Methods for controlling water and sand production in subterranean wells
a technology of subterranean wells and water supply, applied in the direction of fluid removal, borehole/well accessories, chemistry apparatus and processes, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the fluid production capacity of the producing zone, and affecting the stability of the subterranean well
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
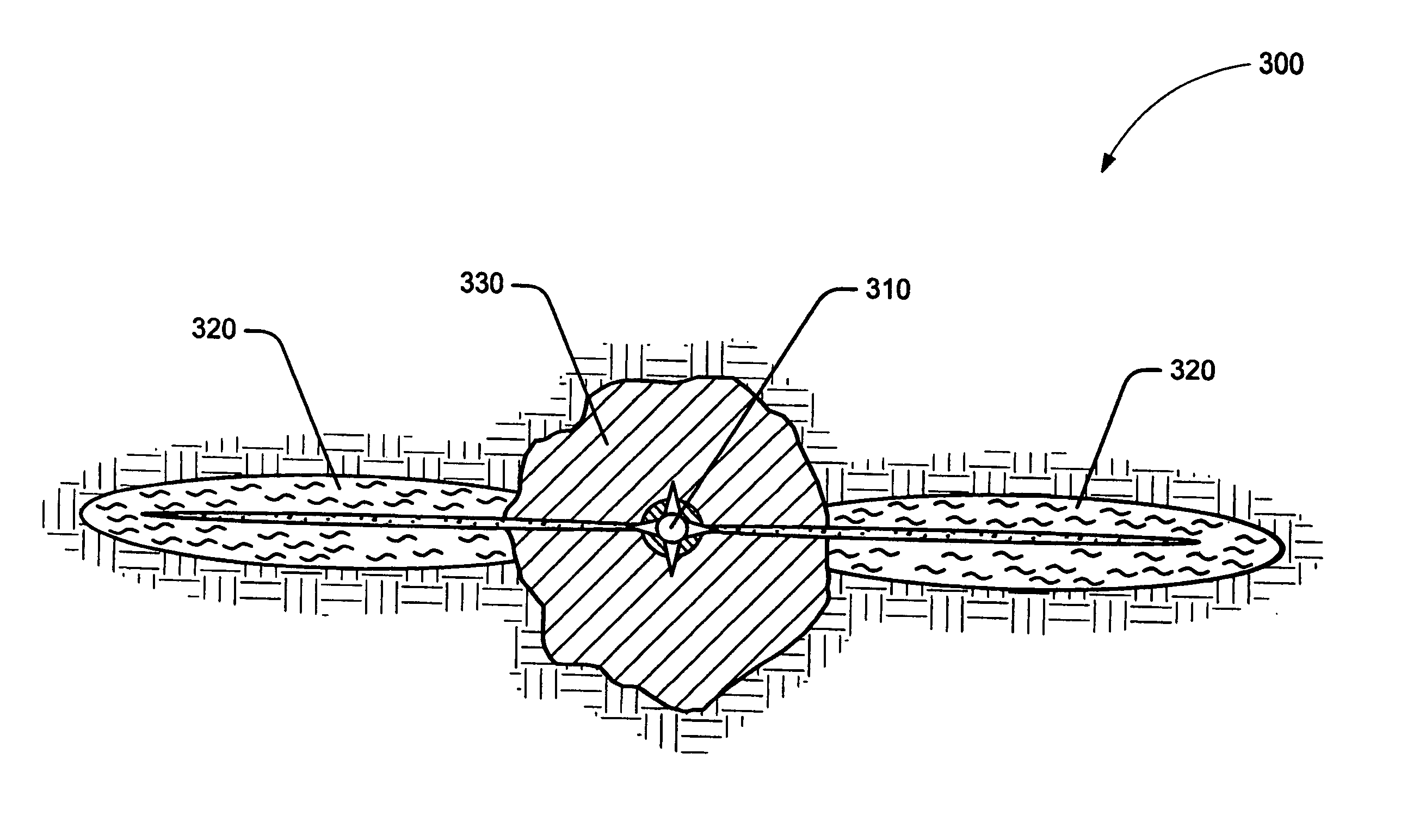
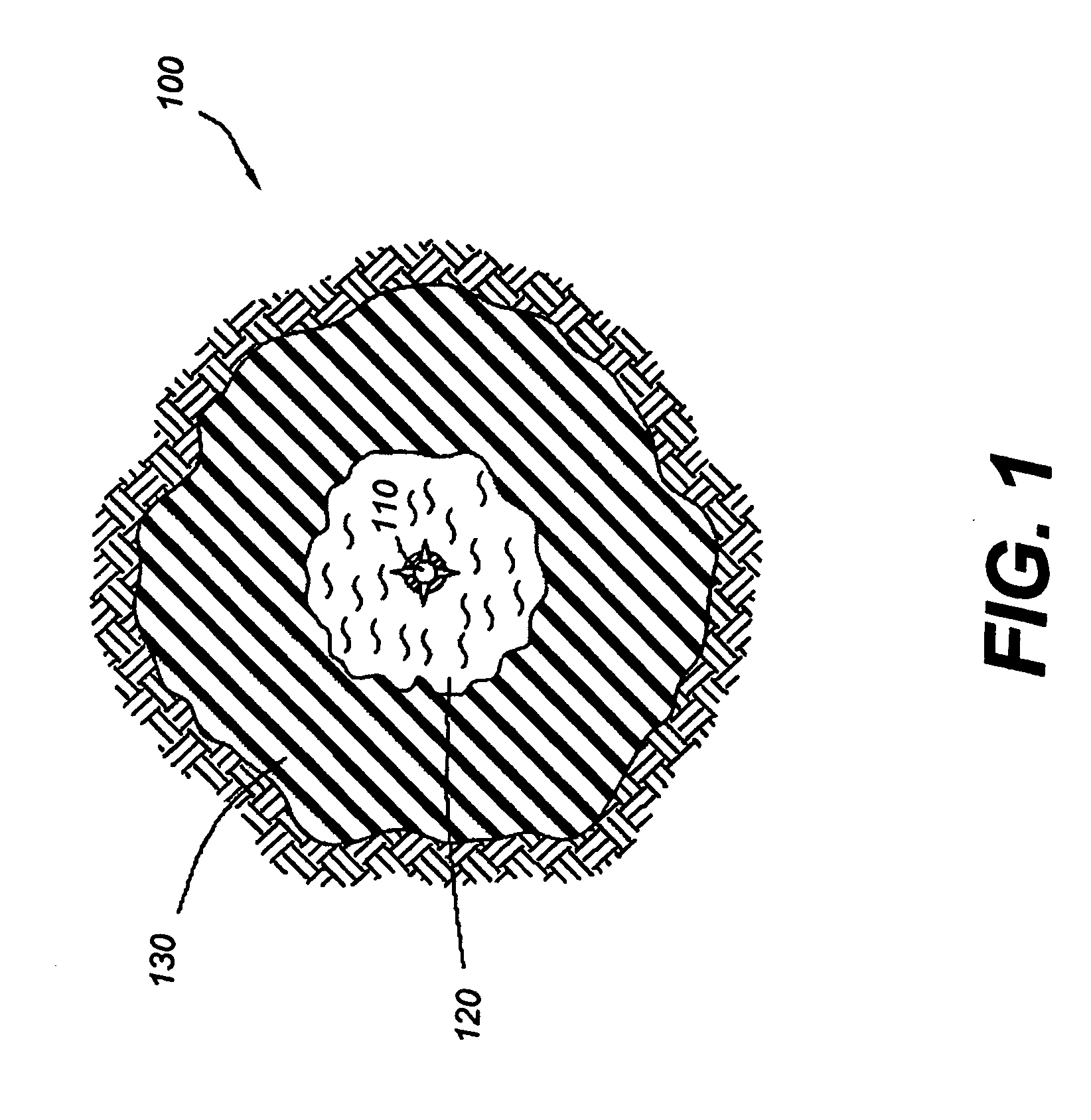
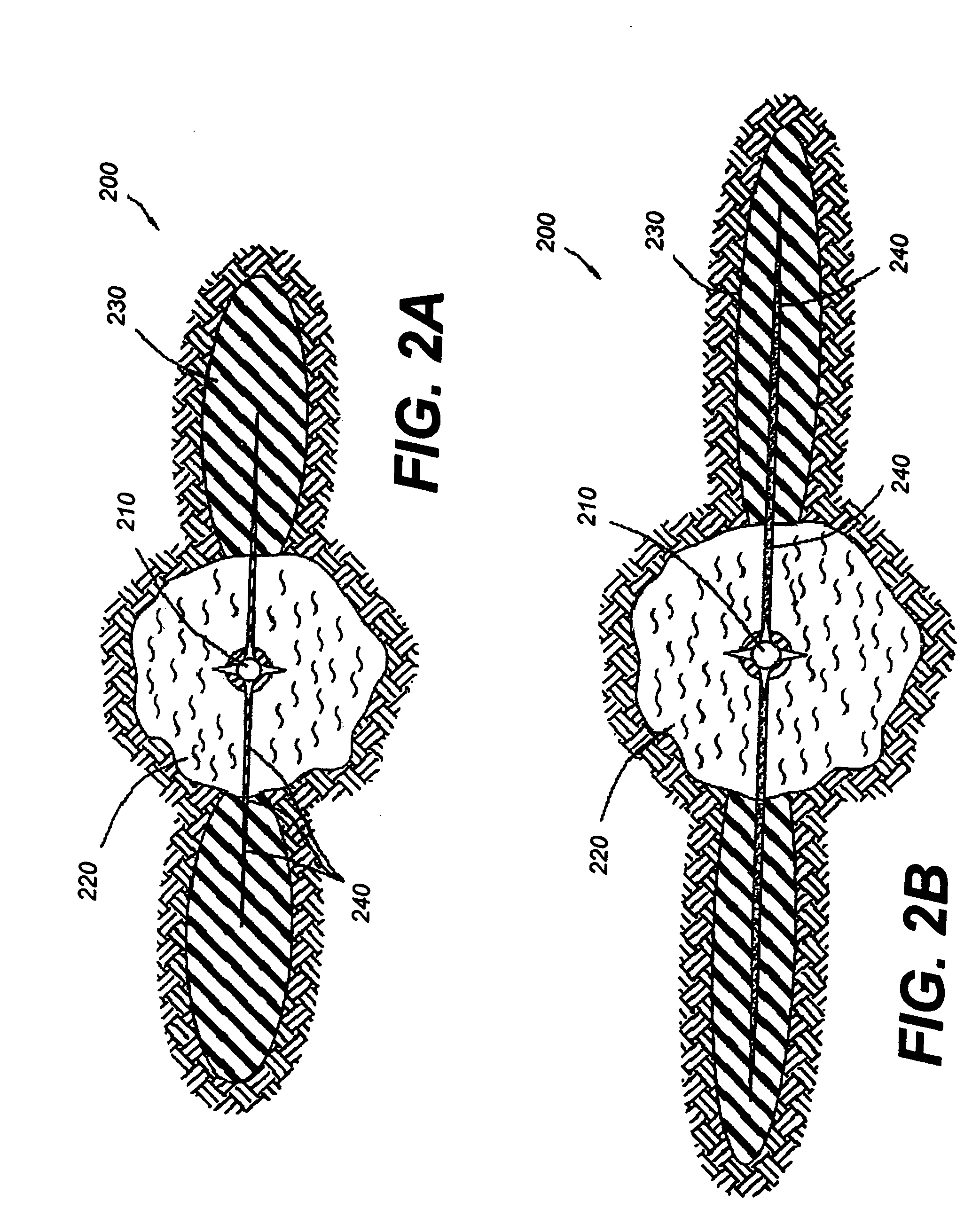
[0018] The present invention relates to the stabilization of subterranean formations. More particularly, the present invention relates to methods for stabilizing unconsolidated portions of a subterranean formation and controlling the production of water from those portions.
I. METHODS OF THE PRESENT INVENTION
[0019] One embodiment of the present invention describes a method of stabilizing an unconsolidated subterranean formation that is penetrated by a well bore comprising introducing a consolidating agent into the subterranean formation so as to transform a portion of the subterranean formation surrounding the well bore into a consolidated region; and introducing a relative permeability modifier fluid into the subterranean formation through the well bore so as to penetrate at least a portion of the consolidated region. The relative permeability modifier fluid, in some embodiments, may penetrate beyond the consolidated region.
[0020] Another embodiment of the present invention descr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com