Accurate one-point positioning method for single-frequency GPS receiver
A GPS receiver, precise single-point positioning technology, applied in the direction of positioning, beacon systems using radio waves, measuring devices, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
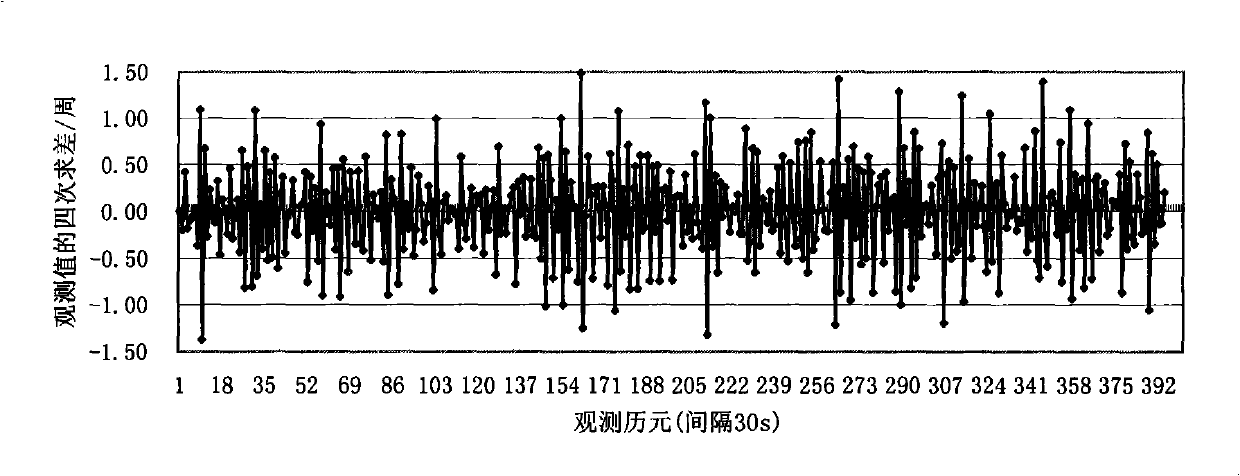
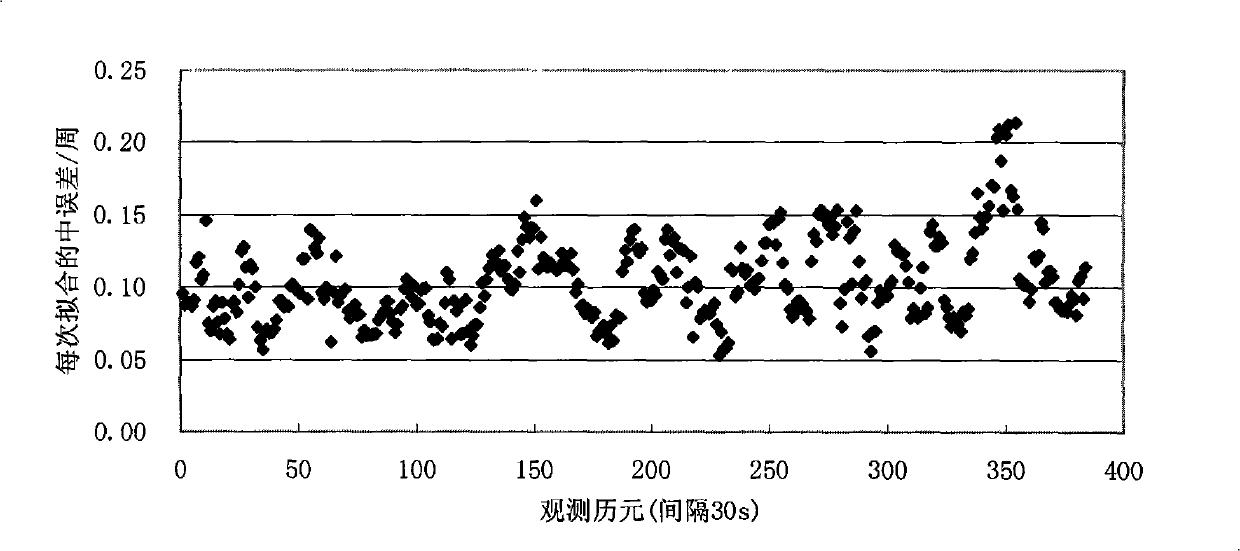
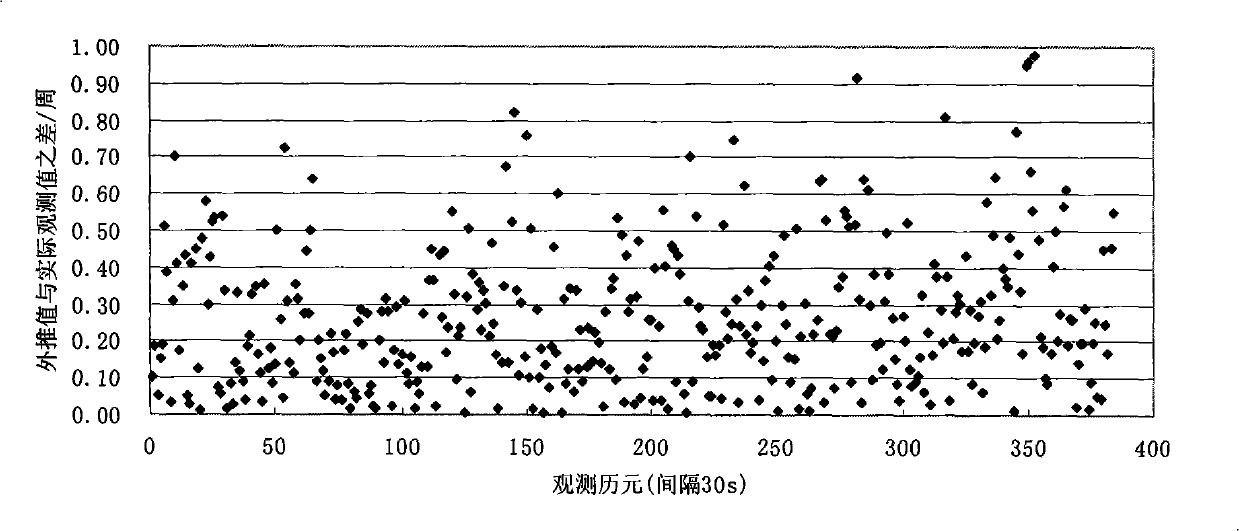
[0124] refer to Figure 12 , a precise single-point positioning method for a single-frequency GPS receiver, comprising a GPS data reading and preprocessing step, an error correction solution step, and a result output step, the preprocessing step including detecting and repairing a cycle slip, The detection and repair steps of the cycle slip include:
[0125] 1) The m carrier phase observations without cycle slip φ i Bring into formula (1) for polynomial fitting;
[0126] i=1,2,...m; m>(n+1)
[0127] (1)
[0128] The polynomial coefficients in the formula are obtained by the least square method, and according to the fitted residual V i Calculate the error:
[0129] σ ( j ) = V i V i m -...
Embodiment 2~3
[0224] Examples 2-3: Comparison of solution accuracy between grid model and semi-sum correction method
[0225] In this embodiment, the data of IGS tracking stations BJFS (bjfs0150.07O) and WUHN (wuhn0150.07O) on January 15, 2007 are respectively solved by ionospheric grid model and half-sum correction method. In the data processing, only the L1 and C / A code data in the observed values are used for the calculation of the data of the IGS tracking station. Statistical results such as Figure 8-11 shown.
[0226] As can be seen from the figure:
[0227] 1) Using the grid model to correct, the accuracy of 5 decimeters can be achieved in the N and E directions. But the accuracy in the U direction is about 1 meter;
[0228] 2) Using the semi-sum correction, the accuracy of about 2 decimeters can be achieved in the N, E, and U directions;
[0229] 3) It is obvious that the semi-sum correction method achieves higher accuracy than the grid model correction method. The main reas...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com