Patents
Literature
236 results about "External defibrillators" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
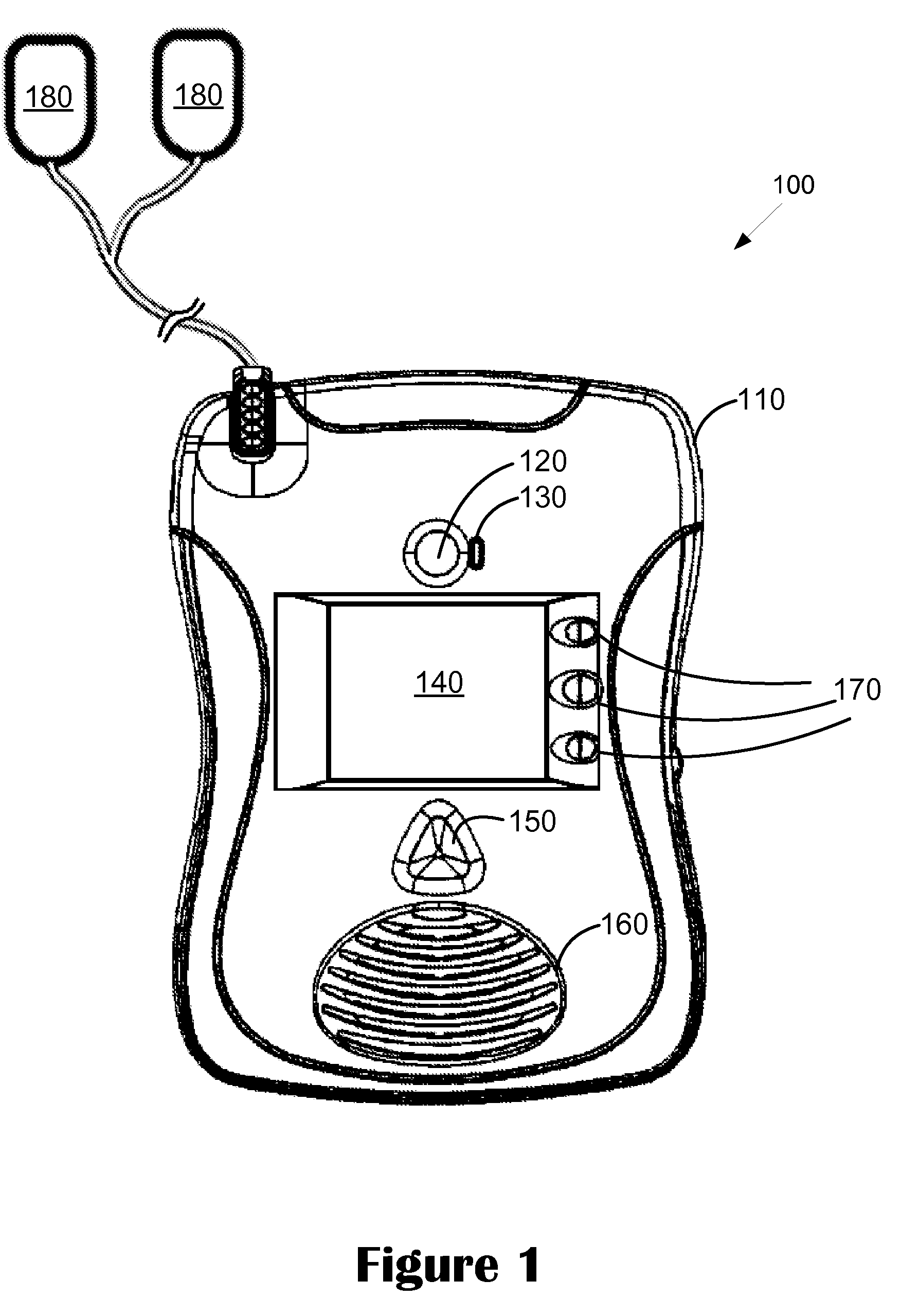
Advanced automatic external defibrillator powered by alternative and optionally multiple electrical power sources and a new business method for single use AED distribution and refurbishment
InactiveUS20040143297A1Improve reliabilityRapid and easy deploymentData processing applicationsHeart defibrillatorsEngineeringAutomatic external defibrillator
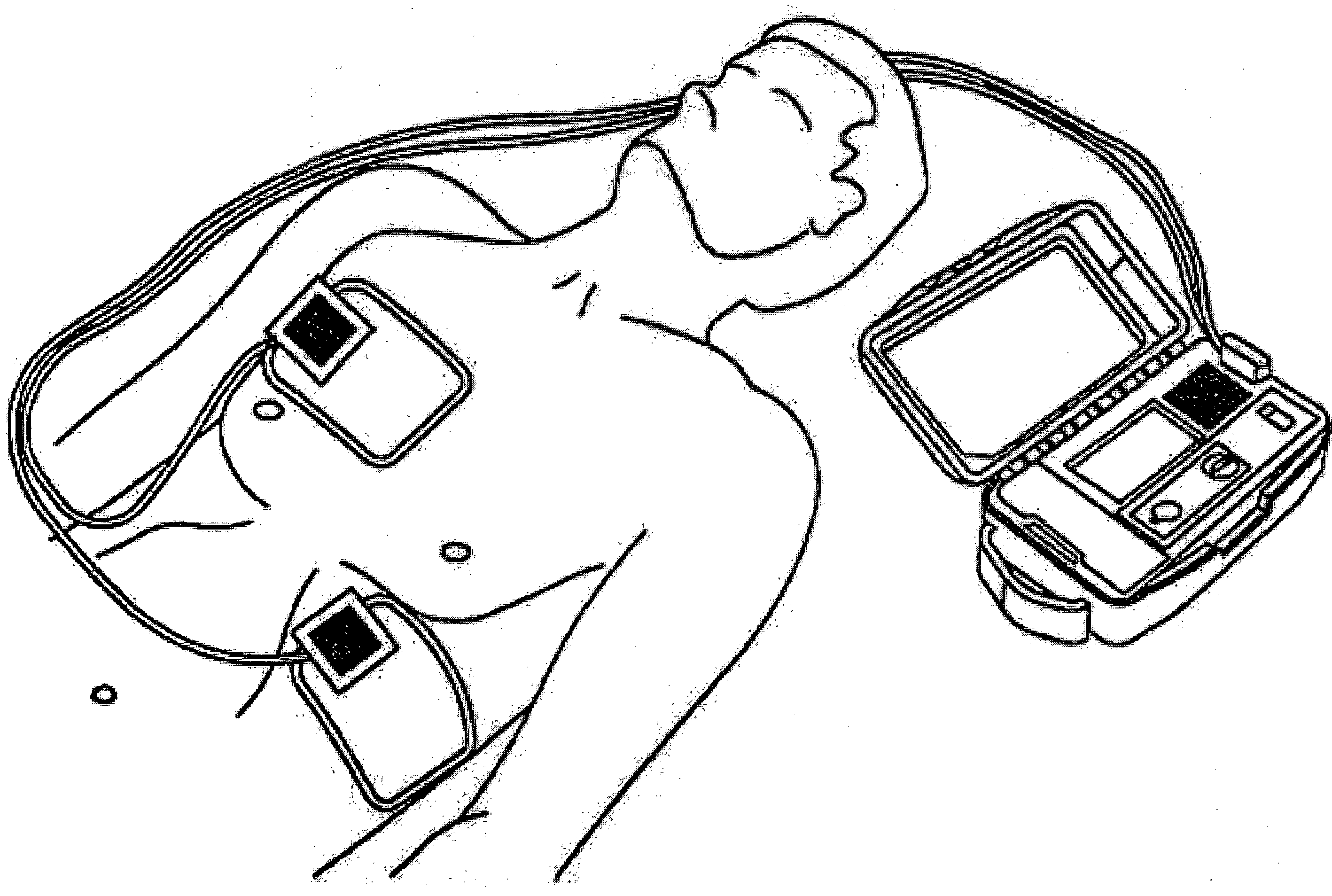
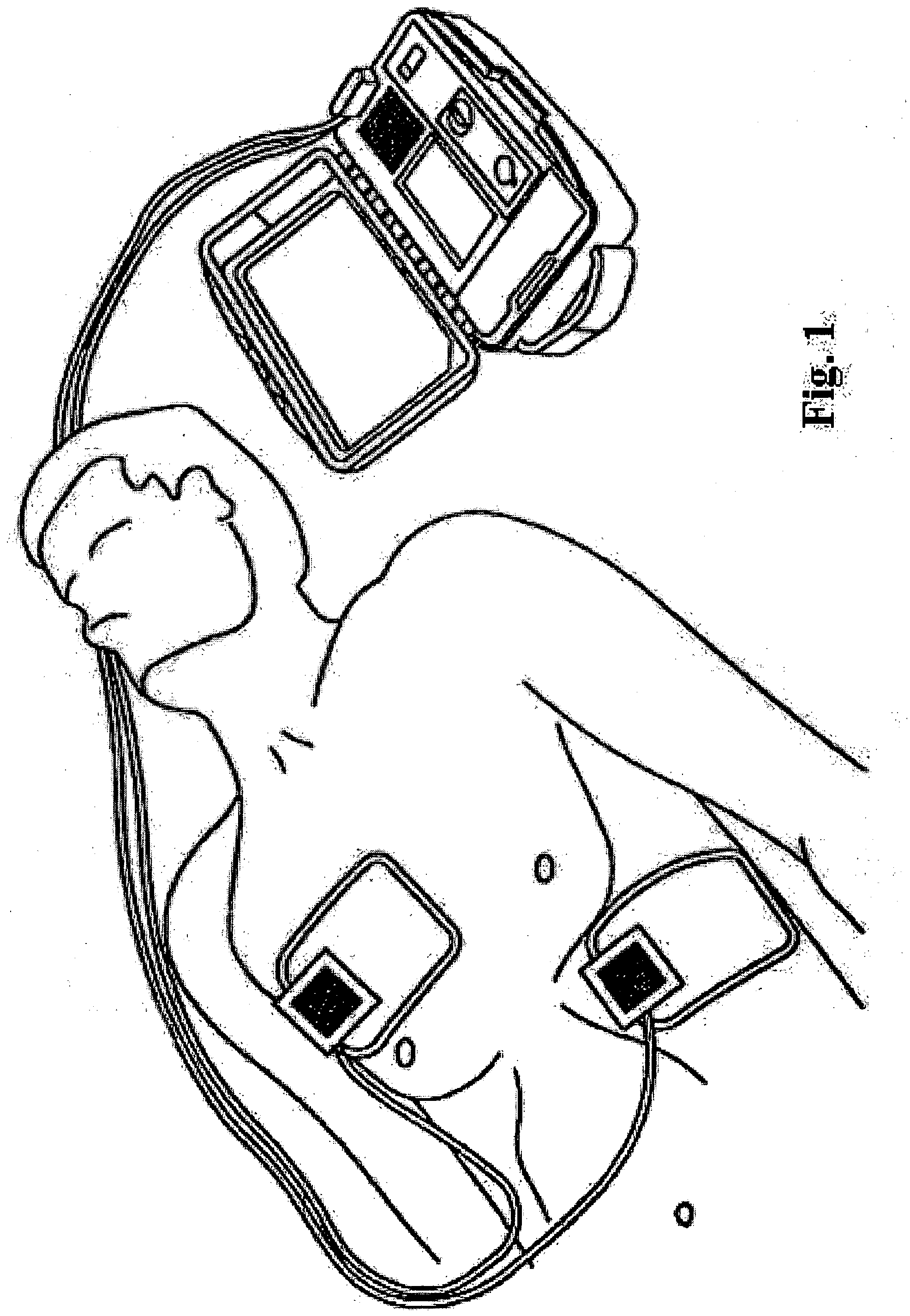
An AED being powered by 120 / 240 VAC electrical power alone, being powered by external DC power alone, or any in combination with or without internal-integral battery power, and further an AED access service business method for sales of access to AEDs. The inventive AED, in addition to the defibrillator circuitry comprises a long, tangle free power access cord to be plugged into an external source of AC or DC power and optionally, additional sets of body surface and alternative electrodes positioned in the esophagus and / or heart. The AED has additional advanced capabilities including the ability to deliver rapid sequential shocks through one or more sets of patient electrodes, and the optional mode of shock delivery whereby the shock is delayed while the AED continues to analyze the patients ECG waveform and delays the defibrillation shock or sequence of shocks until the ECG analysis indicates conditions are optimum for successful defibrillation.
Owner:RAMSEY MAYNARD III
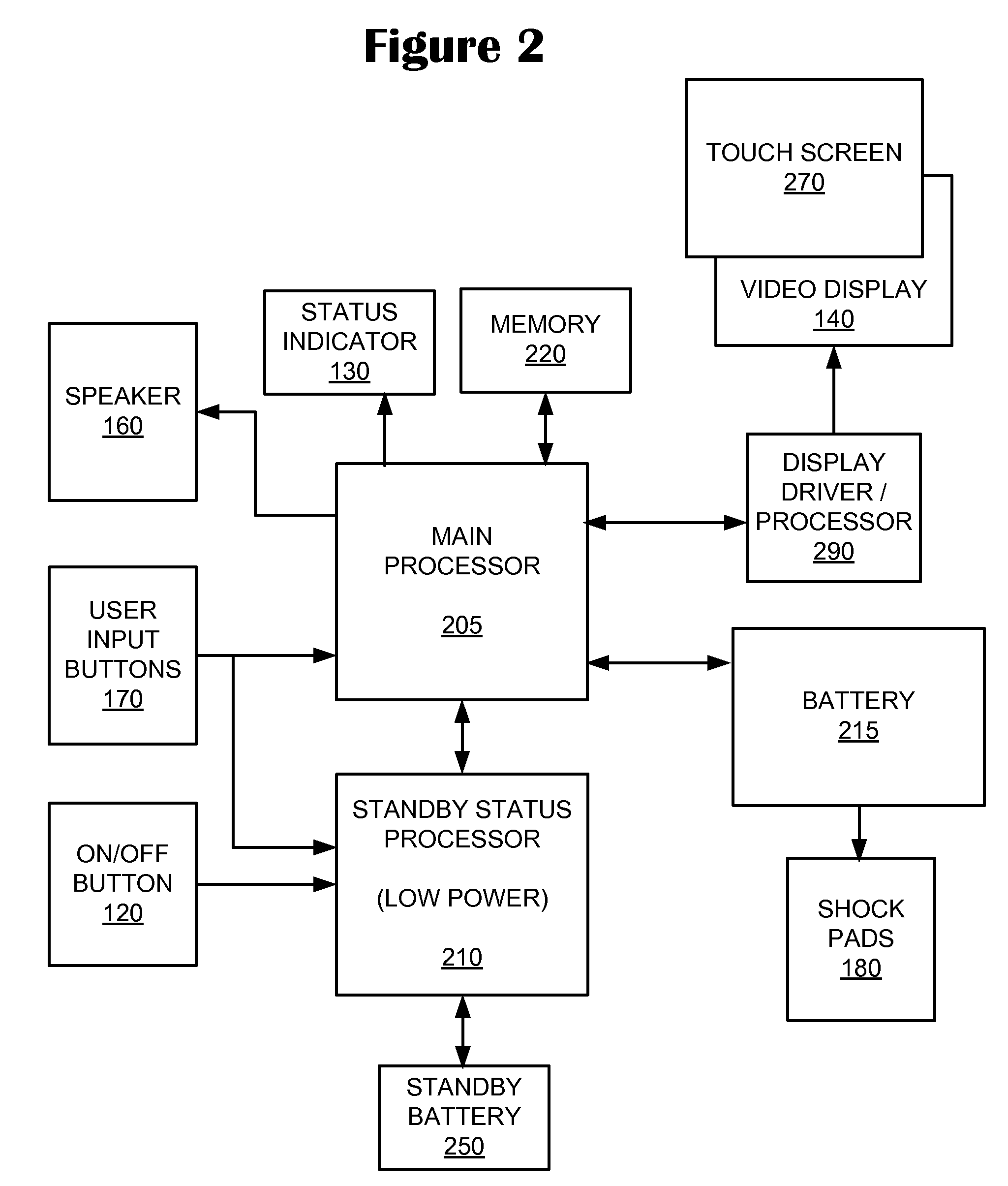
System and Method for Conditioning a Lithium Battery in an Automatic External Defibrillator
An inventive system and method de-passivates a direct current (DC) power source of an Automatic External Defibrillator (AED), such as an AED lithium battery. The system includes a main processor and standby processor. The standby processor monitors the age and usage of the battery. Based on the status of the monitored parameters, the system executes a conditioning discharge to remove a layer of salt crystals on the DC power source.
Owner:DEFIBTECH
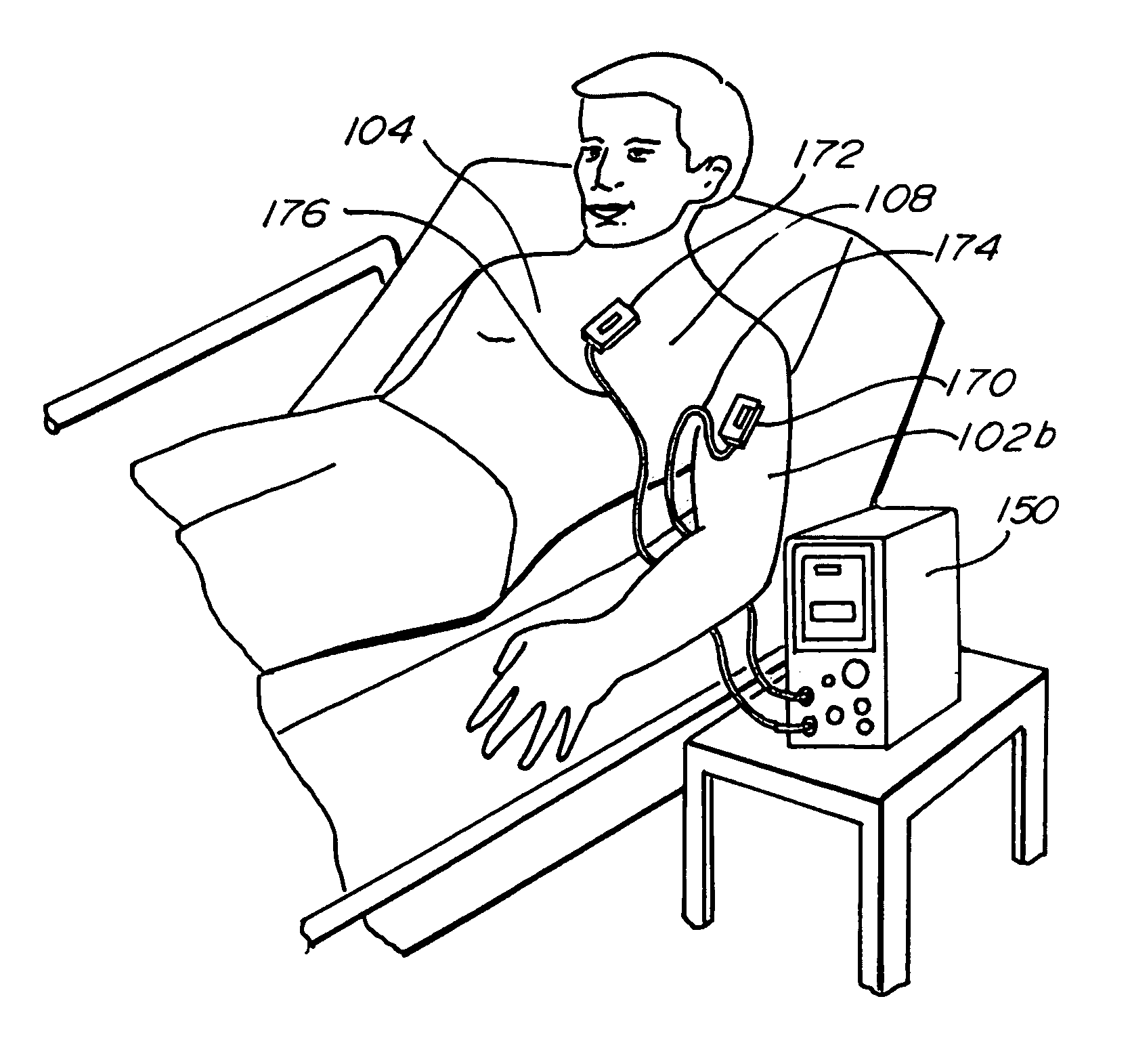
Method of applying electrical signals to a patient and automatic wearable external defibrillator
InactiveUS7065401B2Lower impedanceLoss is particularly problematicHeart defibrillatorsExternal electrodesElectricityProximate
A system, apparatus, and method of delivering a defibrillation pulse to the heart of a patient generally includes positioning a pair of electrodes on the exterior surface of the patient's body such that at least one of the electrodes is placed on a limb, e.g., arm or leg, of the patient in a position proximate to the patient's torso. An electrical defibrillation pulse is then delivered through the electrodes, into the limb, enabling the electrical defibrillation pulse to travel from the limb to the heart of the patient.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
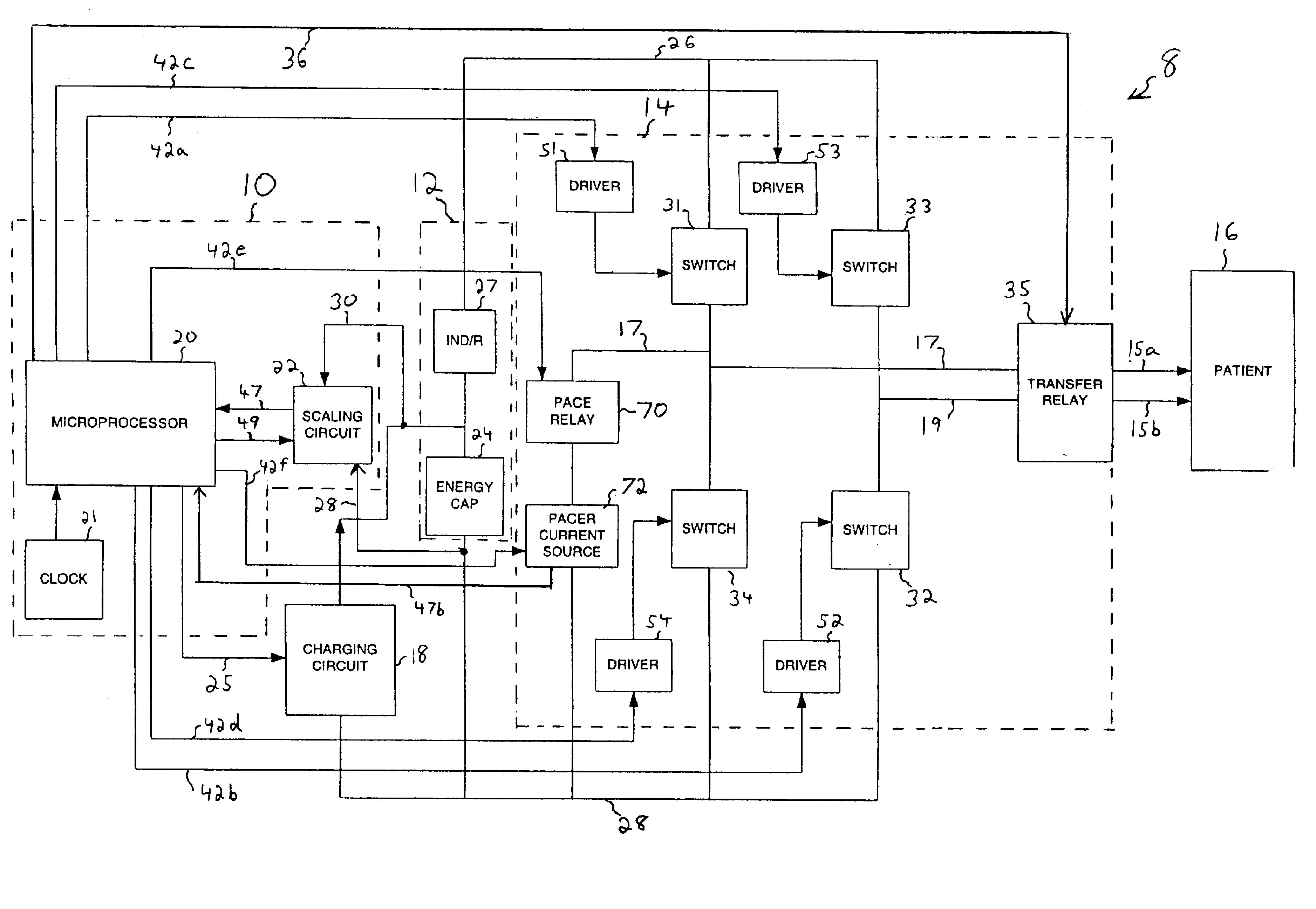
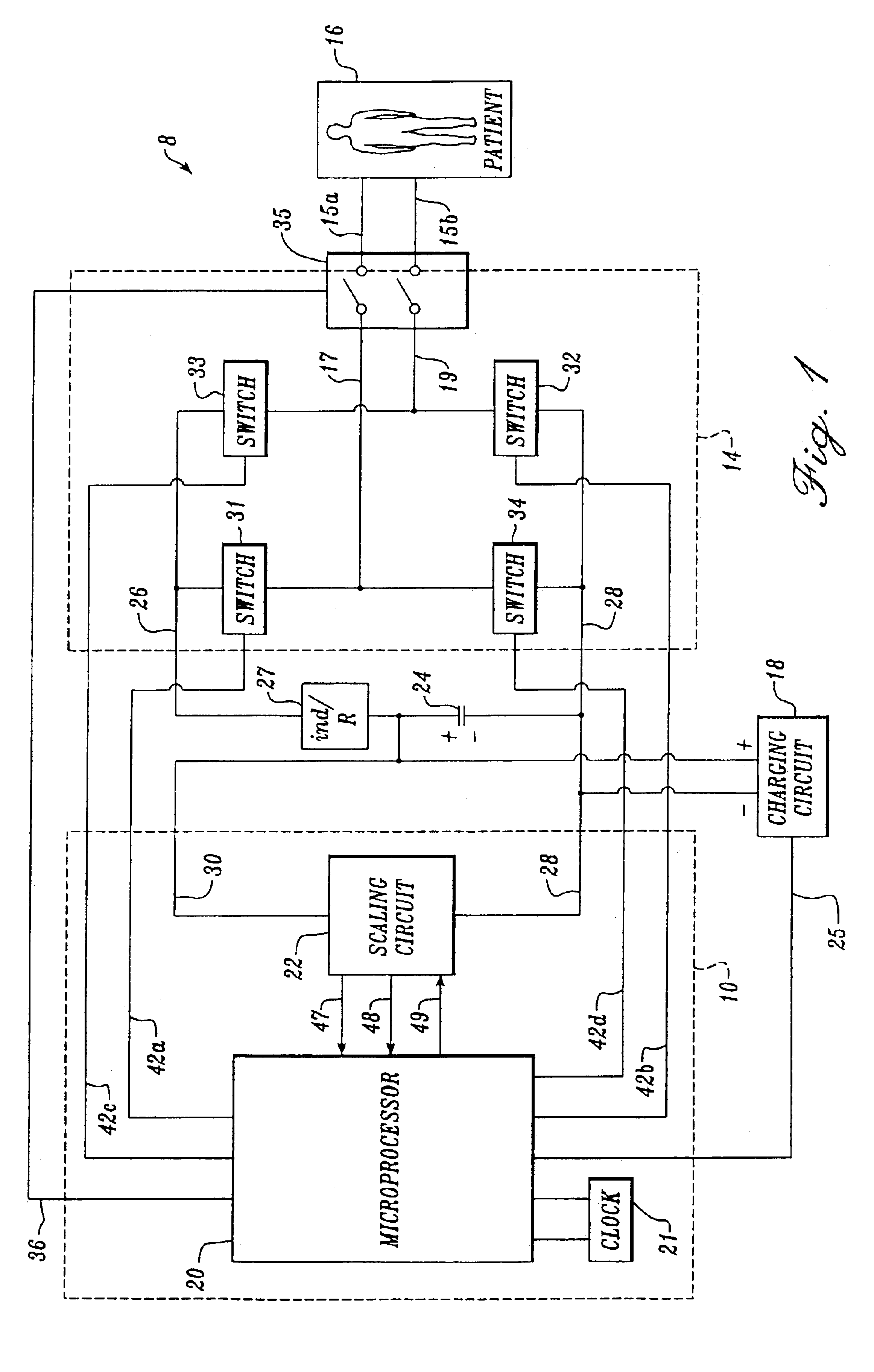
External Defibrillator
ActiveUS20080033495A1Minimal maintenancePrevent implantationHeart defibrillatorsElectricityElectrical battery
An external defibrillator having a battery; a capacitor electrically communicable with the battery; at least two electrodes electrically communicable with the capacitor and with the skin of a patient; a controller configured to charge the capacitor from the battery and to discharge the capacitor through the electrodes; and a support supporting the battery, capacitor, electrodes and controller in a deployment configuration, the defibrillator having a maximum weight per unit area in the deployment configuration of 0.1 lb / in2 and / or a maximum thickness of 1 inch. The support may be a waterproof housing.
Owner:ELEMENT SCI
External defibrillator
ActiveUS20100241181A1Improve portabilityImprove accessibilityHeart defibrillatorsElectricityElectrical battery
A variety of arrangements and methods relating to a defibrillator are described. In one aspect of the invention, a defibrillator includes two paddles that each include a defibrillator electrode covered in a protective housing. The two paddles are sealed together using a releasable seal to form a paddle module such that the housings of the paddles form the exterior of the paddle module. An electrical system including at least a battery and a capacitor is electrically coupled with the paddles. The battery is arranged to charge the capacitor. The capacitor is arranged to apply a voltage at the defibrillator electrodes, which generates an electrical shock for arresting a cardiac arrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIOTHRIVE
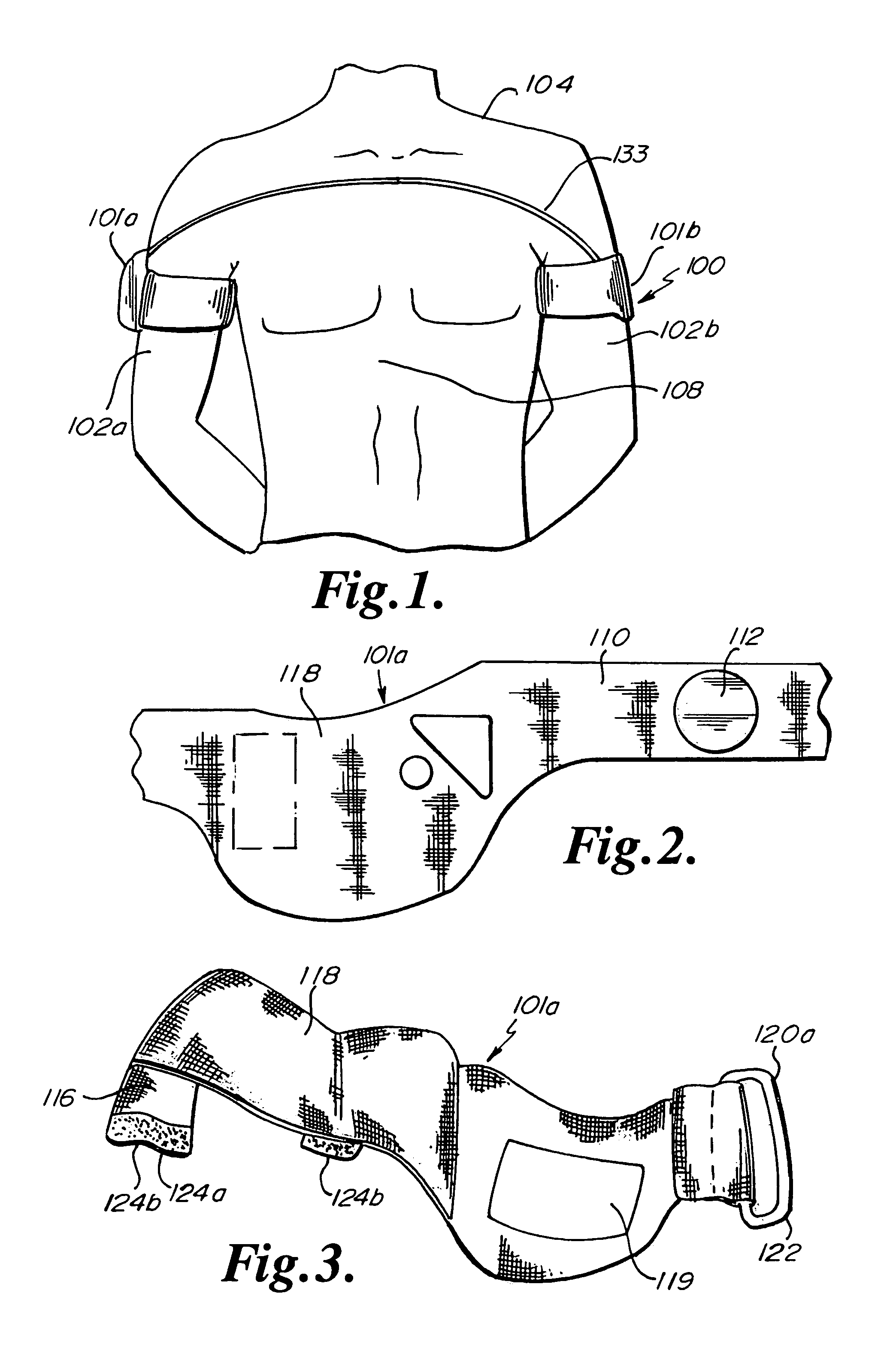
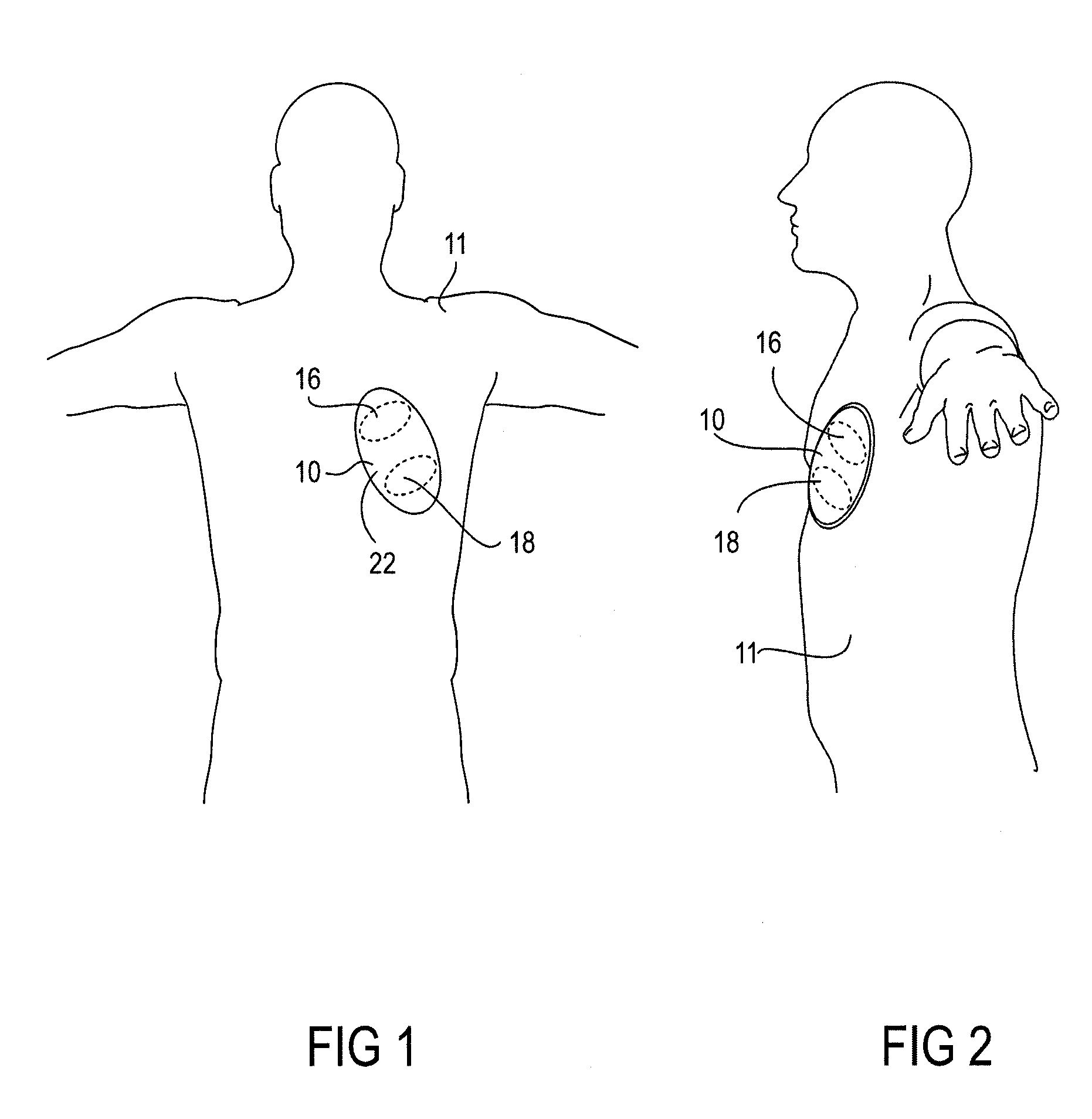
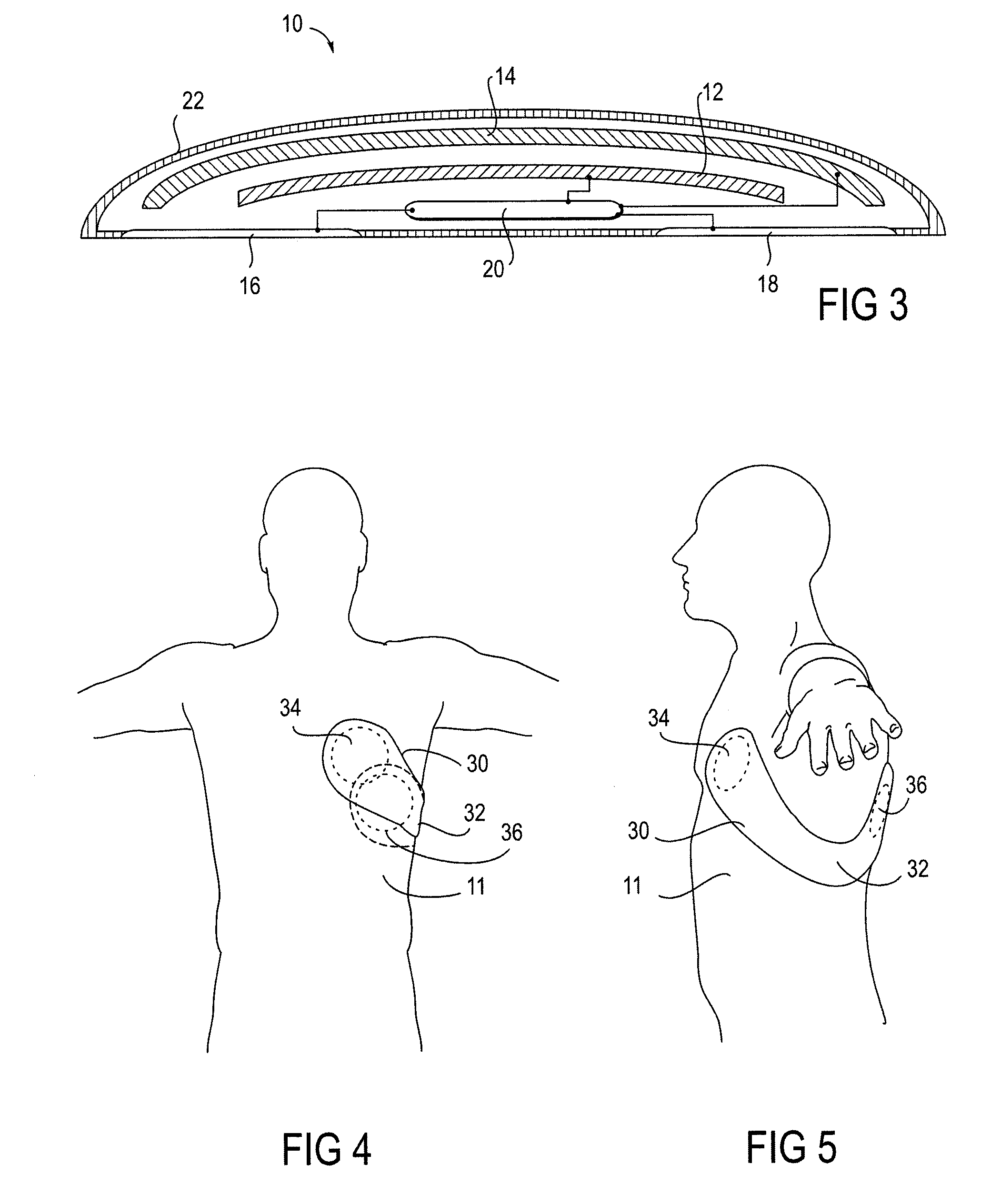
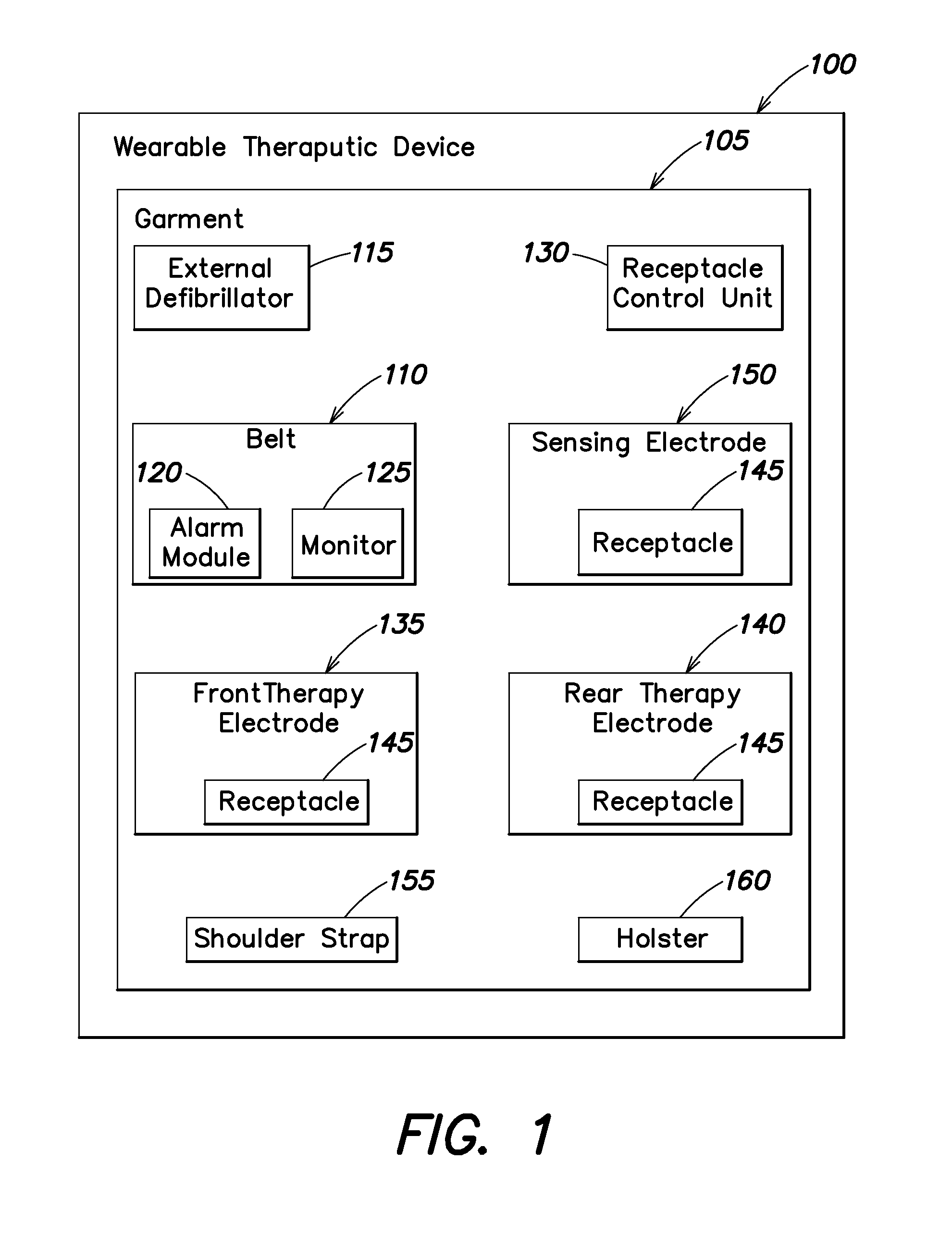
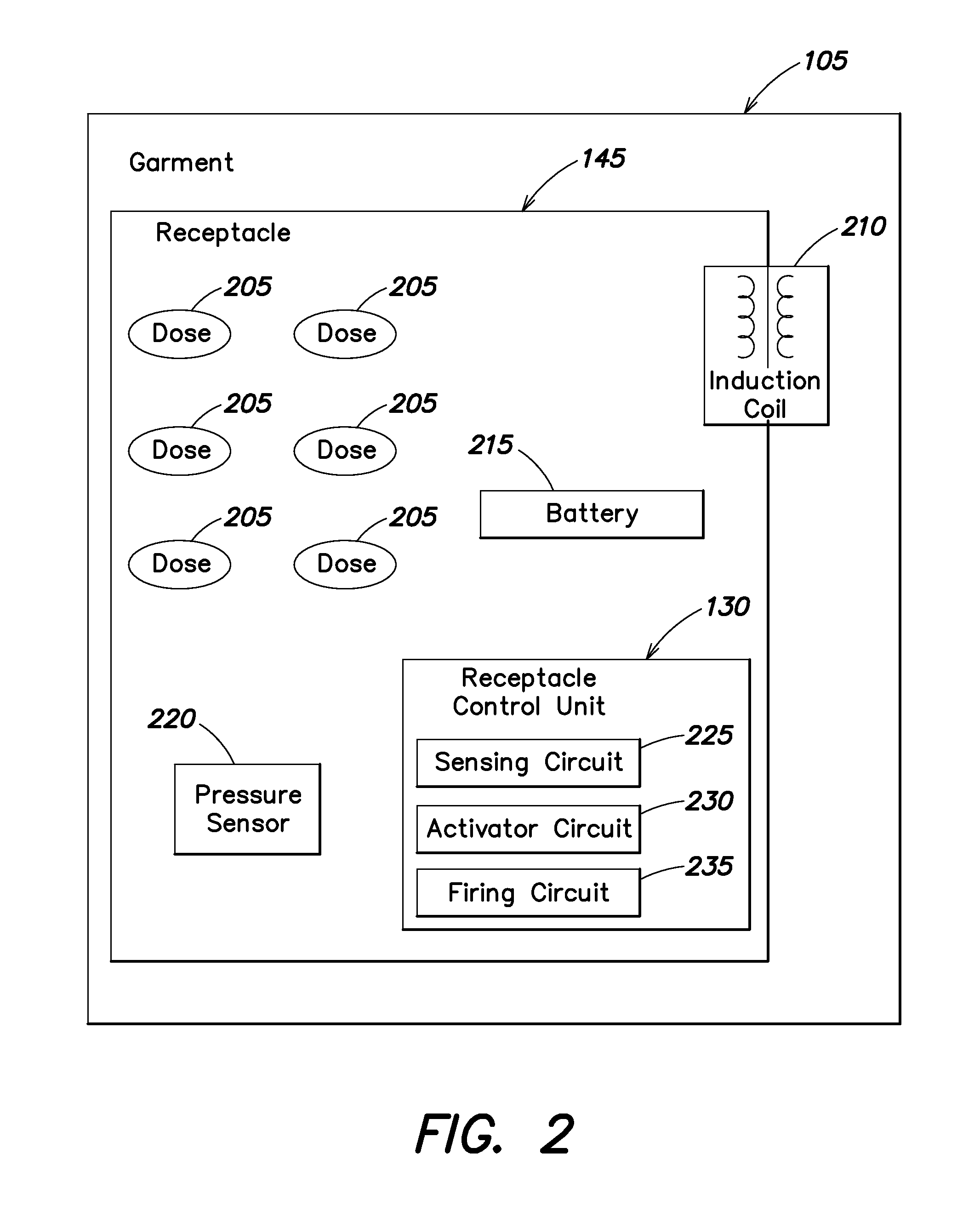
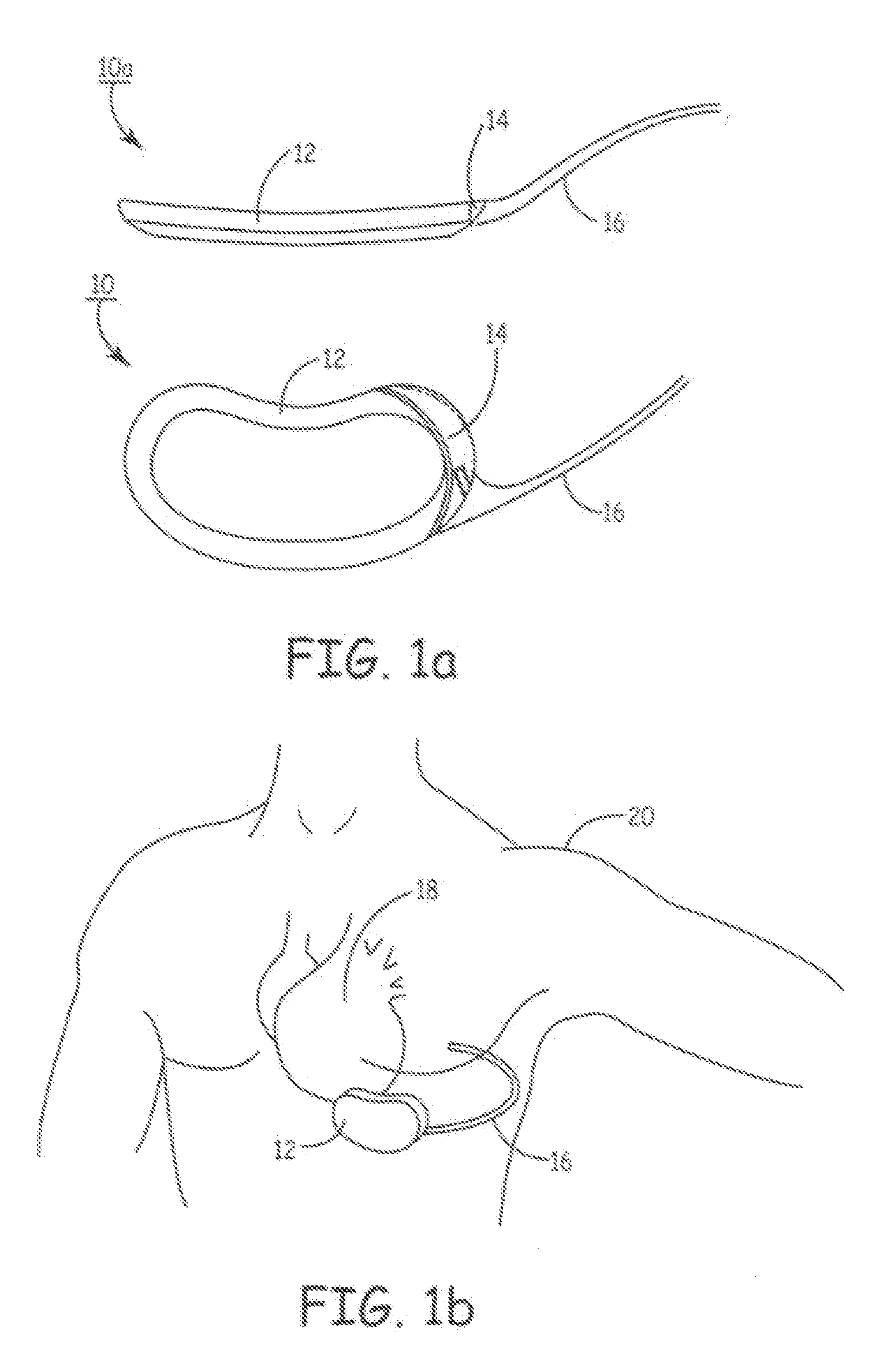
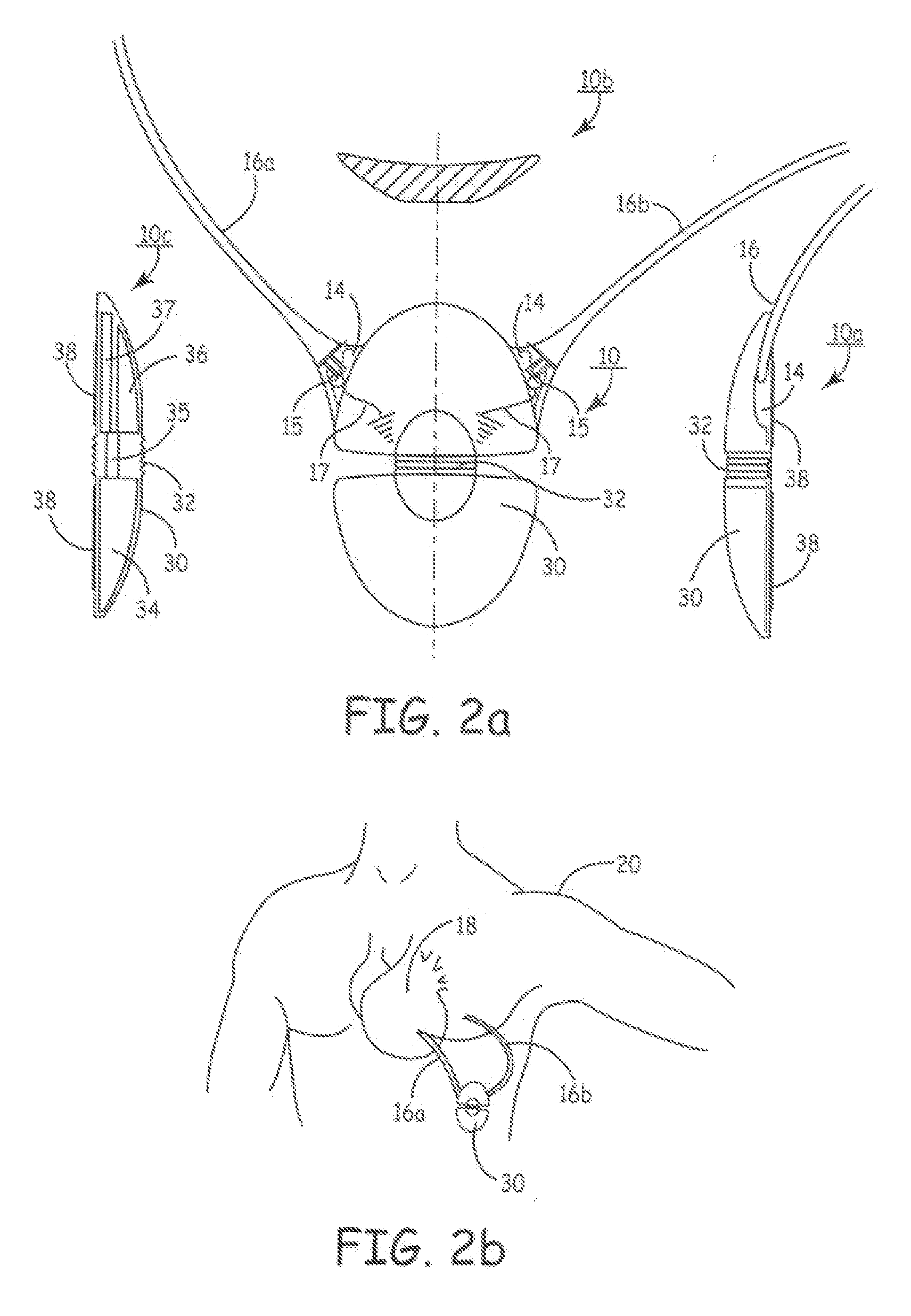
Wearable therapeutic device
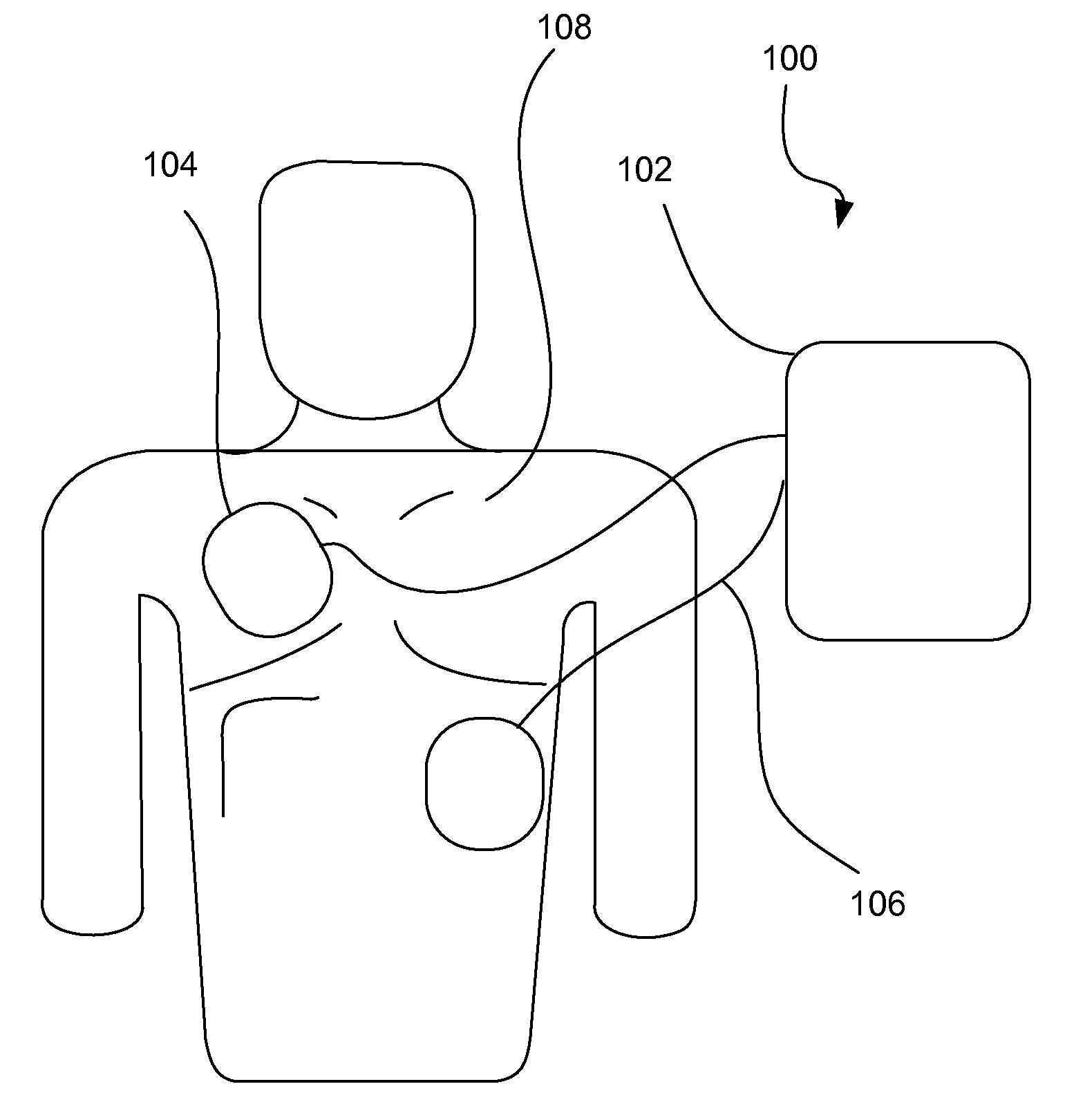
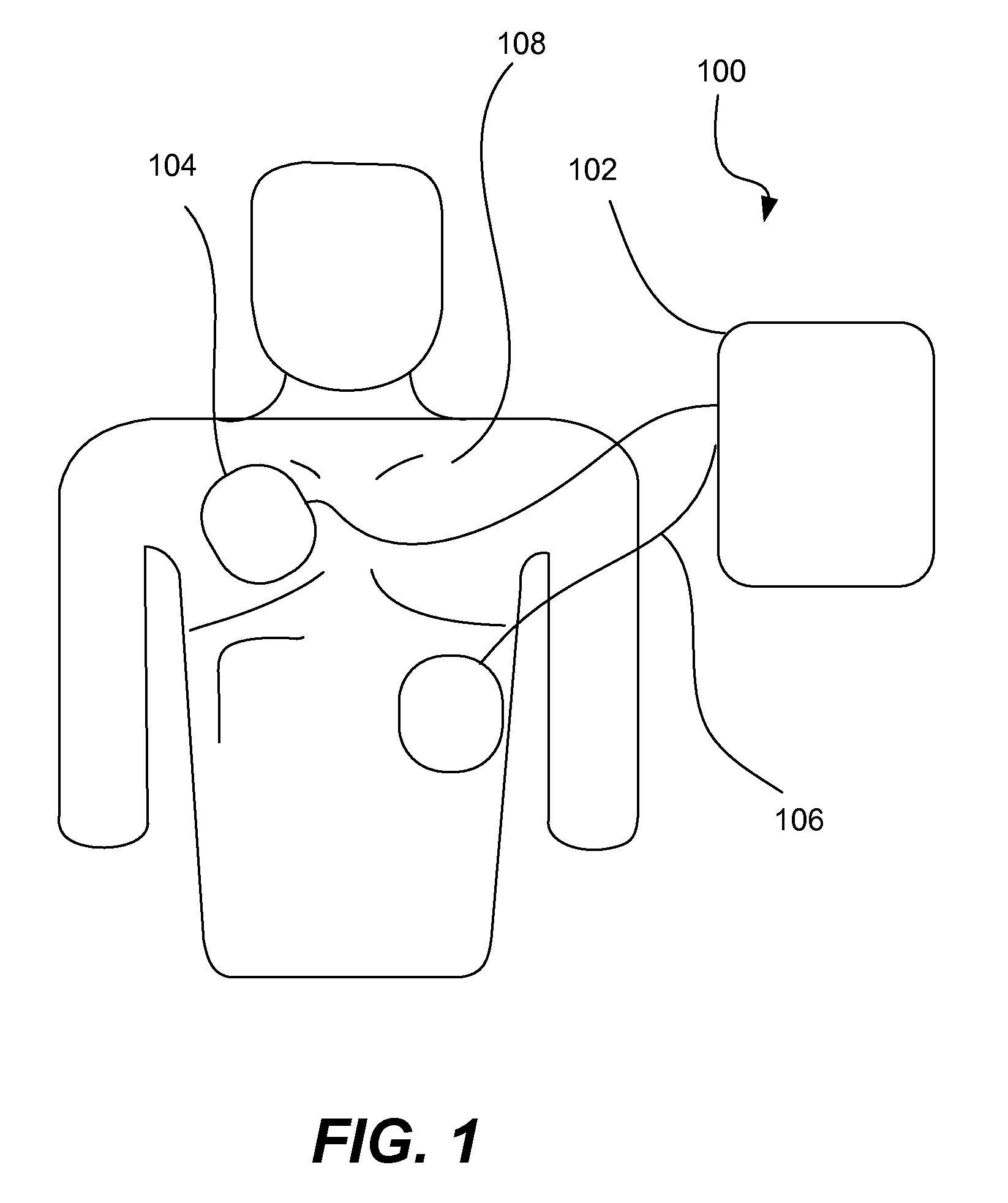
A wearable therapeutic device that includes a garment configured to contain an external defibrillator. The garment is configured to house at least one of an alarm module and a monitor and to house a first therapy electrode and a second therapy electrode. The garment is also configured to releasably receive a receptacle that contains a conductive fluid proximate to at least one of the first therapy electrode and the second therapy electrode, and to electrically couple the receptacle with the garment.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
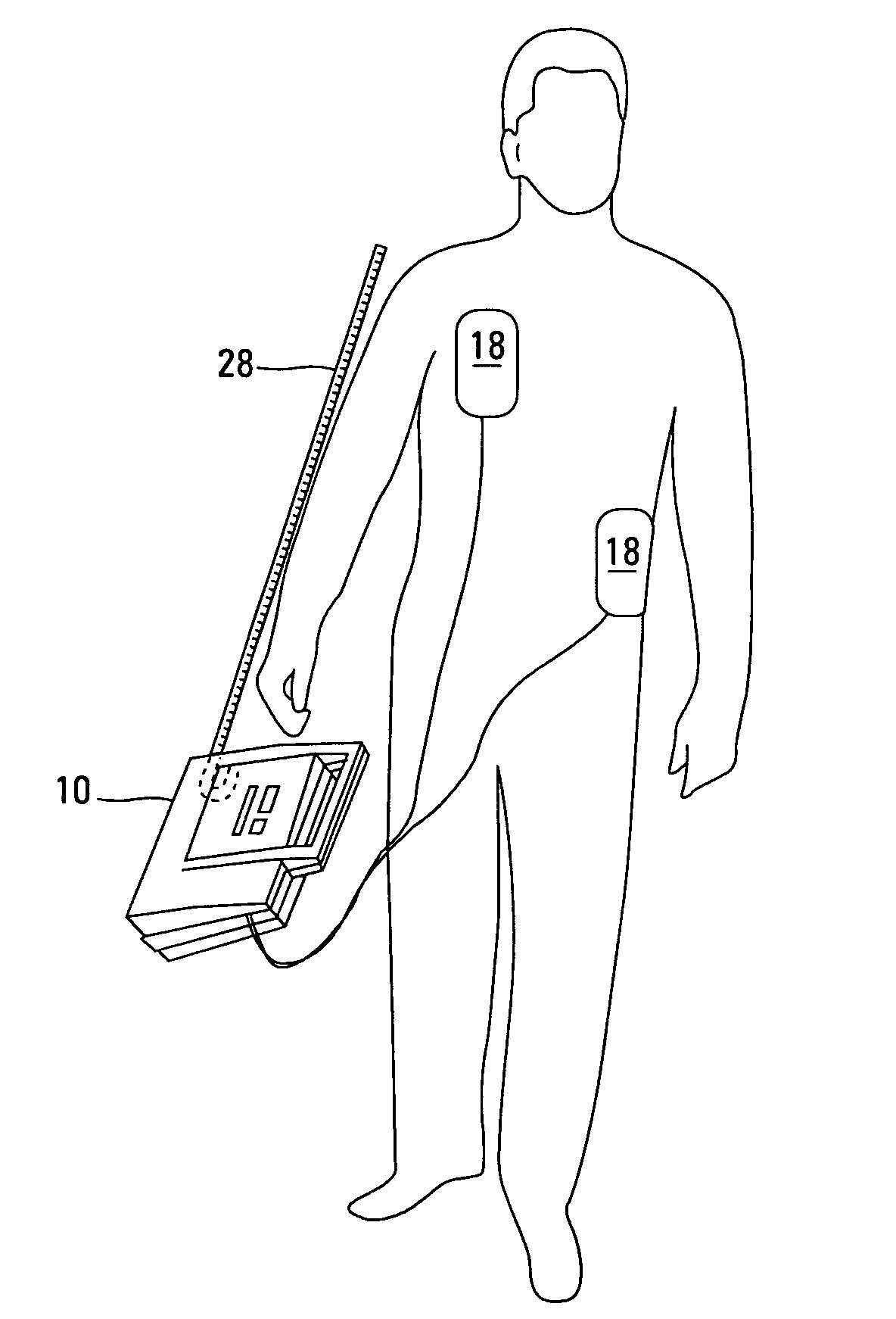
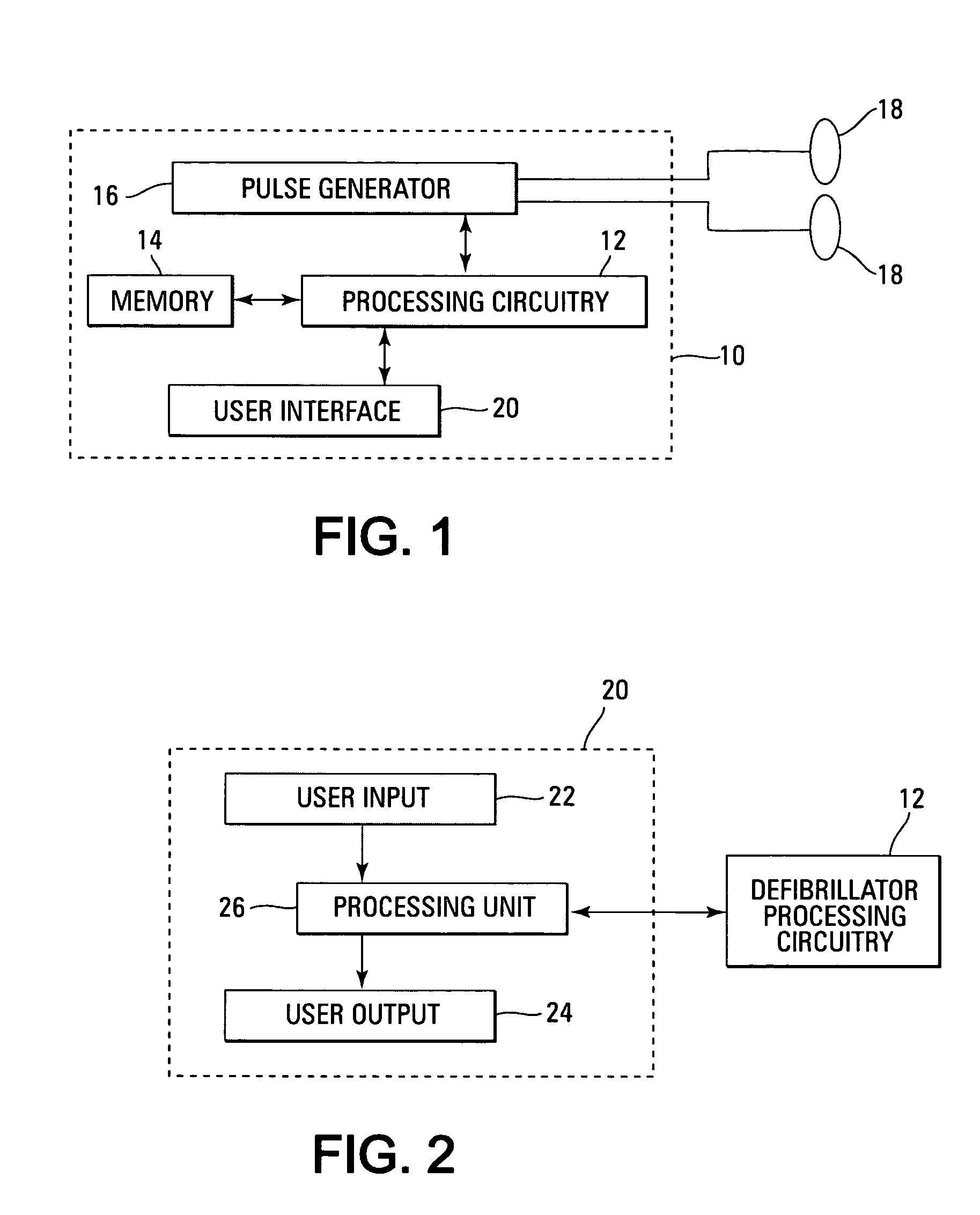
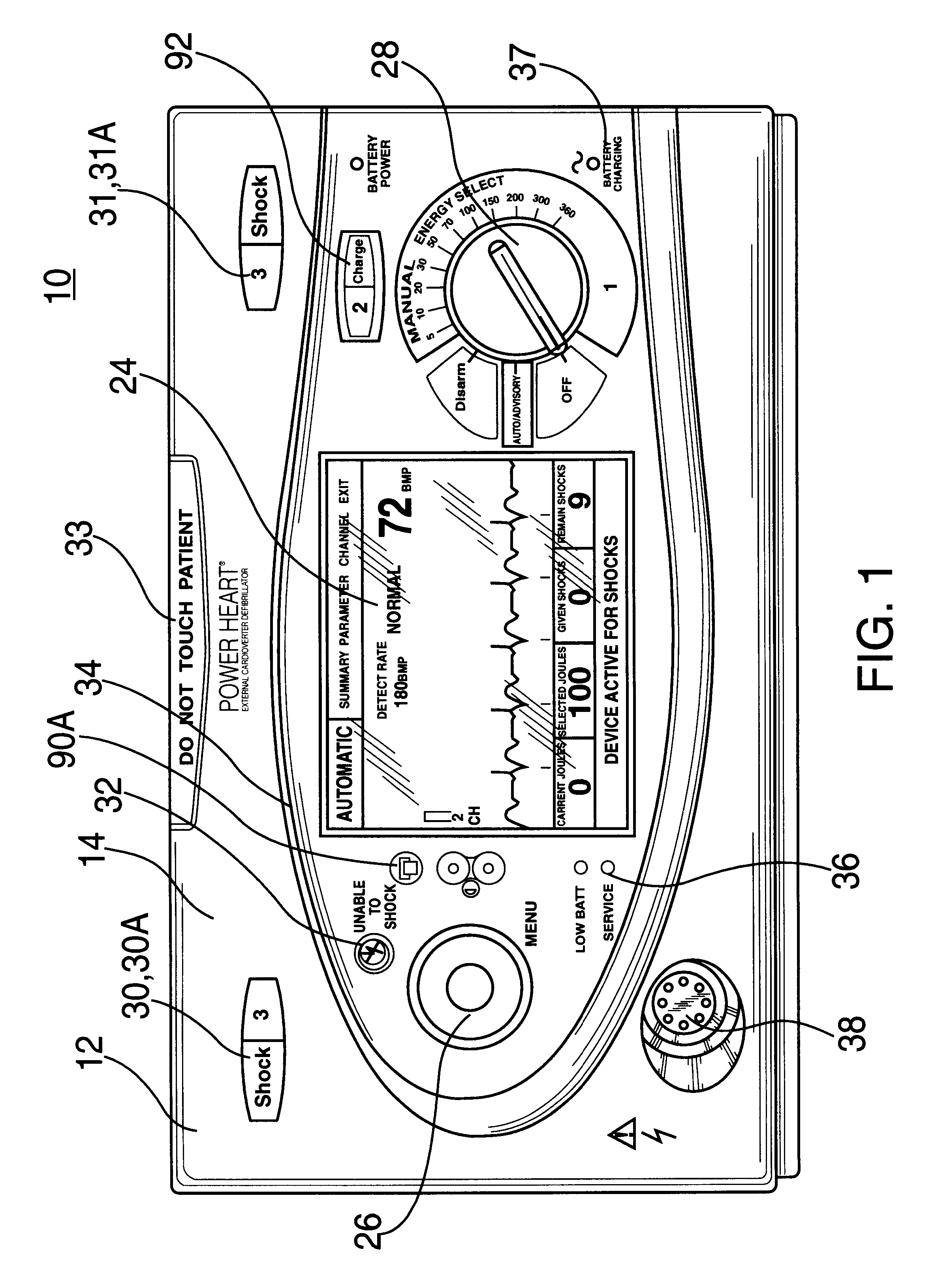
Automated external defibrillator with user interface for adult and pediatric applications
An automated external defibrillator automatically determines the type of patient to which it is attached based on patient-specific information entered by the user. The defibrillator includes electrodes that are adapted for placement on a patient, a pulse generator connected to the electrodes, and processing circuitry that controls the defibrillation pulse delivery from the pulse generator. The automated external defibrillator causes a defibrillation pulse to be delivered to the patient in accordance with the determined patient type. A user interface having a user input connected to the processing circuitry enables the user of the defibrillator to enter patient-specific information. The user may enter the patient-specific information by interacting with the user input during a time period in relation to a prompt from the defibrillator. In another aspect, data pertaining to identification of the type of patient connected to the electrodes may be recorded with event data in a memory.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
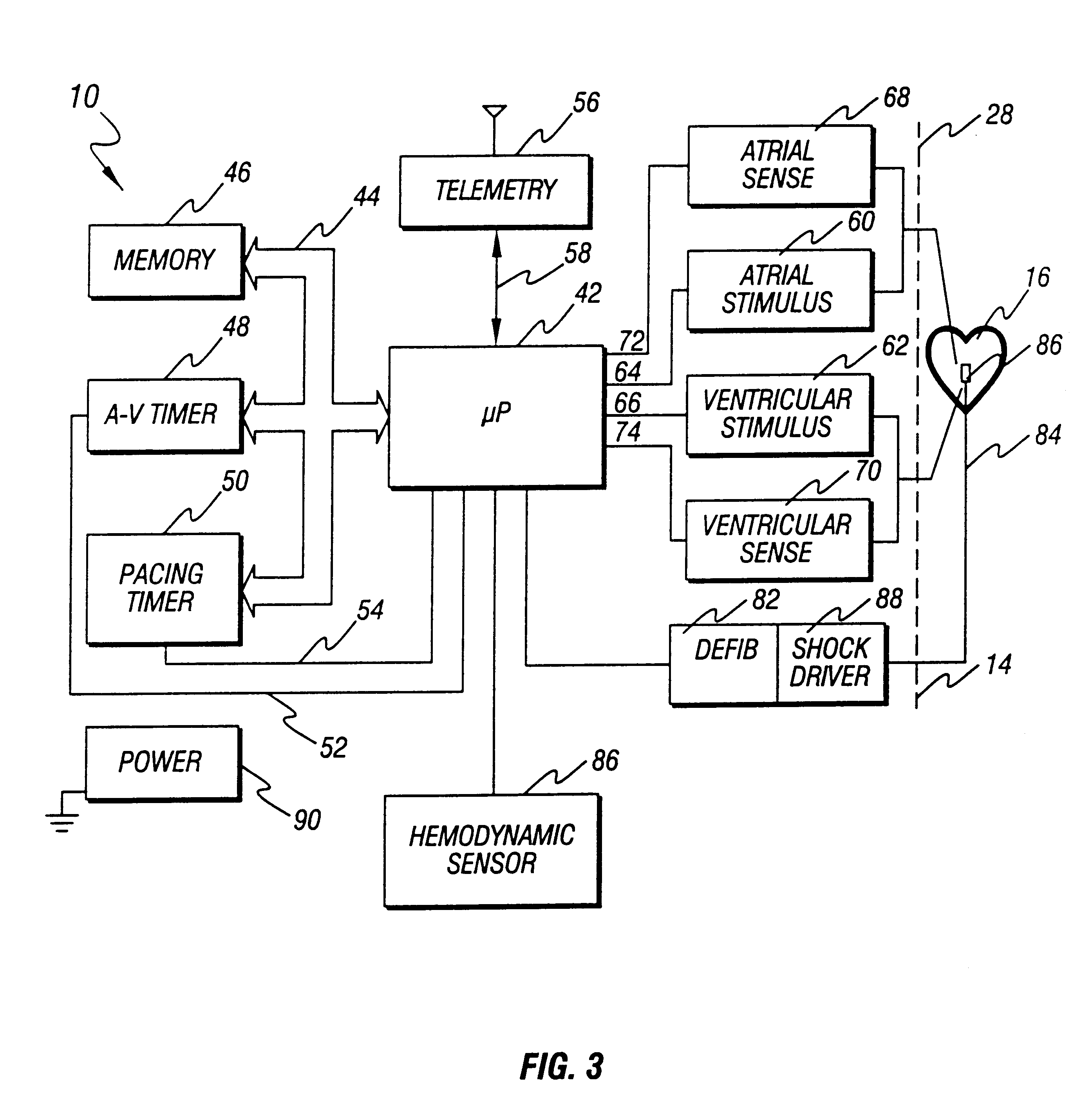
Method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac electromechanical dissociation
InactiveUS6298267B1Heart defibrillatorsCardiac arrest- pulseless electrical activityPulseless electrical activity
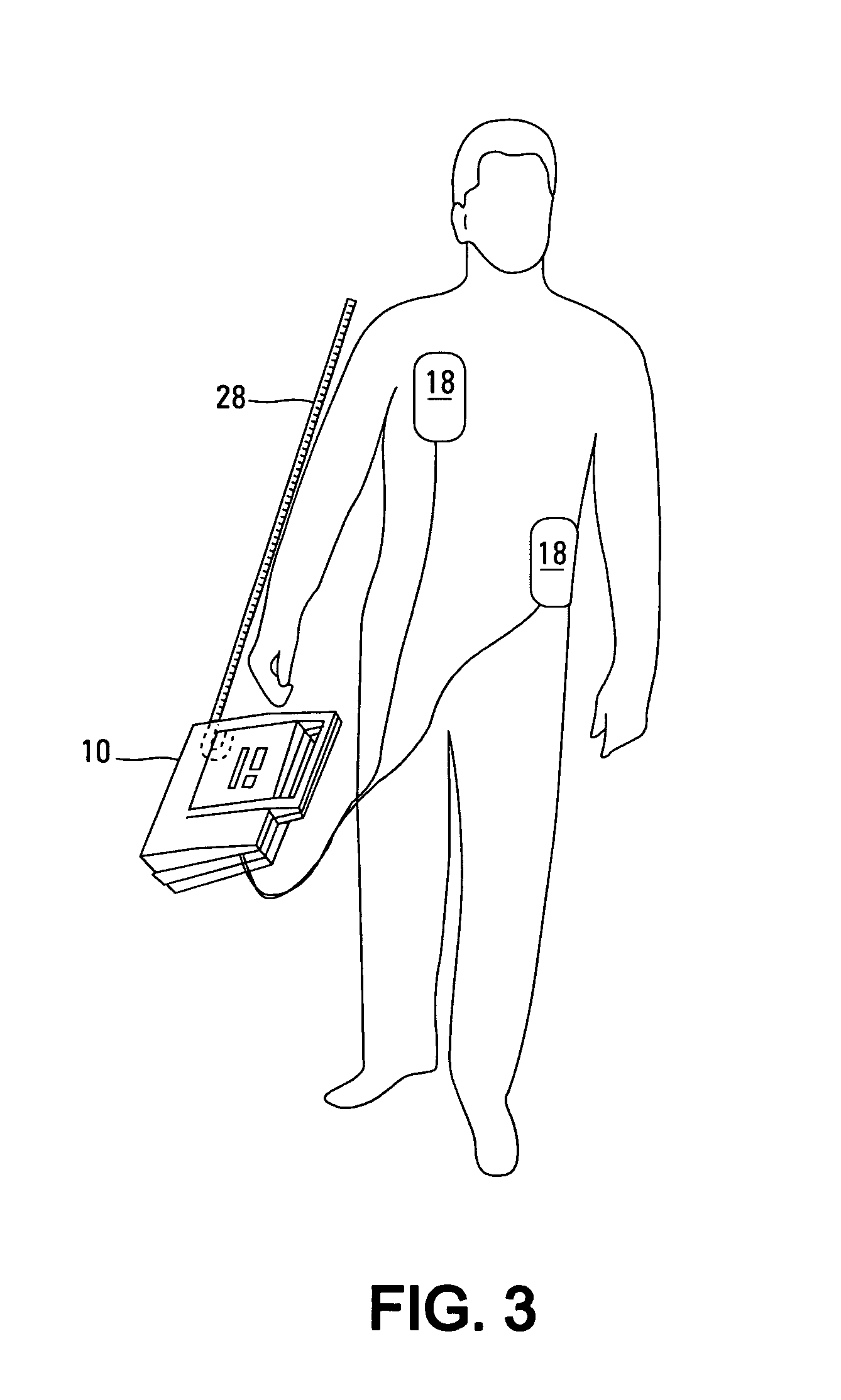
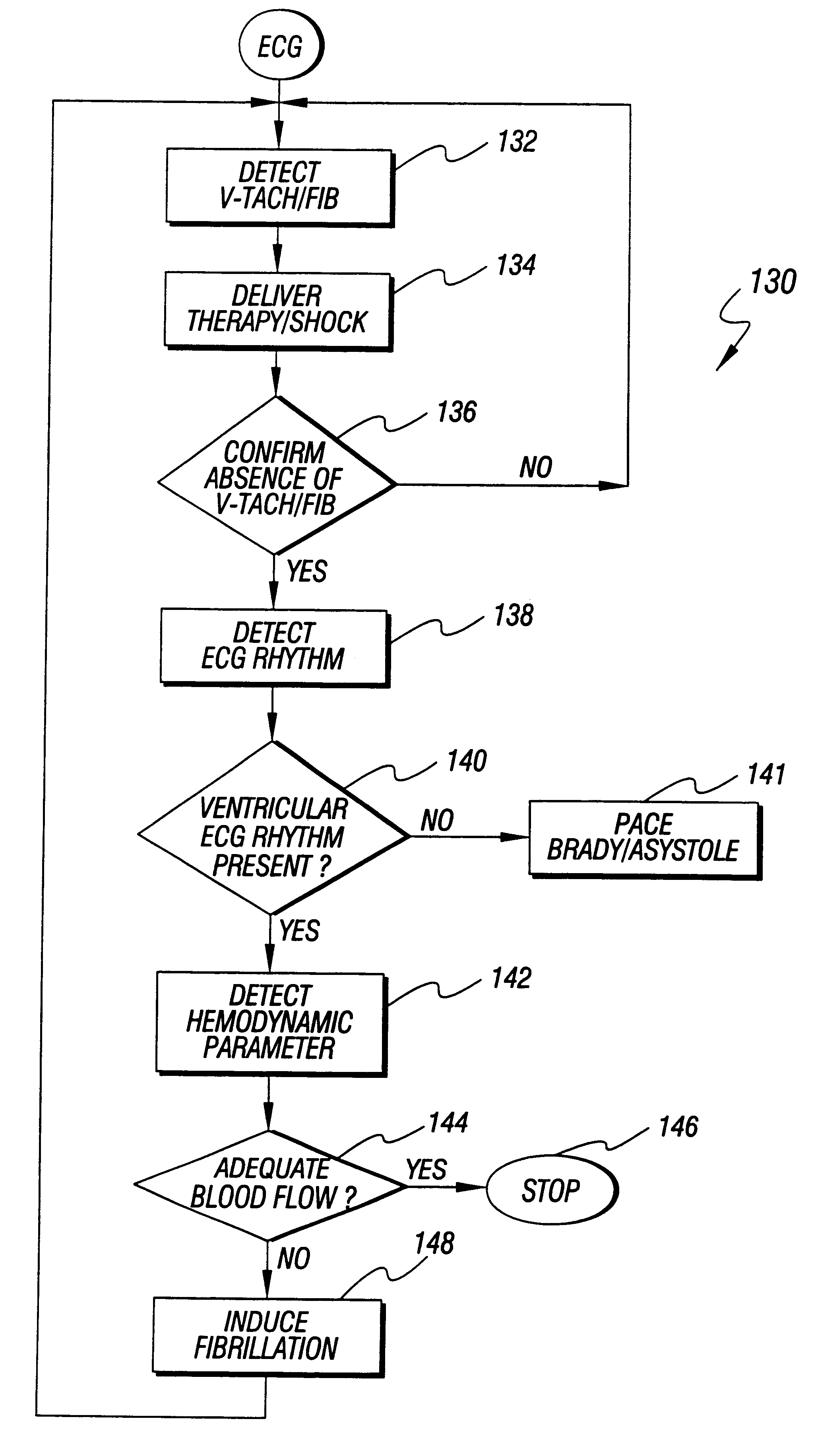
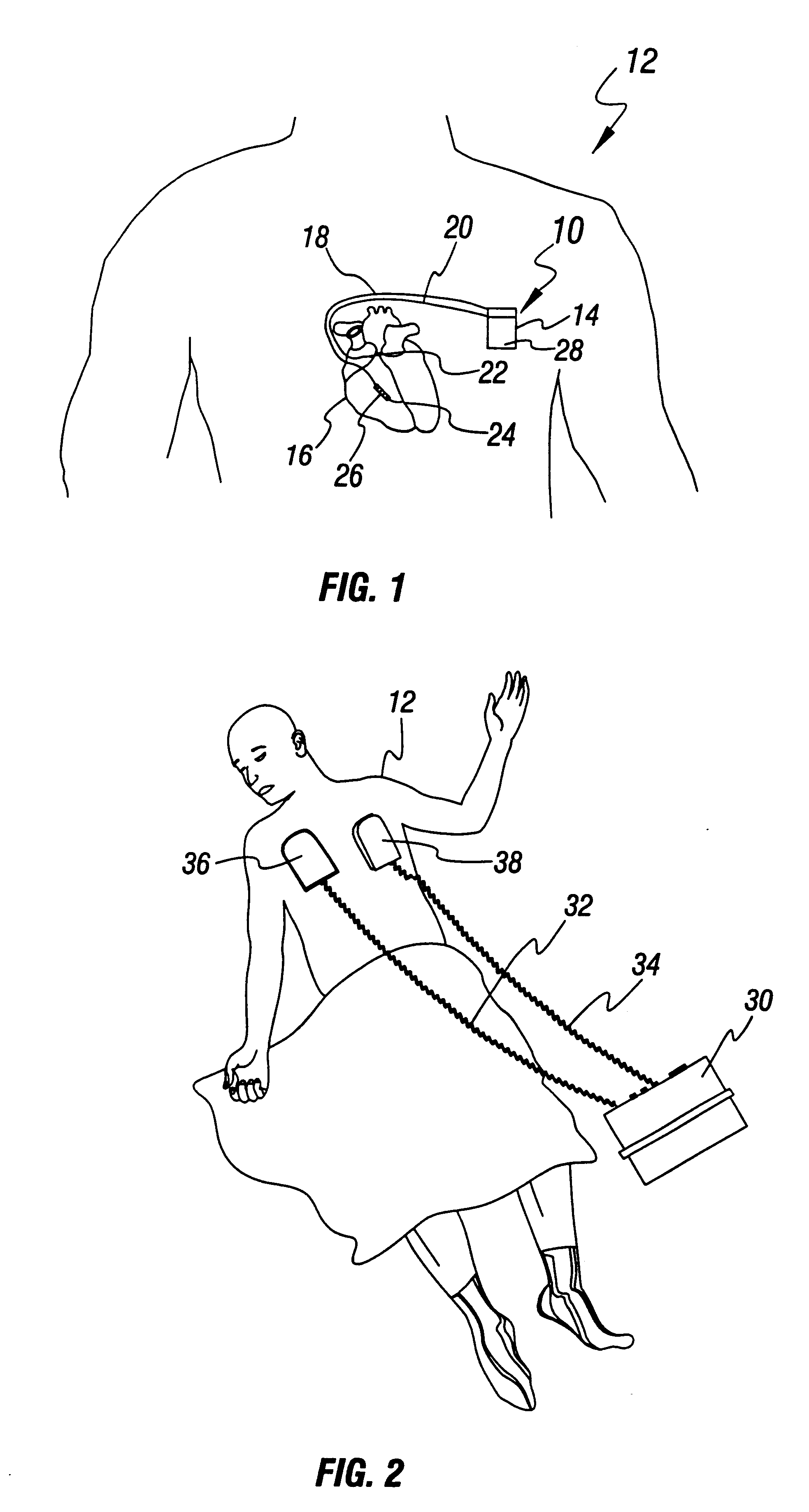
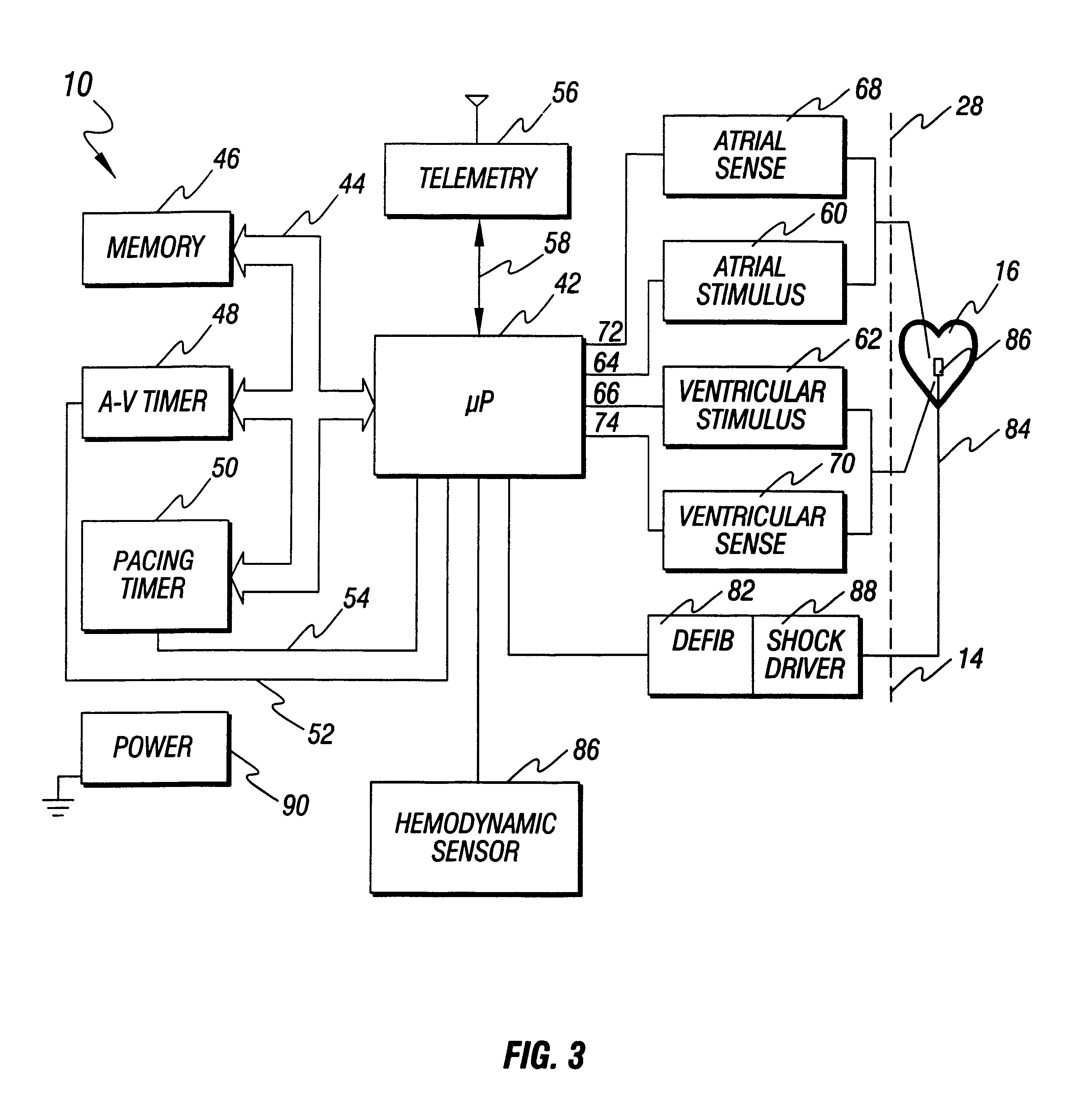
An apparatus and method for treating post-defibrillation electromechanical dissociation ("EMD") or pulseless electrical activity ("PEA"). A first embodiment comprises an implantable defibrillator with the capability of detecting and treating post defibrillation EMD. The stimulator / defibrillator has one or more leads with electrodes and at least one electrode for defibrillation. A sense circuit senses the electrical condition of the heart of the patient. A second sensor senses a parameter correlated to the state of blood flow. The cardiac stimulator / defibrillator detects and terminates ventricular tachyarrhythmia or fibrillation. If the stimulator / defibrillator detects the presence of electrical rhythm in the heart correlated, however, with inadequate blood flow to sustain life (EMD), the device provides an output to stimulate the heart to overcome EMD. The device may also be an external defibrillator. The method for treating the heart to restore blood flow where electromechanical dissociation occurs after termination of a ventricular tachyarrhythmia or ventricular fibrillation comprises identifying electromechanical disassociation after termination of a ventricular tachyarrhythmia or a fibrillation and inducing or re-inducing ventricular fibrillation and subsequently applying defibrillating shocks to terminate the fibrillation.
Owner:INTERMEDICS
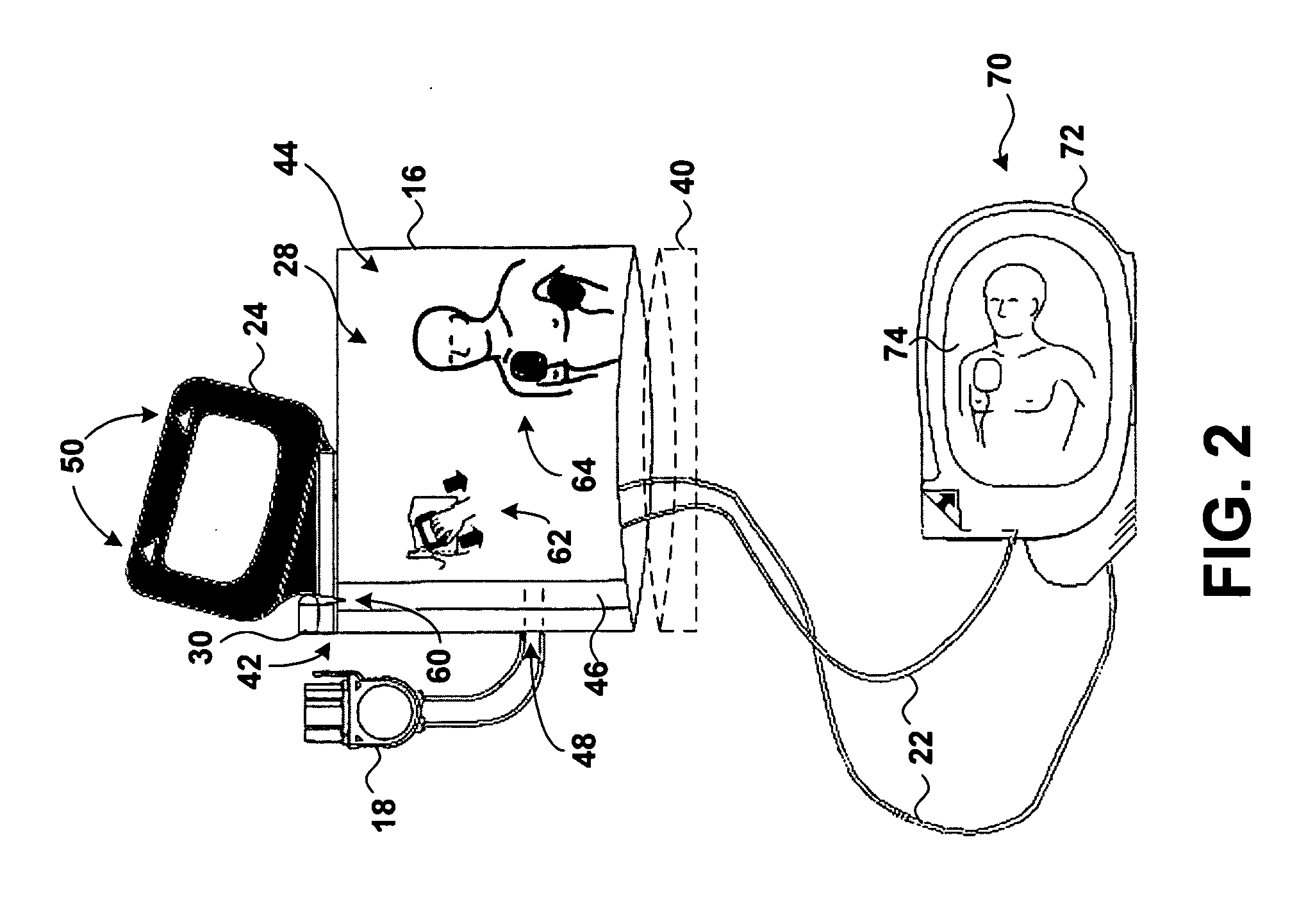
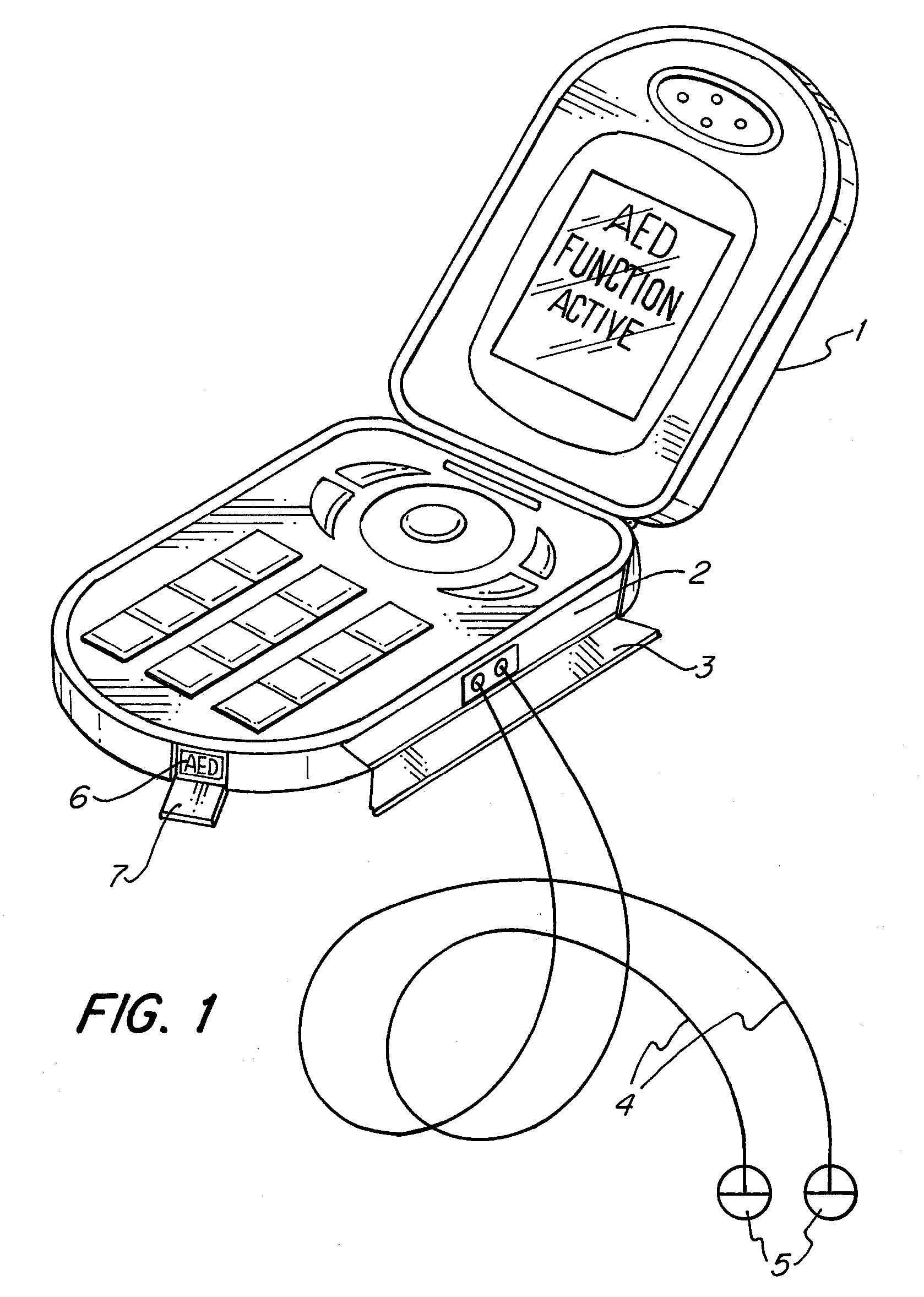
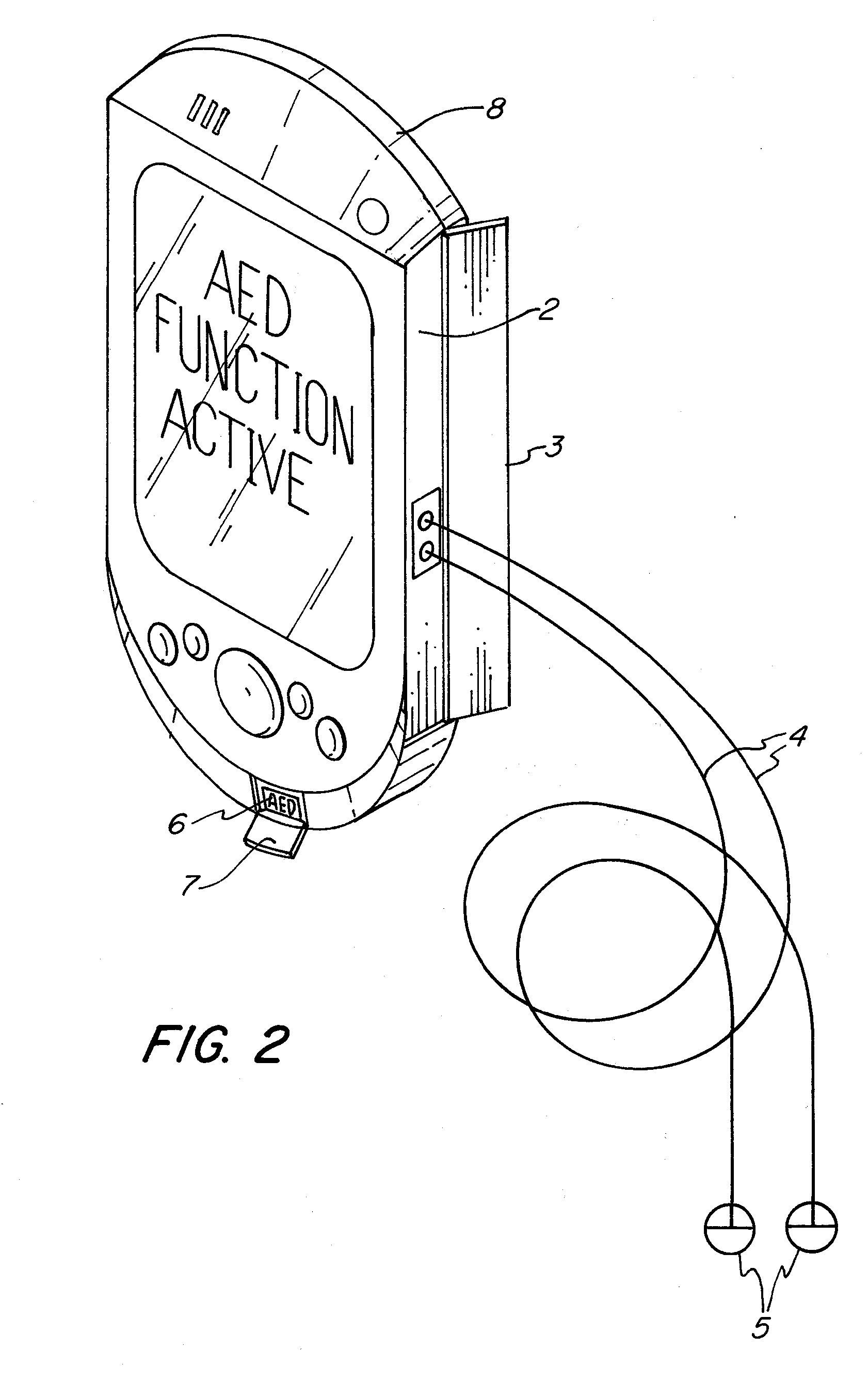
Method and apparatus for remote-operated automated external defibrillator incorporated into a hand-held device
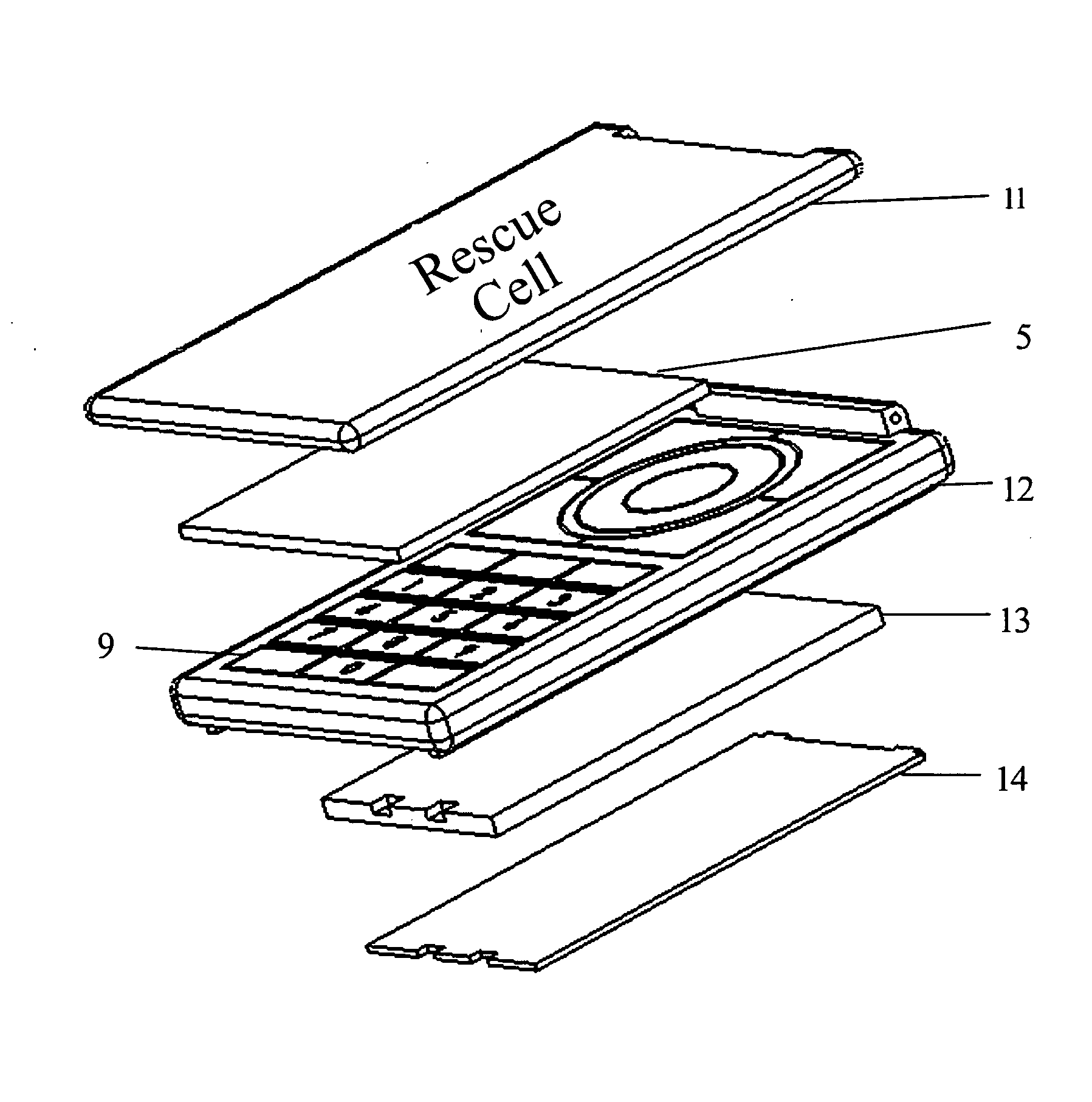
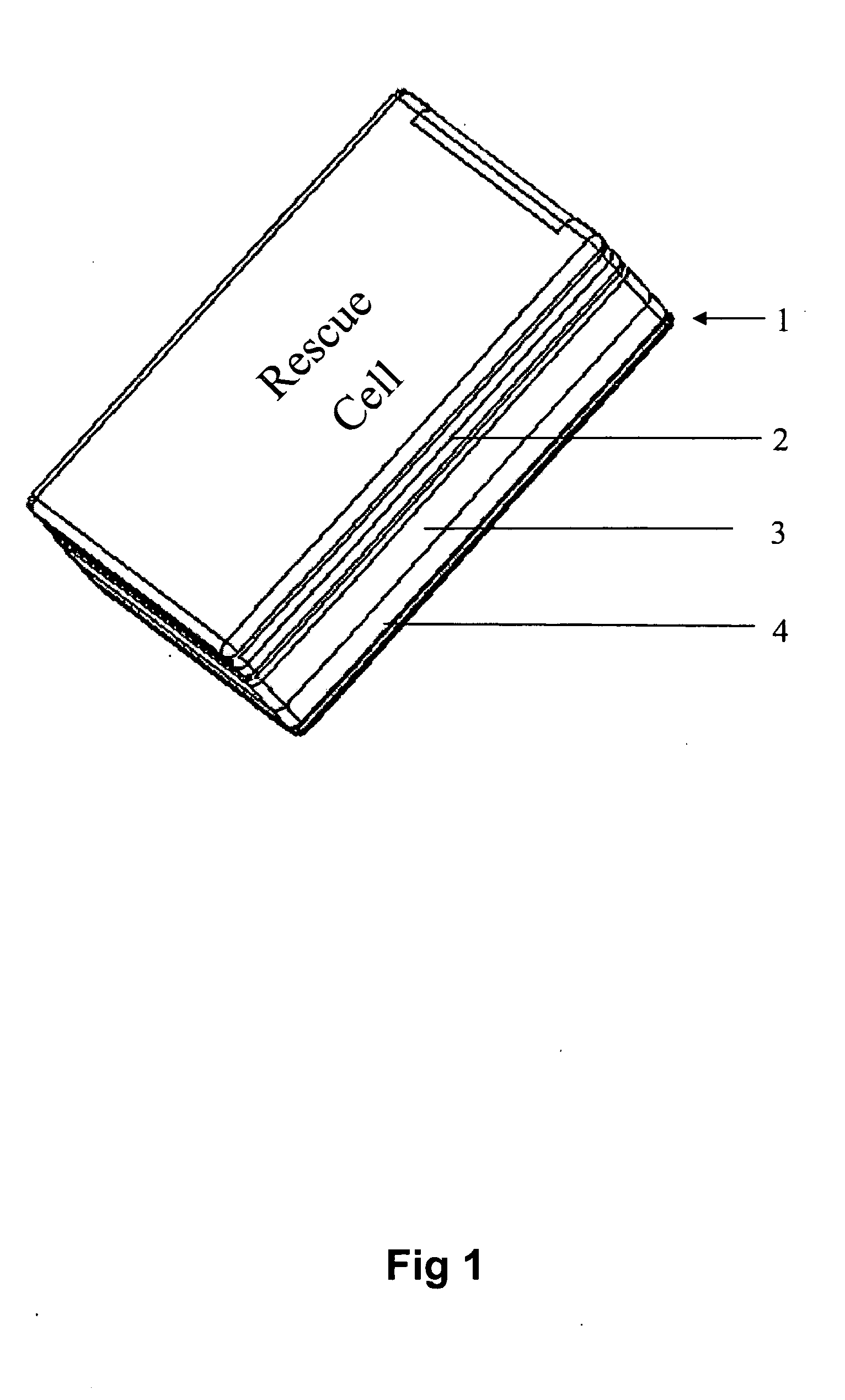
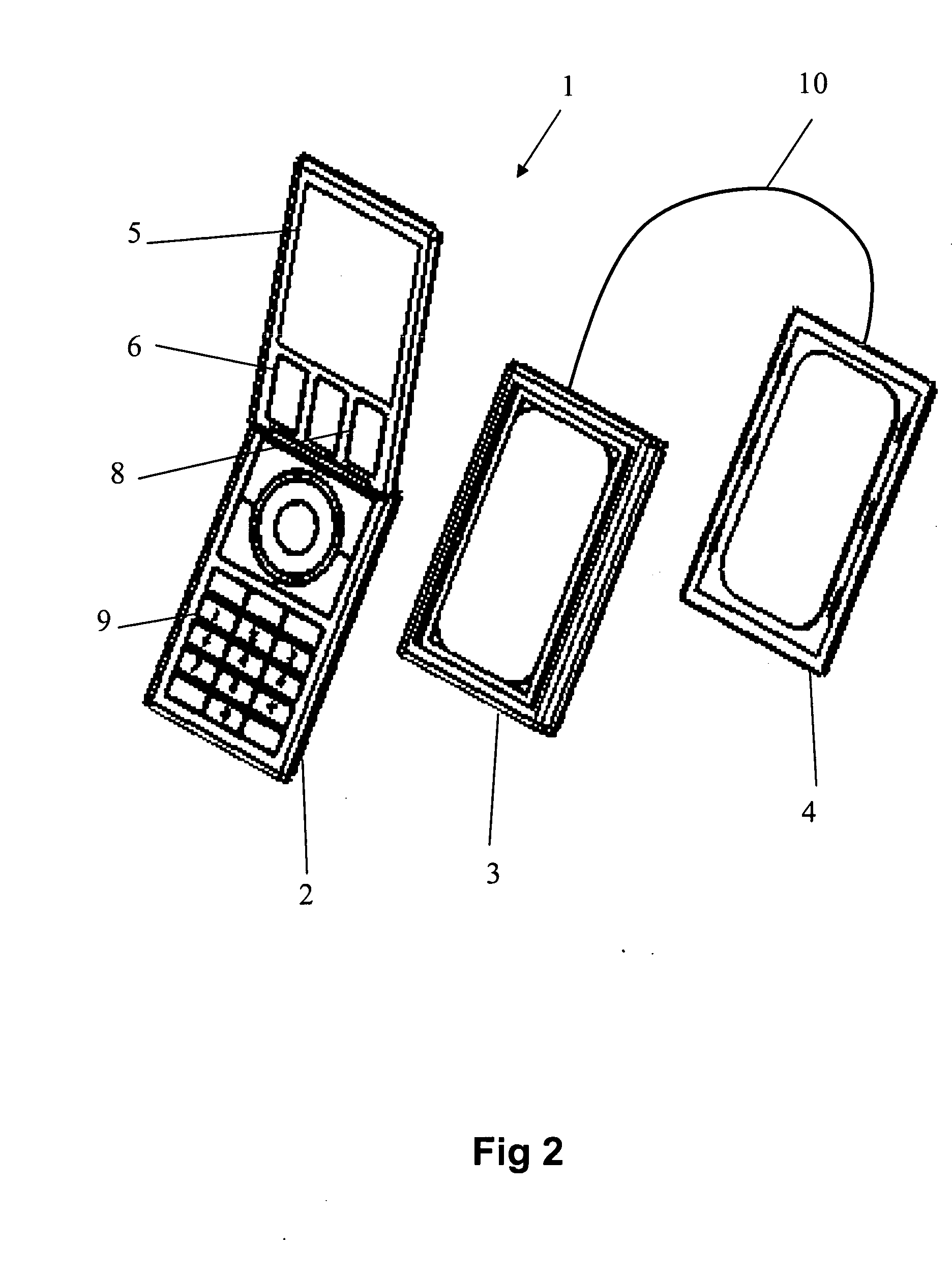
The apparatus according to the current invention, referred herein as “Rescue Cell” is an AED integrated into a handheld device such as mobile phone; pocket PCs, Personal Digital Assistant (PDA), etc. Rescue Cell device according to embodiments of the present invention is portable; it is integrated into a device that is in regular use by most people. A user of a Rescue Cell is likely to carry his Rescue Cell device with him during his daily routine and to have the device at hand most of the time. Thus, there is high likelihood of the Rescue Cell to be available to him in case of cardiac emergency to himself or to someone near him.
Owner:SHAVIT ITAI +2
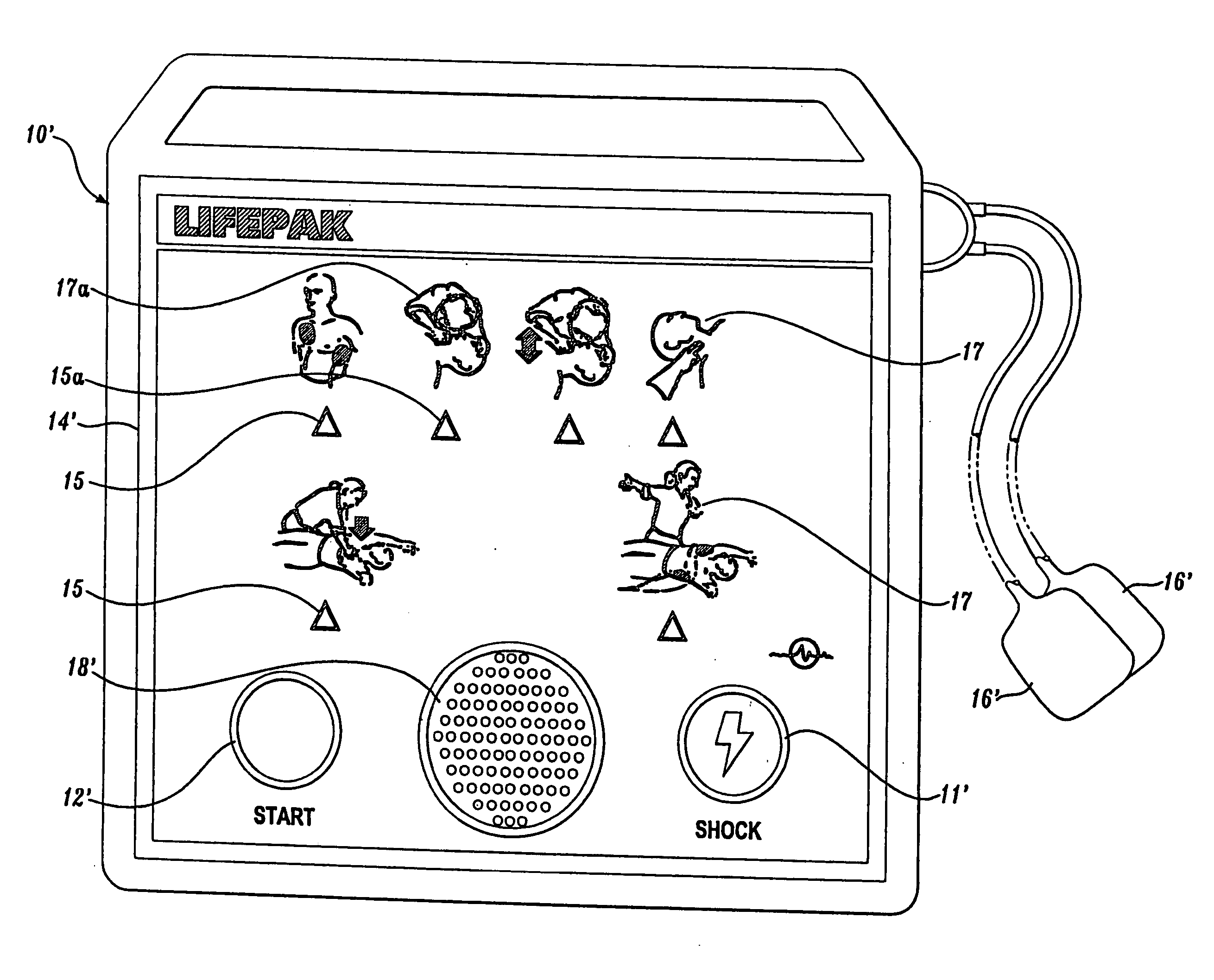
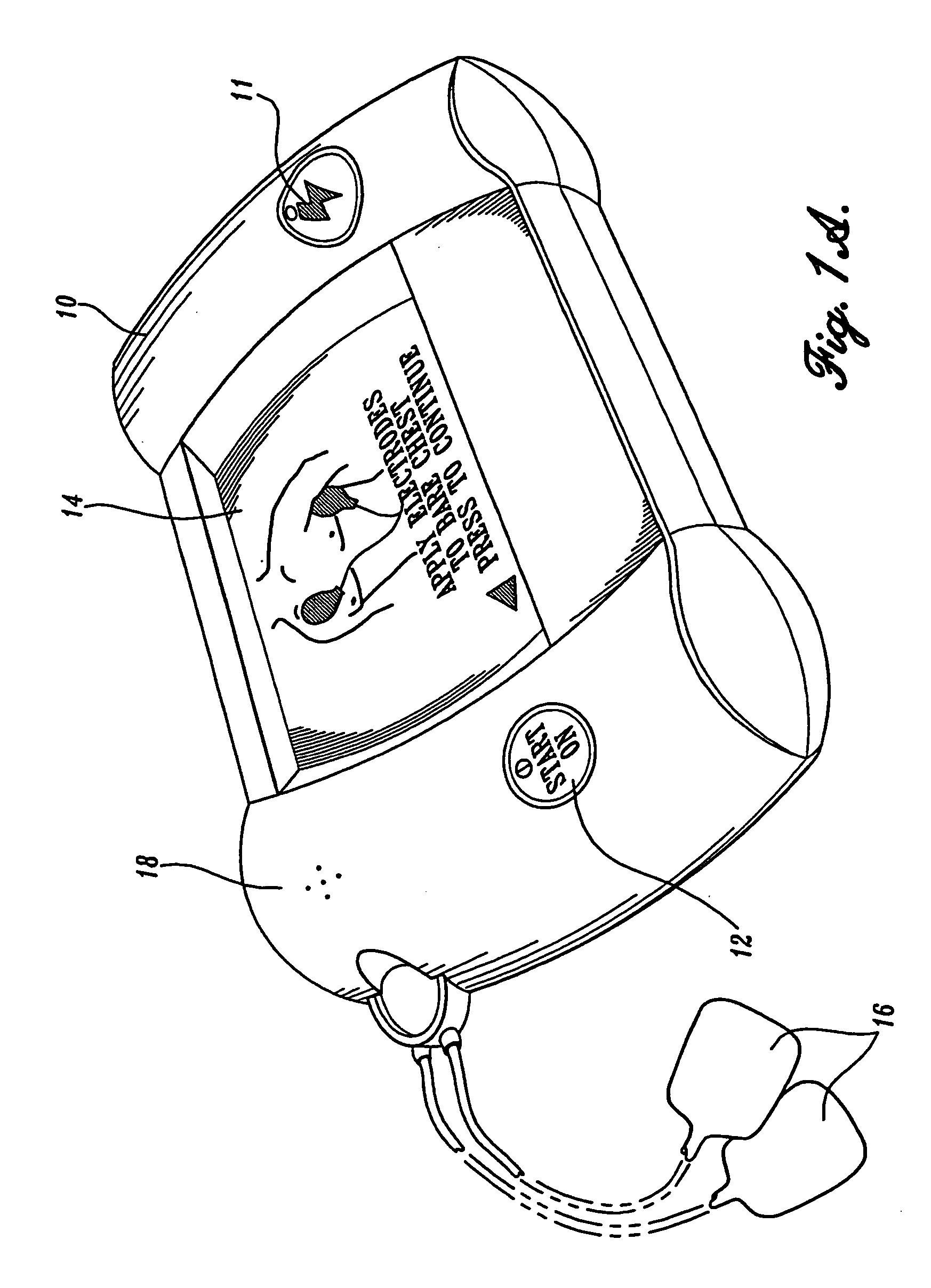
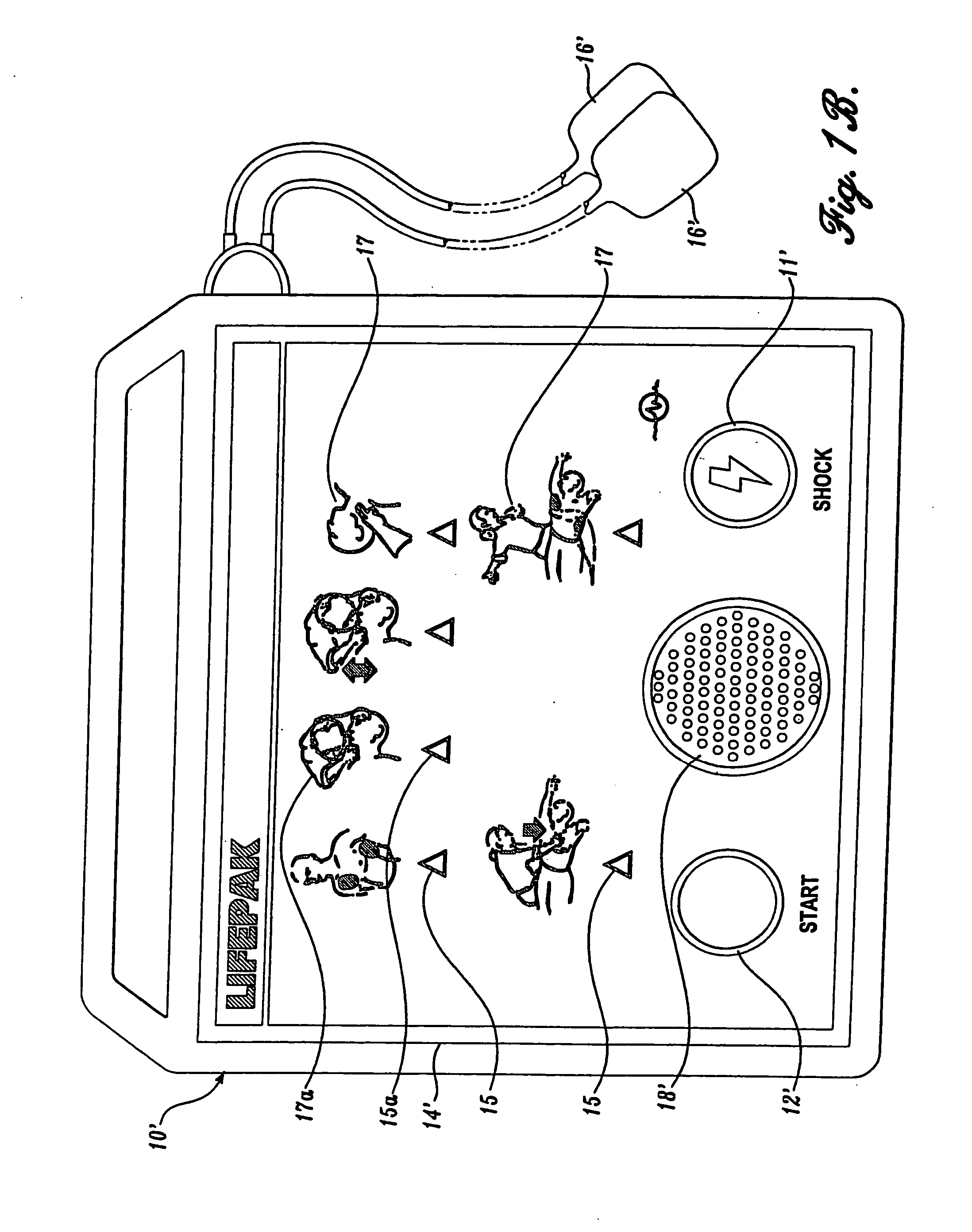
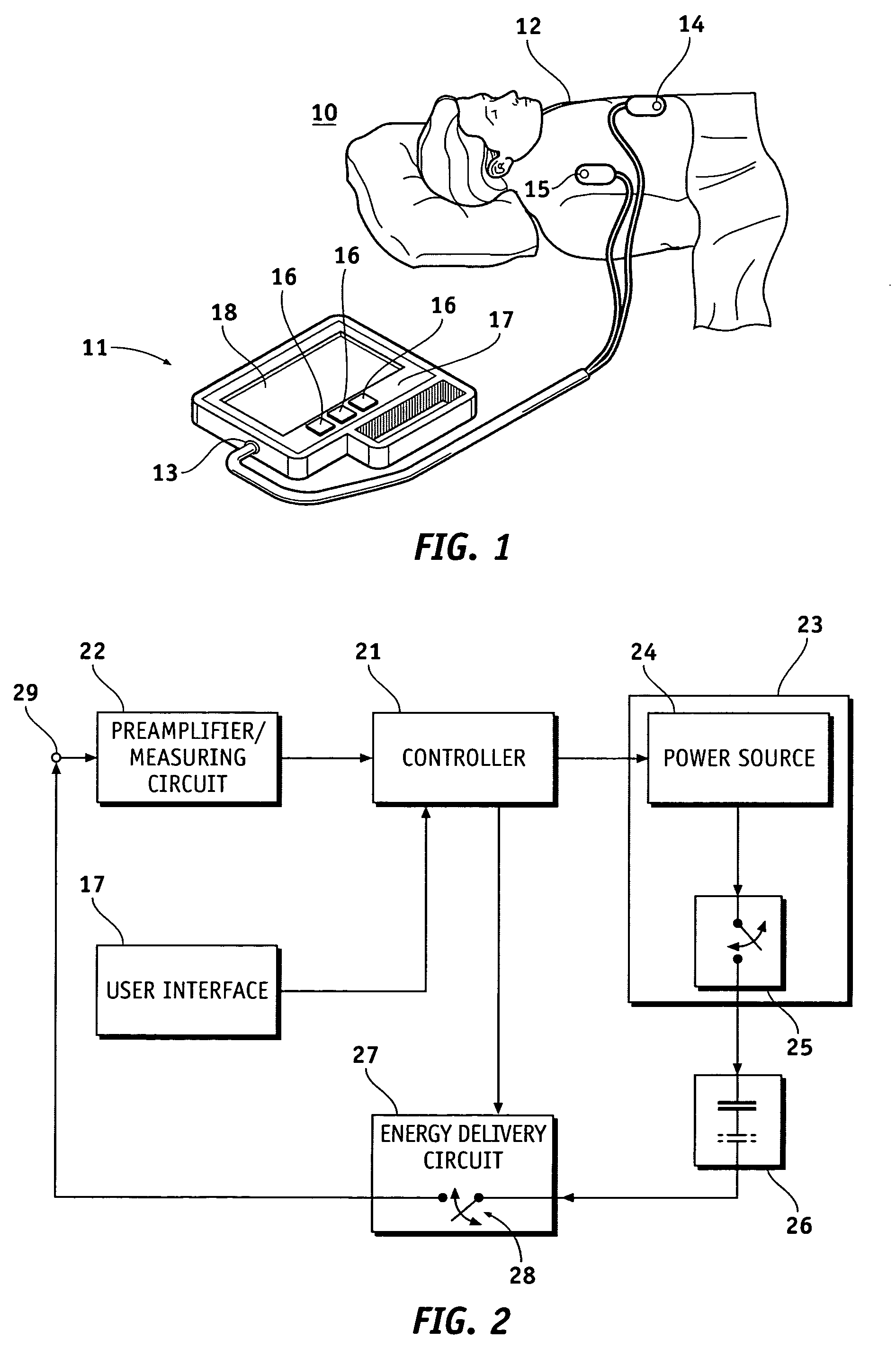
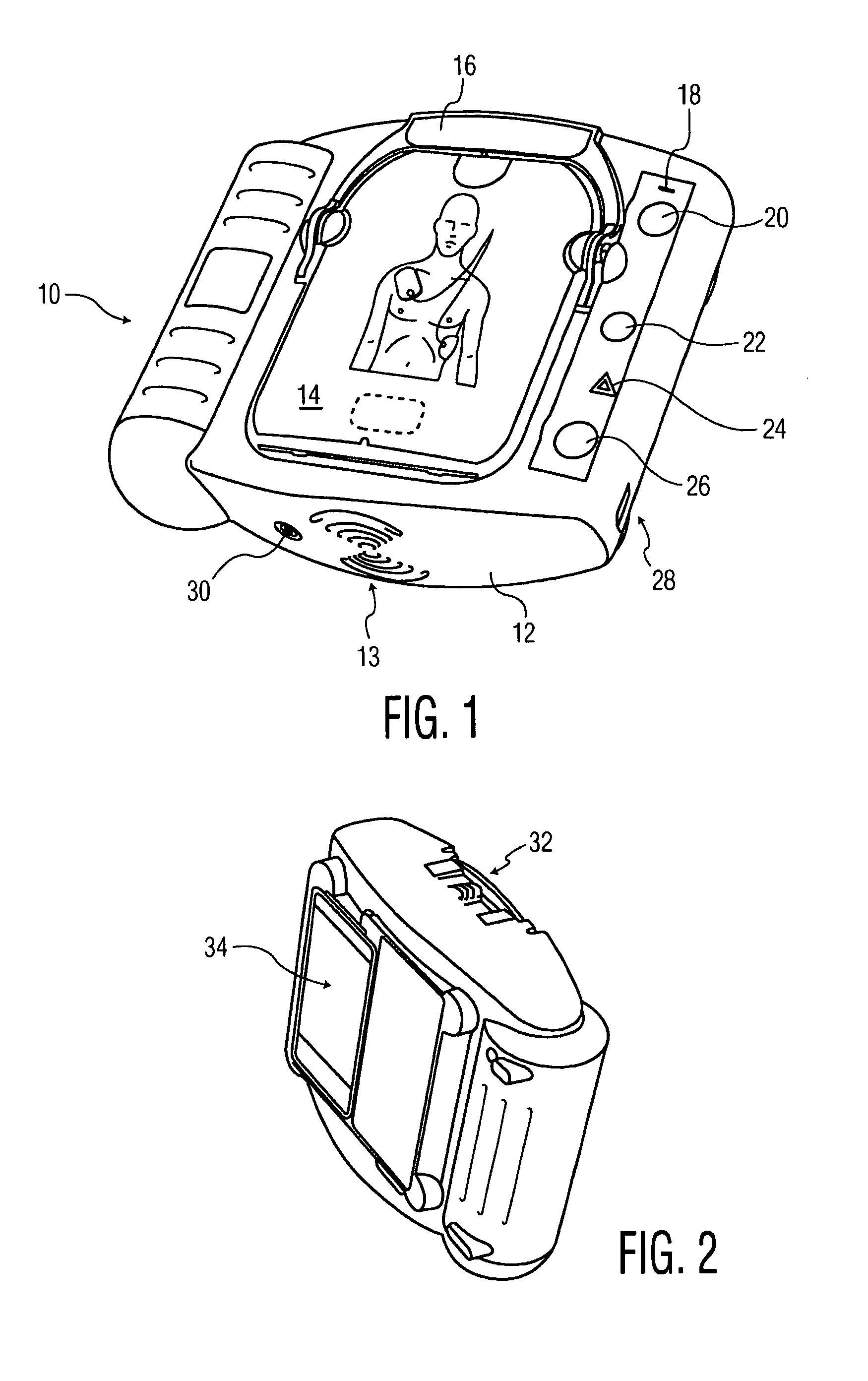
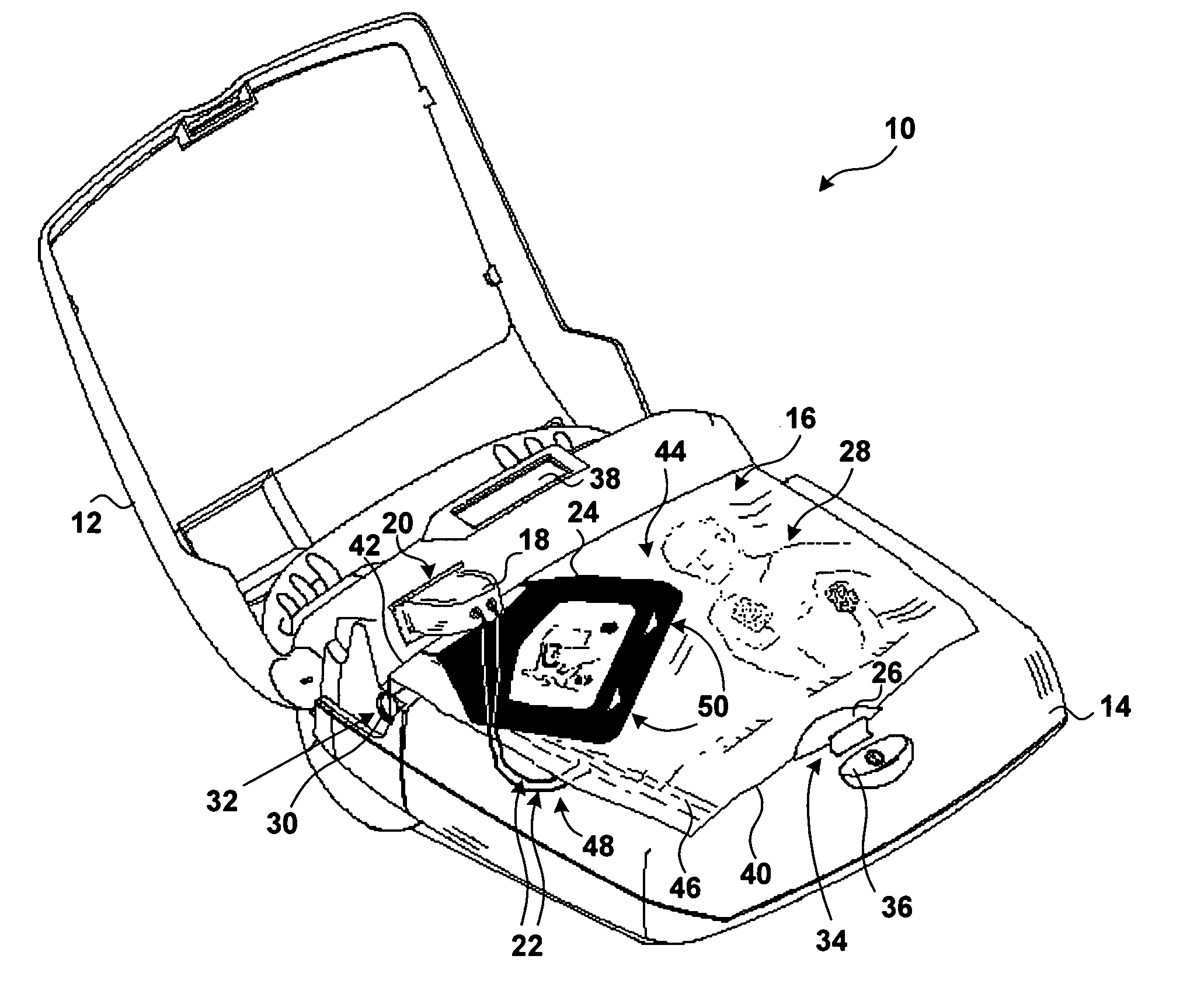
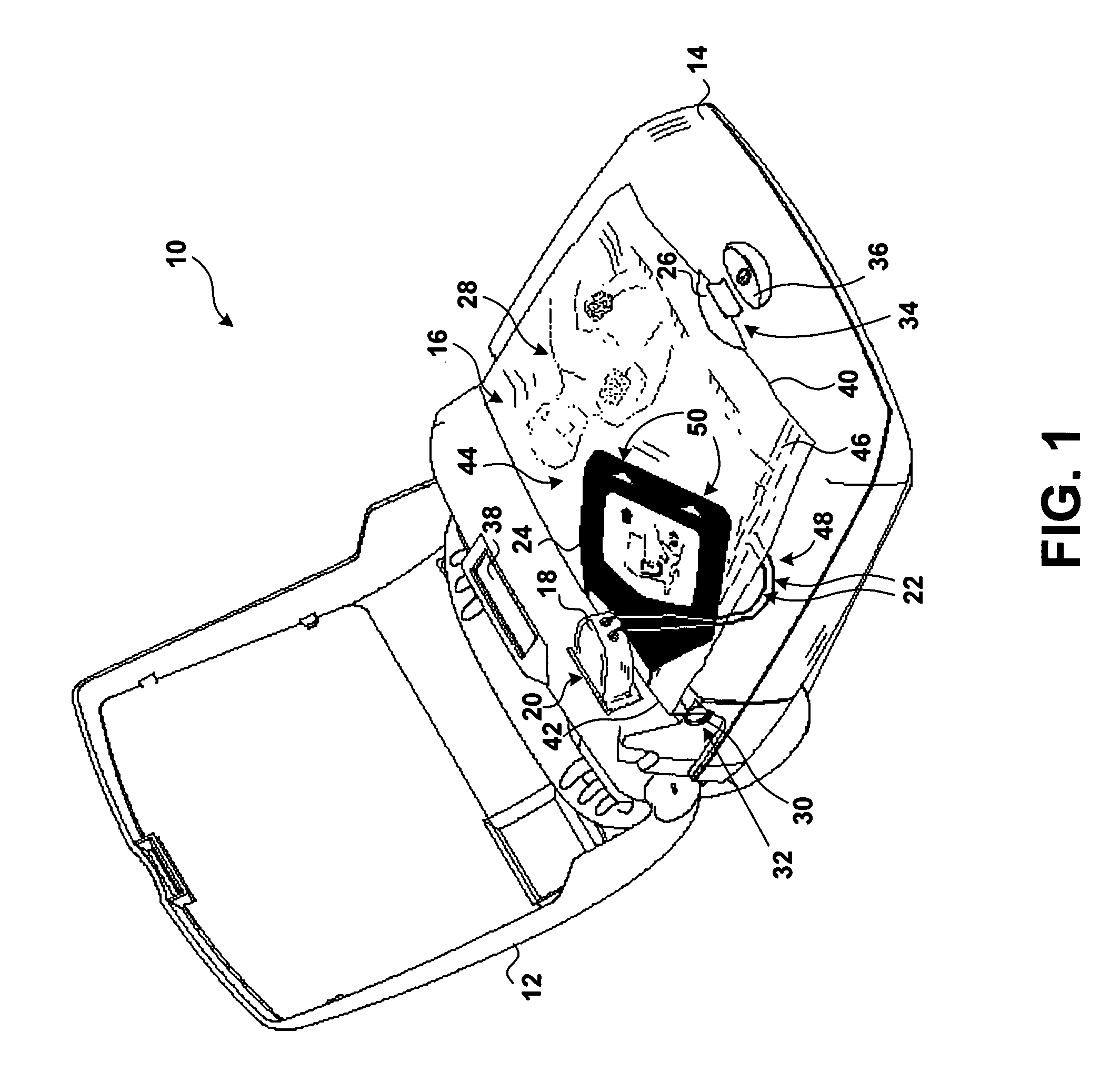
Visual and aural user interface for an automated external defibrillator
An automated external defibrillator (AED) (10) designed for use by a rescuer with minimal or no training during a medical emergency is provided. The AED implements a user interface program (22) which guides the rescuer through operation of the AED and application of CPR and defibrillation therapy to a patient by displaying a series of visual instructions on a graphic display (14) or other visual output device, and by providing additional aural instructions via a speaker (18) or other aural output device. The rescuer merely needs to press a start button (12) to initiate operation of the AED and begin CPR and defibrillation instruction.
Owner:WEST AFFUM HLDG DAC
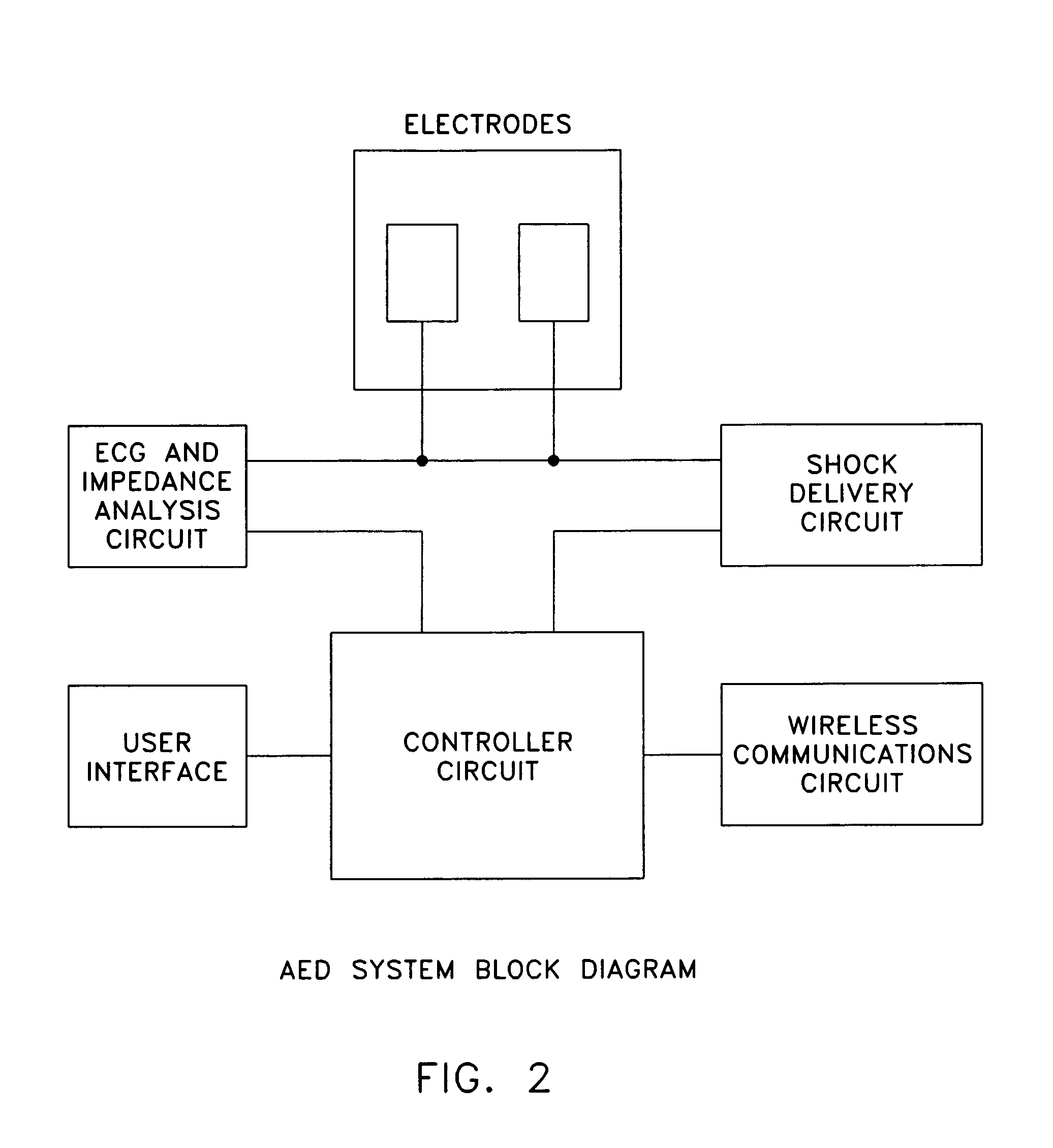
Automated external defibrillator (AED) system with multiple patient wireless monitoring capability for use in mass casualty incidents
InactiveUS20080177341A1Enhanced interactionElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringEmergency medicineAutomated external defibrillator
An Automated External Defibrillator (AED) with wireless patient monitoring capability. The AED is used in conjunction with a monitoring chest strap that transmits the patient's ECG and other parameters over a wireless network to the AED. The AED is capable of monitoring several patients simultaneously for use in mass casualty incidents. The AED notifies and indicates to the operator when a patient requires defibrillation therapy. The device is ready to shock once the defibrillation electrodes are applied.
Owner:ACCESS CARDIOSYST
External defibrillator
ActiveUS8615295B2Lower resistanceEnsure sterility and safetyHeart defibrillatorsElectricityElectrical battery
A variety of arrangements and methods relating to a defibrillator are described. In one aspect of the invention, a defibrillator includes two paddles that each include a defibrillator electrode covered in a protective housing. The two paddles are sealed together using a releasable seal to form a paddle module such that the housings of the paddles form the exterior of the paddle module. An electrical system including at least a battery and a capacitor is electrically coupled with the paddles. The battery is arranged to charge the capacitor. The capacitor is arranged to apply a voltage at the defibrillator electrodes, which generates an electrical shock for arresting a cardiac arrhythmia.
Owner:CARDIOTHRIVE
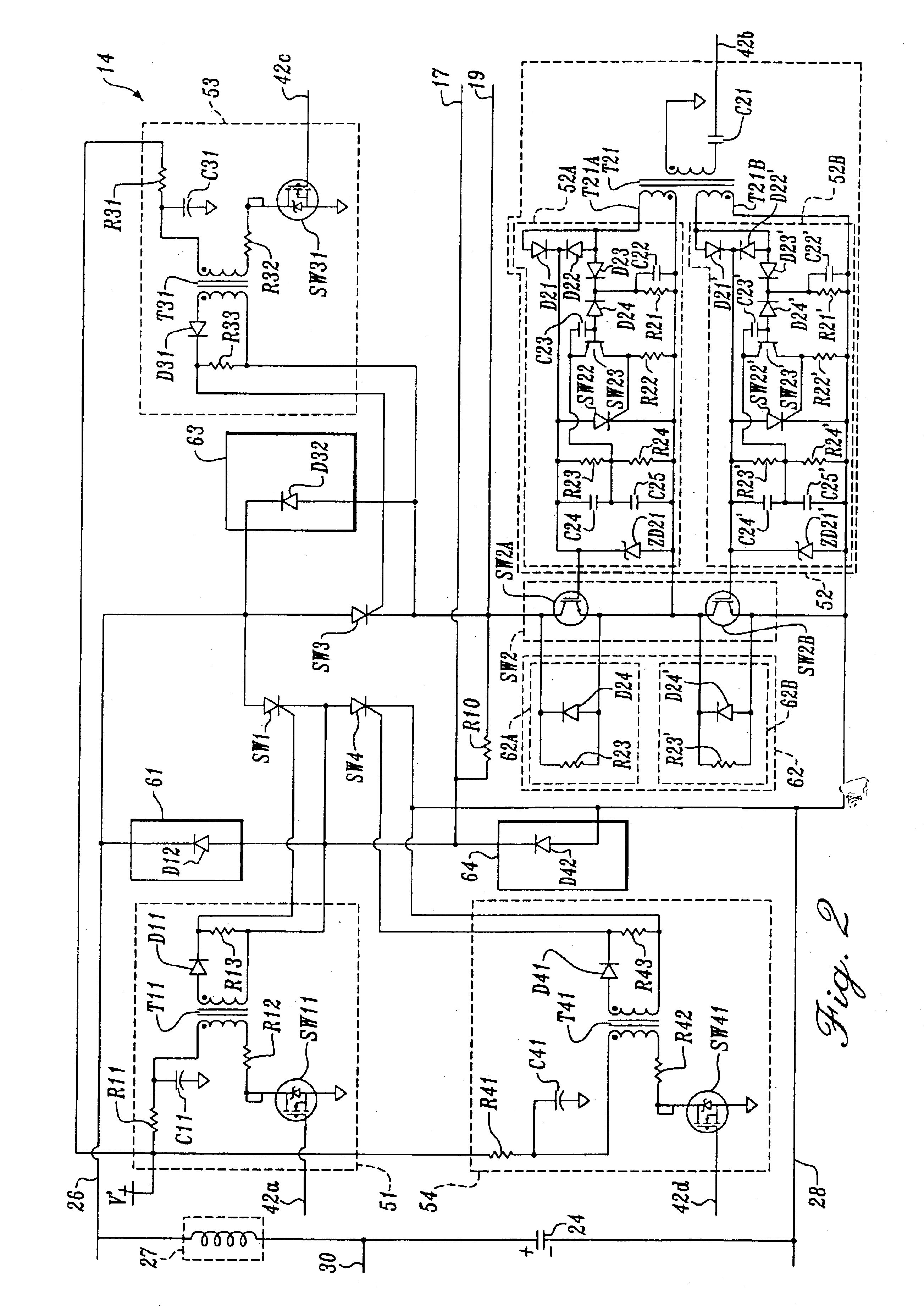
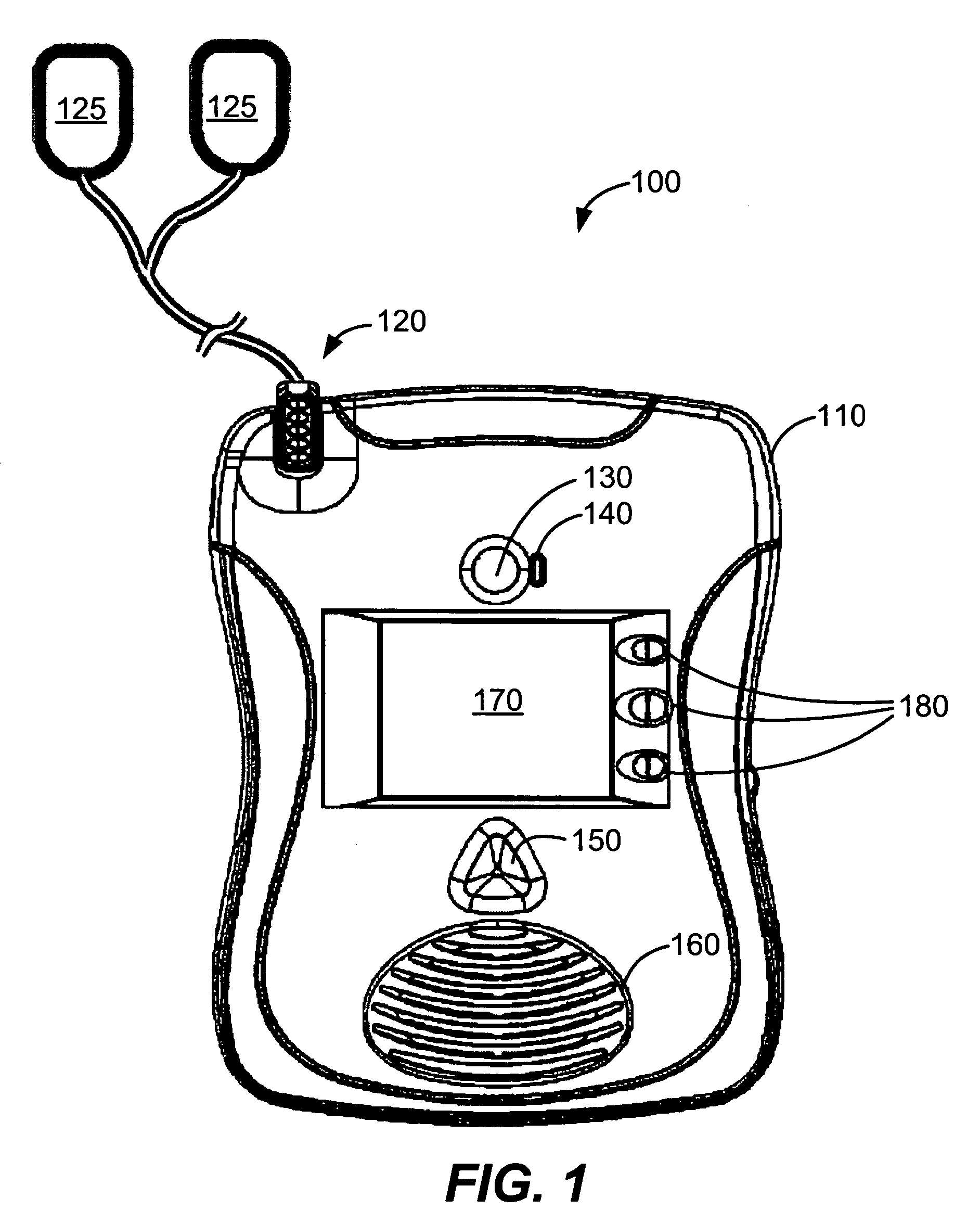
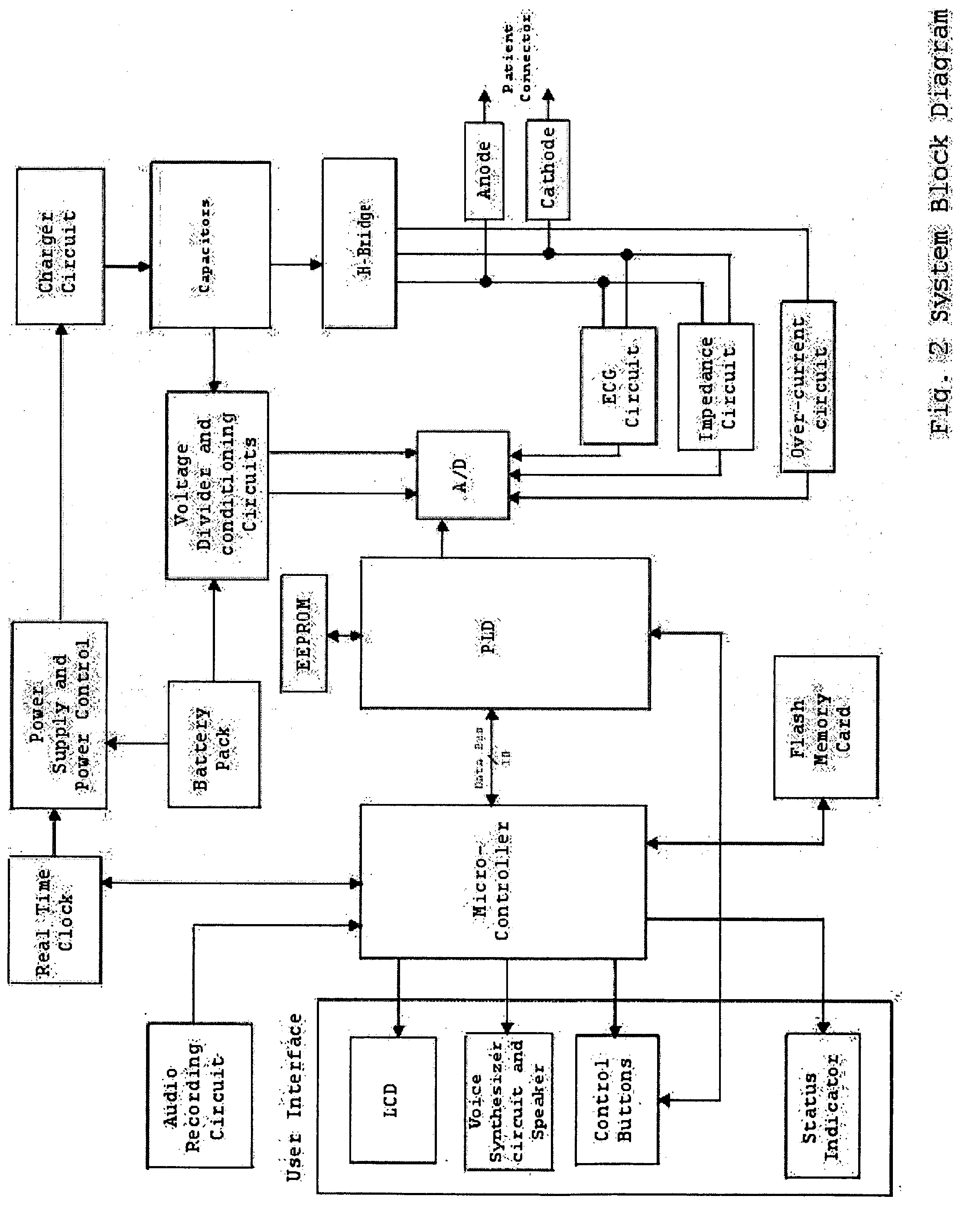
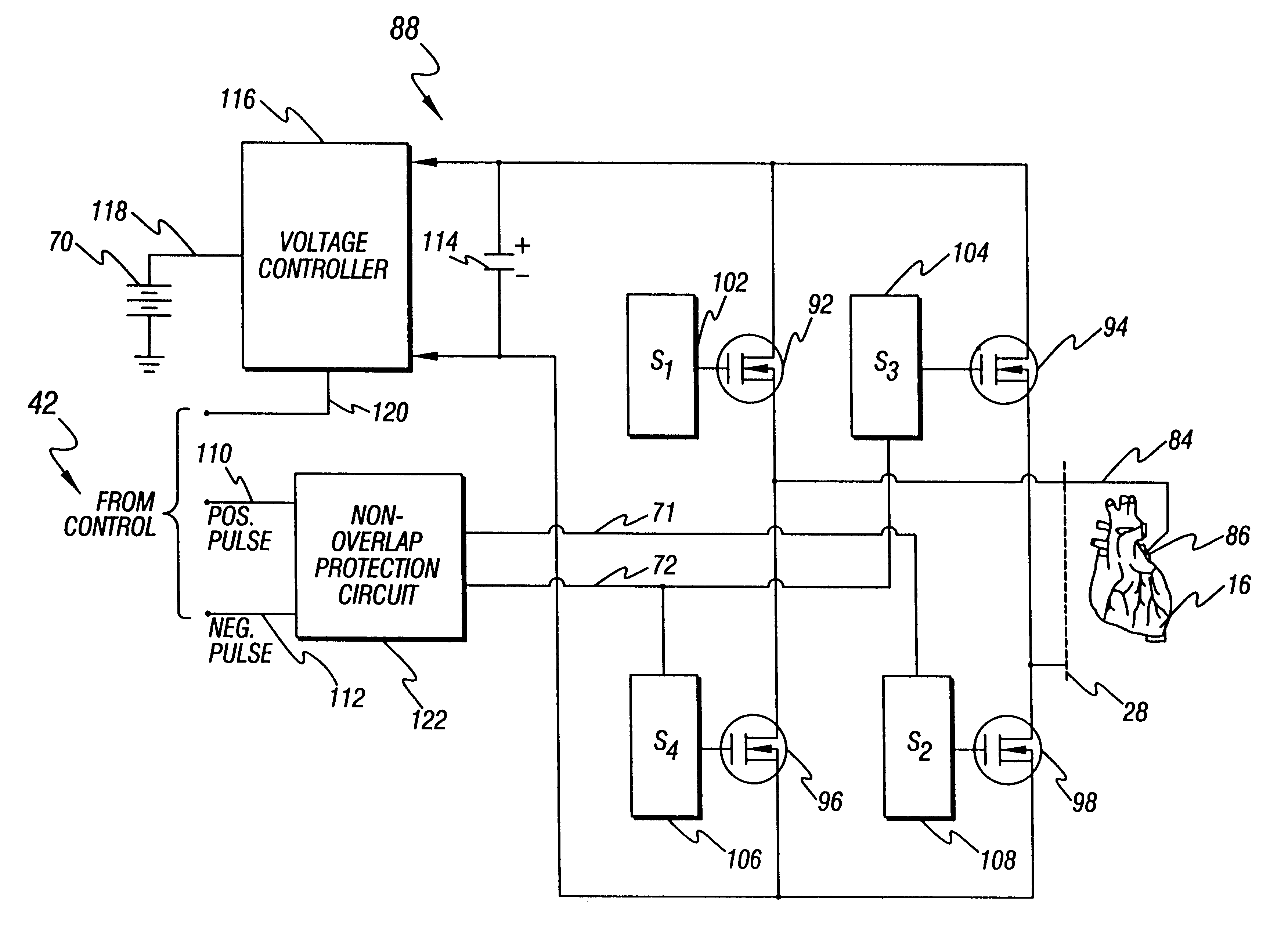
H-bridge circuit for generating a high-energy biphasic waveform in an external defibrillator using single SCR and IGBT switches in an integrated package
An external defibrillator with an output circuit having four legs arrayed in the form of an “H” (an “H-bridge”) is disclosed. The output circuit is designed to be able to conduct a range of defibrillation pulse energies, from below 50 joules to above 200 joules. Each leg of the output circuit contains a solid-state switch. By selectively switching on pairs of switches in the H-bridge, a biphasic defibrillation pulse may be applied to a patient. The switches in three of the legs of the H-bridge output circuit are preferably SCR switches, while the fourth leg includes an IGBT switch. In one embodiment, a single power switch is utilized in each of the legs of the H-bridge output circuit, and are included in a single integrated module or package. The use of single semiconductor switches in an integrated surface mountable module or package simplifies the assembly and manufacturing of the defibrillator device. The use of a single IGBT in a leg of the H-bridge (as opposed to two or more IGBTs in series) also greatly simplifies the drive circuitry required to turn on and off the IGBT.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Automatic external cardioverter/defibrillator with tachyarrhythmia detector using a modulation (amplitude and frequency) domain function
InactiveUS6289243B1Reduce probabilityIncrease probabilityHeart defibrillatorsSensorsVentricular TachyarrhythmiasMedical emergency
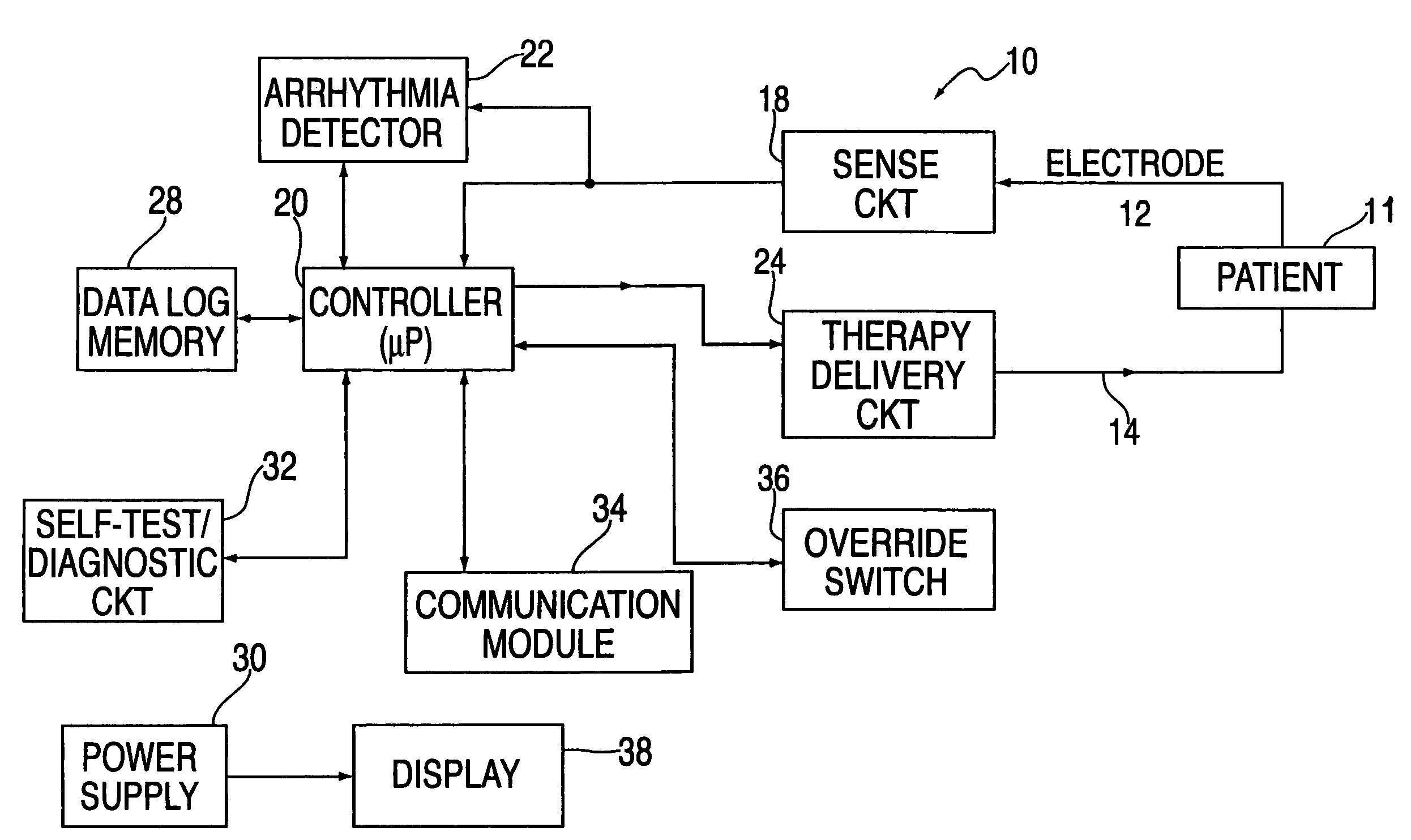
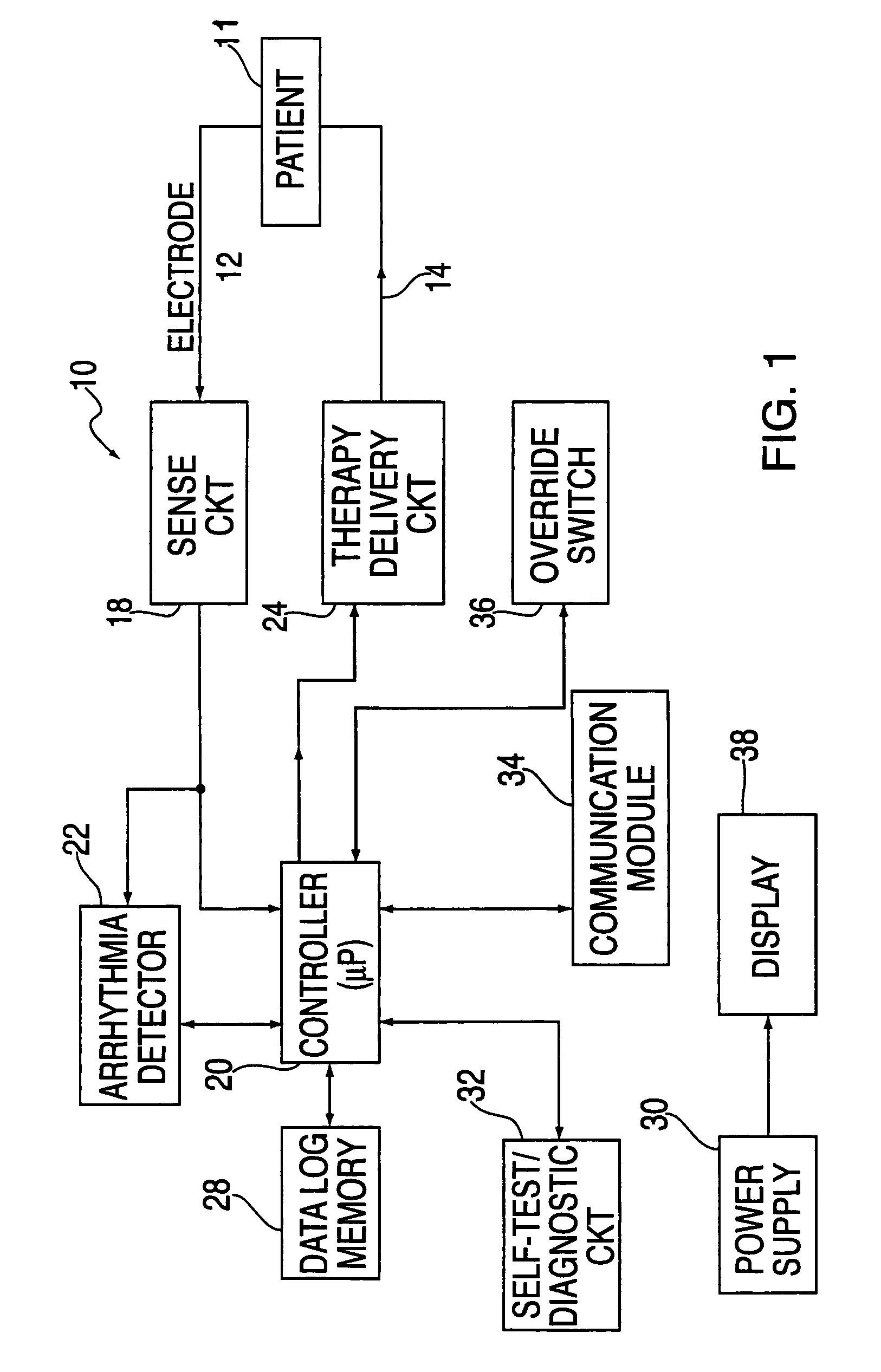
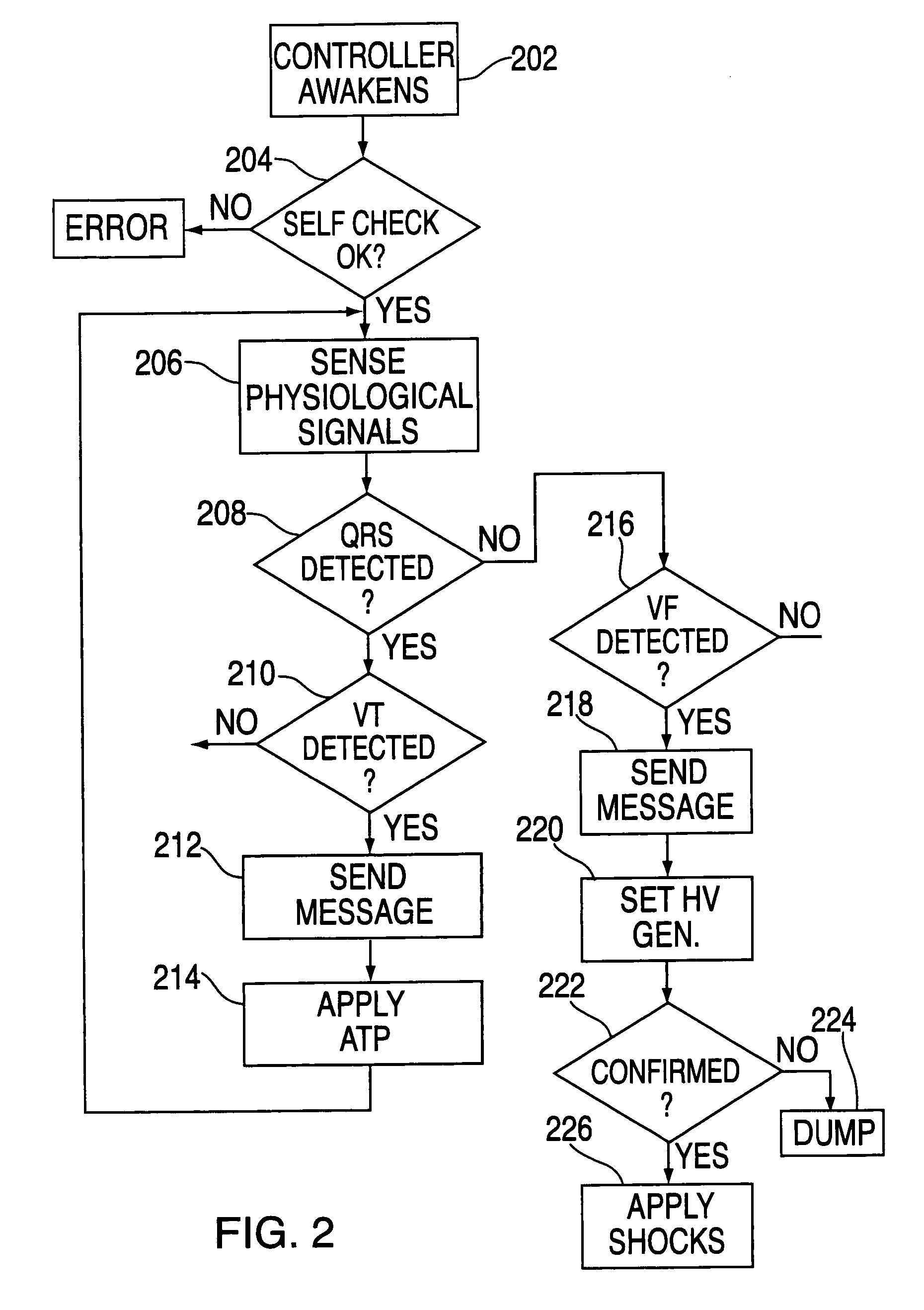
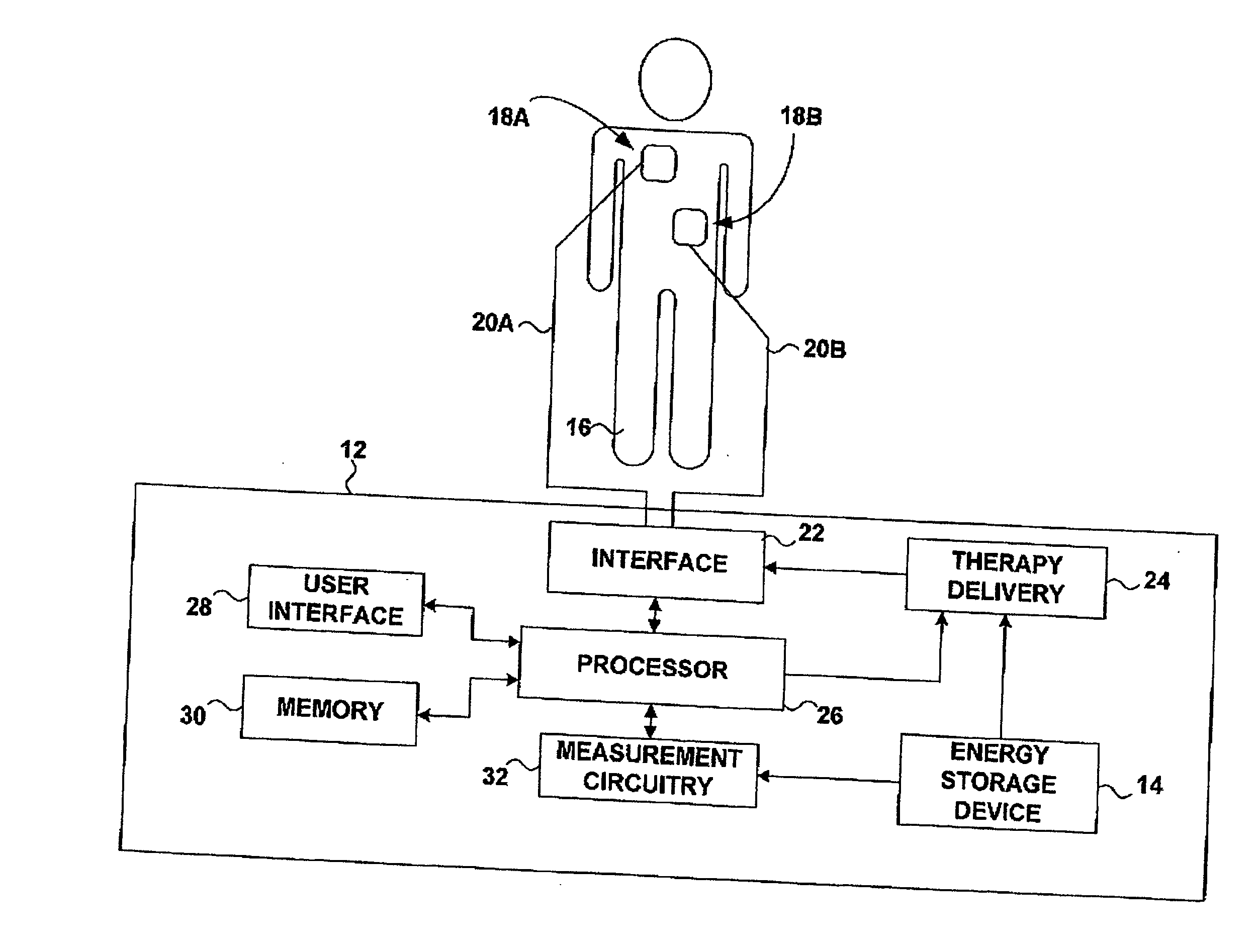
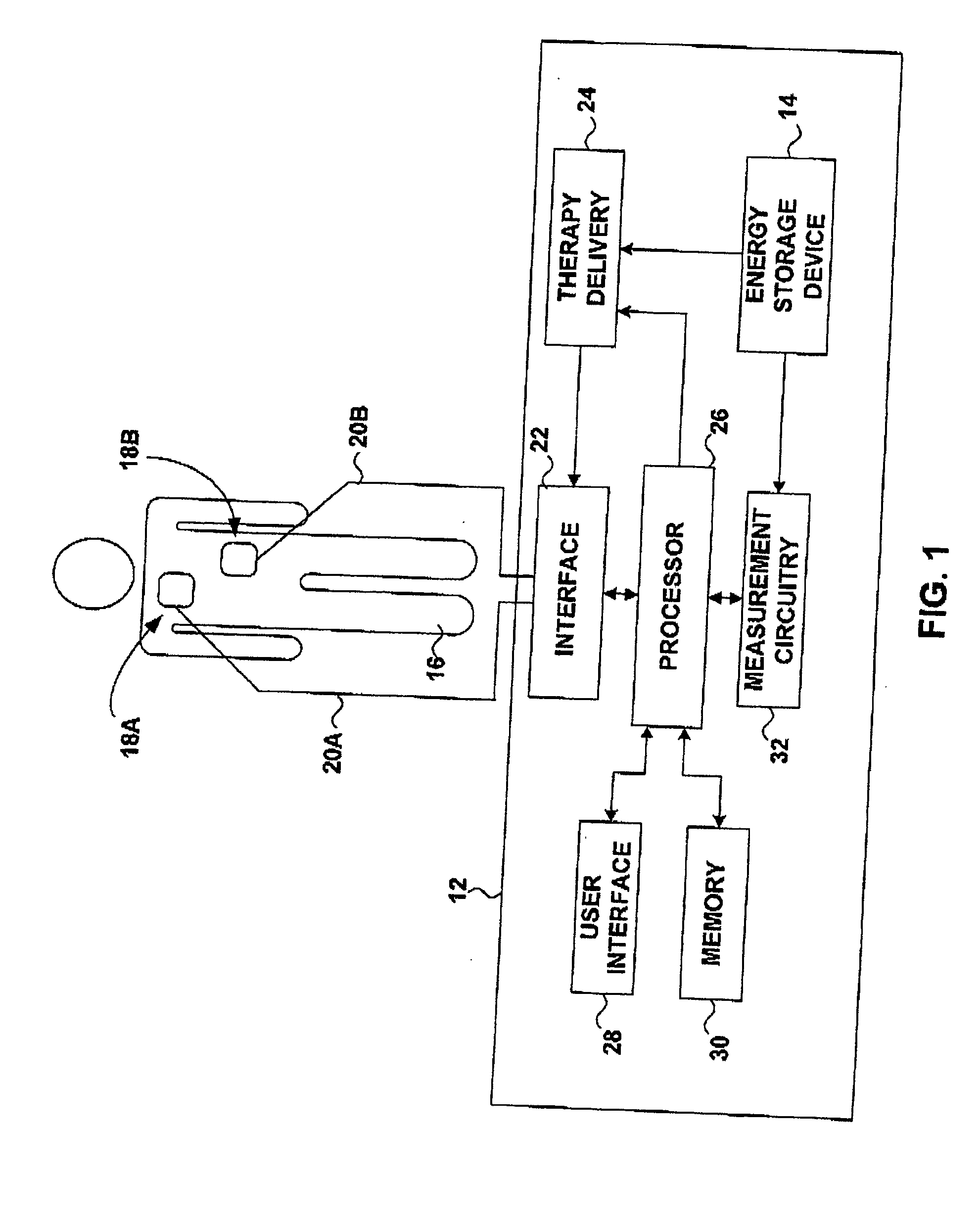
An external defibrillator includes a detector used to detect a life threatening condition of a patient, a controller operating the defibrillator automatically and a therapy delivery circuit that delivers appropriate therapy. Advantageously a parameter is derived from the cardiac signals sensed in the patient, the parameters being used to differentiate between shockable events such as ventricular tachyarrhythmia and other events such as SVT. The defibrillator is attached to a patient by an attendant and once it is attached, the defibrillator is adapted to monitor the patient and when a life threatening condition is detected, to apply therapy automatically, i.e., without any involvement by the patient or the attendant.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
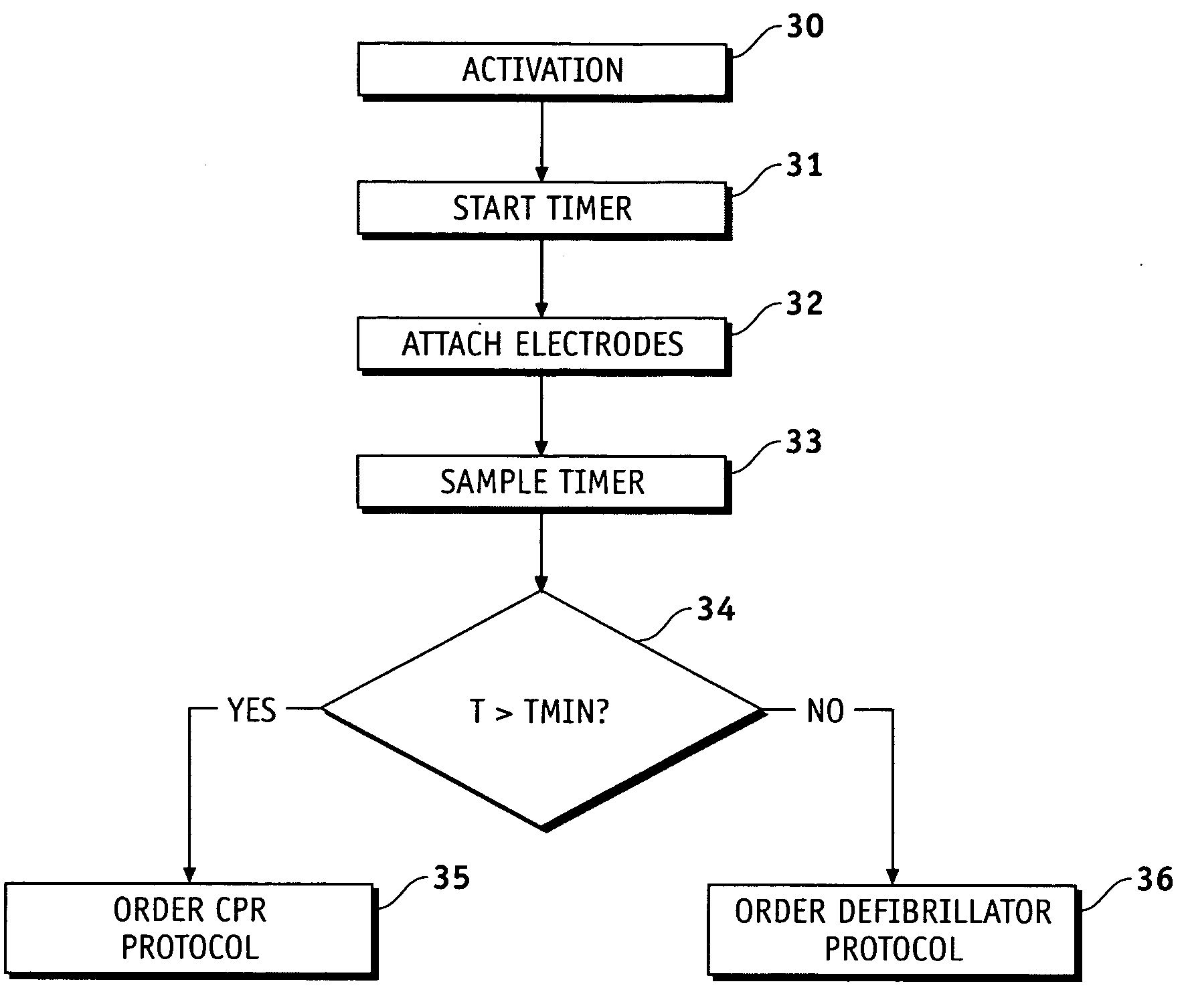
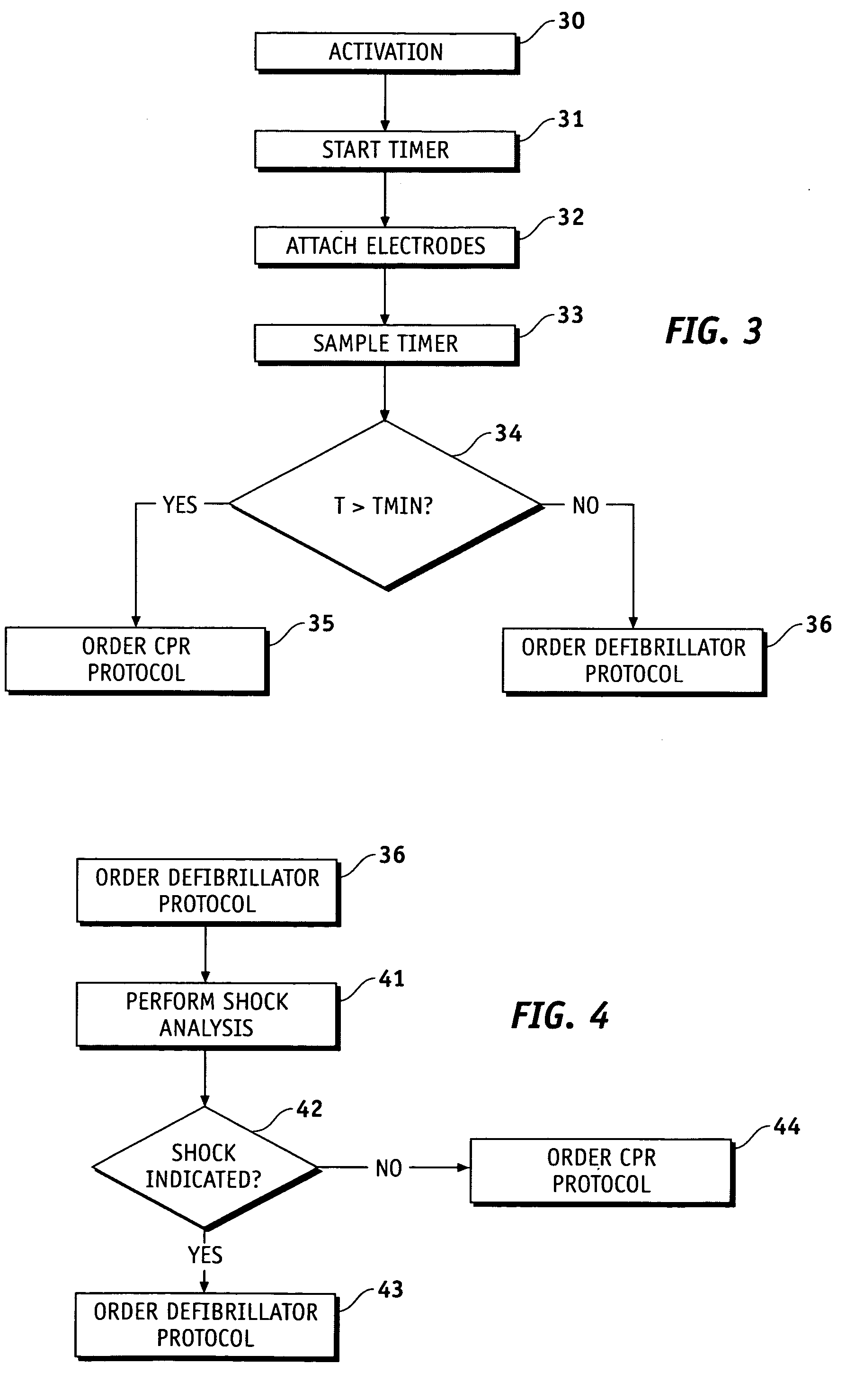
Medical device with resuscitation prompts depending on elapsed time
ActiveUS20060129191A1Physical therapies and activitiesHeart defibrillatorsProper treatmentBiological activation
Methods and apparatus are provided for determining a defibrillation treatment protocol in an external defibrillator using a measurement of elapsed time. The present invention provides a defibrillator with a timer function. Upon activation of the defibrillator, an internal timer begins to run. By closely associating the activation of the defibrillator with the onset of the patient's attack, and by making allowances for inherent time differences between these events, the timer provides a measure of the elapsed time between the onset of the patient's emergency and the presentation of the defibrillator at the patient's side. Using this measure of elapsed time, the defibrillator determines an appropriate treatment therapy, such as CPR or defibrillation therapy.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
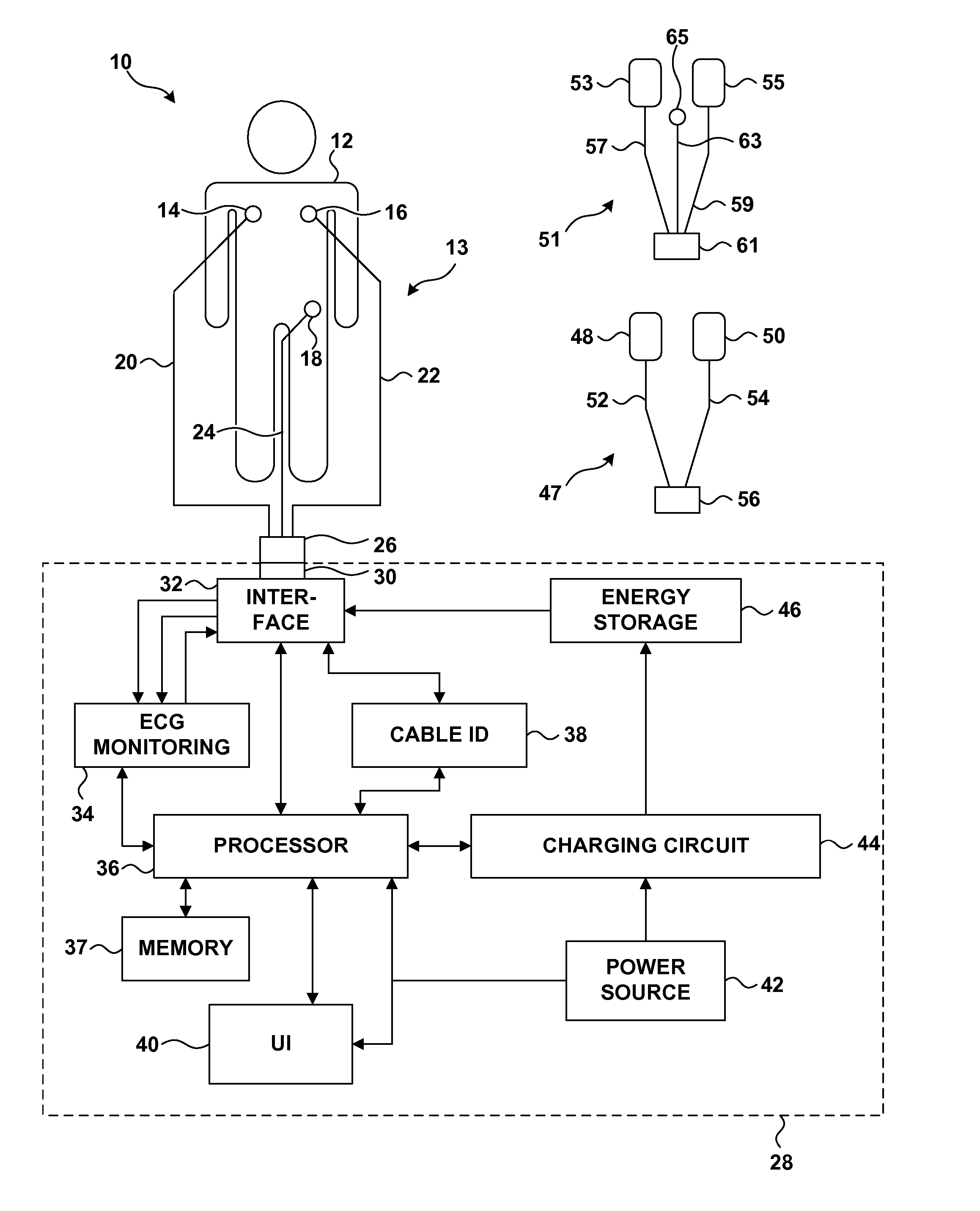
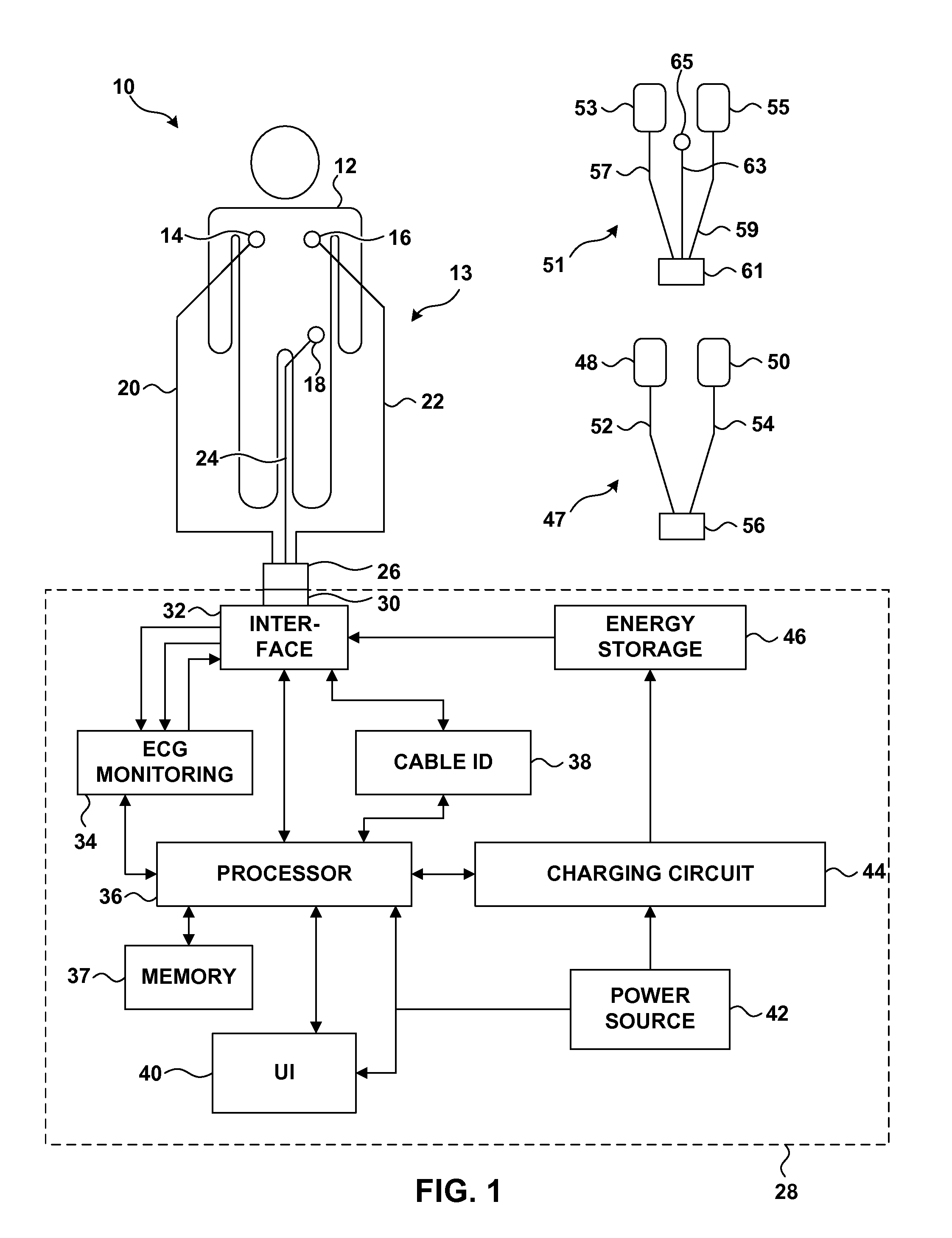
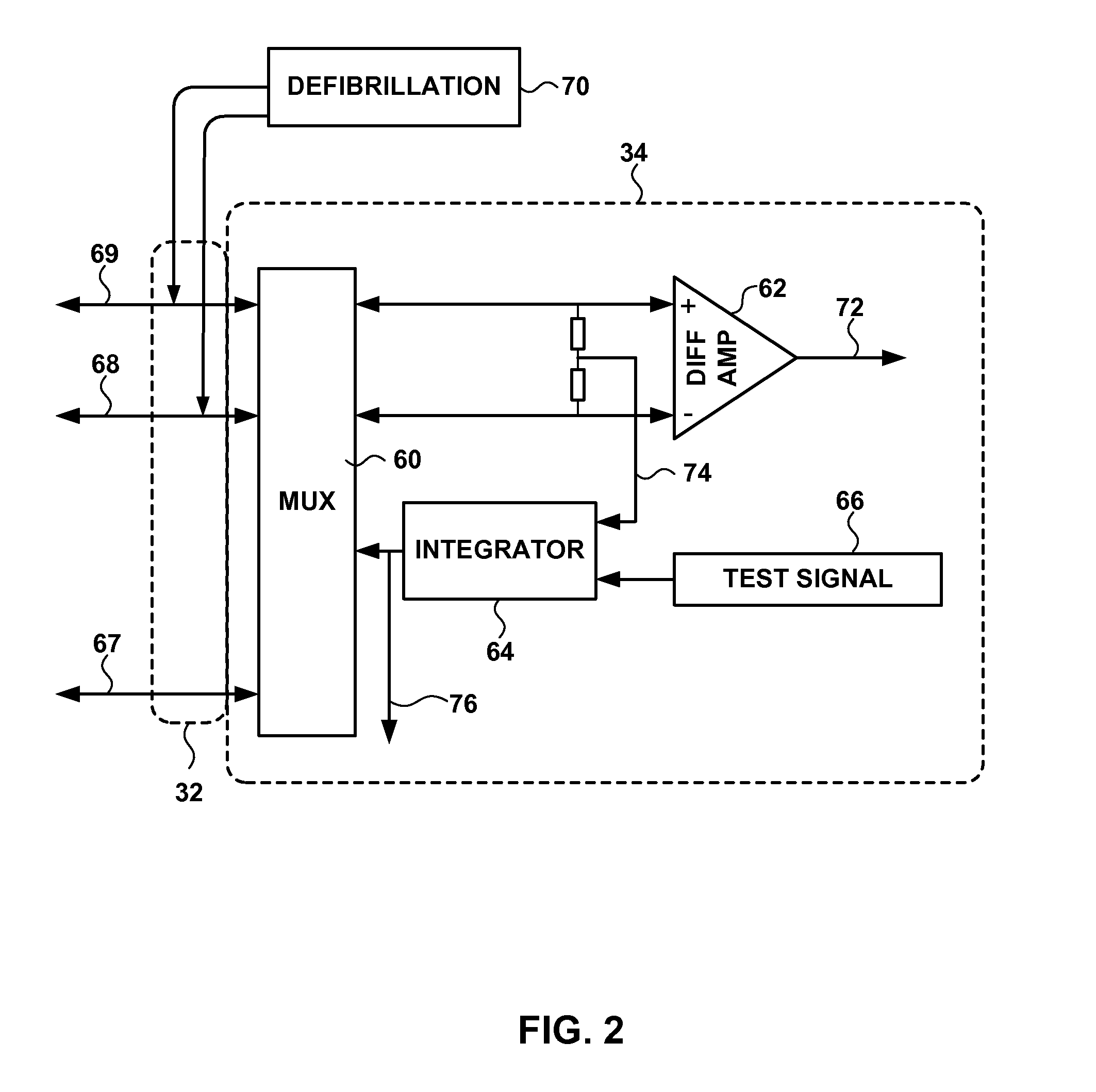
Electrocardiogram Monitoring
Techniques for determining whether one or more leads are not adequately connected to a patient, e.g., for ECG monitoring, are described. The techniques involve injection of an integrated signal (which includes a test signal) into one lead, and monitoring the driven lead and the response at the other leads, including the common mode and the difference between the other leads. These “lead-off” detection techniques may be provided by an external defibrillator that provides three-wire ECG monitoring. Techniques for determining a type of a cable coupled to a defibrillator are also described. The cable-type identification may allow a defibrillator to, for example, operate in either a three-wire ECG monitoring mode or a therapy mode, based on whether a three-wire ECG cable or a defibrillation cable is coupled to the defibrillator.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Public access defibrillator
InactiveUS6993386B2Easy to useProviding therapyHeart defibrillatorsPublic access defibrillatorMedical emergency
A publically available external defibrillator includes a detector used to detect a life threatening condition of a patient, a controller operating the defibrillator automatically and a therapy delivery circuit that delivers appropriate therapy. The defibrillator is attached to a patient by any attendant or bystander and once it is attached, the defibrillator is adapted to monitor the patient and when a life threatening condition is detected, to apply therapy automatically, i.e., without any involvement by the patient or the attendant.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
External defibrillator
An external defibrillator having a battery; a capacitor electrically communicable with the battery; at least two electrodes electrically communicable with the capacitor and with the skin of a patient; a controller configured to charge the capacitor from the battery and to discharge the capacitor through the electrodes; and a support supporting the battery, capacitor, electrodes and controller in a deployment configuration, the defibrillator having a maximum weight per unit area in the deployment configuration of 0.1 lb / in2 and / or a maximum thickness of 1 inch. The support may be a waterproof housing.
Owner:ELEMENT SCI
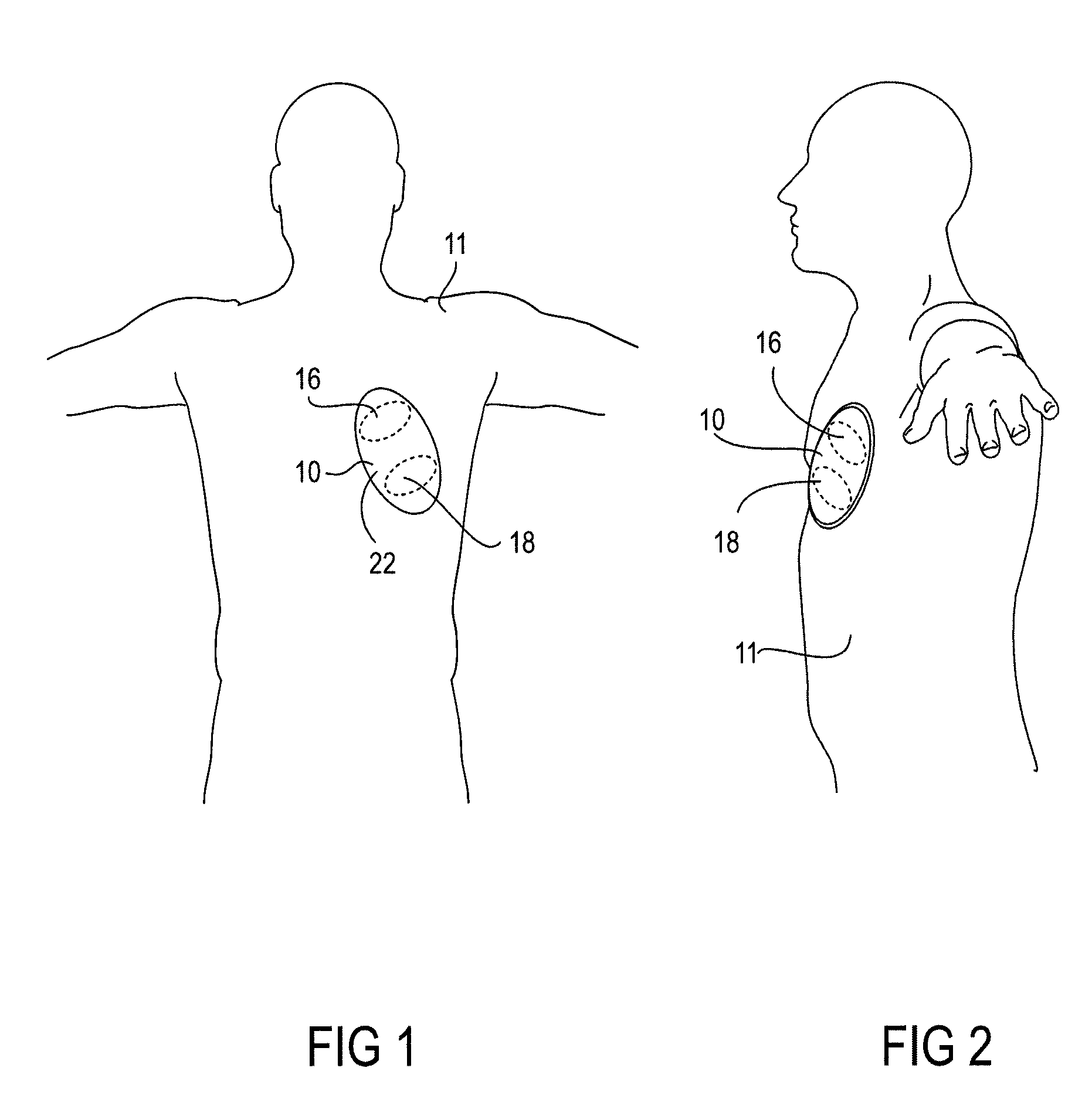
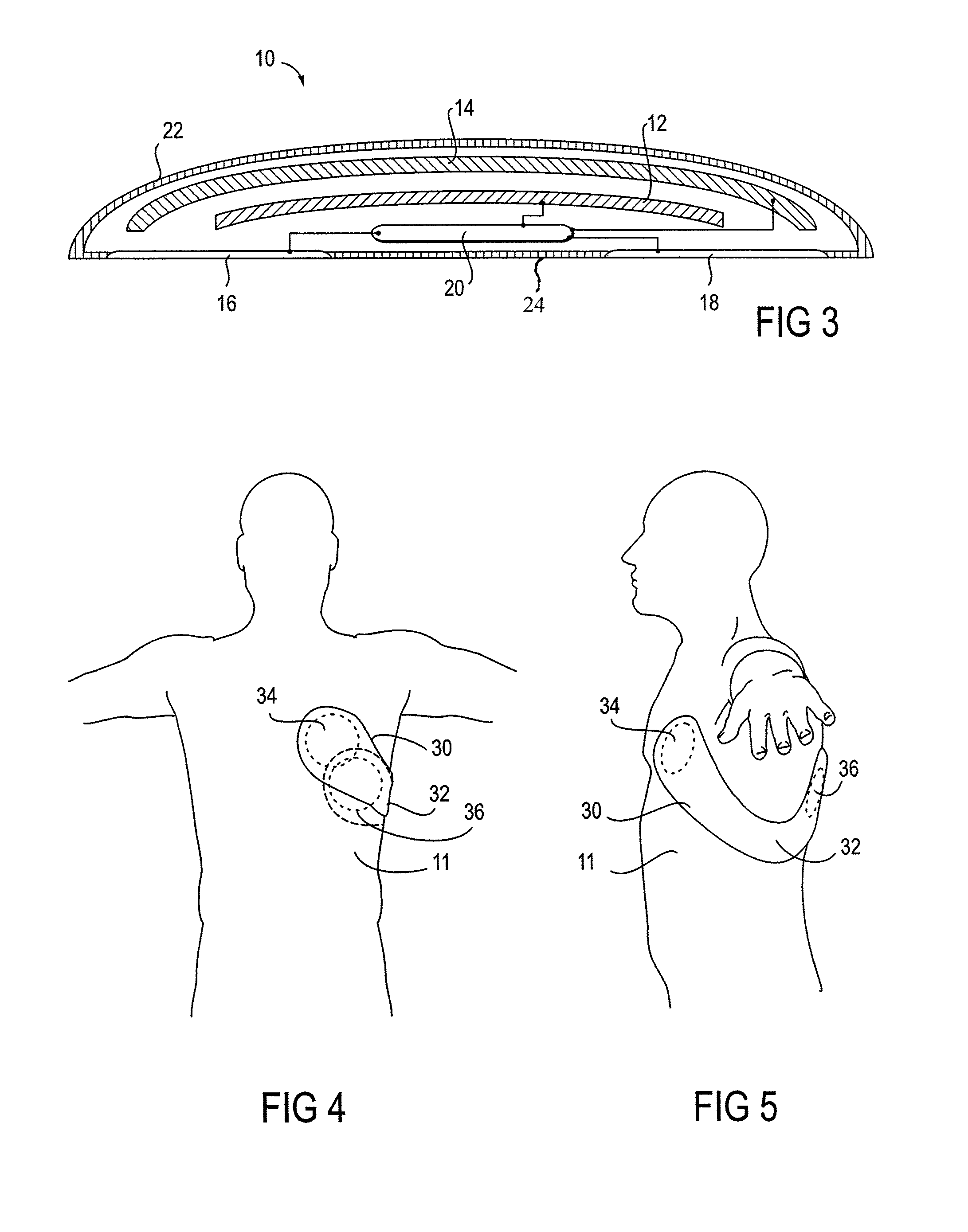
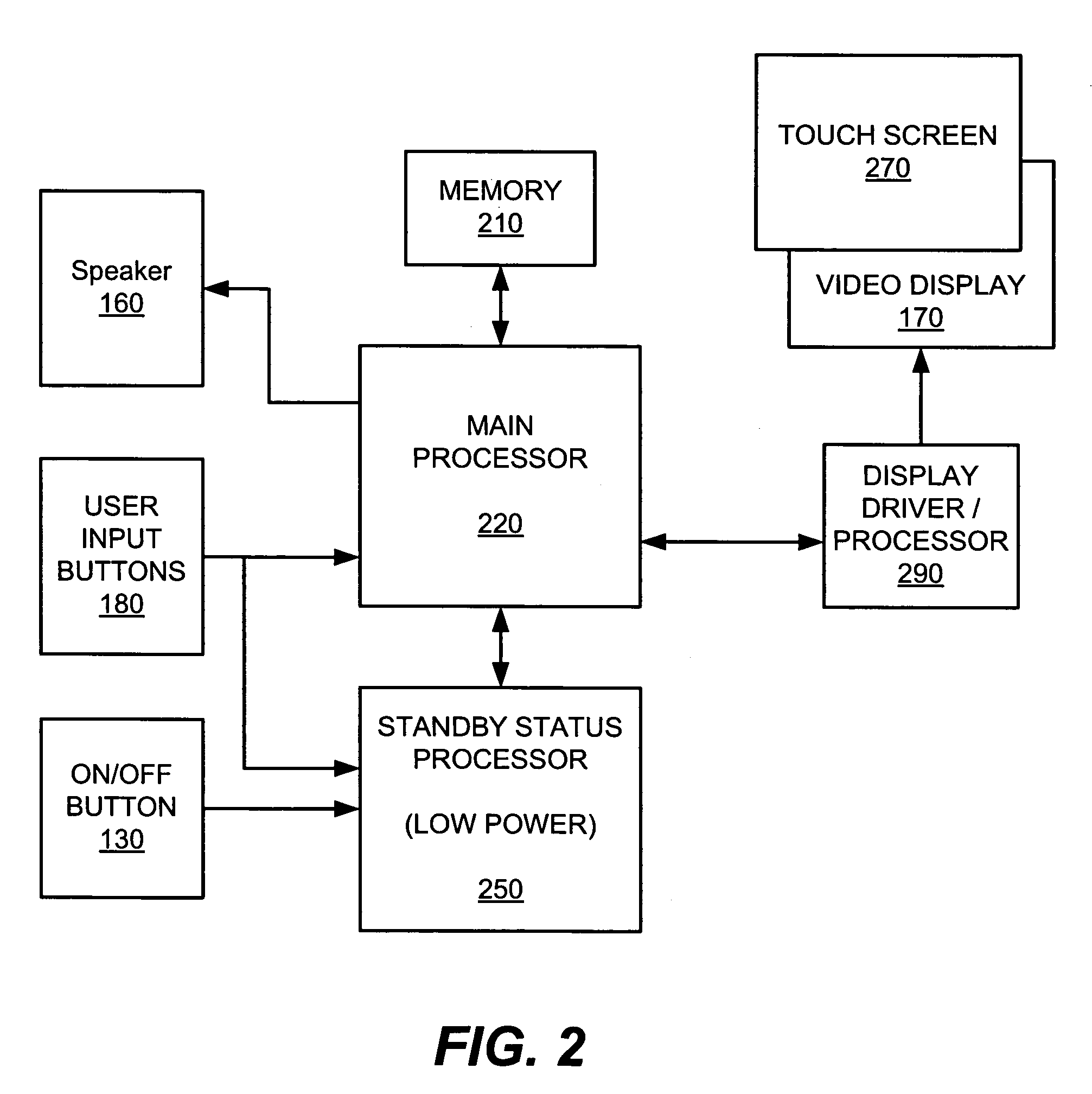
System and method for presenting defibrillator status information while in standby mode
ActiveUS7627372B2Save battery powerRich presentationHeart defibrillatorsGraphicsGraphical user interface
Owner:DEFIBTECH
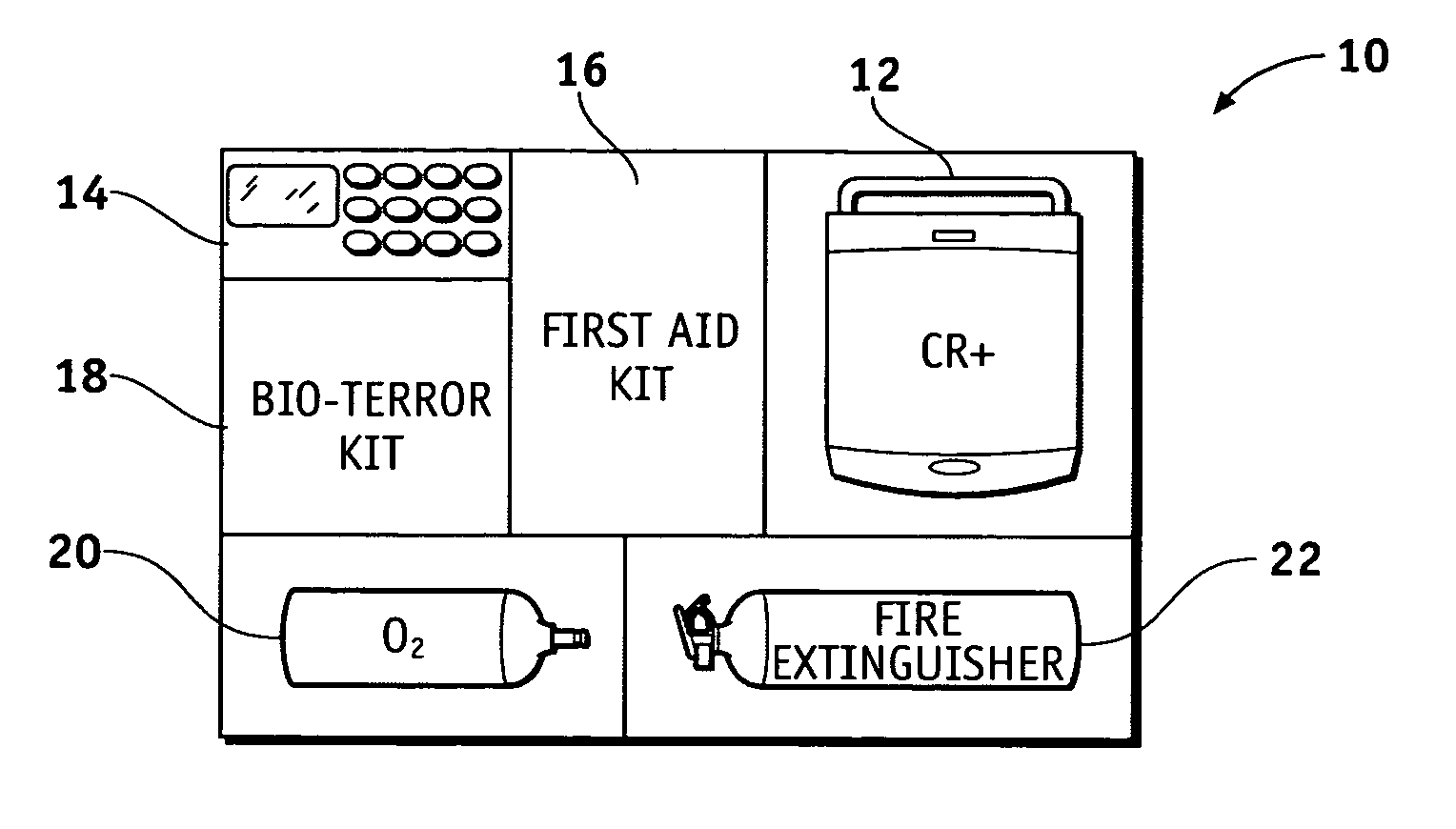
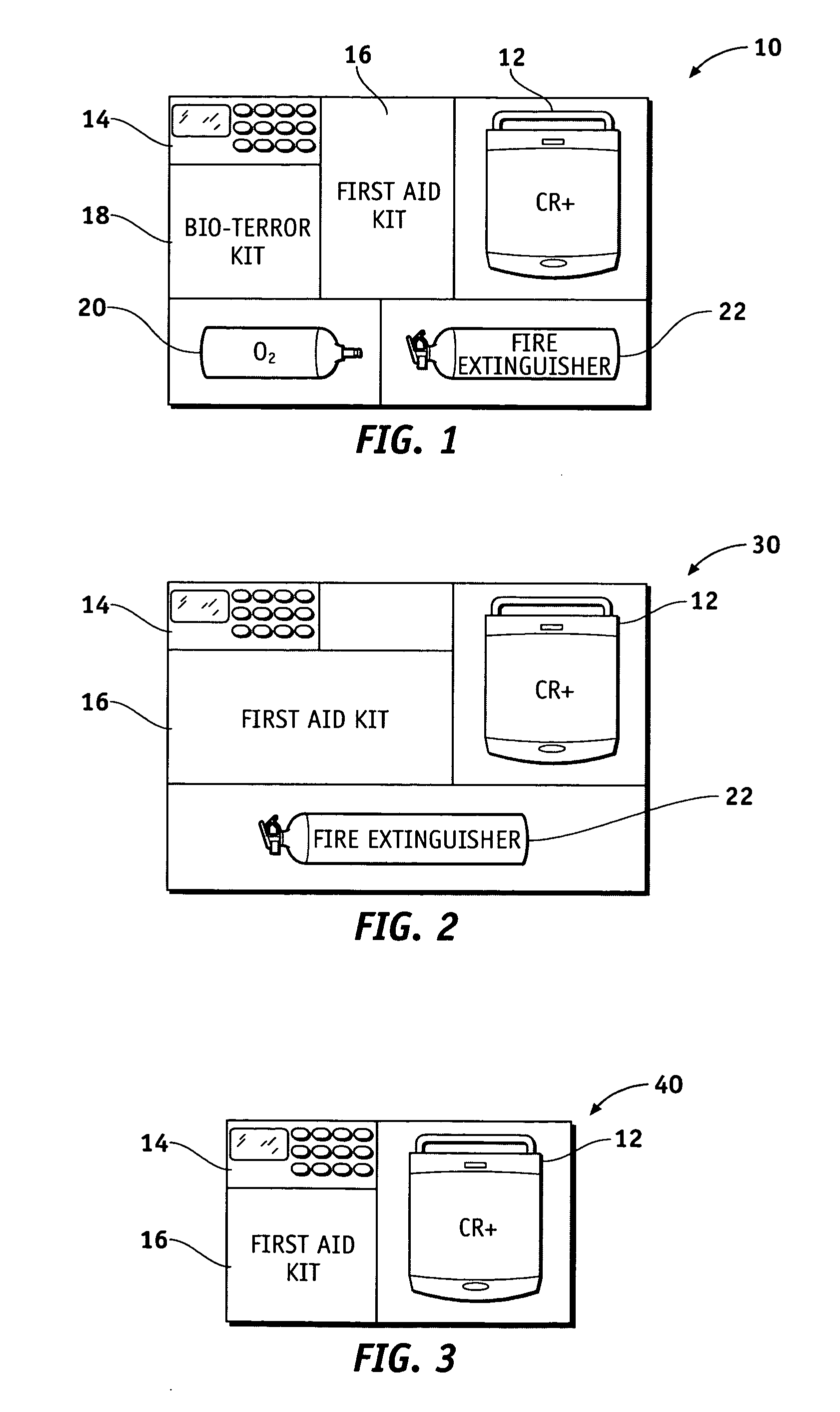
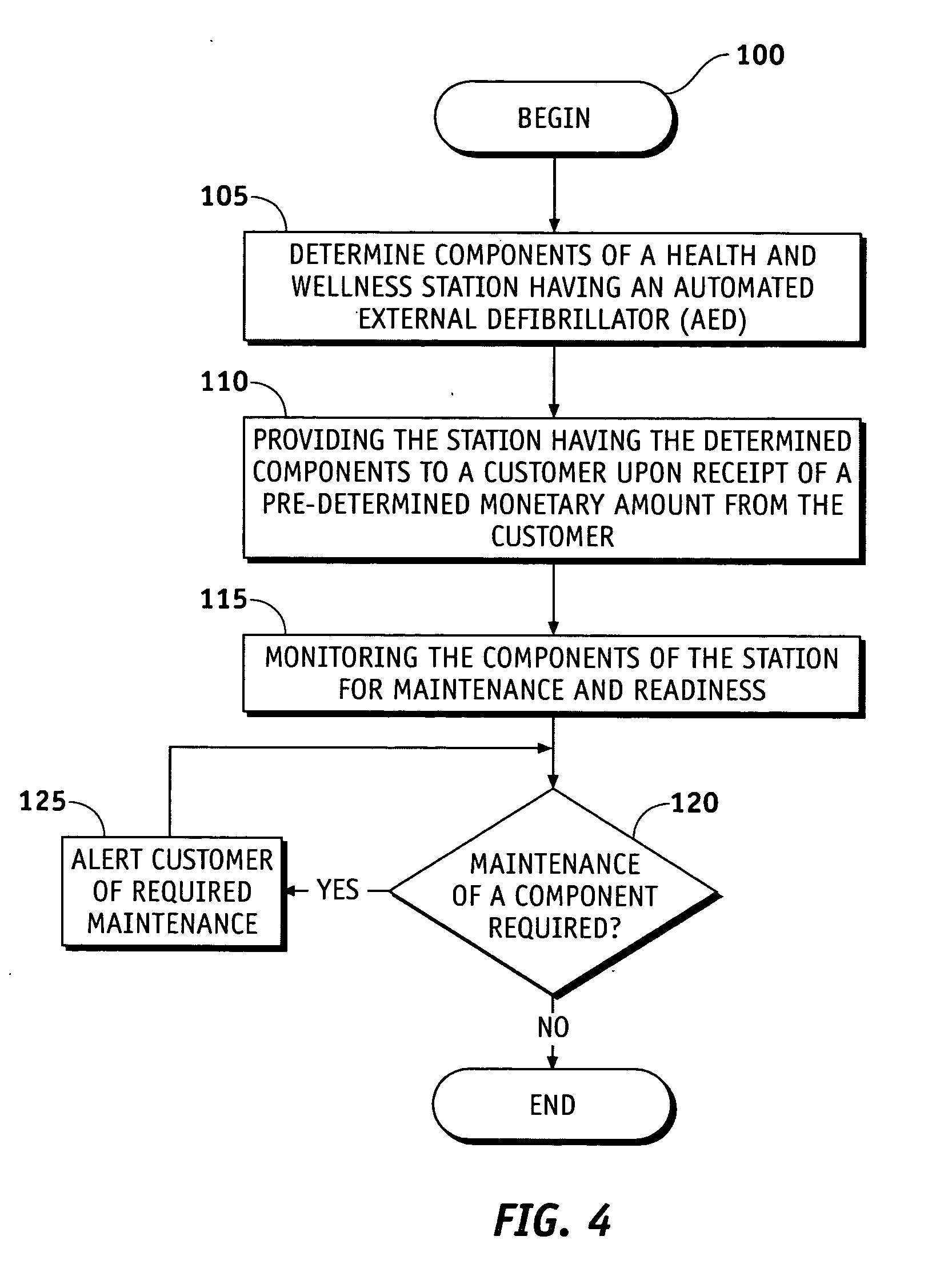
Health and wellness station
InactiveUS20050246199A1Medical communicationData processing applicationsEngineeringFire extinguisher
A health and wellness station having a plurality of emergency response resources incorporated into a single unit is provided to a customer. A method is provided of deploying the health and wellness station and includes the steps of determining components for the health and wellness station, providing a station having the determined components to a customer, and monitoring the components of the station for maintenance and readiness. The station includes an automated external defibrillator (AED) and may have any variety of additional resources, such as a bioterror response kit, a first aid kit, a fire extinguisher, a security system, an oxygen dispenser, and other domestic preparedness items.
Owner:MEDTRONIC PHYSIO CONTROL MFG
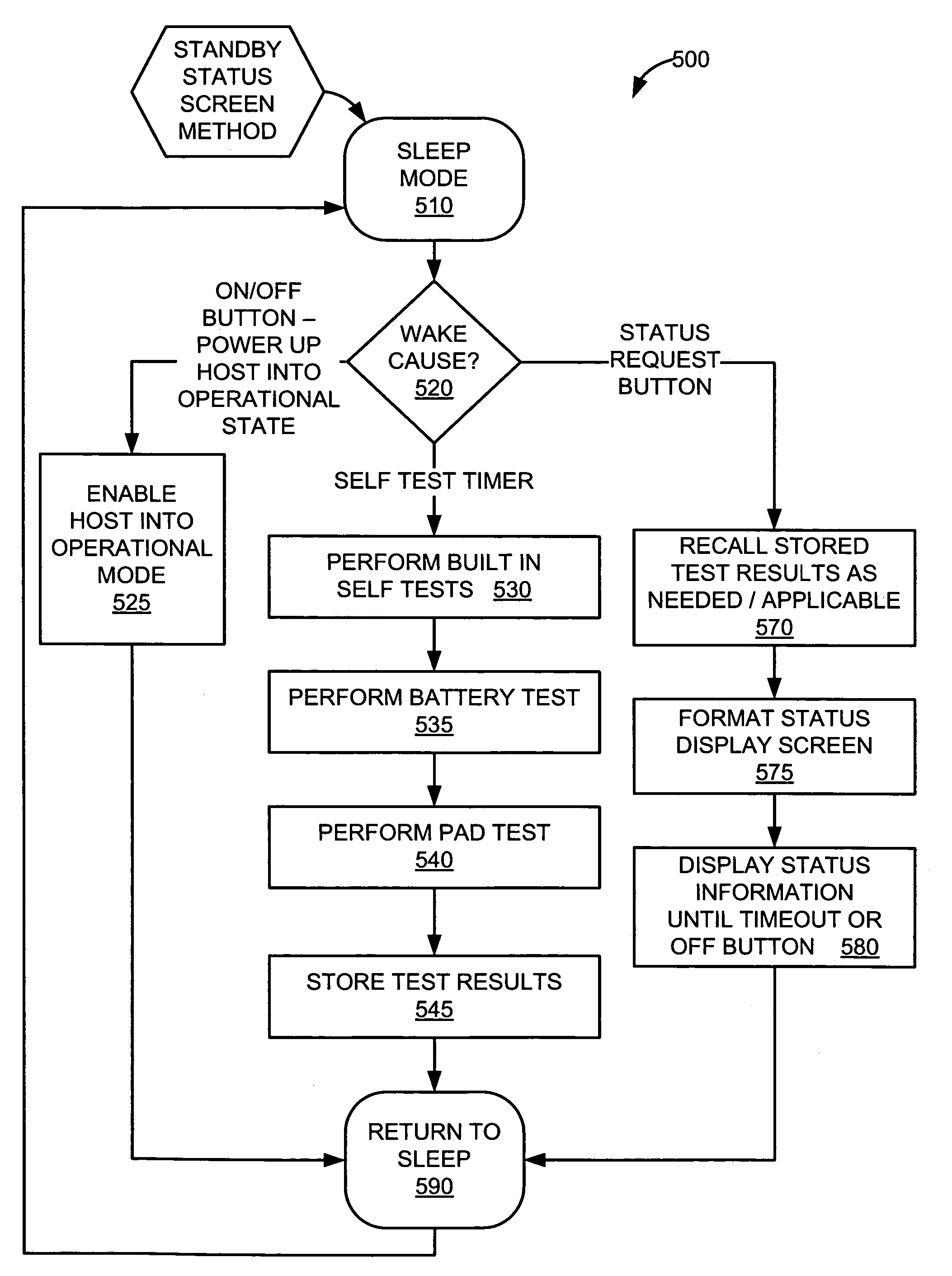
System and method for performing self-test in an automatic external defibrillator (AED)
InactiveUS20060136000A1Reliable electrical connectionHeart defibrillatorsAutomatic external defibrillatorComputer science
An automatic external defibrillator with an intelligent self-test system that ensures device readiness. The self-test system conditionally runs functional tests based on knowledge of device use, time of day, pre-programmed information, operational features and previous events. The condition of the defibrillator is indicated visually, audibly or both based on the results of the self-test performed.
Owner:SCION MEDICAL
OTC automatic external defibrillator with quick install battery
ActiveUS8086306B2Heart defibrillatorsCell component detailsElectricityAutomatic external defibrillator
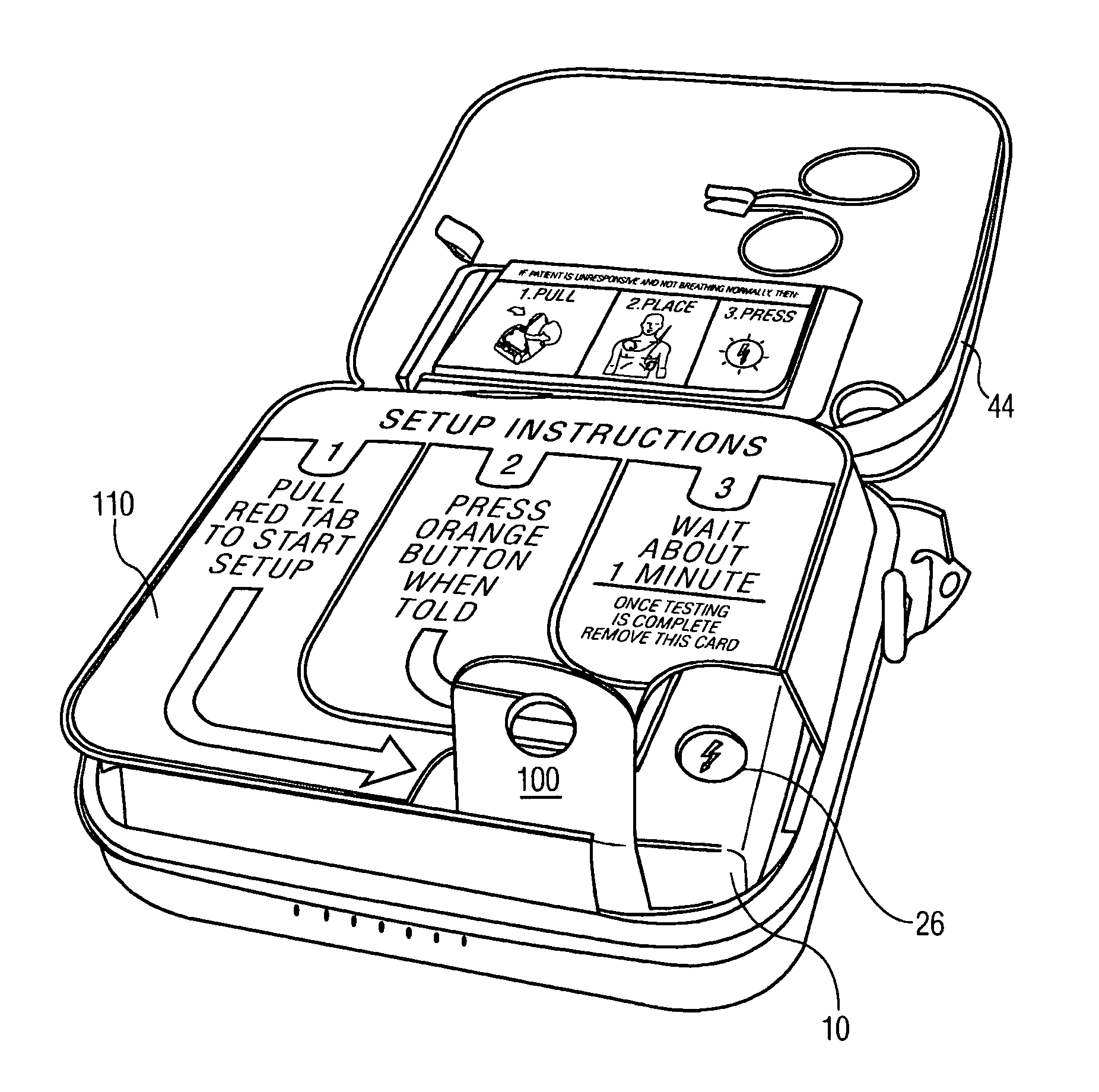
An automatic external defibrillator is shipped from the manufacturer with the battery installed in the battery compartment of the AED. During shipment a removable tab is located between a battery terminal and an electrical contact inside the battery compartment. Upon receipt of the AED the user pulls the tab to remove it from the battery compartment. This completes the circuit between the AED and its battery and the AED begins a self-test. A packaging panel covers the controls of the AED to prevent actuation of controls during the self-test. The packaging panel includes instructions for setup of the AED including indication of a control to actuate during or at the conclusion of the self-test.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Method and apparatus for treatment of cardiac electromechanical dissociation
An apparatus and method for treating post-defibrillation electromechanical dissociation ("EMD"). A first embodiment comprises an implantable defibrillator, which may include cardioversion and pacemaker capabilities, which has the capability of detecting and treating post defibrillation EMD. The stimulator / defibrillator has one or more leads with electrodes. At least one electrode for defibrillation may be an endocardial or epicardial electrode or other suitable defibrillation electrode. A sense circuit senses the electrical condition of the heart of the patient. A hemodynamic sensor senses a parameter correlated to the state of blood flow. The cardiac stimulator / defibrillator detects ventricular tachyarrhythmia including fibrillation and terminates ventricular tachyarrhythmia. After termination of the ventricular tachyarrhythmia, the stimulator / defibrillator can detect the presence of electrical rhythm in the heart correlated, however, with inadequate blood flow to sustain life. Under such conditions, the device provides an output to stimulate the heart to overcome electromechanical dissociation and restore adequate blood flow. The device may also be an external therapy device, as part of, or in conjunction with an external defibrillator. The method for treating the heart to restore blood flow where electromechanical dissociation occurs after termination of a ventricular tachyarrhythmia or ventricular fibrillation comprises identifying electromechanical disassociation after termination of a ventricular tachyarrhythmia or a fibrillation and providing electrical therapy, the therapy comprising a series of packets of electrical pulses.
Owner:INTERMEDICS
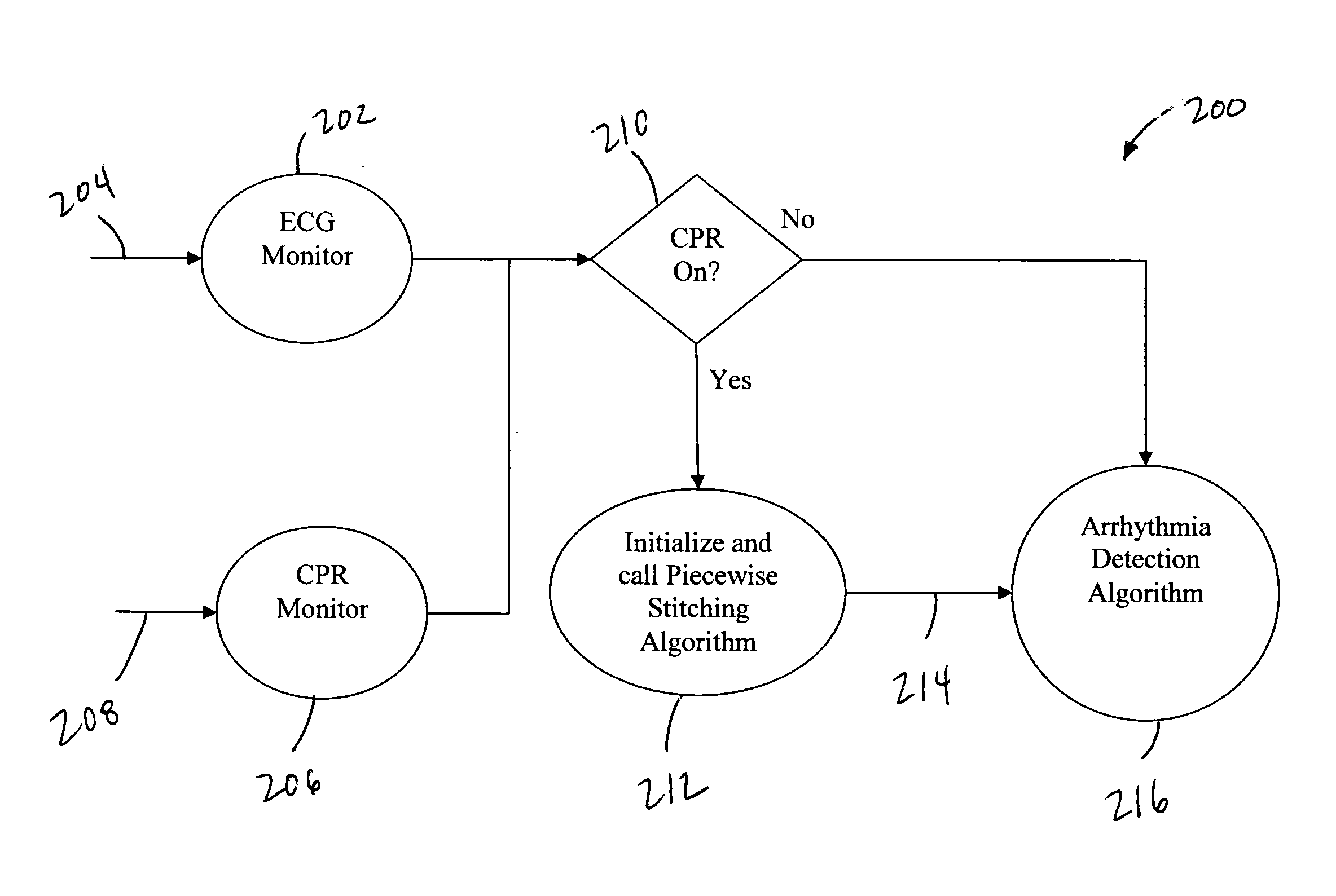
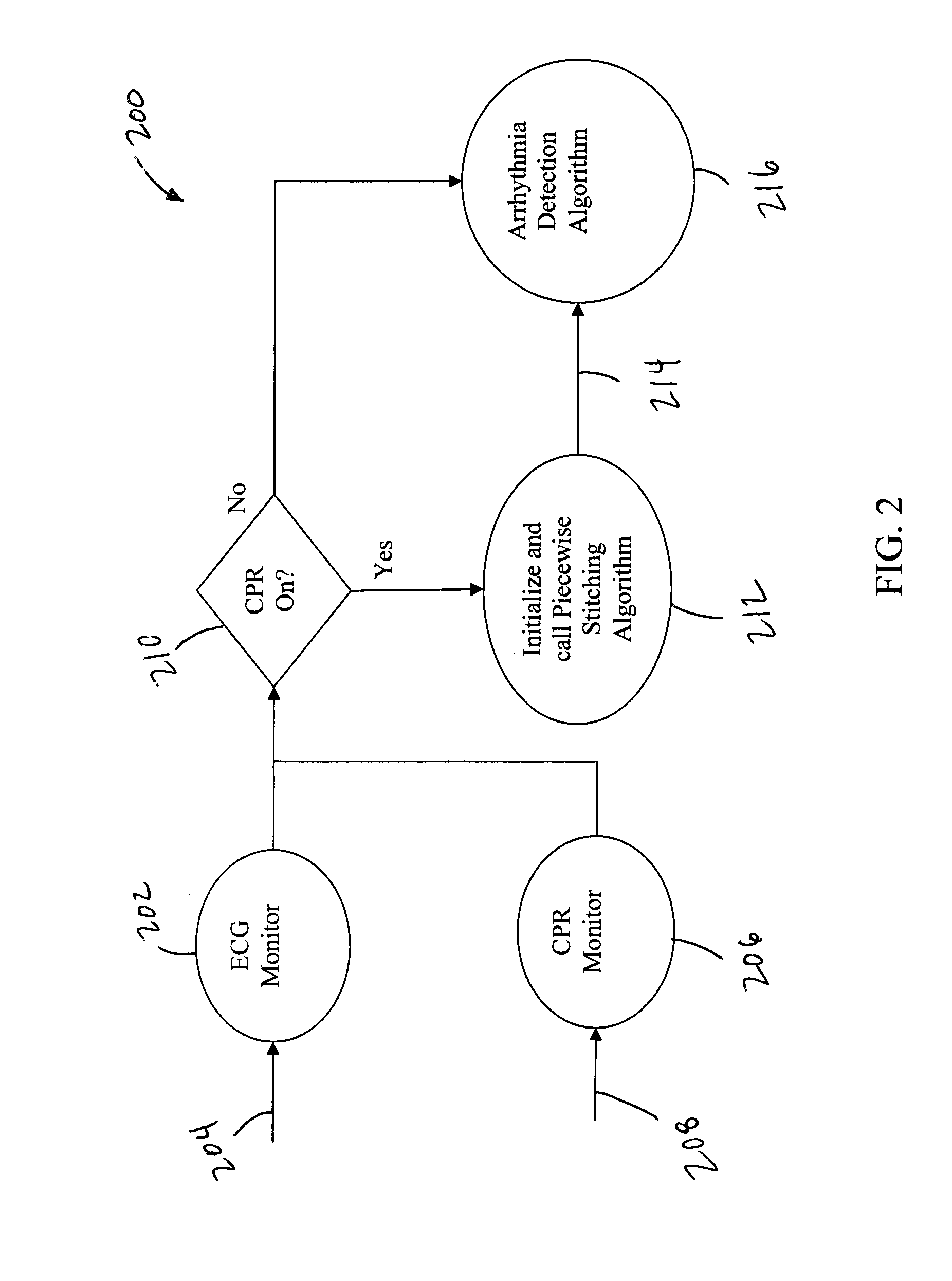
True ECG measurement during cardio pulmonary resuscitation by adaptive piecewise stitching algorithm
ActiveUS20110105930A1Optimize filteringOptimize sensingElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringAutomated external defibrillatorECG Measurement
A method and apparatus utilizing a piecewise stitching adaptive algorithm (PSAA) to filter signal artifacts, such as those induced by cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) from sensed signals in real-time. PSAA is a method of estimating artifact component present in a first signal that is highly correlated with a second signal. The PSAA may utilize autocorrelation and cross-correlation calculations to determine signal sample windows in the first and second signals. The PSAA may estimate a signal artifact in a primary signal segment based on the determined correlations between the primary signal and an artifact signal. The PSAA may remove the estimated signal artifact from the primary signal. In the absence of an artifact signal, PSAA is able to estimate artifacts in the first signal utilizing filters. The PSAA may be implemented in Automated External Defibrillators, Monitor Defibrillators or other devices capable sensing highly correlated signals such as, for example, ECG and CPR signals.
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
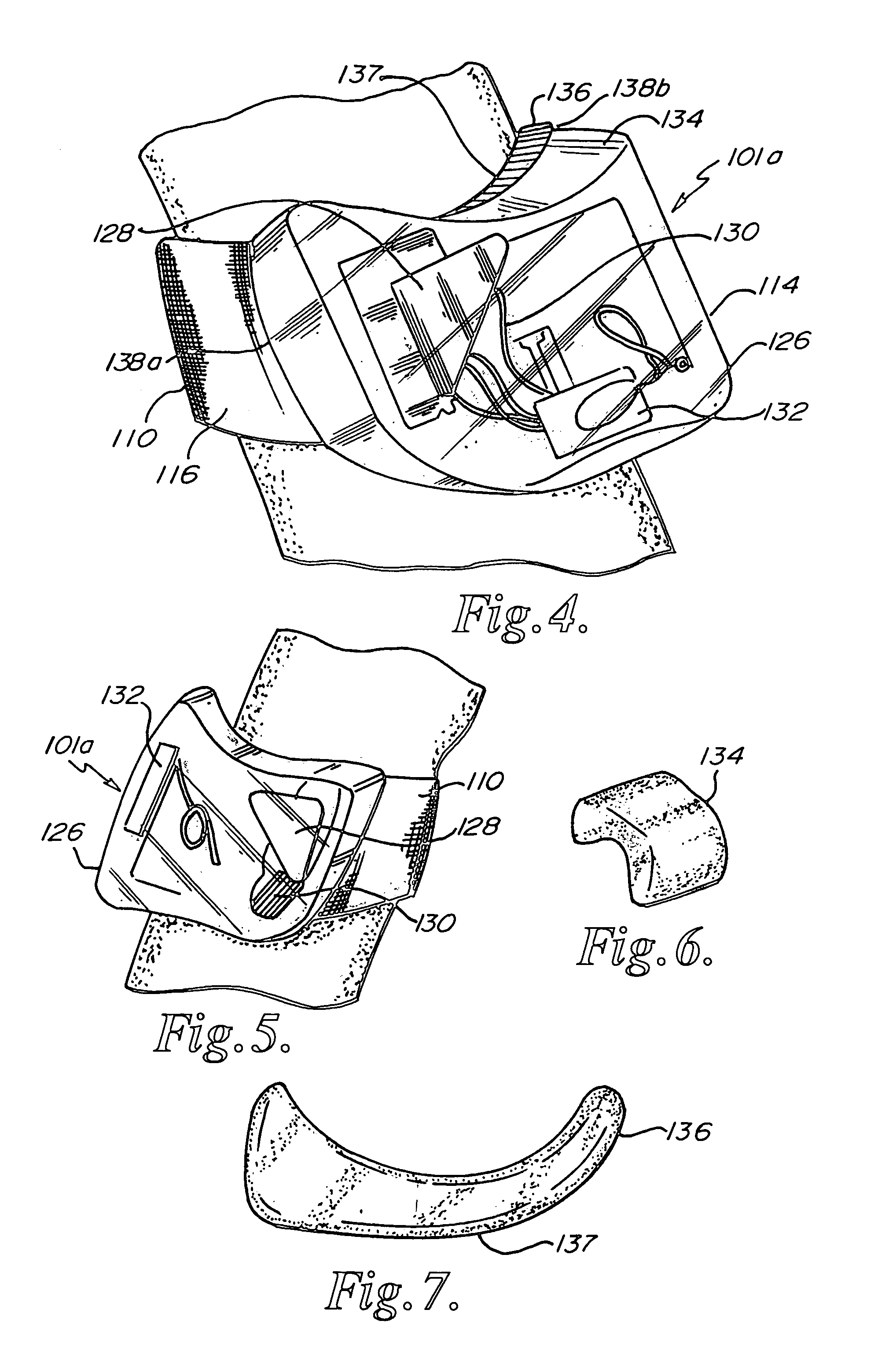
Methods and Apparatus for Selectively Shunting Energy in an Implantable Extra-Cardiac Defibrillation Device
InactiveUS20080183230A1Sufficient massEasy to implantSubcutaneous electrodesExternal electrodesPatient comfortThoracic cavity
The disclosure provides methods and apparatus for simultaneously providing protection to an implantable medical device, such as an extra-cardiac implantable defibrillator (EID), while allowing efficacious therapy delivery via an external defibrillator (e.g., an automated external defibrillator, or AED). Due to the orientation of the electrodes upon application of therapy via, for example, via an AED the structure of the EID essentially blocks therapy delivery. In addition, but for the teaching of this disclosure sensitive circuitry of an EID can be damaged during application of external high voltage therapy thus rendering the EID inoperable. EIDs are disclosed that are entirely implantable subcutaneously with minimal surgical intrusion into the body of the patient and provide distributed cardioversion-defibrillation sense and stimulation electrodes for delivery of cardioversion-defibrillation shock and pacing therapies across the heart when necessary. Configurations include one hermetically sealed housing with one or, optionally, two subcutaneous sensing and cardioversion-defibrillation therapy delivery leads or alternatively, two hermetically sealed housings interconnected by a power / signal cable. The housings are generally dynamically configurable to adjust to varying rib structure and associated articulation of the thoracic cavity and muscles. Further the housings may optionally be flexibly adjusted for ease of implant and patient comfort. One aspect includes partially insulating a surface of an EID that faces away from a heart while maintaining a major conductive surface facing the heart.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
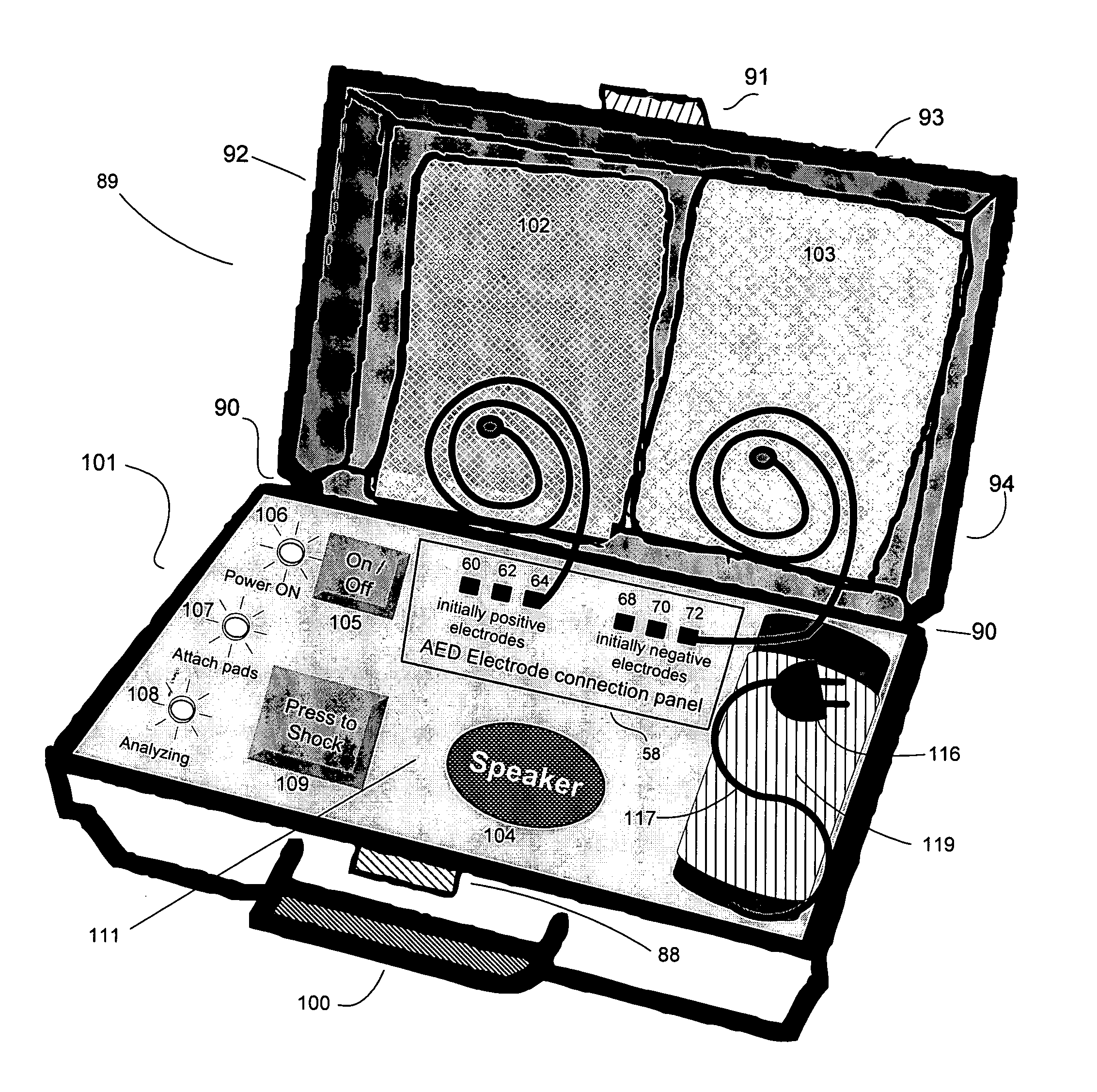
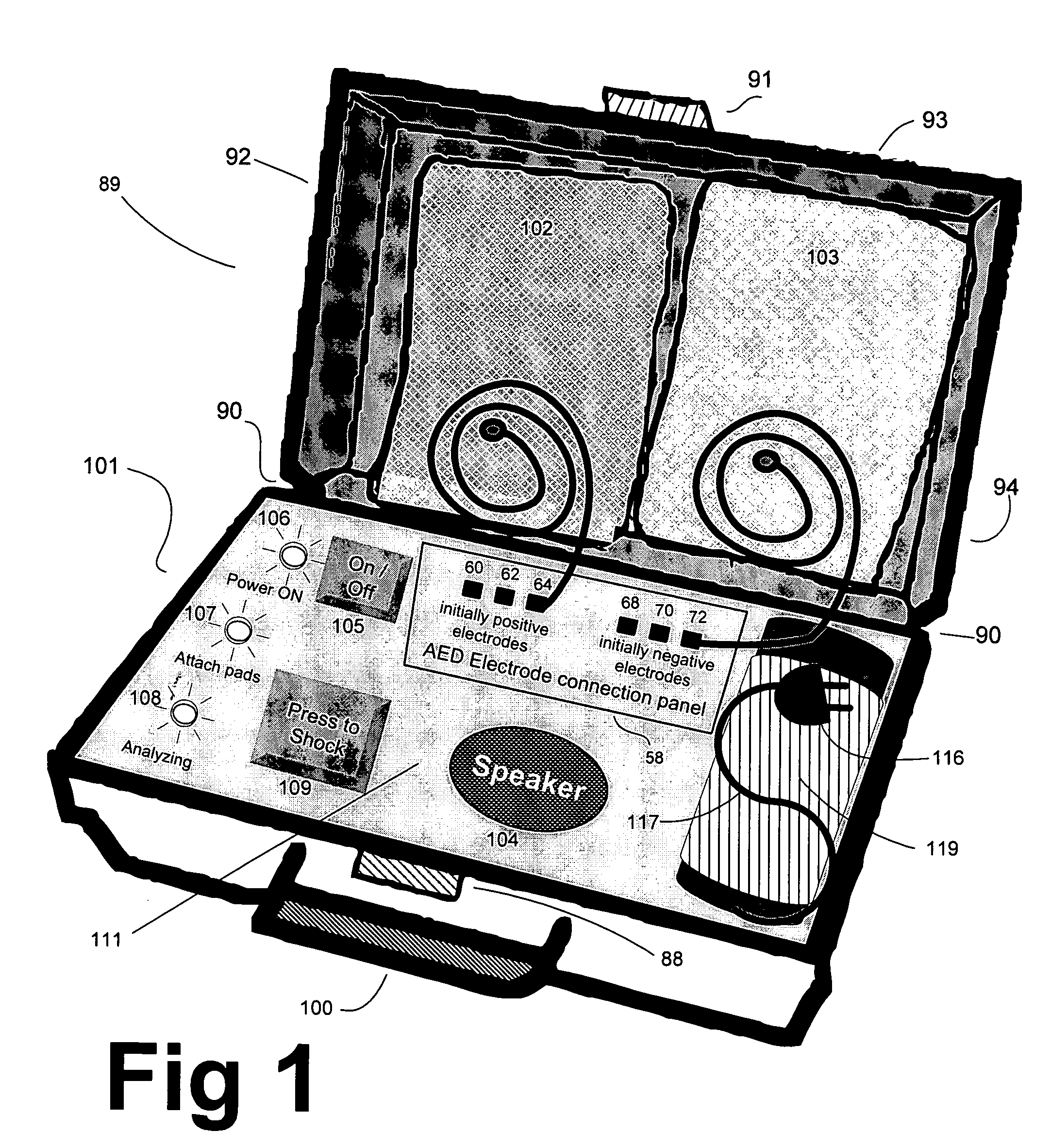
Easy-to-use electrode and package
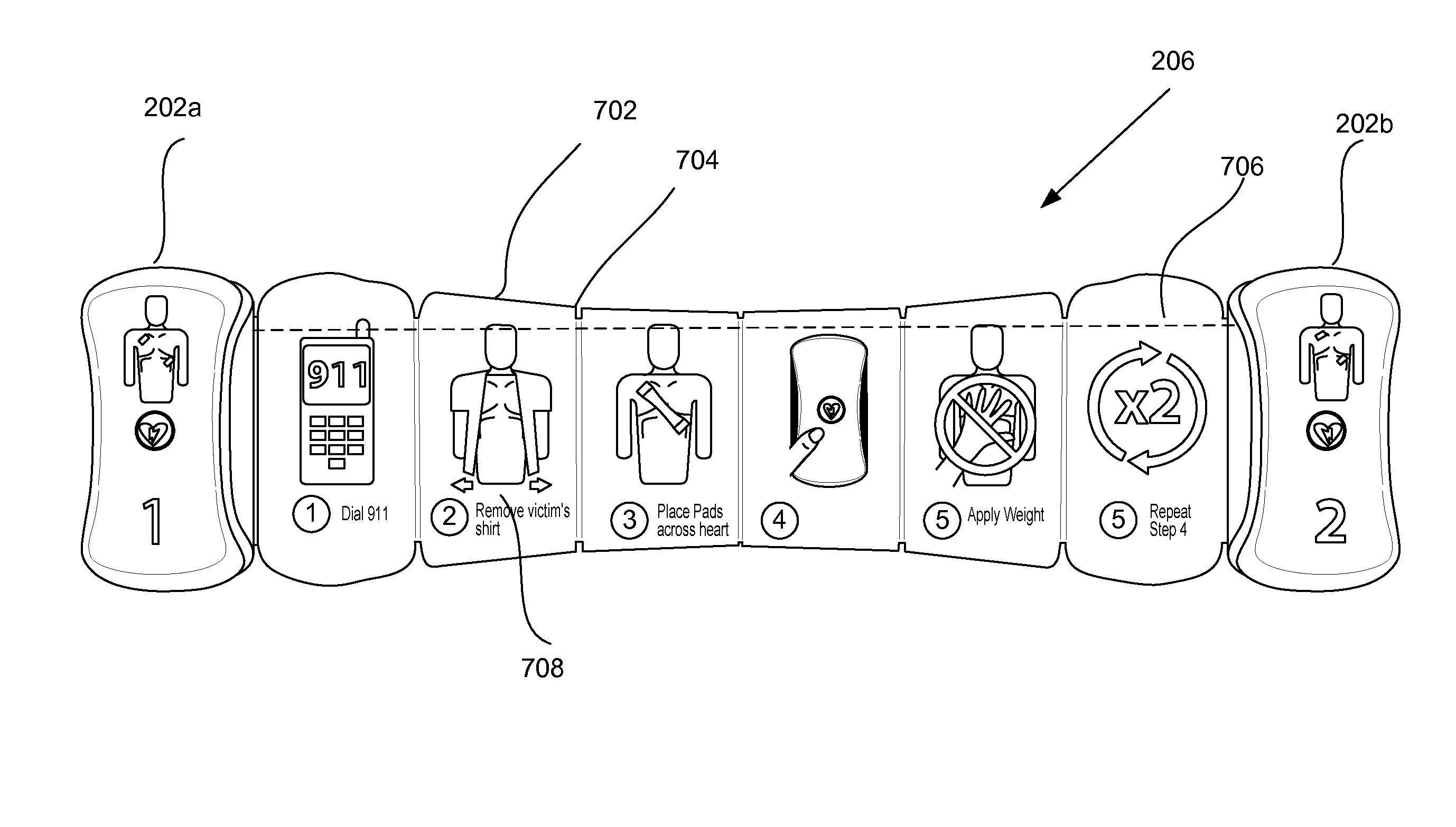
InactiveUS20060206152A1Easy to openIncrease chances of survivalHeart defibrillatorsEmergency medicineAutomated external defibrillator
The invention presents techniques for making the operation of an automated external defibrillator easier to understand for an operator. The automated external defibrillator includes defibrillation electrodes packaged in a sealed, easy-to-open pouch. Visual cues such as instructive pictures show the operator how to open the pouch, retrieve the defibrillation electrodes and correctly position the electrodes on a patient's chest.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
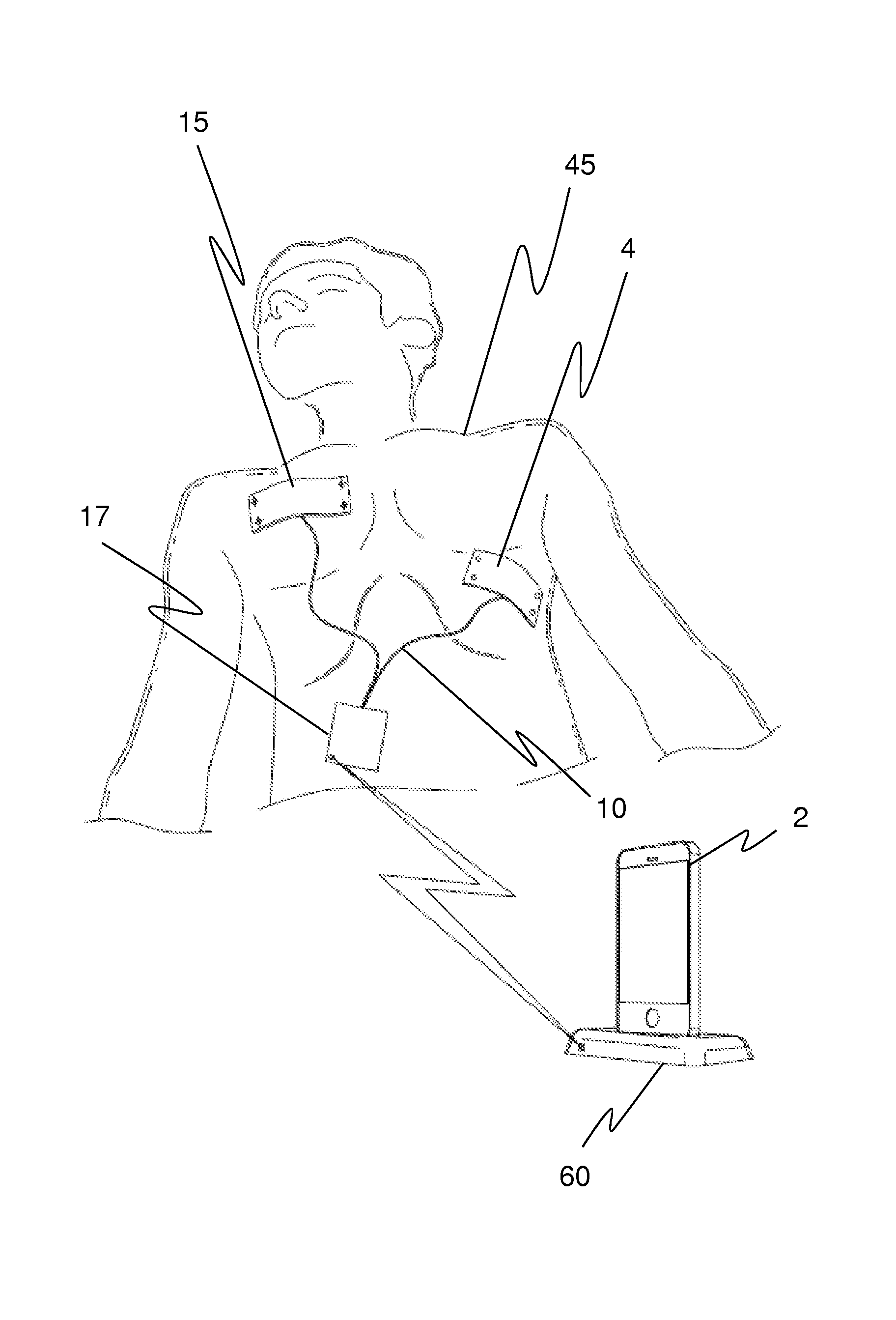
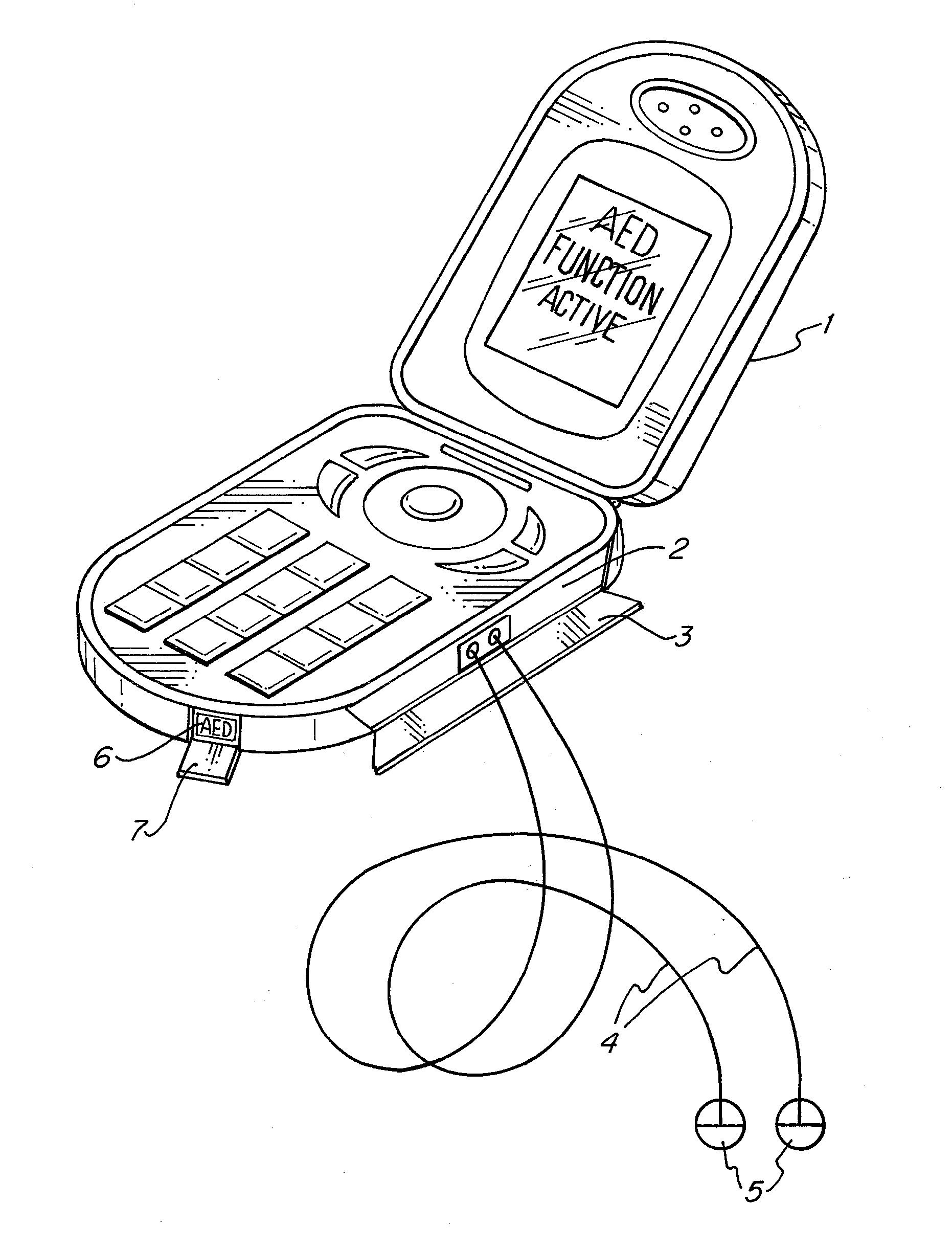
Method and apparatus of remotely-operated automated external defribrallator incorporated into a handheld device
A rescue cell apparatus used for cardiac defibrillation of a patient, the apparatus comprising: a hand held device for sending and receiving communication signals and configured to be used as a remote control to administer a defibrillation pulse to the patient for cardiac defibrillation; a defibrillator unit having a sensor electronic pad positionable on the patient, the sensor electronic pad adapted to deliver the defibrillation pulse; and a second electronic pad, connectable by an electrical wire to the defibrillator unit, the second electronic pad positionable on the patient and adapted to detect ECG signals and to deliver the defibrillation pulse to the patient; and an image recognition module configured in the handheld device, and adapted to verify positioning of the sensor electronic pad and the second electronic pad on the patient before defibrillation.
Owner:EINY GILAD
Method and system for atrial defibrillation
InactiveUS20060100669A1Increase surface areaIncrease contactHeart defibrillatorsInternal electrodesAtrial fibrillationCatheter device
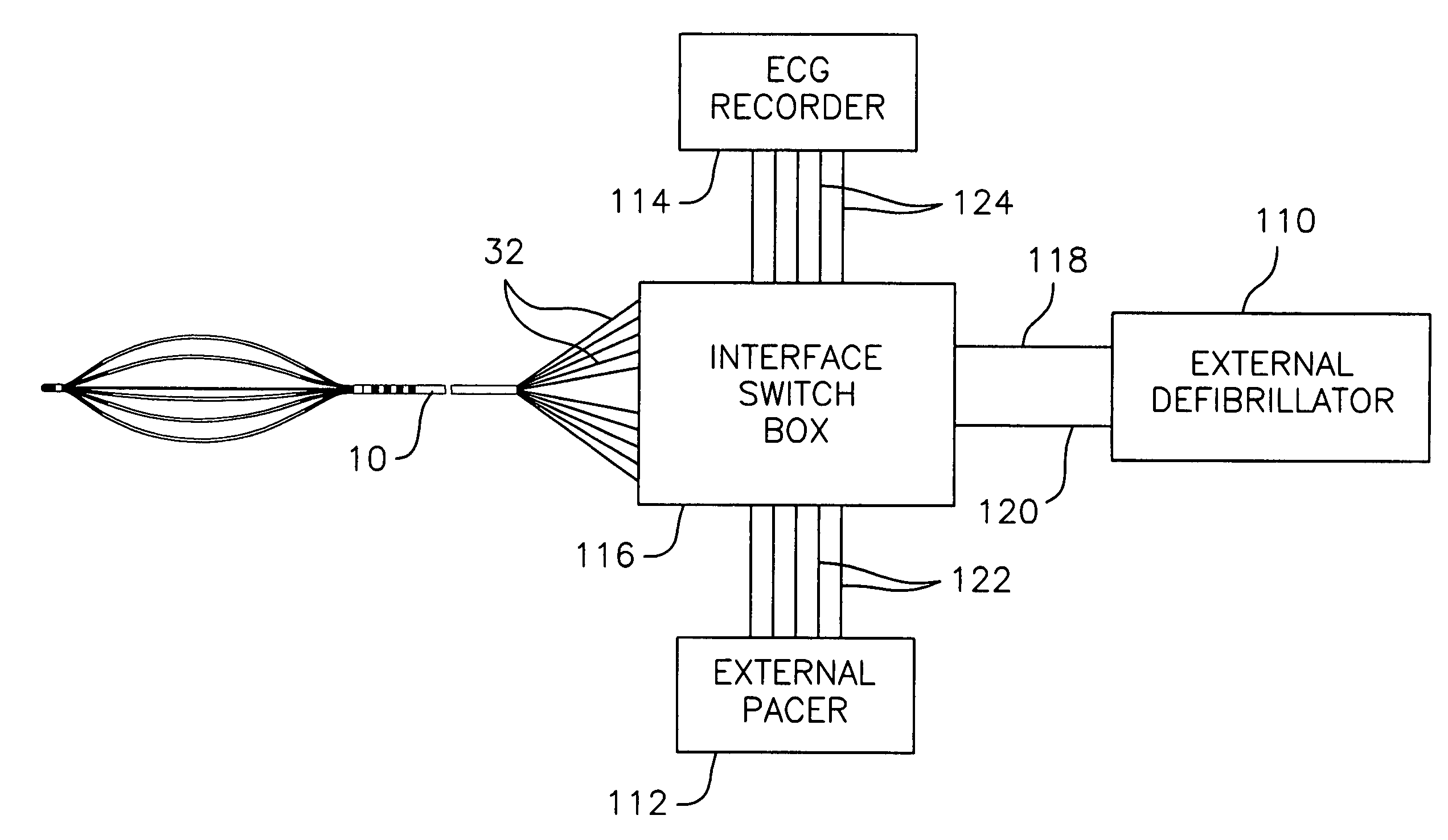
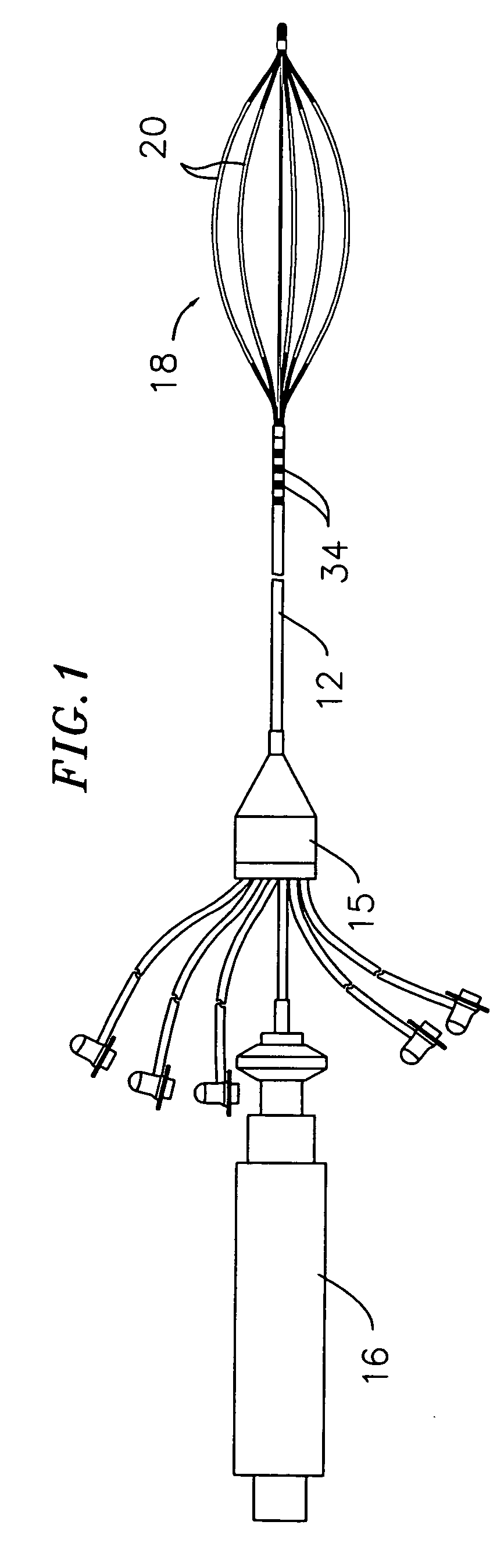
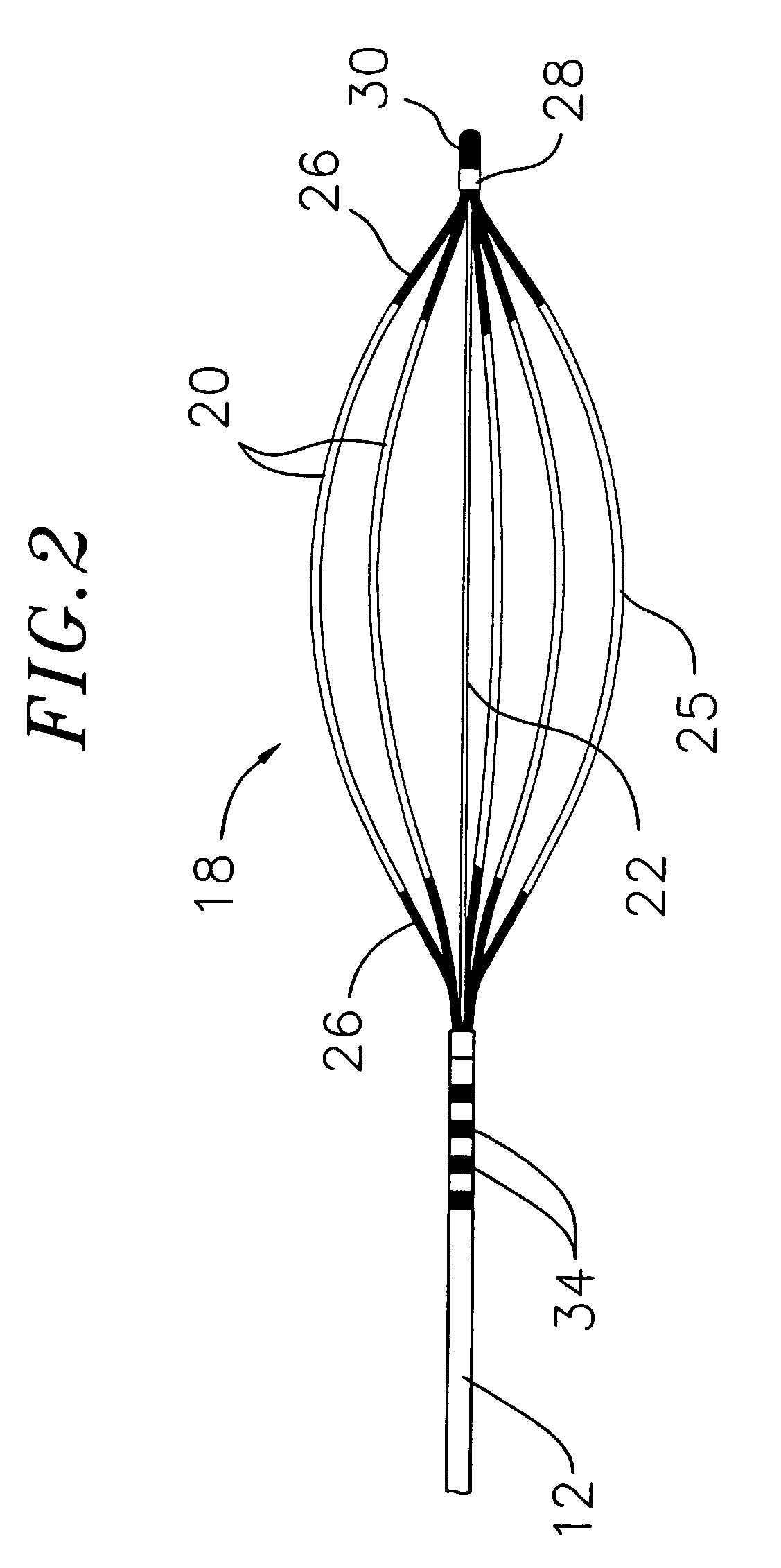
A method and system for atrial defibrillation in a patient are provided. The method comprises introducing into the patient a catheter comprising an elongated catheter body having proximal and distal ends and at least one lumen therethrough, and a basket-shaped electrode assembly at the distal end of the catheter body. The electrode assembly has proximal and distal ends and comprises a plurality of spines connected at their proximal and distal ends, each spine comprising an elongated spine electrode along its length. The electrode assembly has an expanded arrangement wherein the spines bow radially outwardly and a collapsed arrangement wherein the spines are arranged generally along the axis of the catheter body. The method further comprises introducing the electrode assembly into the heart of the patient and applying defibrillation energy to the tissue through one or more of the elongated electrodes. The system comprises a catheter as described above in combination with an external defibrillator electrically connected to the catheter.
Owner:BIOSENSE WEBSTER INC
Common Notebook, Laptop Computer, Tablet PC, PDA and Cell Phone With Automated External Defibrillator (AED) Capability and Methods for Adapting A Common Notebook, Laptop Computer, Tablet PC, PDA and Cell Phone To Enable Each to be Used as an Automated External Defibrillator
ActiveUS20110046688A1Increase chances of survivalShorten the timeHeart defibrillatorsDigital data authenticationTablet computerEmergency medicine
A notebook, laptop computer, tablet PC (personal computer) or desktop computer having an automated external defibrillator (AED) capability, and methods of utilizing the notebook, laptop computer or tablet PC (personal computer) defibrillator to treat victims of sudden cardiac arrest. A notebook, laptop computer or tablet PC (personal computer) having the technology to enable each to be used as an automated external defibrillator (AED). Methods and apparatuses for implementing the common notebook, laptop computer, tablet PC, common cell phone and the common personal digital assistant (PDA) as an automated external defibrillator (AED).
Owner:COMPTOLIFE
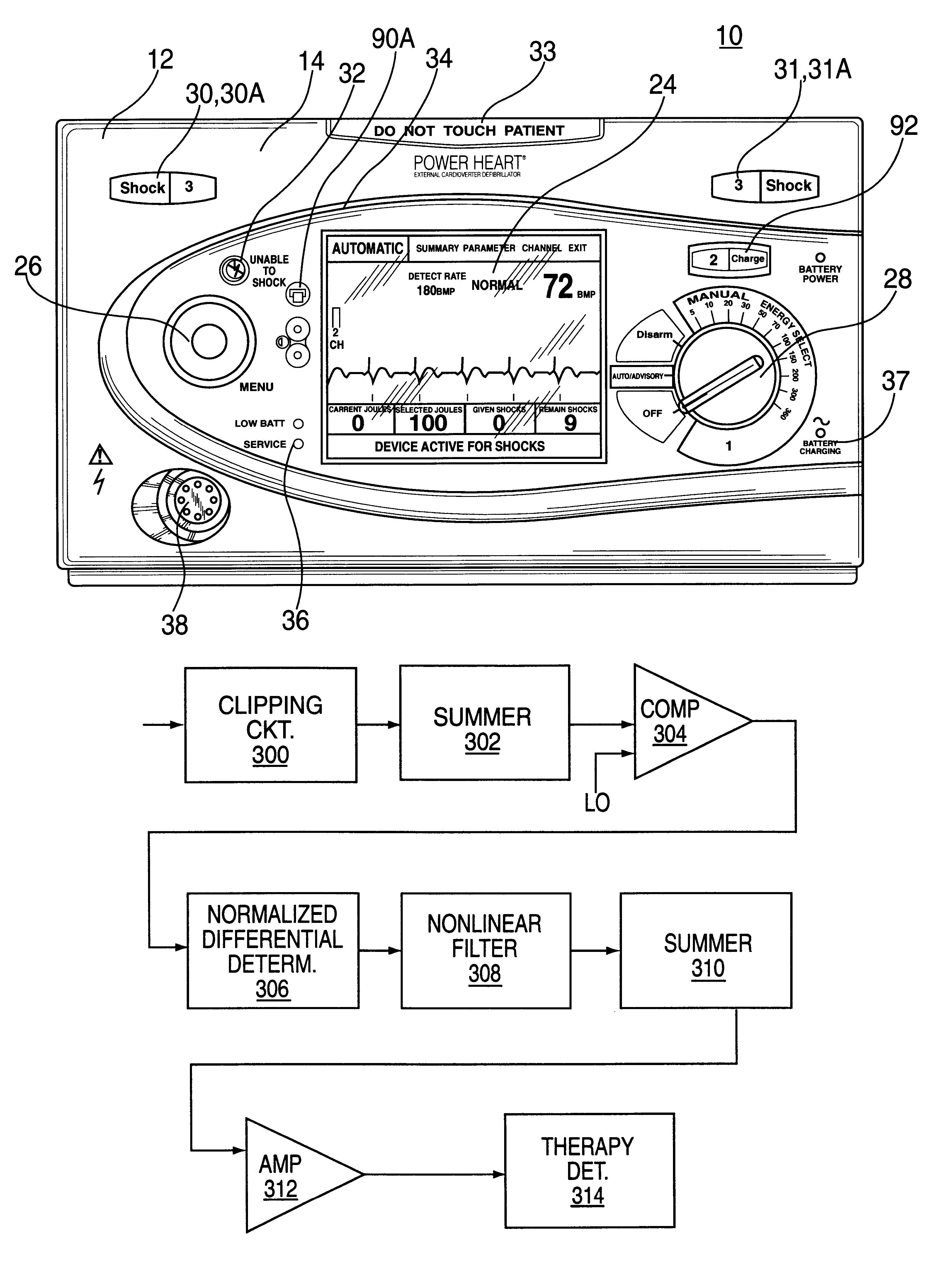
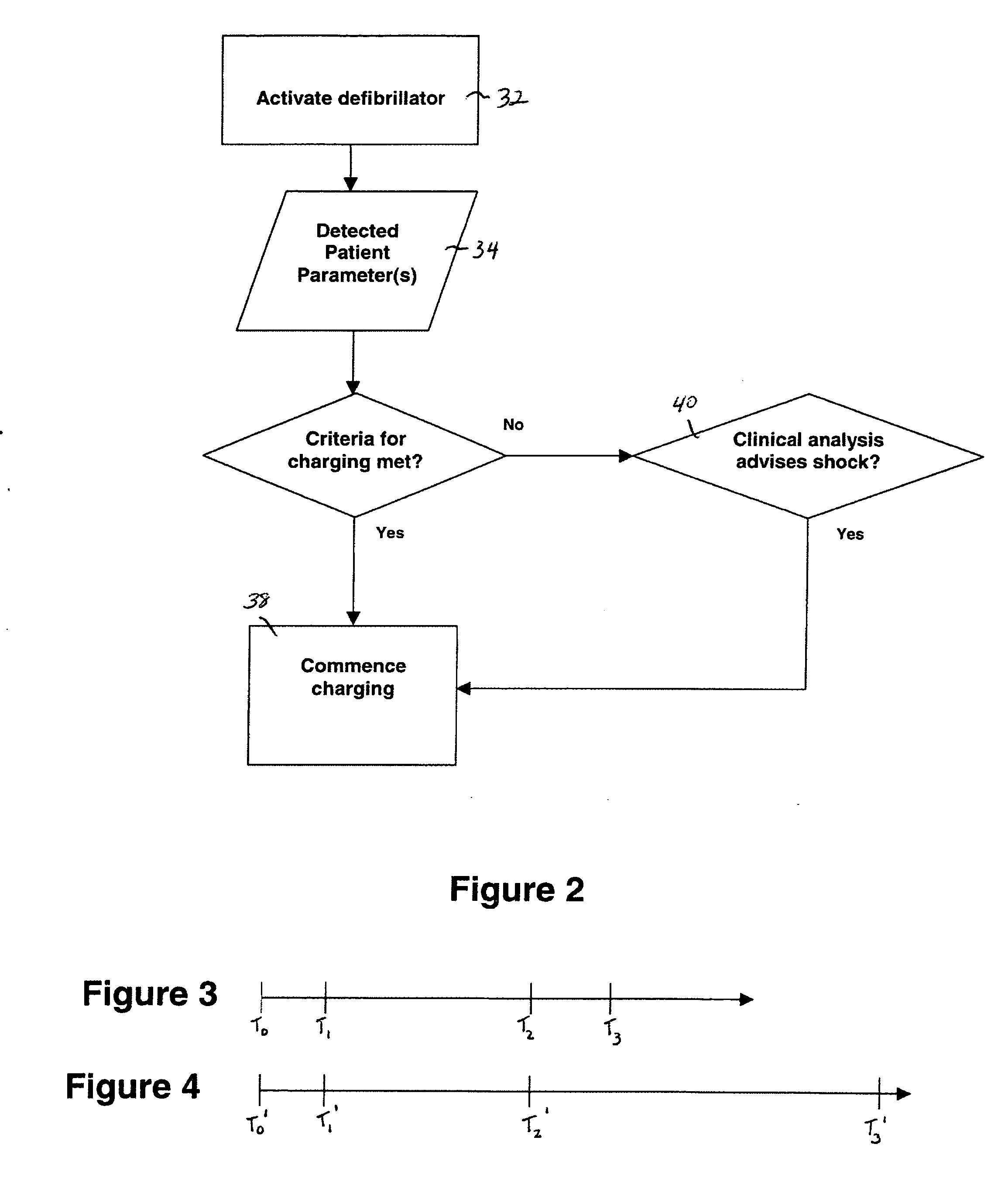
External defibrillator with charge advisory algorithm
A method of delivering electrical therapy to a patient by a medical device includes activating the medical device and performing a first analysis of a first set of data signals sensed by the medical device. If the first analysis shows the first set of data signals meets a first criterion, then charging of an energy delivery circuit is commenced circuit upon completion of the first analysis. A second analysis of a second set of data signals from the patient is performed, and if the second analysis determines that the second set of data signals meet a second criterion, the therapy is delivered. The steps of performing the first analysis and performing the second analysis may be begun at substantially the same time. The step of charging may overlap in time with the step of performing a second analysis. The medical device may be an external defibrillator and the therapy may be a defibrillating shock.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com