Patents
Literature
45results about How to "Simple and precise manner" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
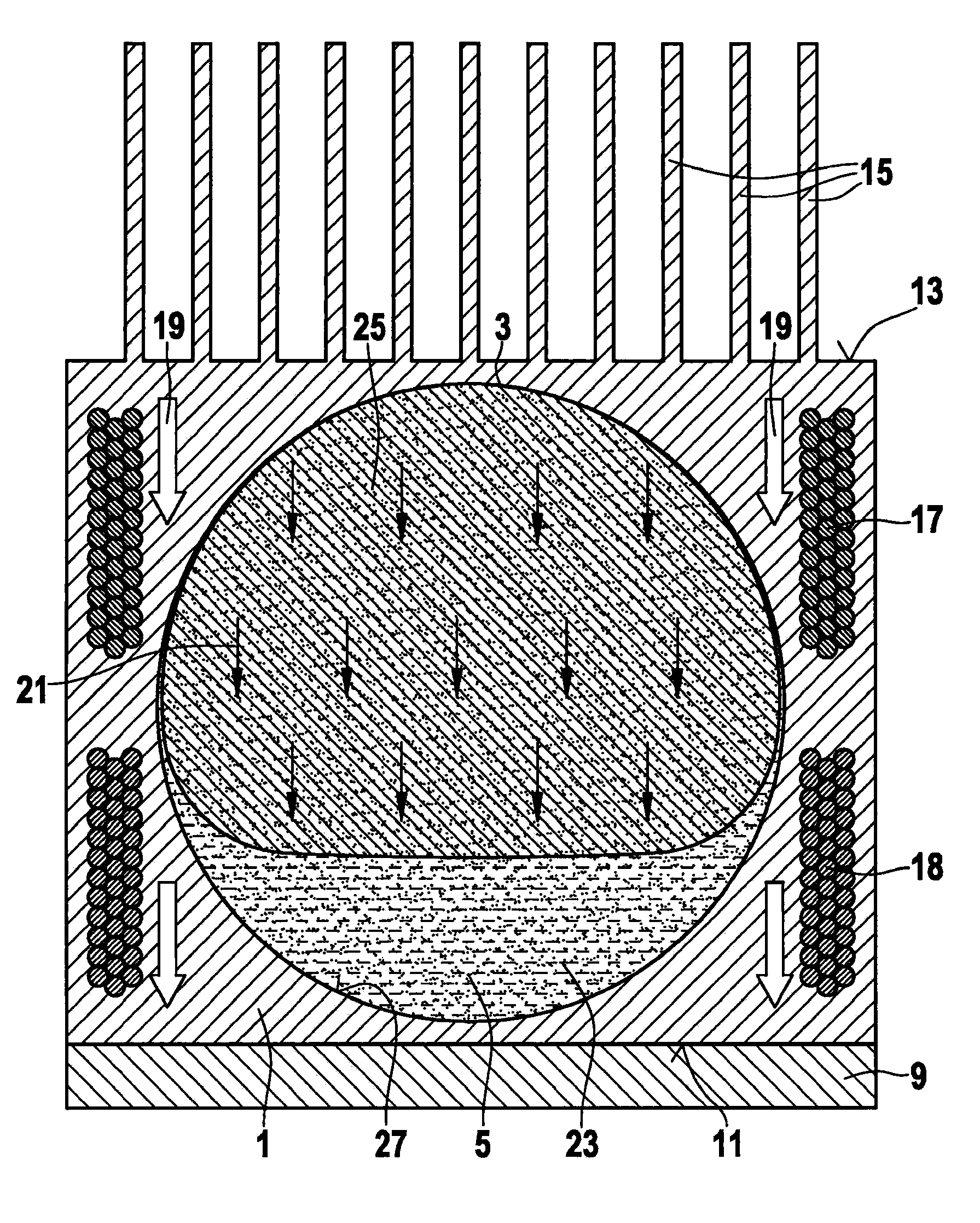
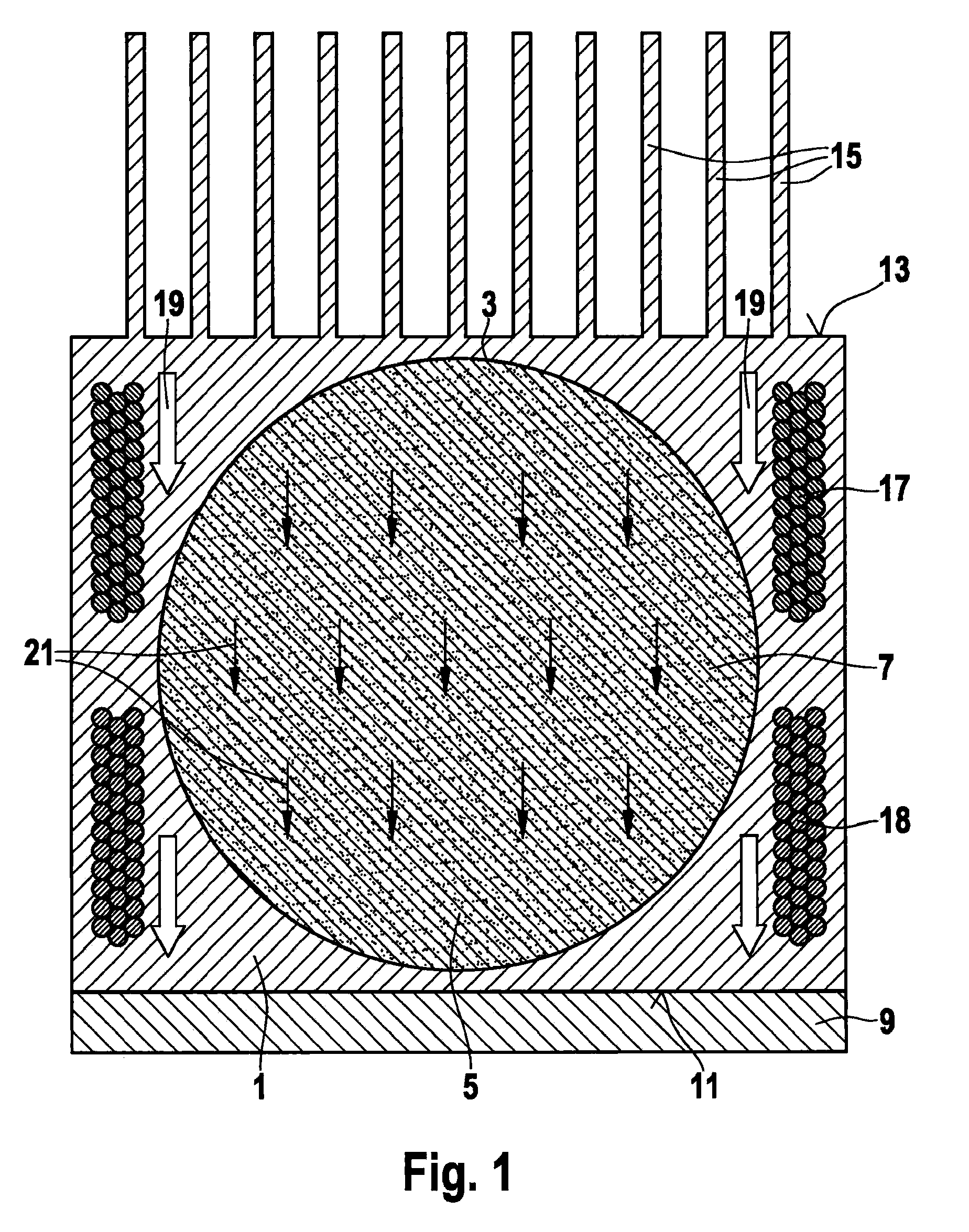
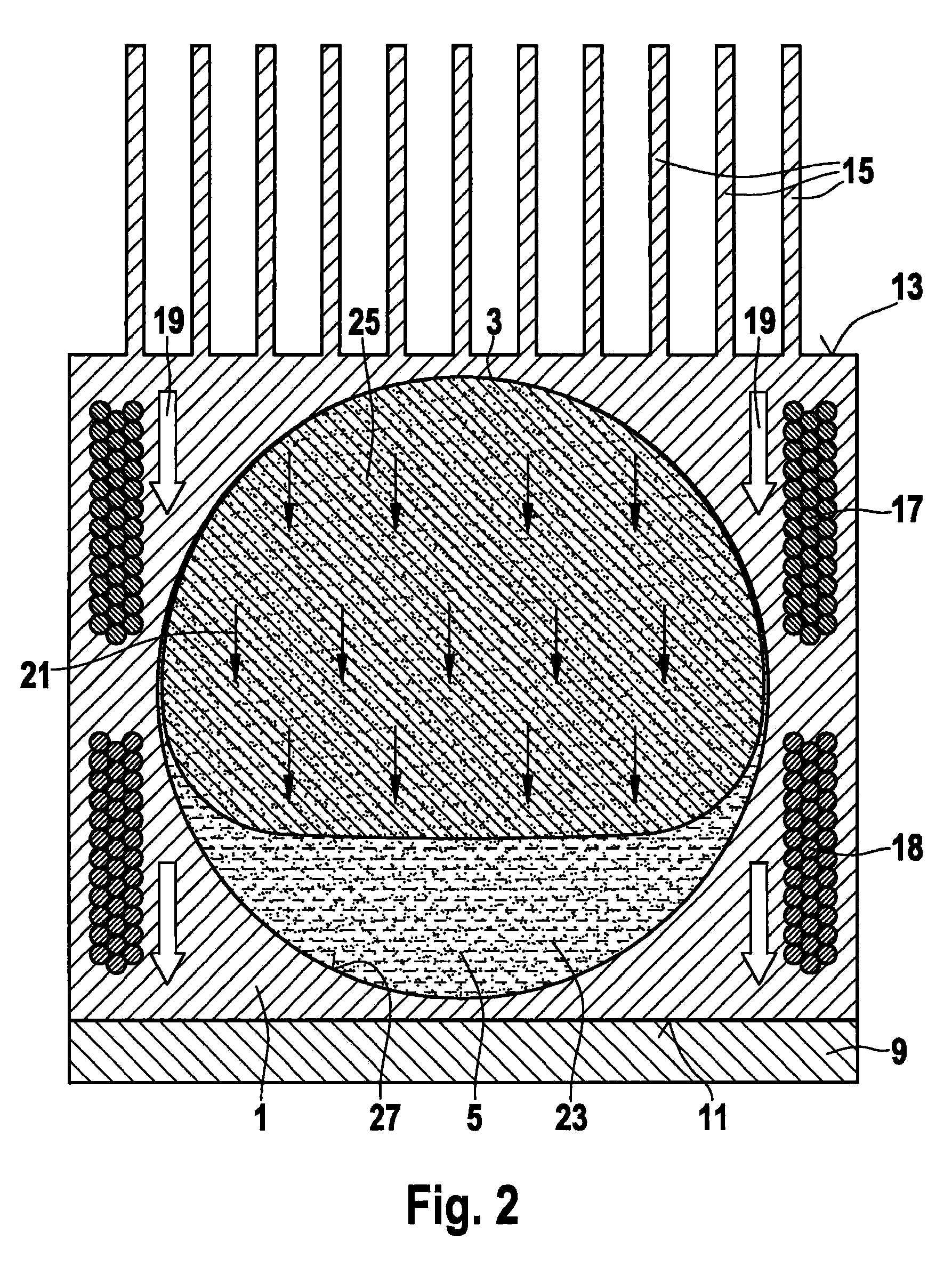
Method of manufacturing an electrowetting-based variable-focus lens
InactiveUS20090021842A1Precise positioningSimple and precise mannerOptical articlesLensElectricityRefractive index
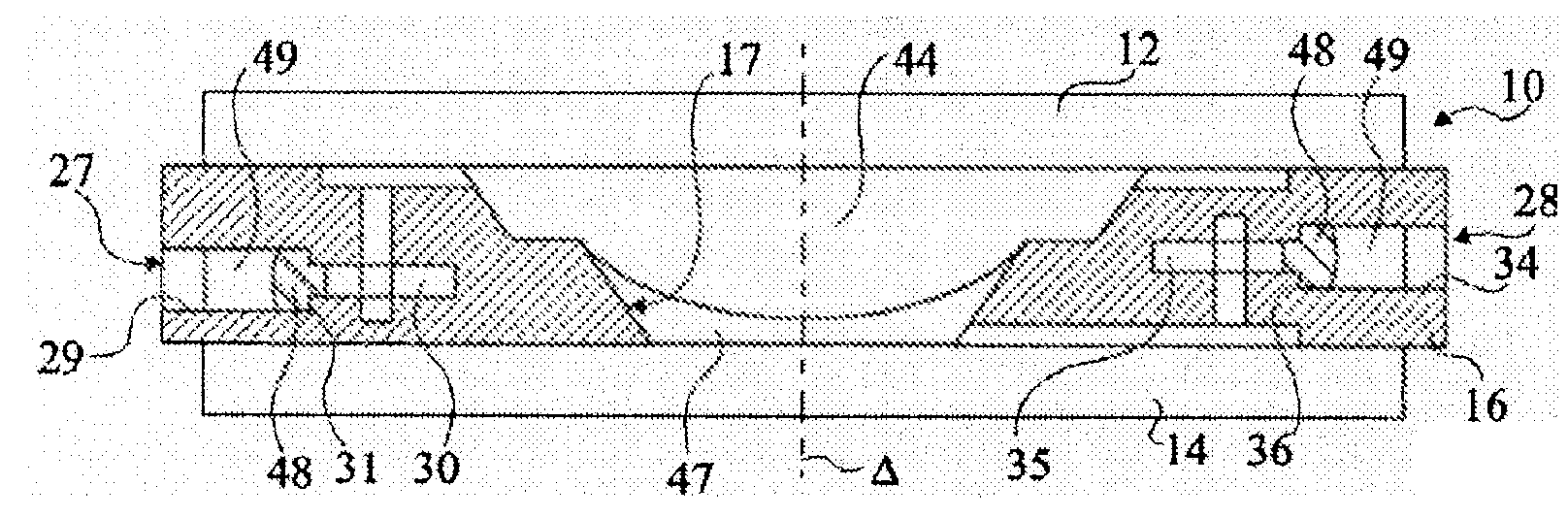
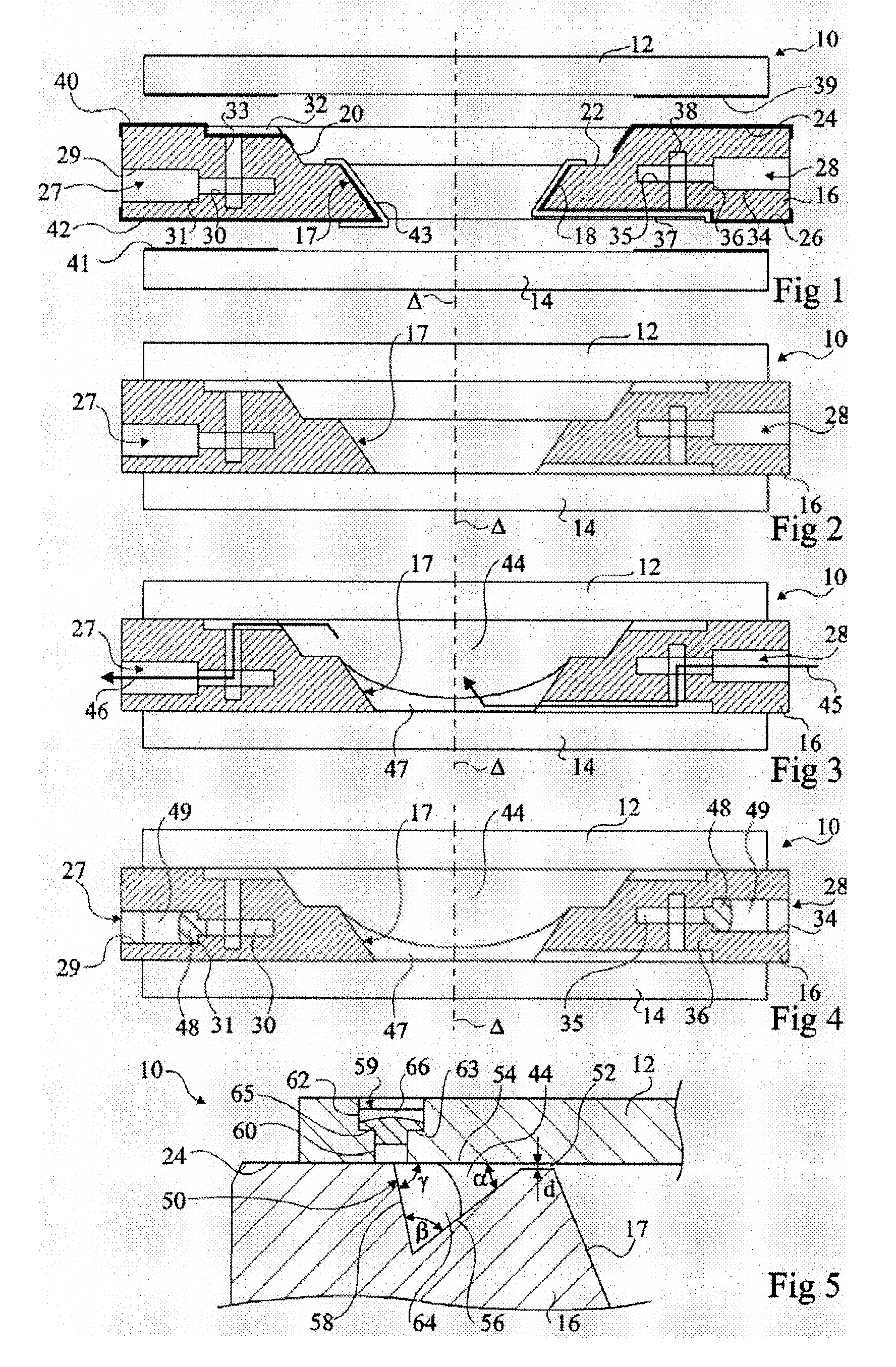
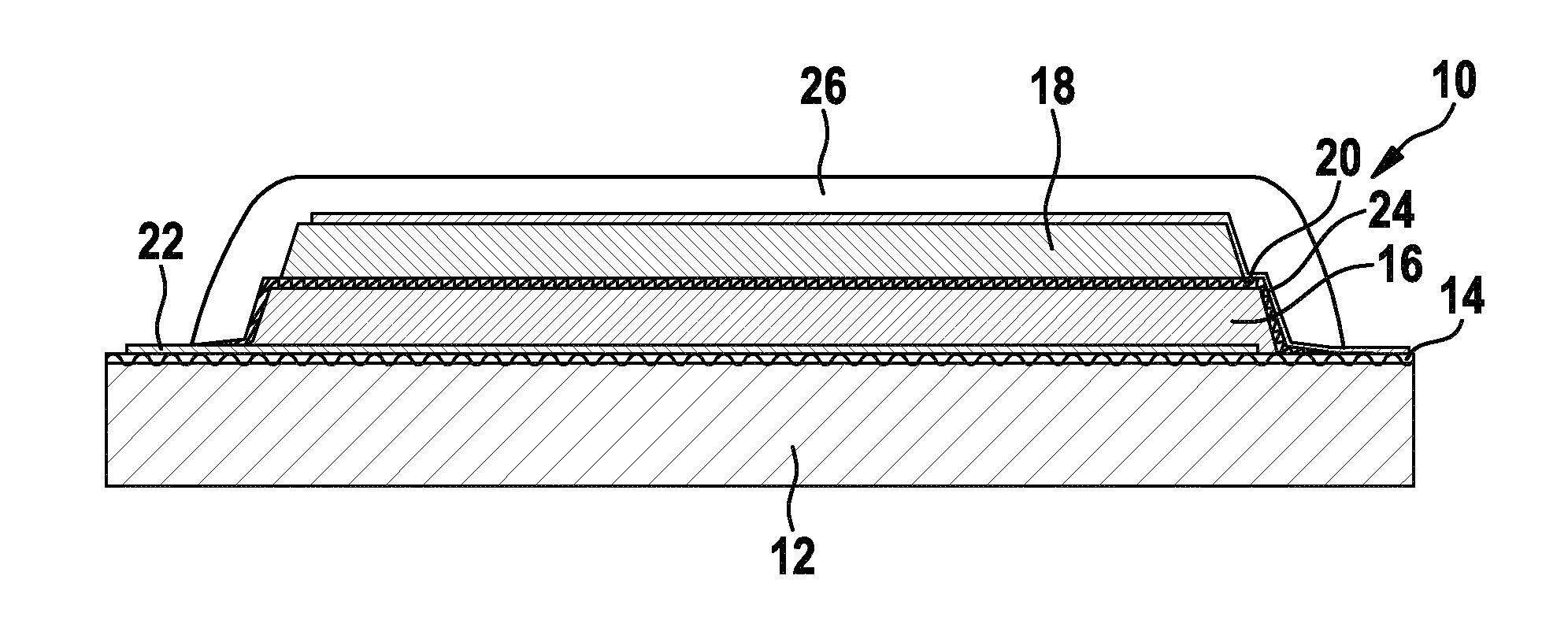
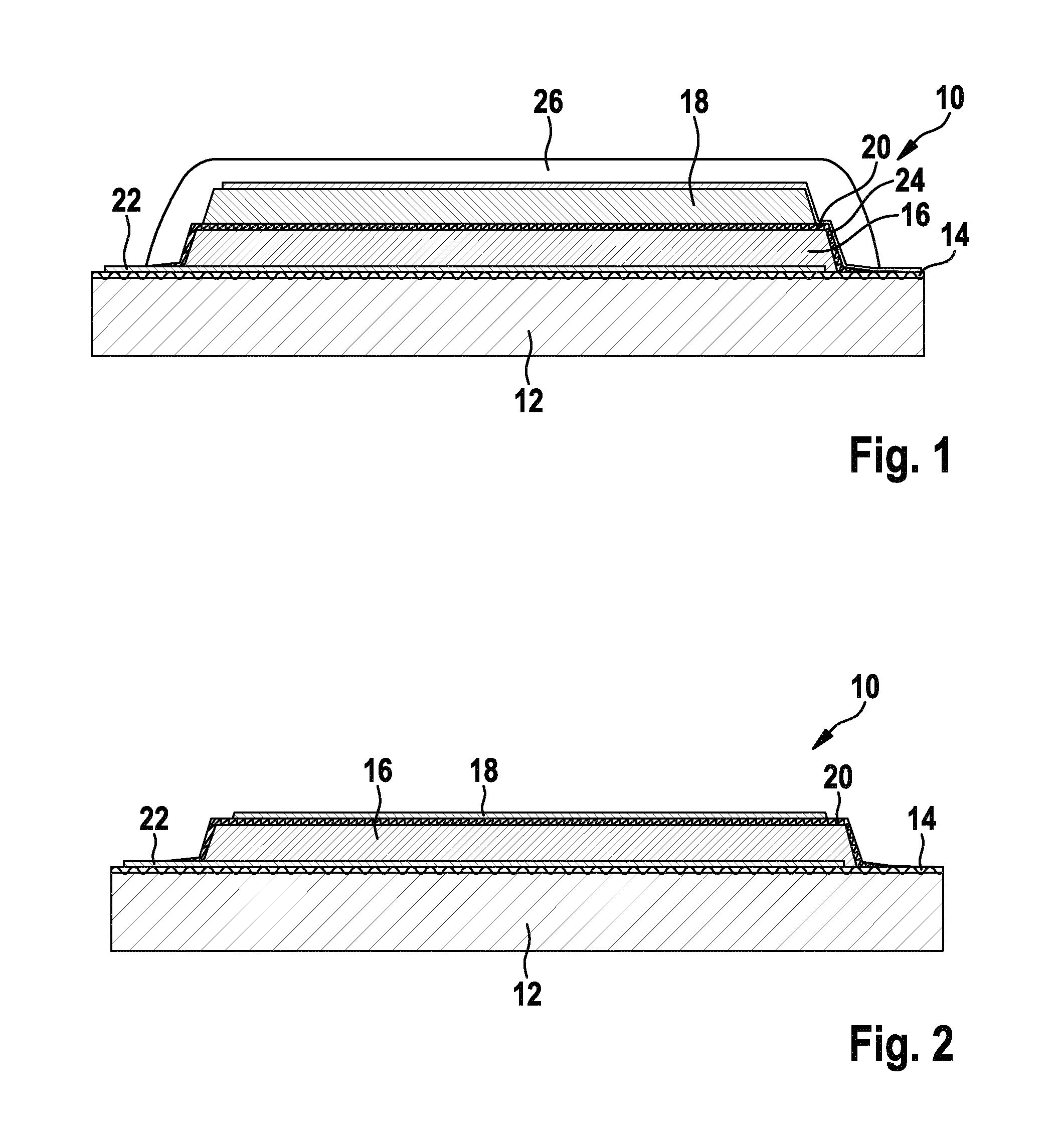
The present invention relates to a method of manufacturing an electrowetting-based variable-focus lens, comprising: (a) providing an enclosure having a cavity (17) and at least one channel (27, 28; 59) communicating at one end with the cavity and at the other end emerging at the exterior surface of the lens; (b) filling the cavity with first and second liquids (44, 47) that are immiscible and of different refractive indices via the channel; and (c) hermetically scaling the channel.
Owner:VARIOPTIC SA
Layer system, energy store, and method for manufacturing an energy store
ActiveUS20140178769A1Increase powerImprove stabilityFinal product manufactureSolid electrolyte cellsSolid state electrolytePhysics
A layer system includes at least three layers, the three layers including a top electrode layer, a bottom electrode layer, and an electrolyte layer situated between the top electrode layer and the bottom electrode layer. The electrolyte layer has a solid-state electrolyte, and at least one of the top and bottom electrode layers includes a paste-like composite layer. A layer system of this type may be used to manufacture in particular energy stores, such as rechargeable lithium-ion accumulators, having an enhanced capacity. Moreover, a method for producing a layer system or an energy store is described.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for the production of structural components from fiber-reinforced thermoplastic material
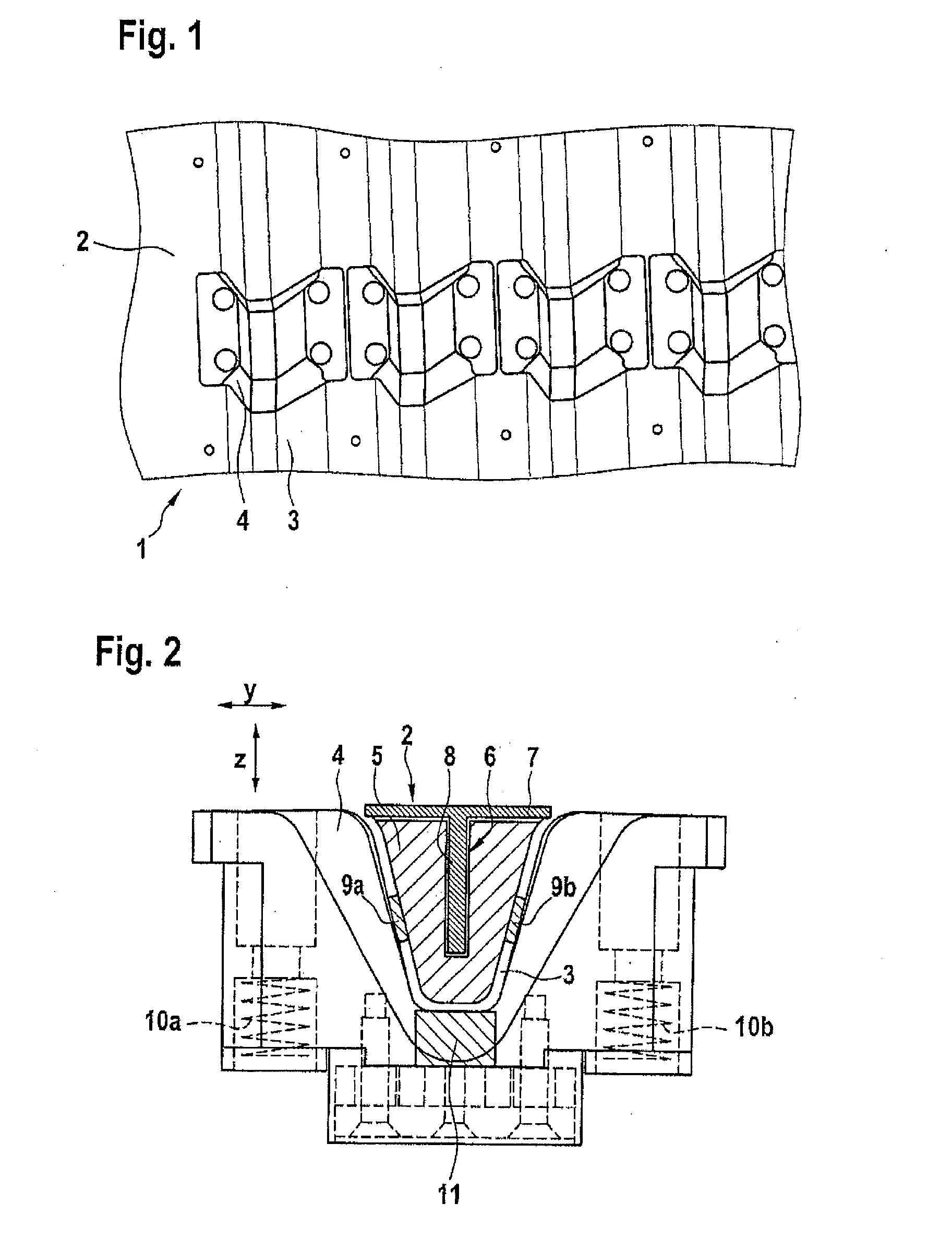
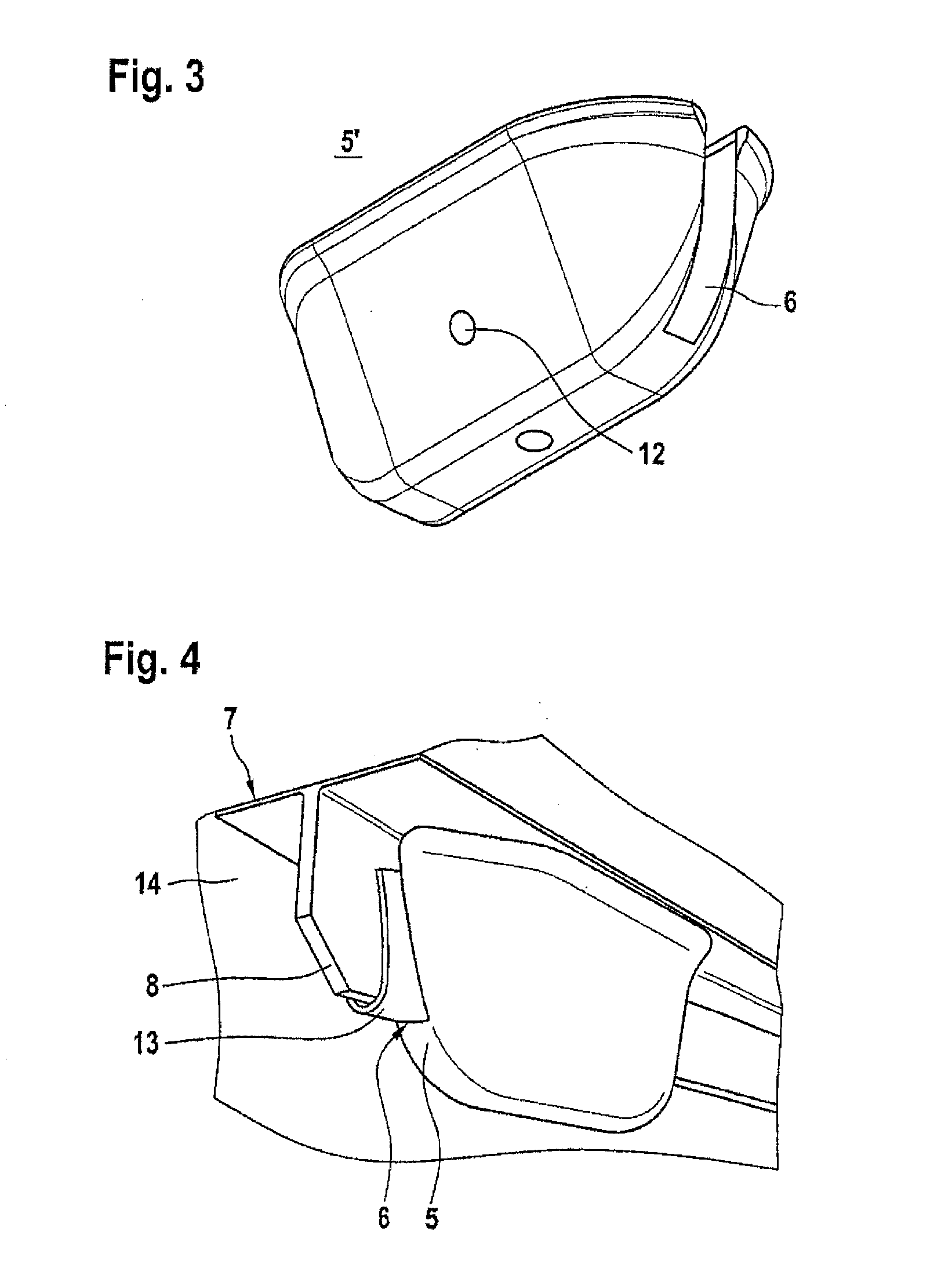
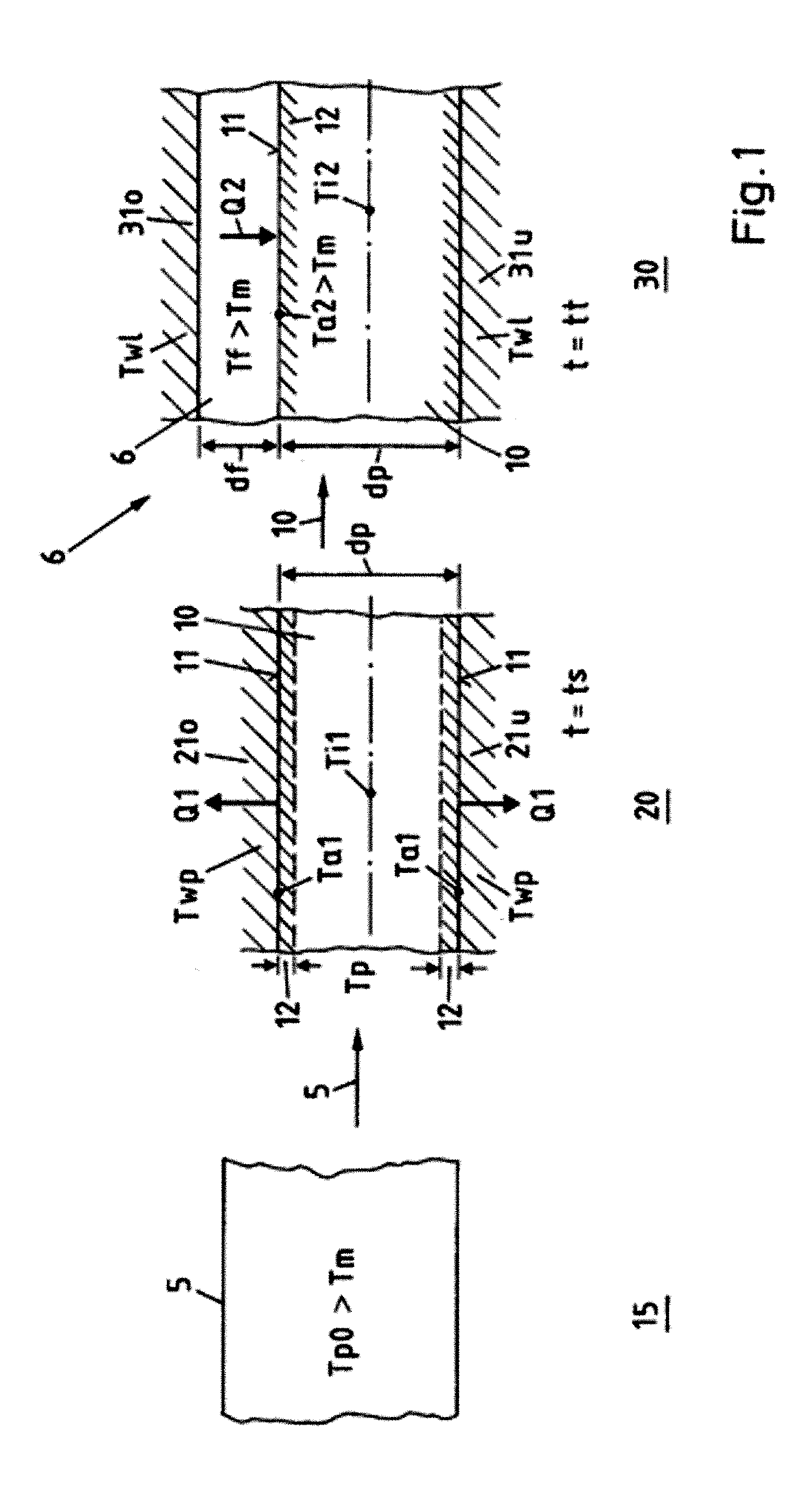
ActiveUS7470388B2Efficient cost-effectiveShort cycleVehicle seatsWood working apparatusSingle stageEngineering
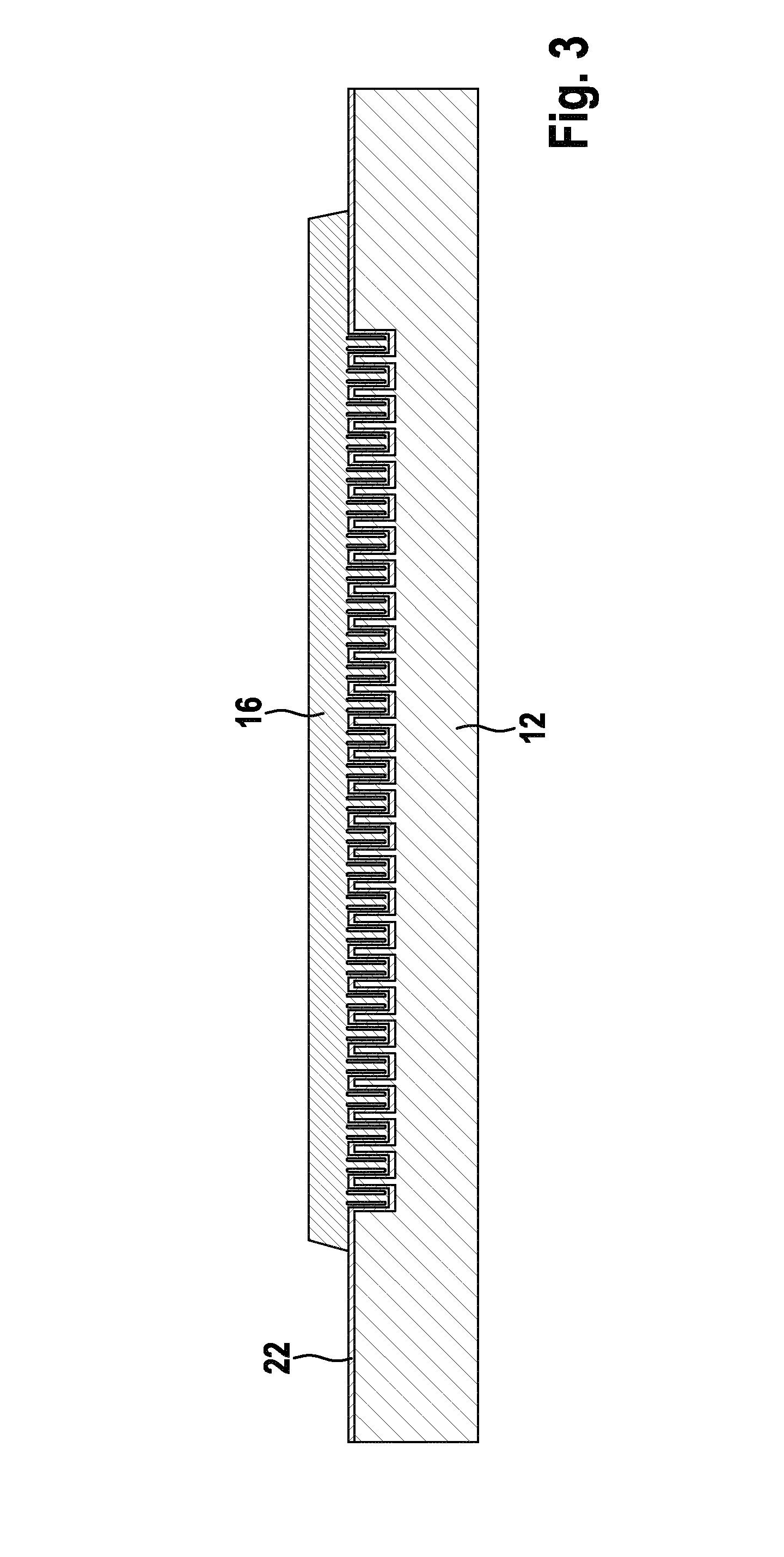
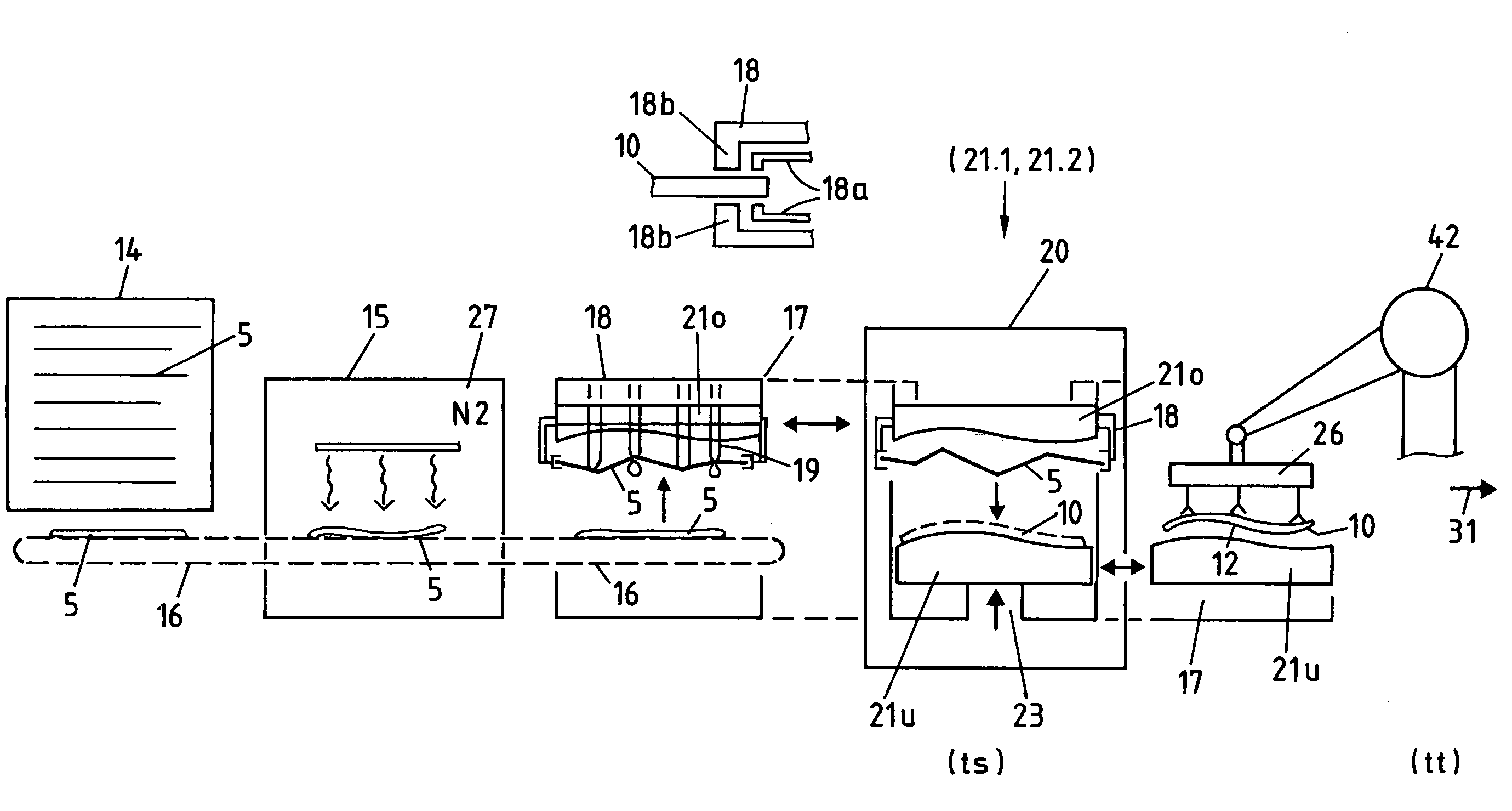
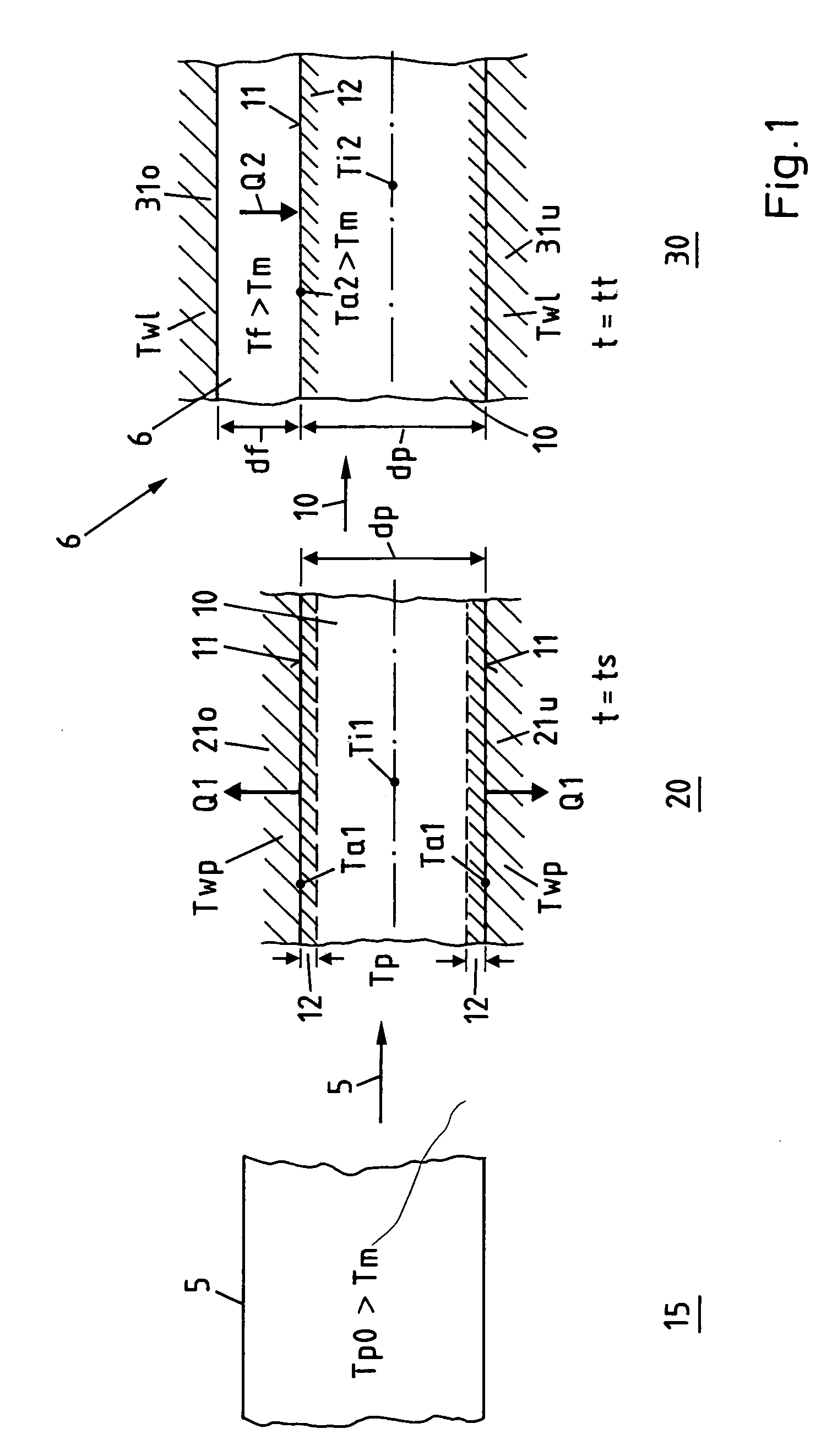
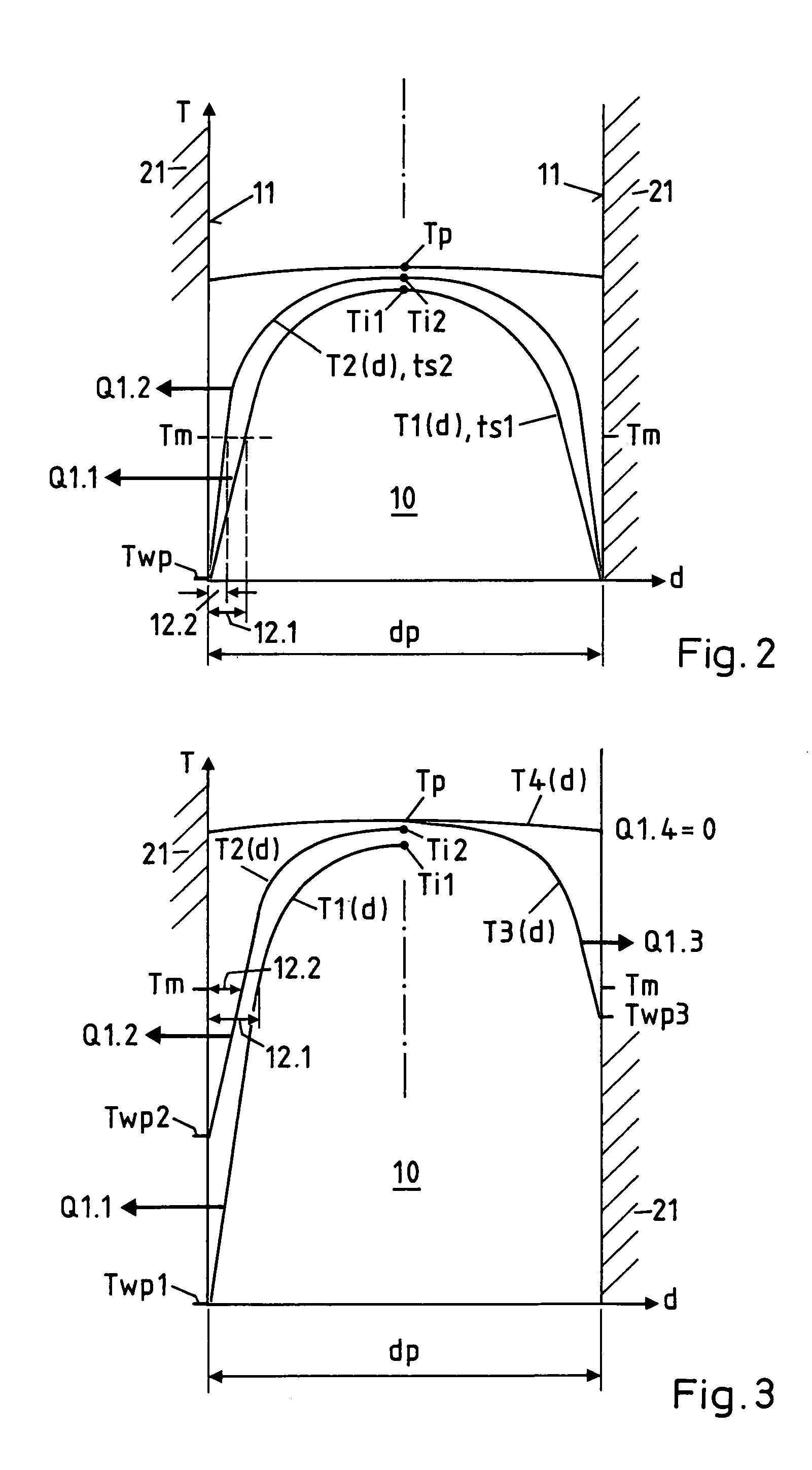
The method enables the series production of light structural components out of long-fiber thermoplastic material (LFT) with integrated continuous fiber (CF)-reinforcements in a single stage LFT-pressing step. In this, CF-tapes (5) are melted open and transferred into a profile tool (21) of a CF-profile forming station (20), there are pressed for a short time period and shaped into the required CF-profile (10). In doing so, by means of contact with the thermally conditioned profile tool (21) on the profile surface (11) a shock-cooled, dimensionally stable, thin casing layer (12) is formed and the inside of the CF-profile remains melted. Following a defined short shock-cooling period (ts), the CF-profile (10) is transferred into an LFT-tool (31) and pressed together with an introduced molten LFT-mass (6). In doing so, the casing layer (12) is melted open again on the surface (11) and is thermoplastically bonded together with the surrounding LFT-mass.
Owner:WEBER TECH
Device for the contactless transfer of electrical energy
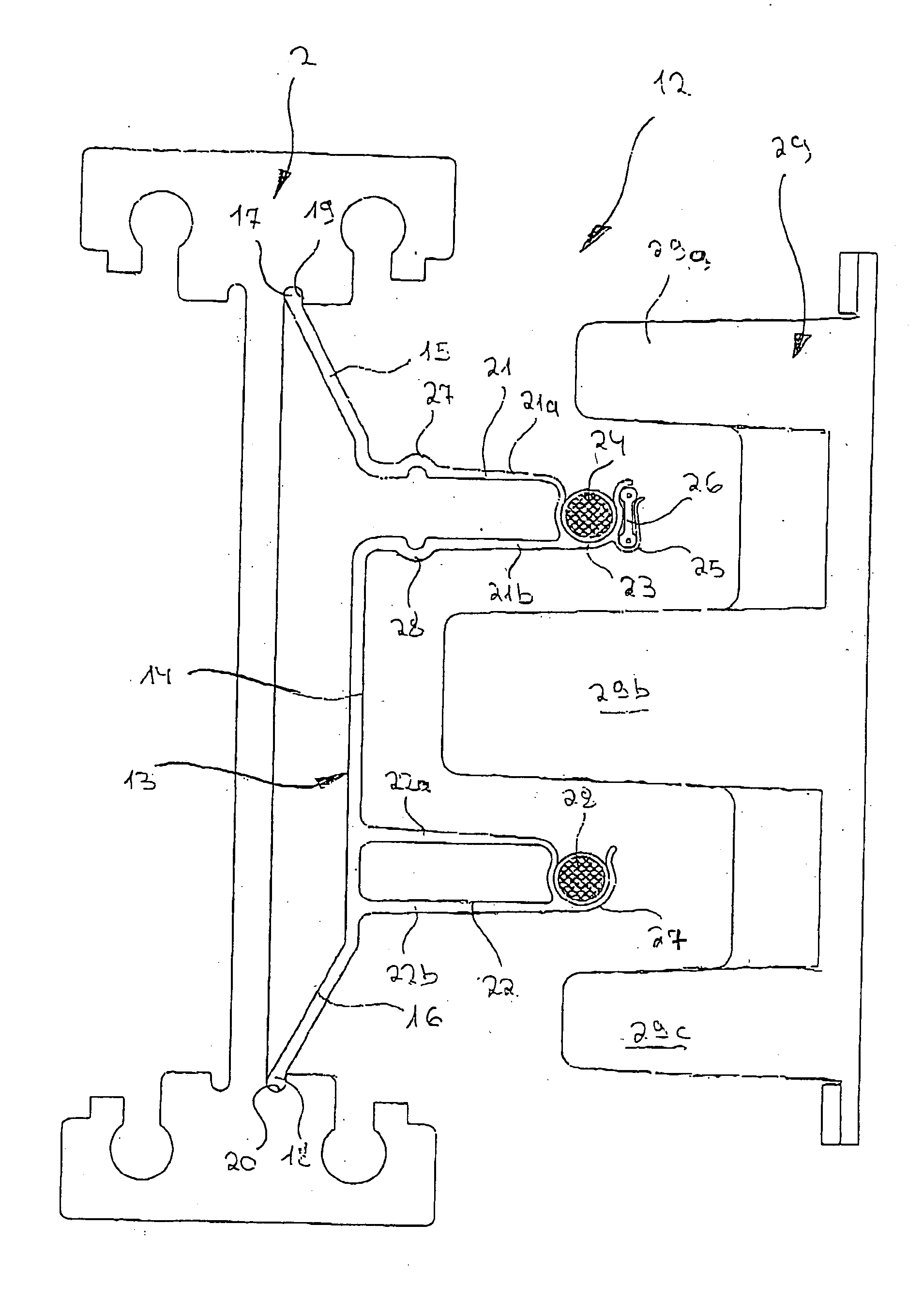
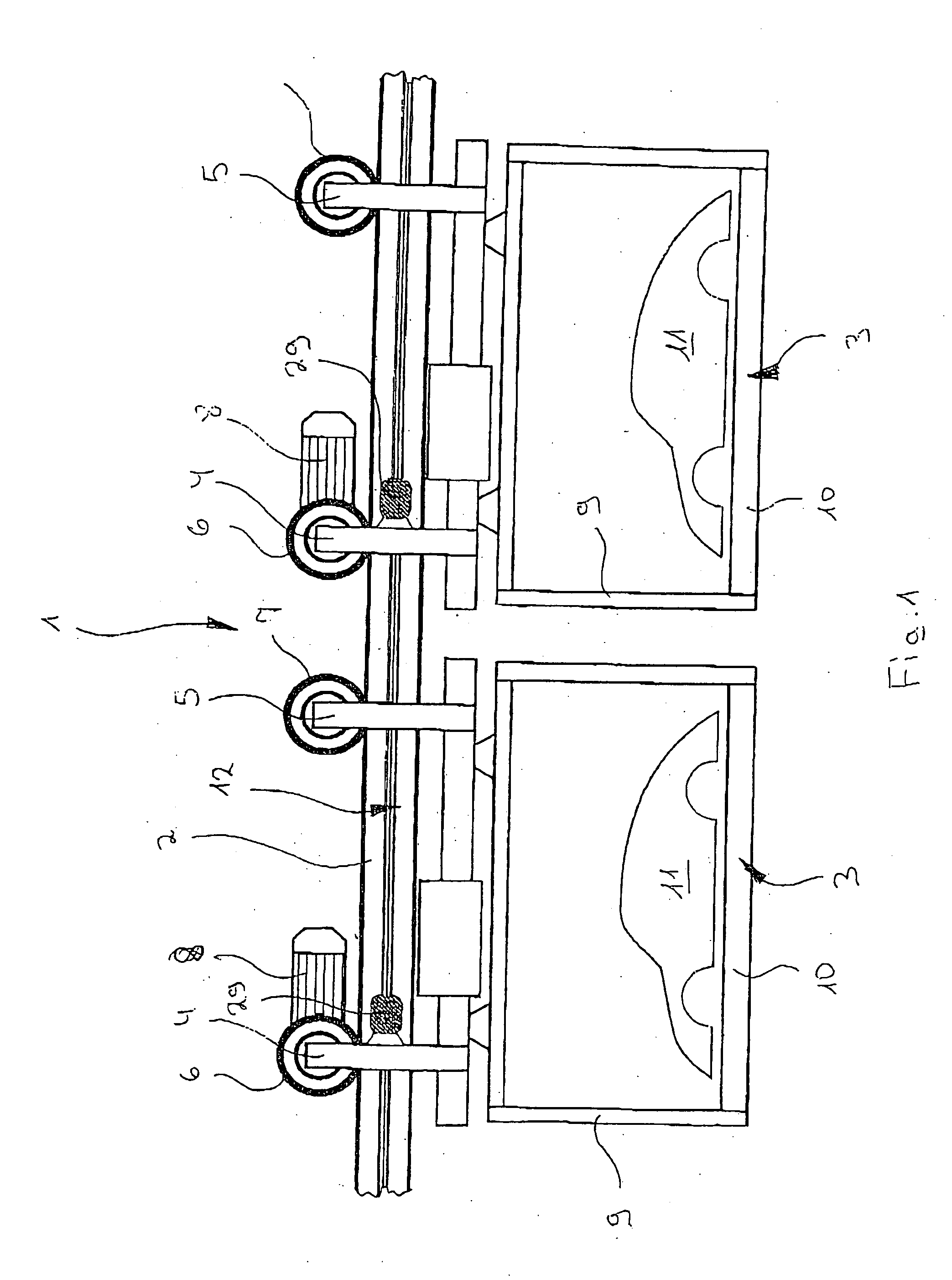
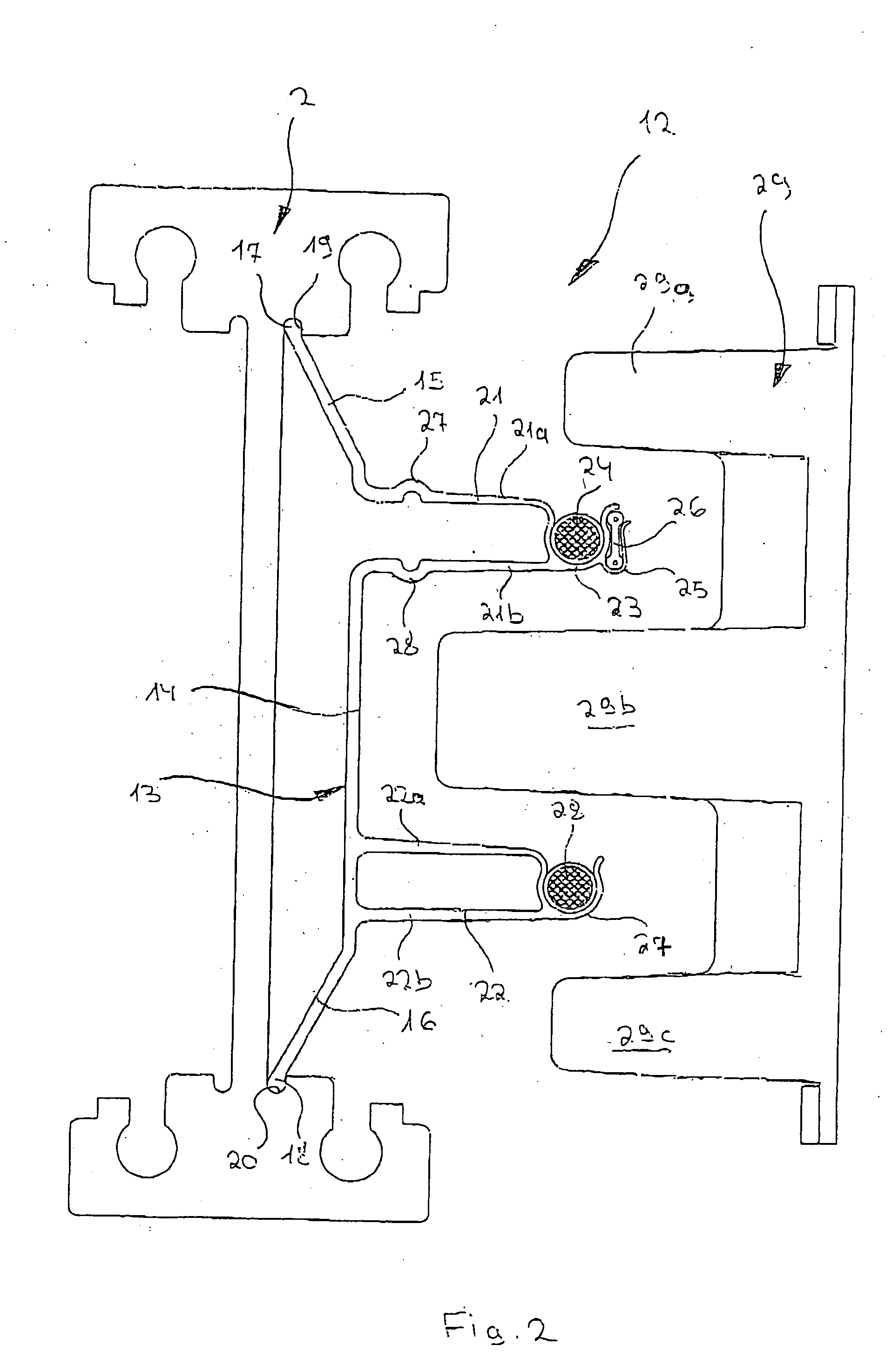
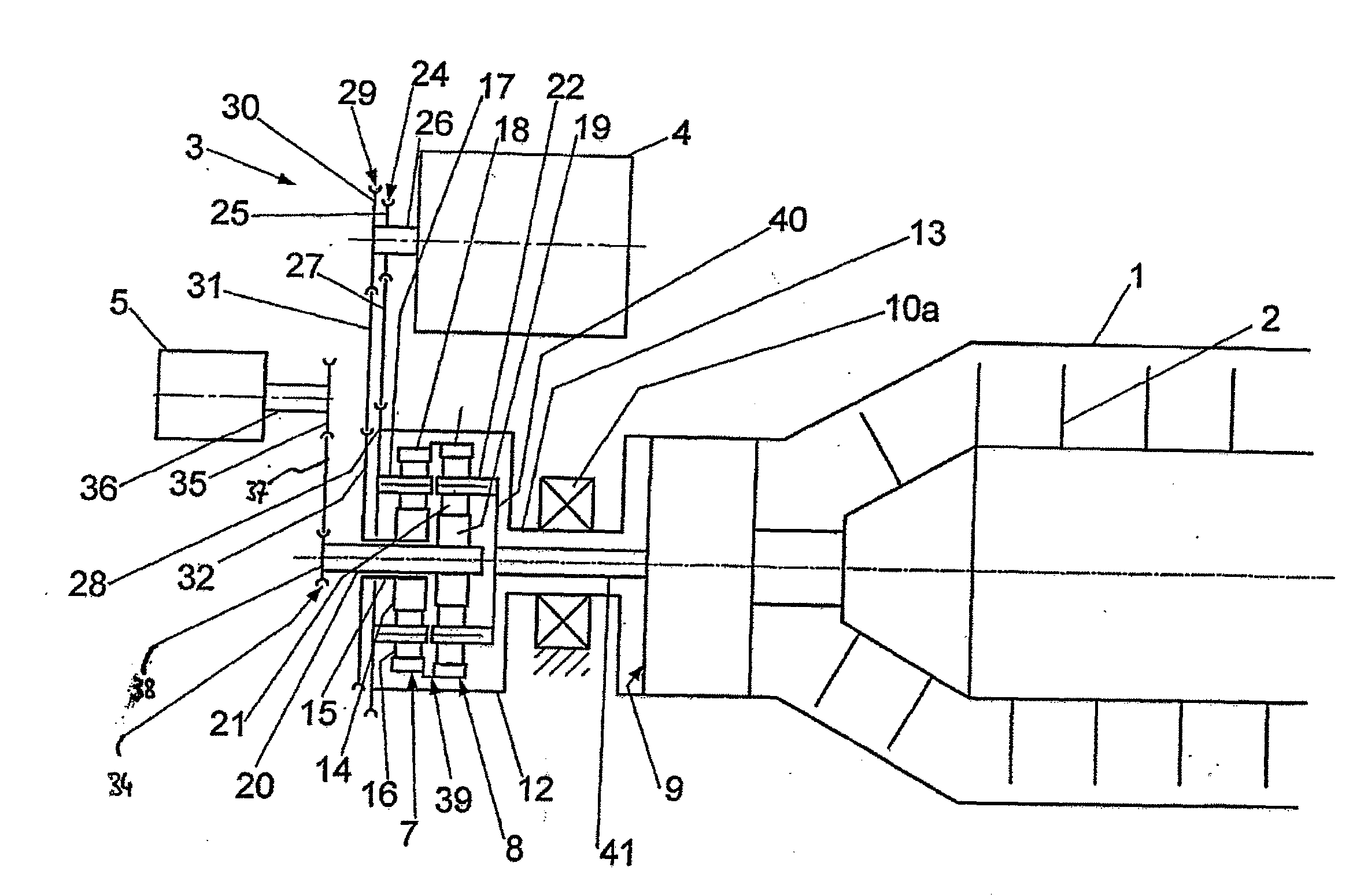
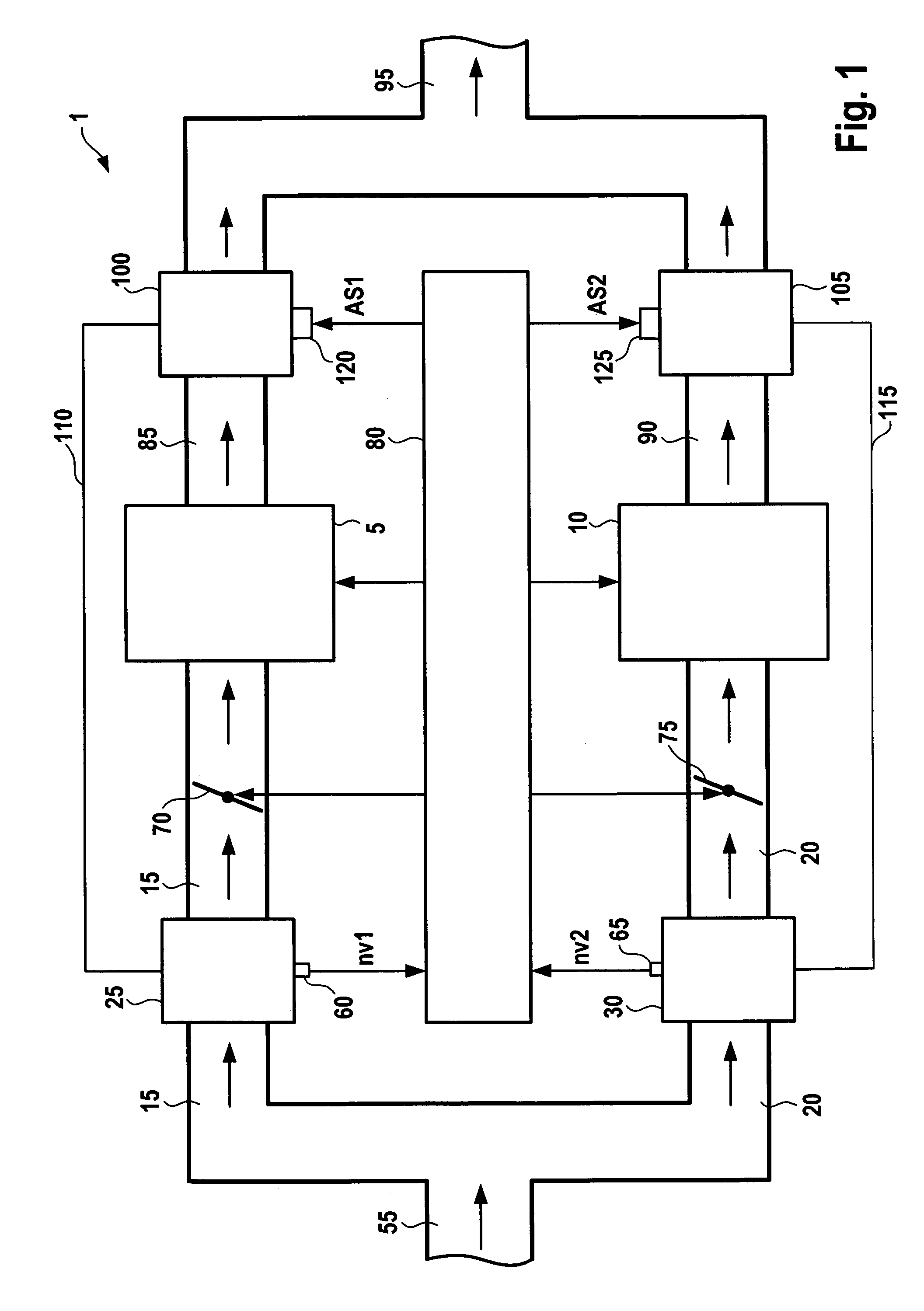
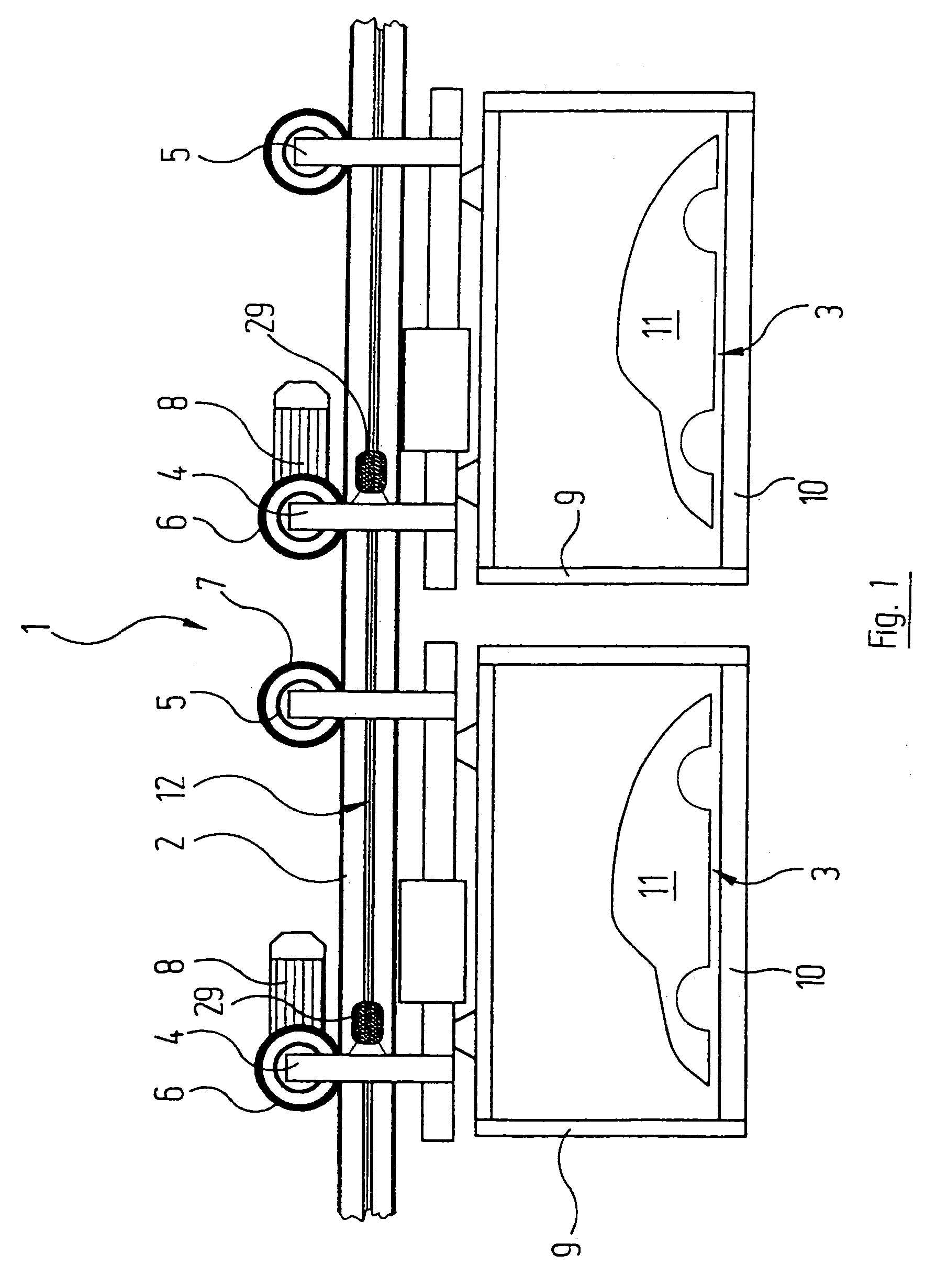
InactiveUS20050098404A1Easily be locked to railSimple and precise mannerRail devicesElectromagnetic wave systemElectric energyHead parts
A device is described with which electrical energy can be transferred from a power cable running along a stationary rail of a transport system to a moving element that can be driven along the rail. Each moving element has for this purpose a transfer head which works inductively together with the power cable. The power cable is attached with the aid of carrier profile which extends substantially along the entire length of the rail and is fixed in a releasable manner to the rail, which element has at least one a trough-like holder open to the side in which the power cable is laid. The power cable is thus relatively easily and accurately laid, avoiding hanging loops of cable which could be damaged by abrasion by the passing transfer heads of the moving elements.
Owner:EISENMANN MASCHENBAU
Helical conveyor centrifuge having a drive device
ActiveUS20090247384A1Accurate settingSimple and compact structureRotary centrifugesToothed gearingsGear wheelScrew conveyor
A helical conveyor centrifuge, such as a solid-bowl or sieve-bowl centrifuge, includes a rotatable drum, a rotatable screw disposed within the drum, and a centrifuge drive for rotating the drum and the screw. The centrifuge drive is configured to set a differential speed between drum and screw. The centrifuge drive includes a first motor, a second motor, and a gearing arrangement disposed between the motors and also between the drum and the screw. The gearing arrangement includes a gearing arranged downstream of the motors and has a first gear, a second gear and a third gear stage. The first and second gear stages include at least four shafts. Torques are either introduced into or are taken off from the first and second gear stages. The first and second gear stages are disposed in a housing and driven by at least three of the at least four shafts.
Owner:GEA MECHANICAL EQUIP
Laser machining device
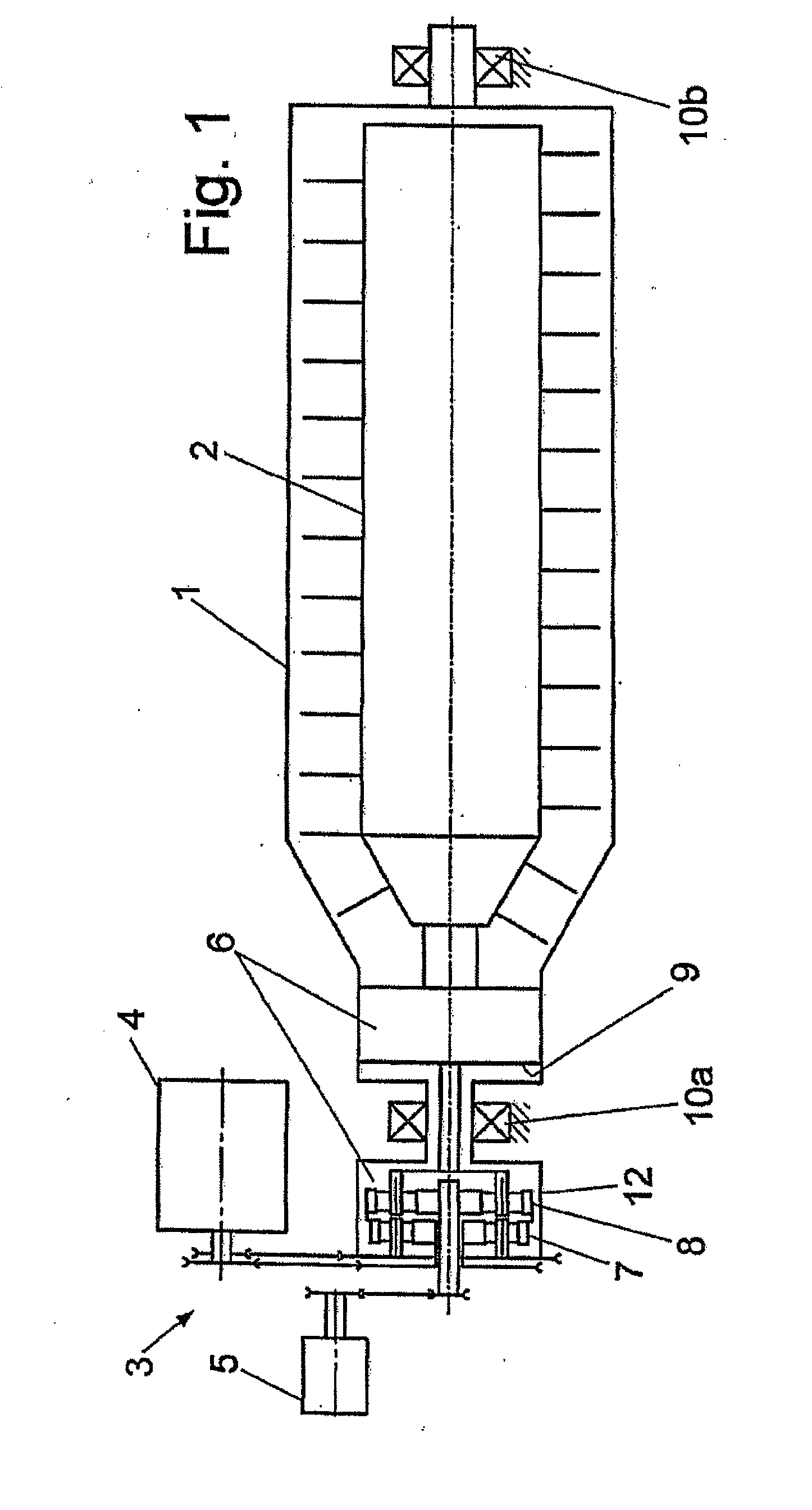
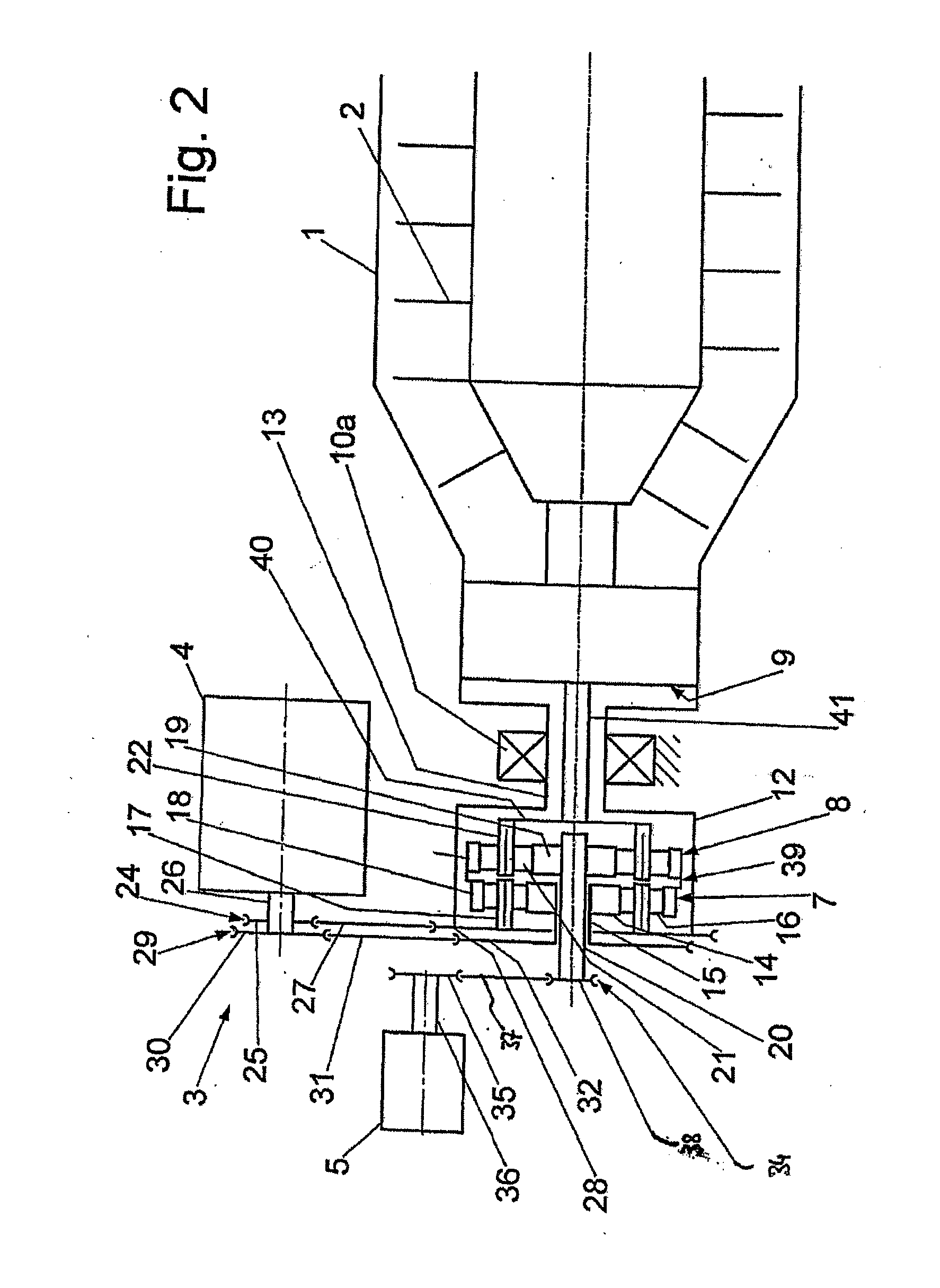
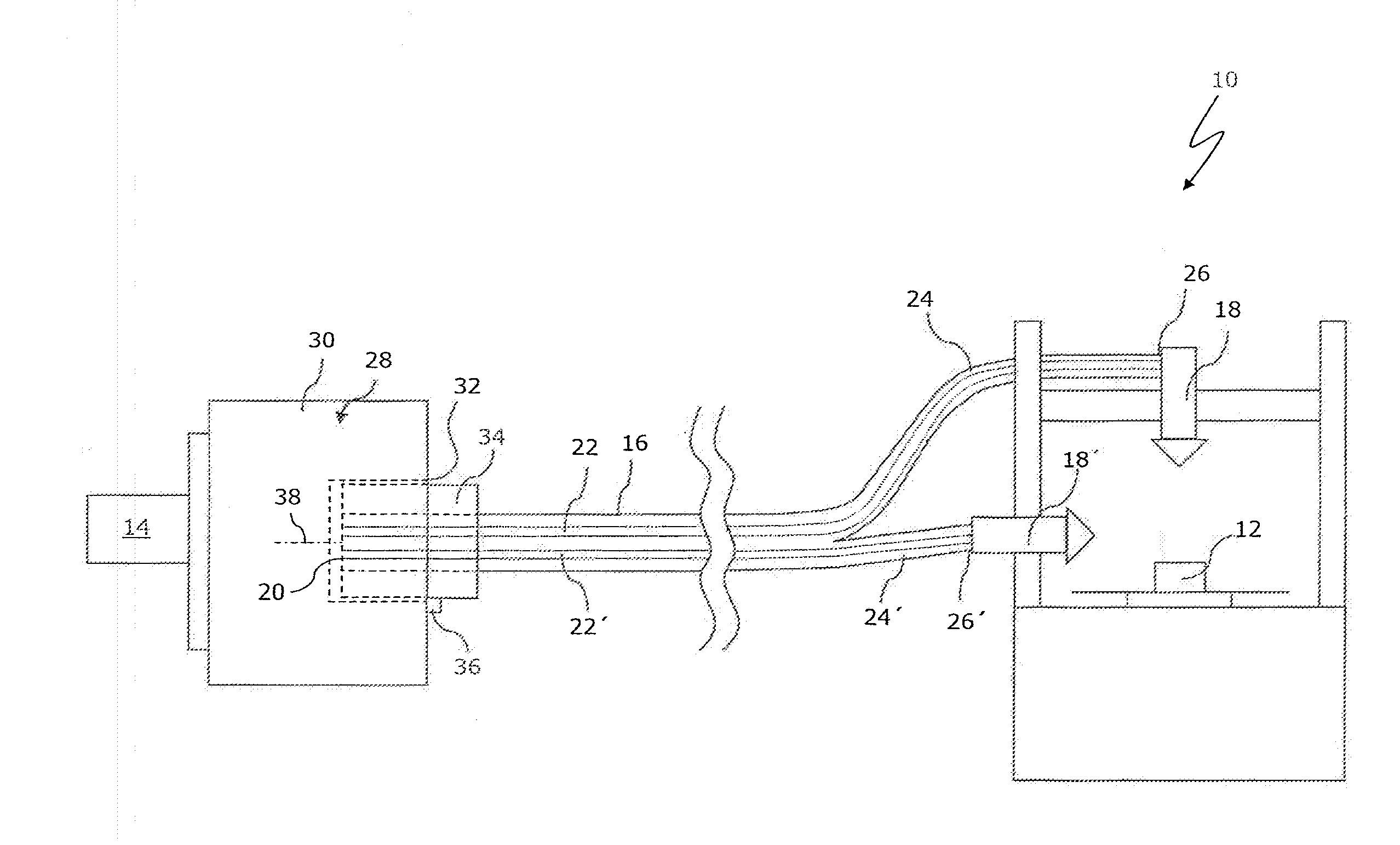
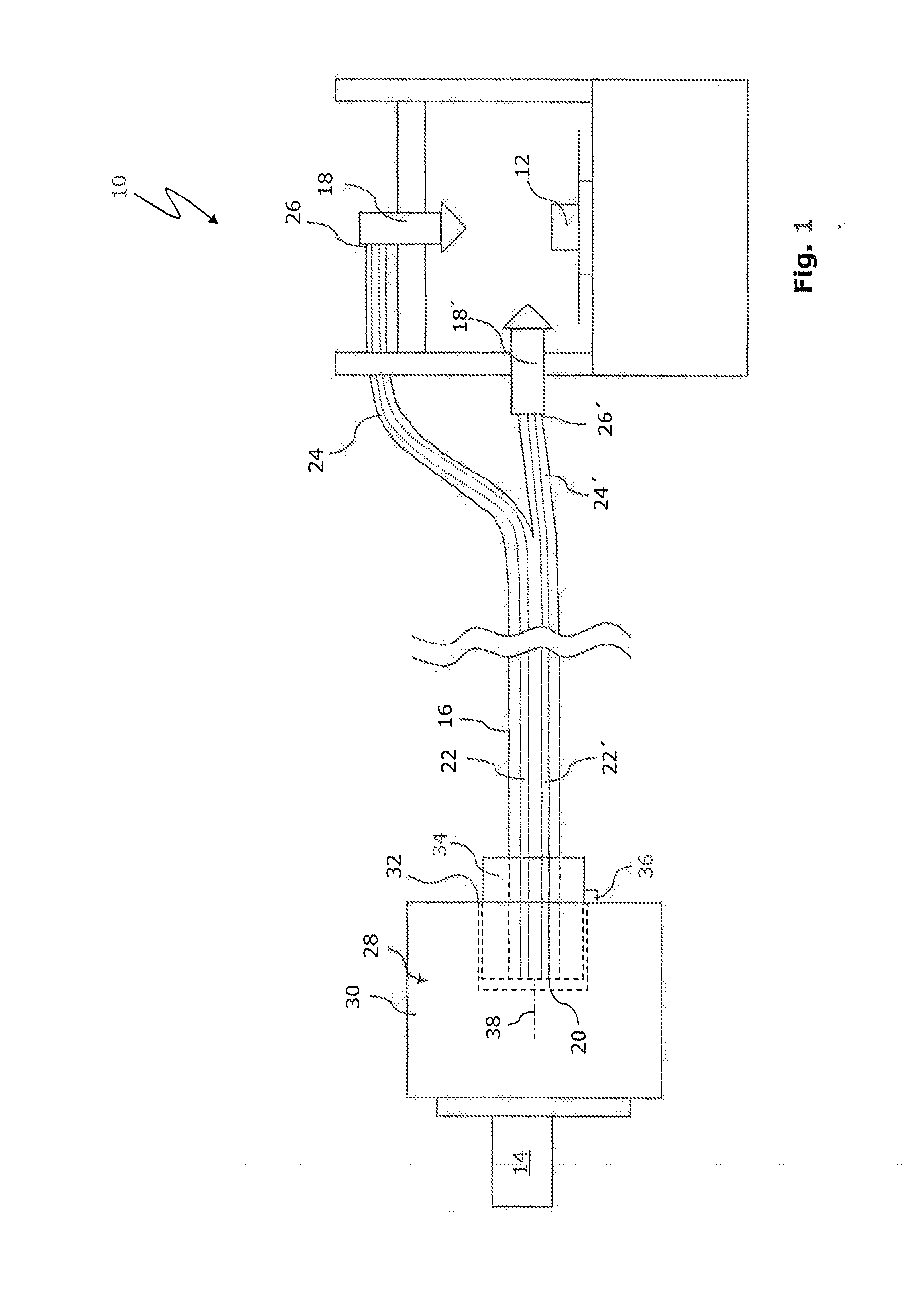
ActiveUS20140021178A1Simple and precise mannerSimple and precise deflectionCoupling light guidesBundled fibre light guideLaser processingOptoelectronics
There is proposed a laser machining device (10) for a laser workpiece machining operation, having a laser (14) for producing laser radiation (50), and having at least two laser tools (18, 18′), to which the laser radiation (50) can be supplied by means of an optical-fibre cable (16). According to the invention, the optical-fibre cable (16) has an input-side end (20) having at least two optical fibre cores (22, 22′) and a plurality of output-side ends (26, 26′) each having one of the optical fibre cores (22, 22′), the optical fibre cores (22, 22′) each being connected to one of the laser tools (18, 18′). A switching device (28) is preferably provided for selectively coupling the laser radiation (50) in one or more of the optical fibre cores (22, 22′) of the optical-fibre cable (16).
Owner:TRUMPF LASERSYST FOR SEMICON MFG
Flap Type Nano/Micro Mechanical Device and Fabrication Method Thereof
InactiveUS20070279140A1Limit thickness of dielectric layerEnsure conductivityWave amplification devicesImpedence networksCMOSCapacitance
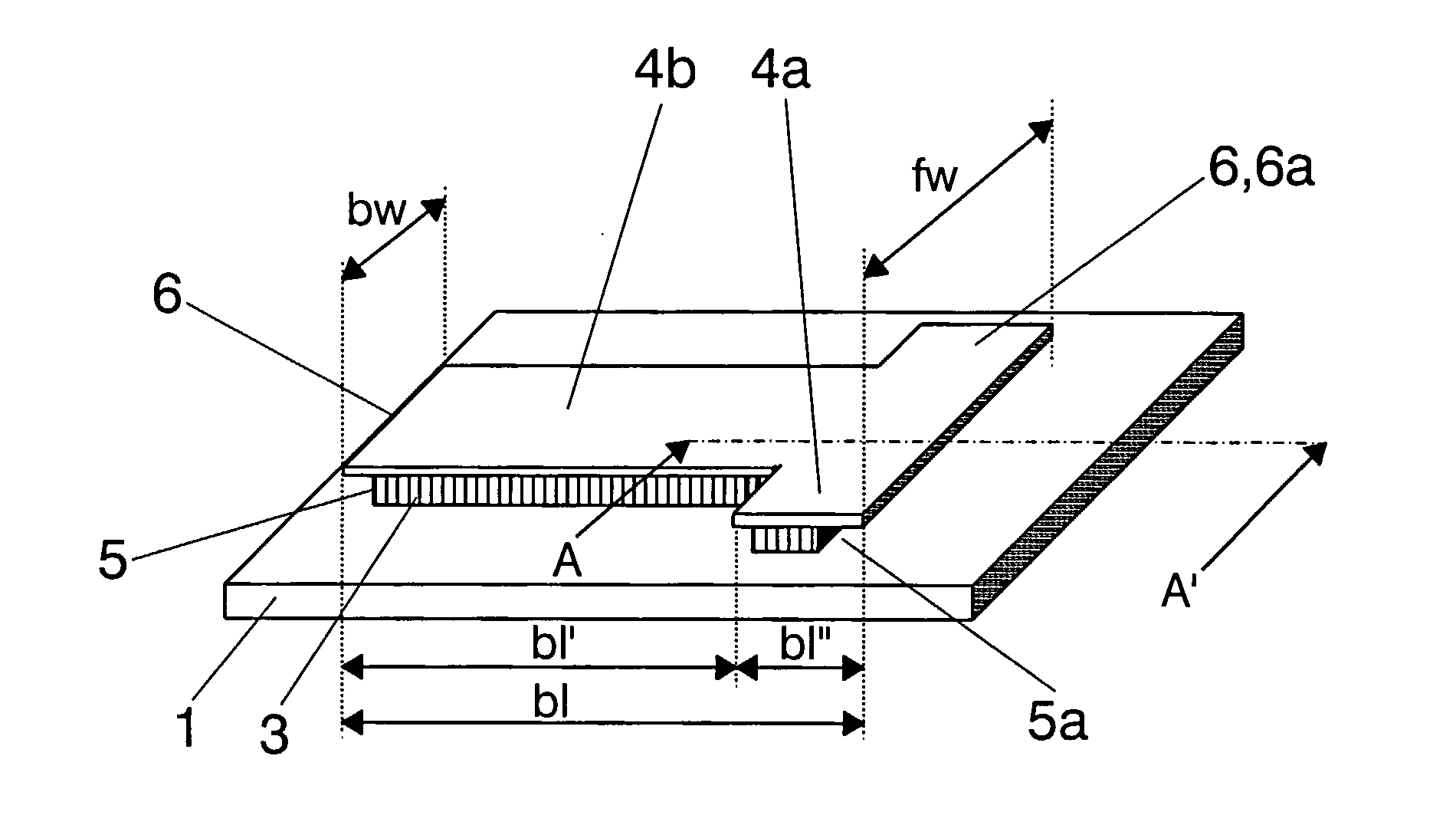
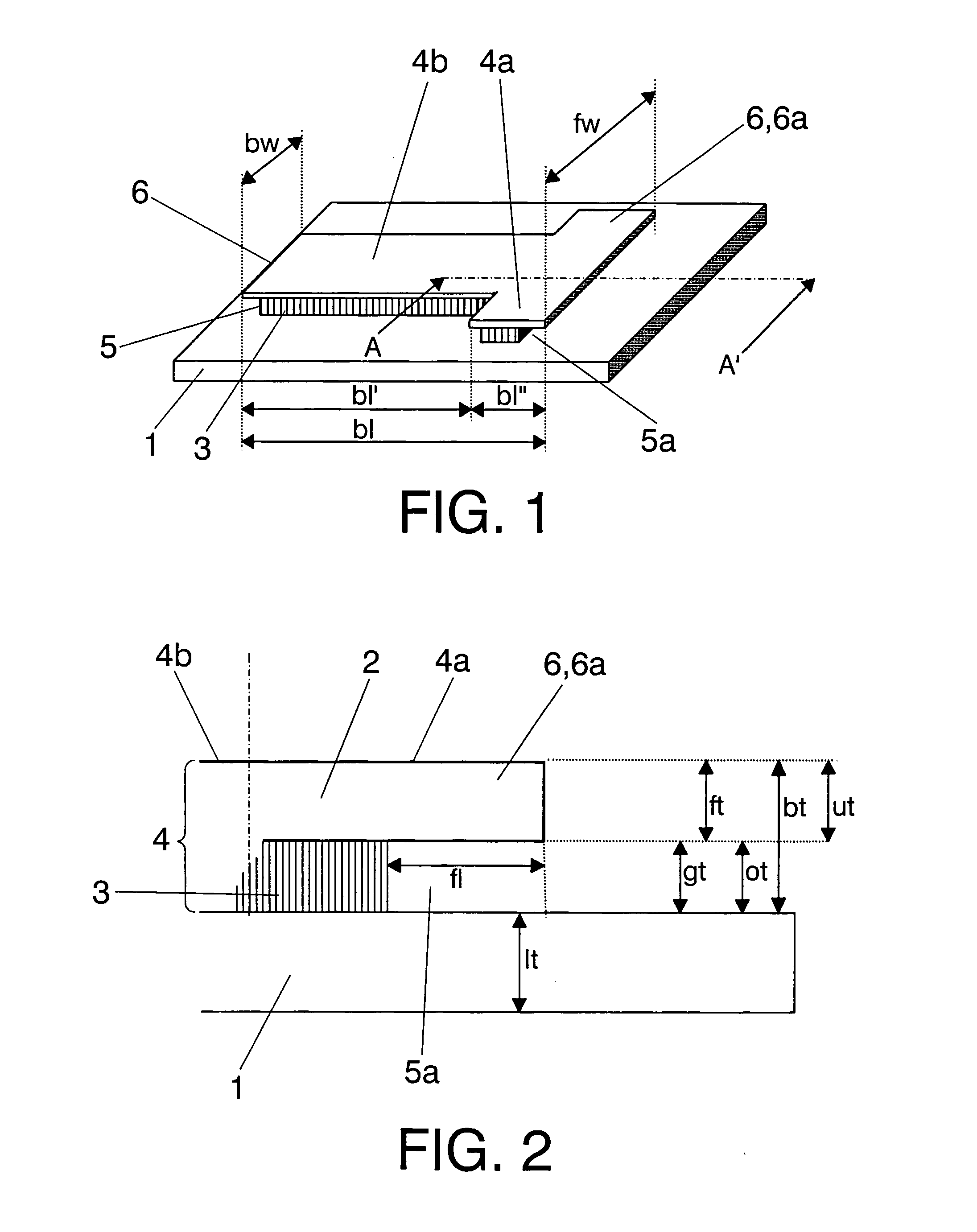
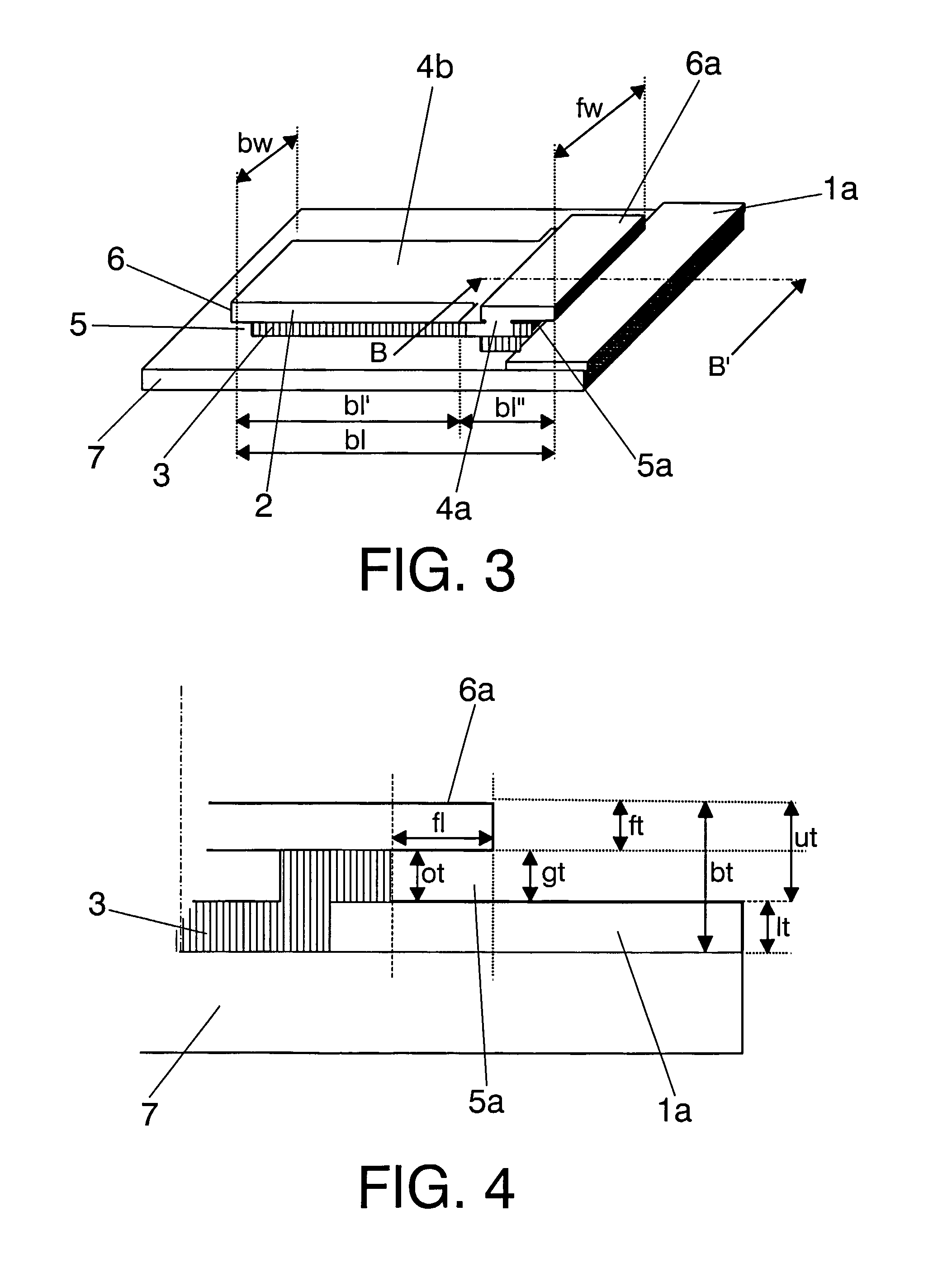
A μ-flap type nano / micro mechanical device with a lower electrode 1,1a, 1b, an upper electrode layer 2, an dielectric layer 3 arranged between the lower electrode 1,1a,1b and the upper layer 2, such that the dielectric layer 3 and said upper electrode layer—2 form a layered body 4, the layered body 4 comprising a horizontal recess 5 in a side portion of the dielectric layer 3, and an overhanging portion 6 of reduced thickness over the recess 5 that forms a gap 5a; such that the overhanging portion 6 forms a μ-flap 6a which extends over the gap 5a. The device is a capacitative-based device in which the mechanical motion can be measured at room temperature and without monolithic integration thereof with an integrated circuit but that can be easily integrated with complementary metal oxide semiconductor (CMOS) circuitry.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method for partial lamination of flexible substrates
InactiveUS20130316122A1Simple processPrecise positioningLamination ancillary operationsOrnamental structuresEngineering
Owner:HERAEUS PRECIOUS METALS GMBH & CO KG
Electrical limitation of a steering gear travel path
InactiveUS20130124043A1Easy to repeatSimple and precise mannerDigital data processing detailsSteering initiationsLimit valueControl theory
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Folding unit having a folding roller adjustment means
InactiveUS20050239624A1Simple and precise mannerMechanical working/deformationFunction indicatorsMeasurement pointEngineering
A folding unit has at least one pair of folding rollers including an adjustable folding roller and a stationary folding roller or two adjustable folding rollers. At least two pressure measuring devices are associated to one adjustable folding roller, the pressure measuring devices being arranged at a distance from one another and measuring pressure values when a sheet passes therethrough. The pressure values correspond to pressures which are exerted on said sheet by the adjustable folding roller at two measurement points which are spaced apart transversely with respect to a sheet running direction. The pressure measuring devices forward measured pressure values to a processing device. Each adjustable folding roller is connected kinematically to a corresponding drive at two connection points which are spaced apart transversely with respect to the sheet running direction. The drives are controllable by the processing device on the basis of the pressure values measured by said pressure measuring devices during the sheet pass, in order to attain an optimum roller nip width between the folding rollers.
Owner:MASCHEBAU OPPENWEILER BINDER
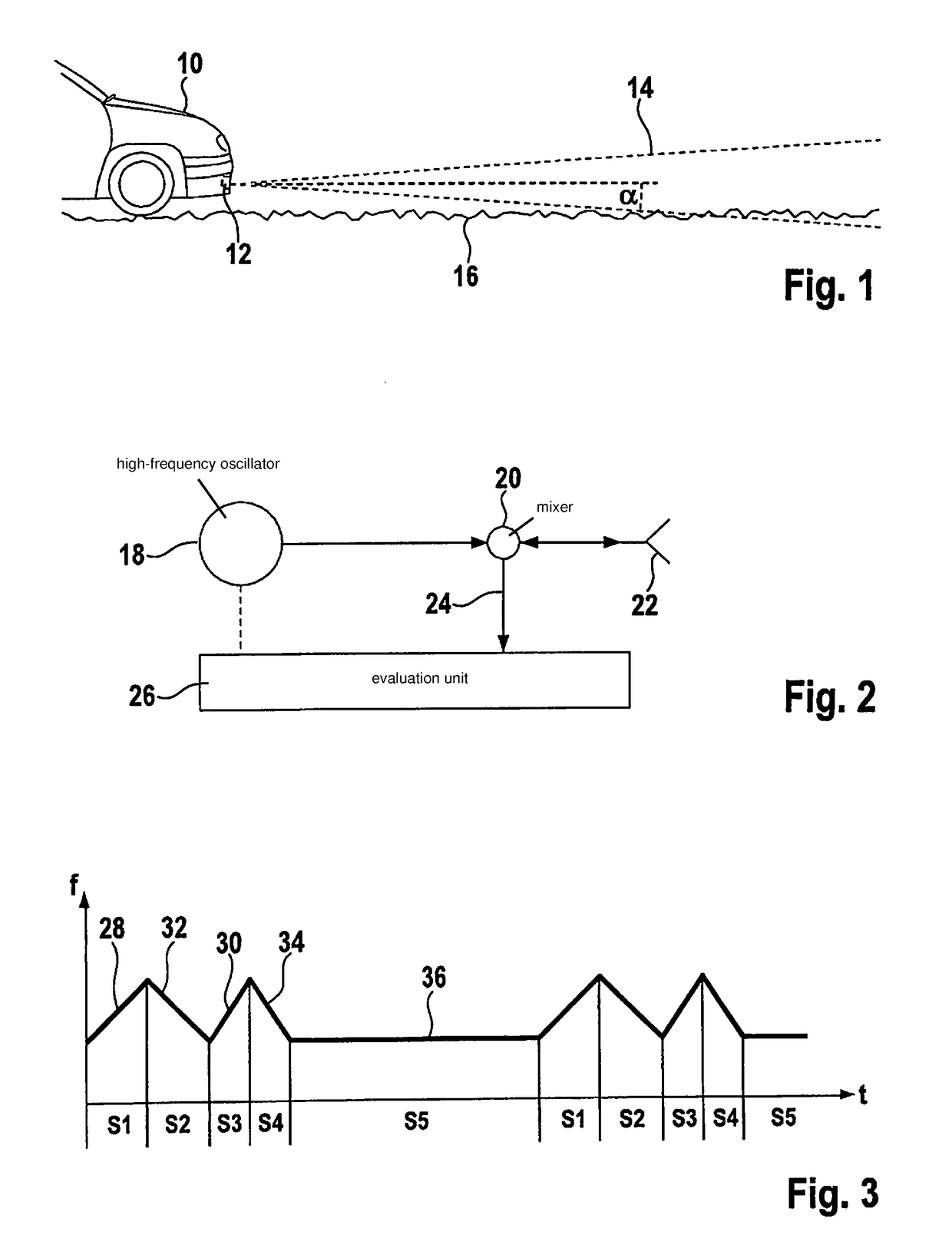
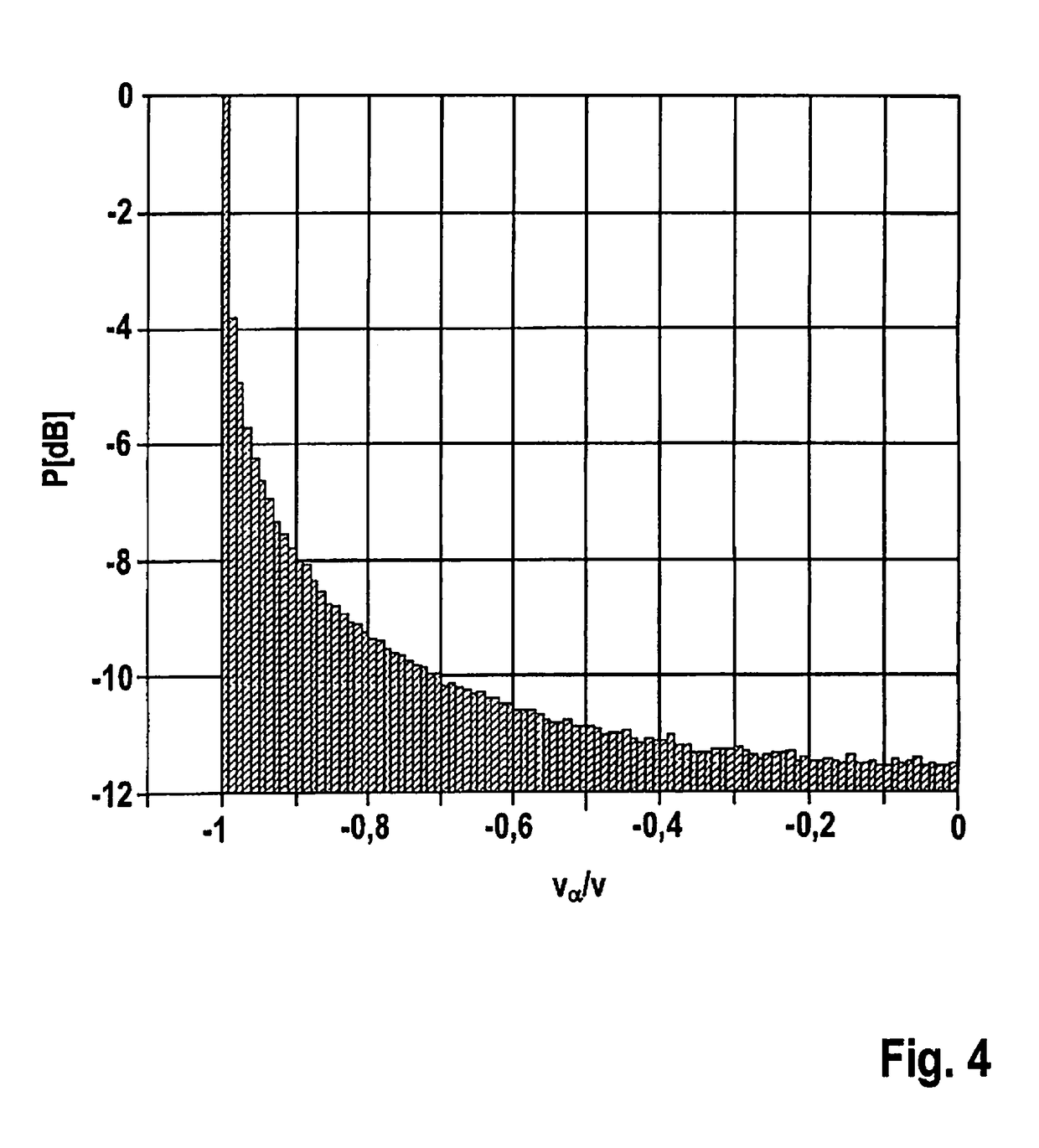
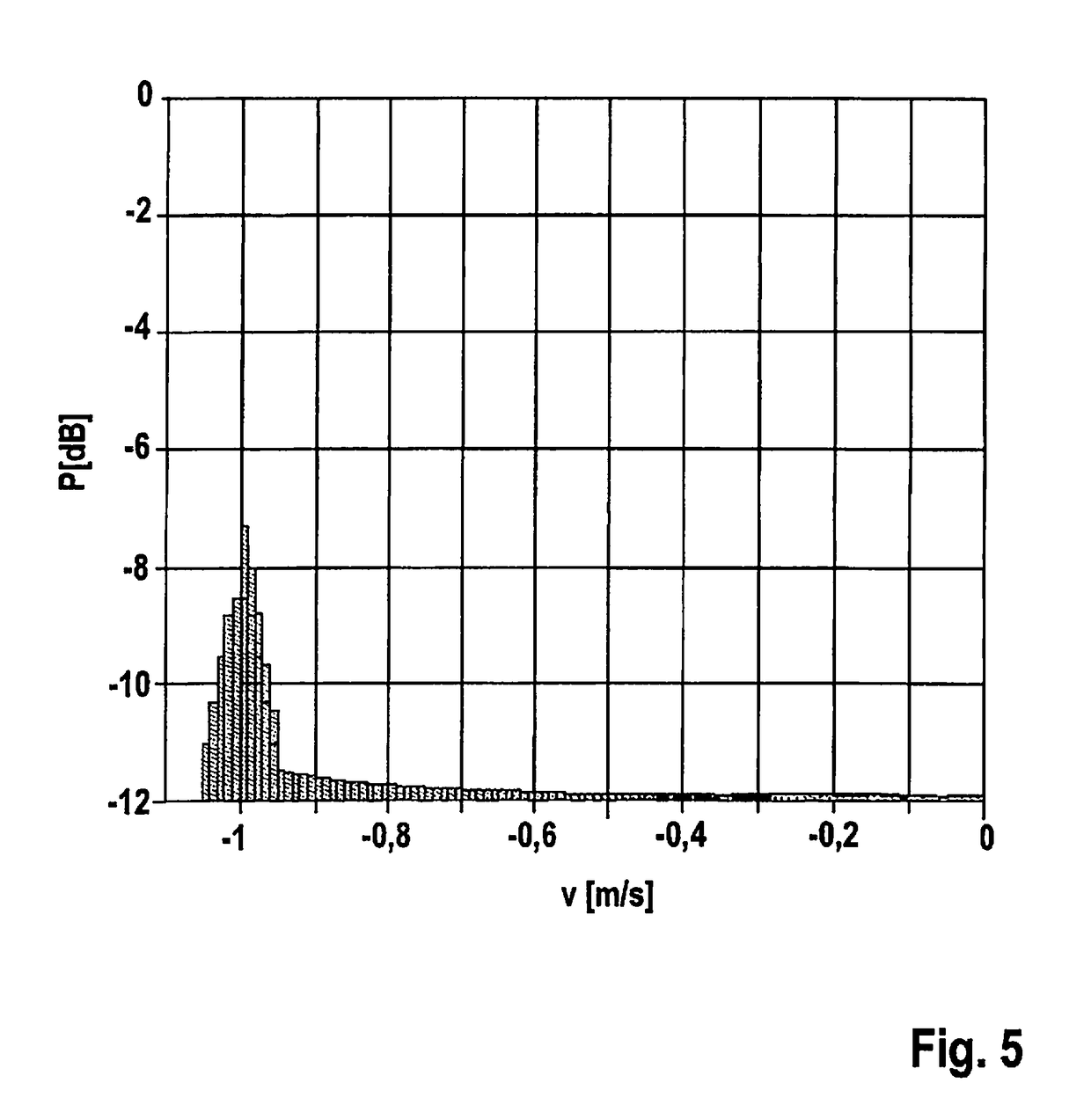
Fmcw radar sensor for motor vehicles
ActiveUS20180356511A1Simple and precise mannerHighly accurate mannerRadio wave reradiation/reflectionModulation patternRadar
An FMWC radar sensor for motor vehicles, having a high-frequency oscillator, which is developed to generate a frequency-modulated transmit signal that has a periodically repeating series of modulation sequences having different modulation patterns, and having an evaluation device for evaluating the received radar echo according to the FMCW principle, wherein the series of the modulation sequences includes a special class of modulation sequences whose duration is longer than that of any other modulation sequence not belonging to this class and whose frequency swing is smaller than that of any other modulation sequence, and the evaluation device is developed to carry out a measurement of the ego velocity of the vehicle on the basis of a radar echo that is received from non-moving objects during the modulation sequences that belong to the special class.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Apparatus for the production of an aircraft fuselage shell consisting of a fibre composite
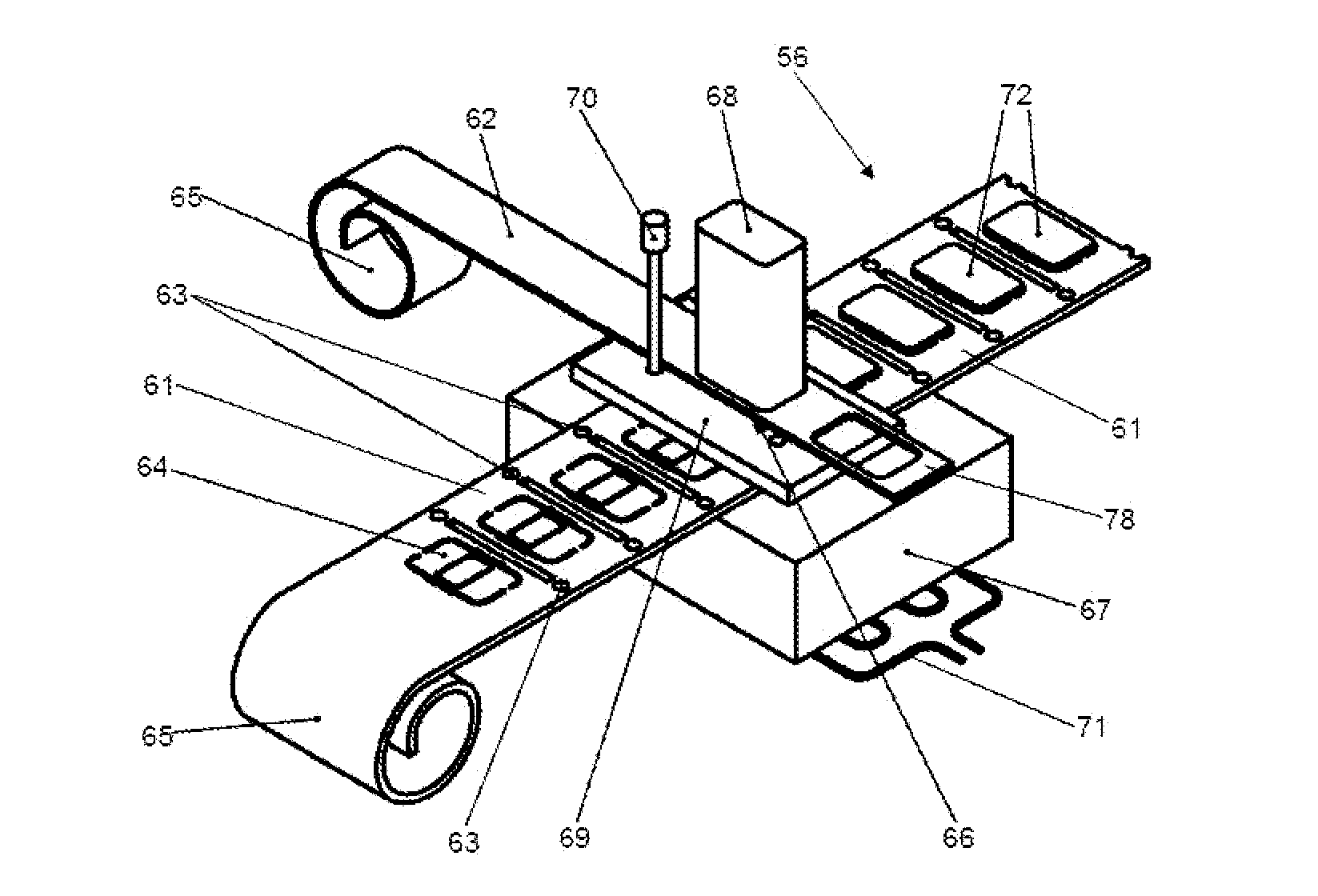
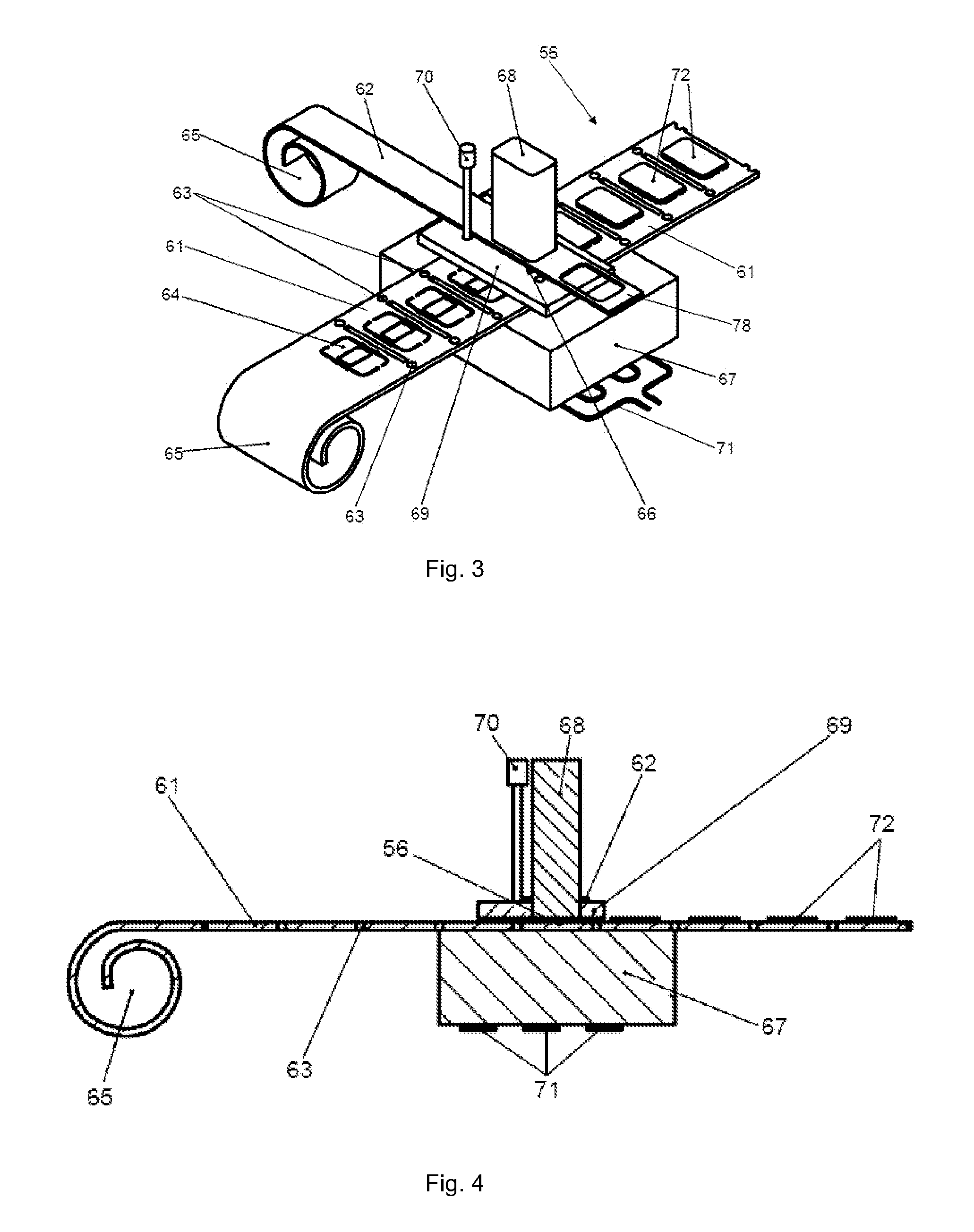
ActiveUS8746315B2Simple and precise mannerIncrease productionMechanical working/deformationLaminationFibrous compositesSubstructure
An apparatus for the production of a fuselage shell for an aircraft made of fiber composite, which is to be equipped with a plurality of stringers disposed spaced apart for reinforcement, comprising a main frame to form a supporting substructure having an outwardly curved mounting surface for positive mounting, having longitudinal mounting grooves for receiving of formed parts for deformably positioning the stringers relative to the mounting surface, wherein a plurality of short formed parts spaced apart from each other are disposed in each mounting groove, and which are adjustable relative to the corresponding mounting groove in the transverse direction (Y) by means of adjusters, and which can be raised in the vertical direction (Z) by means of lifters for guiding the stringers in the direction of a laminating adhesive bonding unit brought over the mounting surface.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Device for transmitting torques
InactiveUS20120118081A1Simple and precise mannerReduce effortWork measurementTorque measurementMechanical engineeringTorque transmission
Owner:THYSSENKRUPP EGM
Apparatus for the production of an aircraft fuselage shell consisting of a fibre composite
ActiveUS20120279662A1Simple and precise mannerIncrease productionEfficient propulsion technologiesWeight reductionEngineeringFibrous composites
An apparatus for the production of a fuselage shell for an aircraft made of fibre composite, which is to be equipped with a plurality of stringers disposed spaced apart for reinforcement, comprising a main frame to form a supporting substructure having an outwardly curved mounting surface for positive mounting, having longitudinal mounting grooves for receiving of formed parts for deformably positioning the stringers relative to the mounting surface, wherein a plurality of short formed parts spaced apart from each other are disposed in each mounting groove, and which are adjustable relative to the corresponding mounting groove in the transverse direction (Y) by means of adjusters, and which can be raised in the vertical direction (Z) by means of lifters for guiding the stringers in the direction of a laminating adhesive bonding unit brought over the mounting surface.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Method for the Production of Structural Components from Fiber-Reinforced Thermoplastic Material
ActiveUS20050266224A1Fast conductionImprove relationshipVehicle seatsWood working apparatusSingle stageEngineering
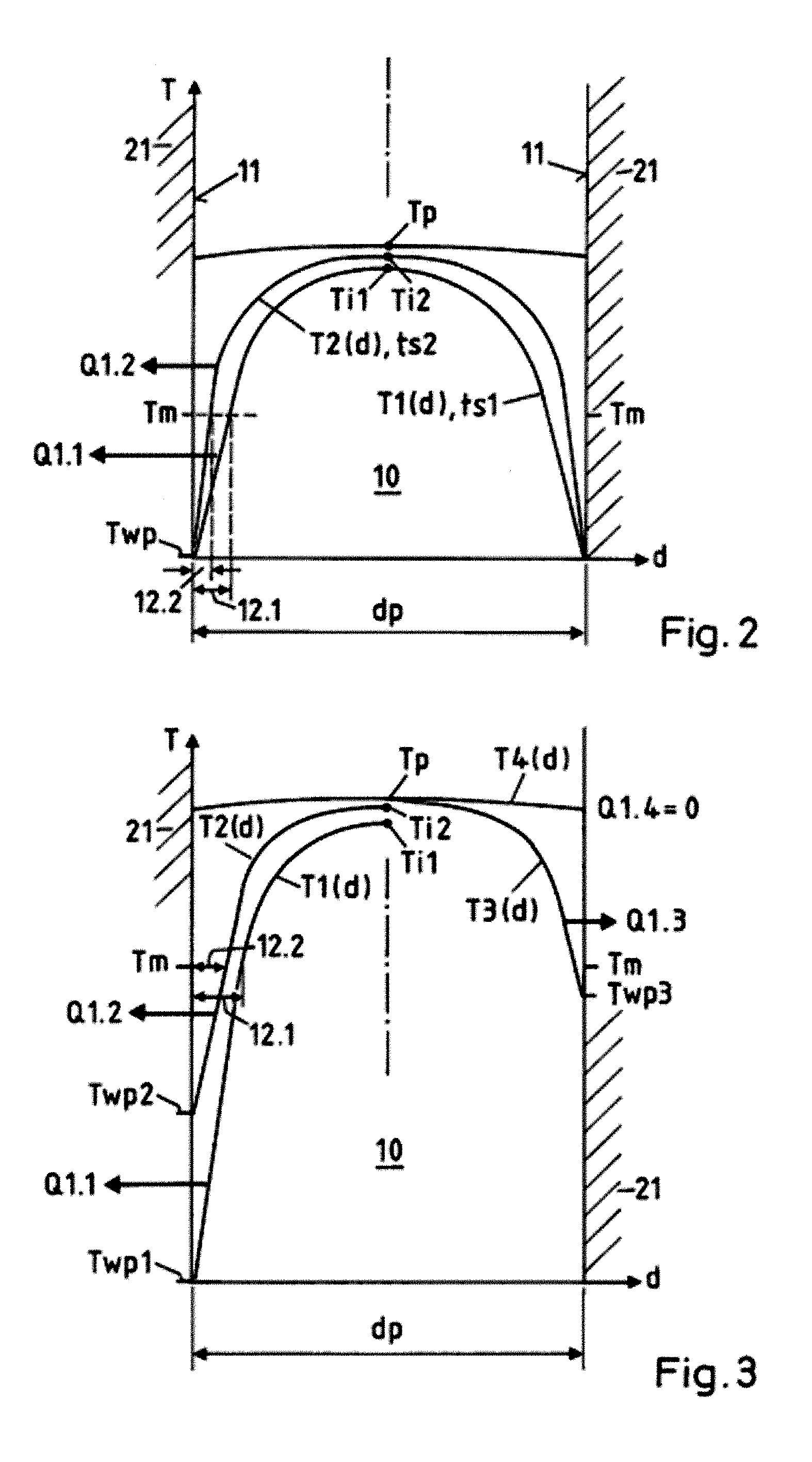
Abstract of the DisclosureThe method enables the series production of light structural components out of long-fiber thermoplastic material (LFT) with integrated continuous fiber (CF) - reinforcements in a single stage LFT - pressing step. In this, CF - tapes (5) are melted open and transferred into a profile tool (21) of a CF - profile forming station (20), there are pressed for a short time period and shaped into the required CF - profile (10). In doing so, by means of contact with the thermally conditioned profile tool (21) on the profile surface (11) a shock-cooled, dimensionally stable, thin casing layer (12) is formed and the inside of the CF - profile remains melted. Following a defined short shock-cooling period (ts), the CF - profile (10) is transferred into an LFT - tool (31) and pressed together with an introduced molten LFT - mass (6). In doing so, the casing layer (12) is melted open again on the surface (11) and is thermoplastically bonded together with the surrounding LFT - mass.
Owner:WEBER TECH
Method for Determining a Pressure at the Output of an Exhaust Gas System
ActiveUS20120109494A1Improve accuracySimpler and precise mannerAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlFresh airInternal combustion engine
In a method for determining a pressure at the output of an exhaust gas system of an internal combustion engine system of a vehicle, a mass flow through the internal combustion engine system and an ambient pressure at a fresh air supply of the internal combustion engine system are detected. The pressure at the output of the exhaust gas system is determined as a function of the mass flow, the ambient pressure and throttling of the mass flow through the internal combustion engine system.
Owner:VOLKSWAGEN AG
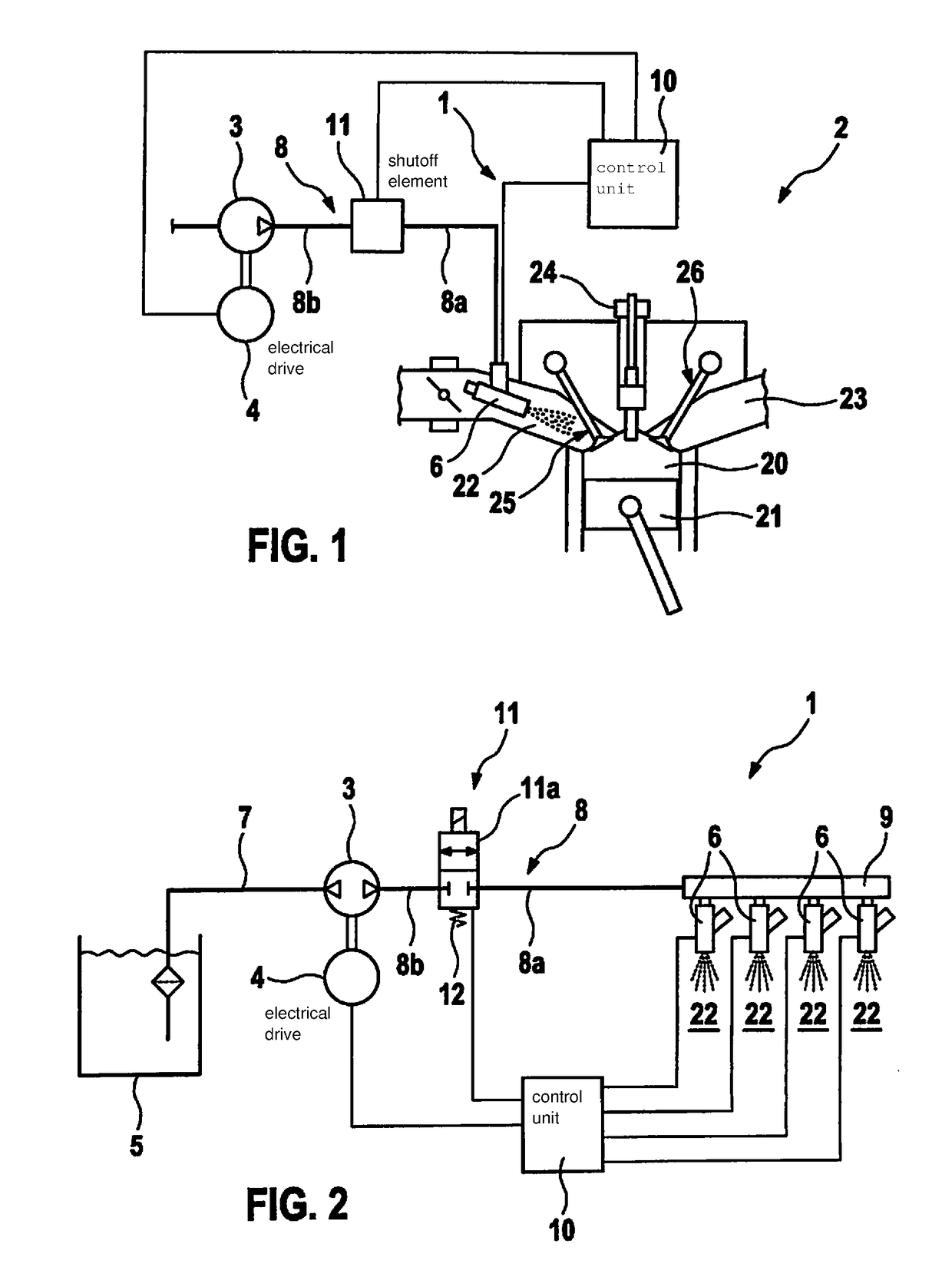
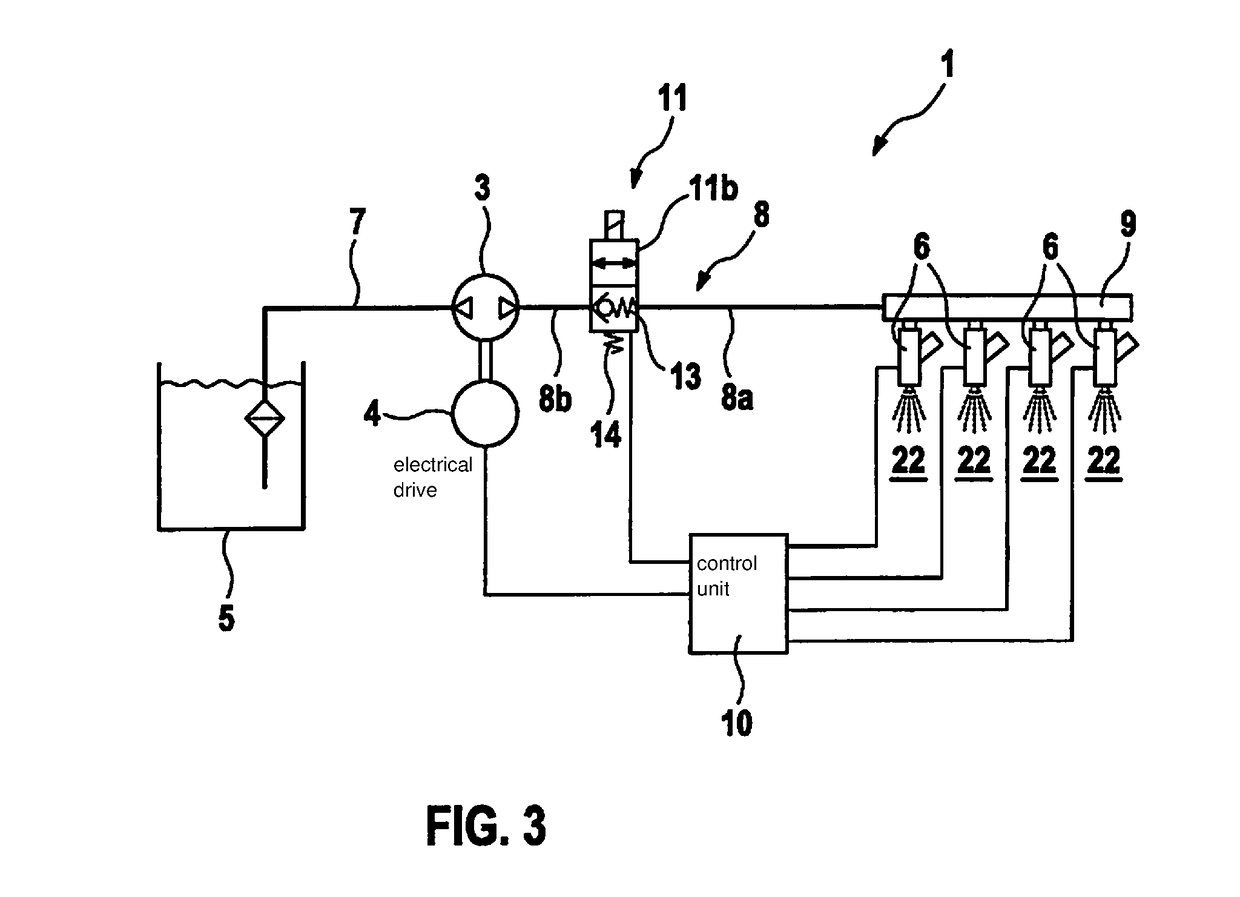
Water injection device of an internal combustion engine
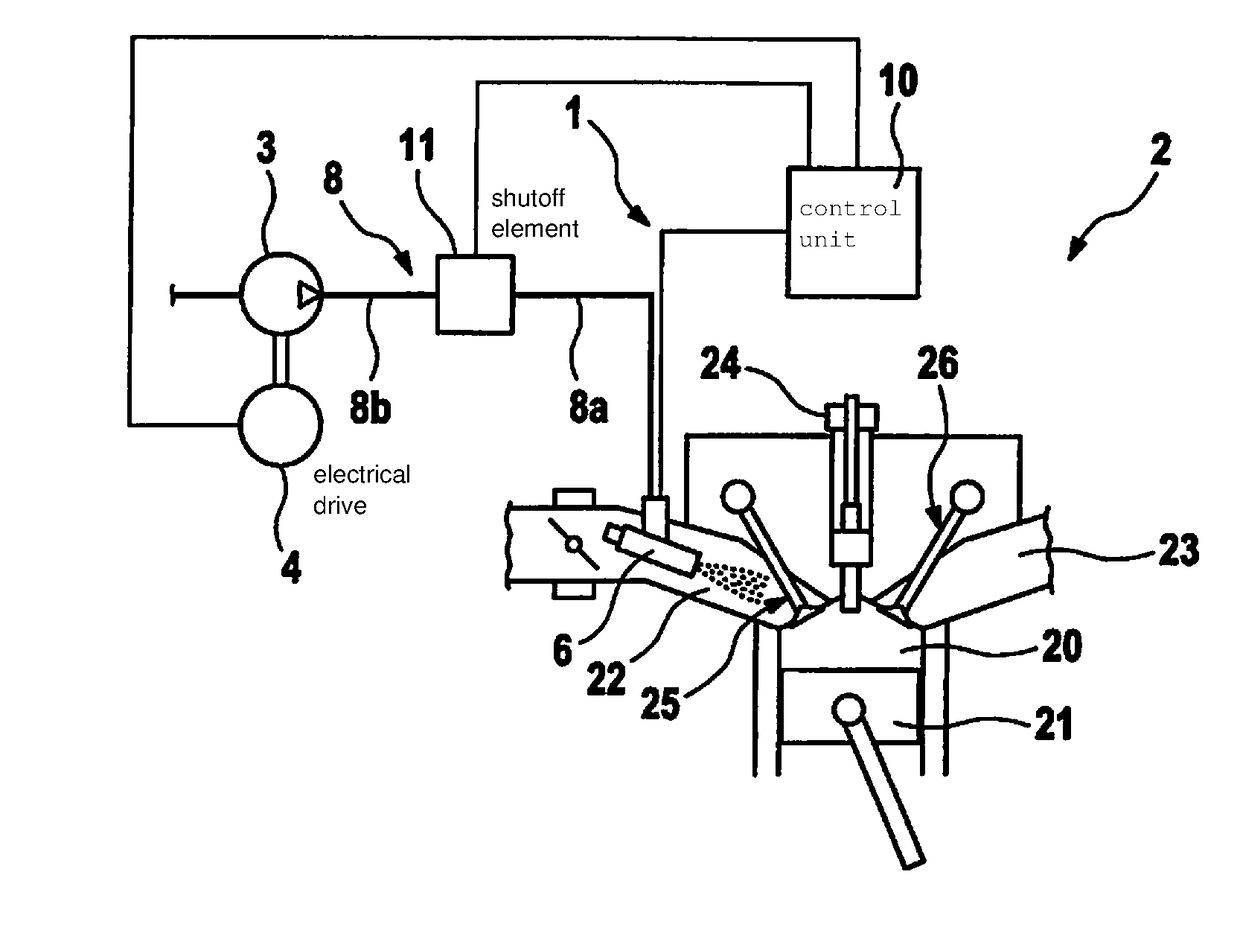
ActiveUS20180119649A1Short pressure build-up timeAvoid knocking tendencyInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExternal combustion engineSystem pressure
A water injection device of an internal combustion engine, including a water tank for storing water, at least one water injector, a conveying element for conveying water from the water tank into the water injector, and a shut-off element, which is situated in an area between the conveying element and the water injector, and which is configured to maintain a system pressure between the shut-off element and the water injector at a level such that water situated in the area is prevented from evaporating. An internal combustion engine, which includes a water injection device.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
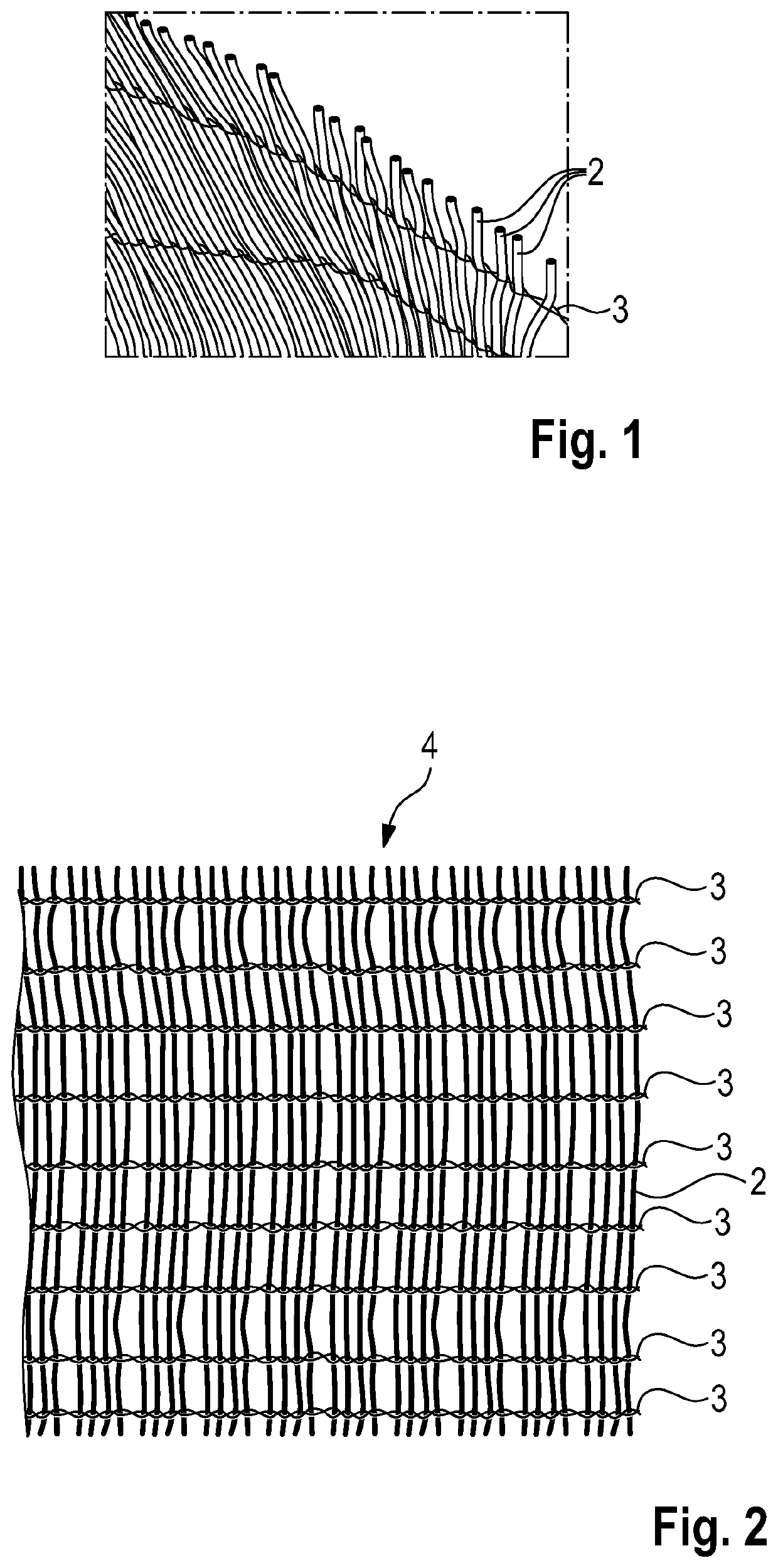
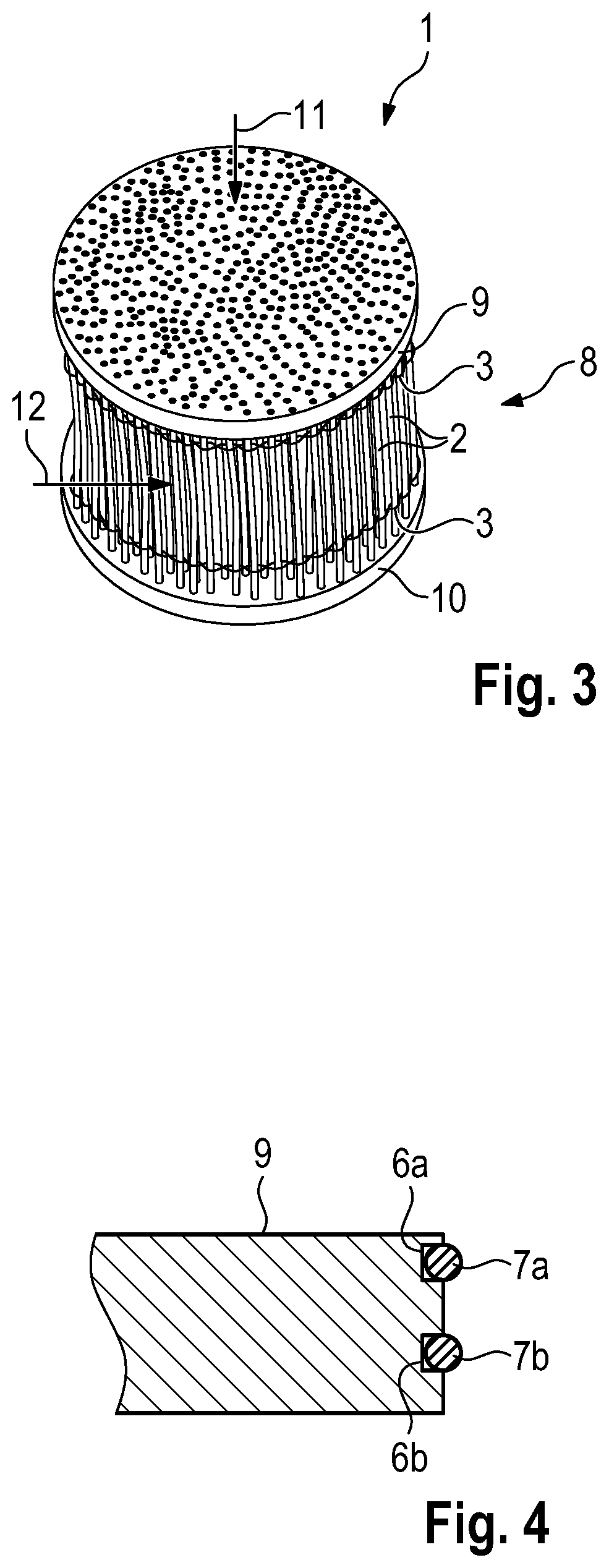
Method for producing a microchannel bundle heat exchanger
ActiveUS11135688B2High degree of automationSimple and precise mannerStationary tubular conduit assembliesWoven fabricsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A method for producing a microchannel bundle heat exchanger (1) includes providing a multiplicity of tubular microchannels (2); incorporating the microchannels (2) in a weaving device; interweaving the tubular microchannels (2) with a plurality of warp wires (3) in the weaving device, and generating at least one heat exchanger mat (4) from the tubular microchannels (2) which are connected to one another by means of the warp wires (3); shaping at least one heat exchanger pack (8) from the at least one heat exchanger mat (4), in particular by folding and / or rolling up the heat exchanger mat (4); and adhesively bonding the tubular microchannels (2) at two mutually opposite end sides (9, 10) of the heat exchanger pack (8).
Owner:DR ING H C F PORSCHE AG
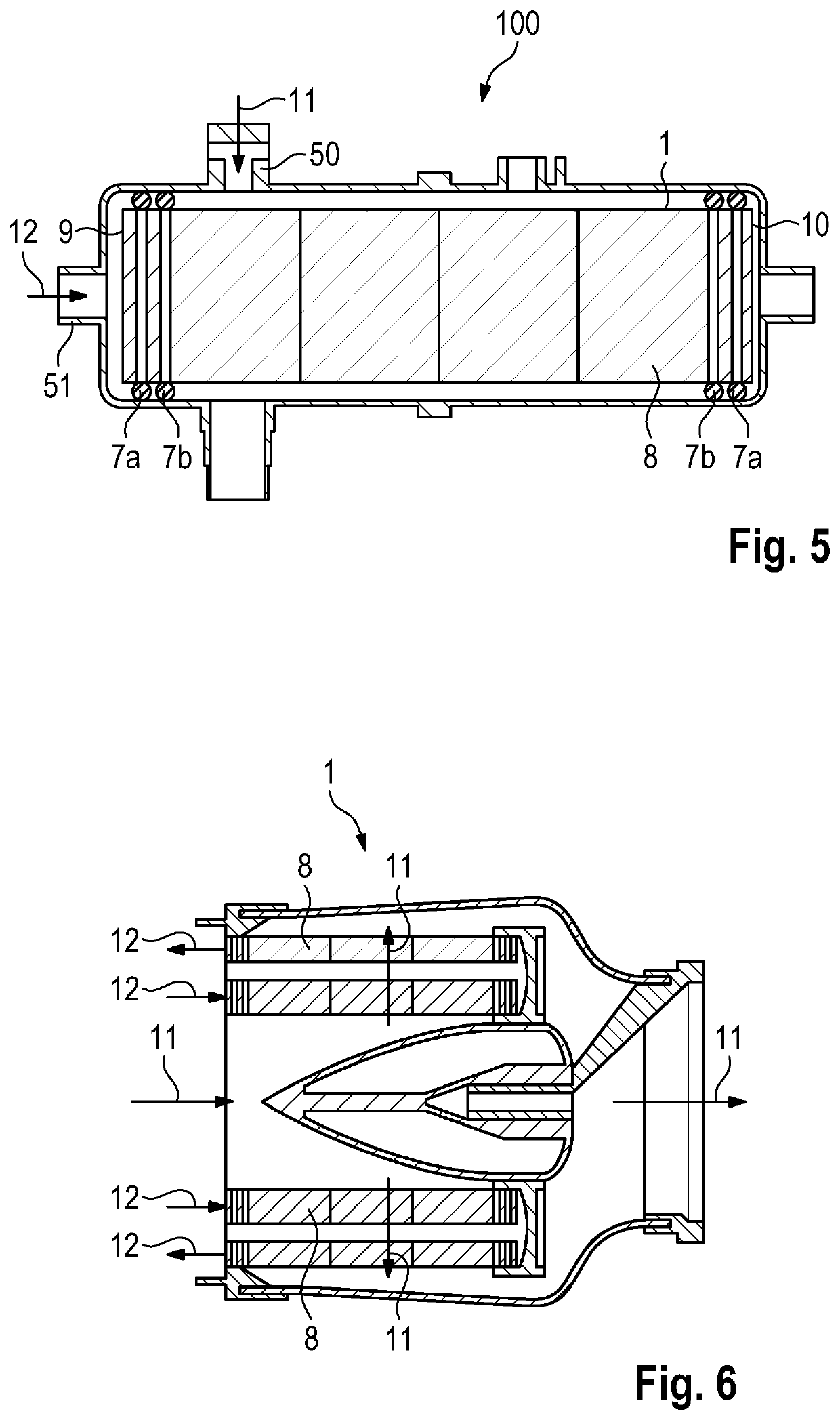
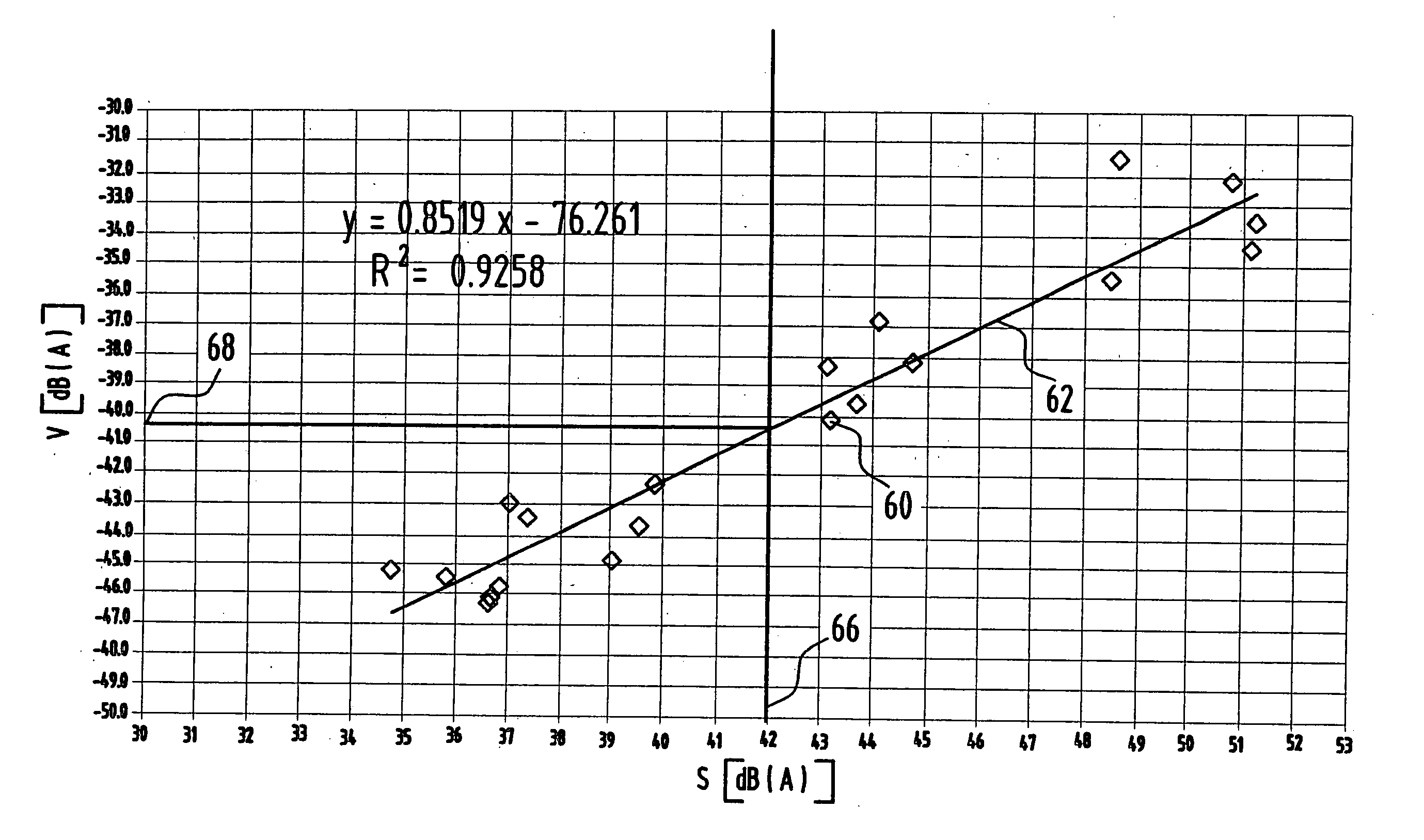
Measuring method to determine the noise emission of an electric motor and measuring device
InactiveUS20050092090A1Simple and precise mannerVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingMeasurement deviceNoise level
A measuring method to determine the noise emission of an electric motor is proposed in which the vibrational excitation of the running electric motor is measured by a laser vibrometer device and this measured vibrational excitation is correlated with a noise level.
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Helical conveyor centrifuge having a planetary gear drive device
ActiveUS7883457B2Large differential speedSimple and precise mannerRotary centrifugesToothed gearingsGear driveGear wheel
A helical conveyor centrifuge, such as a solid-bowl or sieve-bowl centrifuge, includes a rotatable drum, a rotatable screw disposed within the drum, and a centrifuge drive for rotating the drum and the screw. The centrifuge drive is configured to set a differential speed between drum and screw. The centrifuge drive includes a first motor, a second motor, and a gearing arrangement disposed between the motors and also between the drum and the screw. The gearing arrangement includes a gearing arranged downstream of the motors and has a first gear, a second gear and a third gear stage. The first and second gear stages include at least four shafts. Torques are either introduced into or are taken off from the first and second gear stages. The first and second gear stages are disposed in a housing and driven by at least three of the at least four shafts.
Owner:GEA MECHANICAL EQUIP
Method and device for operating an internal combustion engine having at least two cylinder banks
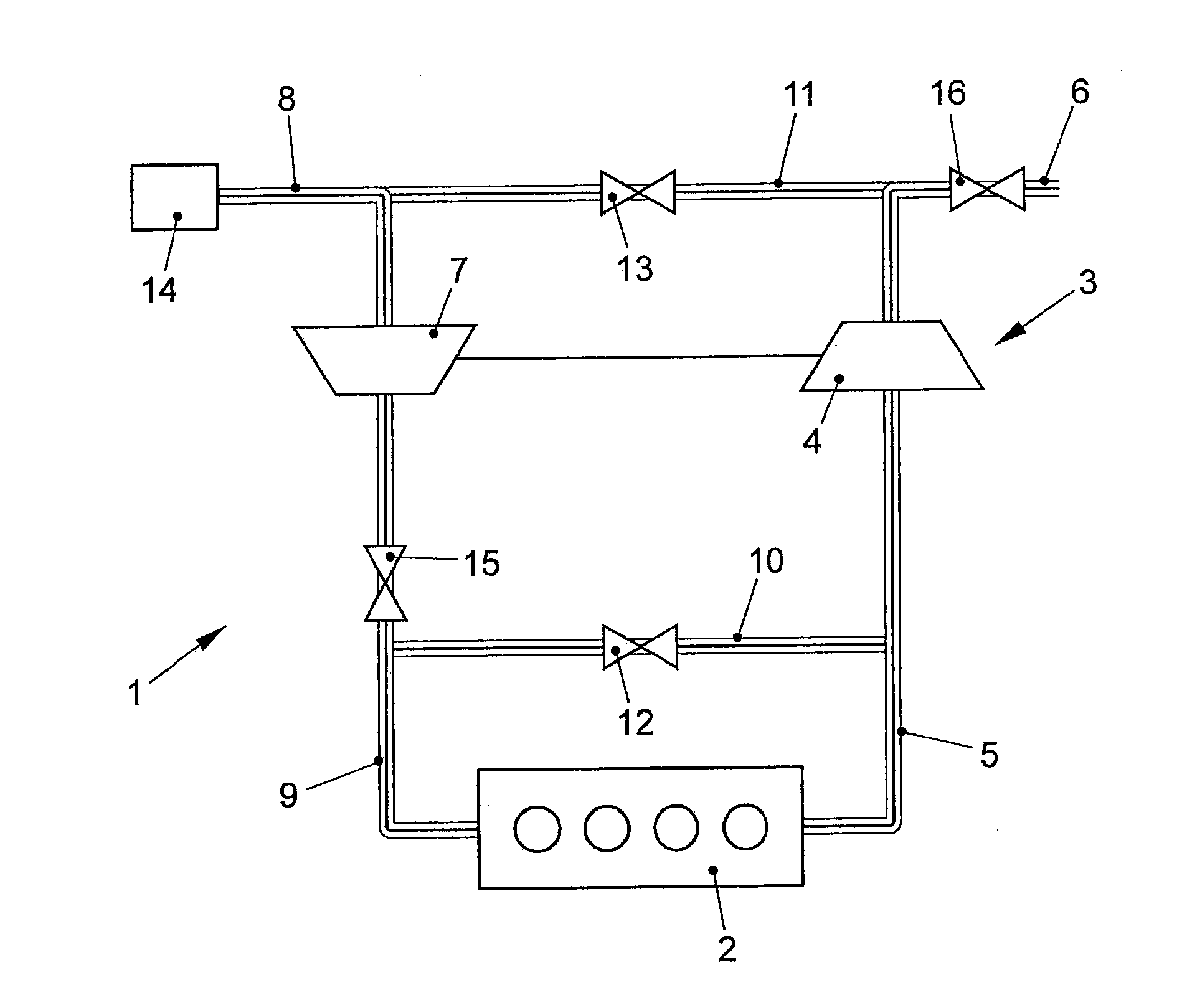
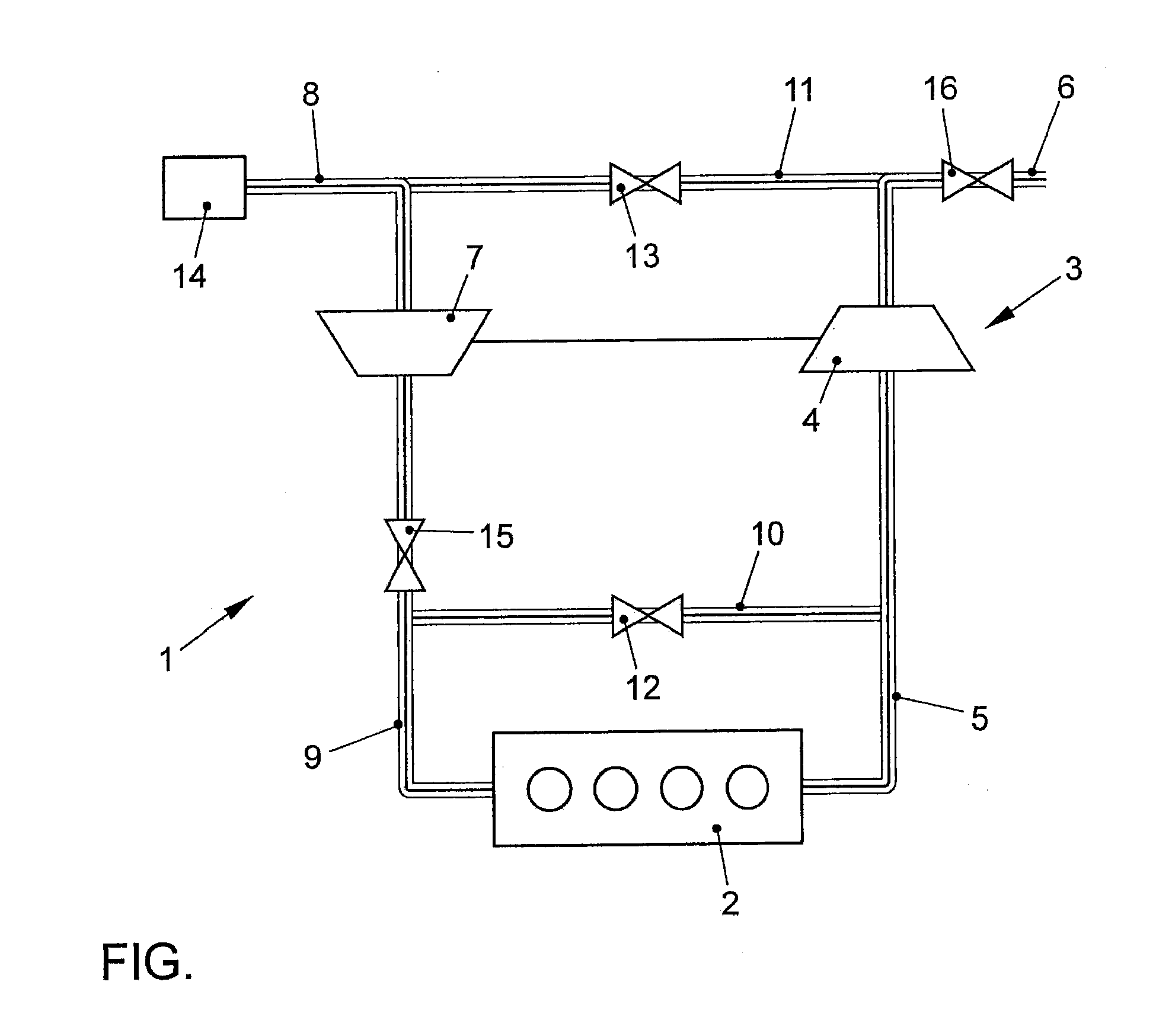
InactiveUS7165538B2Simple and precise mannerGood synchronizationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineControl theory
A method and a device for operating an internal combustion engine having at least two cylinder banks are provided, each of the at least two cylinder banks having an air supply with an individual compressor, and a coordination of the compressors is possible in a simple and precise manner. In this context, a shared setpoint value is predefined for a characteristic variable for the rotational speed of a first compressor in a first air supply of a first cylinder bank, and a characteristic variable for the rotational speed of a second compressor in a second air supply of a second cylinder bank. An actual value of the characteristic variable for the rotational speed of the first compressor and an actual value for the characteristic variable for the rotational speed of the second compressor are corrected to the shared setpoint value.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Device for the contactless transfer of electrical energy
InactiveUS7137494B2Simple and precise mannerAvoid scratchesRail devicesElectromagnetic wave systemPower cableTransport system
A device with which electrical energy can be transferred from a power cable running along a stationary rail of a transport system to a moving element that can be driven along the rail. Each moving element has for this purpose a transfer head which works inductively together with the power cable. The power cable is attached with the aid of carrier profile which extends substantially along the entire length of the rail and is fixed in a releasable manner to the rail, which element has at least one a trough-like holder open to the side in which the power cable is laid. The power cable is thus relatively easily and accurately laid, avoiding hanging loops of cable which could be damaged by abrasion by the passing transfer heads of the moving elements.
Owner:EISENMANN MASCHINENBAU GMBH & CO KG
Protection apparatus for a manipulation device on a handling device, as well as handling device
ActiveUS10086512B2Simple and precise mannerProgramme-controlled manipulatorNumerical controlMechanical engineeringRobot
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Method for diagnosis of a temperature control means of a battery pack
ActiveUS20210184282A1Simple and precise mannerCell temperature controlCells structural combinationTemperature controlBattery cell
A method for diagnosis of a temperature control means (30) of a battery pack (10) that comprises a plurality of battery cells (20) and a plurality of temperature sensors for measuring temperatures of the individual battery cells (20), the battery cells (20) being arranged side by side in the battery pack (10), in a longitudinal direction (12) of the battery pack (10), and mechanically connected to each another, and the battery cells (20) being arranged on the temperature control means (30) and mechanically and thermally connected to it. A battery management system, and / or a battery pack (10) may be configured to execute the method. A vehicle may be fitted with a battery pack that carries out the method.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Measuring method to determine the noise emission of an electric motor and measuring device
InactiveUS7165456B2Simple and precise mannerVibration measurement in solidsMachine part testingMeasurement deviceNoise level
Owner:MINEBEA CO LTD
Fastening system with eccentric
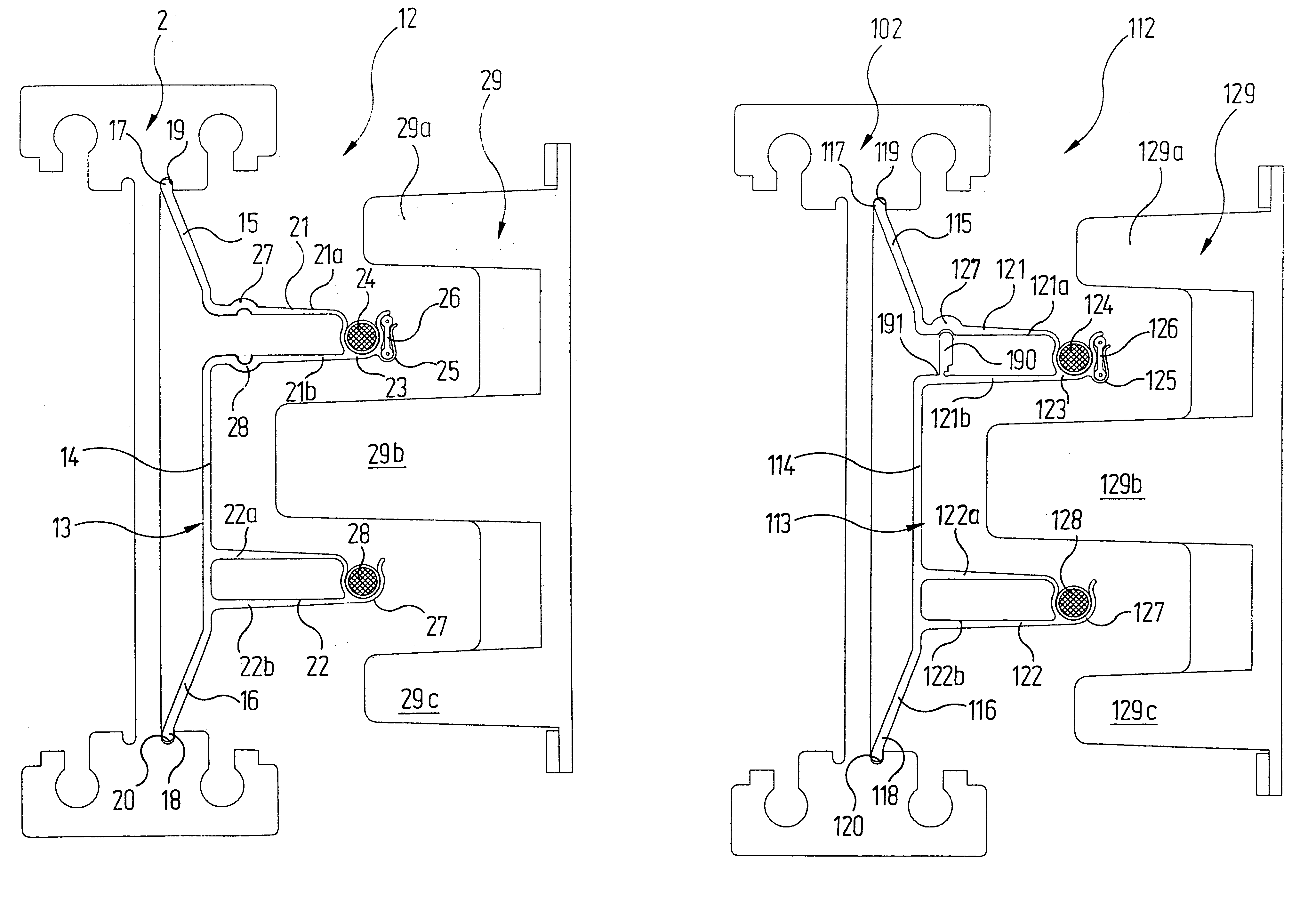
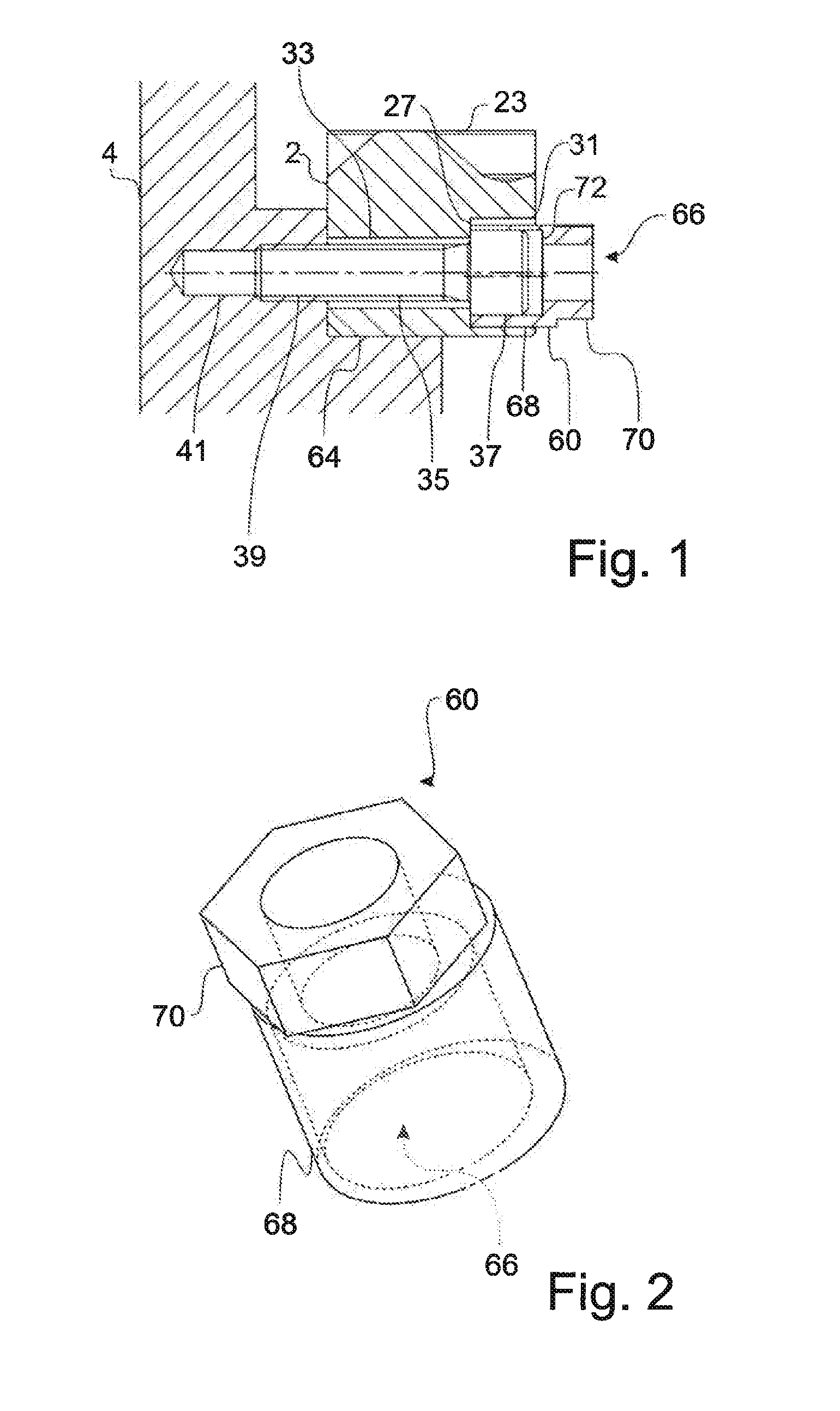
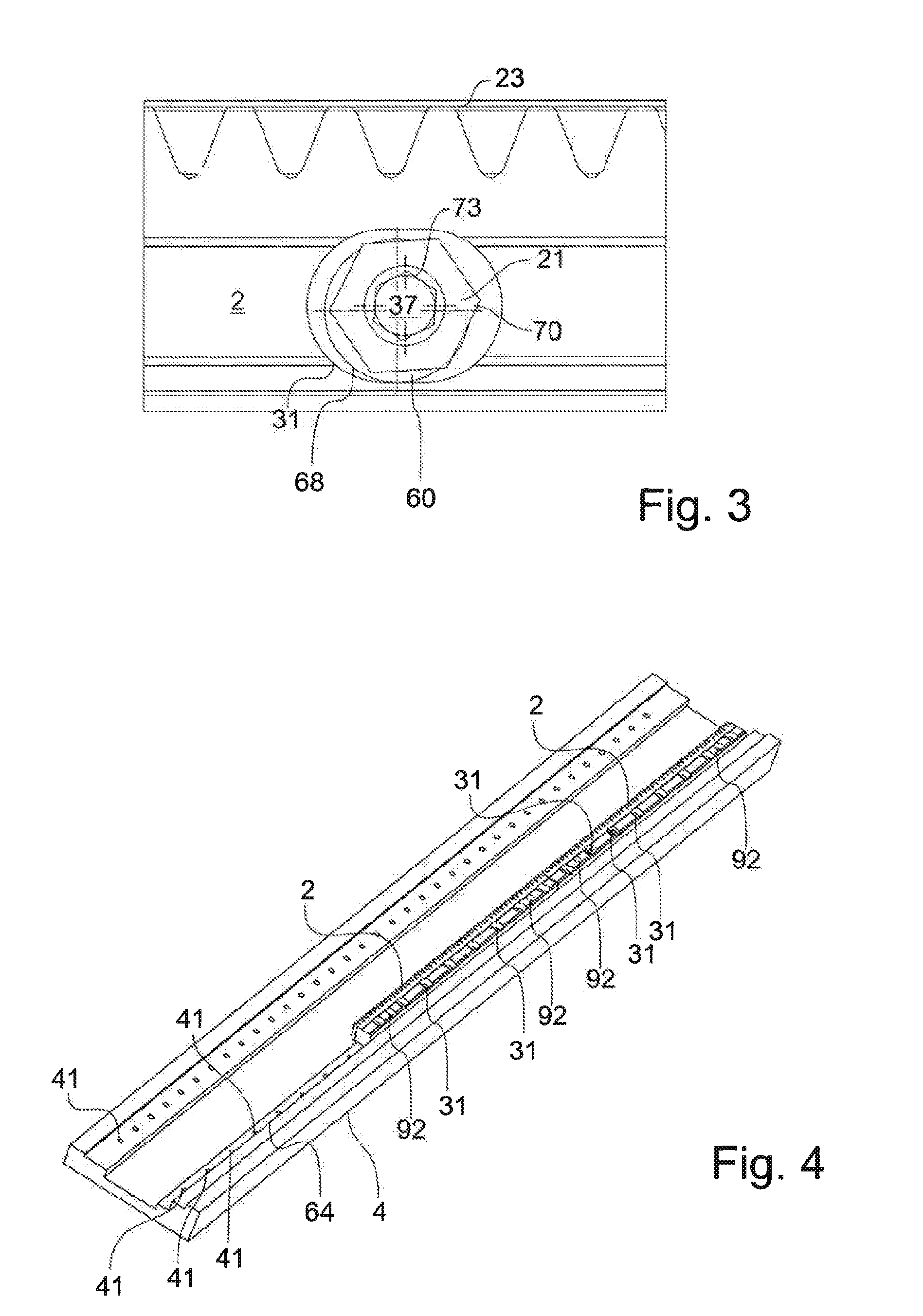
ActiveUS9273712B2Improve convenienceImprove securityLinear bearingsNutsLinear machineMechanical engineering
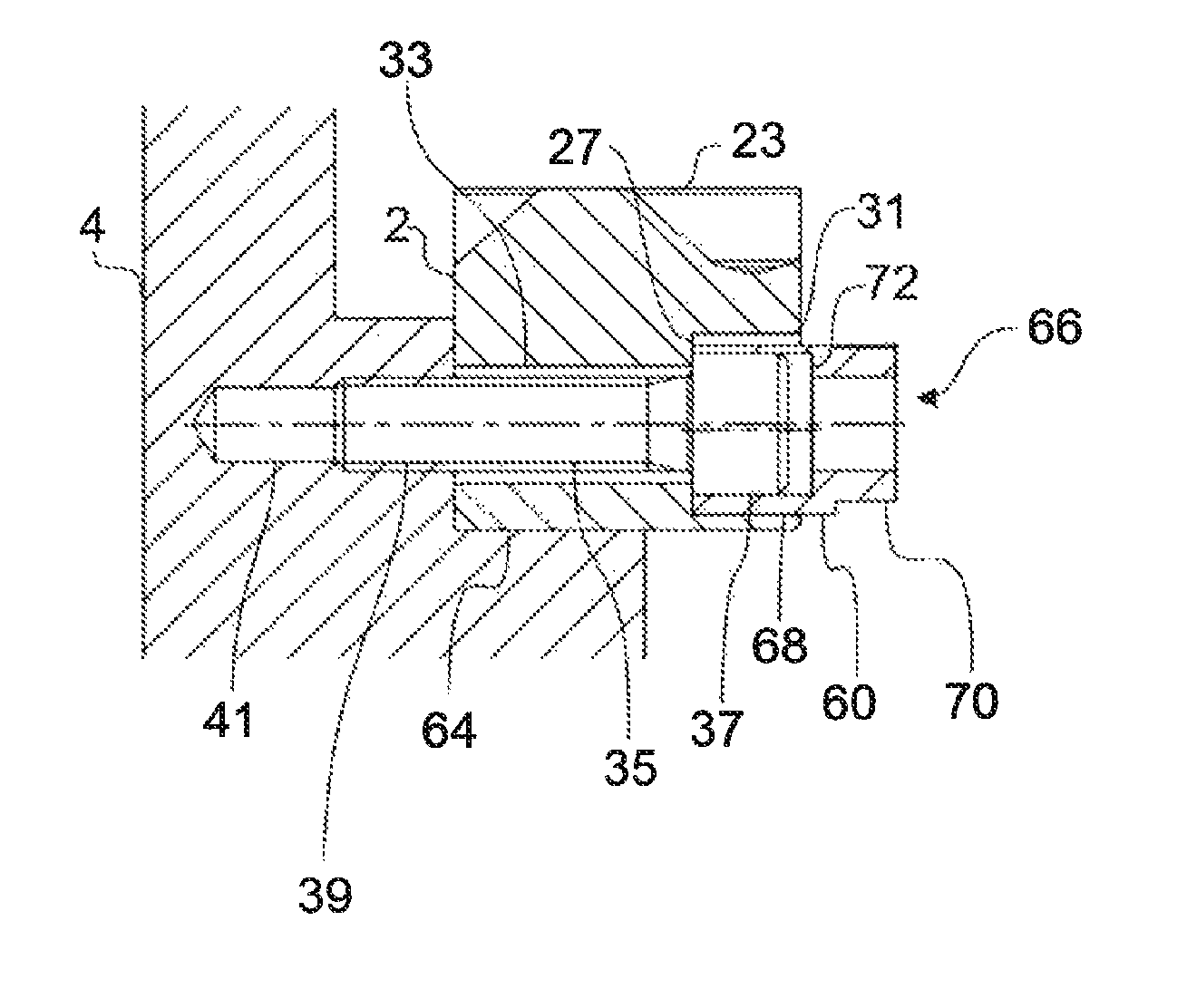
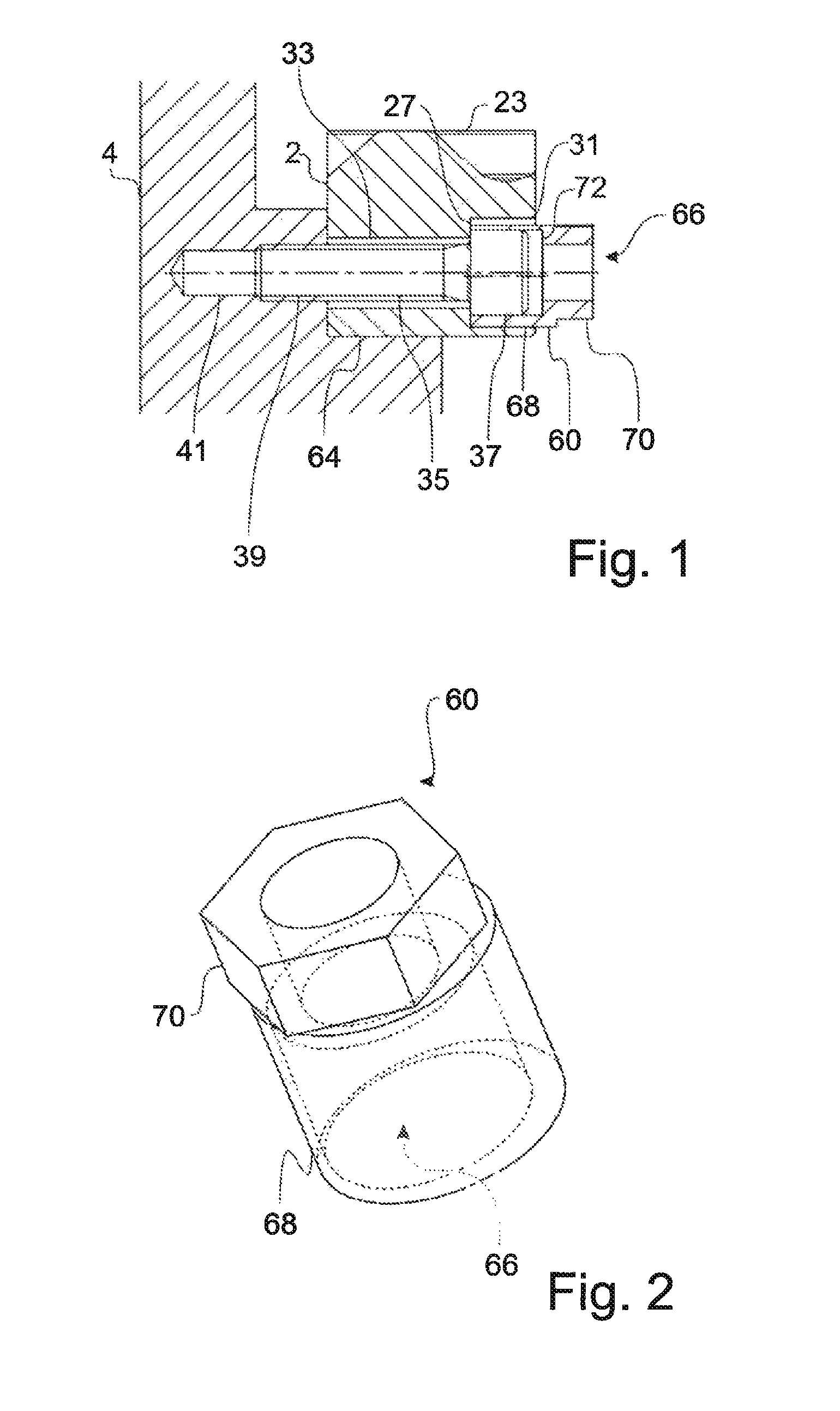
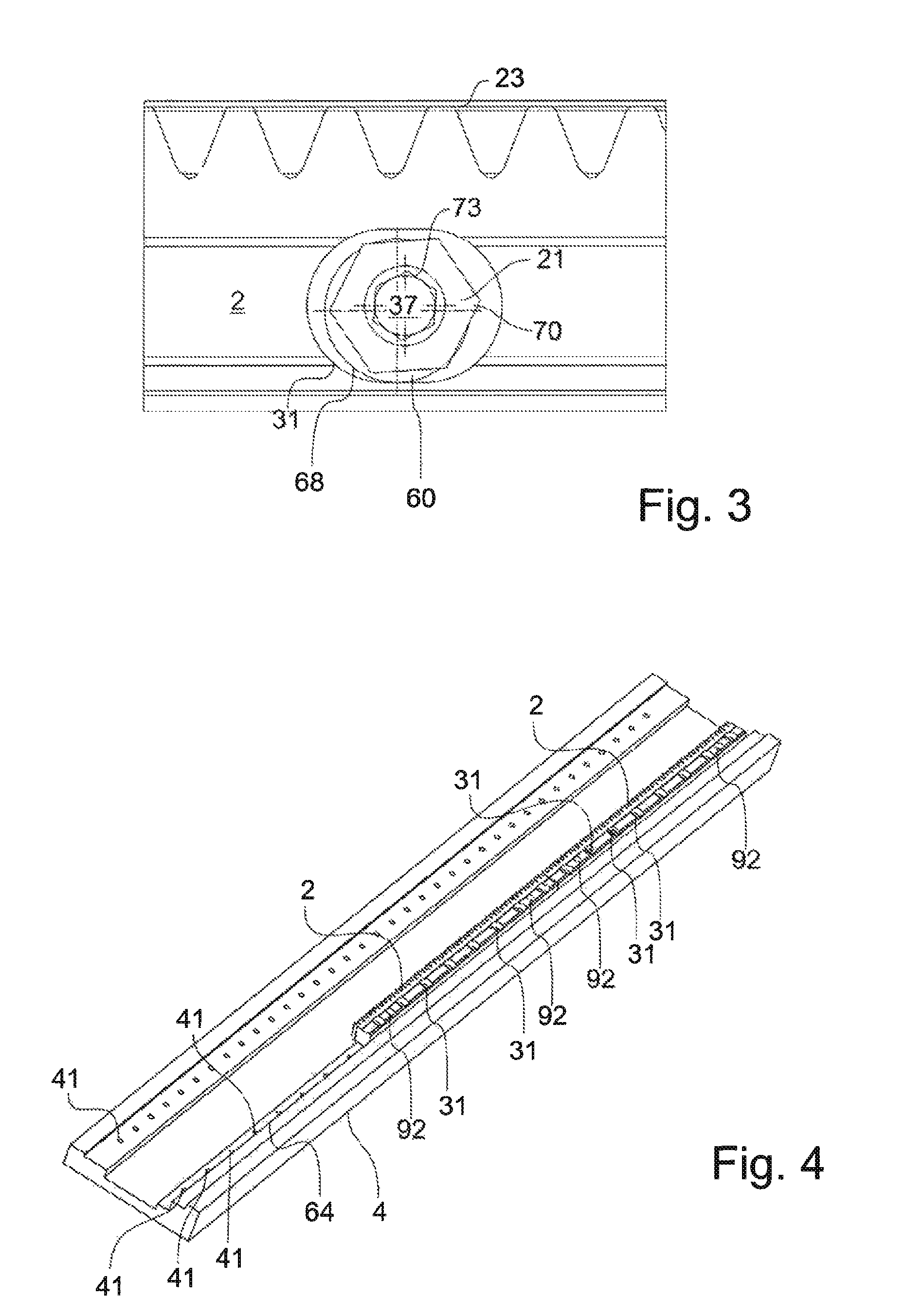
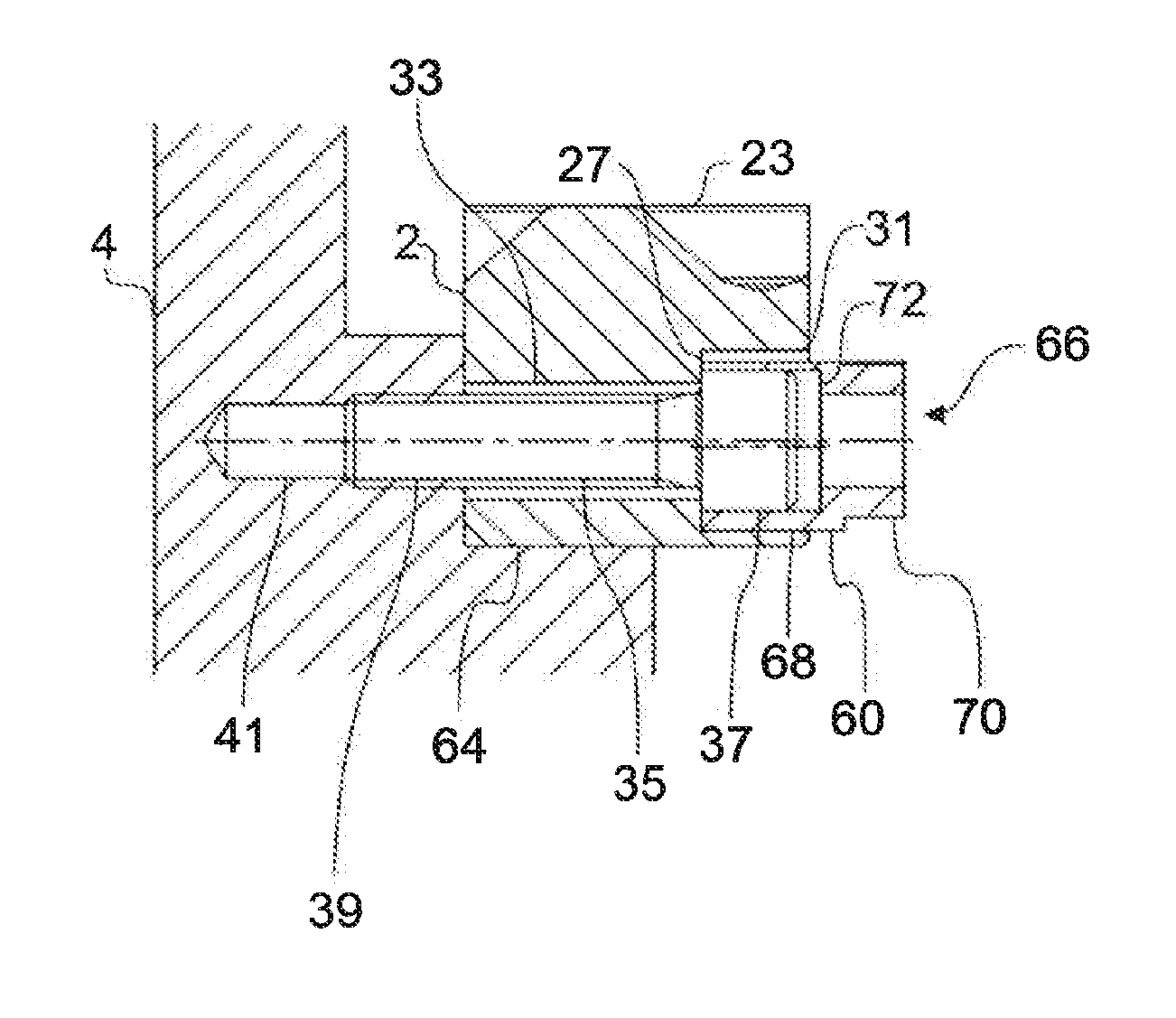
Fastening system for a linear machine element (2, 102) for fastening in a machine foundation (4), having a clamping element which has a shank (35) and a head (37), wherein the diameter of the head (37) is greater than the diameter of the shank (35), and having an eccentric (60) which comprises a sleeve (68) with an eccentric bore (66) and a torque-transmitting element (70), wherein the outer diameter of the head (37) is smaller than the inner diameter of the bore (66) or at least substantially corresponds to the inner diameter of the bore (66).
Owner:WITTENSTEIN SE
Fastening system with eccentric
ActiveUS20150043990A1Improve convenienceImprove securityLinear bearingsShaftsEngineeringLinear machine
Fastening system for a linear machine element (2, 102) for fastening in a machine foundation (4), having a clamping element which has a shank (35) and a head (37), wherein the diameter of the head (37) is greater than the diameter of the shank (35), and having an eccentric (60) which comprises a sleeve (68) with an eccentric bore (66) and a torque-transmitting element (70), wherein the outer diameter of the head (37) is smaller than the inner diameter of the bore (66) or at least substantially corresponds to the inner diameter of the bore (66).
Owner:WITTENSTEIN SE
Rotary anode for a rotary anode x-ray tube and method for manufacturing a rotary anode
ActiveUS20120163549A1Heat flow is limitedHigh power densityX-ray tube electrodesX-ray tube target materialsInhomogeneous materialOptoelectronics
A rotary anode for a rotary anode X-ray tube has an anode disc with a supporting portion. A focal track is located in the vicinity of an outer diameter of the anode disc. The supporting portion has inhomogeneous material properties along a radial coordinate of the anode disc to provide a high mechanical load capacity in the area of an inner diameter of the anode disc and a high thermal load capacity at the focal track. These measures provide for a rotary anode for a rotary anode X-ray tube that meets the extreme thermal and mechanical loads during operation. Further, a method for manufacturing such a rotary anode is described as well.
Owner:PLANSEE SE
Method for manufacturing deicing acoustic skin for an aircraft acoustic panel, using a fiber spacing device
PendingUS20200101681A1Low costSimple and precise mannerEngine manufactureEngine fuctionsFiberMechanical engineering
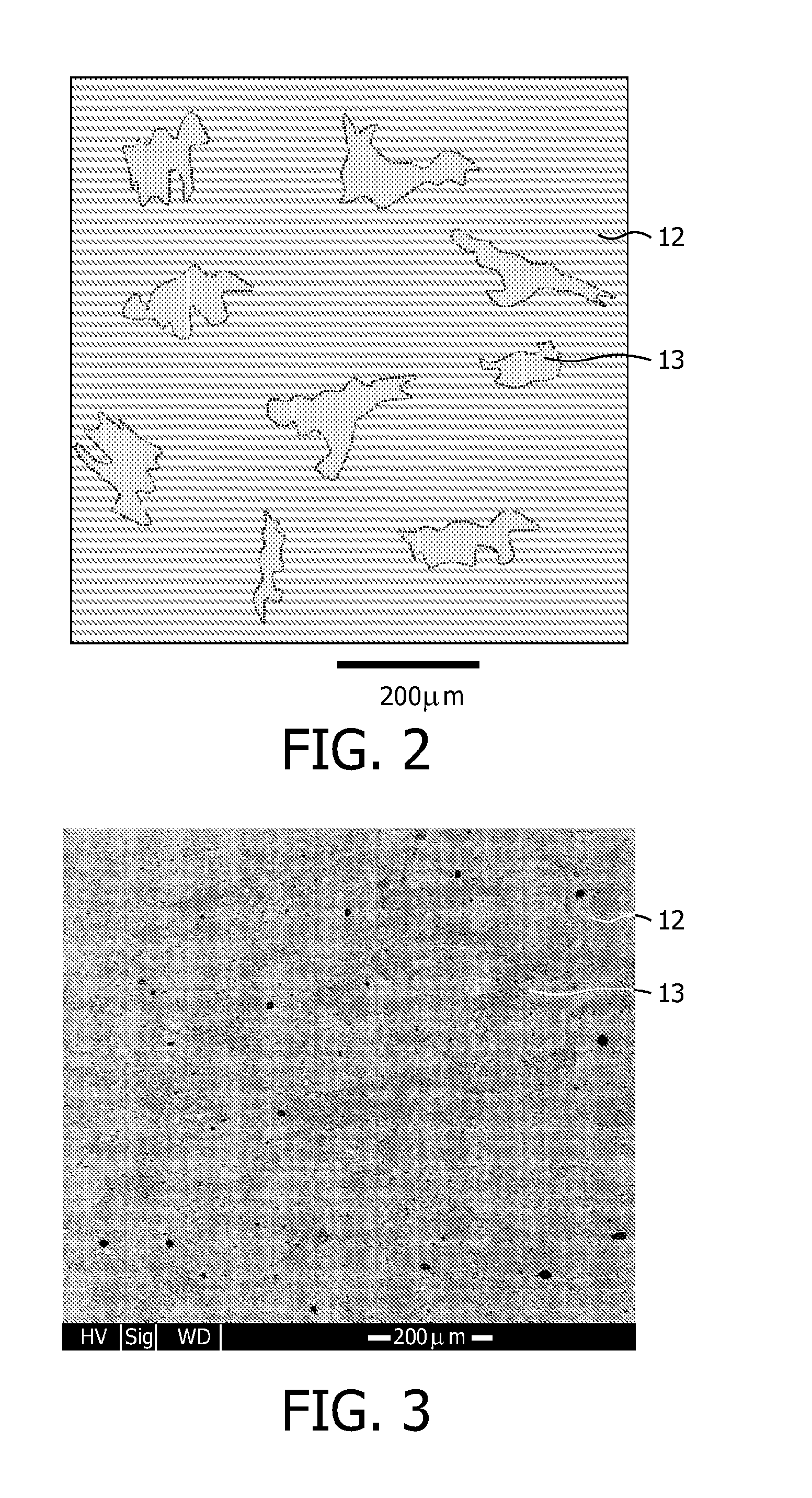
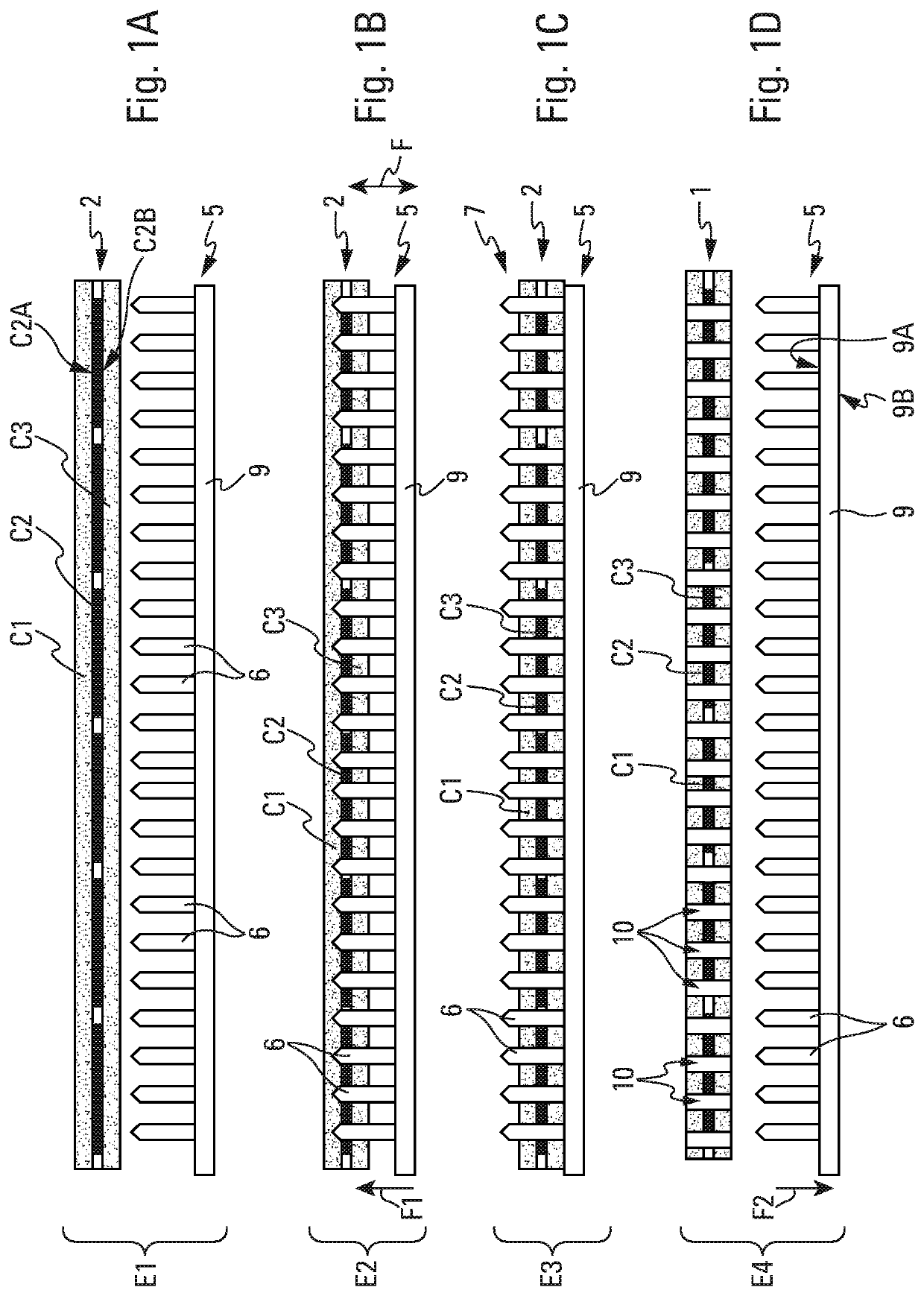
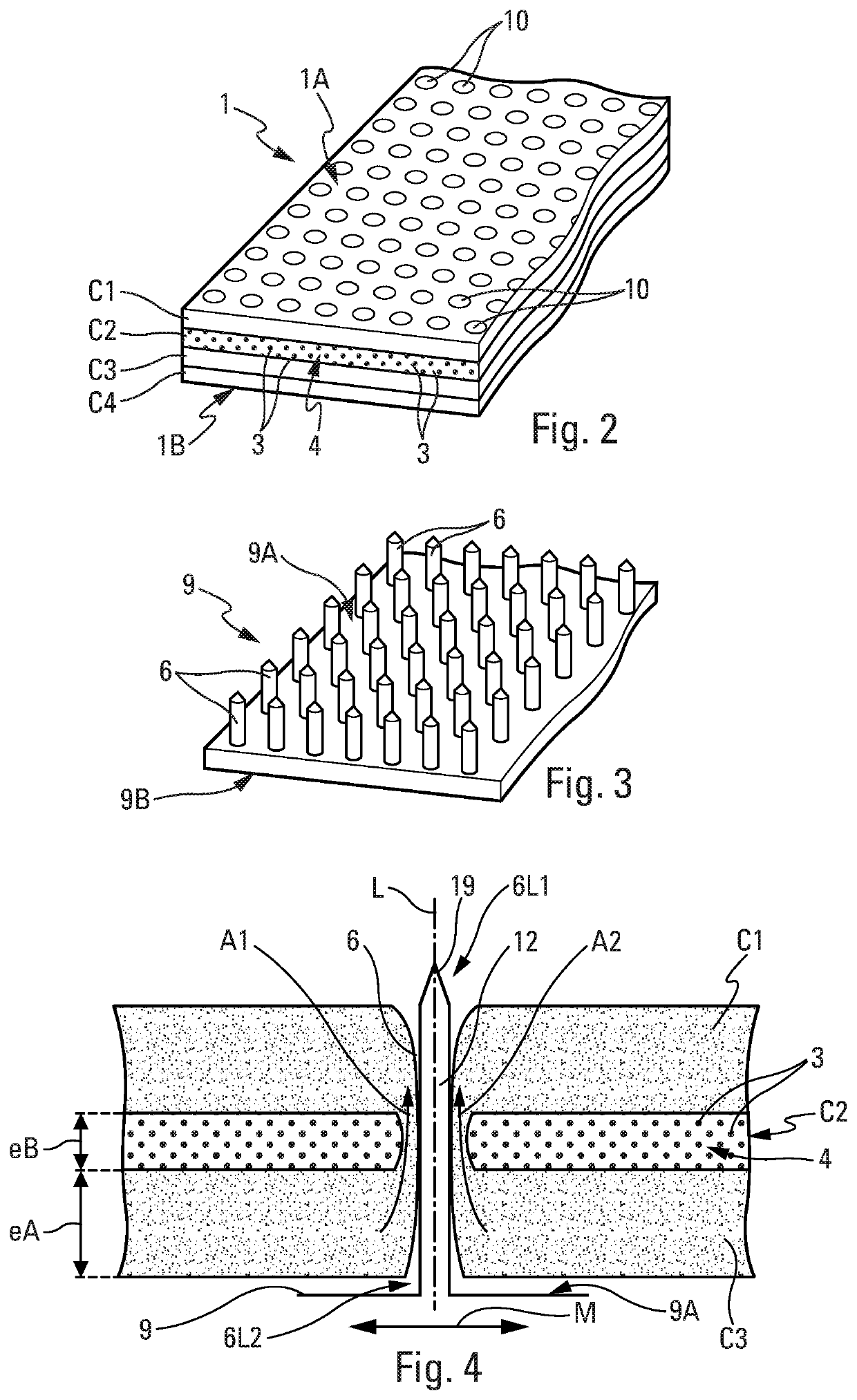
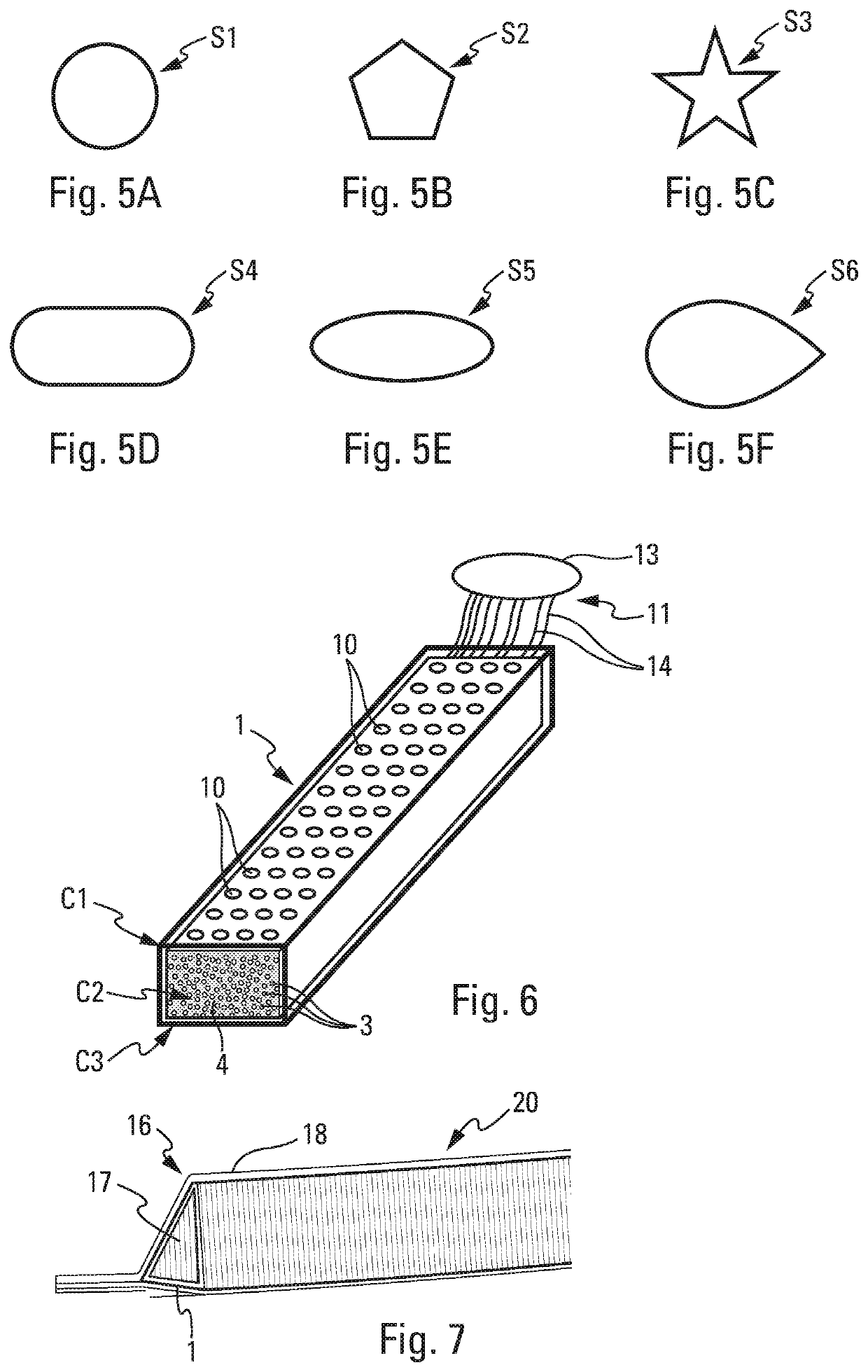
A method for manufacturing deicing acoustic skin for an aircraft acoustic panel, using a fiber spacing device. The manufacturing method includes at least one step for manufacturing a layer assembly having a deicing layer supplied with electrically conductive fibers embedded in a resin and two insulating layers arranged on either side of the deicing layer, and a baking step. The method provides for fitting, during baking, a spacing device on the layer assembly, the spacing device having pins passing through said layer assembly, perforations being produced at the locations of the pins after the withdrawal of the spacing device, the fitting of the spacing device making it possible to produce perforations with desired sizes and shapes, in a simple and effective manner, and with a reduced manufacturing duration.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS (SAS)
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com