect provides at least two RF lenses or cavities, one before a specimen and one after the specimen.
Owner:BOARD OF TRUSTEES OPERATING MICHIGAN STATE UNIV
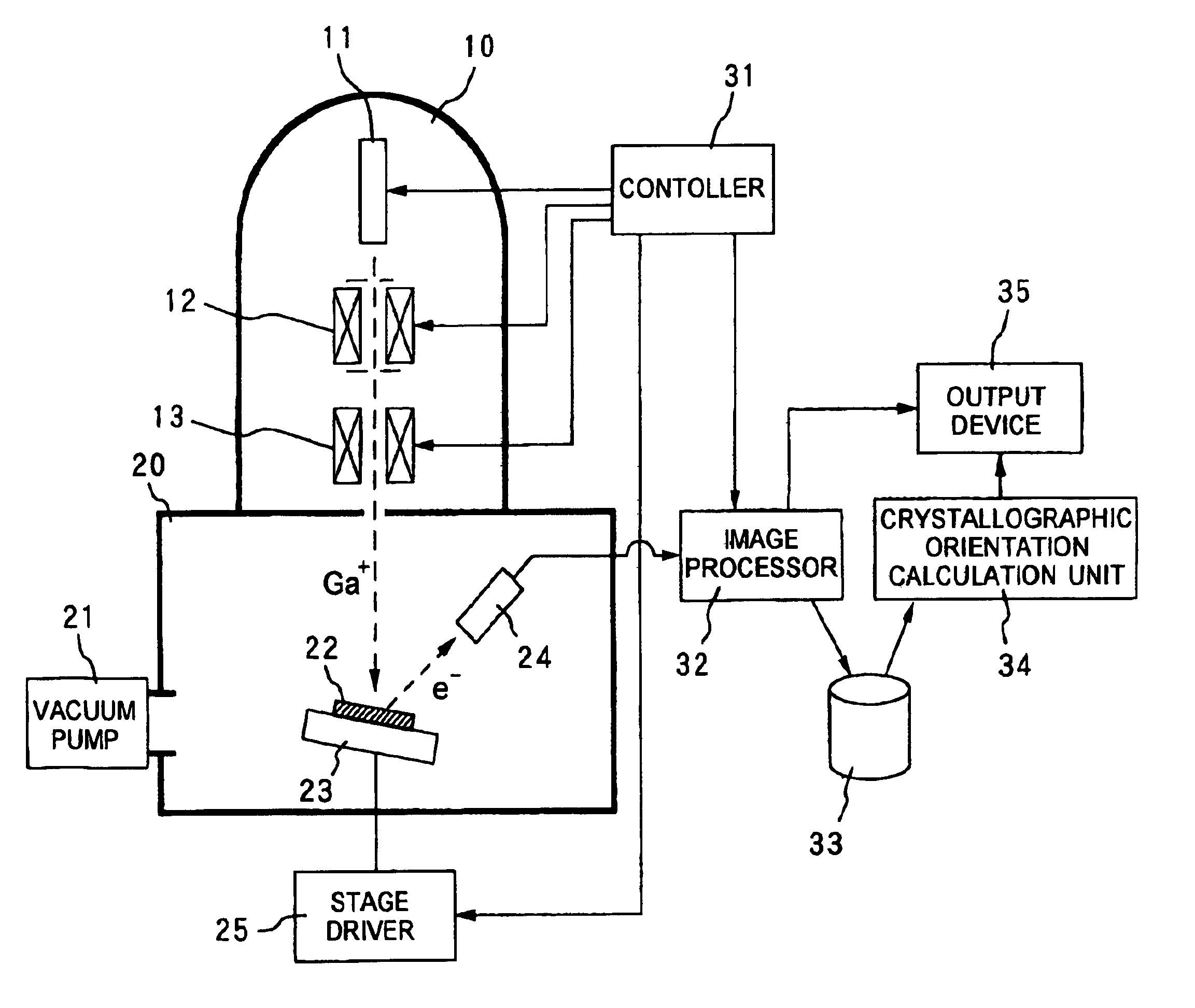
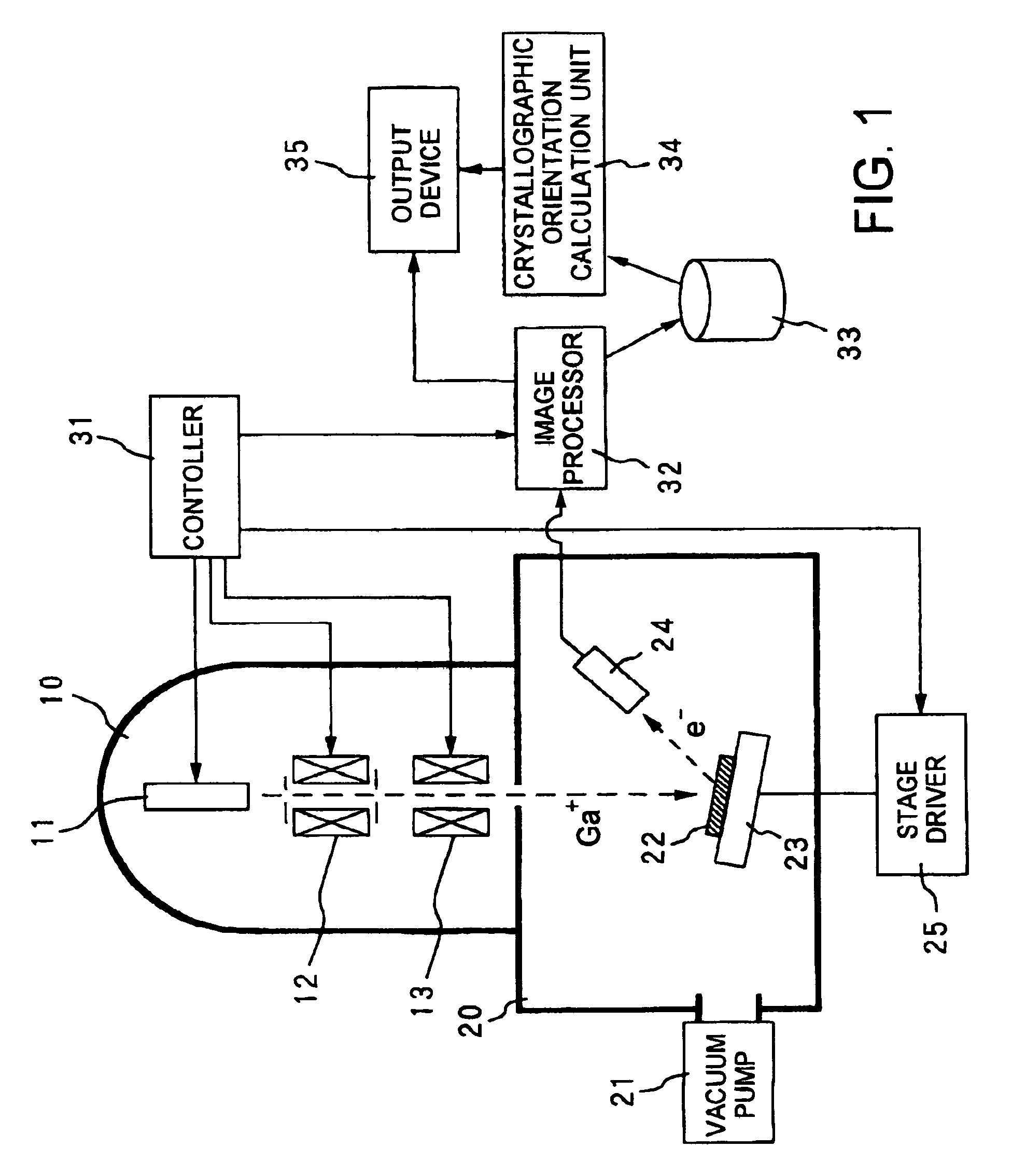
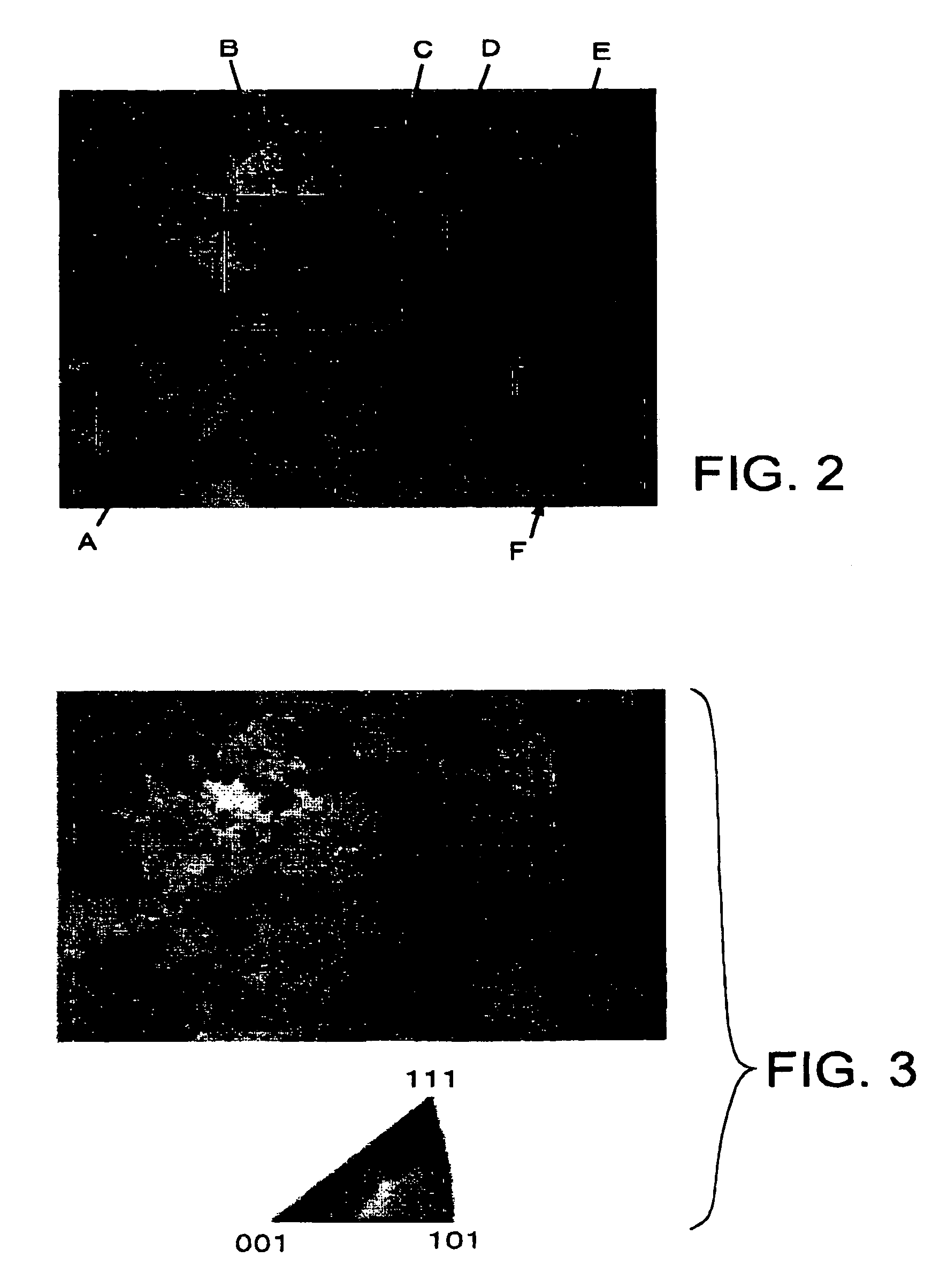
Method and apparatus for crystal analysis
InactiveUS7091484B2High resolutionSimple processMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotometryCrystal systemAngle of incidence
The method of measuring crystallographic orientations, crystal systems or the like of the surface of a specimen has steps of: irradiating the specimen with an ion beam; measuring the secondary electrons generated by the irradiation of the ion beam; repeating the irradiation of the ion beam and the measurement of the secondary electrons with each variation in an angle of incidence of the ion beam with respect to the specimen; and determining the crystalline state based on the variation in the amount of the secondary electrons corresponding to the variation of the angle of incidence.
Owner:TDK CORPARATION
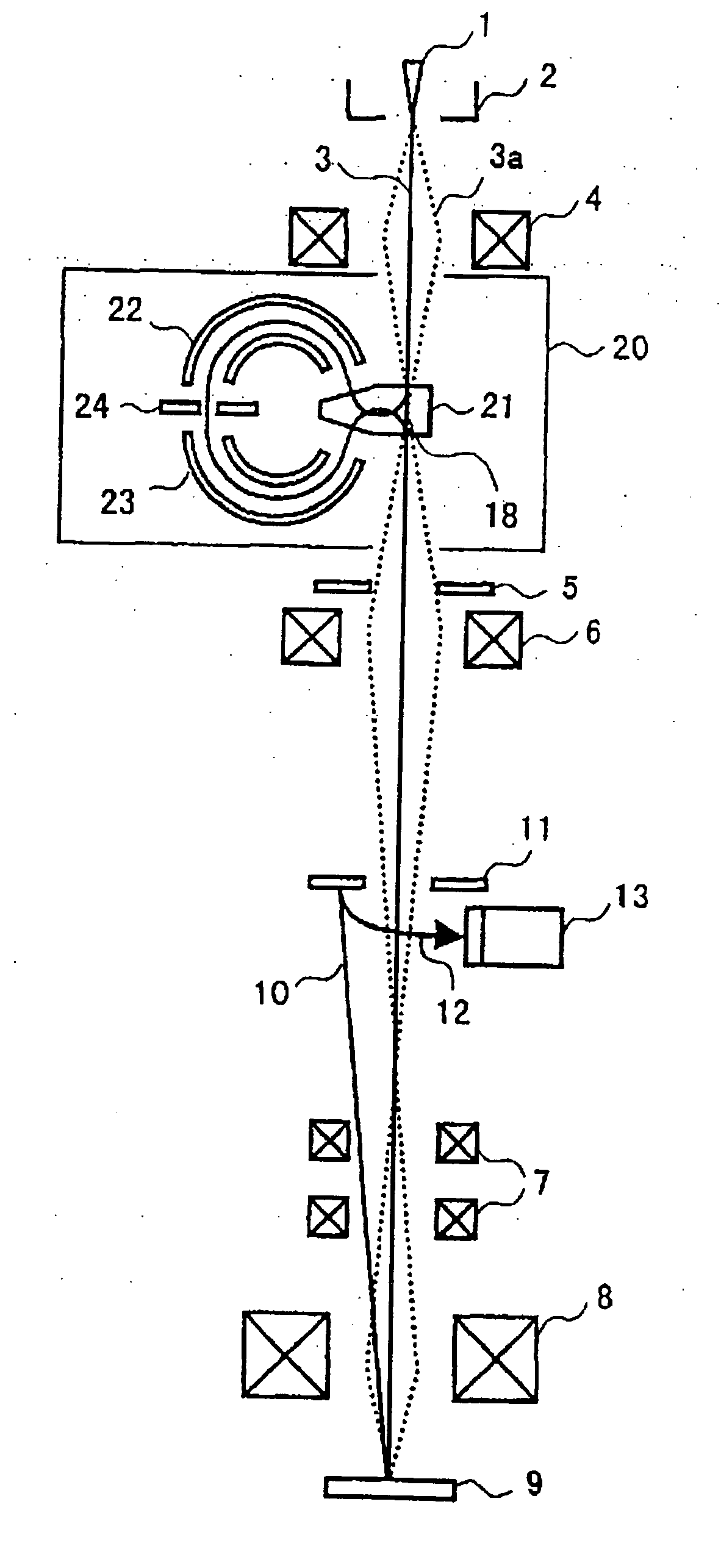
Monochromator and scanning electron microscope using the same
InactiveUS20060219910A1High resolutionAberration suppressionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesObject pointEnergy dispersion
An invention providing a scanning electron microscope composed of a monochromator capable of high resolution, monochromatizing the energy and reducing chromatic aberrations without significantly lowering the electrical current strength of the primary electron beam. A scanning electron microscope is installed with a pair of sectorial magnetic and electrical fields having opposite deflection directions to focus the electron beam and then limit the energy width by means of slits, and another pair of sectorial magnetic and electrical fields of the same shape is installed at a position forming a symmetrical mirror versus the surface containing the slits. This structure acts to cancel out energy dispersion at the object point and symmetrical mirror positions, and by spatially contracting the point-converged spot beam with a converging lens system, improves the image resolution of the scanning electron microscope.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Electron Spectrometer and Measurement Method
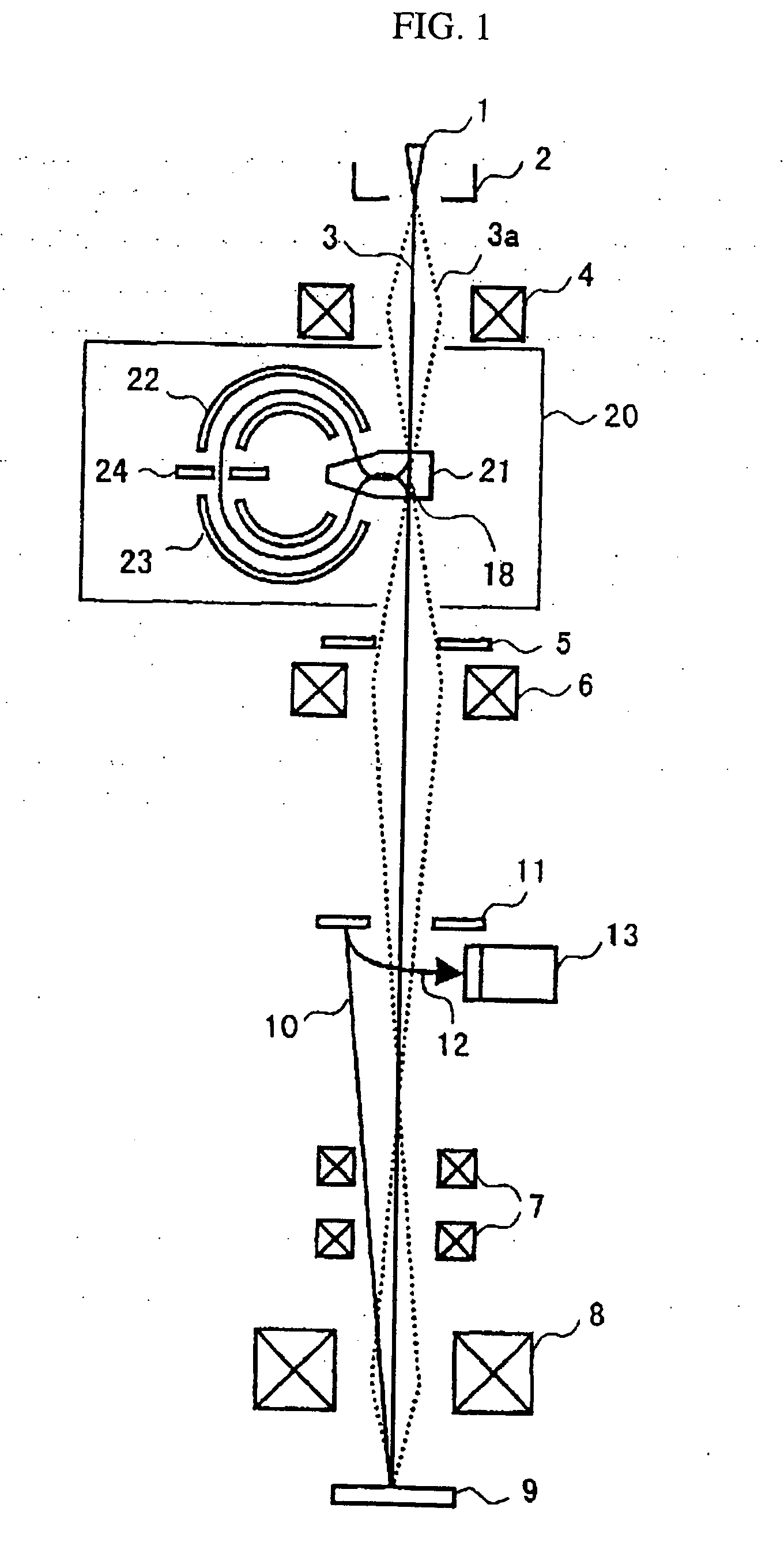
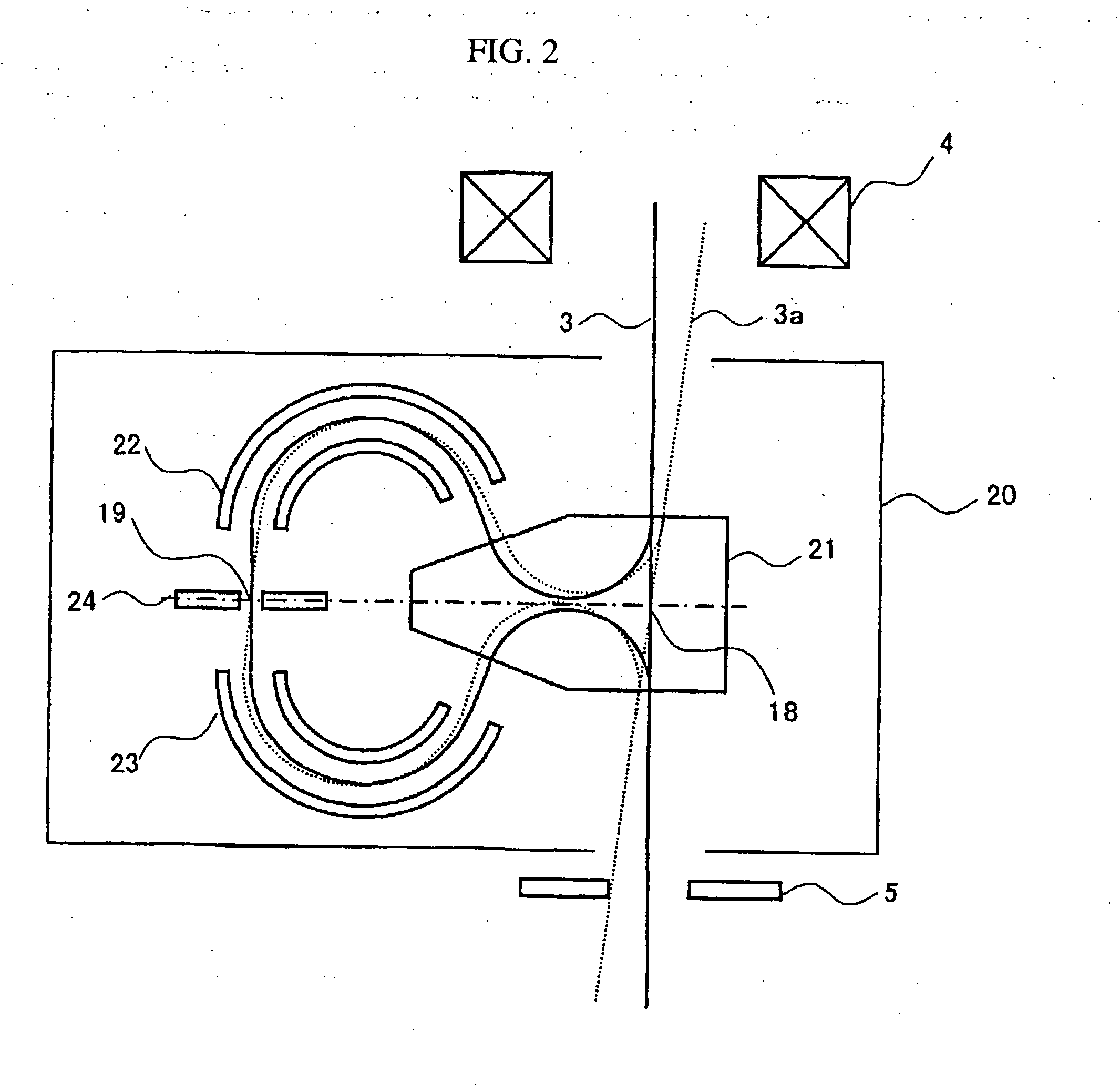
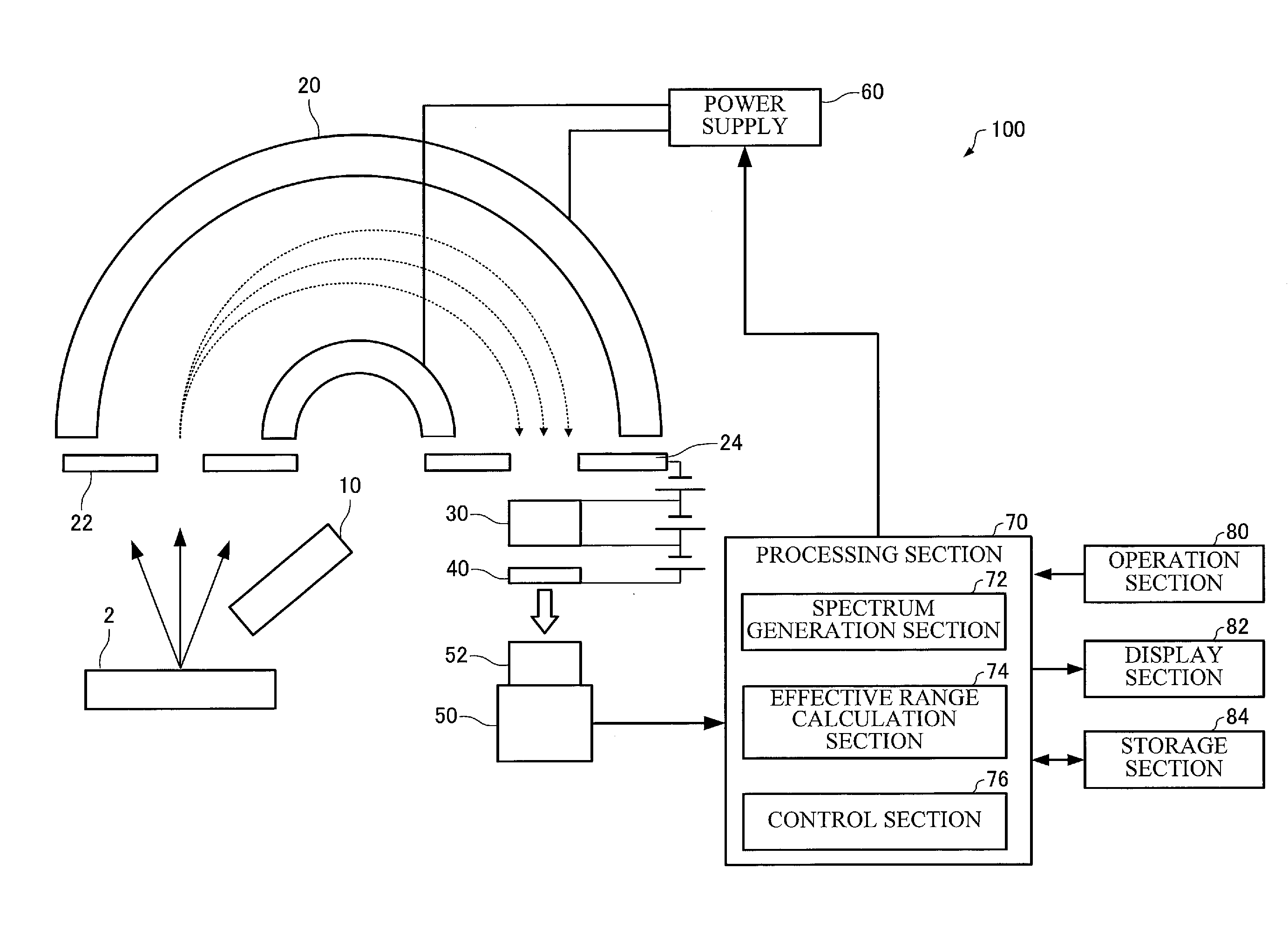
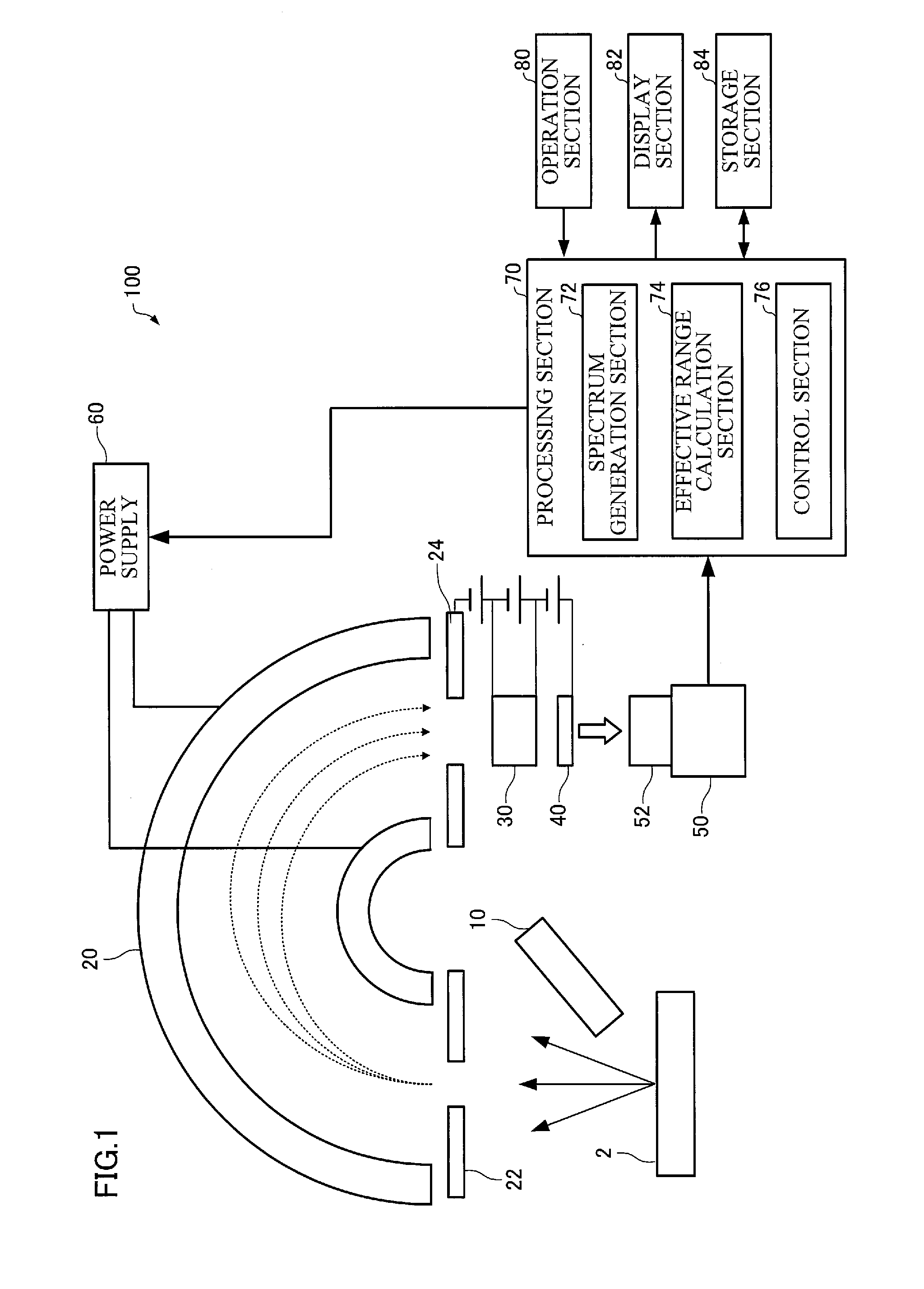
ActiveUS20160268119A1Accurately effective rangeAccurate calculationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging particle spectrometryCamera imageFluorescence
An electron spectrometer includes: an energy analyzer section that energy-analyzes electrons emitted from a specimen; a micro-channel plate that amplifies the electrons analyzed by the energy analyzer section; a fluorescent screen that converts the electrons amplified by the micro-channel plate into light; a camera that photographs the fluorescent screen; and an effective range calculation section that calculates an effective range of the fluorescent screen within a camera image photographed by the camera, the effective range calculation section performing a process that acquires a plurality of the camera images photographed while causing the energy analyzer section to analyze the electrons with a different center energy, a process that converts the plurality of camera images respectively into a plurality of spectra, and a process that calculates the effective range of the fluorescent screen within the camera image based on the plurality of spectra.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Spectroscopy and imaging system
ActiveUS20210033551A1Reduce aberrationOptimise the electron opticsSpectrometer detectorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEnergy analyserParticle physics
An apparatus and method for characterisation of a sample via spectroscopy and / or imaging. The apparatus comprises a first detector for imaging or spectroscopy, a second detector for imaging or spectroscopy, and a toroidal capacitor type electrostatic energy analyser. The toroidal capacitor type electrostatic energy analyser comprises a first and a second entrance aperture arranged such that charged particles emitted from a sample and passing through the first entrance aperture traverse a first trajectory through the toroidal capacitor type electrostatic energy analyser to be incident at the first detector, and charged particles emitted from a sample and passing through the second entrance aperture traverse a second trajectory through the toroidal capacitor type electrostatic energy analyser to be incident at the second detector. A deflection assembly arranged between the sample and the analyser may be used to direct charged particles emitted from the sample towards the first and / or second entrance aperture of the analyser.
Owner:VG SYST
Device and method for electron transfer from a sample to an energy analyzer and electron spectrometer device
ActiveUS20200303177A1Wide range of anglesReduce aberrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron/ion optical arrangementsOptical spectrometerOptical axis
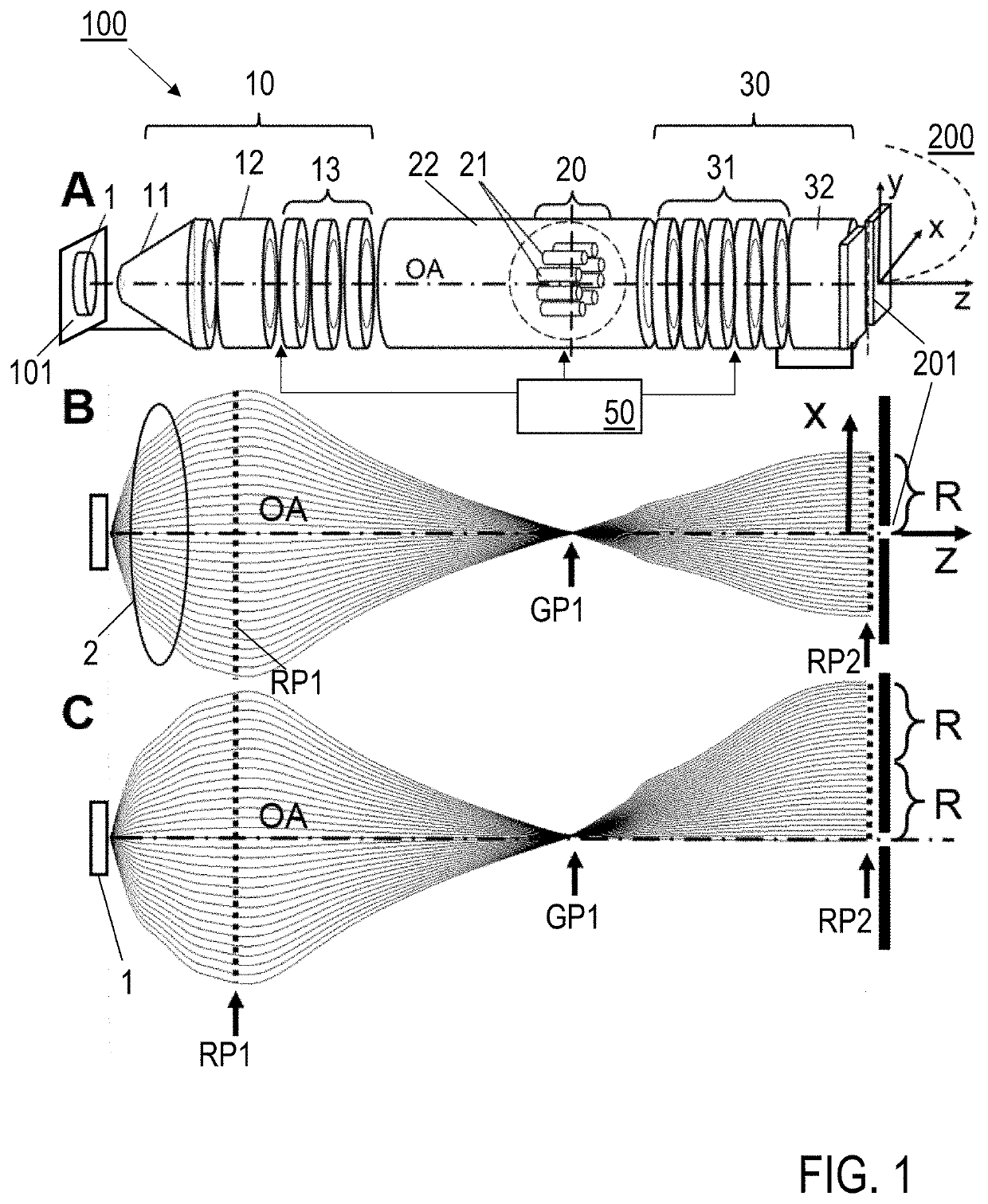
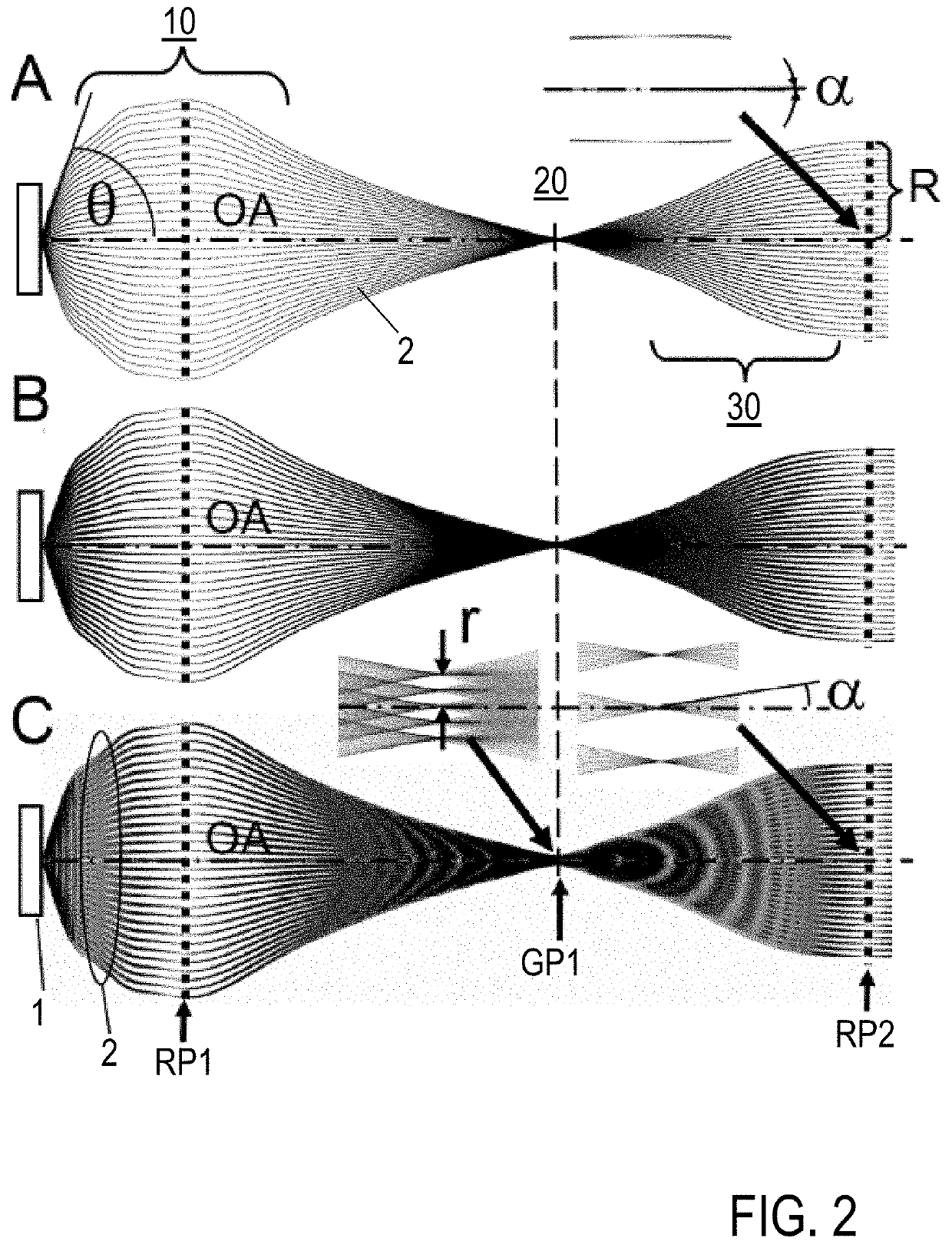
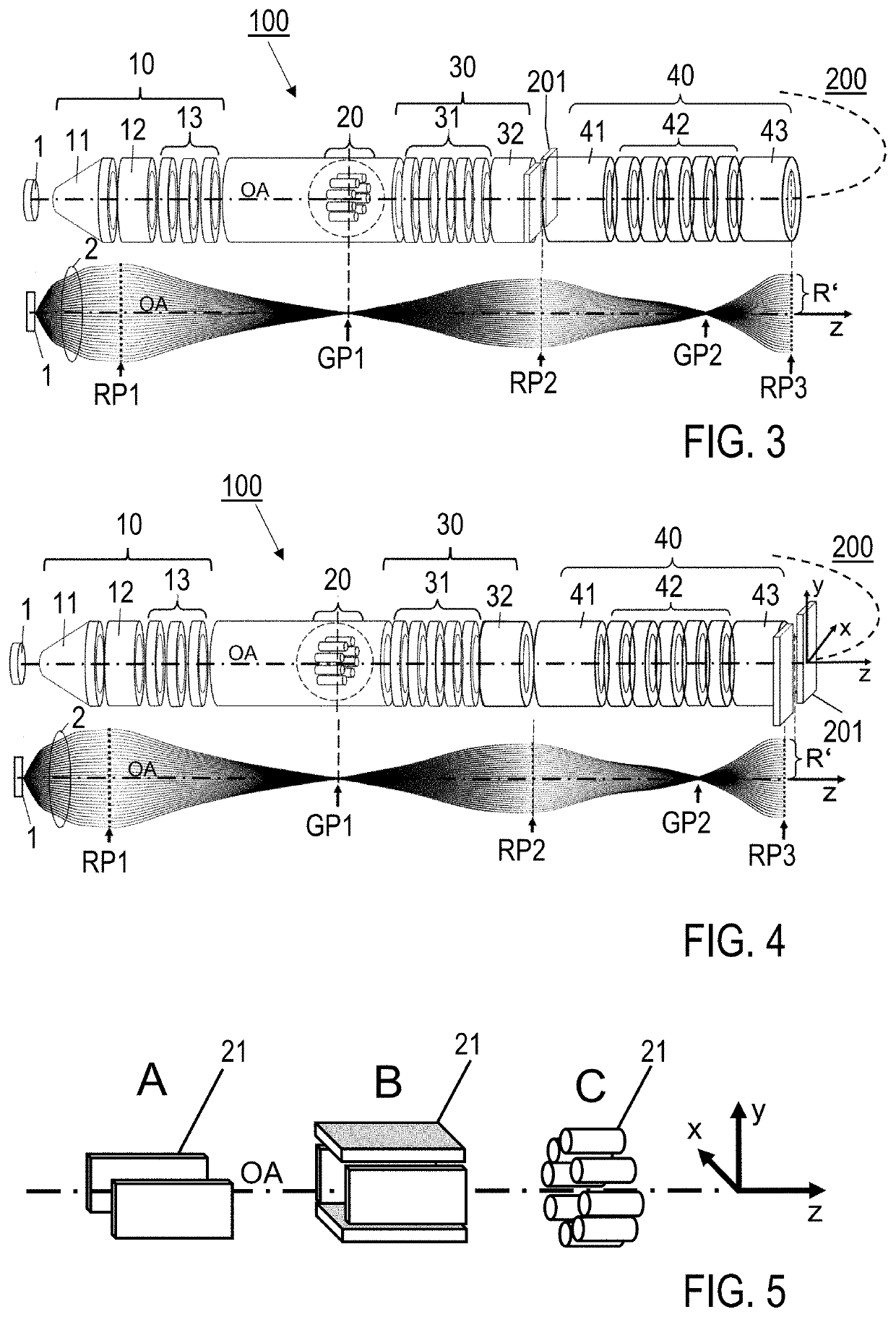
An electron imaging apparatus 100 is disclosed, which is configured for an electron transfer along an electron-optical axis OA of an electron 2 emitting sample 1 to an energy analyzer apparatus 200, and comprises a sample-side first lens group 10, an analyzer-side second lens group 30 and a deflector device 20, configured to deflect the electrons 2 in an exit plane of the electron imaging apparatus 100 in a deflection direction perpendicular to the electron-optical axis OA. An electron spectrometer apparatus, an electron transfer method and an electron spectrometry method are also described.
Owner:SPECS SURFACE NANO ANALYSIS
Accelerator mass spectrometry device for simultaneously measuring isotopes
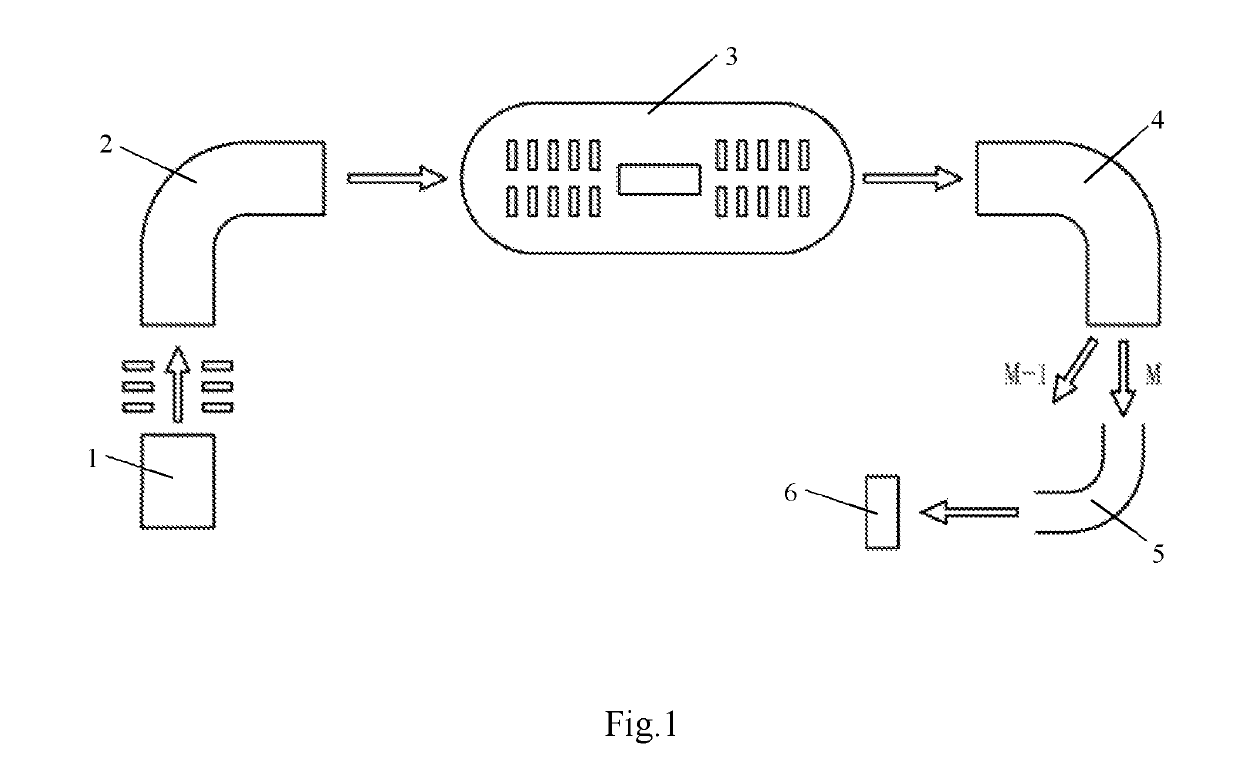
ActiveUS10395910B2Promote popularizationSimple structureIon sources/gunsStatic spectrometersMass analyzerAccelerator mass spectrometry
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com