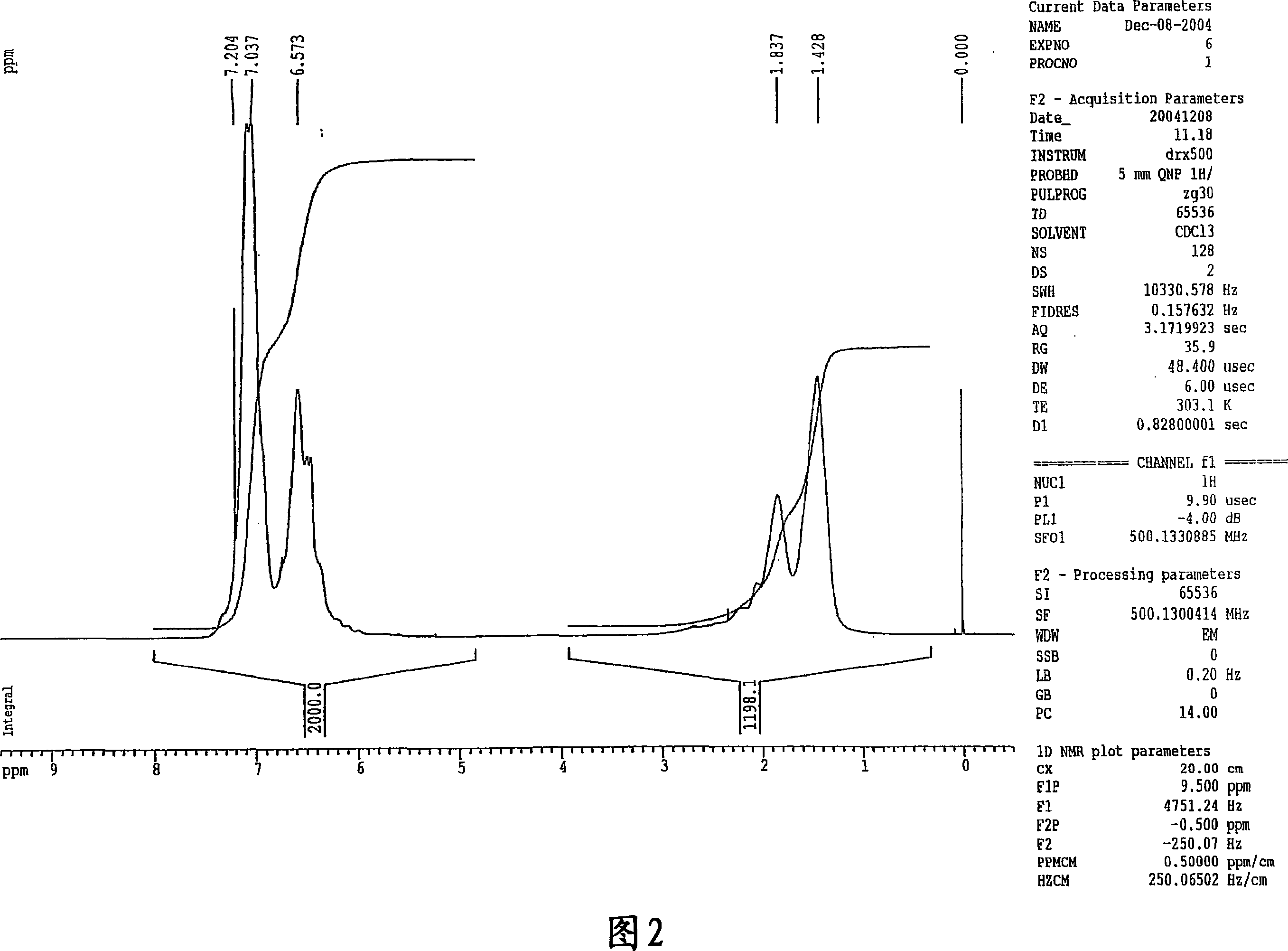
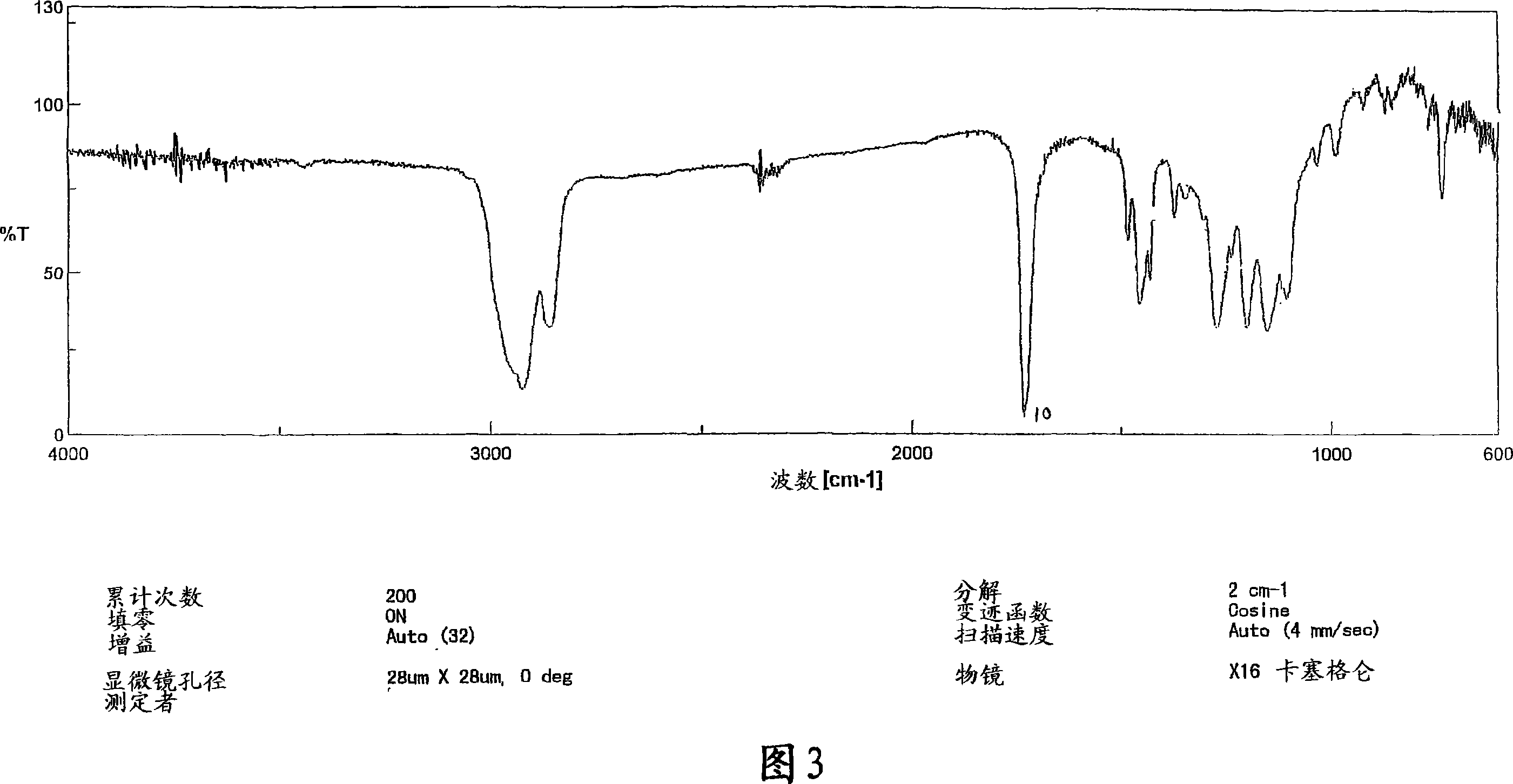
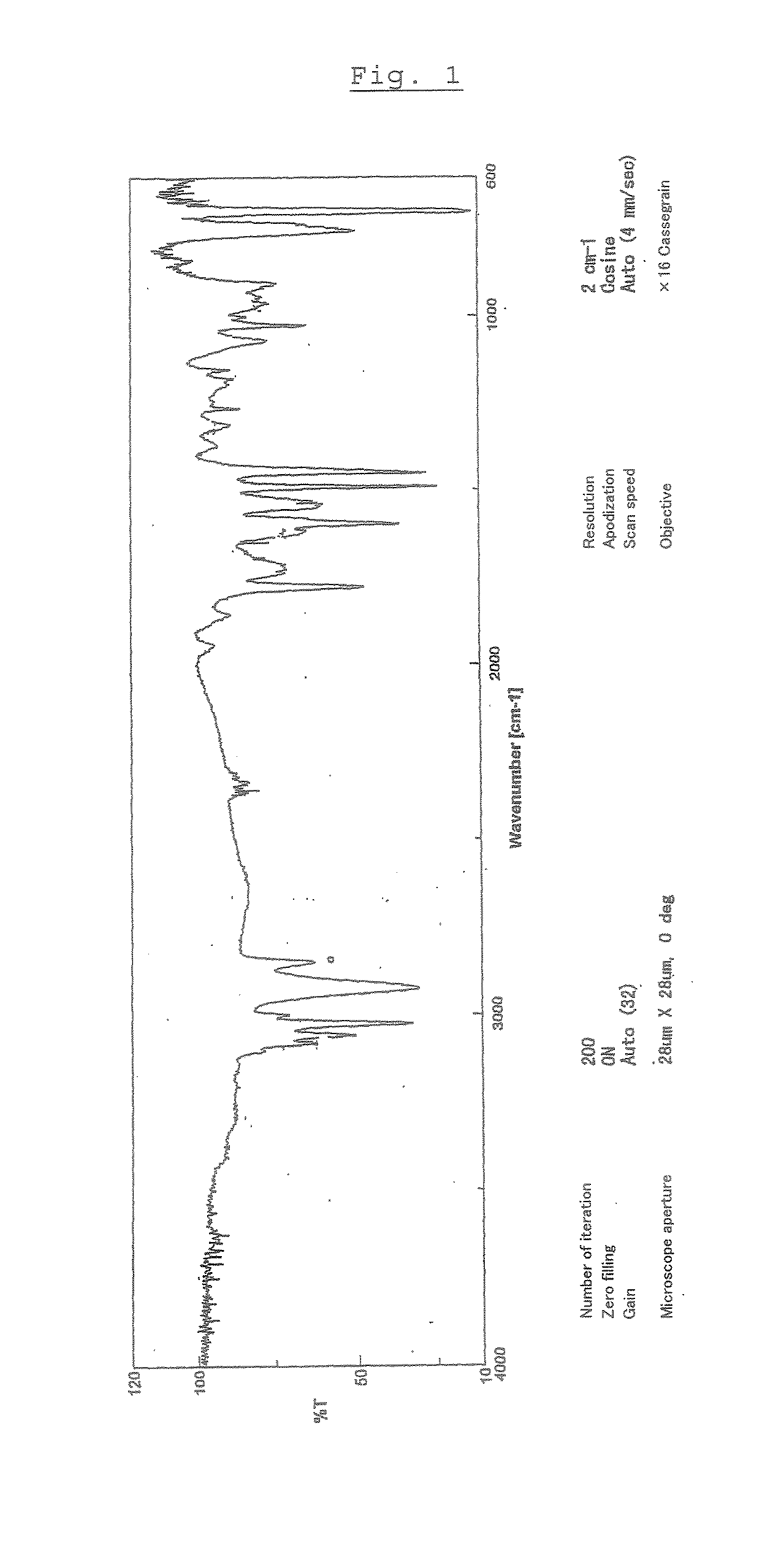
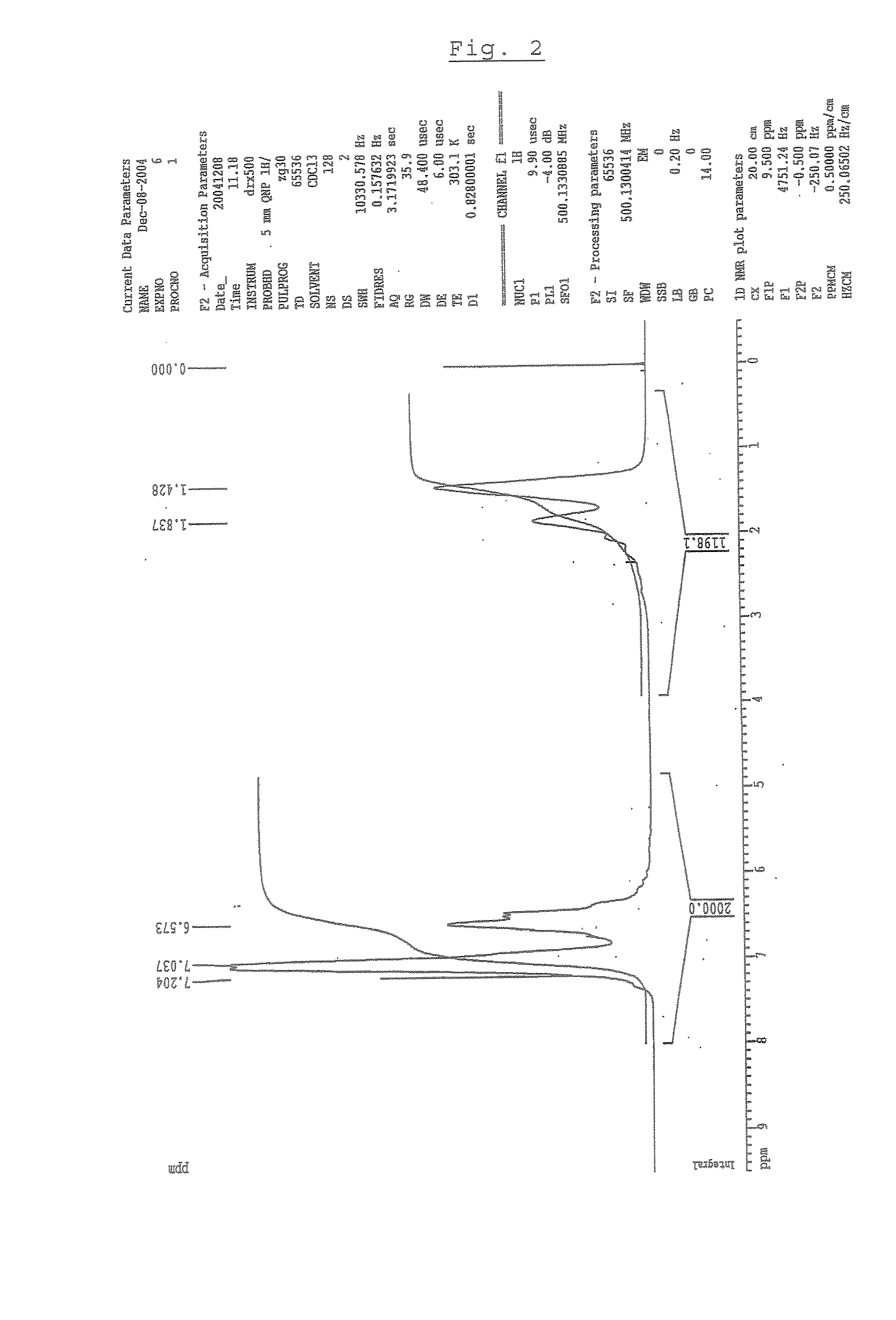
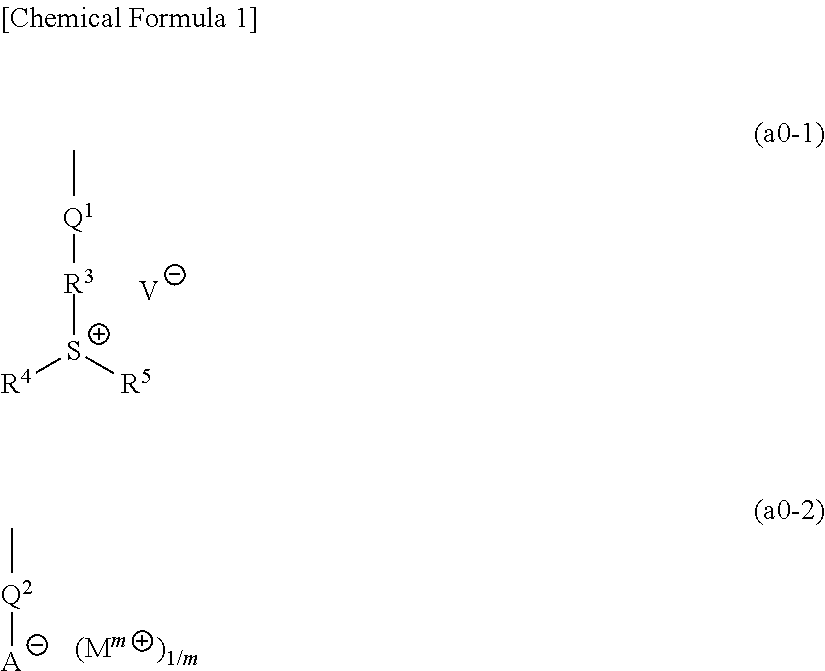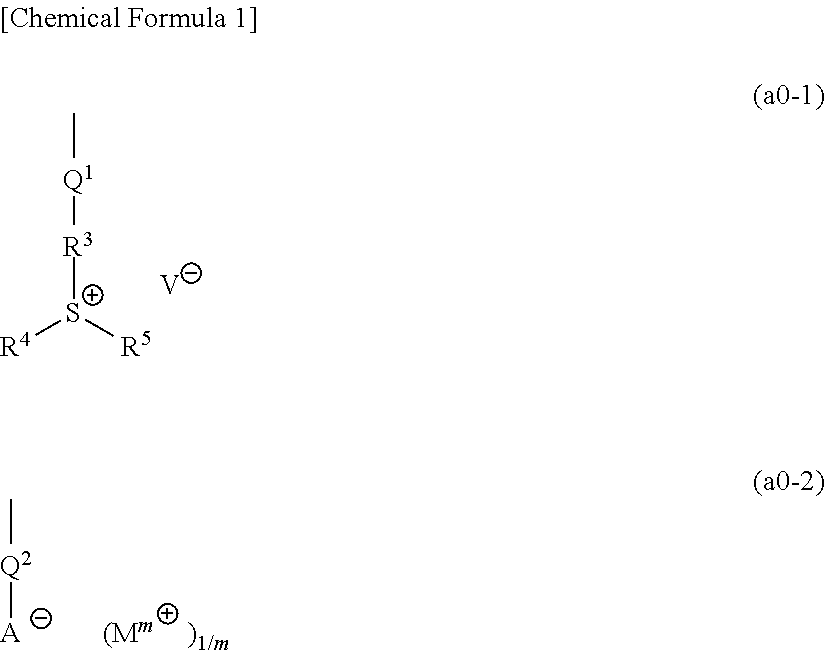Patents
Literature
75 results about "Polycyclic group" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In mathematics, a polycyclic group is a solvable group that satisfies the maximal condition on subgroups (that is, every subgroup is finitely generated). Polycyclic groups are finitely presented, and this makes them interesting from a computational point of view.
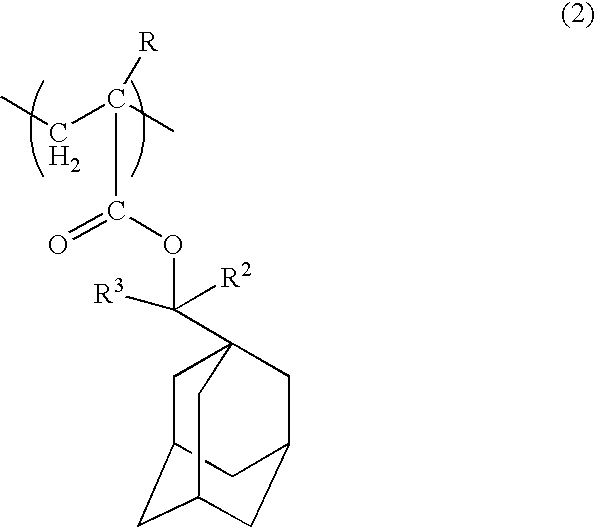
Positive resist composition and method of forming resist pattern from the same
InactiveUS20040110085A1Small line edge roughnessHigh resolutionRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityMethacrylate
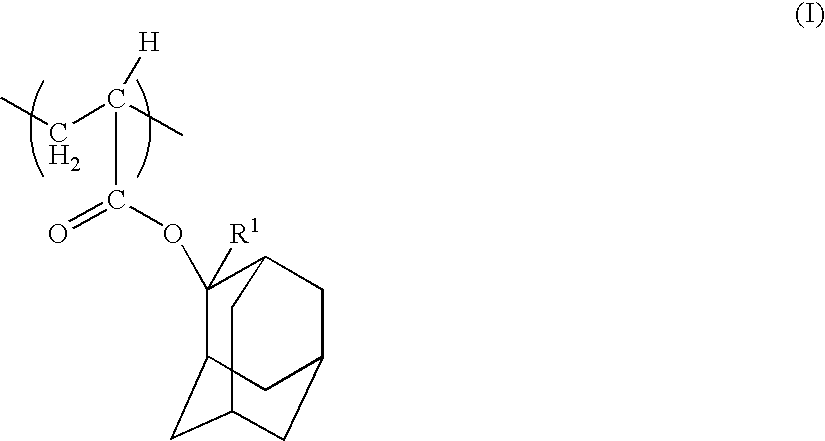
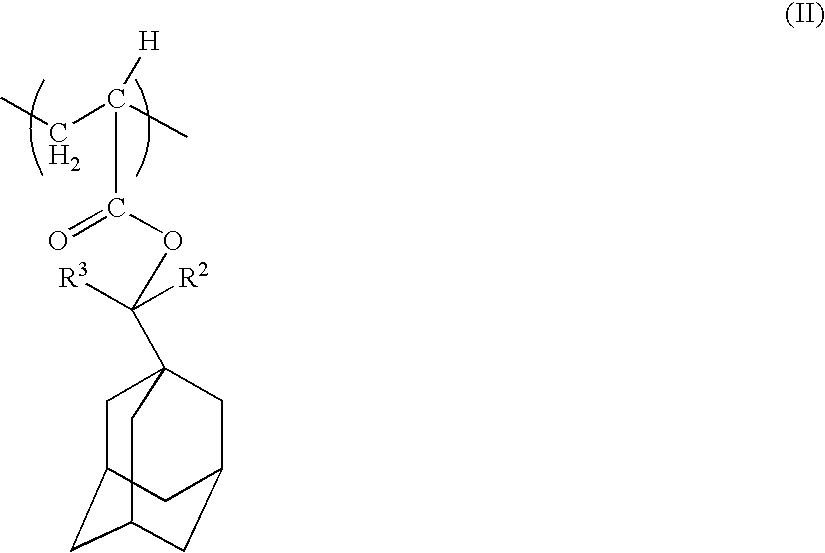
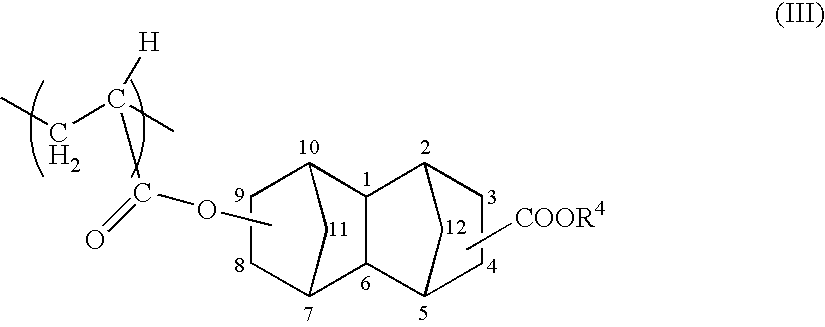
There is provided a positive type resin composition comprising (A) a resin component comprising within the principal chain a structural unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester and incorporating an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group on an ester side chain section, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, and (C) an organic solvent, wherein the component (A) comprises both a structural unit derived from a methacrylate ester and a structural unit derived from an acrylate ester. According to such a resist composition, a resist pattern can be formed which displays little surface roughness and line edge roughness on etching, and also offers excellent resolution and a wide depth of focus range.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Positive resist composition and method of forming resist pattern
InactiveUS20040058269A1High resolutionIncreased focus rangePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsSolubilityResist
There is provided a positive type resist composition formed by dissolving (A) a resin component with a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester in the principal chain, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, and (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, in an organic solvent component (C), wherein the resin component (A) is a copolymer comprising (a1) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group, (a2) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a lactone containing monocyclic group or polycyclic group, (a3) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a hydroxyl group containing polycyclic group, and (a4) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a polycyclic group which is different from the unit (a1), the unit (a2) and the unit (a3). This composition provides a chemically amplified positive type resist composition which displays excellent resolution, enables the depth of focus range of an isolated resist pattern to be improved, and enables the proximity effect to be suppressed.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Phenylcarbazole compounds and organic electroluminescence devices using the same
ActiveUS20060020136A1Improve efficiencyExtend your lifeOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescencePolycyclic group
A phenylcarbazole compound of formula (1) below is provided, where each of R1 and R2 is independently a monosubstituted or polysubstituted functional group selected from the group consisting of hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C4-C30 heterocyclic group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 condensed polycyclic group, wherein groups adjacent to R1 and R2 bind and form a saturated or unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon group, and Ar is a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group or a C6-C30 heteroaryl group, wherein the substituent R4 is defined herein. Also included is an organic electroluminescence device comprising the above phenylcarbazole compounds.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Phenylcarbazole compounds and organic electroluminescence devices using the same
ActiveUS7431997B2Improve efficiencyExtend your lifeOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensArylHydrogen atom
A phenylcarbazole compound of formula (1) below is provided,where each of R1 and R2 is independently a monosubstituted or polysubstituted functional group selected from the group consisting of hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C4-C30 heterocyclic group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 condensed polycyclic group, wherein groups adjacent to R1 and R2 bind and form a saturated or unsaturated cyclic hydrocarbon group, and Ar is a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group or a C6-C30 heteroaryl group, wherein the substituent R4 is defined herein. Also included is an organic electroluminescence device comprising the above phenylcarbazole compounds.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Compound for organic electro-luminescence device and organic electro-luminescence device using the compound
InactiveUS6329084B1Organic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensOrganic electroluminescenceLight emission
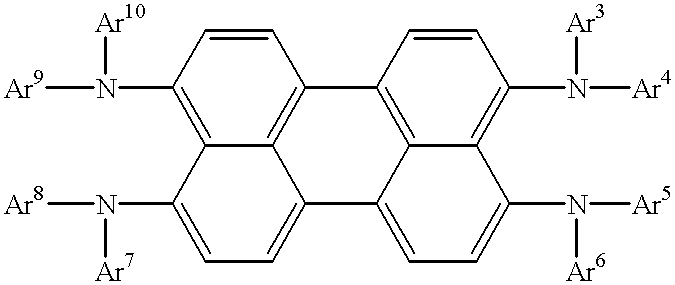
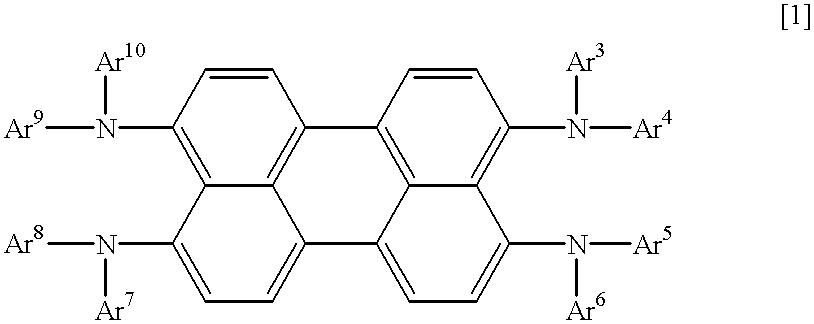
Compounds for organic EL devices which emit light of red, have a high light emission brightness and have a long lifetime of light emission, and organic EL devices using the above compounds, the light-emitting materials being compounds of the formula [1],wherein each of Ar3 to Ar10 is independently a substituted or non-substituted aromatic monocyclic group, a substituted or non-substituted fused polycyclic group or a substituted or non-substituted aromatic heterocyclic group, provided that Ar3 and Ar4 may integrally bond to each other, that Ar5 and Ar6 may integrally bond to each other, that Ar7 and Ar8 may integrally bond to each other, and that Ar9 and Ar10 may integrally bond to each other.
Owner:TOYO INK SC HOLD CO LTD
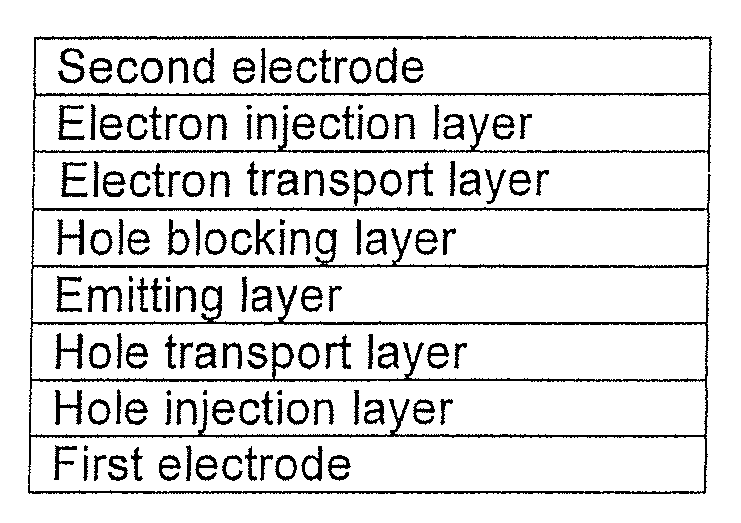
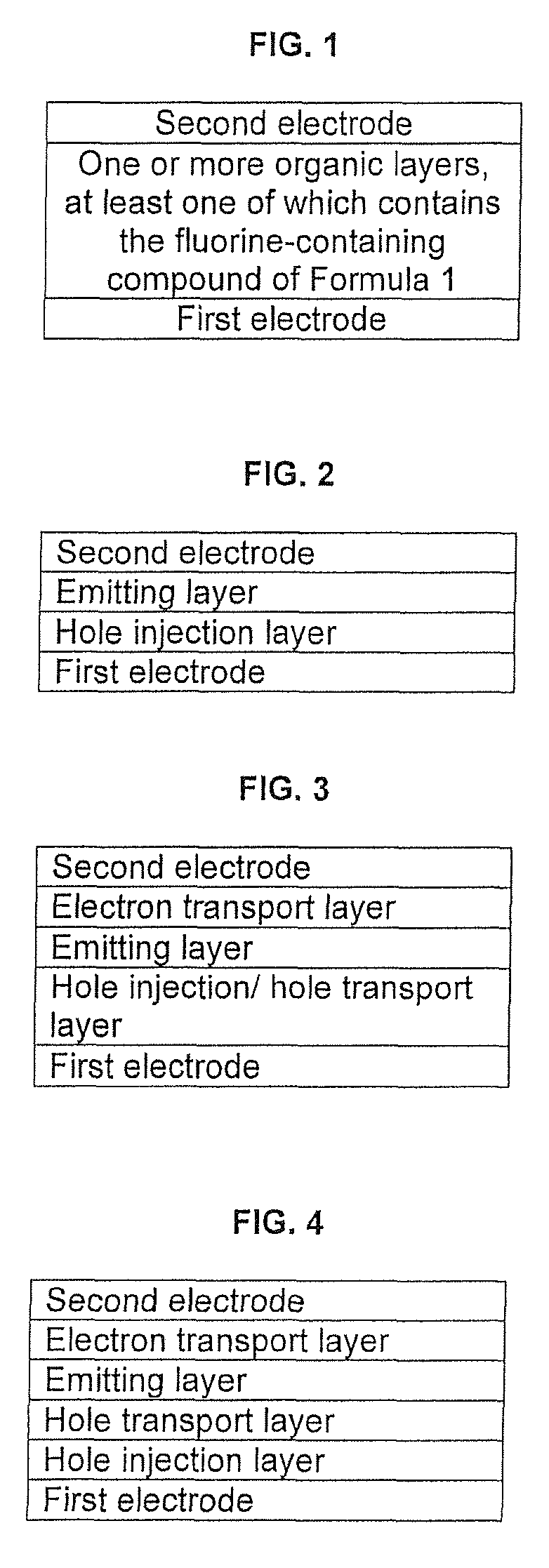
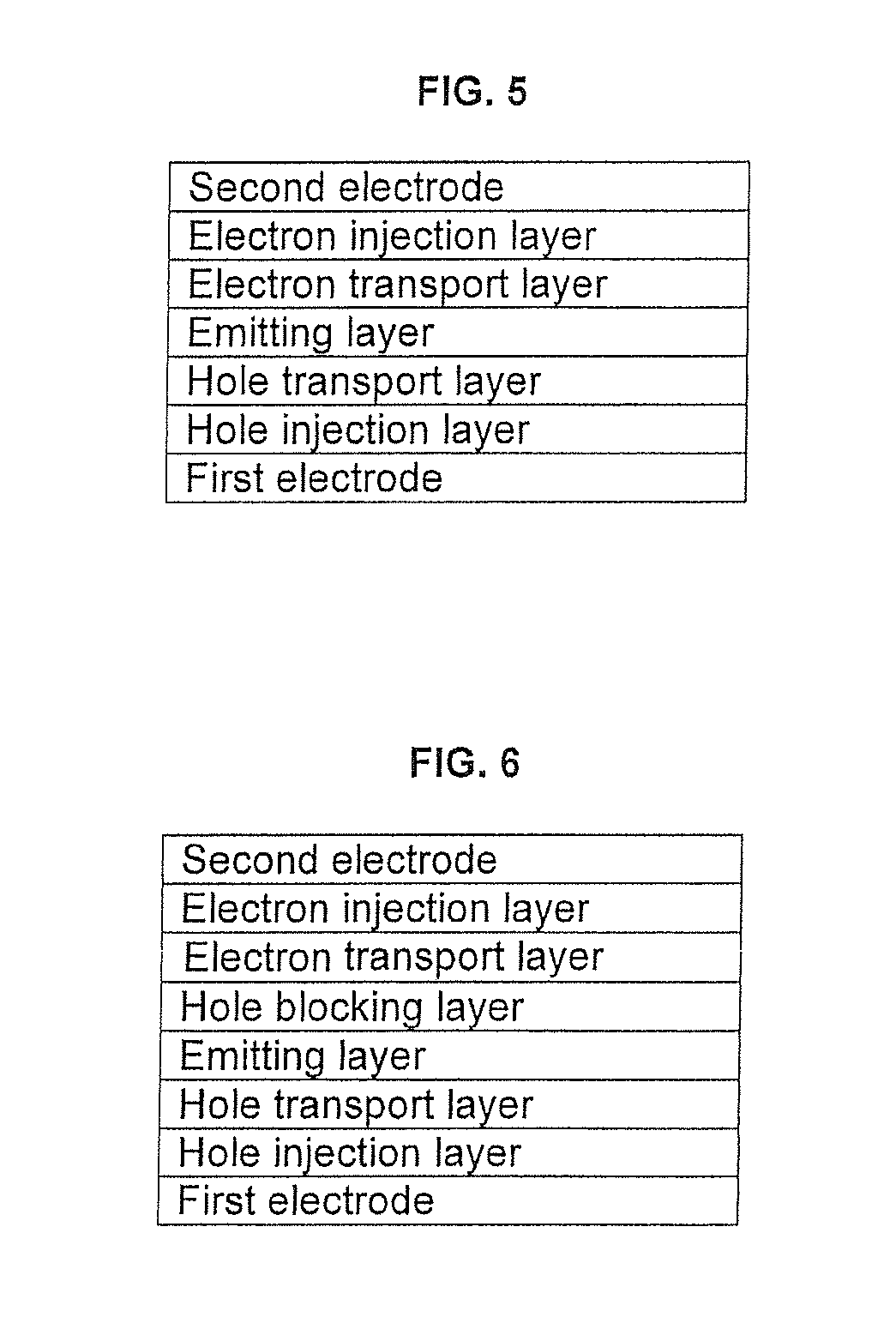
Fluorine-containing compound and organic light-emitting device employing the same
ActiveUS20080169755A1Electrical stabilityHigh charge transport performanceOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensArylHydrogen atom
A fluorine-containing compound is represented by Formula 1 below:wherein R1a, R1b, R2a, and R2b are each independently a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted C4-C30 heteroaryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 condensed polycyclic group, a hydroxy group, halogen, a cyano group, or a substituted or unsubstituted amino group, and adjacent groups selected from R1a, R1b, R2a, and R2b may join together to form a saturated or unsaturated carbon ring; n and m are each independently an integer of 0 to 5; Ar1a and Ar1b are each independently a C6-C30 aryl group which is unsubstituted or substituted by at least one fluorine or a C4-C30 heteroaryl group which is unsubstituted or substituted by at least one fluorine; and Ar2 is a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group or a substituted or unsubstituted C2-C30 heteroaryl group. The fluorine-containing compound has good electrical characteristics and charge transport capability, and thus, is useful as a hole injection material, a hole transport material, and / or an emitting material for fluorescent or phosphorescent devices capable of producing light of a full spectrum of colors, including red, green, blue, and white. Thus, the fluorine-containing compound can be used to produce organic light-emitting devices with high efficiency, a low driving voltage, high brightness, and a long lifetime.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Fluorinated polymers, photoresists and processes for microlithography
InactiveUS20050203262A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingResistUltraviolet
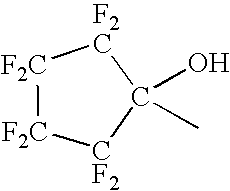
Fluorinated polymers useful in photoresist compositions and associated processes for microlithography are described. These polymers and photoresists have a fluoroalcohol functional group that simultaneously imparts high ultraviolet (UV) transparency and developability in basic media. The polymers also have a repeat unit derived from a C1-C25 alkyl hydroxymethylacrylate comonomer, e.g., tert-butyl hydroxymethylacrylate, or a C5-C50 polycyclic alkyl acrylate in which the polycyclic group contains a hydroxy group, e.g., hydroxyadamantyl acrylate. The materials of this invention have high UV tansparency, particularly at short wavelengths, e.g., 193 nm and 157 nm, which makes them highly useful for lithography at these short wavelengths.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Positive resist composition and method of forming resist pattern
InactiveUS6982140B2High resolutionIncreased focus rangePhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsSolubilityResist
There is provided a positive type resist composition formed by dissolving (A) a resin component with a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester in the principal chain, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, and (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, in an organic solvent component (C), wherein the resin component (A) is a copolymer comprising (a1) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group, (a2) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a lactone containing monocyclic group or polycyclic group, (a3) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a hydroxyl group containing polycyclic group, and (a4) a unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester comprising a polycyclic group which is different from the unit (a1), the unit (a2) and the unit (a3). This composition provides a chemically amplified positive type resist composition which displays excellent resolution, enables the depth of focus range of an isolated resist pattern to be improved, and enables the proximity effect to be suppressed.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
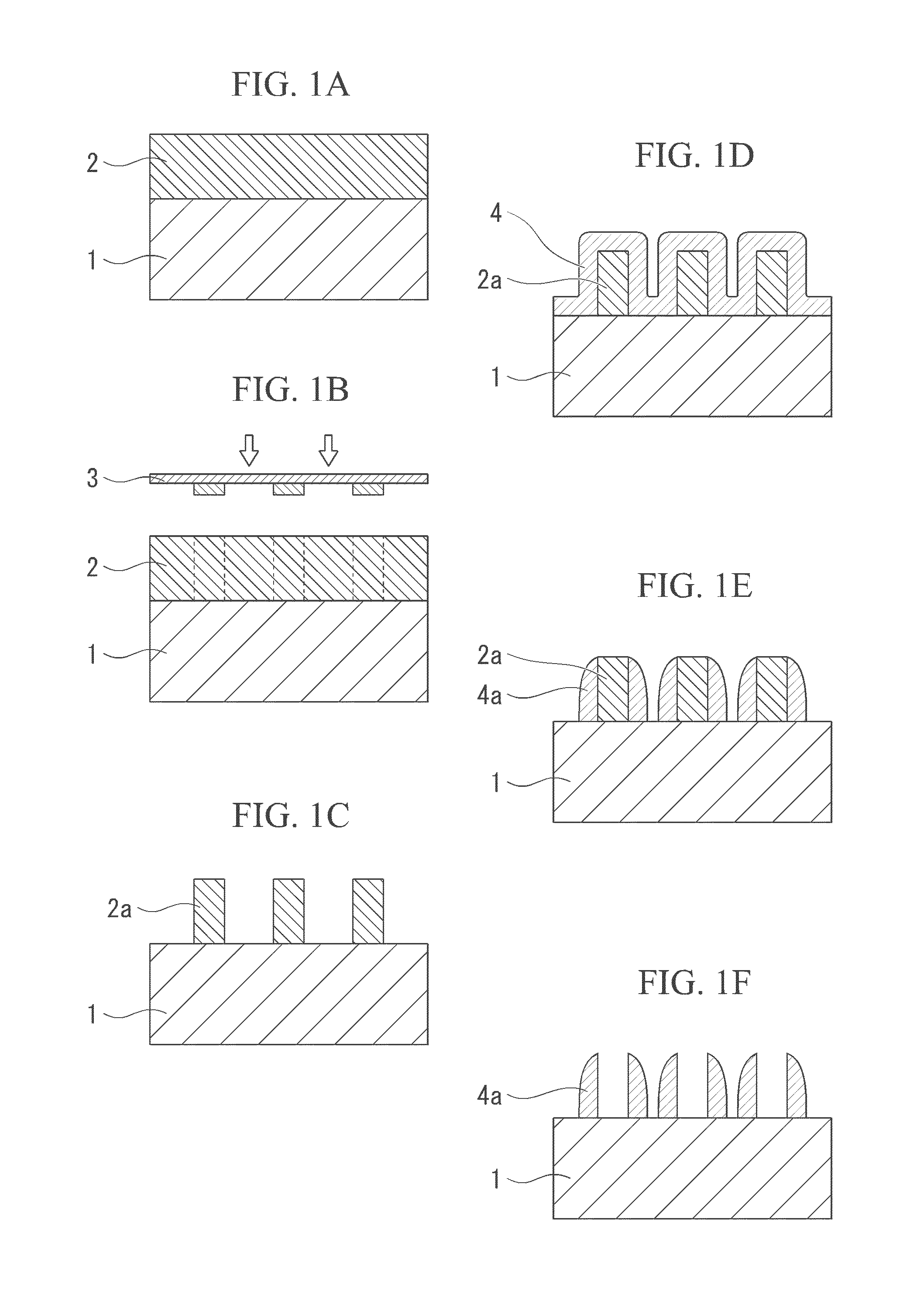
Method of forming pattern
ActiveUS20130209941A1Improve uniformitySimple processSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusSolubilityResist
A method of forming a pattern including applying a resist composition to a substrate to form a resist film, and then subjecting the resist film to exposure and development, thereby forming a first pattern containing a resist film; forming a SiO2 film on the surface of the first pattern and the substrate; subjecting the SiO2 to etching such that the SiO2 film remains only on a side wall portion of the first pattern; and removing the first pattern, thereby forming a second pattern containing the SiO2 film. Thr resist composition contains a base component that exhibits changed solubility in a developing solution under action of an acid, and an acid generator component that generates acid upon exposure, the base component containing a resin component containing a structural unit having an acid decomposable group which exhibits increased polarity by the action of acid and has no polycyclic group.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD +1
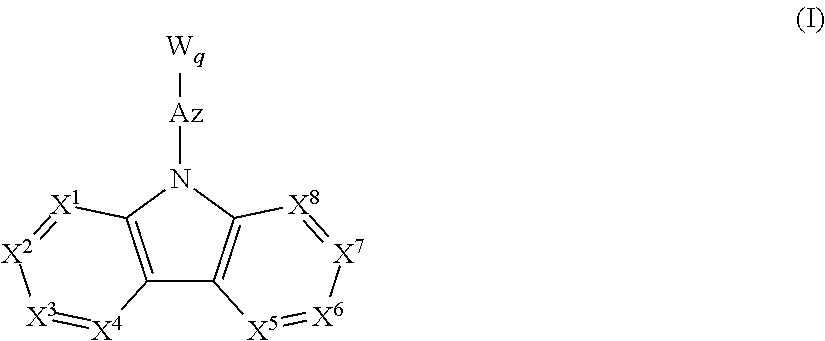
Material for organic electroluminescence device, and organic electroluminescence device using the same
A material for an organic electroluminescence device represented by the following formula (I):wherein X1 to X8 are a nitrogen atom, CH, CHal or CRa; Az is a nitrogen-containing six-membered ring or a fused polycyclic group including a nitrogen-containing six-membered ring; W is an aromatic hydrocarbon group having 6 to 30 ring carbon atoms which is substituted by at least one cyano group or a heterocyclic group having 5 to 30 ring atoms which is substituted by at least one cyano group.
Owner:IDEMITSU KOSAN CO LTD
Phenanthroimidazole symmetric derivative host material and electroluminescent device
ActiveCN104987309AReduce the starting voltageReduce the driving voltageOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesArylHydrogen atom
The invention relates to a phenanthroimidazole symmetric derivative host material. The structure of the host material is represented by formula I, and can be used to form an organic electroluminescent device with the advantages of high luminescence efficiency, low driving voltage, long life, high brightness and high color purity. In the formula I, R1 and R2 are respectively independently selected from the hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl groups, C1-C30 cycloalkyl groups, C1-C30 saturated alkyl groups, substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyloxy groups, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl groups, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryloxy groups, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 arylamino groups, substituted or unsubstituted C2-C30 heterocyclic groups, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 fused polycyclic groups, hydroxy groups, cyan groups or substituted or unsubstituted amino groups.
Owner:NANJING TOPTO MATERIALS CO LTD
Positive resist composition
InactiveUS20060063102A1Good body shapeGood yieldSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material auxillary/base layersSolubilityLithography process
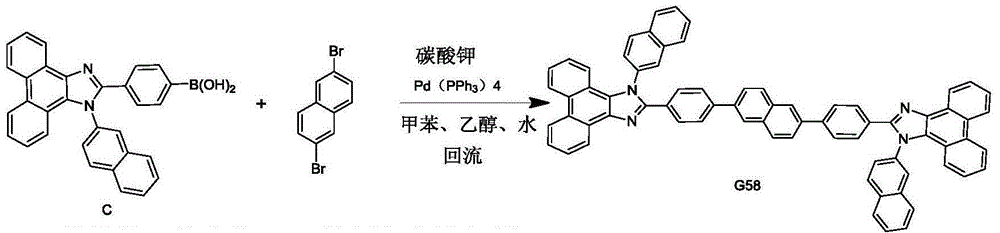
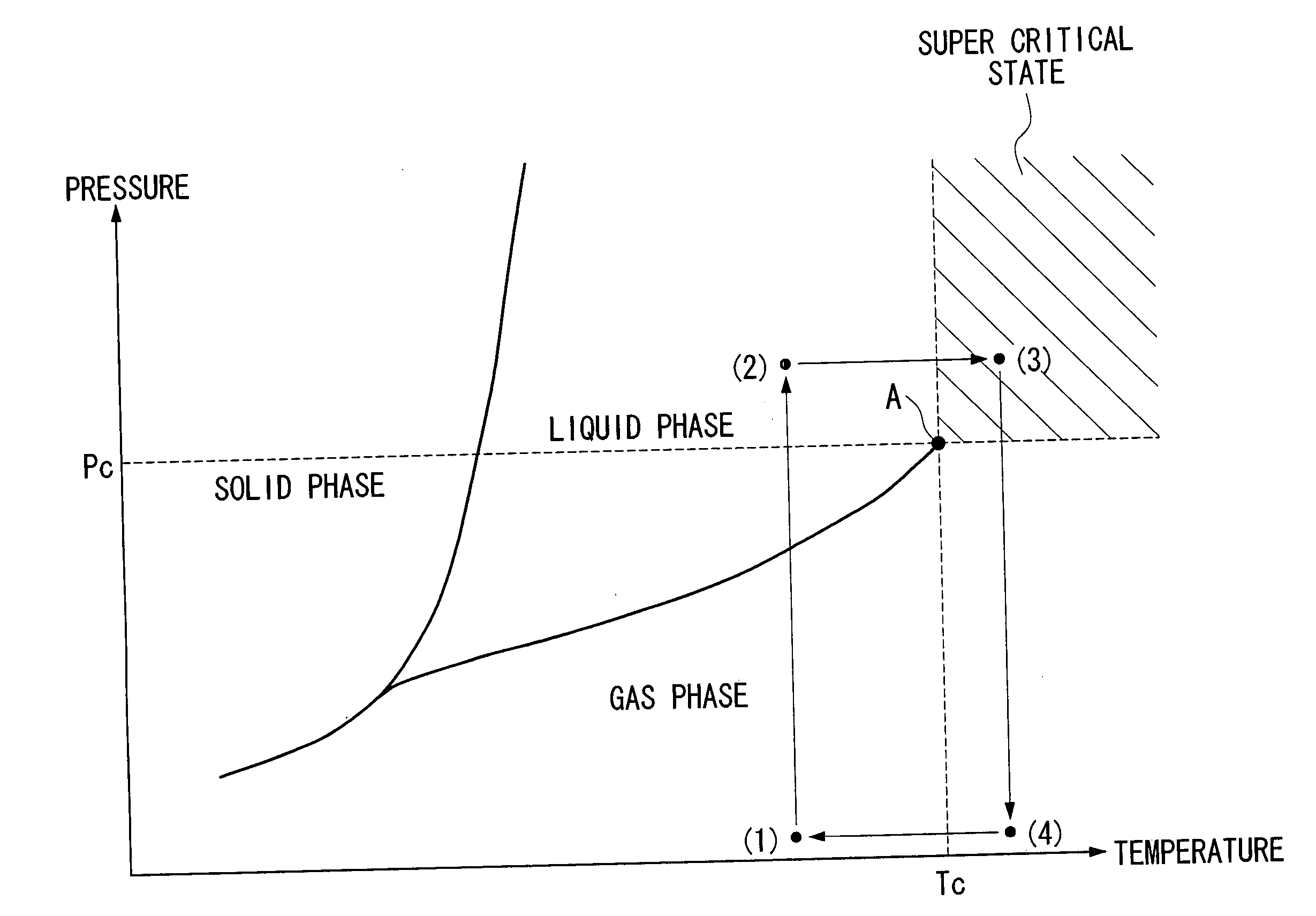
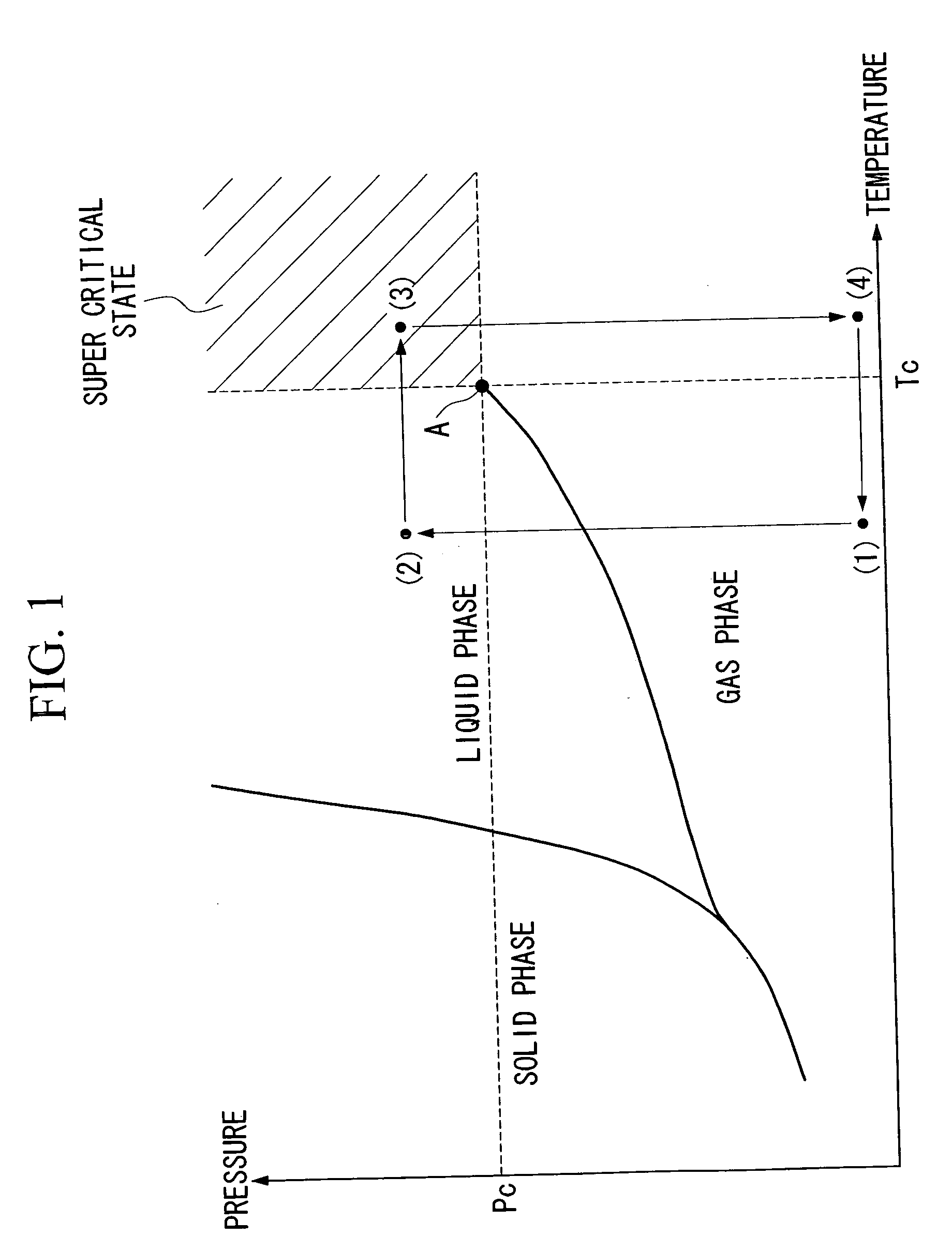
There is provided a positive resist composition which, during resist pattern formation, can prevent the collapse of very fine resist patterns during the drying step following developing. This positive resist composition is used in a resist pattern formation method comprising a step, within the lithography process, for substituting a liquid remaining on the substrate following alkali developing with a critical drying liquid, and then drying this critical drying liquid by causing passage through a critical state. The positive resist composition comprises a resin component (A), which has an alkali-soluble unit content of less than 20 mol %, contains an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group, and displays increased alkali solubility under action of acid, an acid generator component (B) that generates acid on exposure, and an organic solvent (C) for dissolving the components (A) and (B), and moreover, the component (A) comprises a structural unit (a1) containing an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group, a structural unit (a2) containing a lactone unit, and a structural unit (a3) containing a polycyclic group with an alcoholic hydroxyl group.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Positive type resist composition and resist pattern formation method using same
InactiveUS20060127808A1Small surface roughnessLittle line edgeRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMethacrylateSolubility
There is provided a positive type resin composition comprising (A) a resin component comprising within the principal chain a structural unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester and incorporating an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group on an ester side chain section, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, and (C) an organic solvent, wherein the component (A) comprises both a structural unit derived from a methacrylate ester and a structural unit derived from an acrylate ester. According to such a resist composition, a resist pattern can be formed which displays little surface roughness and line edge roughness on etching, and also offers excellent resolution and a wide depth of focus range.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Polymer compound, resist composition and dissolution inhibitor agent containing the polymer compound
ActiveUS20050130056A1Radiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistPolymer science
Provided are a polymer compound having high transparency for use in a photoresist composition for microfabrication of the next generation, a resist composition using the polymer compound as a base polymer, and a dissolution inhibitor agent composed of the polymer compound. To ensure etching resistance, an alicyclic group is introduced into a side chain portion. Hydrogen atoms on the ring of the alicyclic group are highly fluorinated to ensure transparency to light of 157 nanometer wavelength, represented by an adsorption coefficient equal to or less than 3.0 μm−1. As the alicyclic group, a polycyclic group is preferably used. Hydrogen atoms are highly fluorinated by preferably substituting all hydrogen atoms on the ring by fluorine atoms, that is, forming a perfluoroalicyclic group. The resist composition is formed by using the polymer compound as a base polymer and further, the dissolution inhibitor agent is formed of the polymer compound.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Silsesquioxane resin, positive resist composition, resist laminate, and method of forming resist pattern
InactiveUS20090068586A1Transparent highIdeal for useOrganic chemistryPhotosensitive materialsHydrogen atomAliphatic hydrocarbon
A silsesquioxane resin, a positive resist composition, a resist laminate, and a method of forming a resist pattern that are capable of suppressing a degas phenomenon are provided, and a silicon-containing resist composition and a method of forming a resist pattern that are ideally suited to immersion lithography are also provided. The silsesquioxane resin includes structural units represented by the general shown below [wherein, R1 and R2 each represent, independently, a straight chain, branched, or cyclic saturated aliphatic hydrocarbon group; R3 represents an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a hydrocarbon group that includes an aliphatic monocyclic or polycyclic group; R4 represents a hydrogen atom, or a straight chain, branched, or cyclic alkyl group; X represents an alkyl group of 1 to 8 carbon atoms in which at least one hydrogen atom has been substituted with a fluorine atom; and m represents an integer from 1 to 3].
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Organic compound and electroluminescent device using same
InactiveCN104045595AHigh purityReduce the starting voltageOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesArylHydrogen atom
The invention discloses an organic compound. The organic compound has a structure represented by a formula I shown in descriptions, wherein R1 is substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryloxy, phenyl, biphenyl, naphthyl or anthryl; R2 is independently selected from a monosubstituted or polysubstituted substituent, a hydrogen atom, substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl, substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkoxy, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryloxy, substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 arylamino, a substituted or unsubstituted C2-C30 heterocycle, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 fused polycyclic group, hydroxyl, cyan and substituted or unsubstituted amino. The invention further discloses an electroluminescent device using the organic compound.
Owner:BEIJING GREEN GUARDEE TECH
Organic light-emitting device including anthracene derivatives
ActiveCN101267022AImprove formation efficiencyReduce the driving voltageOrganic chemistrySolid-state devicesArylAnthracene
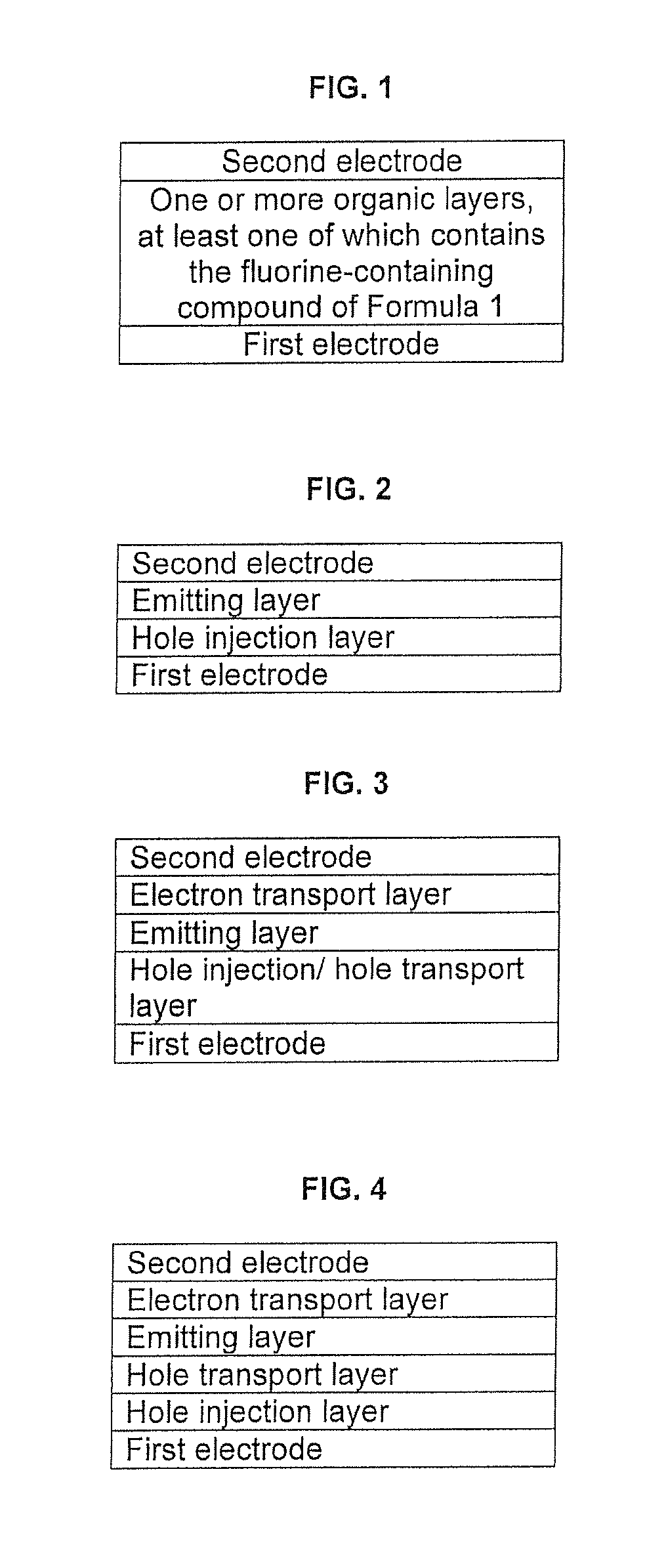
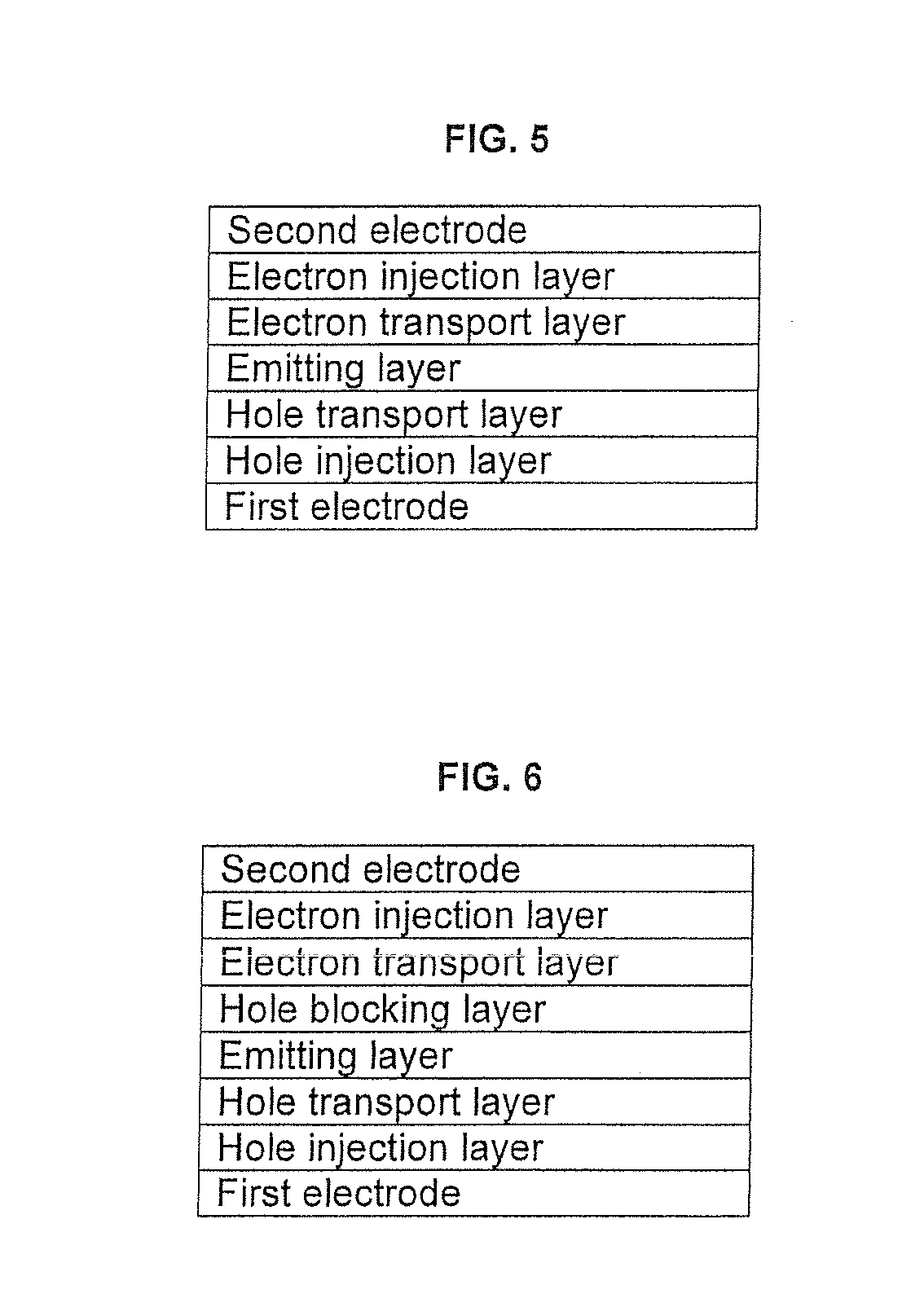
Provided is an organic light-emitting device including: a first electrode; a second electrode; and one or more organic layers interposed between the first electrode and the second electrode. At least one of the organic layers includes one or more anthracene derivatives represented by Formula 1 below: wherein R 1 and R 2 are each independently a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted C4-C30 heteroaryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 condensed polycyclic group, a hydroxyl group, halogen, a cyano group, or a substituted or unsubstituted amino group.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Heterocyclic compound and organic light-emitting device including the same
ActiveUS20140151650A1Improve luminous efficiencyImprove power efficiencySilicon organic compoundsSolid-state devicesArylHydrogen atom
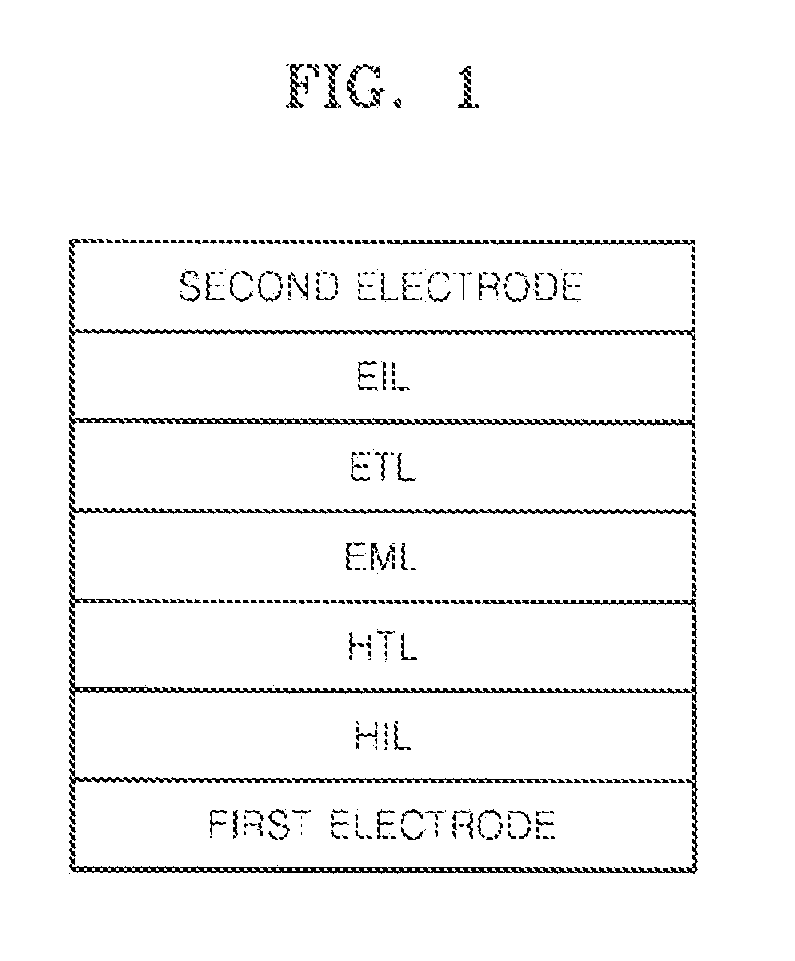
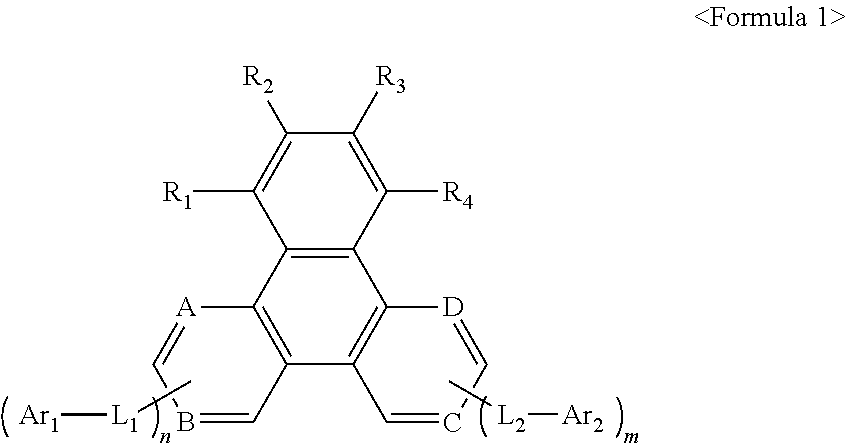
A heterocyclic compound represented by Formula 1 below and an organic light-emitting device including the heterocyclic compound are described.In Formula 1, R1 to R4 may be each independently one of a hydrogen atom, a deuterium atom, C5-C60 alkyl, C5-C60 aryl and C6-C60 condensed polycyclic; L1 and L2 may be each independently one of a single bond, C5-C60 aryl, C3-C60 heteroaryl and C6-C60 condensed polycyclic; Ar1 and Ar2 may be each independently one of C5-C60 aryl, C3-C60 heteroaryl and C6-C60 condensed polycyclic; A, B, C and D may be each independently one of —CH═ and —N═, excluding that all A, B, C and D are —CH═; and m and n may be each independently an integer of 0 to 3, excluding that all m and n are zero, wherein any of the above alkyl groups, aryl groups, condensed polycyclic groups and heteroaryl groups may be substituted or unsubstituted.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Positive type resist composition and resist pattern formation method using same
InactiveUS20050095535A1Small surface roughnessLittle line edgeRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolubilityMethacrylate
There is provided a positive type resin composition comprising (A) a resin component comprising within the principal chain a structural unit derived from a (meth)acrylate ester and incorporating an acid dissociable, dissolution inhibiting group containing a polycyclic group on an ester side chain section, for which the solubility in alkali increases under the action of acid, (B) an acid generator component which generates acid on exposure, and (C) an organic solvent, wherein the component (A) comprises both a structural unit derived from a methacrylate ester and a structural unit derived from an acrylate ester. According to such a resist composition, a resist pattern can be formed which displays little surface roughness and line edge roughness on etching, and also offers excellent resolution and a wide depth of focus range.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Heterocyclic compound and an organic light emitting device comprising the same
ActiveUS7846559B2High color purityHigh color reproductionOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensArylOrganic light emitting device
A heterocyclic compound represented by Formula 1 below:X is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, boron, and phosphorous; and Ar1, Ar2, Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently selected from the group consisting of a C6-C30 substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, a C6-C30 substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a C4-C20 substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, and a C6-C20 fused polycyclic group.The heterocyclic compound can be included in emission layers of top emission and bottom emission organic light emitting devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Resist composition and method of forming resist pattern
ActiveUS8883396B2Good body shapeHigh sensitivityPhotosensitive materialsPhotoprinting processesResistStructural unit
A resist composition containing a base component (A) which generates an acid upon exposure and exhibits changed solubility in a developing solution by the action of acid, wherein the base component (A) contains a copolymer (A1) having a structural unit (a0) containing a group represented by the following general formula (a0-1) or (a0-2), a structural unit (a11) containing an acid-decomposable group which exhibits increased polarity by the action of acid and contains a polycyclic group, and a structural unit (a12) containing an acid-decomposable group which exhibits increased polarity by the action of acid and contains a monocyclic group. Each of the groups —R3—S+(R4)(R5) and Mm+ in the formula has only one aromatic ring as a whole or has no aromatic ring.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Heterocyclic compound and an organic light emitting device comprising the same
ActiveUS20090128013A1High color purityHigh color reproductionOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensArylOrganic light emitting device
A heterocyclic compound represented by Formula 1 below:X is selected from the group consisting of nitrogen, boron, and phosphorous; and Ar1, Ar2, Ar3 and Ar4 are each independently selected from the group consisting of a C6-C30 substituted or unsubstituted aryl group, a C6-C30 substituted or unsubstituted aryloxy group, a C4-C20 substituted or unsubstituted heterocyclic group, and a C6-C20 fused polycyclic group.The heterocyclic compound can be included in emission layers of top emission and bottom emission organic light emitting devices.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
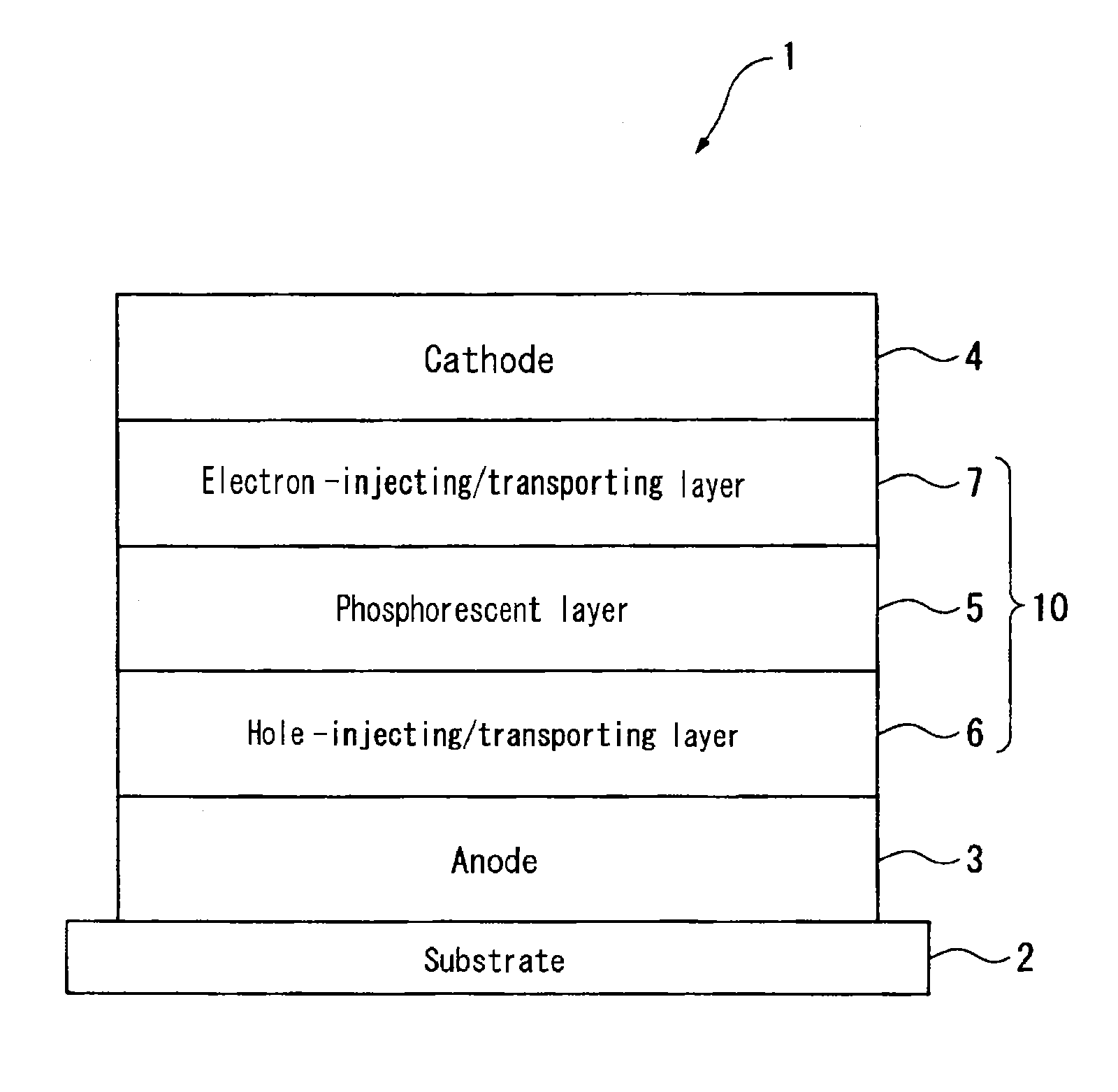
BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME
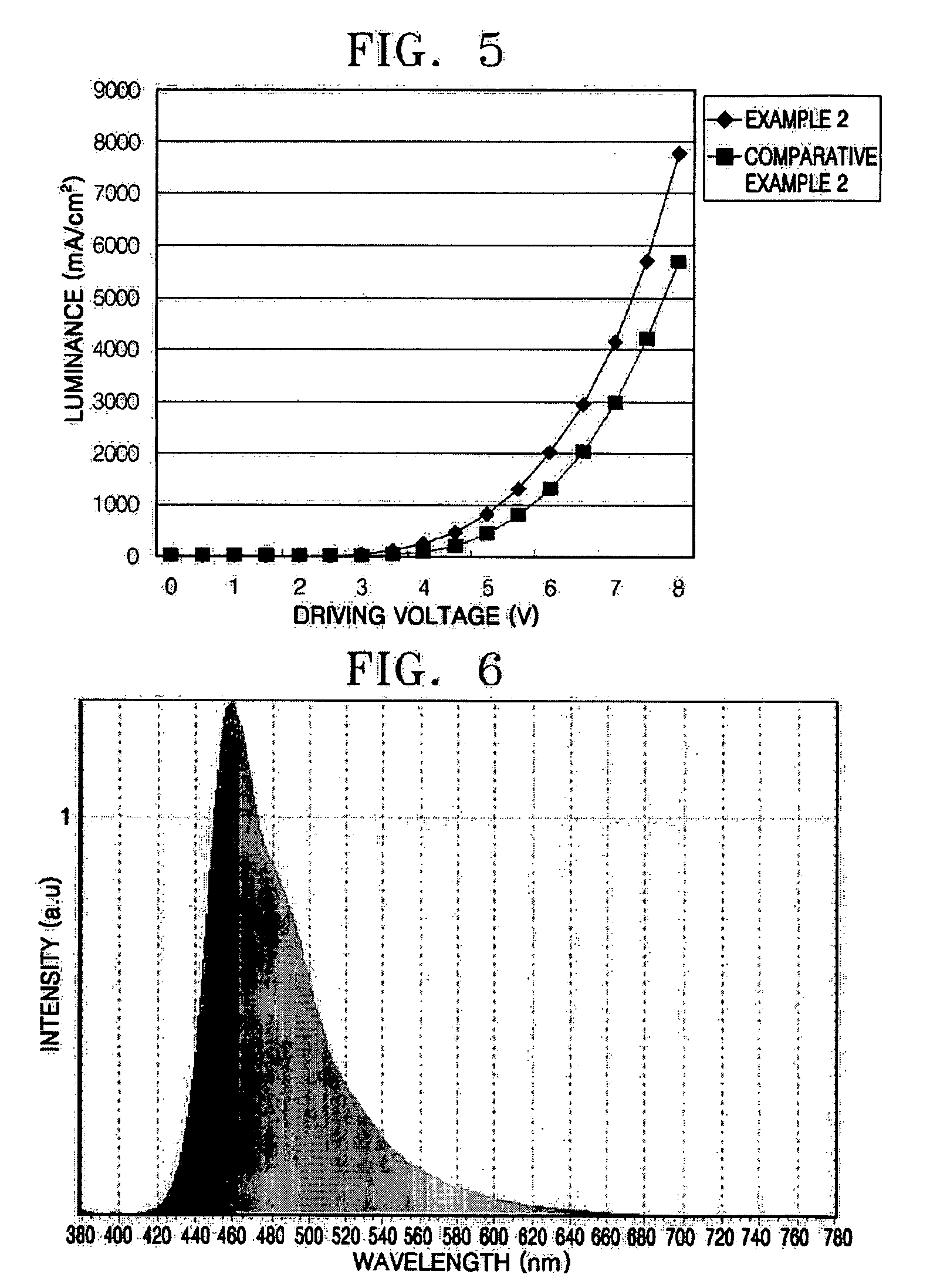
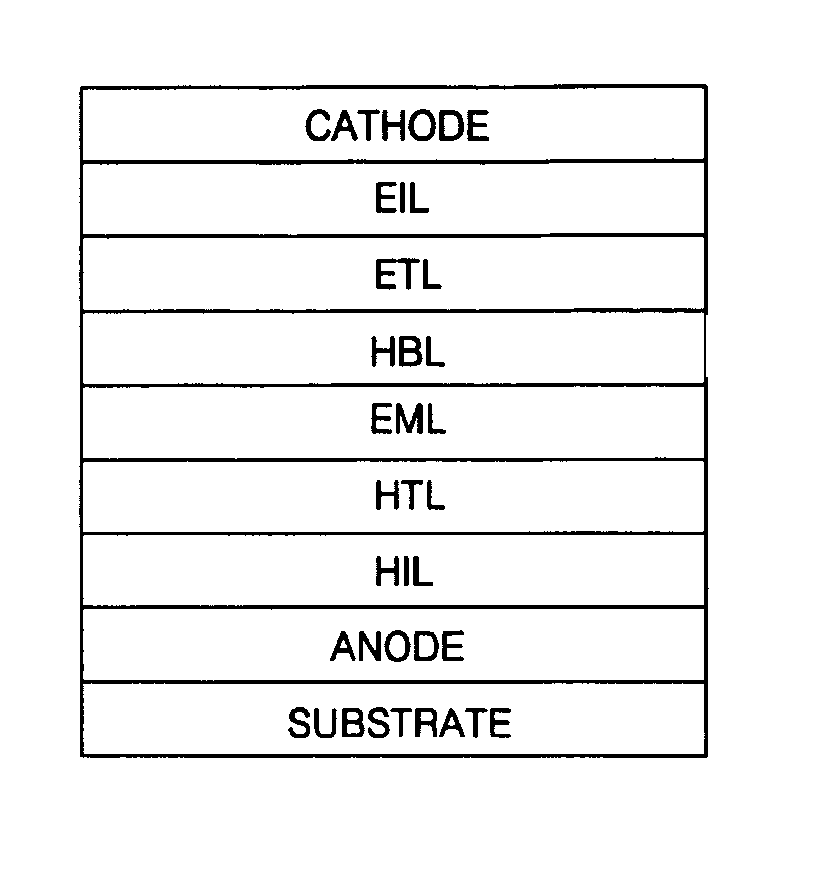
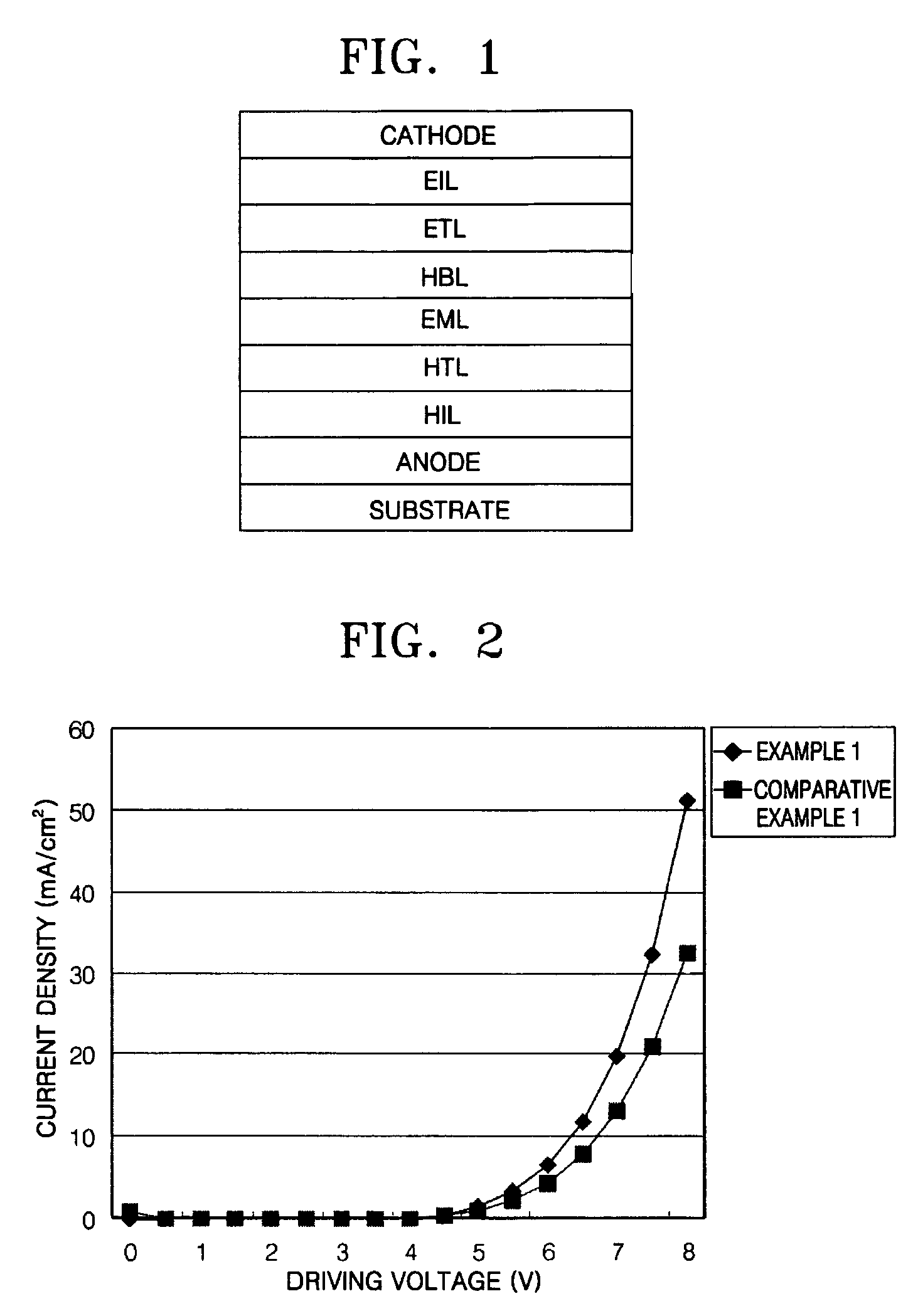
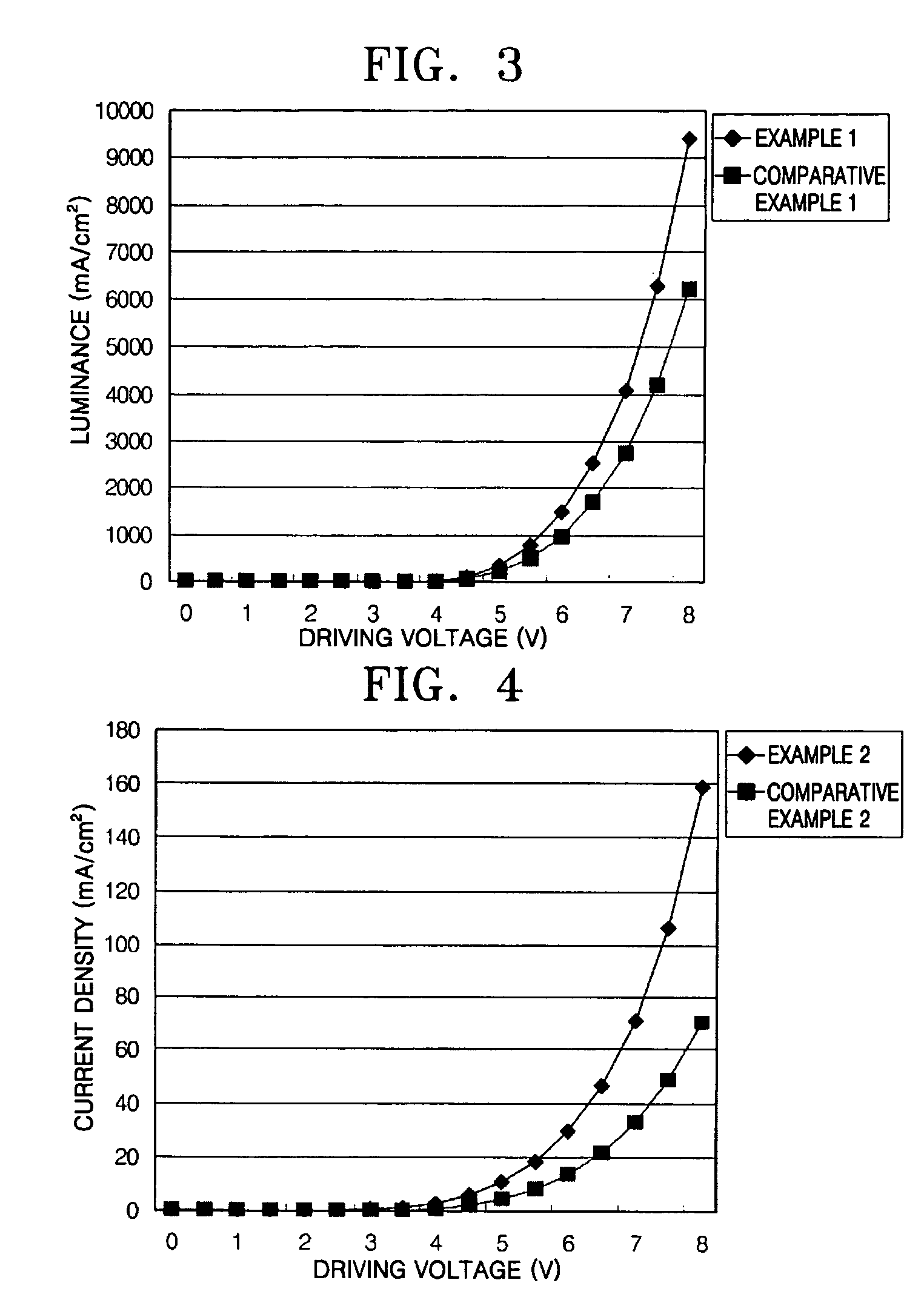
InactiveUS20110049479A1Shine wellIncreased durabilityLiquid crystal compositionsOrganic chemistryFluoranthenePolycyclic group
Provided are a novel benzo[a]fluoranthene compound and an organic light emitting device having extremely good light emitting efficiency, extremely good luminance, and durability. The benzo[a]fluoranthene compound is represented by the following general formula (I):wherein: at least one of R11 to R22 represents Rm represented by the following general formula (i):Rm=—X1—Ar1 (i)wherein X1 represents a substituted or unsubstituted phenylene group, or a substituted or unsubstituted, divalent monocyclic heterocyclic group, and Ar1 represents one of the following groups (a) and (b): (a) a substituted or unsubstituted fused polycyclic group, and (b) a composite substituent formed by combining two or more of a benzene ring, a monocyclic heterocyclic ring, and a fused polycyclic ring, the composite substituent being permitted to have a substituent.
Owner:CANON KK
Resist composition and method of forming resist pattern
ActiveUS20130137048A1High sensitivityMaintain good propertiesPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusSolubilityPolymer science
A resist composition containing a base component (A) which generates an acid upon exposure and exhibits changed solubility in a developing solution by the action of acid, wherein the base component (A) contains a copolymer (A1) having a structural unit (a0) containing a group represented by the following general formula (a0-1) or (a0-2), a structural unit (a11) containing an acid-decomposable group which exhibits increased polarity by the action of acid and contains a polycyclic group, and a structural unit (a12) containing an acid-decomposable group which exhibits increased polarity by the action of acid and contains a monocyclic group. Each of the groups —R3—S+(R4)(R5) and Mm+ in the formula has only one aromatic ring as a whole or has no aromatic ring.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
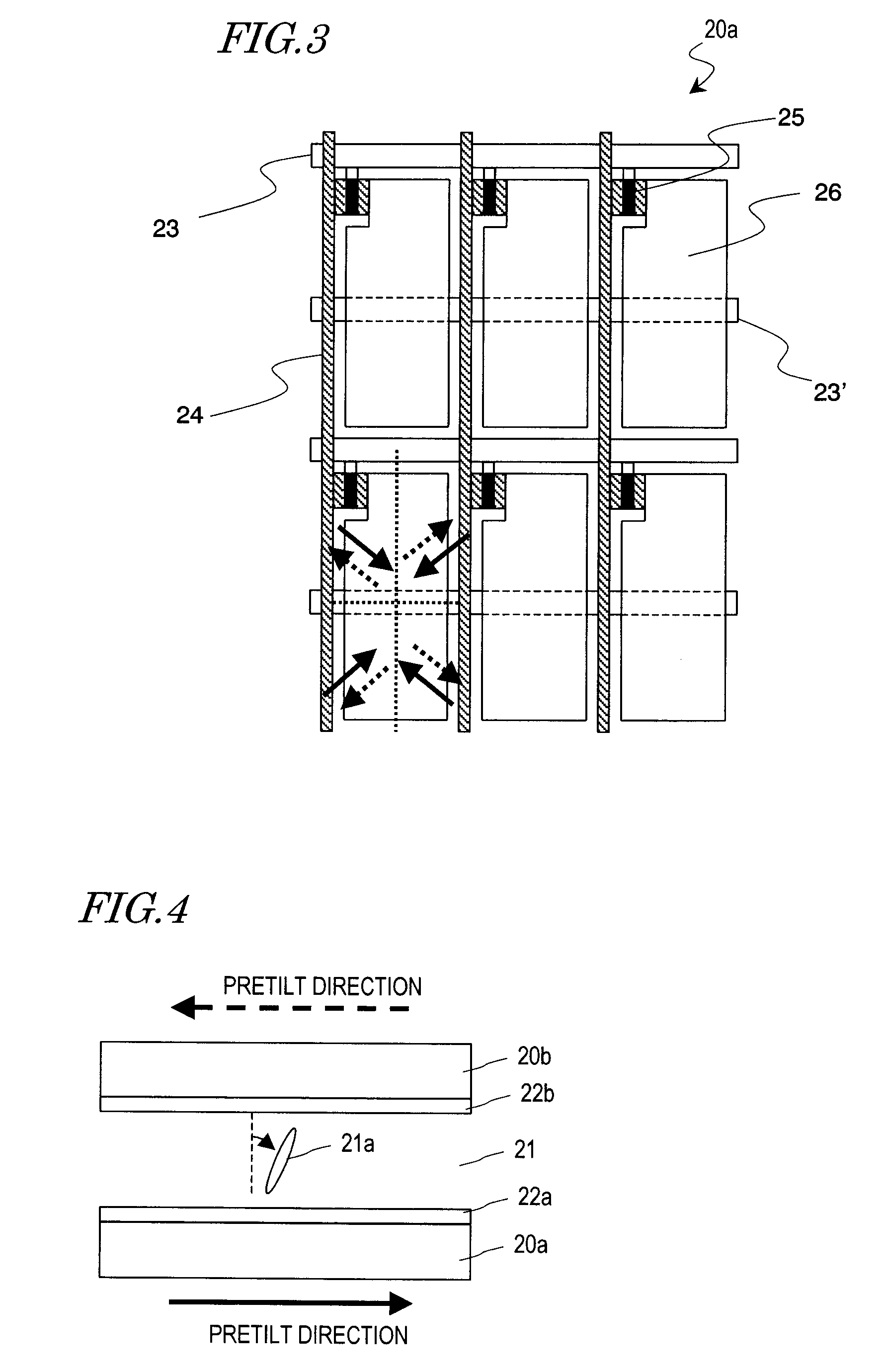
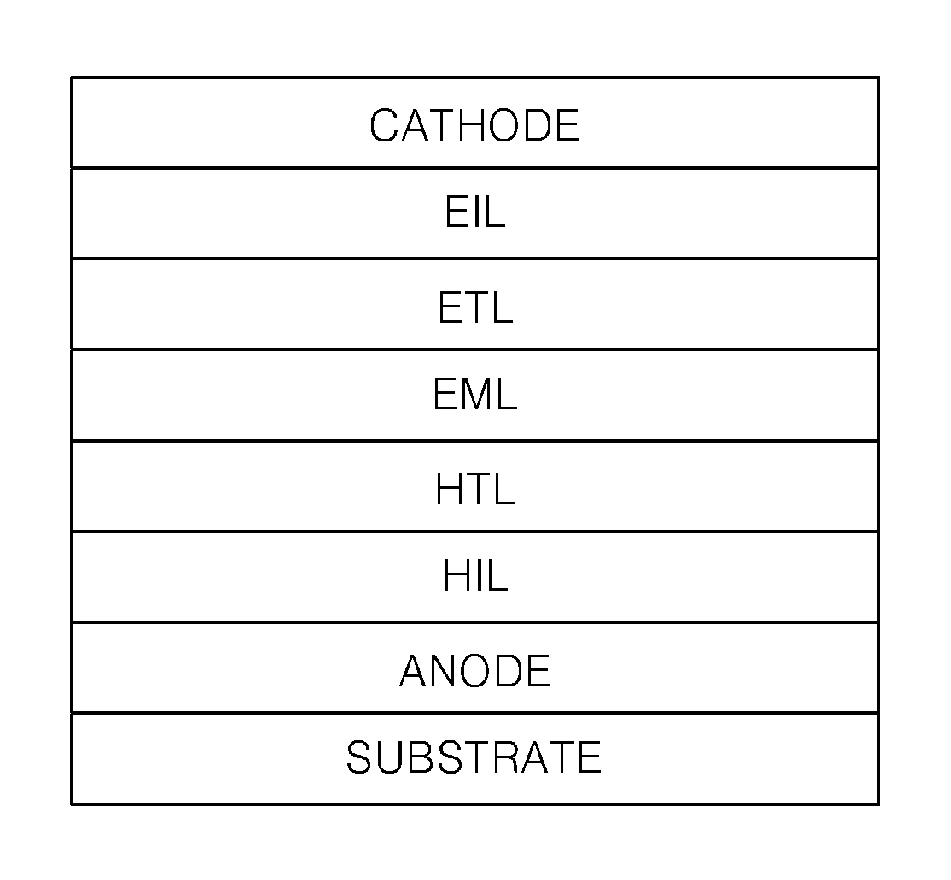
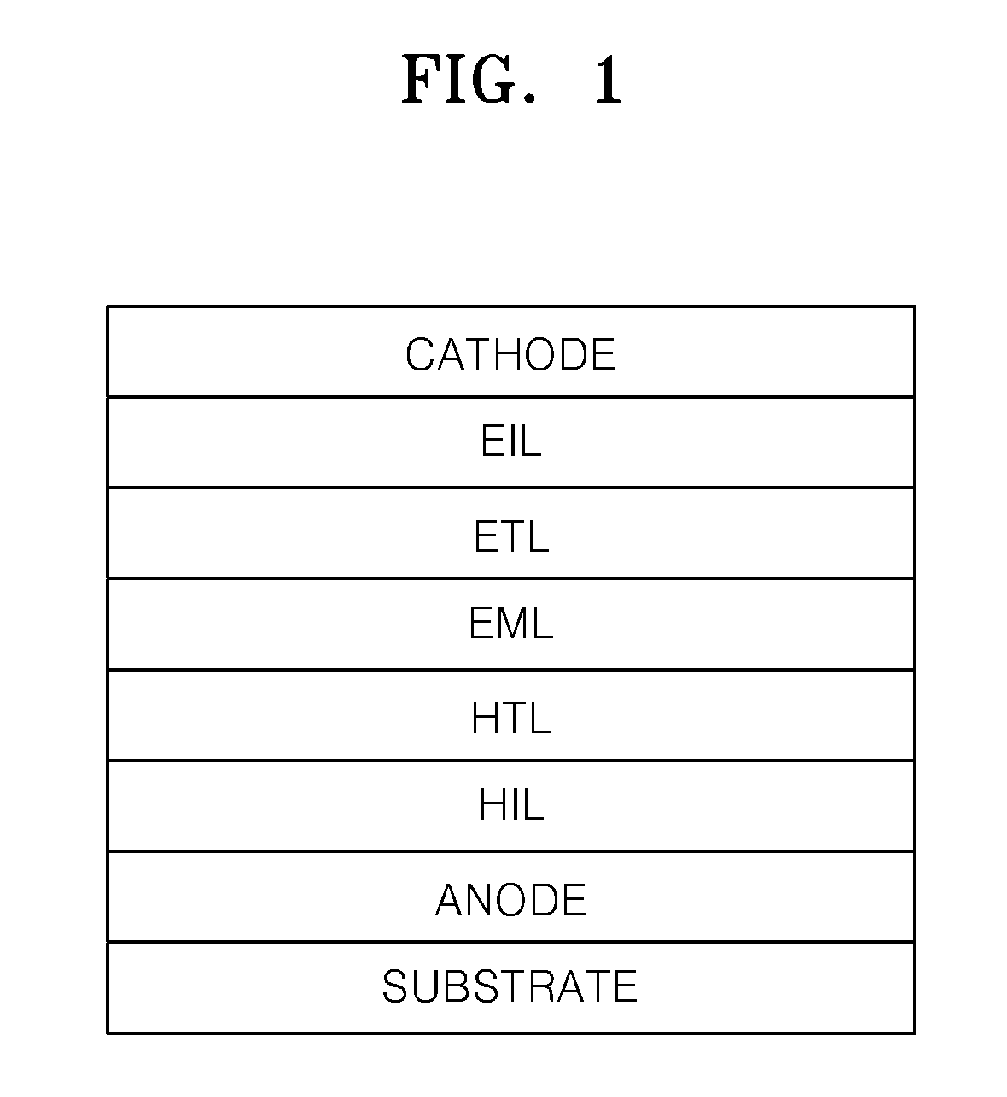
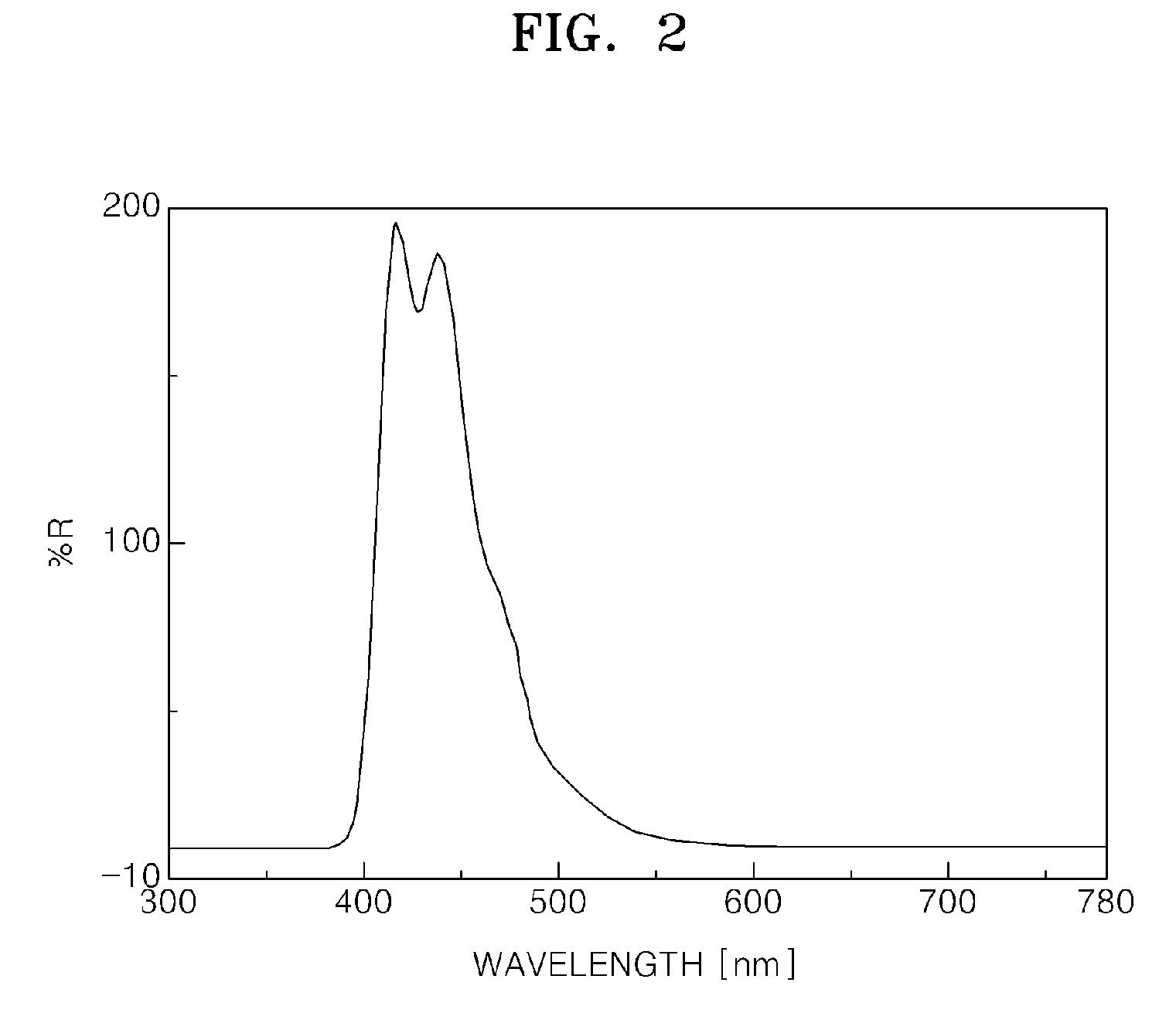
Liquid Crystal Display Device and Electronic Device Having the Same
ActiveUS20080100776A1Improve reliabilityHigh quality displayLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingLiquid-crystal displayPolycyclic group
A liquid crystal display device according to the present invention includes an illuminator and a liquid crystal panel for performing displaying by using light which is emitted from the illuminator. The liquid crystal panel includes a pair of substrates and a liquid crystal layer provided therebetween. The liquid crystal layer is formed of a liquid crystal material which contains molecules having at least one of a carbon-carbon triple bond and a polycyclic group. The illuminator includes a light source causing primary generation of at least blue light, among other light which is used for displaying.
Owner:SHARP KK
Fluorine-containing compound and organic light-emitting device employing the same
ActiveUS7867631B2Electrical stabilityHigh charge transport performanceOrganic chemistryDischarge tube luminescnet screensArylHalogen
A fluorine-containing compound is represented by Formula 1 below:wherein R1a, R1b, R2a, and R2b are each independently a hydrogen atom, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkyl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C1-C30 alkoxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryloxy group, a substituted or unsubstituted C4-C30 heteroaryl group, a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 condensed polycyclic group, a hydroxy group, halogen, a cyano group, or a substituted or unsubstituted amino group, and adjacent groups selected from R1a, R1b, R2a, and R2b may join together to form a saturated or unsaturated carbon ring; n and m are each independently an integer of 0 to 5; Ar1a and Ar1b are each independently a C6-C30 aryl group which is unsubstituted or substituted by at least one fluorine or a C4-C30 heteroaryl group which is unsubstituted or substituted by at least one fluorine; and Ar2 is a substituted or unsubstituted C6-C30 aryl group or a substituted or unsubstituted C2-C30 heteroaryl group. The fluorine-containing compound has good electrical characteristics and charge transport capability, and thus, is useful as a hole injection material, a hole transport material, and / or an emitting material for fluorescent or phosphorescent devices capable of producing light of a full spectrum of colors, including red, green, blue, and white. Thus, the fluorine-containing compound can be used to produce organic light-emitting devices with high efficiency, a low driving voltage, high brightness, and a long lifetime.
Owner:SAMSUNG DISPLAY CO LTD
Positive resist composition and method for resist pattern formation
ActiveUS20090042129A1Excellent lithography characteristicLower Level RequirementsPhotosensitive materialsRadiation applicationsResistMethacrylate
A positive resist composition includes a resin component (A) that exhibits increased alkali solubility under the action of acid, and an acid generator component (B) that generates acid upon exposure, wherein the resin component (A) is a mixture of a copolymer (A1) that includes a structural unit (a1) derived from an acrylate ester that contains an acid-dissociable, dissolution-inhibiting group, a structural unit (a2) derived from a methacrylate ester that contains a lactone-containing monocyclic group, and a structural unit (a3) derived from an acrylate ester that contains a polar group-containing polycyclic group, and a copolymer (A2) that has a different structure from the copolymer (A1) and has a lower hydrophilicity than the copolymer (A1).
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Thermoplastic resin composition, optical film, and process for producing film
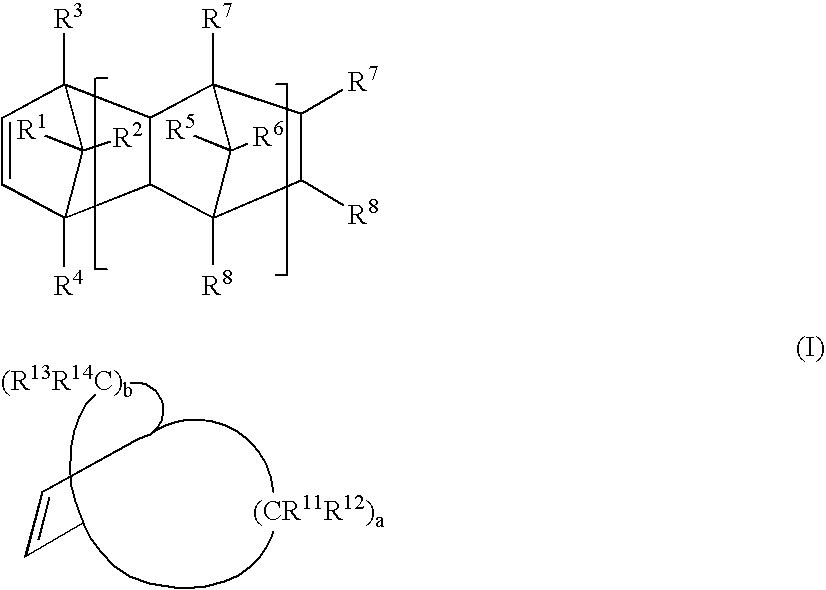
A thermoplastic resin composition which is inhibited from suffering phase separation and readily gives an optical film having excellent transparency; an optical film comprising the composition as a major ingredient; a retardation film which is a film formed by stretching the optical film, shows a positive wavelength dependence, and has a low photoelastic coefficient and transparency; and a process for producing the retardation film. The thermoplastic resin composition comprises (A) a cyclic-olefin polymer and (B) a vinyl polymer having a unit represented by the following general formula (II). (II) (III) (In the formula (II), at least one of R<1> to R<4> represents a group represented by the general formula (III), and the remainder of R<1> to R<4>, if any, and R<5> and R<6> each represents hydrogen, halogeno, a (substituted) hydrocarbon group optionally having a connecting group containing a heteroatom, or a polar group, provided that R<5> and R<6> may be bonded to each other to form a monocyclic or polycyclic group optionally having a heteroatom or may in cooperation represent a divalent hydrocarbon group; and Y represents a divalent hydrocarbon group.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Resist composition, method of forming resist pattern, and polymeric compound
ActiveUS20150198880A1Good body shapeEasy to shapePhotosensitive material processingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentResistStructural unit
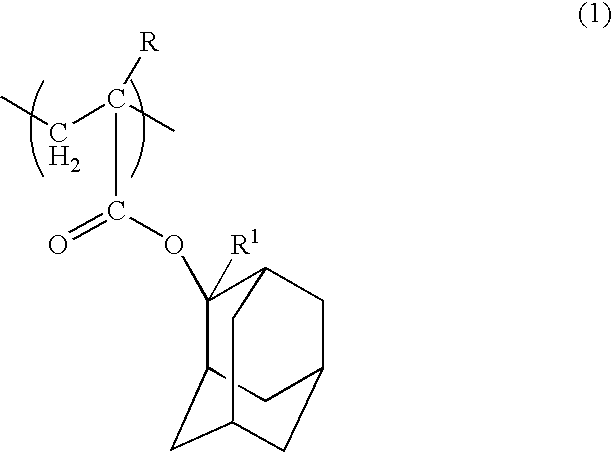
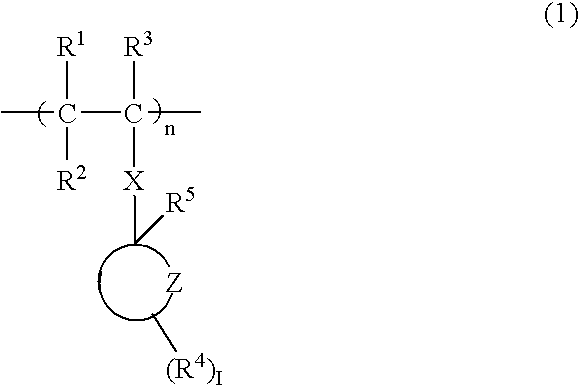
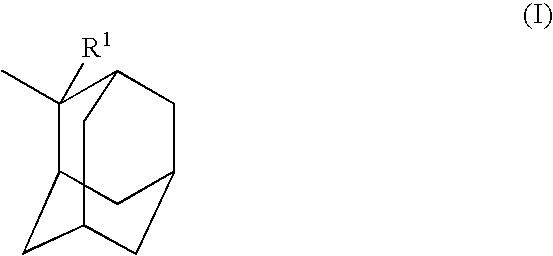
A polymeric compound including a structural unit (a0) represented by general formula (a0-1) shown below and a polycyclic group-containing structural unit (a2m) other than the structural unit (a0), the structural unit (a2m) containing a lactone-containing polycyclic group, a —SO2-containing polycyclic group or a carbonate-containing polycyclic group, and a resist composition including the same:wherein R0 represents a hydrocarbon group of 1 to 6 carbon atoms which may have a substituent, or a hydrogen atom; Ya0 represents a single bond or a divalent linking group; L represents an ester bond; and Ra0 represents a polycyclic group having a bridged ring polycyclic skeleton or a condensed ring polycyclic skeleton, which has in its skeleton —C(═O)O— or —SO2—, and at least one of an alkyl group, an alkoxy group, a halogen atom and a halogenated alkyl group.
Owner:TOKYO OHKA KOGYO CO LTD
Thermoplastic Resin Composition, Optical Film, And Process For Producing Film
InactiveUS20080177002A1Good compatibilityHigh transparencyPolarising elementsFlat articlesHalogenHydrogen atom
The present invention is intended to provide a thermoplastic resin composition which is inhibited from suffering phase separation and from which an optical film having excellent transparency is readily obtained, an optical film containing the composition as a main component, a retardation film which is a film obtained by stretching the optical film and exhibits positive wavelength dependence and has a small coefficient of photoelasticity and transparency, and a process for producing the retardation film. The thermoplastic resin composition contains (A) a cycloolefin-based polymer and (B) a vinyl-based polymer having a unit represented by the following formula (II):wherein at least one of R1 to R4 is a group represented by the formula (III), the remainder of R1 to R4 if any, and R5 and R6 are each a hydrogen atom, a halogen atom, a substituted) hydrocarbon group which may have a linkage containing a hetero atom, or a polar group, R5 and R6 may be bonded to each other to form a monocyclic or polycyclic group which may have a hetero atom, or may be united to form a divalent hydrocarbon group and Y is a divalent hydrocarbon group.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com



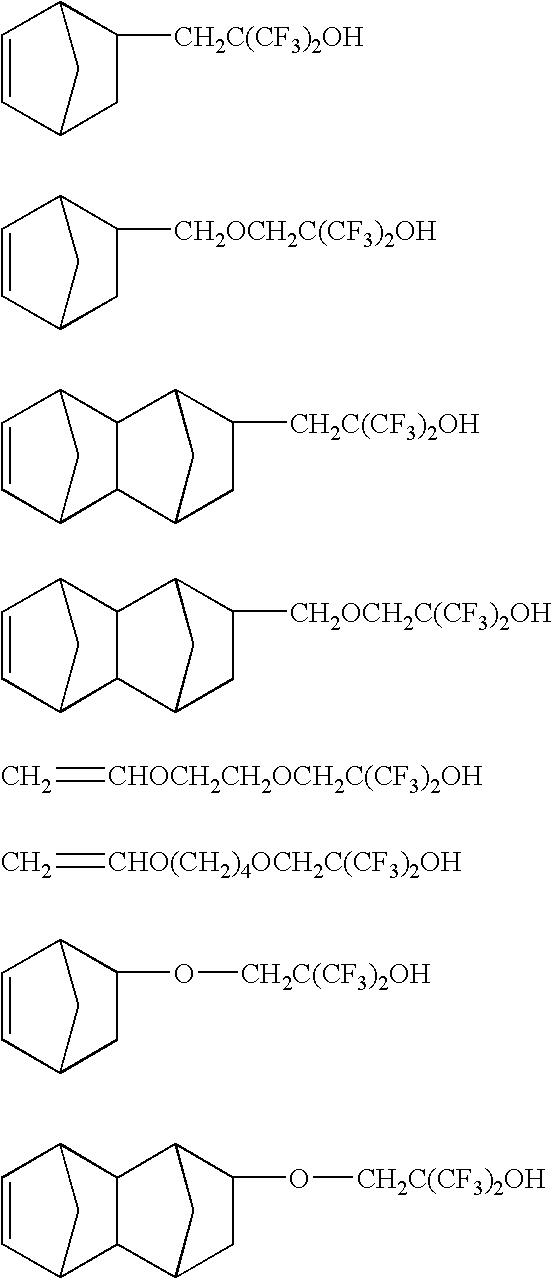


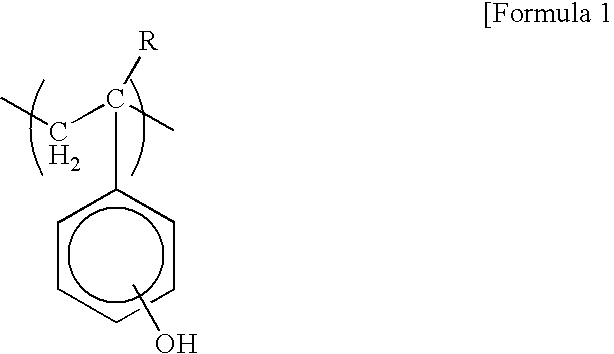
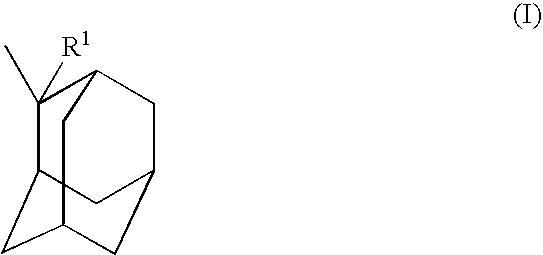
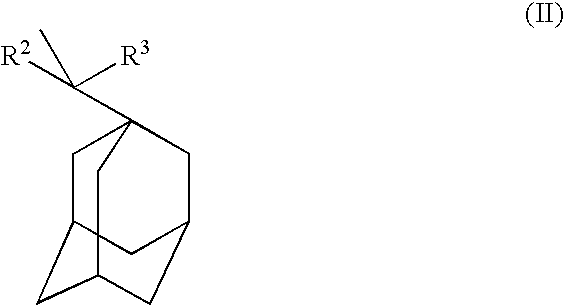
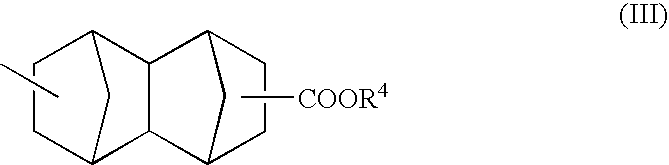
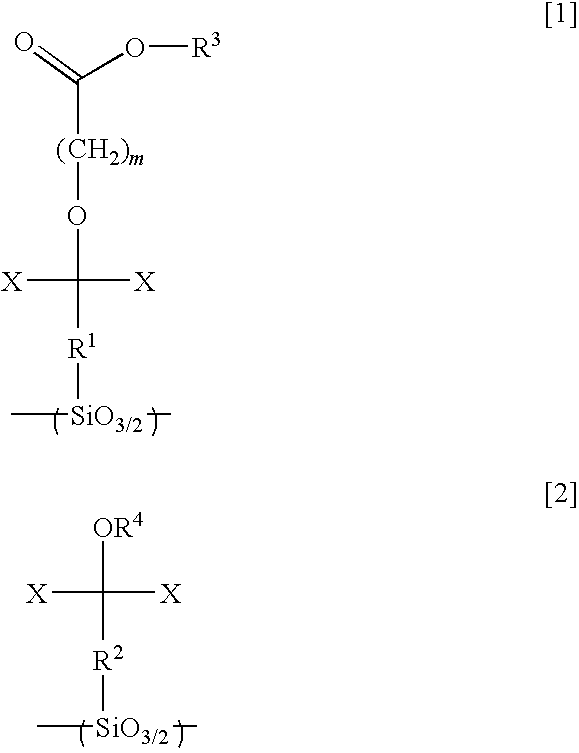
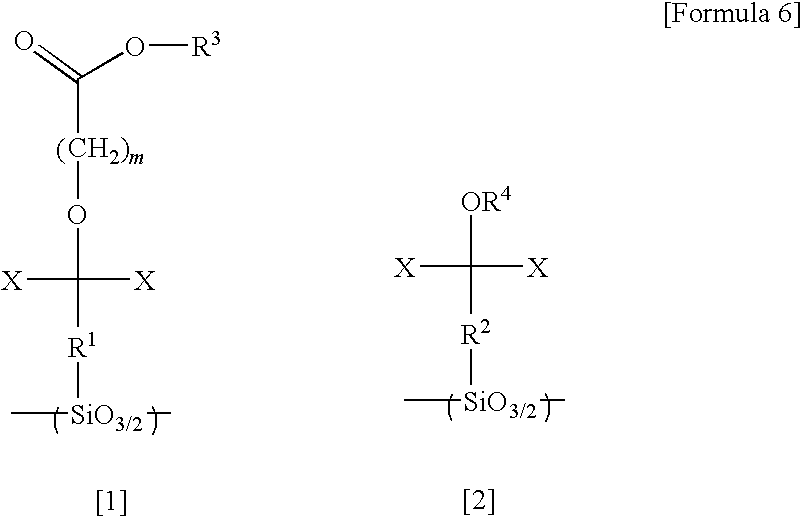




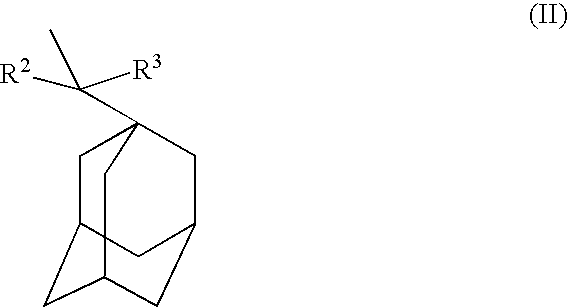
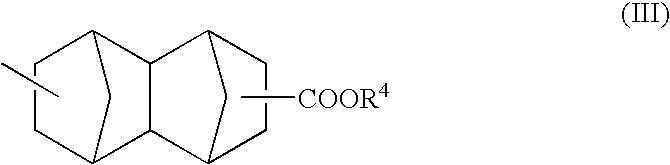
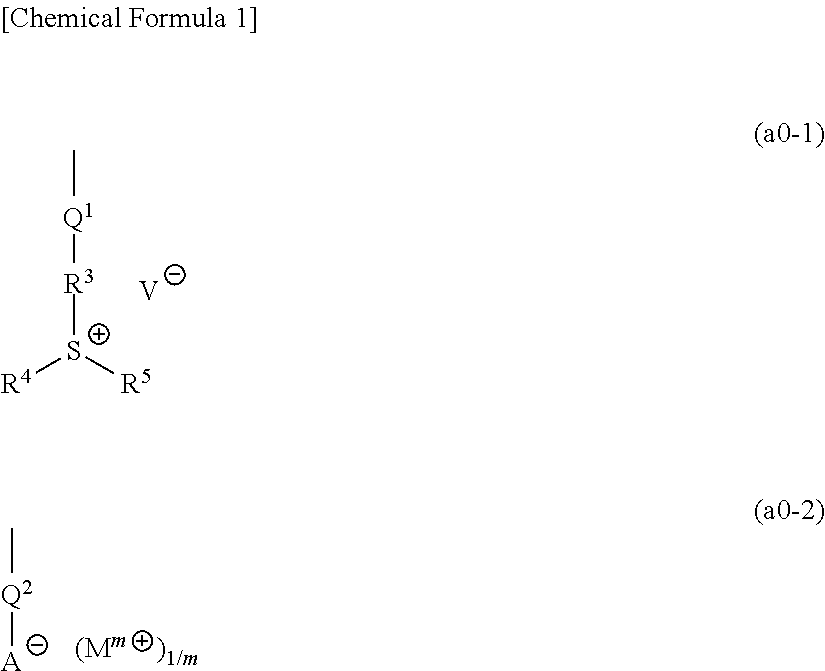
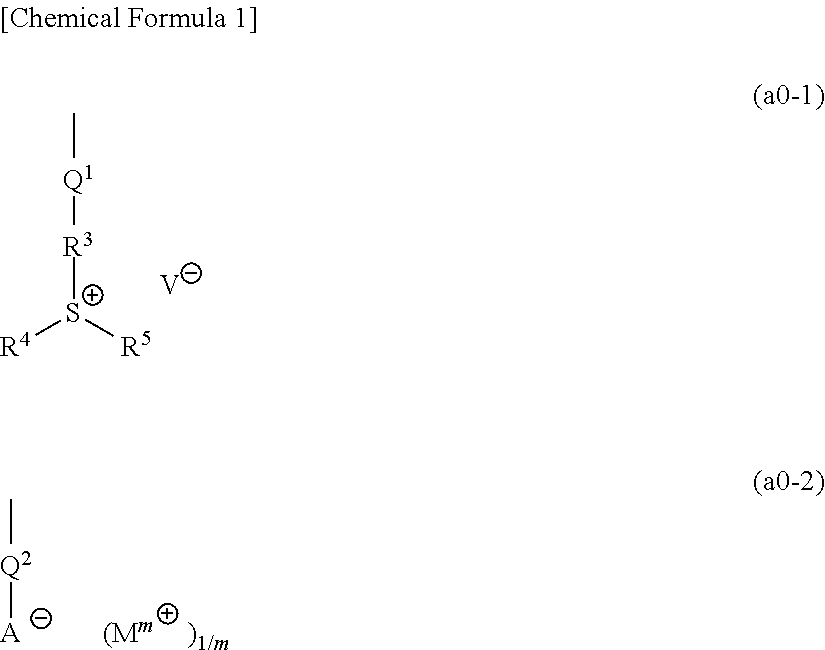

![BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a40de337-30c4-442b-8606-48a561b571aa/US20110049479A1-20110303-D00001.png)
![BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a40de337-30c4-442b-8606-48a561b571aa/US20110049479A1-20110303-D00002.png)
![BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME BENZO[a]FLUORANTHENE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC LIGHT EMITTING DEVICE USING THE SAME](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/a40de337-30c4-442b-8606-48a561b571aa/US20110049479A1-20110303-D00003.png)