Patents
Literature
227results about How to "Improved energy resolution" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
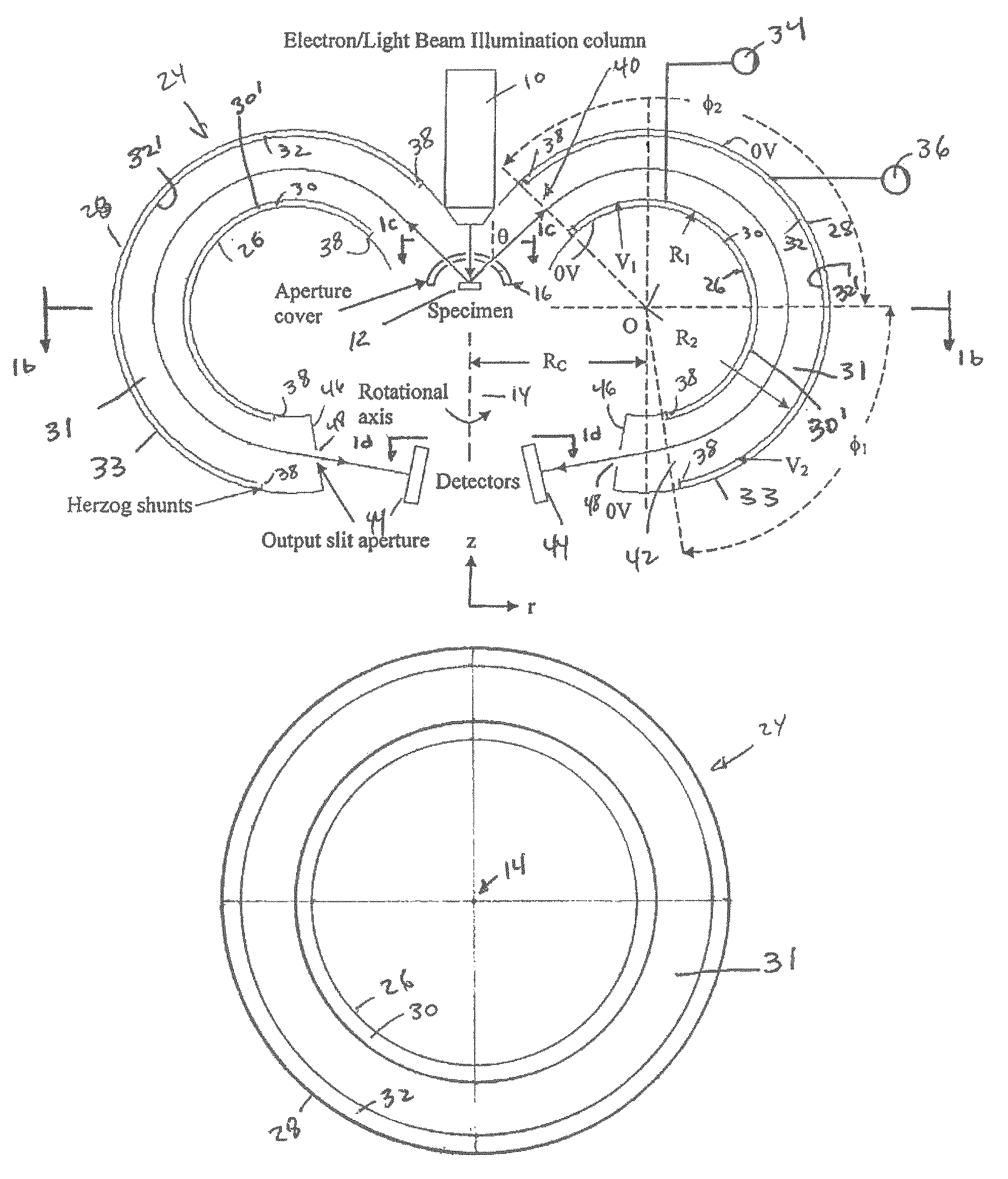
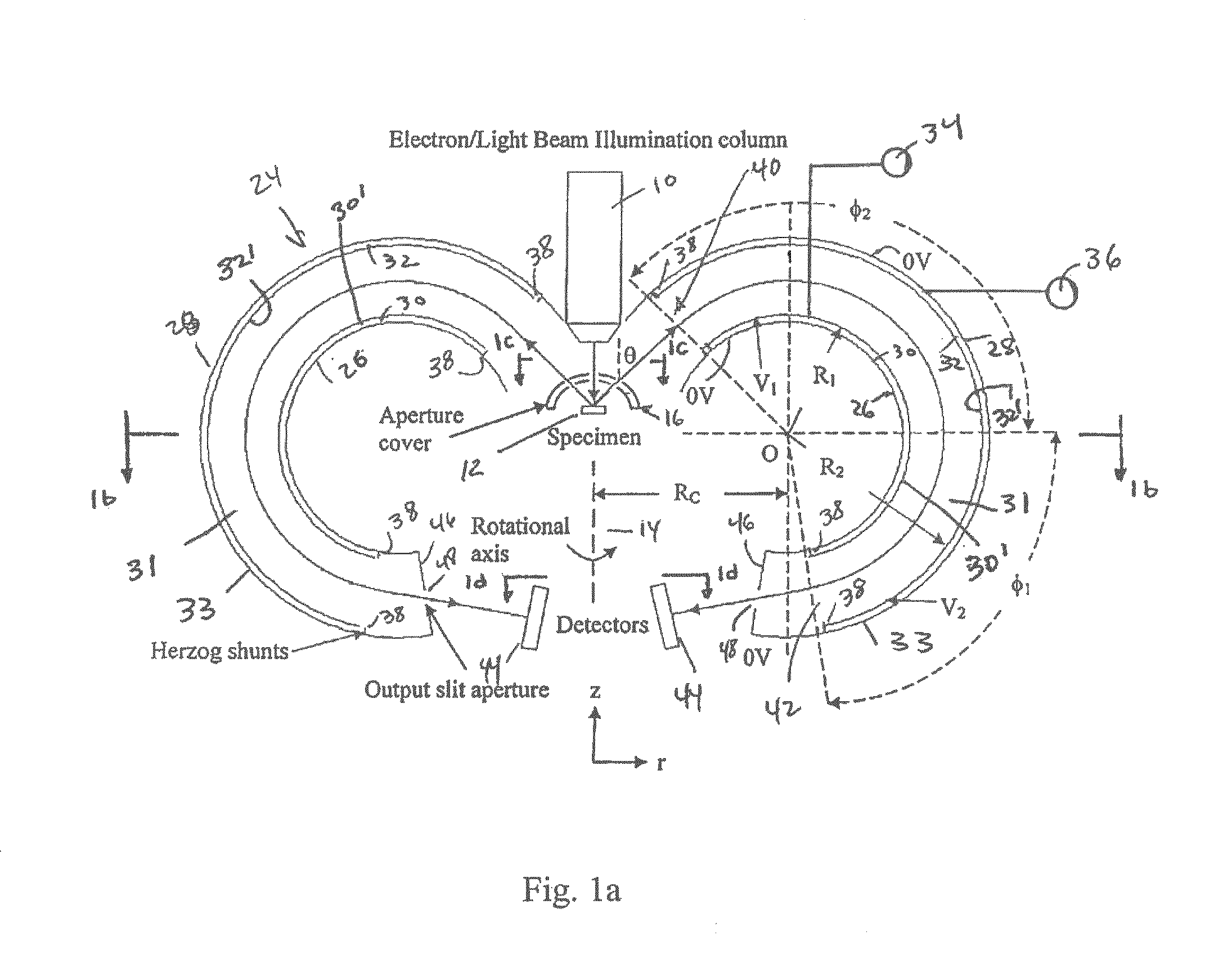
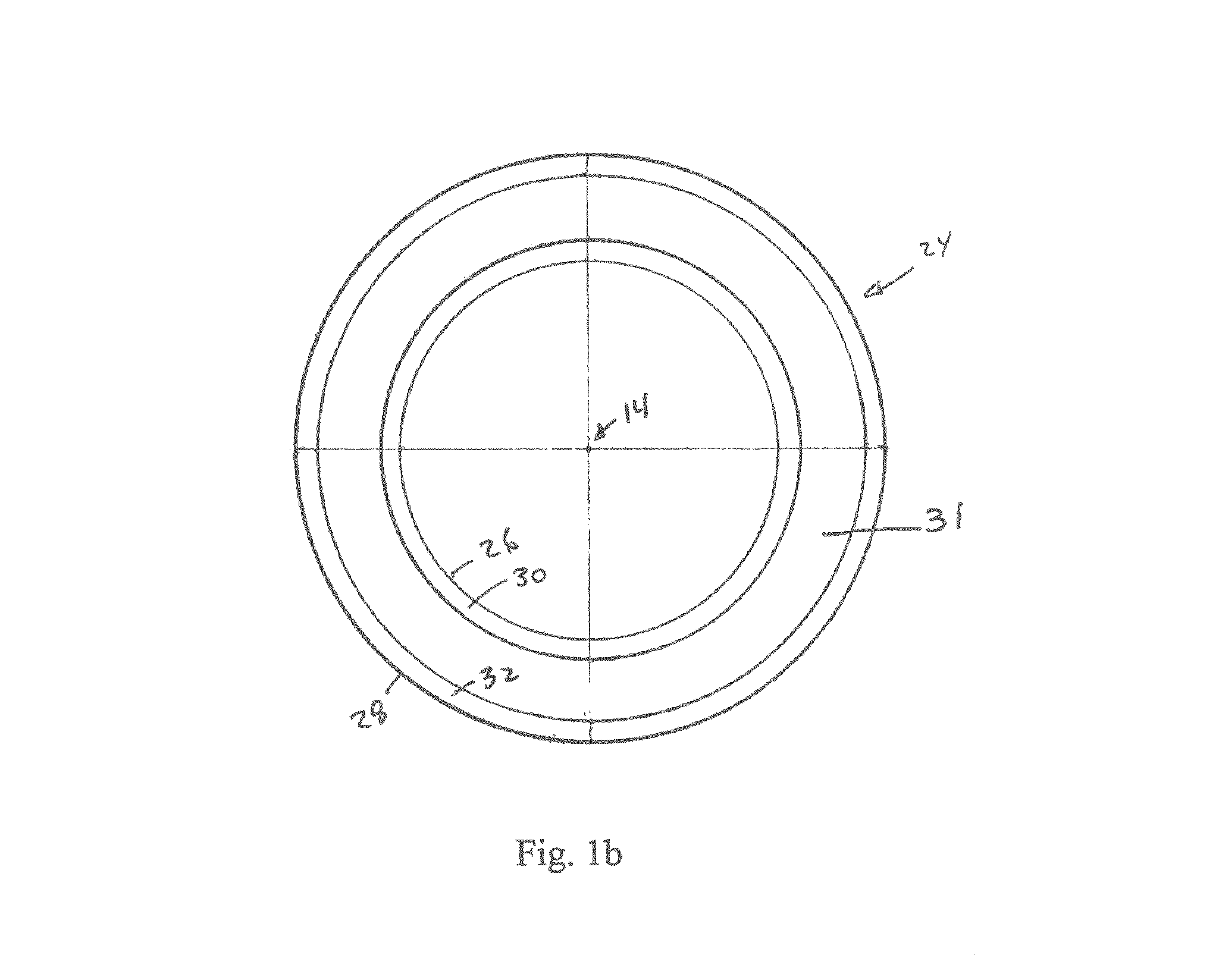
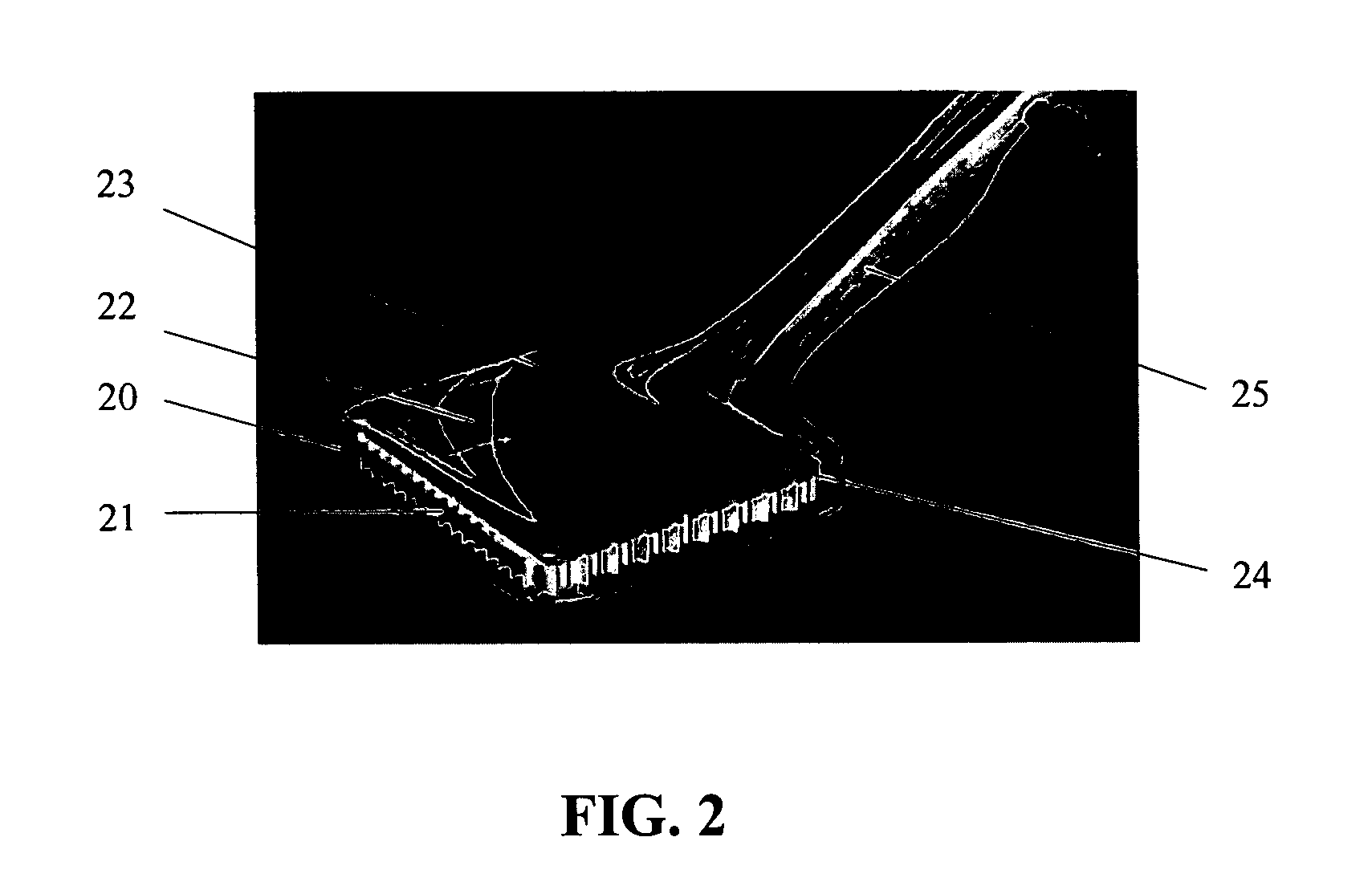
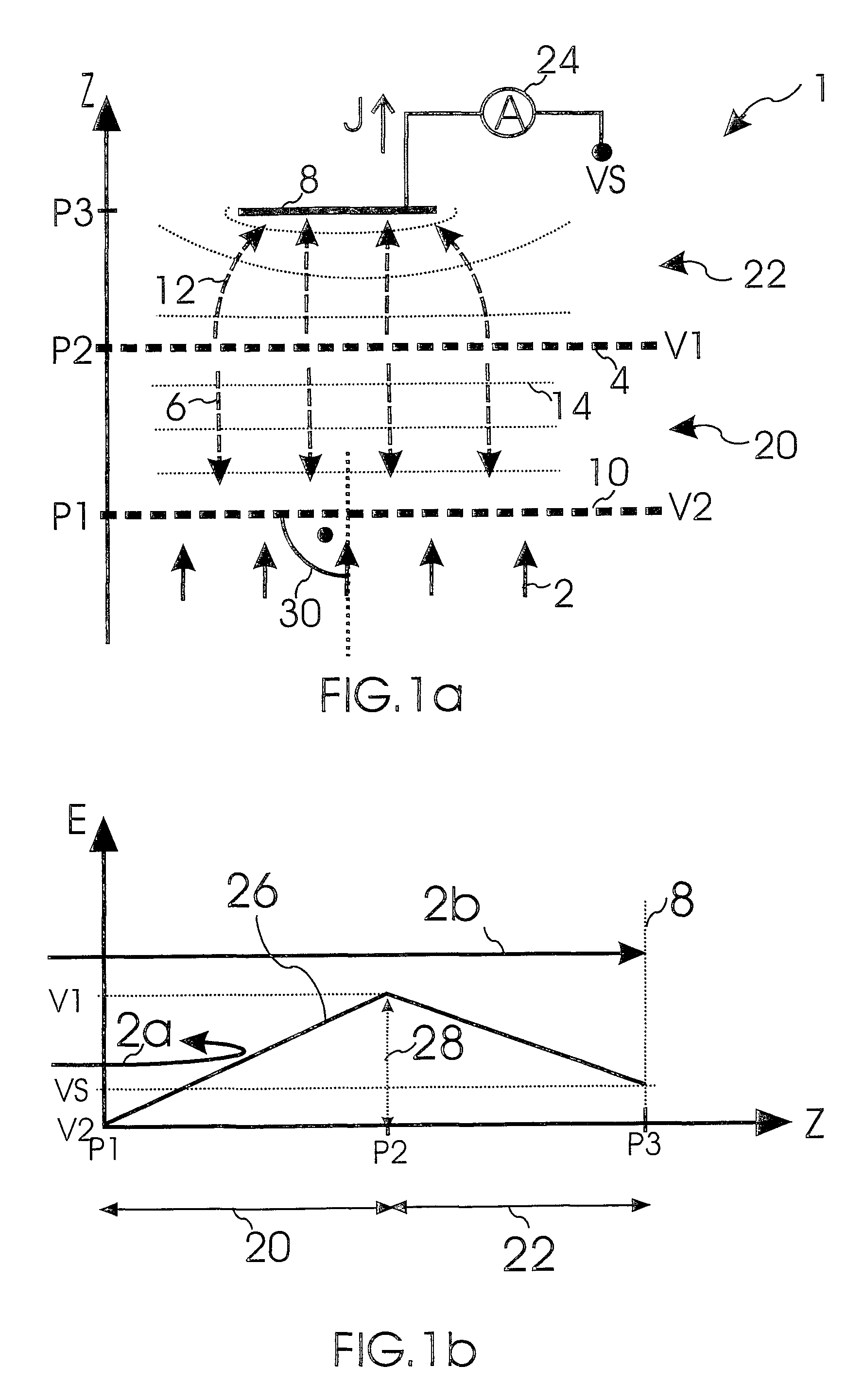
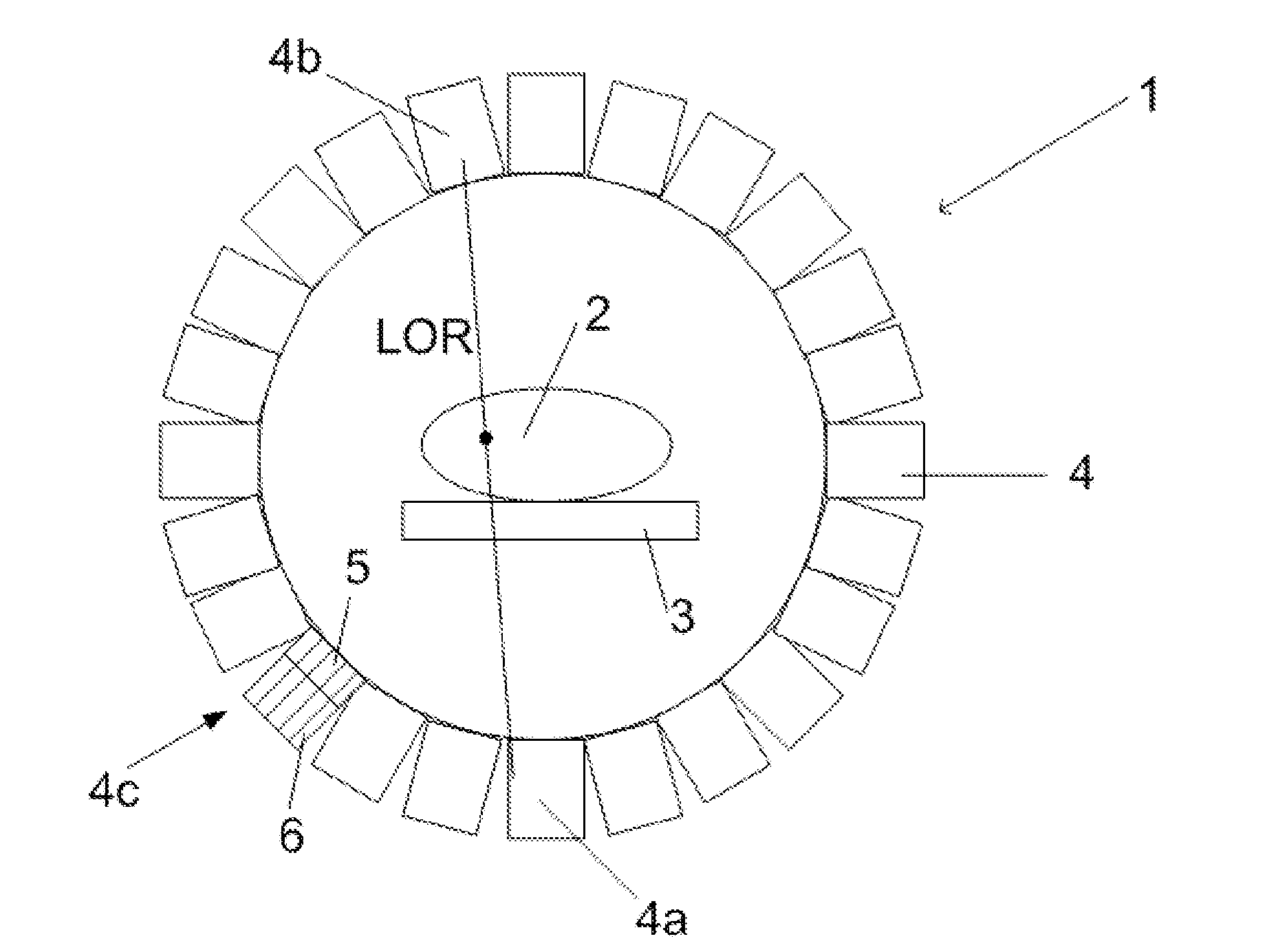
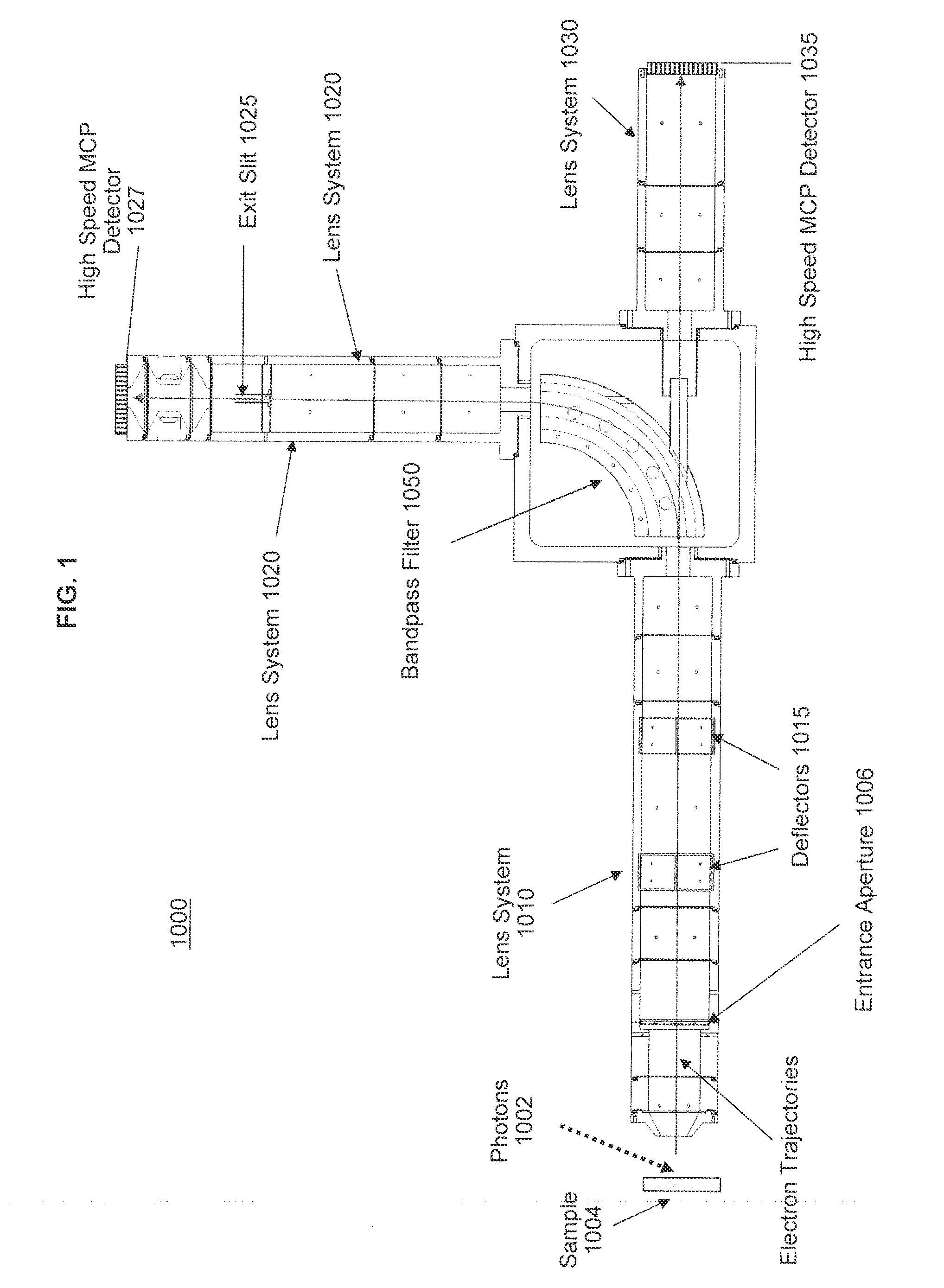
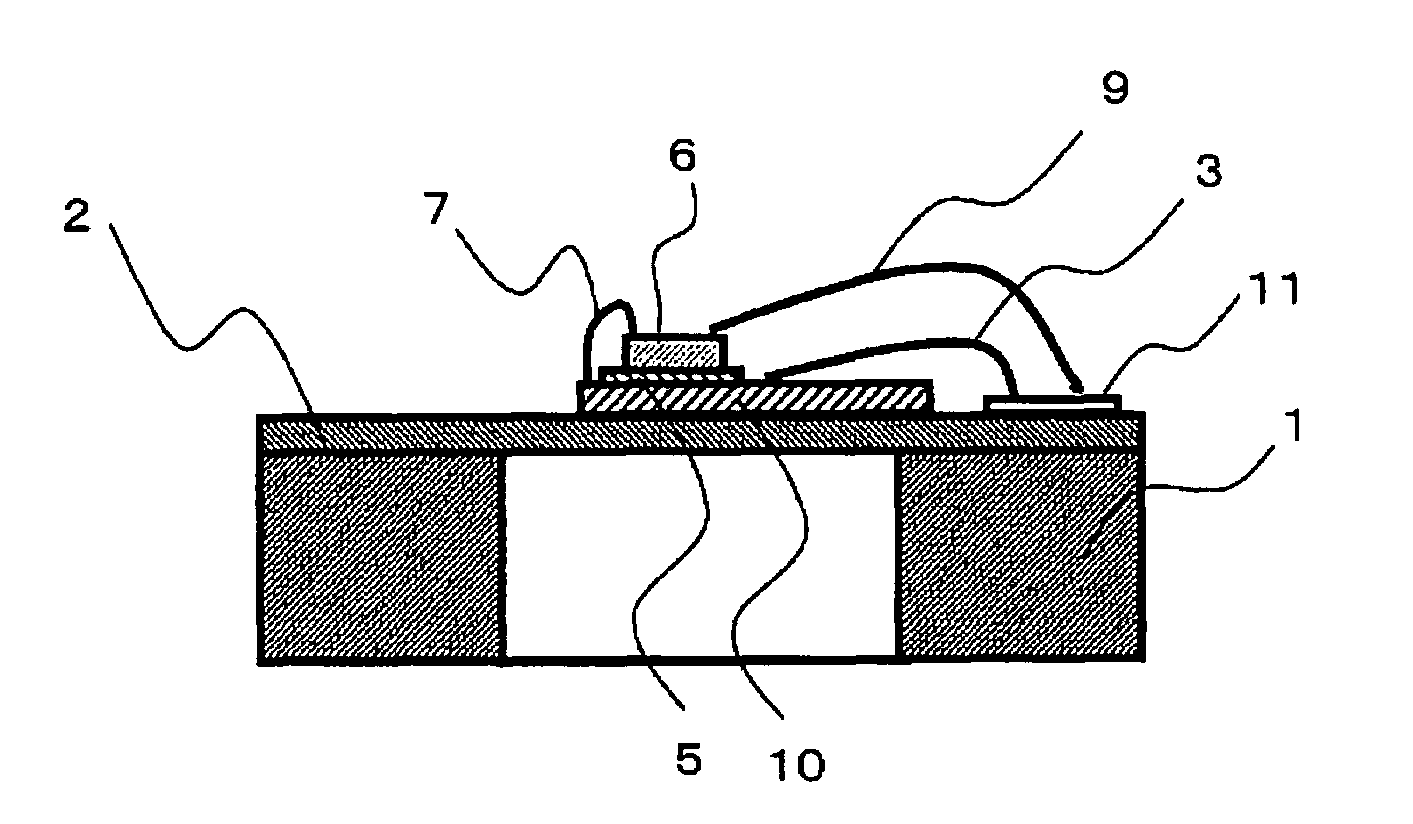
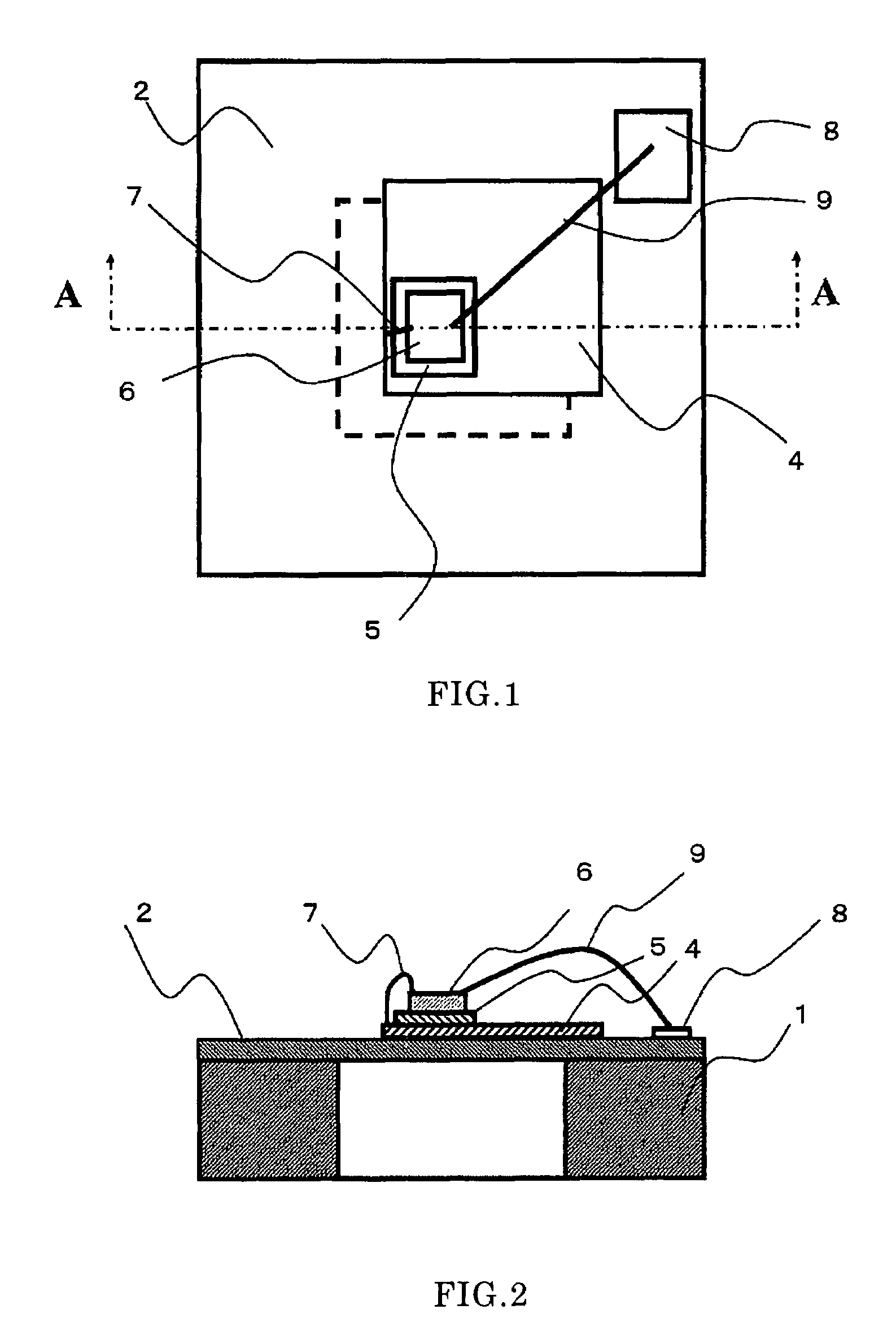
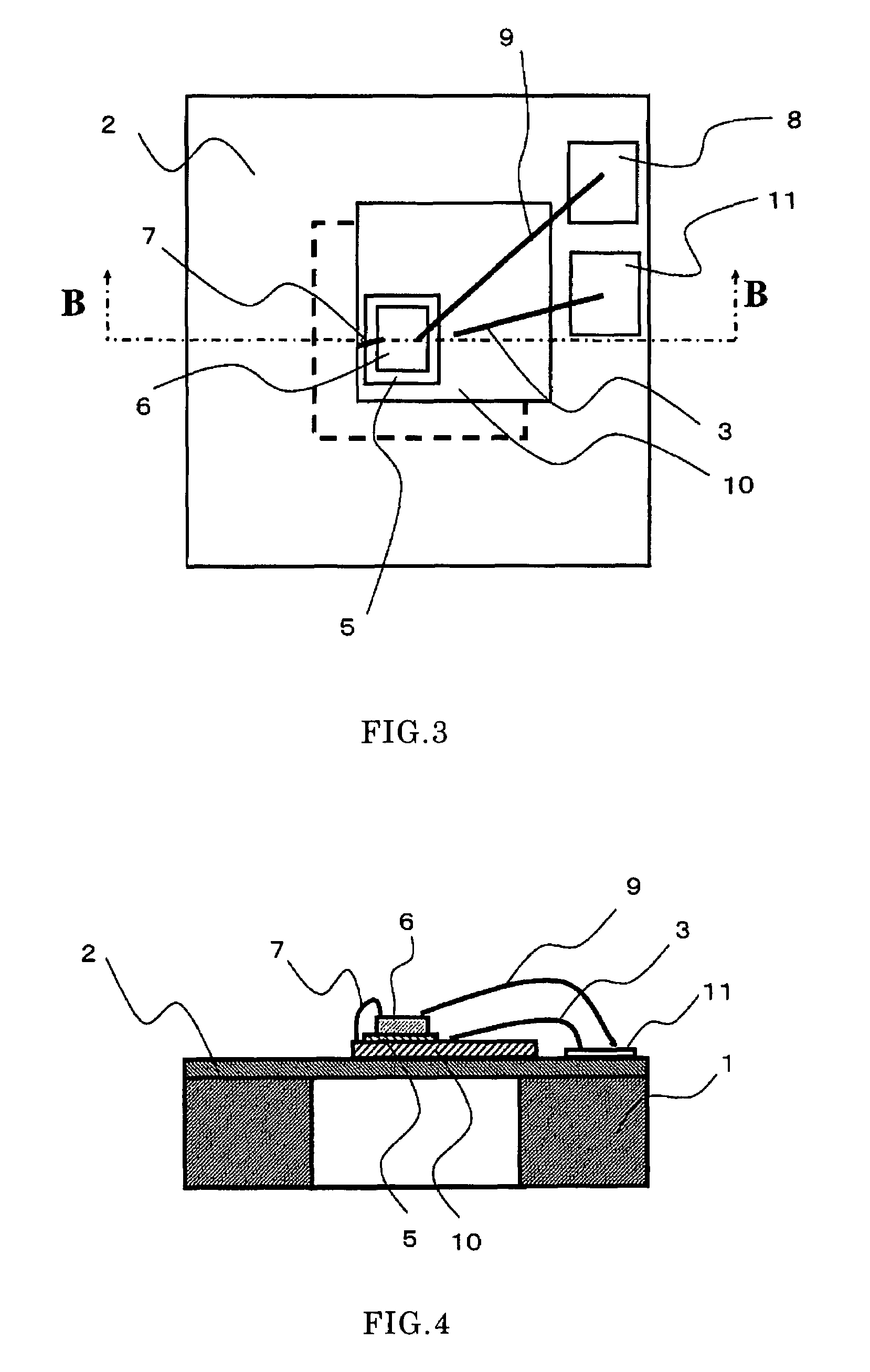
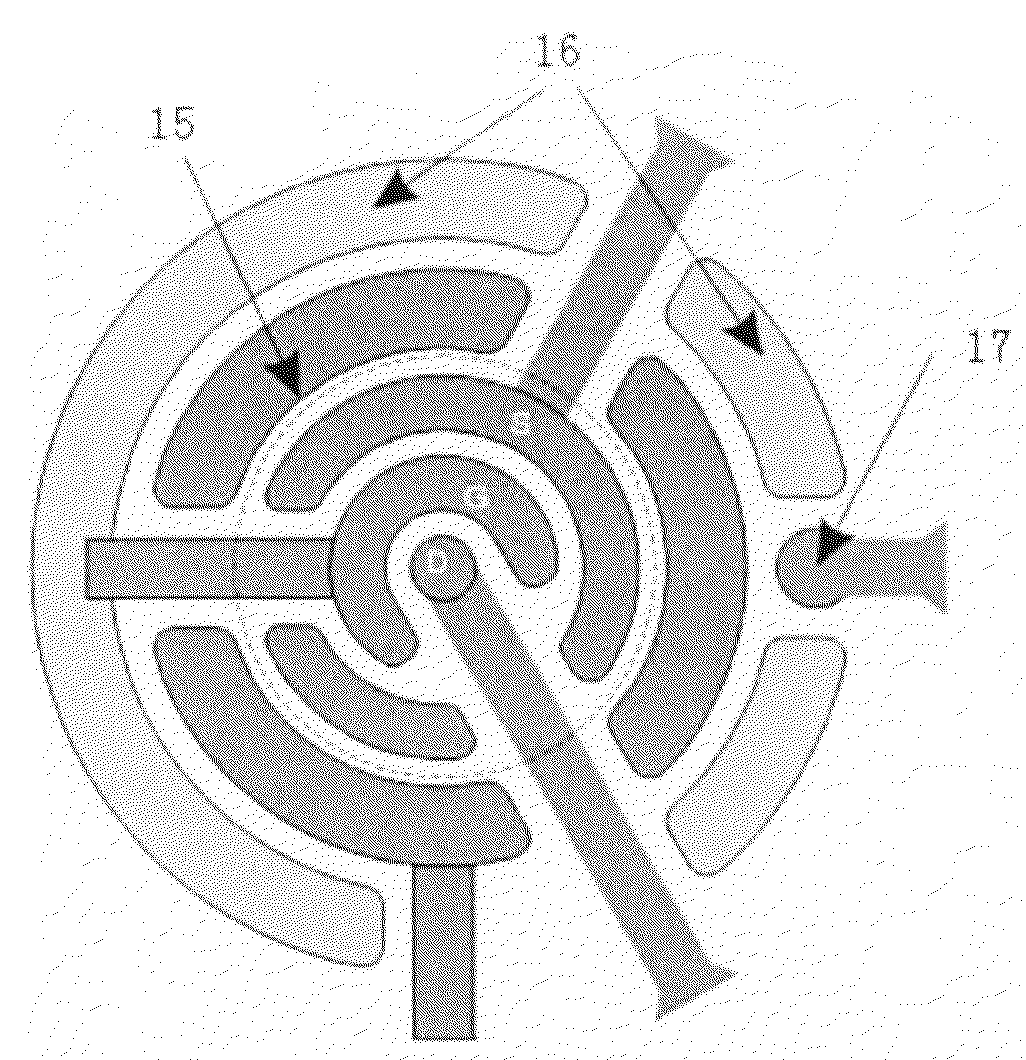
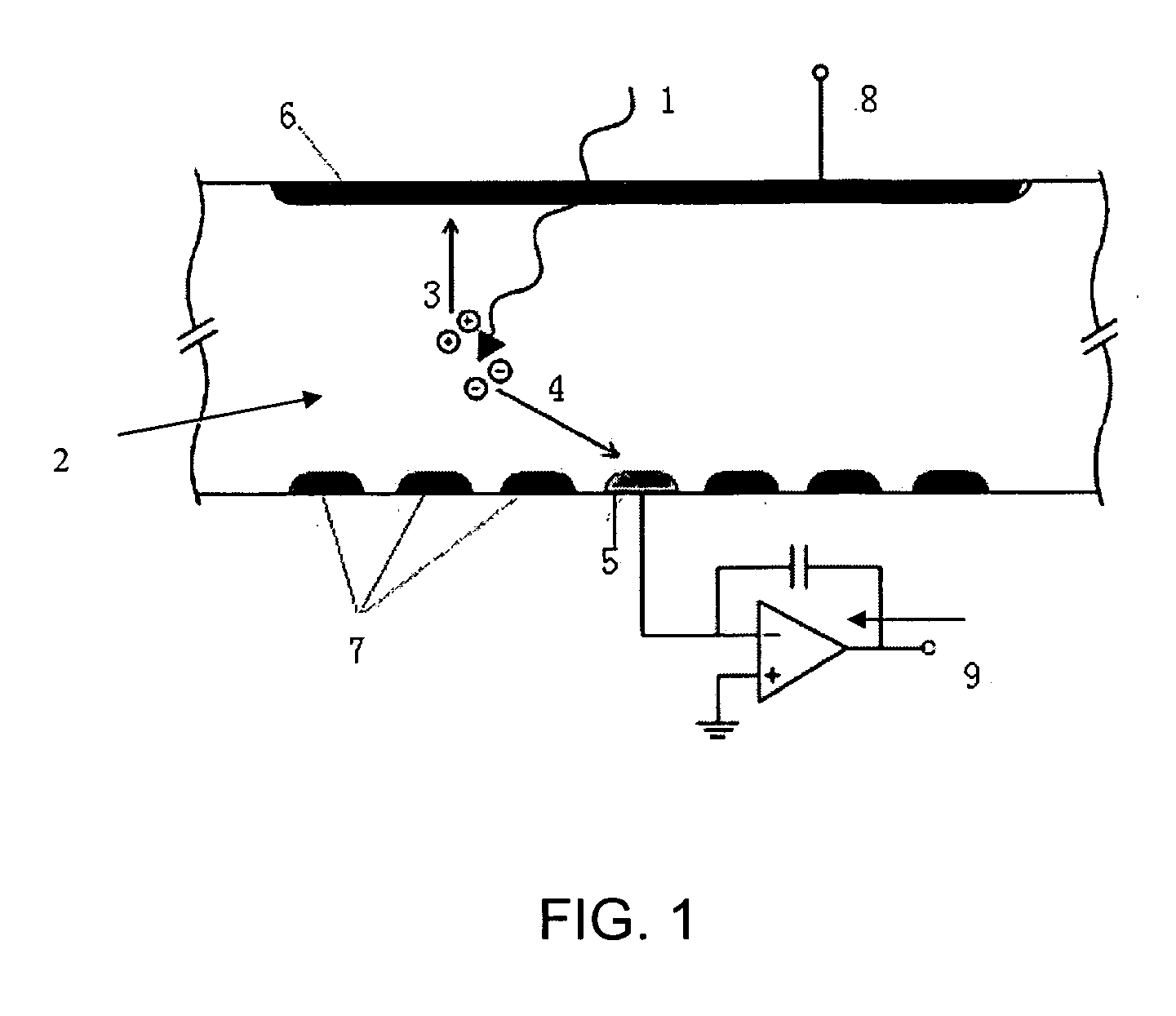
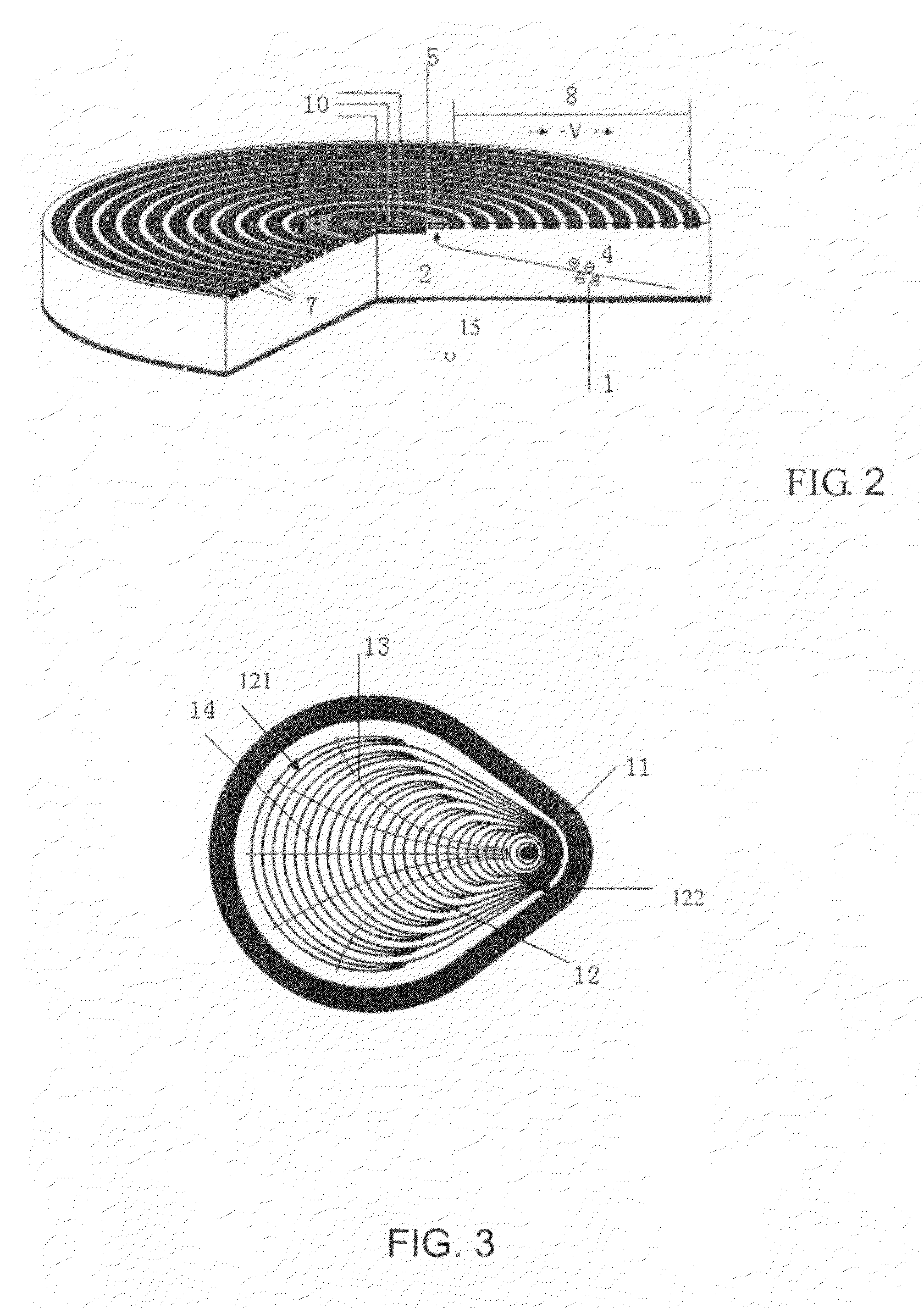
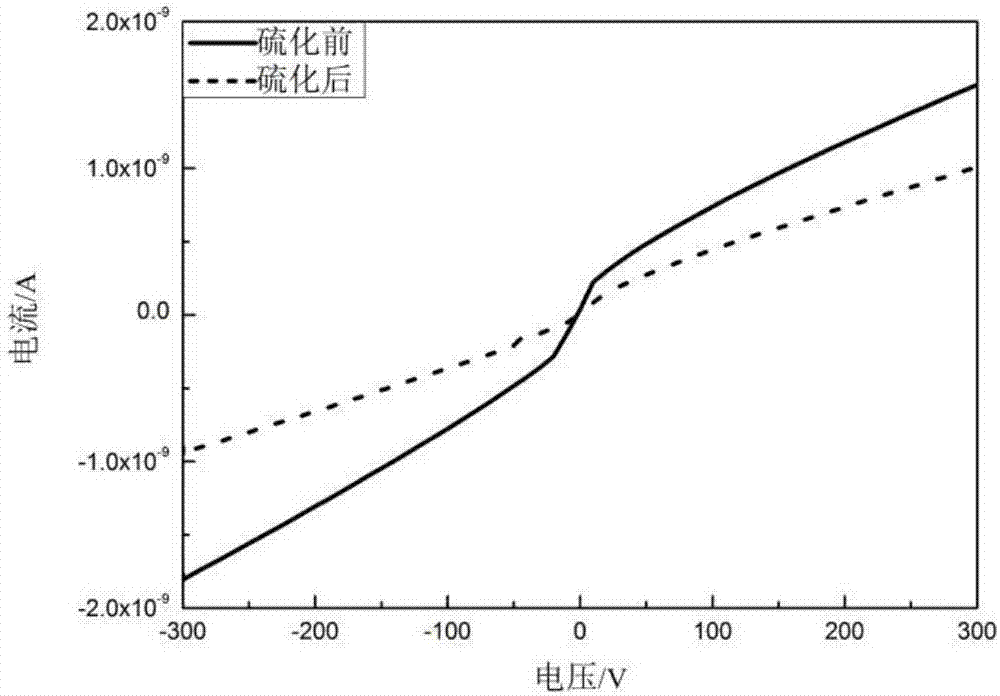
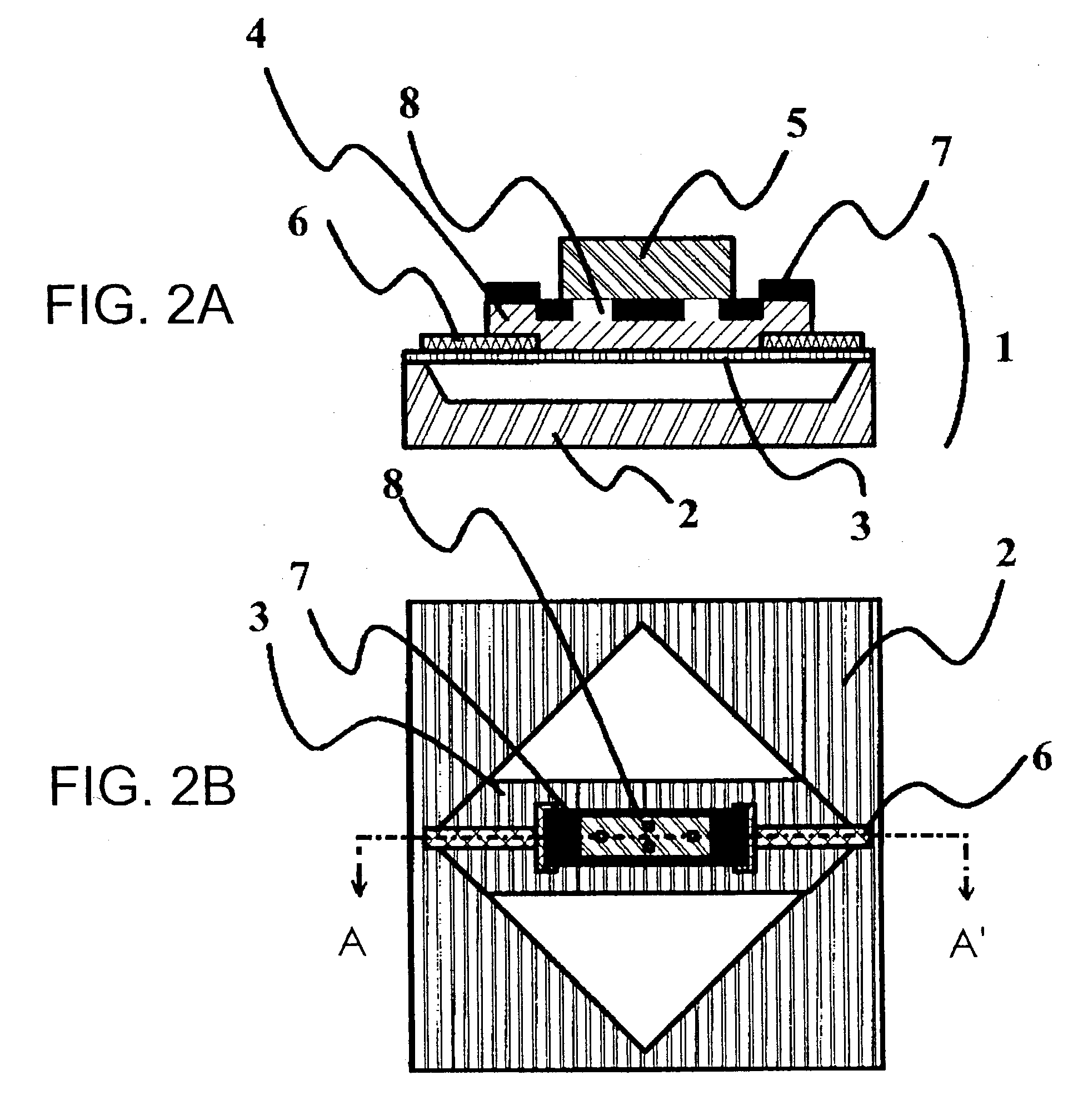
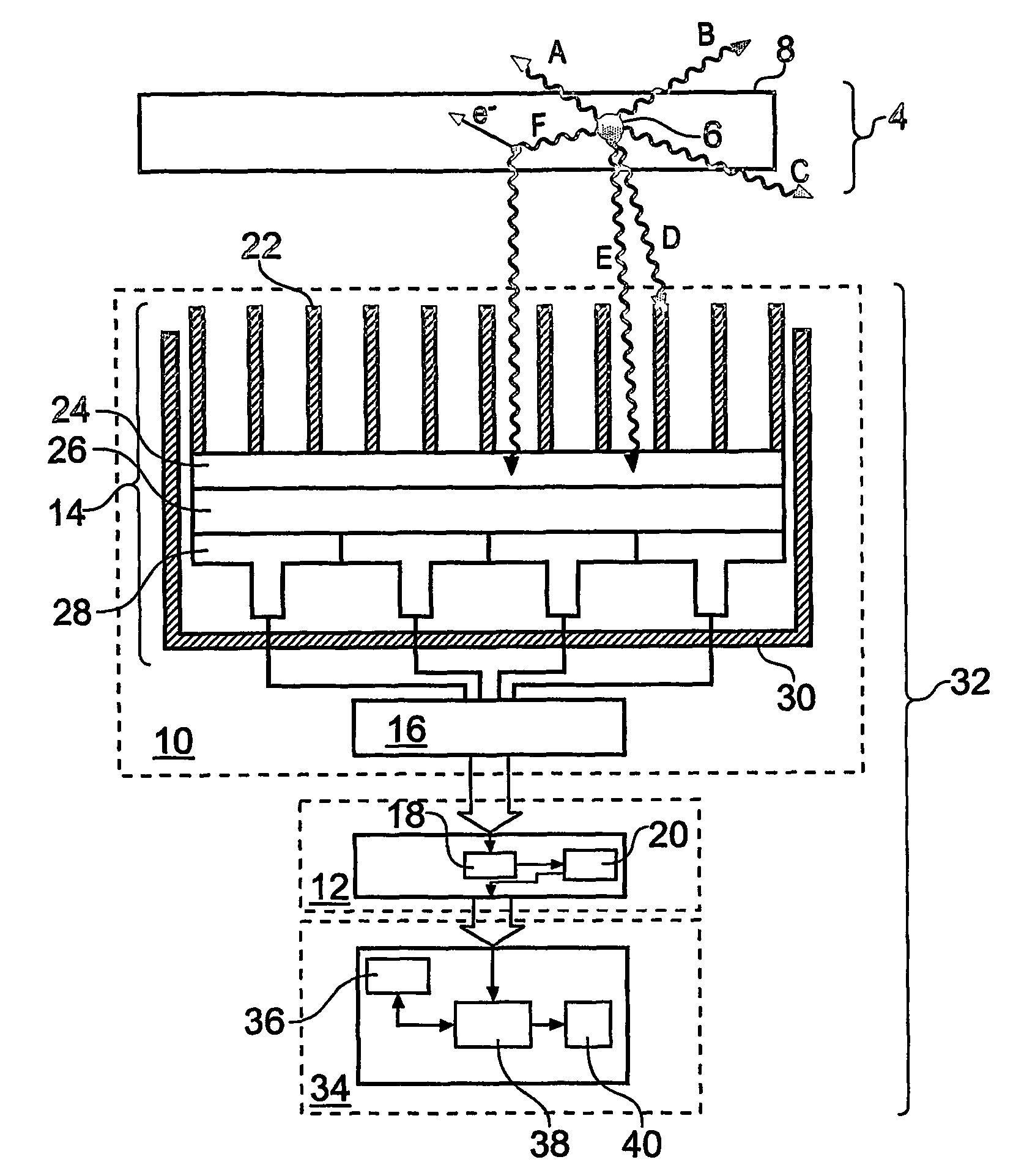
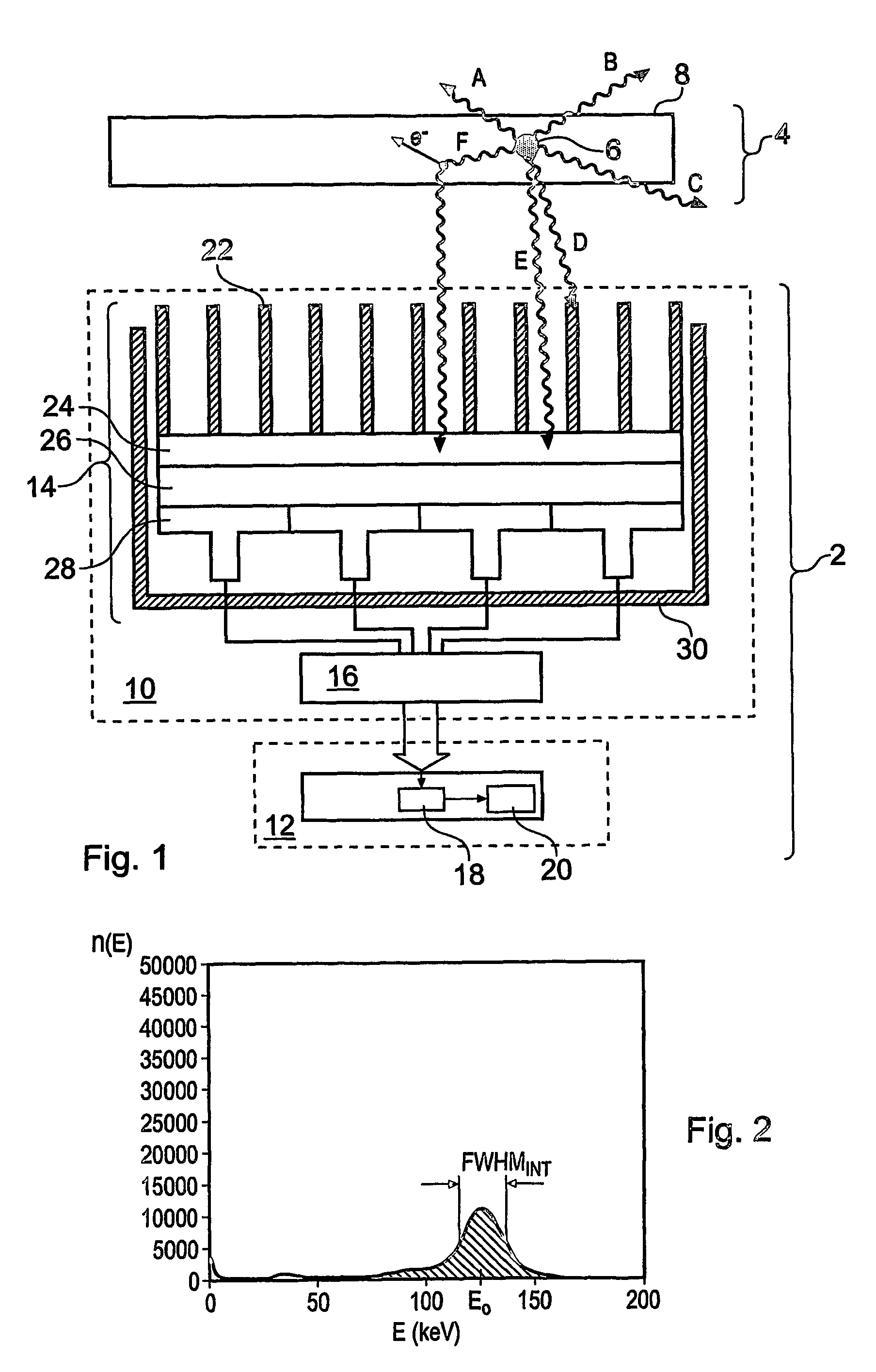
Electrostatic electron spectrometry apparatus
ActiveUS8013298B2Improved energy resolutionHigh simulationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesSpectrometerElectron
An apparatus for spectrometry that includes a spectrometer configured for second order focusing and capable of 2π azimuthal collection.
Owner:NAT UNIV OF SINGAPORE
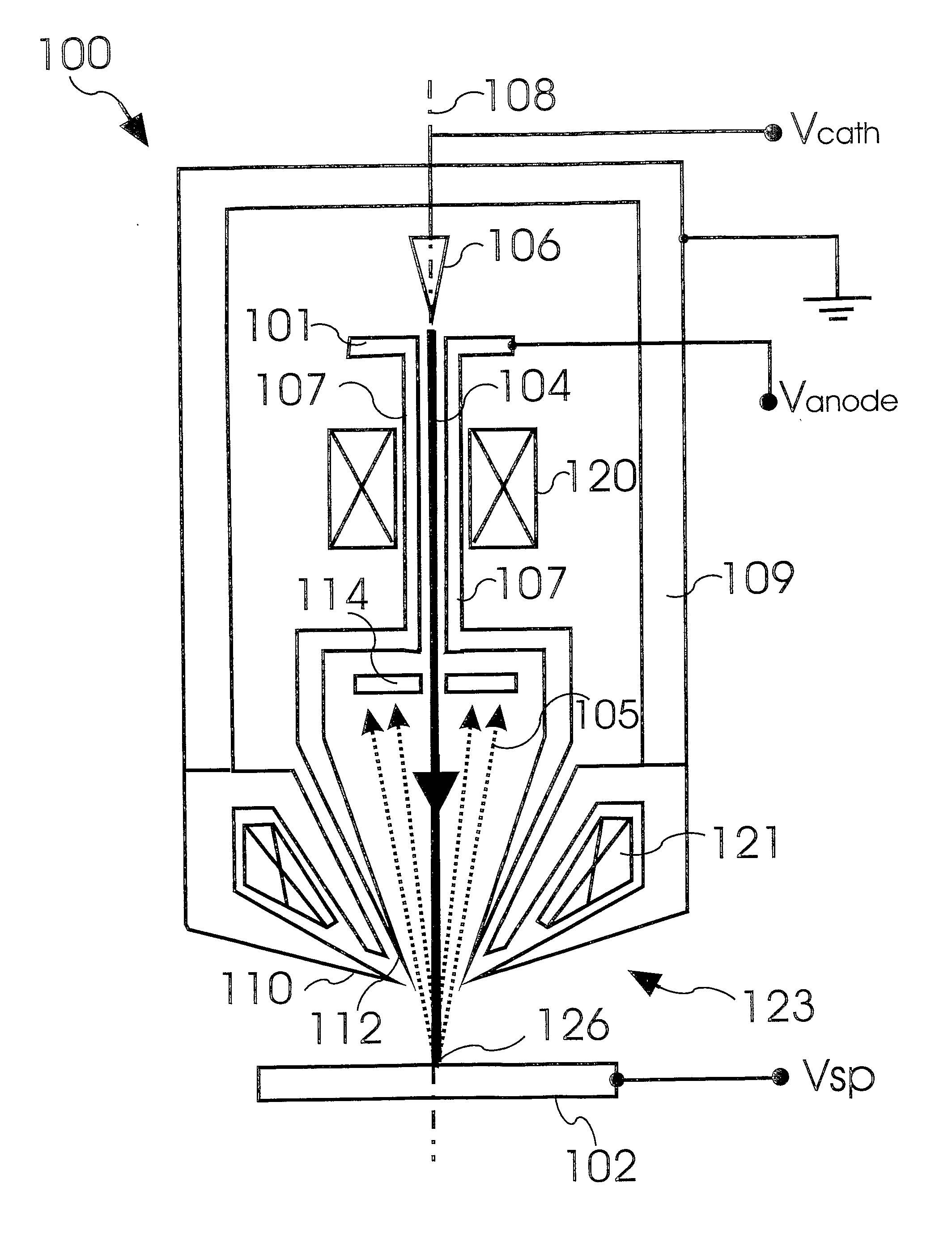
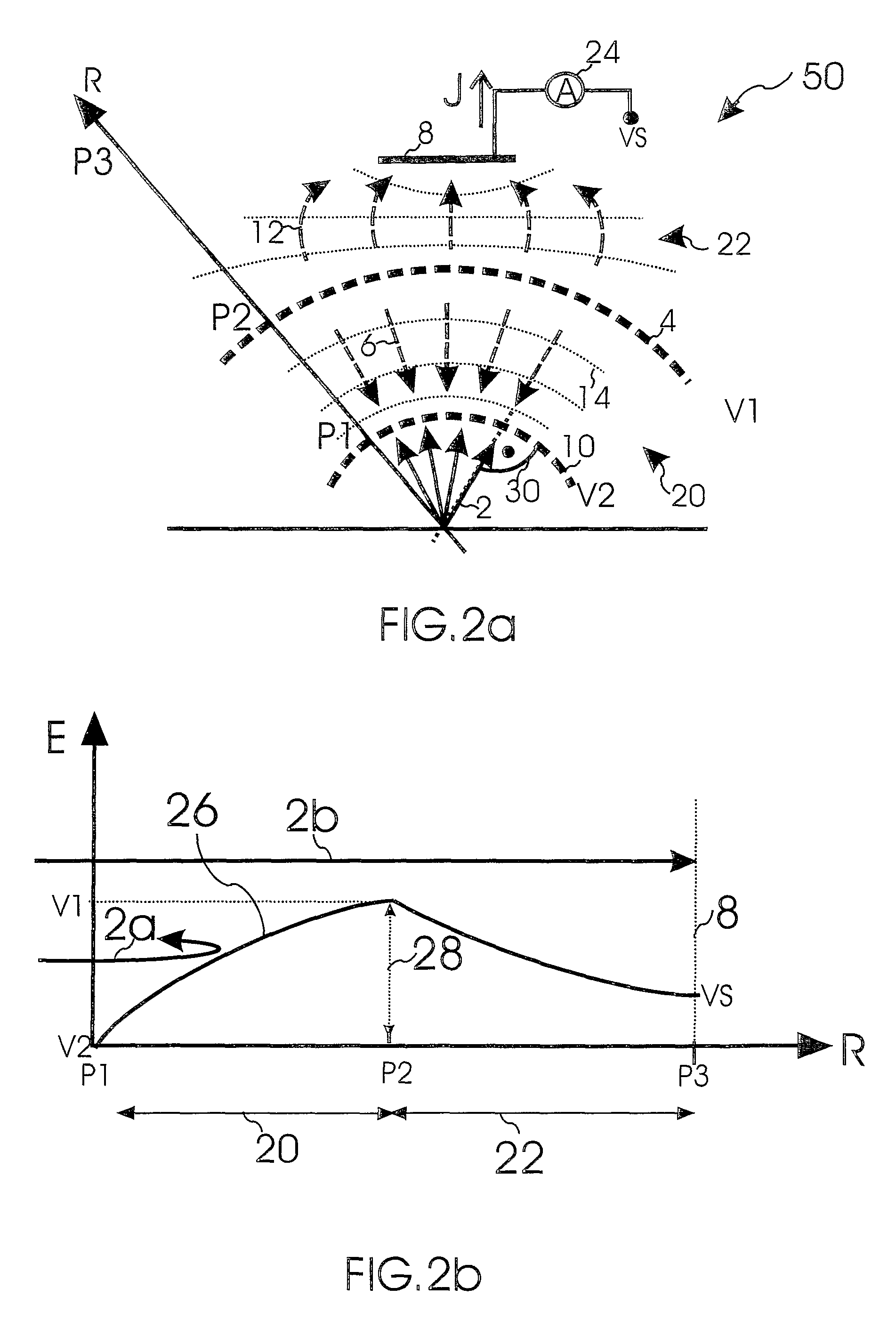
Charged Particle Beam Device With Retarding Field Analyzer
ActiveUS20090200463A1Improve spatial resolutionSmall sizeMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationParticle separator tubesOptical axisImage resolution
The invention provides a charged particle beam device to inspect or structure a specimen with a primary charged particle beam propagating along an optical axis; a beam tube element having a tube voltage; and a retarding field analyzer in the vicinity of the beam tube element to detect secondary charged particles generated by the primary charged particle beam on the specimen. According to the invention, the retarding field analyzer thereby comprises an entrance grid electrode at a second voltage; at least one filter grid electrode at a first voltage; a charged particle detector to detect the secondary charged particles; and at least one further electrode element arranged between the entrance grid electrode and the at least one filter grid electrode. The at least one further electrode element reduces the size of the stray fields regions in the retarding electric field region to improve the energy resolution of the retarding field analyzer. The improvement of the energy resolution is significant, in particular when the beam tube element is part of a high voltage beam tube.
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
Pixelated photon detector
InactiveUS7009183B2Little effectGuaranteed effective sizeSolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical conductorPrinted circuit board
A gamma camera comprising:a plurality of pixelated detectors wherein each pixelated detector provides a detector signal responsive to photons that are incident on it;a plurality of processing circuits that receive said detector signals and provide processed signals responsive to said detector signals; andat least one printed circuit board on which said processing circuits are mounted and having conductors thereon that carry said detector signals to said processing circuits;wherein said processing circuits are mounted on said printed circuit board at locations remote from said detectors; andwherein said plurality of pixelated detectors form a two-dimensional planar array.
Owner:ELGEMS
Method and apparatus for improving PET detectors
ActiveUS7132664B1Highly programmable computing capabilityHighly accurate spatial resolution informationMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyWhole bodyParallel computing
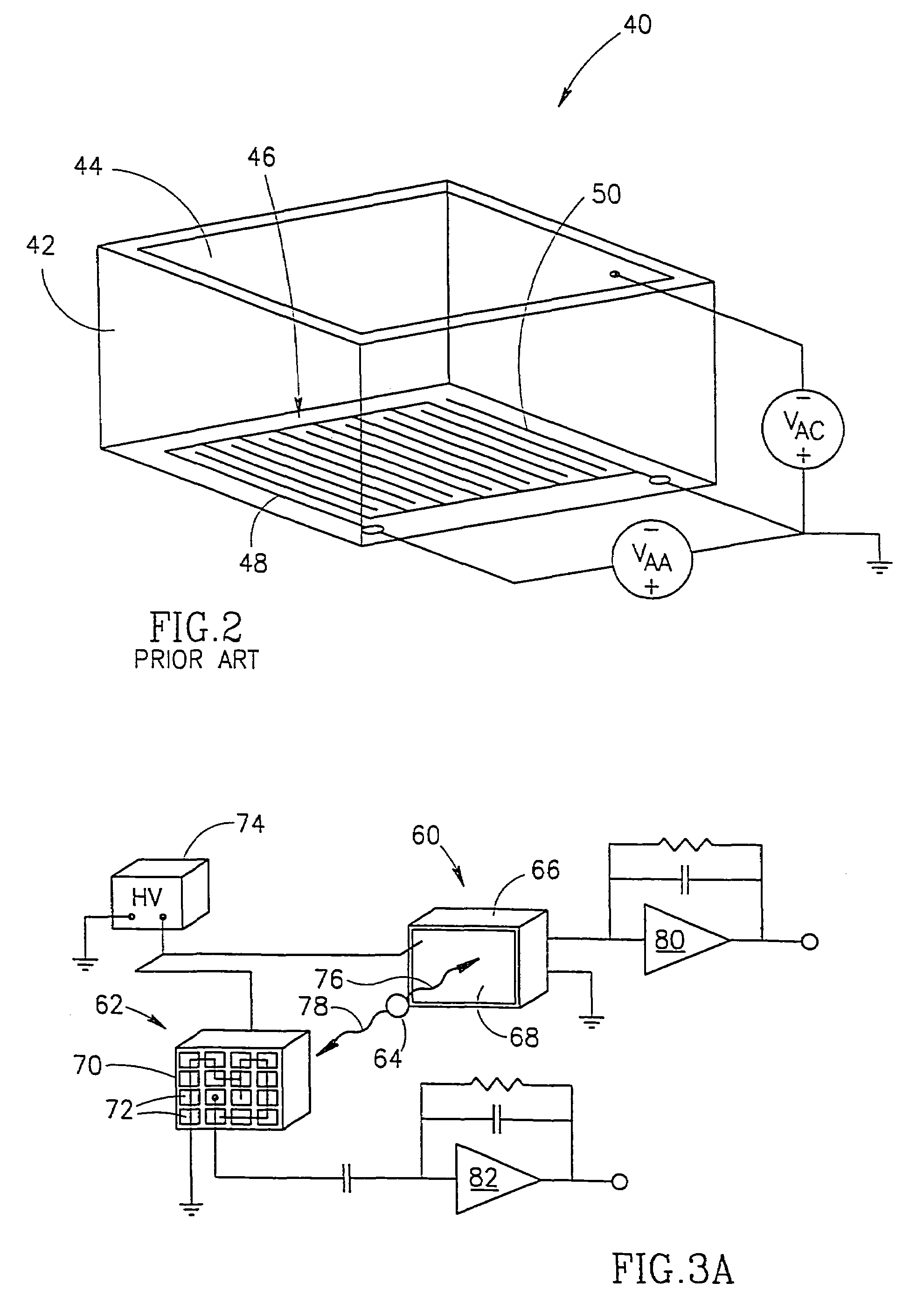
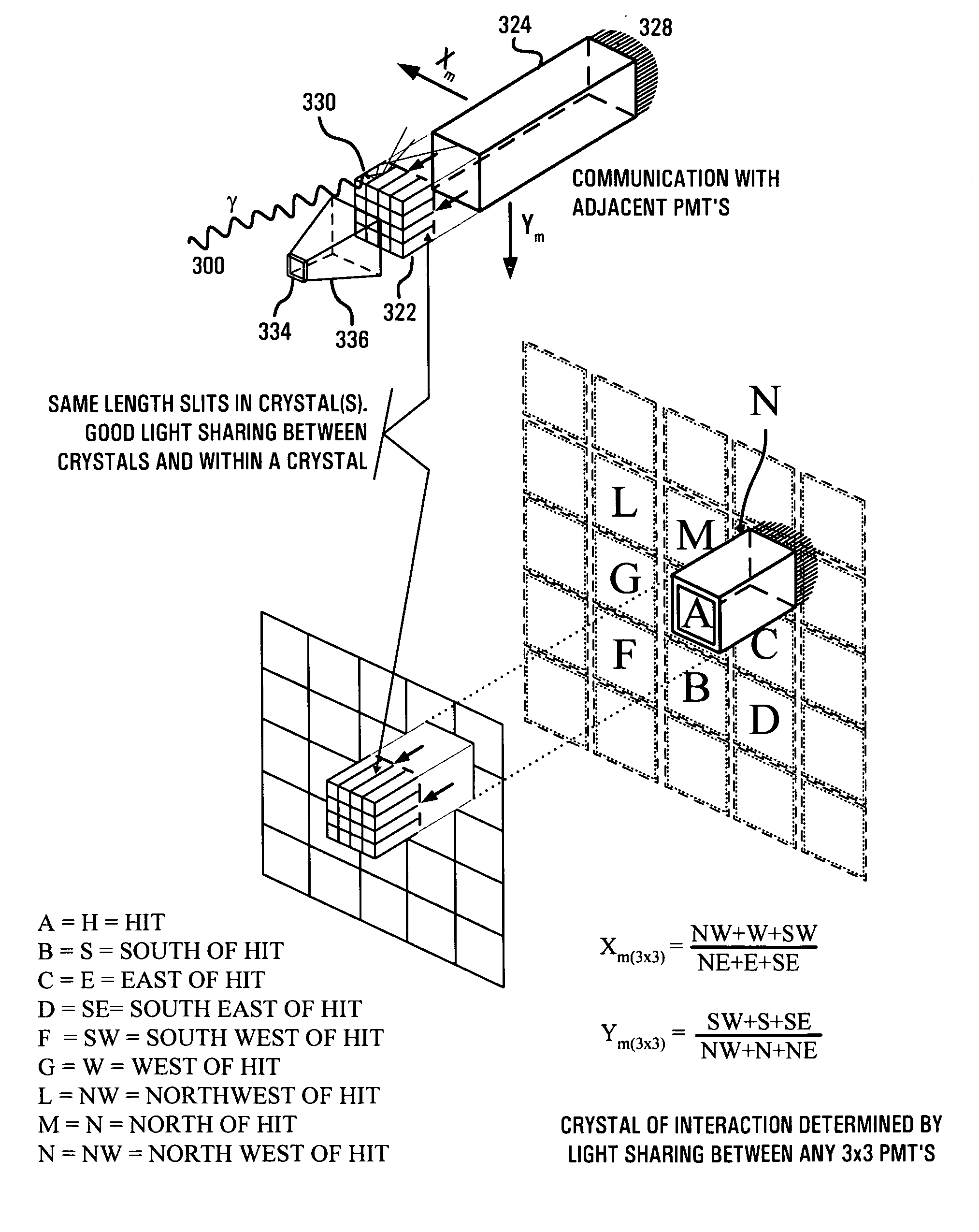
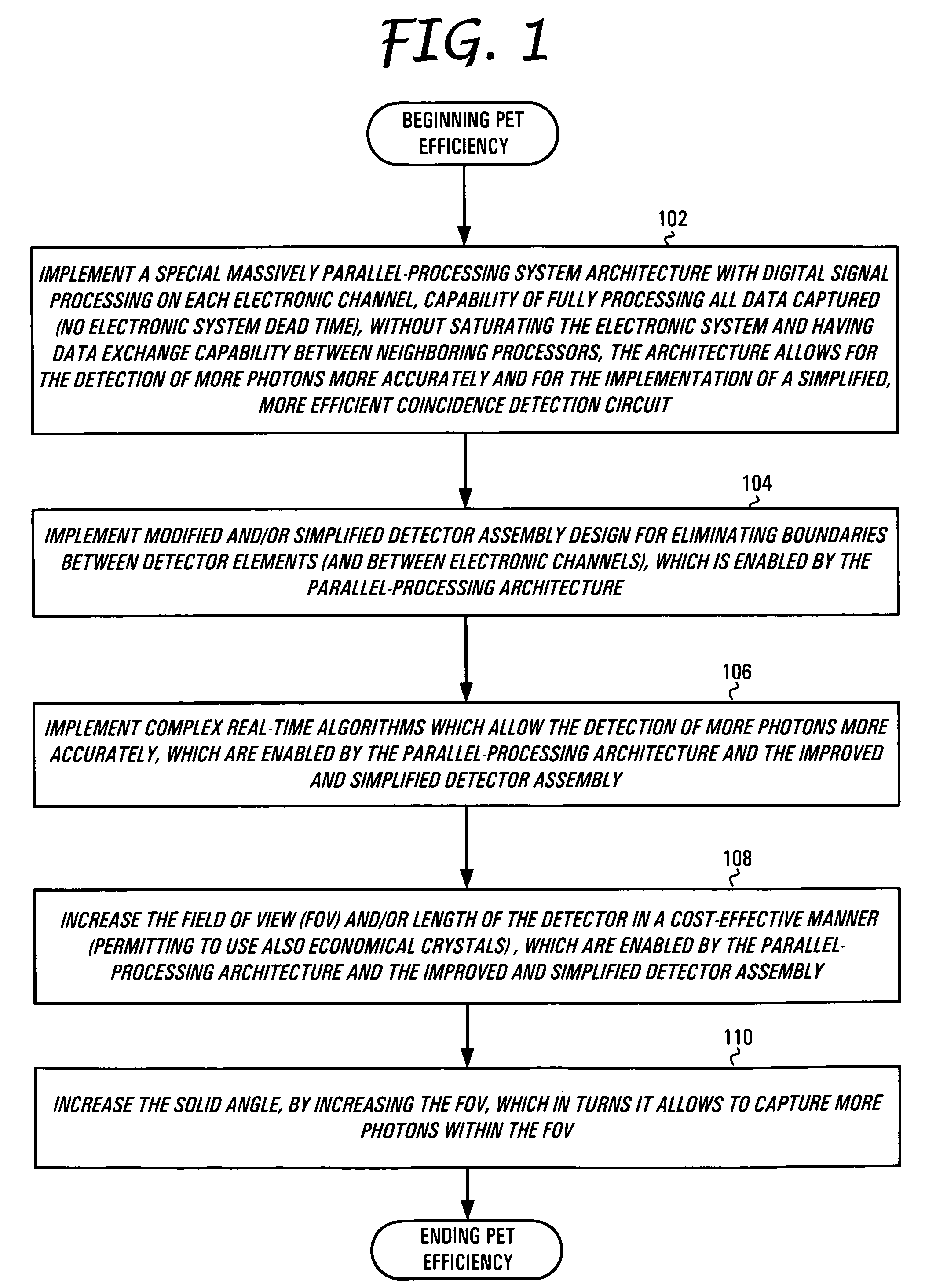
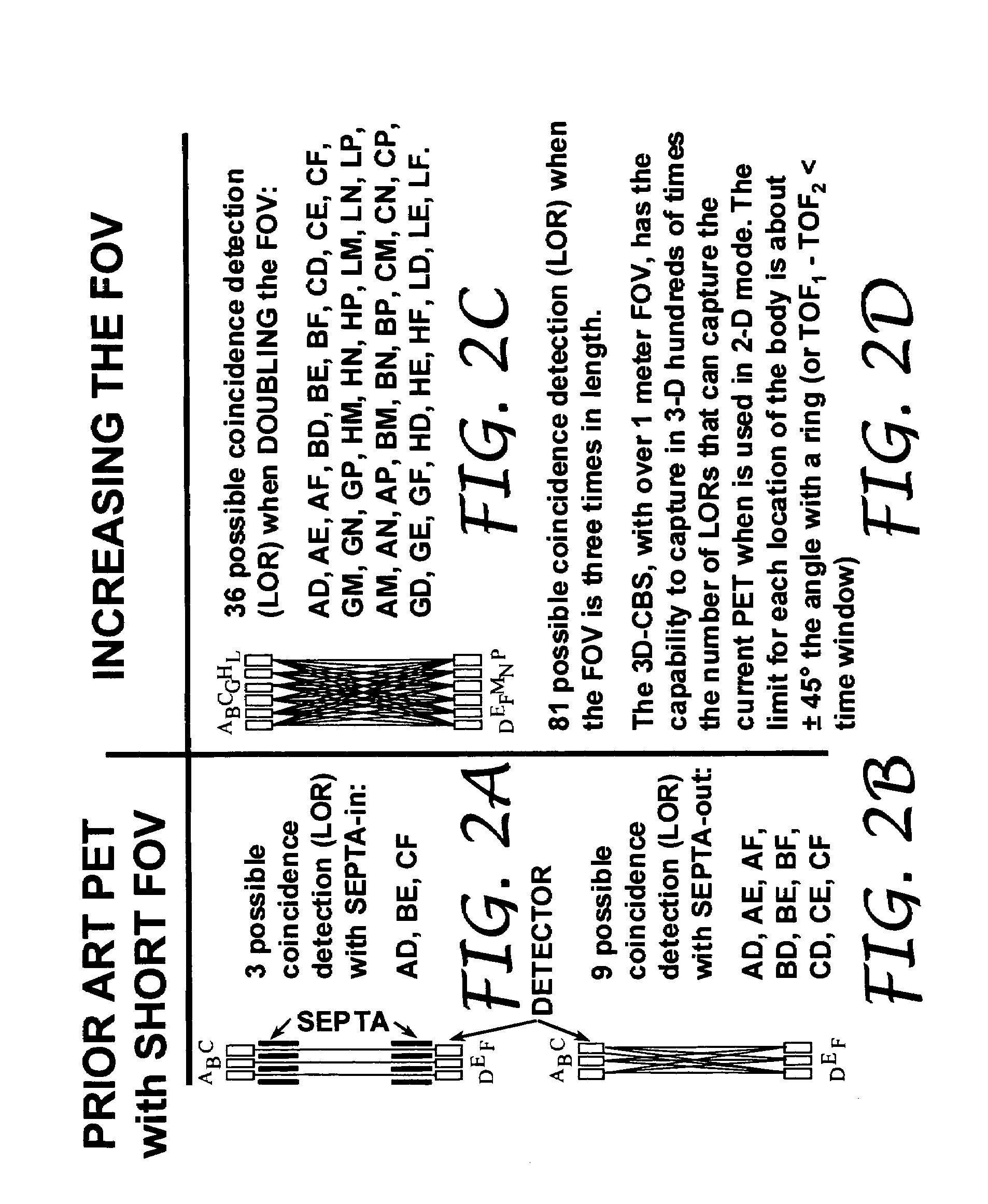
The present invention is directed to a system, method and software program product for implementing 3-D Complete-Body-Screening medical imaging which combines the benefits of the functional imaging capability of PET with those of the anatomical imaging capability of CT. The present invention enables execution of more complex algorithms measuring more accurately the information obtained from the collision of a photon with a detector. The present invention overcomes input and coincidence bottlenecks inherent in the prior art by implementing a massively parallel, layered architecture with separate processor stacks for handling each channel. The prior art coincidence bottleneck is overcome by limiting coincidence comparisons to those with a time stamp occurring within a predefined time window. The increased efficiency provides the bandwidth necessary for increasing the throughput even more by extending the FOV to over one meter in length and the execution of even more complex algorithms.
Owner:CROSETTO DARIO B
Energy-resolving detection system and imaging system
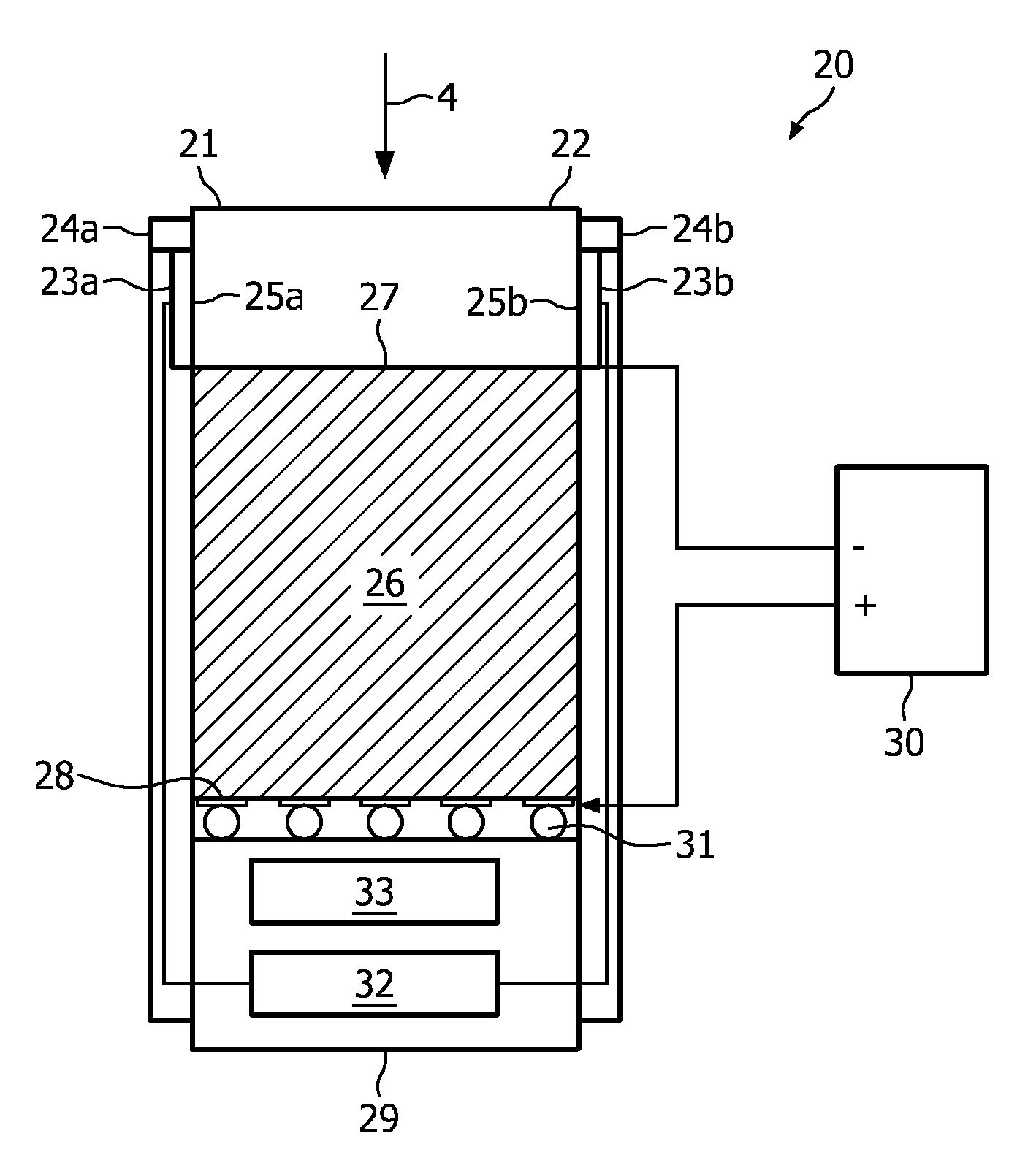
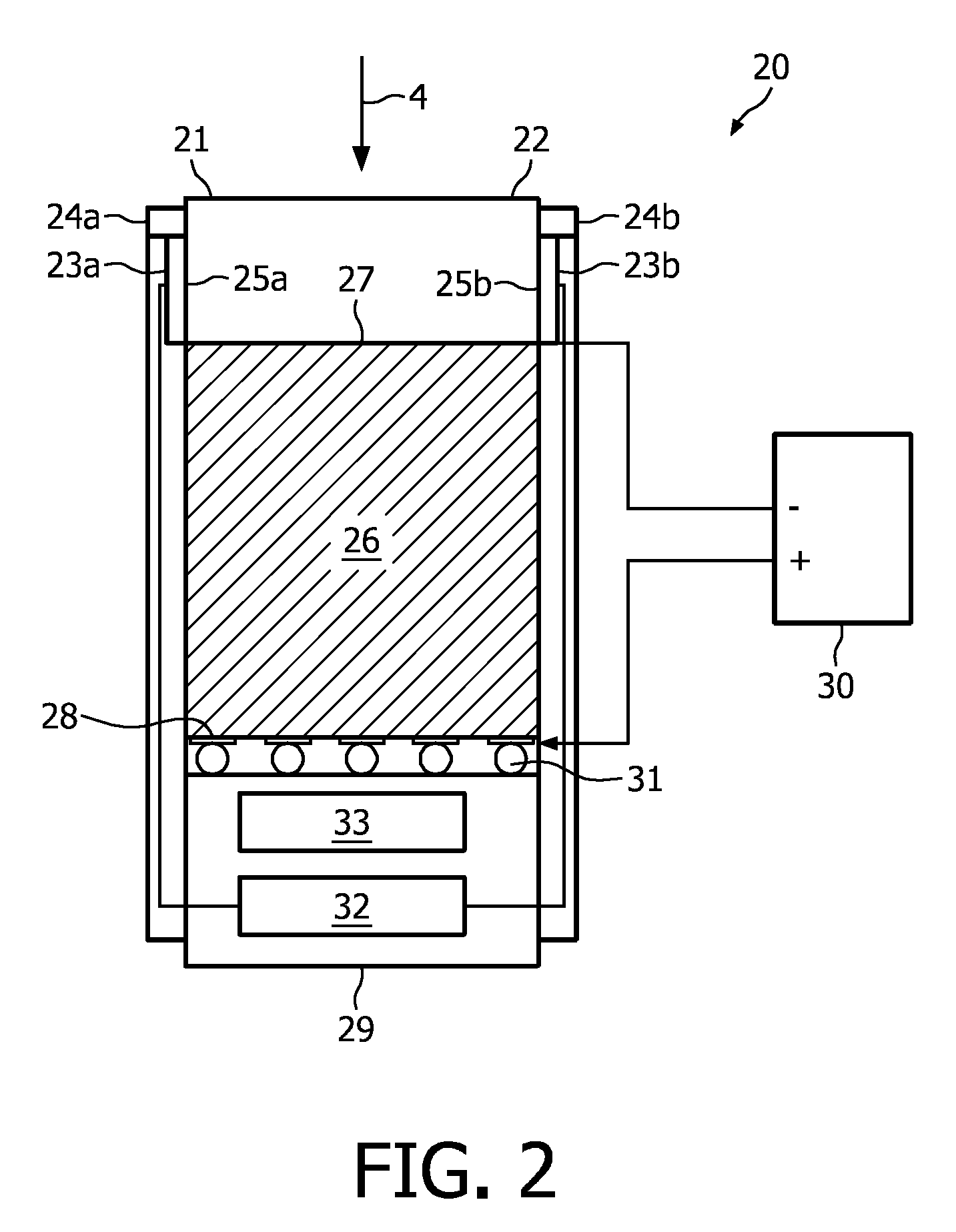
InactiveUS20100012845A1Diminishing effectImproved energy resolutionX-ray spectral distribution measurementSolid-state devicesQuantumPhysics
The invention relates to an energy-resolving detection system for detecting radiation (4). The energy-resolving detection system comprises a first layer (21) for absorbing a part of the radiation (4) and a radiation quanta counting unit comprising a second layer (26) for counting radiation quanta of the radiation (4). A read-out unit (29) is coupled with the radiation quanta counting unit for reading out the radiation quanta counting unit. The first layer (21) and second layer (26) are arranged such that the radiation (4), which is incident on the detection system and which reaches the second layer (26), has passed the first layer (21).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Imaging probe
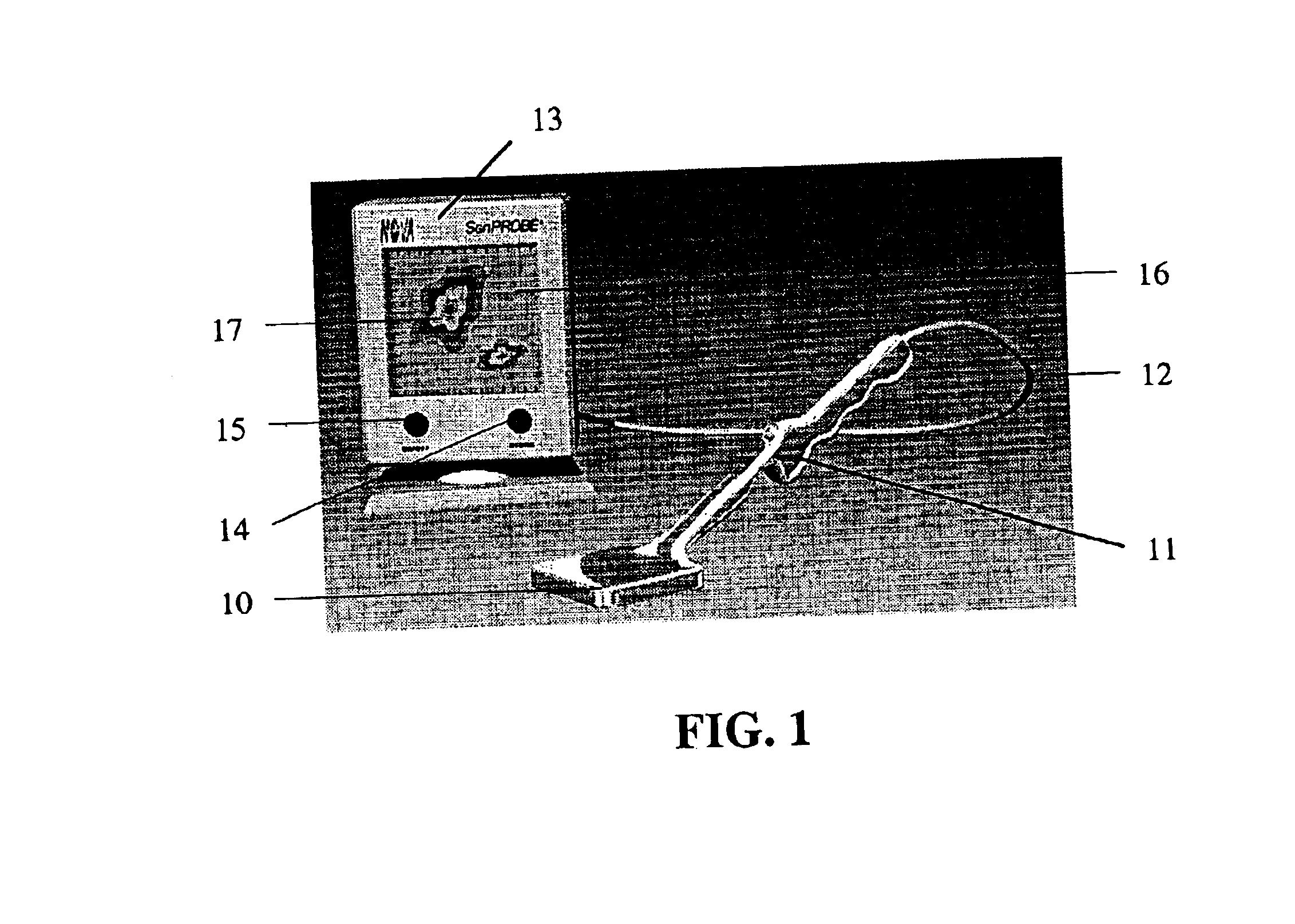
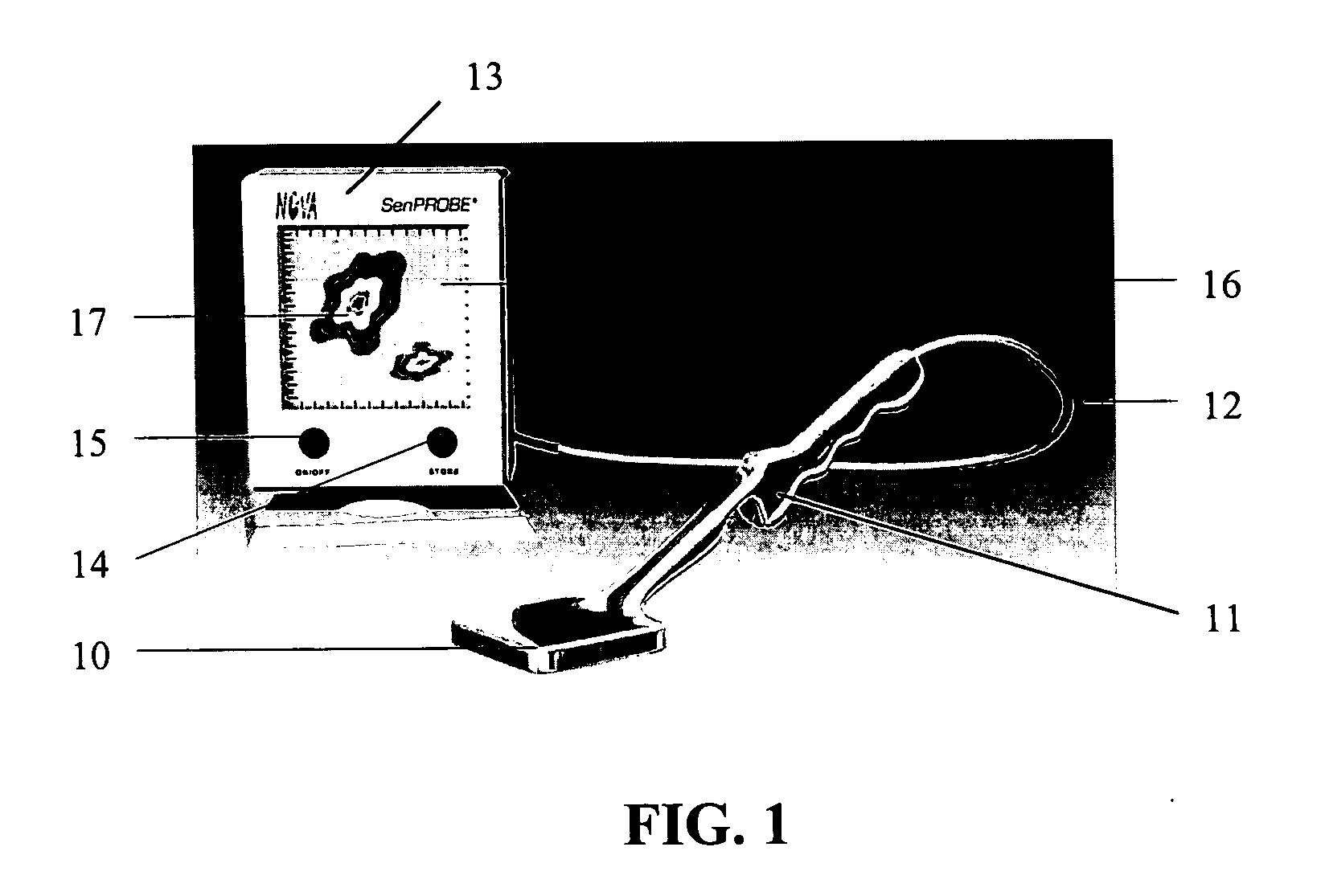
InactiveUS6940070B2High sensitivityImprove quantum efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingLow noiseRadioactive agent
The design of a compact, handheld, solid-state and high-sensitivity imaging probe and a micro imager system is reported. These instruments can be used as a dedicated tool for detecting and locating sentinel lymph nodes and also for detecting and imaging radioactive material. The reported device will use solid state pixel detectors and custom low-noise frontend / readout integrated circuits. The detector will be designed to have excellent image quality and high spatial resolution. The imaging probes have two different embodiments, which are comprised of a pixelated detector array and a highly integrated readout system, which uses a custom multi-channel mixed signal integrated circuit. The instrument usually includes a collimator in front of the detector array so that the incident photons can be imaged. The data is transferred to an intelligent display system. A hyperspectral image can also be produced and displayed. These devices are designed to be portable for easy use.
Owner:NOVA R&D
Imaging probe
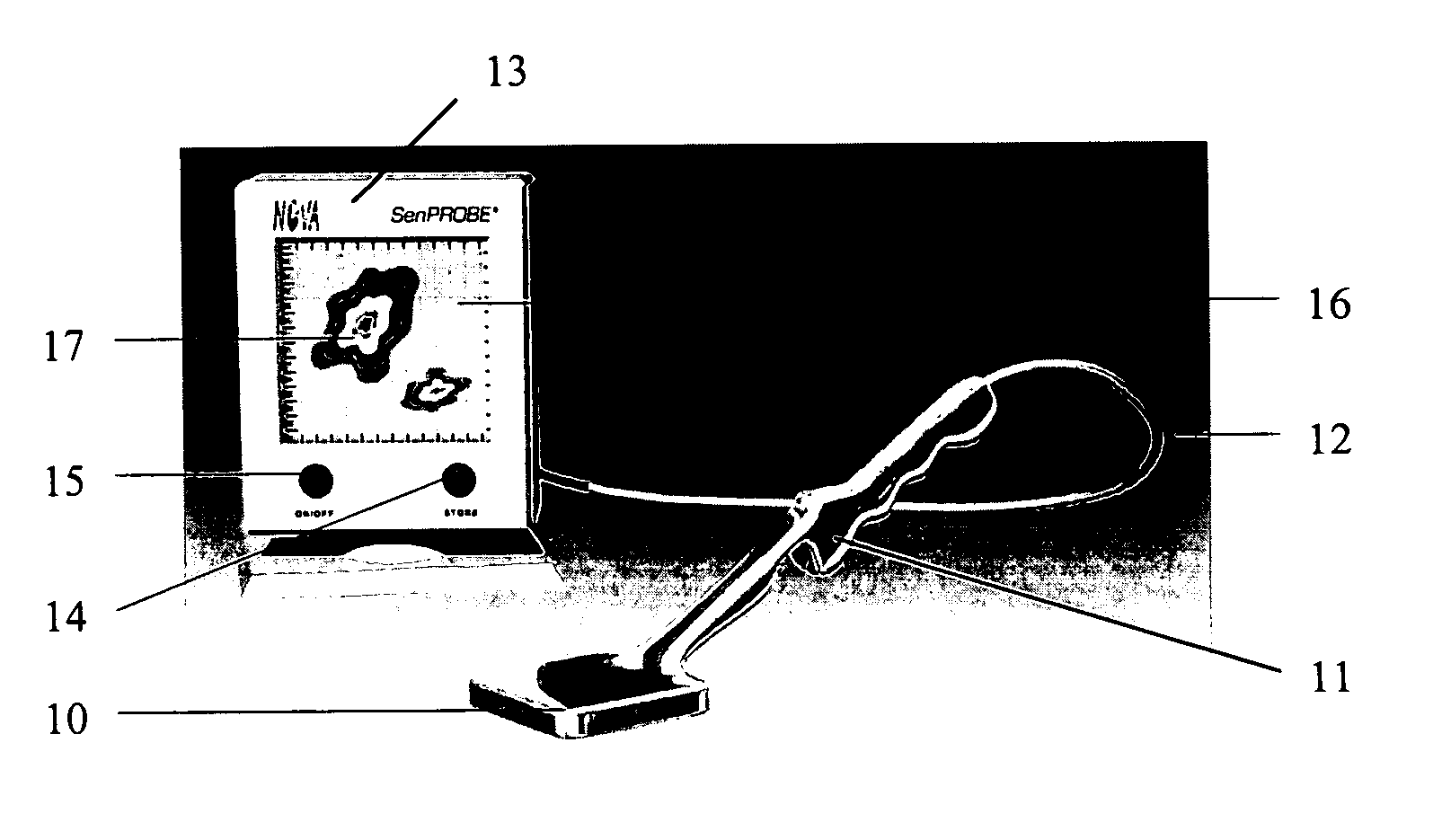
ActiveUS20060036157A1High sensitivityImprove quantum efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsRadioactive agentImaging quality
The design of a compact, handheld, solid-state and high-sensitivity imaging probe and a micro imager system is reported. These instruments can be used as a dedicated tool for detecting and locating sentinel lymph nodes and also for detecting and imaging radioactive material. The reported device will use solid state pixel detectors and custom low-noise frontend / readout integrated circuits. The detector will be designed to have excellent image quality and high spatial resolution. The imaging probes have two different embodiments, which are comprised of a pixelated detector array and a highly integrated readout system, which uses a custom multi-channel mixed signal integrated circuit. The instrument usually includes a collimator in front of the detector array so that the incident photons can be imaged. The data is transferred to an intelligent display system. A hyperspectral image can also be produced and displayed. These devices are designed to be portable for easy use.
Owner:NOVA R&D
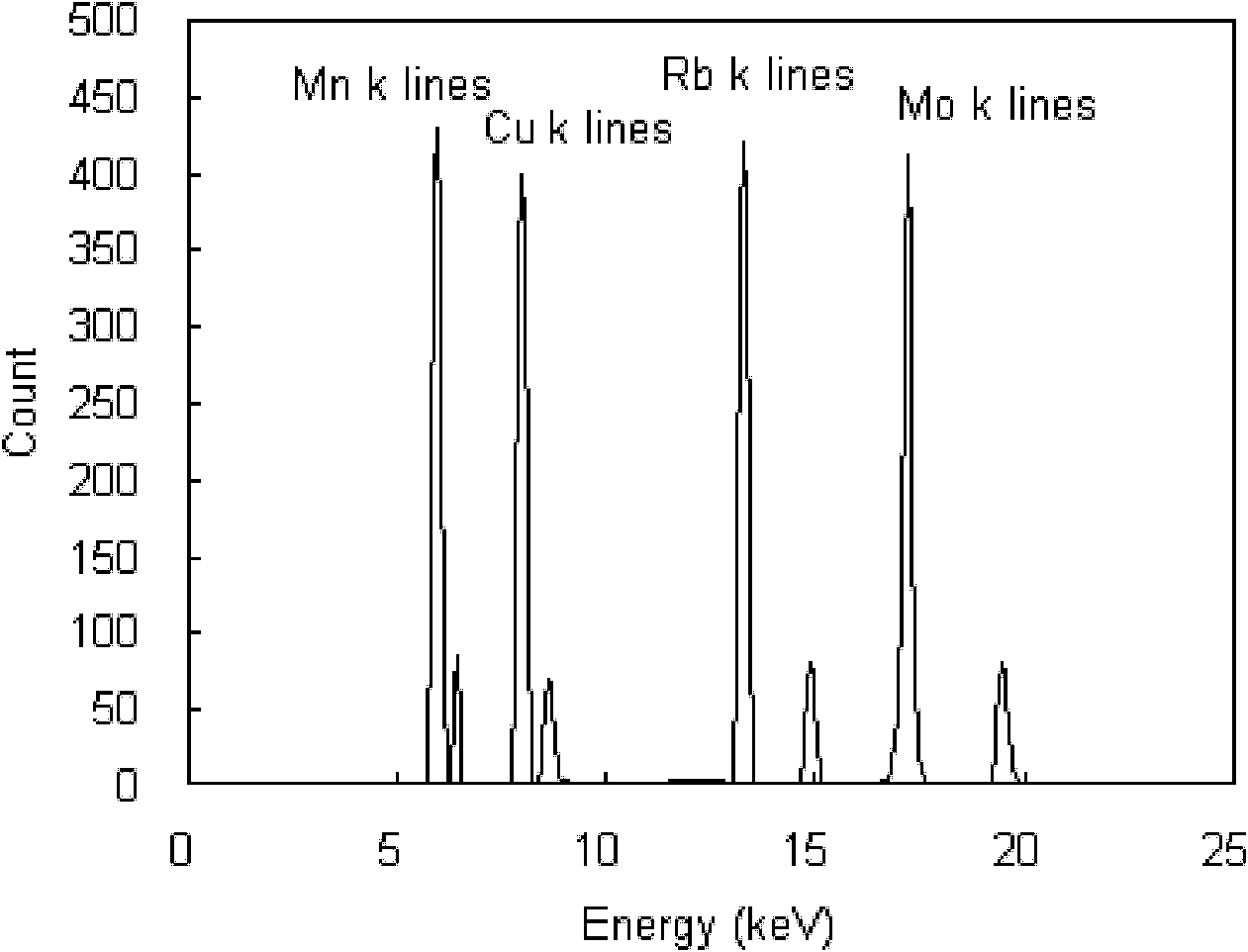
Digital logarithm gamma energy spectrometer
InactiveCN101799554AGuaranteed Energy ResolutionHigh count pass rateX-ray spectral distribution measurementAnti-aliasingProgrammable logic device
The invention discloses a digital logarithm gamma energy spectrometer, which comprises a NaI crystal, a photomultiplier, a high-voltage power supply module, a preamplifier, a logarithmic amplifier, a gain-programmed amplifier, an anti-aliasing active filter, a high-speed analog-digital converter (ADC) and a CPLD programmable logic device, wherein the logarithmic amplifier performs logarithmic operation on received nuclear pulse signals to acquire a high energy section spectral line and a low energy section spectral line; the high-speed analog-digital converter (ADC) performs analog-digital conversion on filtered signals; and the CPLD programmable logic device realizes pulse amplitude analysis, baseline restoration and filtering de-noising to digital signals, and obtains information on corresponding nuclear pulse peak values. The logarithmic amplifier performs logarithmic compression on the nuclear pulse signals to ensure the resolution of the high energy spectral line and the low energy spectral line; and the high-speed analog-digital converter and the CPLD programmable logic device are adopted to realize a digital energy spectrometer and ensure the high counting pass rate and the energy resolution of the energy spectrometer.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Apparatus and method for detection, location, and identification of gamma sources
InactiveUS8067742B2Improve responseIncrease pointsMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPhotodetectorScintillation crystals
An apparatus for detecting and determining a source azimuth for gamma radiation includes at least two scintillation crystals at angular offsets and directed toward a common plane of detection, photodetectors adjacent to each of the scintillation crystals for converting the light response of the scintillation crystals into distinct electrical signals, and a digital processing system configured to analyze spectral data from each electrical signal produced for each crystal. The digital processing system monitors a finite number of spectral windows corresponding to a selected set of radioisotopes, and uses one or more of the electrical signals to determine a signal intensity and a likely source azimuth for a detected radioisotope in the plane of detection. Another scintillation crystal directed outside of the common plane of detection may be used for three-dimensional detection. Related methods for detection and location of gamma ray sources are discussed.
Owner:SPACE MICRO A CORP OF DELAWARE
Charged particle beam device with retarding field analyzer
ActiveUS8203119B2Improve spatial resolutionSmall sizeStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationOptical axisImage resolution
Owner:ICT INTEGRATED CIRCUIT TESTING GESELLSCHAFT FUER HALBLEITERPRUEFTECHNIK GMBH
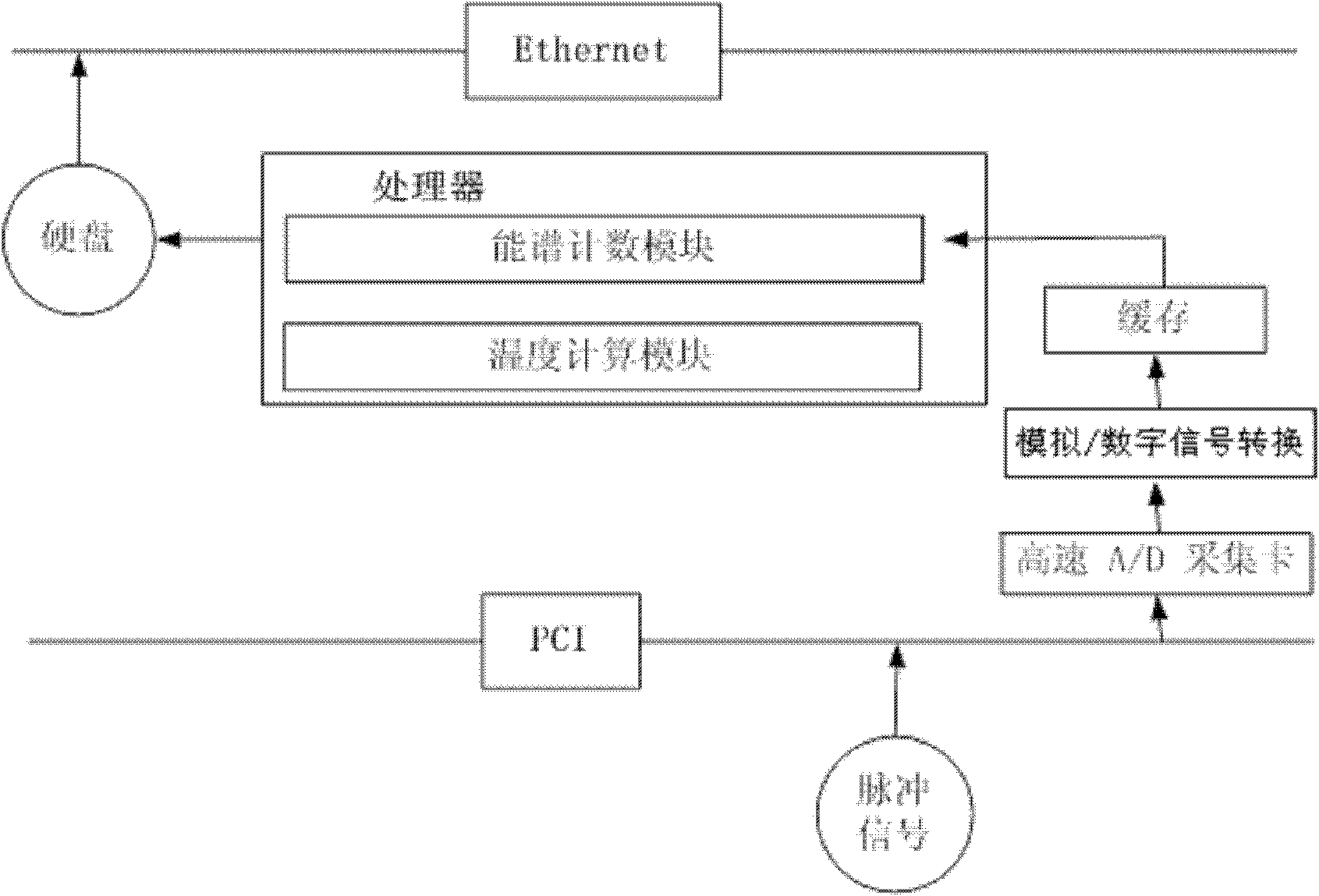
Processing method and device for multi-channel energy spectrum measurement
InactiveCN102279408AEliminate lossesEliminate stacking effectsX-ray spectral distribution measurementPhotonicsDigitization
The invention belongs to the field of plasma diagnosis computer processing, in particular to a processing method and device for multi-channel energy spectrum measurement. The processing method includes the following steps: collecting a pulse signal sent by a probe and converting it into a digital pulse signal; counting and classifying the digitized pulse signal to obtain a count spectrum; converting the count spectrum into an energy spectrum; The energy attenuation produced by the beryllium foil is reduced, and the energy spectrum obtained in the third step is restored; the energy spectrum after reduction is smoothed and peaked and fitted to obtain the electron temperature. The processing device includes a pulse signal generation module, a high-speed acquisition card, an analog / digital signal conversion module, a high-speed cache module, and a processor unit with an energy counting module and a temperature calculation module. The problems of common multi-channel energy spectrum measurement and processing methods, such as high hardware cost, strong equipment specificity, limited number of energy channels, low spatial and temporal resolution, and inability to save original signals, are solved.
Owner:SOUTHWESTERN INST OF PHYSICS
Device for detecting highly energetic photons
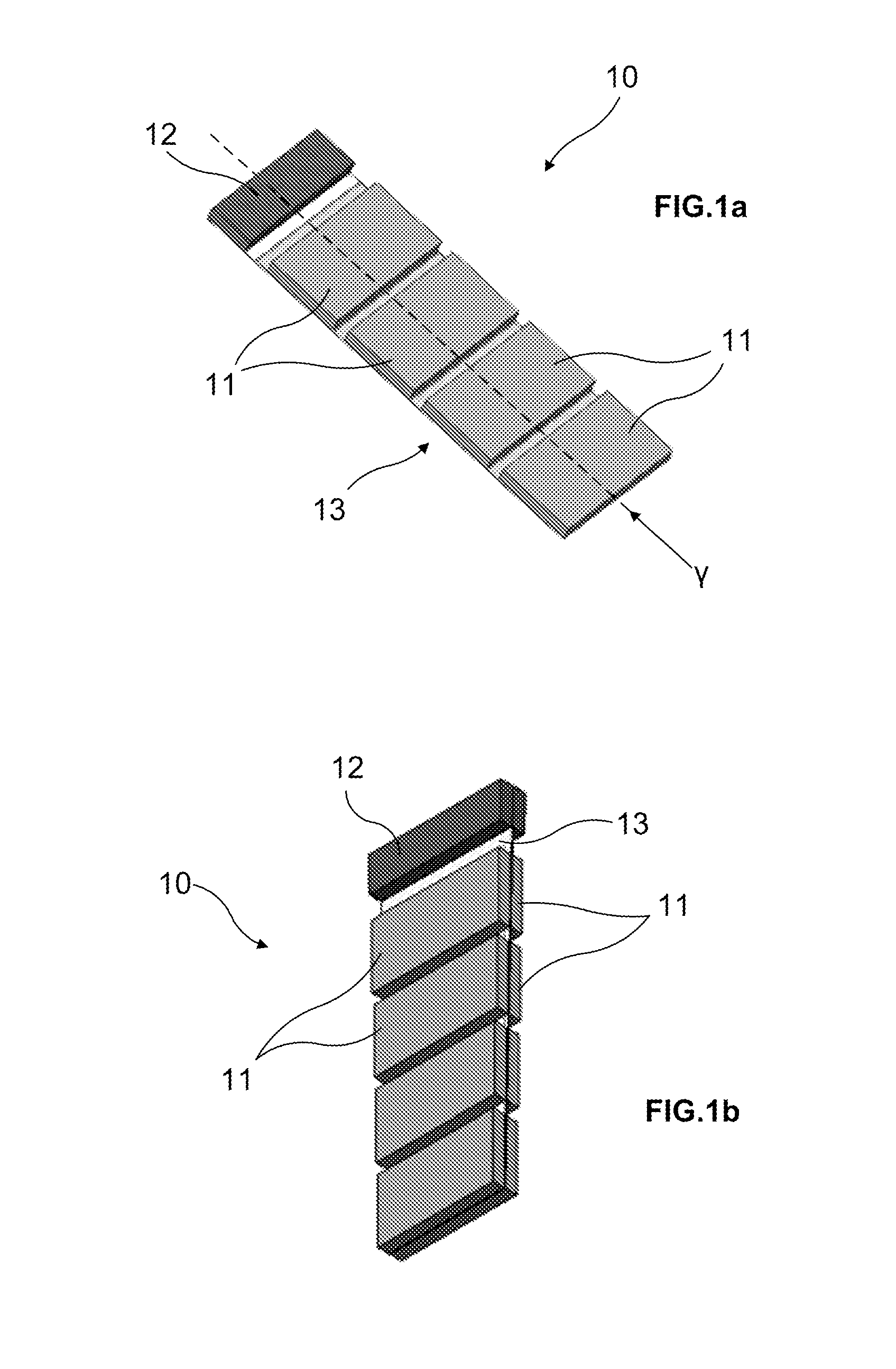
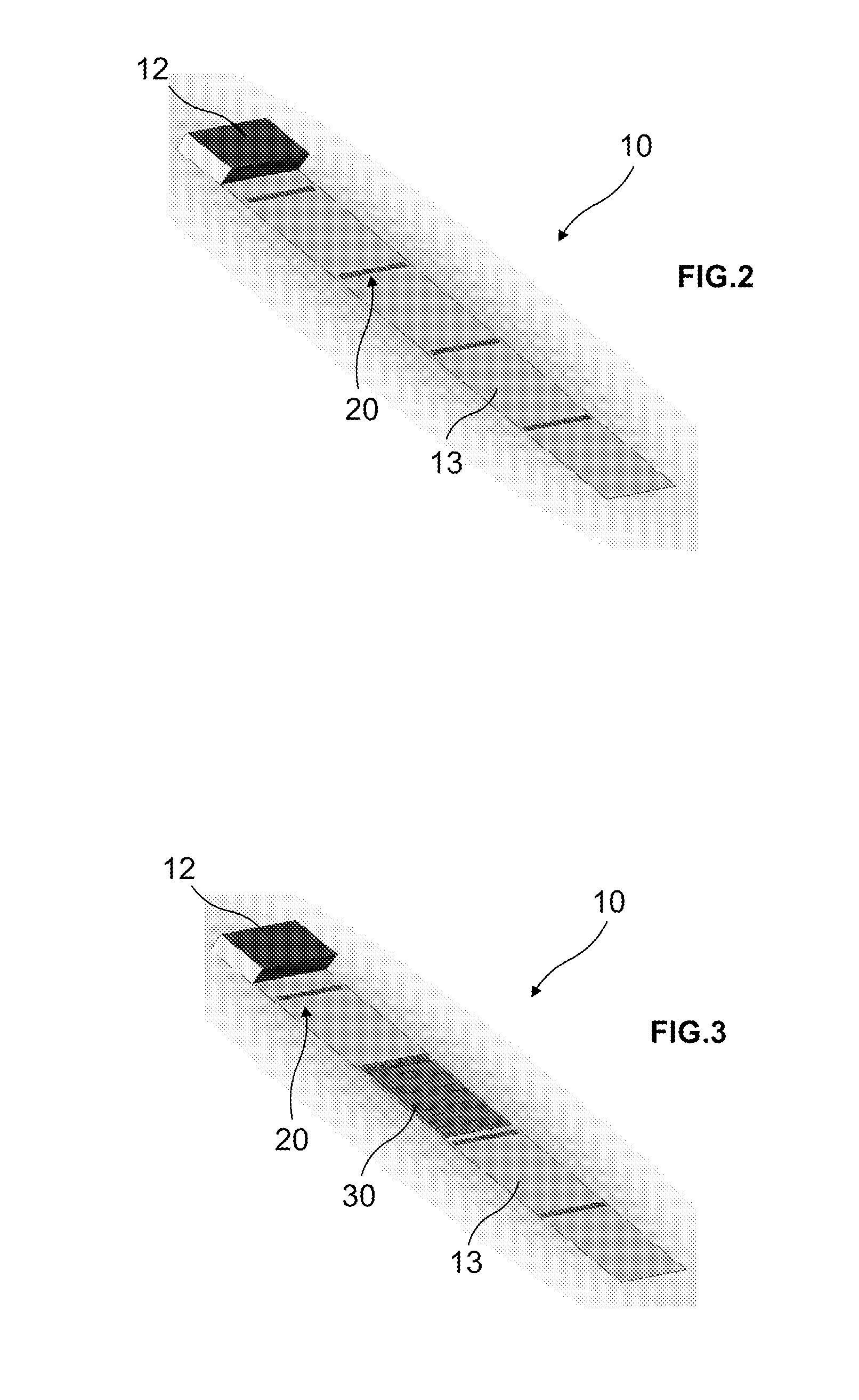
ActiveUS20110253901A1Improve spatial resolutionSolve the low detection efficiencySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansSolid state detectorEngineering
A device (10) for detecting highly energetic photons, comprising one or more pixelated solid-state detectors (11) for detecting the highly energetic photons; means for providing a high voltage for polarizing said solid-state detectors; one or more pixelated readout elements (30), a readout element being connected to each of said one or more pixelated solid-state detectors (11); an input / output element (12) connected to said readout elements (30) for data input and output; and a base layer (13) for mounting the pixelated solid-state detectors (11), the readout elements (30) and the input / output element (12).
Owner:INST DE FISICA D ALTES ENERTIES (IFAE)
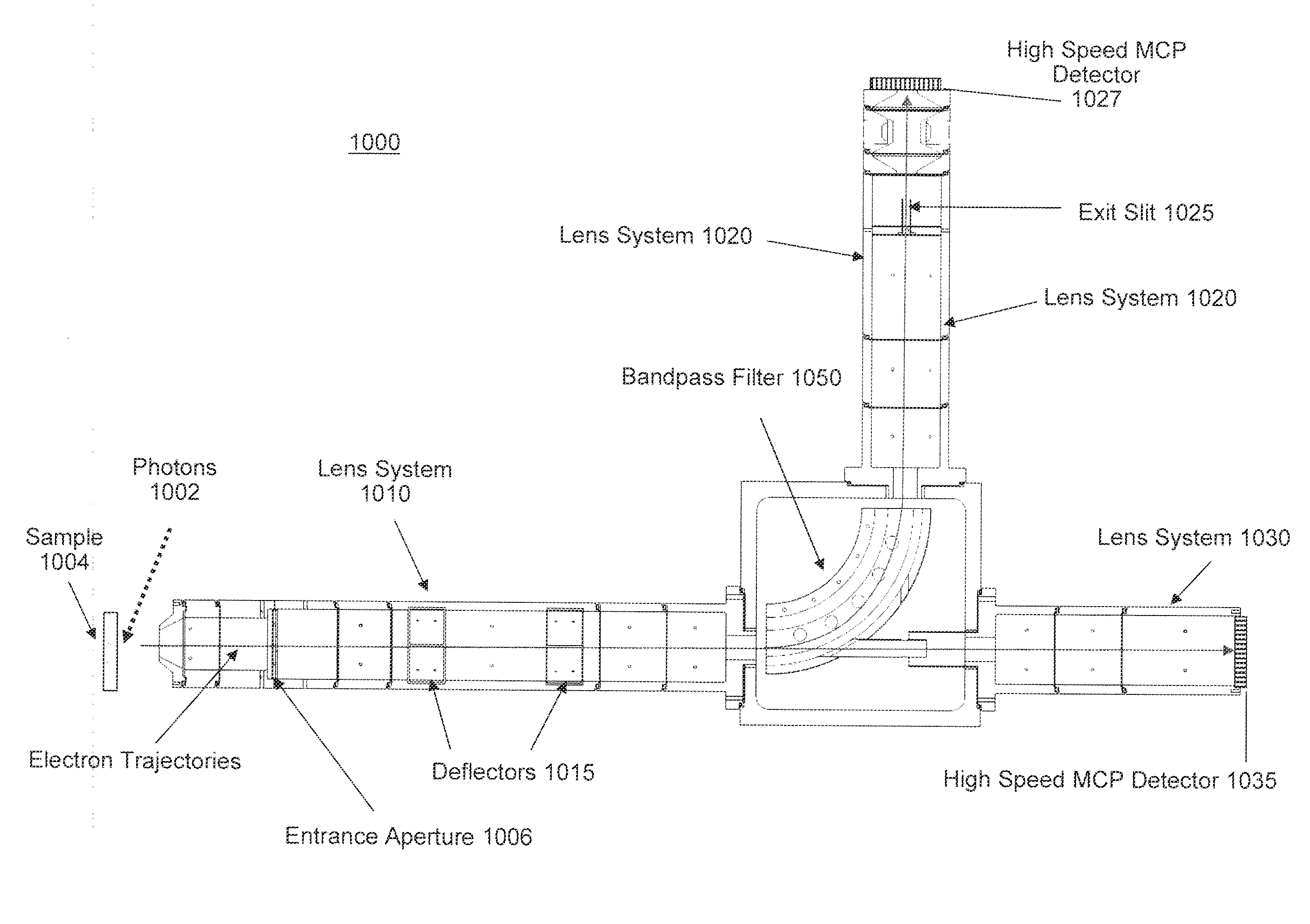
Time-of-Flight Electron Energy Analyzer
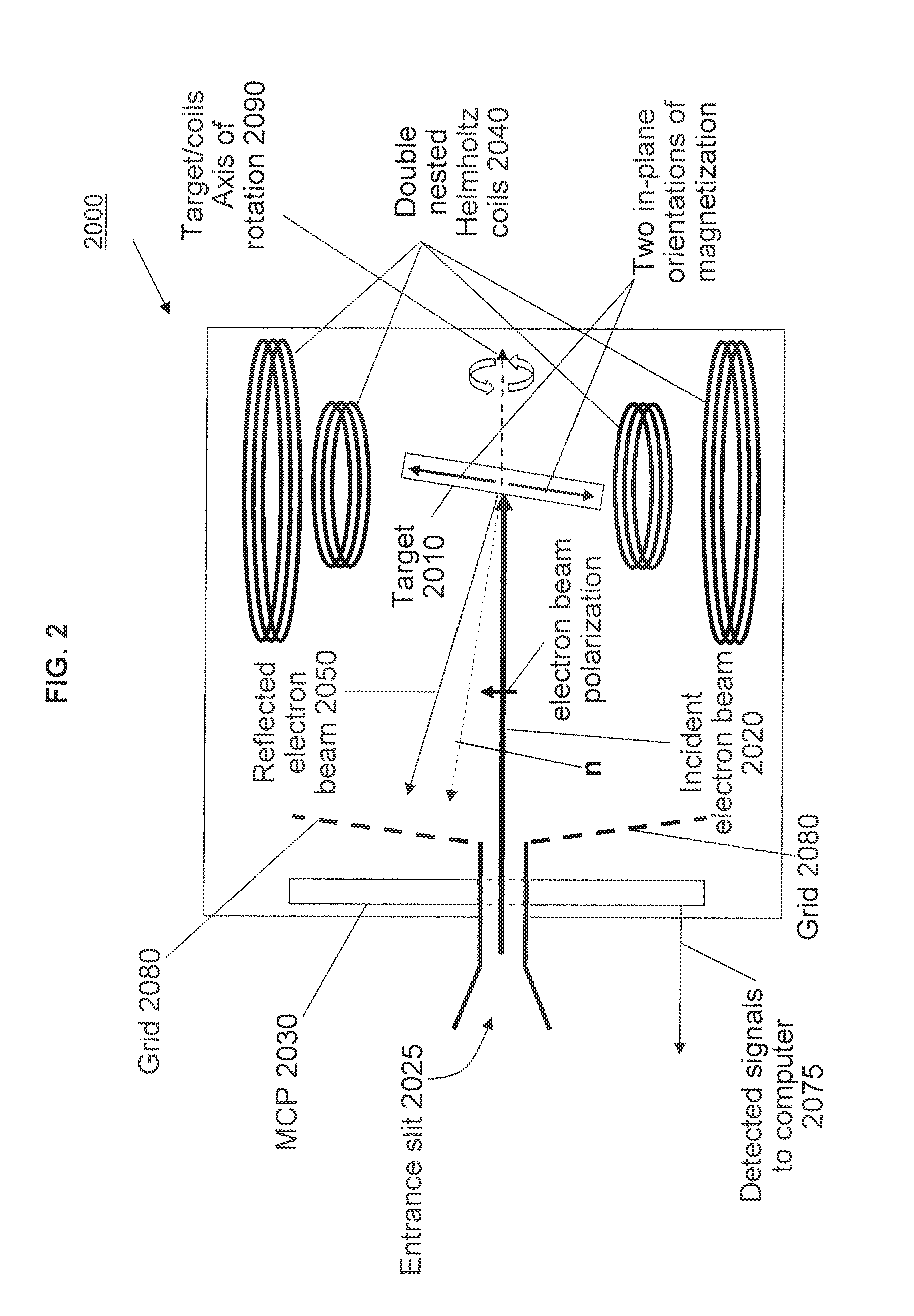
InactiveUS20130126727A1High resolutionImproved energy resolutionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesBandpass filteringTarget surface
A time-of-flight (TOF) photoemission electron energy analyzer includes a TOF spectrometer for measuring an energy spectrum of a beam of electrons photoemitted from a sample and a 90 degree bend bandpass filter for spatially dispersing and filtering electrons according to energy. An exchange scattering electron spin polarimeter for detecting the spin of electrons includes an entrance aperture for admitting an electron beam, a magnetizable target positionable for receiving the electron beam at an angle relative to a target surface normal vector, a pair of Helmholtz coils positioned about the target for magnetizing the target in a selected direction, and a high-speed multi-channel plate (MCP) detector facing toward the target for receiving electrons reflected from the target surface, the MCP outputting a signal corresponding to the spin dependent intensity and time of electrons' arrivals.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Device and method for measuring multi-wavelength characteristic X ray diffraction
InactiveCN104634799AHigh diffraction intensityEliminate attenuationMaterial analysis using radiation diffractionX-rayHigh pressure
The invention relates to a device and a method for measuring multi-wavelength characteristic X ray diffraction of an X ray diffraction spectrum of a measured crystal material sample by selecting a certain characteristic X ray of an X ray tube anode target within a relatively wide wavelength range. The device comprises an X ray tube, a high-pressure generator, a silt, an angle measurer, a detector, a multi-path analyzer, and the like. According to the device and the method disclosed by the invention, large-scale attenuation of the characteristic X ray diffraction due to use of a filter sheet or a crystal monochromator and the like is avoided; required characteristic X rays for measuring needed wavelength can be selected by regulating the tube voltage of the X ray tube and upper and lower thresholds of the multi-path analyzer, so that diffraction rays (characteristic X rays with relatively large wavelengths) on the surface of a sample can be measured in a nondestructive manner, and the diffraction rays (characteristic X rays with relatively small wavelengths) inside the sample can be measured in the nondestructive manner. Moreover, the device is simple and convenient to operate, relatively short in detection time; the characteristic X ray diffraction spectrums obtained by scanning are real and reliable.
Owner:郑琪
Superconducting X-ray detector and X-ray analysis apparatus using the same
InactiveUS7589323B2Reduce sensitivityImproved energy resolutionDigital data processing detailsAnimal undercarriagesSoft x rayHeat flow
To provide a superconducting X-ray detector capable of carrying out a measurement by a high energy resolution by restraining a reduction in a sensitivity by a self magnetic field. A superconducting X-ray detector comprising a temperature detector 6 for detecting a temperature change by heat generated when an X-ray is absorbed, and a heat link 3 for controlling a heat flow amount of escaping the generated heat to a support board i, wherein the temperature detector 6 comprises a heat conducting multilayer thin film, the superconducting X-ray detector is constituted by a structure of providing a superconductor layer 4 above the heat link 3 and providing an insulating member 2 between the superconductor layer 4 and the temperature detector 6, the superconductor layer 4 and the temperature detector 6 are connected by a superconducting wiring 7 and uses materials by which superconducting transition temperatures of the superconductor layer 4 and the superconducting wiring 7 are higher than a superconducting transition temperature of the temperature detector 6.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
Charged particle energy filter
ActiveUS20130112890A1High beam qualityImproved energy resolutionStability-of-path spectrometersBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsLight beamQuadrupole
A multi-element electrostatic chicane energy filter, with the addition of electrostatic quadrupole and hexapole excitations to the dipole elements. A charged particle energy filter according to the present invention with a combination of dipole, quadrupole, and hexapole elements capable of producing a line focus at an aperture reduces space-charge effects and aperture damage. A preferred embodiment allows the filter to act as a conjugate blanking system. The energy filter is capable of narrowing the energy spread to result in a smaller beam.
Owner:FEI CO
Apparatus and method for detection, location, and identification of gamma sources
InactiveUS20100168947A1High light yieldPrecise energy resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansHandling using diaphragms/collimetersPhysicsElectric signal
An apparatus for detecting and determining a source azimuth for gamma radiation includes at least two scintillation crystals at angular offsets and directed toward a common plane of detection, photodetectors adjacent to each of the scintillation crystals for converting the light response of the scintillation crystals into distinct electrical signals, and a digital processing system configured to analyze spectral data from each electrical signal produced for each crystal. The digital processing system monitors a finite number of spectral windows corresponding to a selected set of radioisotopes, and uses one or more of the electrical signals to determine a signal intensity and a likely source azimuth for a detected radioisotope in the plane of detection. Another scintillation crystal directed outside of the common plane of detection may be used for three-dimensional detection. Related methods for detection and location of gamma ray sources are discussed.
Owner:SPACE MICRO A CORP OF DELAWARE
Quantum-imaging system and mode of operation and method of fabrication thereof
ActiveUS7781739B1Quality improvementIncrease catch rateElectric discharge tubesPhotometryOperation modeSpectrometer
A quantum-imaging system for detecting photons, including short-wavelength (<1 nm) photons, is provided. A quantum imaging system can include optical read-out and optical means, and can be configured to perform as both a photon counter and a photon spectrometer. A quantum-imaging system can function as a photon counter and be configured to measure photon beam fluences (e.g., in J / cm2) for both strong beams and weak beams, the latter ones, for example, in the intensity range of 1 pJ / cm2sec, or 0.1 μSv / h. The quantum-imaging system can also function as a photon spectrometer and can be configured to measure photon energies with high energy resolution such as, for example, 1% of photon energy.
Owner:MERCURY MISSION SYST LLC
Method for detecting radiation, device thereof, and positron emission tomography scanner
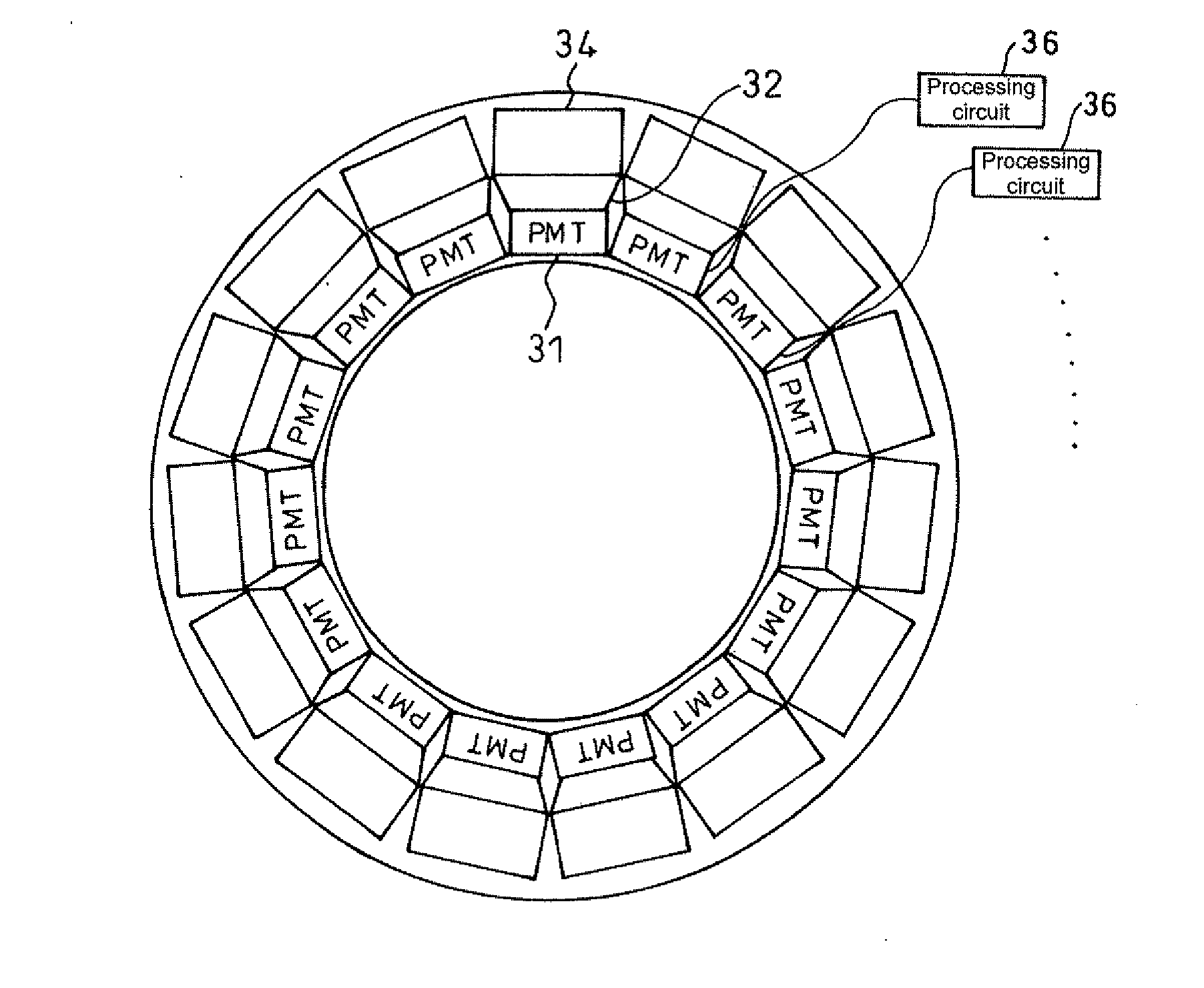
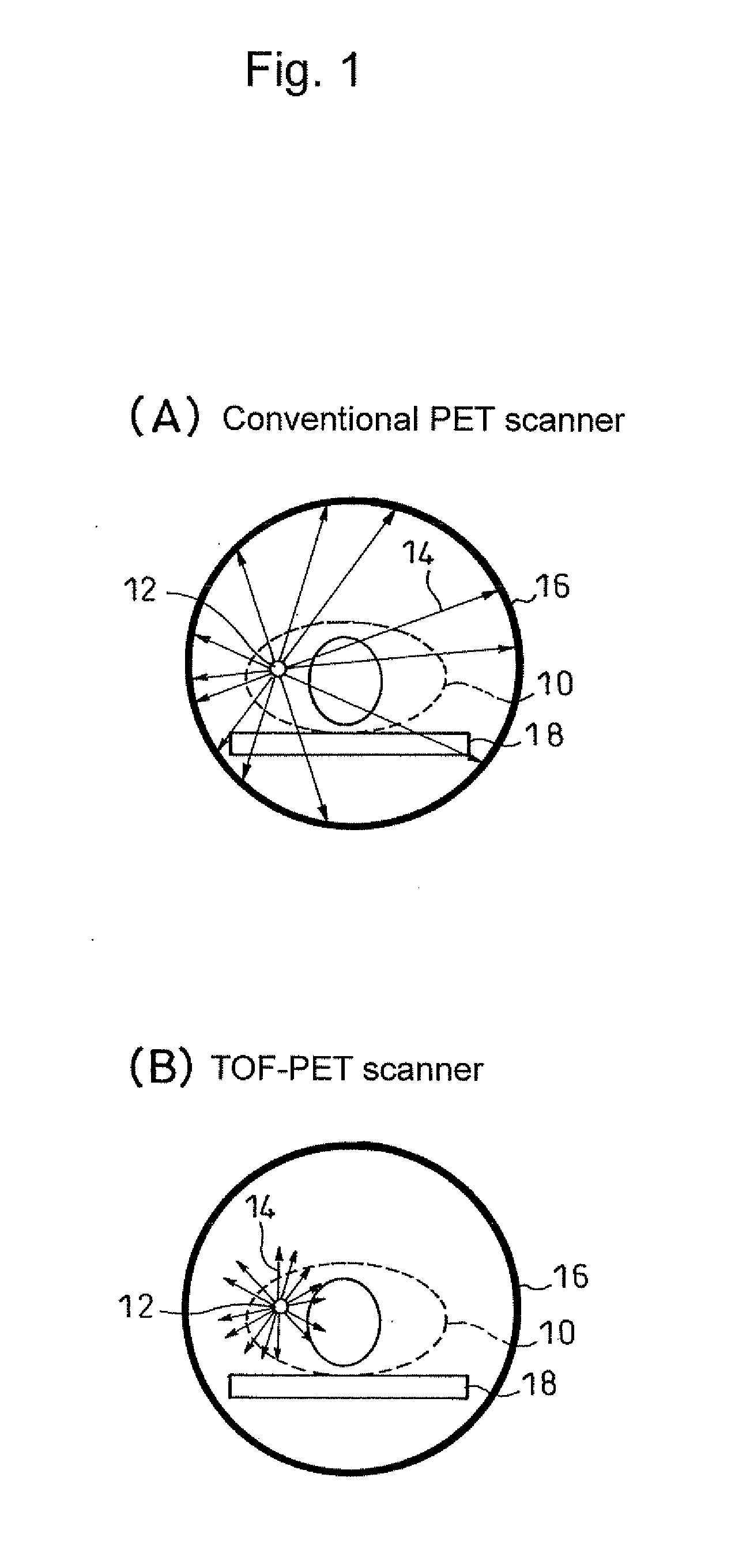
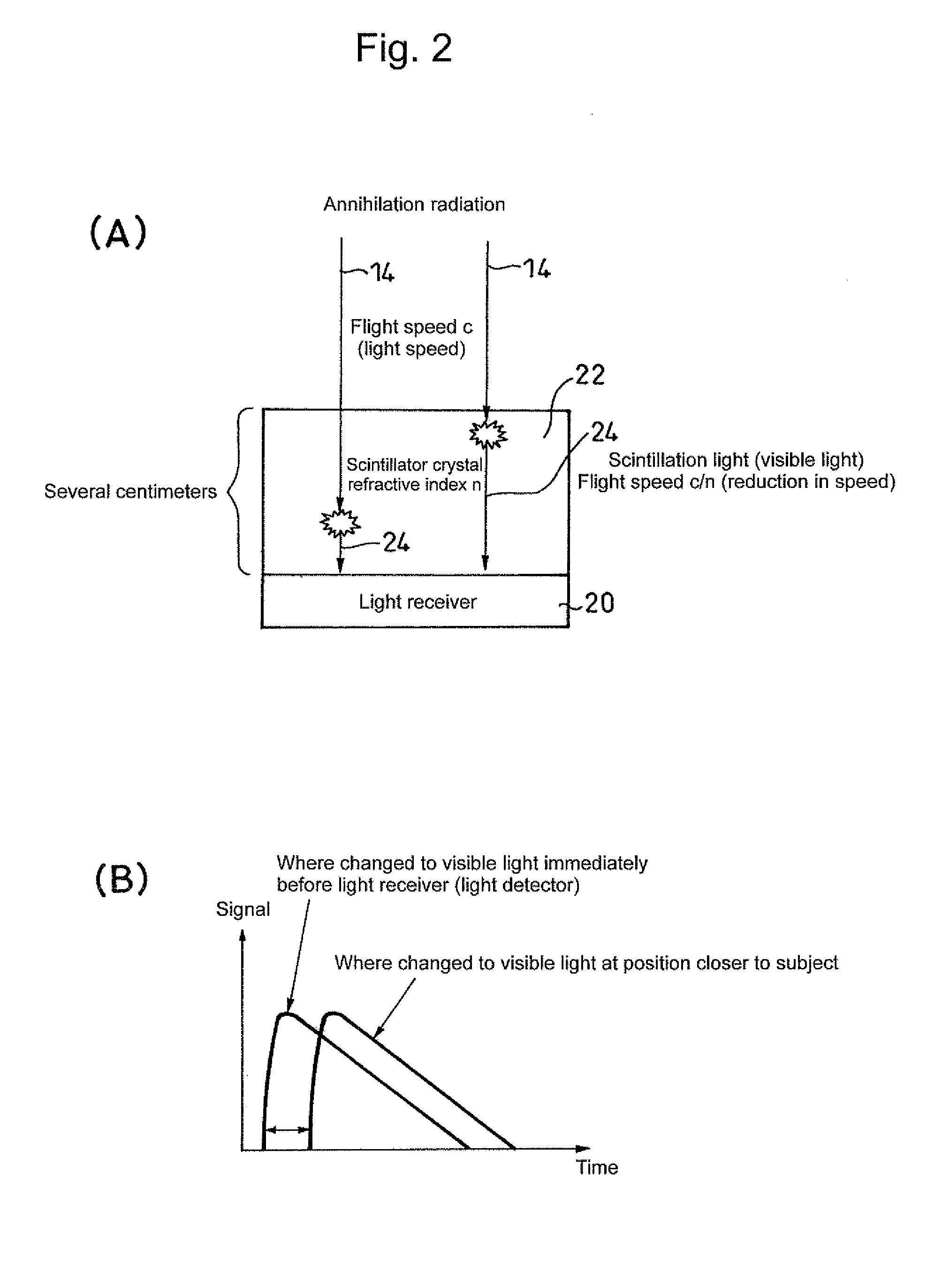
InactiveUS20110001049A1High measurement accuracyResolution timeMaterial analysis by optical meansTomographyScintillatorElectron
A light receiver for detecting incident time is installed on the side of a radiation source of a scintillator (including a Cherenkov radiation emitter), and information (energy, incident time, an incident position, etc.) on radiation made incident into the scintillator is obtained by the output of the light receiver. It is, thereby, possible to identify an incident position and others of radiation into the scintillator at high accuracy.
Owner:NAT INST FOR QUANTUM & RADIOLOGICAL SCI & TECH
Radiological imaging system
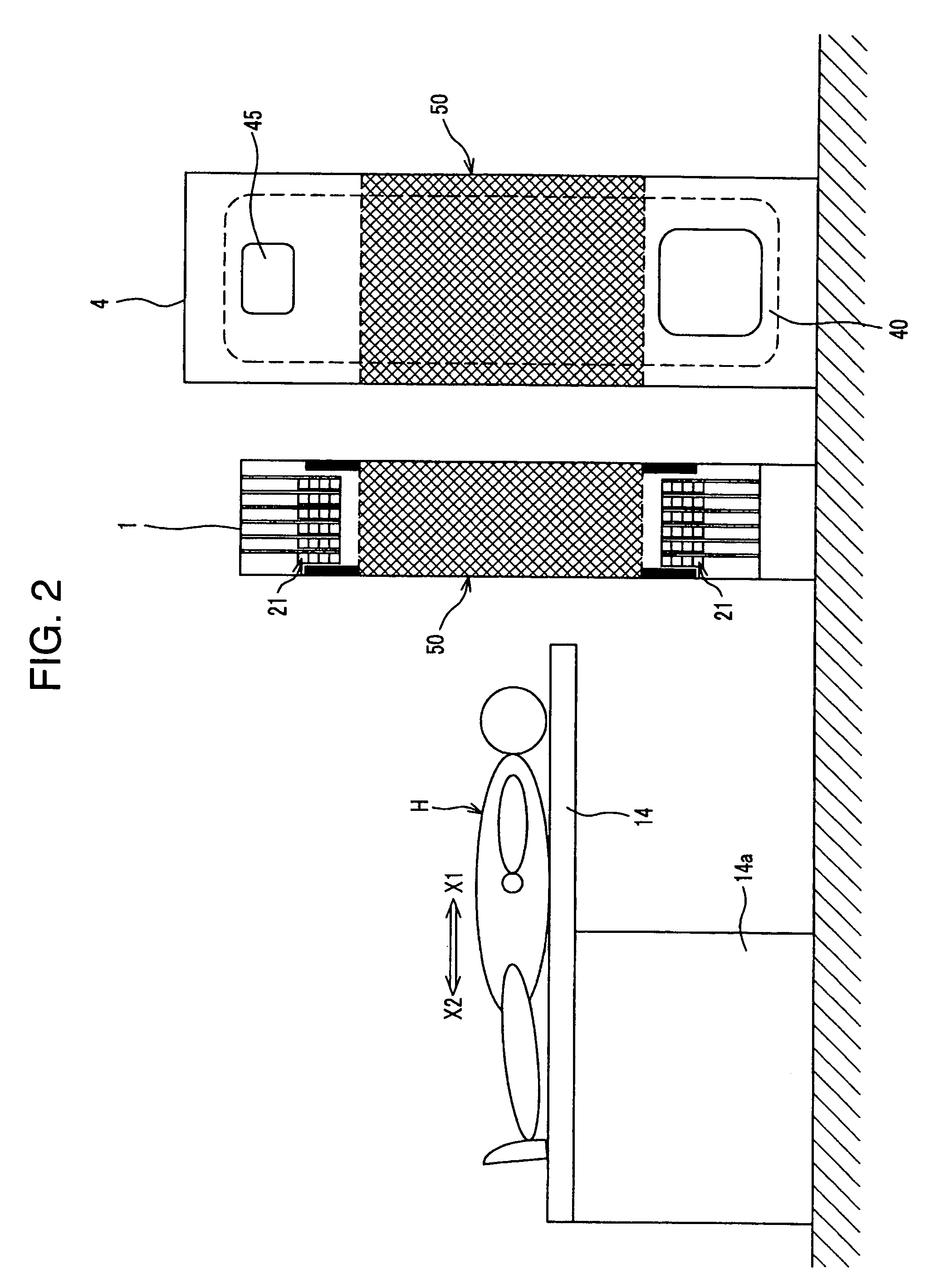
InactiveUS20070057191A1Improve quantitativenessImprove detection accuracyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
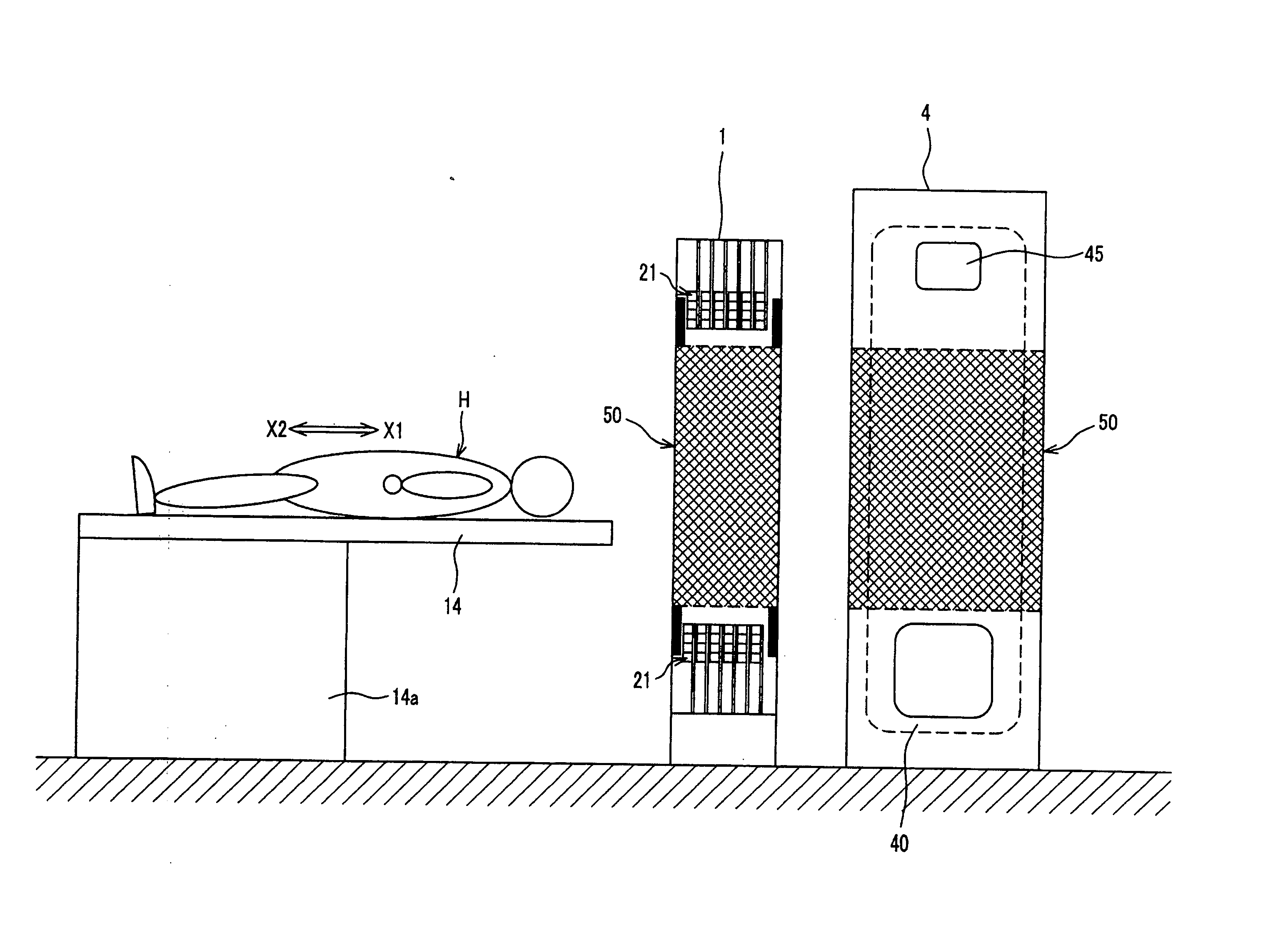
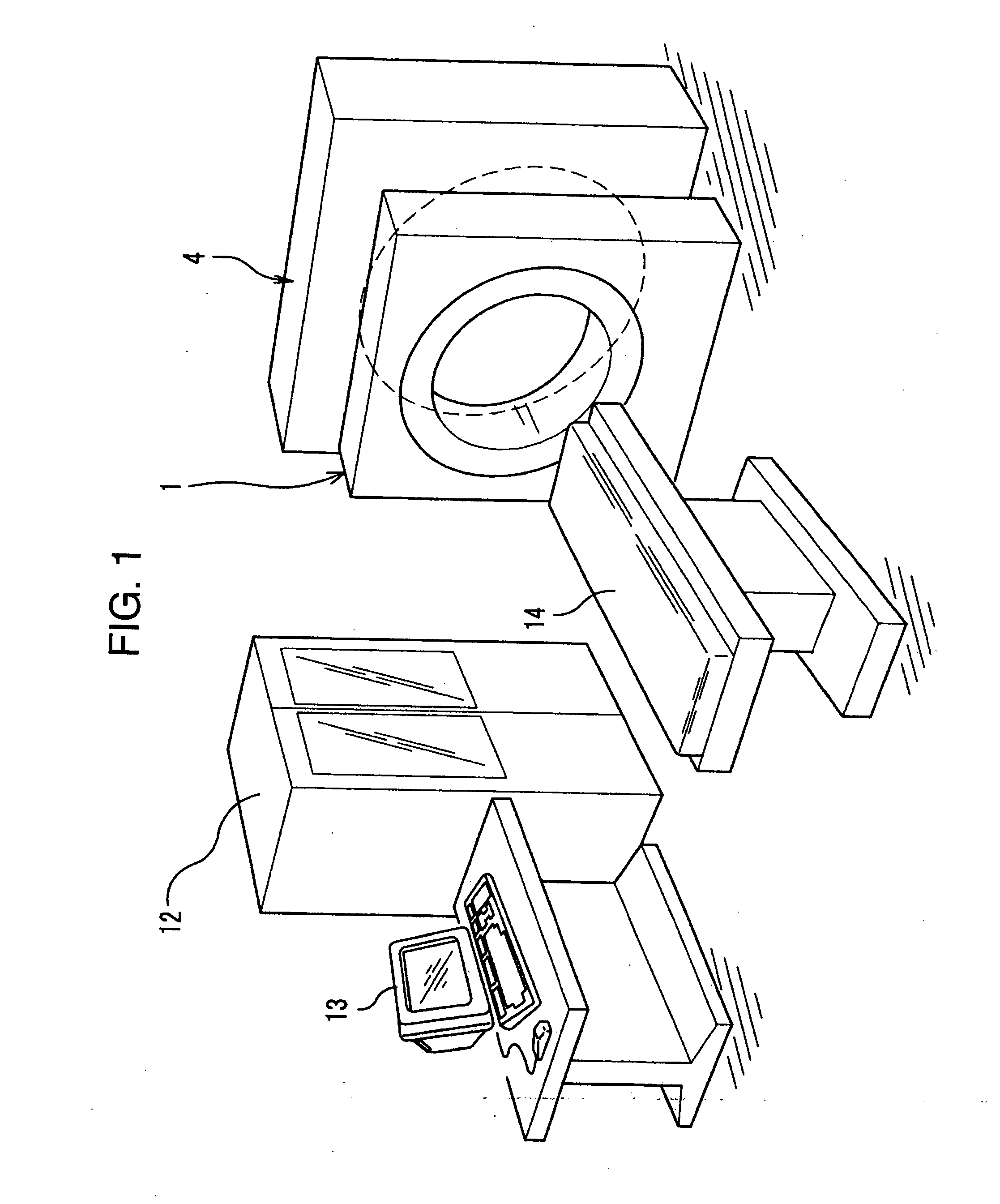
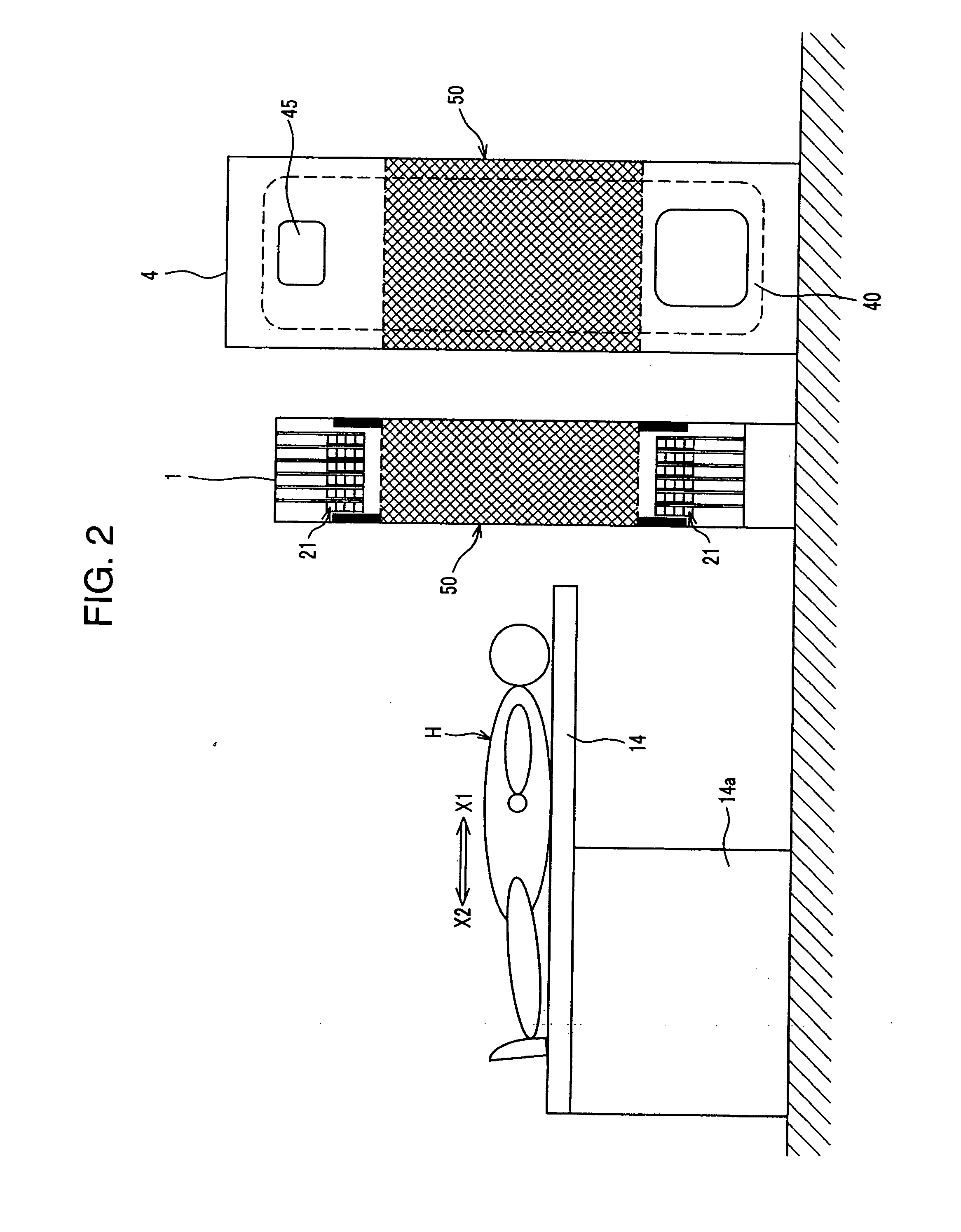
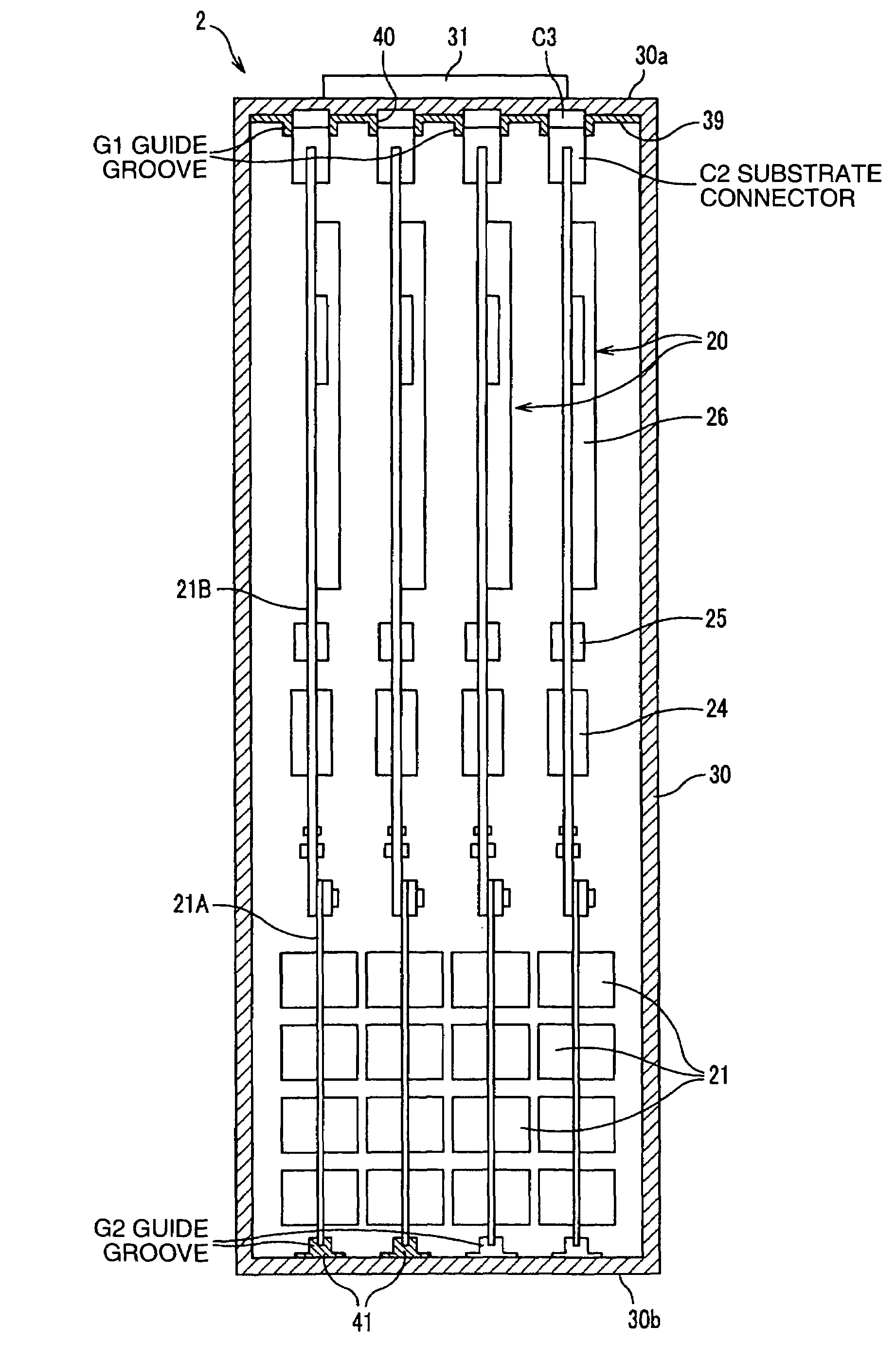
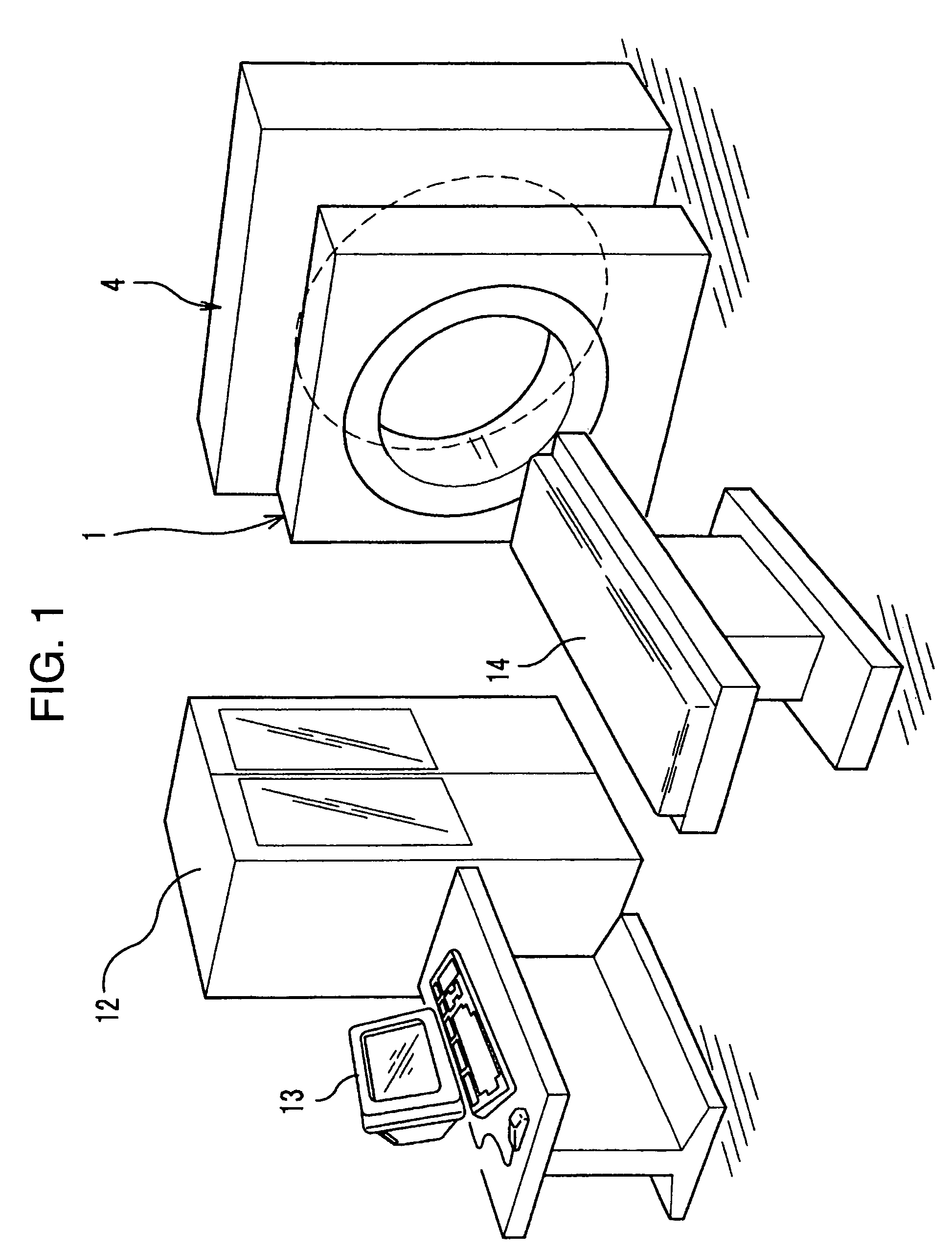
The radiological imaging system which can improve an energy resolution and perform a diagnosis with high accuracy includes a bed for carrying an examinee H, first and second imaging apparatuses and disposed along the longitudinal direction of the bed. The first imaging apparatus has a plurality of semiconductor radiation detectors for detecting γ-rays emitted from the examinee H, arranged around the bed, the second imaging apparatus has an X-ray source for emitting X-rays to the examinee H and a radiation detector for detecting X-rays which have been emitted from the X-ray source and passed through the examinee H, and the bed is shared by the first imaging apparatus and the second imaging apparatus.
Owner:UENO YUUICHIROU +7
Radiological imaging system
InactiveUS7683338B2Improve quantitativenessImprove detection accuracyTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesImage resolutionSemiconductor radiation detectors
The radiological imaging system which can improve an energy resolution and perform a diagnosis with high accuracy includes a bed for carrying an examinee H, first and second imaging apparatuses and disposed along the longitudinal direction of the bed. The first imaging apparatus has a plurality of semiconductor radiation detectors for detecting γ-rays emitted from the examinee H, arranged around the bed, the second imaging apparatus has an X-ray source for emitting X-rays to the examinee H and a radiation detector for detecting X-rays which have been emitted from the X-ray source and passed through the examinee H, and the bed is shared by the first imaging apparatus and the second imaging apparatus.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Quasi-continuous or continuous laser spinning resolving photoelectron energy spectrum analysis device
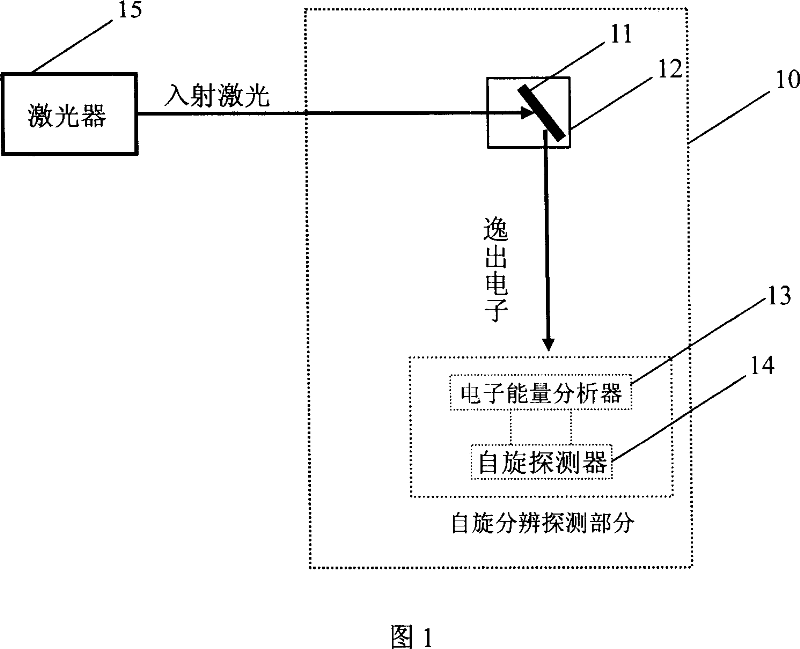
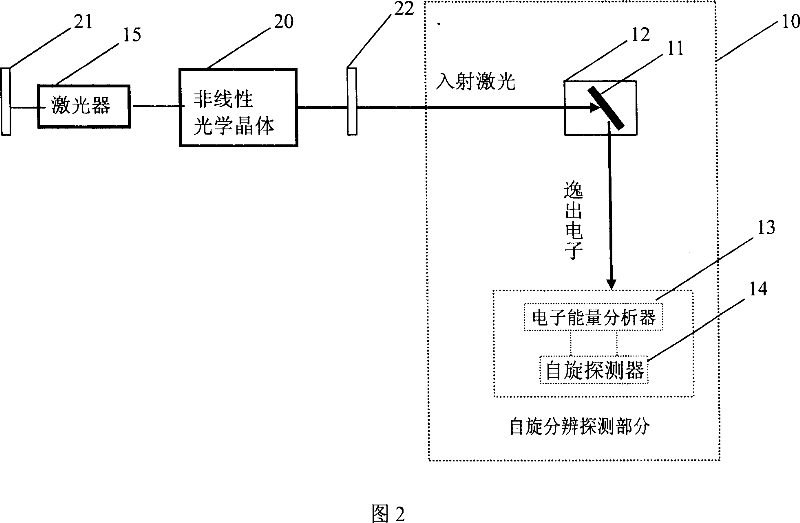
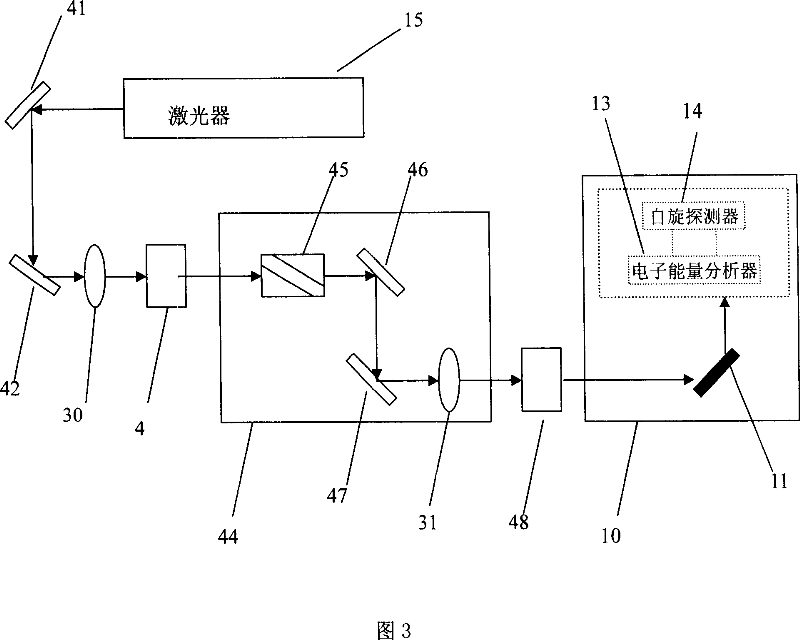
ActiveCN101038330AAchieving a comprehensive descriptionImproved energy resolutionMagnetic property measurementsLaser lightVolt
The invention discloses a quasi-continuous or continuous laser spin photoelectron spectroscopy analyzer, consists of vacuum chamber, specimen stand in the vacuum chamber for fixing and manipulating the specimen, and the electron energy analyzer and spin detector at the side of specimen stand; characterized in that still includes a laser at the laser light inlet of the vacuum chamber, the laser light sent by laser shall be injected into the vacuum chamber from its inlet and injected to the specimen on the specimen stand, the laser photon energy on the specimen is higher than 5 electron-volt; the laser light from the laser is a quasi-continuous laser or continuous laser. The advantage of the invention is improving the energy resolution, and momentum resolution, it is a high efficient, easy to operate, and low cost device for measuring the accurate electron spinning state of materials and even fully describe the electron state of materials.
Owner:INST OF PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Ultra high-resolution radiation detector (UHRD) and method for fabrication thereof
InactiveUS20090026569A1Reduce driftReduce resolutionSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotovoltaic energy generationField-effect transistorP–n junction
An ultra high-resolution radiation detector and method for fabrication thereof, has a detector chip, comprising the so-called drift rings and an amplifier integrated with the diode component, centrally located n-type anode on one surface, the depletion region. The detector chip has a circular field of view, the depletion region which also has a circular field of view by ion implanting symmetrical p-n junctions on the surface of the radiation entrance side of the detector chip, said centrally n-type anode located on the opposite surface of the depletion region, and its position is in the region which outer of the depletion region, said centrally n-type anode was surrounded by a plurality of p-type drift electrode rings, which have an gibbous circularity topology; wherein the focus of said p-type drift electrode rings is the position of the anode, said FET (Field-Effect Transistor) was integrated in the position of the detector's anode and directly coupled to the detector's anode. The p-type drift electrode rings is a plurality of drift rings which have gibbous circularity topology, wherein the gibbous circularity topology is encircled by a majority of a large circularity and a small circularity, wherein the maximum of the depletion region is the opposite surface of the region encircled by the outermost p-type drift electrode ring.
Owner:SHENZHEN SKYRAY INSTR
CdZnTe planar detector surface treatment method
InactiveCN107123698AReduce leakage currentReduce scatterFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesImage resolutionDangling bond
The invention discloses a CdZnTe planar detector surface treatment method and is to solve the technical problem of poor energy resolution of a planar detector obtained after processing of an existing planar detector surface treatment method. The technical scheme is characterized by, after corrosion of a CdZnTe wafer, carrying out passivation on the surface of the CdZnTe wafer through a (NH4)2S solution; carrying out cleaning after passivation through deionized water; and finally, plating an Au electrode onto the two surfaces of the wafer through a vacuum evaporator. Through the passivation method, a Te-rich layer is removed, a CdS layer is deposited on the surface of the wafer, and stoichiometric ratio is improved, thereby reducing scattering of electrons on the surface of the crystal; dangling bonds formed after corrosion are neutralized, thereby reducing leak current on the surface of the CdZnTe wafer, improving energy resolution and improving detection efficiency of the CdZnTe planar detector; and through test, the energy resolution of the CZT planar detector is improved from original energy resolution larger than 6.5% to energy resolution smaller than 4.5%.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Method and appts. for gamma radiation detection imaging
InactiveCN1564022AImprove spatial resolutionHigh resolutionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentPhotocathodeGamma ray
Photocathode is coated by vaporization on surface of scintillating crystal array. Crystal array emits scintillating light caused by gamma rays. Photoelectrons are excitated under action between scintillating light and photocathode material. Photoelectrons are collected and exported. After gain amplification of the signal, Energy and spatial location of gamma rays are calculated from signal of impulse voltage. In the equipment, scintillating crystal array is placed in insulated bracket in vacuum chamber. Photocathode is on one side of the scintillating crystal array, and grid electrode is led out. Microchannel plate and imaging anode are in on another side of photocathode. One end of leading out cable is connected to imaging anode, and the other end is out of vacuum envelope. Features are high resolution in space and energy, and compact size.
Owner:谢舒平 +2
Radiation detector and radiation detection device
ActiveCN103913763AImproved energy resolutionAchieving Single Charge Sensitive PropertiesX-ray spectral distribution measurementSignal processing circuitsSemiconductor
The invention discloses a radiation detector and a radiation detection device comprising the radiation detector. The radiation detector comprises a semiconductor crystal used for sensing radiation, a first anode arranged on the top surface the semiconductor crystal, a second anode arranged on the bottom surface of the semiconductor crystal, and one cathode on at least one side face of the semiconductor crystal. The semiconductor crystal comprises the top surface, the bottom surface and at least one side face. The radiation detection device comprises the radiation detector and a signal processing circuit. The radiation detector achieves the feature of singly-charged flexibility by utilizing the double-anode structure which is simple, and energy resolution is improved.
Owner:NUCTECH CO LTD +1
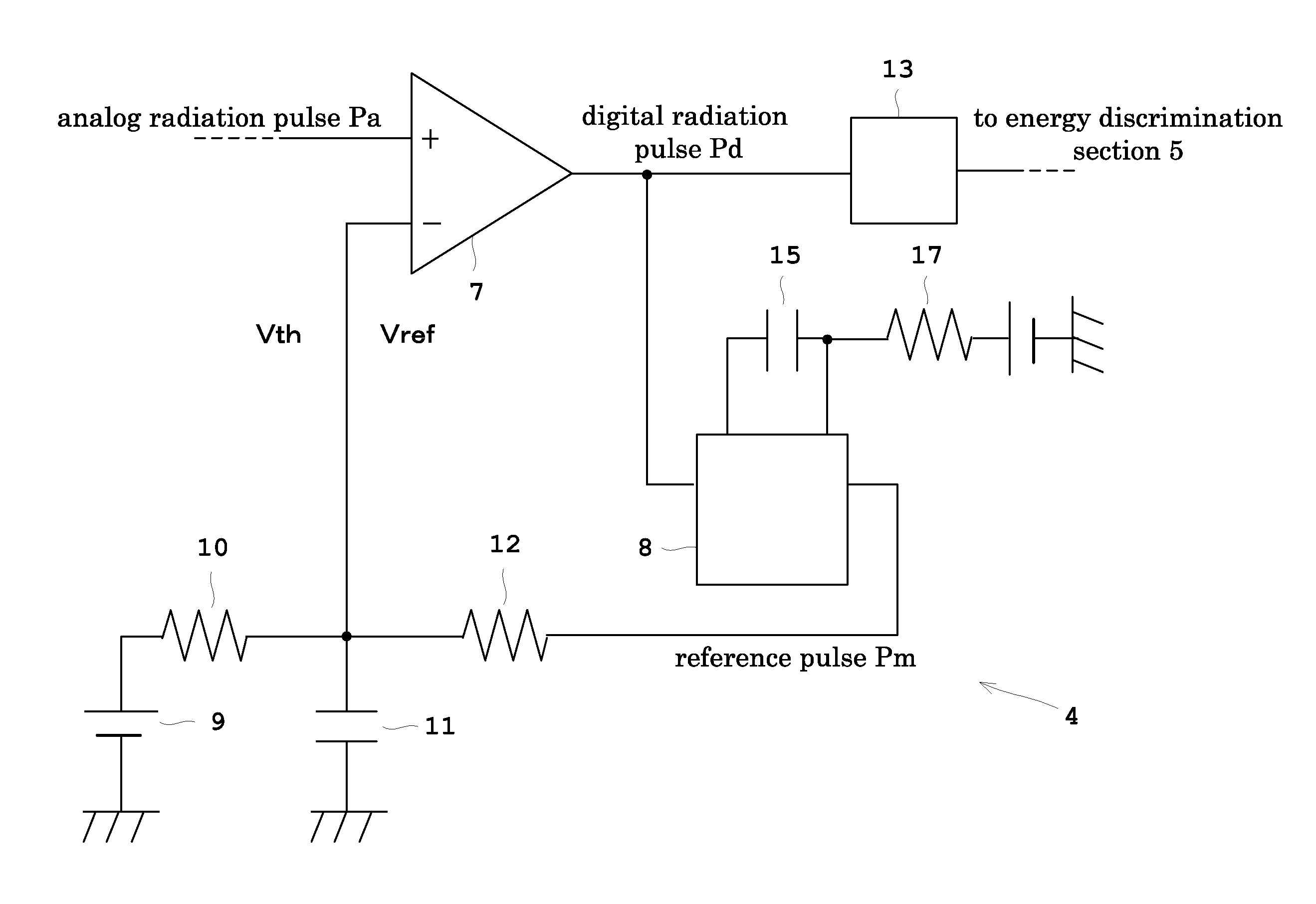
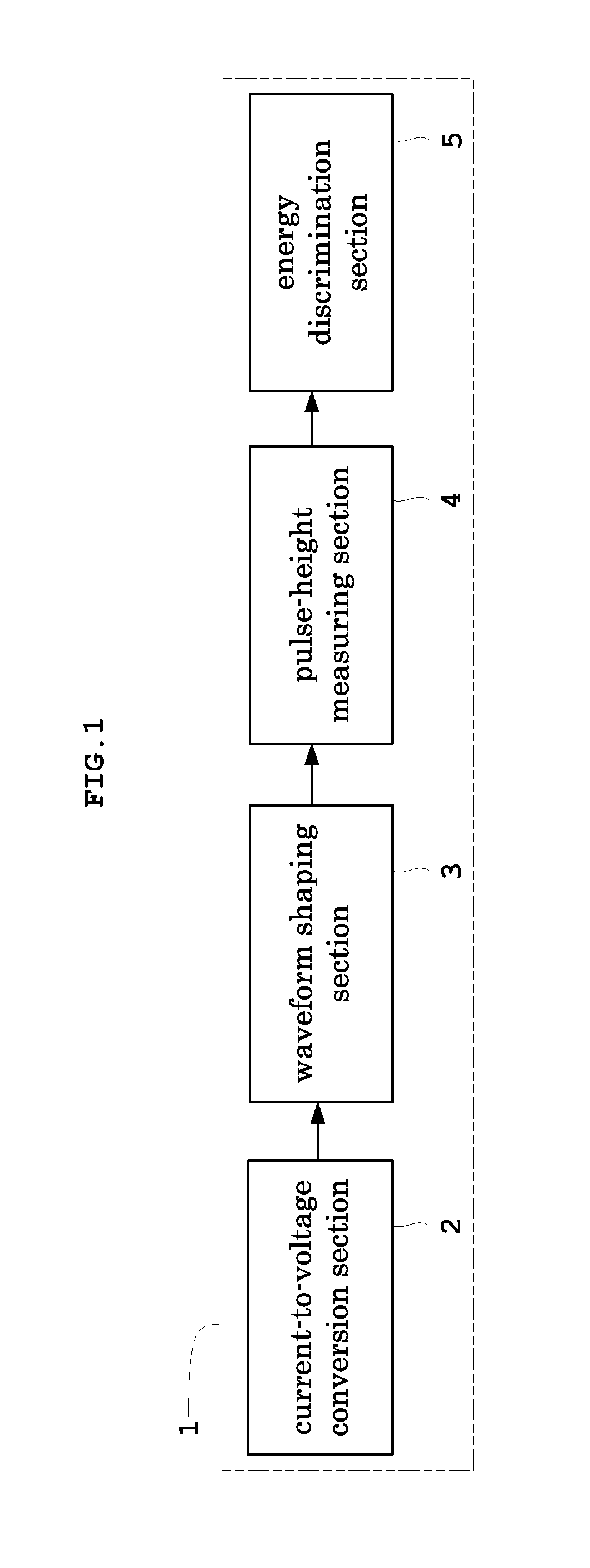
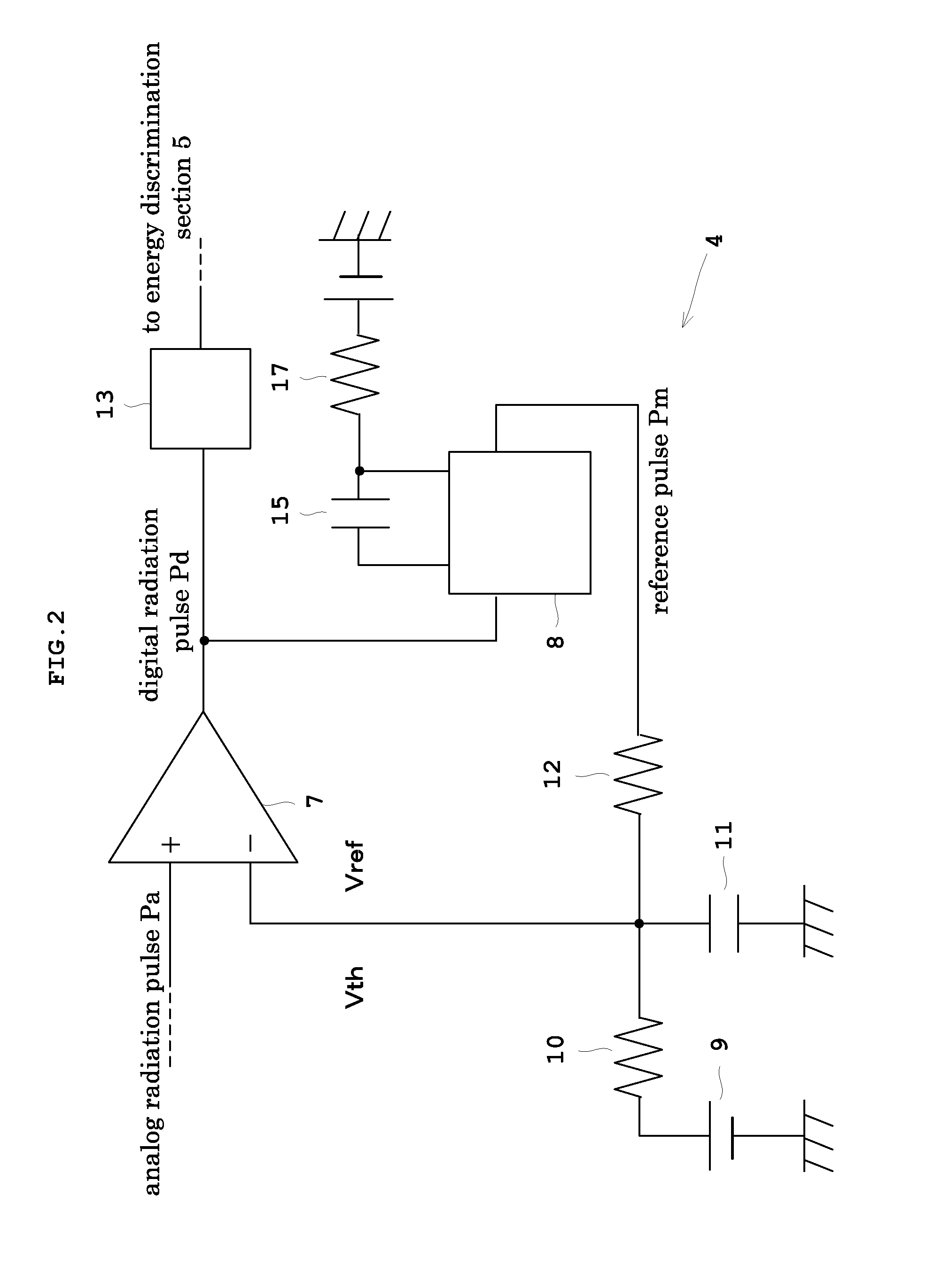
Pulse height analyzer and nuclear medicine diagnosis apparatus provided with the same
ActiveUS20120184848A1Improve linearityImproved energy resolutionPhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansPulse height analyzerRadiation pulse
With a pulse-height analyzer, a reference-pulse generator generates a reference pulse of a given pulse height for a given period of time when an analog radiation pulse inputted to a comparator is higher than an initial threshold. A capacitor and a resistor receive the reference pulse, and then increase an increment threshold for the given period of time from the initial threshold to the given pulse height. Then the increment threshold is set as a reference voltage of the comparator. A pulse time width of the analog radiation pulse is determined through measuring a period of time from timing where the analog radiation pulse exceeds the initial threshold to timing where the analog radiation pulse being attenuated falls below the increment threshold.
Owner:SHIMADZU CORP +1
Calorimeter
InactiveUS20040030505A1Maintenance of superconductivitySuppress mutationThermometer detailsCalorimetric dosimetersX-rayJoule
A superconducting radiation detector uses the abruptness of a superconducting transition edge, converts a slight heat generated by an X-ray into a high signal current, and uses an electrothermal self-feedback mechanism, thereby having a high energy resolution and a high counting rate. In a calorimeter that includes an absorber for absorbing X-rays, a resistor provided under the absorber, a resistance value thereof being changed by heat generated in the absorber, superconducting wires connecting the resistor and an external current detector, and a membrane on which the resistor is superimposed, the resistor being constituted by a superconductor, the calorimeter allowing Joule heat generated by steadily flowing a current in the resistor and the heat generated in the absorber to be thermally balanced and transfer in the membrane, an insulating film is provided between the resistor and the absorber, the film having a hole penetrating the film in the thickness direction.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
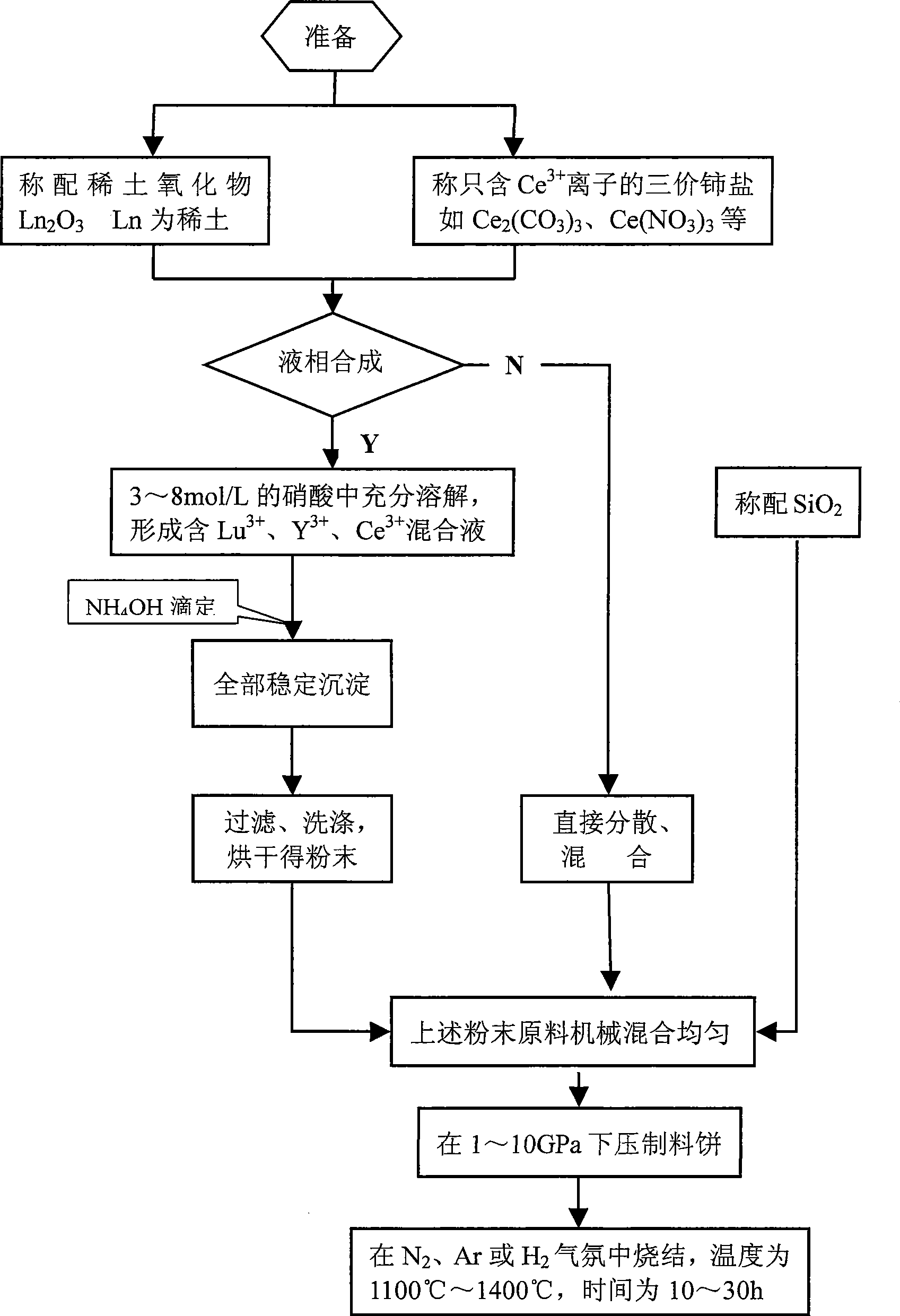
Rare earth silicates polycrystal material doped with Ce<3+> and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN101377020ALower sintering temperatureHigh purityPolycrystalline material growthSingle crystal growth detailsRare earthQuenching
The invention relates to a cerous ion-doped rare earth silicate polycrystal material and a preparation method thereof, which is characterized in that the rare earth silicate is lutecium silicate, yttrium silicate or lutecium and yttrium silicate; the mol percentage of the doped cerous compound is 0.2 percent to 2 percent; the general formula of the doped rare earth silicate is Ln<2(1-x)>Ce2xSiO3, wherein, x is equal to0.002 to 0.02, and Lu is one or two types of Y and Lu. The doped cerous compound is Ce2(CO3)3, Ce(NO3)3, Ce2(C2O4)3, Ce(CH3COO)3 or Ce(OH)3. The polycrystal material is directly synthesized or prepared by doping the cerous compound and liquid-phase mixing. The invention most reduces the introduction of Ce<+4> raw material, eliminates the quenching impact of the Ce<+4> on the luminescence of Ce<+3>, reduces the sintering temperature of the polycrystal material, and improves the scintillation properties of the material, such as light output, energy resolution and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gamma-ray camera system
InactiveUS7504635B2Improved energy resolutionEnhance the imageMaterial analysis by optical meansRadiation diagnosticsEnergy windowImage resolution
A scintillator crystal (26) based gamma-ray camera system is described. The gamma-ray camera system includes a spectra processing component for (34) providing improved energy resolution over that seen in conventional gamma-ray camera systems. The spectra processing component operates to deconvolve detector response functions from observed energy spectra on a pixel by pixel basis. The pixel dependent to detector response functions are obtained by a combination of theoretical simulation, and empirical calibration. By deconvolving pixel specific detector response functions, variations in response of a gamma-ray camera system across its image plane can be accounted for. This offers significant improvements in energy resolution and many of the problems associated with conventional gamma-ray camera systems are reduced. For example, the improved energy resolution allows better rejection of photons associated with Compton scattering events occurring in a source being imaged. This is because a narrower energy window filter can be used without rejecting a significant fraction of non-Compton scattered photons. The spectra processing component can be easily implemented with different types of gamma-ray imagers, for example Anger-type cameras, and may also be retroactively fitted to existing gamma-ray camera systems.
Owner:SYMETRICA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com