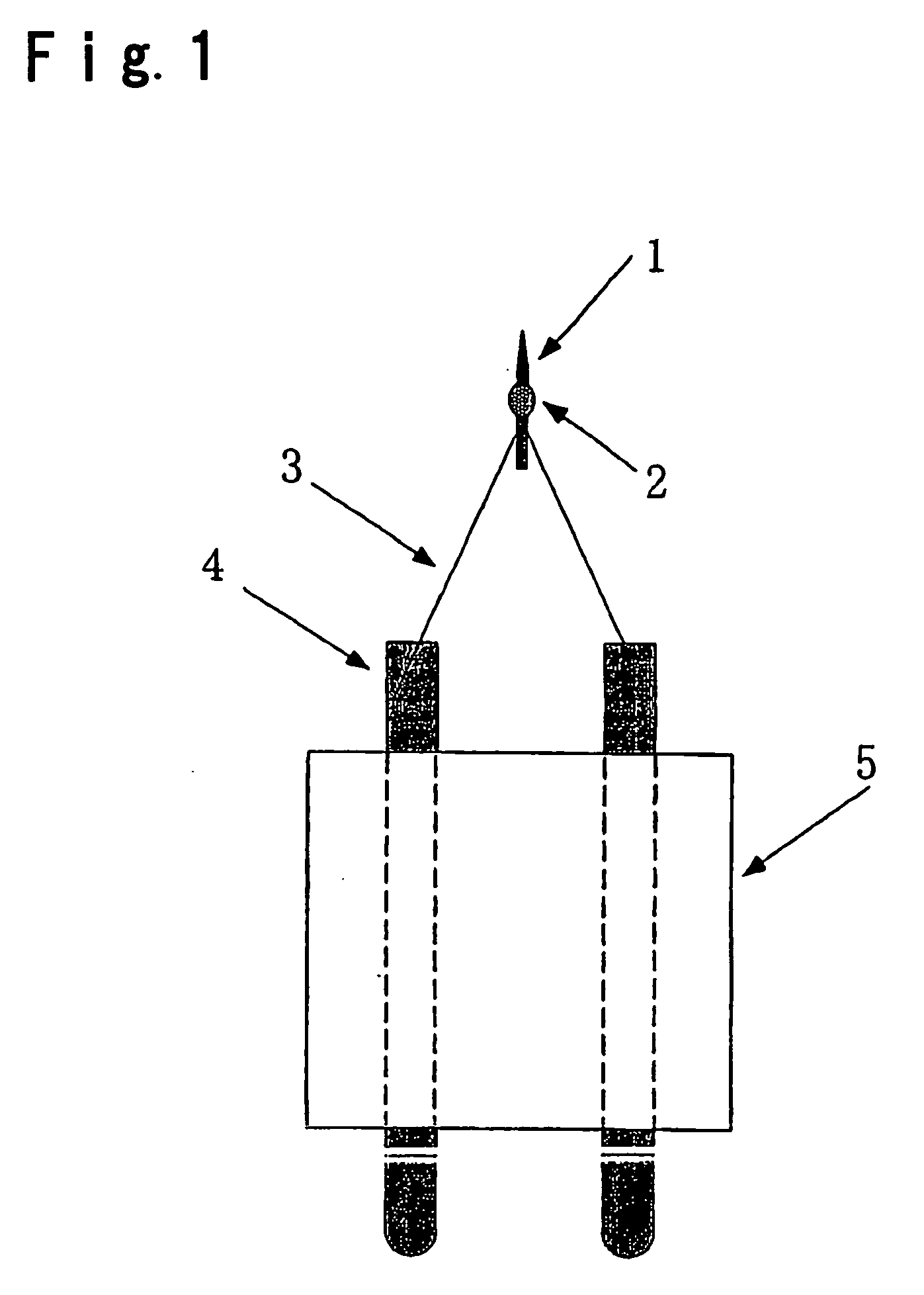
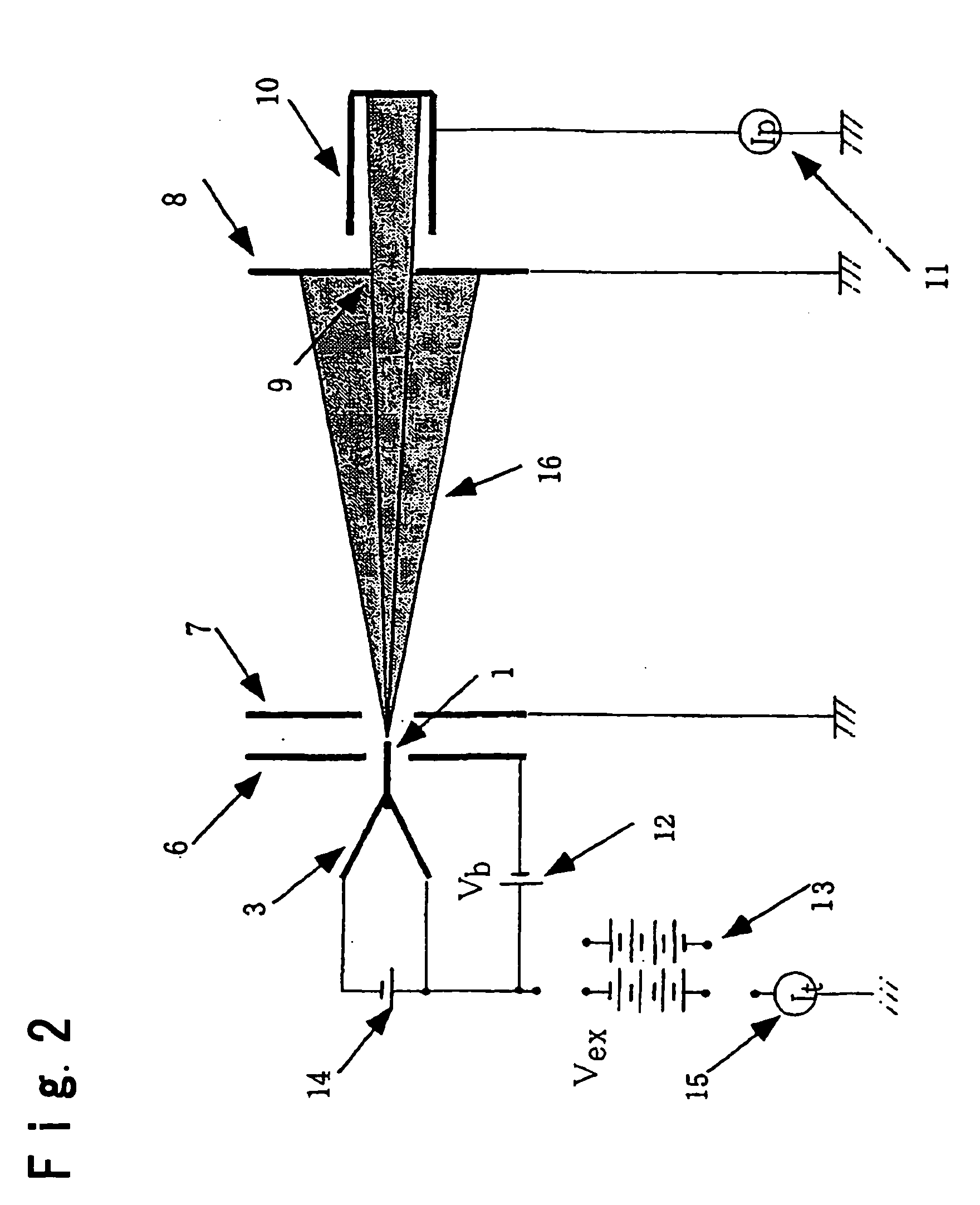
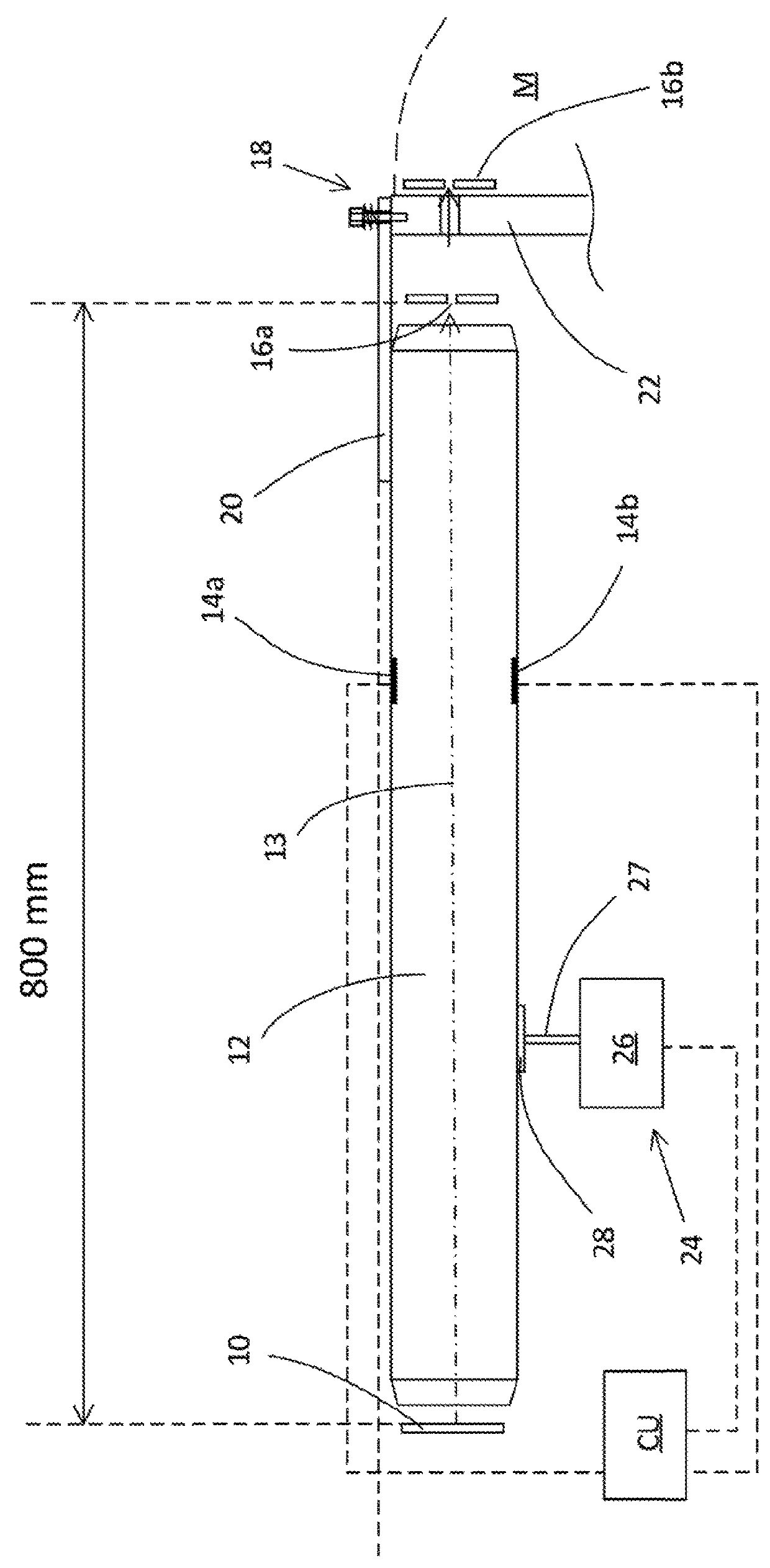
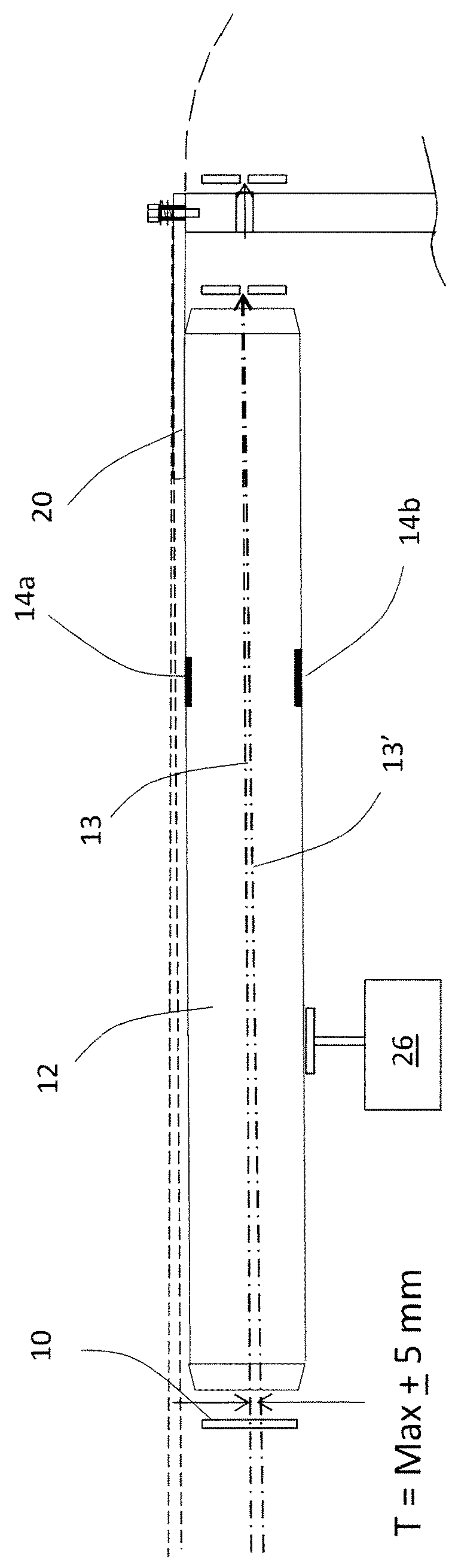
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Electron spectrometer" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
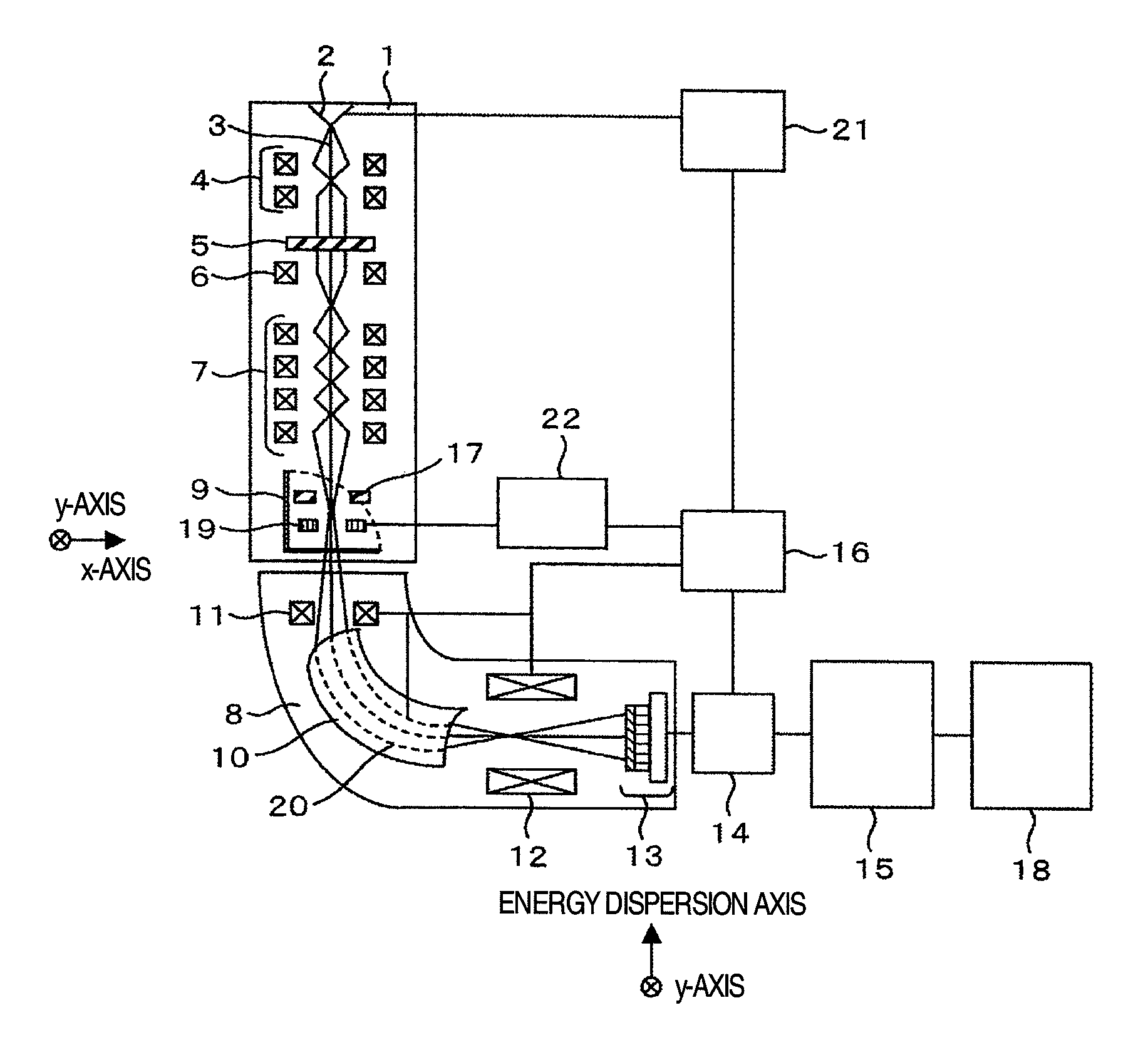
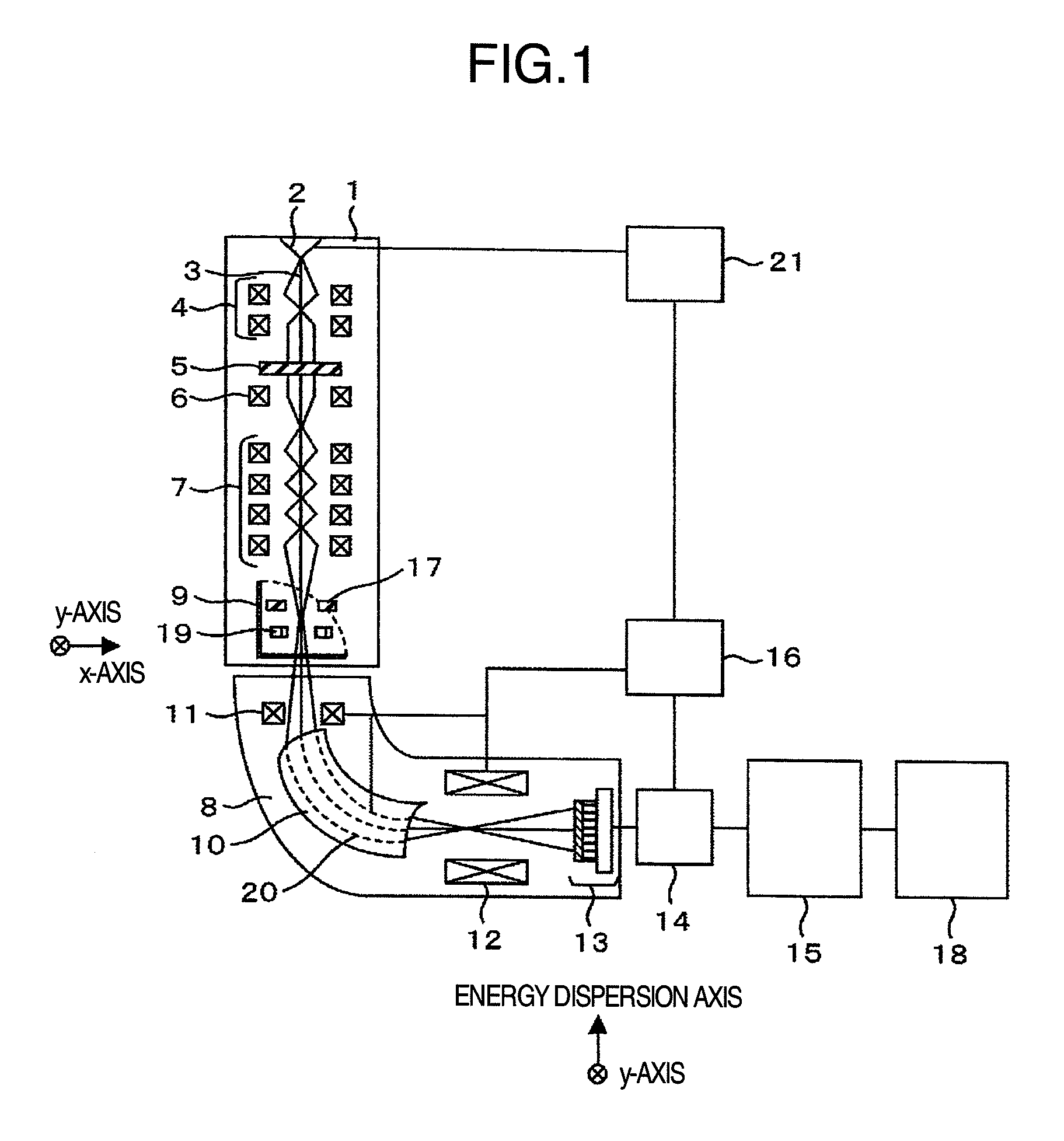
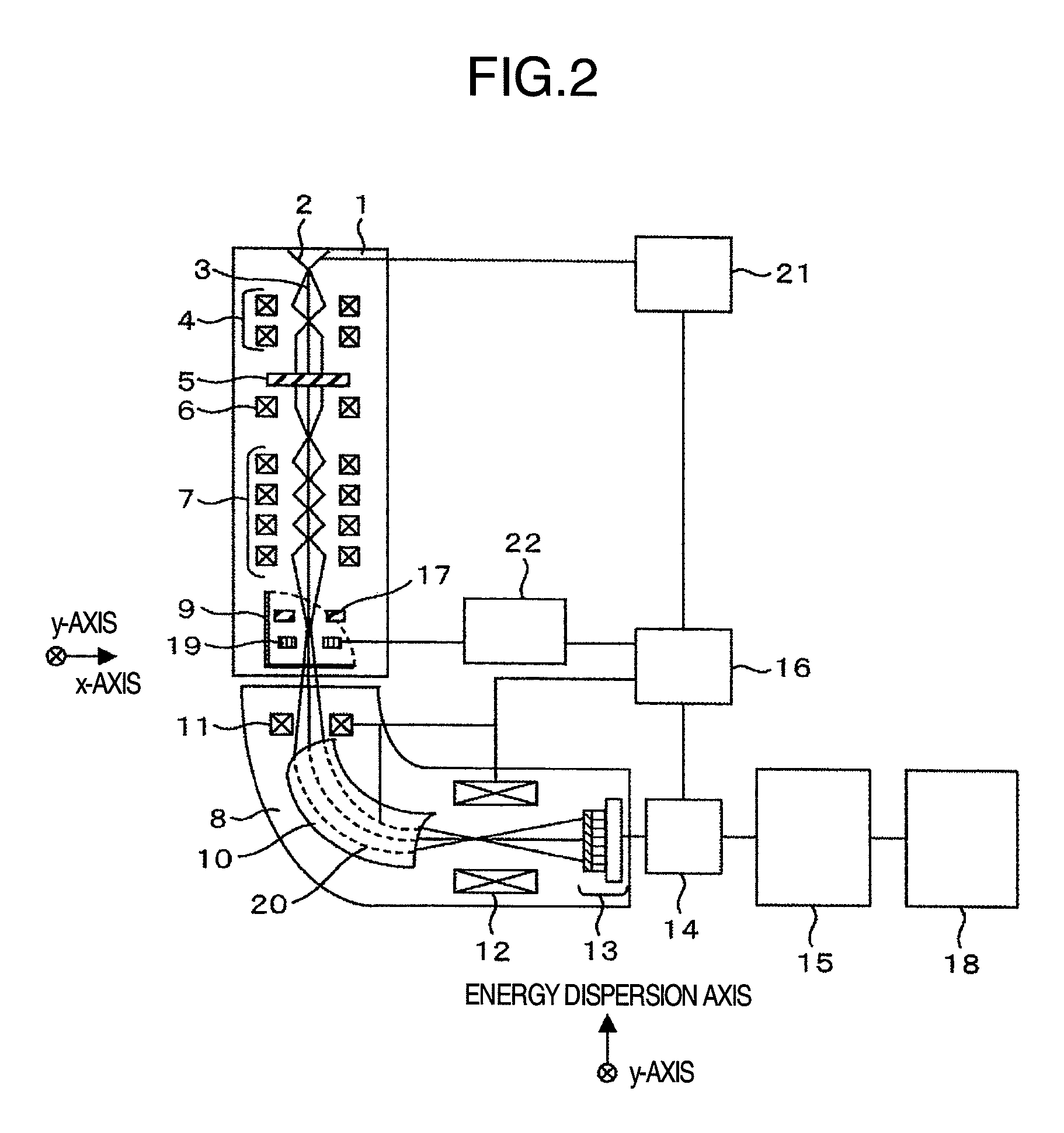
In an electron spectrometer, an incoming beam of electrons is bent with electric or magnetic fields. As higher energy electrons will be bent less by the beam, this produces a spatially distributed range of energies.
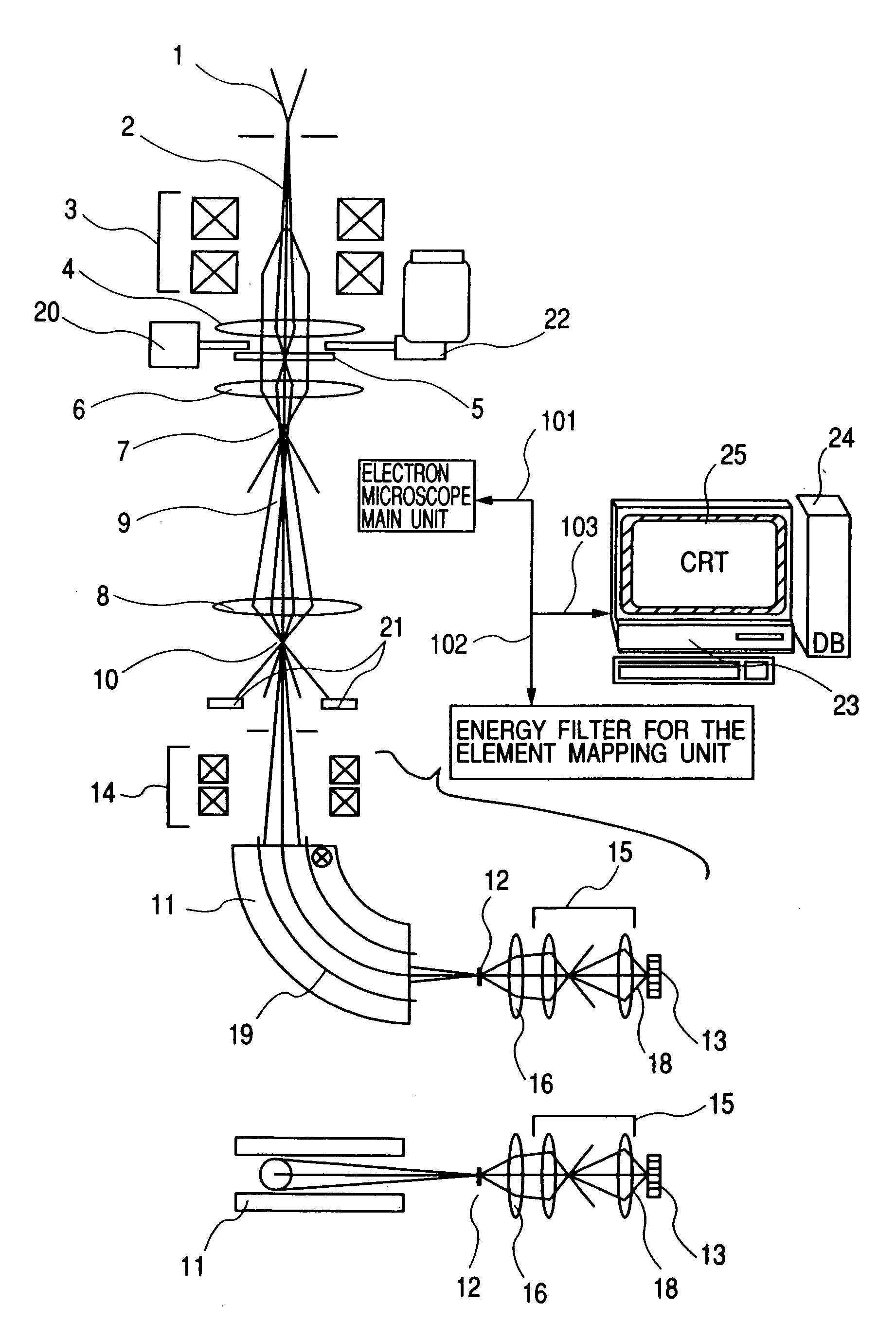
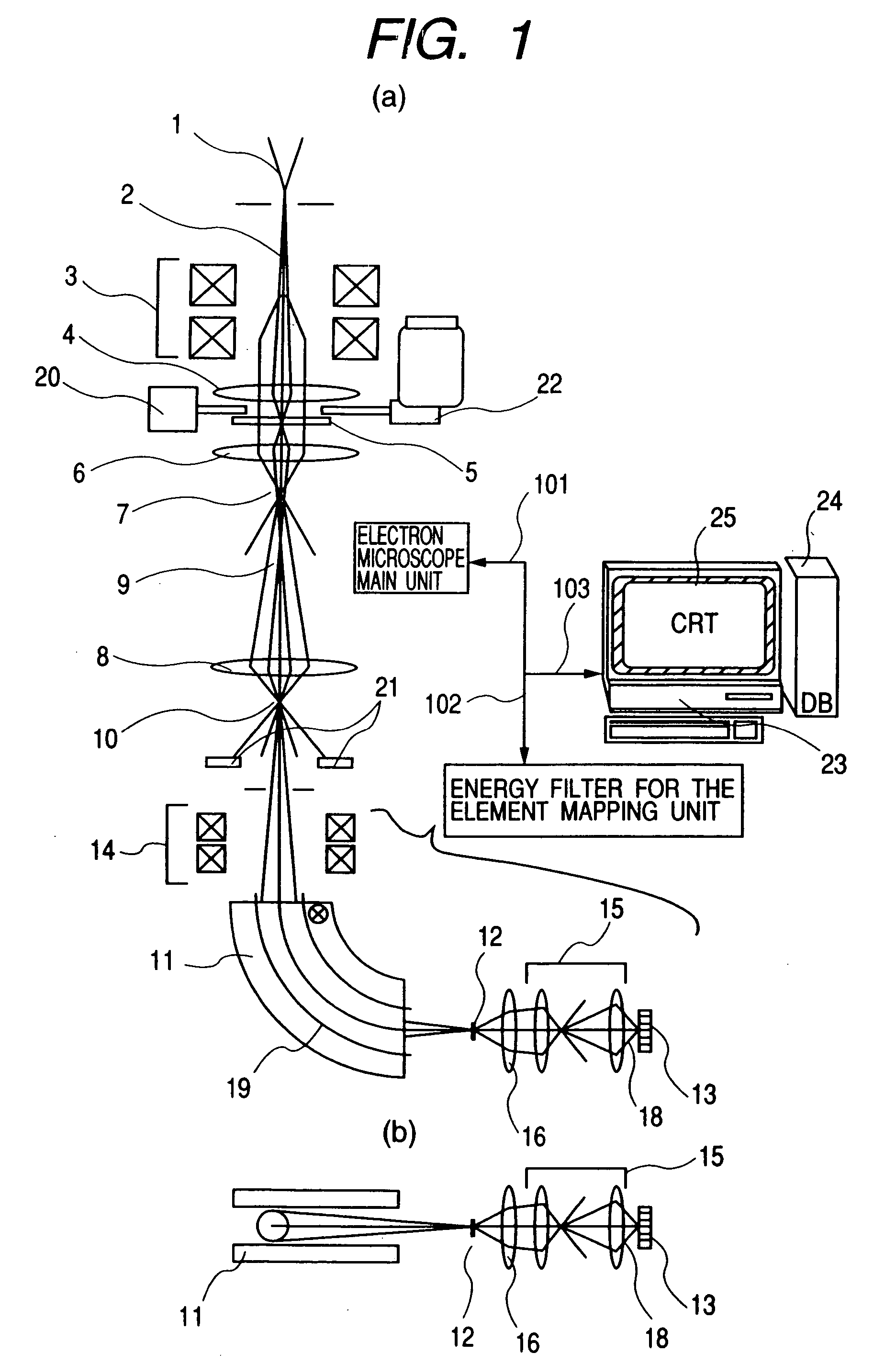
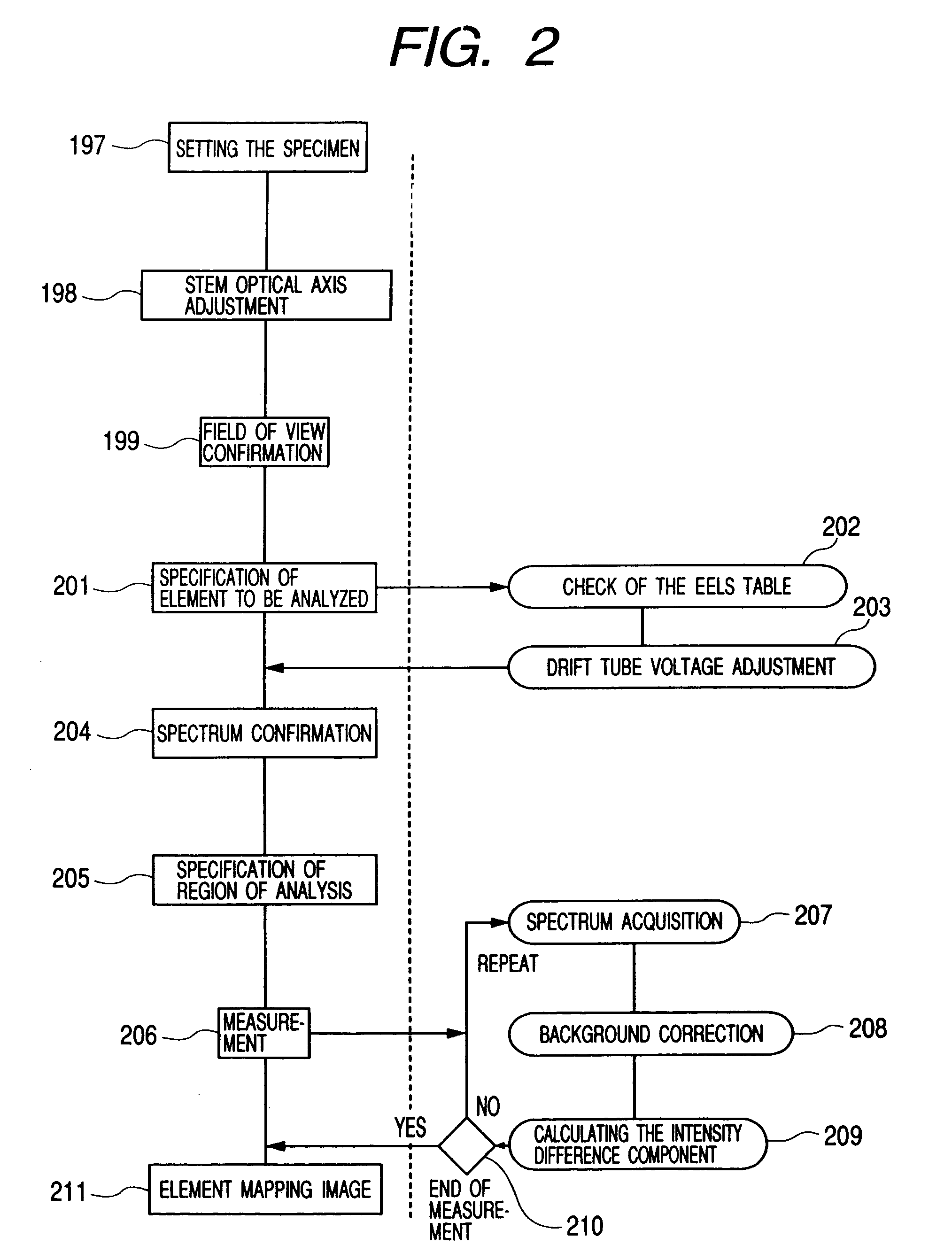
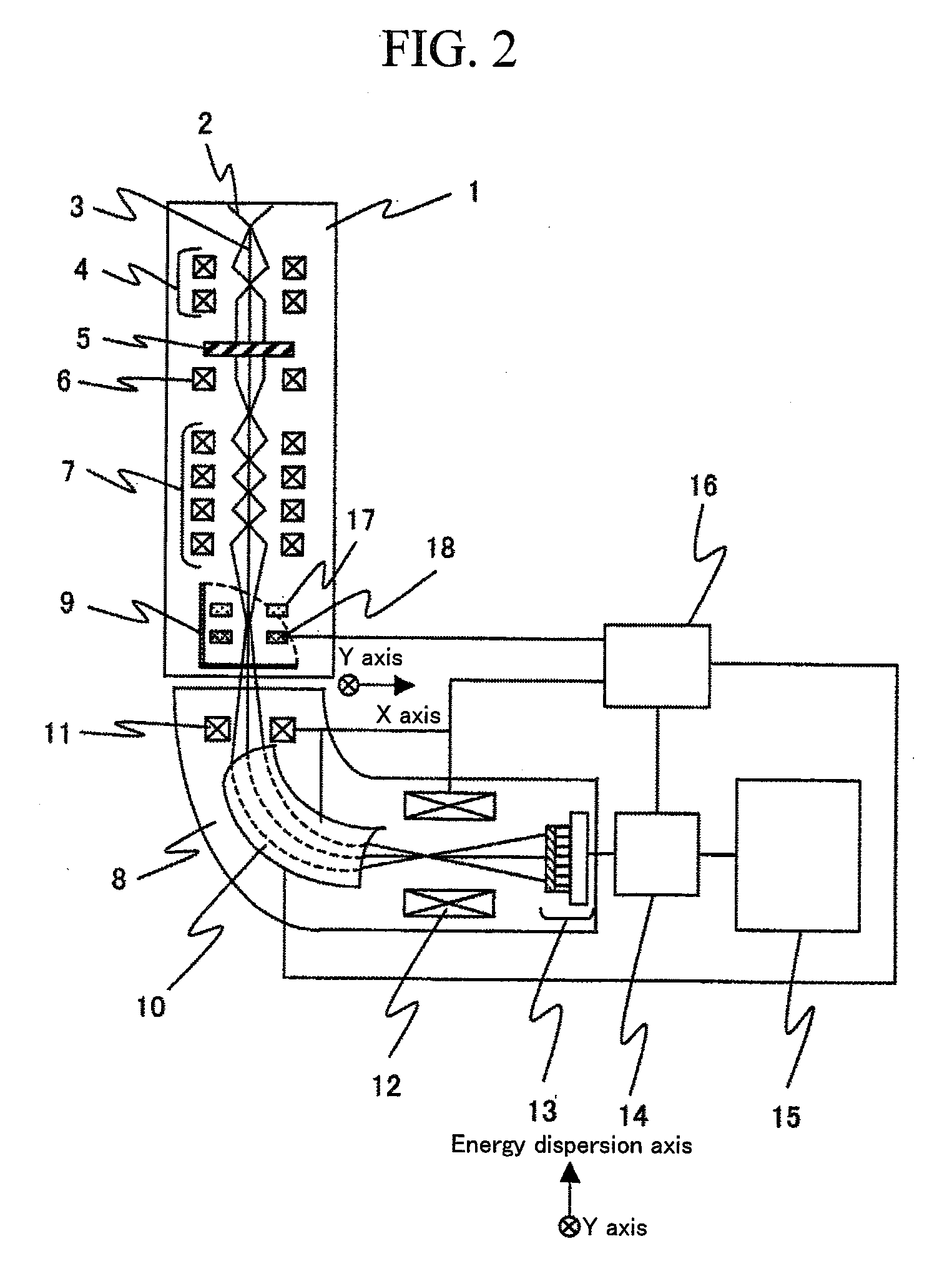
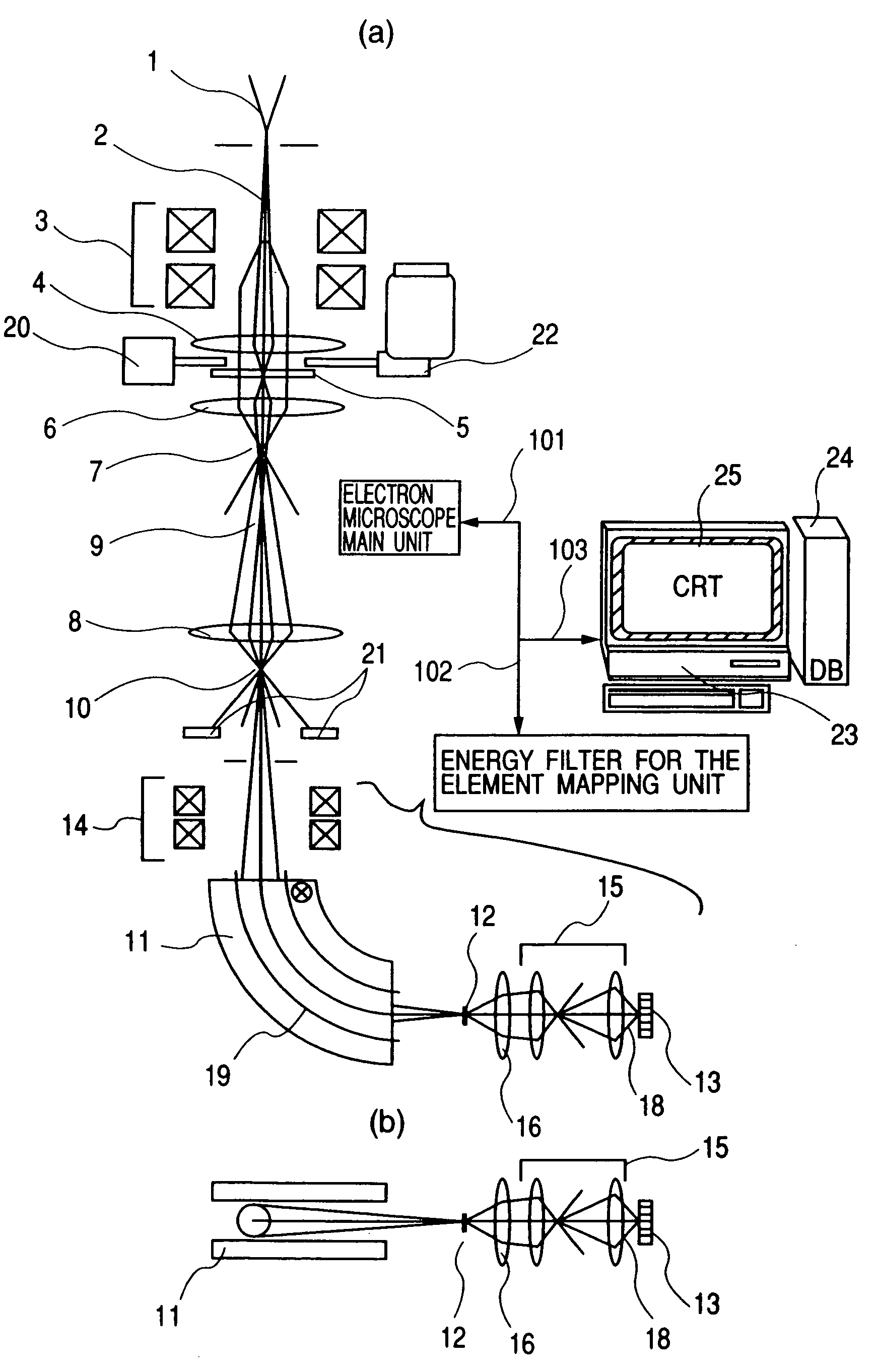
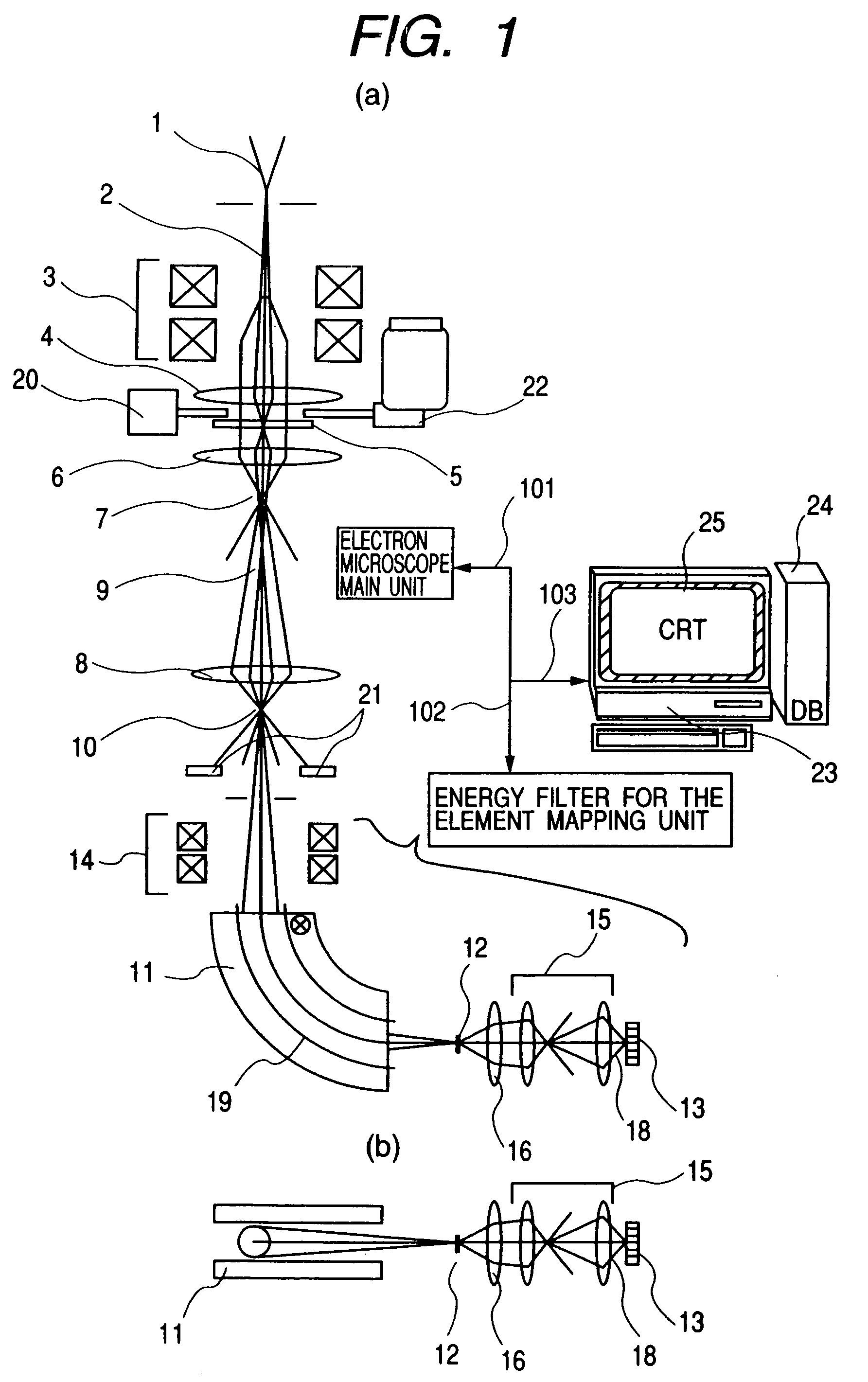
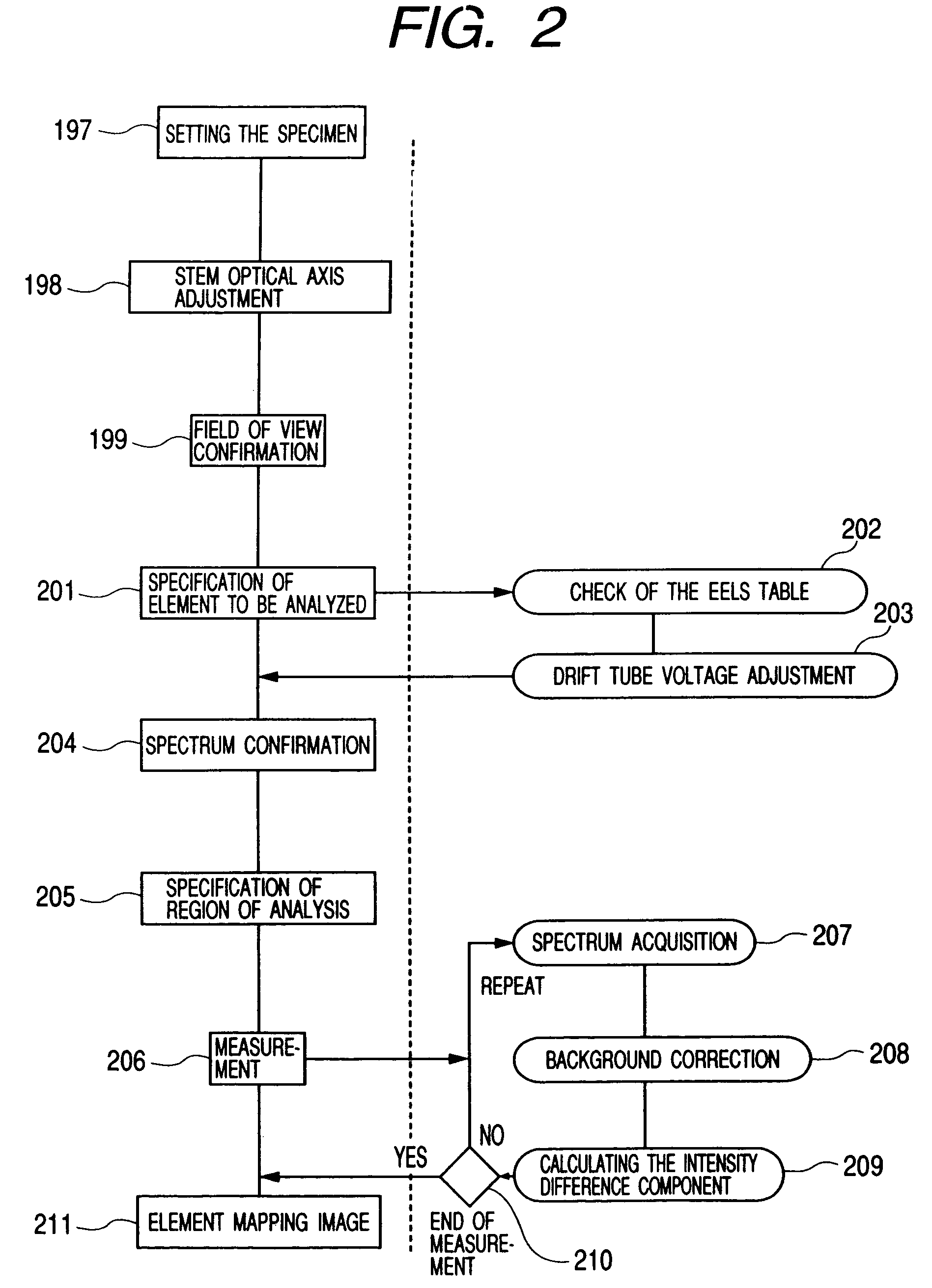
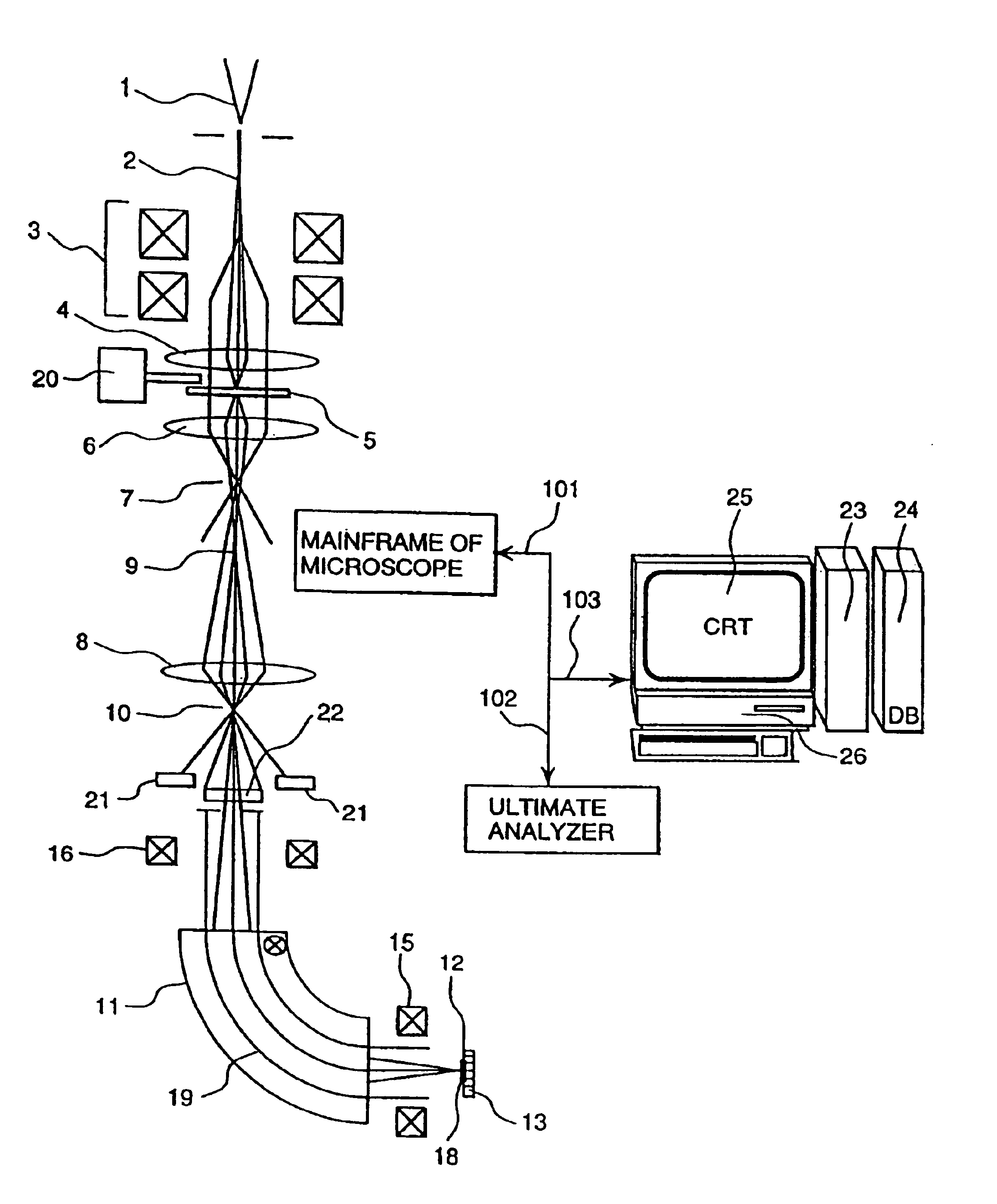
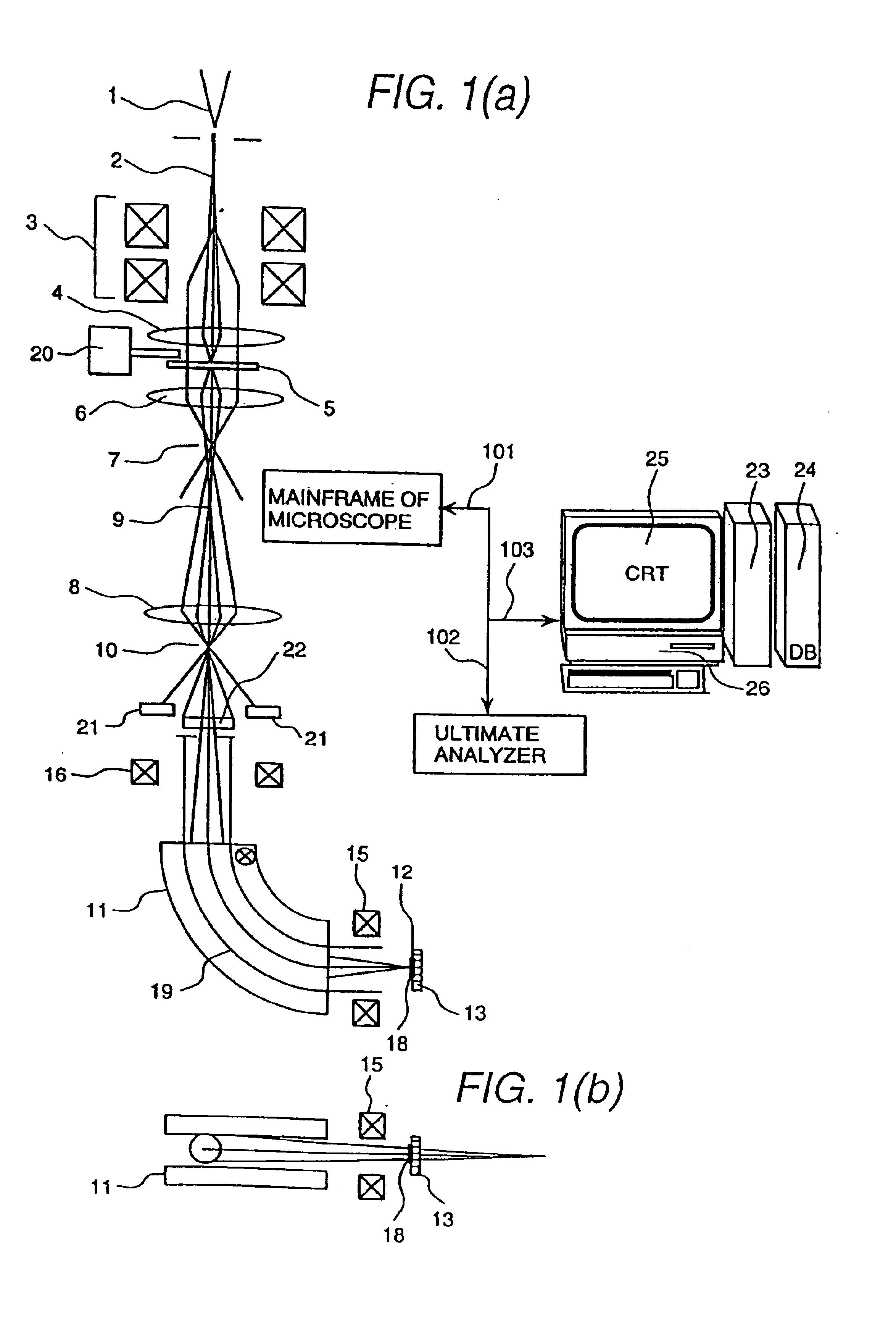
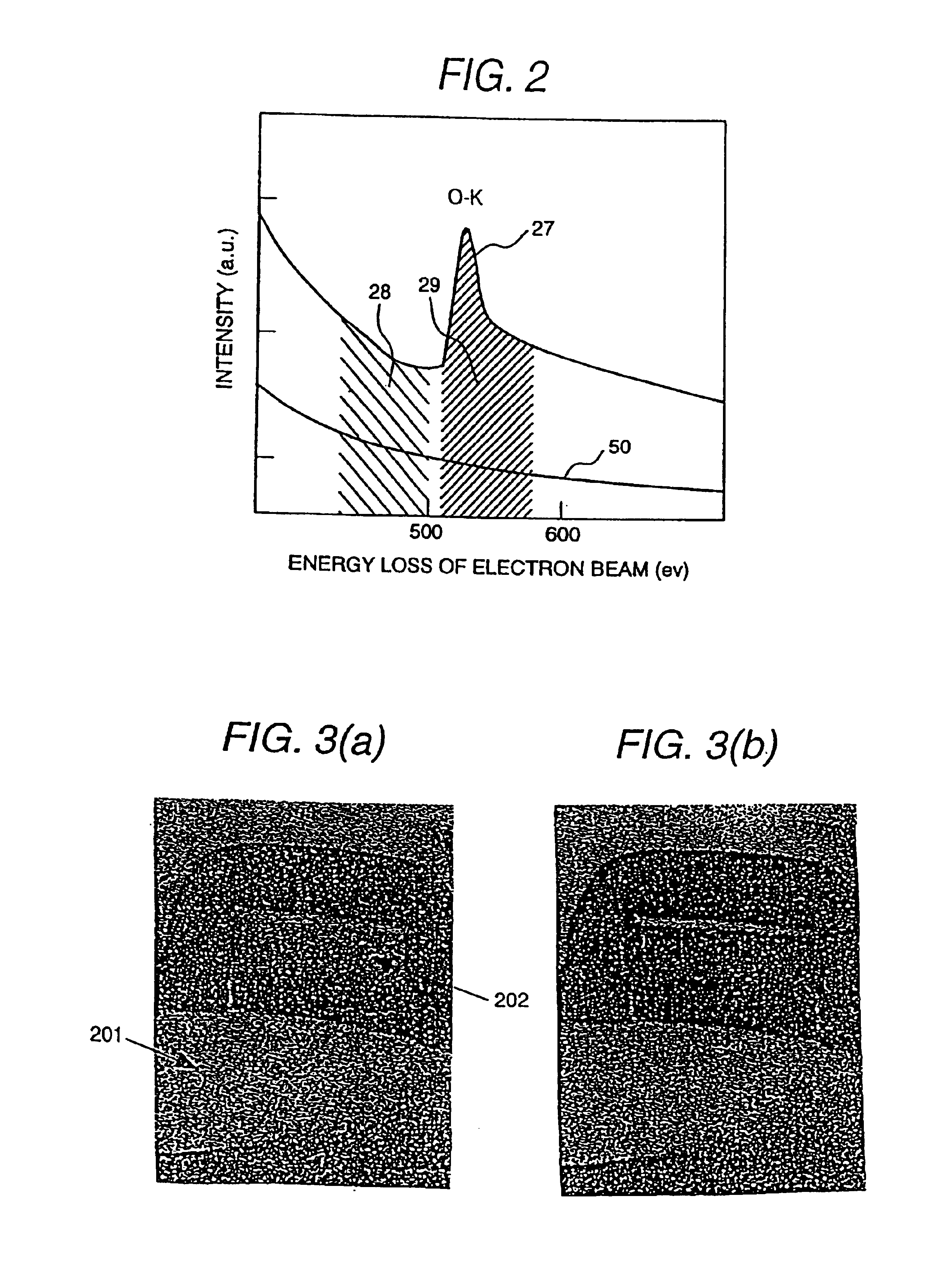
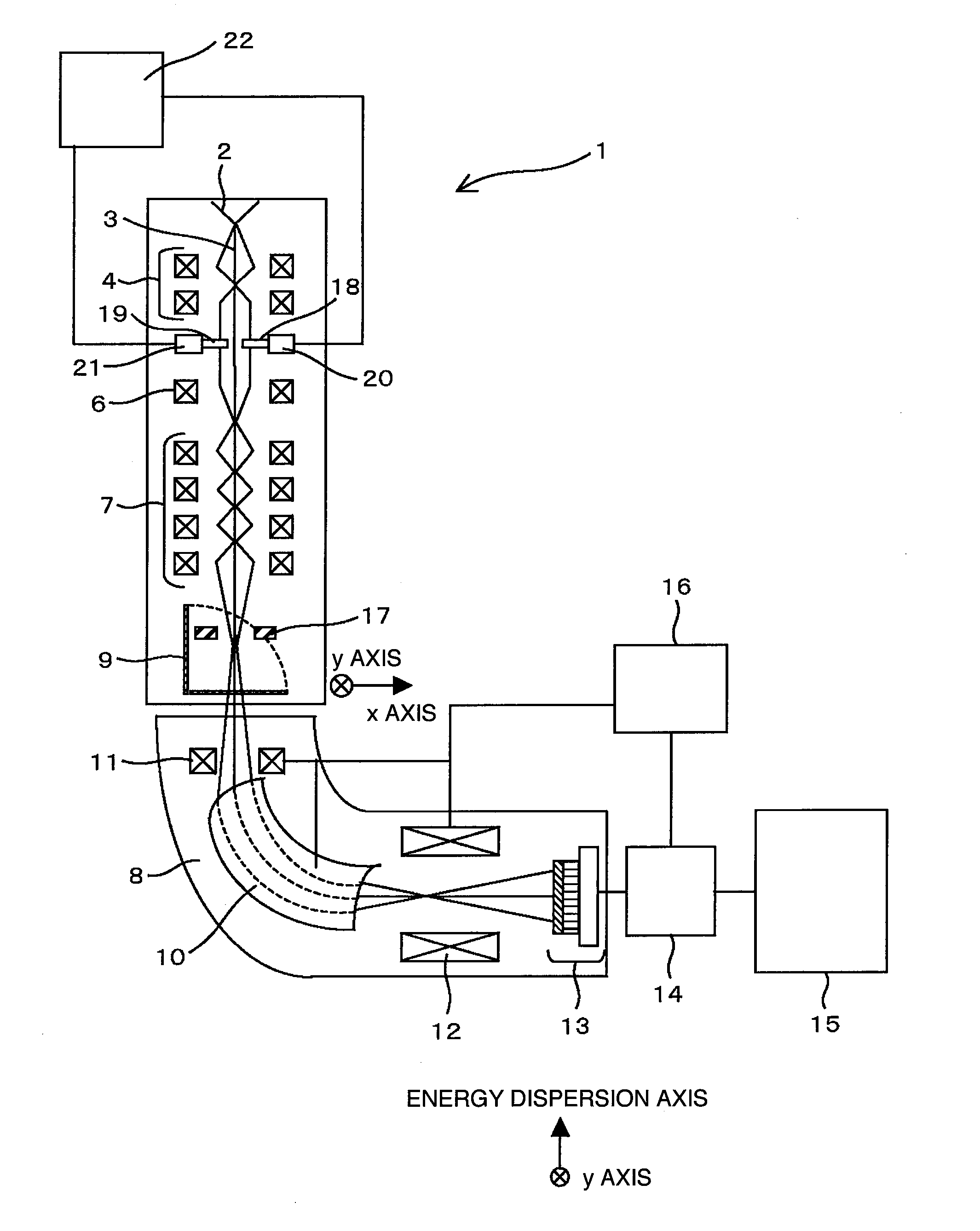
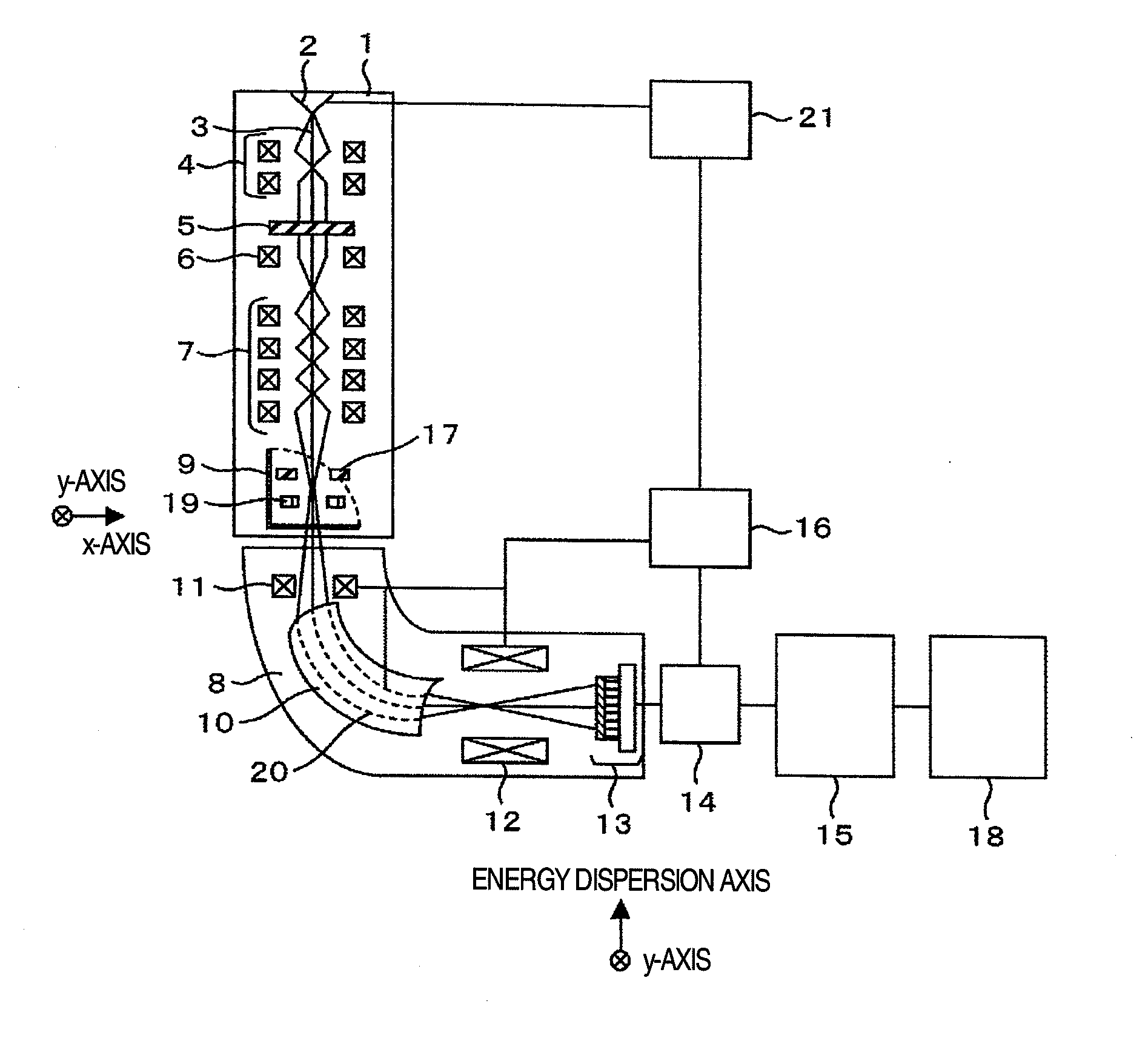
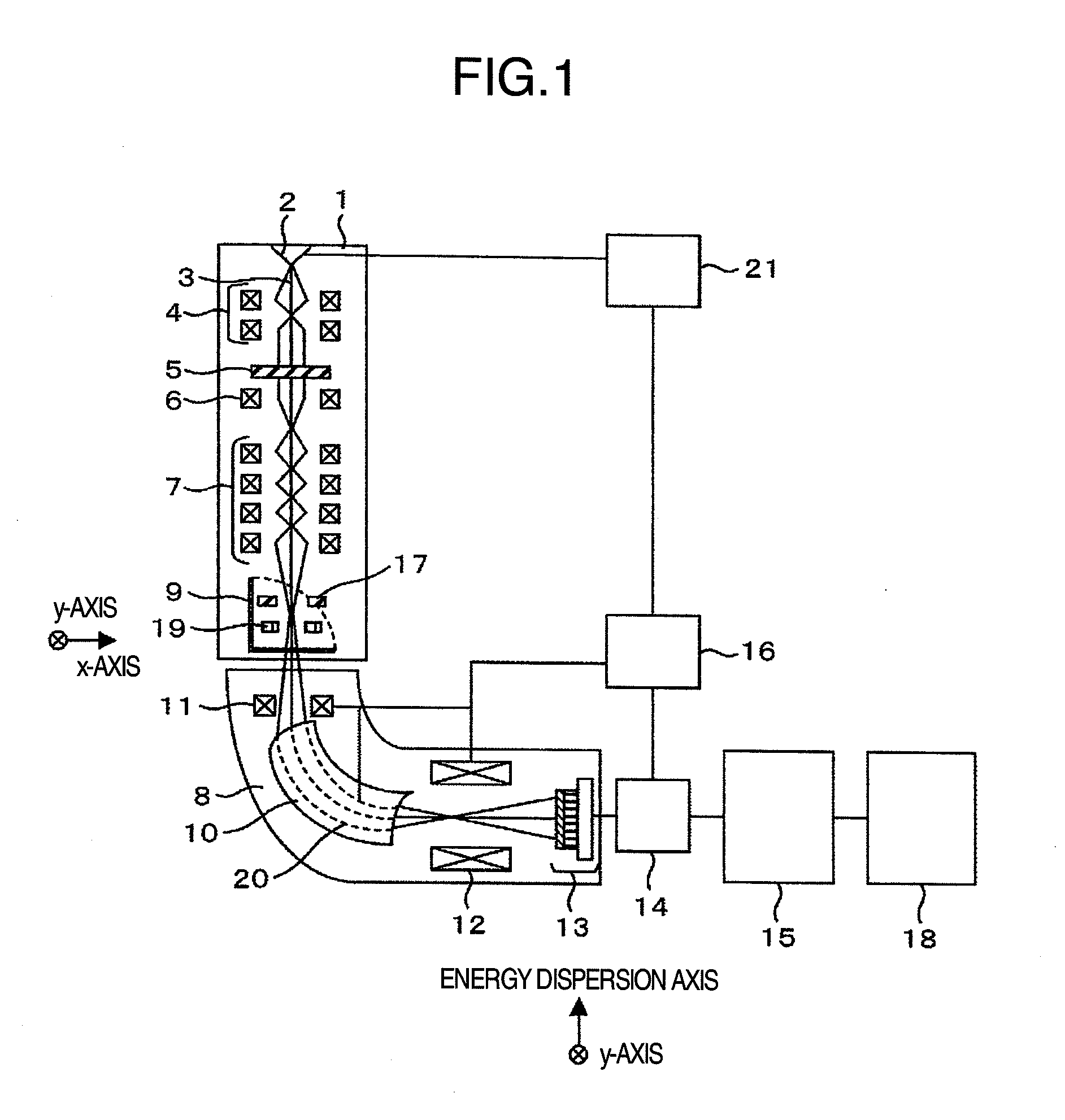
Element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method
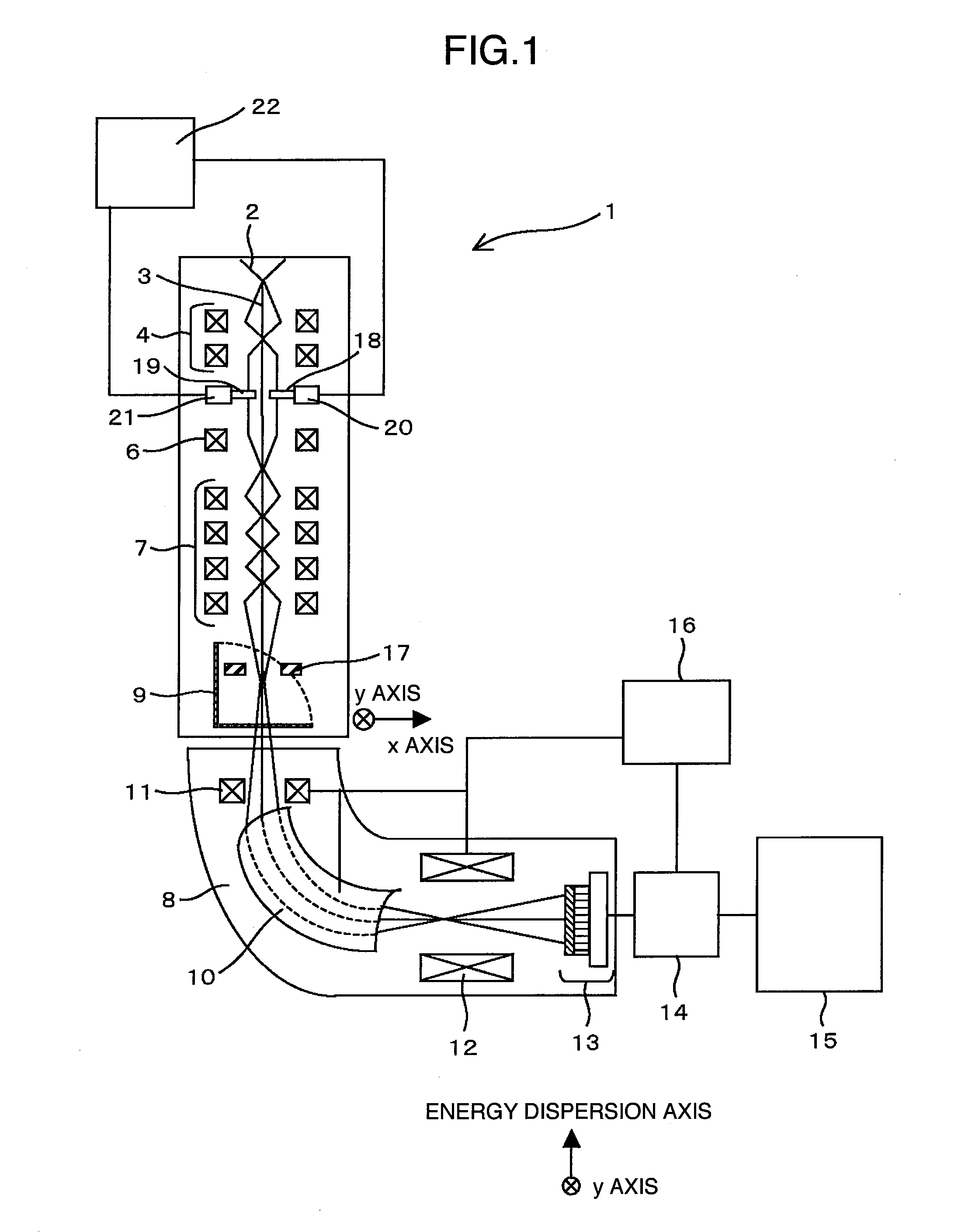
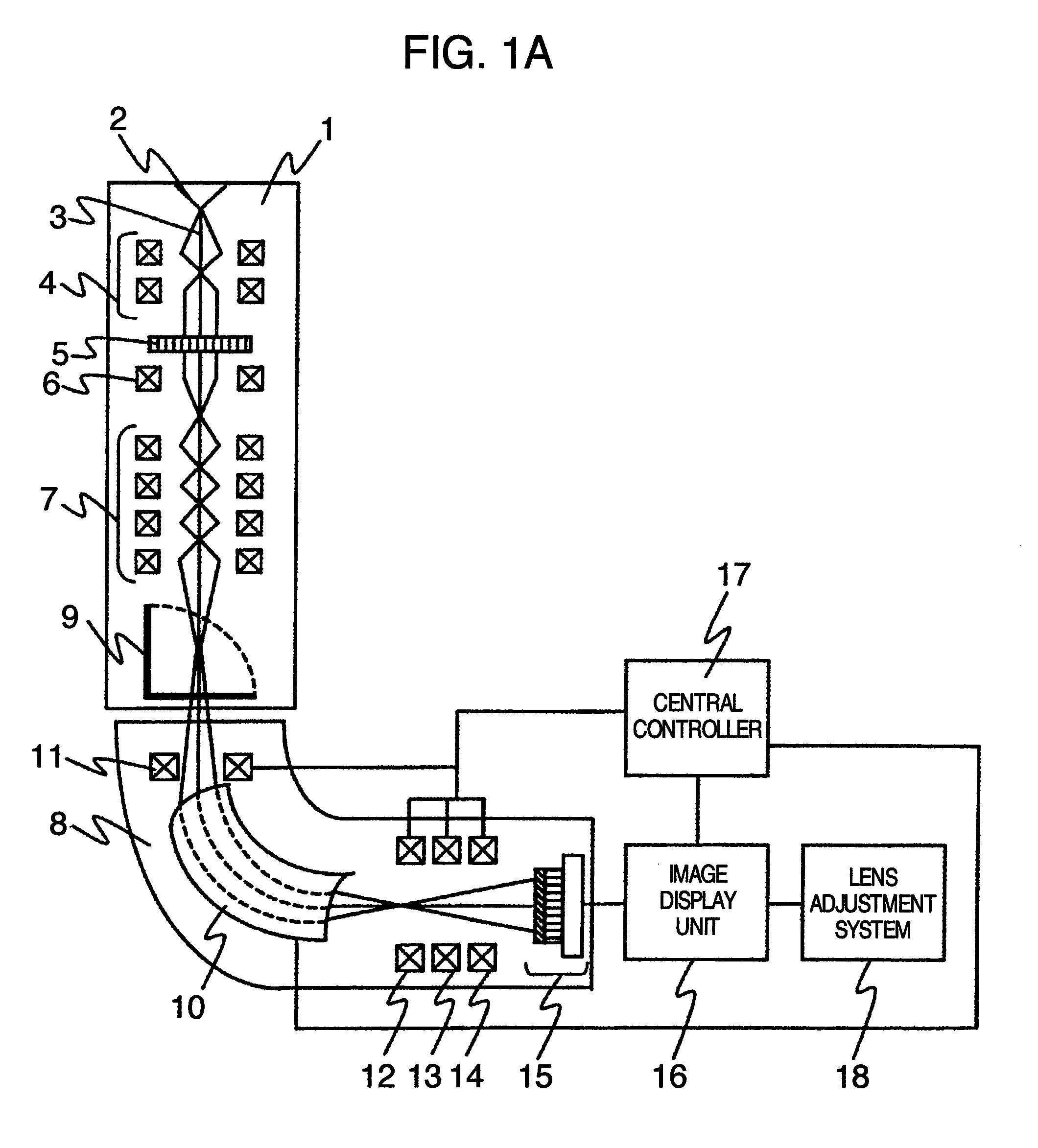
InactiveUS20060011836A1Easy to operateHigh EELS spectrum energy stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeFrequency spectrum
There is provided an element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method that enable to acquire an element mapping image very easily. On the scanning transmission electron microscope, the electron beam transmitted through an object to be analyzed enters into the element mapping unit. The electron beam is analyzed of its energy into spectrum by an electron spectrometer and an electron energy loss spectrum is acquired. Because the acceleration voltage data for each element and window data for 2-window method, 3-window method or contrast tuning method are already stored in a database and accordingly the spectrum measurement is carried out immediately even when an element to be analyzed is changed to another, the operator can confirm a two-dimensional element distribution map immediately. Besides, because every electron beam that enters into an energy filter passes through the object point, aberration strain in the electron spectrometer can be minimized and higher energy stability can be achieved. As a result, drift of the electron energy loss spectrum acquired by analyzing the electron beam into spectrum can be minimized and element distribution with higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
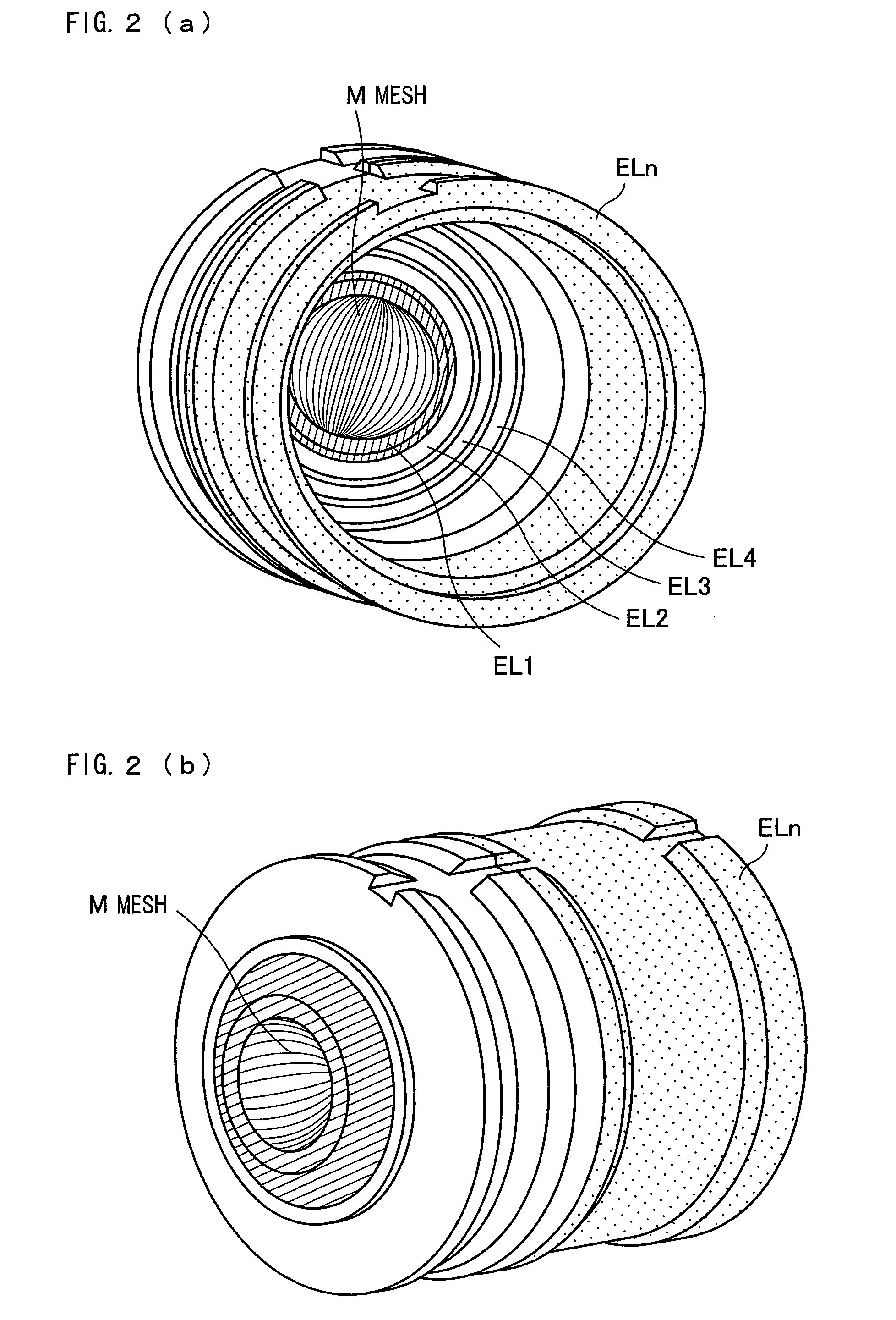
Spherical aberration correction decelerating lens, spherical aberration correction lens system, electron spectrometer, and photoelectron microscope
InactiveUS20100001202A1High sensitivityFunction increaseStability-of-path spectrometersMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationHigh energyDivergence angle
A spherical aberration correction decelerating lens corrects a spherical aberration occurring in an electron beam or an ion beam (hereinafter, referred to as “beam”) emitted from a predetermined object plane position with a certain divergence angle, and said spherical aberration correction decelerating lens comprises at least two electrodes, each of which is constituted of a surface of a solid of revolution whose central axis coincides with an optical axis and each of which receives an intentionally set voltage applied by an external power supply, wherein at least one of the electrodes includes one or more meshes (M) which has a concaved shape opposite to an object plane (P0) and which is constituted of a surface of a solid of revolution so that a central axis of the concaved shape coincides with the optical axis, and a voltage applied to each of the electrodes causes the beam to be decelerated and causes formation of a decelerating convergence field for correcting the spherical aberration occurring in the beam. This makes it possible to provide a spherical aberration correction decelerating lens which converges a beam, emitted from the sample and having high energy and a large divergence angle, onto an image plane.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Transmission Electron Microscope Provided with Electronic Spectroscope
InactiveUS20080203296A1Improve efficiencyEffective correctionThermometer detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationConventional transmission electron microscopeMagnification
In order to correct measurement magnification and measurement position of a spectral image with high efficiency and with high accuracy using an electronic spectroscope and a transmission electron microscope regarding the spectral image formed in two orthogonal axes which are an amount of energy loss axis and a measurement position information axis; a method for correcting magnification and position and a system for correcting magnification and position, both of which are capable of correcting measurement magnification and measurement position of a spectral image with high efficiency and with high accuracy using an electronic spectroscope and a transmission electron microscope regarding the spectral image formed in two orthogonal axes which are an amount of energy loss axis and a measurement position information axis, are provided.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
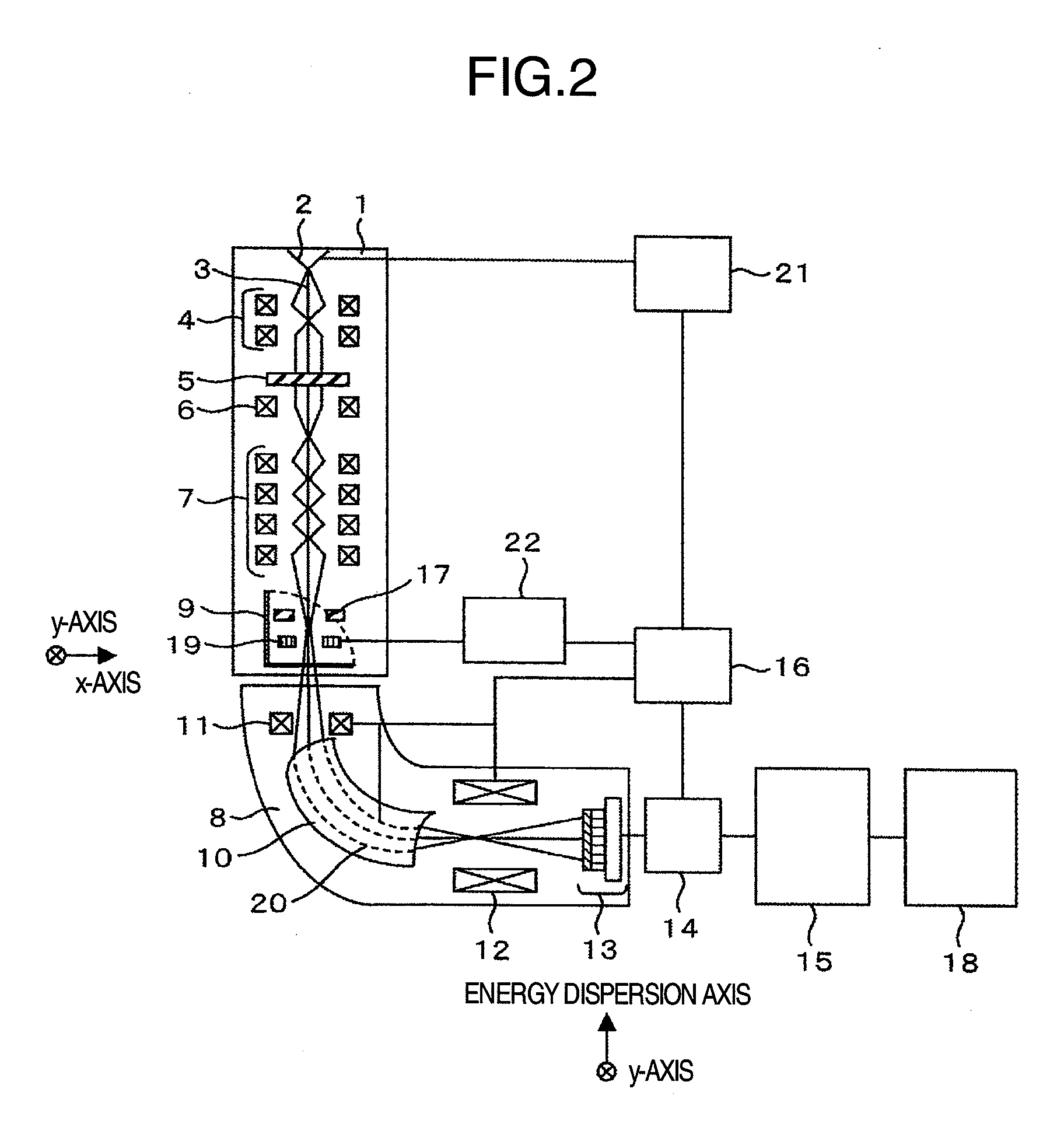
Element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method
InactiveUS7928376B2Easy to operateGood magnetic field stabilityMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPhotoelectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeFrequency spectrum
There is provided an element mapping unit, scanning transmission electron microscope, and element mapping method that enable to acquire an element mapping image very easily. On the scanning transmission electron microscope, the electron beam transmitted through an object to be analyzed enters into the element mapping unit. The electron beam is analyzed of its energy into spectrum by an electron spectrometer and an electron energy loss spectrum is acquired. Because the acceleration voltage data for each element and window data for 2-window method, 3-window method or contrast tuning method are already stored in a database and accordingly the spectrum measurement is carried out immediately even when an element to be analyzed is changed to another, the operator can confirm a two-dimensional element distribution map immediately. Besides, because every electron beam that enters into an energy filter passes through the object point, aberration strain in the electron spectrometer can be minimized and higher energy stability can be achieved. As a result, drift of the electron energy loss spectrum acquired by analyzing the electron beam into spectrum can be minimized and element distribution with higher accuracy can be acquired.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
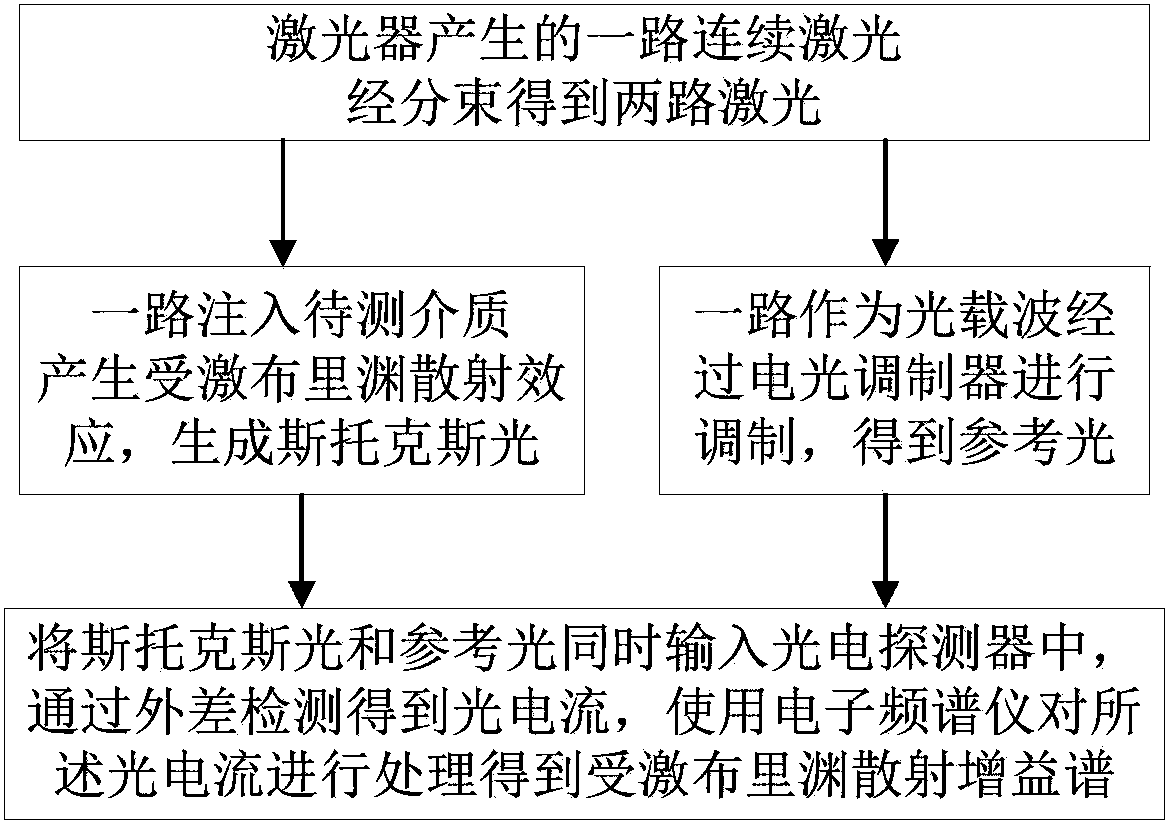
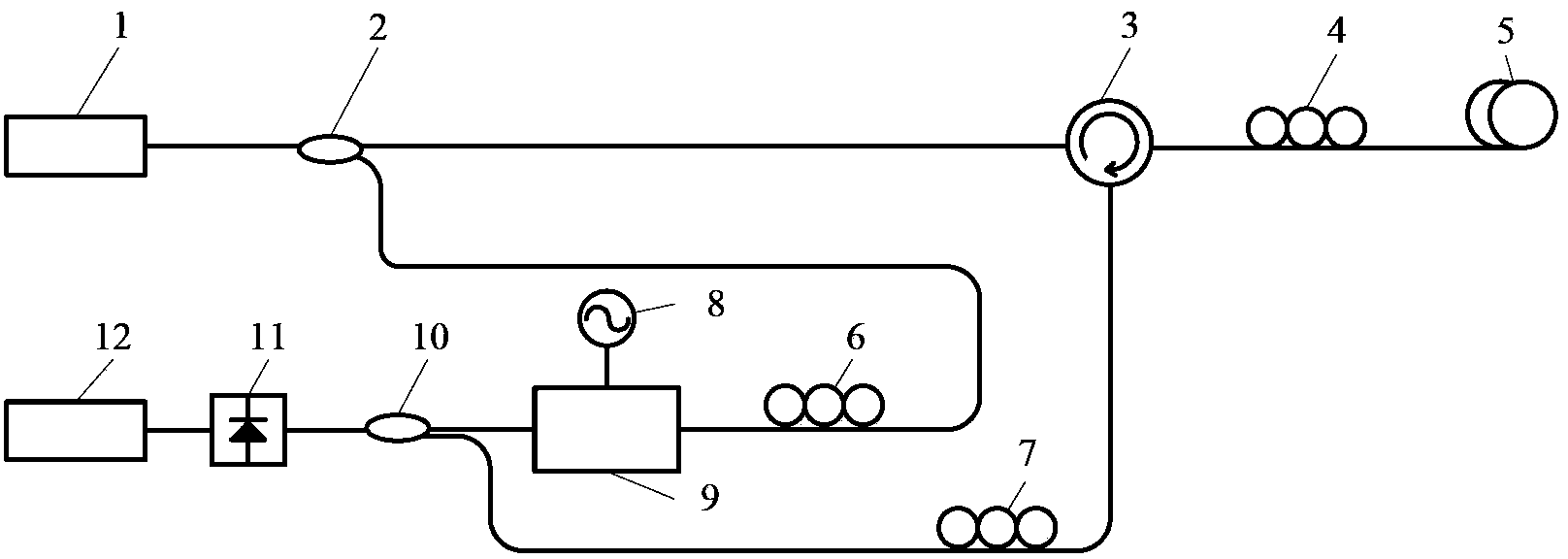
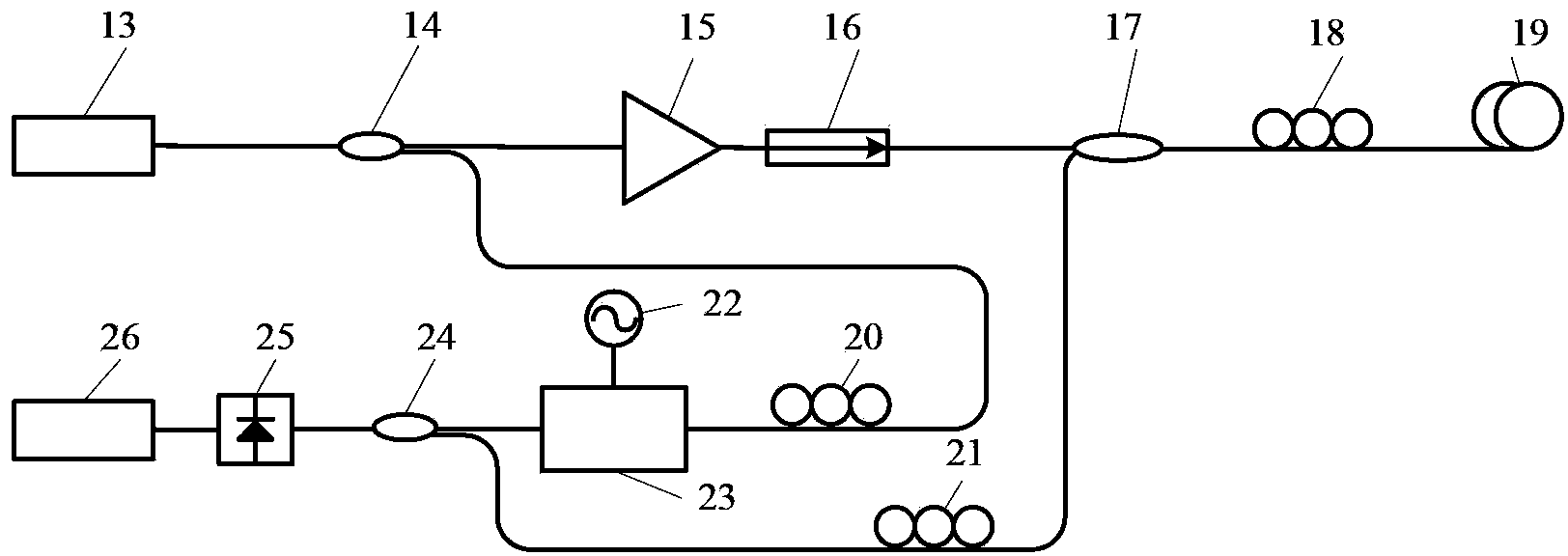
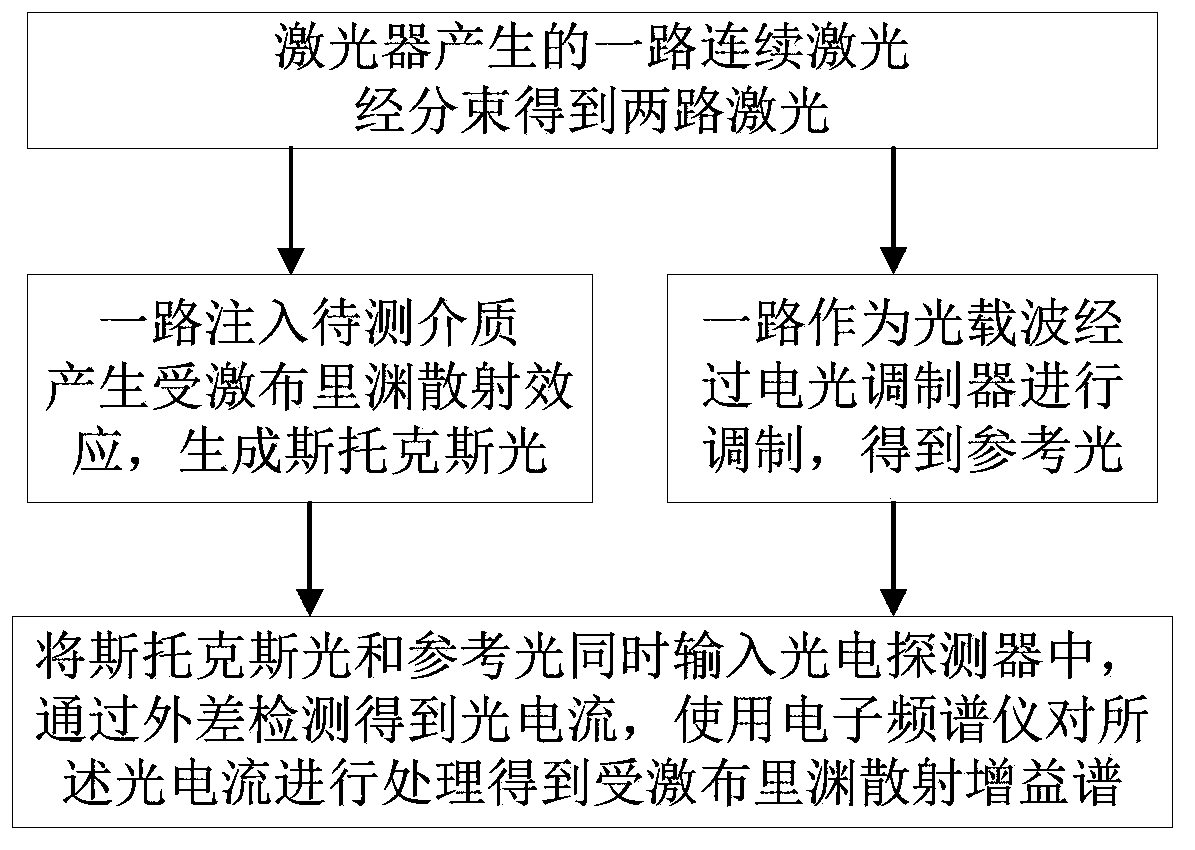
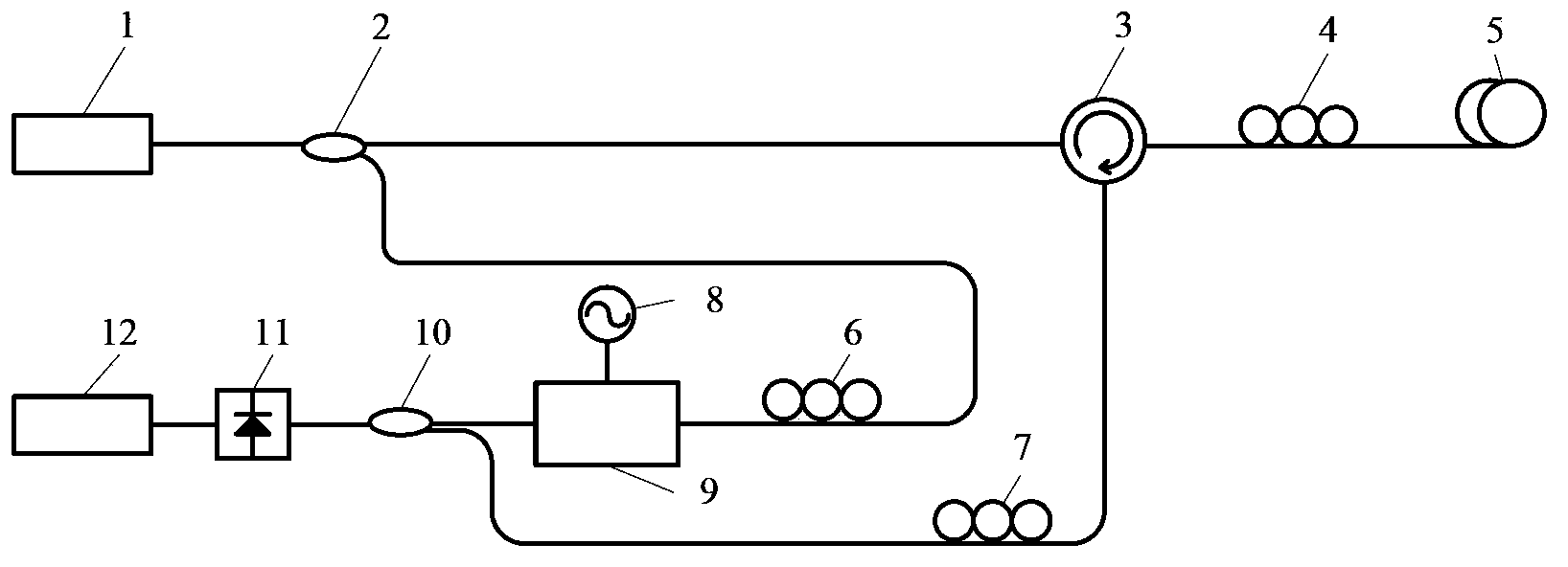
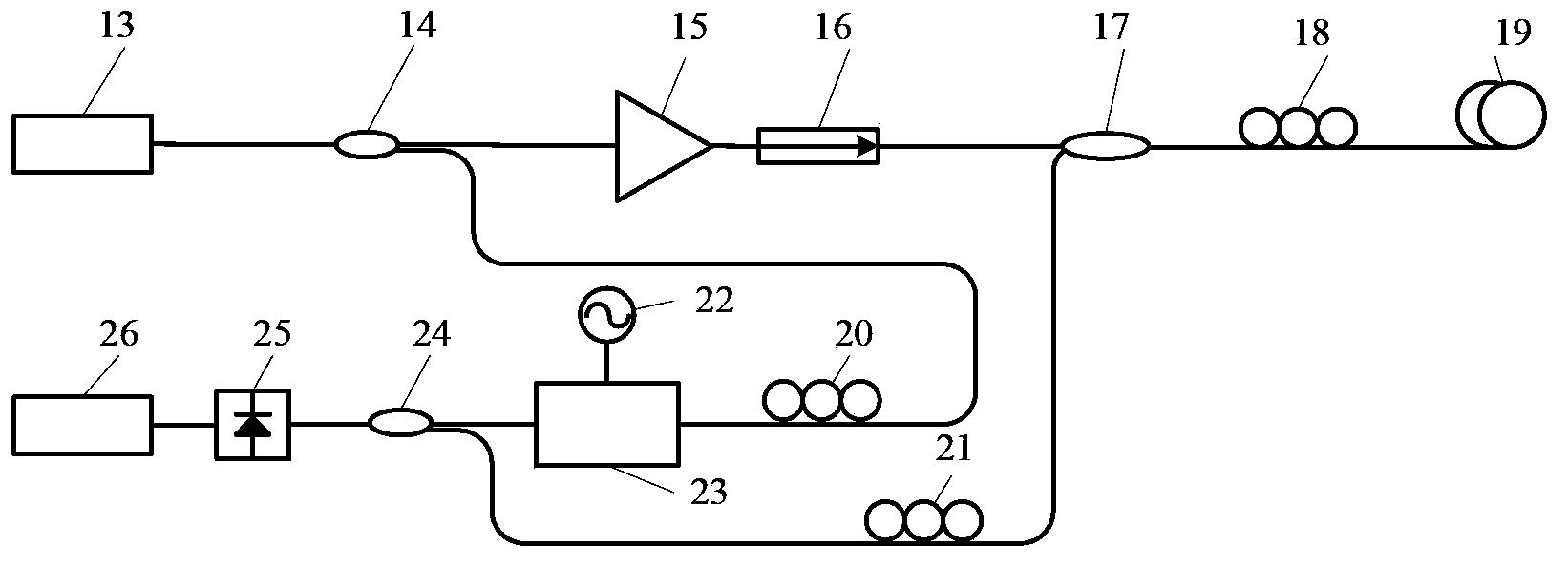
Excited Brillouin scattering gain spectrum measuring method and system thereof
ActiveCN103411675AReduce bandwidth requirementsRealize measurementRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsPhotovoltaic detectorsBeam splitting
The invention discloses an excited Brillouin scattering gain spectrum measuring method which comprises the steps of (1) conducting beam splitting on a beam of continuous laser generated by a laser device to obtain two beams of lasers, using one beam of laser as pumping light to be injected into a medium to be measured, enabling the excited Brillouin scattering effect to be generated in the medium to be measured, generating Stokes light which is opposite to the injected pumping light in transmission direction, using the other beam of laser as a light carrier to be modulated through an electrooptical modulator with loaded periodic electrical signals, and obtaining reference light, and (2) simultaneously inputting the reference light and the stokes light in a photoelectric detector, obtaining the light current through heterodyne detection, and using an electron spectrometer to process the light current to obtain an excited Brillouin scattering gain spectrum. By means of the excited Brillouin scattering gain spectrum measuring method, the bandwidth requirements of using equipment such as the modulator, the detector and the electron spectrometer can be reduced, and measurement on characteristics such as line types and the bandwidth of the excited Brillouin scattering gain spectrum is easily and stably achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electron source
ActiveUS20060076866A1Optical filtersElectric lighting sourcesSingle crystalScanning electron microscope
To provide an electron source to be used for a surface analyzer such as a scanning or transmission electron microscope or an Auger electron spectroscope, or an electron beam lithography machine, particularly for a semiconductor wafer inspection apparatus such as a scanning electron microscope to be used at a low acceleration with an electron beam acceleration voltage of up to 1 kV, CD SEM or DR SEM. An electron source wherein a barium supplying source consisting of a complex oxide comprising barium oxide and an oxide of metal other than barium, is provided at a portion of a single crystal needle of tungsten or molybdenum.
Owner:DENKA CO LTD
Electron spectrometer
ActiveUS9997346B1Improve recording qualityLess distortionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationEnergy spectrometersParticle beamSpectrometer
A charged particle spectrometer of hemispherical analyzer type for analyzing a particle emitting sample, the spectrometer comprising at least a first mechanism configured to move at least a part of the lens with respect to the axis between the sample spot and the analyzer entrance in a coordinate direction synchronously with a deflection of the particle beam.
Owner:MB SCI
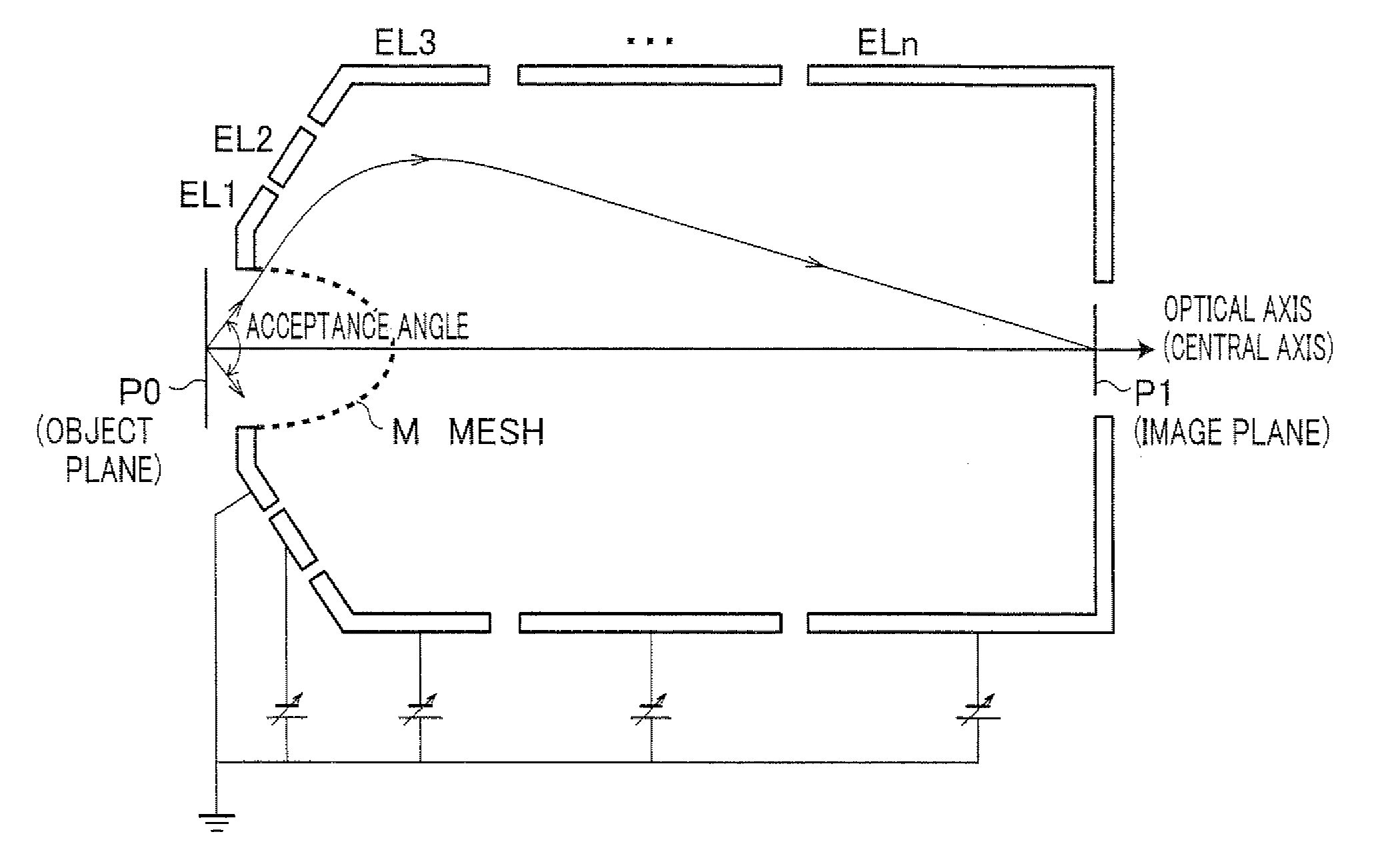
Spherical Aberration Corrected Electrostatic Lens, Input Lens, Electron Spectrometer, Photoemission Electron Microscope And Measuring System
InactiveUS20080135748A1Wide acceptance angleImprove performanceThermometer detailsBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsElectron microscopePhotoelectron microscopy
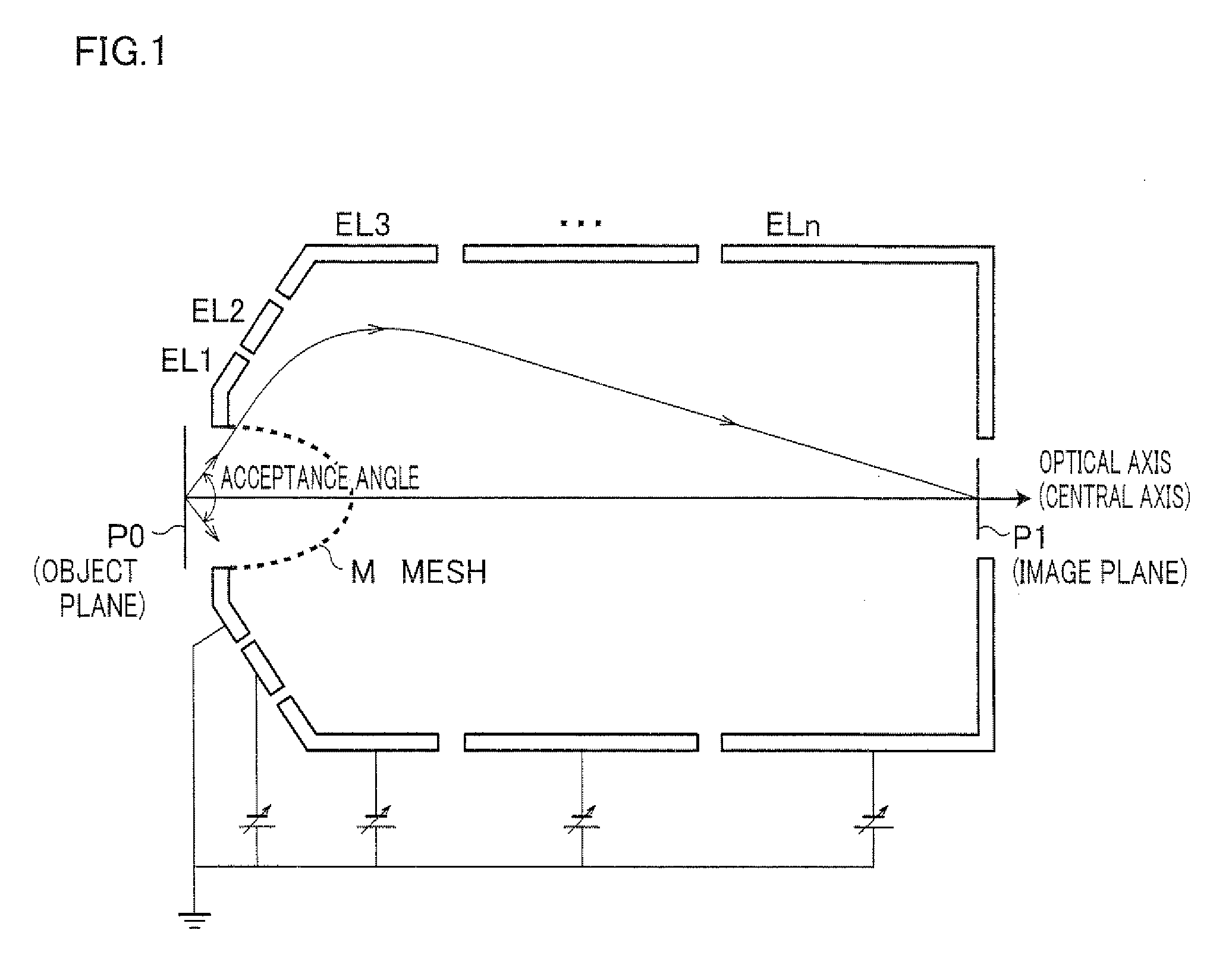
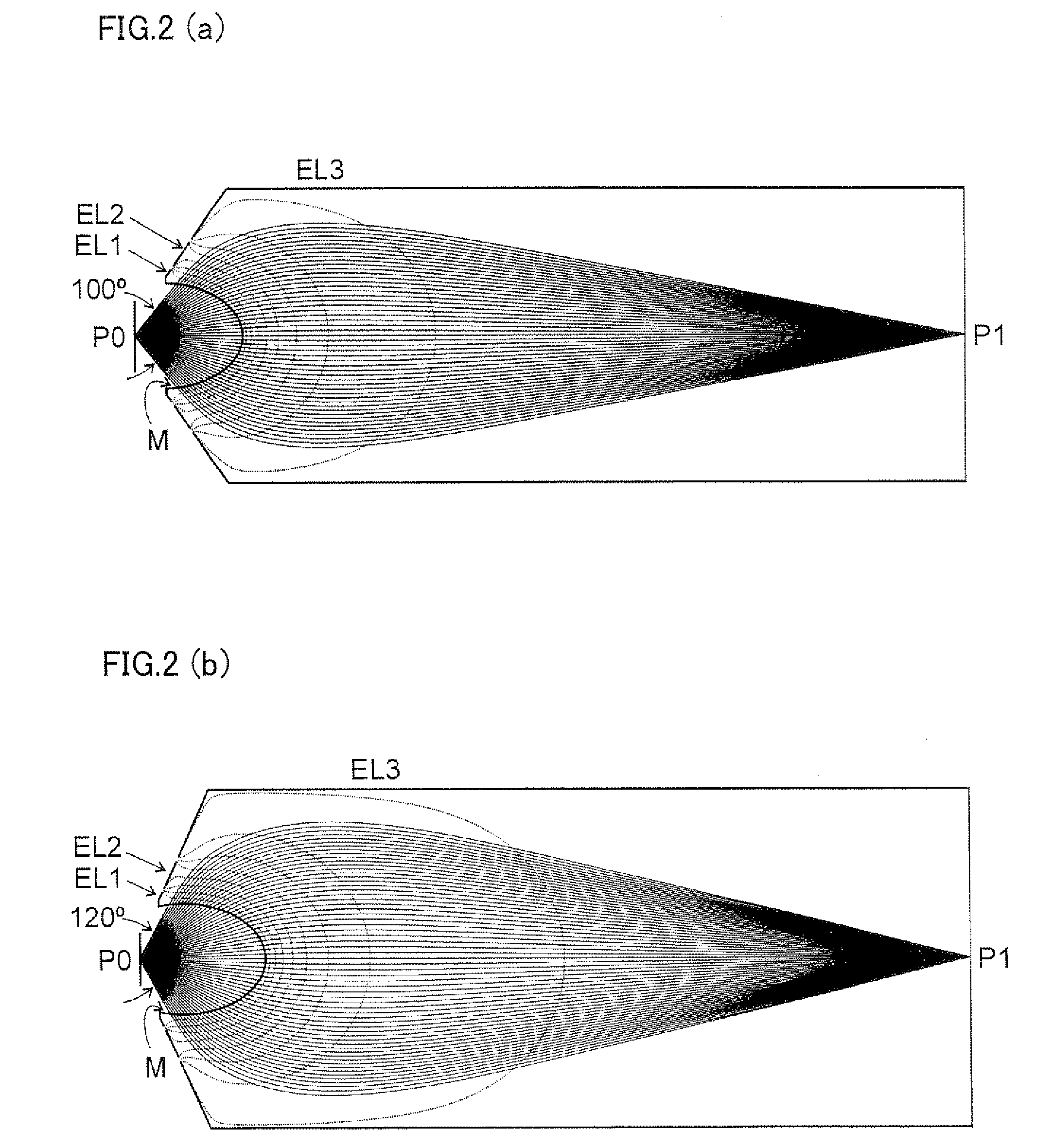
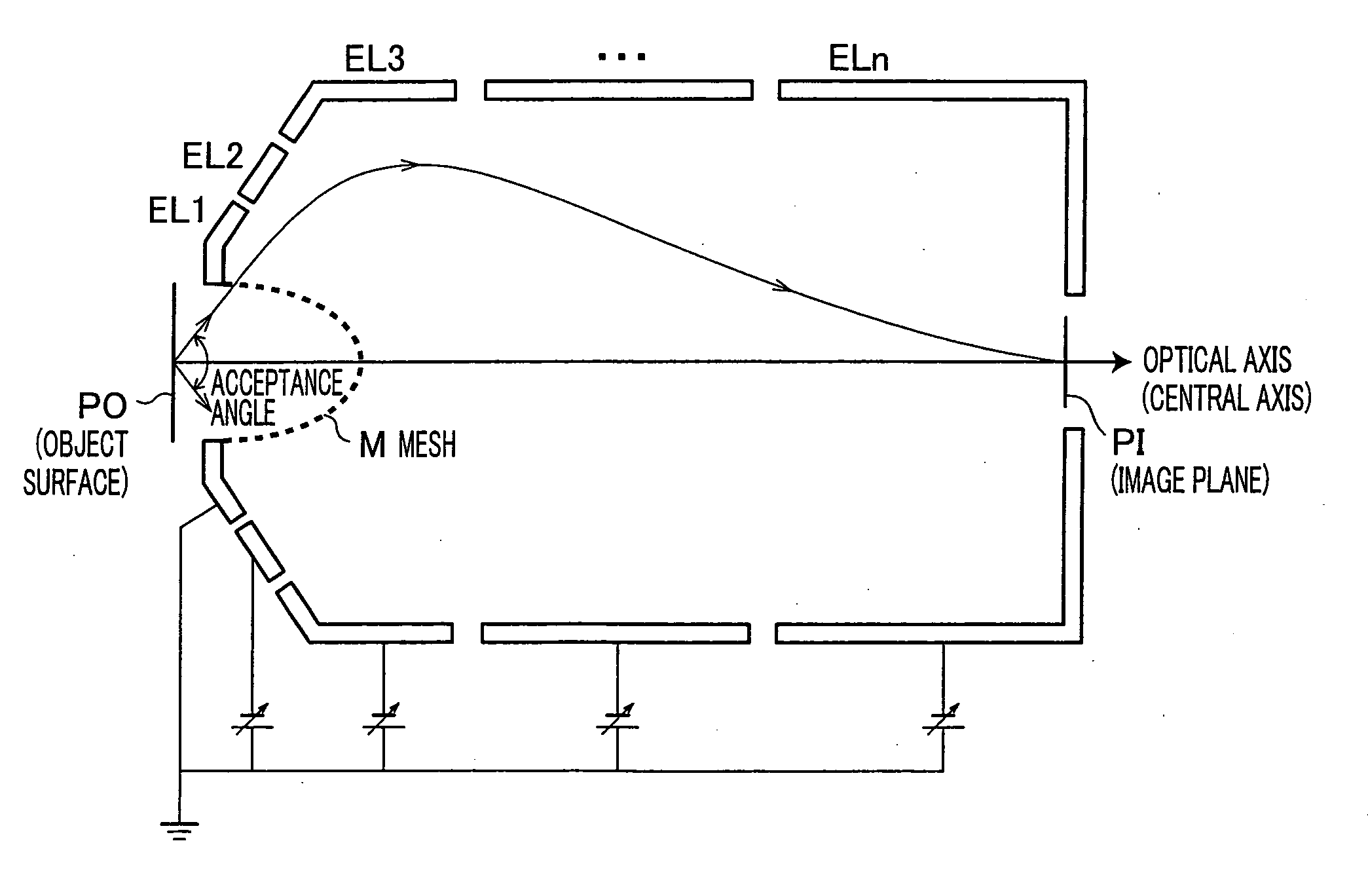
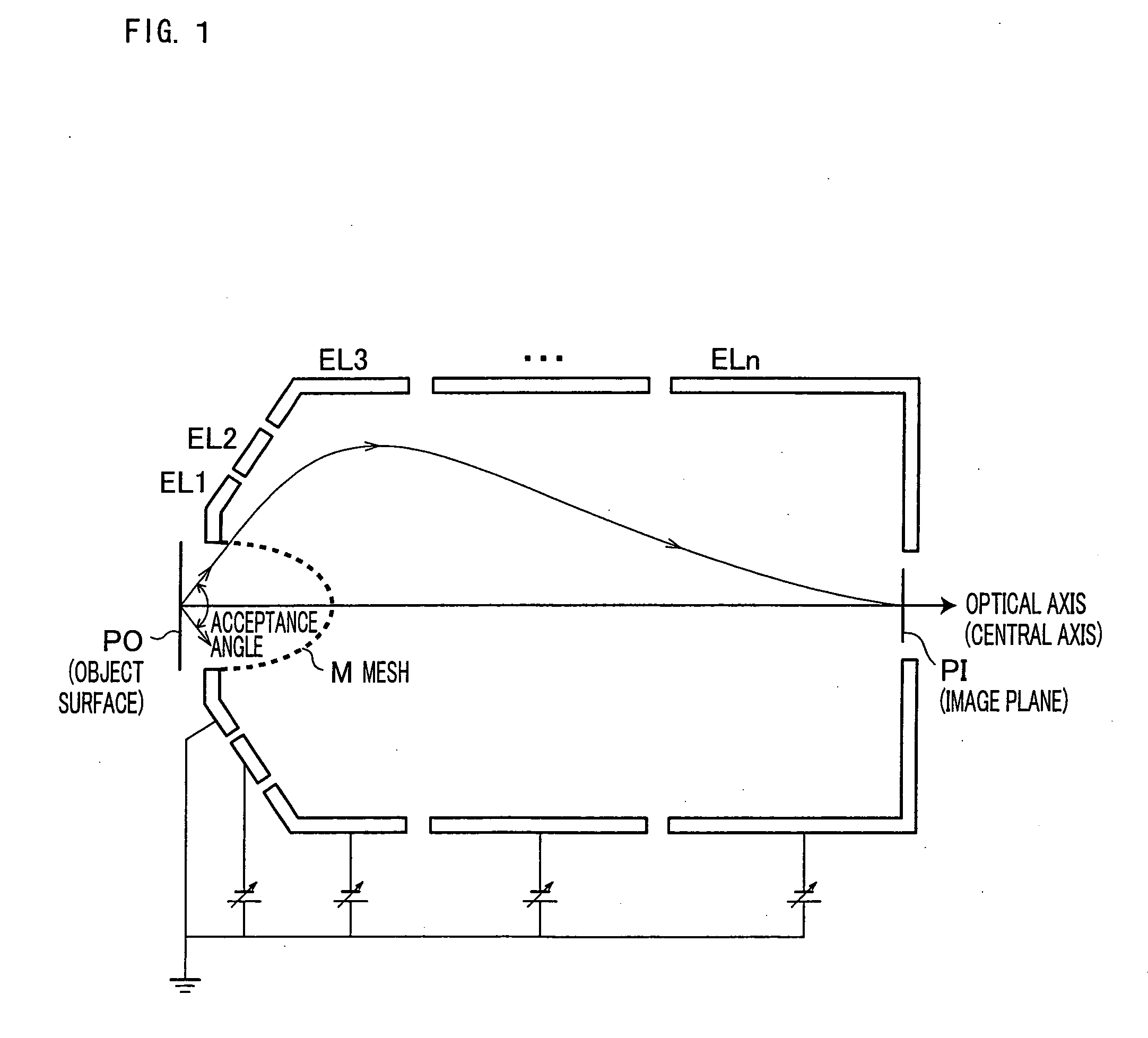
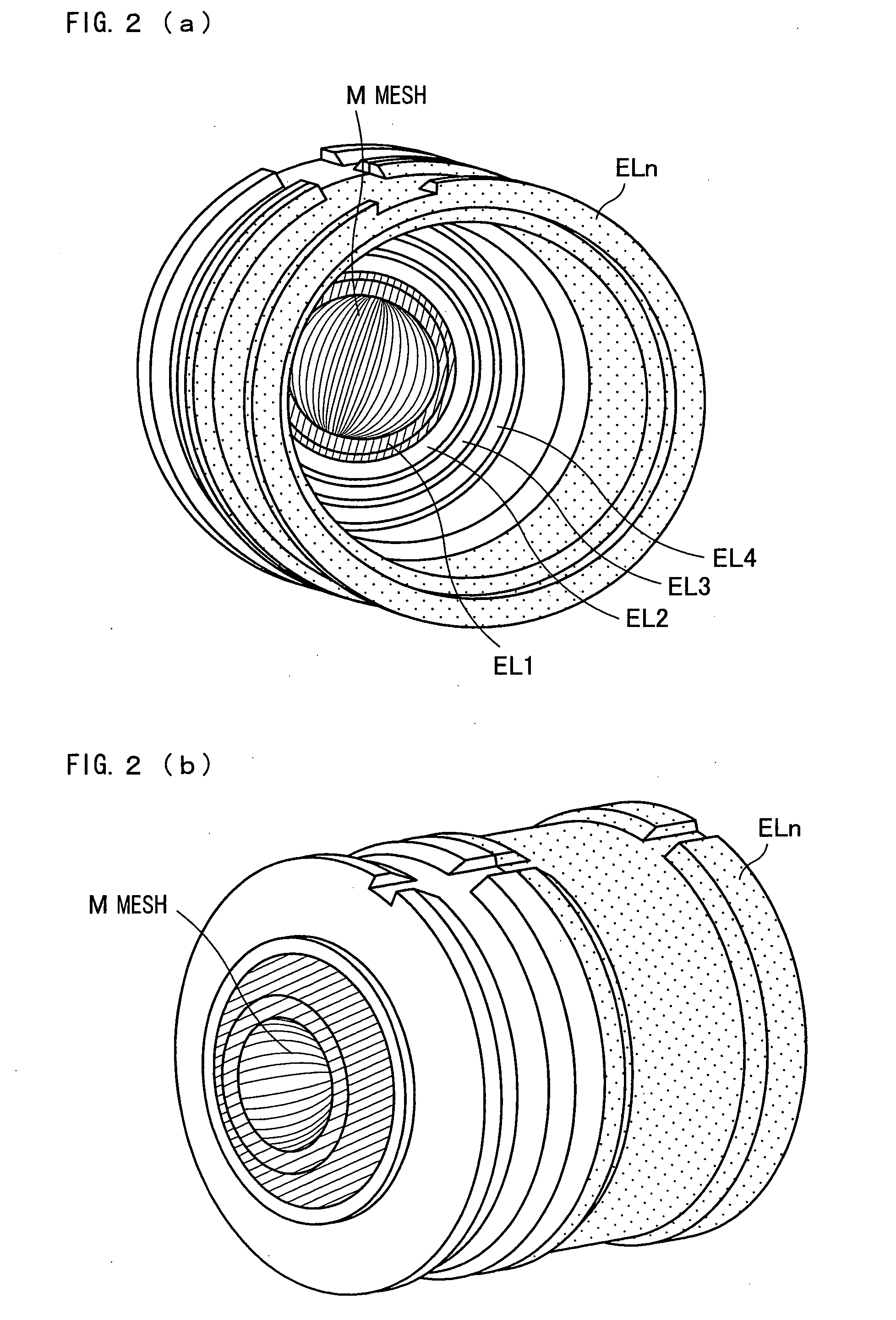
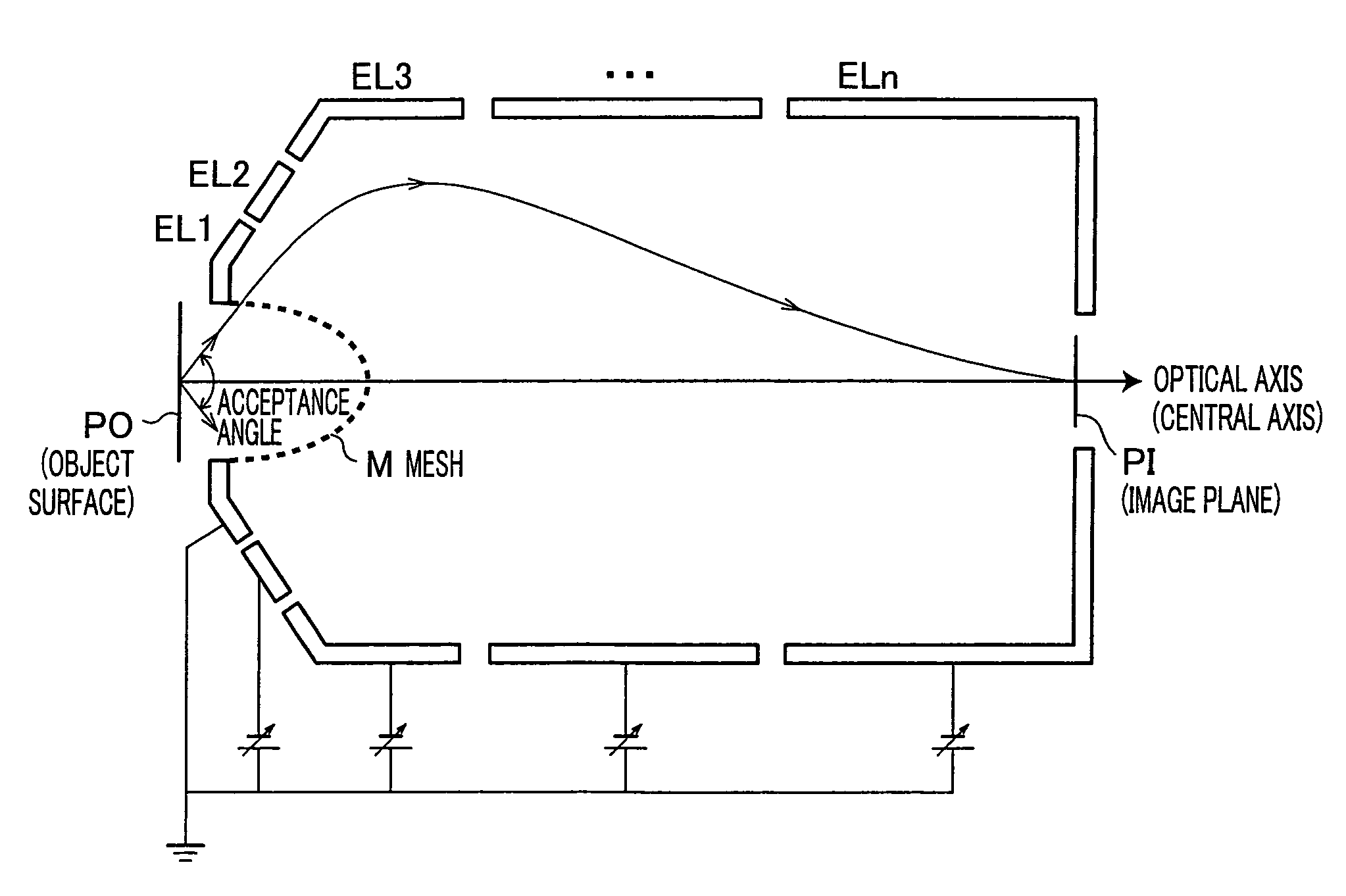
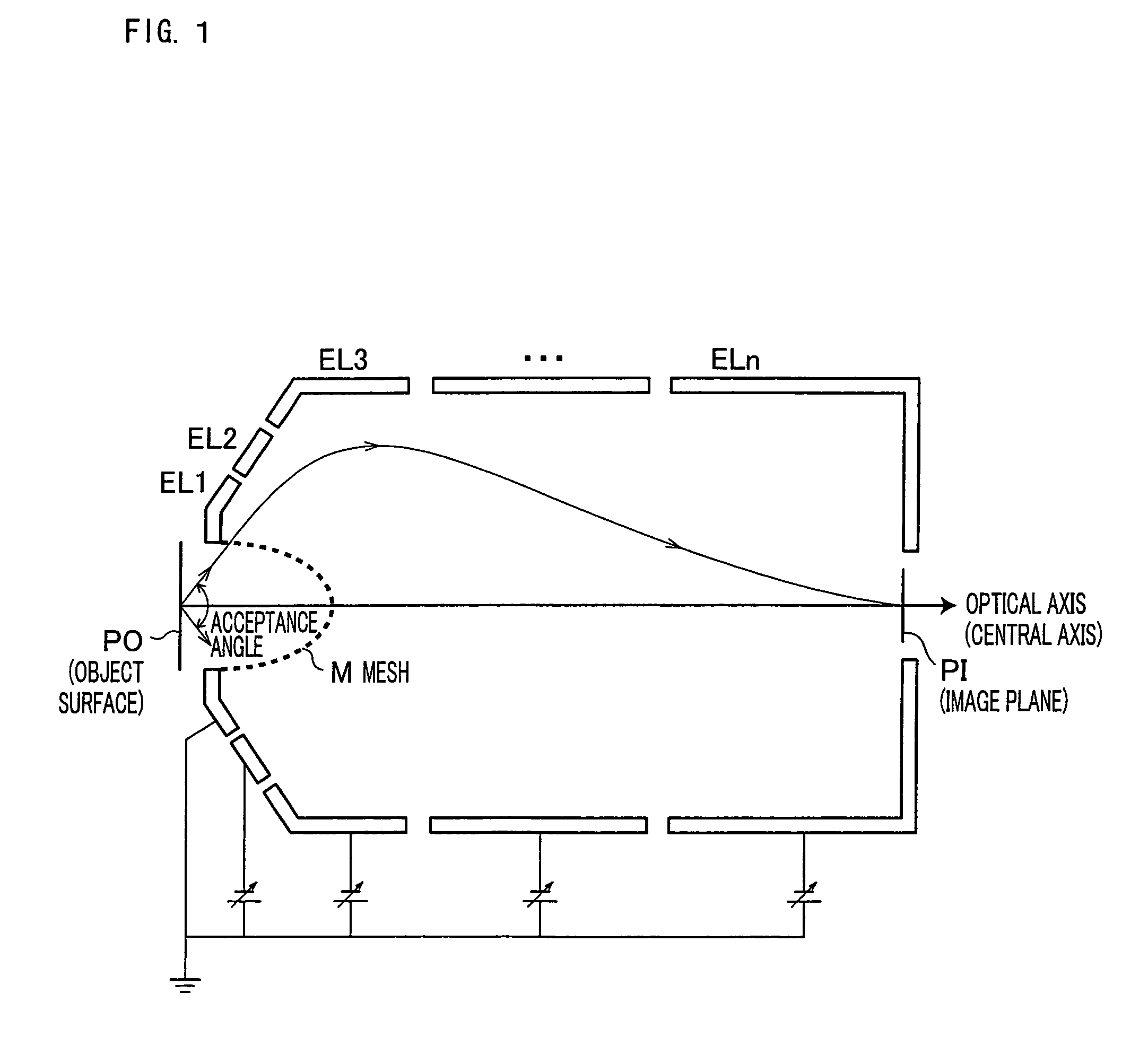
A mesh (M) having an ellipsoid shape or a shape close to the ellipsoid shape is attached to an electrode (EL1) among electrodes (EL1 to ELn). Voltages of the later-stage electrodes (EL2 to ELn) are appropriately set. With this arrangement, a local negative spherical aberration generated by the mesh (M) is cancelled out with a positive spherical aberration. This optimizes an electric field distribution. As a result, this realizes an electrostatic lens whose acceptance angle is extended to about±60°.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
Ultimate analyzer, scanning transmission electron microscope and ultimate analysis method
InactiveUS6933501B2Increase contrastImprove accuracyPhotoelectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationConventional transmission electron microscopeEnergy dispersion
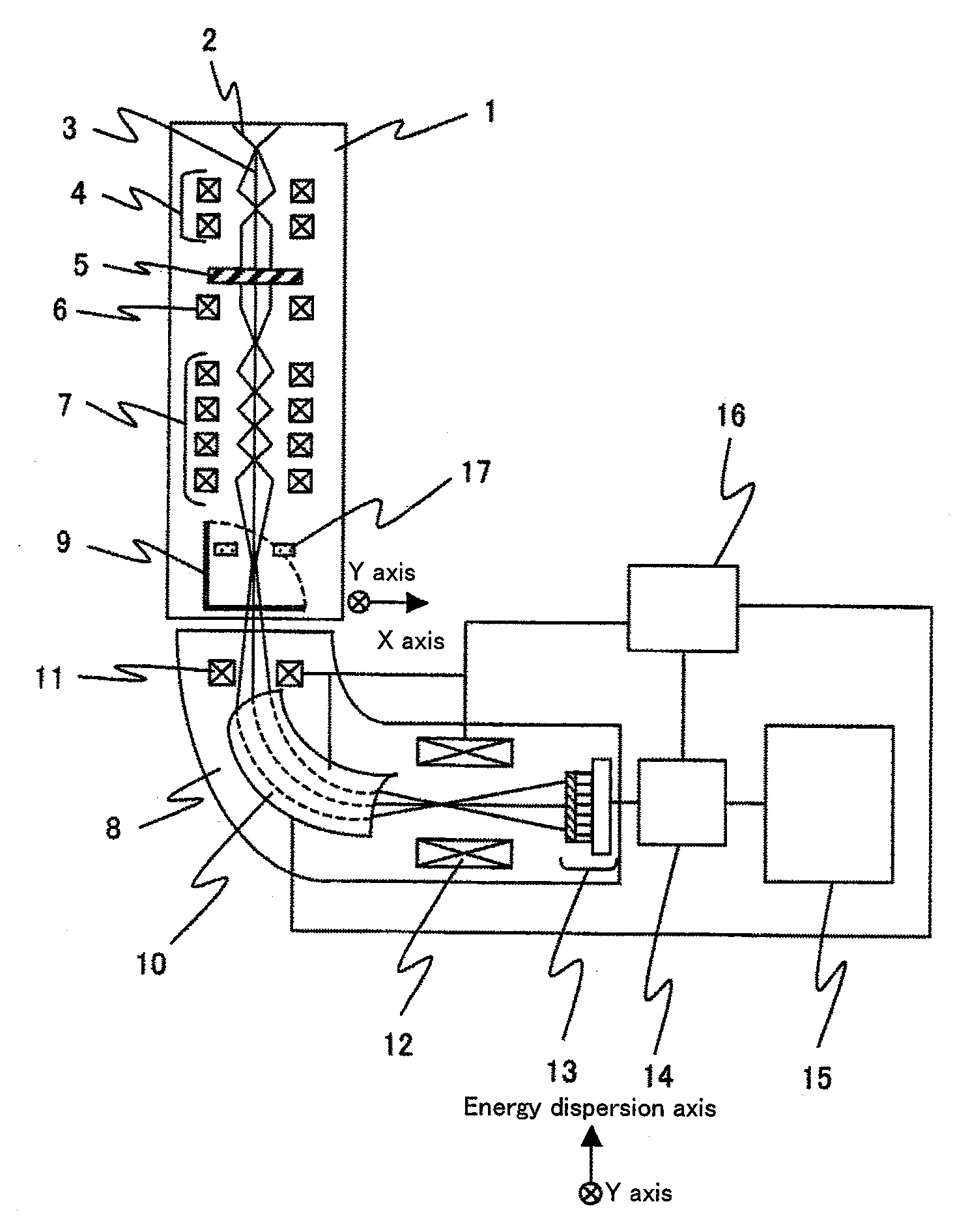
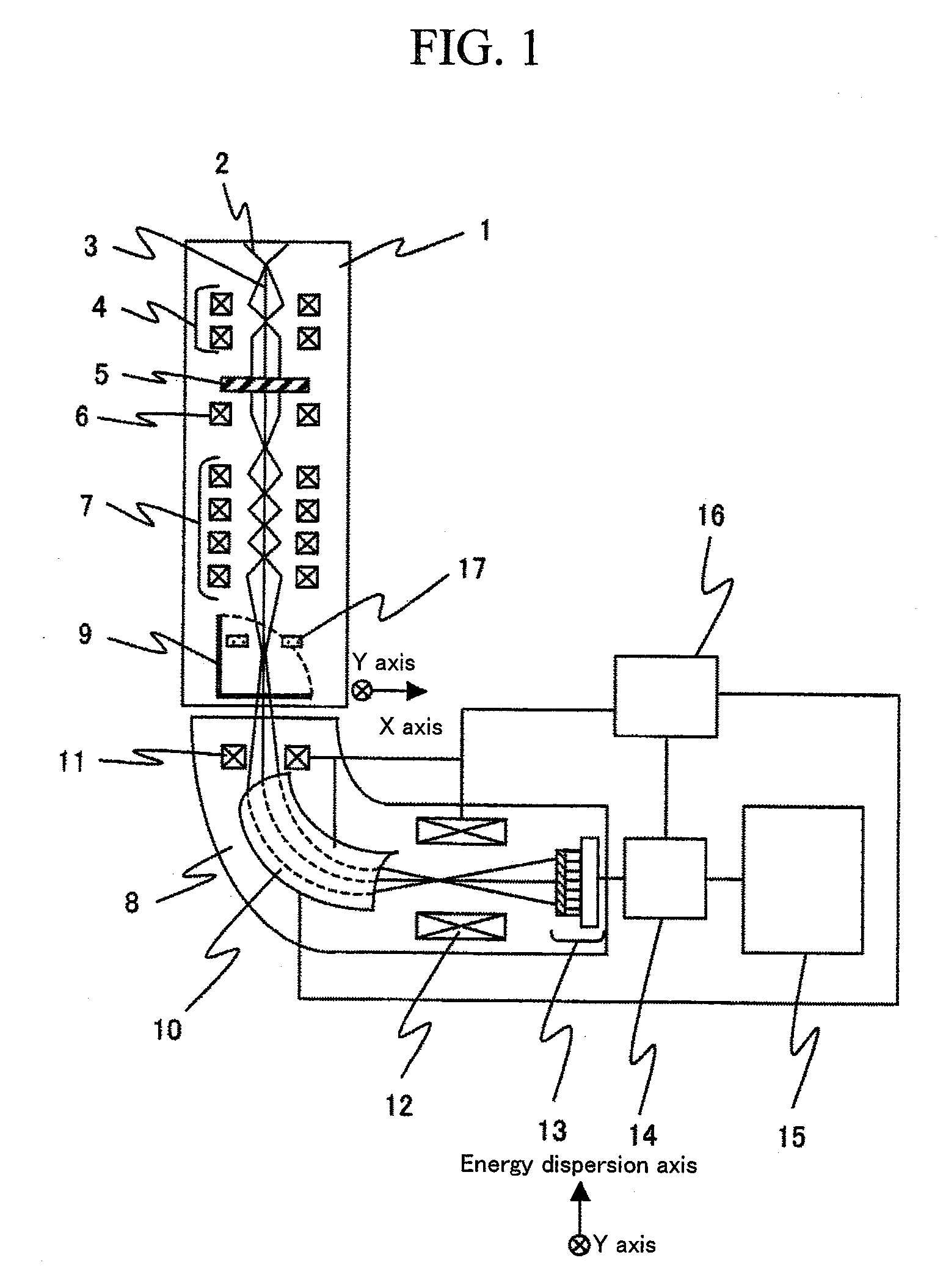
The present invention provides an ultimate analyzer which displays an element distribution image of an object with high contrast and high accuracy. A scanning transmission electron microscope and a method of analyzing elements using the ultimate analyzer is also provided. The ultimate analyzer comprises a scattered electron beam detector for detecting an electron beam scattered by an object; an electron spectrometer for energy dispersing an electron beam transmitted through the object; an electron beam detector for detecting said dispersed electron beam; and a control unit for analyzing elements based on an output signal of the electron beam detected by the electron beam detector and an output signal of the electron beam detected by the scattered electron beam detector.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Transmission electron microscope apparatus comprising electron spectroscope, sample holder, sample stage, and method for acquiring spectral image
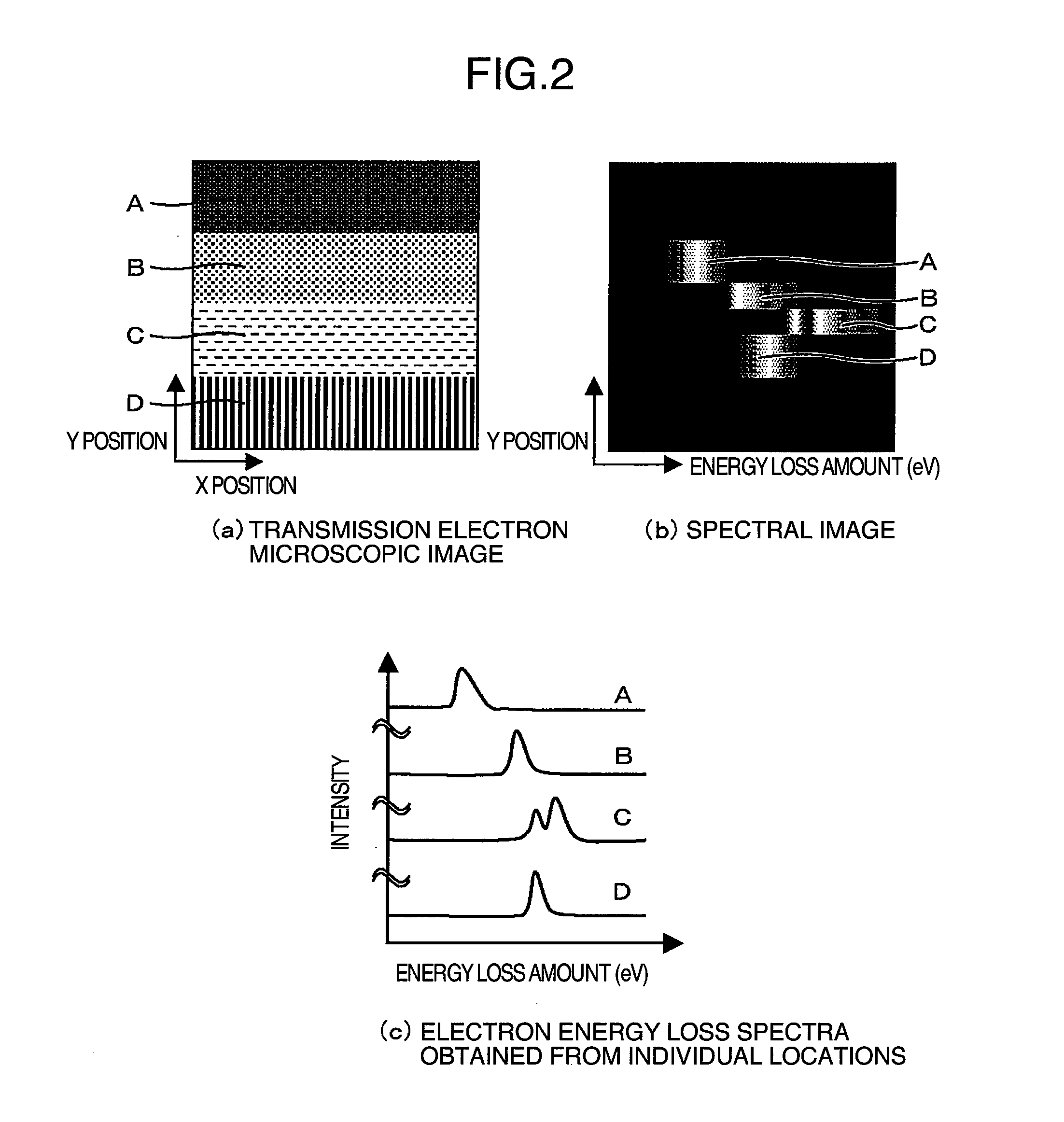
InactiveUS20110155906A1Highly accurate chemical shiftHighly accurate chemical shiftsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesEnergy dispersionElectron energy loss spectra
A transmission electron microscope apparatus, a sample holder and a sample stage and a method for acquiring spectral images as well are provided which can acquire spectral images at a time from a plurality of samples and measure highly accurate chemical shifts from electron energy loss spectra extracted from the spectral images.A transmission electron microscope apparatus comprises an electron gun for emitting an electron beam, a condenser lens for converging the emitted electron beam, a plurality of sample stages radiated with a converged electron beam and adapted to mount samples, a sample movement control unit for moving the sample stages, image-forming lenses for forming an image of an electron beam having transmitted through the plural samples, an electron spectrometer adapted to perform spectrometry of the electron beam in accordance with energy amounts the image-formed electron beam has and deliver spectral images obtained at convergence positions which are different in energy dispersion axis direction and in a direction orthogonal to the energy dispersion axis direction to thereby acquire spectral images from the plural samples at a time, and an image display unit for displaying acquired spectral images.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Electron microscope with electron spectrometer
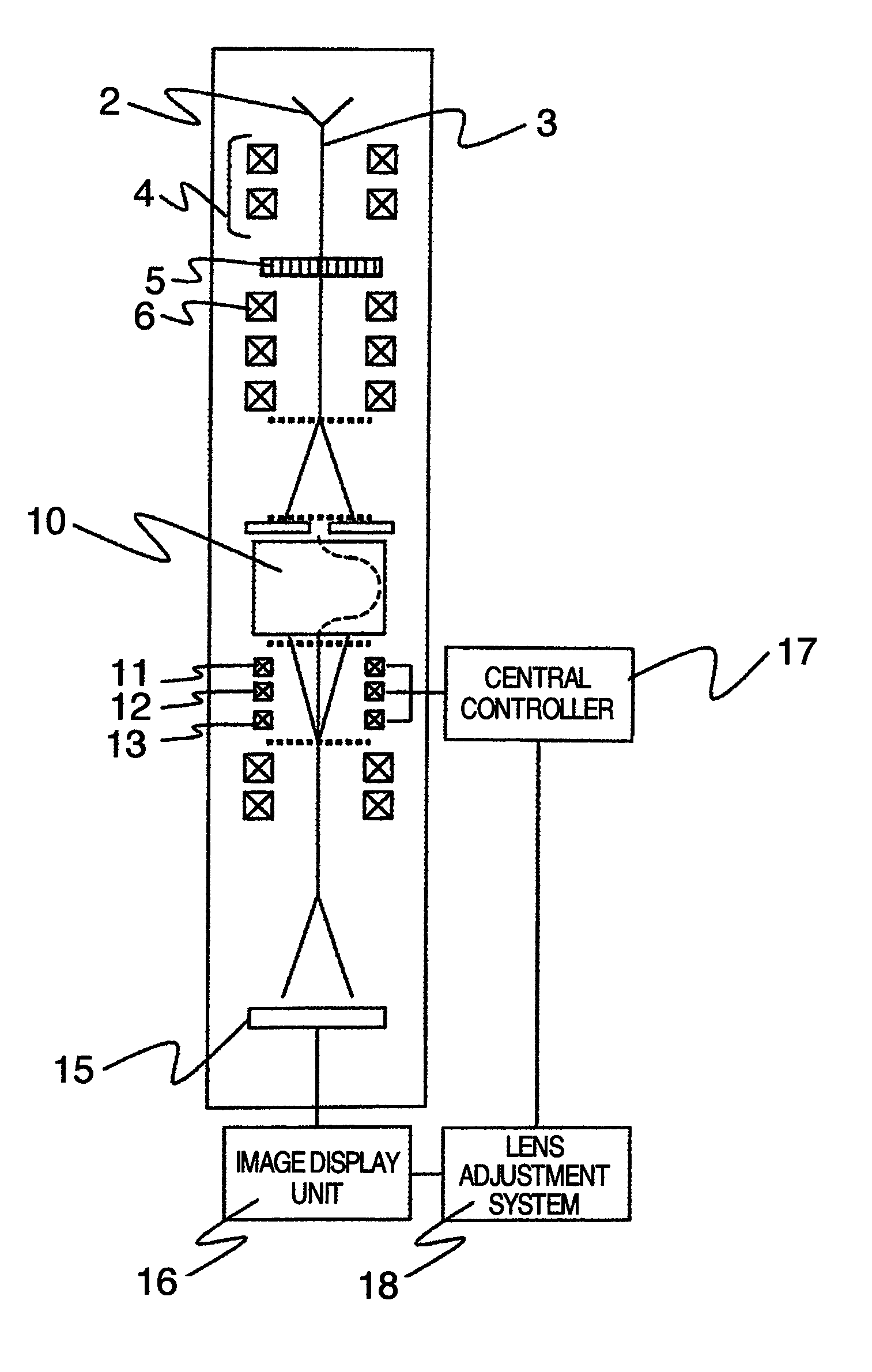
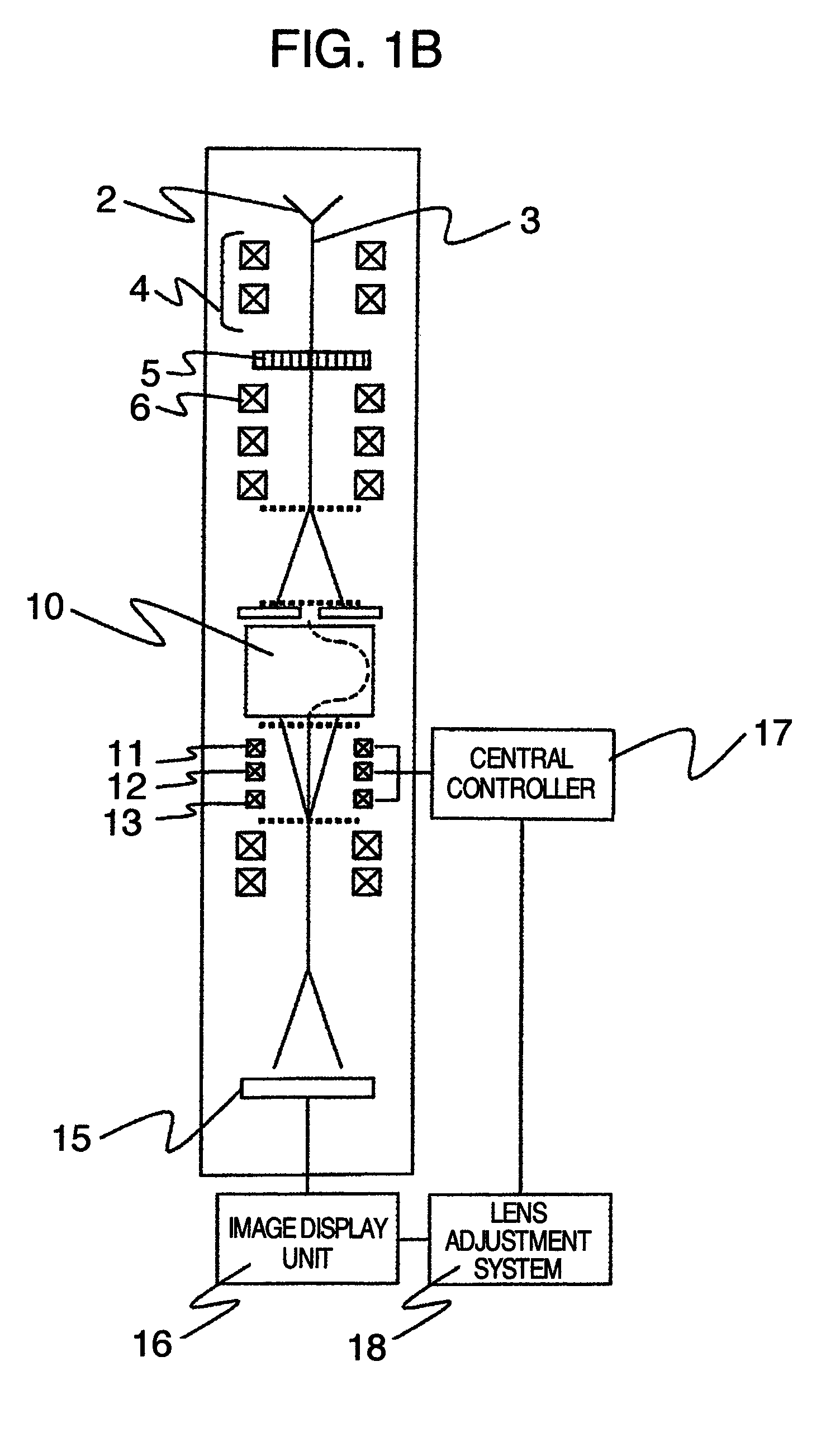
InactiveUS7888641B2Optimal condition adjustment highly efficiently and highly accuratelyRadiation pyrometryMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPower flowSimulation based
A lens adjustment method and a lens adjustment system which adjust a plurality of multi-pole lenses of an electron spectrometer attached to a transmission electron microscope, optimum conditions of the multi-pole lenses are determined through simulation based on a parameter design method using exciting currents of the multi-pole lenses as parameters.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Electron spectrometer
InactiveUS7569816B1Energy spectrometersMaterial analysis by optical meansPhotoelectron microscopyProjection lens
A field terminating imaging electron spectrometer being used for imaging electrons created within a magnetic field such as an image produced with a magnetic projection lens in a photoelectron microscope. The preferred embodiment is a CHA with magnetic input and output lenses.
Owner:BROWNING RAYMOND
Transmission electron microscope having electron spectrometer
InactiveUS20110240854A1Effective correctionImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeEnergy loss
In a spectral image formed by two orthogonal axes, one of which is an axis of the amount of energy loss and the other of which is an axis of positional information, by the use of an electron spectrometer and a transmission electron microscope, distortion in the spectral image of a sample to be analyzed is corrected with high efficiency and high accuracy by comparing electron beam positions calculated from a two-dimensional electron beam position image formed by the two orthogonal axes (the axis of the amount of energy loss and the axis of positional information) with reference electron beam positions, and calculating amounts of the distortion based on the differences of the electron beam positions. Method and apparatus are offered which correct distortion in a spectral image with high efficiency and high accuracy, the image being formed by the two orthogonal axes (the axis of the amount of energy loss and the axis of positional information).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
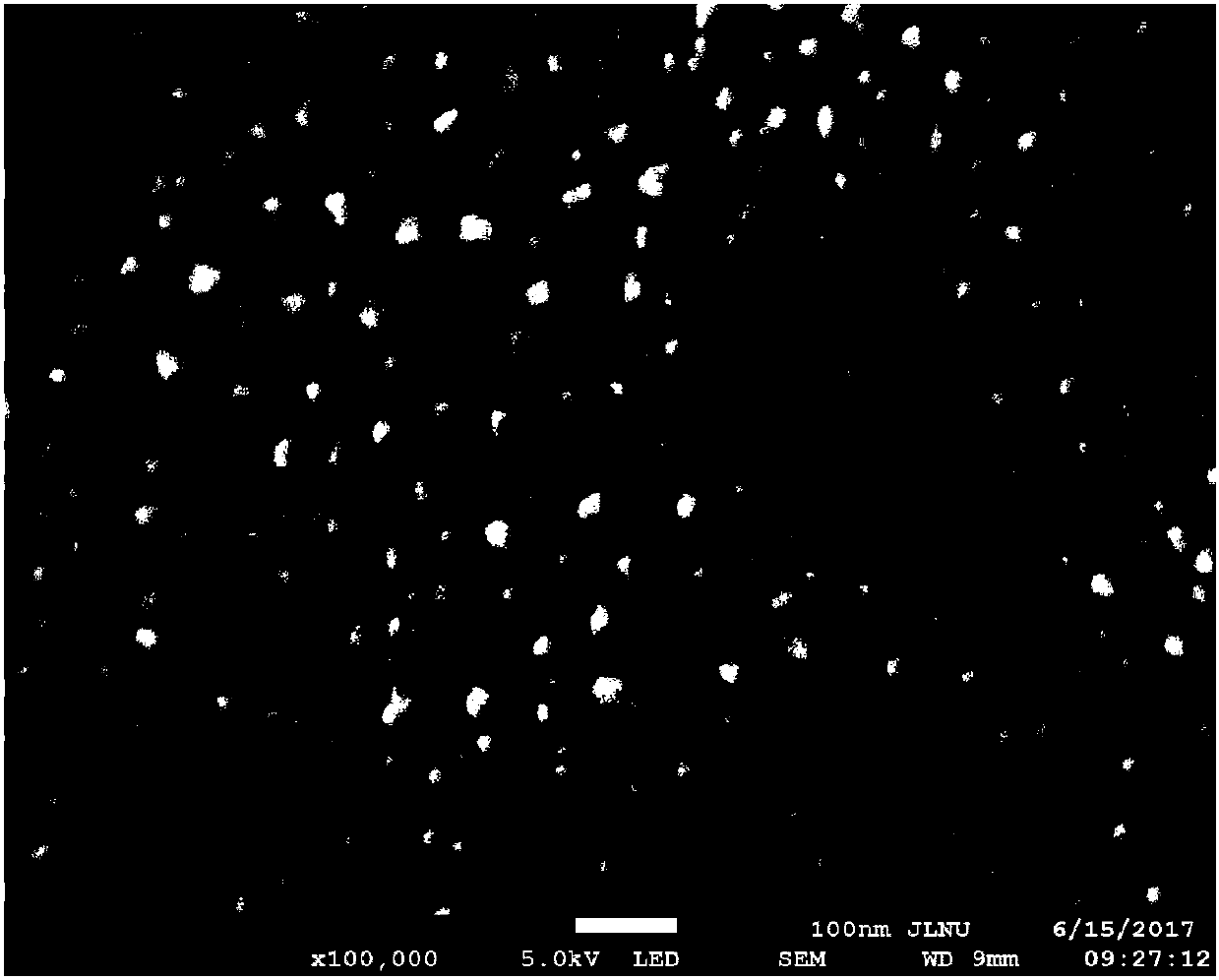
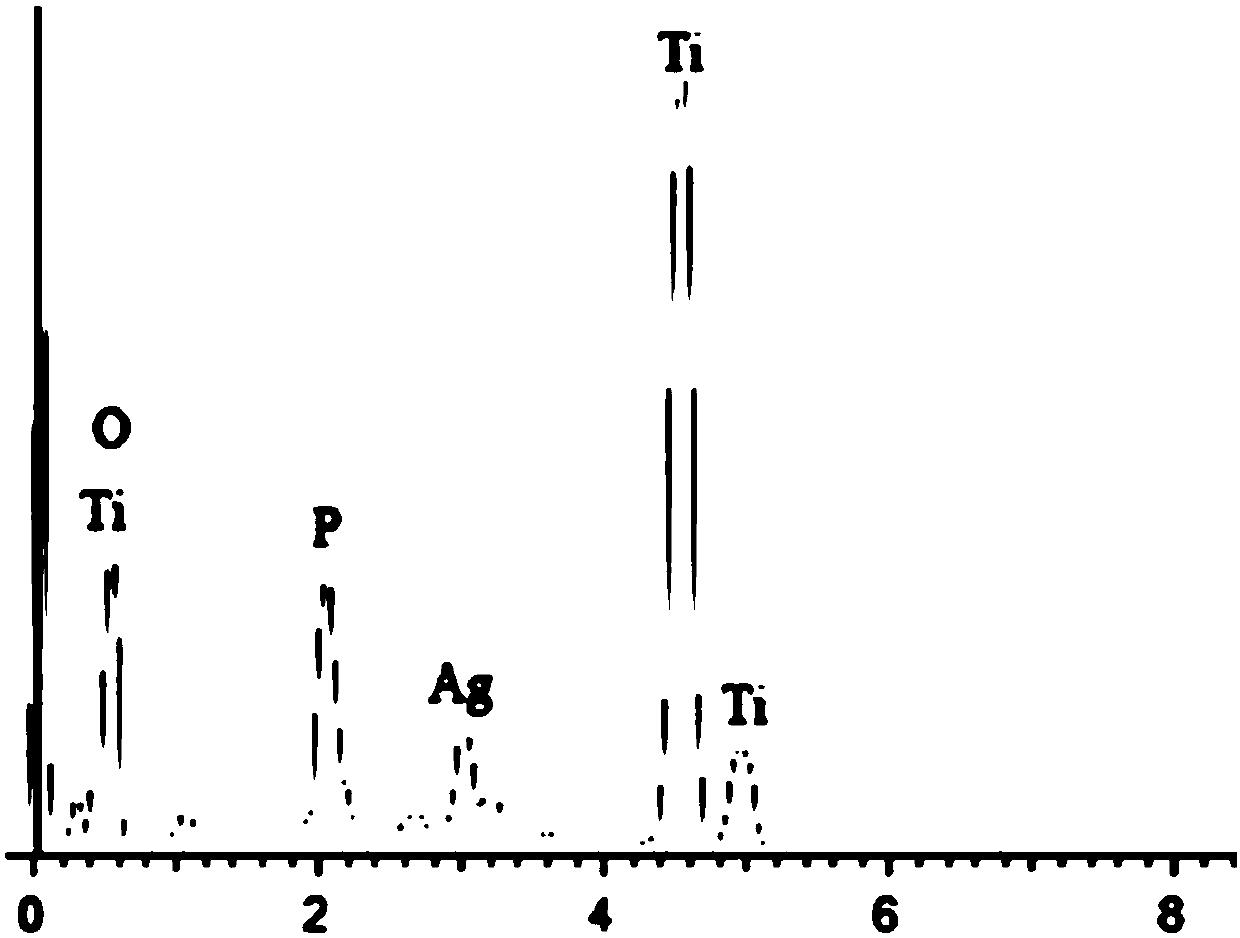
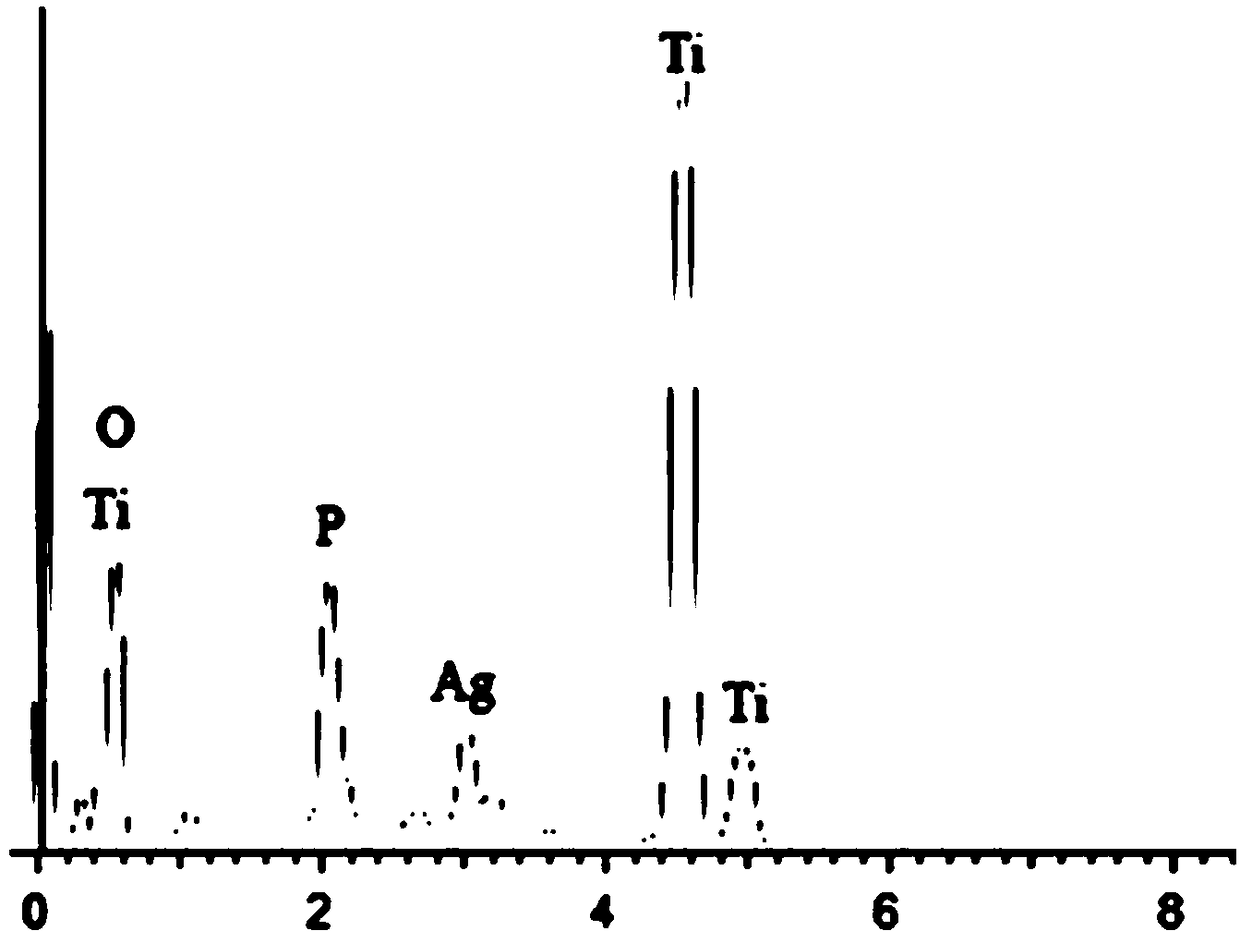
Nanometer Ag3PO4-modified and TiO2 heterojunction photo-catalytic membrane material and preparing method thereof
ActiveCN107675230ARealize continuous preparationSimple methodPhysical/chemical process catalystsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingHeterojunctionPlasma electrolytic oxidation
The invention discloses a nanometer Ag3PO4-modified and TiO2 heterojunction photo-catalytic membrane material and a preparing method thereof and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. Representation is carried out on the prepared material by adopting testing means, such as an X-ray diffractometer, an X-ray photo-electron spectrometer, an ultraviolet spectrograph and a scanning electronic microscope. The process of the method comprises the following steps: first, in an electrolytic solution containing silver ions and phosphate ions, utilizing a micro-arc oxidation technology to prepare a TiO2 membrane containing Ag and P on a Ti plate substrate; then, sintering Ag and P precursors in the membrane through muffle furnace sintering to form Ag3PO4 nanometer particles;and finally forming the nanometer Ag3PO4 / TiO2 heterojunction photo-catalytic membrane. The method has the advantages that the preparing process is simple and easy to control, the operation is convenient, the cost is low, the photocatalytic activity of the membrane is high, and the photocatalytic activity can be regenerated through forging.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
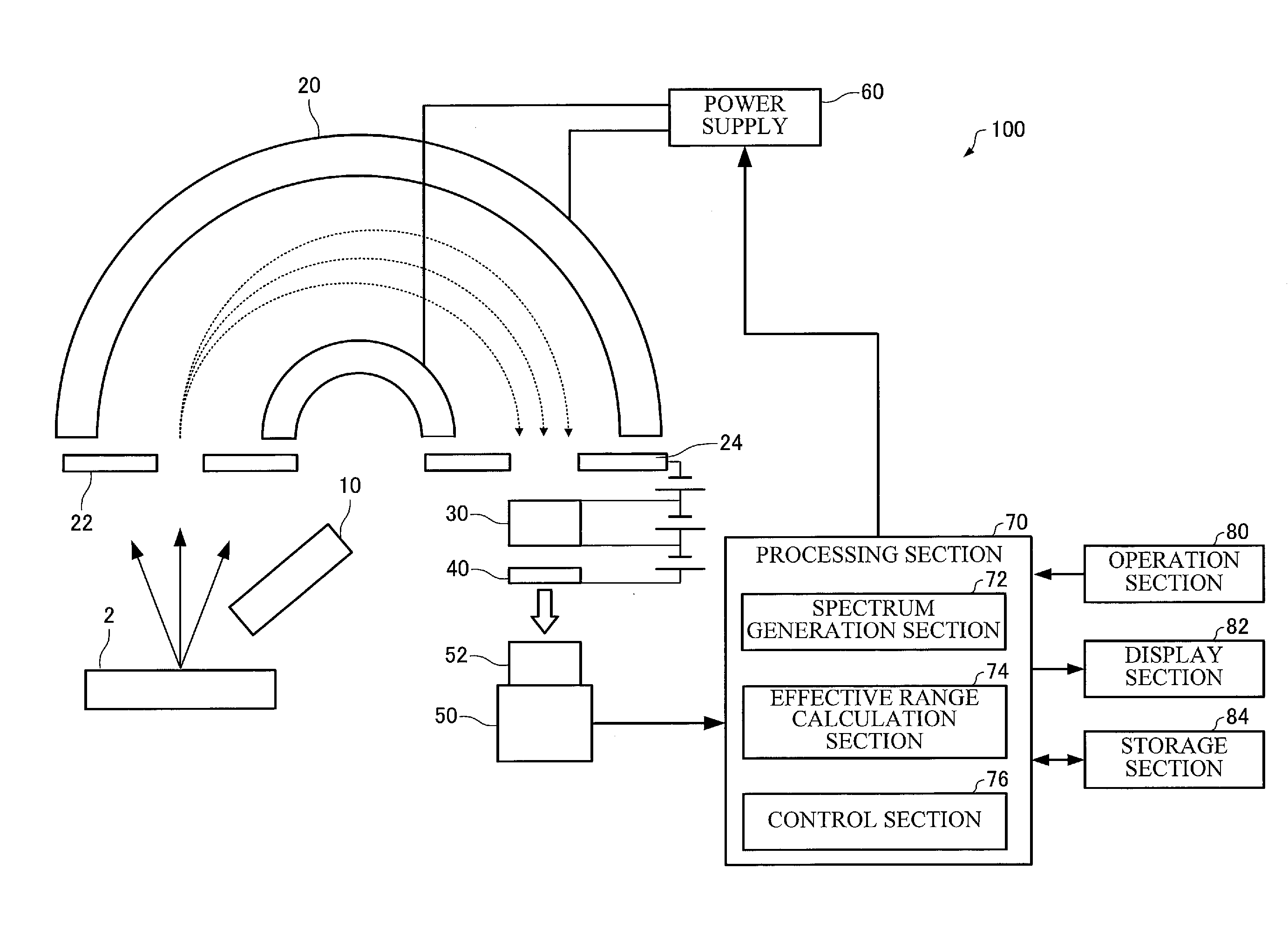
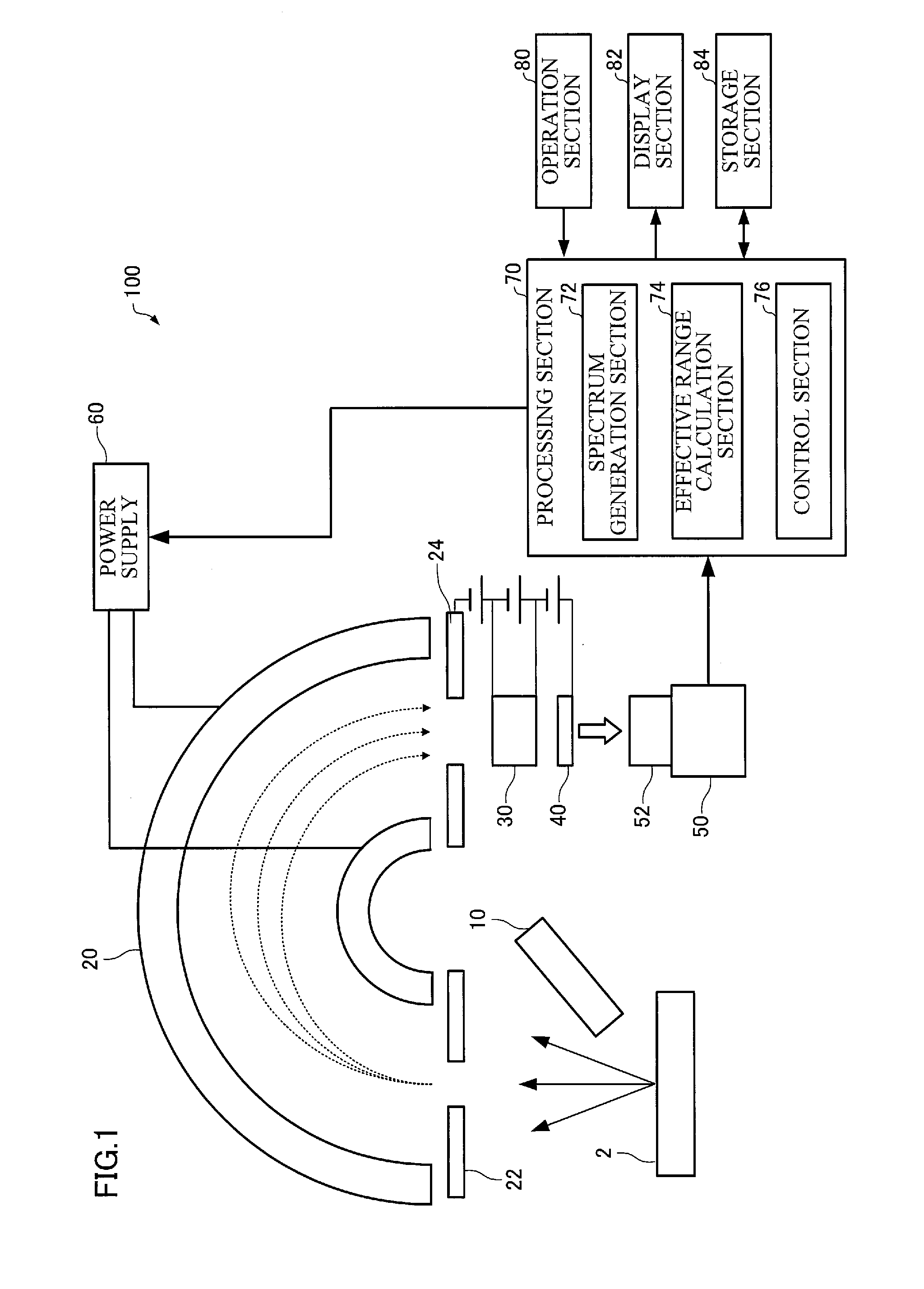
Electron Spectrometer and Measurement Method
ActiveUS20160268119A1Accurately effective rangeAccurate calculationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationImaging particle spectrometryCamera imageFluorescence
An electron spectrometer includes: an energy analyzer section that energy-analyzes electrons emitted from a specimen; a micro-channel plate that amplifies the electrons analyzed by the energy analyzer section; a fluorescent screen that converts the electrons amplified by the micro-channel plate into light; a camera that photographs the fluorescent screen; and an effective range calculation section that calculates an effective range of the fluorescent screen within a camera image photographed by the camera, the effective range calculation section performing a process that acquires a plurality of the camera images photographed while causing the energy analyzer section to analyze the electrons with a different center energy, a process that converts the plurality of camera images respectively into a plurality of spectra, and a process that calculates the effective range of the fluorescent screen within the camera image based on the plurality of spectra.
Owner:JEOL LTD
Device and method for electron transfer from a sample to an energy analyzer and electron spectrometer device
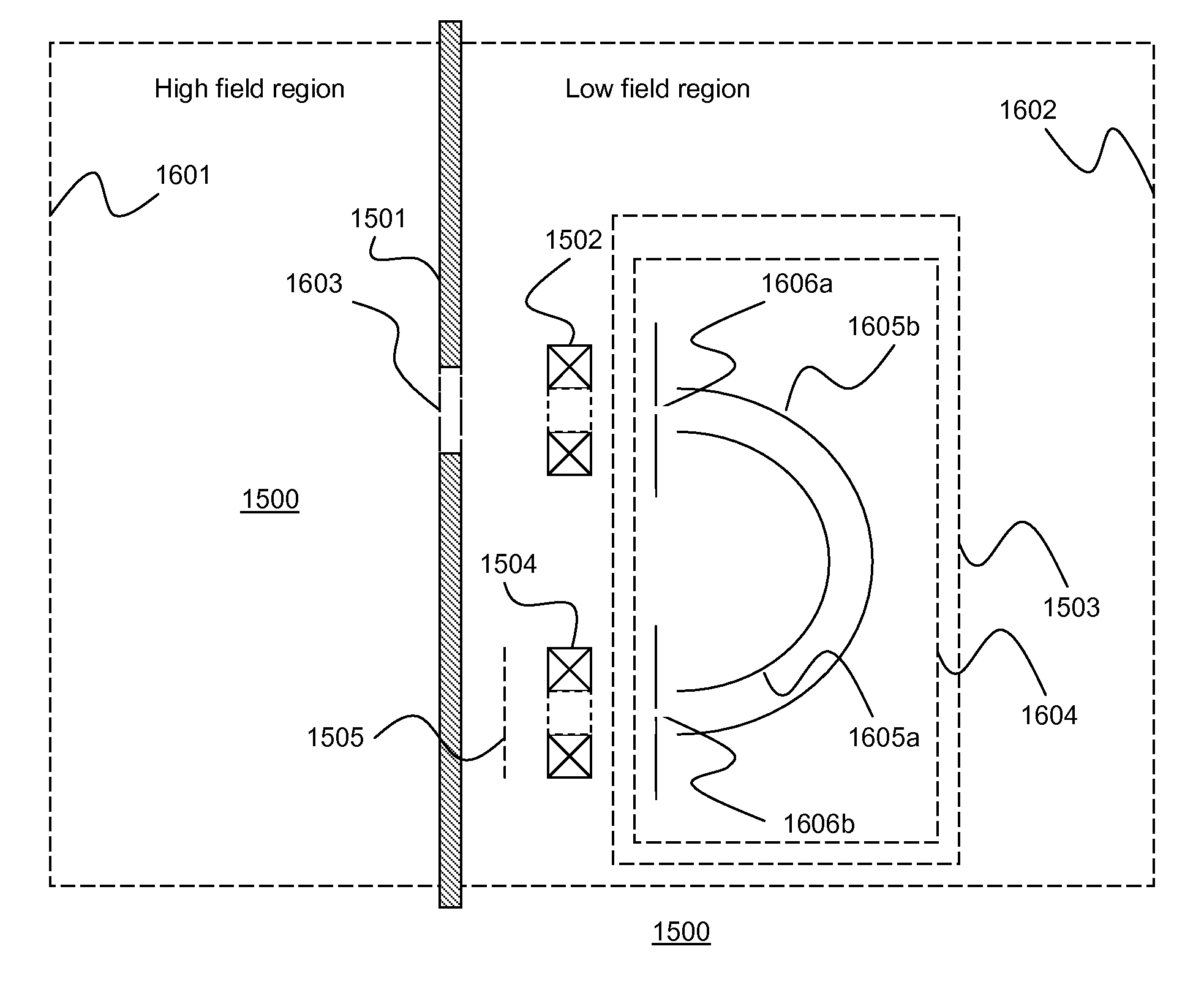
ActiveUS20200303177A1Wide range of anglesReduce aberrationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron/ion optical arrangementsOptical spectrometerOptical axis
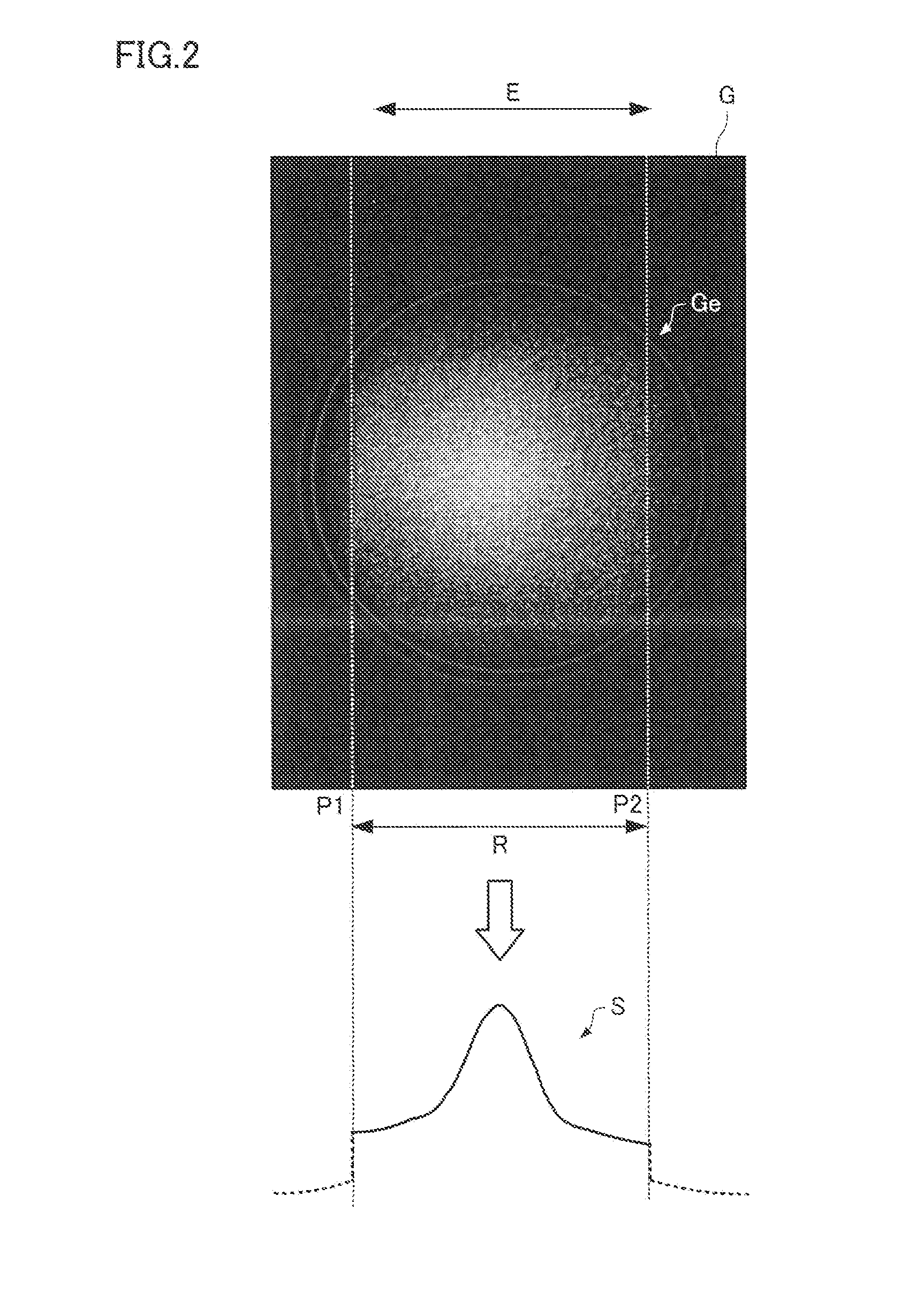
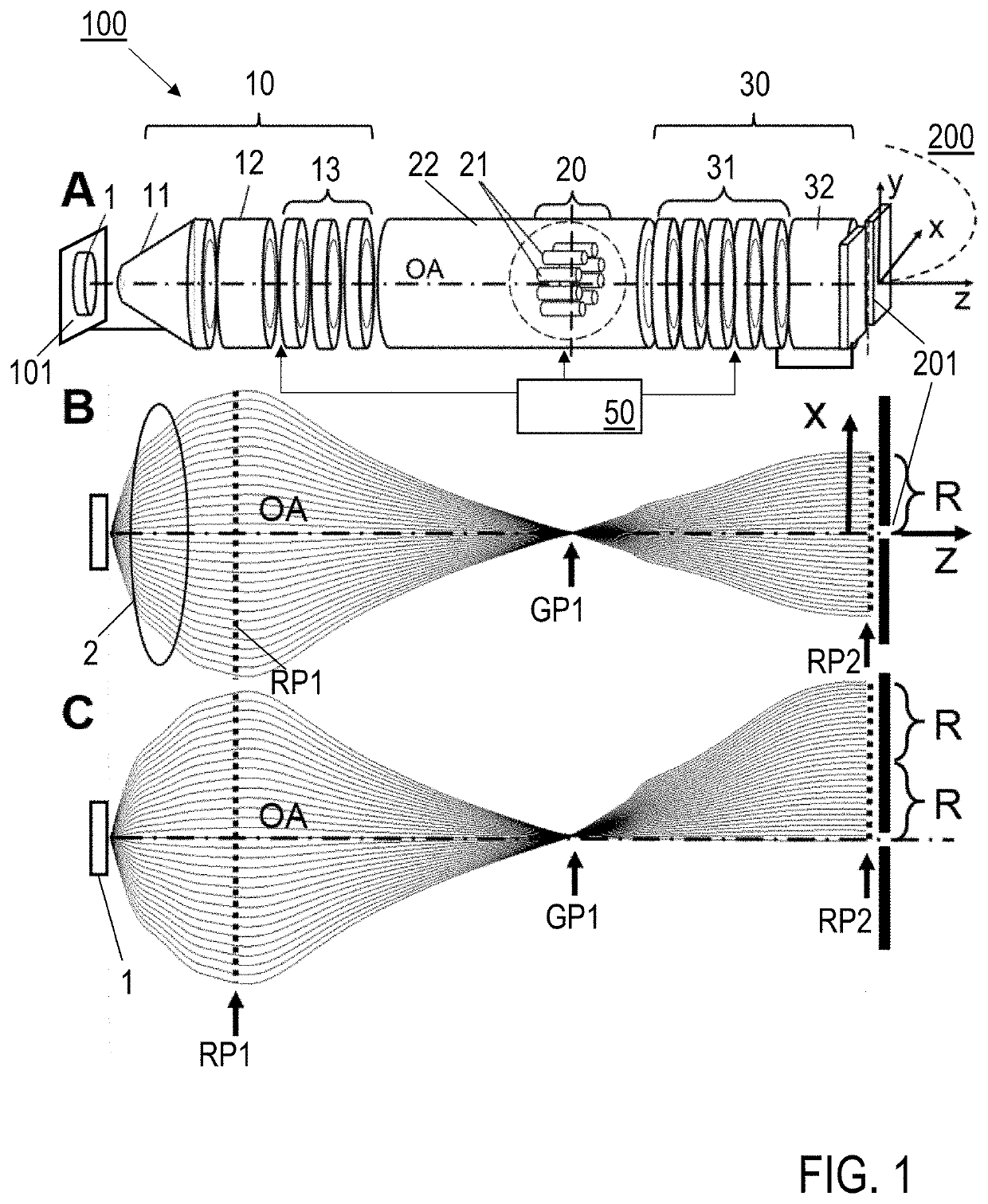
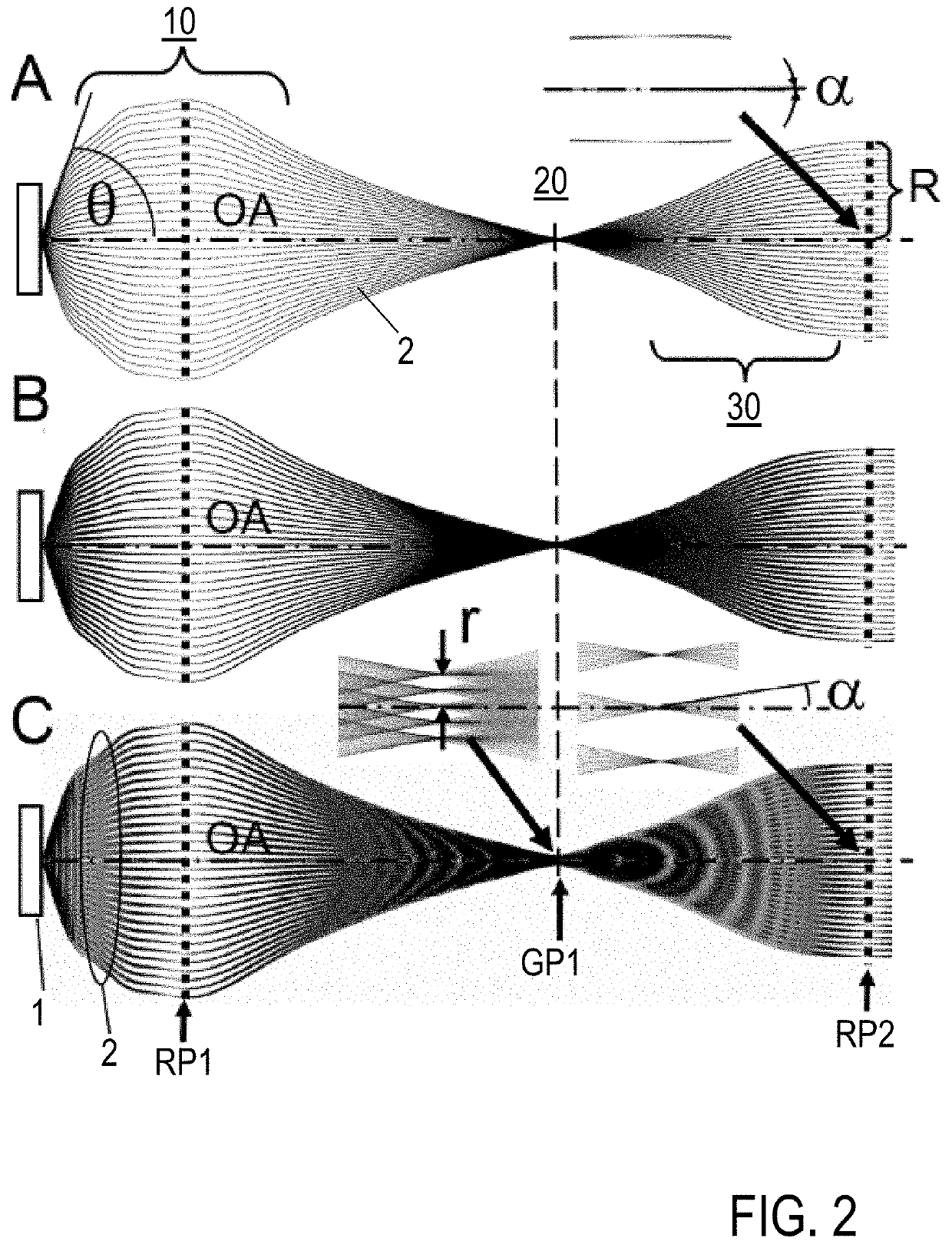
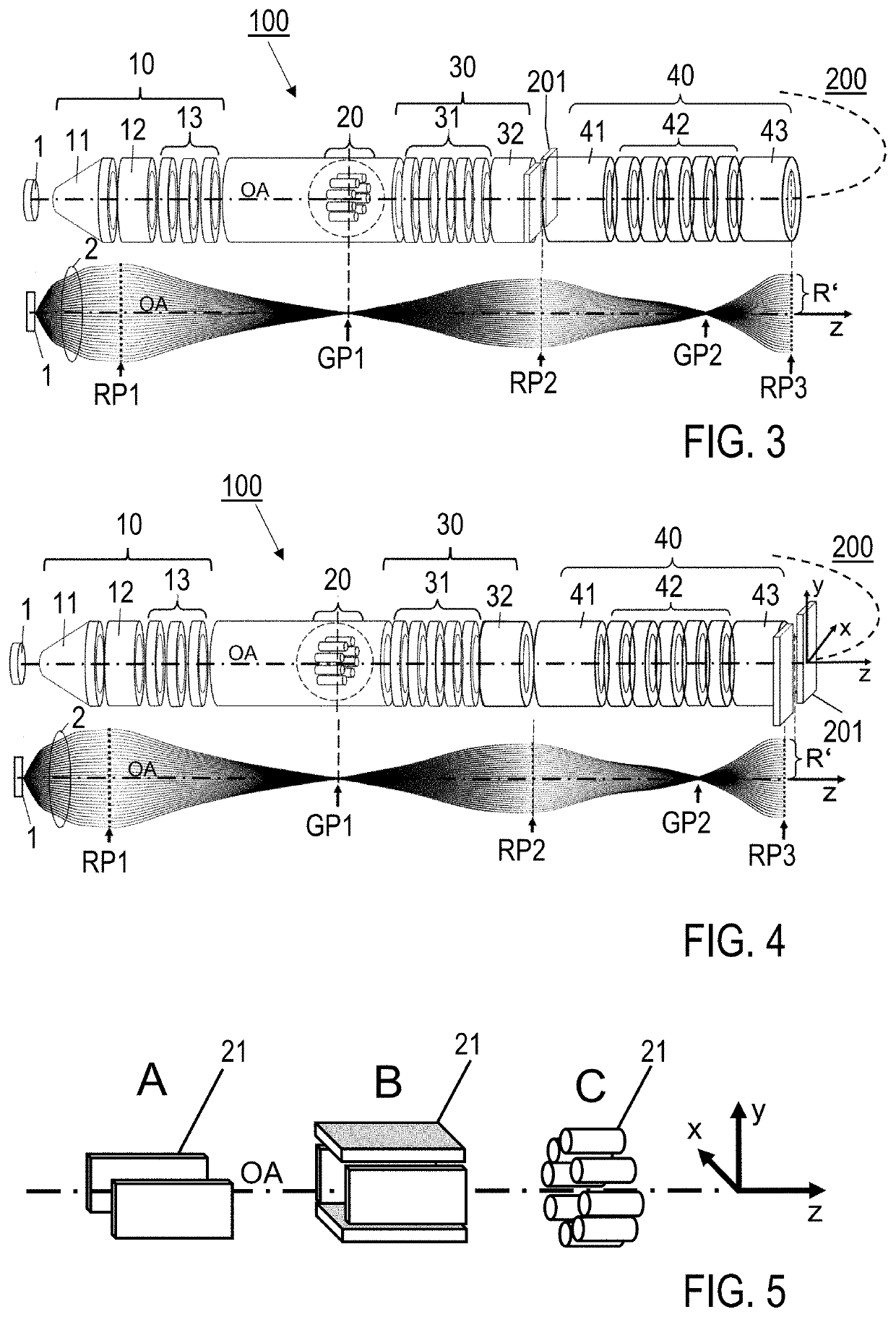
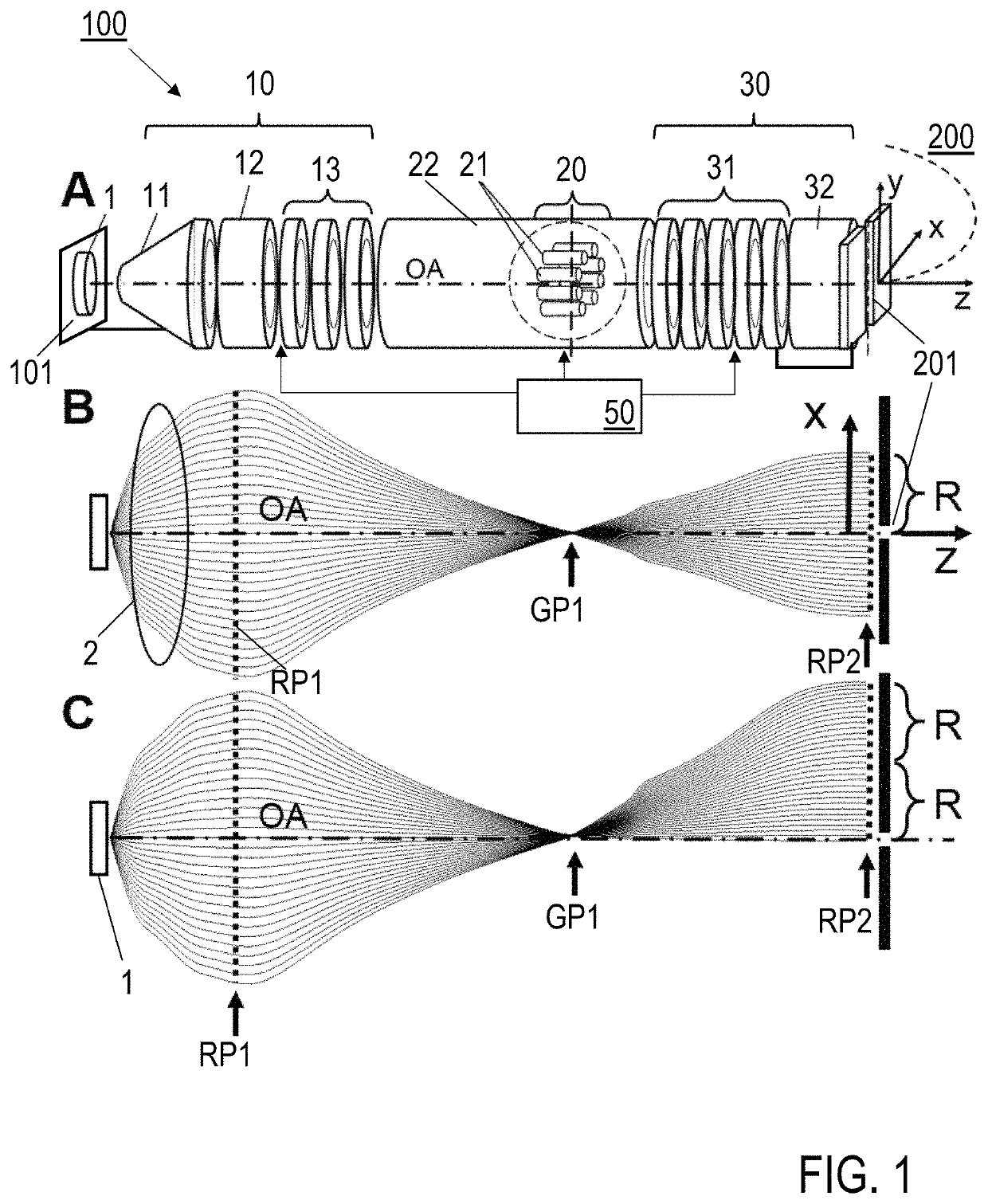
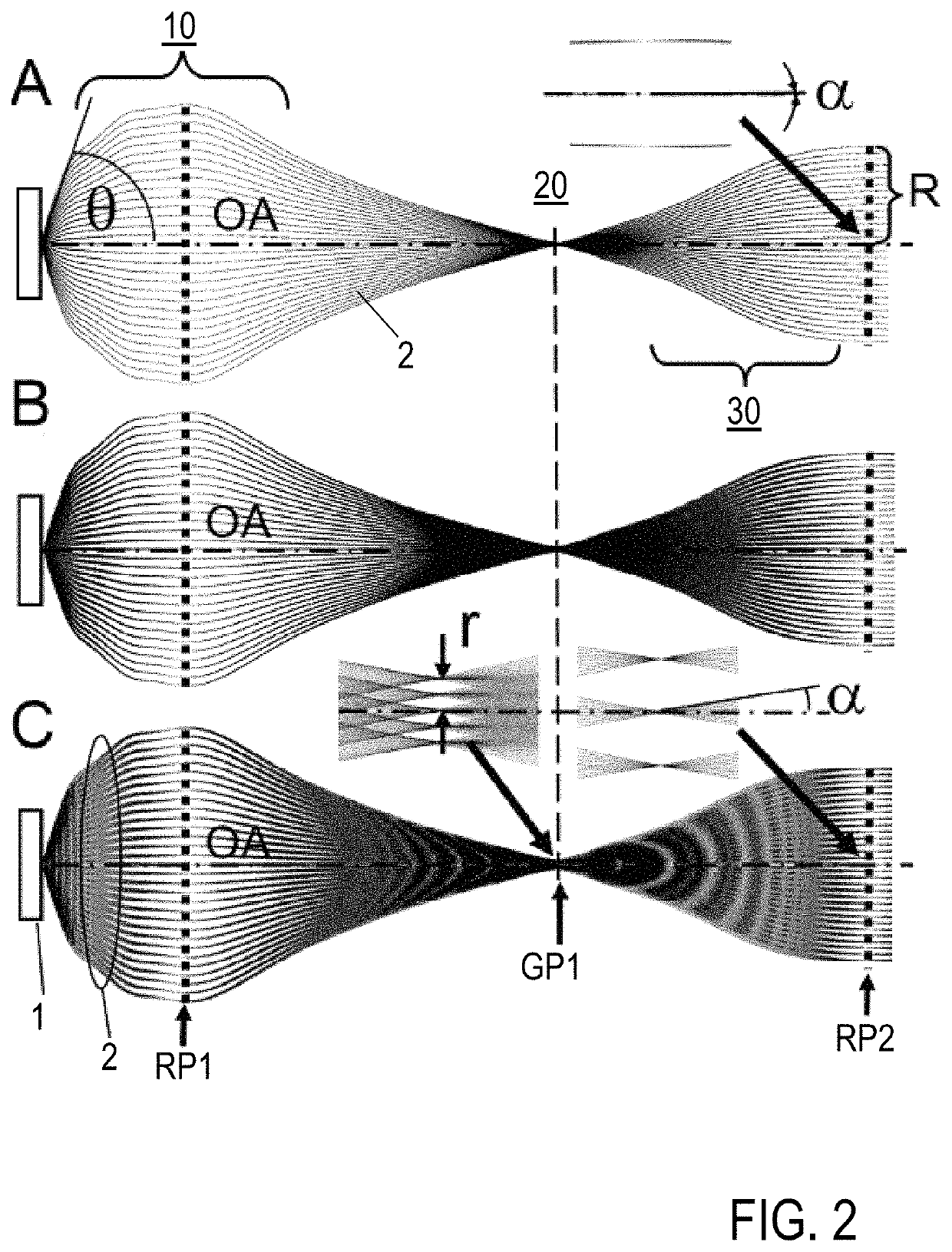
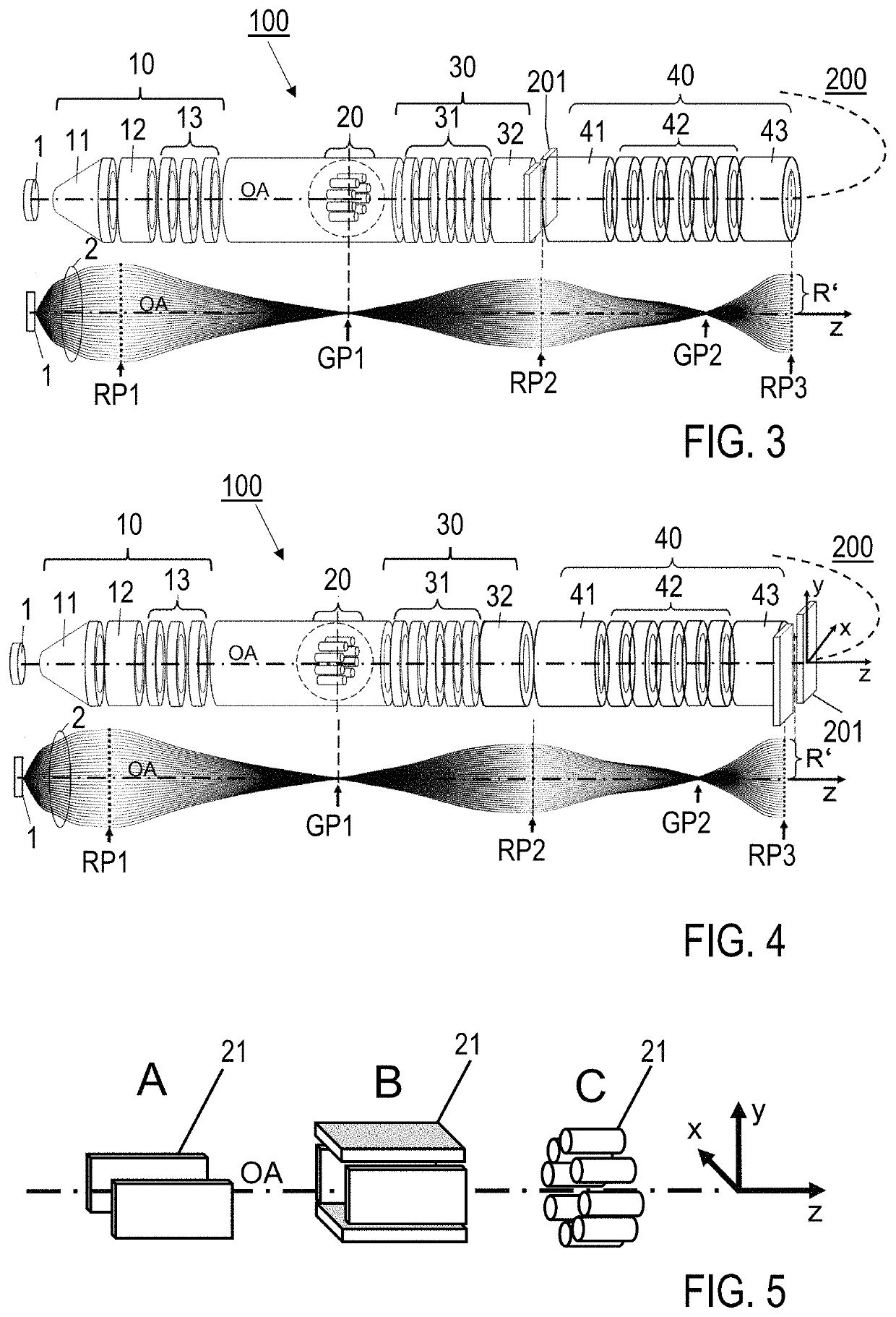
An electron imaging apparatus 100 is disclosed, which is configured for an electron transfer along an electron-optical axis OA of an electron 2 emitting sample 1 to an energy analyzer apparatus 200, and comprises a sample-side first lens group 10, an analyzer-side second lens group 30 and a deflector device 20, configured to deflect the electrons 2 in an exit plane of the electron imaging apparatus 100 in a deflection direction perpendicular to the electron-optical axis OA. An electron spectrometer apparatus, an electron transfer method and an electron spectrometry method are also described.
Owner:SPECS SURFACE NANO ANALYSIS
Transmission electron microscope having electron spectrometer
InactiveUS8436301B2Effective correctionImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectric discharge tubesConventional transmission electron microscopeElectron
In a spectral image formed by two orthogonal axes, one of which is an axis of the amount of energy loss and the other of which is an axis of positional information, by the use of an electron spectrometer and a transmission electron microscope, distortion in the spectral image of a sample to be analyzed is corrected with high efficiency and high accuracy by comparing electron beam positions calculated from a two-dimensional electron beam position image formed by the two orthogonal axes (the axis of the amount of energy loss and the axis of positional information) with reference electron beam positions, and calculating amounts of the distortion based on the differences of the electron beam positions. Method and apparatus are offered which correct distortion in a spectral image with high efficiency and high accuracy, the image being formed by the two orthogonal axes (the axis of the amount of energy loss and the axis of positional information).
Owner:HITACHI HIGH-TECH CORP
Analysis Method and Analysis Apparatus
ActiveUS20210096063A1Spectrometer detectorsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationComputational physicsAnalytical chemistry
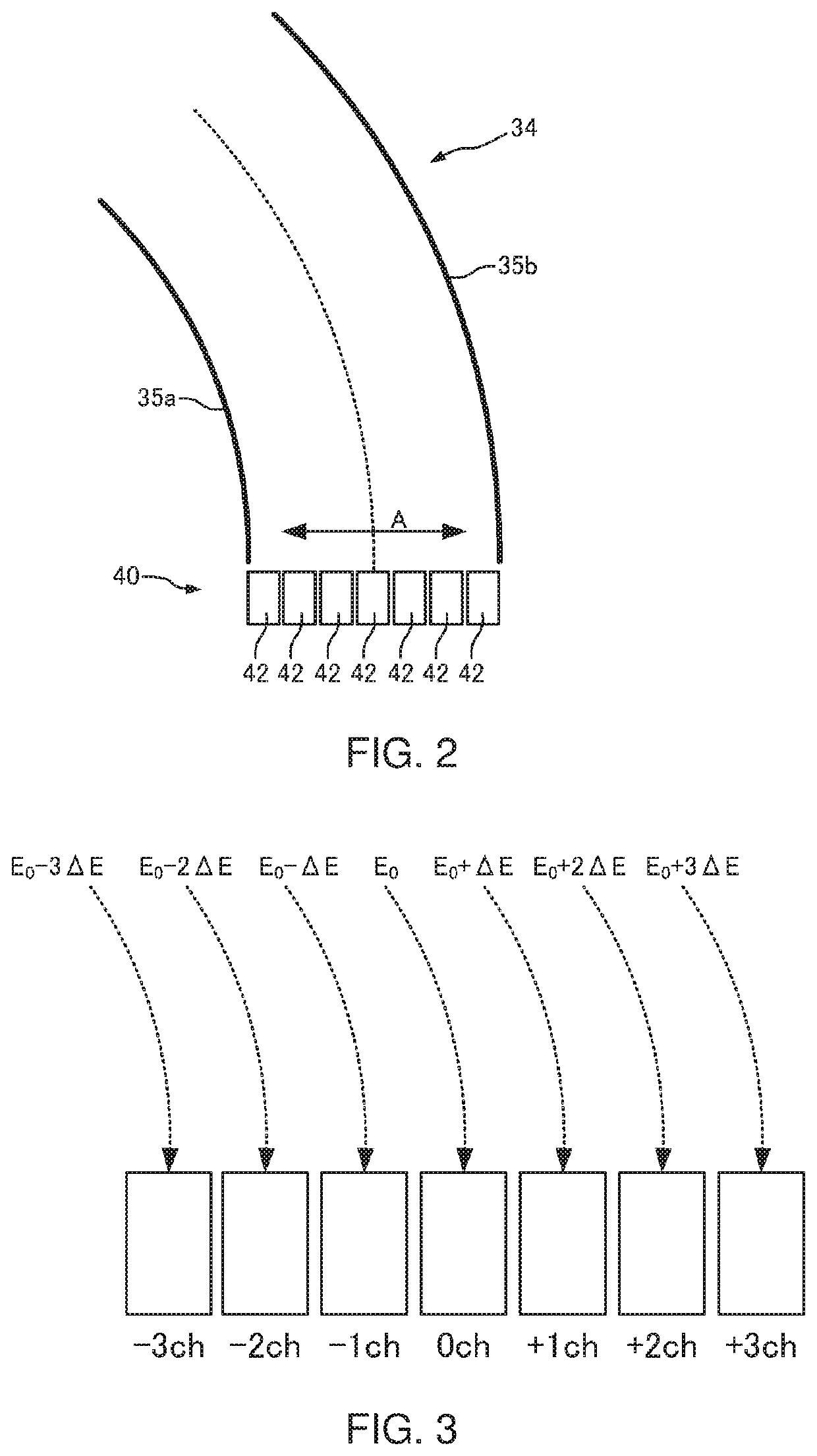
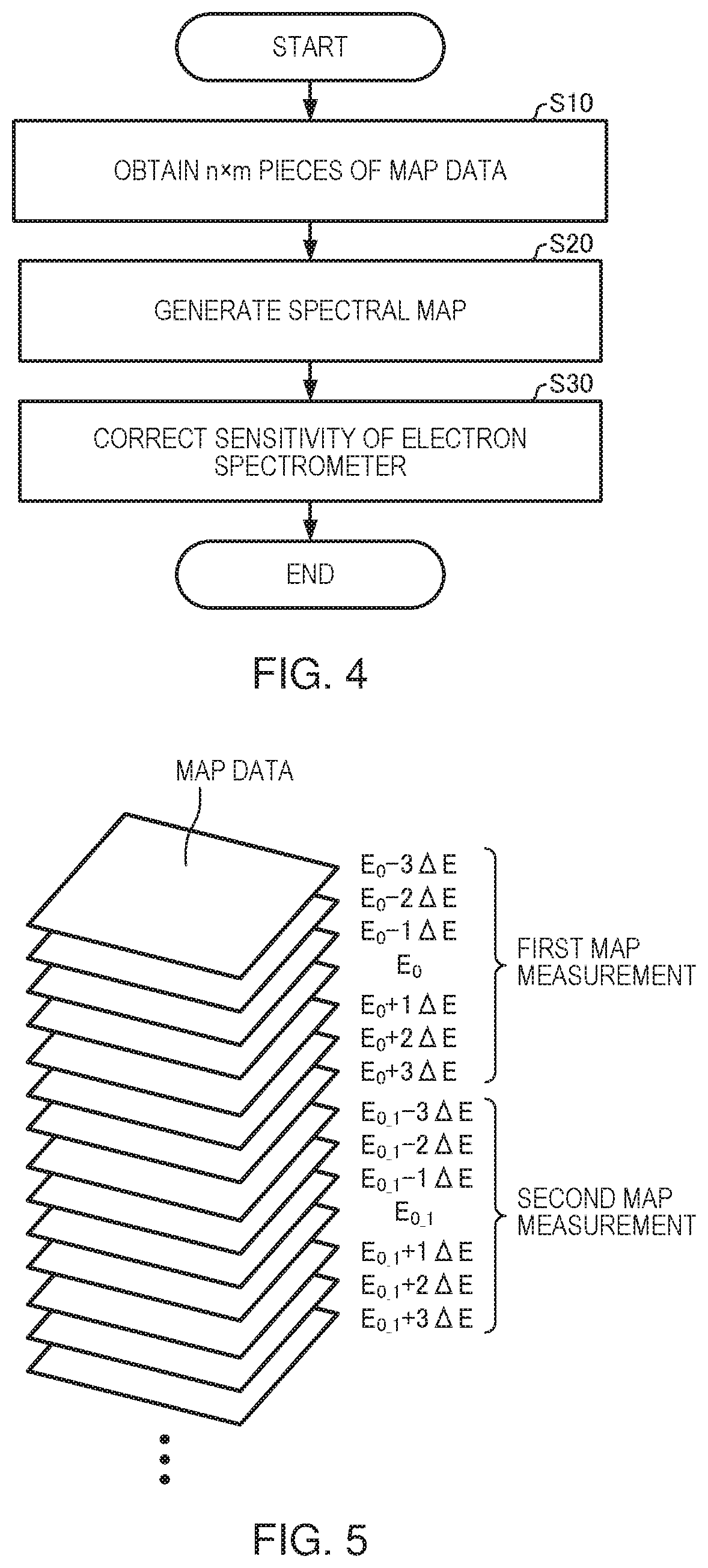
An analysis method includes: obtaining n×m pieces of map data by repeating, m times, a map measurement in which n pieces of map data are obtained by scanning a specimen with a primary probe to detect electrons emitted from the specimen with an electron spectrometer, while measurement energy ranges of an analyzer are varied; and generating a spectral map in which a position on the specimen is associated with a spectrum based on the n×m pieces of map data, the measurement energy ranges of m times of the map measurement not overlapping each other.
Owner:JEOL LTD +1
Spherical aberration corrected electrostatic lens, input lens, electron spectrometer, photoemission electron microscope and measuring system
InactiveUS7655923B2Improve performanceHigh sensitivityThermometer detailsStability-of-path spectrometersElectron microscopePhotoelectron microscopy
A mesh (M) having an ellipsoid shape or a shape close to the ellipsoid shape is attached to an electrode (EL1) among electrodes (EL1 to ELn). Voltages of the later-stage electrodes (EL2 to ELn) are appropriately set. With this arrangement, a local negative spherical aberration generated by the mesh (M) is cancelled out with a positive spherical aberration. This optimizes an electric field distribution. As a result, this realizes an electrostatic lens whose acceptance angle is extended to about ±60°.
Owner:NARA INSTITUTE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY +1
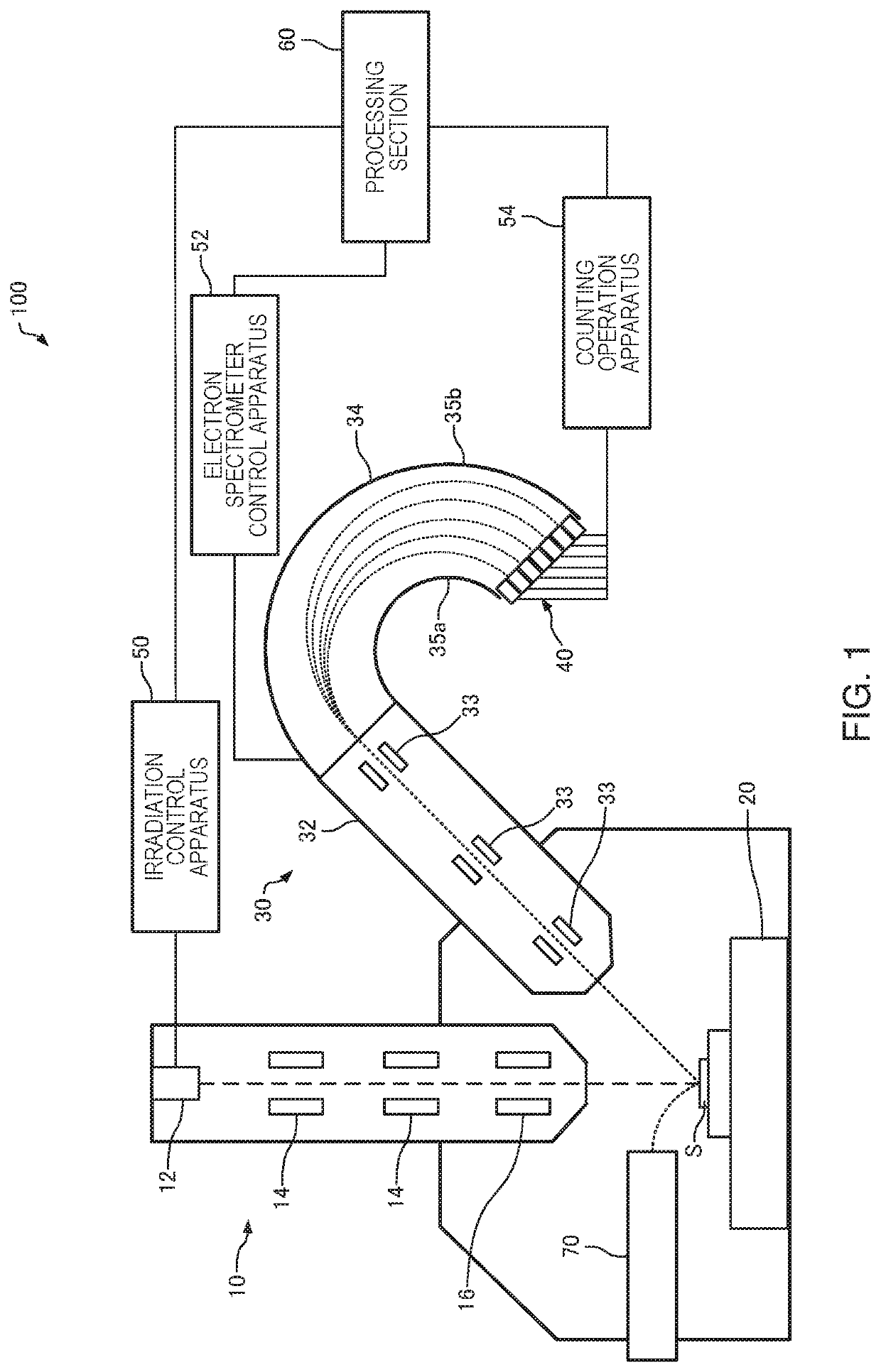
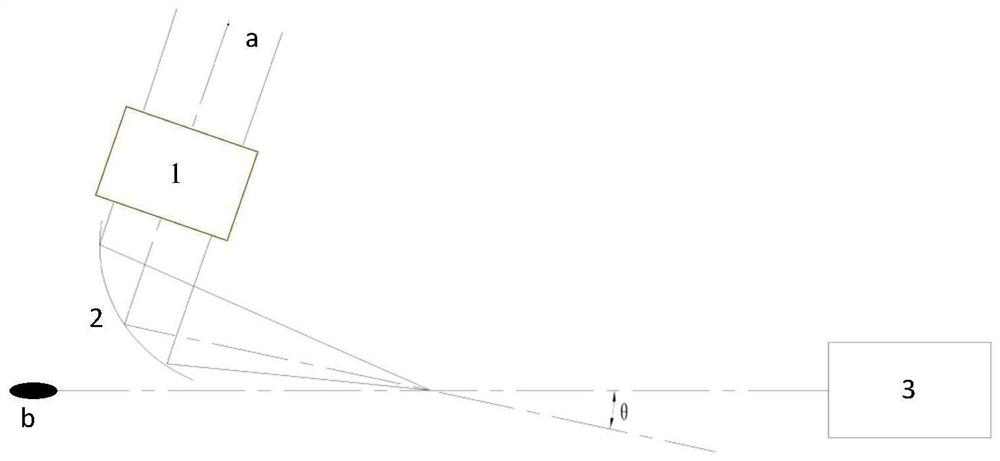
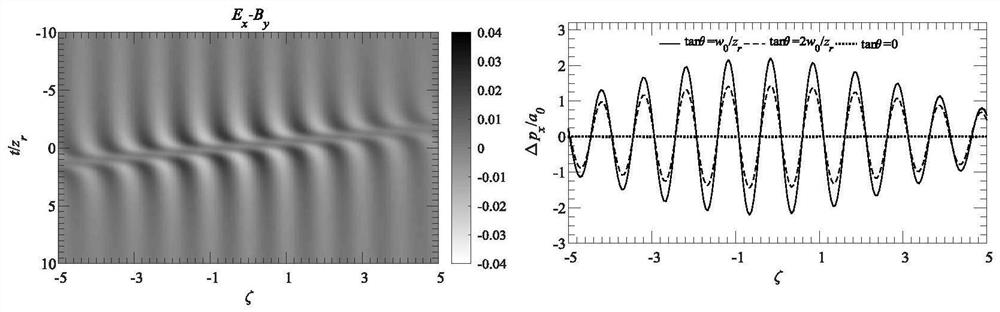
Electron beam transient energy chirp reconstruction method
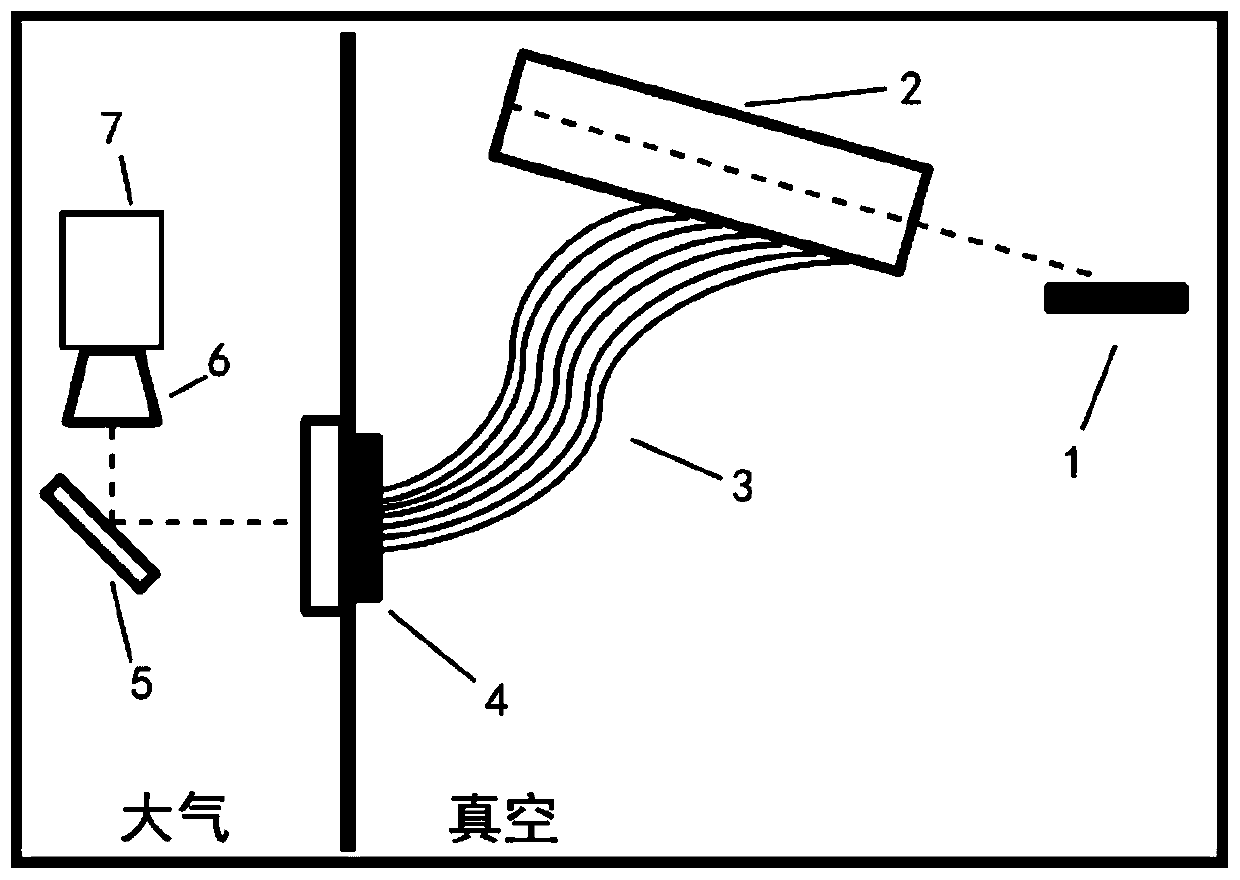
ActiveCN111817786AFast real-time reconstructionEffective diagnosisDistortion/dispersion eliminationElectromagnetic transmittersDivergence angleParticle physics
The invention discloses an electron beam transient energy chirp reconstruction method, and relates to the technical field of electron beam transient energy chirp diagnosis. The electron beam transientenergy chirp reconstruction method comprises steps that a tightly-focused chirped pulse laser a is focused by a delayer (1) and a parabolic mirror (2) and then interacts with a chirped electron beamb, energy spectrum and transverse divergence angle distribution of the chirped electron beam b are analyzed by an electron spectrometer (3), Fourier transform of an energy domain is applied to realizereconstruction of transient energy chirp of the electron beam, and the reconstruction method comprises the steps of A-E. Compared with the prior art, the method has the advantages that firstly, electron beam bunch transient energy chirp can be reconstructed; secondly, the devices are simple and convenient, the method can be realized only by common mature, stable and reliable devices such as the paraboloidal mirror and the electronic spectrometer; thirdly, the expansibility is good, the adopted pulse laser can be expanded to any waveband. The method is of great significance to control optimization of small accelerators and dynamic behavior exploration and optimization of electron beams in various novel accelerators.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Real-time electron spectrometer based on thin film scintillator and optical fiber array
InactiveCN107121693AReduce noiseImprove resolutionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentLow noiseHigh energy
The present invention provides a real-time electron spectrometer based on a thin film scintillator and an optical fiber array. The spectrometer comprises an electron collimating device, a uniform magnetic field device, the thin film scintillator, the optical fiber line-to-plane conversion array and an imaging system; the electron collimating device, the uniform magnetic field device and the thin film scintillator are arranged in a housing; a coaxial hole in the axial direction of the electronic collimating device is formed in the housing; and the coaxial hole is used for assisting the position adjustment of the electron spectrometer. On the basis of a magnetic field deflection-based traditional electron spectrometer, the real-time electron spectrometer integrates advantages such as the real-time detection of the scintillator, low noise and flexibility of plastic optical fibers, high matching degree between the plane fiber array and the image plane of a detector. The electron spectrometer of the present invention is of simplicity and is easy to operate. The real-time electron spectrometer of the invention can diagnose and detect electrons of which the energy ranges from 0.98MeV to 4.55MeV, can be extended to higher energy bands and has a high application value in laser plasma physics.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
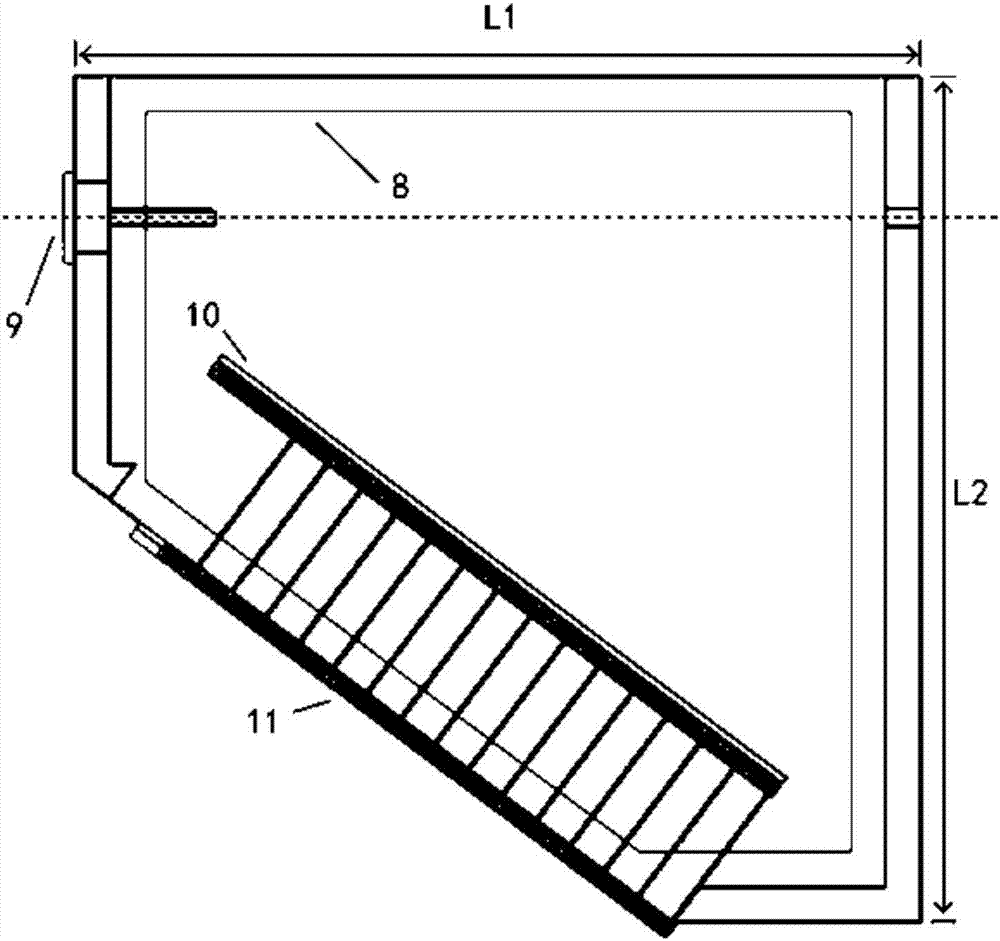
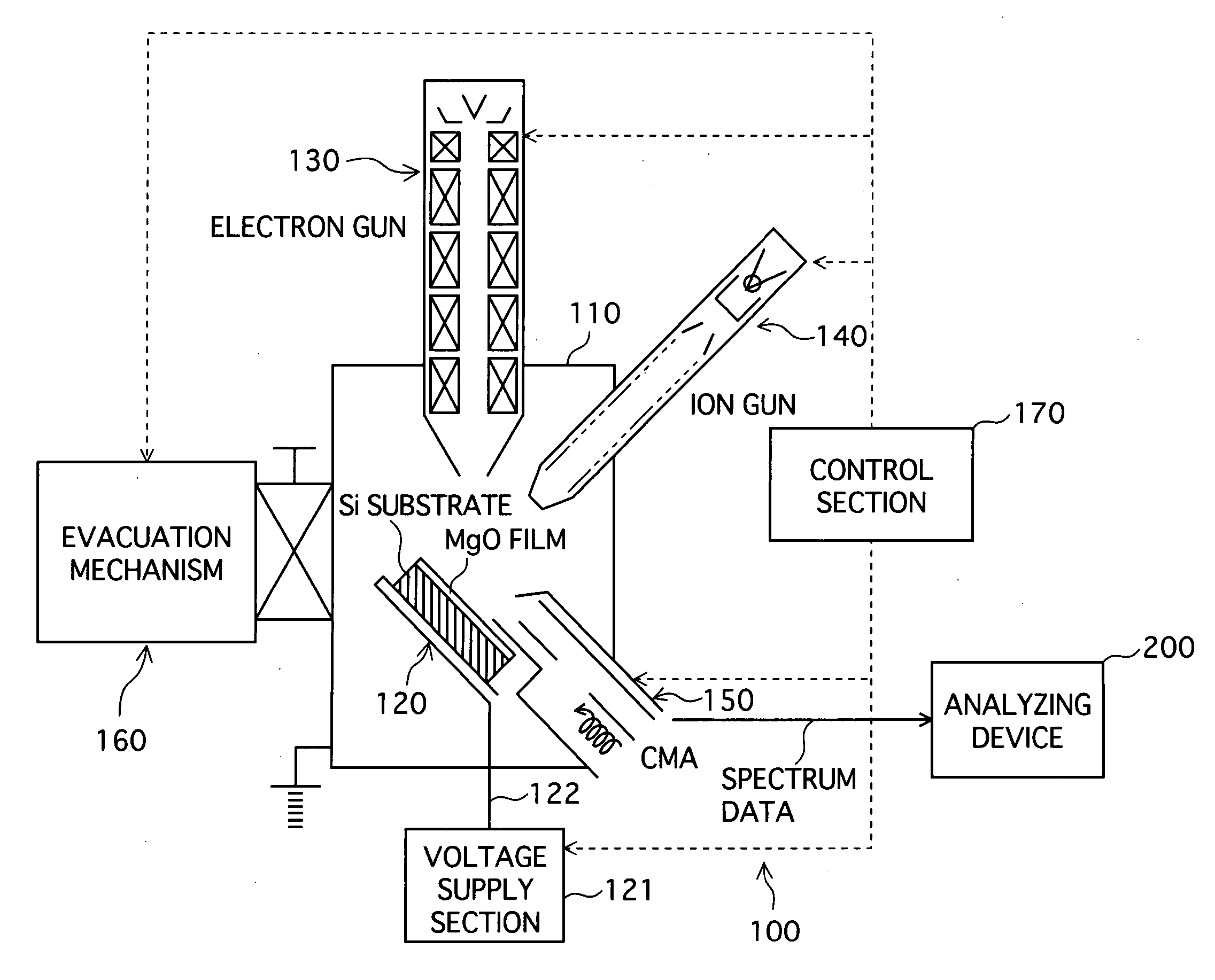
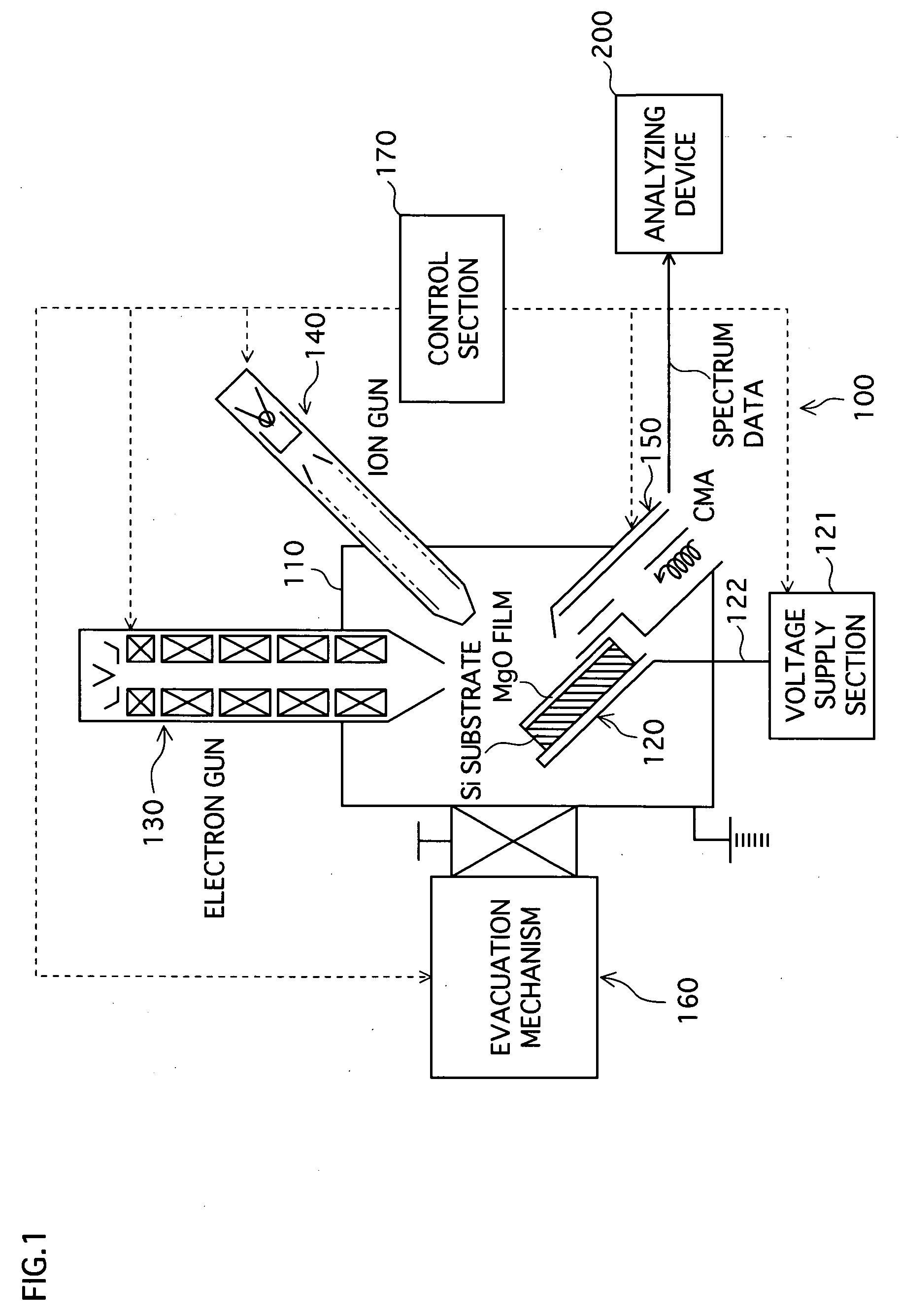
Insulating film measuring device, insulating film measuring method, insulating film evaluating device, insulating film evaluating method, substrate for electric discharge display element, and plasma display panel
InactiveUS20060250147A1Simply and accurately obtainingIncrease productionMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationGas discharge electrodesMeasurement deviceSpectrograph
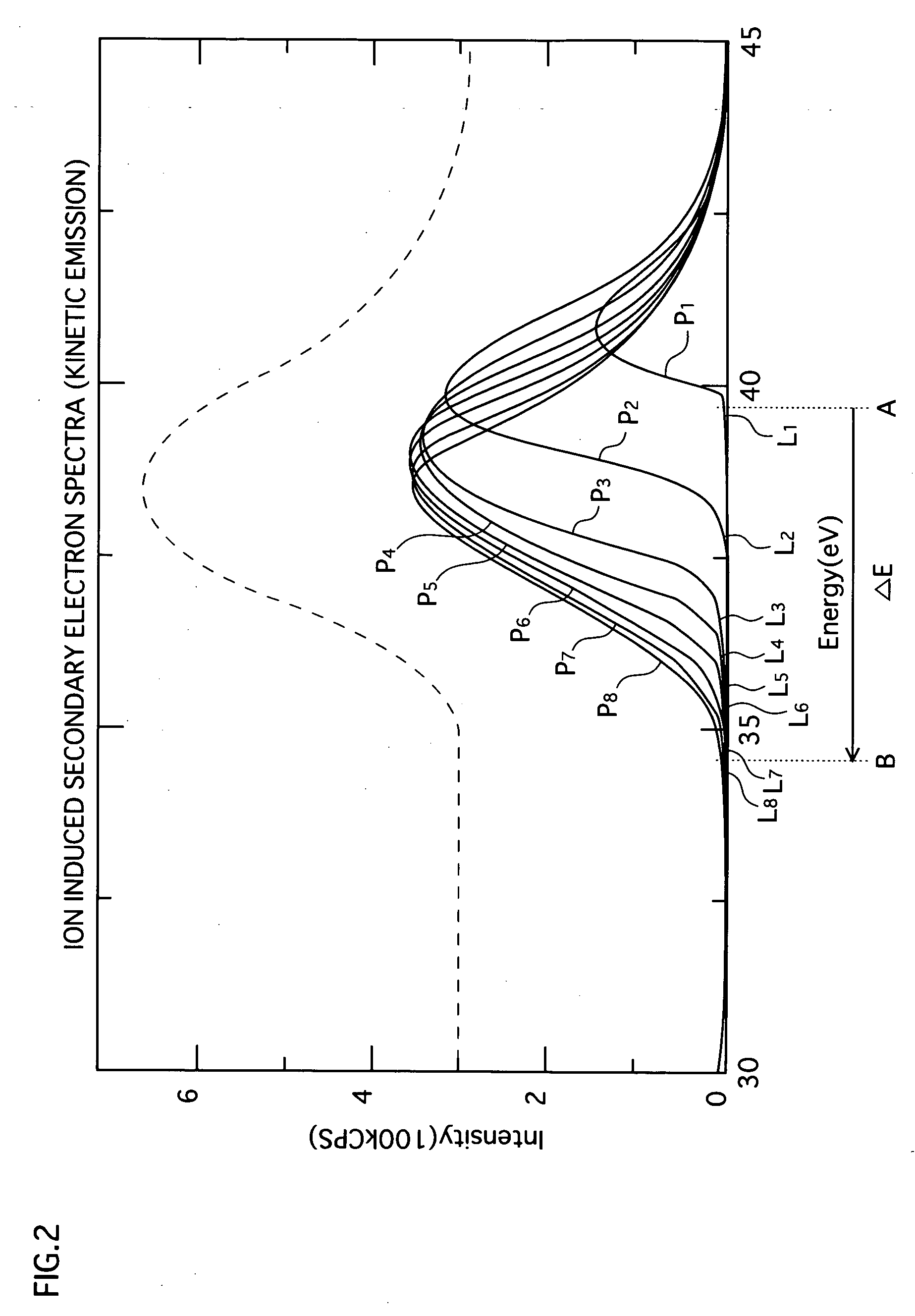
A measuring device, a measuring method, and an evaluating device for easily and accurately obtaining information suitable to evaluate, for example, the discharge characteristic of an insulating film such as an MgO protective layer of a plasma display are provided. An MgO film surface, a sample to be measured, is irradiated with electrons or ions emitted from an electron gun (130) or an ion gun (140). The energy distribution of the secondary electrons emitted from the sample is measured by an electron spectrograph (150), and the spectrum data on the measured secondary electrons is supplied to an analyzing device (200). The analyzing device (200) analyzes the spectrum data and determines information (evaluation values) to evaluate the properties of the sample to be measured.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
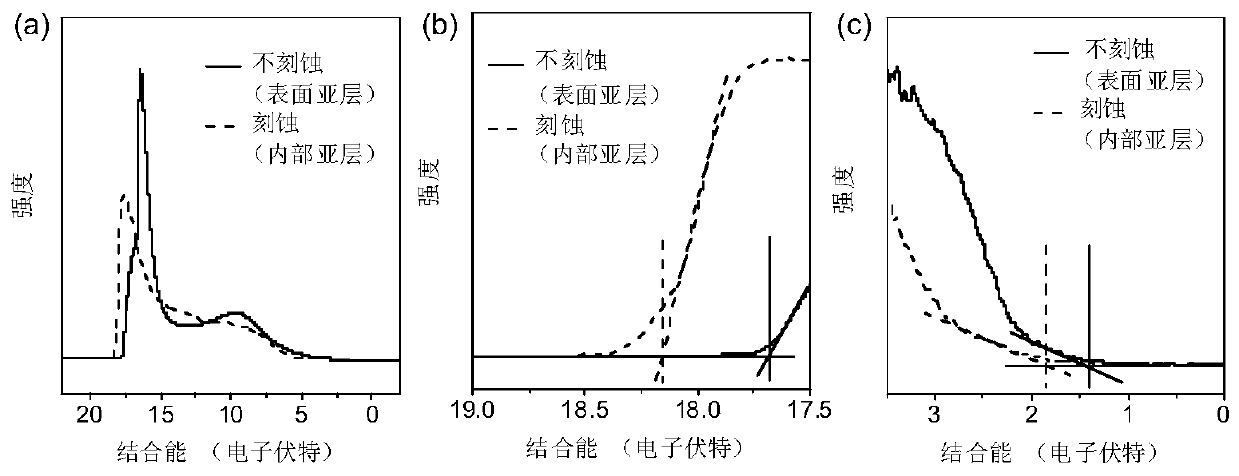
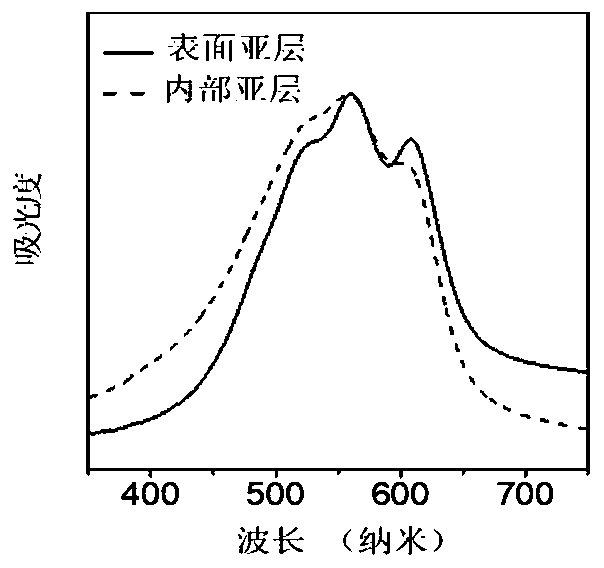
Method for measuring photoelectron spectroscopy of polymer sublayer by utilizing plasma etching
PendingCN111537539ALow costMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUltraviolet lightsPolymer thin films
The invention discloses a method for measuring polymer sublayer photoelectron spectroscopy by plasma etching, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) cleaning two ITO glass substrates, performing blow-drying with nitrogen, carrying out ultraviolet-ozone treatment, and performing modifying in an n-octyl trichlorosilane solution; (2) preparing polymer films on the two modified ITO glass substrates, and respectively marking the polymer films as a film 1 and a film 2; (3) detecting the ultraviolet electron spectrum of the polymer film 1 by using an ultraviolet electron spectrometer, etching the polymer film 2 by using low-pressure (20 Pascal) oxygen plasma, and detecting the ultraviolet electron spectrum of the polymer film 2. According to the invention, the low-pressure oxygen plasma etching technology is combined with an ultraviolet electronic energy spectrum method for detecting the ultraviolet light electron energy spectra, namely sub-layer photoelectron energy spectra, at different depth positions of the polymer semiconductor thin film, and obtaining energy level distribution, thereby facilitating the exploration of the relation between the properties of the polymer semiconductor thin film and the properties of photoelectric devices. The method has good application prospects in the field of thin film analysis.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
A positron-electron magnetic spectrometer with angular resolution
ActiveCN105425277BReasonable structureIngenious designX-ray spectral distribution measurementMeasurement precisionImaging spectrometer
The invention discloses a positron-electron magnetic spectrometer with the angular resolution capability. The positron-electron magnetic spectrometer comprises an alignment hole array, a cylindrical magnet device and a positron-electron recording medium, wherein the alignment hole array is used for leading positrons and electrons into the cylindrical magnet device; the cylindrical magnet device comprises an outer shell, an inner shell and permanent magnets, the permanent magnets are fixed between the outer shell and the inner shell and are radially distributed; a magnetic field loop in which the movement directions of the positrons and the electrons are deflected is formed by space enclosed by all of the permanent magnets; the positron-electron recording medium is used for recording the intensity distribution of the positrons and the electrons on an imaging plane, so as to obtain the angular distribution of the positrons and the electrons and the information of an energy spectrum of the angular distribution. The positron-electron magnetic spectrometer has the advantages of reasonable structure and skillful design, the technical defects of low measurement precision and long time for adjusting a measurement range of an existing magnetic spectrometer are preferably overcome, and the diagnosis precision of an energy spectrum of the angular distribution of the positrons and the electrons is greatly increased, and therefore, the positron-electron magnetic spectrometer is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
A nano-ag3po4 modified tio2 heterojunction photocatalytic film layer material and its preparation method
ActiveCN107675230BRealize continuous preparationSimple methodPhysical/chemical process catalystsSurface reaction electrolytic coatingHeterojunctionMicro arc oxidation
The invention discloses a nanometer Ag3PO4-modified and TiO2 heterojunction photo-catalytic membrane material and a preparing method thereof and belongs to the technical field of nanometer material preparation. Representation is carried out on the prepared material by adopting testing means, such as an X-ray diffractometer, an X-ray photo-electron spectrometer, an ultraviolet spectrograph and a scanning electronic microscope. The process of the method comprises the following steps: first, in an electrolytic solution containing silver ions and phosphate ions, utilizing a micro-arc oxidation technology to prepare a TiO2 membrane containing Ag and P on a Ti plate substrate; then, sintering Ag and P precursors in the membrane through muffle furnace sintering to form Ag3PO4 nanometer particles;and finally forming the nanometer Ag3PO4 / TiO2 heterojunction photo-catalytic membrane. The method has the advantages that the preparing process is simple and easy to control, the operation is convenient, the cost is low, the photocatalytic activity of the membrane is high, and the photocatalytic activity can be regenerated through forging.
Owner:JILIN NORMAL UNIV
Impulse-resolving photo-electron spectrometer and method for impulse-resolving photo-electron spectroscopy
PendingCN111727489ALow costGood momentum resolutionElectron/ion optical arrangementsImaging particle spectrometrySpatially resolvedOptical axis
The invention relates to the field of physics and relates to an impulse-resolving photo-electron spectrometer, by means of which the physical properties can be determined. The aim of the invention isto provide an impulse-resolving photo-electron spectrometer enabling the device components to have a simple structure with a significantly reduced overall volume. The aim of the invention is achievedby means of an impulse-resolving photo-electron spectrometer comprising components arranged one behind the other in the direction of the optical axis at least in a vacuum and which are each at least one electron emission sample and a focusing system, wherein the focusing system consists of at least one electron lens and at least one detector, wherein the electron lens consists of three cylindricalelements, wherein the first cylindrical element has a potential = 0 and the two subsequently arranged cylindrical elements have a potential of being not equal to 0, and wherein the detector is one ormore spatially resolved detectors which are arranged in the focal plane of the electron lens.
Owner:德累斯顿莱布尼茨固体材料研究所
Excited Brillouin scattering gain spectrum measuring method and system thereof
ActiveCN103411675BReduce bandwidth requirementsRealize measurementRadiation pyrometrySpectrometry/spectrophotometry/monochromatorsPhotovoltaic detectorsBeam splitting
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Device and method for electron transfer from a sample to an energy analyzer and electron spectrometer device
ActiveUS11328918B2Wide range of anglesImprove efficiencyMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationElectron/ion optical arrangementsOptical spectrometerOptical axis
An electron imaging apparatus 100 is disclosed, which is configured for an electron transfer along an electron-optical axis OA of an electron 2 emitting sample 1 to an energy analyzer apparatus 200, and comprises a sample-side first lens group 10, an analyzer-side second lens group 30 and a deflector device 20, configured to deflect the electrons 2 in an exit plane of the electron imaging apparatus 100 in a deflection direction perpendicular to the electron-optical axis OA. An electron spectrometer apparatus, an electron transfer method and an electron spectrometry method are also described.
Owner:SPECS SURFACE NANO ANALYSIS
Real-time Electron Spectrometer Based on Thin Film Scintillator and Fiber Array
InactiveCN107121693BReduce noiseImprove resolutionX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentLow noiseHigh energy
The present invention provides a real-time electron spectrometer based on a thin film scintillator and an optical fiber array. The spectrometer comprises an electron collimating device, a uniform magnetic field device, the thin film scintillator, the optical fiber line-to-plane conversion array and an imaging system; the electron collimating device, the uniform magnetic field device and the thin film scintillator are arranged in a housing; a coaxial hole in the axial direction of the electronic collimating device is formed in the housing; and the coaxial hole is used for assisting the position adjustment of the electron spectrometer. On the basis of a magnetic field deflection-based traditional electron spectrometer, the real-time electron spectrometer integrates advantages such as the real-time detection of the scintillator, low noise and flexibility of plastic optical fibers, high matching degree between the plane fiber array and the image plane of a detector. The electron spectrometer of the present invention is of simplicity and is easy to operate. The real-time electron spectrometer of the invention can diagnose and detect electrons of which the energy ranges from 0.98MeV to 4.55MeV, can be extended to higher energy bands and has a high application value in laser plasma physics.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV
Multifunctional sample test bench for X-ray electron spectrometer
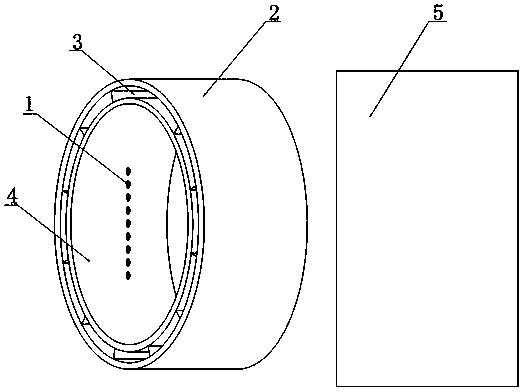
PendingCN113176287AImplement testSolve the problem of unable to collect dataMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationNon magneticTest bench
The invention provides a multifunctional sample test bench for an X-ray electron spectrometer. The multifunctional sample test bench comprises a first test bench and a second test bench which are made of non-magnetic materials, a sample can be placed on the first test bench, and the position of the sample can be adjusted in the horizontal X and Y directions; and the structure of the second test bench is the same as that of the first test bench, and a sample can be placed on the second test bench for position adjustment in the Z direction. The multifunctional sample test bench of the X-ray electron spectrometer solves the problem that an existing X-ray electron spectrometer is difficult to test special-shaped samples or samples with large sizes.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com