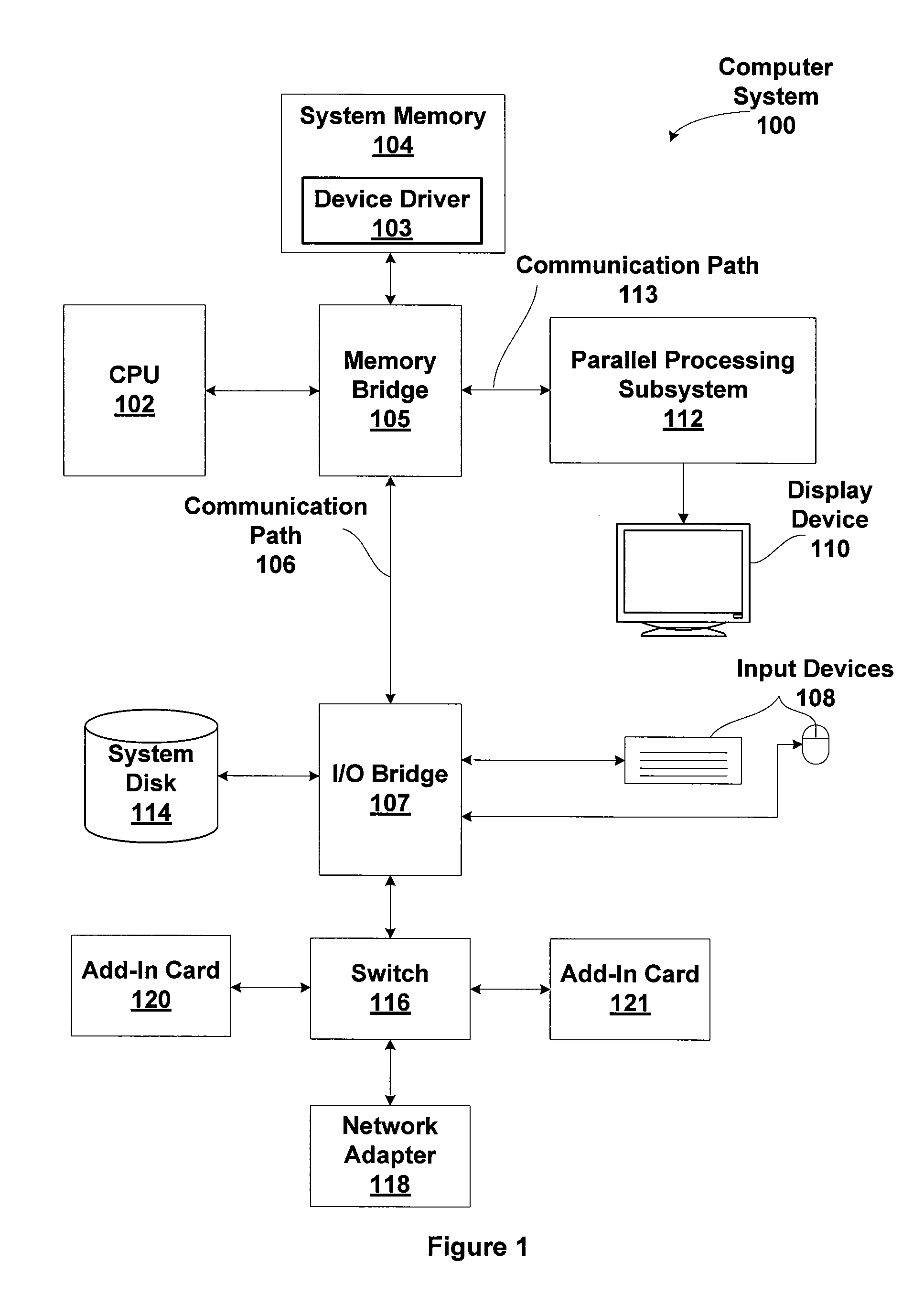
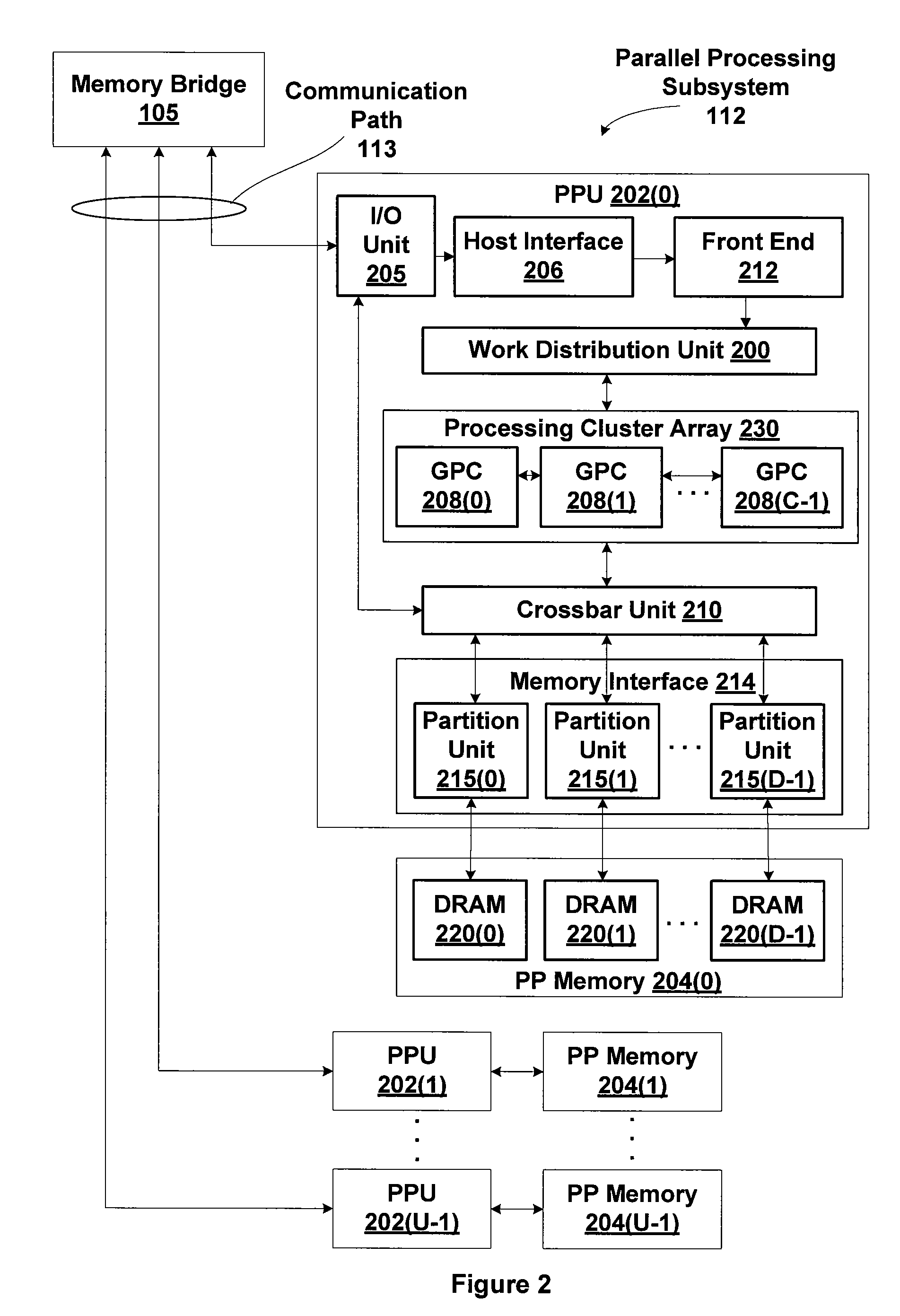
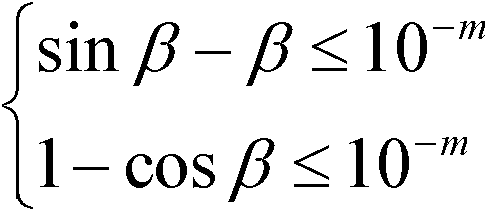Patents
Literature
72 results about "Round-off error" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A roundoff error, also called rounding error, is the difference between the result produced by a given algorithm using exact arithmetic and the result produced by the same algorithm using finite-precision, rounded arithmetic. Rounding errors are due to inexactness in the representation of real numbers and the arithmetic operations done with them. This is a form of quantization error. When using approximation equations or algorithms, especially when using finitely many digits to represent real numbers (which in theory have infinitely many digits), one of the goals of numerical analysis is to estimate computation errors. Computation errors, also called numerical errors, include both truncation errors and roundoff errors.
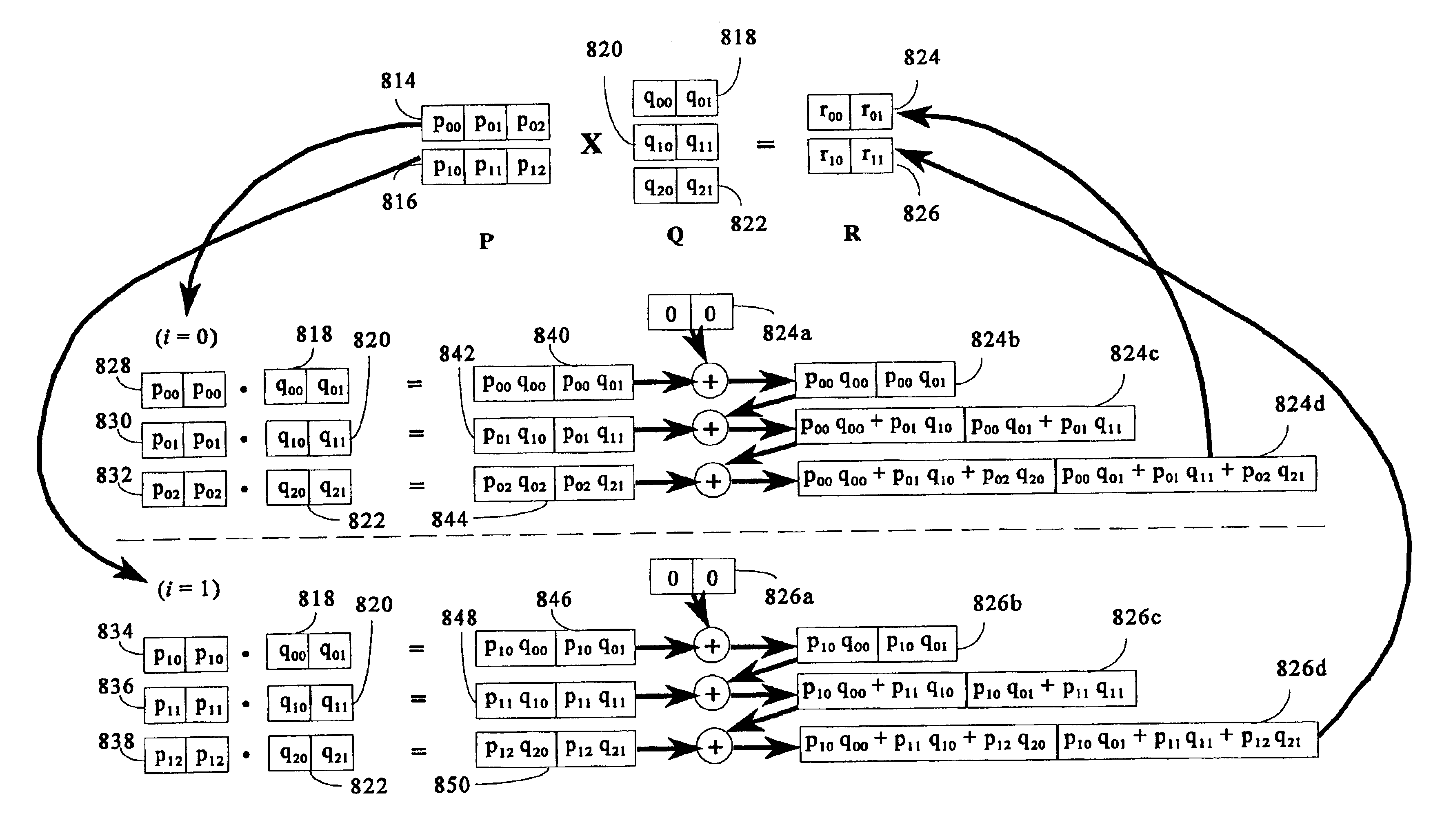
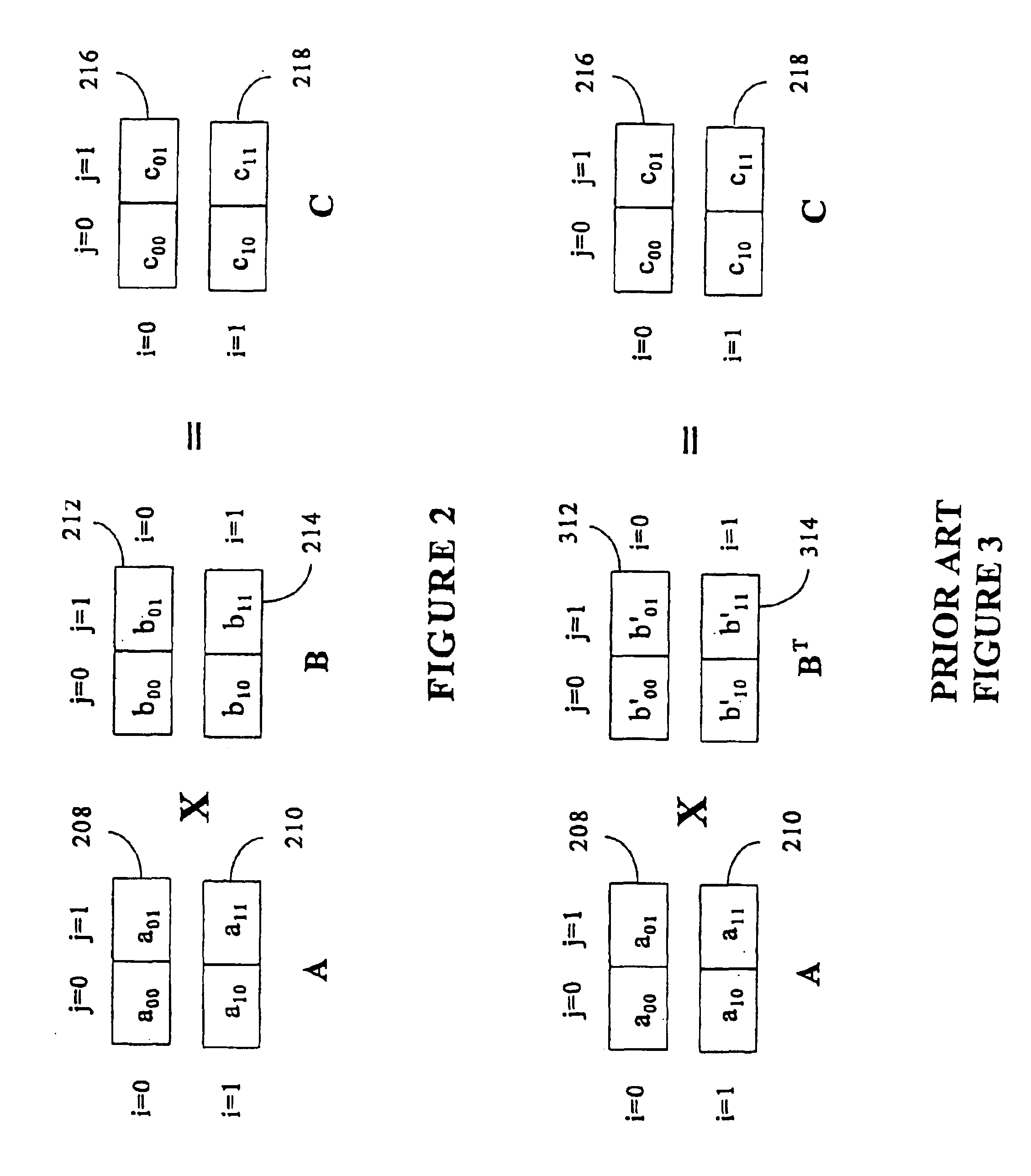
Matrix multiplication in a vector processing system
InactiveUS6901422B1Increase speedMaintaining bit-by-bit compatabilityComputation using non-contact making devicesProgram controlMultiplication of vectorsProcessor register
The present invention is directed to a system and method for multiplication of matrices in a vector processing system. Partial products are obtained by dot multiplication of vector registers containing multiple copies of elements of a first matrix and vector registers containing values from rows of a second matrix. The dot products obtained from this dot multiplication are subsequently added to vector registers which make up a product matrix. In an embodiment of the present invention, each matrix may be divided into submatrices to facilitate the rapid and efficient multiplication of large matrices, which is done in parts by computing partial products of each submatrix. The matrix multiplication performed by the present invention avoids rounding errors as it is bit-by-bit compatible with conventional matrix multiplication methods.
Owner:APPLE INC
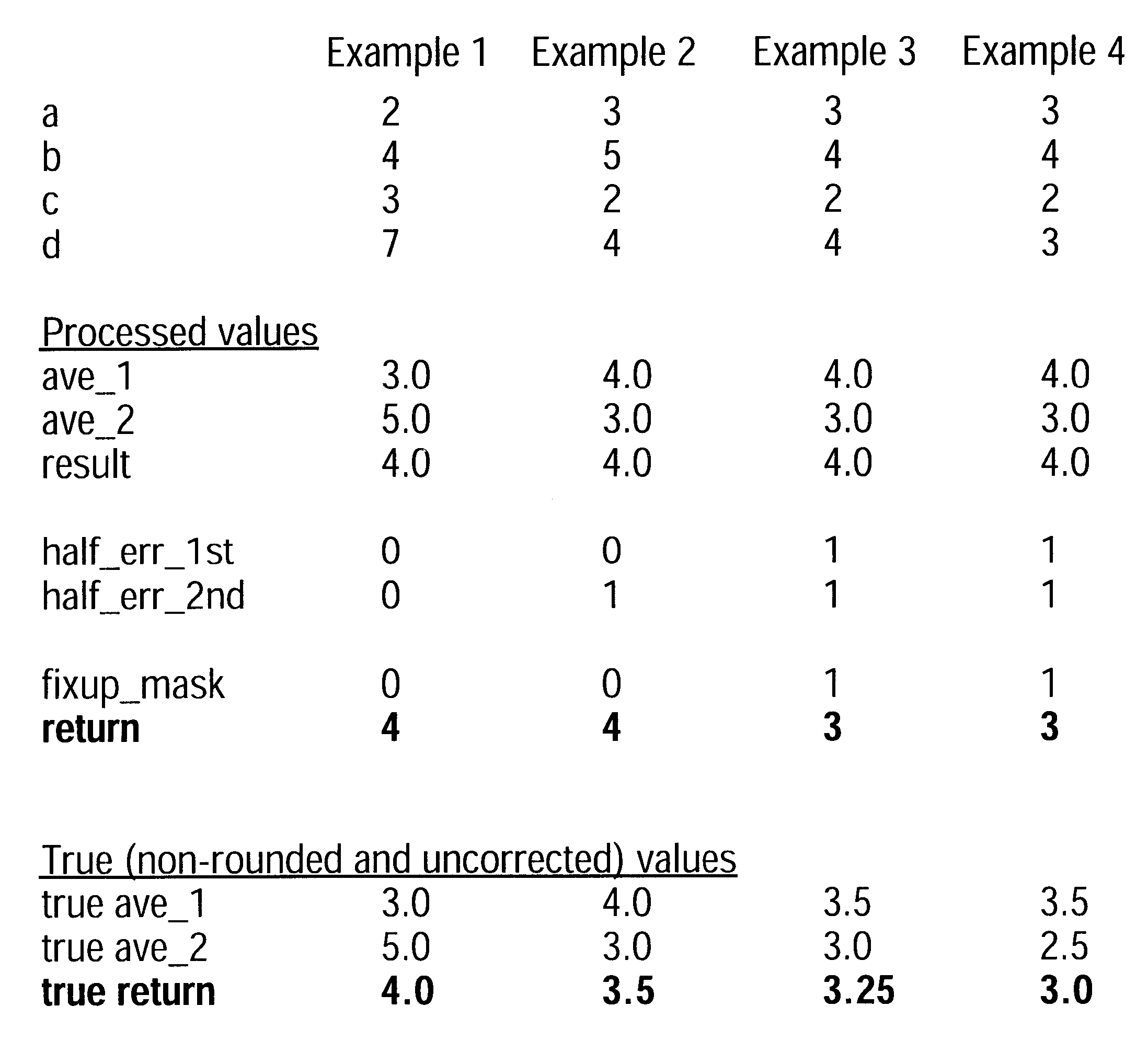
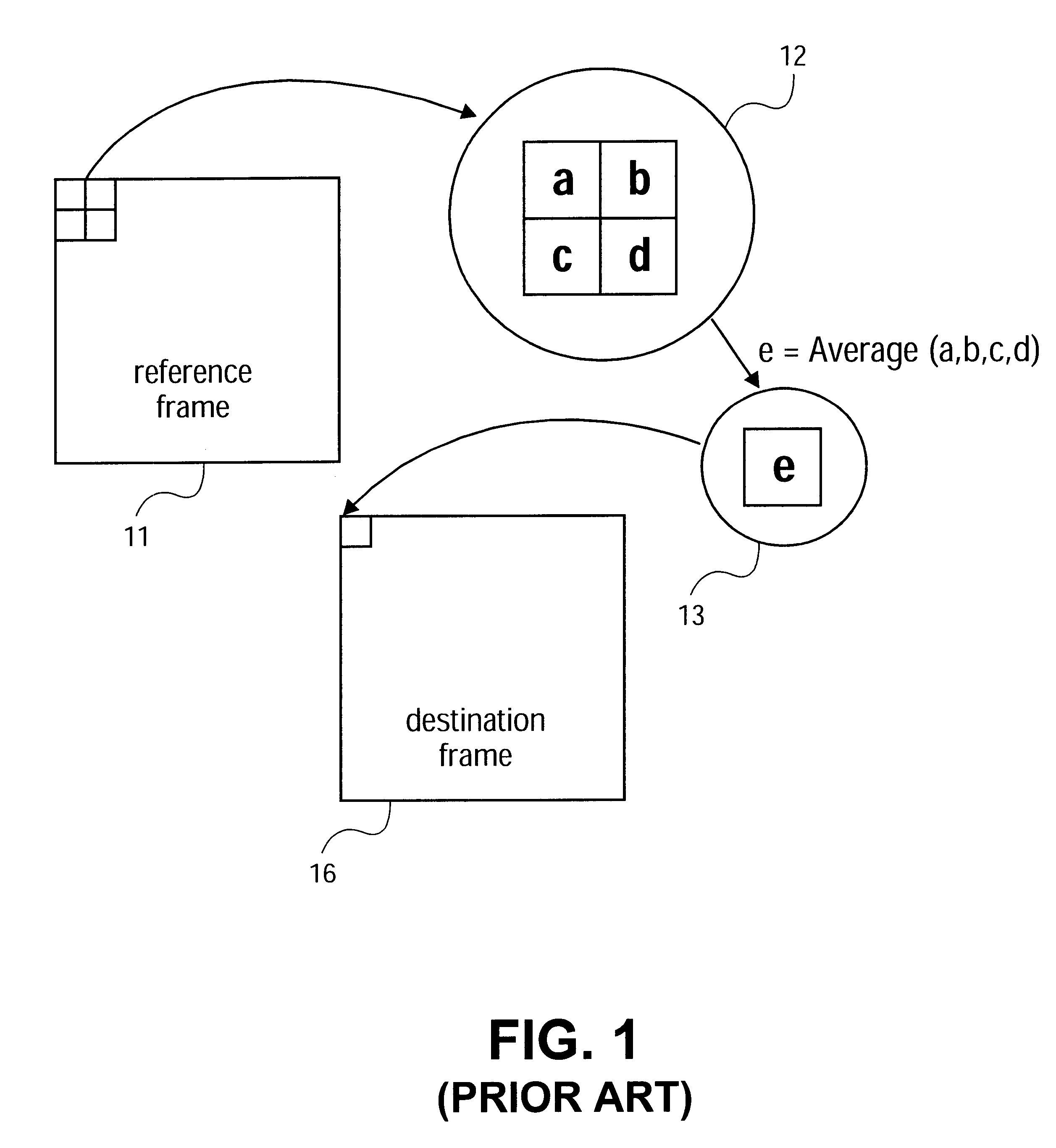
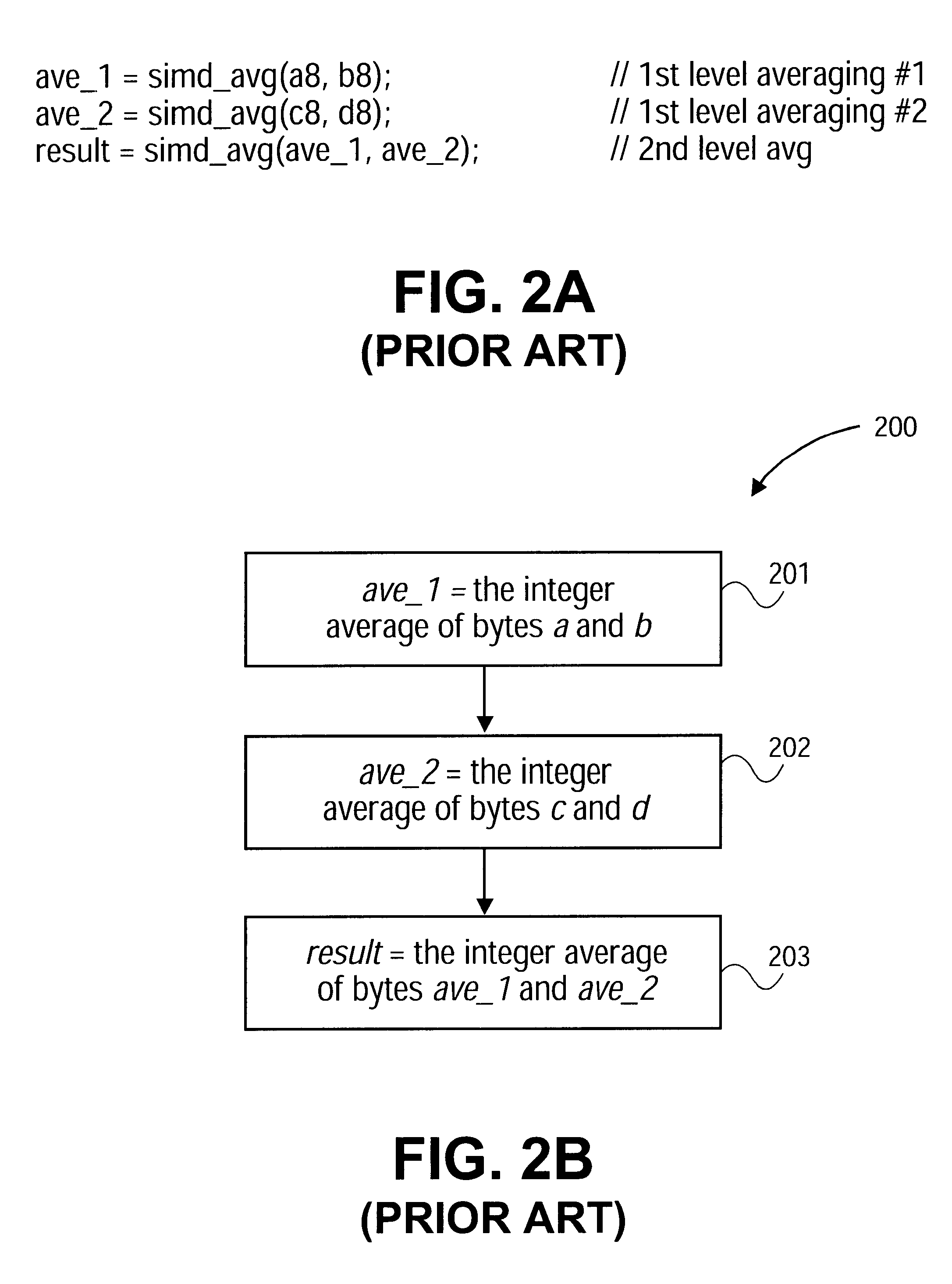
Accurate averaging of elements using integer averaging
InactiveUS6512523B1Character and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsRound-off errorParallel processing
A system and method for efficiently obtaining corrected results when averaging multiple integers together. The invention detects when round off errors occur during integer averaging operations, and determines if the accumulated errors are sufficient to require correction. If so, the result is modified by a correction factor to produce an accurate result. Errors can be detected by examining the even / odd status of pairs of numbers that are being averaged together. The invention can be employed with Single Instruction Multiple Data instructions to process multiple sets of integers in parallel. In one embodiment, the invention is used for averaging pixel values in the compression and / or decompression of digitized moving pictures.
Owner:INTEL CORP
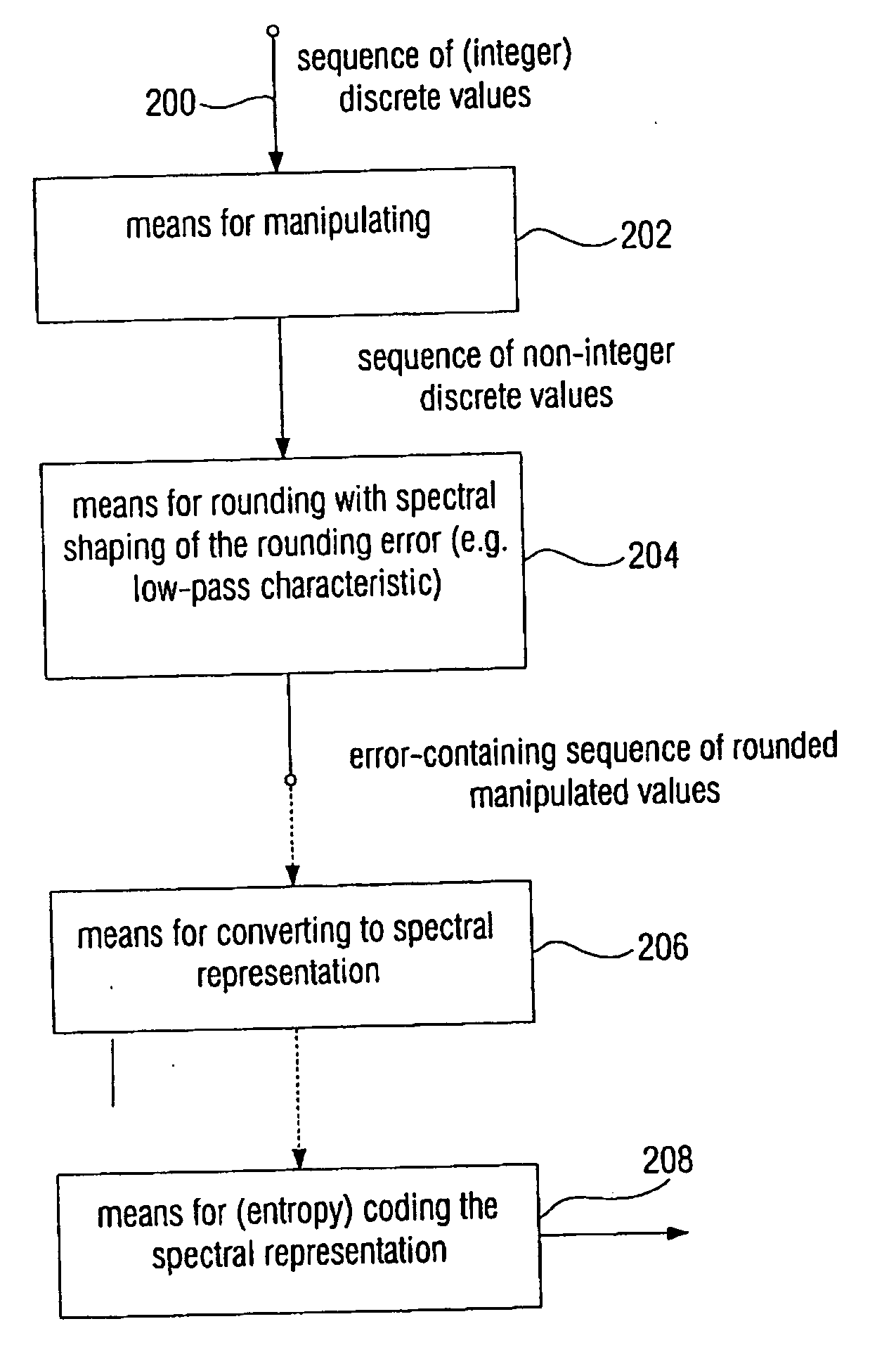
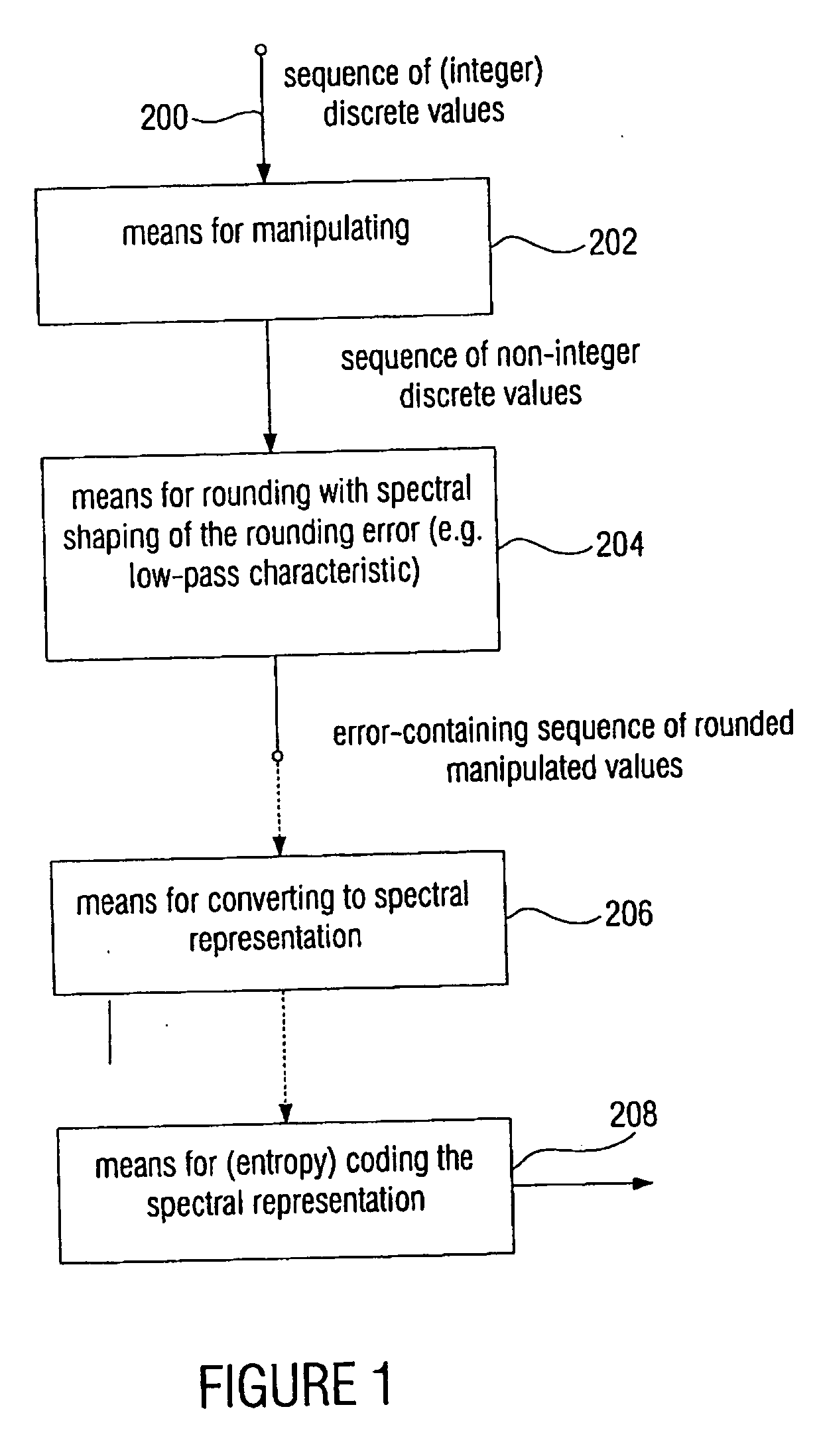
Device and method for processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values
ActiveUS20060210180A1Few rounding errorIncrease the number ofSpeech analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLossless codingFrequency spectrum
When processing a signal having a sequence of discrete values, wherein there is a first frequency range, in which the signal has a high energy, and wherein there is a second frequency range, in which the signal has a low energy, the sequence of discrete values is first manipulated to obtain a sequence of manipulated values, so that at least one of the manipulated values is non-integer. Then the sequence of manipulated values is rounded to obtain a sequence of manipulated values. The rounding is formed to effect a spectral shaping of a generated rounding error so that a spectrally shaped rounding error has a higher energy in the first frequency range than in the second frequency range. By spectrally shaping the rounding error so that the rounding error does not have any energy either in the storage areas where there is no signal energy, an especially efficient coding is obtained particularly in connection with a lossless coding context.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER ANGEWANDTEN FORSCHUNG EV
Method and system for selecting data sampling phase for self timed interface logic
InactiveUS6839861B2Channel dividing arrangementsSynchronisation information channelsComputer scienceTransmitter
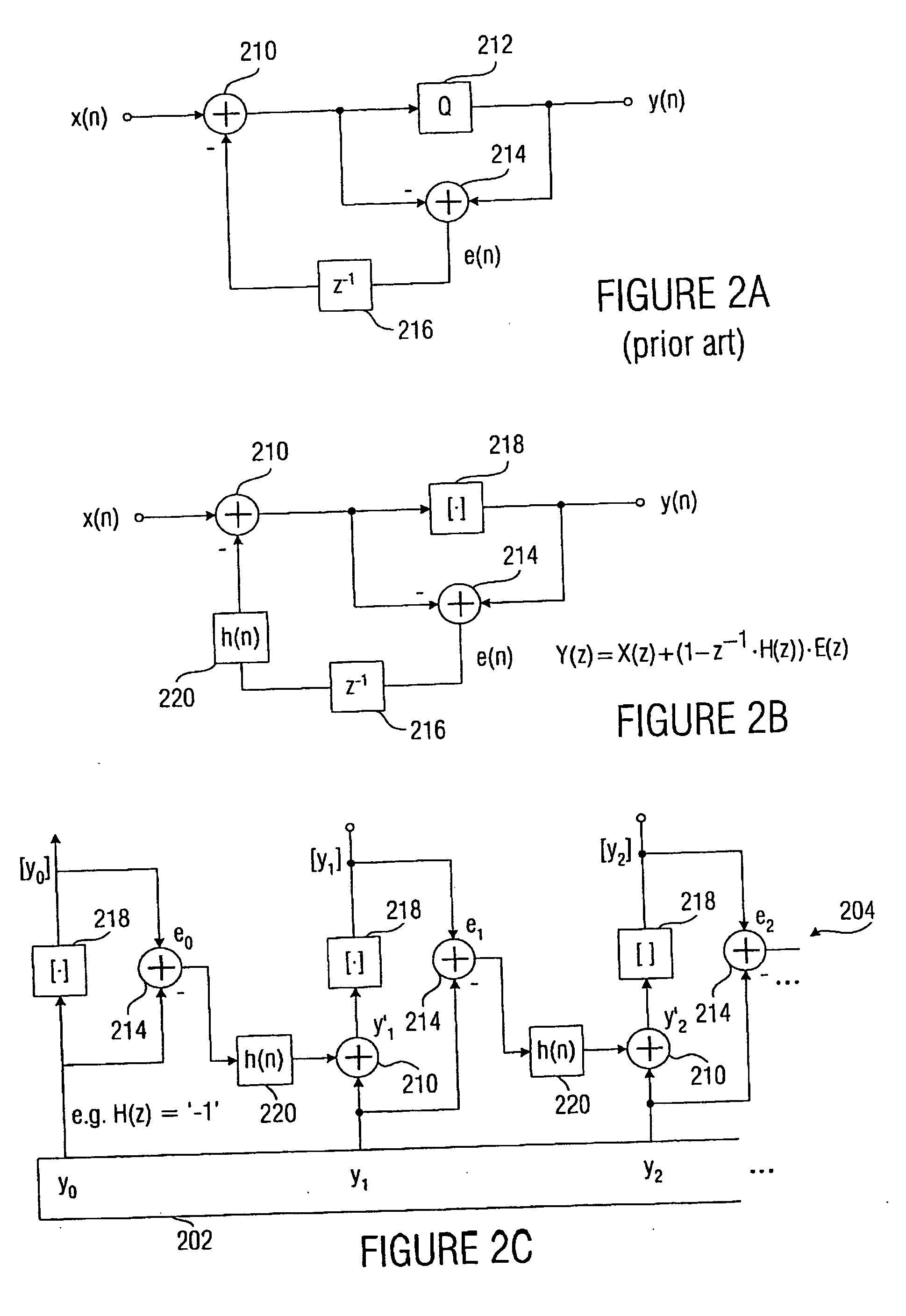
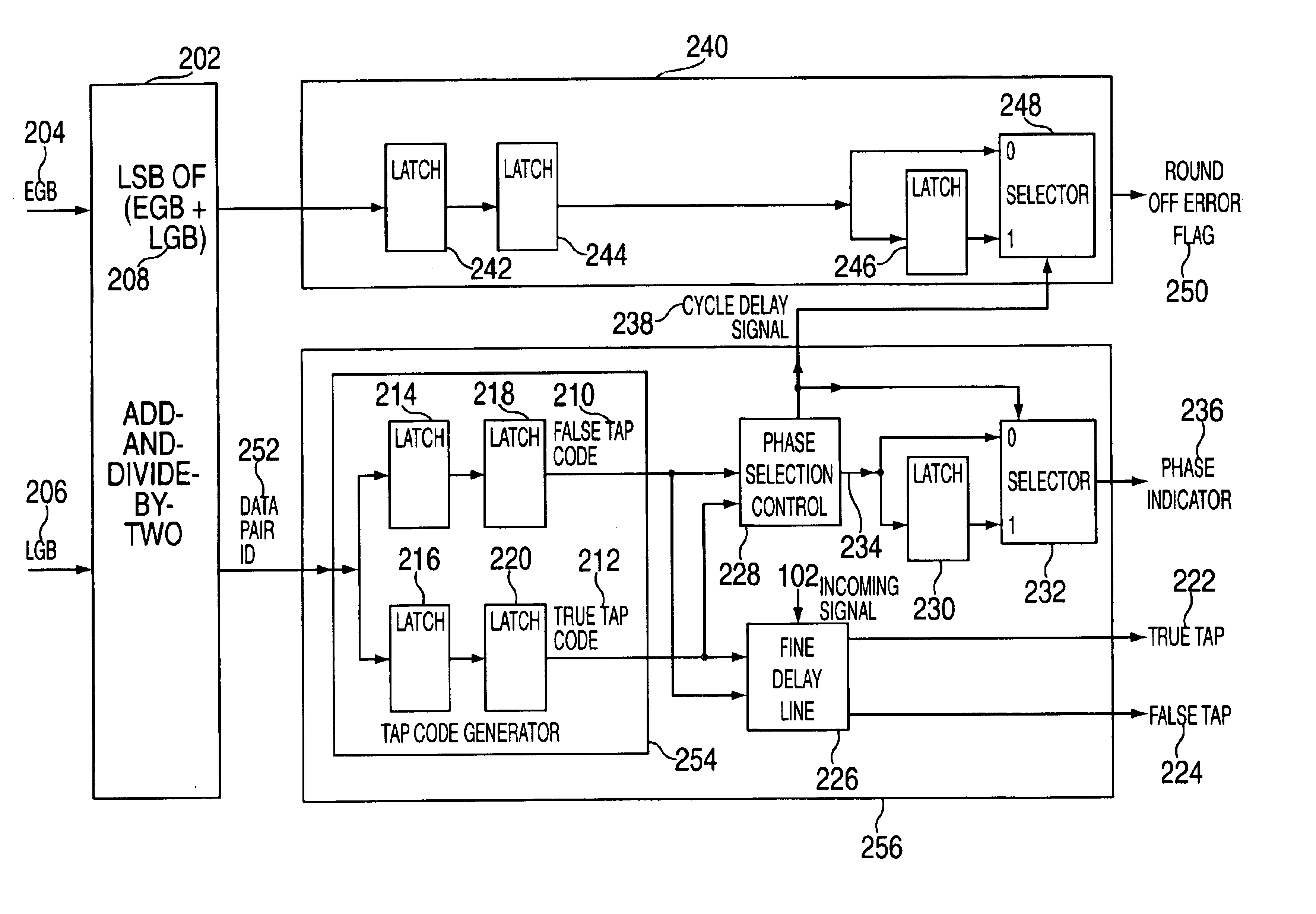
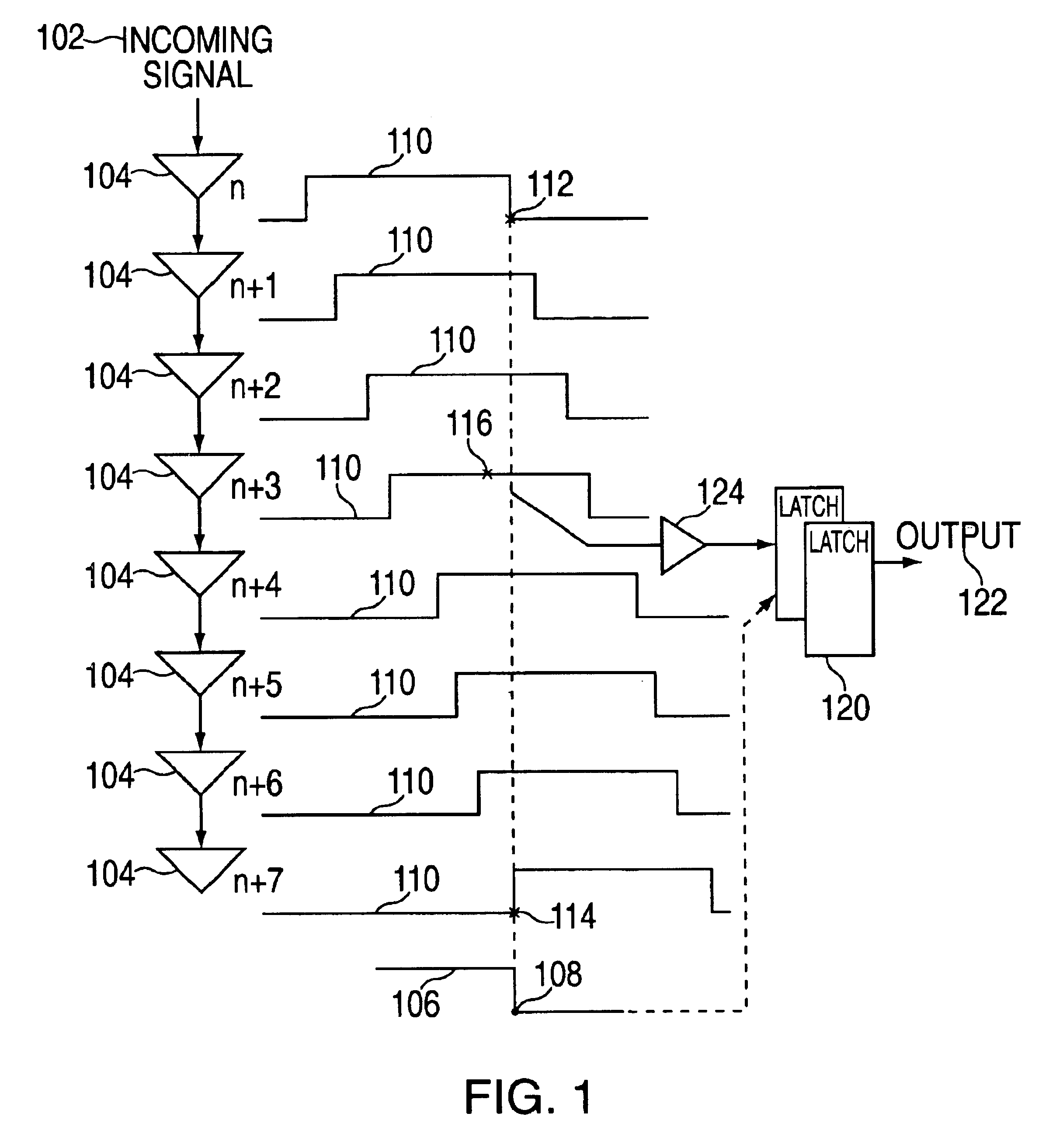
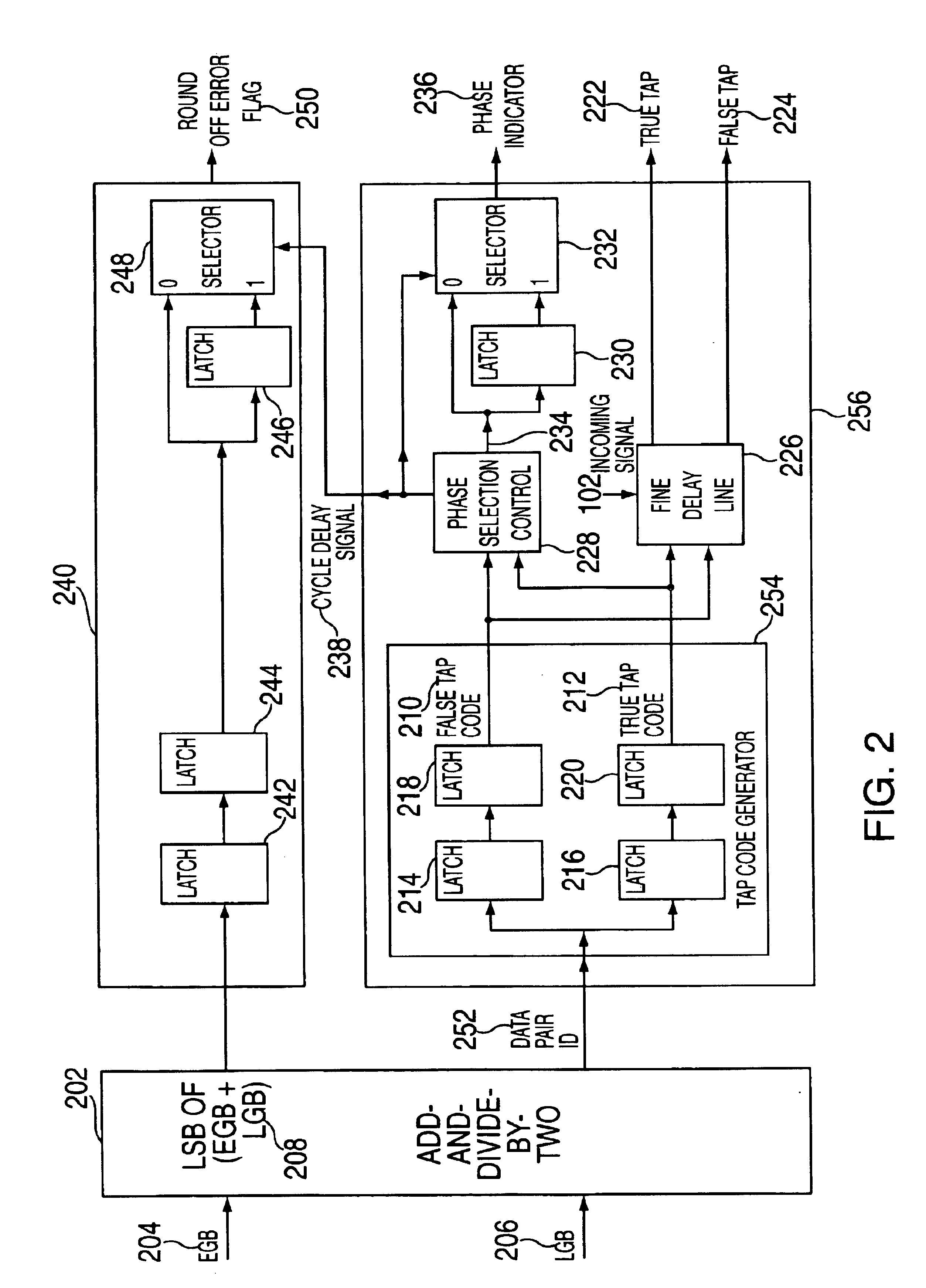
An exemplary embodiment of the present invention is a method for transmitting data among processors over a plurality of parallel data lines and a clock signal line. A receiver processor receives both data and a clock signal from a sender processor. At the receiver processor a bit of the data is phased aligned with the transmitted clock signal. The phase aligning includes selecting a data phase from a plurality of data phases in a delay chain and then adjusting the selected data phase to compensate for a round-off error. Additional embodiments include a system and storage medium for transmitting data among processors over a plurality of parallel data lines and a clock signal line.
Owner:IBM CORP
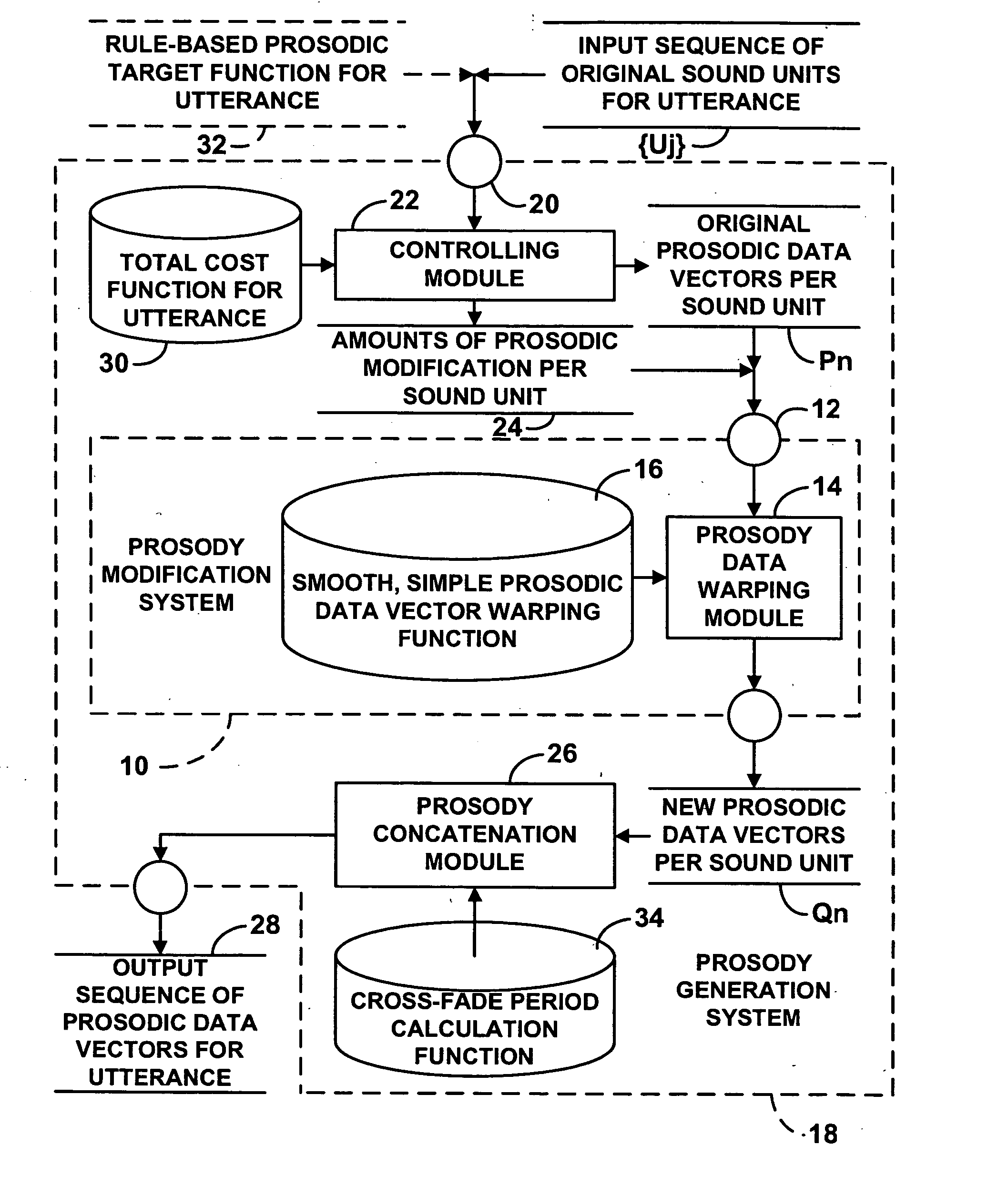
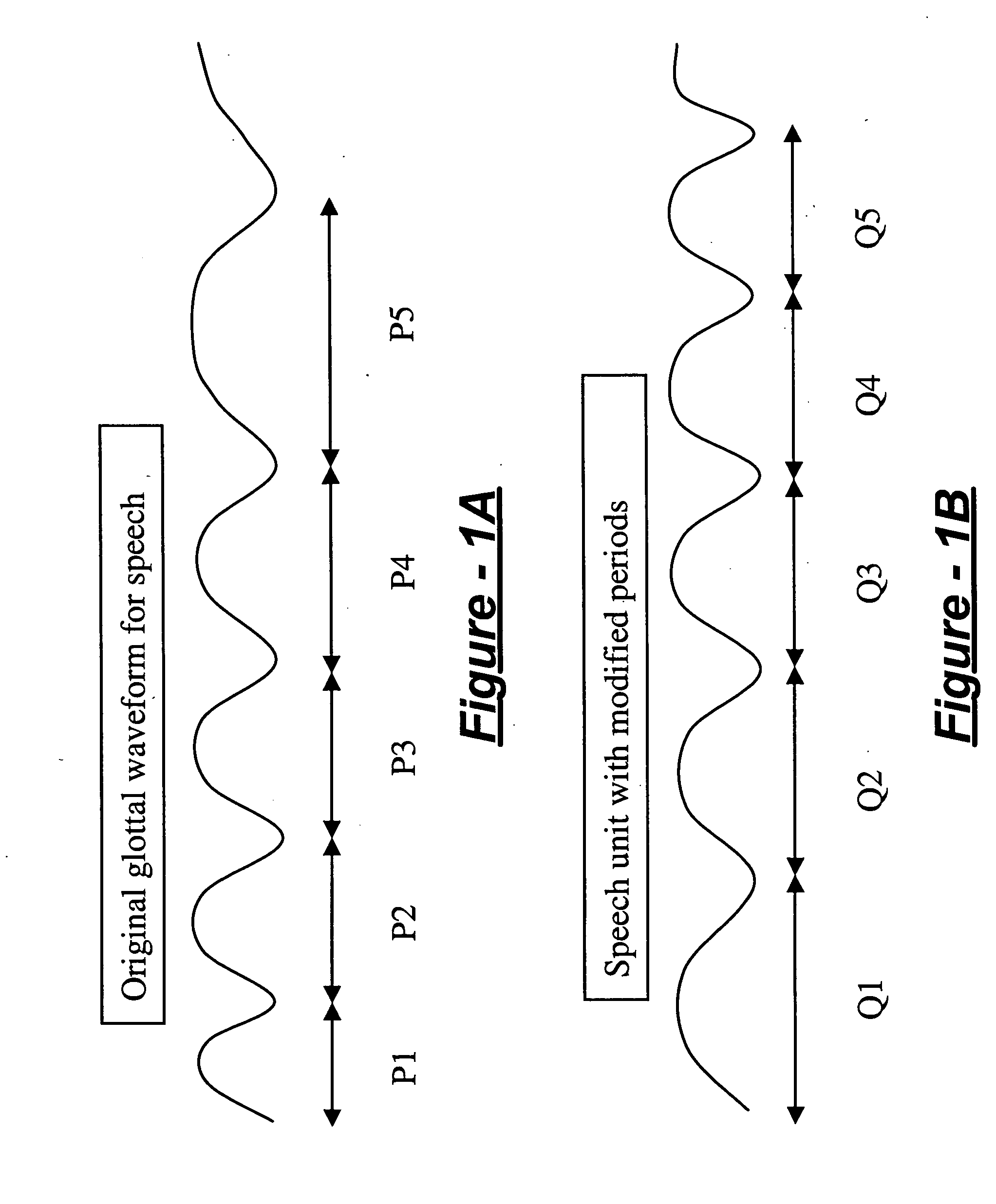
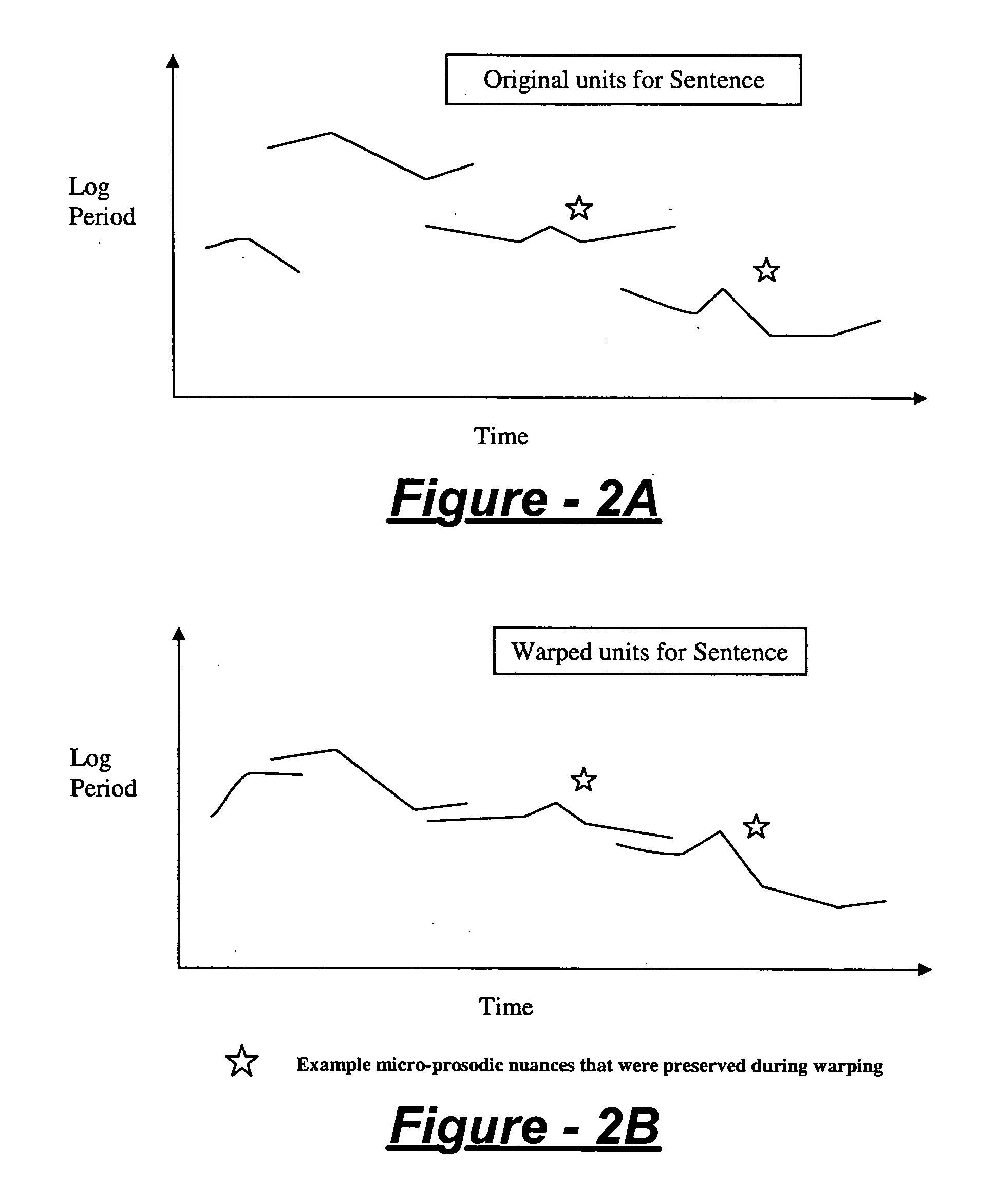
Prosody generation for text-to-speech synthesis based on micro-prosodic data
InactiveUS20060074678A1Avoids round-off errorHigh complexitySpeech synthesisOriginal dataText to speech synthesis
A prosody modification system for use in text-to-speech includes an input receiving a sequence of prosodic data vectors Pn, measured at time Tn, which samples a sound waveform. A prosody data warping module directly derives new prosodic data vectors Qn from the original data vectors Pn using a function, which is controlled by warping parameters A0, . . . Ak, which avoids round-off errors in deriving quantized values, which has derivatives with respect to A0, . . . Ak, Pn, and Tn that are continuous, and which has sufficiently high complexity to model intentional prosody of the sound waveform, and sufficiently low complexity to avoid modeling micro-prosody of the sound waveform. The smoothness and simplicity of the function ensure that micro-prosodic perturbations and errors in measurement of Tn are transferred directly to the output Qn. The errors are thus reversed during re-synthesis and therefore eliminated, resulting in micro-prosodic perturbations being preserved during re-synthesis.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
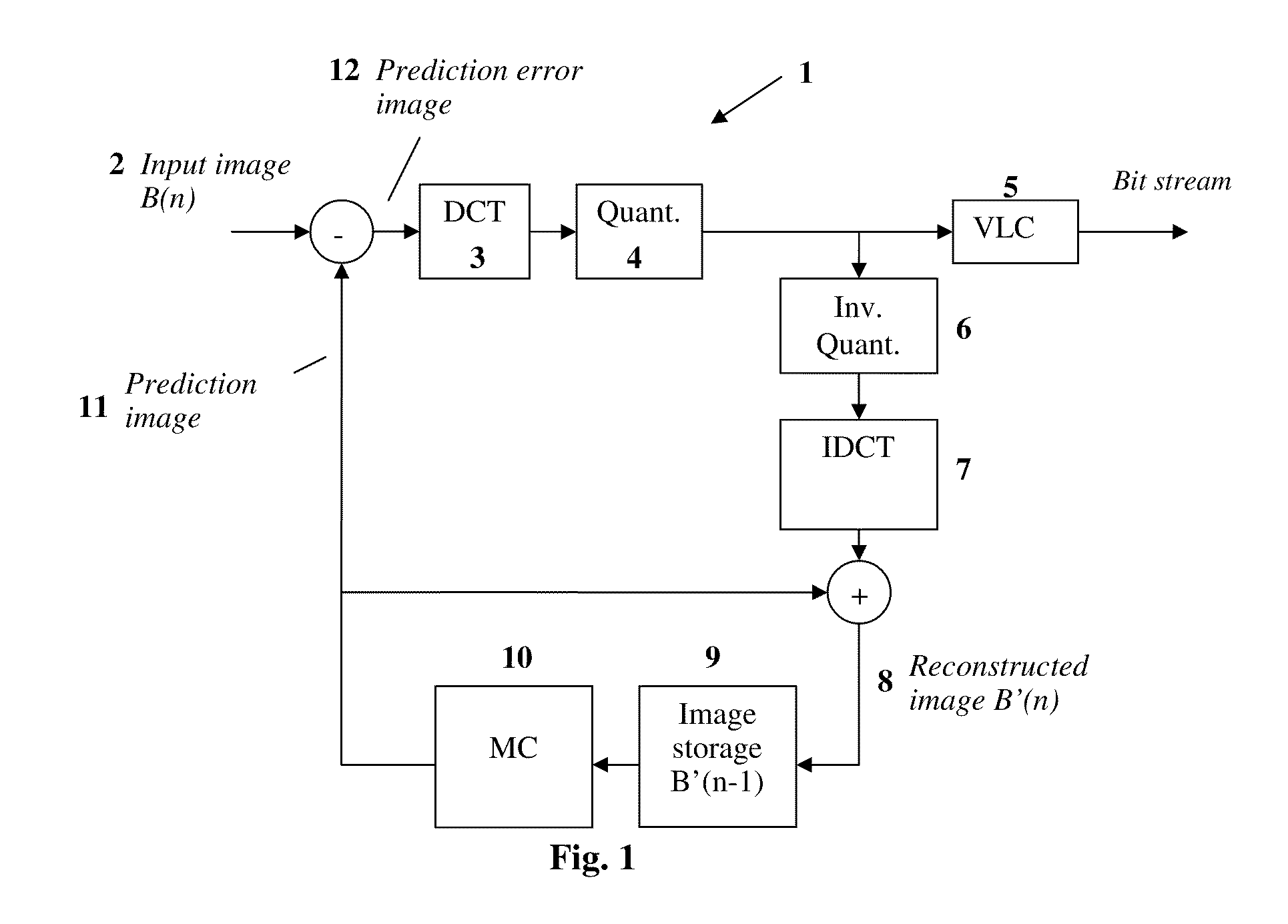
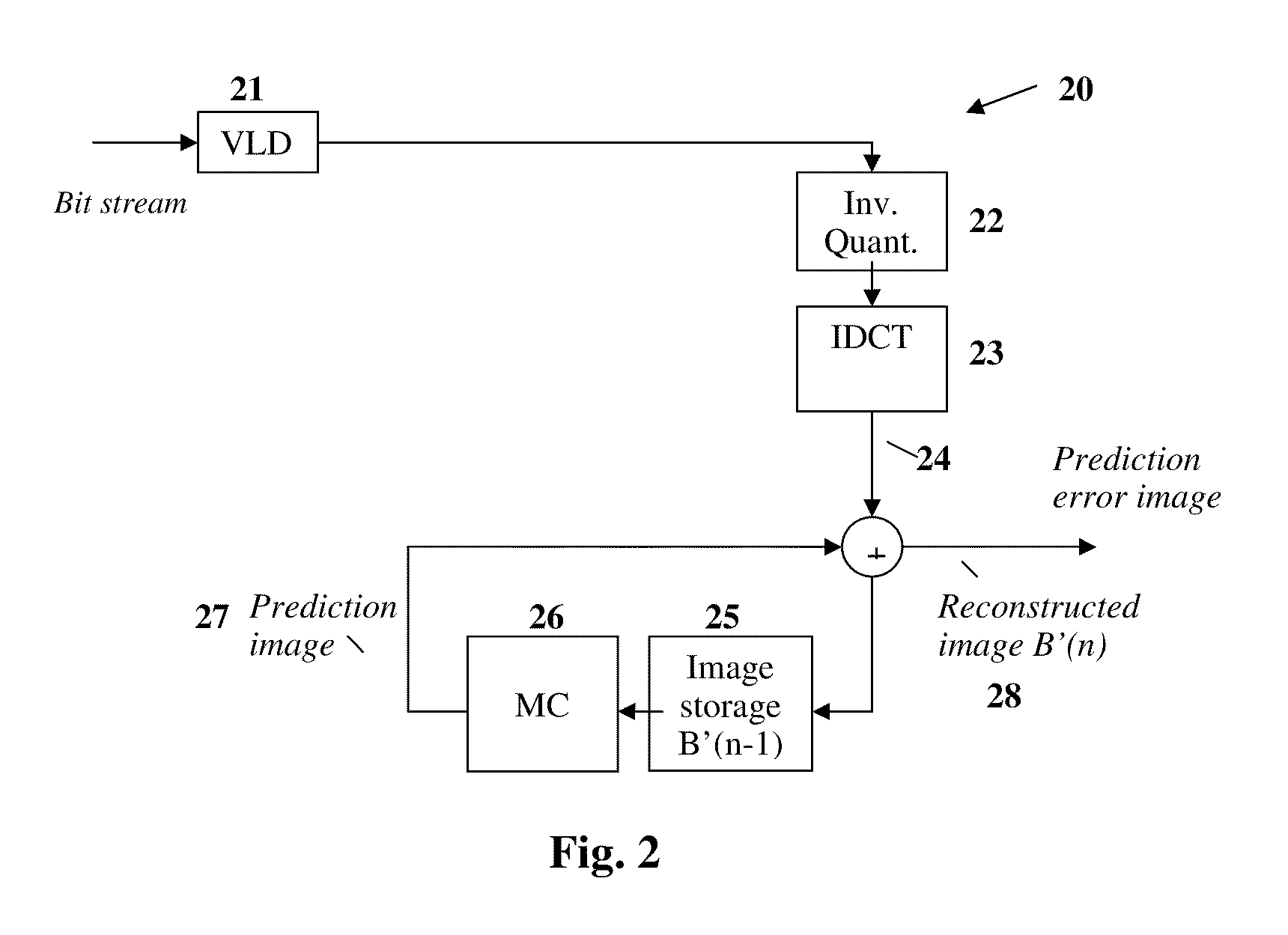
Method and device for avoiding rounding errors after performing an inverse discrete orthogonal transformation
InactiveUS20100208807A1Avoiding rounding errorColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionComputer graphics (images)Errors and residuals
The present invention provides a method for avoiding rounding errors during rounding of values after performing an inverse discrete orthogonal transformation. In a first step, a block of coefficients (F′[u][v]) is transformed into a block of image pixel values (f′[y][x]) by means of an inverse discrete orthogonal transformation, wherein each image pixel comprises an image pixel value. In a second step, a product of the block of image pixel values (f′[y][x]) with a first pixel pattern (A[y][x]) is calculated. In a third step, the product values of the second step are summed up to a first sum (Sum1′). In a fourth step, it is determined whether the first sum (Sum1′) is even or odd. In a fifth step, if the first sum (Sum1′) is even, a block of manipulation values (C[y][x]) is added to or subtracted from the block of image pixel values (f′[y][x]) for generating a manipulated block of image pixel values (f[y][x]), wherein the block of manipulation values (C[y][x]) is formed in such a way that rounding errors are avoided in a subsequent rounding operation.
Owner:ECODISC TECH +1
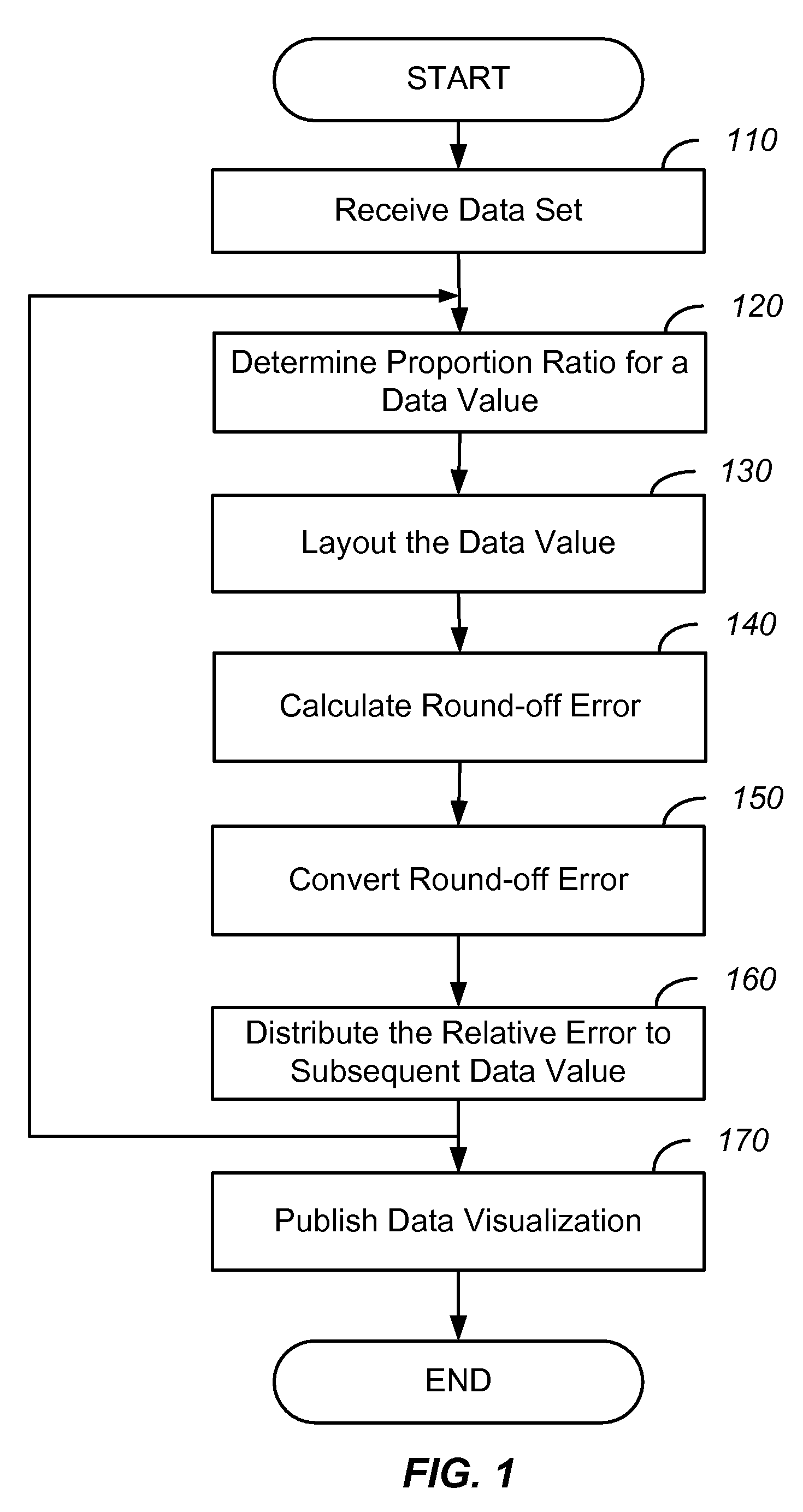
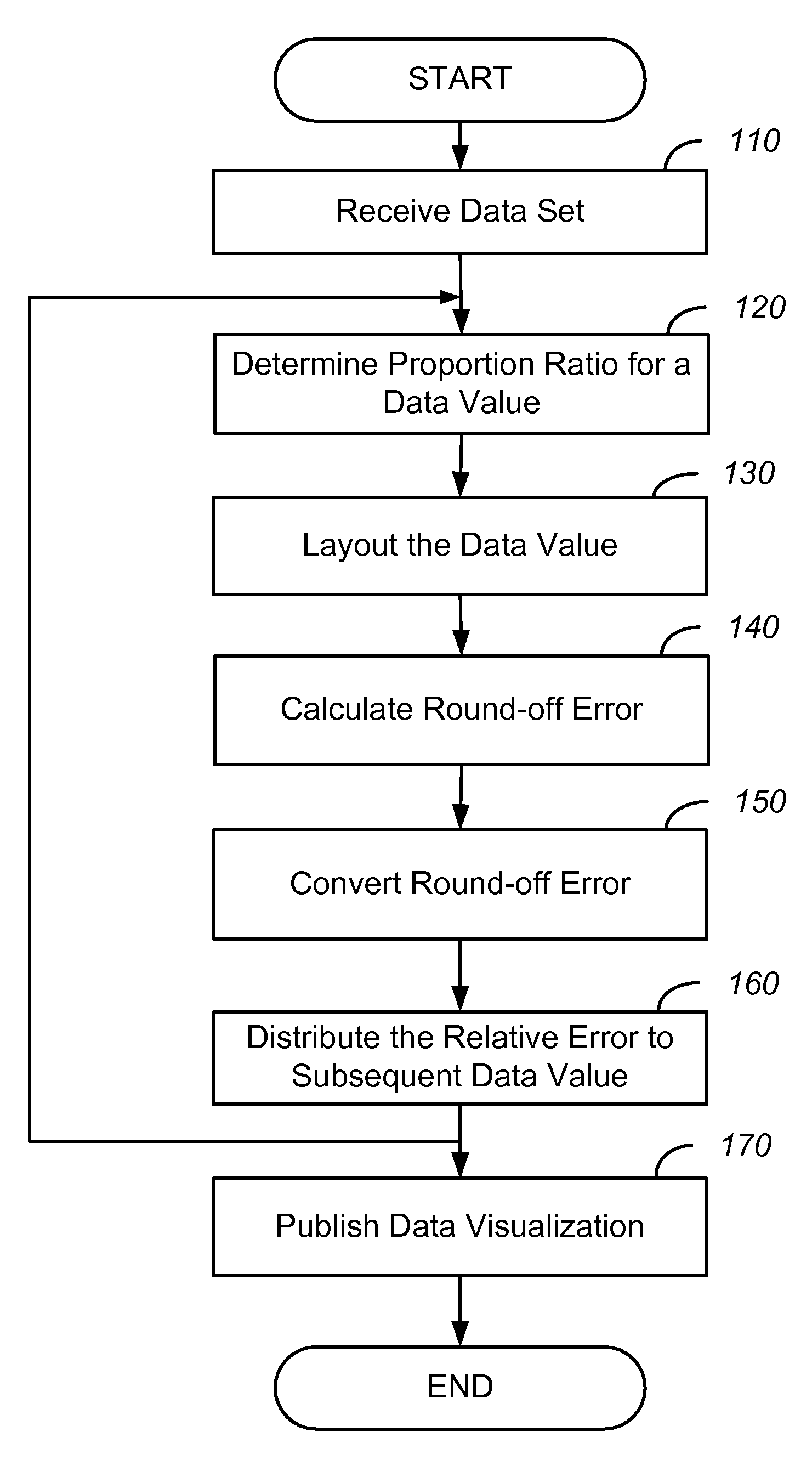
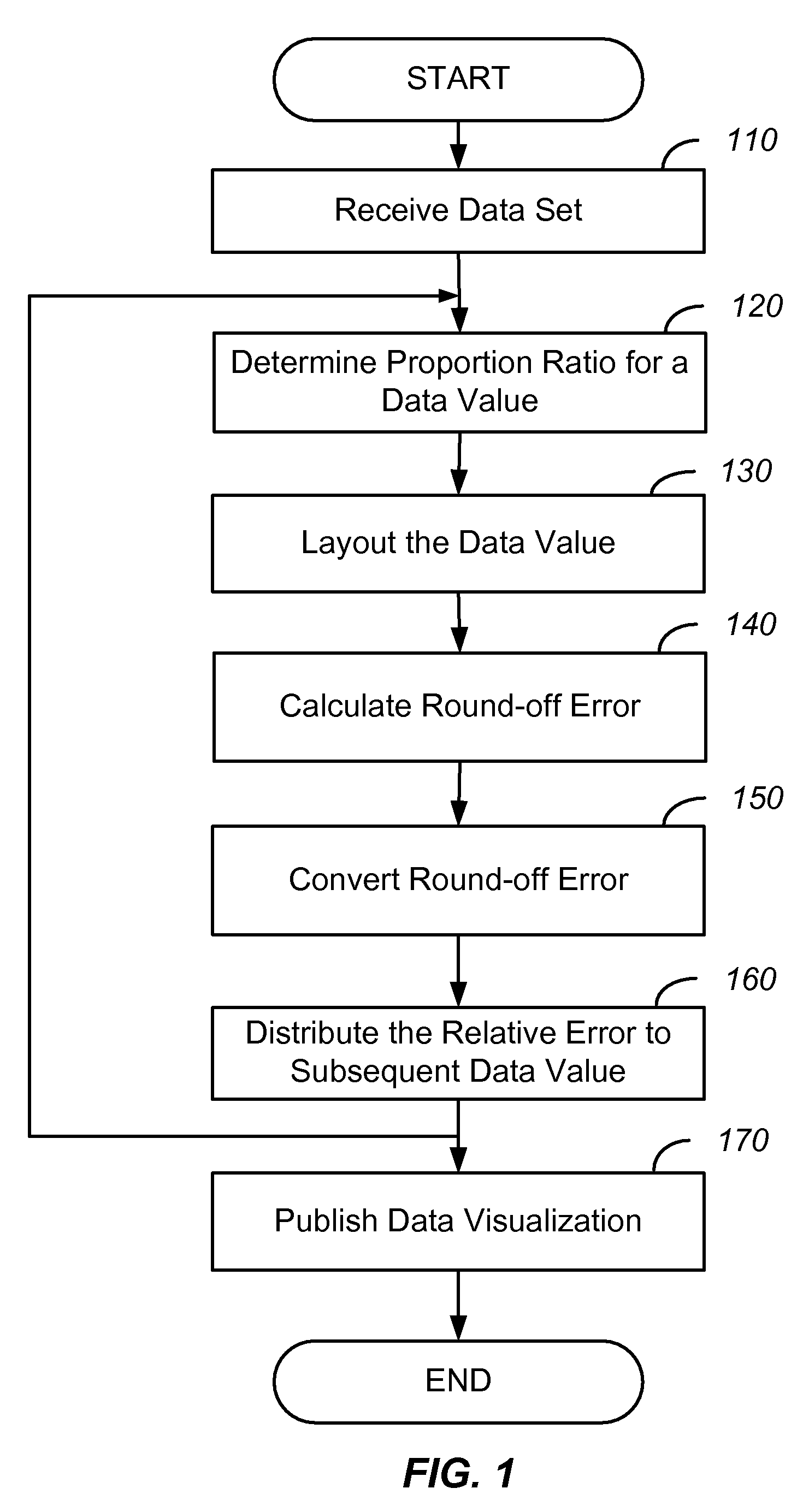
Rendering data visualization with minimal round-off error
ActiveUS20080278496A1Minimal round-off errorMinimize impactDrawing from basic elementsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsData set
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention provide for the rendering of data visualizations with minimal round-off errors. The data visualization method represents a dataset as graphical elements within a graphical layout area by performing layout of a data value within the dataset on the graphical layout area. The data value is positioned on the graphical layout area by determining a floating point position of the data value. A round-off error is calculated by casting the floating point position to an integer position on the graphical layout area. The round-off error is distributed to one or more subsequent data values that are yet to be positioned on the graphical layout area.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Neutral buoyancy robot pose and trajectory control method based on active disturbance rejection
ActiveCN107065564AImprove anti-interference abilitySmall overshootAttitude controlAdaptive controlDifferentiatorActive disturbance rejection control
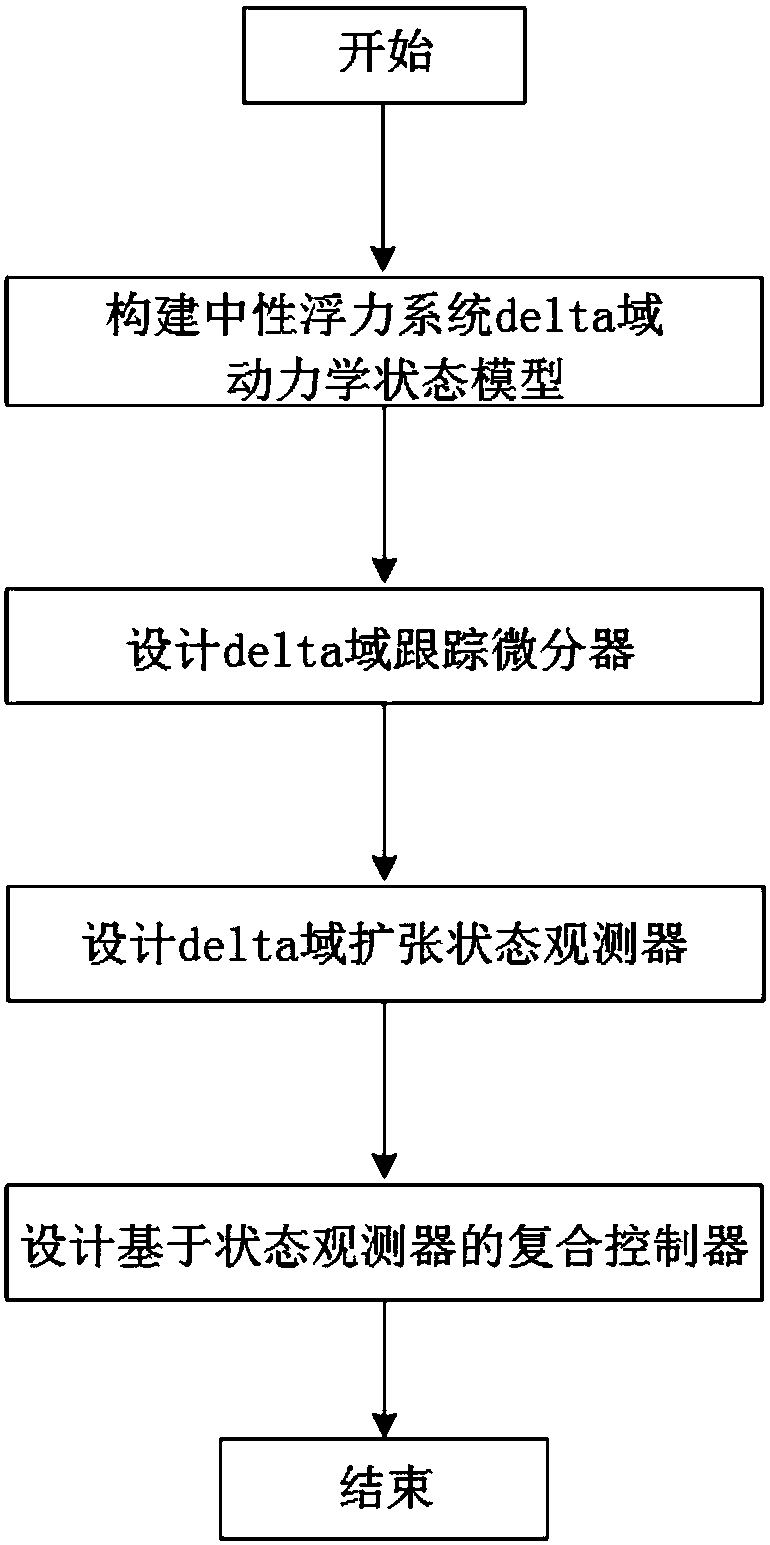
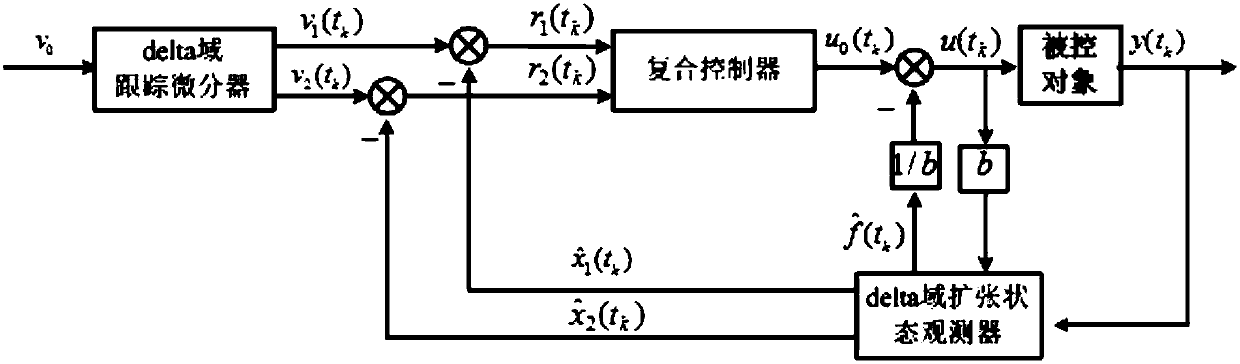
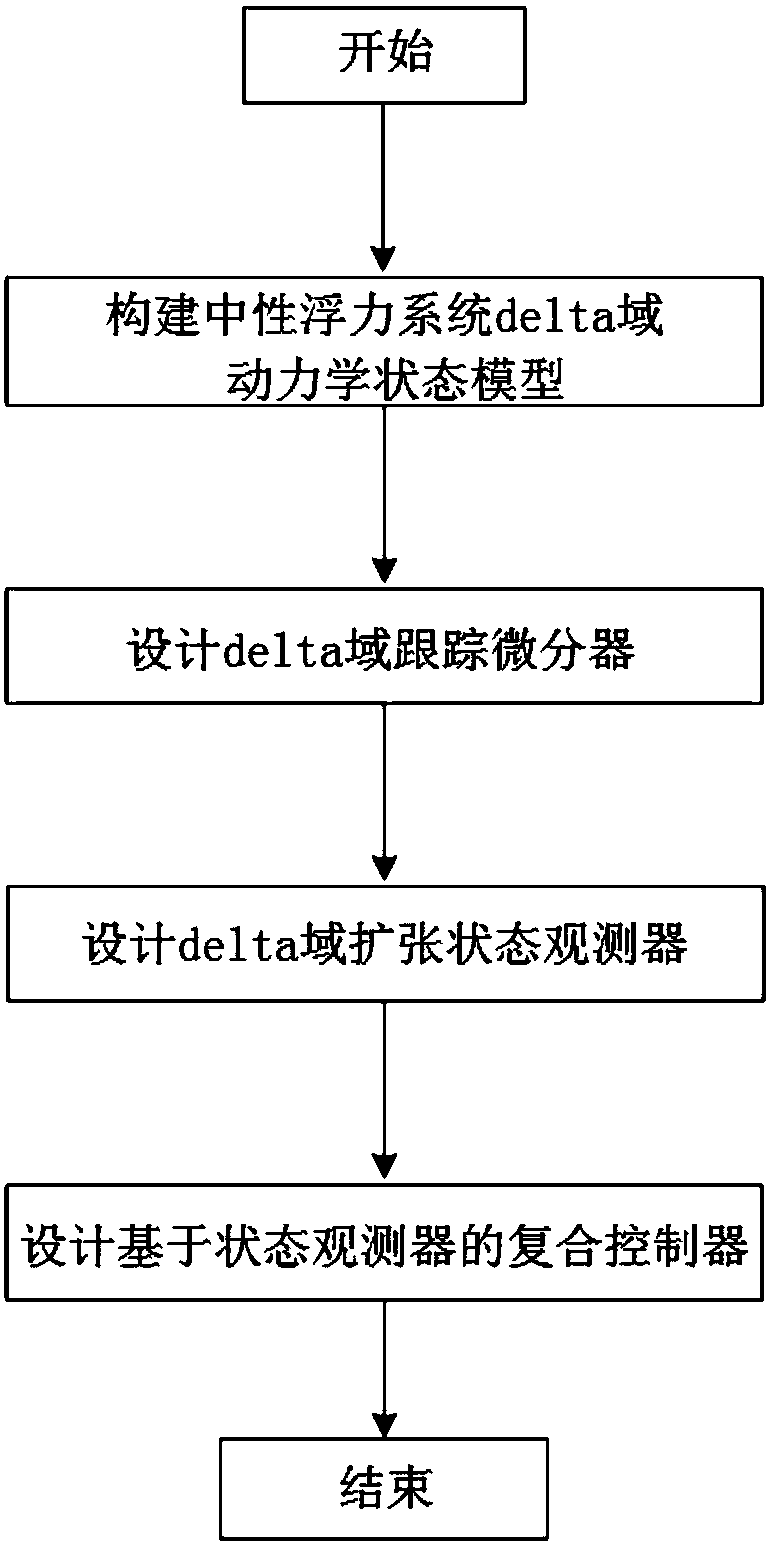
The invention discloses a neutral buoyancy robot pose and trajectory control method based on active disturbance rejection theory, the method aims at a round-off error problem caused by poor robot anti-interference ability and finite word length in a neutral buoyancy system, and delta operator theory is utilized to construct a neutral buoyancy system delta domain dynamic state equation. A delta domain tracking differentiator is designed, and a input signal transient process is arranged. A delta domain extended state observer is designed for coupling terms between water resistance and control forces in the neutral buoyancy system. The output state of the tracking differentiator and the estimation state of the extended state observer are utilized to design a delta domain compound anti-interference controller, and robot pose and trajectory control in the neutral buoyancy system is completed. According to the invention, the extended state observer is utilized to estimate total interference in the neutral buoyancy system and intra-system non-linearly coupled terms, the system anti-interference ability is improved, and the round-off error of the finite word length of system parameters is effectively reduced, and the method can be used in robot pose and trajectory high precision control under microgravity environment.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Multiple-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative passive location method based on improved distance parameterization
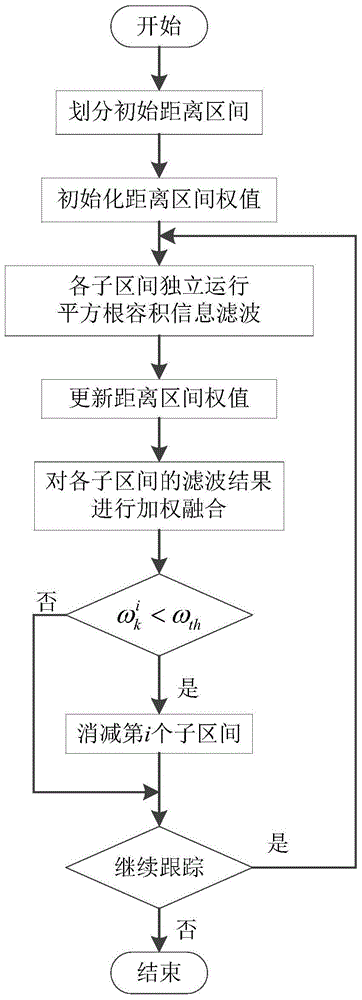
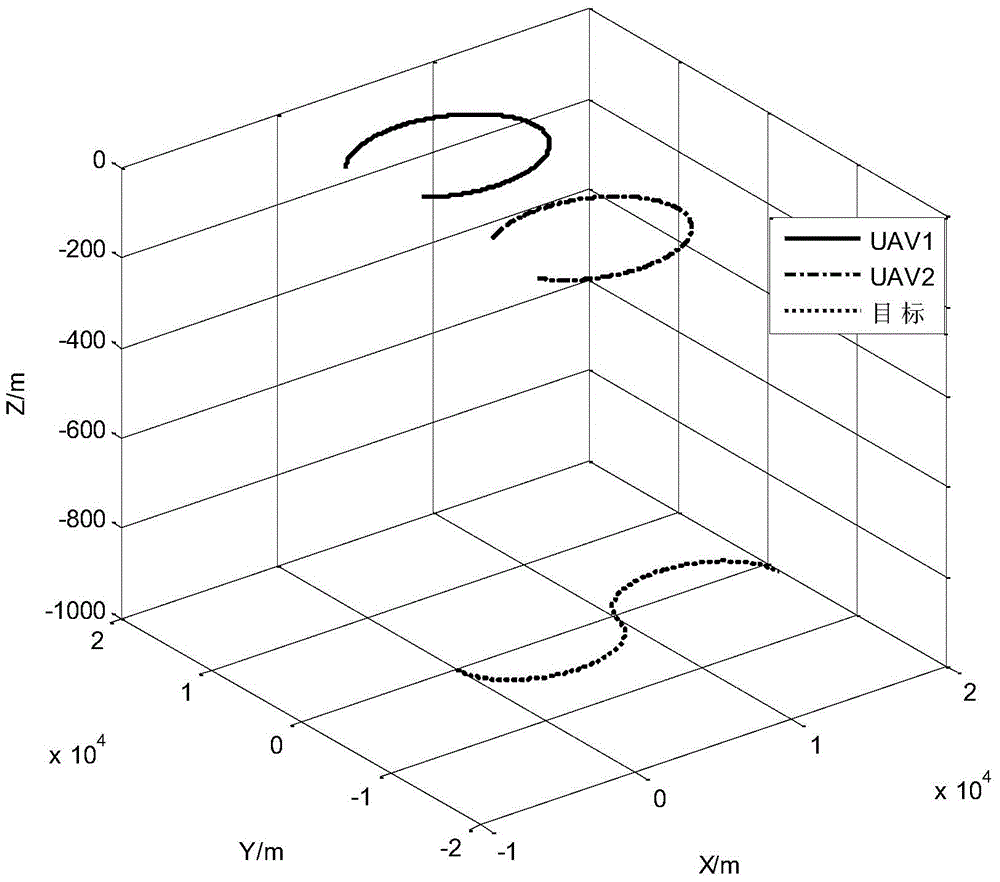
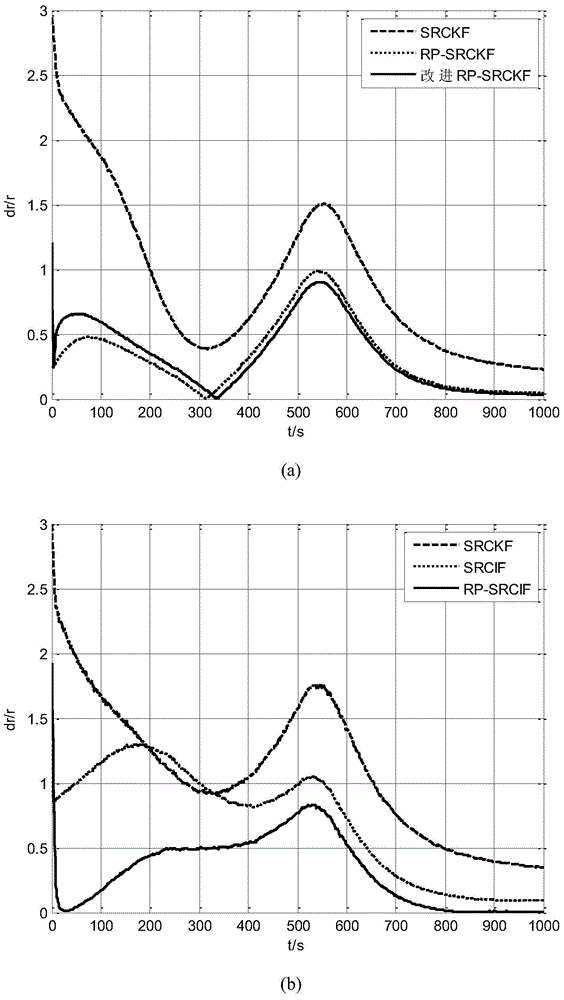
InactiveCN104833949AEliminate indeterminate problemsImprove robustnessPosition fixationUncrewed vehicleErrors and residuals
The invention provides a multiple-unmanned aerial vehicle cooperative passive location method based on improved distance parameterization. First, an initial distance interval is divided, and the weight of the distance interval is initialized; then, squared root cubature information filtering is performed separately on the sub intervals, and the weight of the distance interval is updated; and weighted fusion is performed on filtering results of all the sub intervals to obtain a final location result. The problem that the covariance matrix is not positive definite due to round-off error of a computer is eliminated, and the robustness of the filtering method is improved. Compared with a traditional distance parameterization method, the amount of calculation of the adopted improved distance parameterization method is greatly reduced. The influence of the initial filtering value to the location performance is avoided effectively, and the real-time performance of the filtering method is improved. Information filtering under a fully distributed fusion estimation structure makes fusion estimation calculation easier and improves the location accuracy.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
System and method for symmetric parameterization of independently tessellated patches
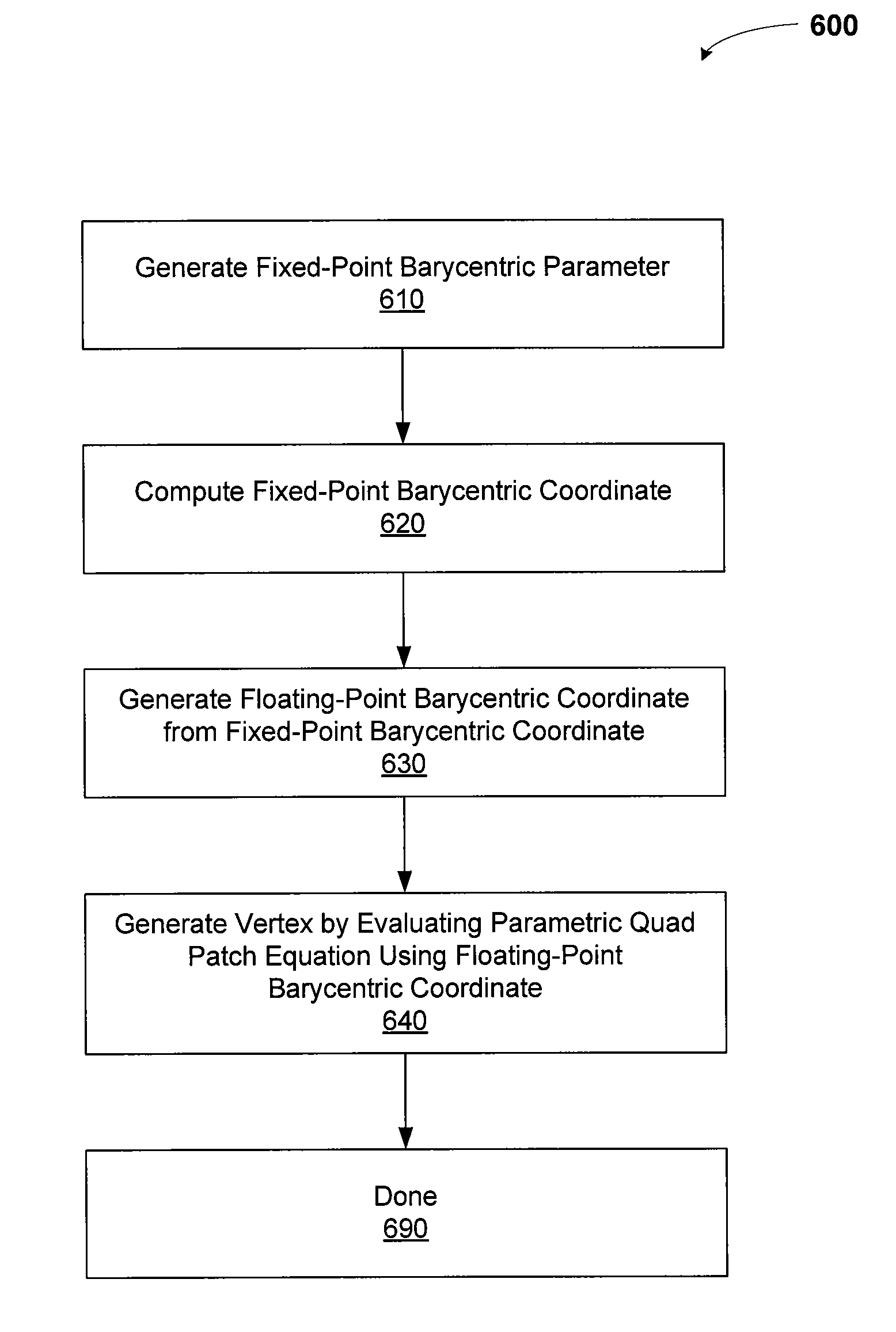
ActiveUS8558833B1Improve performance3D-image rendering3D modellingComputer graphics (images)Floating point
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a technique for consistently evaluating geometric patches with shared boundaries using barycentric coordinates. A barycentric parameter is generated and represented using a fixed-point fraction. The barycentric parameter is then used to generate a fixed-point barycentric coordinate. The fixed-point barycentric coordinate is then converted to a floating-point representation for evaluating the geometric patches. Computing shared boundary splits using fixed-point fractions eliminates inconsistencies in associated barycentric coordinates due to round-off errors. Evaluating geometric patch equations using consistent barycentric coordinates facilitates precise, consistent computation of vertices along shared boundaries.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Rendering data visualization with minimal round-off error
Systems and methods in accordance with various embodiments of the present invention provide for the rendering of data visualizations with minimal round-off errors. The data visualization method represents a dataset as graphical elements within a graphical layout area by performing layout of a data value within the dataset on the graphical layout area. The data value is positioned on the graphical layout area by determining a floating point position of the data value. A round-off error is calculated by casting the floating point position to an integer position on the graphical layout area. The round-off error is distributed to one or more subsequent data values that are yet to be positioned on the graphical layout area.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
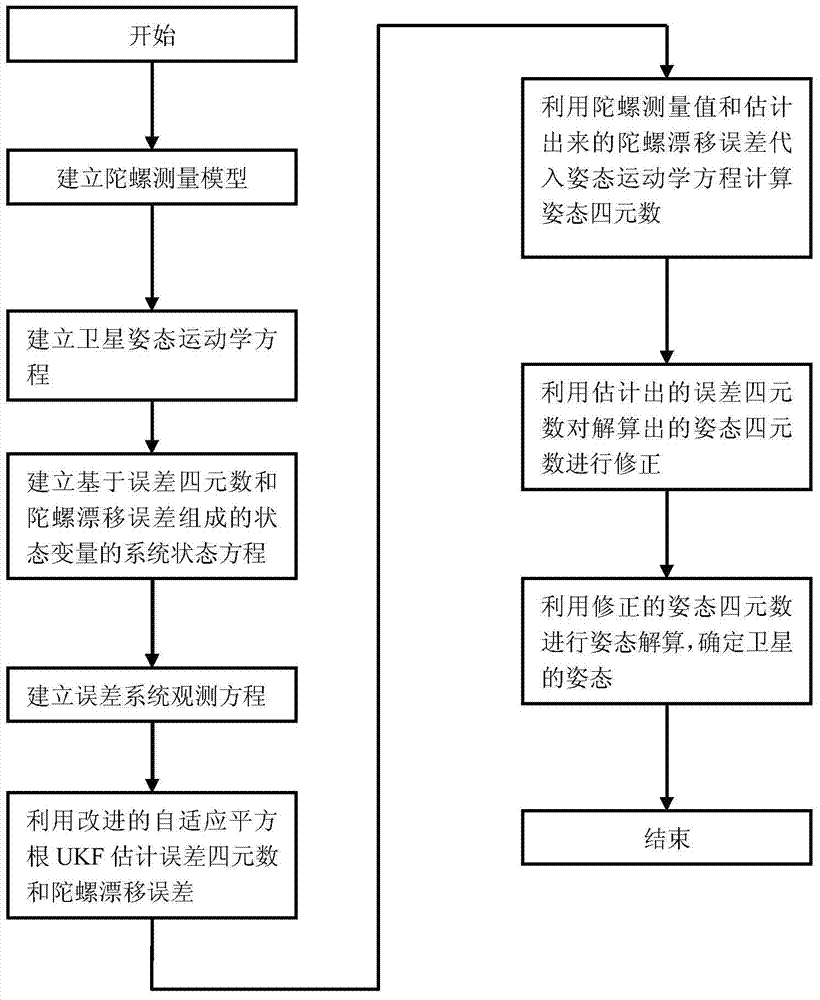
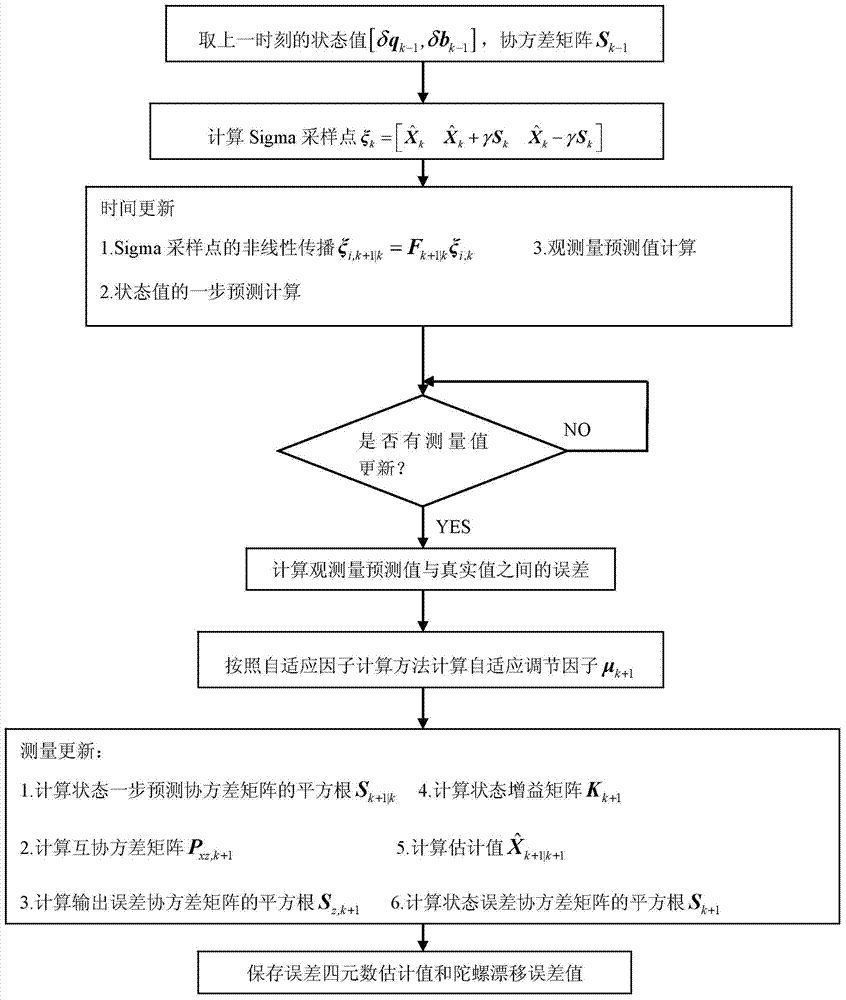
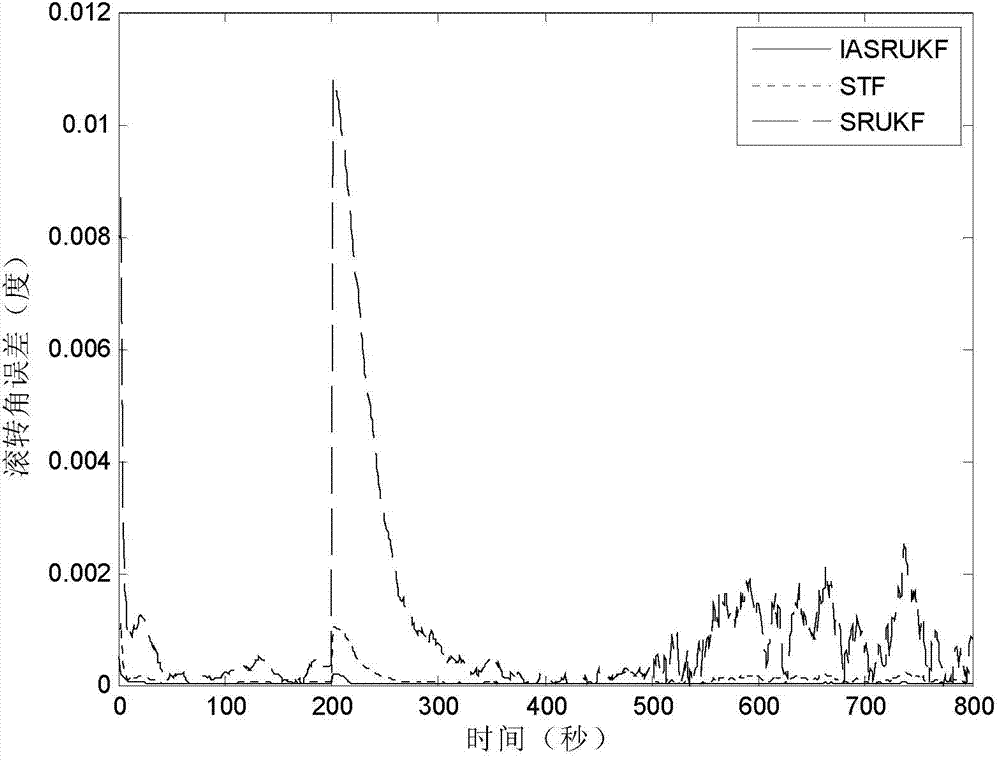
Satellite attitude determining method based on improved self-adaptive square root UKF (Unscented Kalman Filter) algorithm
InactiveCN103940433AImprove stabilityAdaptableInstruments for comonautical navigationKinematics equationsKinematics
The invention relates to a satellite attitude determining method based on an improved self-adaptive square root UKF (Unscented Kalman Filter) algorithm, which belongs to the technical field of satellite attitude determination and solves the problems that a satellite attitude determining system is unstable, the satellite attitude precision is low, and the traceability to an virtual condition of a satellite is weak due to overlarge round-off errors numerically calculated by virtue of existing EKF (Extended Kalman Filter), UKF (Unscented Kalman Filter) and SRUKF (Square Root Unscented Kalman Filter) algorithms when the satellite attitude determining system suffers from uncertain interferences and is influenced by noise. The satellite attitude determining method comprises the main realization processes: estimating an error quaternion and a gyroscopic drift error by virtue of the improved self-adaptive square root UKF; substituting gyroscopic measurement value and the estimated gyroscopic drift error into an attitude kinematical equation to calculate an attitude quaternion; correcting the calculated attitude quaternion by virtue of the estimated error quaternion; carrying out attitude resolving by virtue of the corrected attitude quaternion so as to determine the attitude of the satellite. The satellite attitude determining method is suitable for the technical field of the satellite attitude determination.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Rendering stroke pairs for graphical objects
InactiveUS20070216689A1Reduce the possibilityFilling planer surface with attributesGraphicsExternal reference
The principles of the present invention relate to rendering stroke pairs. A graphical object includes at least a first stroke and a second similarly oriented second stroke collectively representing a stroke pair. A calculated distance between the first stroke and the second stroke is constrained (e.g., to a center line between the strokes) to mitigate the possibility of rounding errors causing the represented stroke pair to be inappropriately rendered. After the stroke pair is constrained, controls points of the individual strokes can be adjusted so that the individual strokes are appropriately rendered at their respective constrained locations. The adjusted stroke pair is constrained between external reference points for appropriate rendering relative to other graphical objects. The graphical object, including the adjusted constrained stroke pair, is rendered at an output device.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
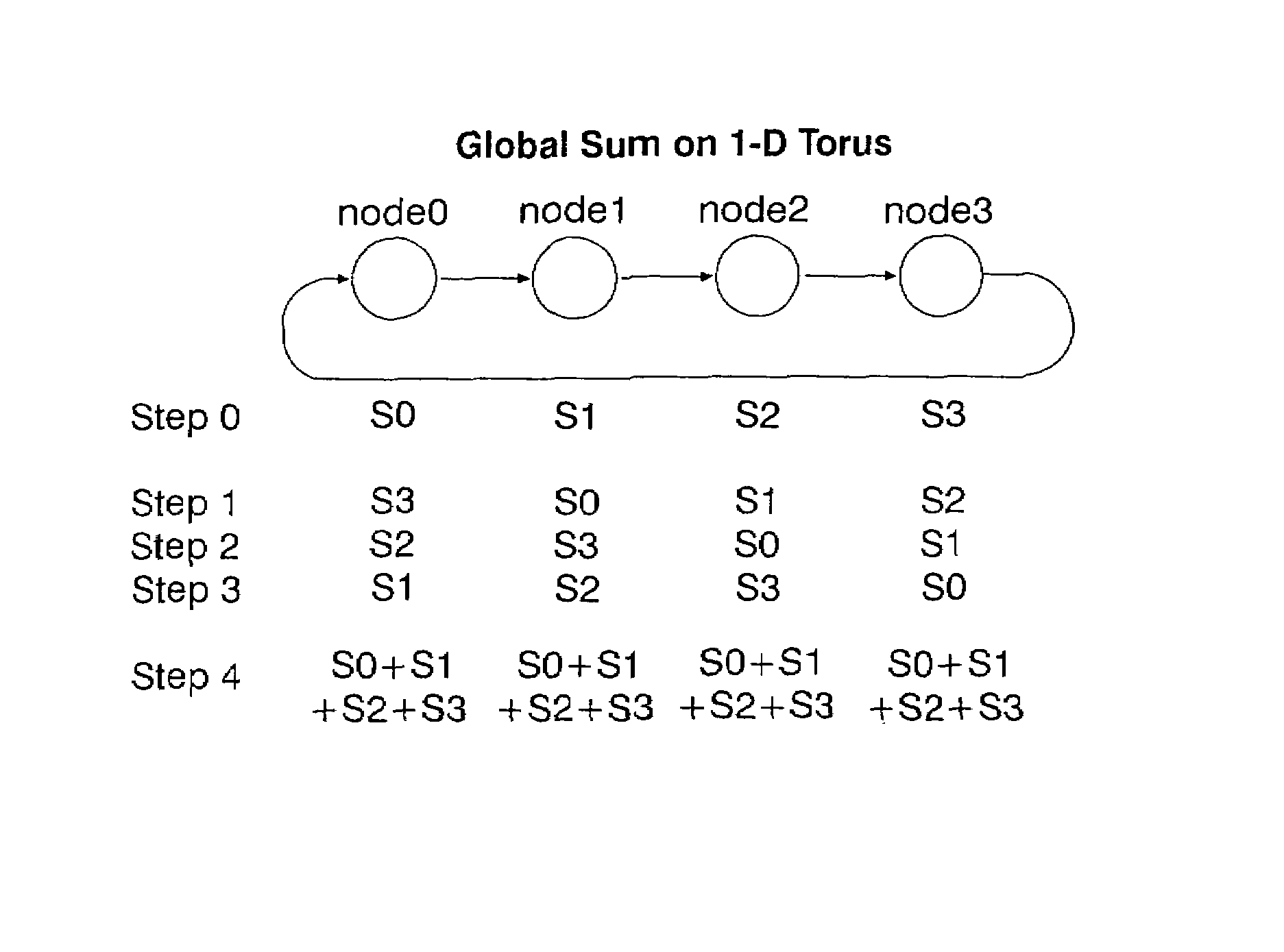
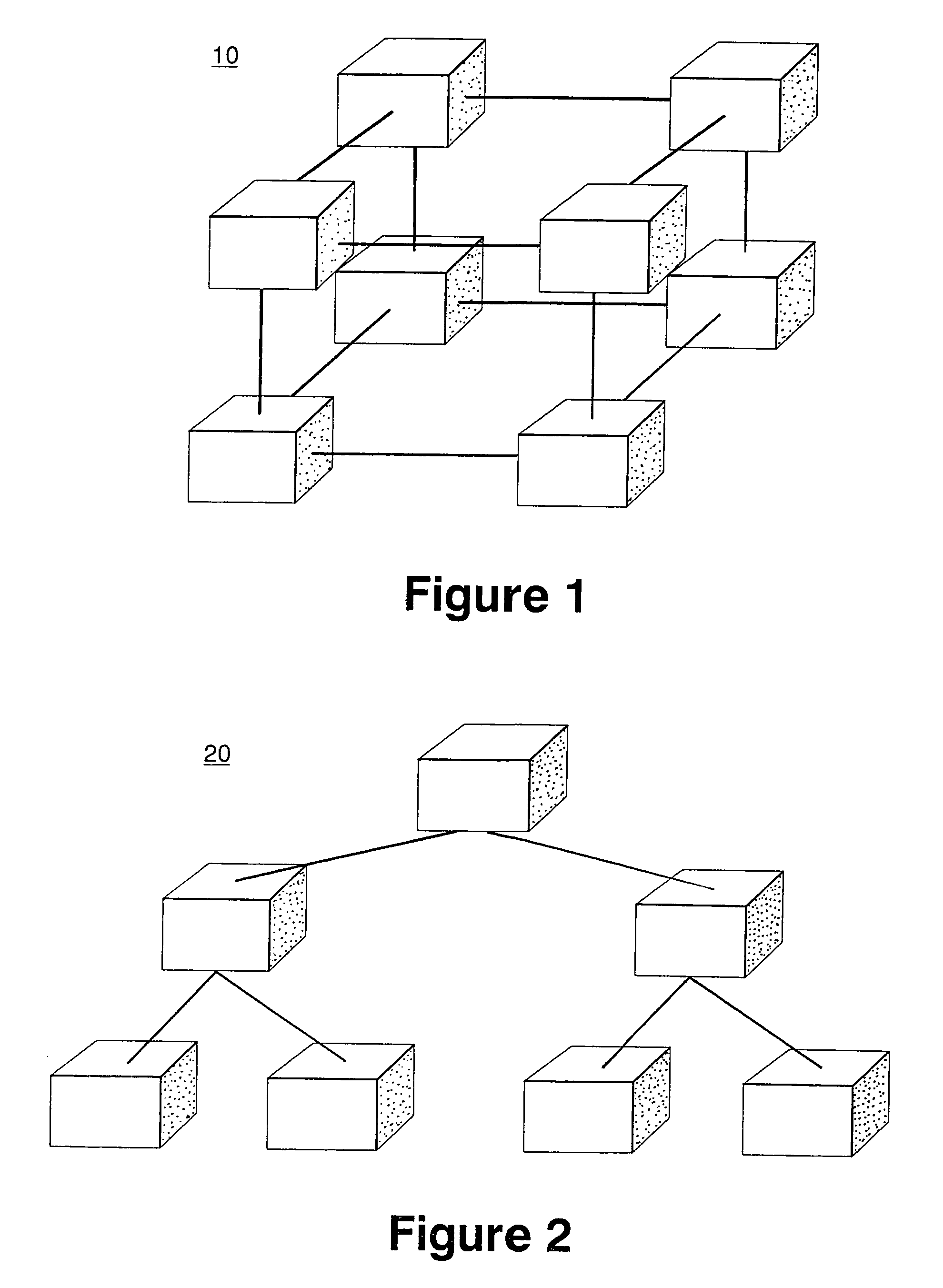
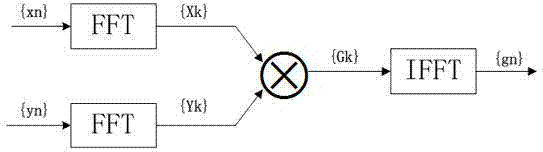
Arithmetic functions in torus and tree networks
InactiveUS7313582B2Accelerated programImprove efficiencyError preventionDigital data processing detailsNODALAbsolute minimum
Methods and systems for performing arithmetic functions. In accordance with a first aspect of the invention, methods and apparatus are provided, working in conjunction of software algorithms and hardware implementation of class network routing, to achieve a very significant reduction in the time required for global arithmetic operation on the torus. Therefore, it leads to greater scalability of applications running on large parallel machines. The invention involves three steps in improving the efficiency and accuracy of global operations: (1) Ensuring, when necessary, that all the nodes do the global operation on the data in the same order and so obtain a unique answer, independent of roundoff error; (2) Using the topology of the torus to minimize the number of hops and the bidirectional capabilities of the network to reduce the number of time steps in the data transfer operation to an absolute minimum; and (3) Using class function routing to reduce latency in the data transfer. With the method of this invention, every single element is injected into the network only once and it will be stored and forwarded without any further software overhead. In accordance with a second aspect of the invention, methods and systems are provided to efficiently implement global arithmetic operations on a network that supports the global combining operations. The latency of doing such global operations are greatly reduced by using these methods.
Owner:IBM CORP
Circuit structure using number theoretic transform for calculating cyclic convolution
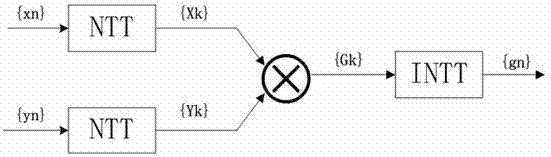
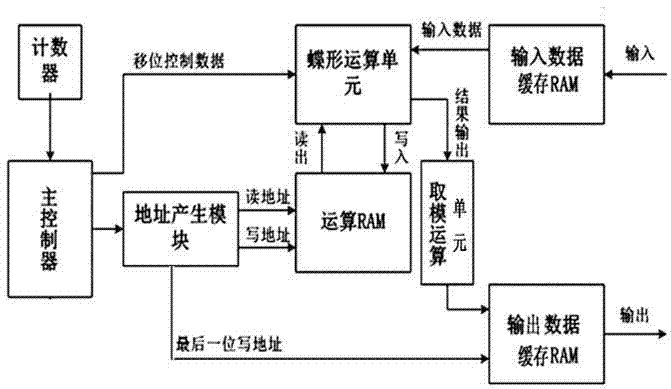
ActiveCN103870438AEliminate rounding errorsReduce areaComputations using residue arithmeticComplex mathematical operationsBase functionCircuit design
The invention belongs to the technical field of integrated circuit design, and particularly relates to a circuit structure using number theoretic transform for calculating cyclic convolution. The circuit structure comprises an input data buffer memory RAM (random-access memory), an output data buffer memory RAM, an operation RAM, a counter, a main controller, an address generating module, a butterfly-shaped operation module, a mold take-up operation unit and the like. According to the circuit structure, only addition (subtraction) and displacement operation is needed in the transform, and multiplication is not needed, so the operation speed is accelerated, the round-off error caused by FFT (fast Fourier transform) is also eliminated through FNT (Fermat number theoretic transform), and the high-precision convolution can be obtained; and in addition, the base function access is not needed, so the storage space is saved, the circuit structure belongs to a circuit structure capable of realizing fast cyclic convolution at smaller chip area and lower power consumption, and the circuit structure can be preferably applied to the fields of image filtering and image processing.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
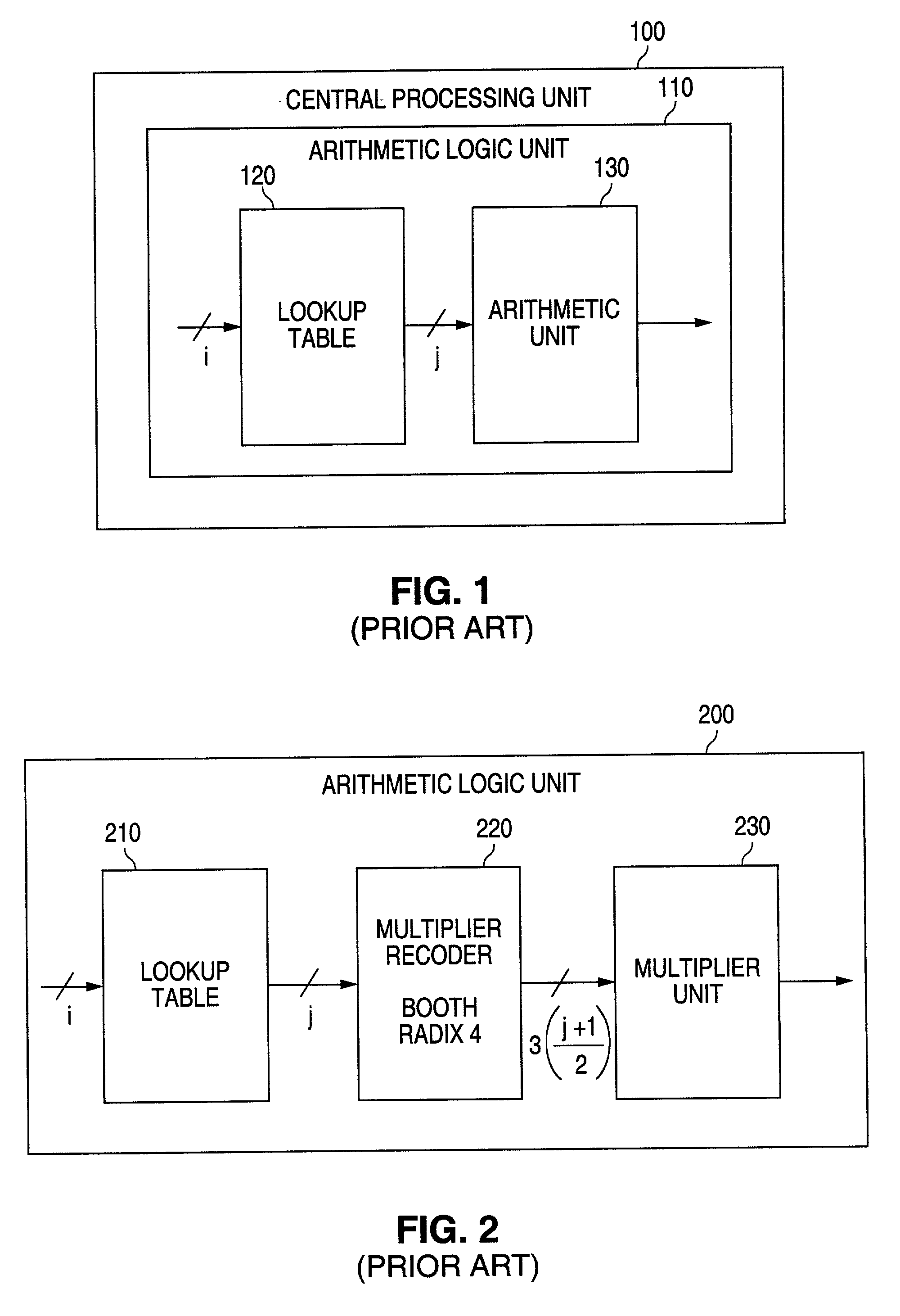
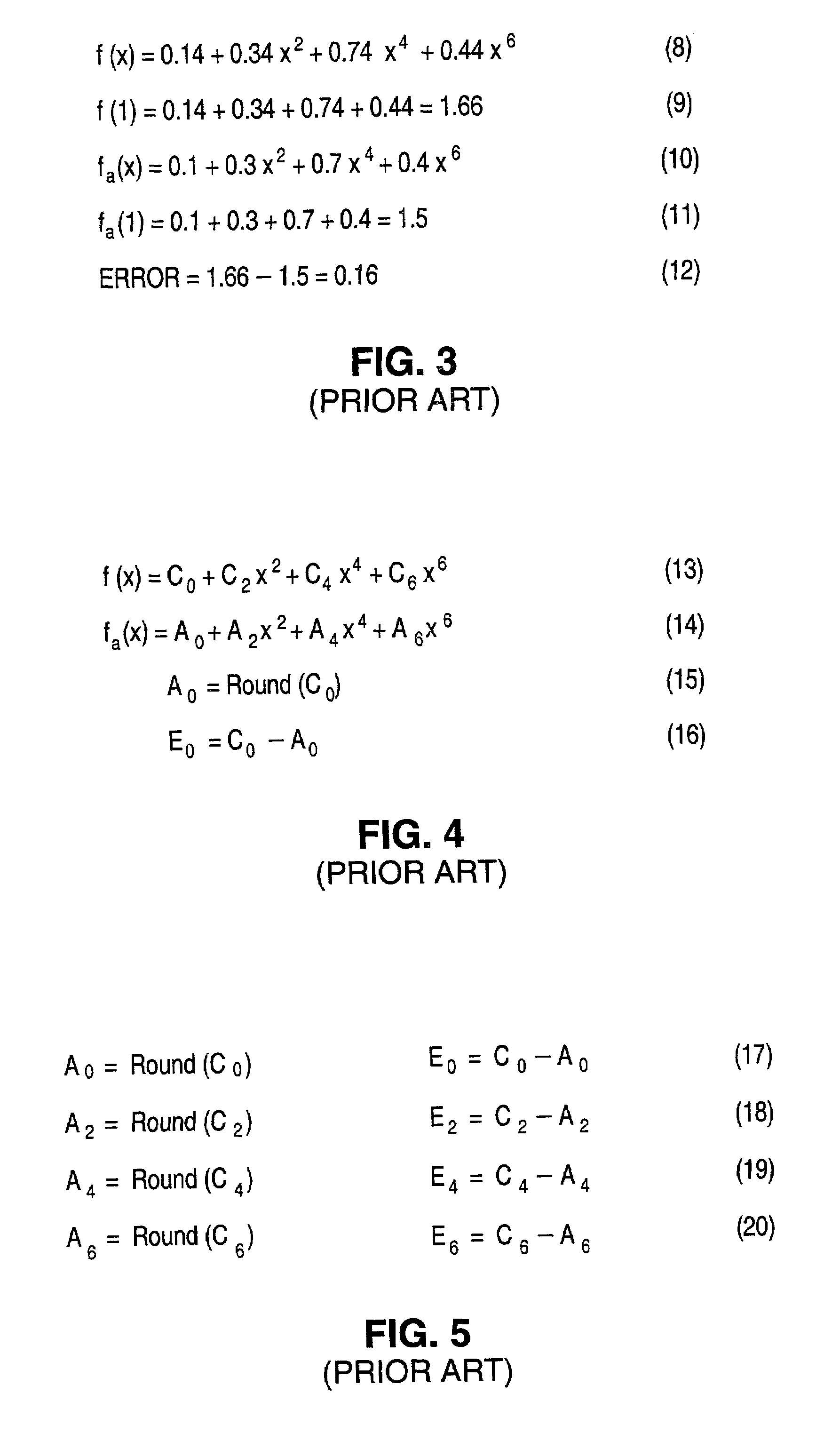
Apparatus and method for minimizing accumulated rounding errors in coefficient values in a lookup table for interpolating polynomials
InactiveUS6978289B1Error minimizationDigital function generatorsComplex mathematical operationsComputer hardwareLookup table
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
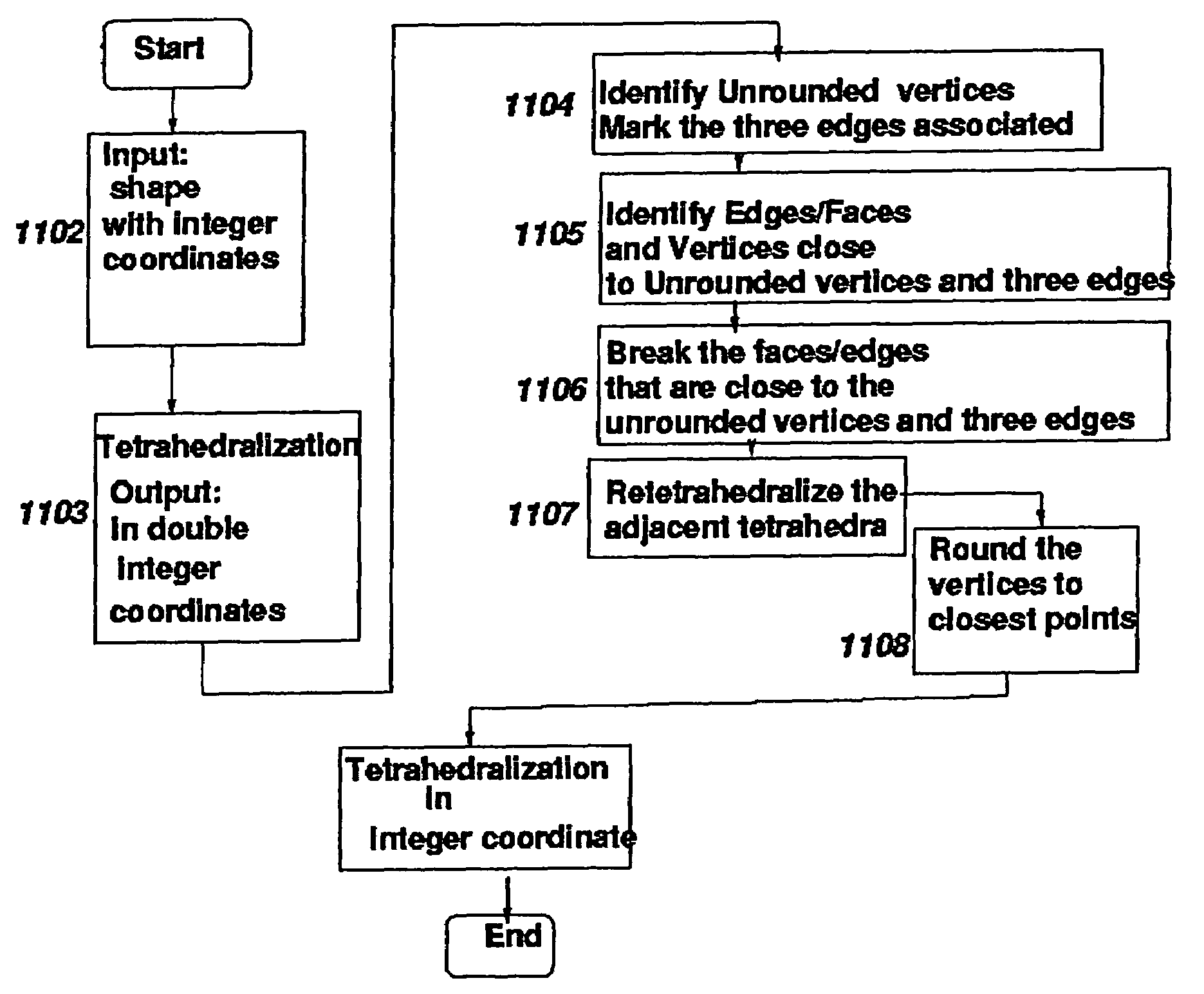
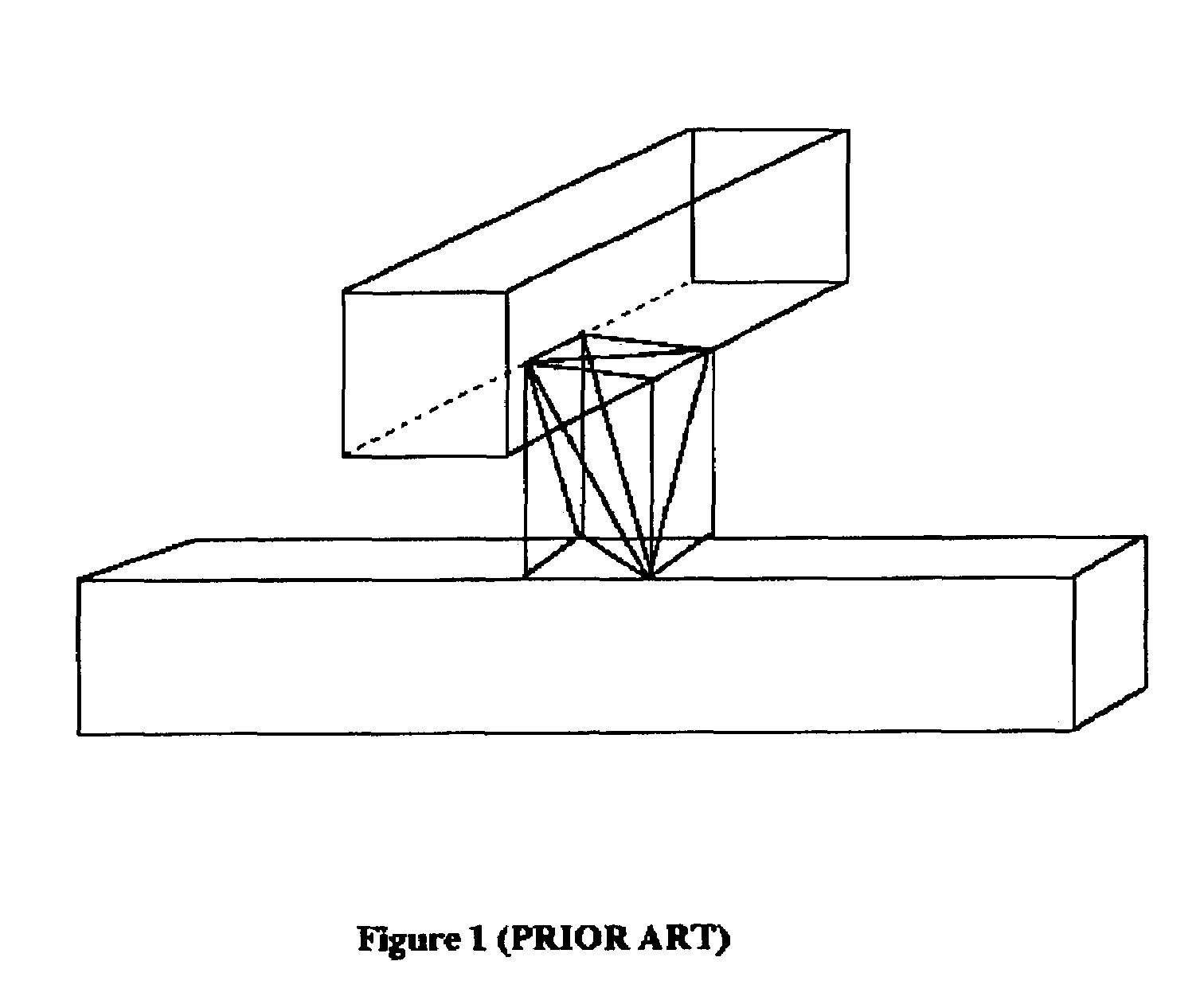
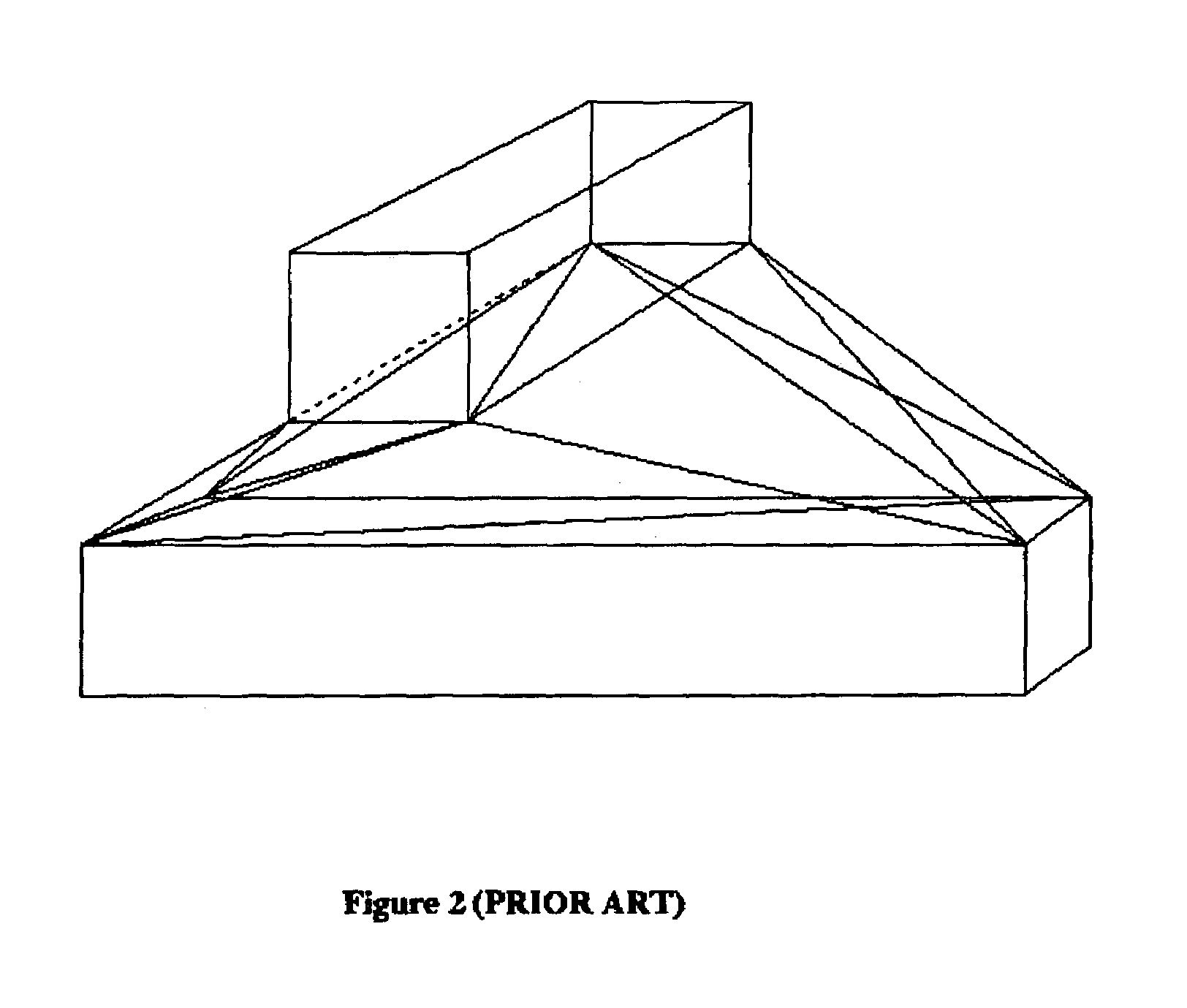
Robust tetrahedralization and triangulation method with applications in VLSI layout design and manufacturability
ActiveUS7075532B2Avoid volumePrevent inconsistency in processDetecting faulty computer hardwareCathode-ray tube indicatorsTopological consistencyElement analysis
A tetrahedralization and triangulation method used with the proximity based rounding method to satisfy topological consistency of tetrahedralization with the bounded precision of a digital computer is described. Tetrahedralization is applied to a VLSI design, and more specifically for solving Maxwell's equation to extract parasitic capacitances and 3-D optical proximity correction applications. The exactness of solving Maxwell's equation and finite element analysis depends on the correctness of the topological properties of the tetrahedralization. Among the important aspects of the correctness of the topological properties is the absence of spurious intersection of two or more tetrahedra. In a typical digital computer, numbers are represented using finite sized words. Round-off errors occur when a long number is represented using the finite word size. As a result, tetrahedralization loses its topological consistency. The proximity based rounding method finds potential locations of spurious intersections and pre-corrects these locations to avoid the generation of any topological inconsistencies.
Owner:TWITTER INC
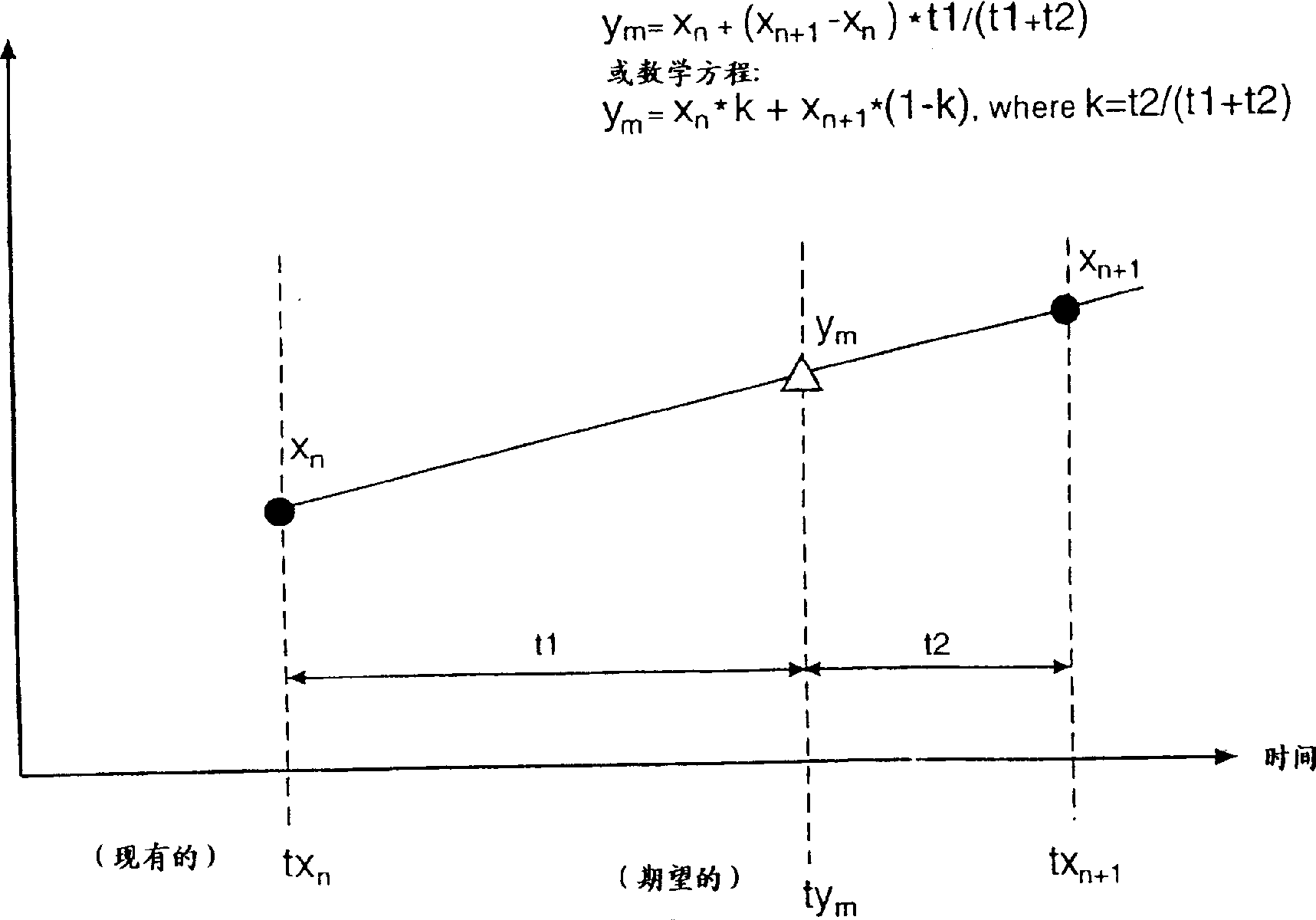
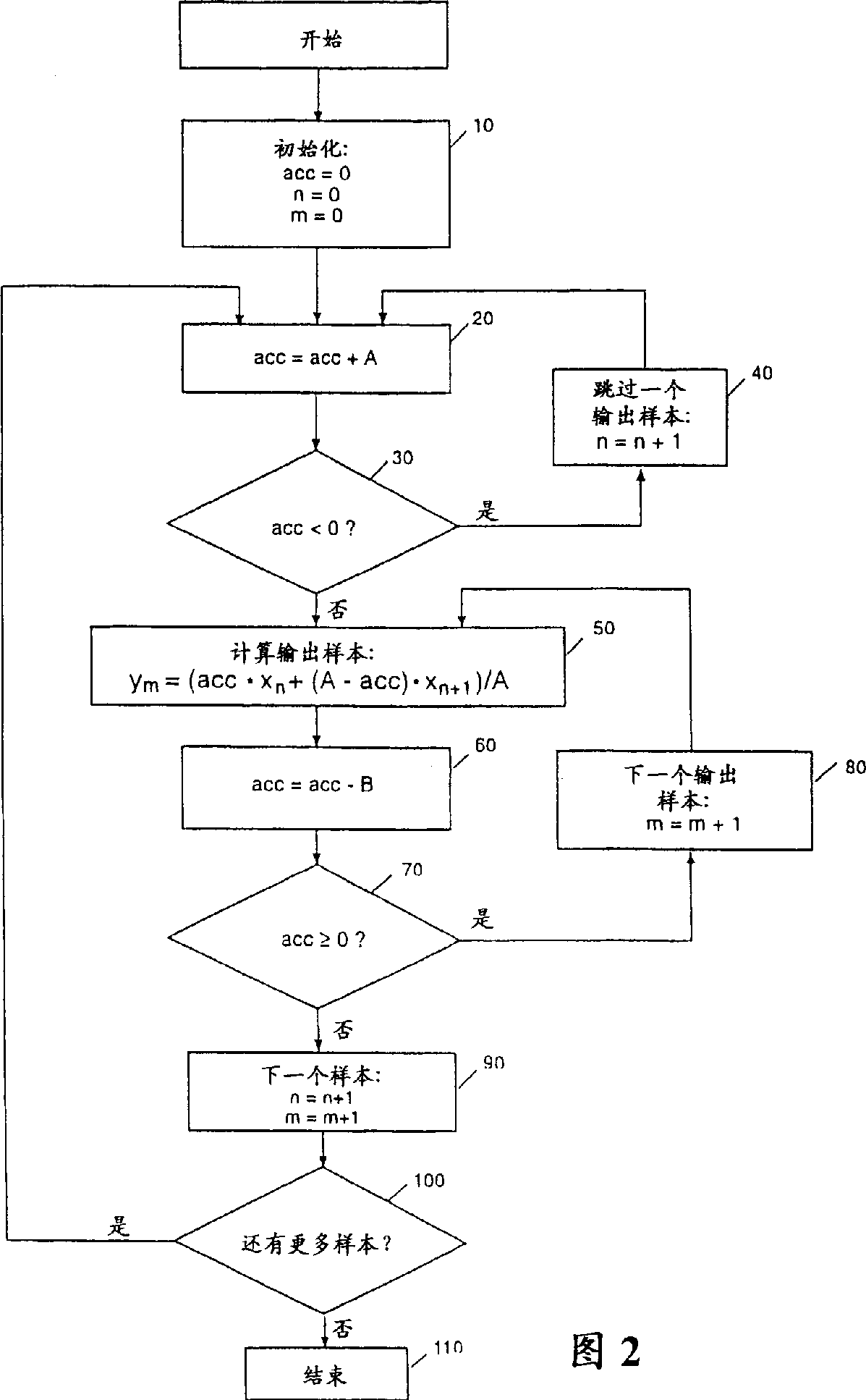
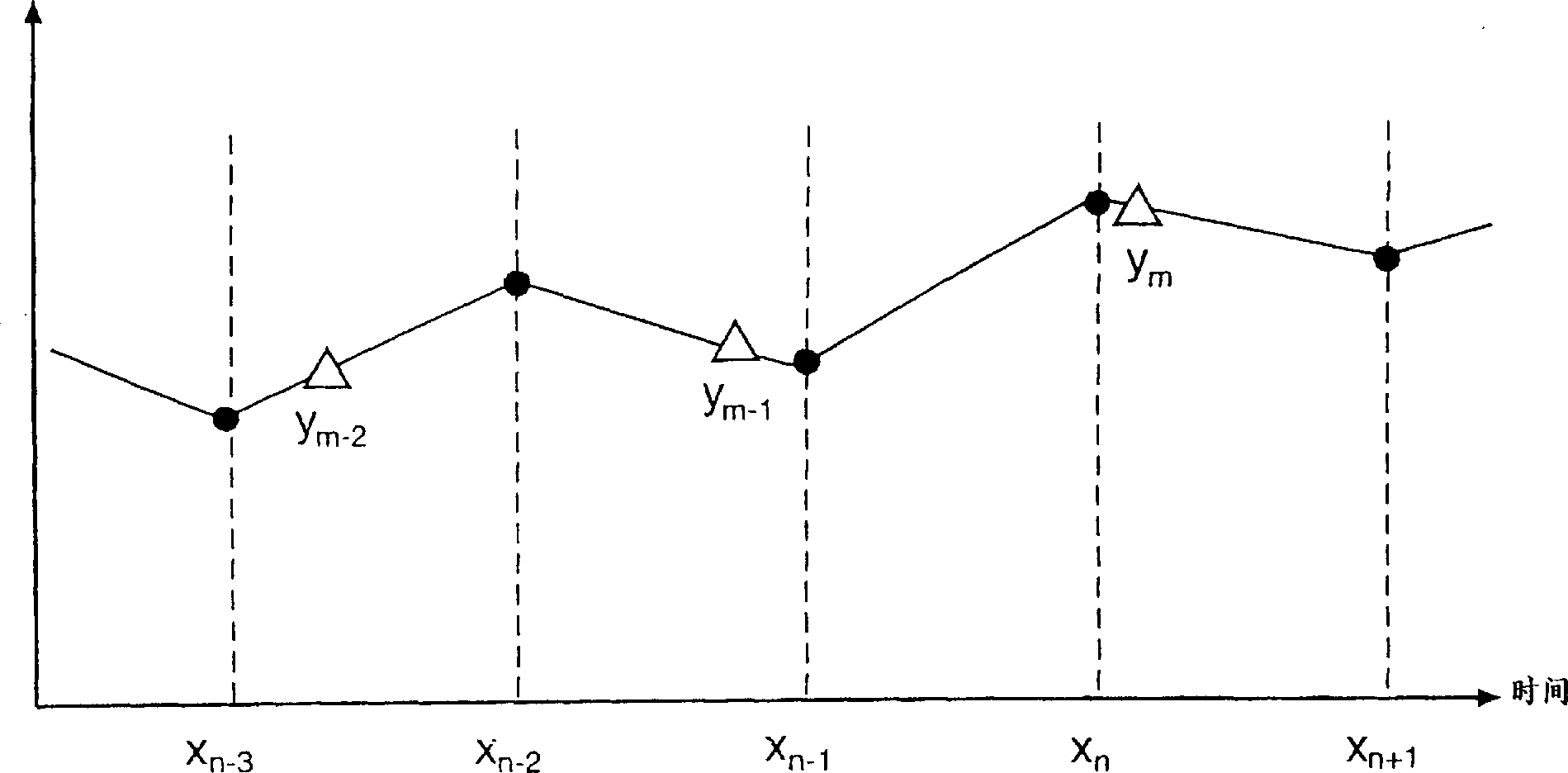
Sample rate converter
A sample rate converter (200) is described for converting an input data stream including a plurality of input samples (X) at one sample rate to an output data stream including a plurality of output samples (Y) at another sample rate. The converter uses an interpolation approach that utilizes an integer accumulator (220) to track the timing relation between input samples and output samples. Based on the value of the accumulator, the method determines if the correct input samples are being used to calculate the current output sample. If so, the output sample is calculated as a function of the input samples and the accumulator value. The converter provides the robustness of a table based conversion approach without the need to precalculate and store a table, simplifies the calculations involved, and is less sensitive to numeric round off errors.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
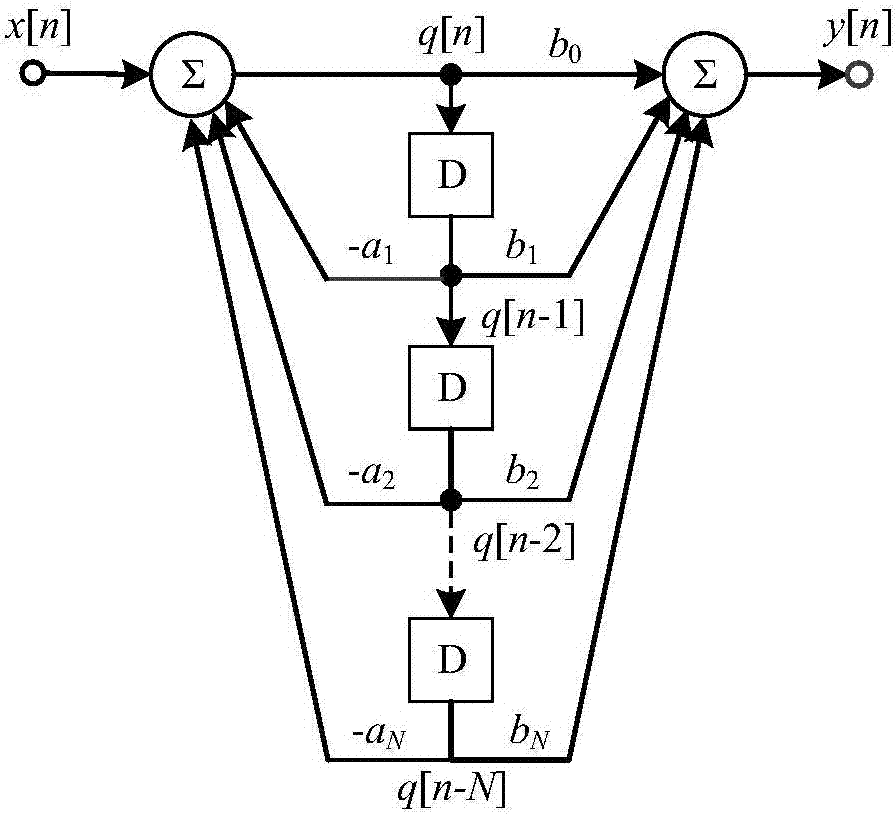
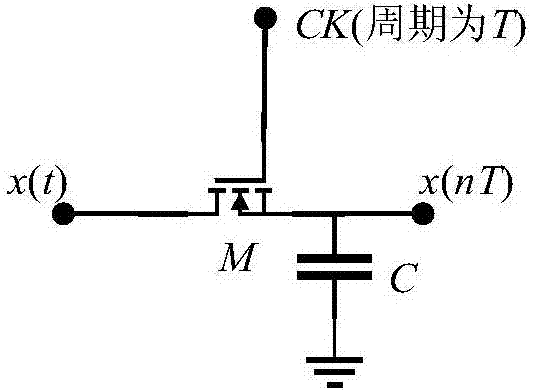
Programmable IIR filter analog hardware implementation method based on memristor
InactiveCN107241080AChange the filter coefficientChange filter characteristicsDigital technique networkCapacitanceFeedback circuits
The invention discloses a programmable IIR filter analog hardware implementation method based on a memristor, which comprises the following steps of: (1) sampling an analog input signal by utilizing a switched capacitor circuit to obtain a digital sampled signal of the analog input signal; (2) carrying out delay on the sampled digital signal by using a single-cycle delay circuit to obtain a delayed signal of the intermediate digital signal; (3) according to a direct type structure of an IIR filter, establishing two parts of circuits by utilizing a cross matrix structure of the memristor and an adder, and respectively using two parts of circuits as a feedback circuit and weighted summation output; and (4) selecting and setting a resistance value of the memristor, completing setting of filter parameters, inputting a to-be-filtered analog signal, and obtaining a filter signal at an output end of an operational amplifier. According to the programmable IIR filter analog hardware implementation method disclosed by the invention, the circuits are programmable, a round-off error can be reduced, a filtering speed is also not limited to an analog-digital converter, the complex multiplication calculation is avoided, all the calculations are in parallel, and the programmable IIR filter analog hardware implementation method can be used for implementing a high-order IIR filter.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
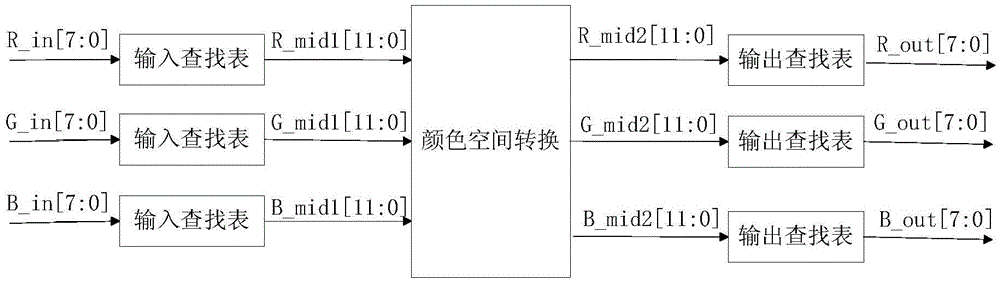
Image color correction method and device based on FPGA
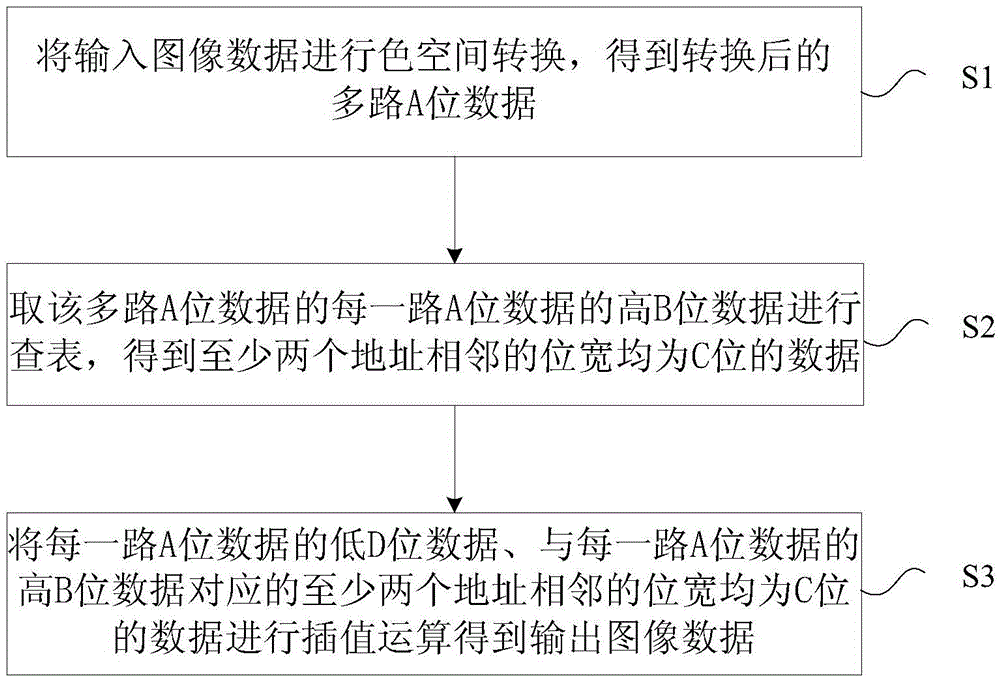
InactiveCN105657386AReduce rounding errorsSolve the errorColor signal processing circuitsPicture signal generatorsPattern recognitionColor correction
The invention provides an image color correction method and device based on an FPGA. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out color space conversion on input image data to obtain converted multiple paths of A bit data; extracting high B bit data of each path of A bit data in the multiple paths of A bit data to carry out table look-up to obtain at least two data with adjacent addresses and bit widths of C bits; and carrying out an interpolation operation on the low D bit data of each path of A bit data and the at least two data with adjacent addresses and bit widths of C bits of each path of A bit data to obtain output image data. The image color correction method provided by the invention is used for solving the problem in related technology of relatively large error and lost image details caused by GAMMA correction and color space conversion in the case of limited FPGA resources, so as to reduce the rounding errors in an image color correction process and perfect the dark image details after the color space conversion.
Owner:BEIJING TIMES OSEE TECH CO LTD
Interval prediction control modeling and optimizing method based on soft constraints
Provided is an interval prediction control modeling and optimizing method based on soft constraints. The control method comprises the following steps: (1) a quadratic performance index including a constraint item, a control item and an economic item is established based on a process prediction model; (2) whether an overall optimization method is feasible is judged by solving a slack variable; (3) a method for solving a soft constraint slack variable when a control model output constraint is not feasible is provided, and adjustment of the range of a feasible region when an interval prediction control model output constraint is not feasible is realized; and (4) a boundary feasible sequence quadratic programming method is adopted to solve the problem that poor initial point selection causes calculation amount increase of the method or difficulty in finding an optimal solution, the problem that the positive definiteness of a Hessian matrix is destroyed due to the influence of round-off error in calculation, and the like, and to figure out the optimal control input. A complicated multivariable system control model can be established, the control law can be solved accurately and quickly based on soft constraint adjustment, and good control on a multivariable system can be achieved.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
Method for calibrating power supply and tuning power supply unit
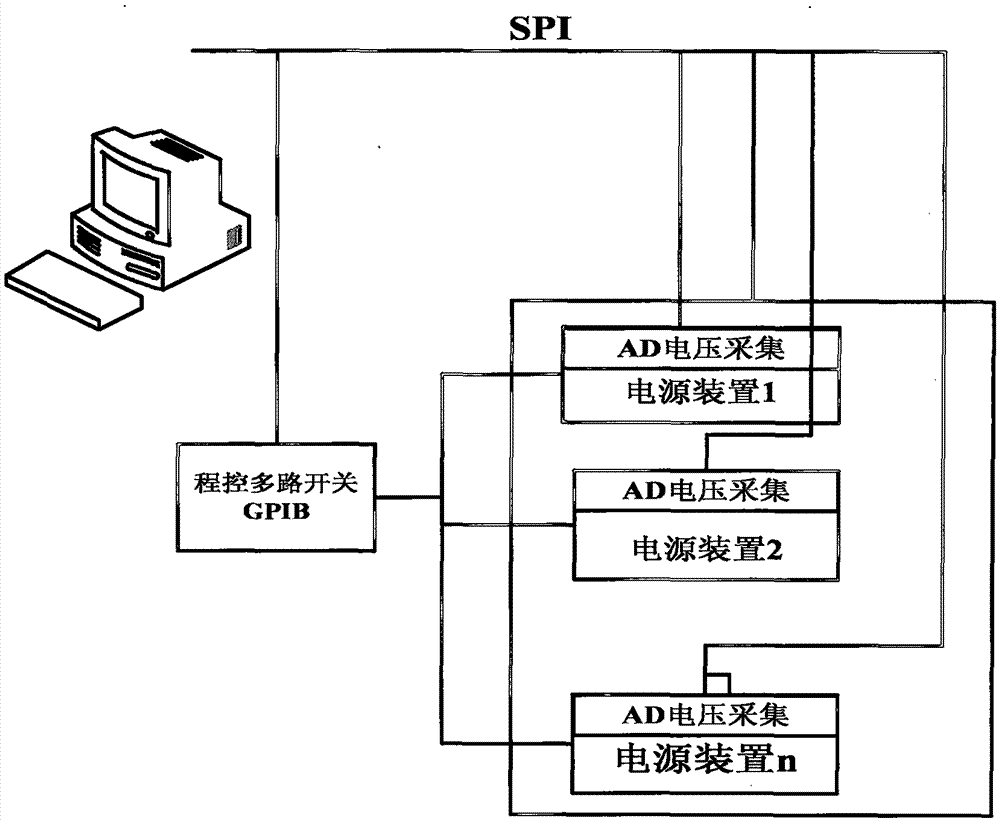
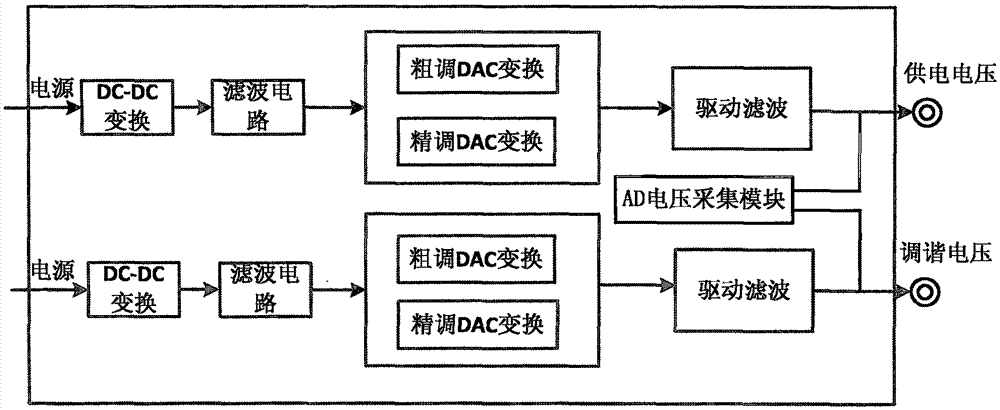
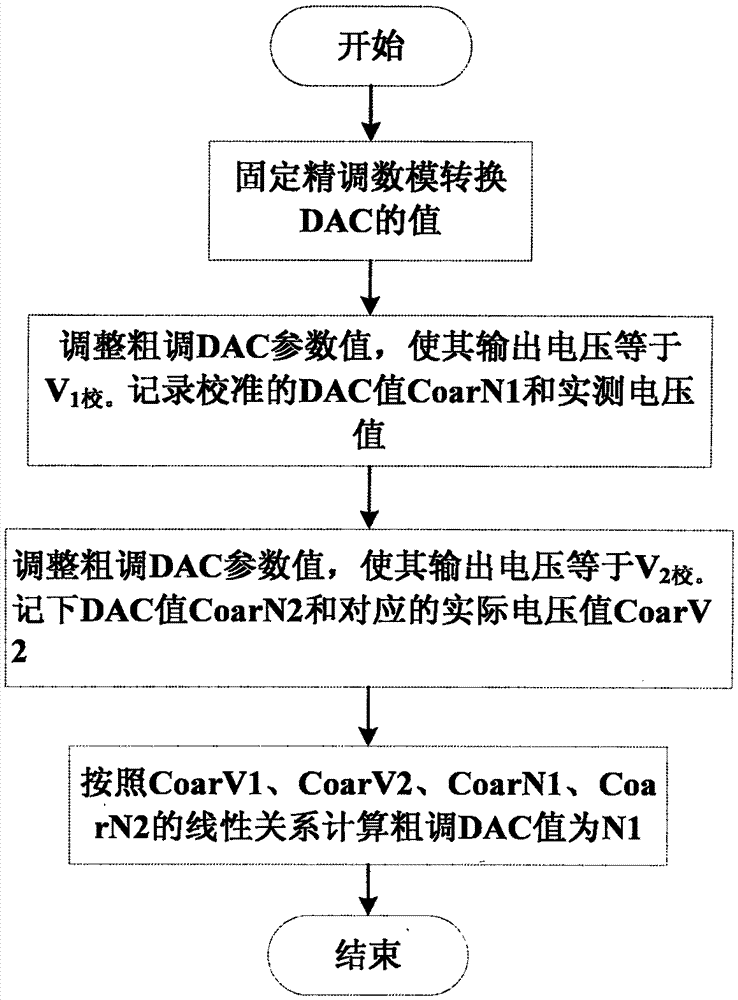
ActiveCN105446409AImprove accuracyIncrease workloadElectric variable regulationArray data structureEngineering
The invention discloses a method for calibrating a power supply and tuning power supply unit. A calibrating system comprises the power supply and tuning power supply unit, a computer and a program-controlled multi-channel switch. The power supply and tuning power supply unit is internally provided with an AD voltage acquisition module, the two-stage digital-to-analogue conversion combination is utilized to adjust power output voltage, the voltage output range is adjusted by coarse tuning digital-to-analogue conversion, and the round-off error compensation is performed by fine tuning digital-to-analogue conversion. The voltage output is divided into a plurality of output ranges in the calibrating process, and the voltage output is calibrated respectively in each range. An array{Vi, N1i, N2i} of the voltage, the fine tuning digital-to-analogue conversion value N1 and the fine tuning digital-to-analogue conversion value N2 is obtained by calibrating a plurality of points, a curvilinear equation can be obtained by utilizing Chebyshev curve fitting, and the digital-to-analogue conversion value is calculated through the arrangement of the curvilinear equation.
Owner:THE 41ST INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP
Reduction of rounding errors during the processing of digital image data
InactiveUS20050036678A1Reduce in quantityIncrease clock frequencyImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionMultiplexer
In order to avoid rounding errors as a result of restricted accuracy of the processing unit in a video processing arrangement, a comparison is carried out between processed image data and unprocessed image data. For this purpose, the unprocessed image data is buffer-stored in a memory and is supplied together with the processed image data to a comparator, which compares the difference between the processed image data and the unprocessed image data with a threshold value Either the processed image data or the unprocessed image data is produced at the output of the arrangement, by means of a multiplexer, as a function of the result of the comparison. A rounding element between the processing unit and the multiplexer rounds the processed image data before it is emitted, if the processing stage has not itself carried out a rounding process.
Owner:GVBB HLDG R L
Construction method of dropper in full-compensatory elastic chain type hanger in contact network of rapid transit railway
InactiveCN102358212AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed installation qualityTrolley linesContact networkSimultaneous equations
The invention relates to a construction method of a dropper in a full-compensatory elastic chain type hanger in a contact network of a rapid transit railway. The construction method comprises the following steps: performing mathematical modeling by taking a contact hanger within any span of an anchor section as an object, wherein each node on a strength-bearing cable corresponds to the position of one dropper, a cable unit is formed between every two nodes, the coordinate of the i-th node is (xi, yi), and the concentrated load of the i-th node is GJi, i=0,1,2...; establishing an entire stiffness matrix of the cable units according to a brand new expression of the cable unit formed between the i-th node and the (i+1)th node and a longitudinal force balancing equation of the i-th node; solving the simultaneous equations, thereby acquiring a vertical coordinate yi of the i-th node; acquiring a length of the dropper corresponding to the i-th node according to a dropper length equation: Ci=yi-Hi; and finally correcting, prefabricating the dropper, determining the mounting position of the dropper and performing construction. The construction method provided by the invention has the advantages that a rounding error generated in the prior art is efficiently avoided and the accuracy of calculated data is higher.
Owner:中铁建电气化局集团南方工程有限公司
Power system dynamic state estimation method based on singular value decomposition CDKF
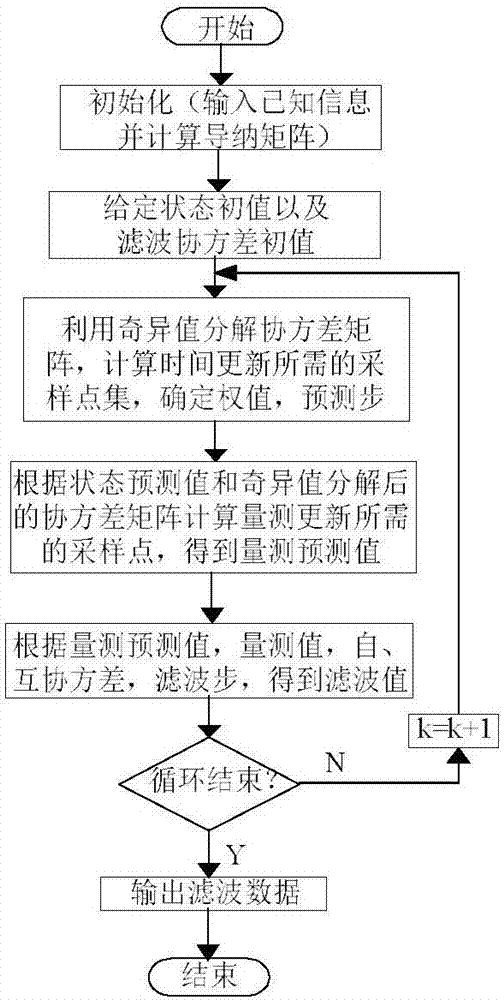
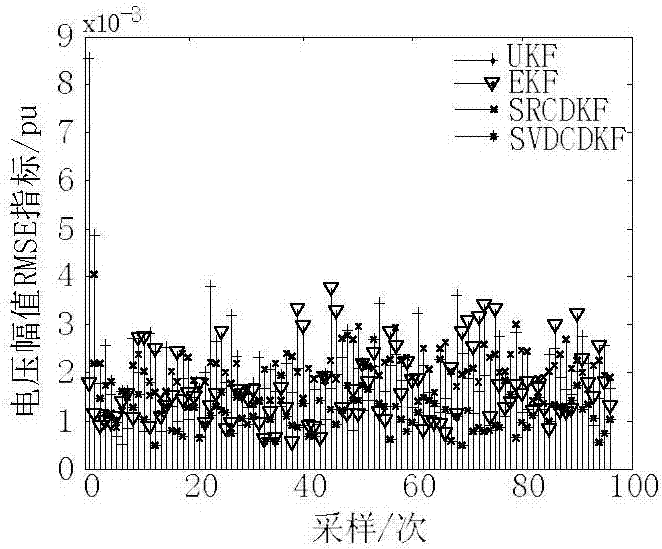
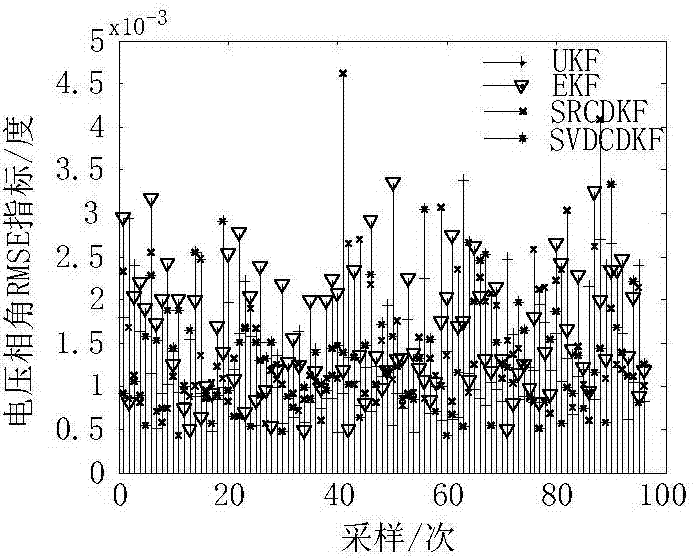
ActiveCN107025609AIncreased complexitySolve the problem of losing positive concentrationResourcesNumerical stabilityRounding
The invention discloses a power system dynamic state estimation method based on singular value decomposition CDKF. First, a singular value decomposition (SVD) technology is introduced to central difference Kalman filtering CDKF, and Collins basic decomposition of a covariance matrix in CDKF is replaced with singular value decomposition. Then, with the help of the Stering interpolation formula, the derivation of a nonlinear function is approximated by a polynomial, and a first-order or second-order derivation formula in a Taylor expansion is replaced with a central difference formula. Through the method, the problem that the covariance matrix is not positive definite due to calculation error and rounding error is solved. The numerical stability of the method is improved. Complex deviation is avoided. Calculation is simple, parameter adjustment is easy, and the filtering precision is high. The results show that the method has higher numerical stability than a square root form method and has higher filtering precision than an extended Kalman filter method and an unscented Kalman filter method.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
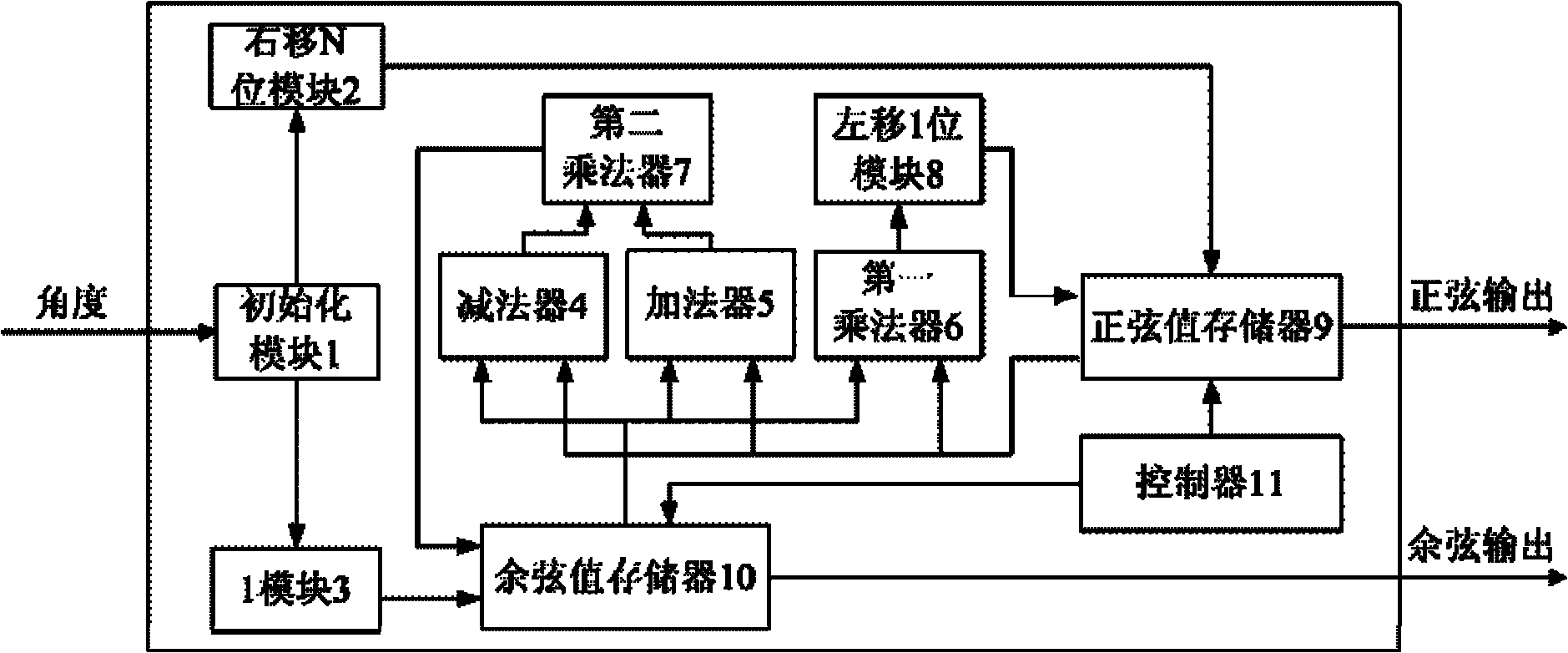
Sine-cosine function IP core capable of reconfiguring spaceborne computer and control method thereof
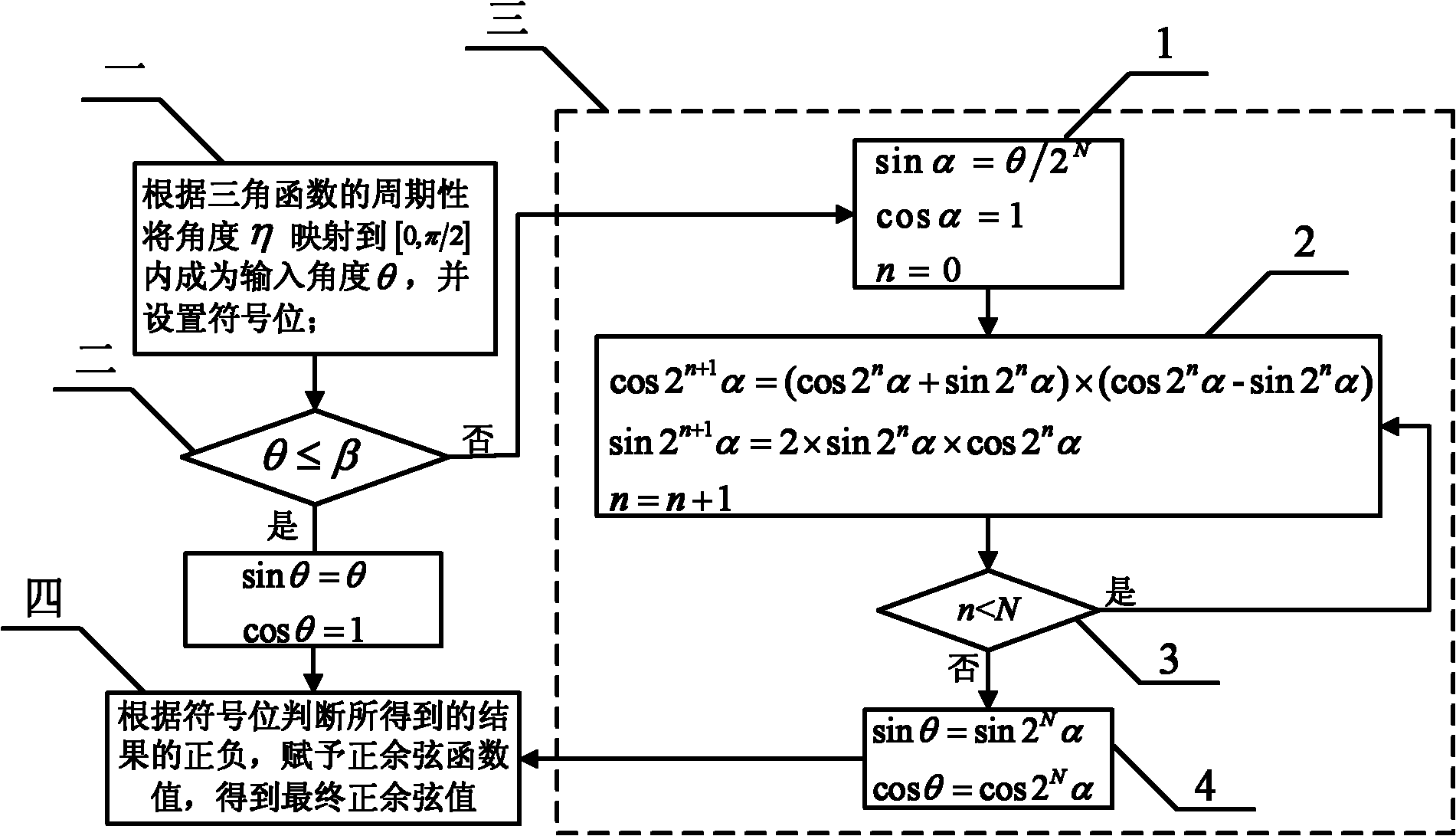
InactiveCN102156626AImprove performanceCalculation speedDigital data processing detailsBinary multiplierAttitude control
The invention relates to a sine-cosine function IP core capable of reconfiguring a spaceborne computer and a control method thereof, relating to the technical field of aerospace electronics, and solving the problems that the result of initial value assignment is largely influenced due to rounding errors, and the larger the angle is, the more the iteration times is needed. An initializing module is connected with a right-shift N-bit module and a module 1, the module 1 is connected with a cosine value storing device, the right-shift N-bit module is connected with a sine value storing device, the cosine value storing device and the sine value storing device are connected with a subtracter-adder and a first multiplier, the subtracter-adder is connected with a second multiplier and then is connected with the cosine value storing device, the first multiplier is connected with a left-shift 1-bit module and then is connected with the sine value storing device, and the a controller is connected with the sine value storing device and the cosine value storing device. The control method comprises the following steps of: mapping eta into [0, pi / 2] to generate theta; judging whether theta is less than and equal to beta; if theta is less than and equal to beta, directly assigning the value and carrying out the last step; otherwise, carrying out the iteration operation, and obtaining an assigned initial value according to an approximate rule; calculating by utilizing a double-angle formula, judging whether n is less than N; if n is less than N, calculating again; otherwise, finishing the operation; finally assigning a sine / cosine function value according to the positive / negative result obtained by the sign bit judgment. The invention is applied to attitude control.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
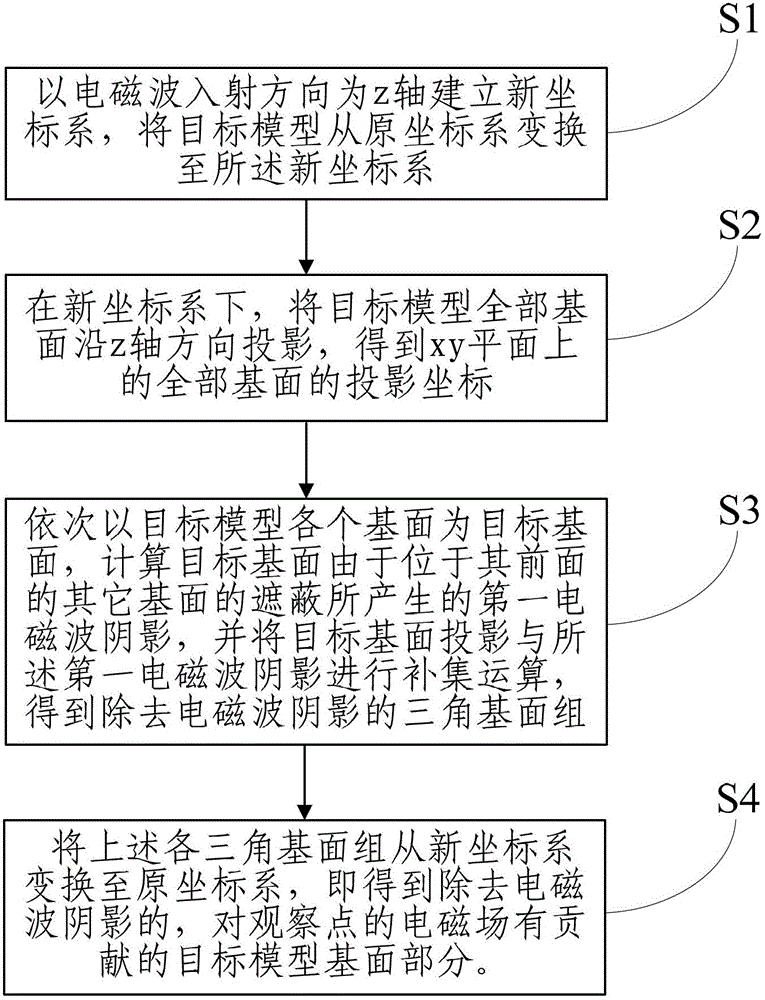
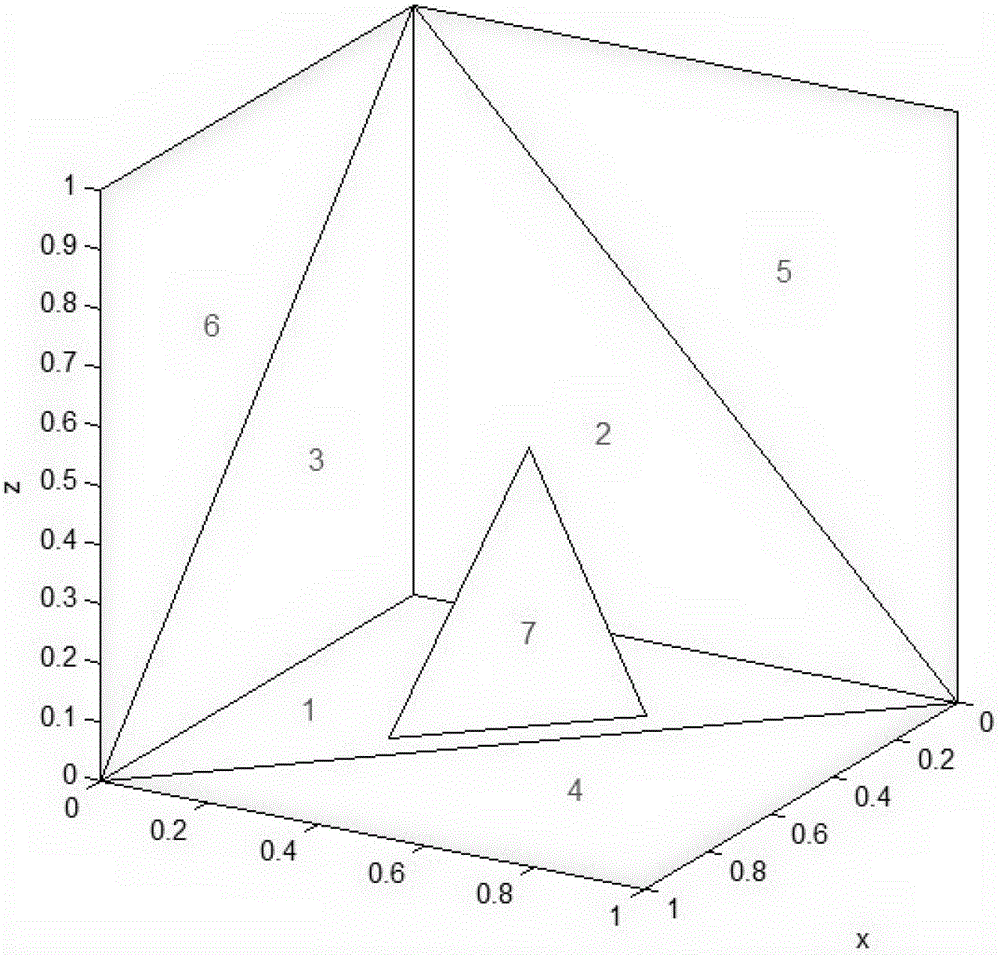
Large-scale complicated target model oriented electromagnetic wave shadow processing method
InactiveCN104008217APrecise and clear boundariesOvercoming Boundary Rounding ErrorsSpecial data processing applications3D modellingClassical mechanicsMesh grid
The invention relates to the technical field of electromagnetic wave shadow processing, in particular to a large-scale complicated target model oriented electromagnetic wave shadow processing method. The method does not need grid subdivision in advance, obtained electromagnetic wave shadows have accurate and clear boundaries, accordingly electromagnetic wave shadow boundary round-off errors produced by grid subdivision accuracy by adopting a grid division method are eliminated. In addition, the method does not need any hypothesis and is suitable for electromagnetic wave shadow processing of any complicated target model. In addition, due to the fact that the method does not need beforehand grid subdivision, coordinate information of the electromagnetic wave shadows is only saved in the electromagnetic wave shadow processing process, and occupied system memory and required operation amount can be minimized. Therefore, the method is suitable for electromagnetic wave shadow processing of large-scale complicated target models.
Owner:BEIJING MUNICIPAL INST OF LABOUR PROTECTION
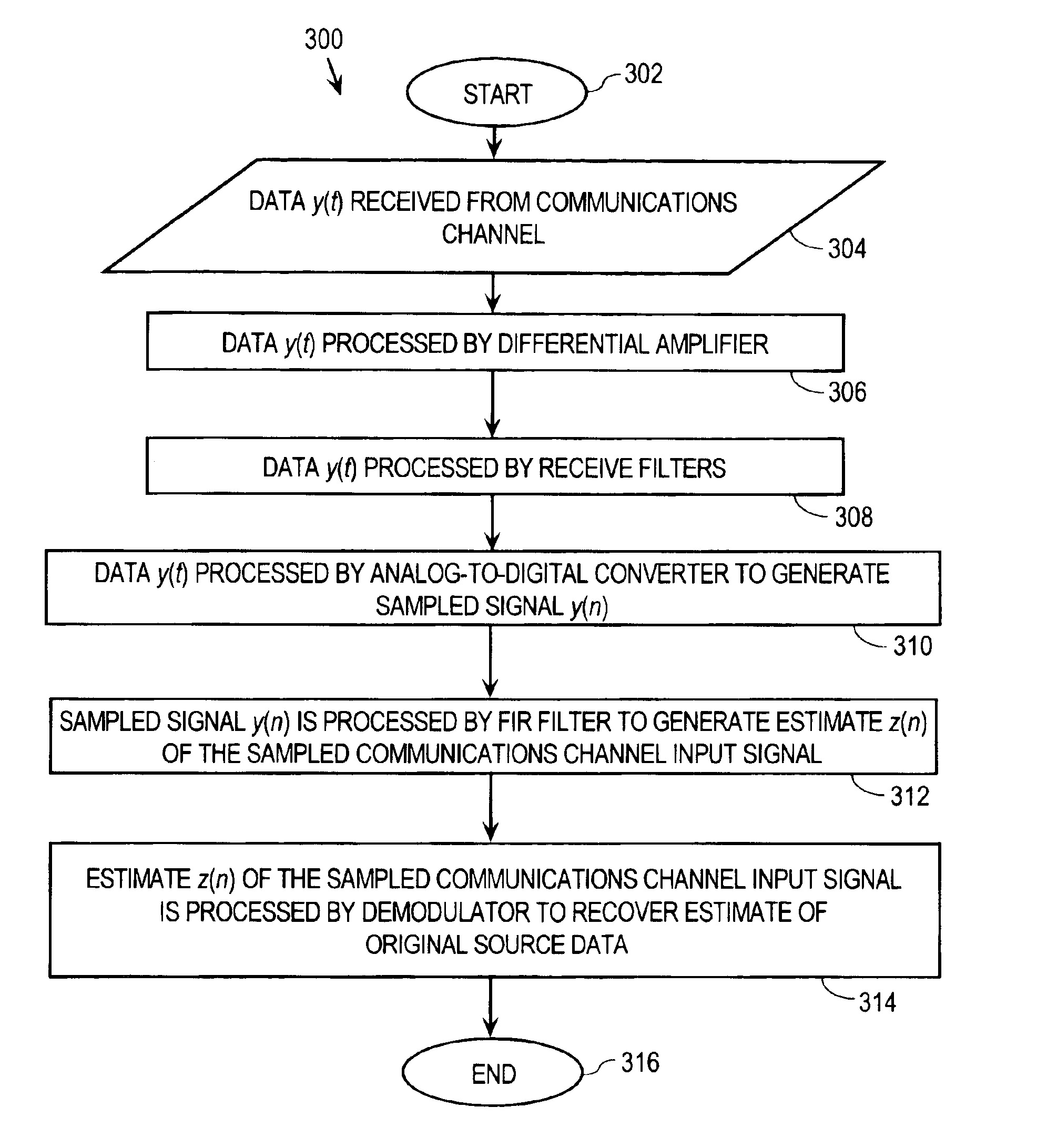
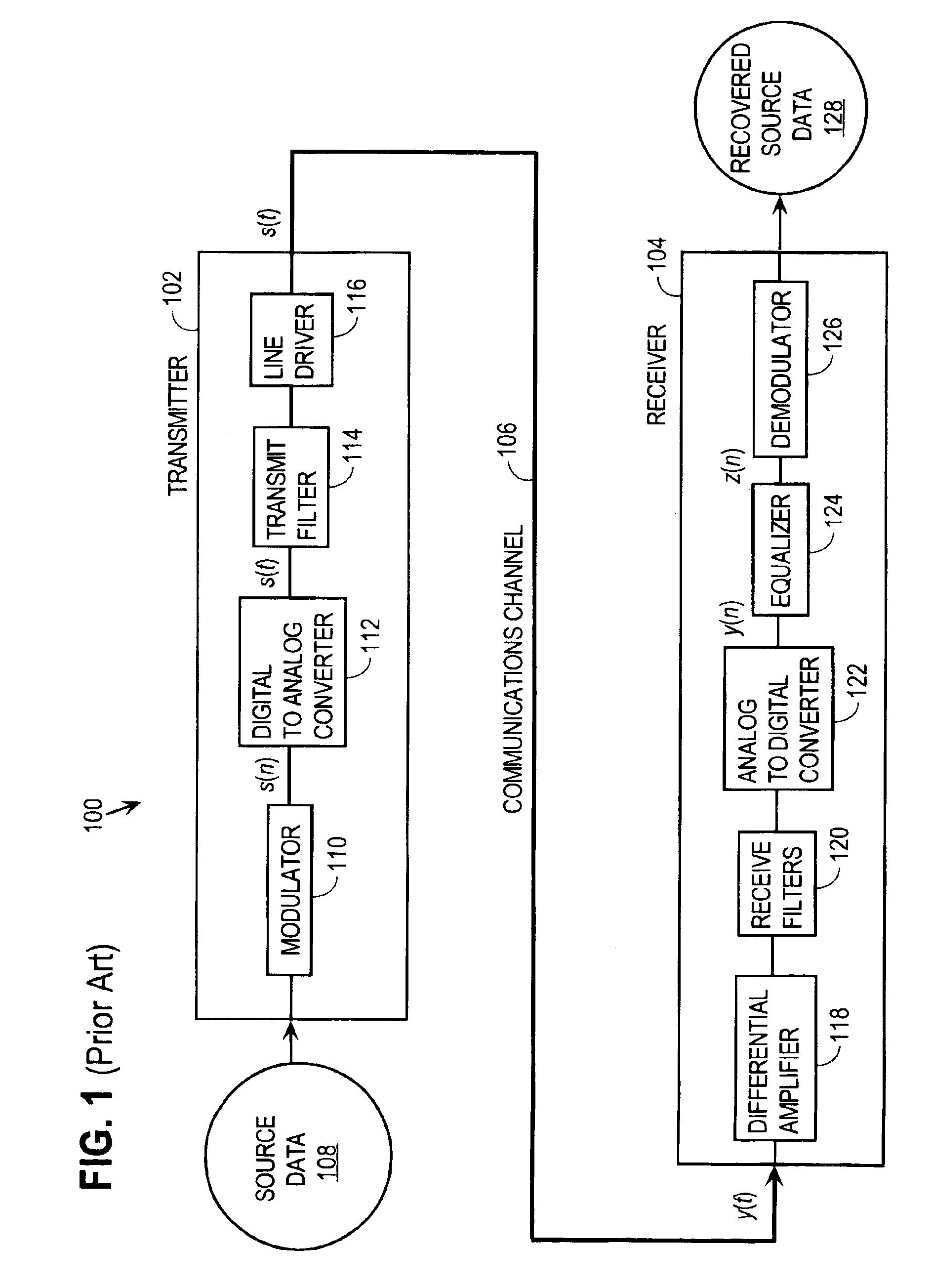
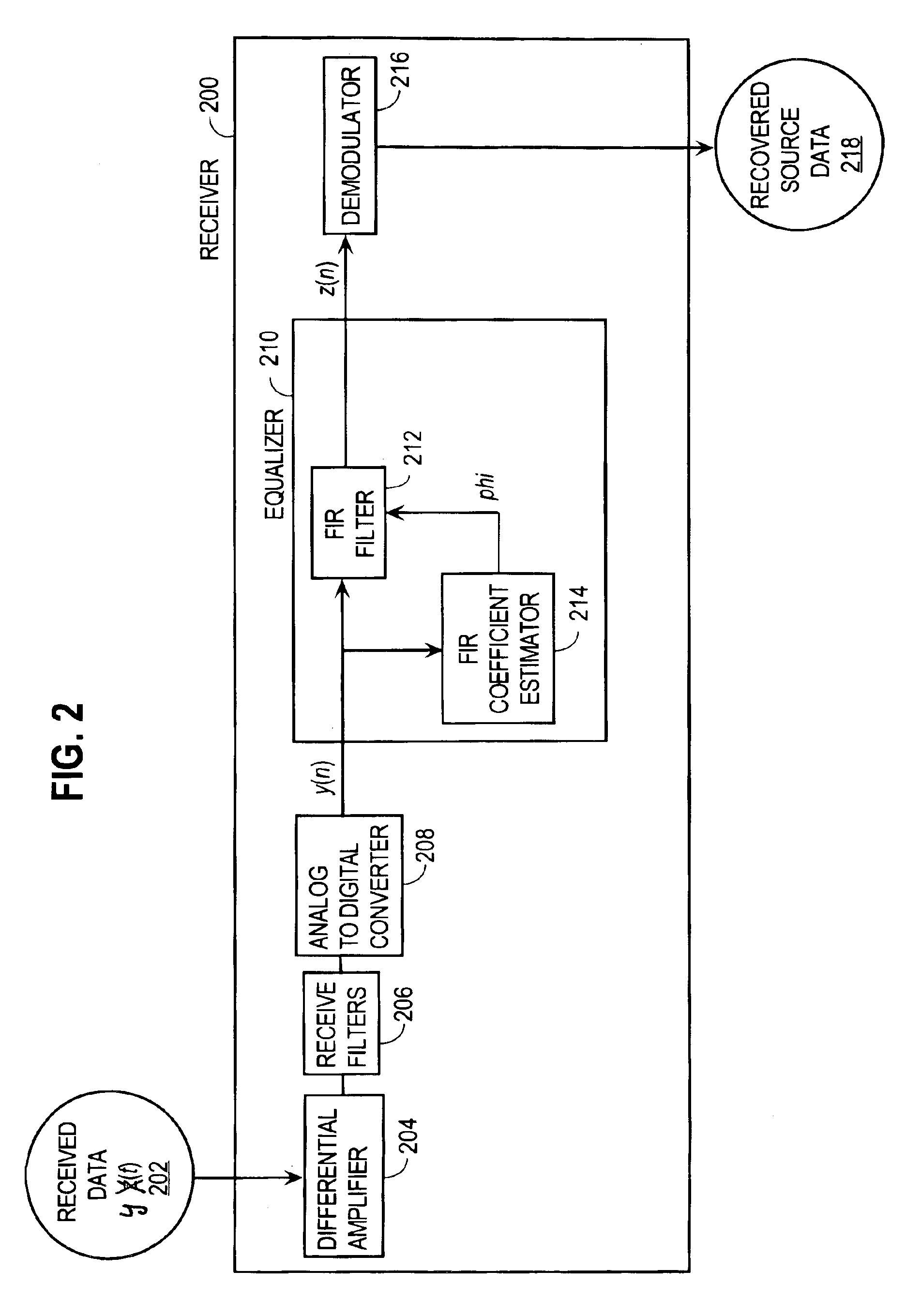
Approach for processing data received from a communications channel in finite precision arithmetic applications
InactiveUS6983030B2Minimize degradationMaximize channel capacityTransmission control/equlisationMulti-frequency code systemsFinite impulse responseTime domain
An approach for processing data received from a communications channel in finite precision arithmetic applications generally involves equalizing received data in the time domain prior to demodulation using finite impulse response (FIR) filtering. FIR coefficients used in FIR filtering are selected to minimize SNR degradation attributable to ISI and roundoff errors due to finite precision arithmetic, thereby maximizing channel capacity. The approach considers the communications channel noise attributable to crosstalk, white noise and analog to digital converter quantization noise, ISI attributable to failure of the equalizer coefficients to completely eliminate ISI, round off noise due to the use of finite precision arithmetic in the equalizer and roundoff noise due to the use of finite precision arithmetic in the FFT algorithm.
Owner:CALLAHAN CELLULAR L L C
Low complexity linear iteraction multiple users detecting device and method
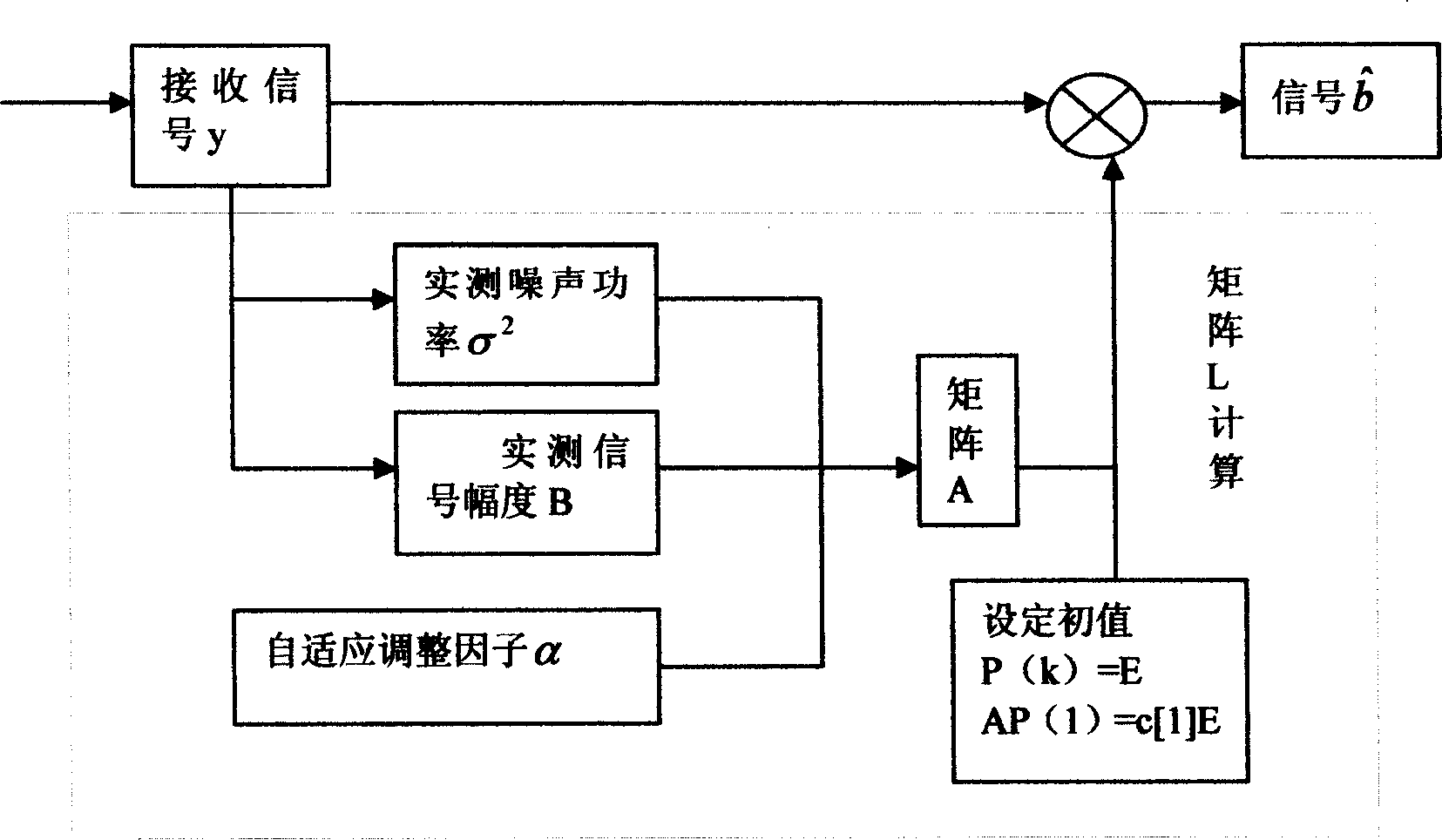
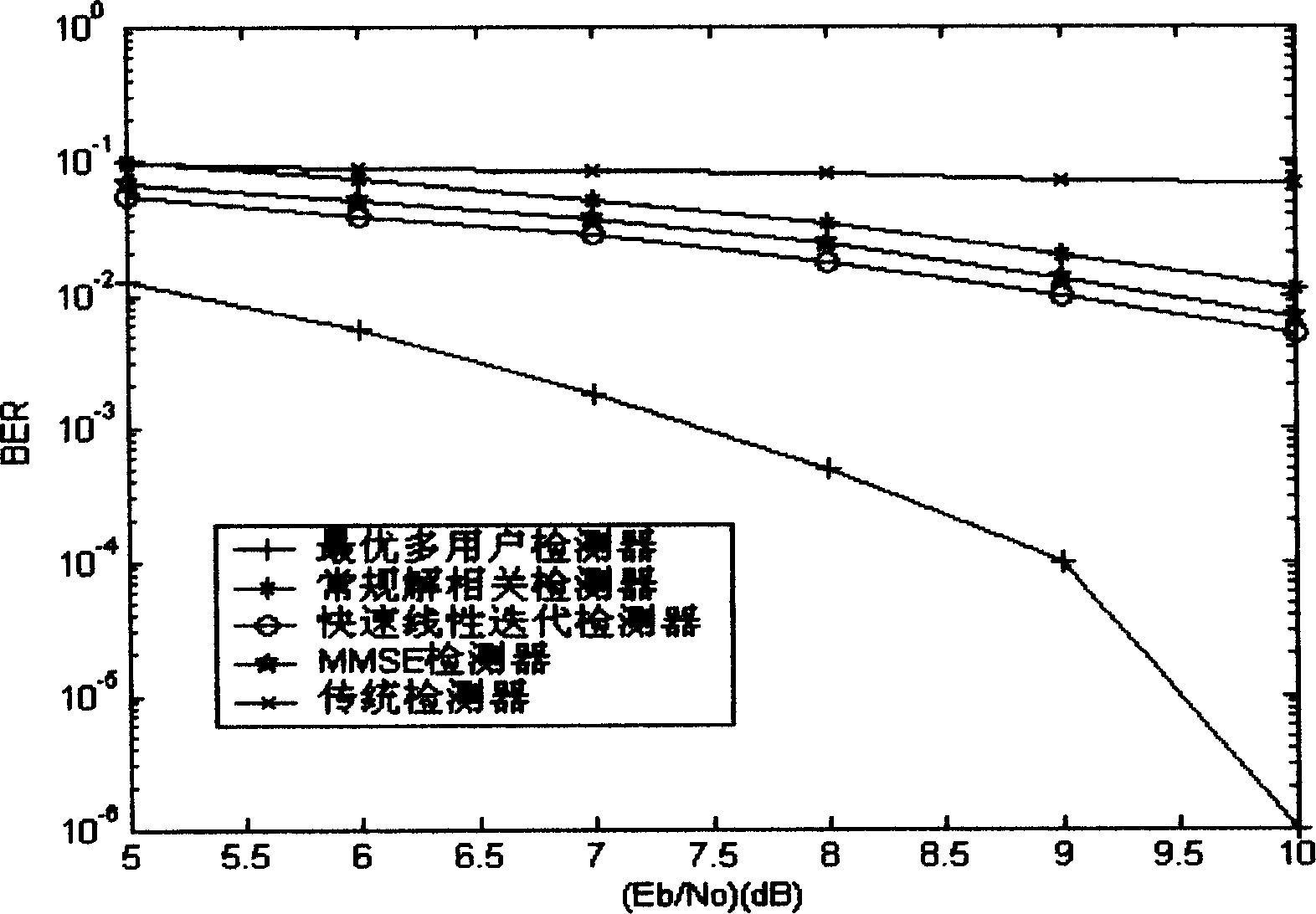
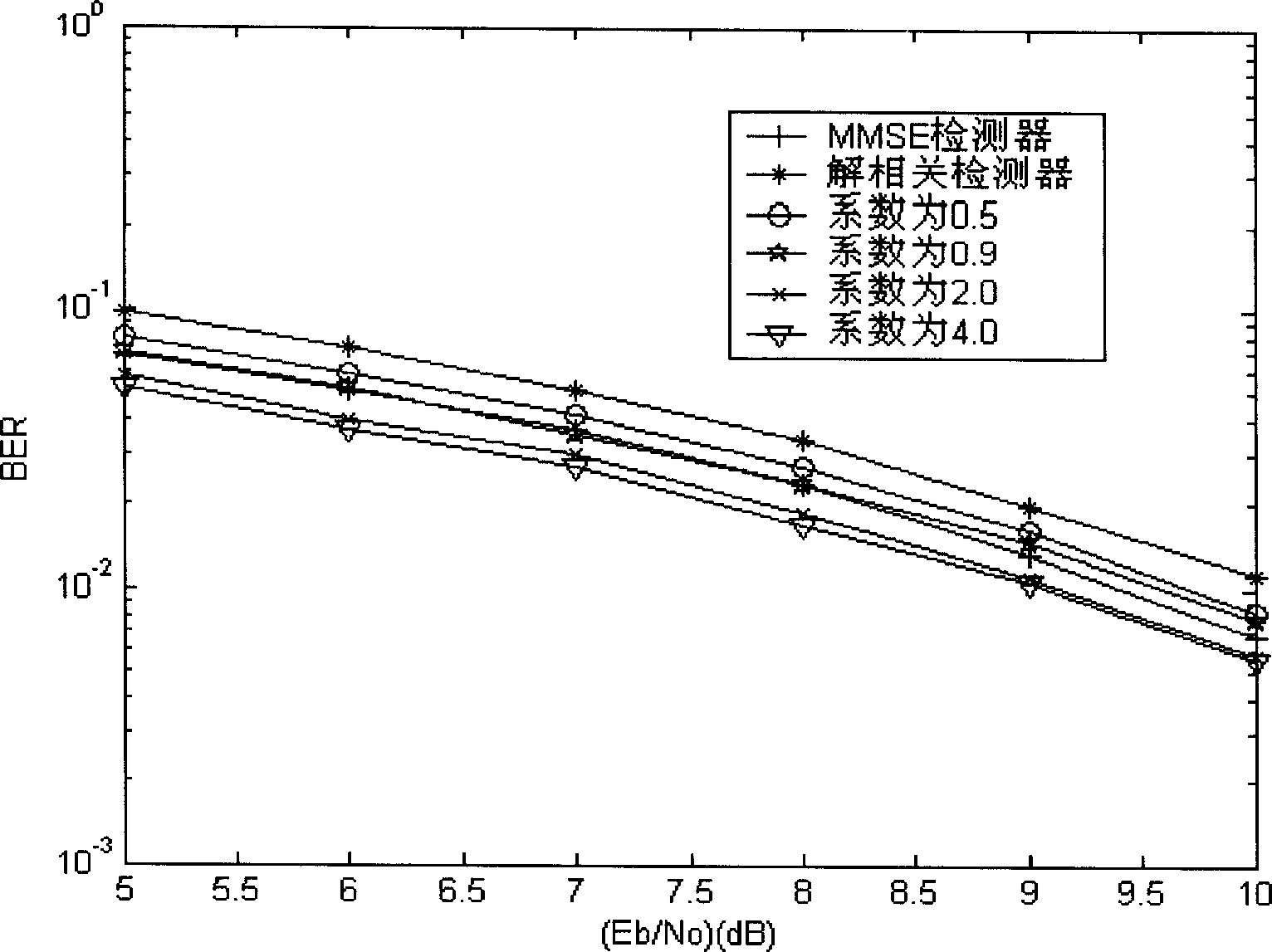
InactiveCN1901388AReduce computational complexityQuick implementationTransmissionRound complexityLow complexity
This invention provides a linear iterative multi-user test device of low complexity and a method, which avoids computation of matrix inversion by a series of circulated iteration, since the method reduces the round-off error in the computation, the computation accuracy is increased greatly at the same time when reducing computation volume and reduces noises resulted from MAI to resume multi-user information very well.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA ZHONGSHAN INST
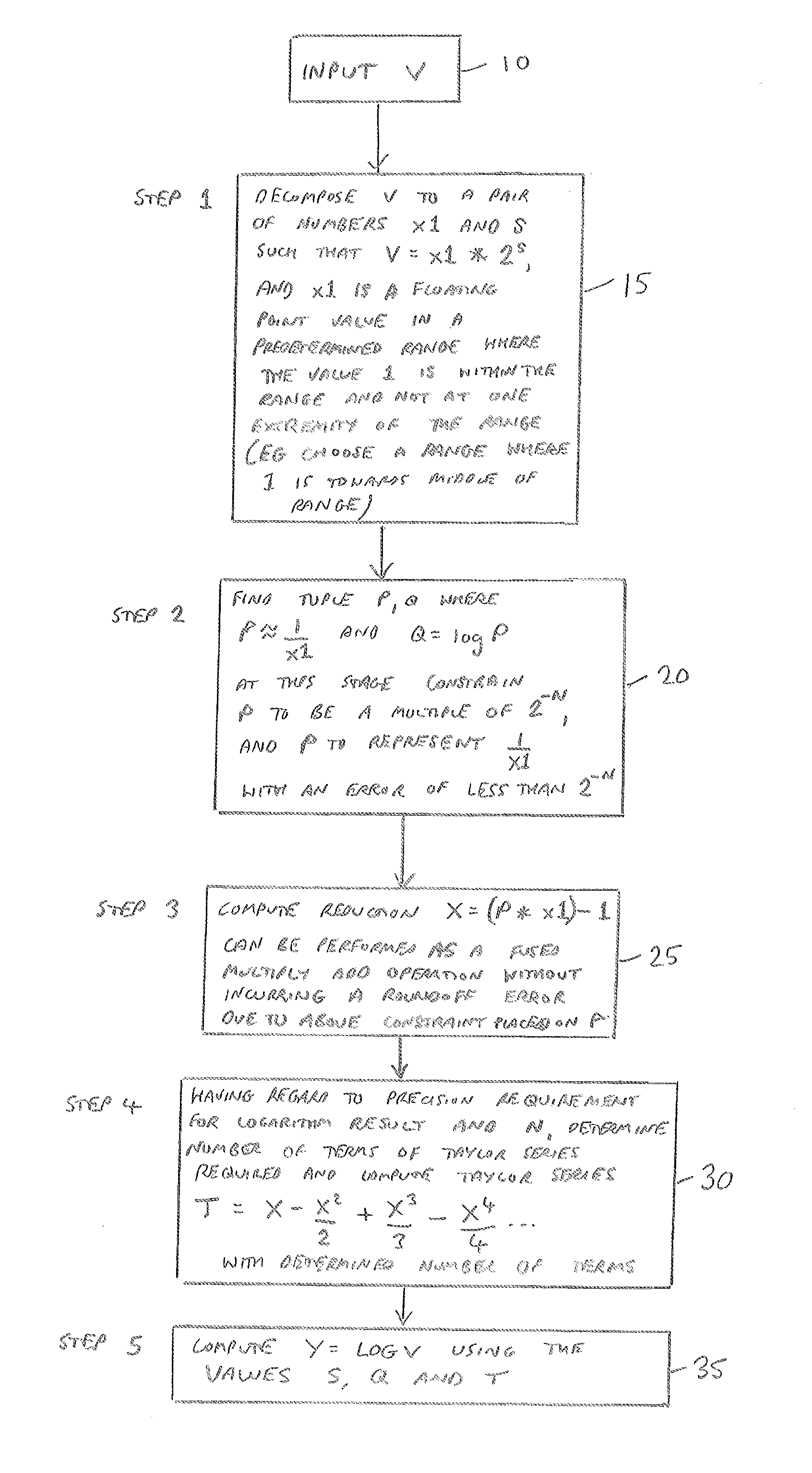
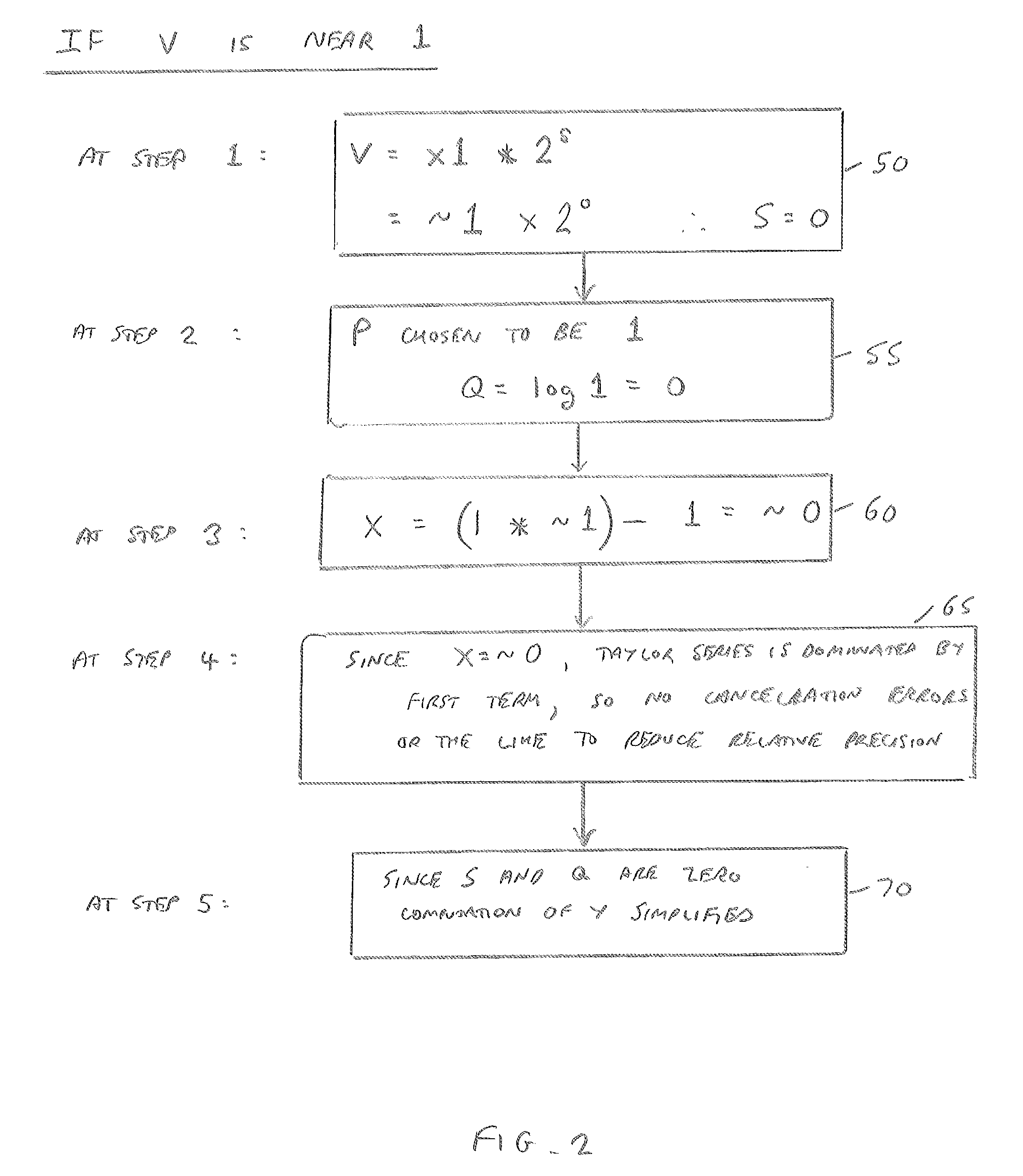
Apparatus and method for inhibiting roundoff error in a floating point argument reduction operation
An apparatus and method are provided for inhibiting roundoff error in a floating point argument reduction operation. The apparatus has reciprocal estimation circuitry that is responsive to a first floating point value to determine a second floating point value that is an estimated reciprocal of the first floating point value. During this determination, the second floating point value has both its magnitude and its error bound constrained in dependence on a specified value N. Argument reduction circuitry then performs an argument reduction operation using the first and second floating point values as inputs, in order to generate a third floating point value. The use of the specified value N to constrain both the magnitude and the error bound of the second floating point value causes roundoff error to be inhibited in the third floating point value that is generated by the argument reduction operation. This enables such an argument reduction operation to be used as part of a more complex computation, such as a logarithm computation, with the inhibiting of roundoff error in the argument reduction result allowing the overall result to exhibit small relative error across the whole representable input range.
Owner:ARM LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com