Shockable rhythm recognition algorithm based on grid projection distribution dispersion
A recognition algorithm and dispersion technology, applied in medical science, sensors, diagnostic recording/measurement, etc., can solve the problems of incompatibility between sensitivity and specificity, poor sensitivity, high hardware requirements, etc., to improve sensitivity and specificity, and simplify calculations Complexity, the effect of meeting application requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0035] The present invention will be further described below through specific examples.
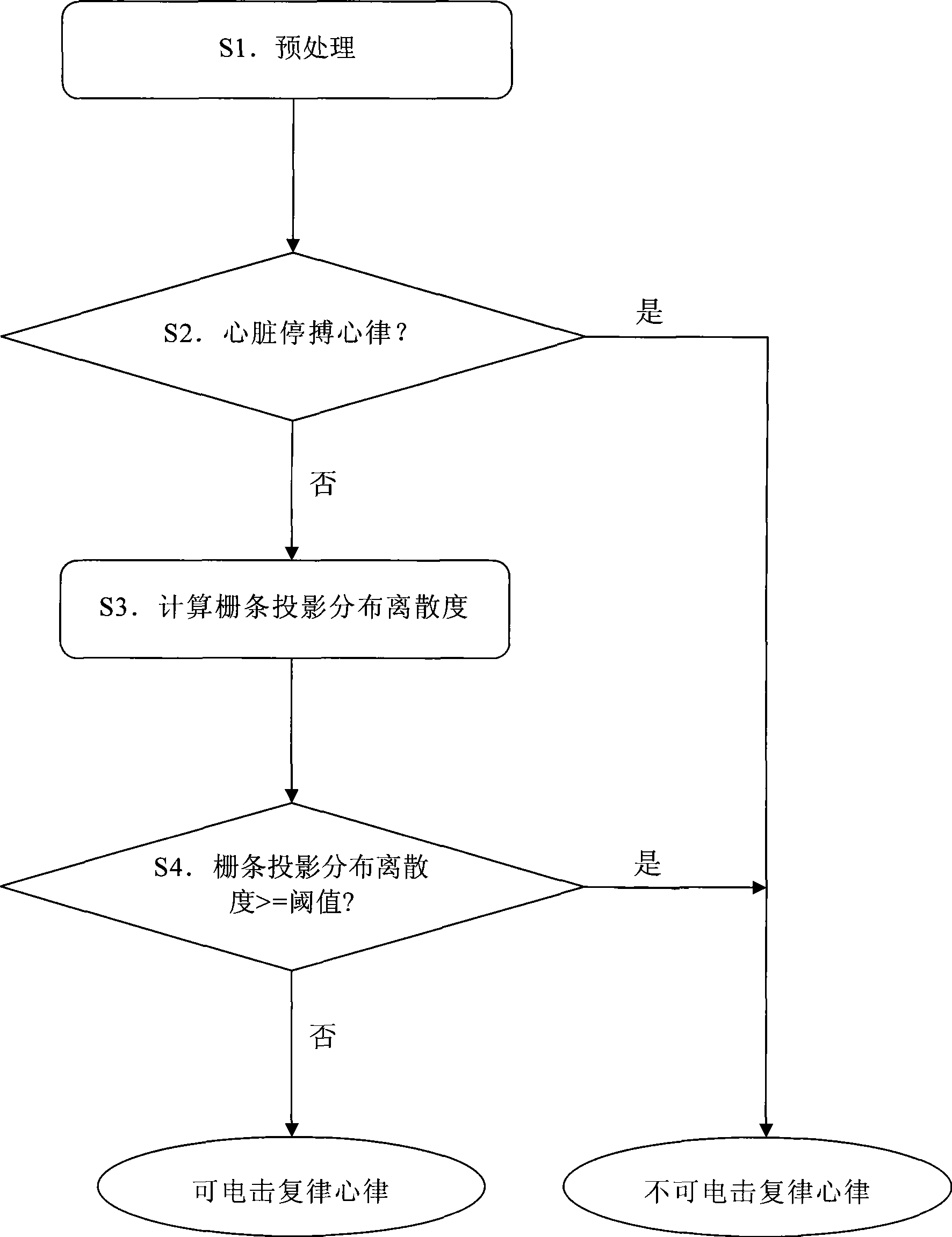
[0036] Present embodiment is a kind of possible realization of the present invention on personal computer (PC) and matrix laboratory (MatrixLaboratory, Matlab) platform, and by MIT arrhythmia database (MITDB), Clayton University ventricular rhythm Arrhythmia Database (CUDB) and MIT Malignant Ventricular Arrhythmia Database (VFDB) are used to test and compare on the test data set composed of three standard databases. The specific steps of this embodiment are as follows:
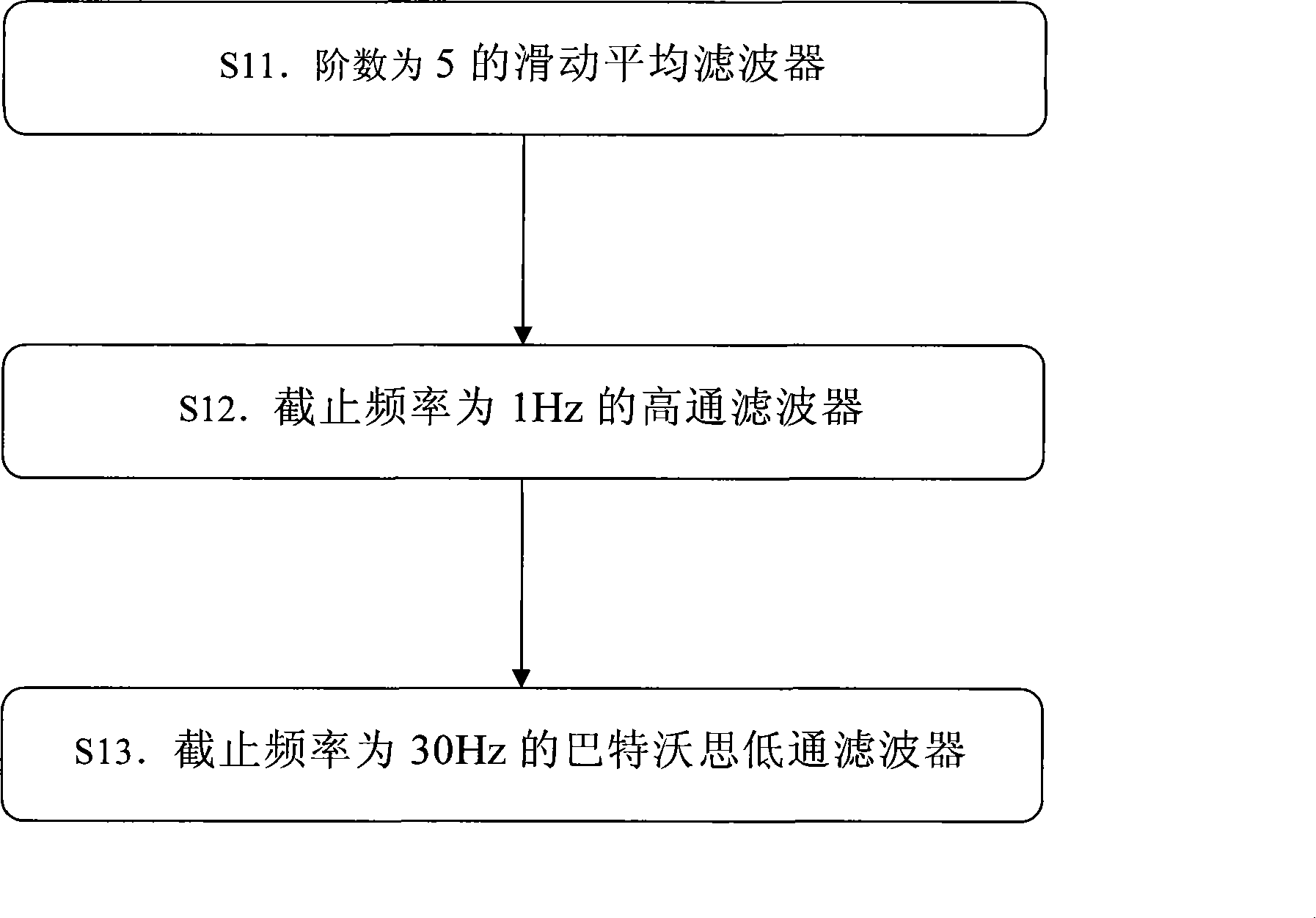
[0037] 1. Preprocessing the ECG signal:
[0038] a) Use a 5th-order moving average filter to filter out high-frequency noise such as scatter noise and myoelectric noise;
[0039] b) Use a high-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 1 Hz to suppress baseline drift;
[0040] c) Use a Butterworth low-pass filter with a cutoff frequency of 30Hz to further filter out irrelevant high-frequency components.
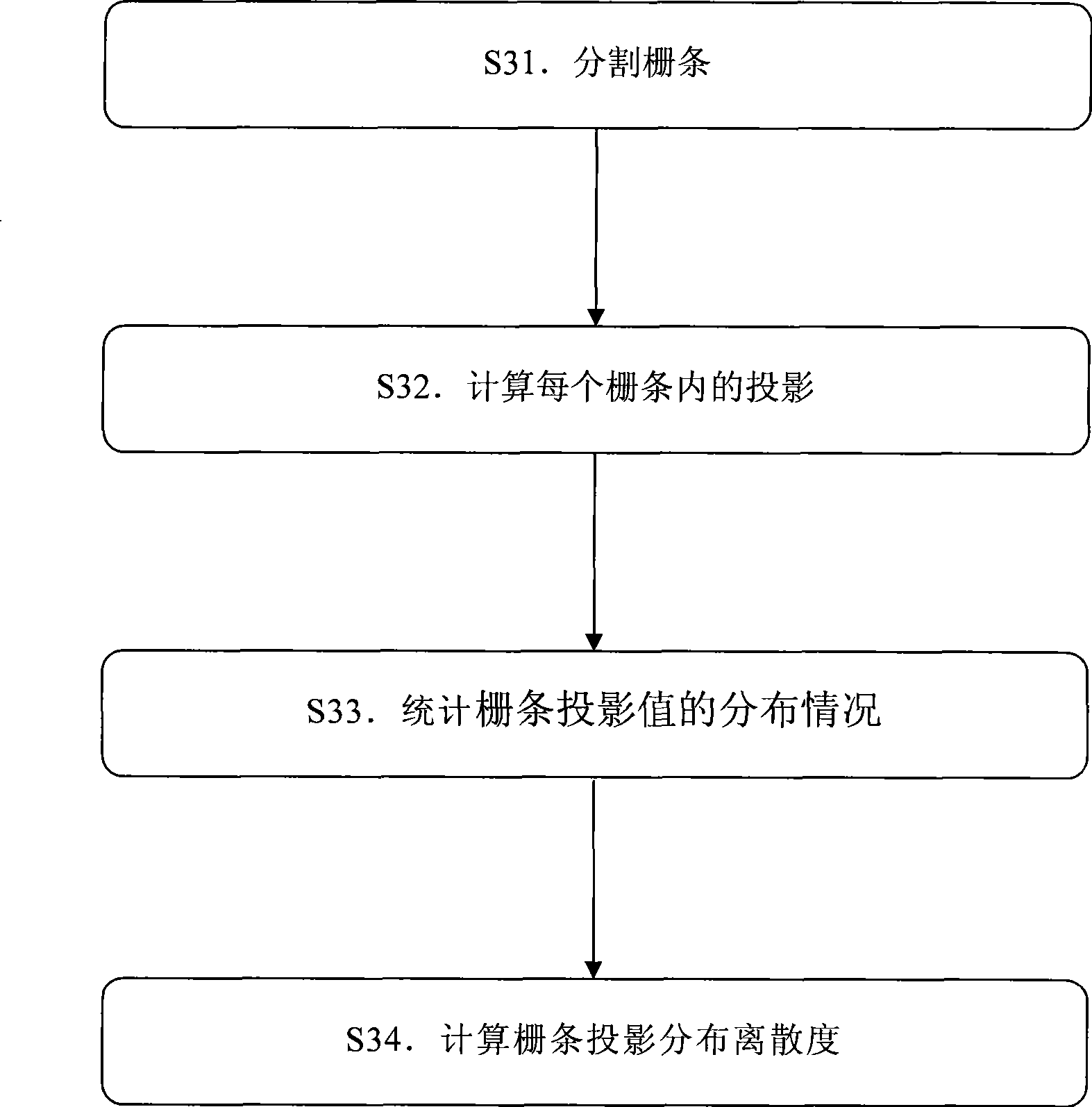
[0041] 2. Recogn...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com