Peripherally inserted central catheter positioning algorithm based on intracardiac electrogram
A central venous catheter and positioning algorithm technology, applied in catheters, medical science, sensors, etc., can solve problems such as inability to detect catheters and catheter tip position lag in time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
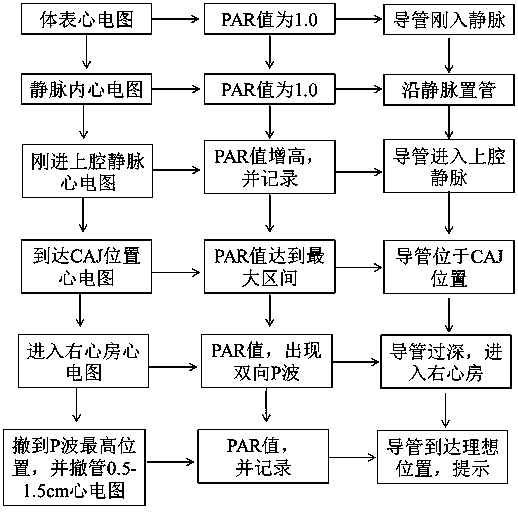
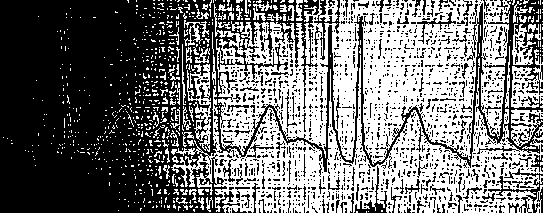
[0031] figure 1 It is a structural diagram of an algorithm for establishing correspondence between the intracavity electrocardiogram and the position of the catheter tip. When the catheter tip is in a peripheral vein (axillary vein, subclavian vein, brachiocephalic vein), an ECG is obtained, such as figure 2 , and measure the P wave amplitude of the electrocardiogram at this time as P1. There is no significant difference between the P wave amplitude of the electrocardiogram at this position and the body surface electrocardiogram, and the PAR value is about 1.0. When the catheter was advanced in the vein, but the catheter tip did not enter the superior vena cava, there was no change in P wave amplitude, and the PAR value was approximately 1.0. However, when the tip of the catheter just entered the superior vena cava, the P wave amplitude suddenly increased significantly. At this time, the P wave amplitude of the electrocardiogram was P2, and the PAR value also increased signi...
Embodiment 2
[0034] Image 6It is a structural diagram of an algorithm for establishing correspondence between the intracavity electrocardiogram and the position of the catheter tip. When the catheter tip is located in the peripheral vein (axillary vein, subclavian vein, brachiocephalic vein), the electrocardiogram is measured, and the ratio of P wave to QRS wave amplitude of the electrocardiogram at this time is measured, and the PQAP value is recorded. When the catheter was advanced intravenously but the catheter tip did not enter the superior vena cava, there was no change in P wave amplitude and no change in PQAP values. When the catheter tip just entered the superior vena cava, the P wave amplitude suddenly increased significantly, and the PQAP value also increased significantly. As the catheter tip advances in the superior vena cava, the recorded PQAP value gradually increases; when the catheter tip is located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium, the P wav...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Confirming the position of the tip of the catheter according to a parameter may cause deviations in insertion due to individual differences. PAR and PQAP values can be used as dual parameters to guide catheter placement. When both the PAR value and the PQAP value enter the ideal range, it means that the tip of the catheter is placed in the ideal area to further improve the accuracy rate.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com