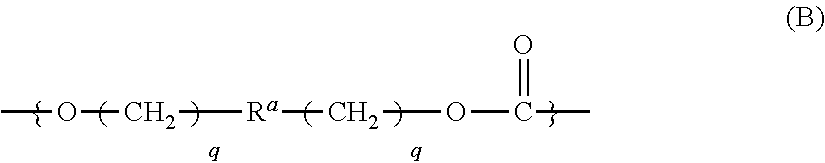Patents
Literature
173 results about "Photoelasticity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Photoelasticity describes changes in the optical properties of a material under mechanical deformation. It is a property of all dielectric media and is often used to experimentally determine the stress distribution in a material, where it gives a picture of stress distributions around discontinuities in materials. Photoelastic experiments (also informally referred to as photoelasticity) are an important tool for determining critical stress points in a material, and are used for determining stress concentration in irregular geometries.
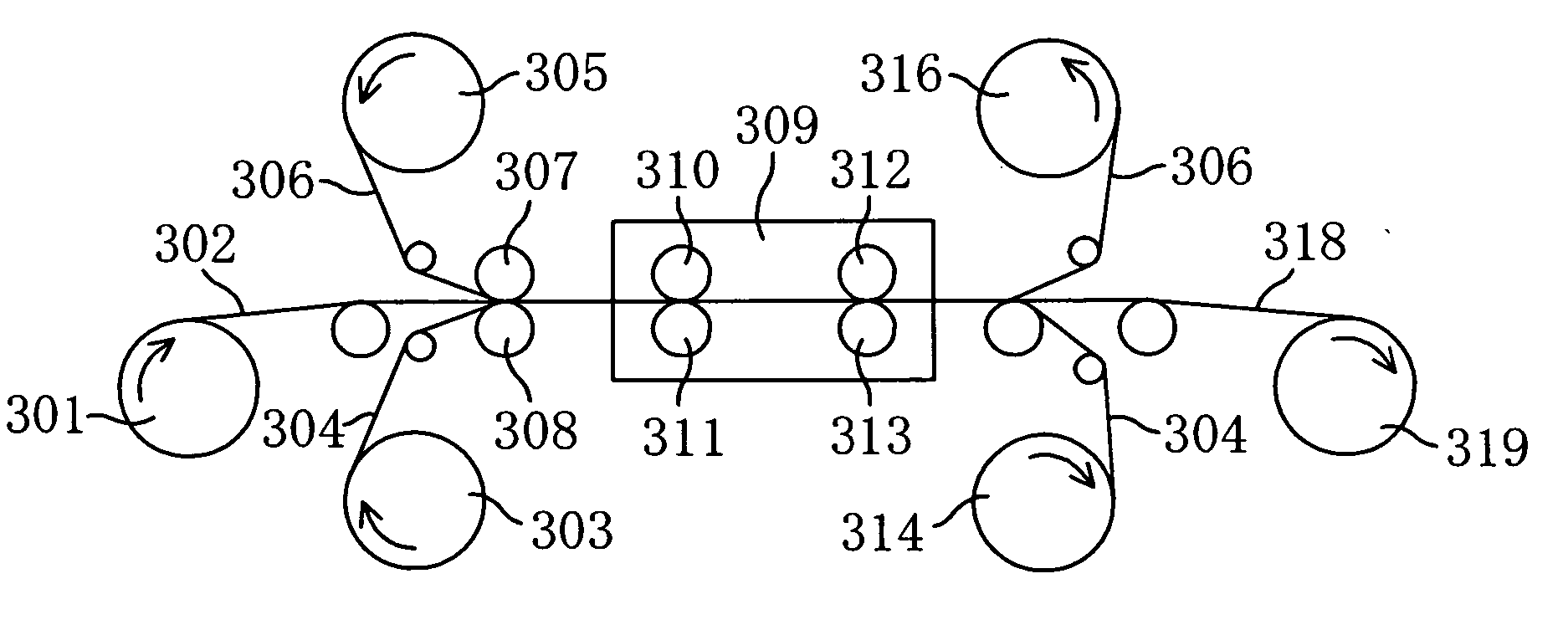
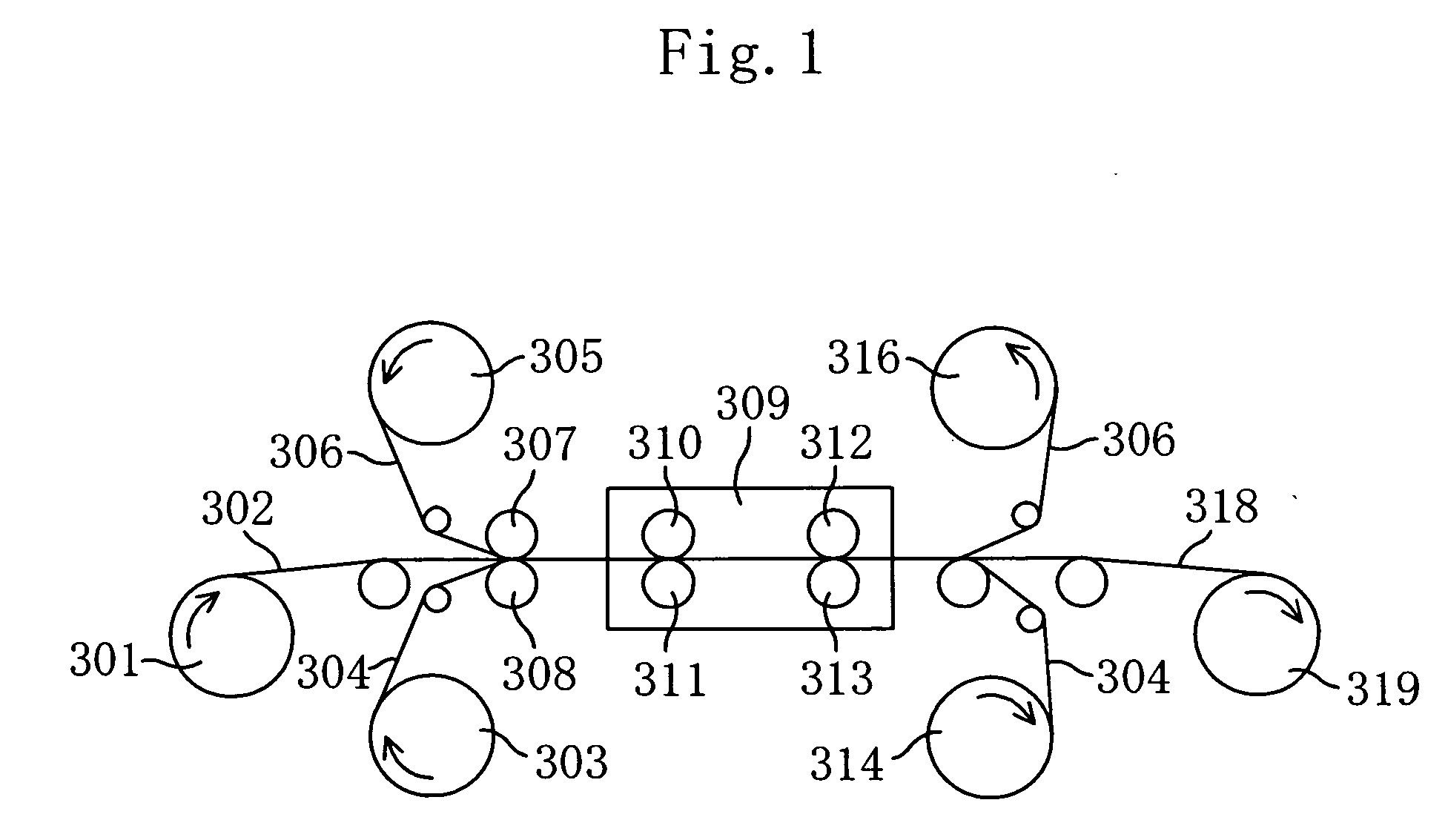
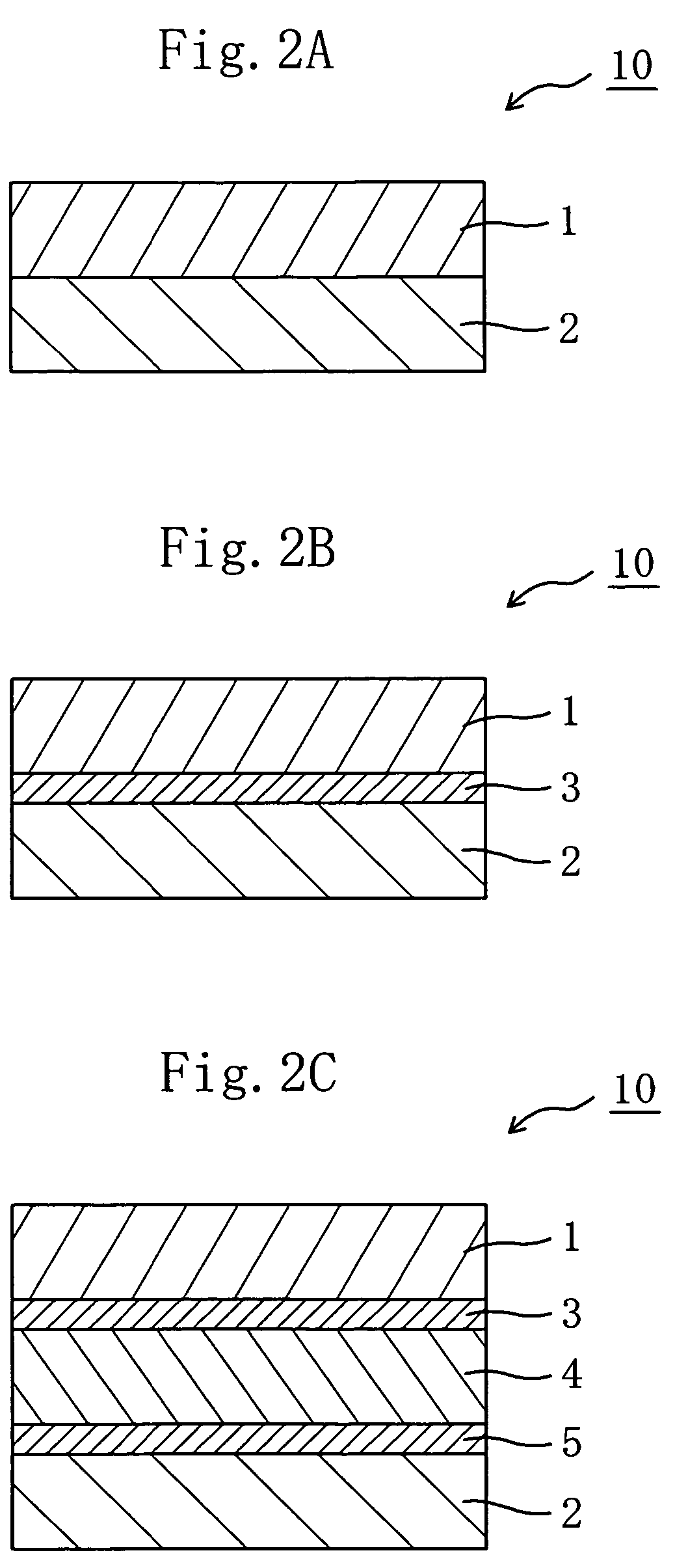
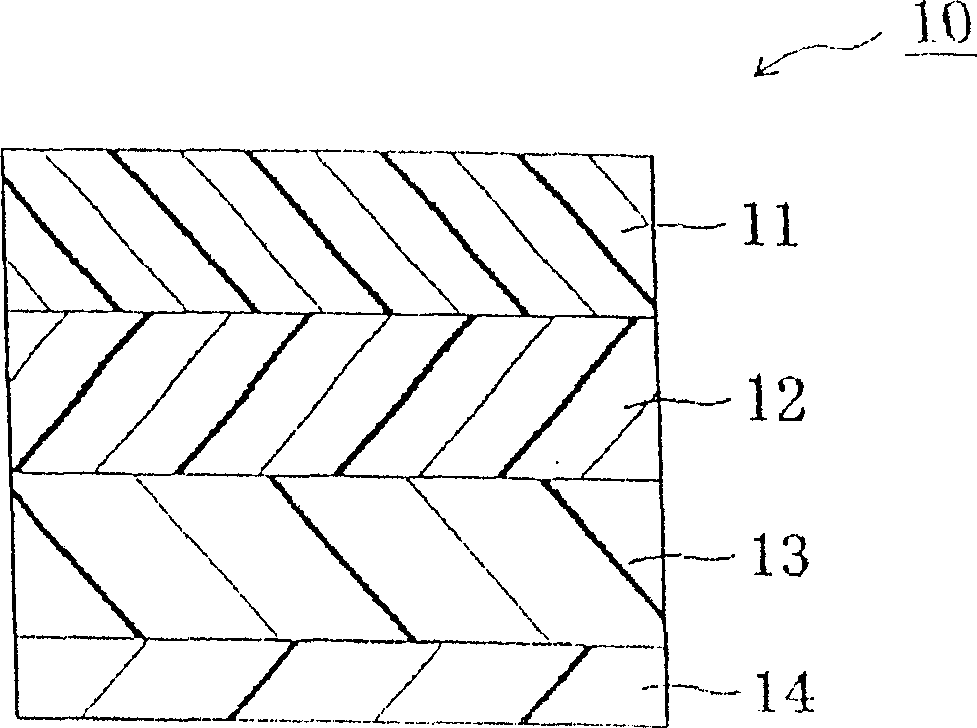
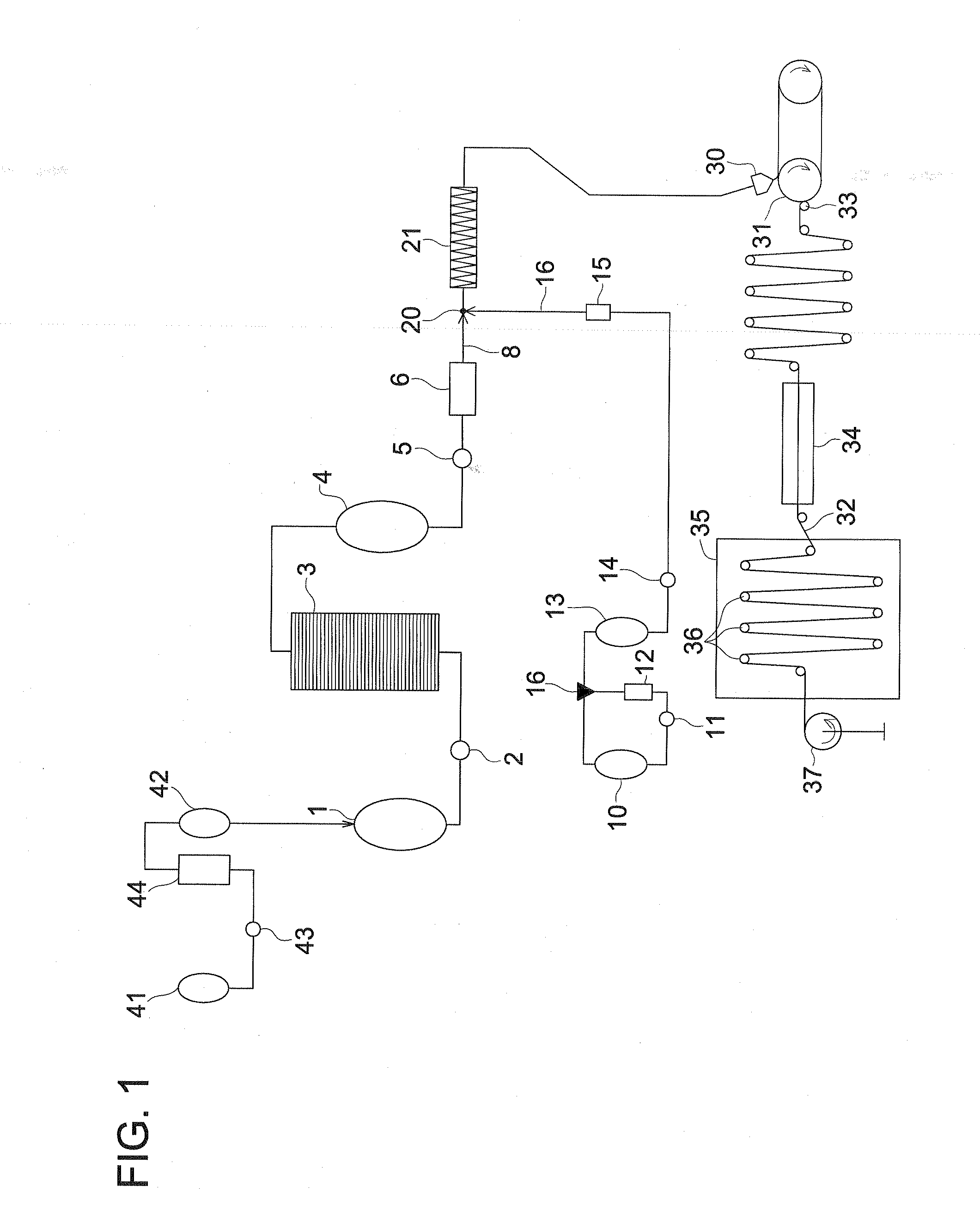
Retardation film, polarizing element, liquid crystal panel, and liquid crystal apparatus
InactiveUS20060177607A1Good molding effectImproved display property displayLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingIn planeLength wave
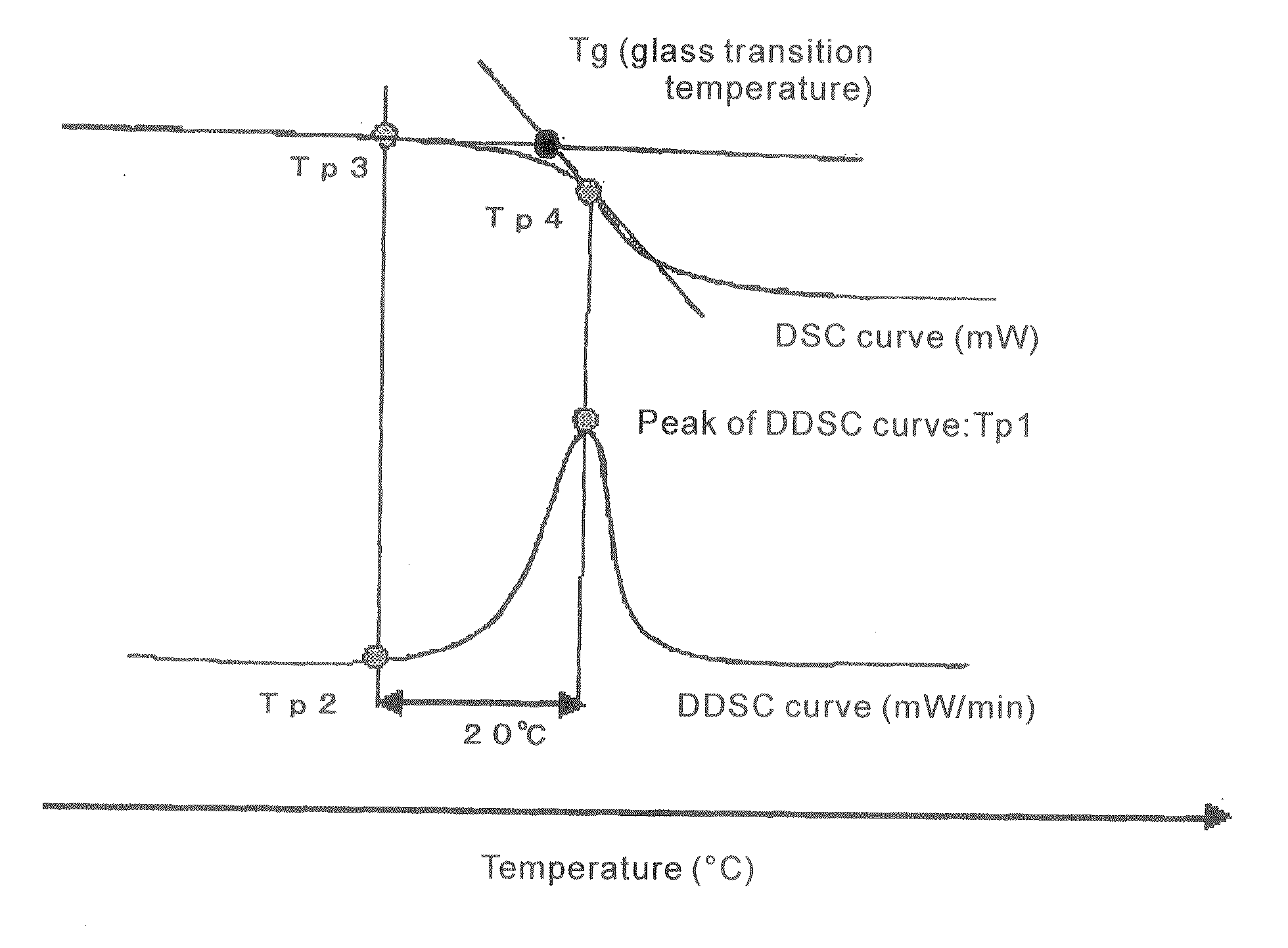
There is provided a retardation film including a stretched film of a polymer film having an absolute value of photoelastic coefficient (m2 / N) of 50×10−12 or less measured by using light of a wavelength of 550 nm at 23° C., which satisfies the following expressions (1) and (2):Re[450]<Re[550]<Re[650] (1)Rth[550]<Re[550] (2).In the expressions (1) and (2): Re[450], Re[550], and Re[650] respectively represent in-plane retardation values measured by using light of wavelengths of 450 nm, 550 nm, and 650 nm at 23° C.; and Rth[550] represents a thickness direction retardation value measured by using light of a wavelength of 550 nm at 23° C.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method and system for assembling a solar cell using a plurality of photovoltaic regions
InactiveUS20070056626A1Easily use processLight weightPV power plantsPhotovoltaic energy generationElastomerEngineering
A solar cell device. The device has a housing member. The device also has a lead frame member coupled to the housing member. In a preferred embodiment, the lead frame member has at least one photovoltaic strip thereon, which has a surface region and a back side region. The device has an optical elastomer material having a first thickness overlying the surface region of the photovoltaic surface. The device has a second substrate member comprising at least one optical concentrating element thereon. The optical concentrating element has a first side and a second side. The device has a first interface within a vicinity of the surface region and the first thickness of the optical elastomer material and a second interface within a vicinity of the second side and the optical elastomer material. In a specific embodiment, the optical concentrating element is coupled to the surface region of the photovoltaic strip such that the optical elastomer material is in between the surface region of the photovoltaic strip and the second side of the optical concentrating element. In a specific embodiment, the device has a spacing comprising essentially the optical elastomer material between the second side of the optical concentrating element and the surface region of the photovoltaic strip. The device has a plurality of particles having a predetermined dimension (e.g., non-compressible and substantially non-deformable particles) spatially disposed overlying the surface region of the photovoltaic strip and within a second thickness of the optical elastomer material to define the spacing between the surface region and the second side of the optical concentrating element. In a specific embodiment, the first interface is substantially free from one or more gaps (e.g., air gaps and / or pockets) and the second interface substantially free from one or more gaps to form a substantially continuous optical interface from the first side of the optical concentrating element, through the first interface, and through the second interface to the photovoltaic strip.
Owner:SOLARIA CORP
Optical compensation film, viewing angle compensation integral type polarizing plate and liquid crystal display apparatus
ActiveUS6881457B2Excellent viewing angle compensation functionIncreased durabilityLiquid crystal compositionsDomestic cooling apparatusCellulose ester membraneLiquid-crystal display
An optical compensation film comprising a cellulose ester film is disclosed. In the film, (a) each of photoelastic coefficient C(md) in a mechanical direction and photoelastic coefficient C(td) in the transverse direction of the cellulose ester film is 1×10−9 to 1×10−13 Pa−1 and C(md)<C(td), (b) retardation R0 within the plane of the cellulose film defined by Formula (I) is 20 to 70 nm, (c) retardation Rt of the cellulose ester film in a thickness direction, defined by Formula (II) is 70 to 400 nm, and (d) both of a dimensional variation ratio S(md) in the mechanical direction and a dimensional variation ratio S(td) in the transverse direction of the cellulose ester film prior to and after being allowed to stand at ambient conditions of 80° C. and 90 percent relative humidity for 50 hours are −1 to 1 percent, and |S(md)|>|S(td)|.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA INC
Resin film, production method thereof, polarizing plate and liquid crystal display device
InactiveUS20070290168A1Small photoelastic coefficientImprove adhesionLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingIn planeLiquid-crystal display
A resin film has a photoelastic coefficient of from 0 to 30×10−8 cm2 / N; and Re satisfying the following formulae (1) to (4):20 nm<Re(548)<300 nm : Formula (1)0.5<Re(446) / Re(548)<1 : Formula (2)1.0<Re(629) / Re(548)<2.0 : Formula (3)0.1%≦[{Re(548) at 25° C., 10% RH−Re(548) at 25° C., 80% RH} / Re(548) at 25° C., 60% RH]≦20%, : Formula (4)wherein Re(λ) represents an in-plane retardation at a wavelength of λ.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Fluorophosphate optical glass
ActiveCN105016619AIncrease refractionLow photoelastic coefficientOptical elementsGratingPhotoelasticity
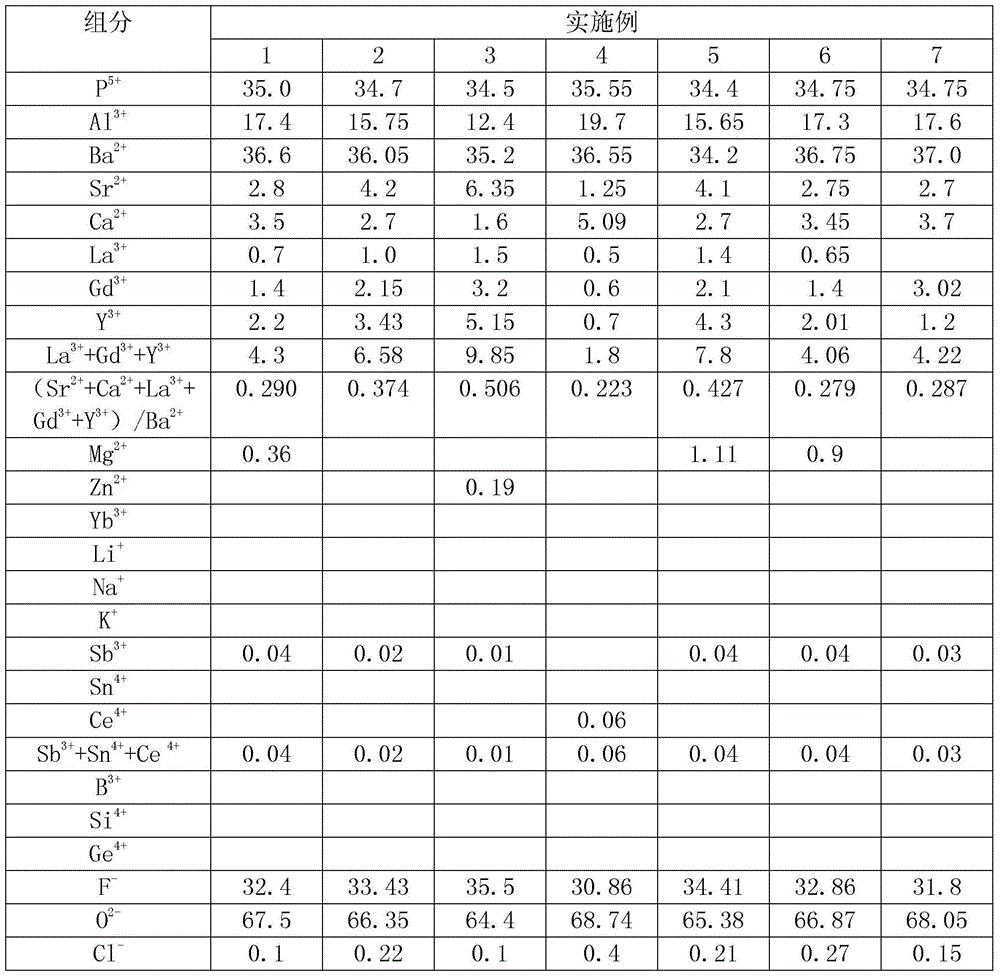
An optical glass, having a refractive index nd which is greater than 1.59, an abbe number υd which is greater than 67, a low photoelastic coefficient and good chemical stability and grinding performance. The fluorophosphate optical glass contains, by cation percentage contents: P5+: 30%-40%, Al3+: 12%-20%, Ba2+: 30%-40%, Ca2+: 1.3%-12%, Sr2+: 1%-10%, La3+: 0%-5%, Gd3+: 0%-6%, Y3+: 0%-10% and contains, by anion percentage contents: F+: 25%-40%, O2-: 60%-75%. The optical glass is applicable to manufacturing methods such as precision moulding, secondary hot-press forming and cold processing, and to manufacturing optical elements such as a high-performance spherical, aspheric and planar lens and a prism and an optical grating.
Owner:CDGM OPTICAL GLASS
Resin composition for optical material
InactiveUS20080266493A1High birefringenceSmall absolute valuePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsChemistryOptical materials
An optical material having a high birefringence and a small absolute value of a photoelastic coefficient is provided by use of a resin composition for an optical material comprising a resin (a) having a positive photoelastic coefficient and a negative inherent birefringence and a resin (b) having a negative photoelastic coefficient and a negative inherent birefringence.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
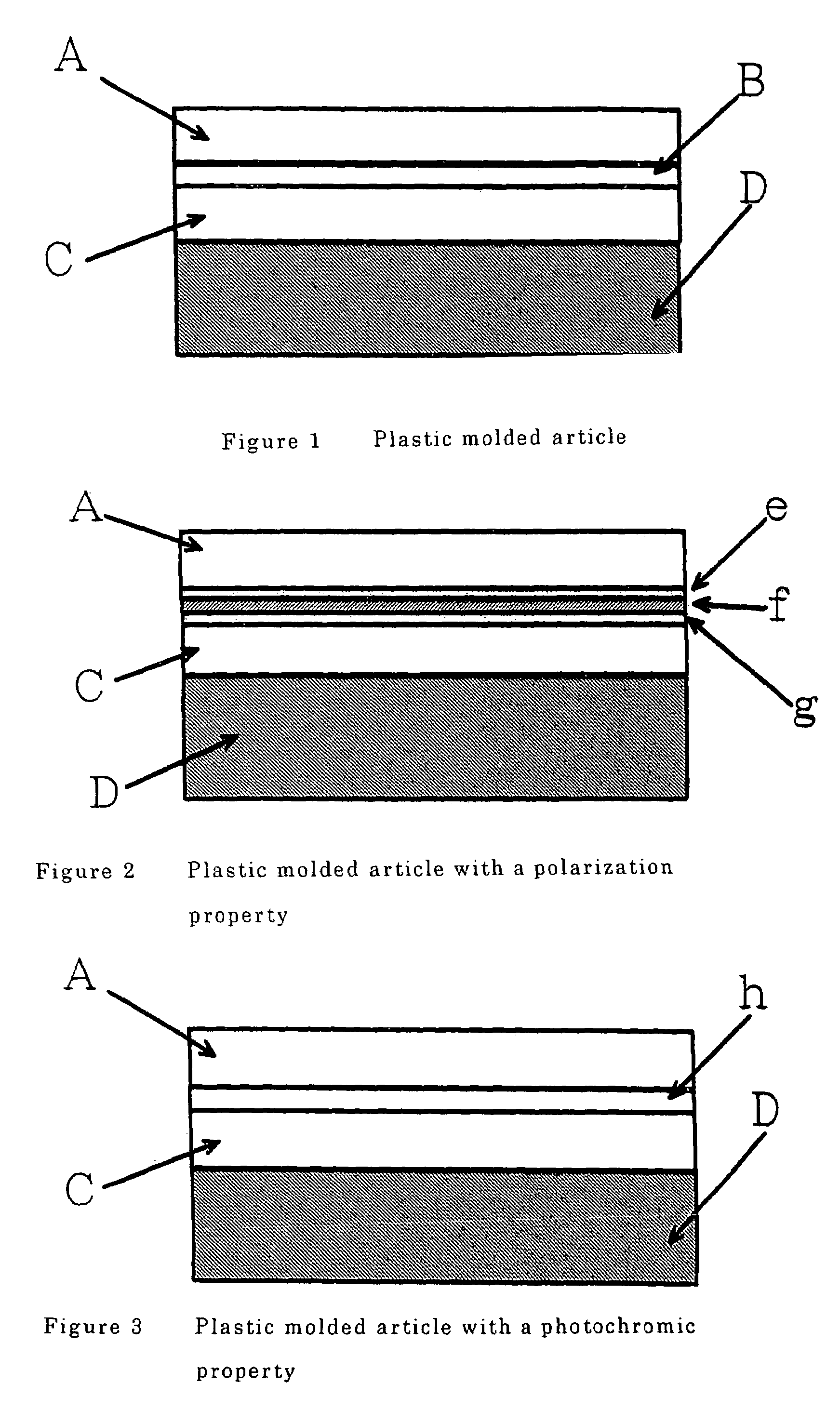
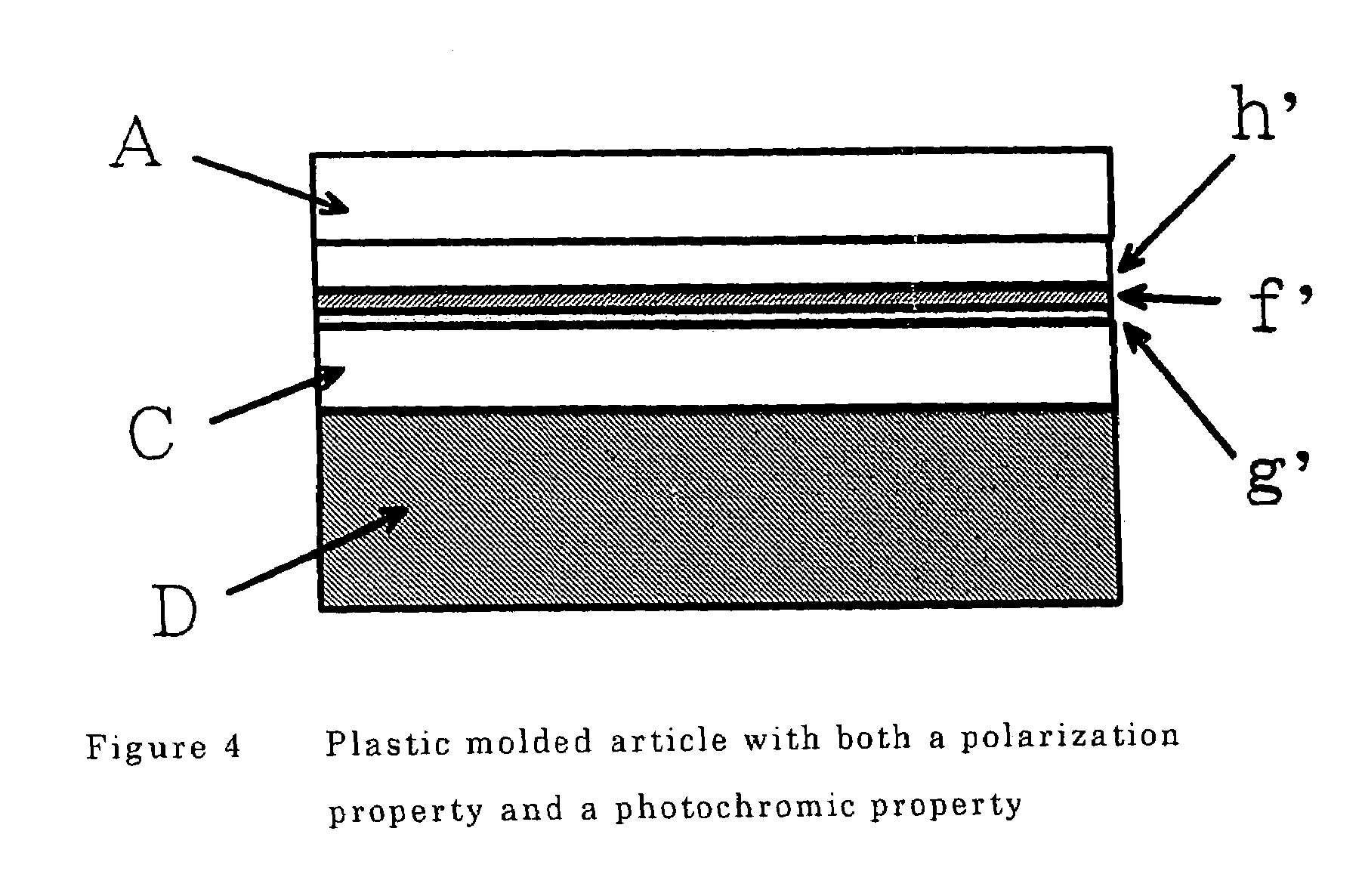
Plastic molded product having photochromic characteristic and/or polarizing characteristics
InactiveUS7118806B2Improve abilitiesMaintain good propertiesPhotosensitive materialsSynthetic resin layered productsPolymer sciencePhotoelasticity
A plastic molded article laminated a layer with a photochromic property and / or a layer with a polarization property on at least one side of a base material, said base material being a polycarbonate having a photoelastic constant of 55×10−12 m2 / N or below.
Owner:MITSUBISHI GAS CHEM CO INC
Retardation film, polarizing element, liquid crystal panel, and liquid crystal apparatus
InactiveUS7625612B2Good molding effectImproved display property and display uniformityLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingIn planeLength wave
There is provided a retardation film including a stretched film of a polymer film having an absolute value of photoelastic coefficient (m2 / N) of 50×10−12 or less measured by using light of a wavelength of 550 nm at 23° C., which satisfies the following expressions (1) and (2):Re[450]<Re[550]<Re[650] (1)Rth[550]<Re[550] (2).In the expressions (1) and (2): Re[450], Re[550], and Re[650] respectively represent in-plane retardation values measured by using light of wavelengths of 450 nm, 550 nm, and 650 nm at 23° C.; and Rth[550] represents a thickness direction retardation value measured by using light of a wavelength of 550 nm at 23° C.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Optical Compensation Layer-Attached Polarizing Plate, Liquid Crystal Panel, Liquid Crystal Display, Image Display, and Method for Producing Optical Compensation Layer-Attached Polarizing Plate
InactiveUS20080043332A1Improve productivityLow costPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planePolarizer
An optical compensation layer-attached polarizing plate of the invention comprises a polarizing plate, an optical compensation layer (1) and another optical compensation layer (2) that are laminated in this order, wherein the optical compensation layer (1) has the relation nx1>ny1=nz1, comprises a resin with a photoelastic coefficient absolute value of at most 2.0×10−11 m2 / N, and has an in-plane retardation (nx1−ny1)d1 in the range of 200 nm to 300 nm, the optical compensation layer (2) has the relation nx2>ny2>nz2, comprises a resin with a photoelastic coefficient absolute value of at most 2.0×10−11 m2 / N, and has an in-plane retardation (nx2−ny2)d2 in the range of 90 nm to 160 nm, a slow axis of the optical compensation layer (1) makes an angle of 10° to 30° with an absorption axis of the polarizing plate, and a slow axis of the optical compensation layer (2) makes an angle of 75° to 95° with the absorption axis of the polarizing plate. The optical compensation layer-attached polarizing plate can provide viewing angle compensation and broadband circular polarization for a VA mode liquid crystal cell, can form a thin product, and can reduce uneven heat-up.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method of enhancing measurement of stress in glass
ActiveUS7583368B1Improve viewing effectOptical interferencePolarisation-affecting propertiesPhase-affecting property measurementsPhotoelasticityColor changes
A detection system for measuring glass that has been placed under strain and the resulting stress lines in the glass has a light source of individual elements configured to create a light distribution. The light distribution has a discontinuity which enhances the viewing of a photoelastic effect in the glass. The light source creates a viewable optical interference (i.e., color changes) which results from stress lines in the glass.
Owner:ELECTRONICS DESIGN MARKET INC
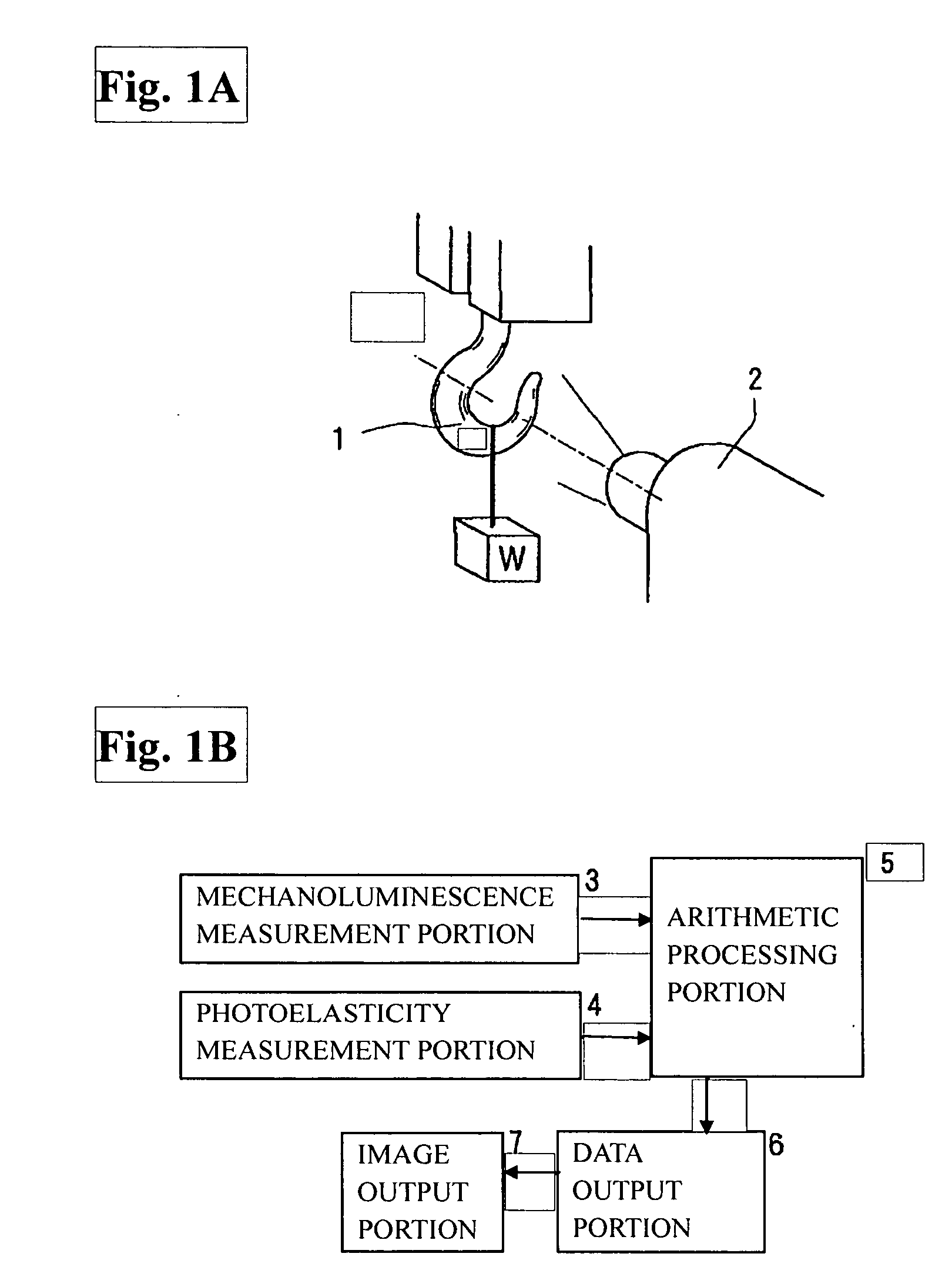
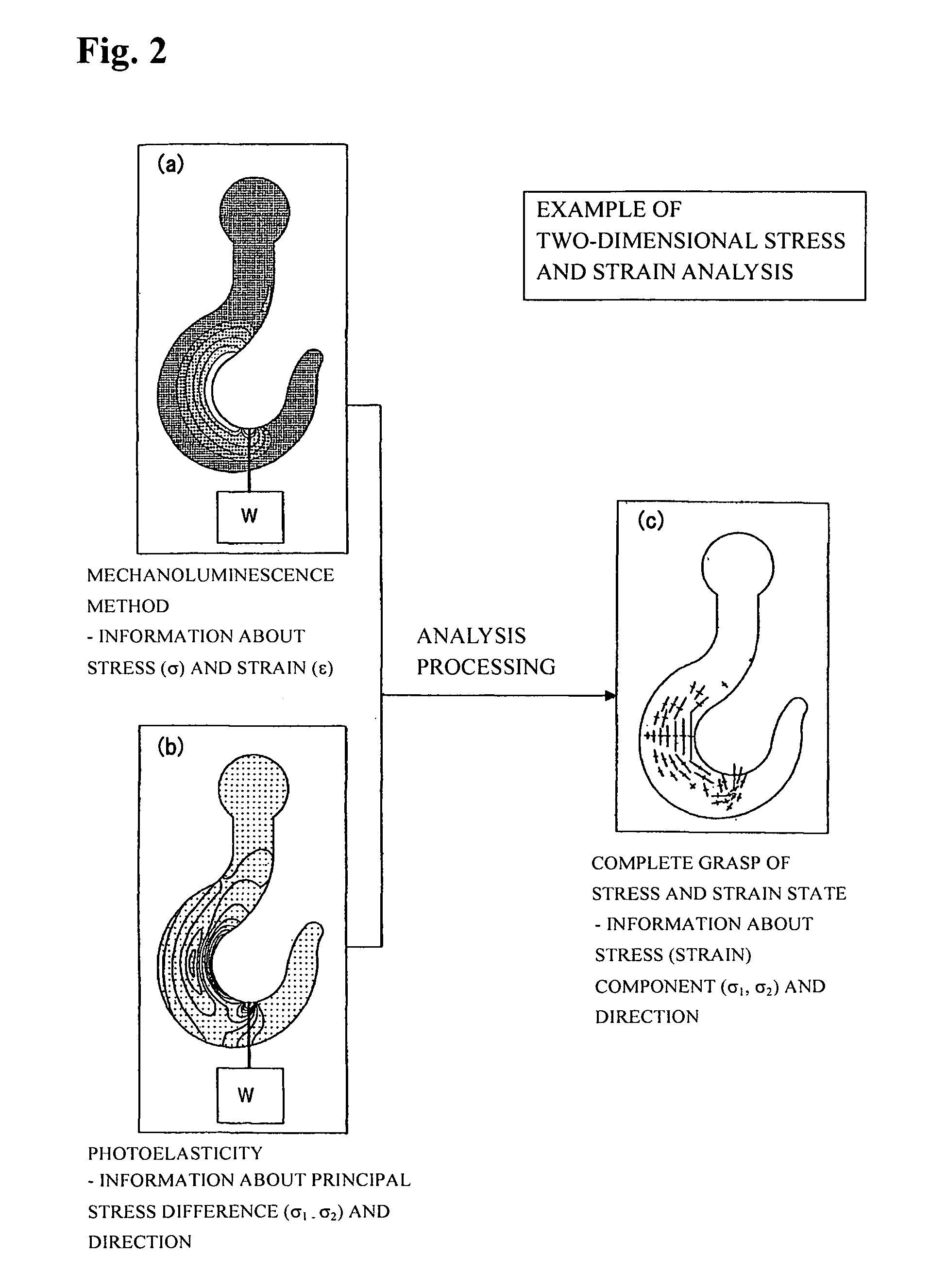
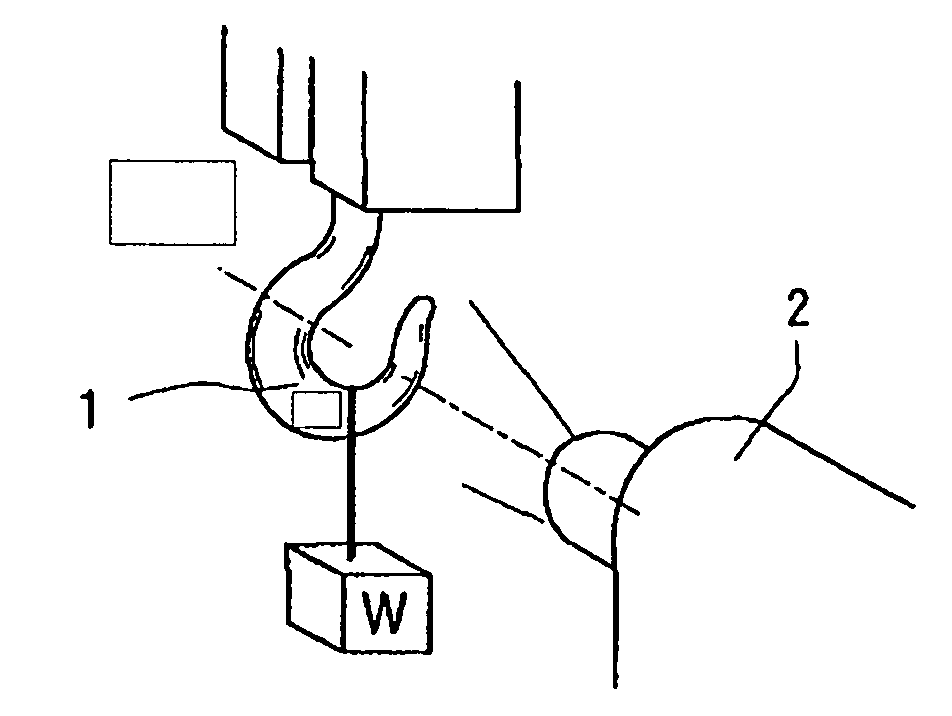
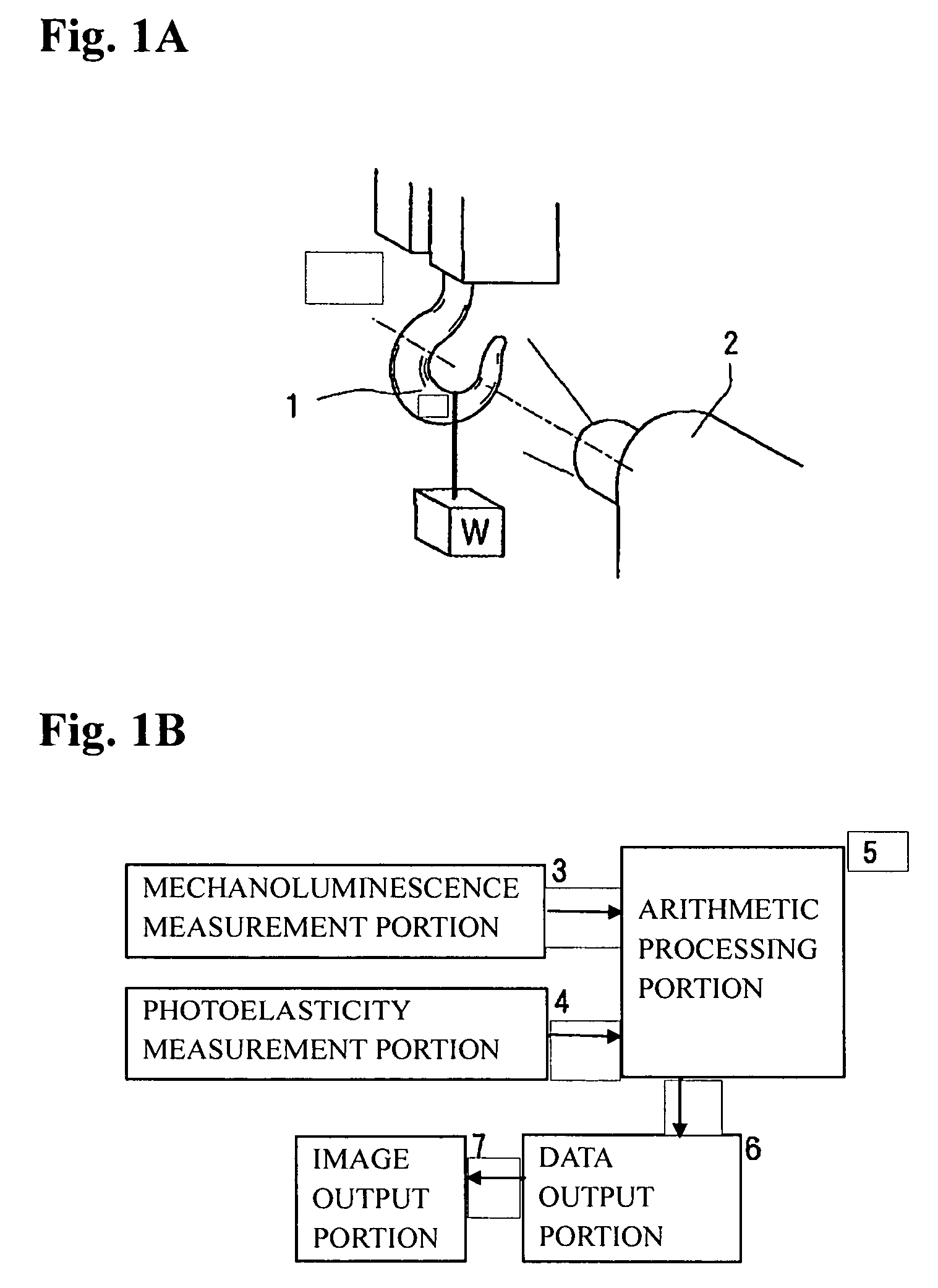
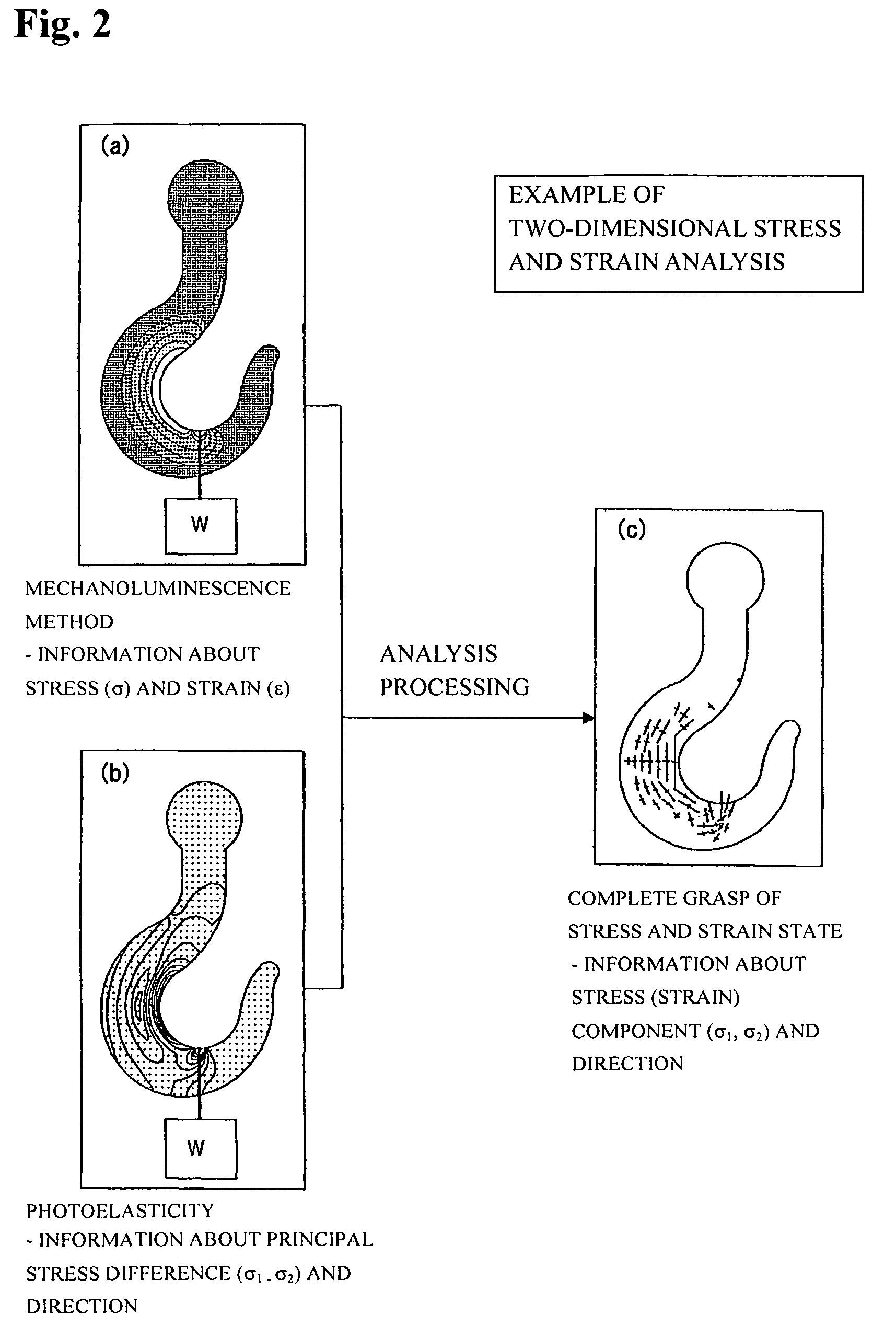
Stress and strain analysis method and its equipment
InactiveUS20070186674A1Detailed stress measurementForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress measurementIt equipment
Provided are a stress analysis method and stress analysis equipment that enable a detailed stress measurement, by using both a photoelasticity measurement method and a stress measurement (mechanoluminescence measurement) which utilizes a mechanoluminescent substance to measure a stress state of an object. Physical quantities that are measurable include individual principal stress component and a principal stress direction. The photoelasticity measurement method alone cannot measure individual principal stress component values.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
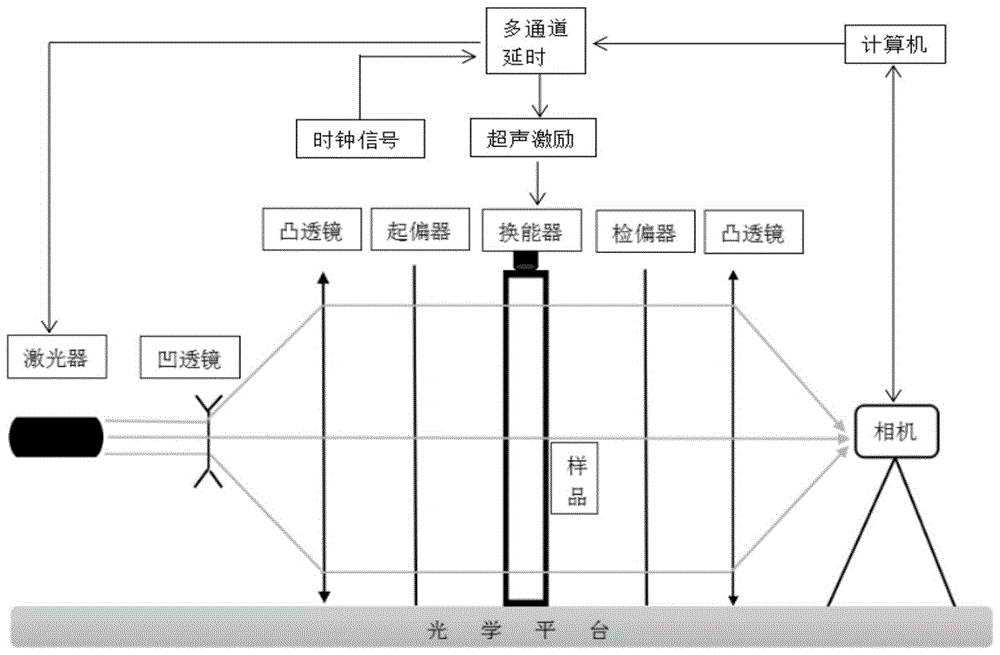
Stress measuring method based on dynamic photoelastic system
InactiveCN105675186AAcquire Ultrasonic Absolute Stress QuicklyEasy to operateForce measurement by measuring optical property variationStress measuresStress measurement
The invention relates to a stress measuring method based on a dynamic photoelastic system. The method comprises that dark-field imaging is carried out, and a first light intensity value of a stress measuring point is obtained; bright field imaging is carried out, and a second light intensity value of the stress measuring point is obtained; dark compensation field imaging is carried out to obtain a third light intensity value of the stress measuring point; the phase difference of birefringence caused by stress is obtained on the basis of the first, second and third light intensity values; and on the basis of the phase difference, different stress values of the stress measuring point are calculated. A laser vibration meter is used to verify the accuracy of a result measured via the method; the measuring method which is a new rotation polarizer method is characterized by a simple optical system, simple operation and the accurate result; and the measuring method can serve as a brand new method to measure the internal stress of a transparent solid, and can be applied to small stress measurement.
Owner:INST OF ACOUSTICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
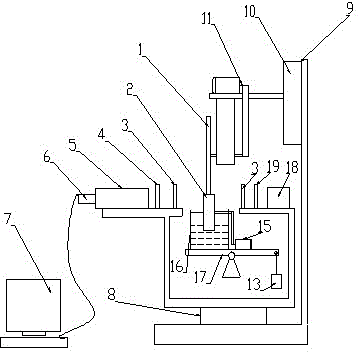
Measuring method and measuring device of elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact pressure based on photoelasticity
ActiveCN103063355AReal-time measurementReal-time display of pressure distributionFluid pressure measurement by optical meansPhotoelasticityImage resolution
The utility model discloses a measuring method and a measuring device of elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact pressure based on photoelasticity. According to the measuring method of the elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact pressure based on the photoelasticity, a friction test sample of elastohydrodynamic lubrication is made of transparent photoelasticity materials, a friction area is irradiated by polarized light, the friction area is observed in an amplified mode through a microscope in the direction of a light source after a polarizing film is detected, photoelasticity strips appear in a friction pair in the contact area irradiated by the polarized light, oil film pressure in the contact area can be displayed and measured in real time after calculating and marking, and resolution ratio of the pressure is determined by the amplification ability of the microscope which is used and the resolution ratio of a camera. The measuring device of the elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact pressure based on the photoelasticity comprises a collimation light source, a polarizer, the friction contact area, an analyzer, a stereoscopic microscope and an imaging recording device in sequence in the light path direction. According to the measuring method and the measuring device of the elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact pressure based on the photoelasticity, distribution of pressure in the elastohydrodynamic lubrication line contact area can be measured with high resolution ratio and in real time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Optical glass having a small photoelastic constant
An optical glass having a small photoelastic constant (β) suitable for parts for polarizing optical system and light polarization control elements and having a refractive index (nd) within a range from 1.60 to 1.68 and an Abbe number (ν d) within a range from 40 to less than 65 comprises, as atoms constituting the optical glass, P5-10mol %Al1-3mol %Ba8-13mol %,Gd1-5mol %Nb0.1-3mol %F15-35mol % andO40-52mol %.
Owner:OHARA
Method and Apparatus For Examining A Semiconductor Wafer
InactiveUS20120007978A1Improve the effect of practiceIncreased riskSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansStress measurementEngineering
The edges of semiconductor wafers are examined by an imaging method and the positions and forms of defects on the edge are determined, and in addition, a ring-shaped region on the flat area of the semiconductor wafer, the outer margin of which is ≦10 mm from the edge, is examined by means of photoelastic stress measurement and the positions of stressed regions in the ring-shaped region are determined, wherein the positions of the defects and the positions of the stressed regions are compared with one another, and the defects are classified in classes on the basis of their form and the results of the photoelastic stress measurement.
Owner:SILTRONIC AG
Optical film
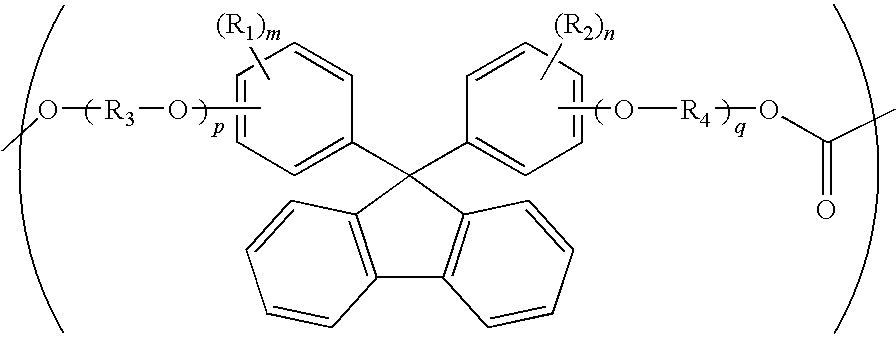
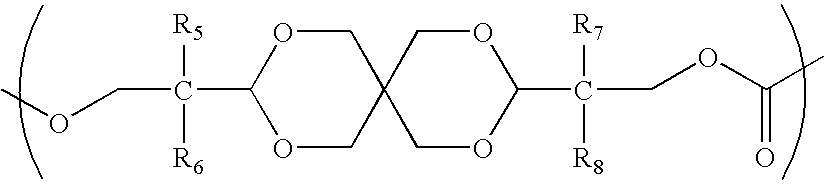
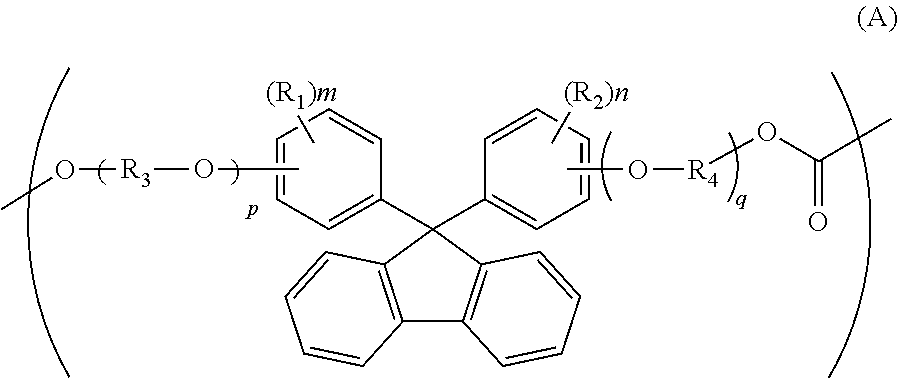
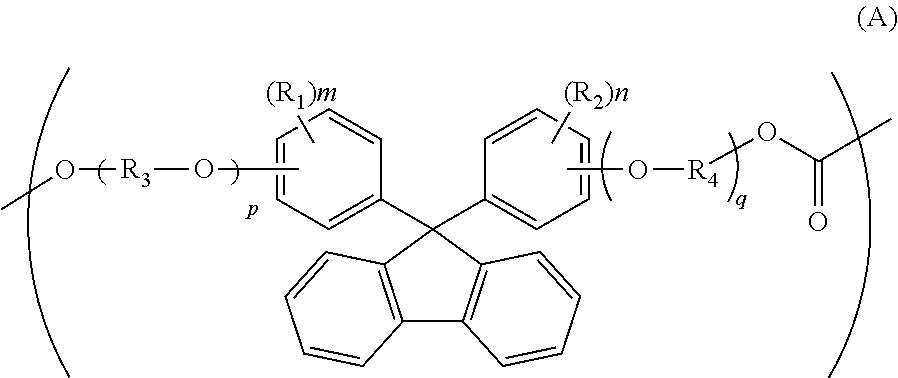
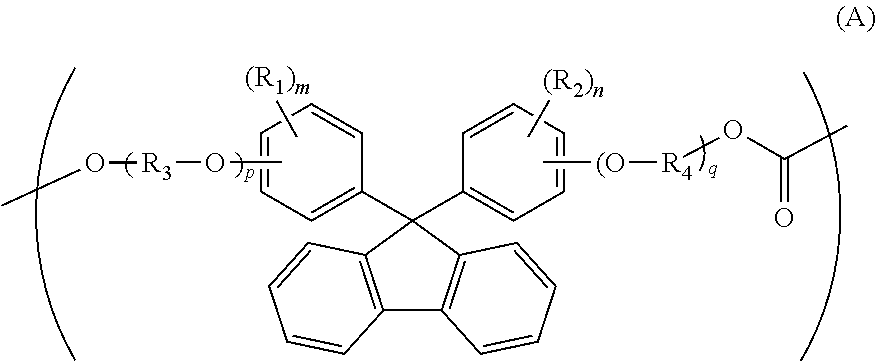
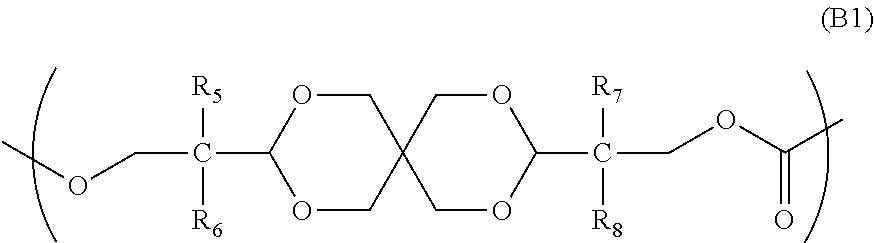
ActiveUS20100104777A1Low photoelastic constantSmall retardationLiquid crystal compositionsPolarising elementsPolycarbonateBisphenol-A-polycarbonate
It is an object of the present invention to provide an optical film which has reverse chromatic dispersibility that its retardation becomes smaller as the wavelength becomes shorter and a low photoelastic constant.The optical film is made of a polycarbonate copolymer containing a unit (A) represented by the following formula:wherein R1 and R2 are each independently a hydrogen atom, hydrocarbon group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms or the like, R3 and R4 are each independently a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms or the like, “m” and “n” are each independently an integer of 0 to 4, and “p” and “q” are each independently an integer of 0 or more,and a unit (B) represented by the following formula:wherein R5 to R8 are each independently a hydrogen atom or alkyl group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms,the (A / B) molar ratio of the unit (A) to the unit (B) is 10 / 90 to 90 / 10 and which satisfies the following expression (1):R(450)<R(550)<R(650) (1)wherein R(450), R(550) and R(650) are retardation values within the plane of the film at wavelengths of 450 nm, 550 nm and 650 nm, respectively.
Owner:TEIJIN CHEM LTD
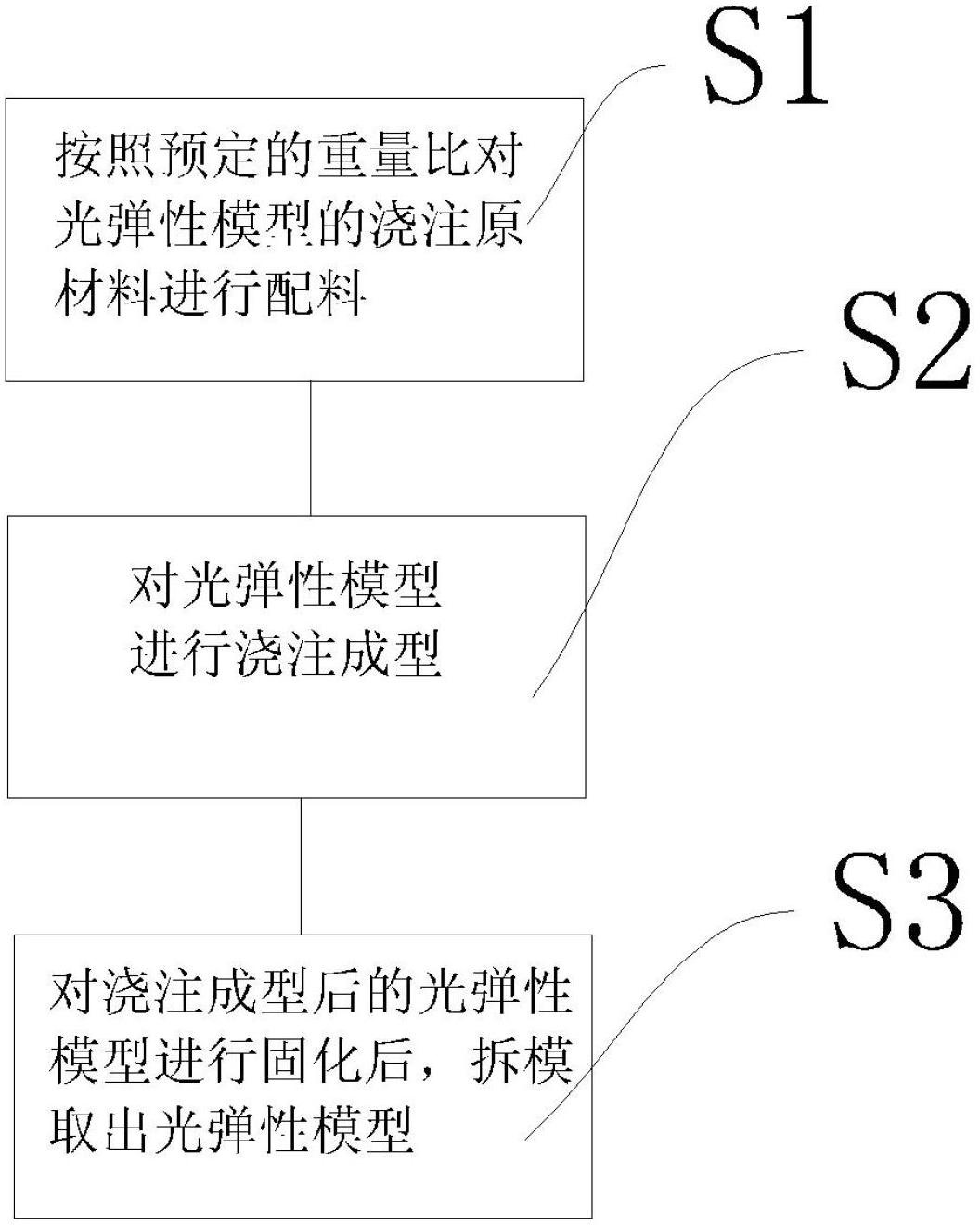
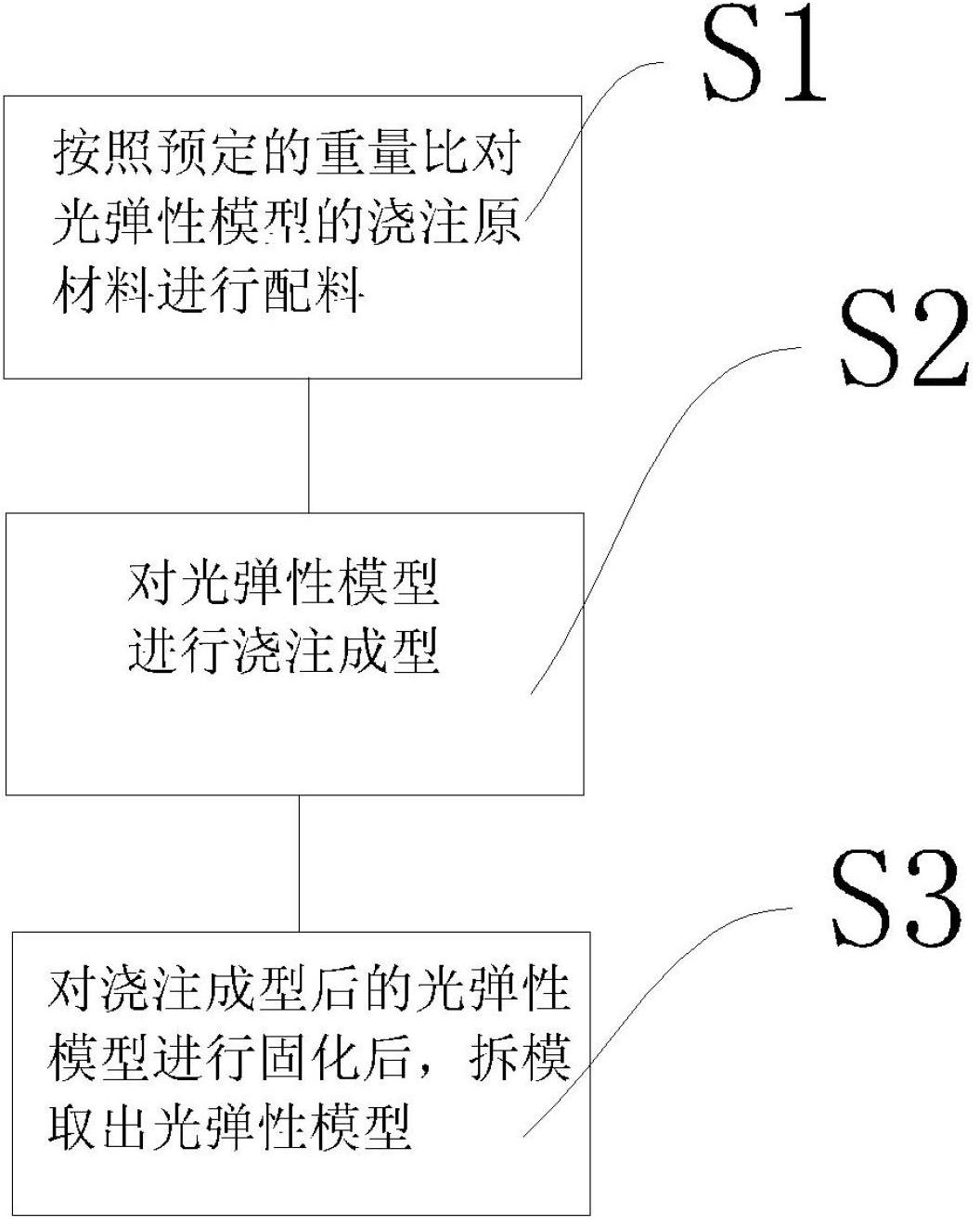
Vacuum casting process method of photoelastic model
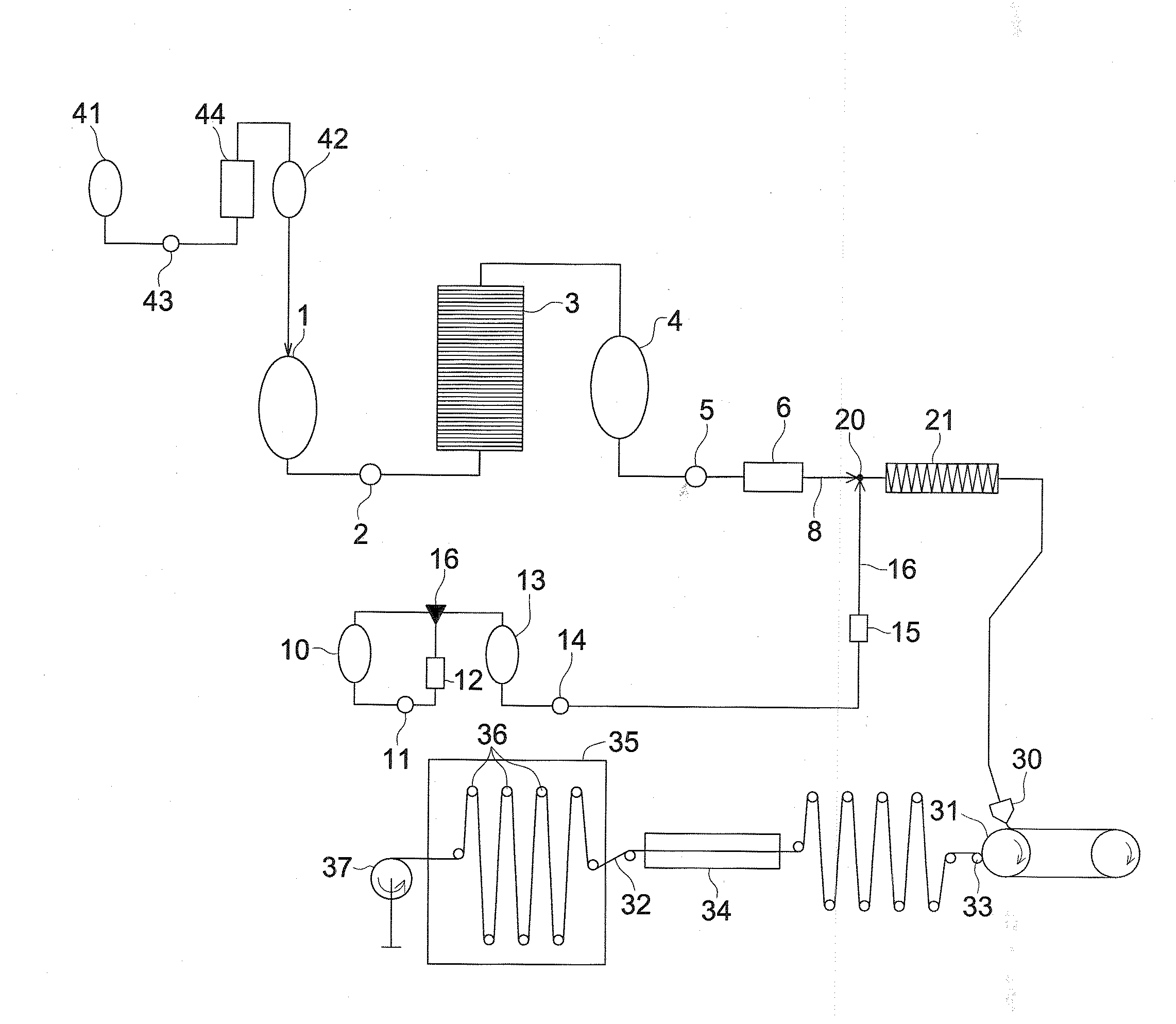
The invention relates to a vacuum casting process method of a photoelastic model. A vacuum casting forming machine and a silicon rubber female mold arranged in the vacuum casting forming machine are used for casting forming, the automation degree is high, the errors are few, and in addition, the harm to human bodies by harmful gas released in the casting process because of artificial participation is avoided. The process comprises the following steps that: step 1, epoxy resin 128 and succnic acid are respectively weighed according to the weight proportion being 100:30-35 in accordance with the photoelastic model to be cast, in addition, the epoxy resin 128 and the succnic acid are uniformly mixed under the vacuum condition of a vacuum stirring temperature control room, the purity of raw materials is improved, and the nonuniformity of materials is avoided; step 2, after a forming chamber of the model is subjected to vacuum pumping, the poxy resin 128 and the succnic acid uniformly mixed in the step 1 are filled into the silicon rubber female mold, and the casting forming is carried out; and step 3, the photoelastic model after the cast forming is solidified.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION POWER MACHINE INST
Optical film
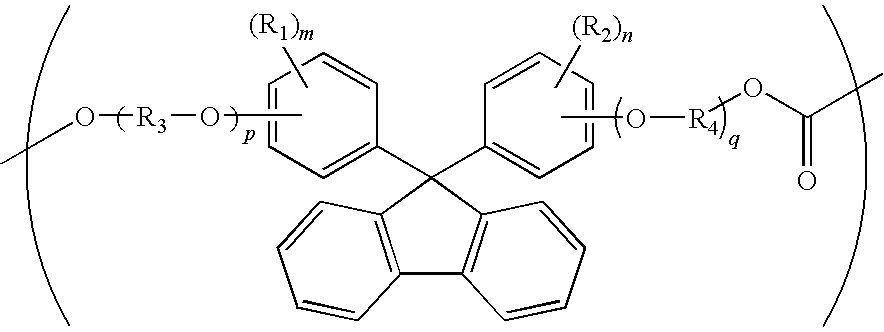
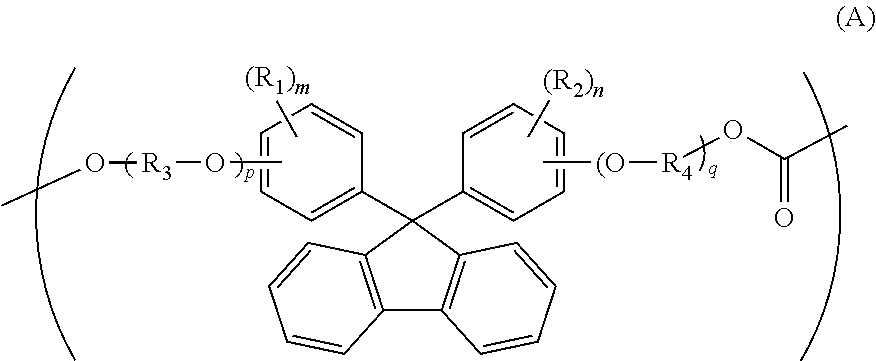
ActiveUS20110288261A1Low photoelasticityImproved melt processabilityPolarising elementsCeramic shaping apparatusIn planeHalogen
The object of this invention is to provide an optical film formed of a copolycarbonate having a desired chromatic dispersion and low photoelasticity and having excellent melt processability.The optical film comprises a copolycarbonate composed of 25 to 90 mol % of unit (A) of the following formula,wherein each of R1 and R2 is independently a hydrogen atom, a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms or a halogen atom, each of R3 and R4 is independently a hydrocarbon group having 1 to 10 carbon atoms, each of m and n is independently an integer of 0 to 4, and each of p and q is independently an integer of 0 or more,and 10 to 75 mol % of unit (B) of the following formula,wherein Ra is a monocyclic or polycyclic alicyclic hydrocarbon group having 4 to 20 carbon atoms, the alicyclic hydrocarbon group may contain a hetero atom or may have a bridge structure, and q is 0 or 1,the optical film satisfying the following expression (1),R(450)<R(550)<R(650) (1)wherein R(450), R(550) and R(650) are in-plane retardation values of the film at wavelengths of 450 nm, 550 nm and 650 nm.
Owner:TEIJIN CHEM LTD
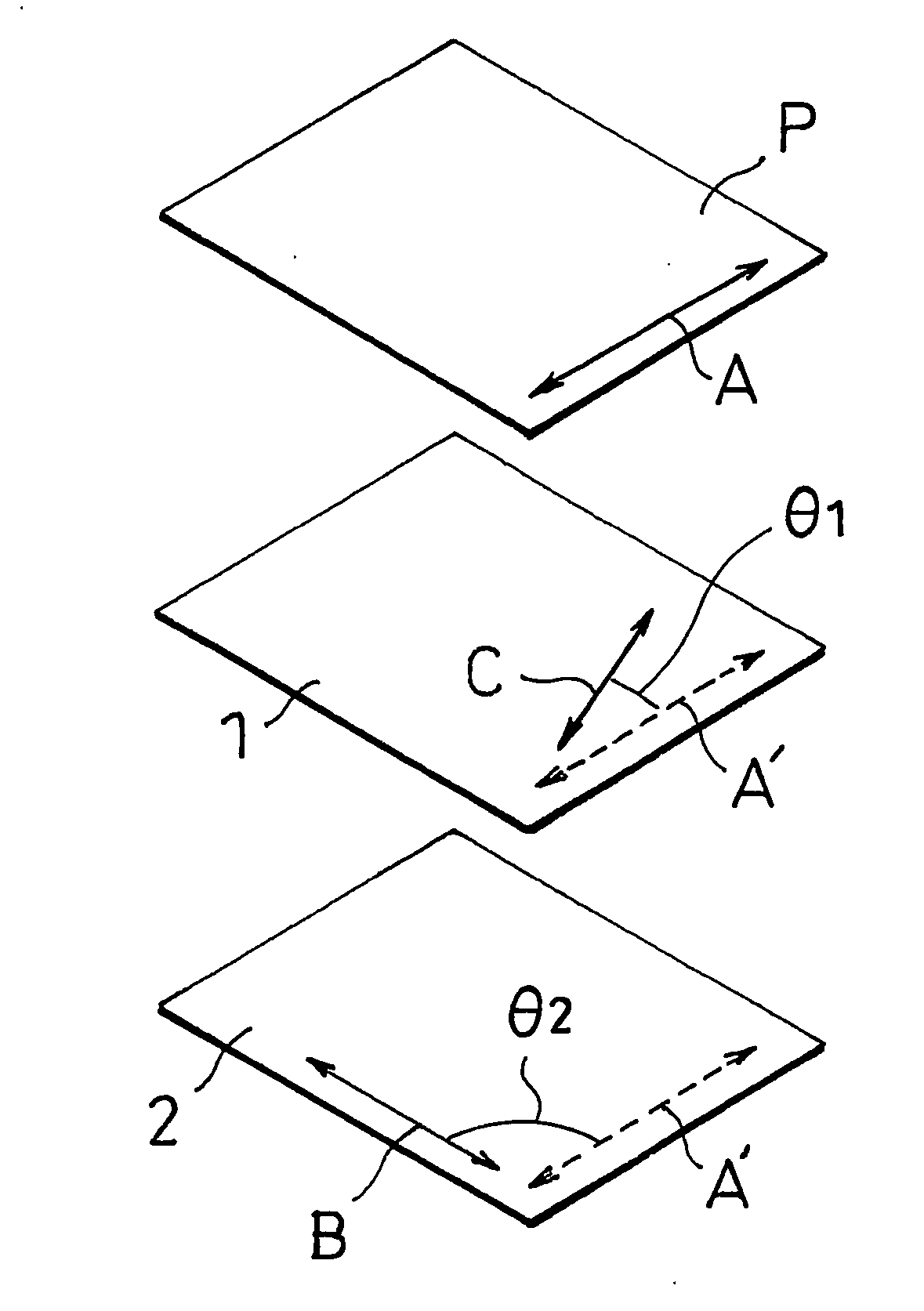
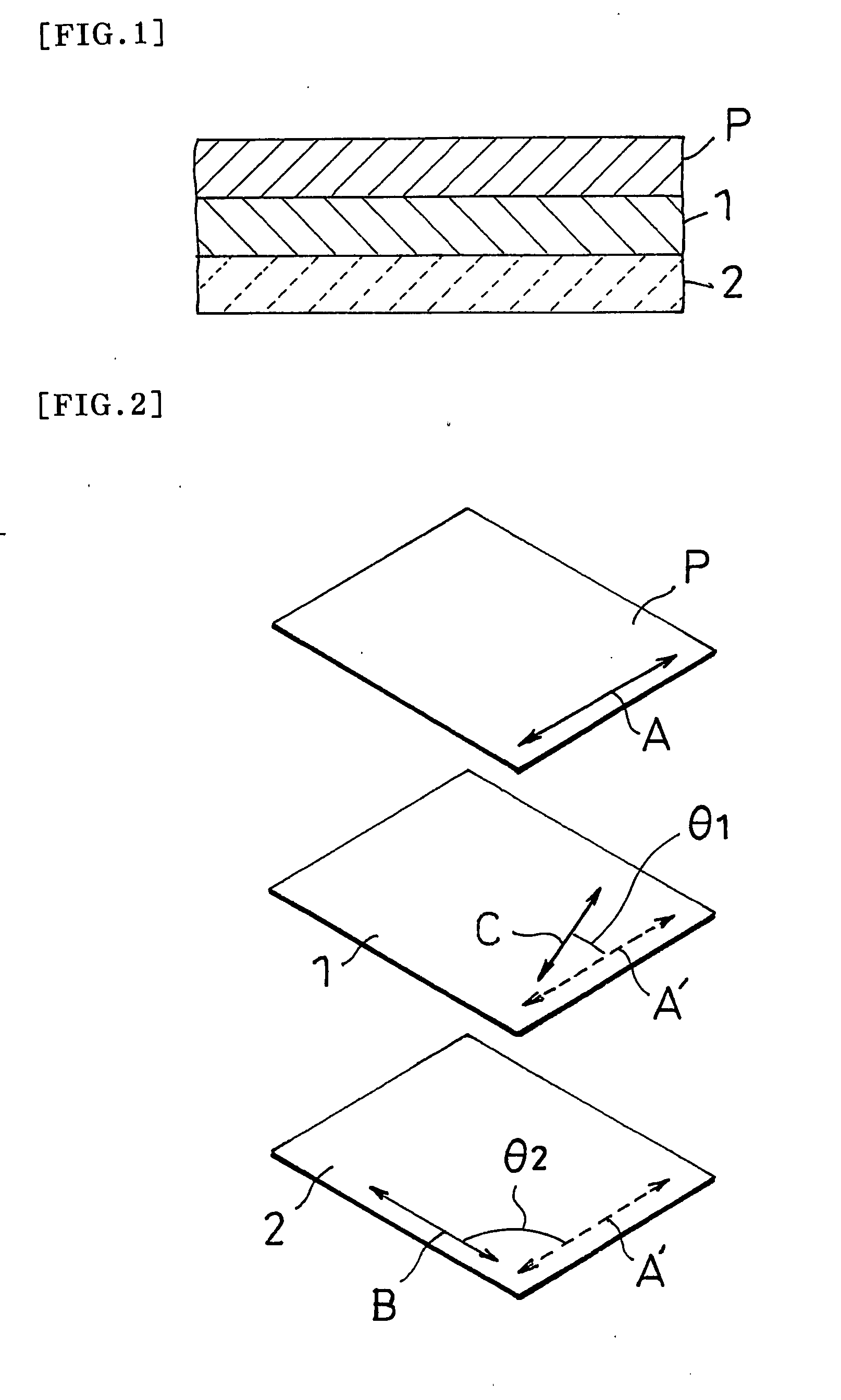
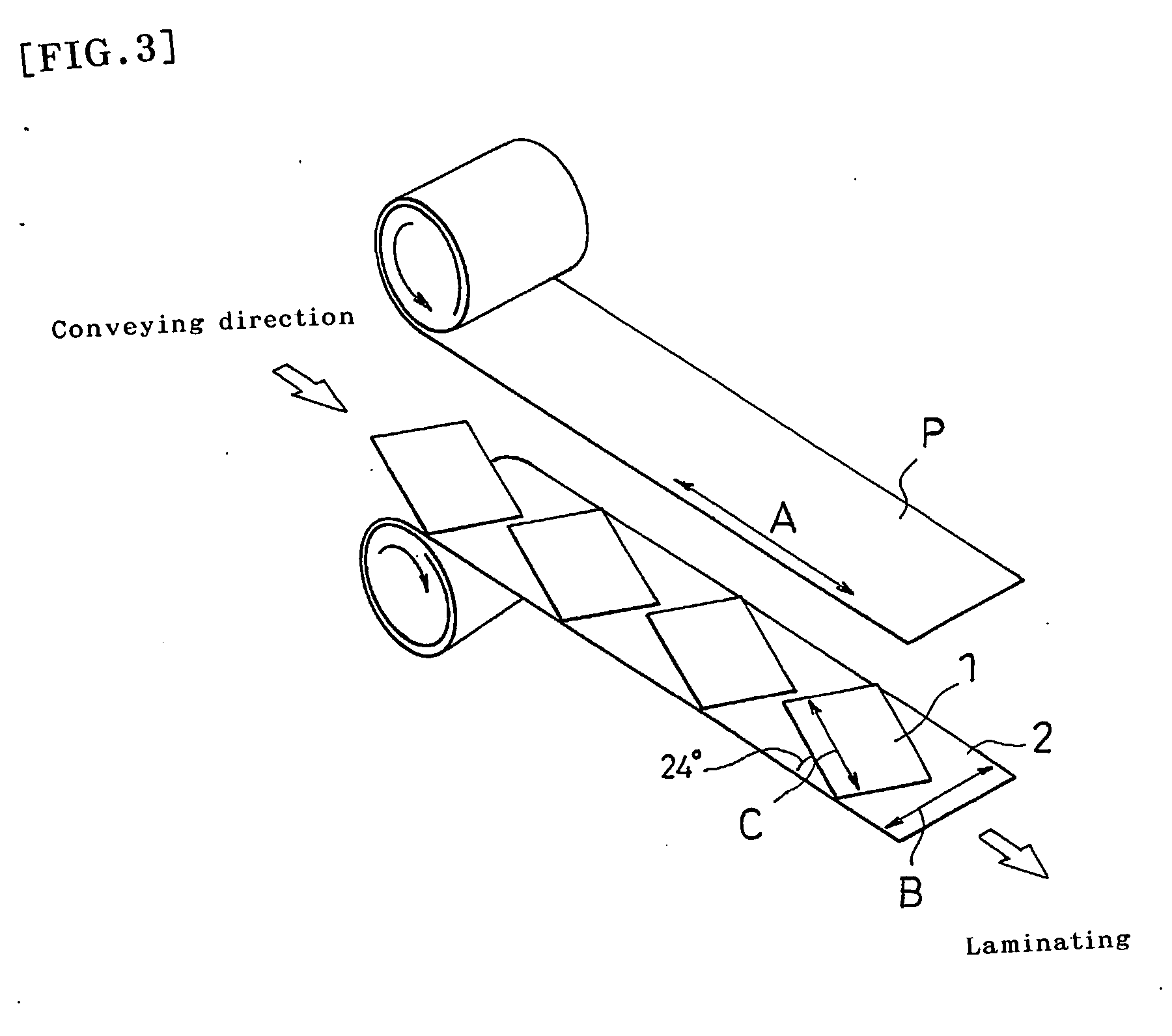
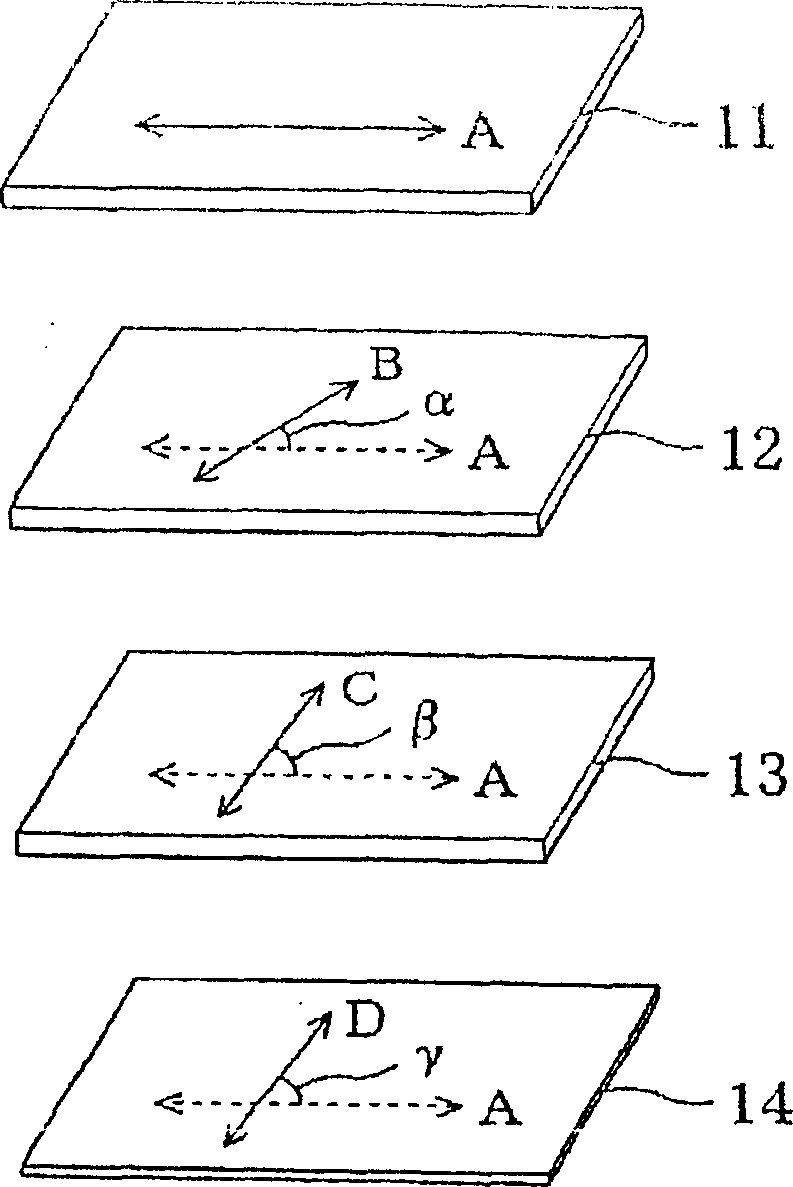
Polarizing plate with optical compensating layer, and image display using the same
ActiveCN1906509AReduce thicknessImprove light leakagePolarising elementsNon-linear opticsIn planePhase difference
A polarizing plate with an optical compensation layer capable of appropriately preventing leakage of light in black display while preventing thermal unevenness and contributing to reduction in thickness, and an image display employing it. The polarizing plate with an optical compensation layer comprises a polarizer, a first optical compensation layer, a second optical compensation layer, and a third optical compensation layer arranged in this order. The first, second and third optical compensation layers respectively have a predetermined absolute value of photoelastic coefficient, refractive index distribution, in-plane phase difference and / or phase difference in the thickness direction, respectively. The angle between the absorption axis of the polarizer and the lag axis of the first optical compensation layer is 10-30 DEG, the angle between the absorption axis of the polarizer and the lag axis of the second optical compensation layer is 70-95 DEG, and the angle between the absorption axis of the polarizer and the lag axis of the third optical compensation layer is 70-95 DEG.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
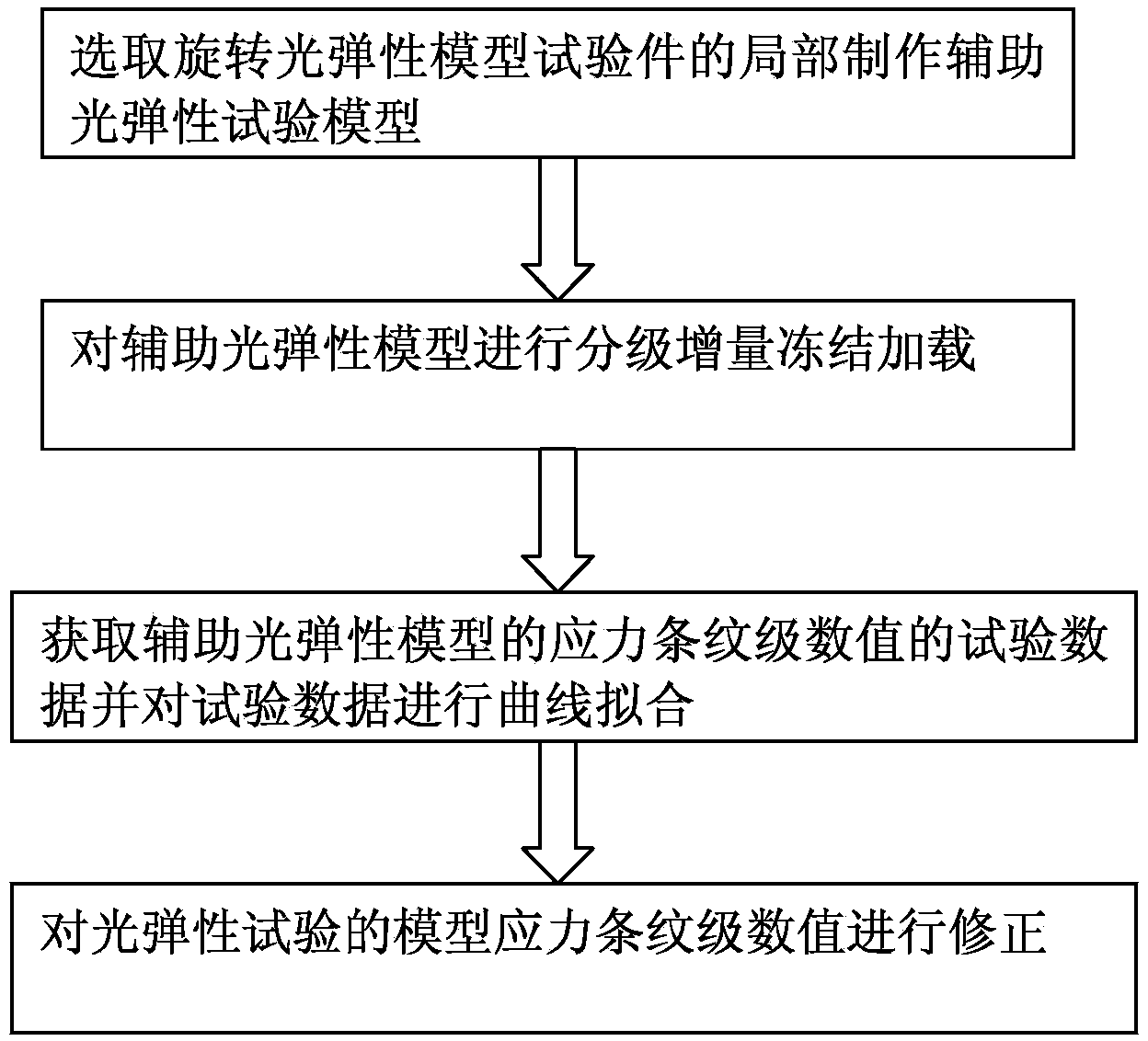
Method for processing stress-fringe-order numerical values of photoelastic model
ActiveCN103968979AHigh precisionReduce processing costsForce measurement by measuring optical property variationPhotoelasticityStress level
The invention discloses a method for processing stress-fringe-order numerical values of a photoelastic model. The method comprises the following steps that (1) part of a rotating photoelastic model test piece is selected, and a manufacturing method same as the method for manufacturing the photoelastic model is used for manufacturing an auxiliary photoelastic model; (2) rotating centrifugal force acting on the auxiliary photoelastic model is converted into tension, and the auxiliary photoelastic model is subjected to classified increment freezing loading; (3) test data of stress-fringe-order numerical values of the auxiliary photoelastic model subjected to classified increment freezing loading are acquired, and are subjected to curve fitting; (4) the stress-fringe-order numerical values of the photoelastic model are corrected by using fitting data variables. The stress-fringe-order numerical values of the photoelastic model obtained through the method are more close to the real stress level.
Owner:CHINA AVIATION POWER MACHINE INST
Stress and strain analysis method and its equipment
InactiveUS7509872B2Detailed stress measurementForce measurement by measuring optical property variationMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesStress measurementIt equipment
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
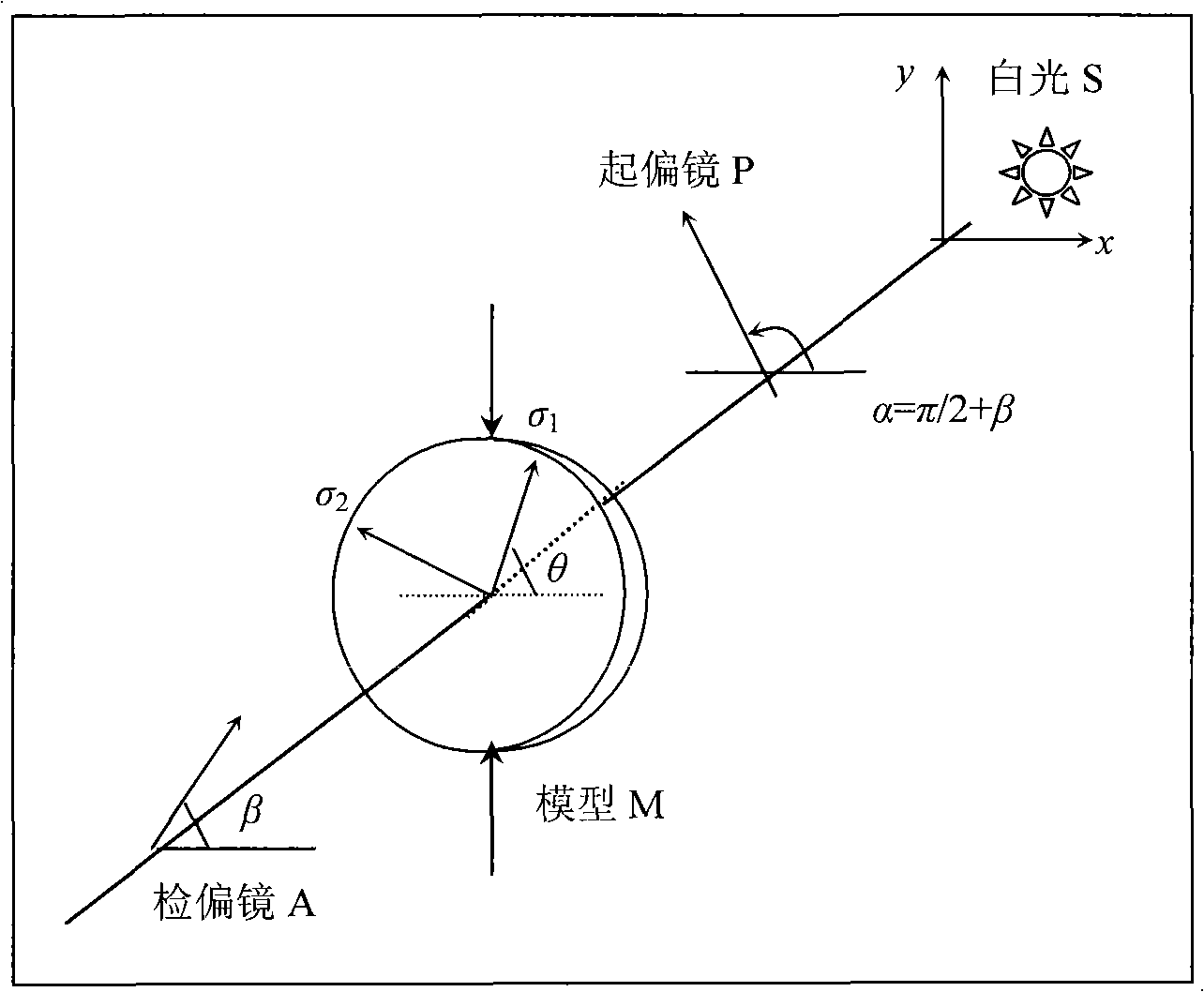
Digital photoelasticity full field shear stress automatic determination method
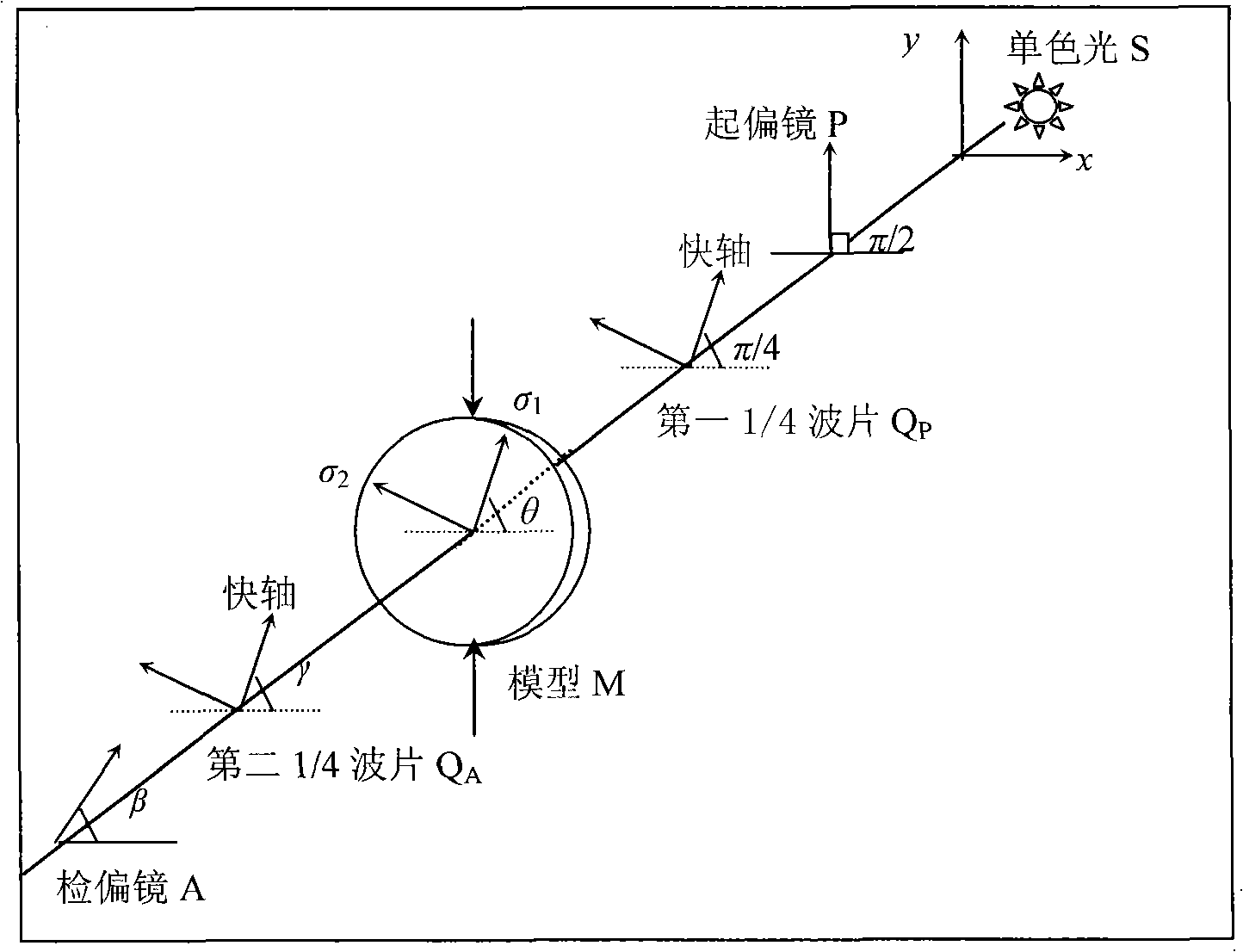
InactiveCN101266215AImprove work efficiencyAvoid tedious laborMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing mechanical meansElastomerPrincipal stress
The invention provides a full-court shearing stress automatic determining method in digital photoelasticity, belonging to a photoelectricity non-destructive test field, comprising: laying the detected photoelasticity body in a photoelastical gauge to apply load, and adjusting the optical field being orthogonal plane polarization field under the white light incidence and respectively collecting four phase shift images when an analyser and a polarizer synchronistically rotate to 0, Pi / 8, Pi / 4 and 3Pi / 8; obtaining the phase diagram of first major principal stress (-Pi / 2,Pi / 2) using four step color phase-shift method; adjusting the optical field being orthogonal circular polarization field user homogeneous light incidence and collecting six phase shift images when the analyser and the second 1 / 4 wave plate respectively rotate to (Pi / 4,0), (3Pi / 4,0), (0,0), (Pi / 4,Pi / 4), (Pi / 2,Pi / 2) and (3Pi / 4,3Pi / 4); combining the phase diagram of first major principal stress and using the improved six phase shift method to obtain isochromatic line packing phase diagram without 'distortion' and performing packing and calculating the full-court shearing stress. The full-court shearing stress can be automatically calculated and the work efficiency is increased and the complicated work of manually data collecting and processing is prevented.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
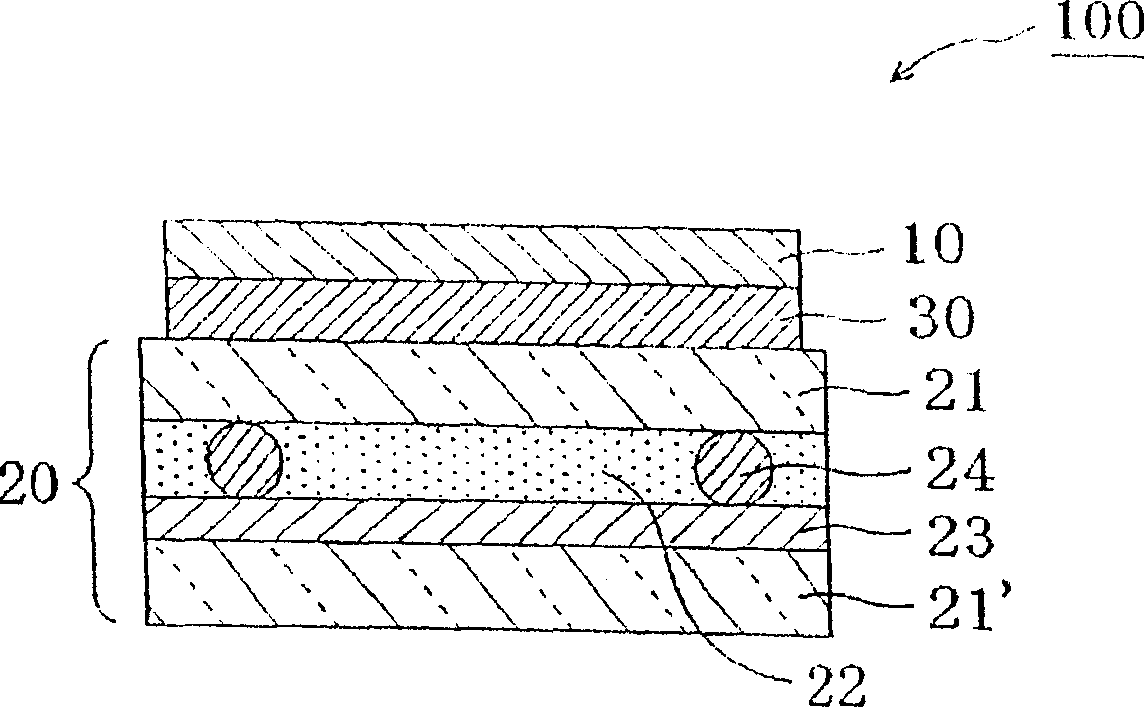
Laminated optical film, elliptically polarizing plate, and image viewing display
The invention provides an optical film which is capable of suppressing the coloring of display image even when the display image is viewed obliquely with respect to the normal direction of a screen and is capable of displaying an image having minimized gradation reversed region, and is excellent in durability. The multilayer optical film is constituted by laminating: an optical film (1) which is obtained by stretching a polymer film comprising polycarbonate base resin and styrene type resin, has an absolute value of photoelasticity coefficient of 2.0x10<-11> to 6.0x10<-11> m<2> / N and has controlled three-dimensional refractive index so as to obtain the Nz coefficient satisfying Nz <= 0.9 and the front retardation satisfying Re >= 80 nm; an optical film (2) showing an optically positive uniaxial property; and an optical film (3) made of a material showing an optically negative uniaxial property, comprising a part in which the material is obliquely aligned, and having a thickness of 30 to 90 mum.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Photoelastic layer with integrated polarizer
In accordance with the present invention, a photoelastic layer for detecting stress and strain is described. The photoelastic layer comprises a photoelastic material that when strained refracts light anisotropically. The photoelastic layer further comprises an integrated polarizer attached on top of the photoelastic material. Also in accordance with the present invention, a photoelastic monitoring device is described for structural monitoring. The photoelastic monitoring device is made out of a photoelastic material or comprises a photoelastic material attached to a base material. The photoelastic monitoring device further comprises an integrated polarizer attached or coated directly over at least a portion of the photoelastic material. The photoelastic monitoring device is designed to be attached to a structure or a part. The monitoring device is attached to the structure in such a way that stresses and strains from the structure are transmitted into the photoelastic monitoring device. When a certain predetermined stress or strain is reached, the monitoring device may deform plastically. The plastic deformation can then be detected in the photoelastic material using the integrated polarizer. Also in accordance with the present invention, a method is described for photoelastic analysis. The method comprises providing a photoelastic material to be analyzed for stresses and strains. An integrated polarizer is attached directly on top of at least a portion of the photoelastic material. The integrated polarizer is attached in such a way such that the photoelastic material can be illuminated with regular light through the integrated polarizer, and such that light can be reflected back through the photoelastic material and back through the integrated polarizer to the observer or the detector. The method comprises illuminating the polarizer with light, and viewing the reflections of light that have traveled through the integrated polarizer, through the photoelastic material, and been reflected back through the photoelastic material and back through the integrated polarizer. Observing or detecting fringe patterns in the reflected light indicate the presence of strain or plastic deformation in the photoelastic material.
Owner:SIMPSON STRONG TIE
Laminated optical film, elliptically polarizing plate, and image viewing display
InactiveCN1573373ASynthetic resin layered productsPolarising elementsPhotoelasticityRefractive index
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Acryl resin containing film, polarizing plate by use thereof and liquid crystal display
ActiveUS20100291376A1Increase productionReduce colorLiquid crystal compositionsLiquid surface applicatorsColor shiftLiquid-crystal display
An acryl resin-containing film which is transparent and highly heat-resistant and has been significantly improved in brittleness is disclosed, satisfying the following equations (1) to (4), exhibiting a tension softening point of 105 to 145° C. and a photoelastic coefficient of −5.0×10−8 to 8.0×10−8 cm2 / N, while causing no ductile fracture. There is also disclosed a liquid crystal display which has achieved an improved yield in works of stamping a polarizing plate or sticking the plate to a panel and reduced color shift occurred depending on viewing angle.|Ro(589)|≦10 nm (1)|Rth(589)|≦20 nm (2)|Ro(480)−Ro(630)|≦5 nm (3)|Rth(480)−Rth(630)|≦10 nm (4)Numerical values of 589, 480 and 630 in parentheses represent the wavelength (nm) of a light used to measure an individual birefringence.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA OPTO
Optical film
InactiveUS20120120356A1Desired wavelength dispersion characteristicLow photoelastic constantPolarising elementsNon-linear opticsPhotoelasticityThin membrane
An optical film having a desired wavelength dispersion characteristic, a low photoelastic coefficient and a desired Nz coefficient.The optical film is formed from a copolymer and meets the following conditions (i) to (v):(i) the thickness (d) is 20 to 80 μm;(ii) the following formulas (1) and (2) are satisfied:0.6<R(450) / R(550)<1 (1)1.01<R(650) / R(550)<1.40 (2)(R(450), R(550) and R(650) are retardations within the plane of the film at respective wavelengths);(iii) R(550) is 120 to 160 nm;(iv) the birefringence (Δn) is not less than 1.5×10−3; and(v) the Nz coefficient represented by the following formula (4) is 1.18 to 2.40:Nz=(nx−nz) / (nx−ny) (4)(nx, ny and nz are 3-dimensional birefringences of the film).
Owner:TEIJIN KASEK KK
Thermoplastic Resin Composition and Optical Films Made Therefrom
InactiveUS20080095955A1Increase dependenceLow water absorptionLiquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingPolymer scienceCycloalkene
The thermoplastic resin composition of the present invention comprises (A) a cycloolefin-based polymer and (B) a vinyl-based polymer having a polar group, has a glass transition temperature of not lower than 100° C. and has a difference in glass transition temperature between the polymers (A) and (B) of less than 50° C. The optical film of the present invention comprises the thermoplastic resin composition of the invention. According to the present invention, it is possible to improve development of retardation at a low stress in the film stretching while retaining excellent heat resistance and optical properties and maintaining wavelength dispersion properties. The optical film of the invention exhibits properties that the dependence of retardation of a transmitted light on wavelength, said retardation being obtained by stretch orientation of the film, becomes larger as the wavelength becomes longer (positive wavelength dispersion properties), has low water absorption and low coefficient of photoelasticity, and is excellent in adhesion or bonding properties to other materials.
Owner:JSR CORPORATIOON
Resin composition and film thereof
ActiveUS20160053104A1High mechanical strengthSmall birefringenceOptical elementsForeign matterPolymer science
An object of the present invention is to provide a resin material capable of producing a molded body having few defects due to foreign substances, having high mechanical strength, very small in both orientation birefringence and photoelastic birefringence, and having high transparency, and having high transparency even when such a resin material is stretched. Provided is a resin composition containing a resin (A) and a multilayer structure polymer (B), wherein the multilayer structure polymer (B) has a crosslinked polymer layer and a hard polymer layer, and the hard polymer layer has at least two different hard polymer layers, at least one of which is a hard polymer layer (C) opposite in sign of a photoelastic constant to that of the resin (A).
Owner:KANEKA CORP
Computer-to-plate flexible plate and production method thereof
ActiveCN104723717AGood adhesionPlate printingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusNetwork reductionEngineering
The invention discloses a computer-to-plate flexible plate and a production method thereof. The flexible plate comprises a supporting body, a photosensitive elastomer layer, an anti-adhering layer and a protection film, a plate material is directly scanned through a computer and then cleaned with water or a solution prior to being dried in hot wind to be made into a printing plate of the flexible plate, scanning of the computer is performed before stripping of the protecting film or after stripping of the protecting film, the photosensitive elastomer layer is highly sensitive to purple light and ultra violet and can be sufficiently cross-linked and solidified; the protecting film is a transparent thin film. Dynamic integration of rapid laser plate production and fine network reduction is realized, and adhesive strength of the photosensitive elastomer layer of the flexible plate is good.
Owner:LUCKY HUAGUANG GRAPHICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com