Harmonic reject receiver architecture and mixer
a receiver and harmonic rejection technology, applied in the field of electronic signal processing, can solve the problems of undesired channels in the television operating band appearing as interference, ineffective filtering, and particular problems in the operation bandwidth, and achieve the effect of reducing the mixer response to undesired harmonics
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
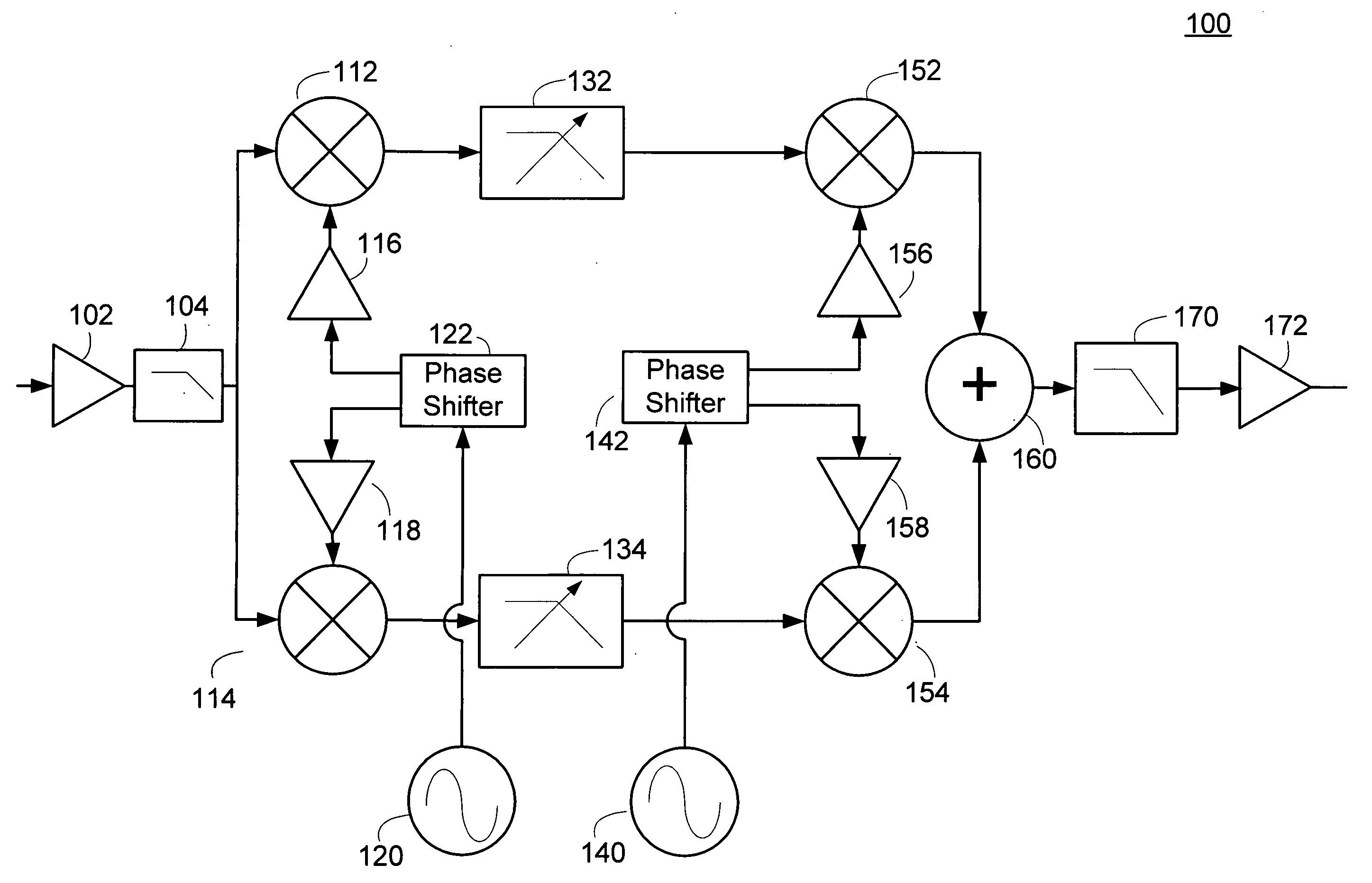
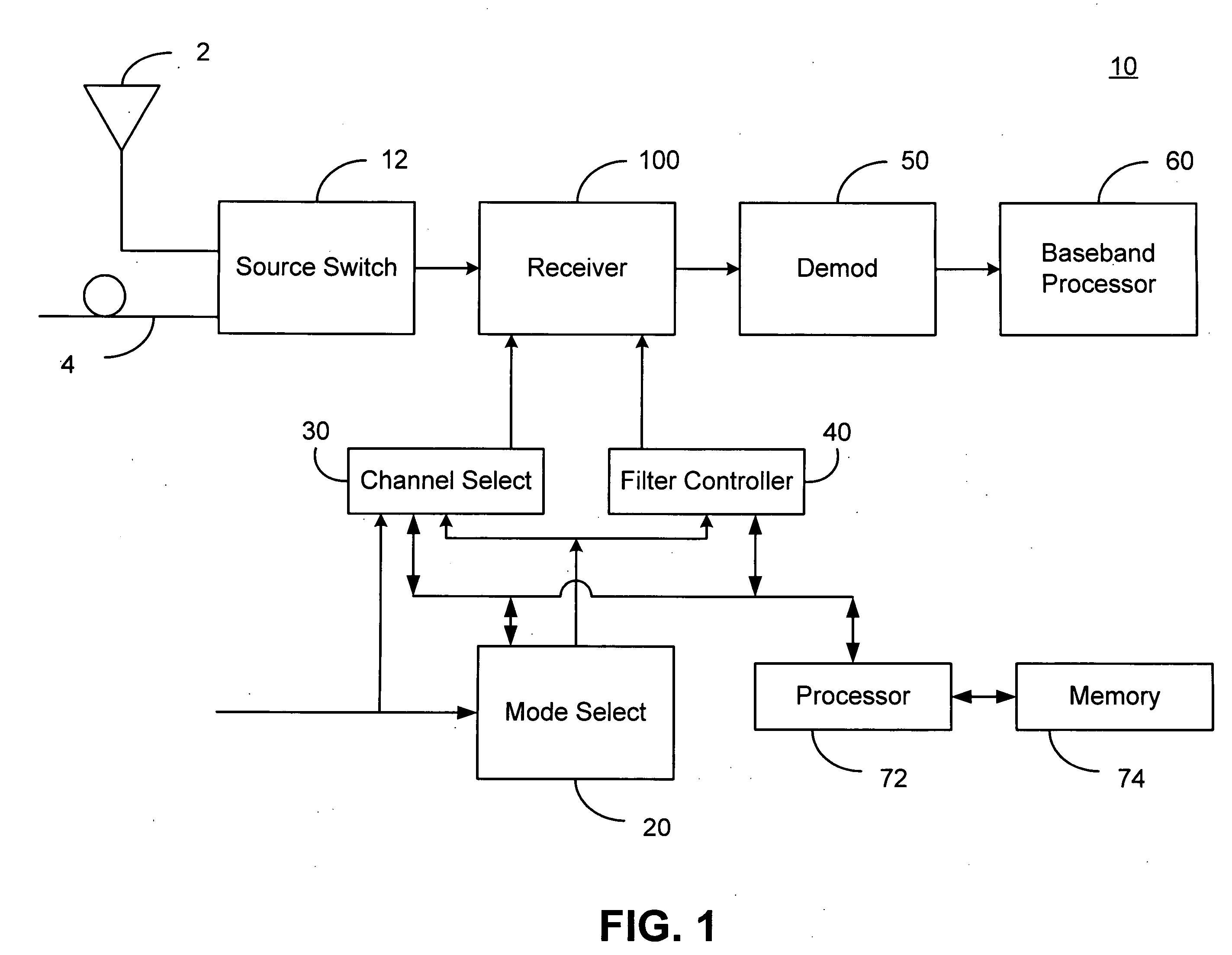
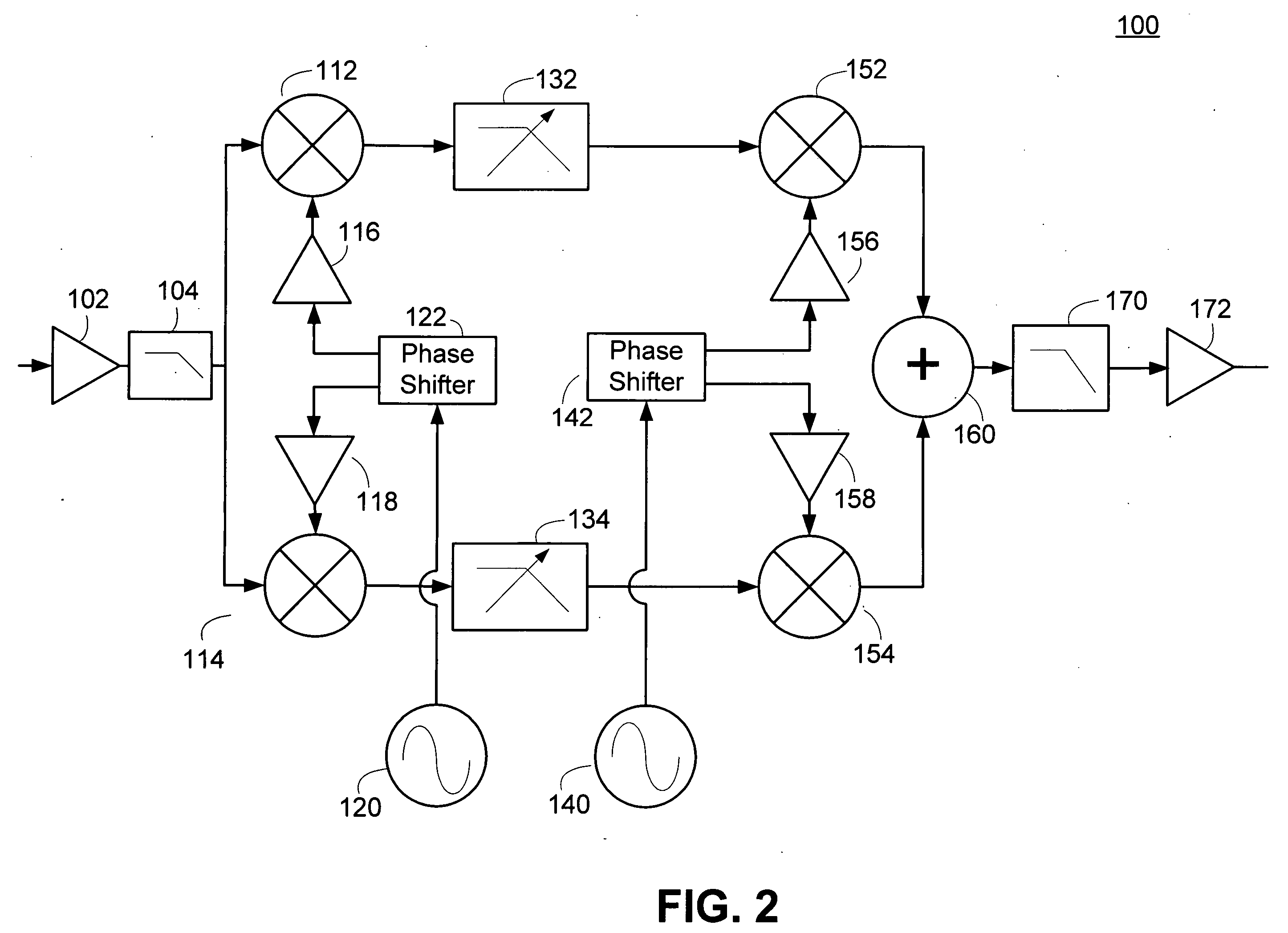
[0020] This disclosure describes harmonic reject mixers and receiver architectures which utilize harmonic reject mixers to permit an efficient implementation of a direct downconversion or low-IF receiver. The current approach to receiver design may employ switching mixers within the receiver front end. This permits the system to achieve low noise and high linearity. However, these switching mixers also efficiently downconvert input signals at undesired harmonic multiples of the local oscillator frequency to the desired output frequency band. The frequency conversion of undesired signals poses a problem which is particularly important for television applications where the desired input range is so wide that the likelihood of undesired harmonics is high. Receiver architectures and methods of processing harmonic rich input signals employing harmonic suppression mixers are disclosed herein. The disclosed receivers, mixers, and methods enable a receiver to achieve the advantages of switc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com