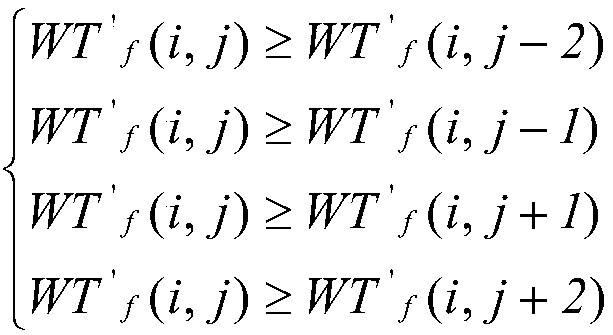Patents
Literature
36 results about "Peak finding" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
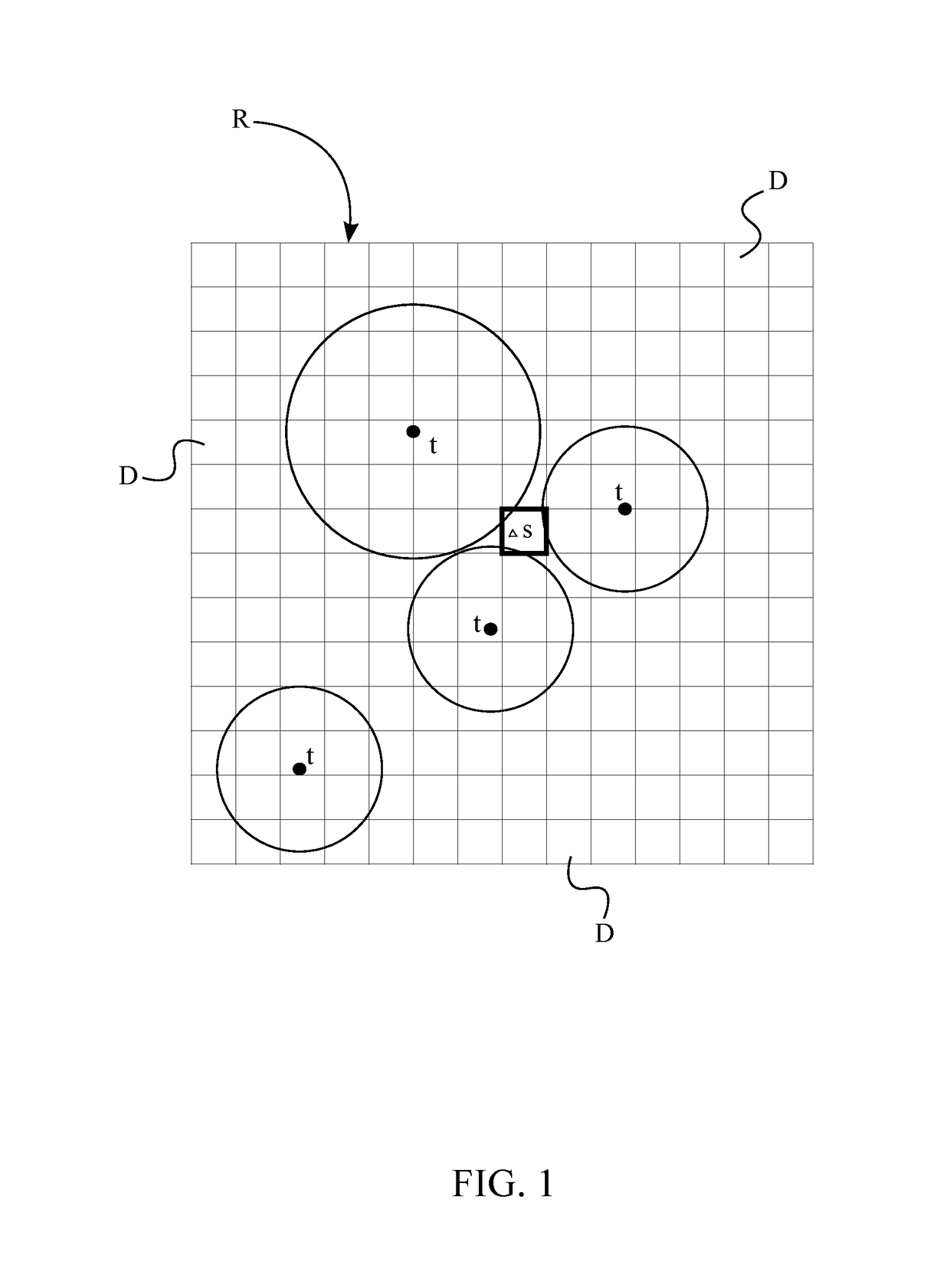
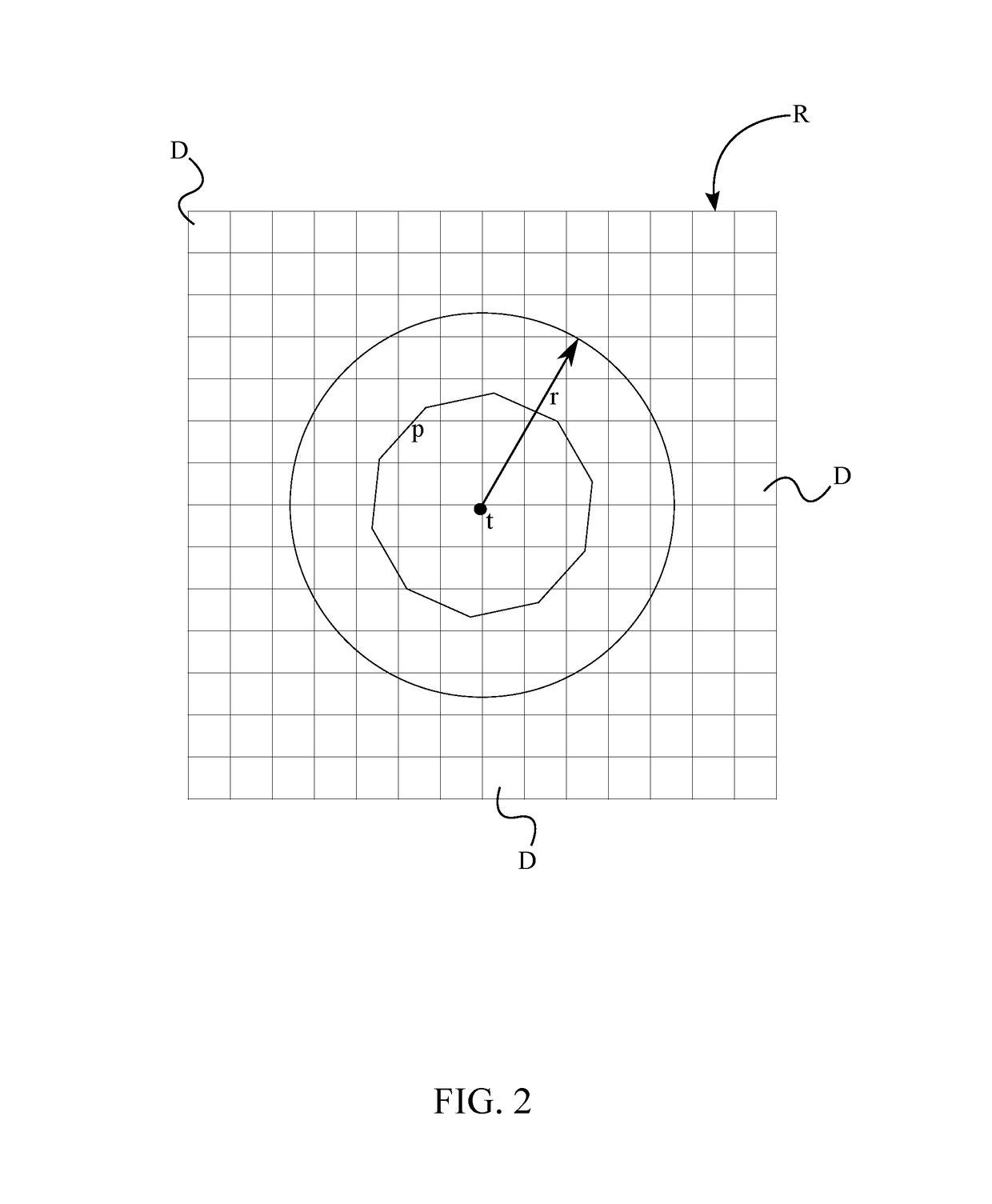
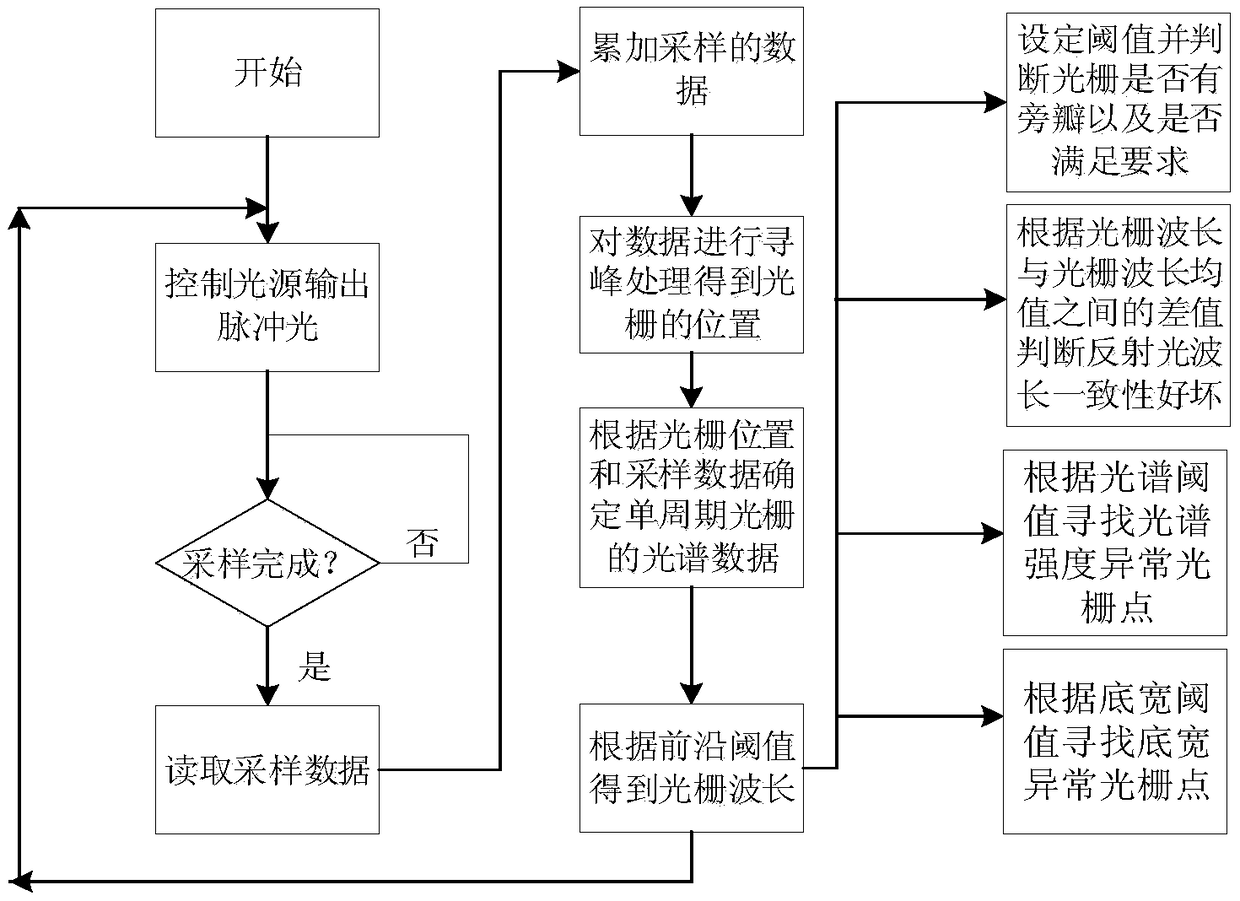
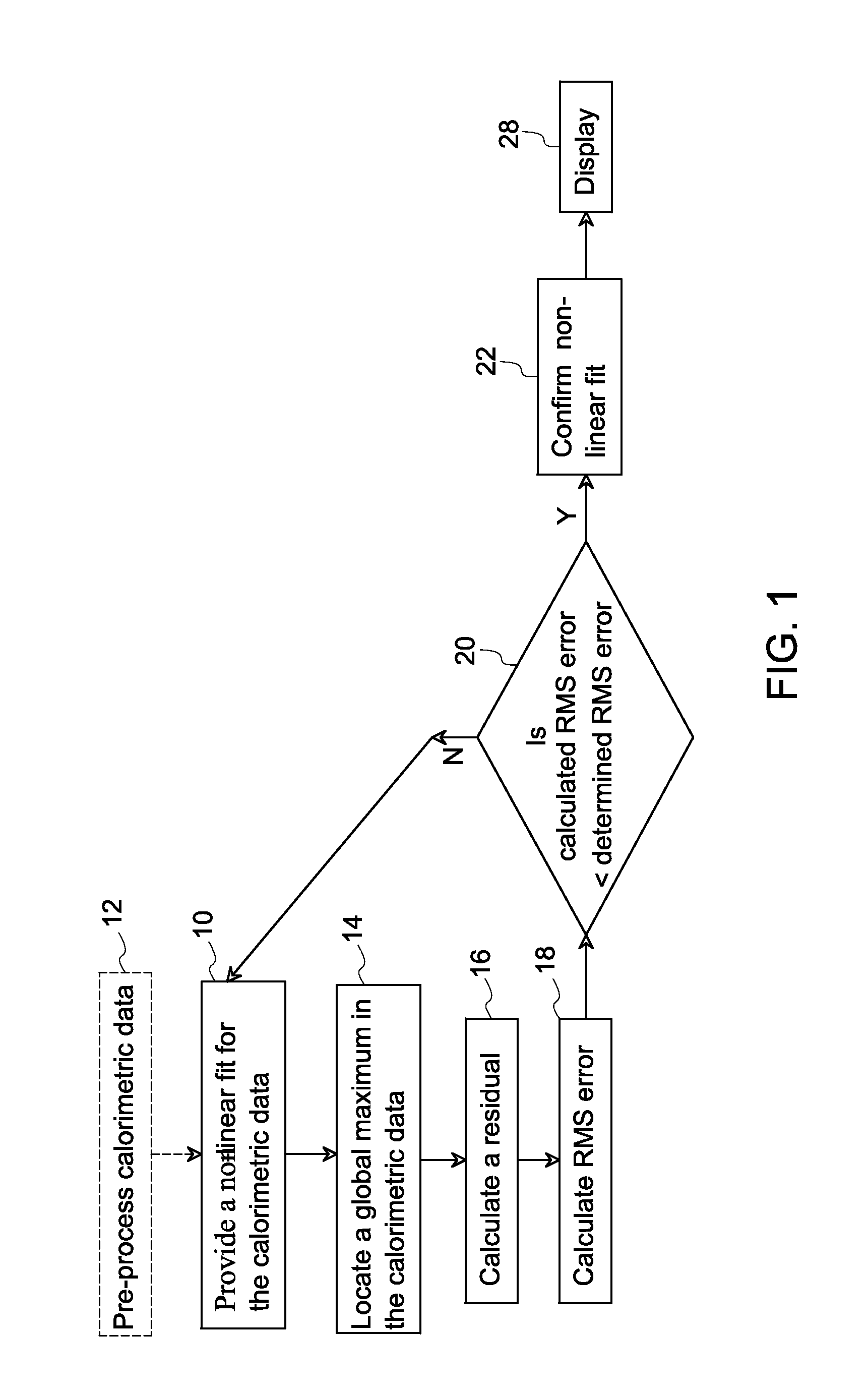
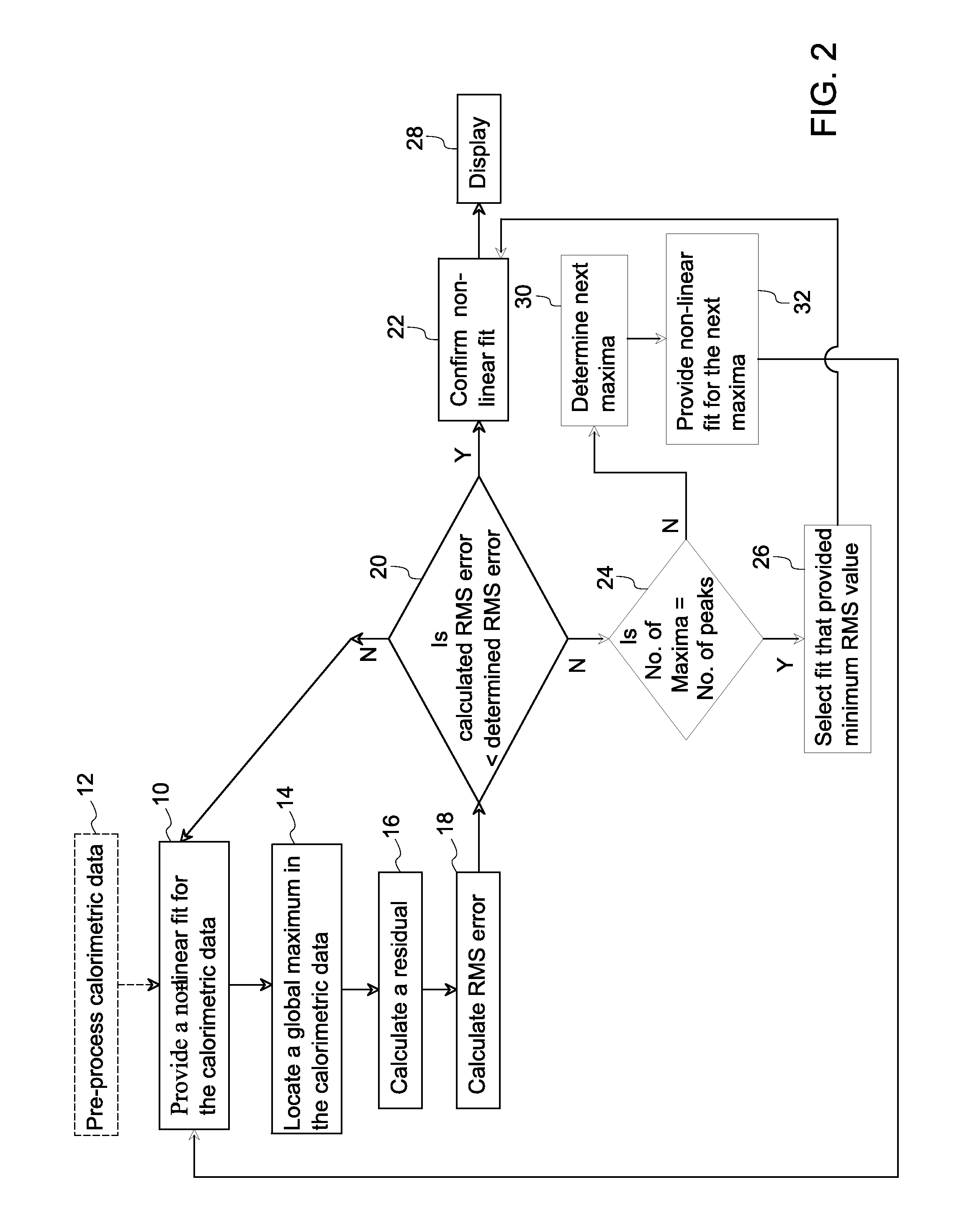
Peak finding in the Find Peaks page include automatic peak finding by the Peak Analyzer and manual peak editing. For automatic peak finding, you can select a method, configure the settings in the Find Peaks Settings branch and then click the Find button. Available methods for auto peak finding include: Local Maximum. Window Search.
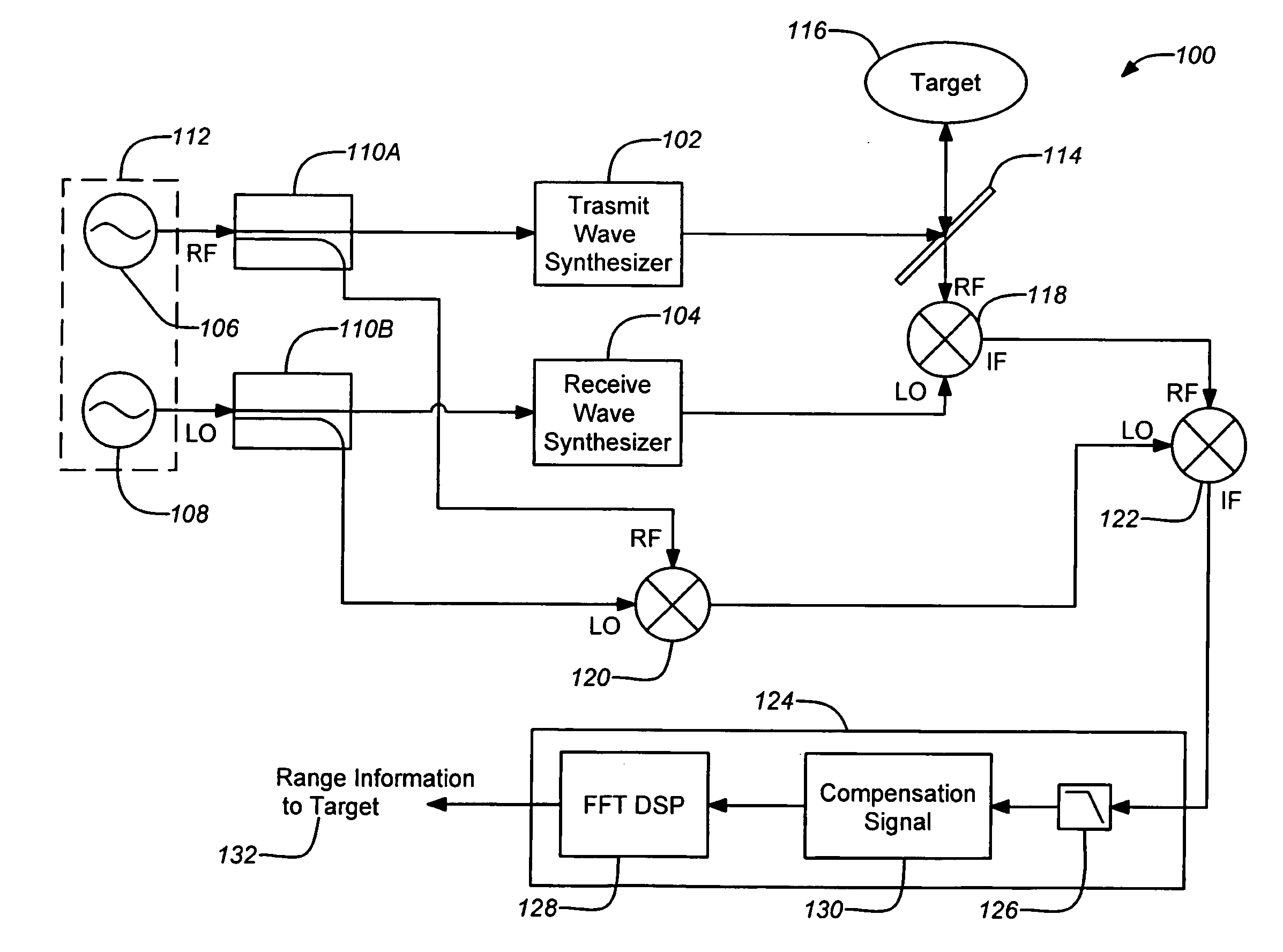
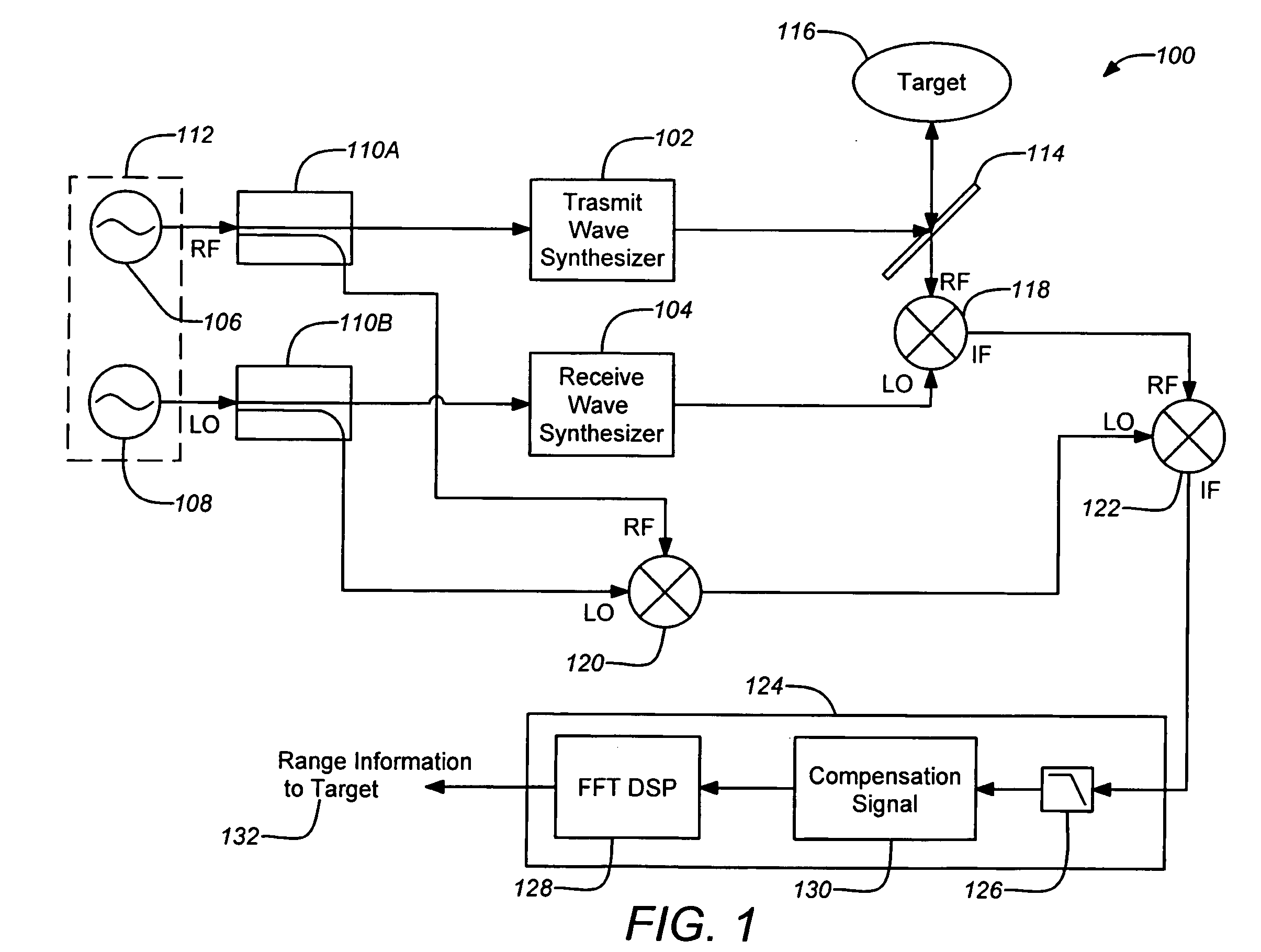
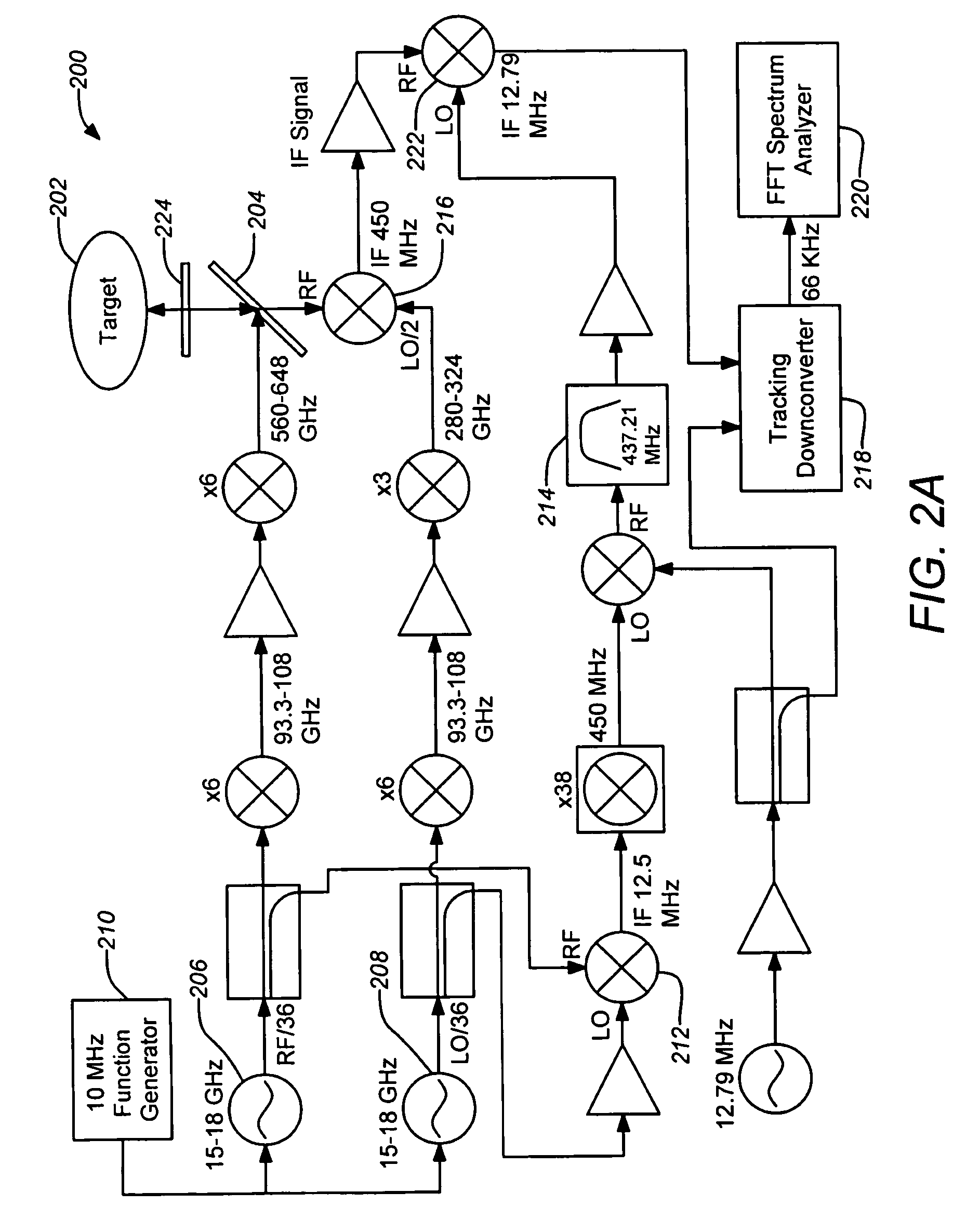
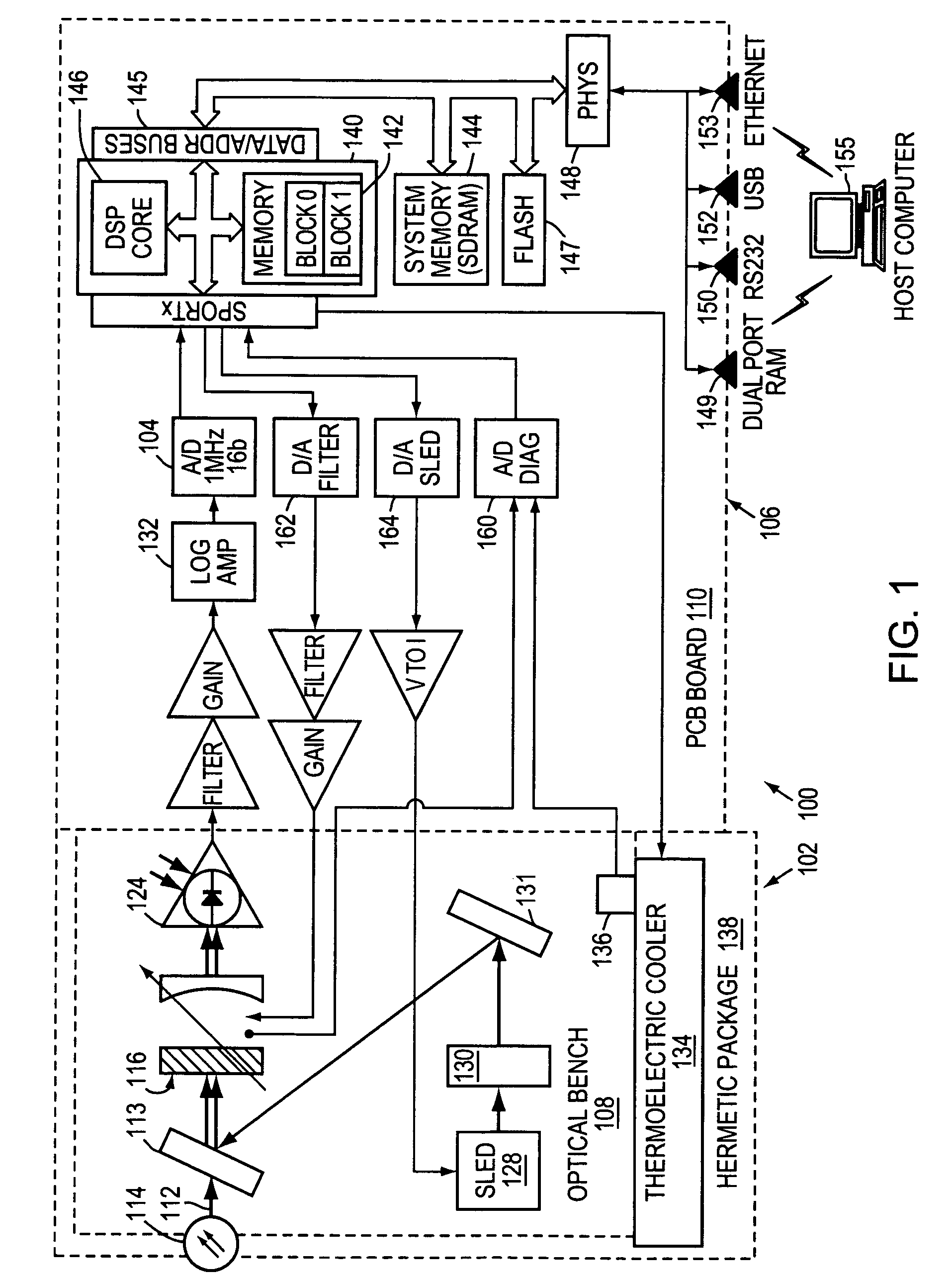
High-resolution three-dimensional imaging radar
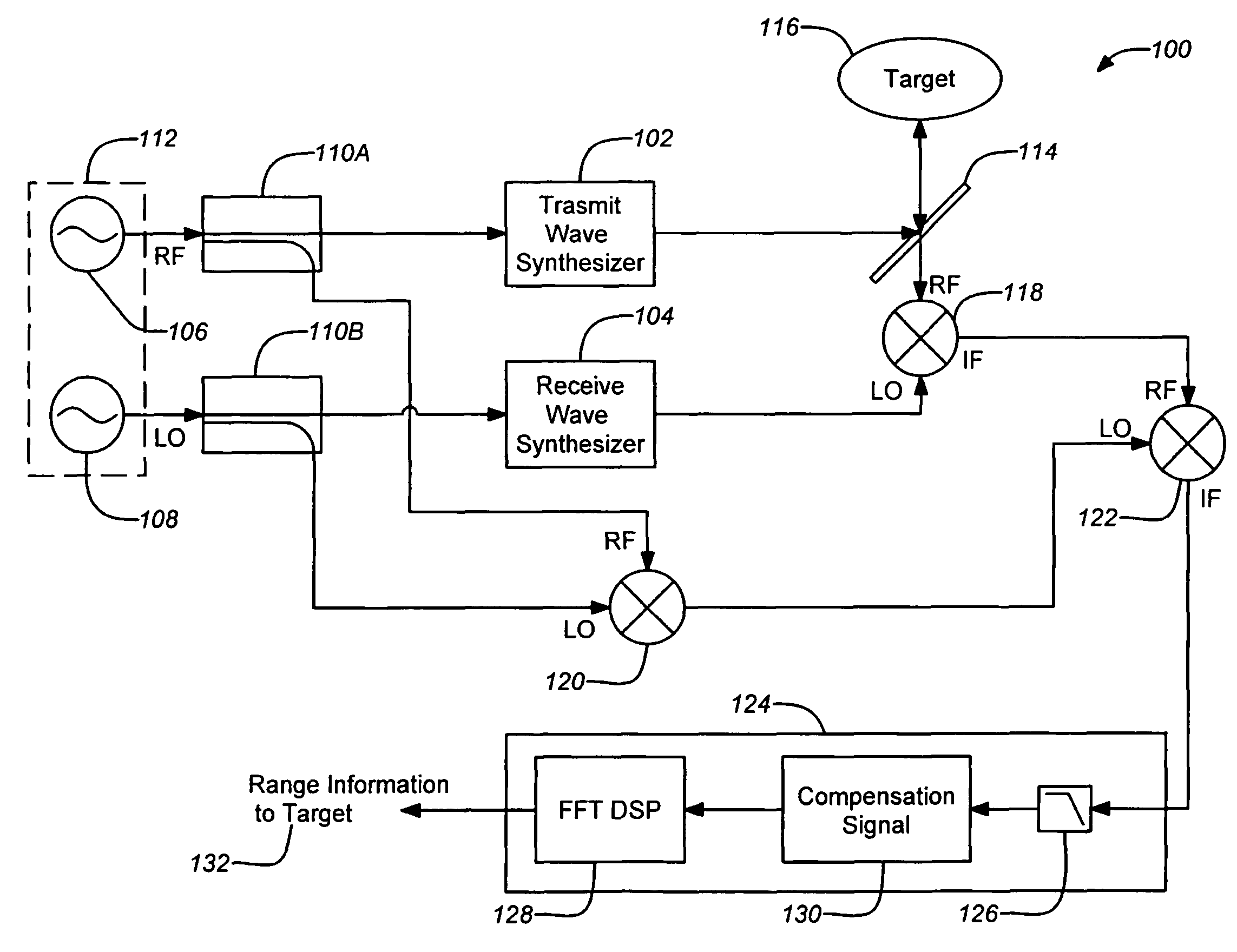
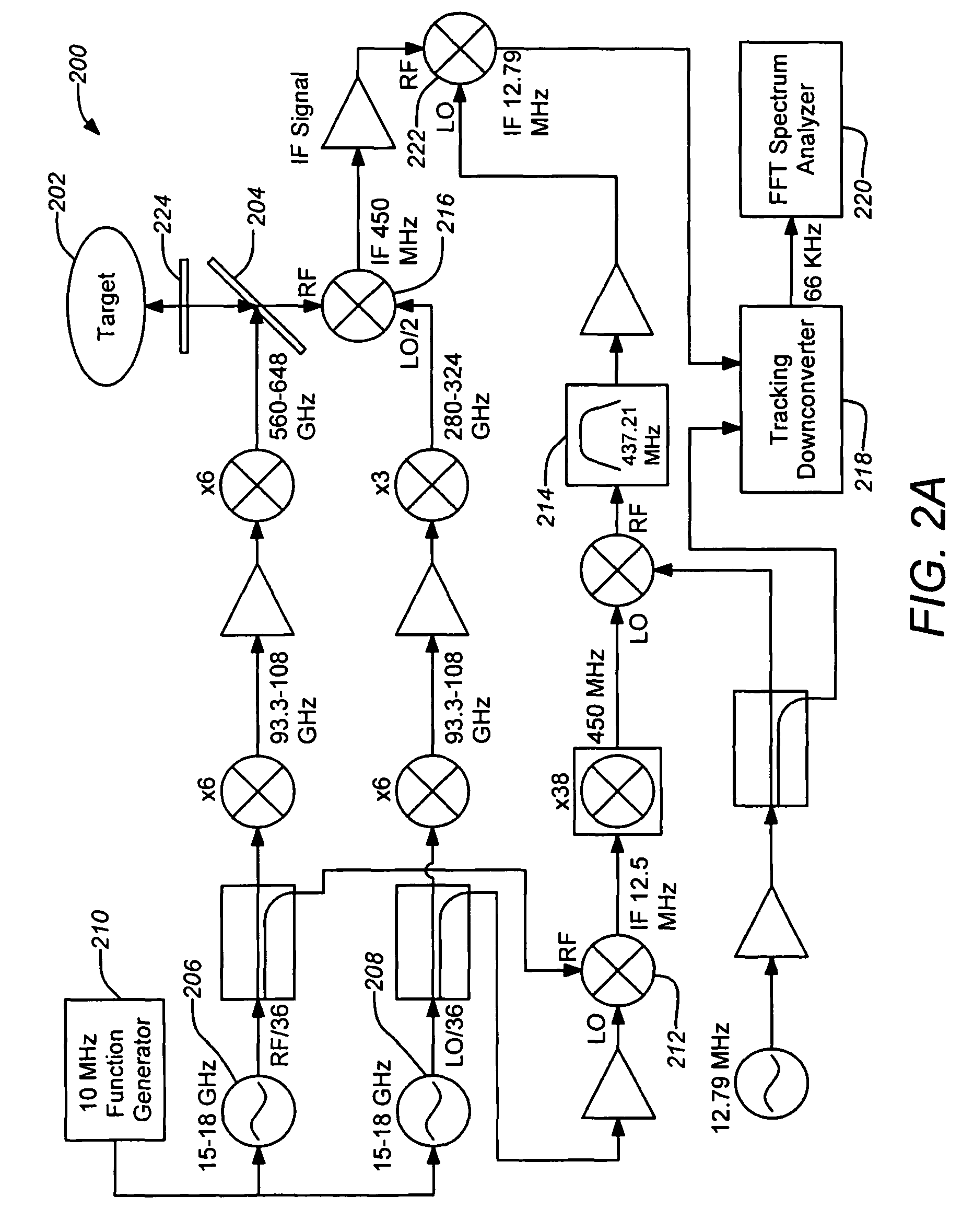
ActiveUS20080304044A1Increase signal powerHigh frequencyOptical rangefindersRadio wave reradiation/reflectionPhase noisePeak value
A three-dimensional imaging radar operating at high frequency e.g., 670 GHz, is disclosed. The active target illumination inherent in radar solves the problem of low signal power and narrow-band detection by using submillimeter heterodyne mixer receivers. A submillimeter imaging radar may use low phase-noise synthesizers and a fast chirper to generate a frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) waveform. Three-dimensional images are generated through range information derived for each pixel scanned over a target. A peak finding algorithm may be used in processing for each pixel to differentiate material layers of the target. Improved focusing is achieved through a compensation signal sampled from a point source calibration target and applied to received signals from active targets prior to FFT-based range compression to extract and display high-resolution target images. Such an imaging radar has particular application in detecting concealed weapons or contraband.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
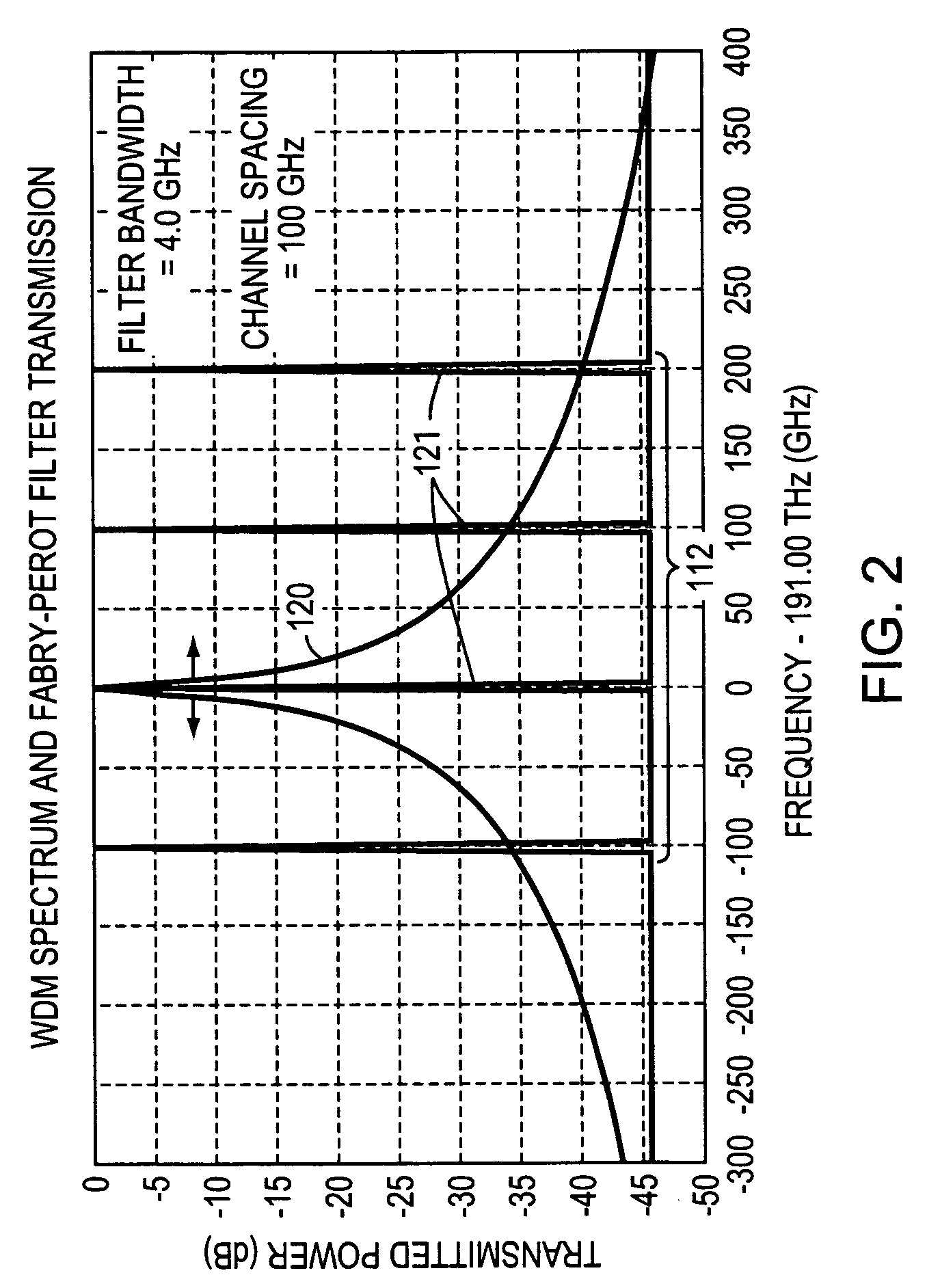
Composite wavelength reference-based fiber bragg grating sensing demodulation device and method
ActiveCN104931081AImprove finenessEasy to find peaksConverting sensor output opticallyGratingBeam splitter
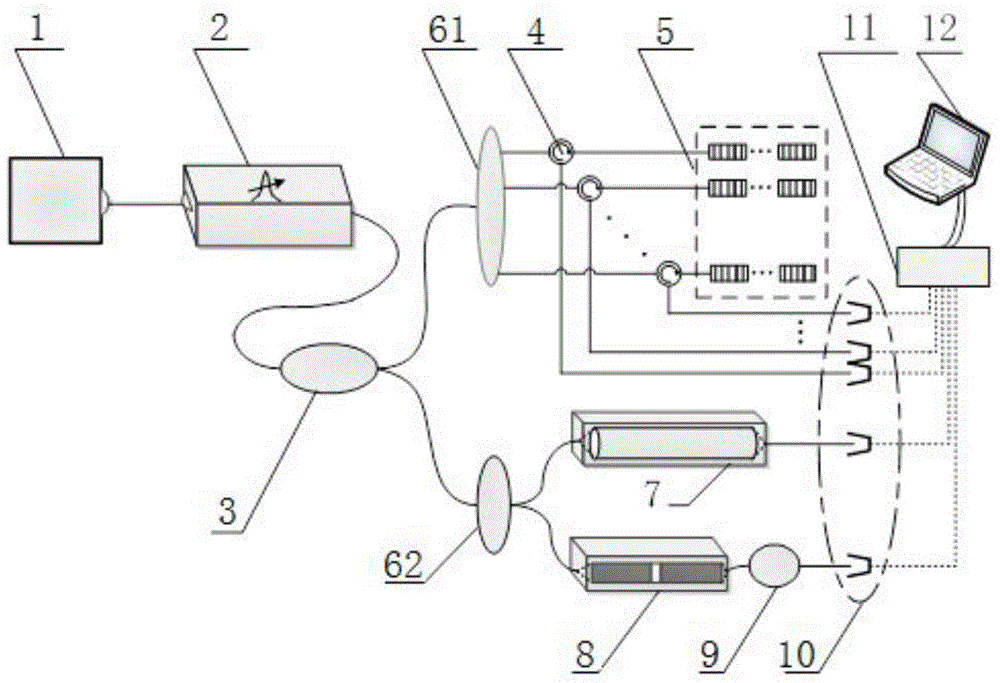
The invention discloses a composite wavelength reference-based fiber bragg grating sensing demodulation device and method. The composite wavelength reference-based fiber bragg grating sensing demodulation device includes a broadband light source (1), a tunable FP filter (2), an optical fiber primary beam splitter (3), an optical fiber circulator (4), an optical fiber grating sensing array (5), a first optical fiber secondary beam splitter (61), a second optical fiber secondary beam splitter (62), an optical fiber air chamber (7), an optical fiber FP etalon (8), a notching filter (9), a photoelectric detection array (10), a data acquisition card (11) and a processing unit (12); and the composite wavelength reference-based fiber bragg grating sensing demodulation device further comprises a sensing link and a wavelength reference link. Compared with the prior art, and according to the composite wavelength reference-based fiber bragg grating sensing demodulation device and method of the invention, equal-interval reference wavelengths can be provided by the optical fiber FP etalon, and therefore, advantages of high fineness of transmission peaks, easiness in peak finding and wide wavelength coverage range can be realized; absolute reference wavelengths provided by the optical fiber air chamber are not affected by environmental factors such as temperature, vibration and impact; and stable fiber bragg grating demodulation is realized.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
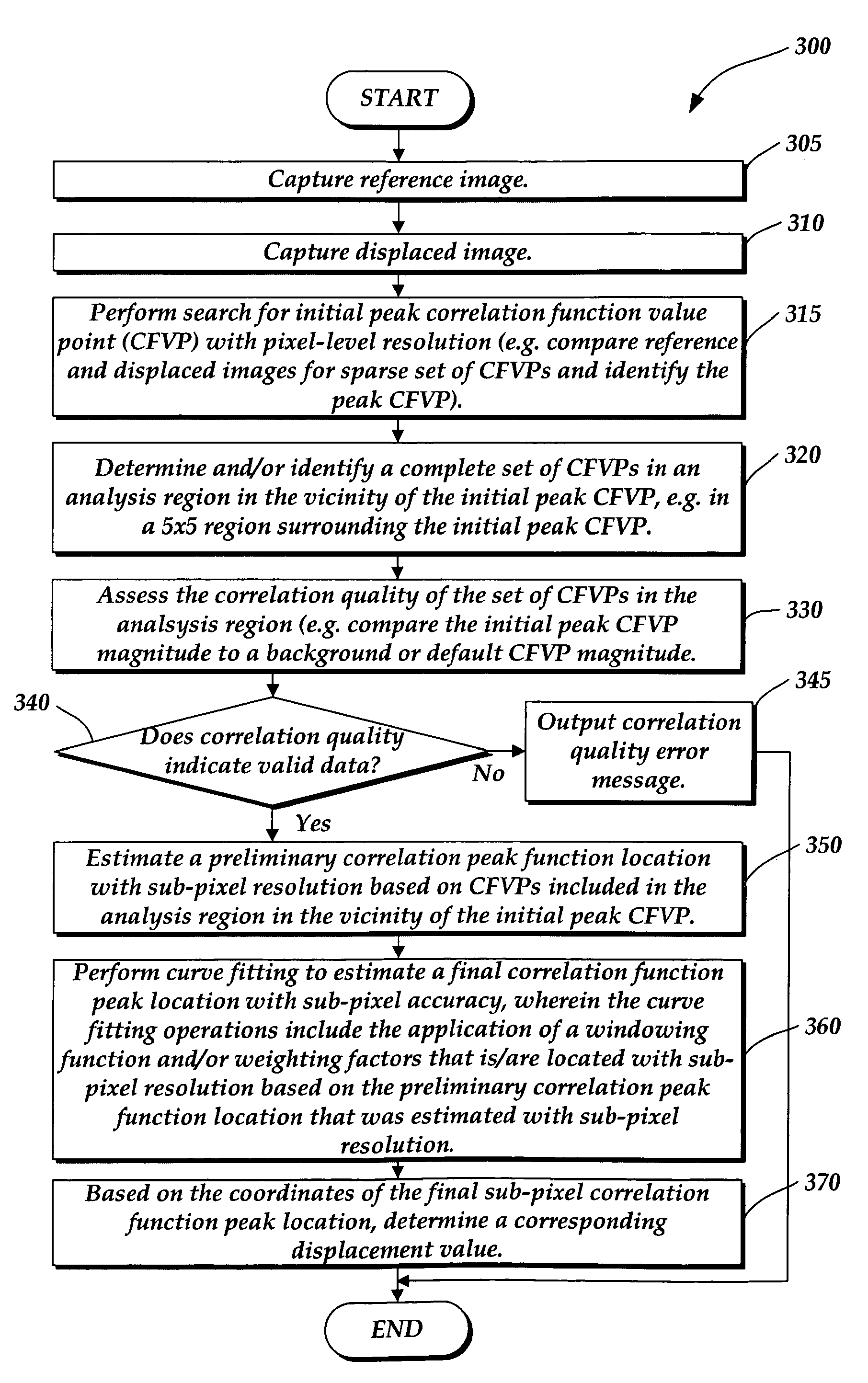
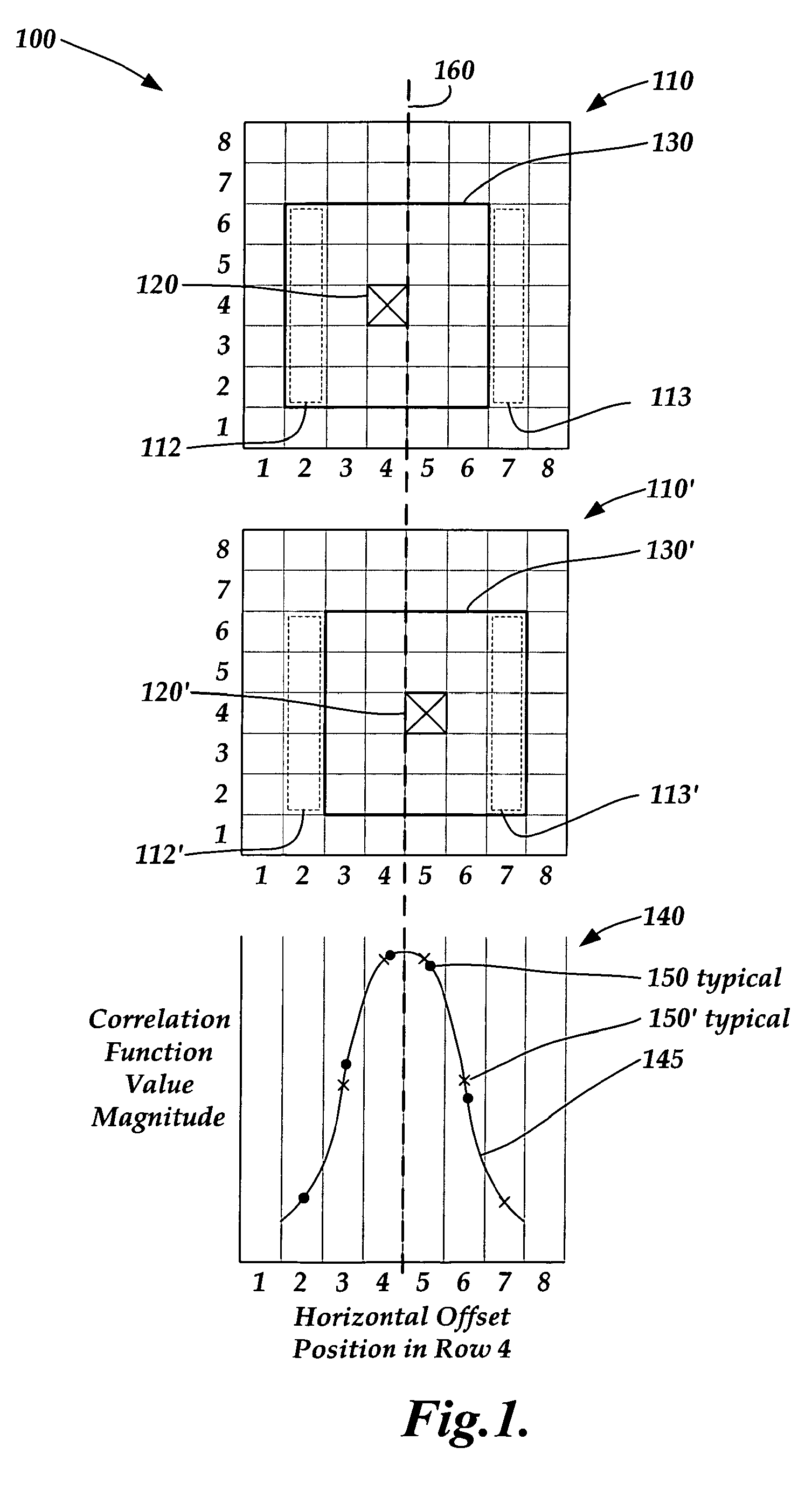
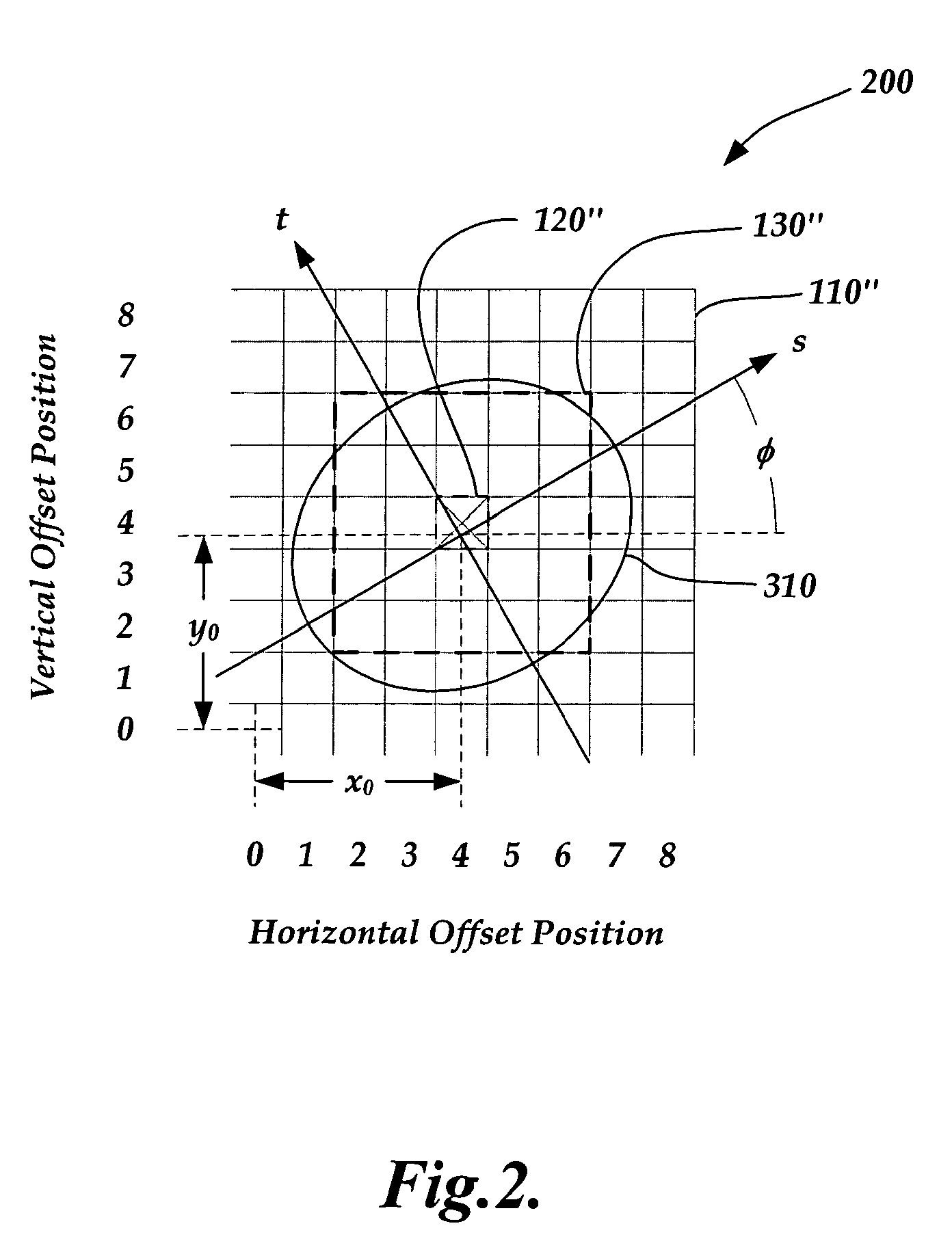
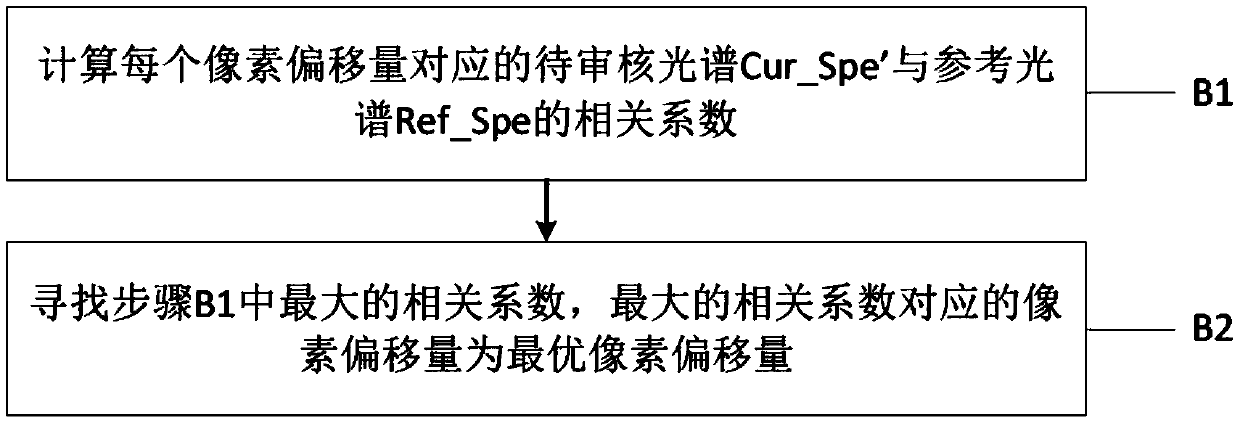
Correlation peak finding method for image correlation displacement sensing
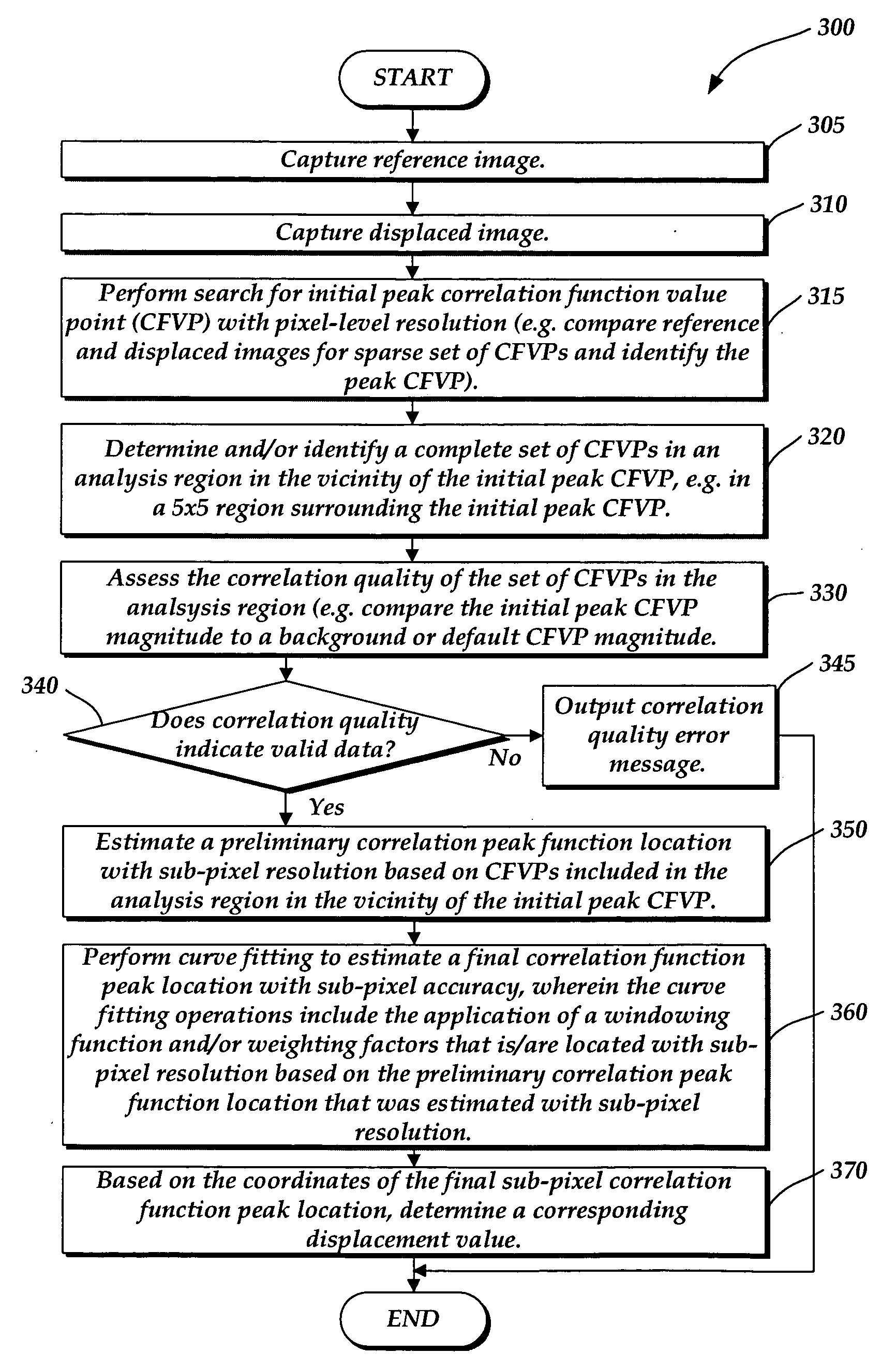
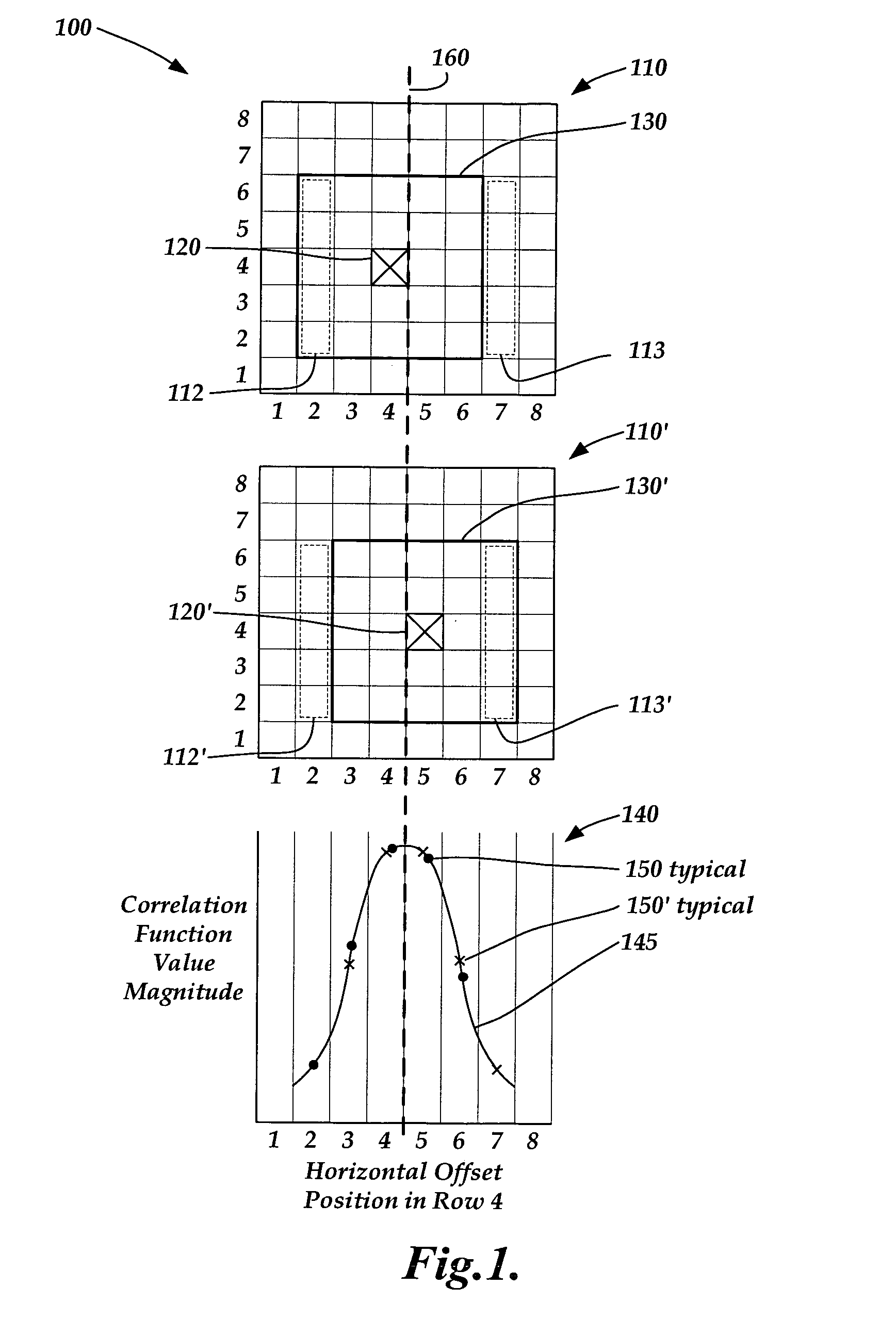
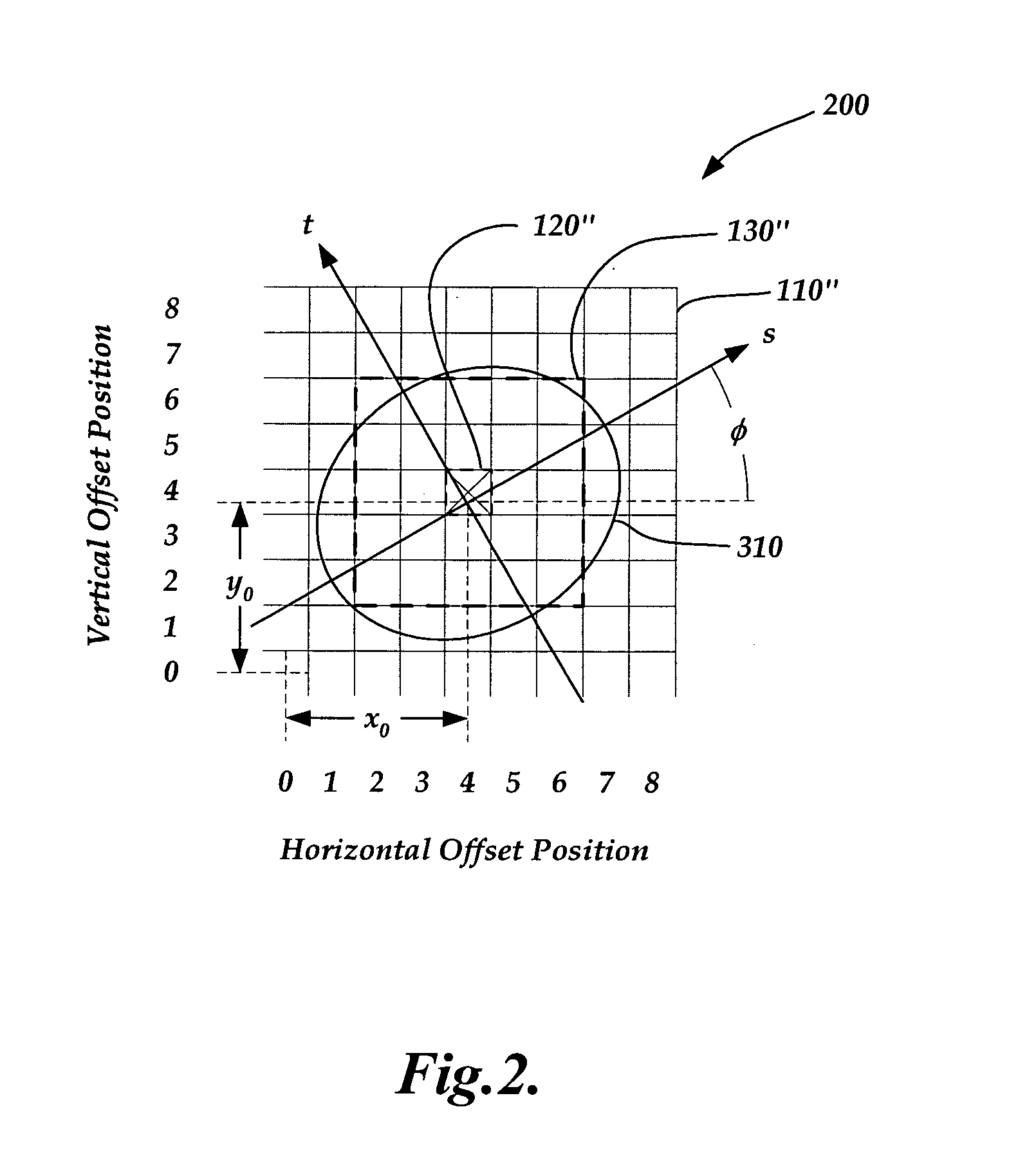
A correlation function peak finding method for an image correlation displacement sensing system is provided. The method may include capturing a reference image and a displaced image, and searching for an initial peak correlation function value point (CFVP) with pixel-level resolution based on correlating the reference image and displaced images at a plurality of offset positions. Then a complete set of CFVPs may be determined at each offset position in an analysis region surrounding the initial peak CFVP. Then a preliminary correlation function peak location is estimated with sub-pixel resolution, based on CFVPs included in the analysis region. Finally, curve-fitting operations are performed to estimate a final correlation function peak location with sub-pixel accuracy, wherein the curve-fitting operations apply a windowing function and / or a set of weighting factors that is / are located with sub-pixel resolution based on the preliminary sub-pixel correlation function peak location.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Correlation peak finding method for image correlation displacement sensing
ActiveUS20080101722A1Type of reductionImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionSub-pixel resolutionPeak finding
A correlation function peak finding method for an image correlation displacement sensing system is provided. The method may include capturing a reference image and a displaced image, and searching for an initial peak correlation function value point (CFVP) with pixel-level resolution based on correlating the reference image and displaced images at a plurality of offset positions. Then a complete set of CFVPs may be determined at each offset position in an analysis region surrounding the initial peak CFVP. Then a preliminary correlation function peak location is estimated with sub-pixel resolution, based on CFVPs included in the analysis region. Finally, curve-fitting operations are performed to estimate a final correlation function peak location with sub-pixel accuracy, wherein the curve-fitting operations apply a windowing function and / or a set of weighting factors that is / are located with sub-pixel resolution based on the preliminary sub-pixel correlation function peak location.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
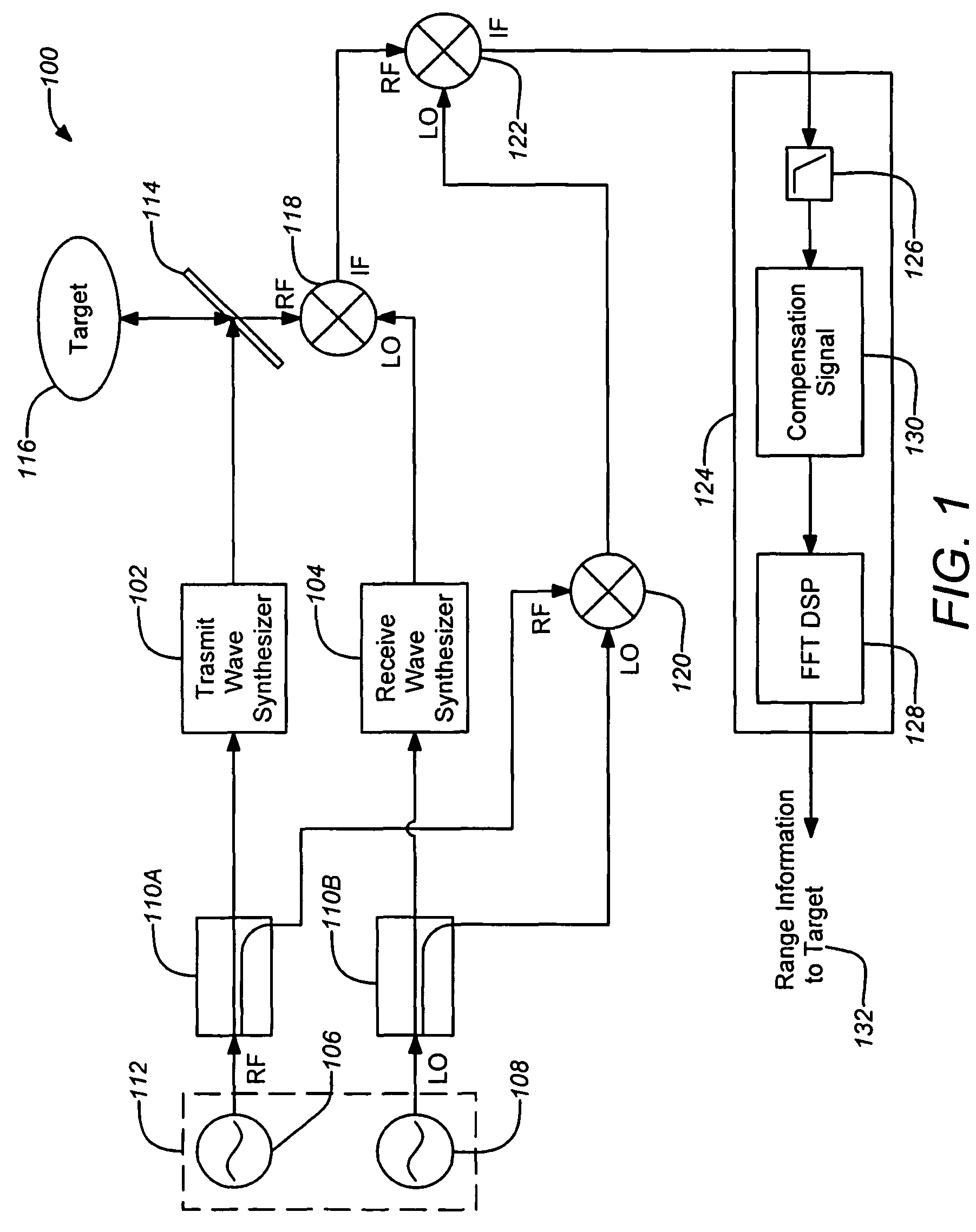
High-resolution three-dimensional imaging radar
A three-dimensional imaging radar operating at high frequency e.g., 670 GHz, is disclosed. The active target illumination inherent in radar solves the problem of low signal power and narrow-band detection by using submillimeter heterodyne mixer receivers. A submillimeter imaging radar may use low phase-noise synthesizers and a fast chirper to generate a frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FMCW) waveform. Three-dimensional images are generated through range information derived for each pixel scanned over a target. A peak finding algorithm may be used in processing for each pixel to differentiate material layers of the target. Improved focusing is achieved through a compensation signal sampled from a point source calibration target and applied to received signals from active targets prior to FFT-based range compression to extract and display high-resolution target images. Such an imaging radar has particular application in detecting concealed weapons or contraband.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
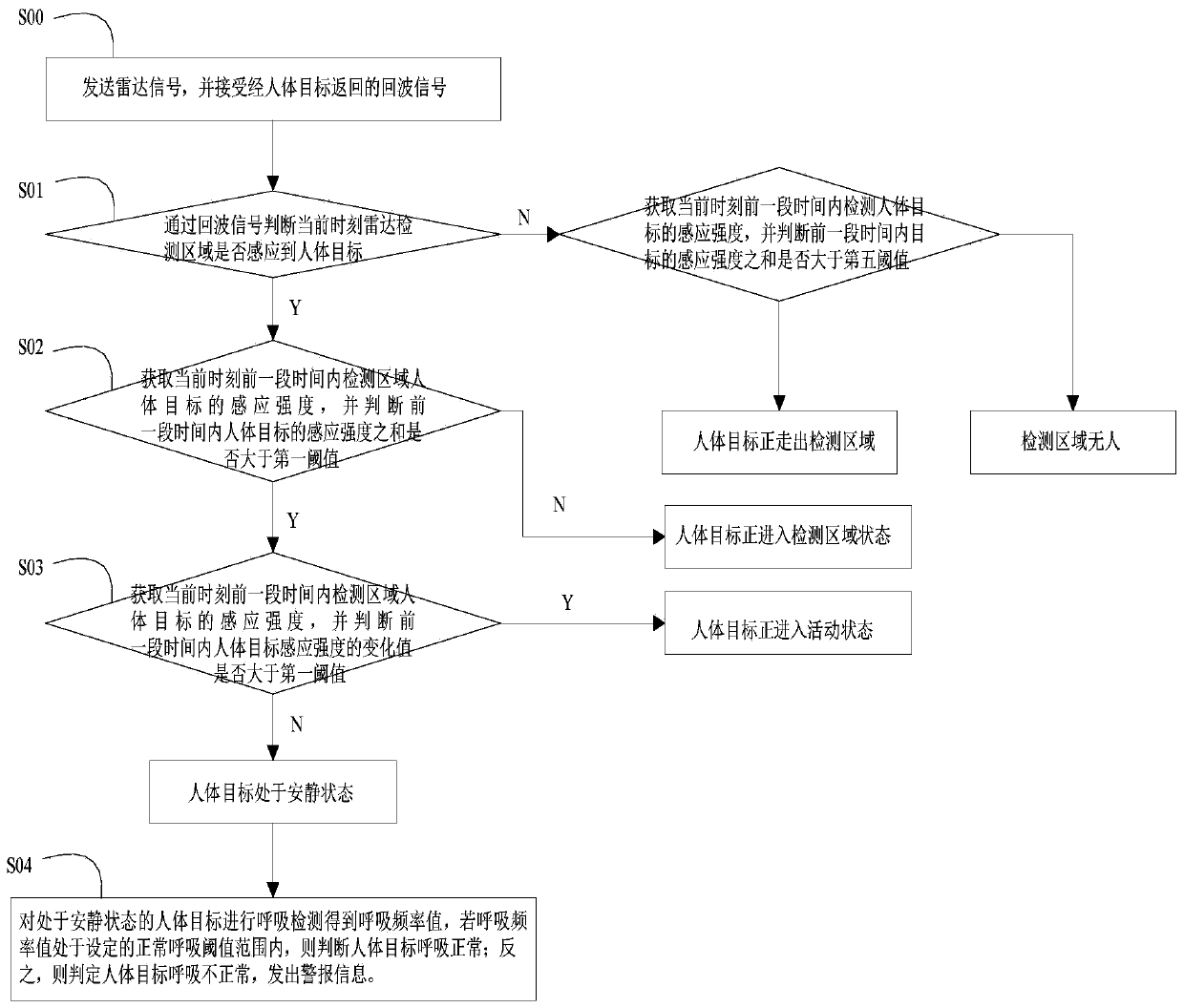
Radar-based non-contact human body breathing detection method and Radar-based non-contact human body breathing detection device
PendingCN110192862AImprove reliabilityEasy to operateRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsHuman bodyRespiratory signal
The invention discloses a radar-based non-contact human body breathing detection method and a radar-based non-contact human body breathing detection device. An intelligent algorithm is used to discriminate the motion posture of a vital sign target in a detection area, and when a human body target is determined in a quiet state, the respiratory detection is started, and a respiratory value is output. In the event of respiratory abnormality, an alarm message is sent to notify the family member or the nursing staff in time, so that the people can be promptly treated, the reliability of the respiratory detection is remarkably improved, and the technical problem that the current non-contact detection breathing method cannot determine and detect the target state of the human body can be solved;by performing a wavelet analysis algorithm, time-domain peak finding and downsampling processing on the sampled echo signals, a respiratory signal can be accurately identified and the respiratory frequency can be obtained, and the method has the advantages of high accuracy and strong real-time performance.
Owner:长沙军民先进技术研究有限公司
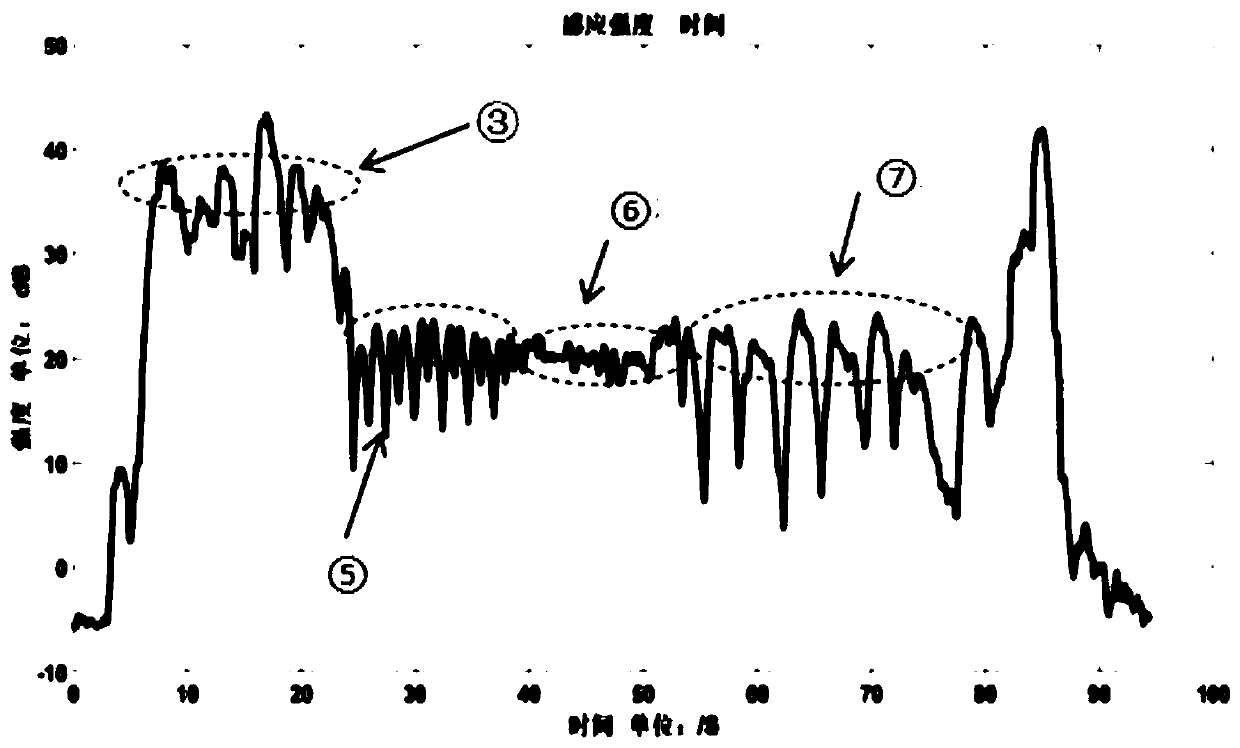
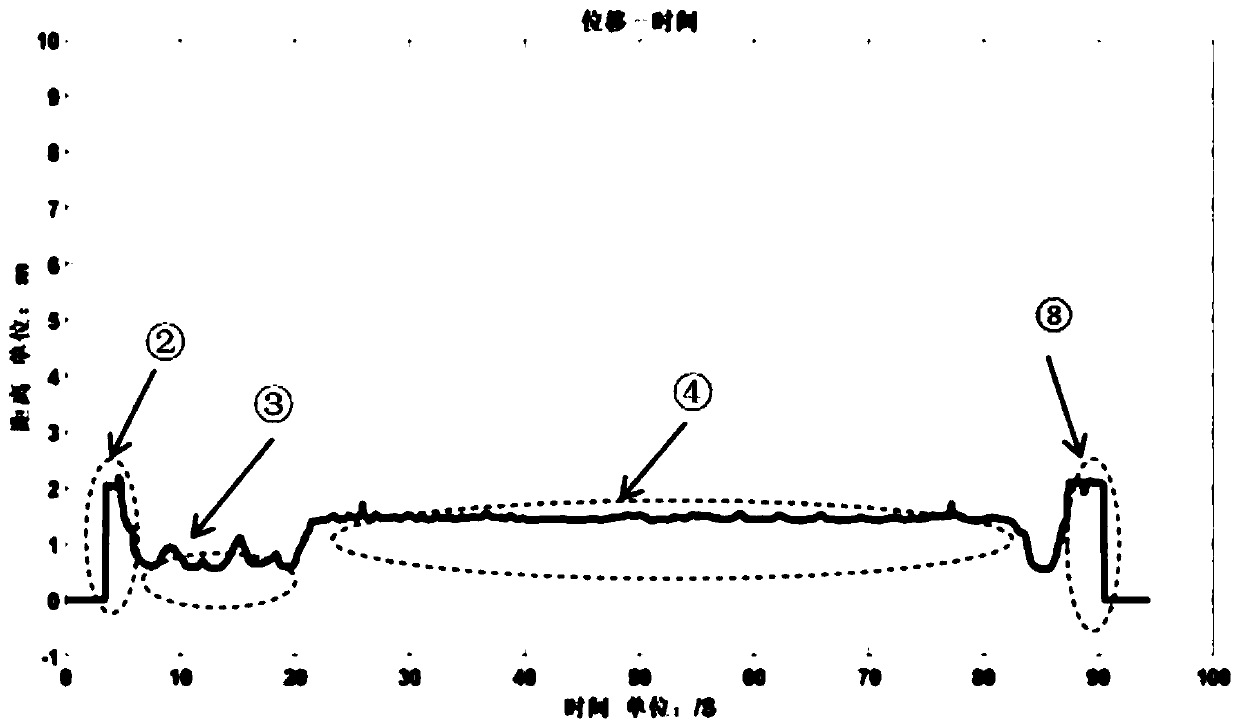
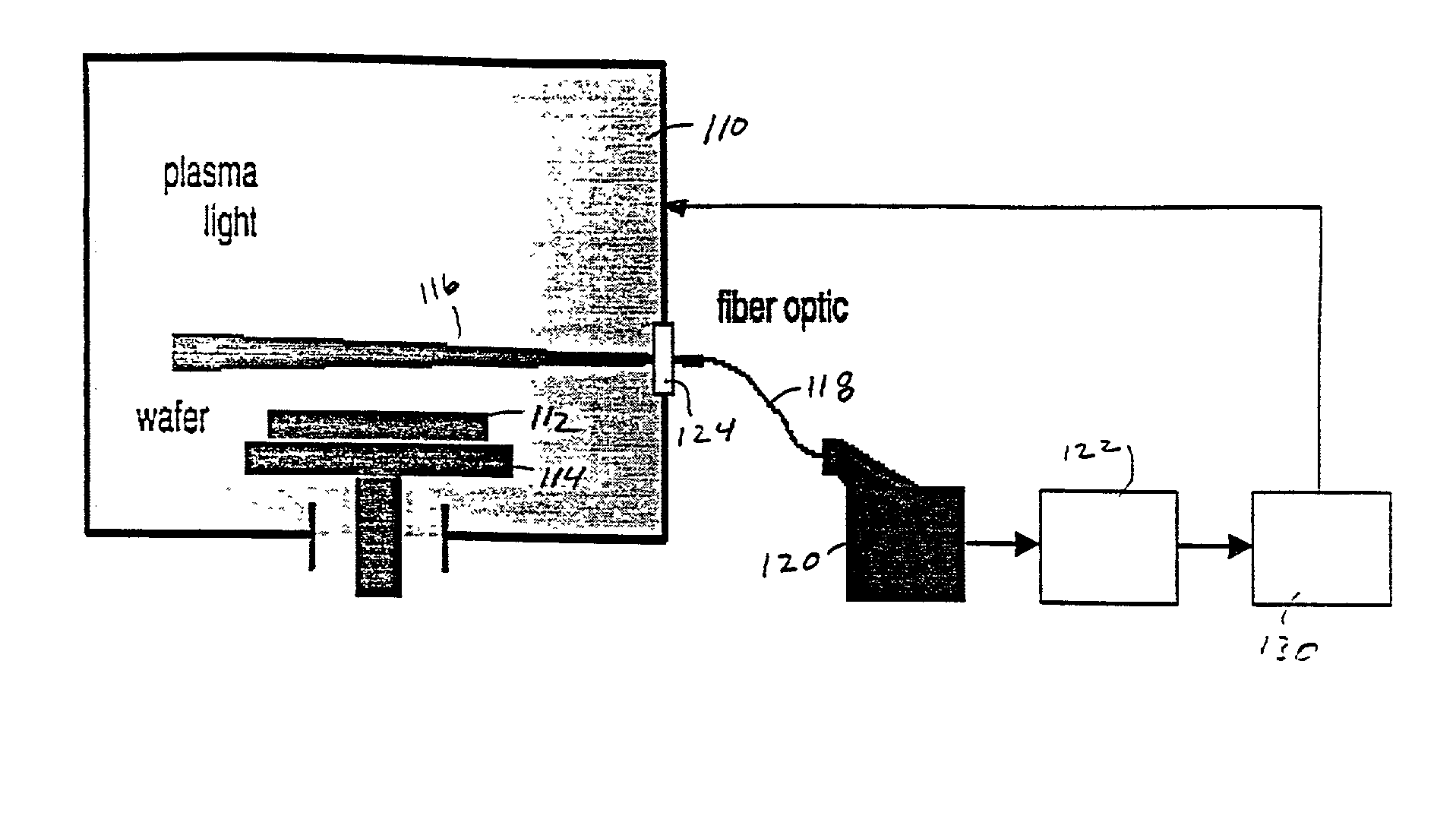
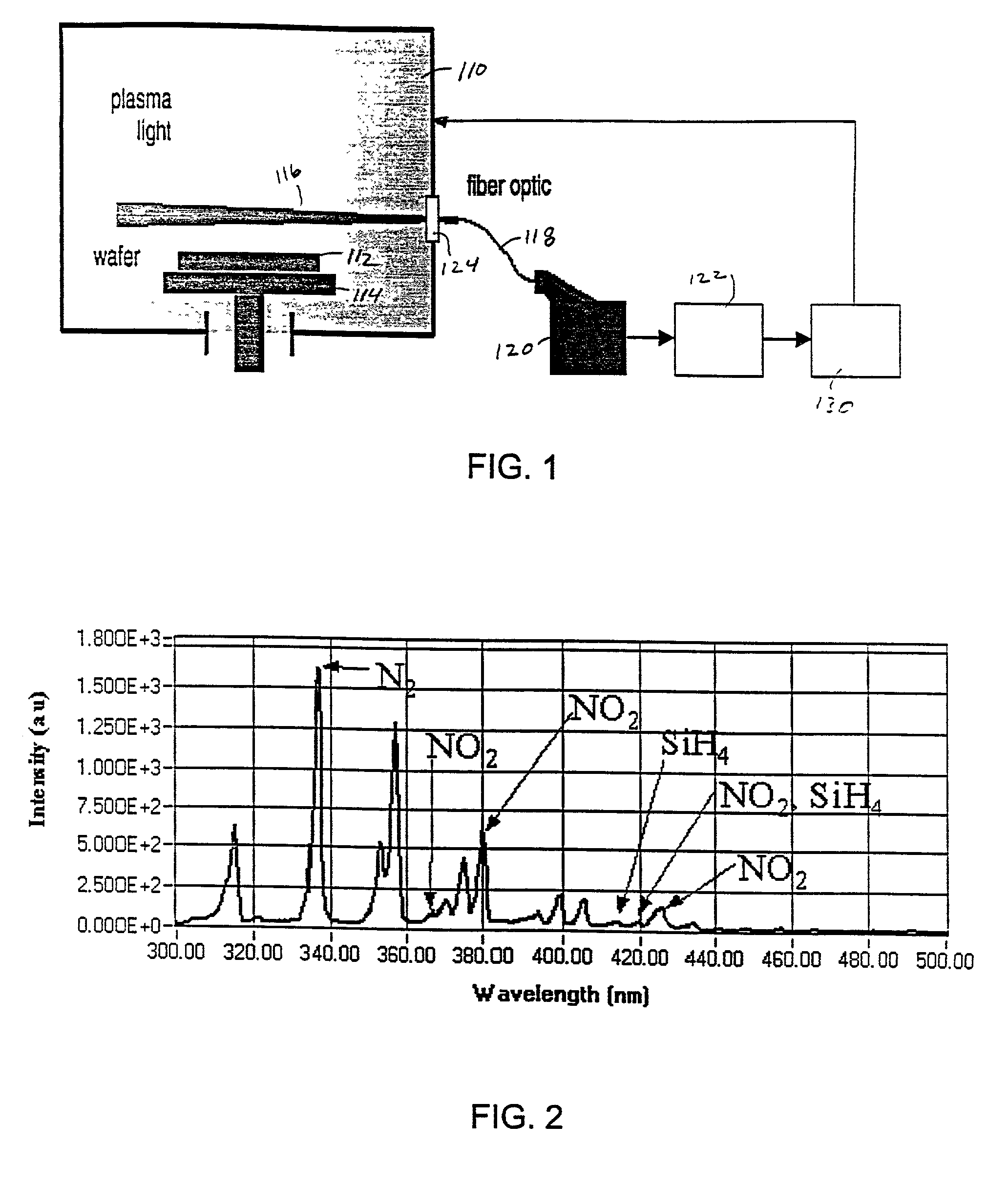
Method and system for event detection in plasma processes
InactiveUS7006205B2Reduce in quantityEasy accessRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationSpectral emissionPeak finding
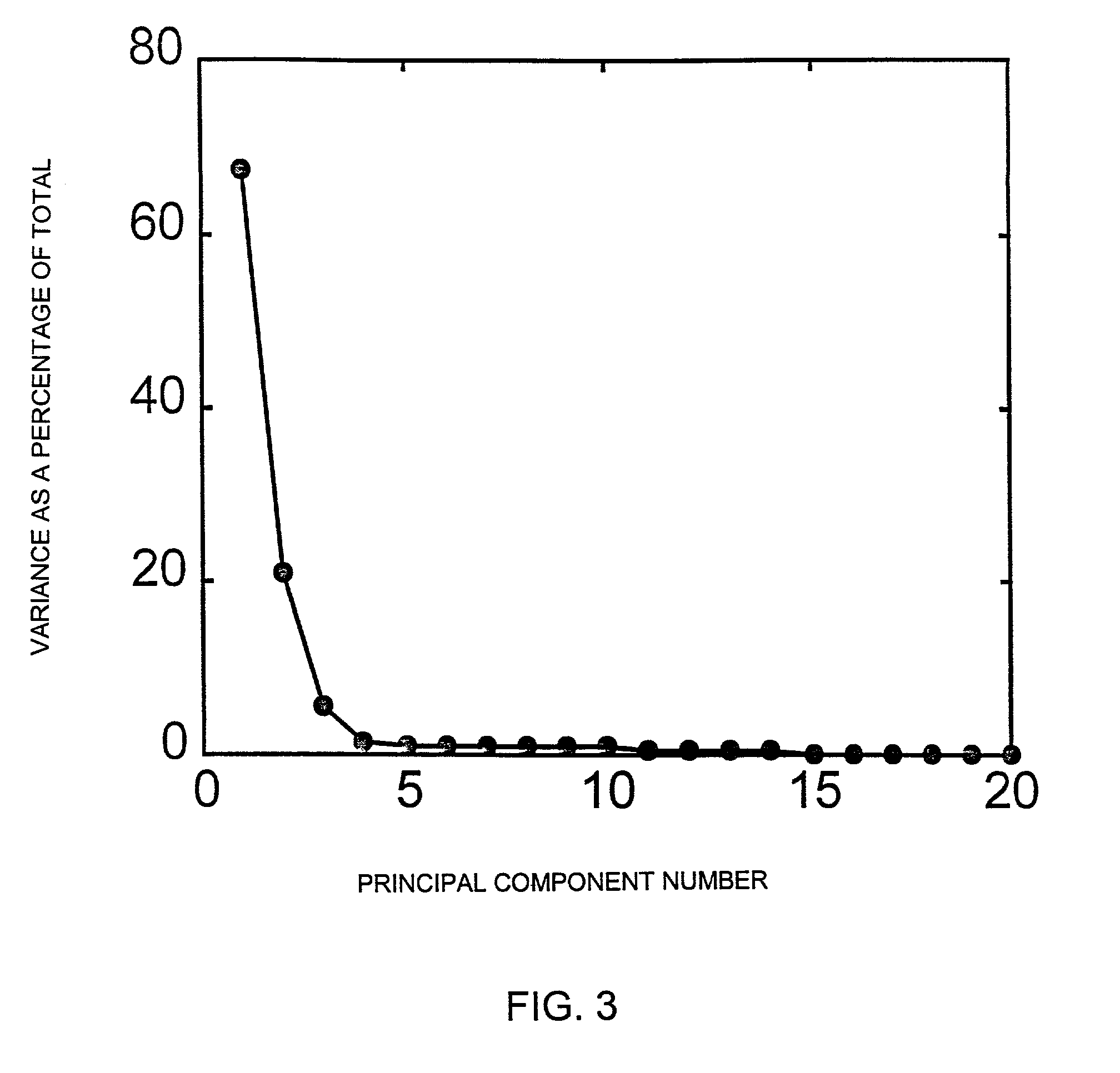
Plasma events are detected by analyzing the spectral emissions of a plasma process of a substrate. A plasma is monitored by a spectrometer which produces plasma emission data which includes an intensity value for each individual wavelength which is a large quantity of information. The plasma emission data is processed with an algorithm or combination of algorithms to reduce the quantity of the plasma emission data. A peak finding algorithm which identifies the wavelengths of light which are associated with a plasma process allowing the other wavelengths to be ignored. A data reduction algorithm provides a single value representative of the intensity of the emitted light from each peak. A noise reduction algorithm removes noise from the spectral signal by eliminating signals at wavelengths which do not exceed a threshold intensity and do not exceed a threshold wavelength span. The data may also be processed with principal component analysis to further reduce the optical emission data. By reducing the optical emission data, the neural network can provide faster data analysis. The neural network of the inventive system identifies the plasma event after being trained and can control the processing equipment when plasma events are detected.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Dual-channel miniature Raman spectrometer
The invention discloses a dual-channel miniature Raman spectrometer, which comprises a near infrared laser diode or a near ultraviolet laser transmitter, a laser beam expanding collimator, an anti-laser laser and Raman light transmission first beam splitter, a zooming and non-zooming cylindrical surface or spherical surface objective lens, an anti-laser Ranman light transmission second beam splitter, a relay optical system, a narrow slit, two spectrum forming lenses, a line array or surface array CCD or CMOS detector, a GPS, and a data processing and wireless receiving and sensing system in sequential connection. After the photo is taken on a target in a laser channel or the sample measurement by optical axis alignment at the Raman channel, data is sent to a mobile phone and a cloud computer in a wireless way for processing of spectrum separation, wave peak finding, spectral database building, substance recognition and the like; the conclusion is fast obtained. The size of the spectrometer is small; the spectrometer can be conveniently carried and used; the measurement result can be seen in places with the Internet; the sensitivity and the resolution ratio are higher than those ofsimilar products.
Owner:ULSEE
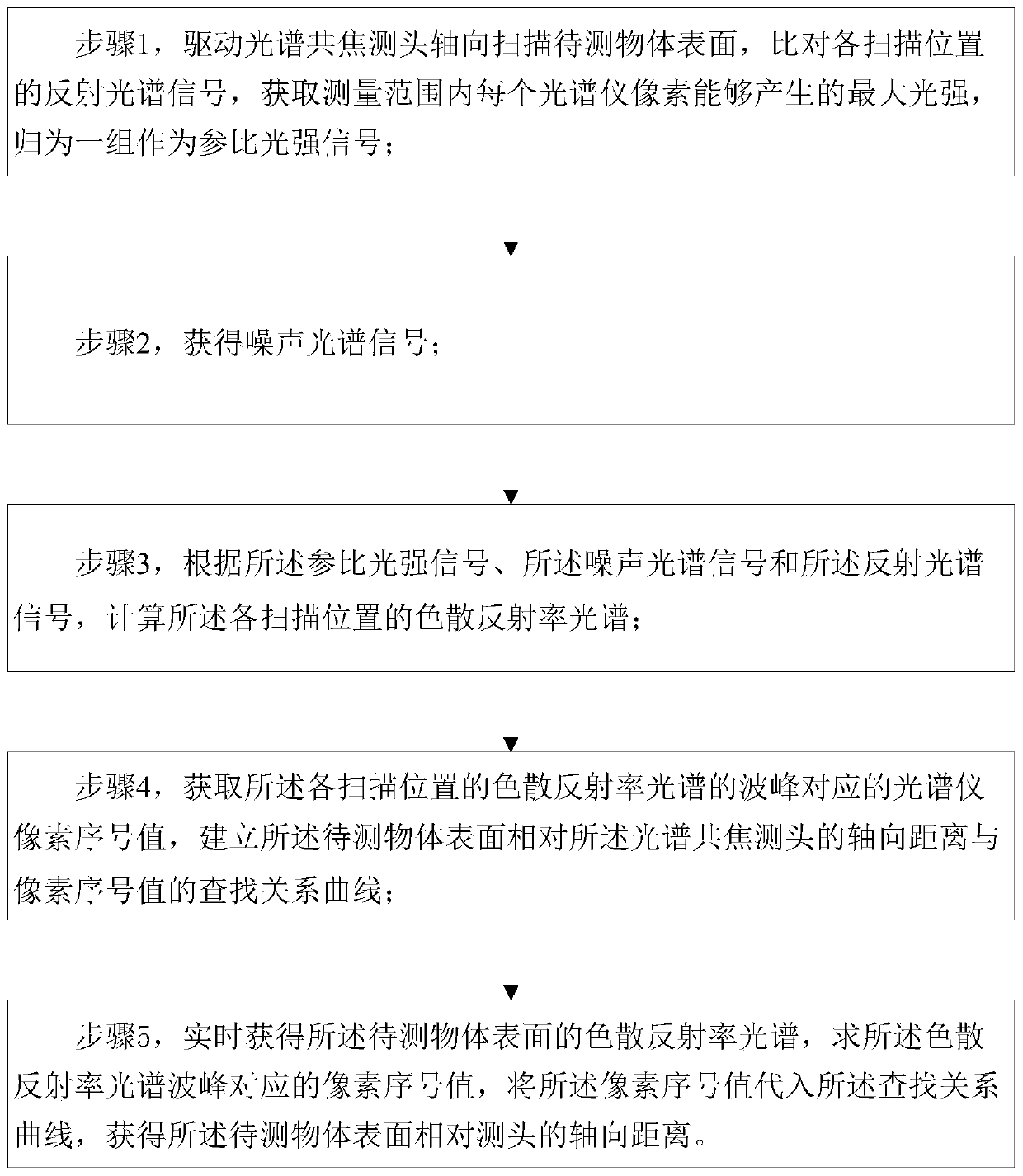
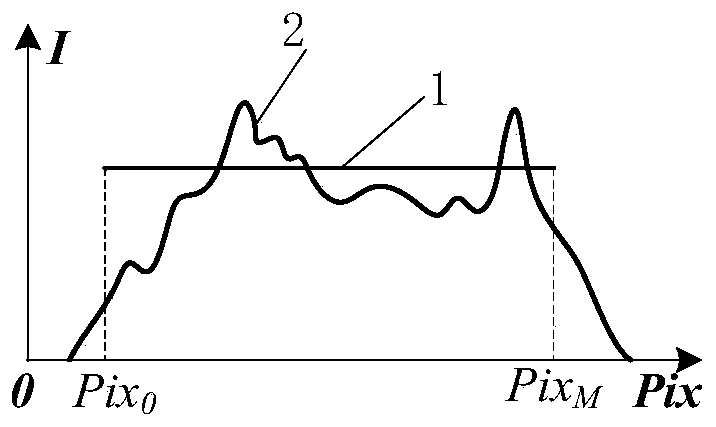
Spectral confocal axial distance detecting method, device and equipment
ActiveCN110044286AHigh solution accuracyMake up strengthUsing optical meansPeak findingReflectance spectroscopy
The invention discloses a spectral confocal axial distance detecting method, device and equipment. The method comprises the following steps of driving a spectral confocal probe to axially scan the surface of an object to be detected, comparing reflected spectral signals of each scanning position, obtaining the maximum light intensity that each spectrometer pixel can generate in the measurement range, and grouping the maximum light intensity as a reference light intensity signal; obtaining a noise spectrum signal; and calculating dispersion reflectance spectrums of the respective scanning positions according to the reference light intensity signal, the noise spectrum signal and the reflection spectrum signal. The spectral confocal axial distance detecting method, device and equipment provided by the invention, by obtaining the maximum light intensity which can be generated by each spectrometer pixel in the measurement range as the reference light intensity signal, calculating the dispersion reflectance by the noise spectrum signal and further performing peak finding on the dispersion reflectance as a focus pixel ordinal value, make up the difference in intensity, transmittance and the like of the light of different wavelengths caused by the light source, and can effectively improve the accuracy of solving the focus pixel ordinal value.
Owner:GUANGXI GUIHUA INTELLIGENT MFG CO LTD
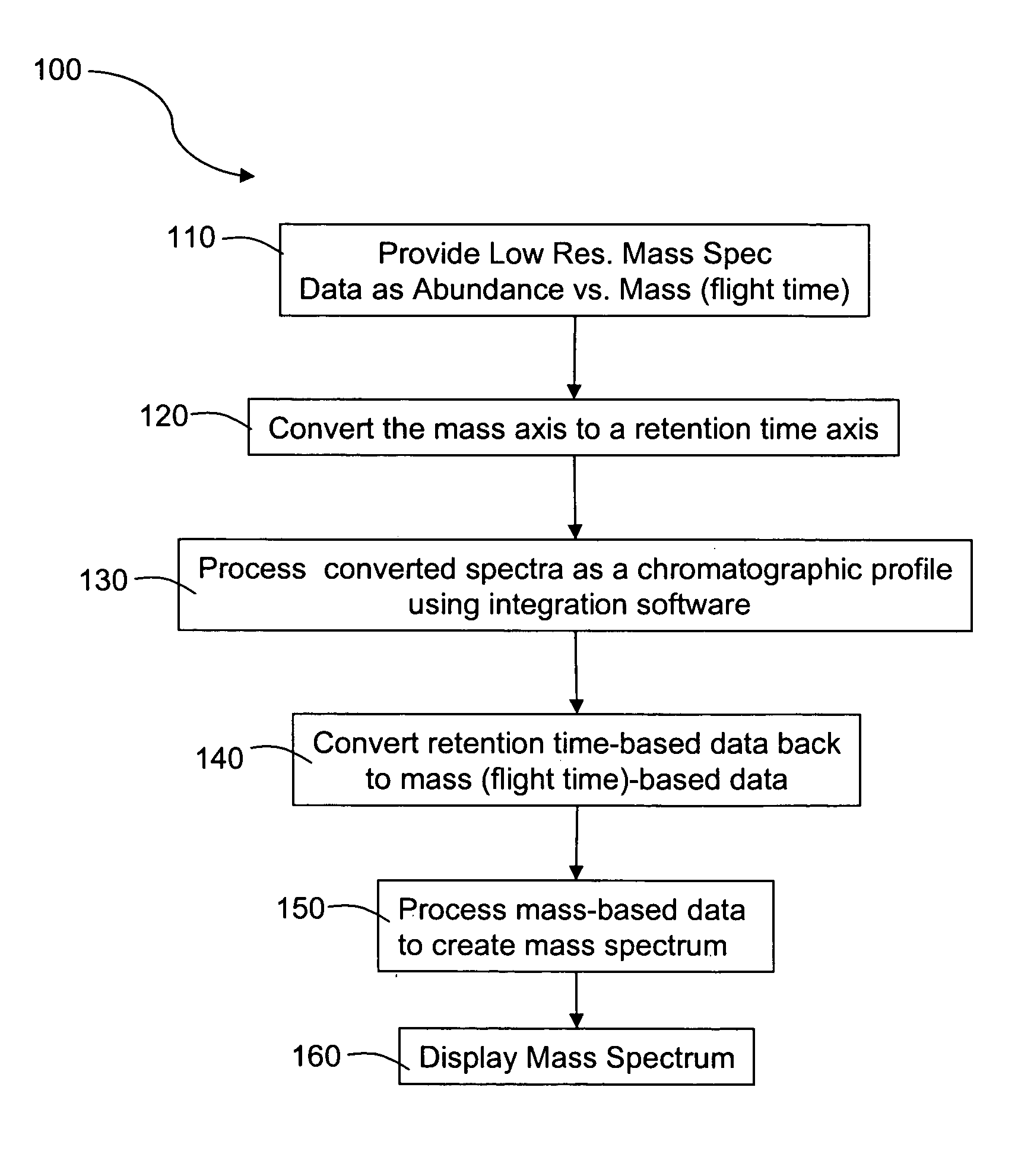
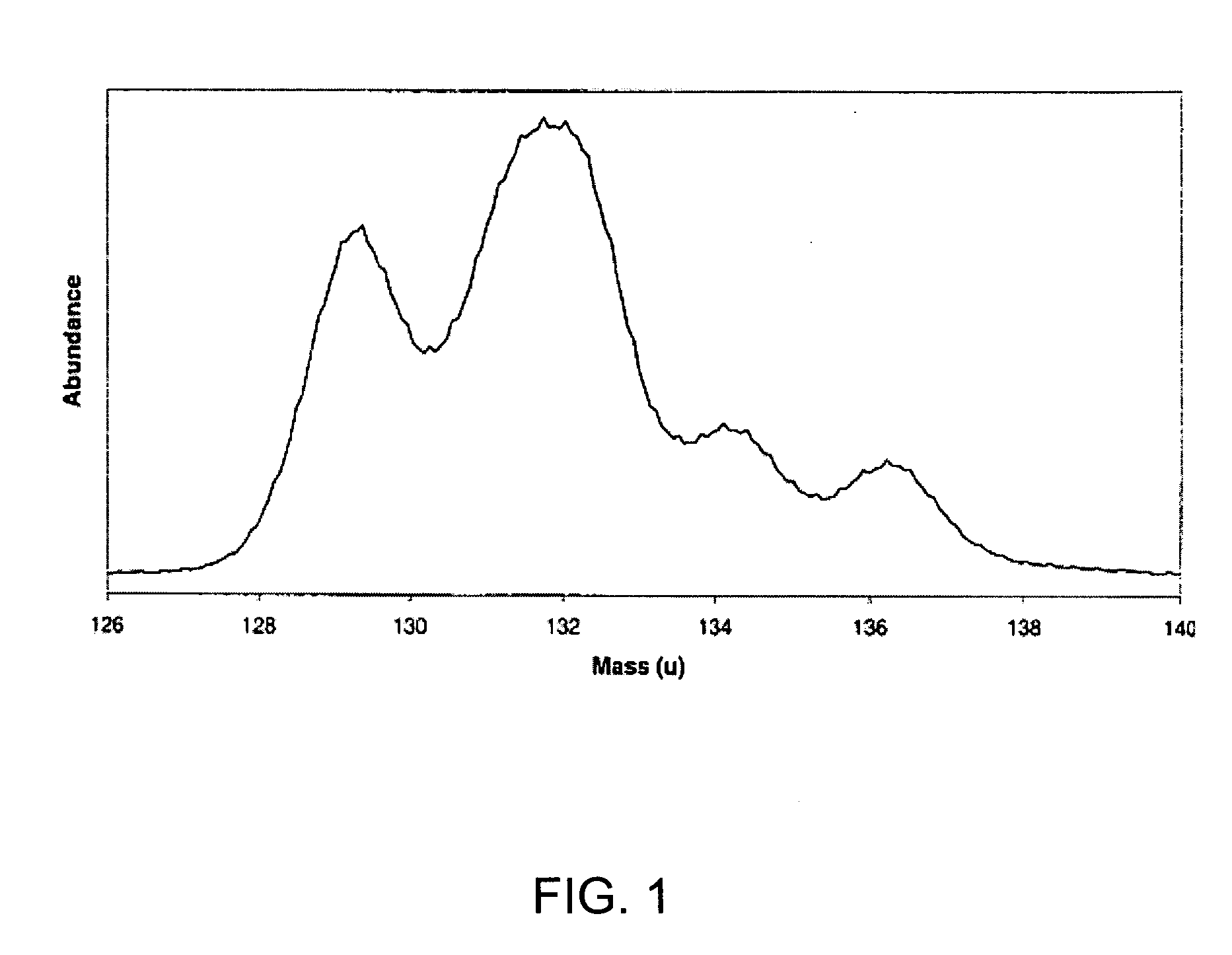
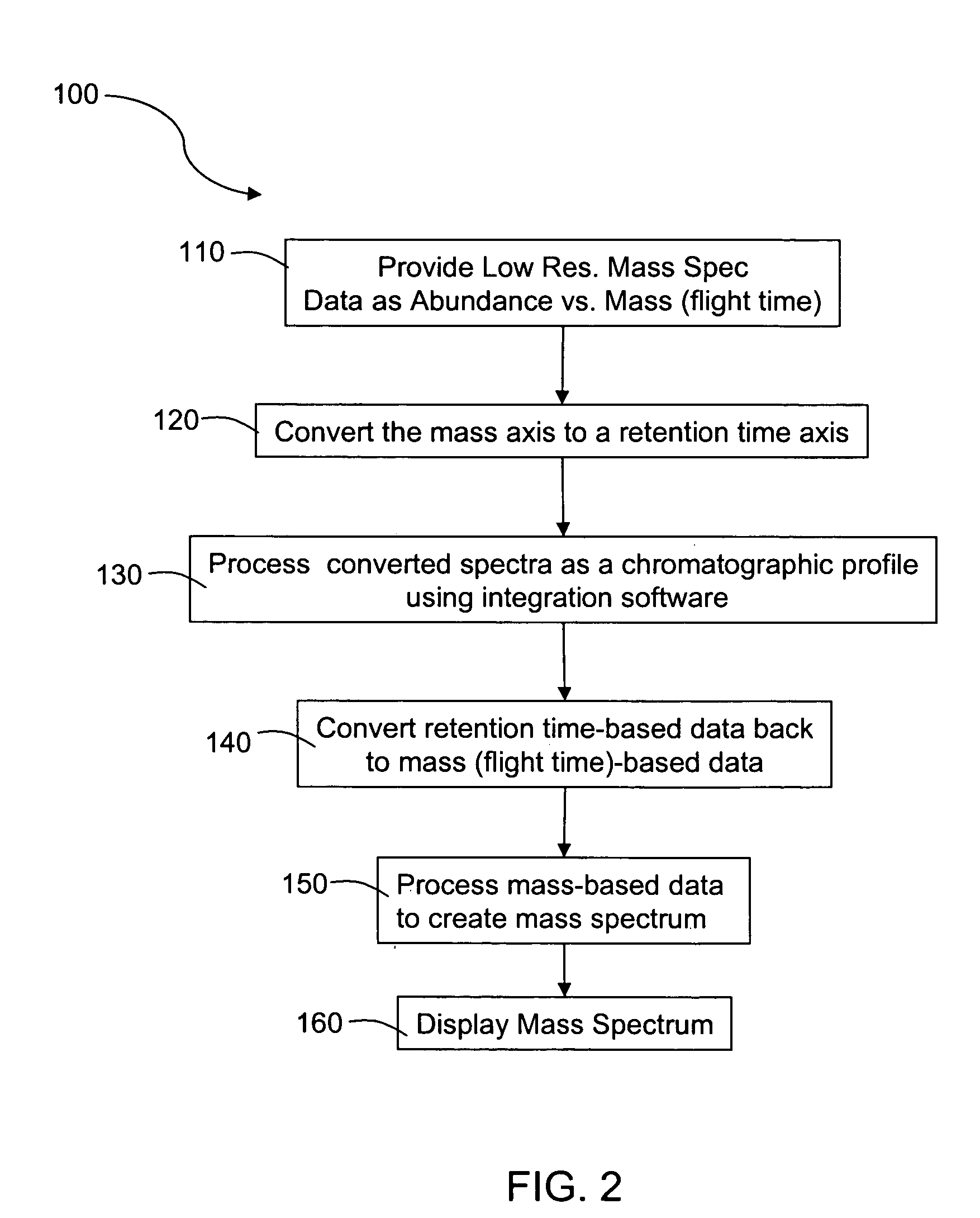
Peak finding in low-resolution mass spectrometry by use of chromatographic integration routines
InactiveUS20080073499A1Particle separator tubesIsotope separationRetention timeProtein mass spectrometry
Methods for processing low resolution mass spectrometry data, including providing the low resolution mass spectrometry data as abundance versus flight time data, converting the flight time axis of the low resolution mass spectrometry data to a calibrated mass axis, and converting that to retention time-based chromatographic data. The time-based data may then be converted back to abundance versus mass data and processed to create a mass spectrum.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Peak positioning method of overlapping fiber bragg grating (FBG) sensing signals
InactiveCN108225385AAccurate removalEliminate low frequency noiseConverting sensor output opticallySingular value decompositionSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
The invention relates to a peak positioning method of overlapping FBG sensing signals, and belongs to the field of optical fiber sensing signal processing research of photoelectric detection. The method comprises the following steps: using continuous wavelet transform to process FBG reflected signals to eliminate the influence of signal noises on peak positioning accuracy; using a wavelet ridge peak finding algorithm to obtain peak initial positioning points of peak overlapping FBG signals with the continuity of extreme values at different scales; improving the wavelet ridge peak finding algorithm through matrix singular value decomposition, extracting wavelet ridges which can represent local characteristic information of the FBG reflected signals, and removing a pseudo maximum value affecting peak positioning; and combining peak energy with a signal-to-noise ratio to obtain accurate peak points of final overlapping peaks. By adopting the method, the peak overlapping problem of the FBGreflected signals can be effectively solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
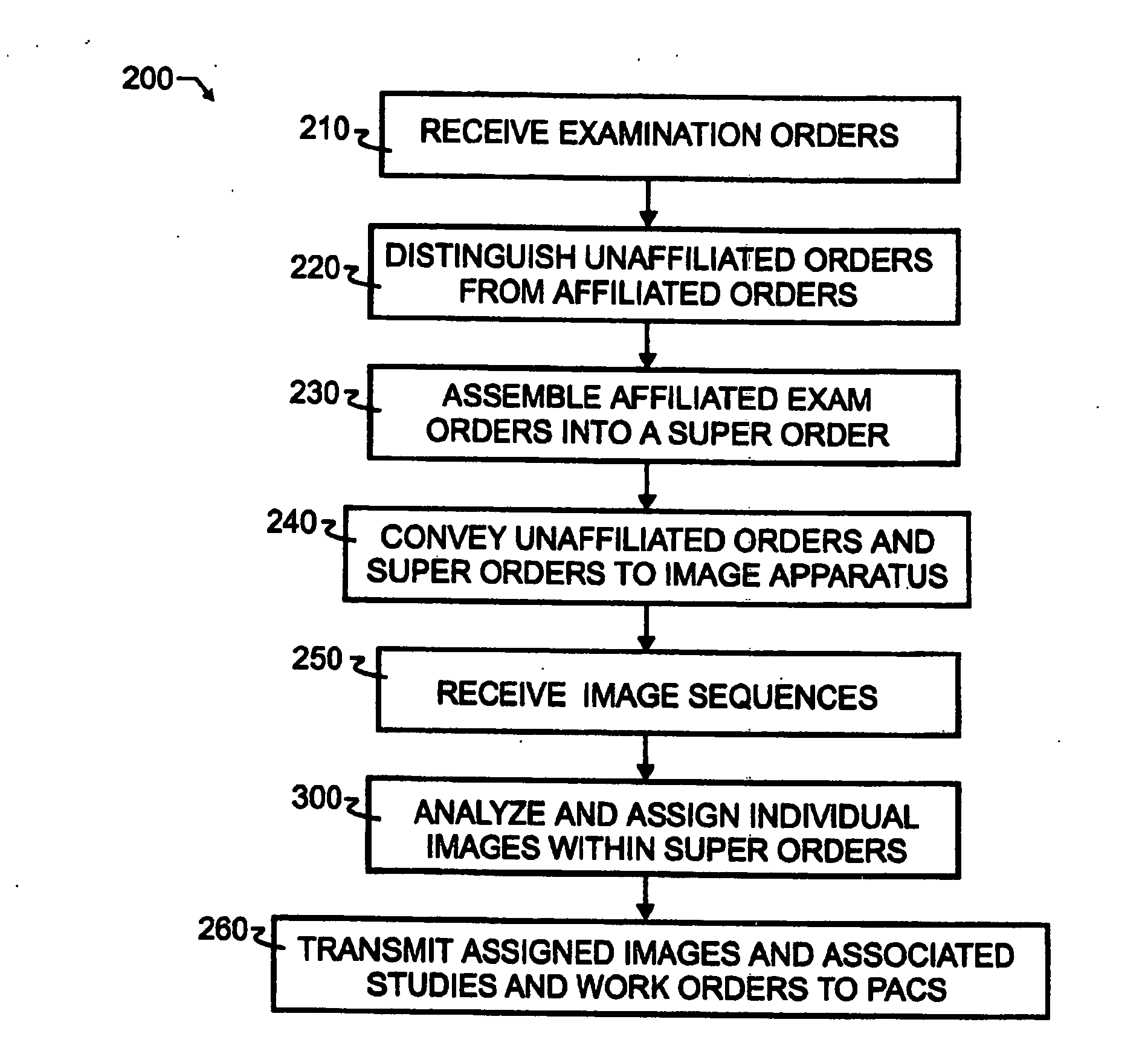
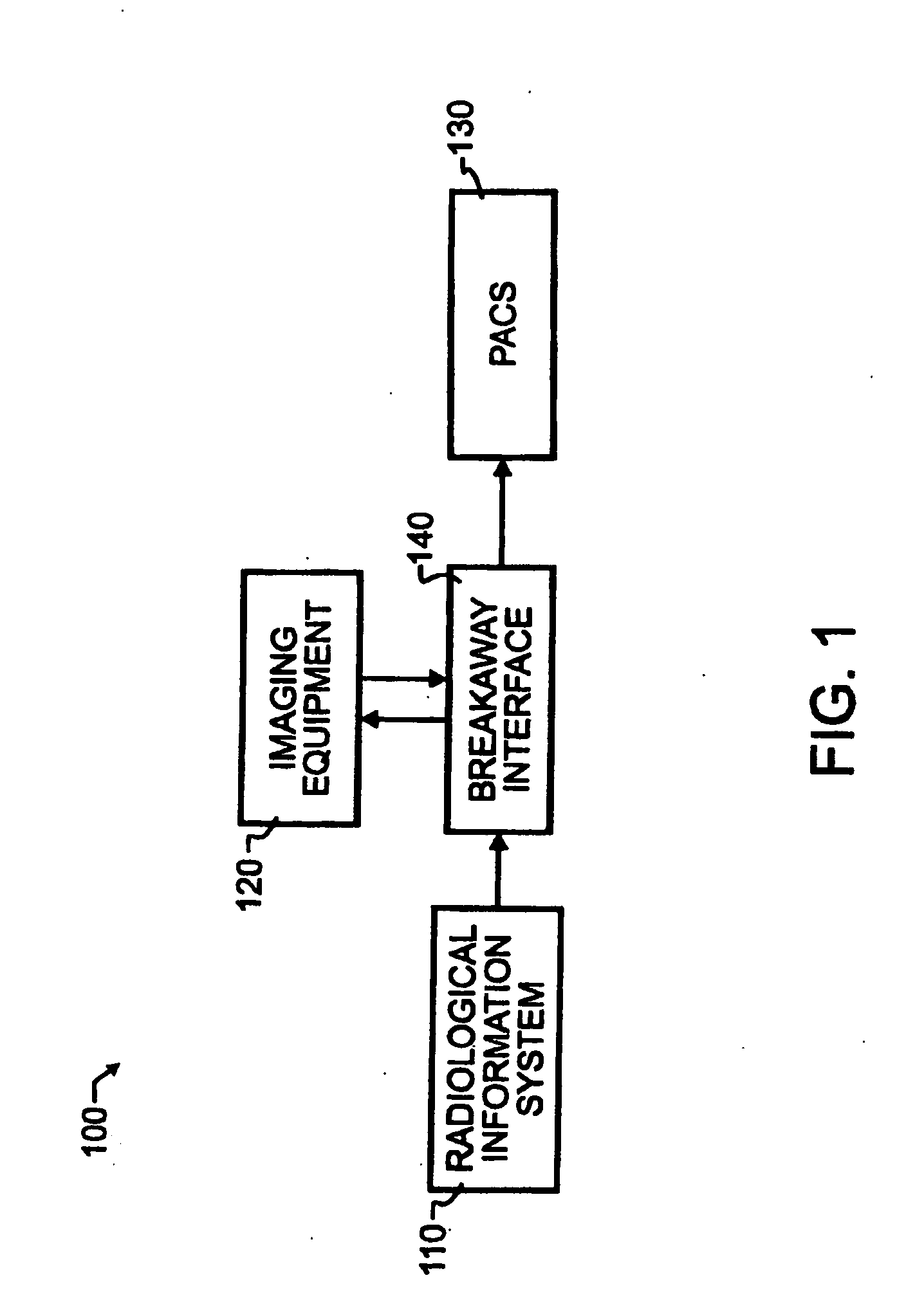
Breakaway interfacing of radiological images with work orders
InactiveUS7756725B2Easy to useImproved and more highly automated communicationComplete banking machinesTelephonic communicationPeak findingSingle image
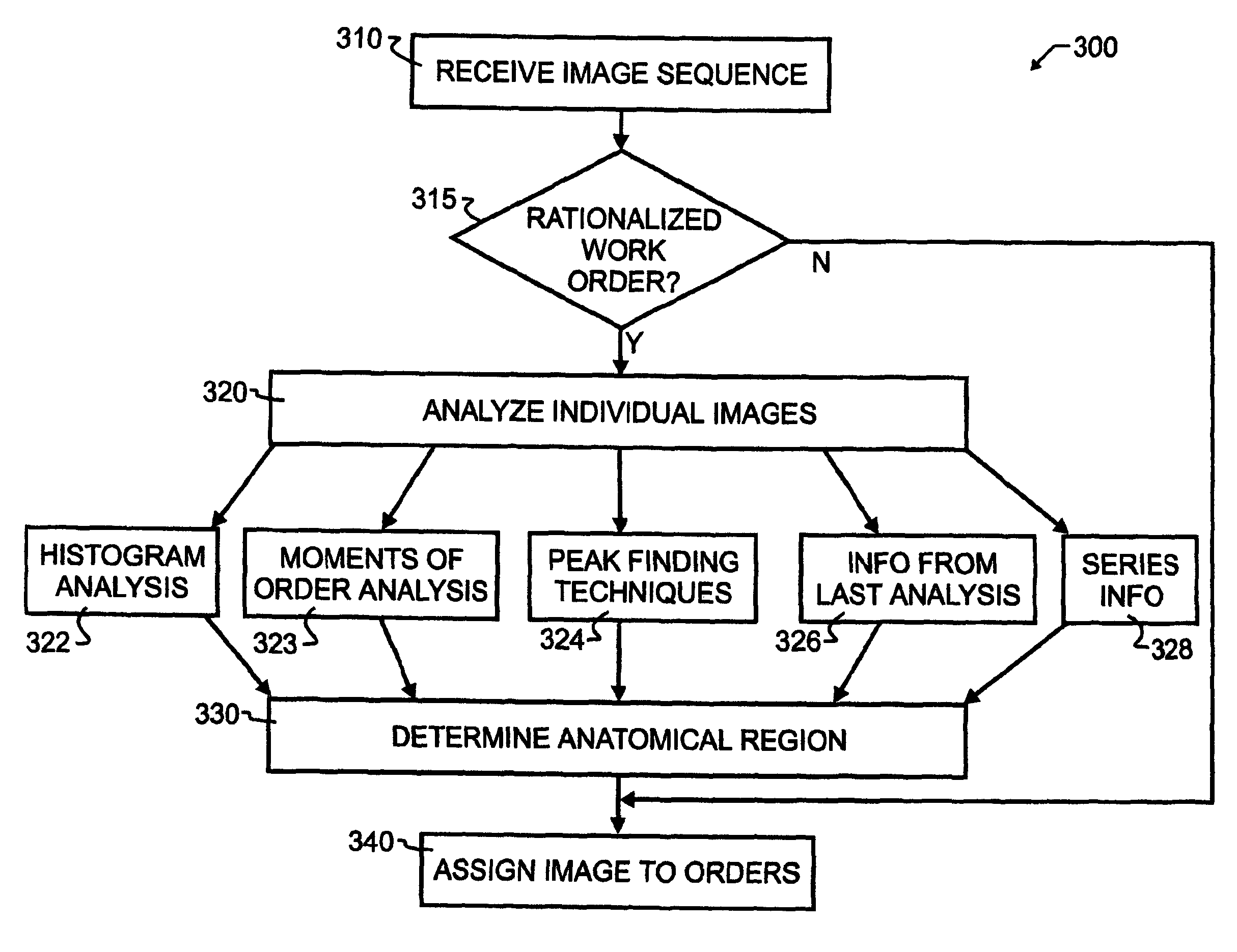
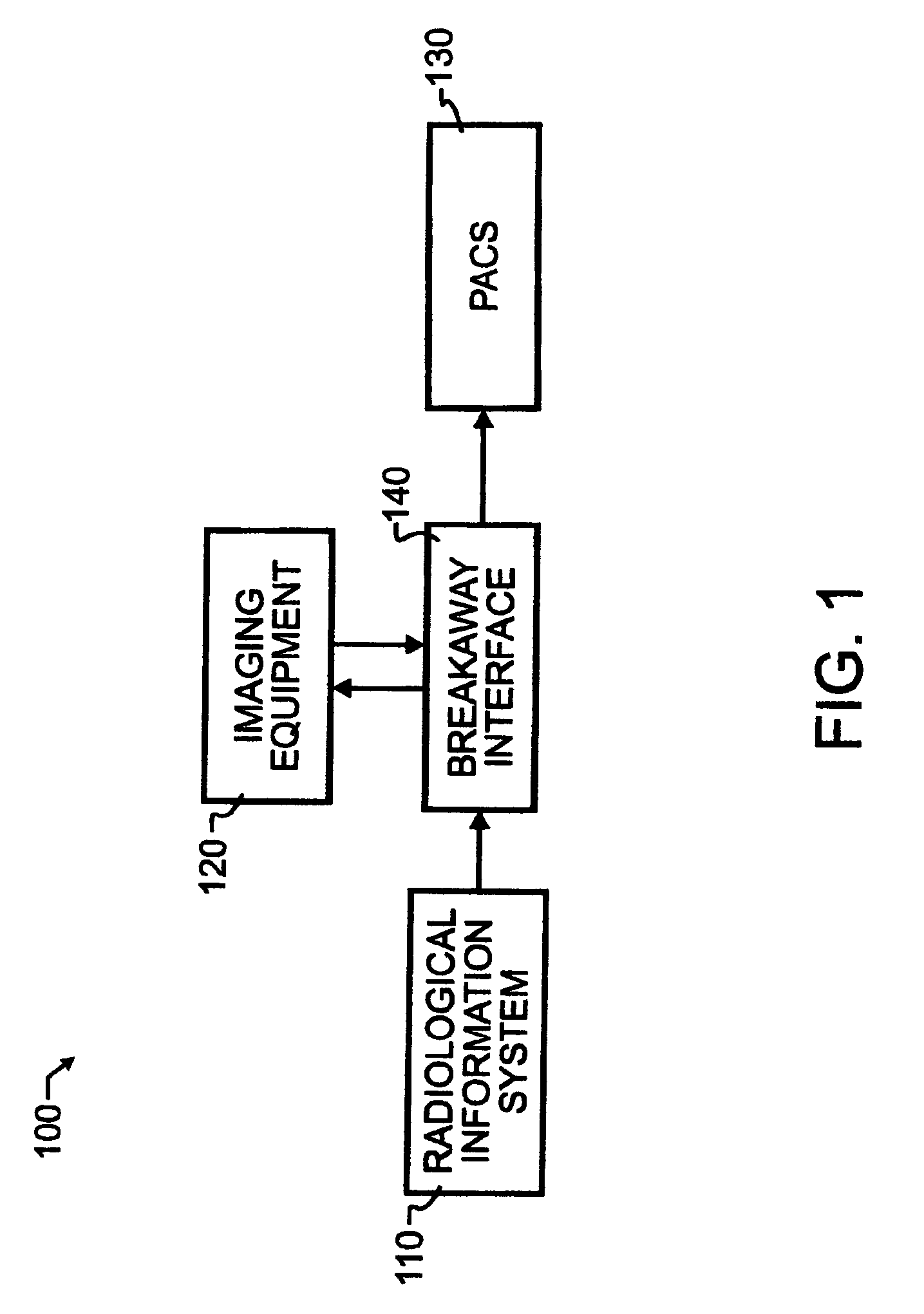
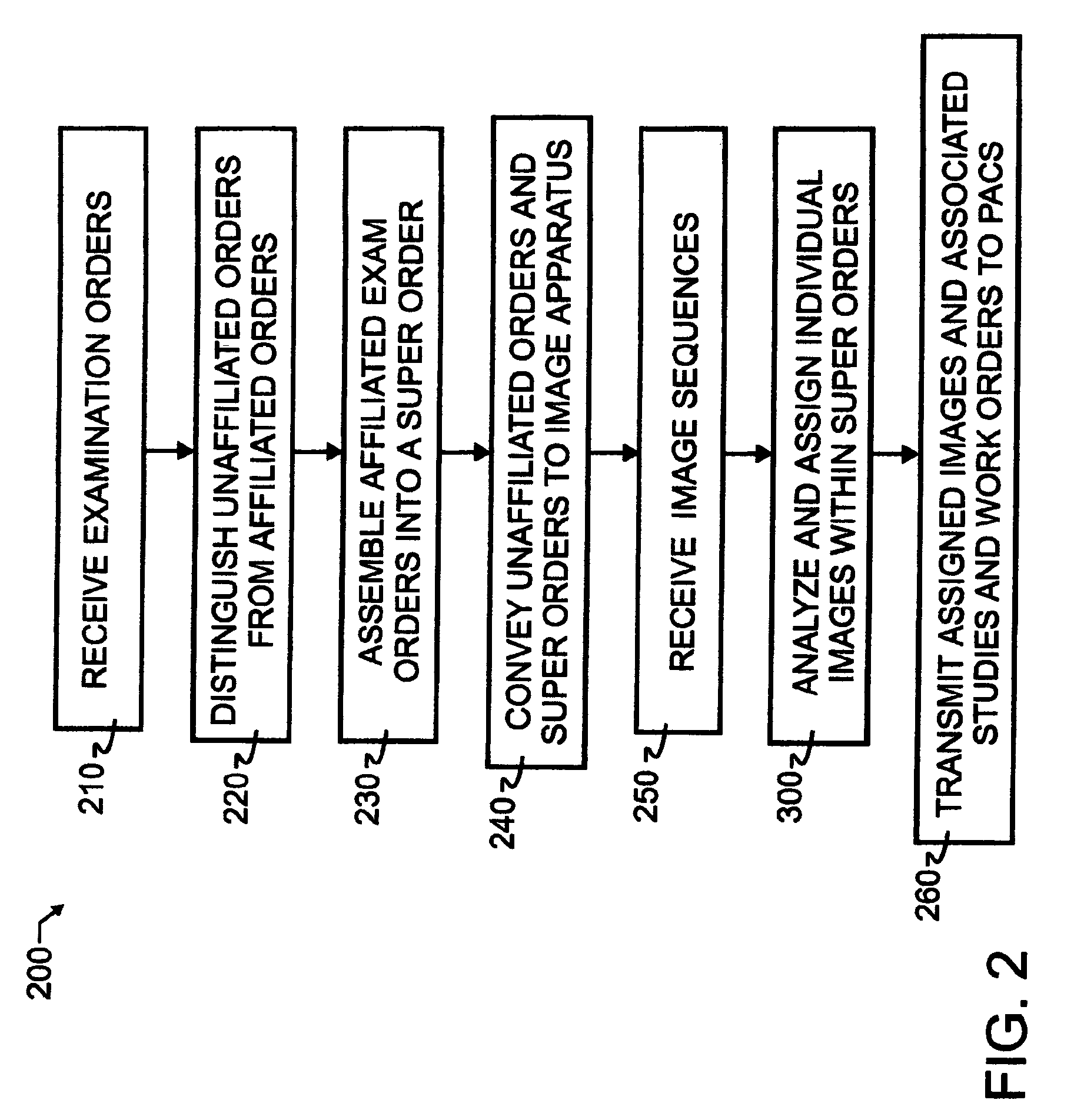
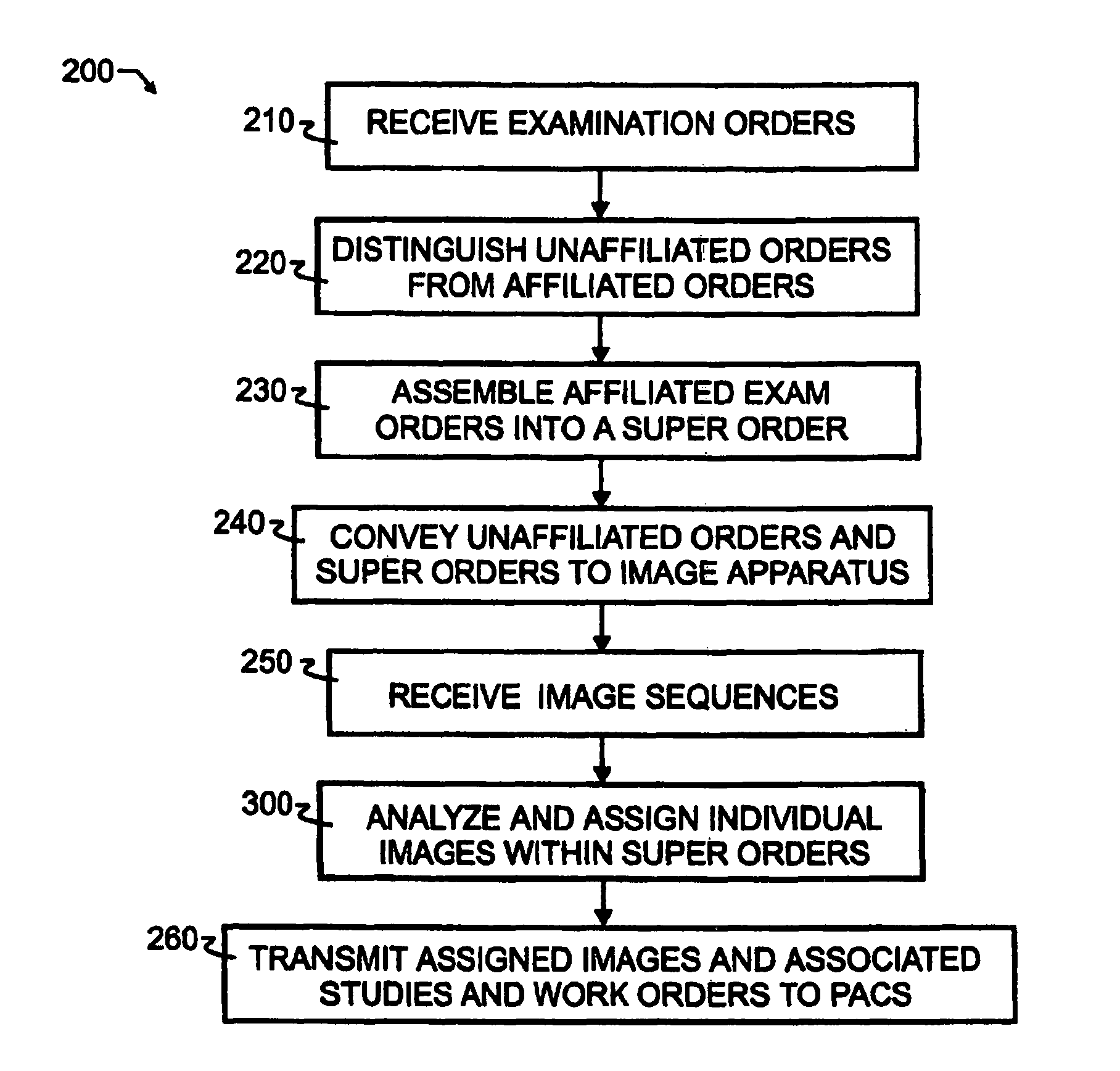
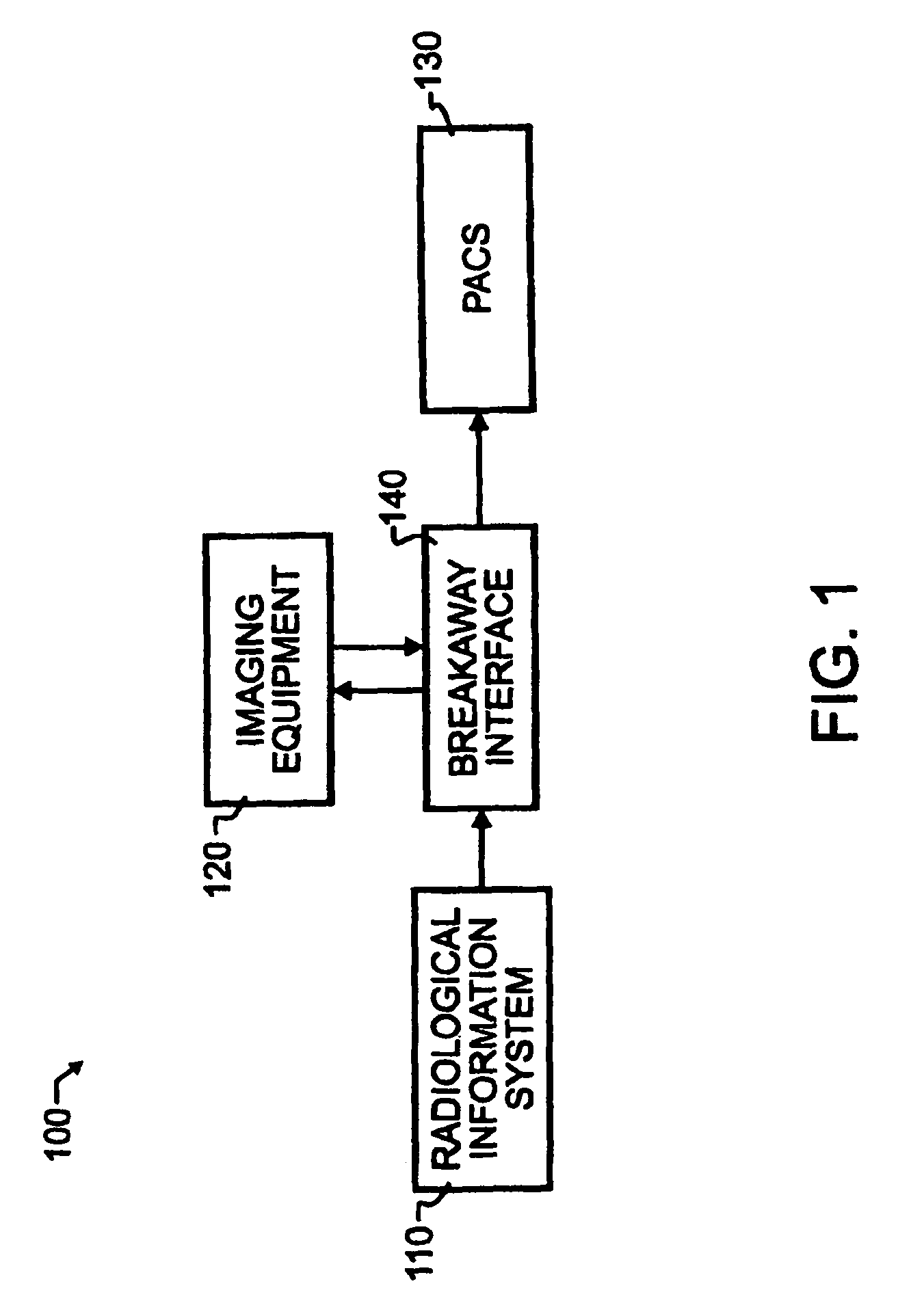
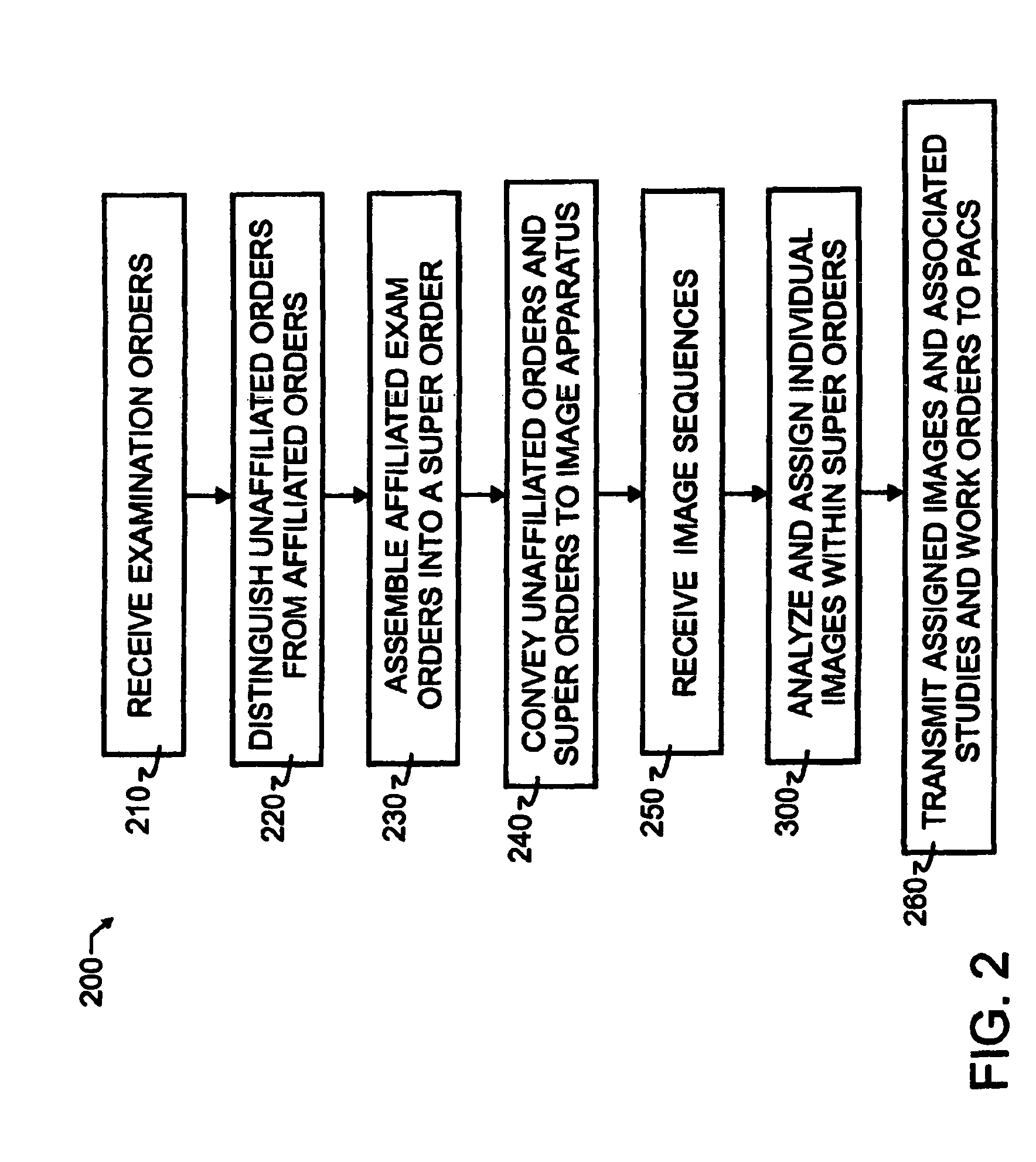
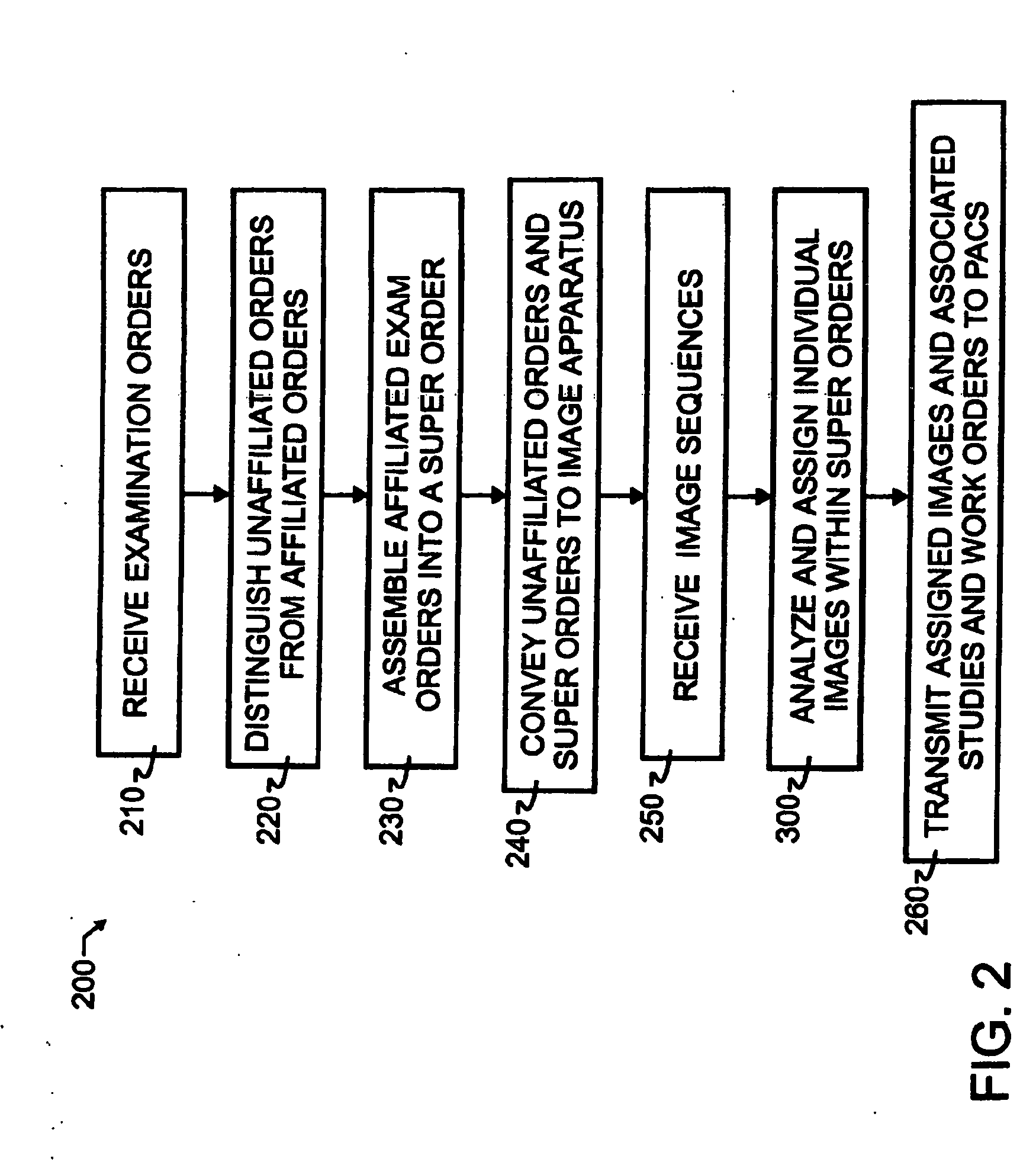
A breakaway interface between radiological information systems, imaging equipment and picture archive and communications systems has automated filtering and handling of multiple study work orders or affiliated work orders, while passing single study work orders through unaltered. The work orders are processed by the breakaway interface to consolidate multiple procedure or multiple study work orders into a single super order, which is then communicated, preferably using DICOM standard protocol, to an imaging machine. The imaging machine returns a single image sequence, and the breakaway interface will then break images away from the single image sequence into a plurality of grouped image sequences. The preferred grouping is based upon anatomical regions, and separate but adjacent anatomical regions will preferably share one or more images at the boundary between the adjacent regions. The exact number of shared images may preferably be preset at the system level. A number of different techniques for analyzing the single image sequence are proposed individually or in combination, including histogram analysis, peak finding techniques, moments of order analysis, evaluating information from one or more previous analyses, and evaluating image sequence series information to distinguish discrete imaging procedures.
Owner:DEJARNETTE RES SYST
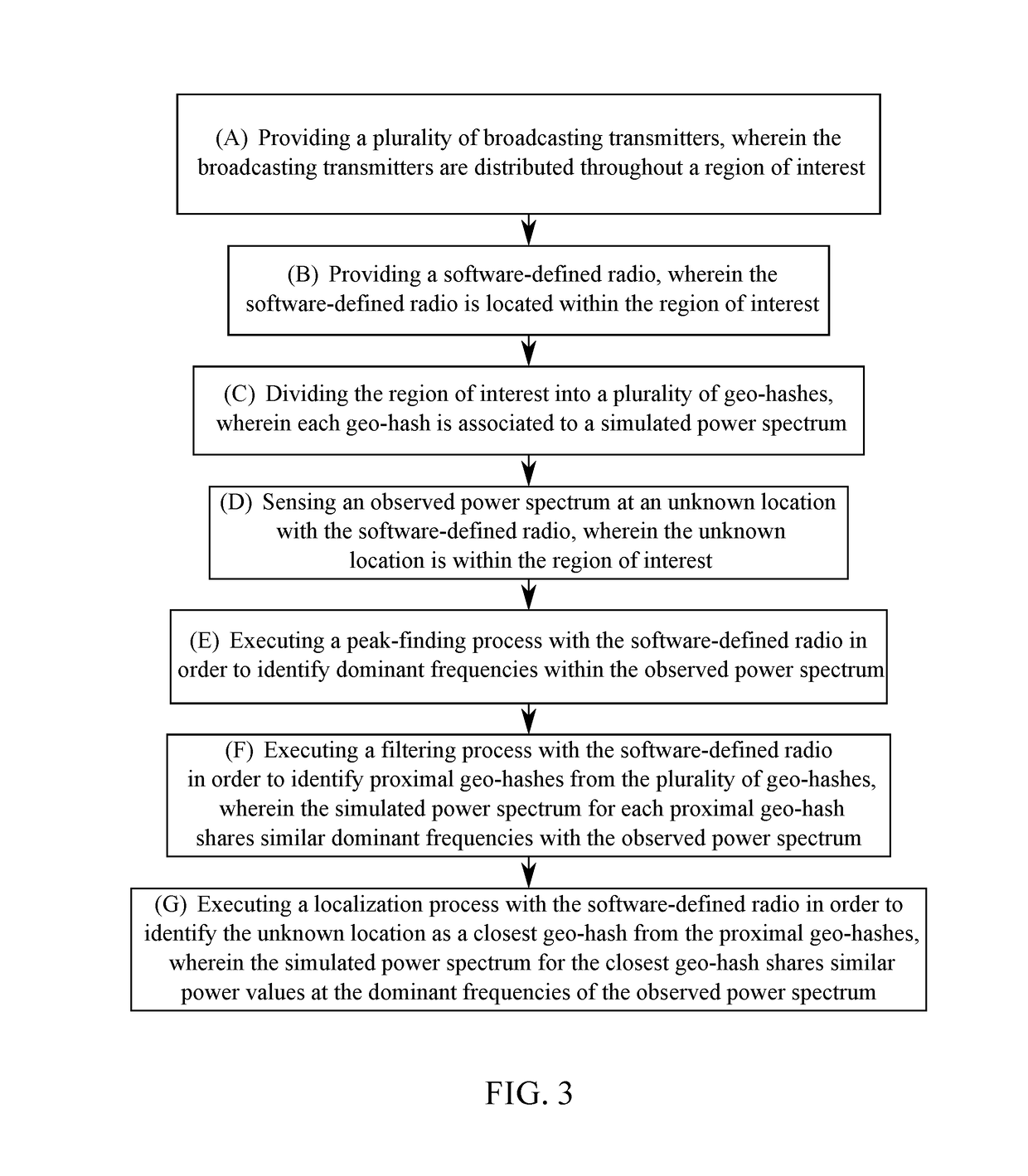
Method for Passive Approximate Localization using Frequency Modulation and Software Defined Radio
A method for localizing for GPS denied environments is provided with a plurality of broadcasting transmitters and a software-defined radio (SDR). A pre-processing stage and a query phase is executed for localizing an unknown location. The results from the preprocessing stage are made available to the query stage. A simulated power spectrum is computed for a region of interest during the pre-processing phase via the plurality of broadcasting transmitters. A transmitter location, a radius of influence, and a power contour plot of each of the plurality of broadcasting transmitters are used for computing the simulated power spectrum. Next, a peak-finding process, a filtering process, and a localization process is executed during the query phase in order to identify the unknown location.
Owner:KUMAR PIYUSH +3
Grating preparation on-line monitoring method and system
ActiveCN109000694AEnable real-time feedbackReal-time monitoring of reflectivityConverting sensor output opticallyGratingPeak finding
The invention provides a grating preparation on-line monitoring method and system. The method comprises the following steps that a j.i matrix is formed by equal-interval grating array data collected in one scanning period, wherein the row of the matrix represents wavelength steps, and the column represents sampling points, j is the total number of the wavelength steps, and i is the number of all the sampling points; peak finding is carried out on the j.i matrix column by column, and the actual position of the grating is obtained; according to the space position information of m gratings, the mcolumns of data in the corresponding positions in the equal-interval grating array data matrix are taken out to obtain a j-m matrix; each column of data is accumulated to obtain a new 1*i matrix [n1,n2, until ni], wherein ni is composed of j data points, and for each ni, [lambda]1-i until [lambda]j-i are compared in sequence to obtain the maximum values [x1, x2 until xi] of each column; assumingthat the initial wavelength of a scanning light source is set to be [lambda] 0, the wavelengths of the gratings to be measured are [lambda 1, lambda 2, until lambda i], wherein [lambda] i is equal to[lambda] 0+ xi / 1000; the weighted average value of the wavelengths of the gratings to be measured is taken to obtain an average wavelength value, and the difference value between the wavelengths of the gratings to be measured and the average wavelength is further obtained; and the wavelength difference value is compared with a standard difference value [delta] in sequence, wherein if the wavelength difference value is larger than the standard deviation value, the grating wavelength is abnormal.
Owner:武汉烽理光电技术有限公司 +1
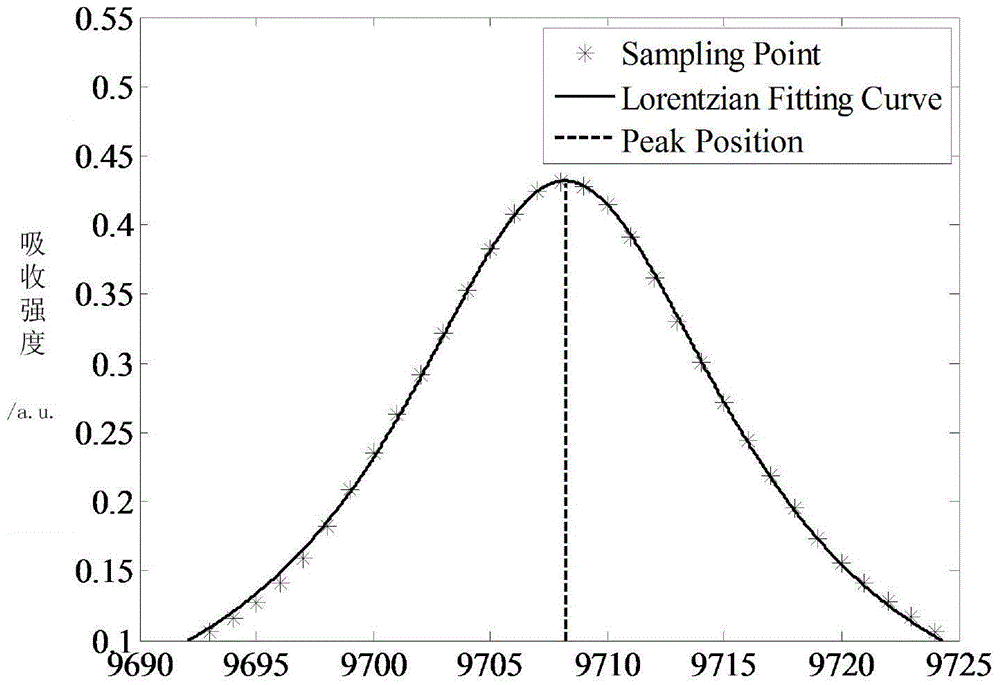
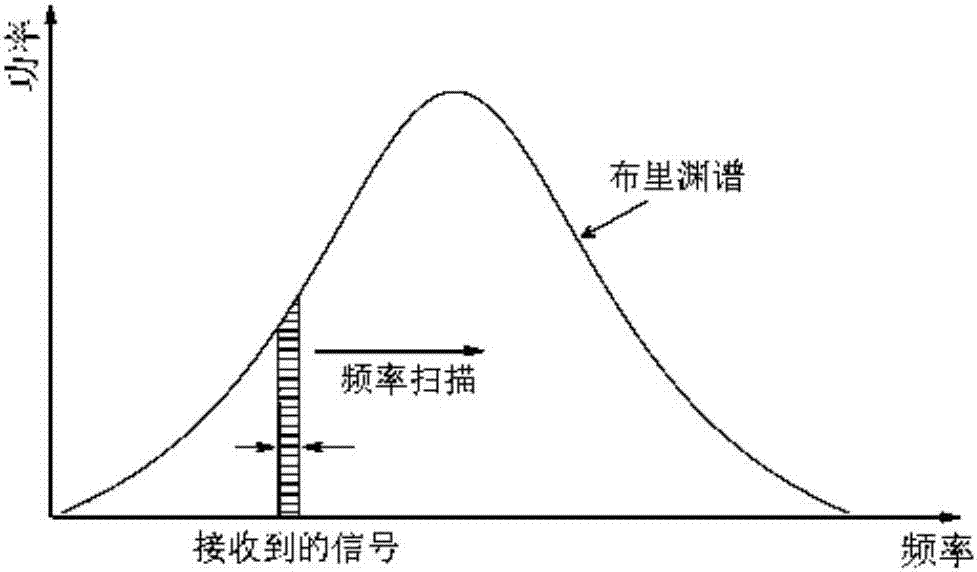
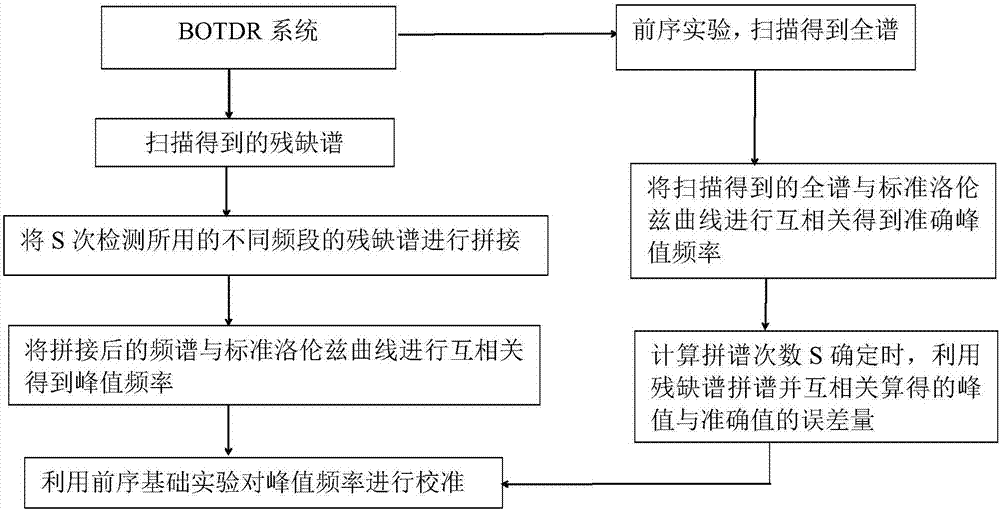
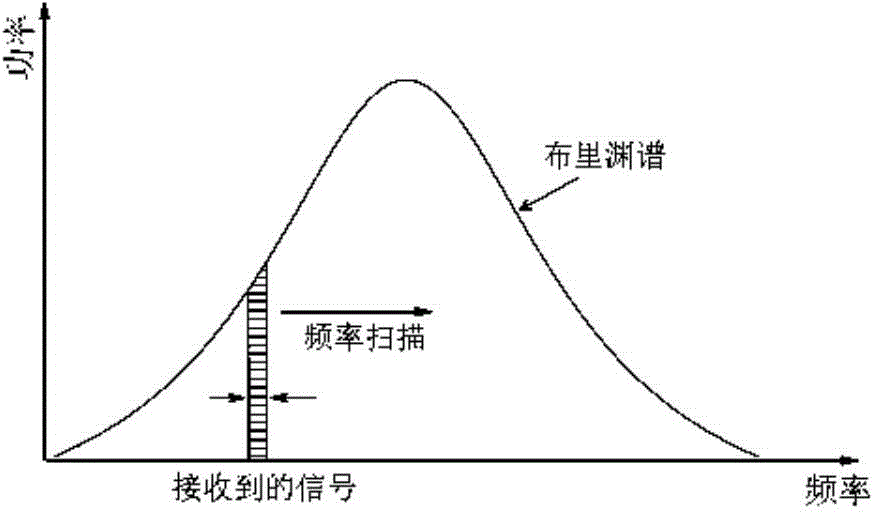
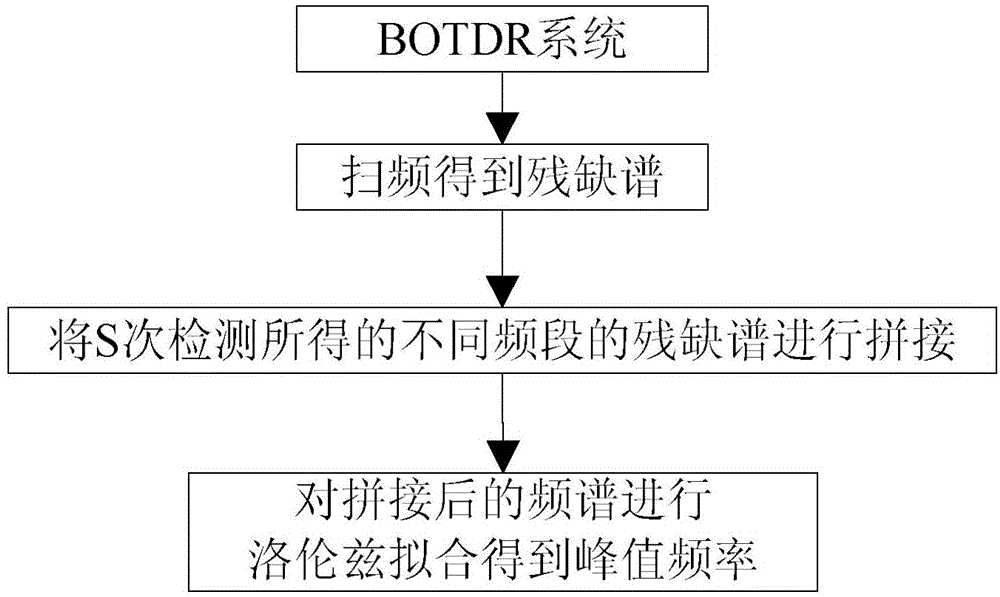
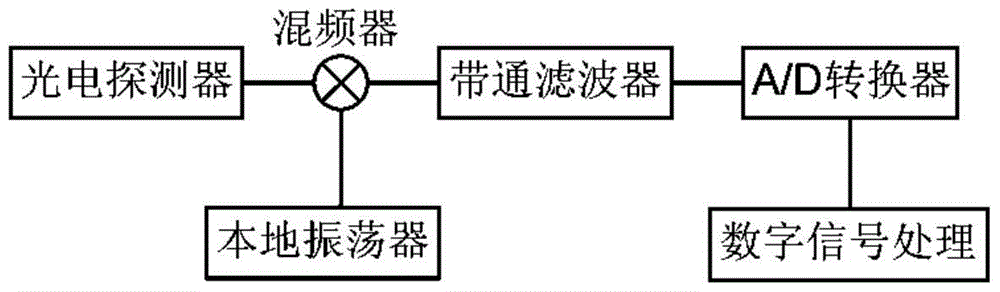
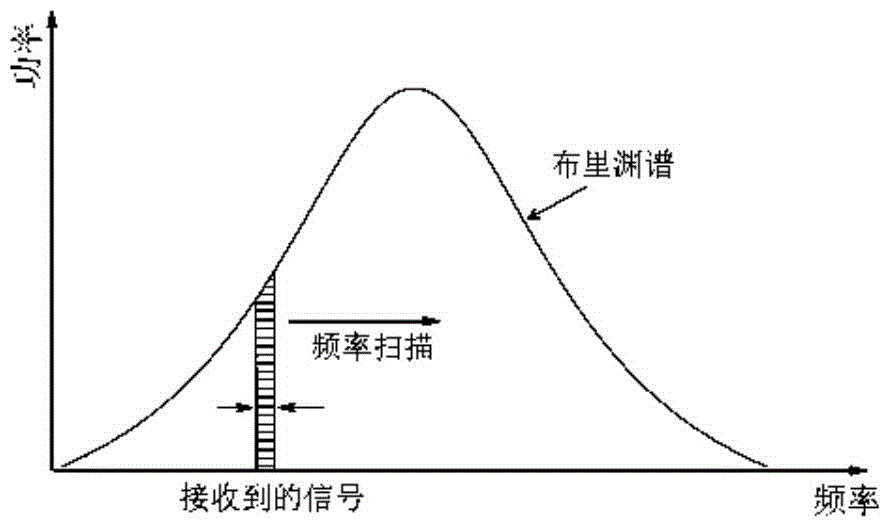
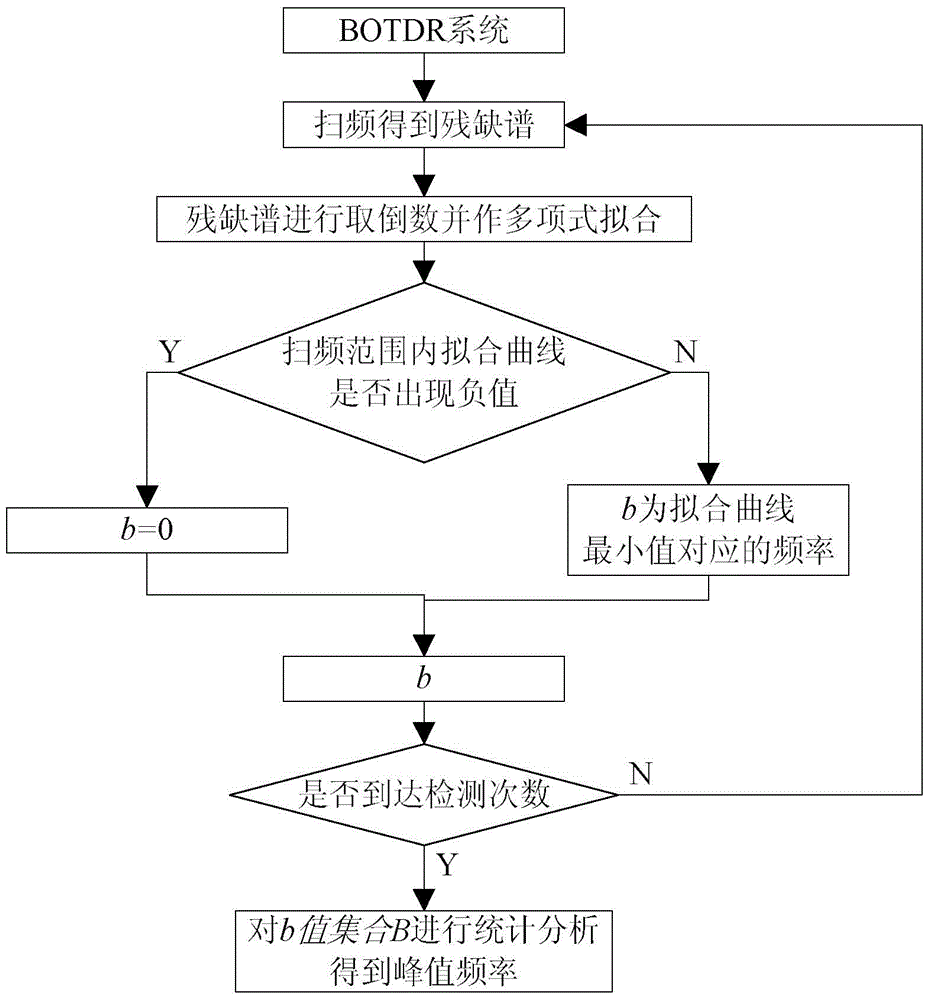
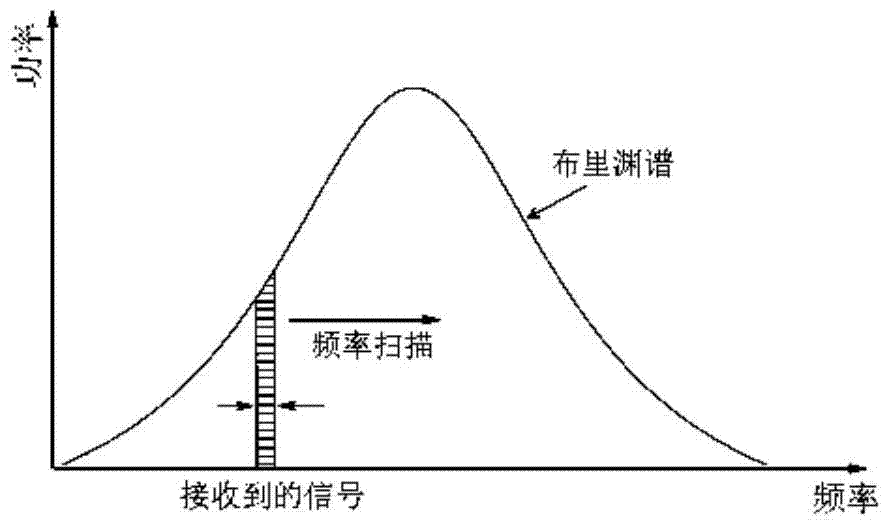
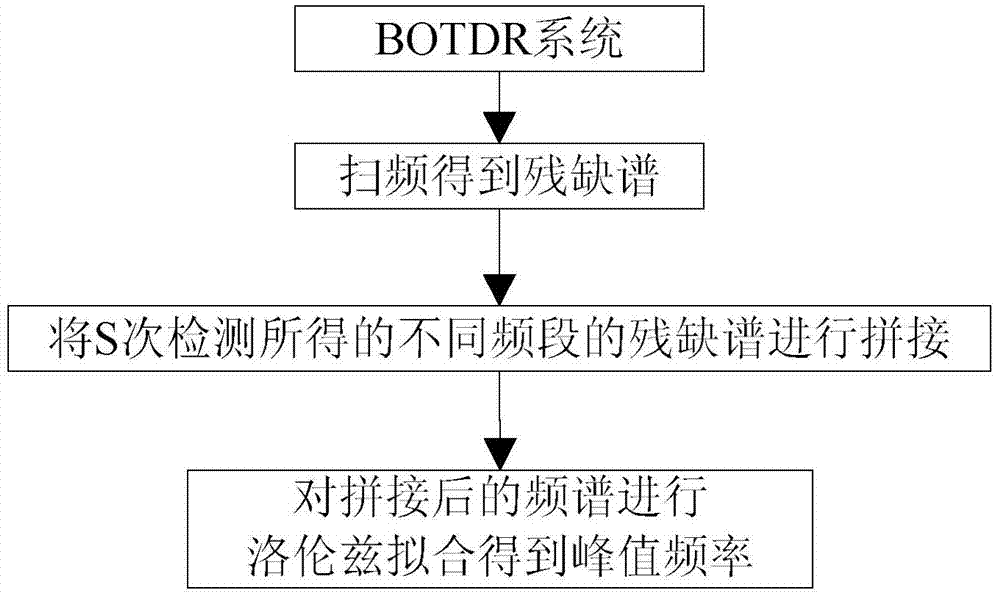
BOTDR cross-correlation peak finding method based on defective spectrum splicing
InactiveCN107084808AMake up for insensitivityImprove Sensing PerformanceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationConverting sensor output opticallyPeak findingPeak value
The invention discloses a BOTDR cross-correlation peak finding method based on defective spectrum splicing. The method comprises steps of in case of a certain scanning frequency, carrying out spectrum splicing on acquired defective spectrums; carrying out correlation operation on the spectrum splicing and standard Lorentzen curves to obtain the real peak value frequency of a Brillouin spectrum; and through a preorder experiment, determining spectrum splicing frequency and optimizing peak finding frequency on the basis of meeting error ranges required in actual application. According to the invention, by carrying out splicing processing on the data after measurement, the cross-correlation algorithm is properly used when the peak value frequency of the Brillouin spectrum by use of the defective spectrums, so efficiency and accuracy for carrying out Brillouin peak finding on the defective spectrums are improved; insensitivity to external interference of rapid change of the BOTDR is overcome; sensing effects of the BOTDR in an extreme environment are improved; and the method has an important meaning for actual engineering application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
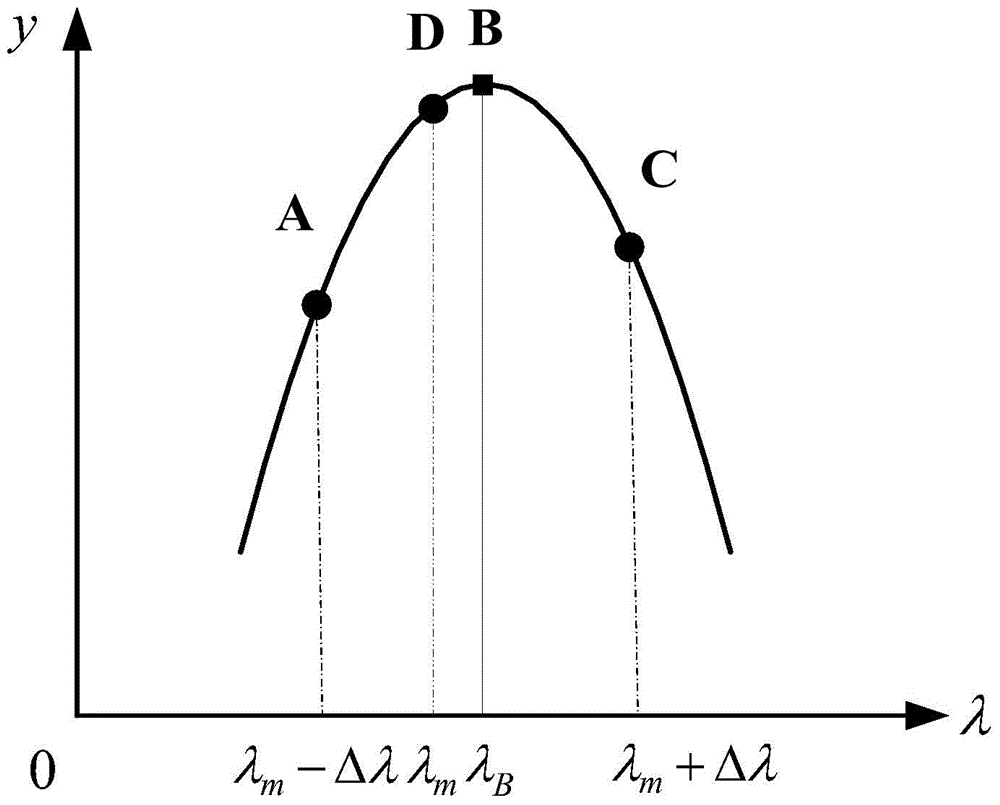
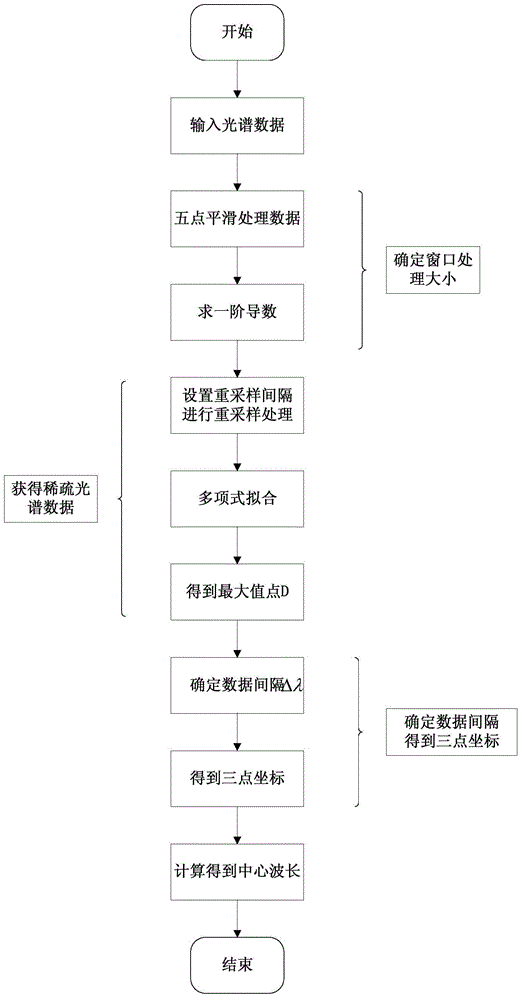
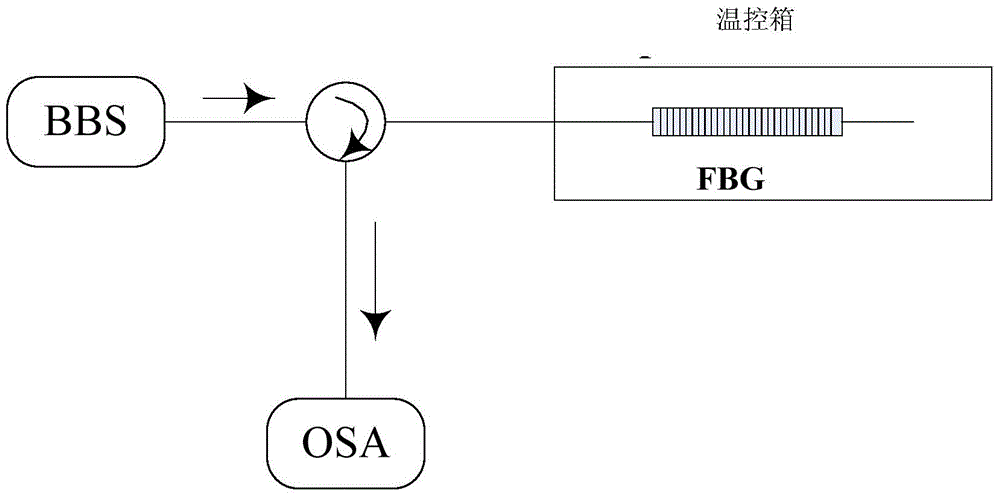
Method of Processing FBG Sensing Signal Using Three-Point Peak-finding Algorithm
ActiveCN103487074BImprove demodulation accuracyProcessing less dataConverting sensor output opticallyPeak findingFiber Bragg grating
The invention relates to an implementation method for processing an FBG (fiber bragg grating) sensing signal based on a three-point peek-seeking algorithm. The method comprises the steps of providing a peek-seeking processing flow, and giving three elements influencing the peek-seeking accuracy according to the flow, wherein reasonable selection of a window size is a key point for improving the peek-seeking accuracy, and the size of a spectral processing window is determined by adopting a derivation method; the spectrum in the window is resampled by arranging sampling intervals, and sparse spectrum data is acquired and subjected to polynomial fitting; a proper wavelength interval delta lambda is selected according to the fitting result, the coordinates of three points can be determined, the peak value of the FBG reflectance spectrum is detected, so that the central wavelength can be acquired, and external physical parameters can be demodulated.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
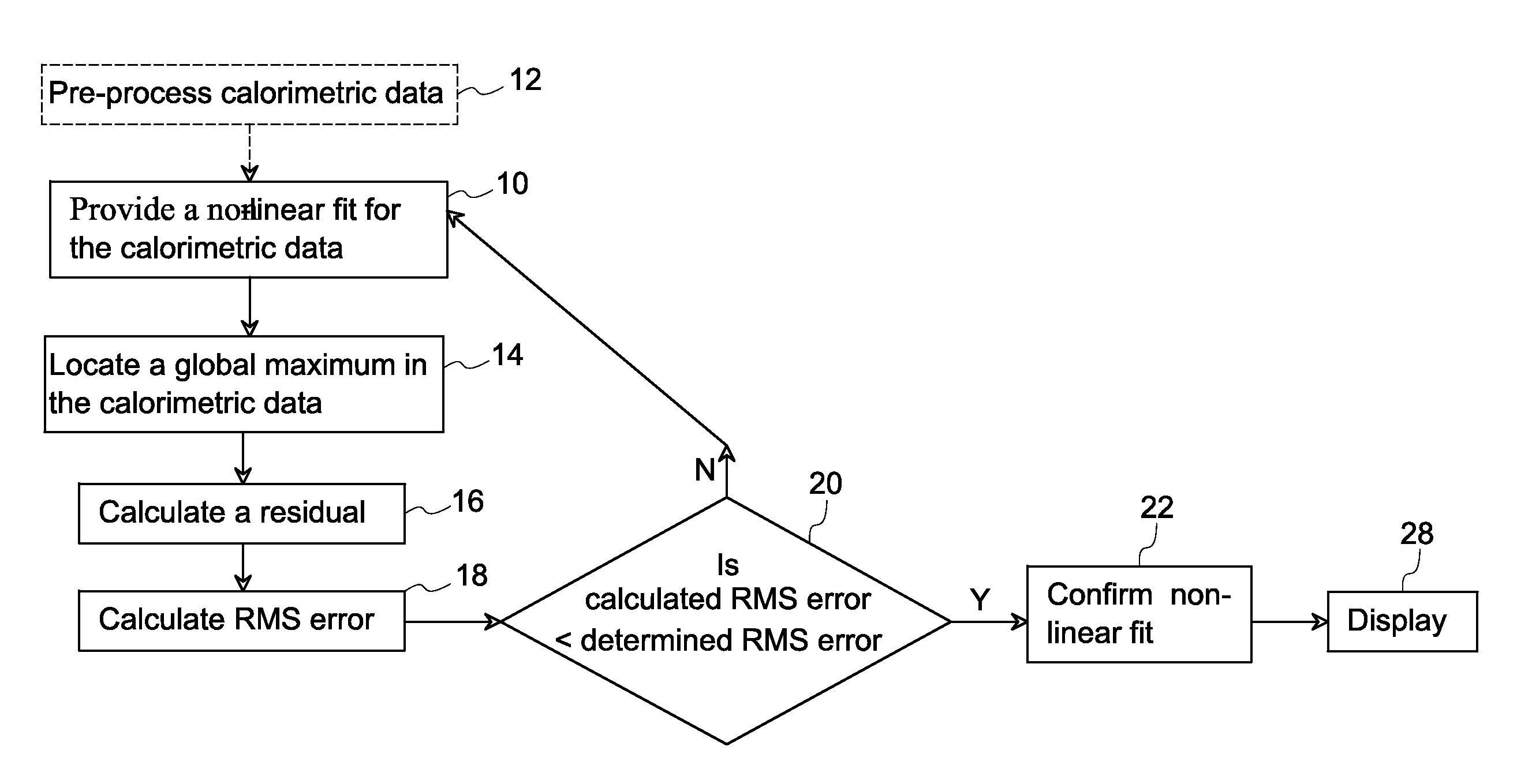
Methods for automatic peak finding in calorimetric data
Owner:MALVERN PANALYTICAL INC
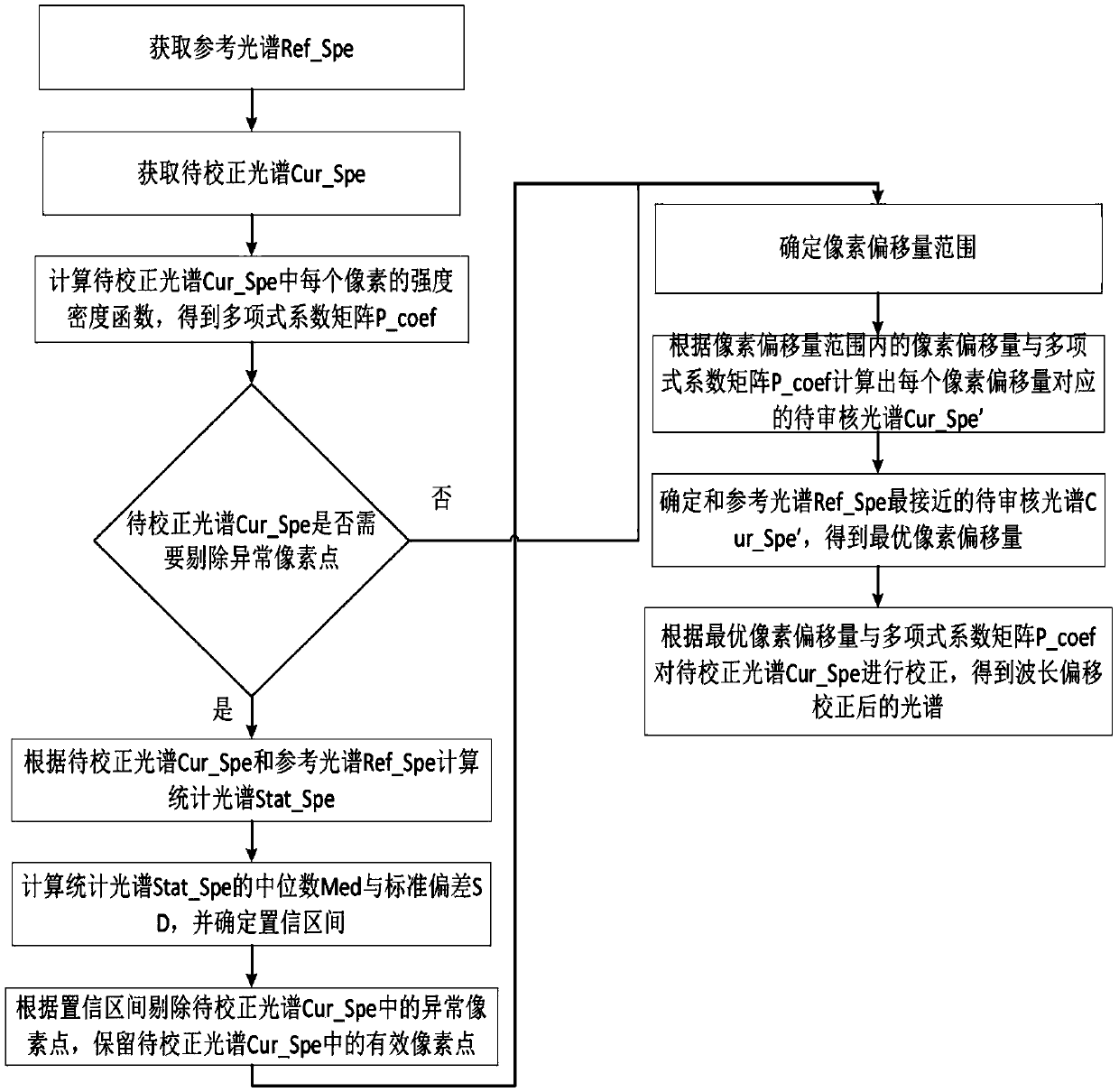
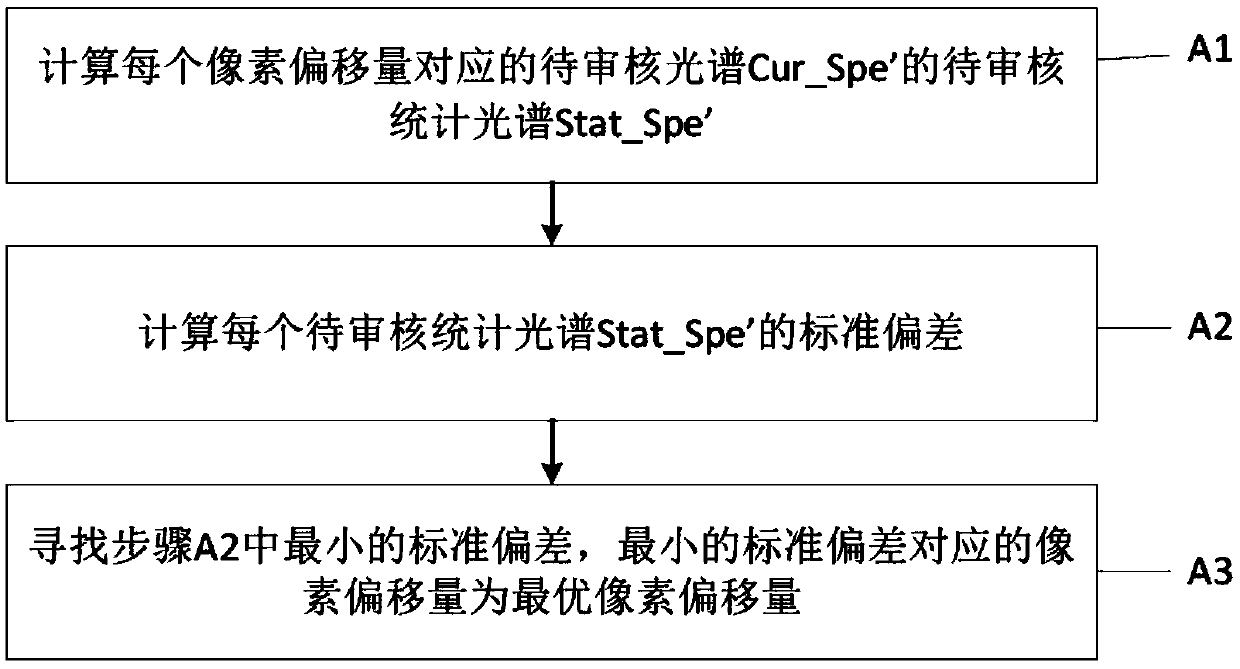
Wavelength offset correction method and device and computer device
ActiveCN109655415AColor/spectral properties measurementsComplex mathematical operationsPeak findingLength wave
The invention discloses a wavelength offset correction method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring a reference spectrum and a spectrum to be corrected; calculating an intensity density function of each pixel in the spectrum to be corrected to obtain a polynomial coefficient matrix, wherein each group of polynomial coefficients in the polynomial coefficient matrix are coefficients ofthe intensity density function of one pixel in the spectrum to be corrected respectively; determining a pixel offset range; calculating a spectrum to be audited corresponding to each pixel offset according to the pixel offset in the pixel offset range and the polynomial coefficient matrix; determining the spectrum to be audited which is closest to the reference spectrum to obtain the optimal pixeloffset; correcting the spectrum to be corrected according to the optimal pixel offset and the polynomial coefficient matrix to obtain the spectrum after wavelength offset correction. The wavelength offset correction method can correct the non-integer multiple pixel offset of the spectral data without depending on a peak finding method. The method also discloses a wavelength offset correction device and a computer device.
Owner:浙江全世科技有限公司
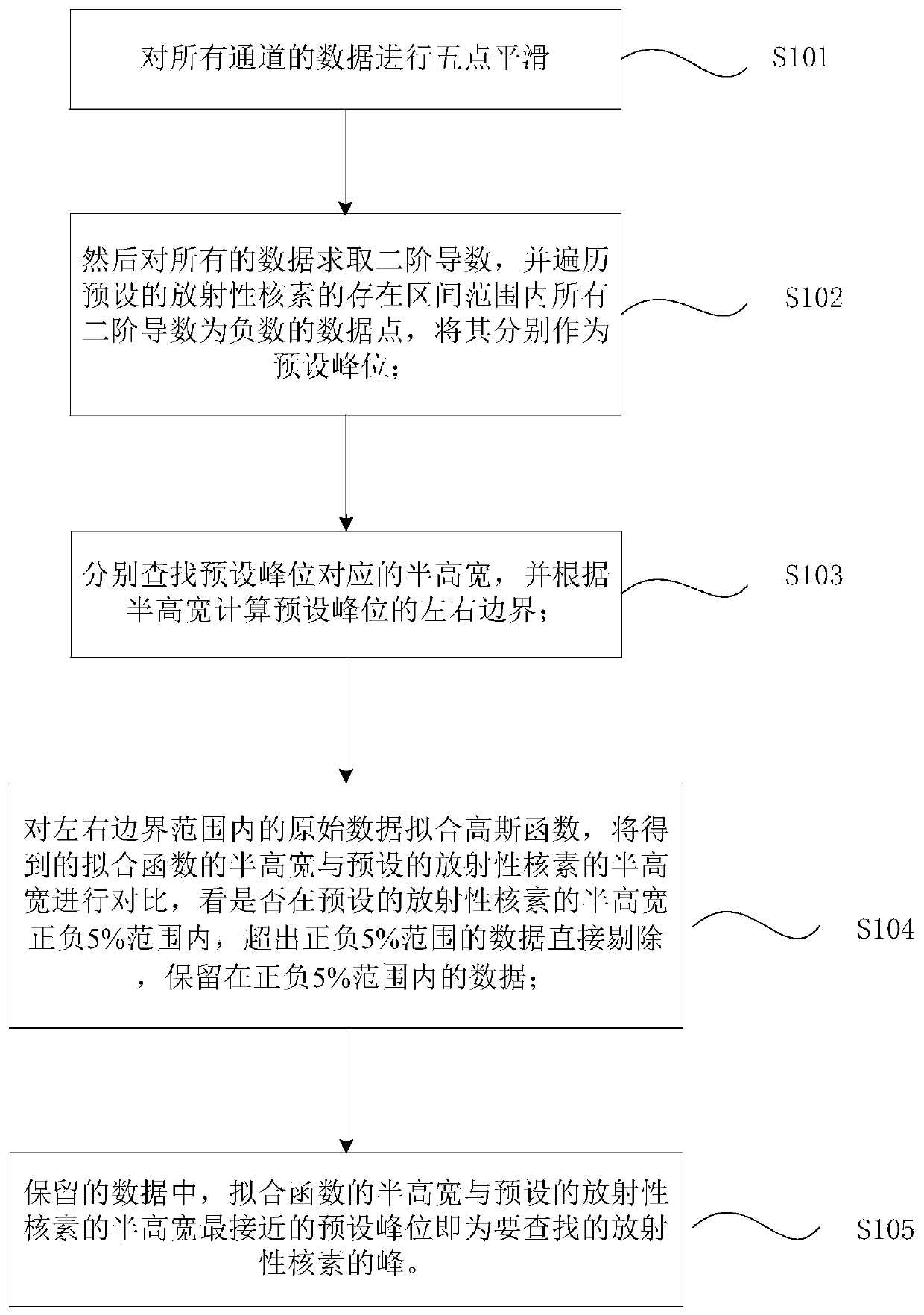
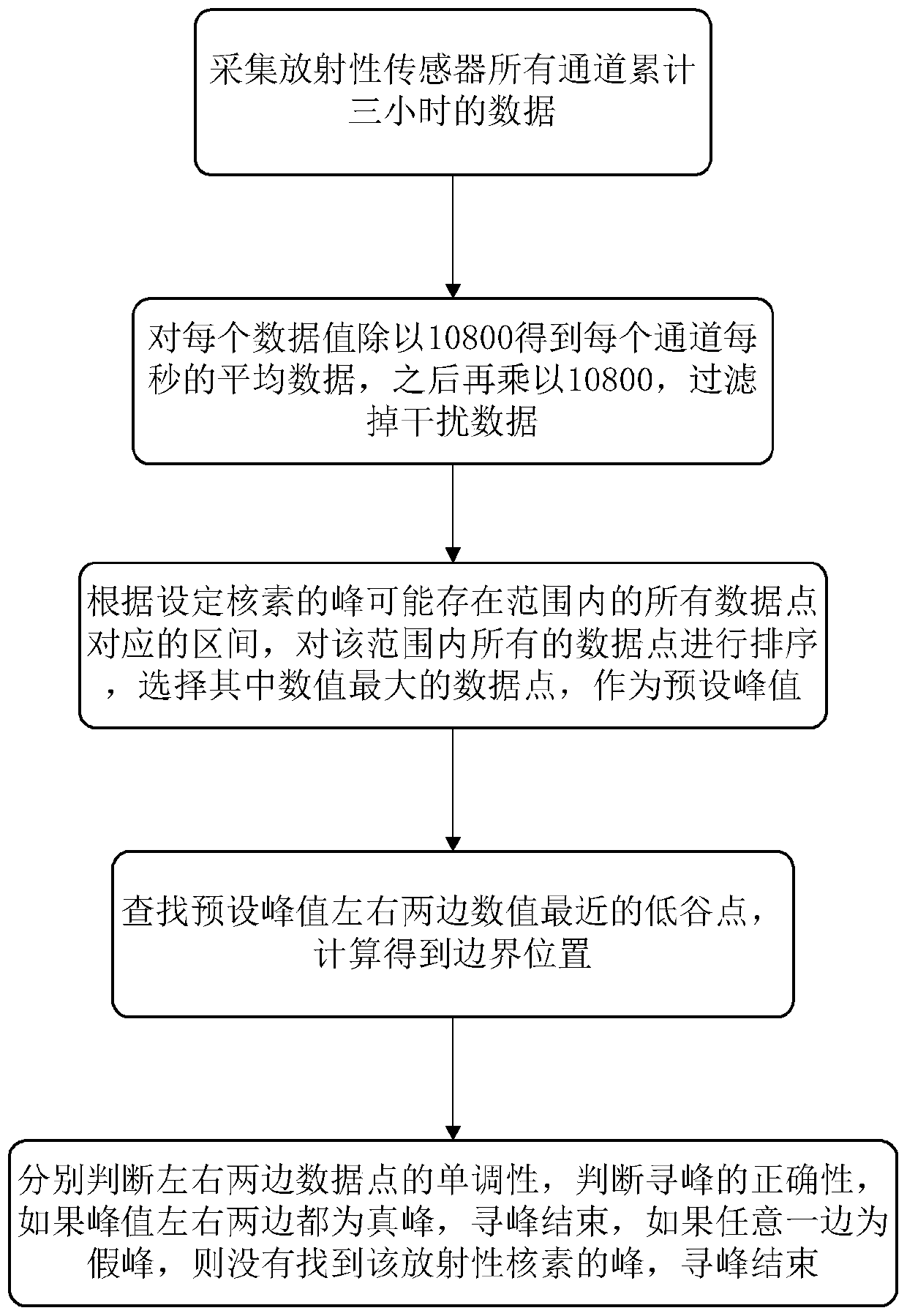
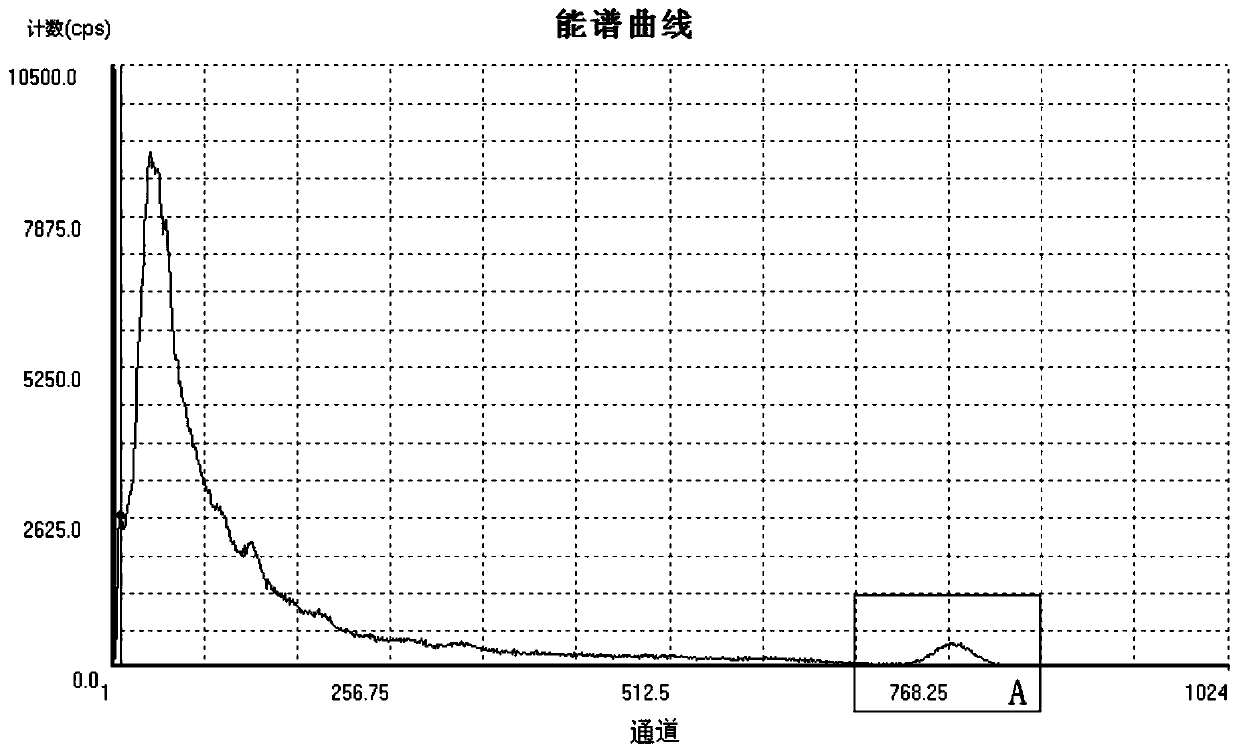
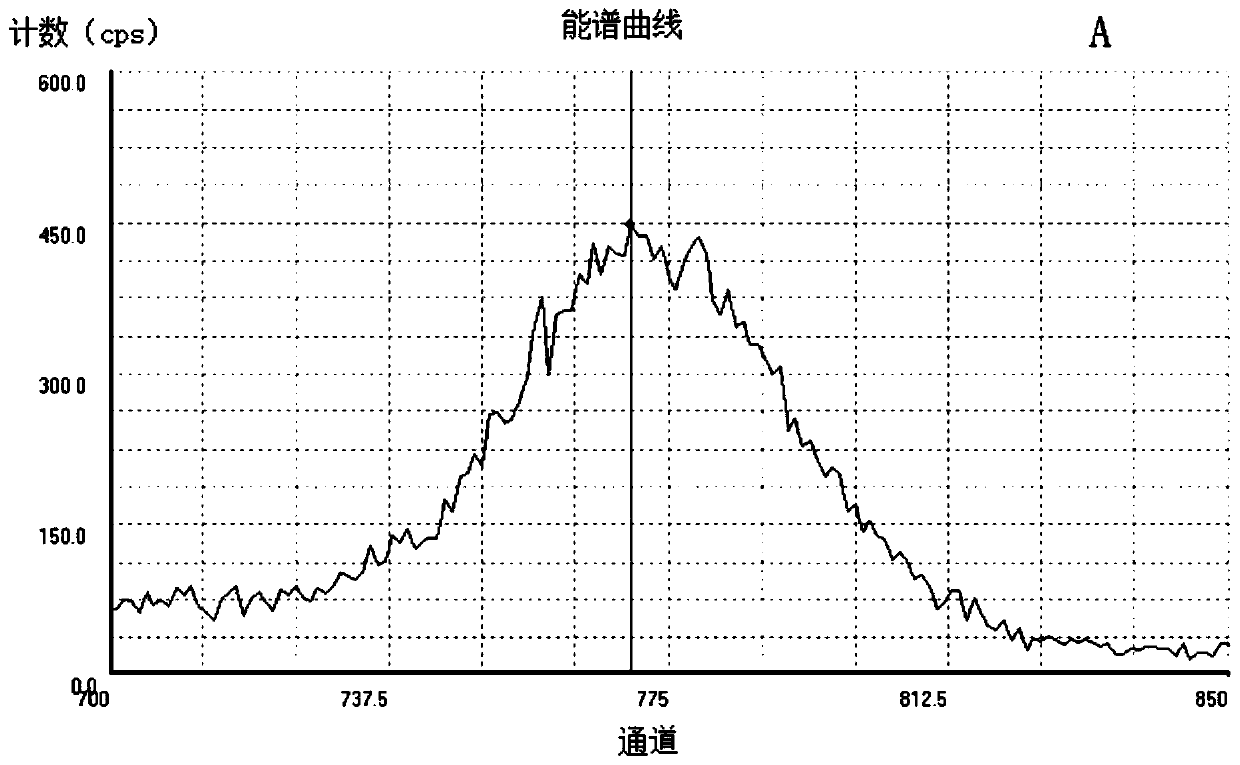
An automatic peak-finding method for seawater radioactivity detection
The invention discloses an automatic peak searching method for seawater radioactivity detection. The method comprises: five-point smoothing of data of all channels is carried out; second-order derivatives for all data are calculated, all second-order derivatives in a preset radionuclide existence zone range are traversed to be negative data points as preset peak positions; left and right boundaries of the preset peak positions are calculated; Gaussian function fitting of original data in the left and right boundary ranges is carried out, the full width at half maximum of each obtained fittingfunction is compared with a preset full width at half maximum of the radionuclide, data exceeding the range of plus or minus 5% are directly eliminated, and the preset peak position with the fitting function having the full width at half maximum closest to the preset full width at half maximum of the radionuclide is determined as a to-be-searched radionuclide peak. The disclosed automatic peak searching method is free from the accumulation time restriction as well as the restriction of the interference of the marine environment; overlapped peaks can be identified; and some obvious false peakscan be filtered automatically. Therefore, the peak searching accuracy is improved.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Breakaway interfacing of radiological images with work orders
InactiveUS8463621B2Easy to useImproved and more highly automated communicationOffice automationMedical imagesPeak findingSingle image
A breakaway interface between radiological information systems, imaging equipment and picture archive and communications systems has automated filtering and handling of multiple study work orders or affiliated work orders, while passing single study work orders through unaltered. The work orders are processed by the breakaway interface to consolidate multiple procedure or multiple study work orders into a single super order, which is then communicated, preferably using DICOM standard protocol, to an imaging machine. The imaging machine returns a single image sequence, and the breakaway interface will then break images away from the single image sequence into a plurality of grouped image sequences. The preferred grouping is based upon anatomical regions, and separate but adjacent anatomical regions will preferably share one or more images at the boundary between the adjacent regions. The exact number of shared images may preferably be preset at the system level. A number of different techniques for analyzing the single image sequence are proposed individually or in combination, including histogram analysis, peak finding techniques, moments of order analysis, evaluating information from one or more previous analyses, and evaluating image sequence series information to distinguish discrete imaging procedures.
Owner:DEJARNETTE RES SYST
Brillouin spectrum peak finding method based on incomplete spectrum splicing
ActiveCN104807568AMake up for insensitivityImprove Sensing PerformanceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationPeak findingPeak value
The invention discloses a Brillouin spectrum peak finding method based on incomplete spectrum splicing. The method comprises performing splicing treatment on measured data, and on the basis of incomplete spectra, obtaining the peak frequency of real Brillouin spectra. The Brillouin spectrum peak finding method based on incomplete spectrum splicing remedies the insensitivity of a BOTDR (Brillouin optical time domain reflectometer) to rapidly-changed external interference, improves the sensing effects of the BOTDR in extreme environments and is significant to practical engineering application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Breakaway interfacing of radiological images with work orders
InactiveUS20100268547A1Improved and more highly automated communicationReduce needOffice automationMedical imagesPeak findingSingle image
A breakaway interface between radiological information systems, imaging equipment and picture archive and communications systems has automated filtering and handling of multiple study work orders or affiliated work orders, while passing single study work orders through unaltered. The work orders are processed by the breakaway interface to consolidate multiple procedure or multiple study work orders into a single super order, which is then communicated, preferably using DICOM standard protocol, to an imaging machine. The imaging machine returns a single image sequence, and the breakaway interface will then break images away from the single image sequence into a plurality of grouped image sequences. The preferred grouping is based upon anatomical regions, and separate but adjacent anatomical regions will preferably share one or more images at the boundary between the adjacent regions. The exact number of shared images may preferably be preset at the system level. A number of different techniques for analyzing the single image sequence are proposed individually or in combination, including histogram analysis, peak finding techniques, moments of order analysis, evaluating information from one or more previous analyses, and evaluating image sequence series information to distinguish discrete imaging procedures.
Owner:DEJARNETTE RES SYST
A Peak Finding Method of Brillouin Spectrum Based on Incomplete Spectrum
ActiveCN104457807BMake up for insensitivityImprove Sensing PerformanceConverting sensor output opticallyFrequency spectrumPeak finding
The invention discloses a Brillouin frequency spectrum peak searching method based on incomplete spectra. According to the practical BOTDR engineering application background, data are processed after measurement is conducted, and thus the real peak frequency of Brillouin frequency spectra is obtained based on the incomplete spectra. By means of the Brillouin frequency spectrum peak searching method, the insensitivity of a BOTDR on external interference which changes quickly is compensated for, the sensing effect of the BOTDR under the extreme environment is improved, and great significance on the practical engineering application is achieved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
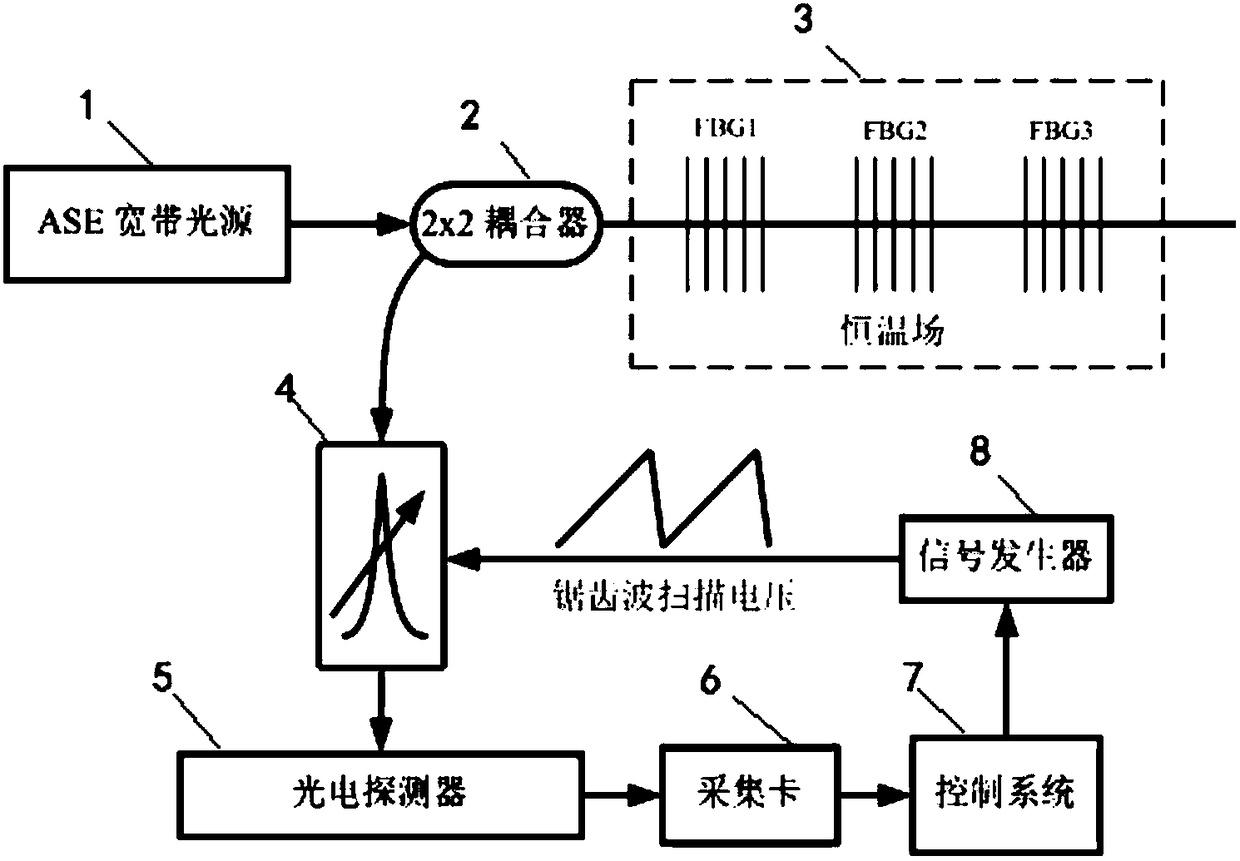
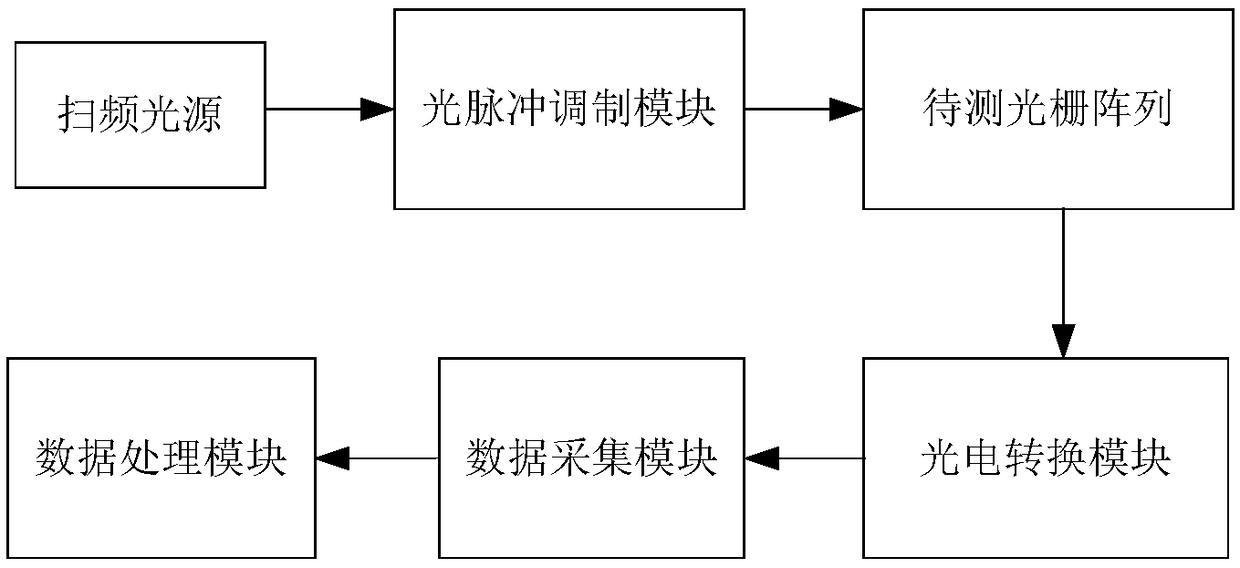
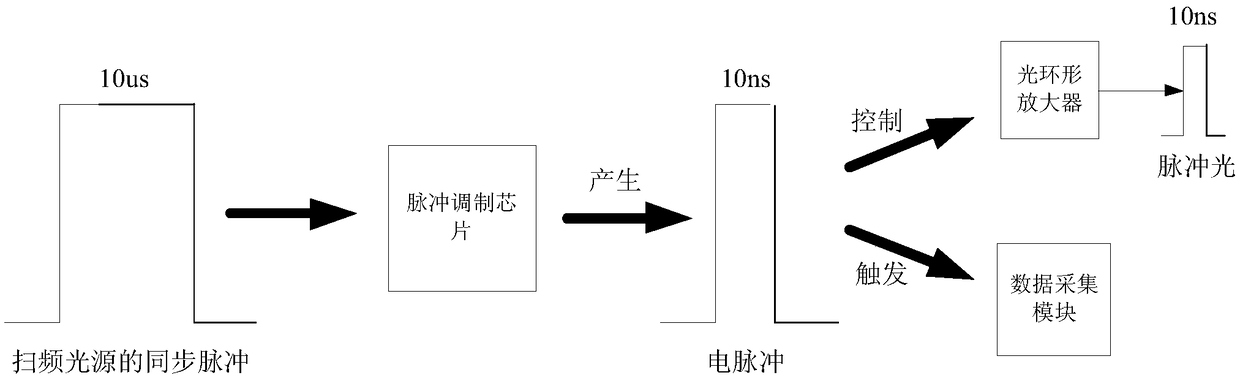
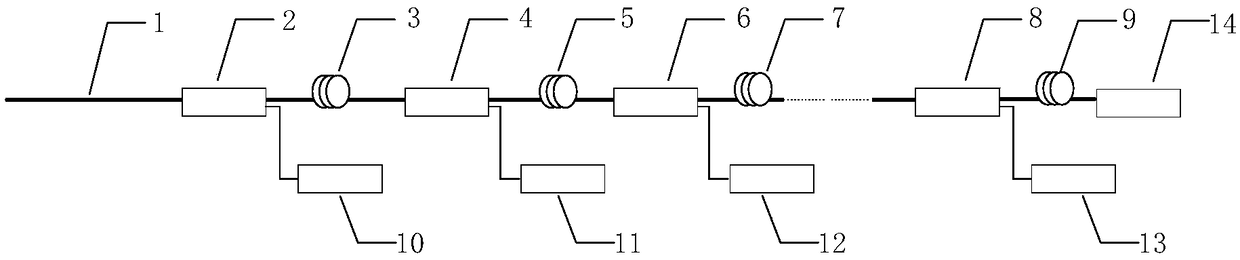
Optical fiber grating sensor array and wavelength demodulating system thereof
InactiveCN109163744AIncrease capacityImprove reusabilityConverting sensor output opticallySensor arrayBeam splitter
The invention discloses an optical fiber grating sensor array and a wavelength demodulating system thereof. The fiber grating sensor array is formed by connecting a plurality of the same optical fibersensor array sections with a main optical fiber connected with an optical fiber delay line through an optical fiber beam splitter with different light splitting ratios. The wavelength demodulation system of the optical fiber grating sensor array is composed of a broadband light source, a tunable filter, a pulsed light modulator, an optical power amplifier, the optical fiber beam splitter, an etalon, an optical detector, a control and signal processing circuit and the like. The wavelength demodulation system of the optical fiber grating sensor array comprises wavelength scanning of the tunablefilter and modulation control of the pulsed light modulator in signal control, and comprises three data processing steps of optical fiber grating sensor array section data division, spectral peak finding and wavelength calculation in data processing. The optical fiber grating sensor array has the characteristics of being high in optical fiber grating sensor capacity, strong in multiplexing capability and the like, thereby having practical engineering values.
Owner:THE 715TH RES INST OF CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND CORP
Brillouin Spectrum Peak Finding Method Based on Incomplete Spectrum Mosaic
ActiveCN104807568BMake up for insensitivityImprove Sensing PerformanceForce measurement by measuring optical property variationPeak findingPeak value
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for passive approximate localization using frequency modulation and software defined radio
A method for localizing for GPS denied environments is provided with a plurality of broadcasting transmitters and a software-defined radio (SDR). A pre-processing stage and a query phase is executed for localizing an unknown location. The results from the preprocessing stage are made available to the query stage. A simulated power spectrum is computed for a region of interest during the pre-processing phase via the plurality of broadcasting transmitters. A transmitter location, a radius of influence, and a power contour plot of each of the plurality of broadcasting transmitters are used for computing the simulated power spectrum. Next, a peak-finding process, a filtering process, and a localization process is executed during the query phase in order to identify the unknown location.
Owner:KUMAR PIYUSH +3
A fast peak-finding method for the detection of radioactive substances in seawater
ActiveCN108333617BIncrease credibilityX/gamma/cosmic radiation measurmentPeak findingRadioactive agent
The invention discloses a rapid peak searching method for radioactive material detection in the seawater. The method comprises the steps of collecting the data of all channels of a radioactive sensorwithin three hours; processing each data value, and filtering out interference data; ranking all data points in an interval according to the interval corresponding to all the data points in the rangeof the peak possible existence range of a preset nuclide, and selecting a data point with the largest numerical value as a preset peak value; searching valley points closest to numerical values at theleft side and the right side of the preset peak value and calculating to obtain boundary positions; respectively judging the monotonicity of data points on the left side and the right side, and judging the correctness of the peak searching; if peaks on the left side and the right side of the peak value are true peaks, ending the peak searching; if anyone of the peaks on the left side and the right side of the peak value is a false peak, judging that no peak of the radionuclide is found out and ending the peak searching. According to the peak searching method disclosed in the invention, the interval range of nuclide distribution can be rapidly and accurately found out. The accuracy and the real-time performance of the measurement result of radioactive materials in the seawater are improved.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
System and method for optical spectrum fast peak reporting
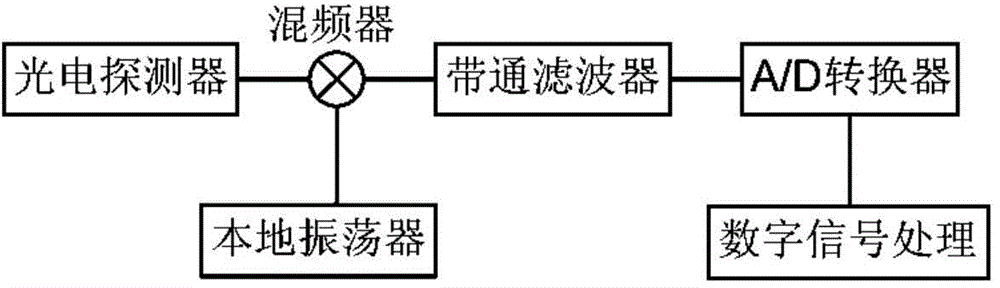
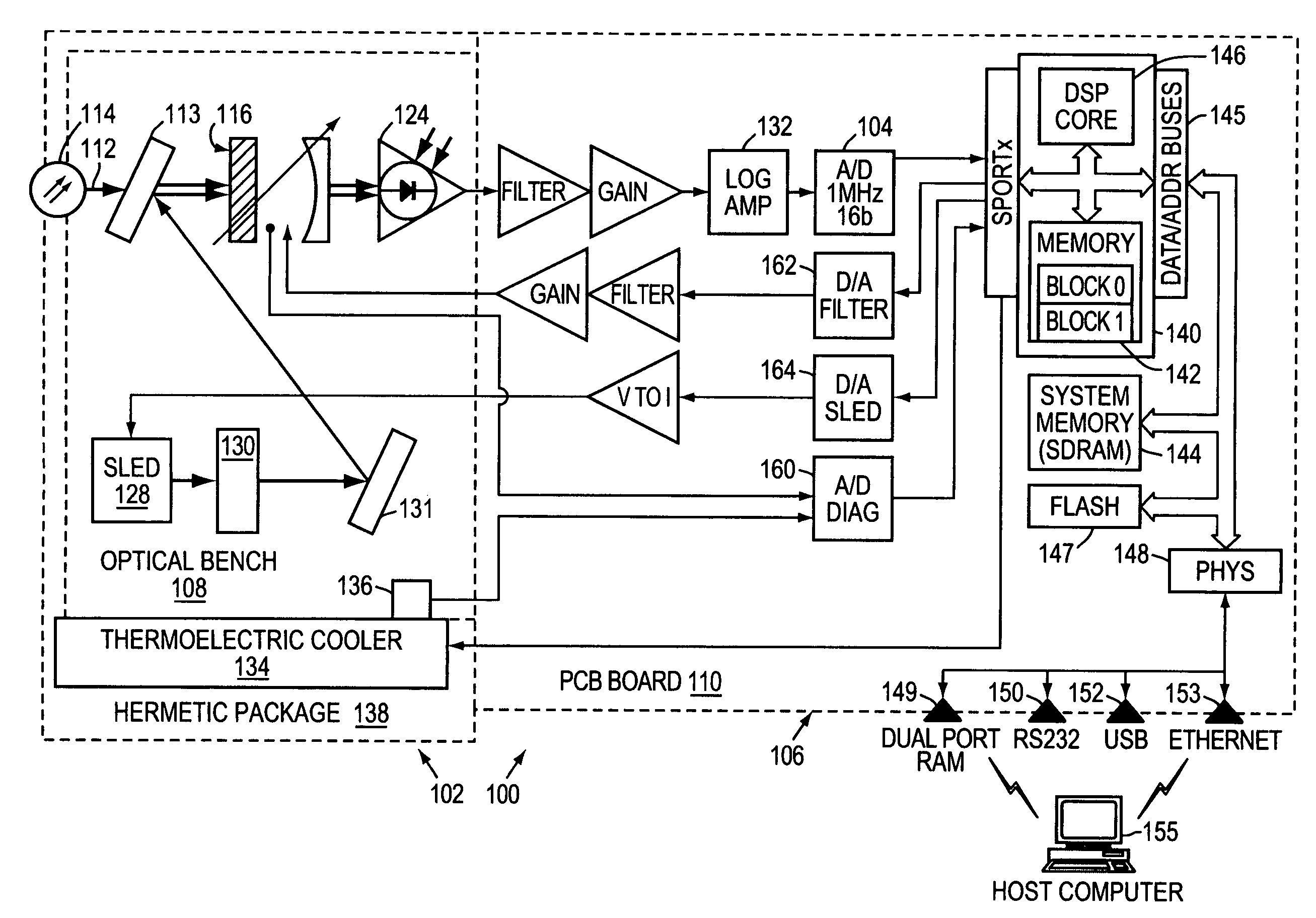
A system and method for fast peak finding in an optical spectrum prioritizes the information it first generates and how the information is then forwarded from the system to a host computer, for example. A spectrum detection subsystem generates a spectrum of an optical signal. An analog-to-digital converter converts the spectrum into sample data. Finally, a data processing subsystem first detects the spectral locations of peaks in the spectrum using the sample data and then uploads the peak information to a host computer before performing processing to determine the shapes of the peaks and / or noise information for the optical signal, for example. The system is thus able to quickly find some information, such as whether or not channels or carriers are present, at what frequency the carriers are operating, and the carriers' power level, and send this information to the host computer. In contrast, information concerning spectral shape or the noise floor sent later in time.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH
A Pulse Amplitude Measuring Circuit and Method for Reducing Counting Loss
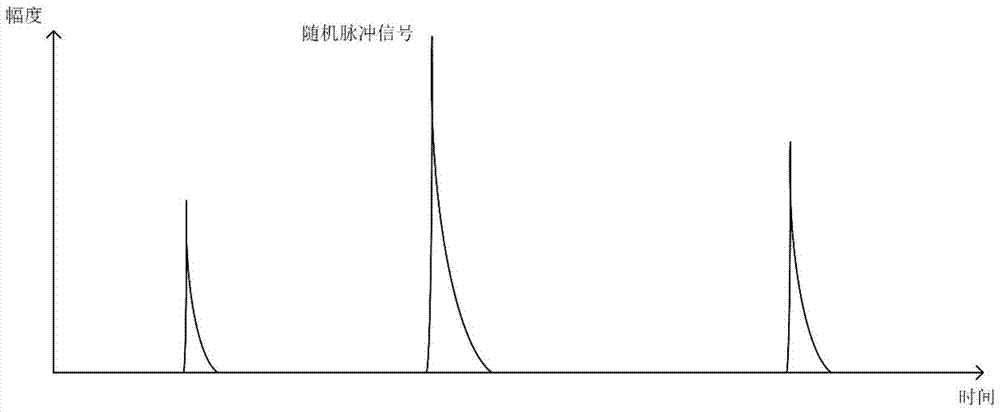
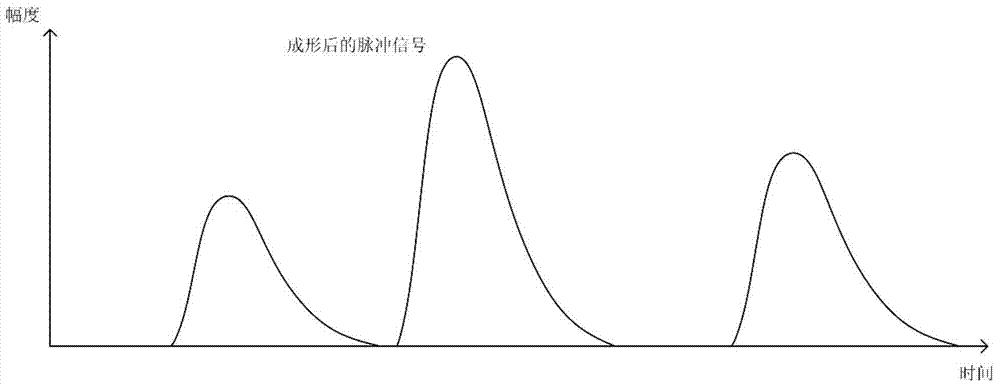
ActiveCN104483557BEasy to handleHigh speedPulse characteristics measurementsCounting ratePeak finding
The invention discloses a pulse amplitude measurement circuit and method for reducing counting losses. The related circuit includes: a shaping amplifier circuit, which is used to widen the random pulse signal output by the nuclear detector into a pulse shape with a flat top that is convenient for amplitude measurement, and Amplify the signal amplitude and output; high-speed AD conversion circuit, used to continuously sample the pulse signal output by the forming amplifier circuit and convert it into digital output; fast peak-seeking and discharge control circuit, used for high-speed AD conversion circuit output Calculate the amplitude of the digital signal waveform, store it after the amplitude calculation is completed, and output the discharge control signal to the signal fast recovery circuit; the signal fast recovery circuit is used to control the forming amplifier circuit according to the received discharge control signal The amplitude of the output pulse returns to the baseline level. The circuit and method disclosed by the invention can reduce the counting rate loss caused by the accumulation effect of the nuclear pulse signal under the condition of high counting rate, and the circuit structure is simple and reliable, and is easy to popularize.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
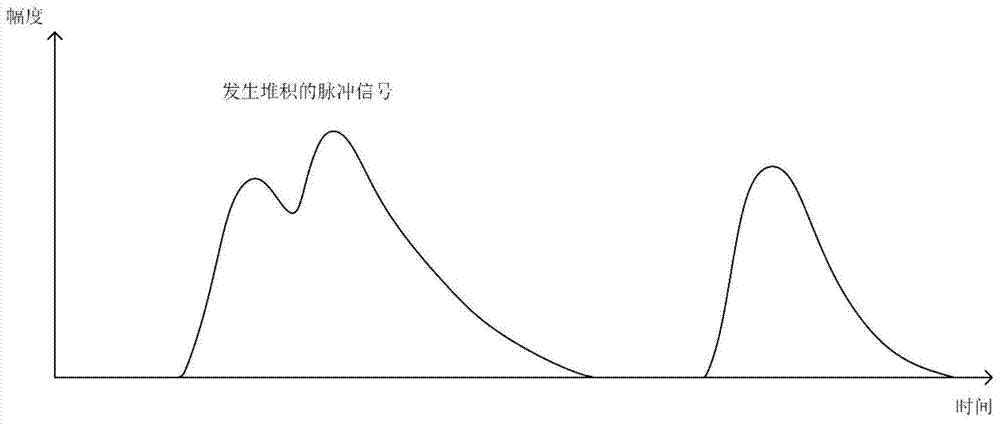
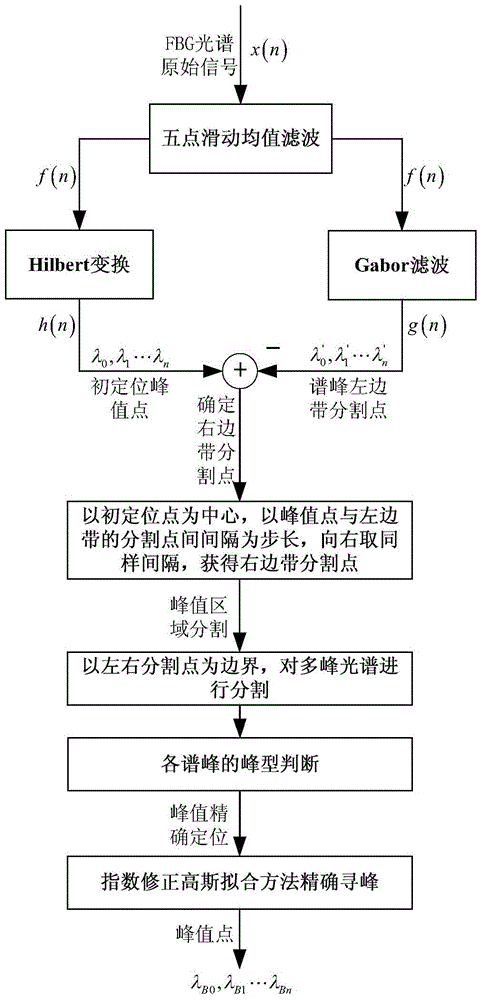
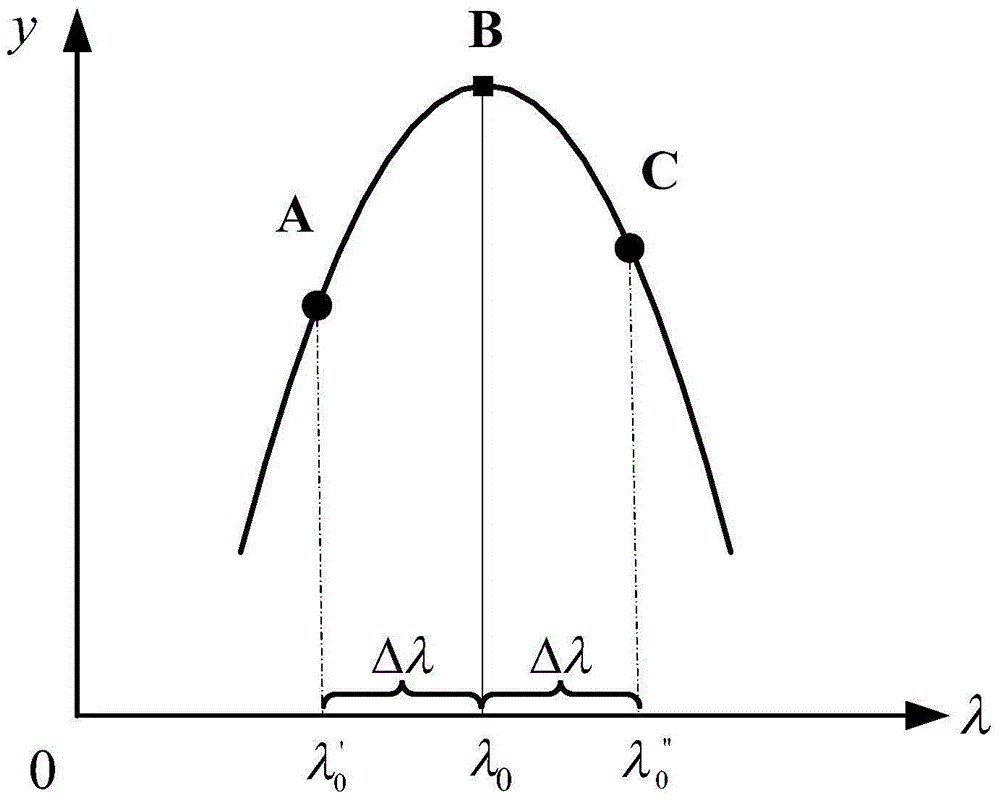
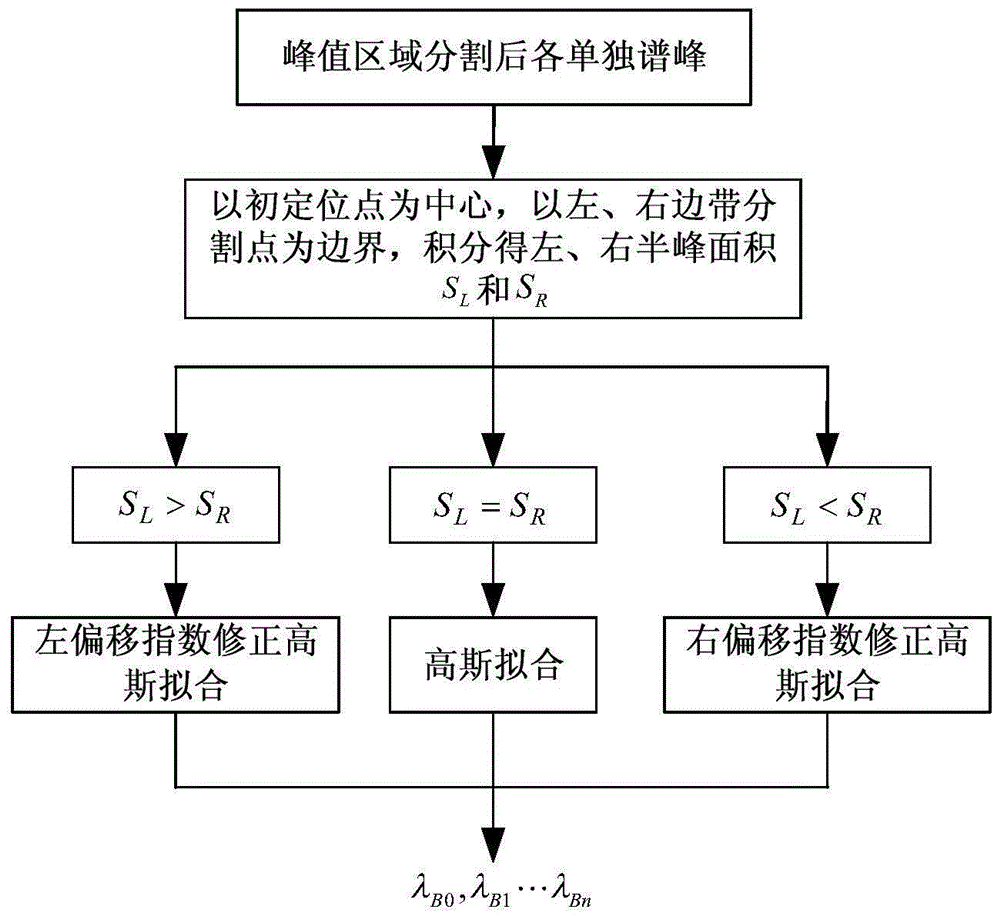
A Multi-peak Adaptive Accurate Peak-finding Method for Distributed FBG Sensor Networks
ActiveCN104634460BImplementing Adaptive Peak Region SegmentationAddresses the shortcoming of pre-determined peak rangesConverting sensor output opticallyFiberPeak value
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com