Patents
Literature
313 results about "Cylinder bank" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Internal combustion piston engines (those with more than one cylinder) are usually arranged so that the cylinders are in lines parallel to the crankshaft. Where they are in a single line, this is referred to as an inline or straight engine.
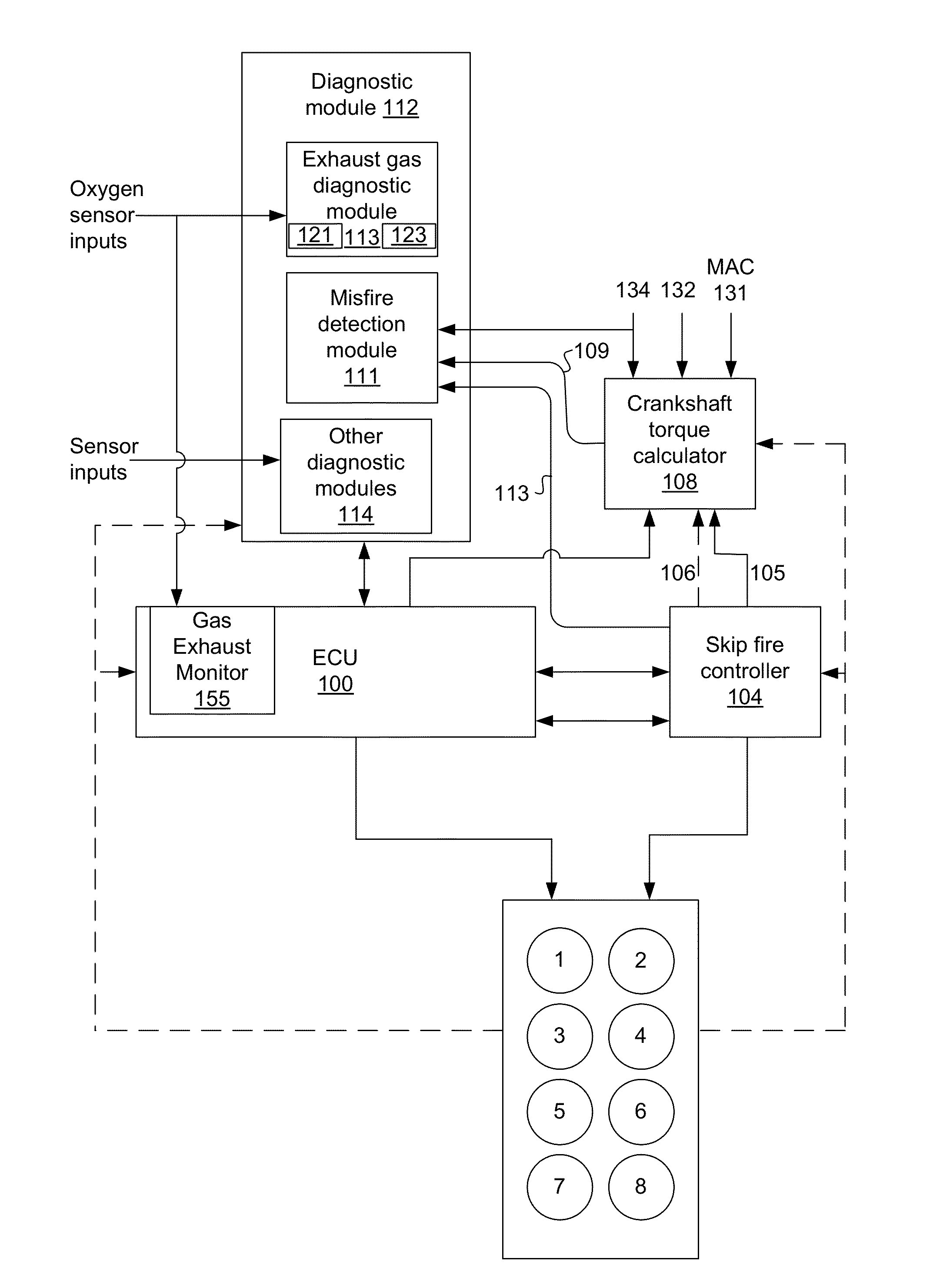
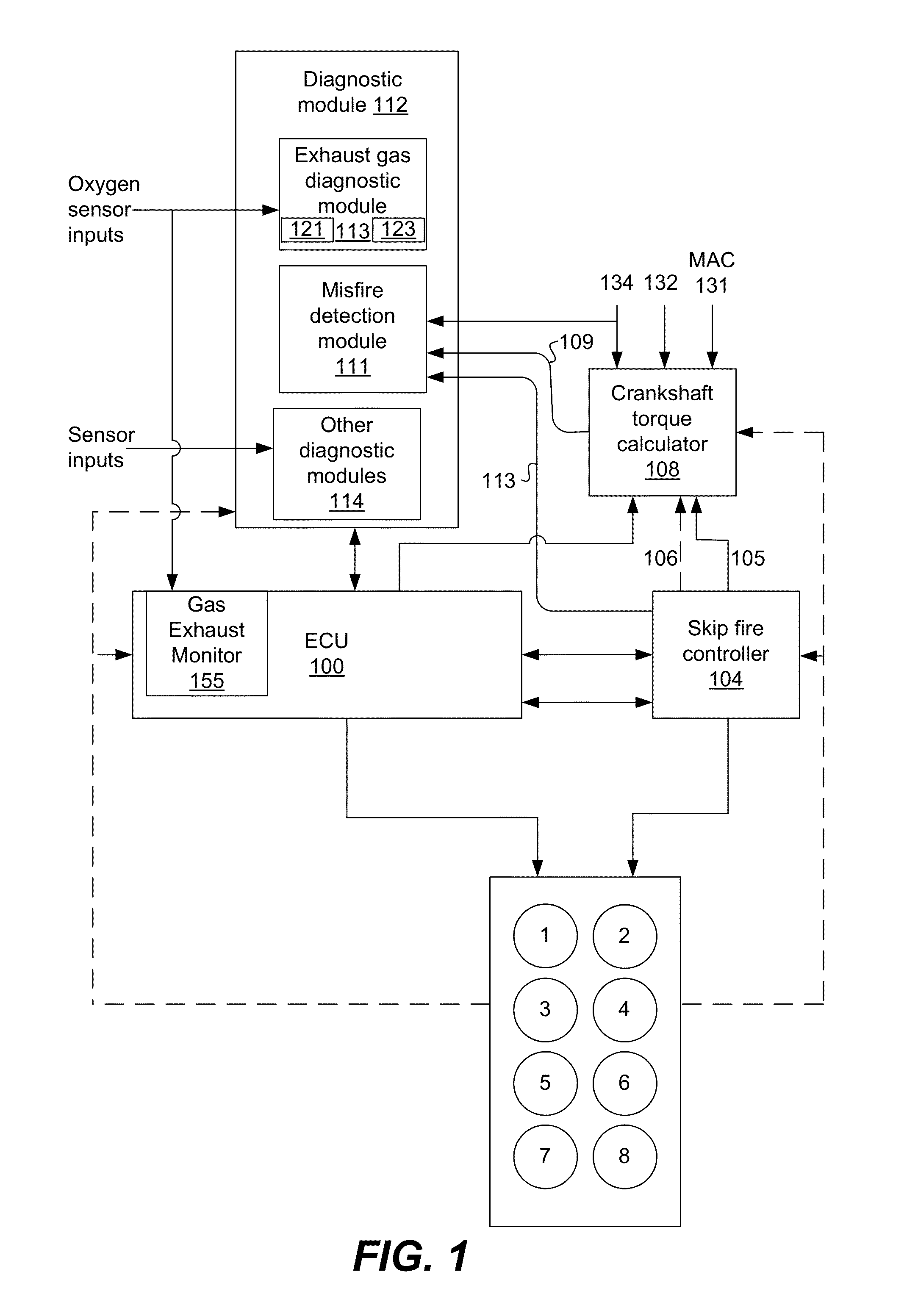
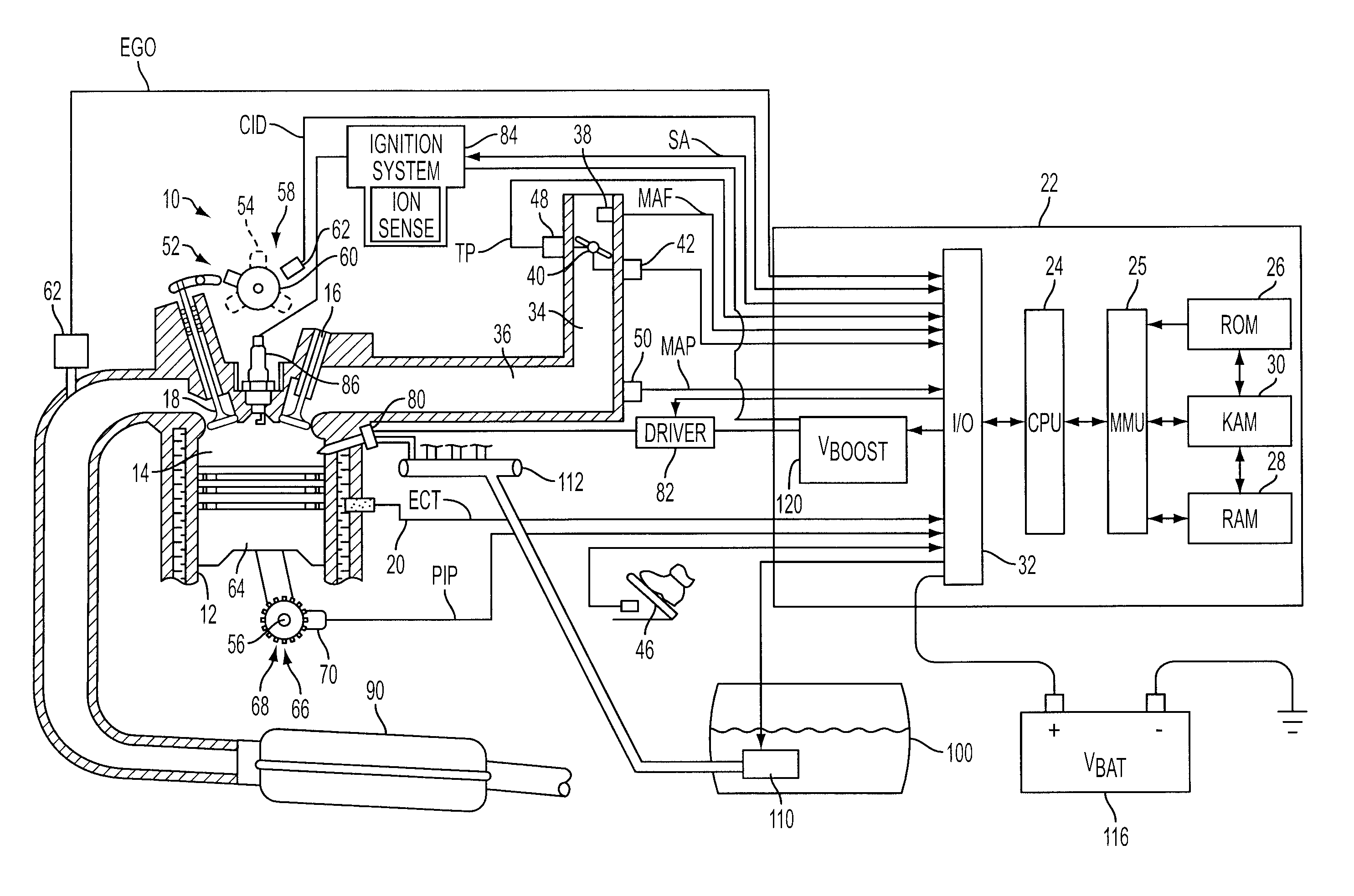
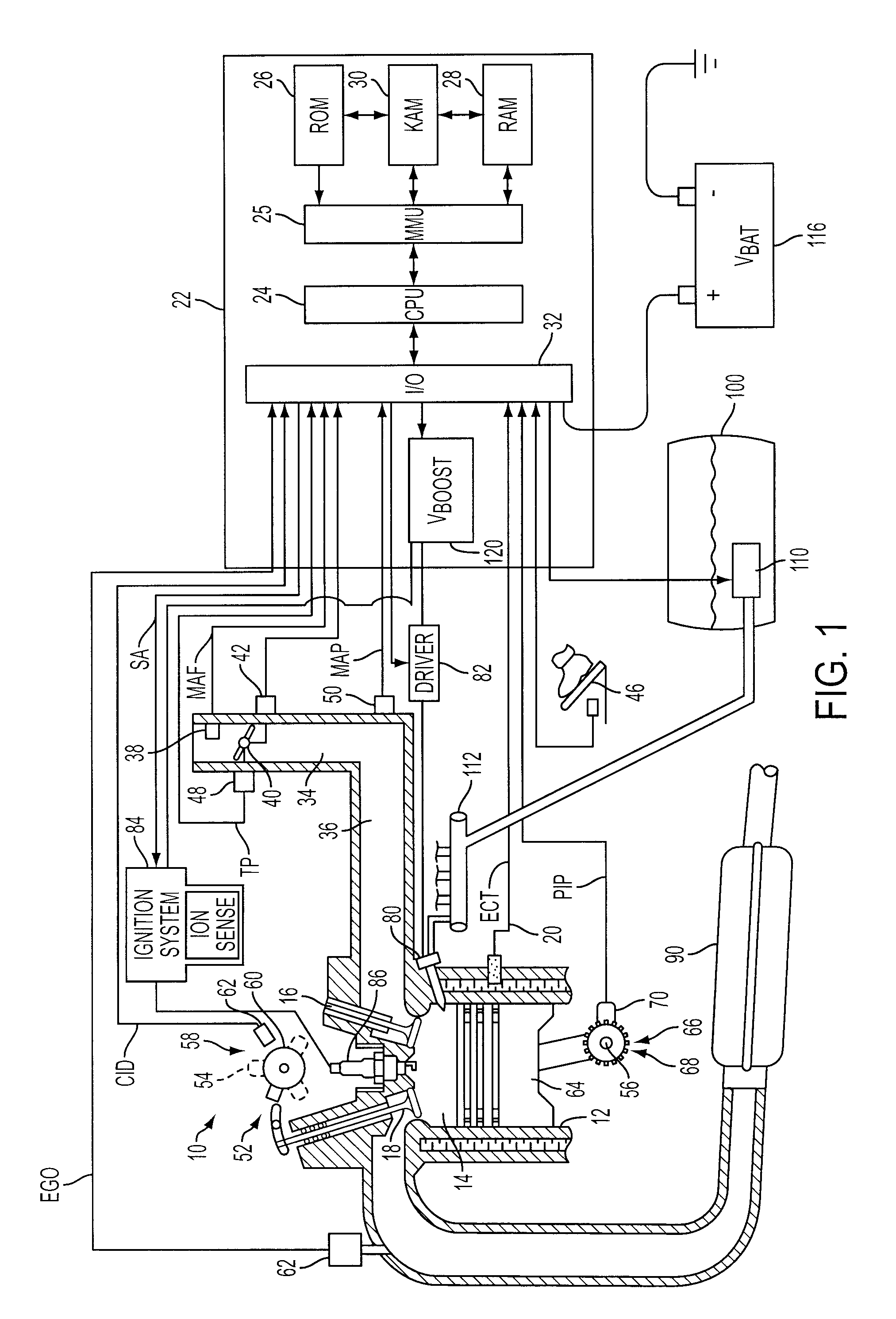
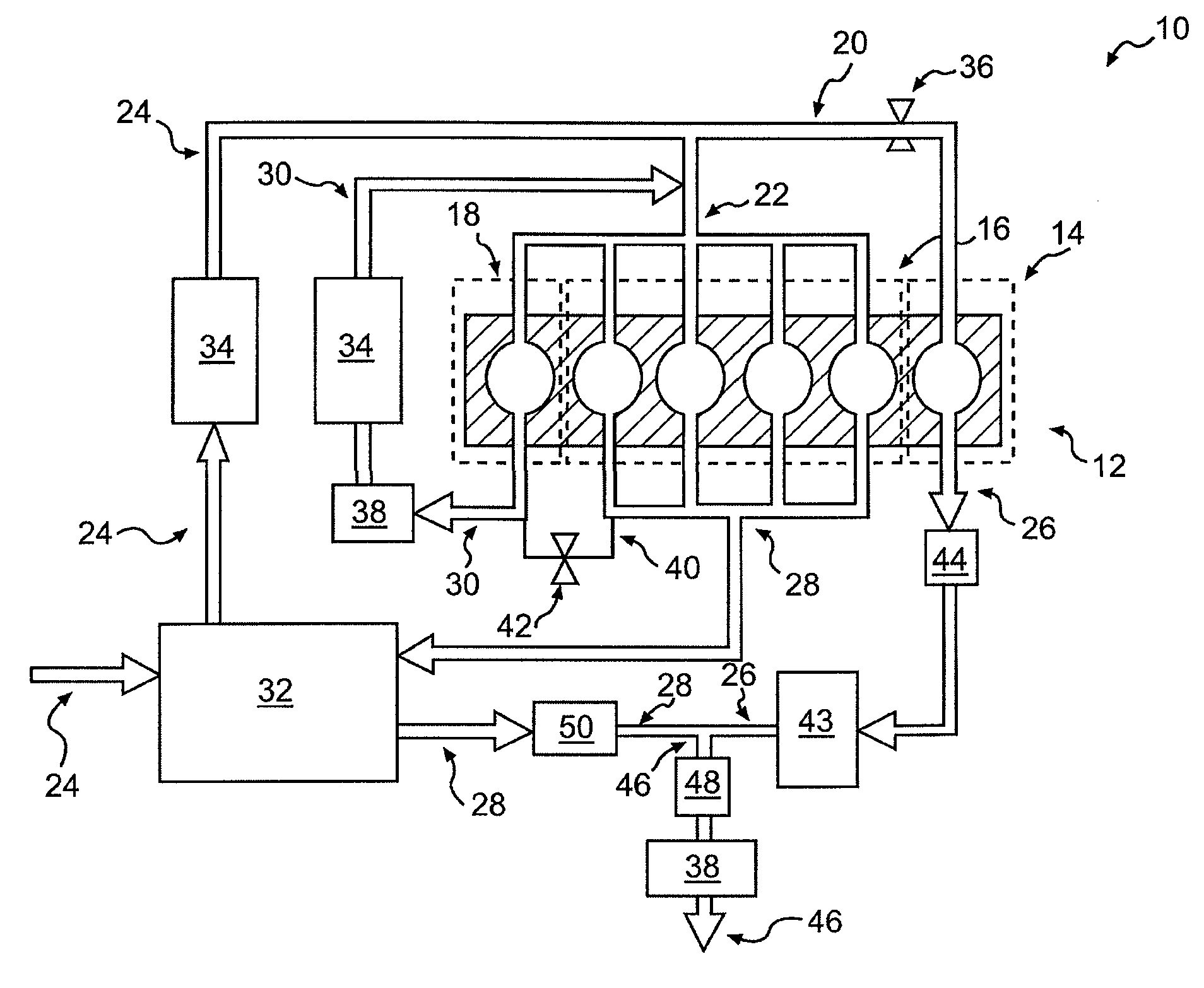
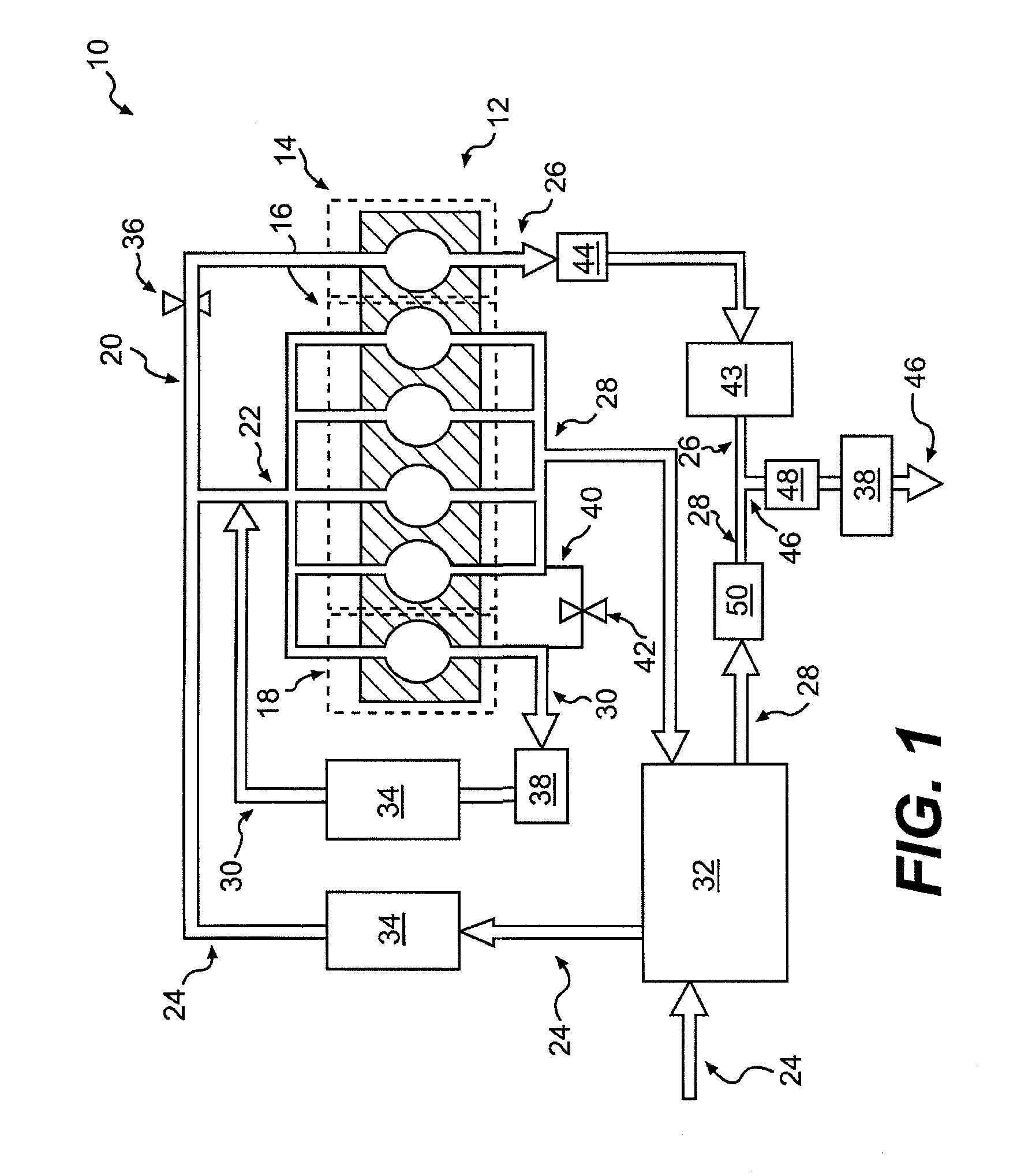
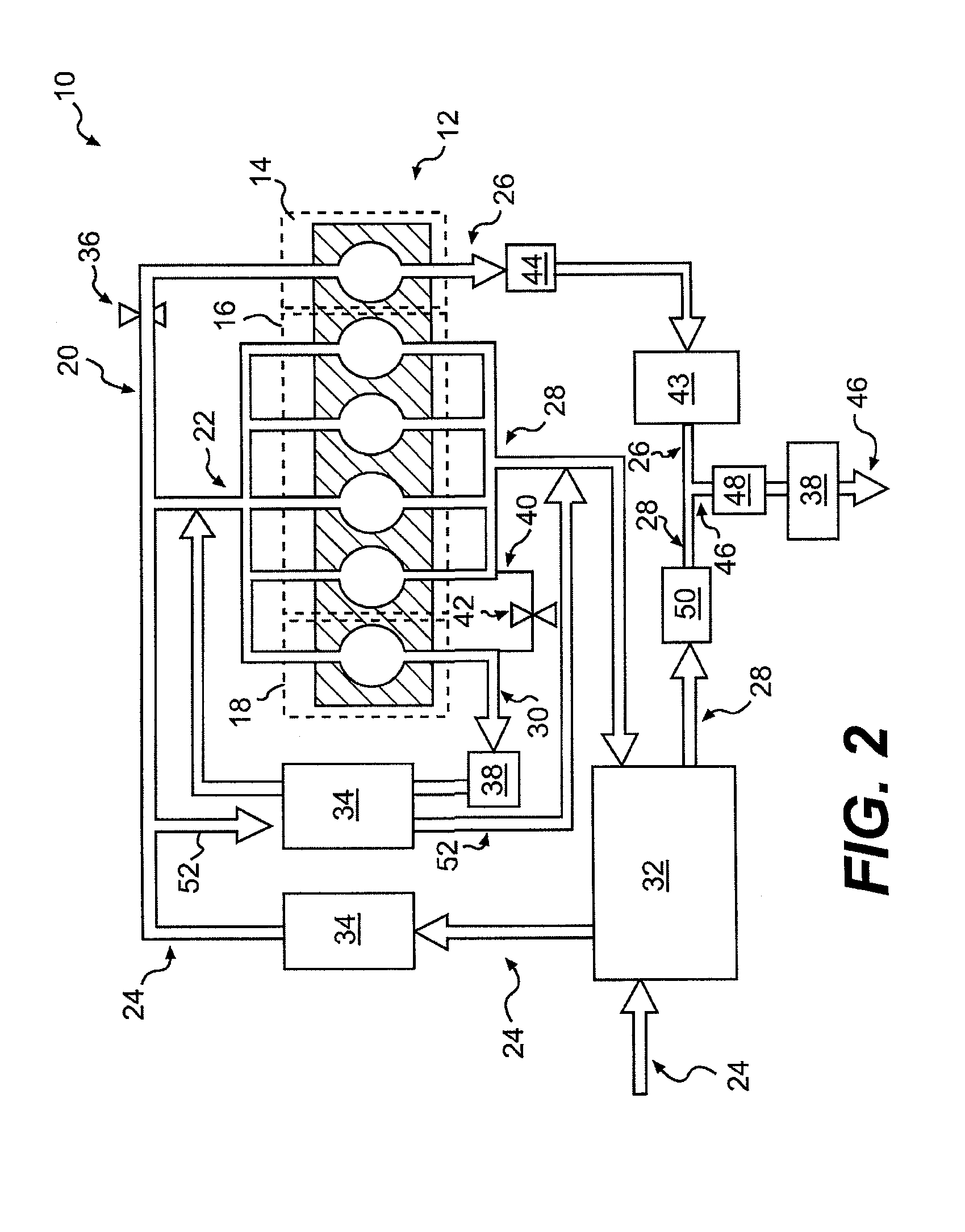
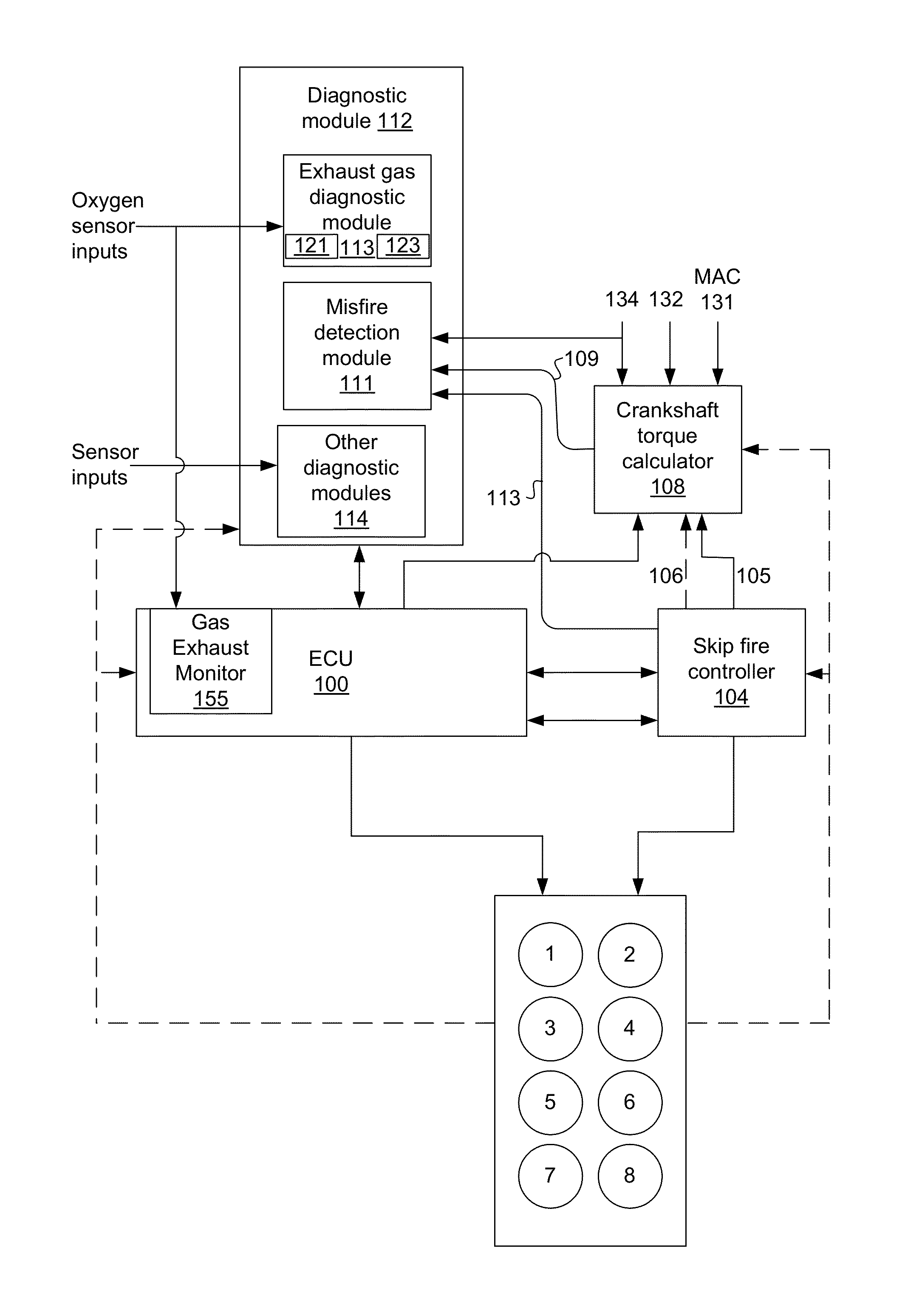
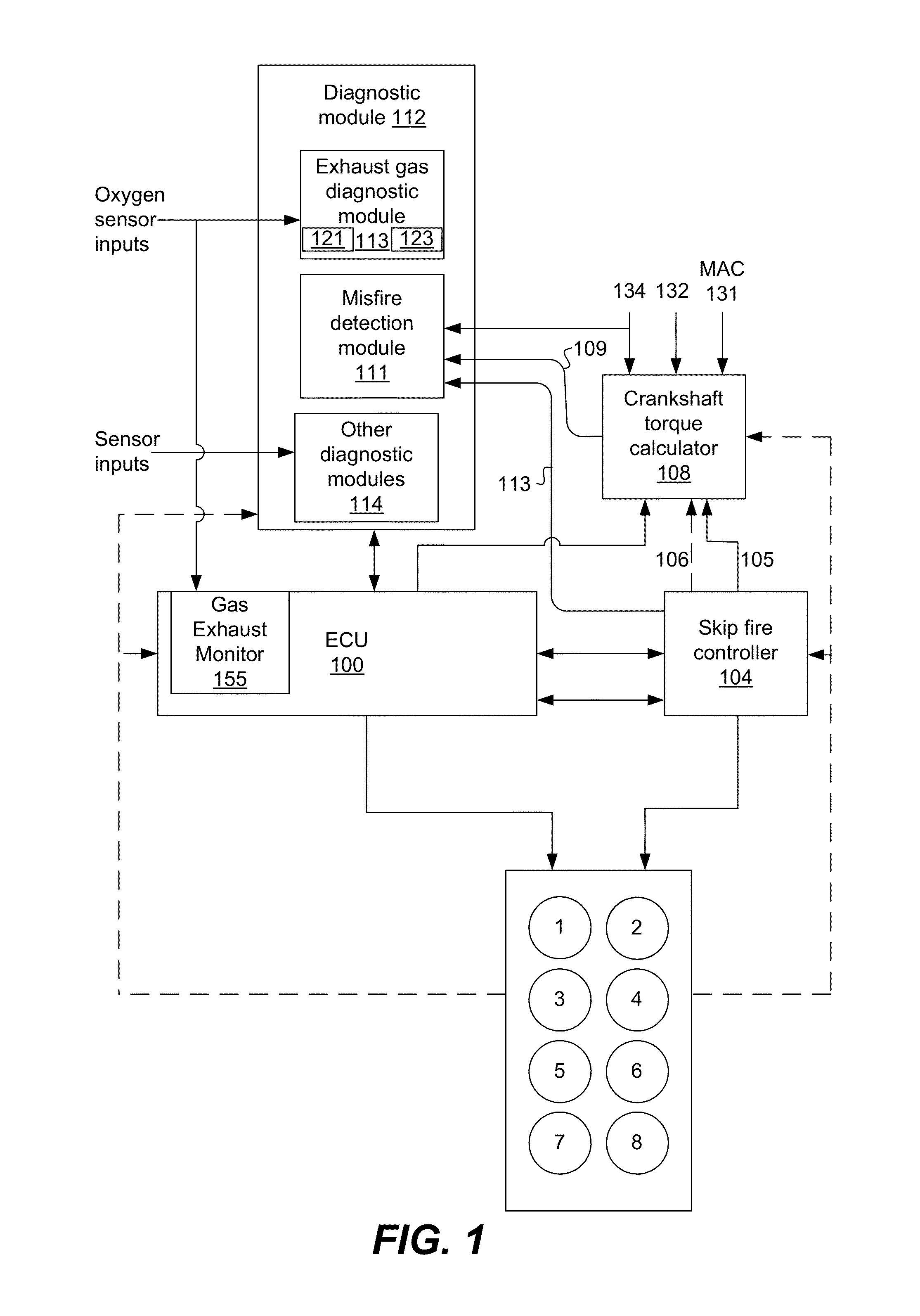
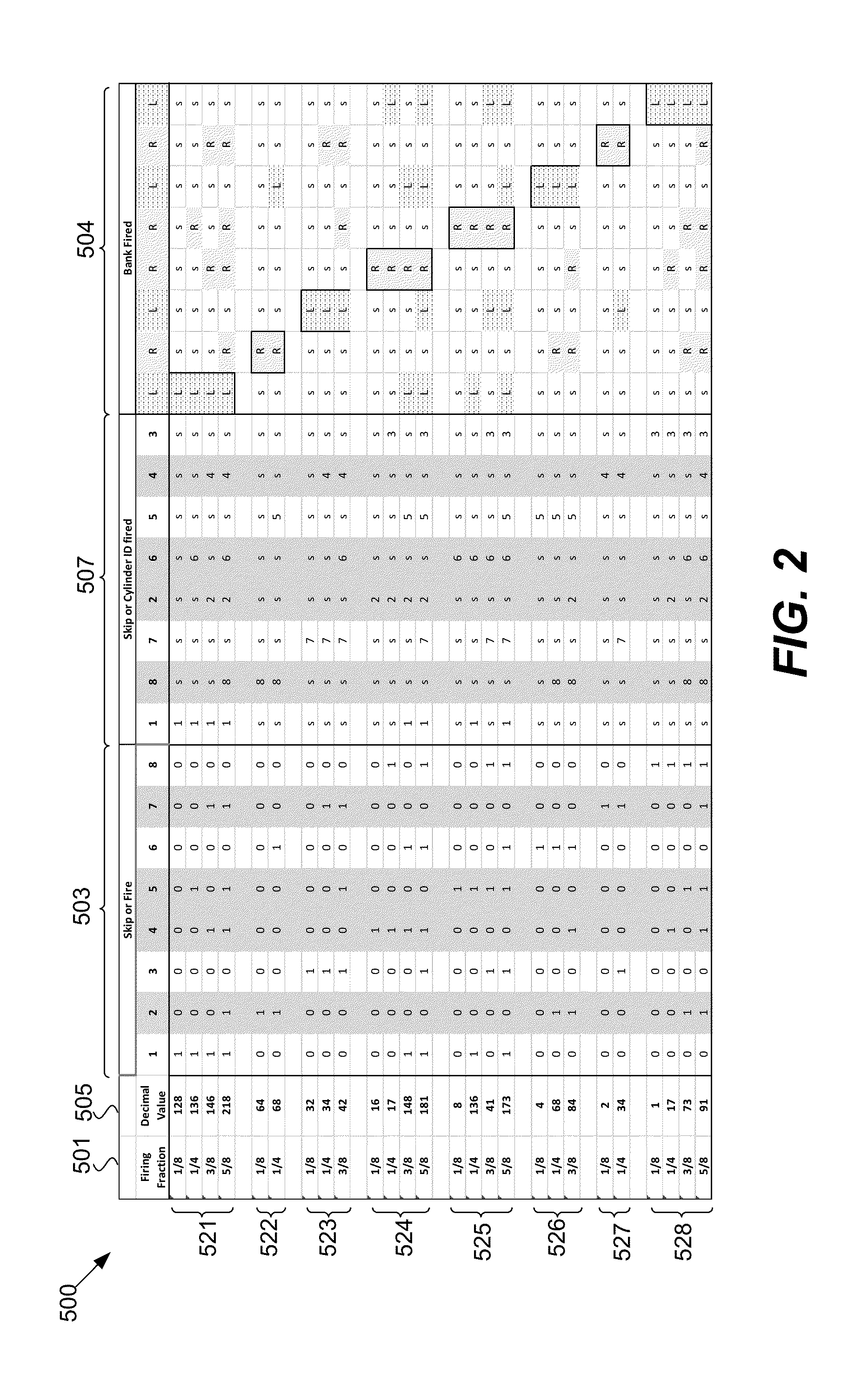
Engine diagnostics with skip fire control
Methods and devices are described for performing engine diagnostics during skip fire operation of an engine while a vehicle is being driven. Knowledge of the firing sequence is used to determine appropriate times to conduct selected diagnostics and / or to help better interpret sensor inputs or diagnostic results. In one aspect, selected diagnostics are executed when a single cylinder is fired a plurality of times in isolation relative to a sensor used in the diagnosis. In another aspect, selected diagnostics are conducted while the engine is operated using a firing sequence that insures that no cylinders in a first cylinder bank are fired for a plurality of engine cycles while cylinders in a second bank are at least sometimes fired. The described tests can be conducted opportunistically, when conditions are appropriate, or specific firing sequences can be commanded to achieve the desired isolation or skipping of one or more selected cylinders.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
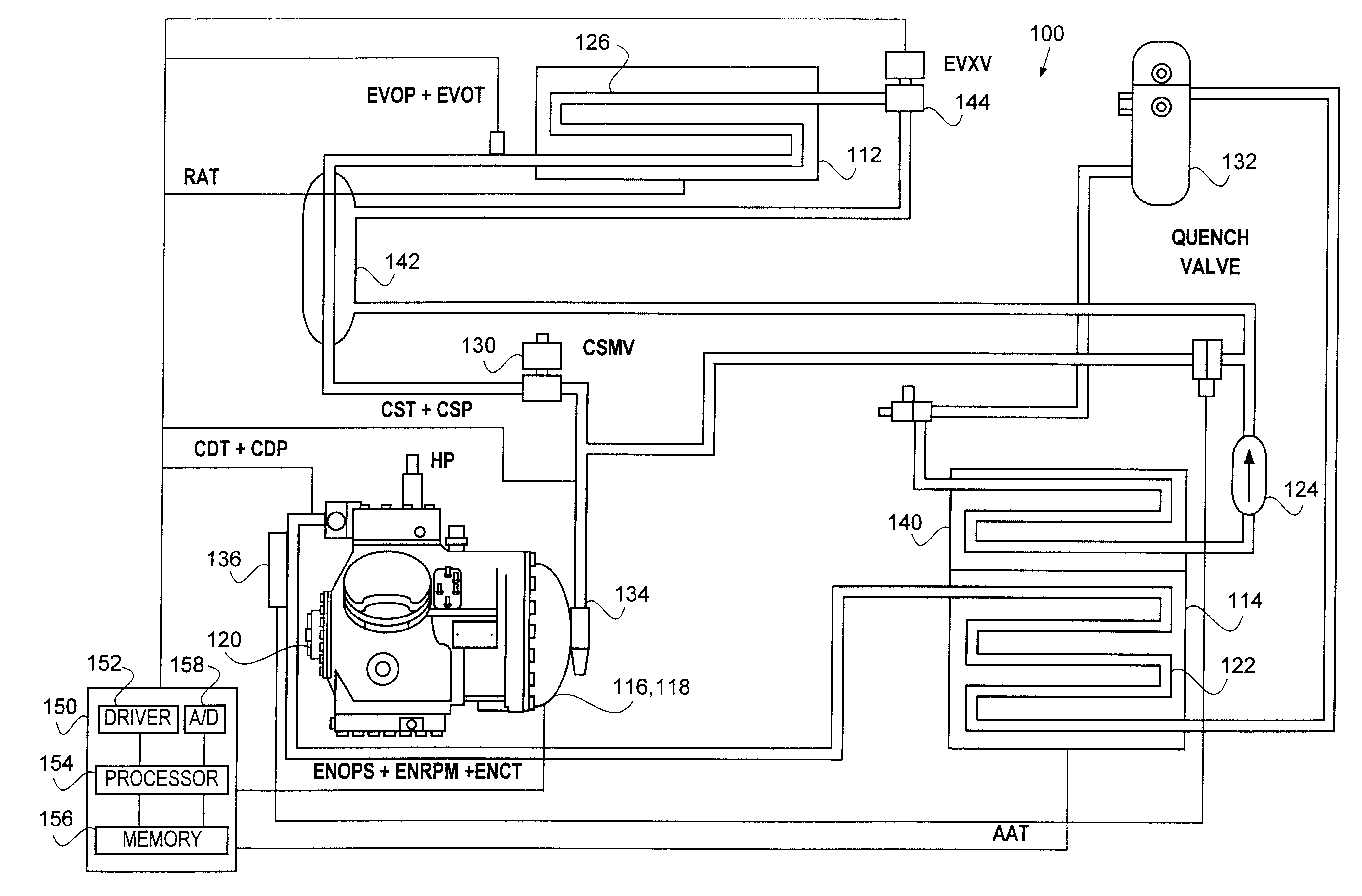
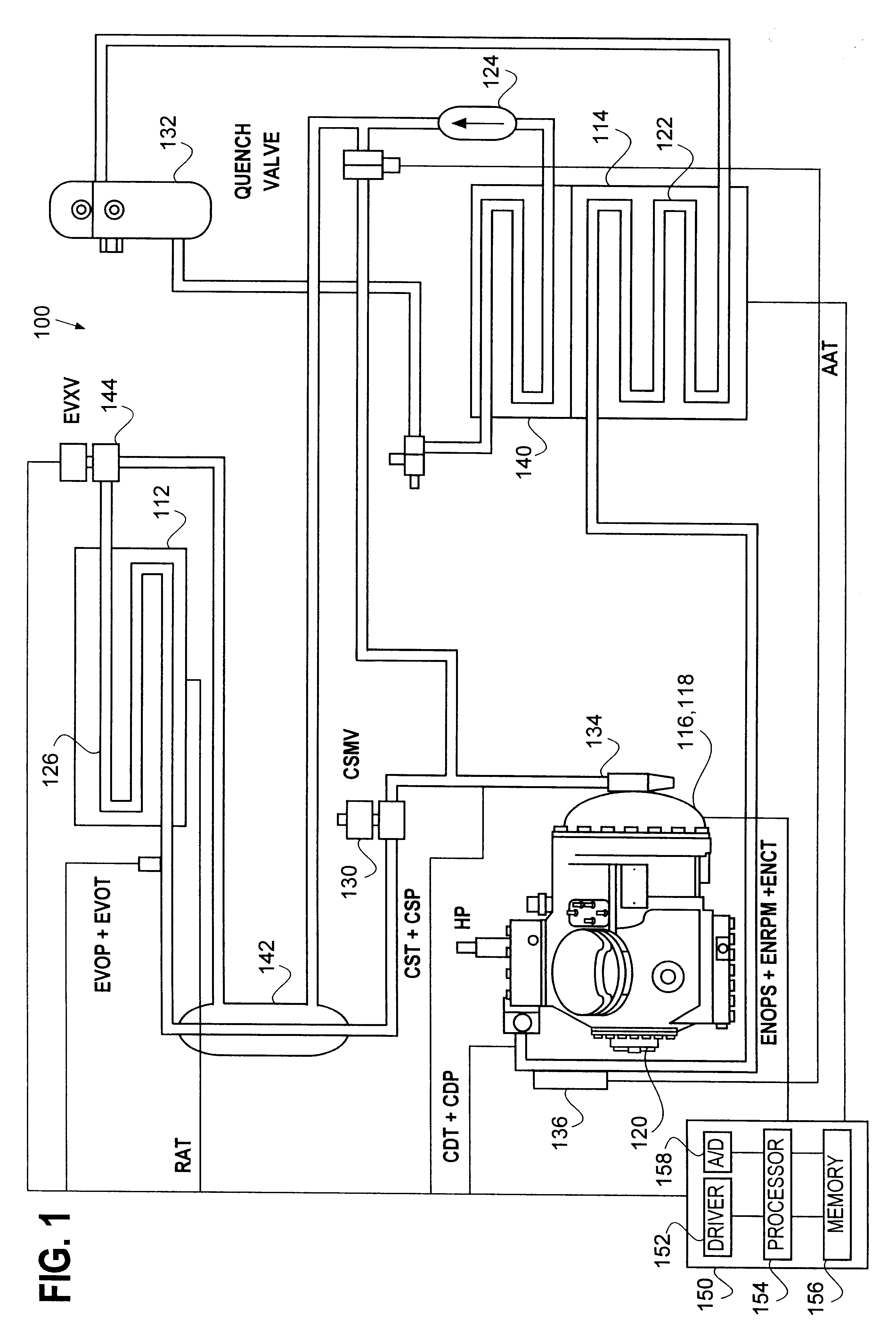
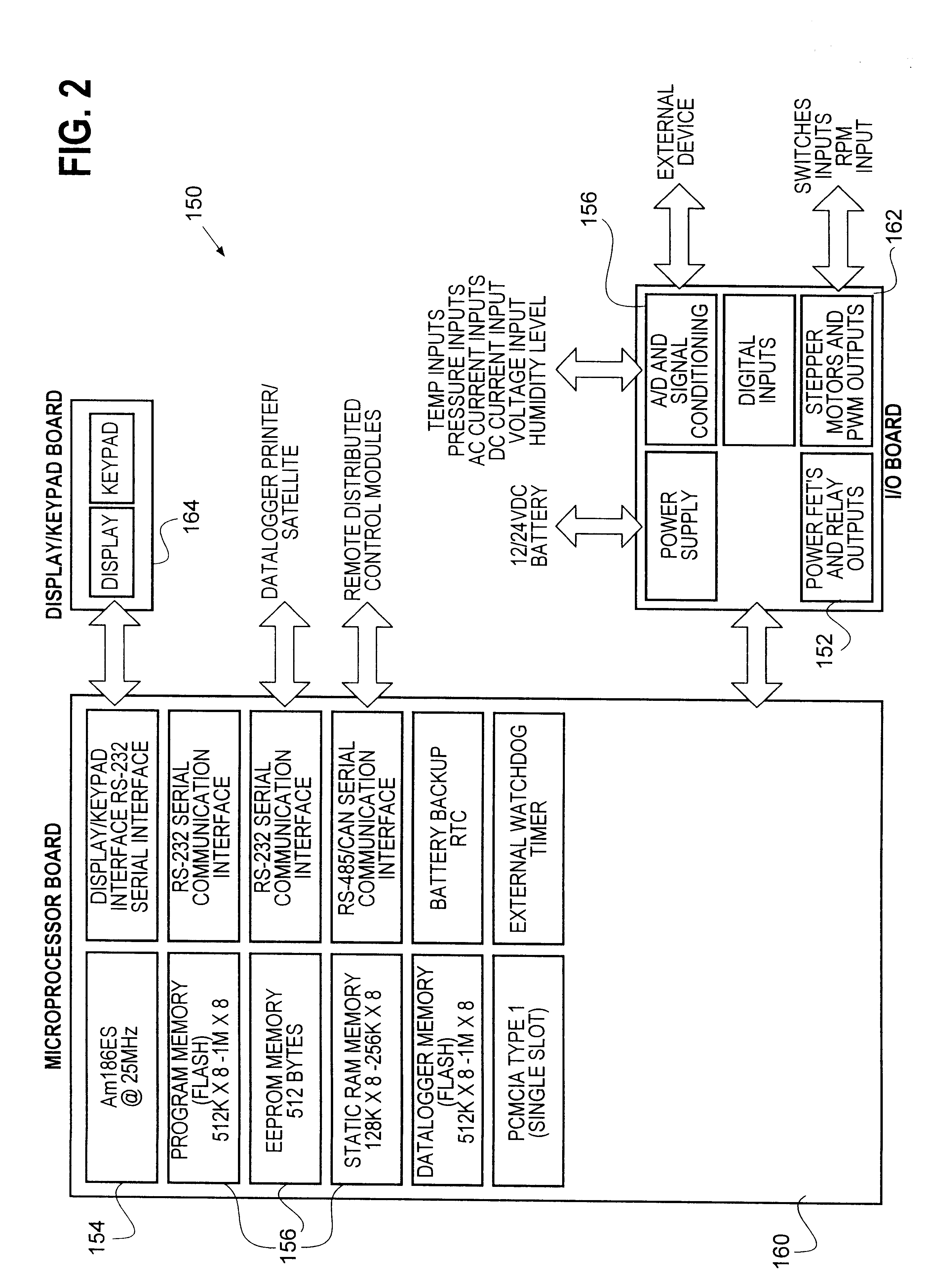
Compressor operating envelope management
InactiveUS6301911B1Precise maintenanceAir-treating devicesMechanical apparatusSolenoid valveEngineering
An process and method for monitoring and selectively controlling the discharge and suction pressures of a compressor within a transport unit is disclosed. Specifically, the present invention teaches the adjustment of the suction modulation valve, the compressor cylinder banks, and the engine speed solenoid in order to bring the operating compressor discharge and suction pressures within the design operating envelope.
Owner:CARRIER CORP
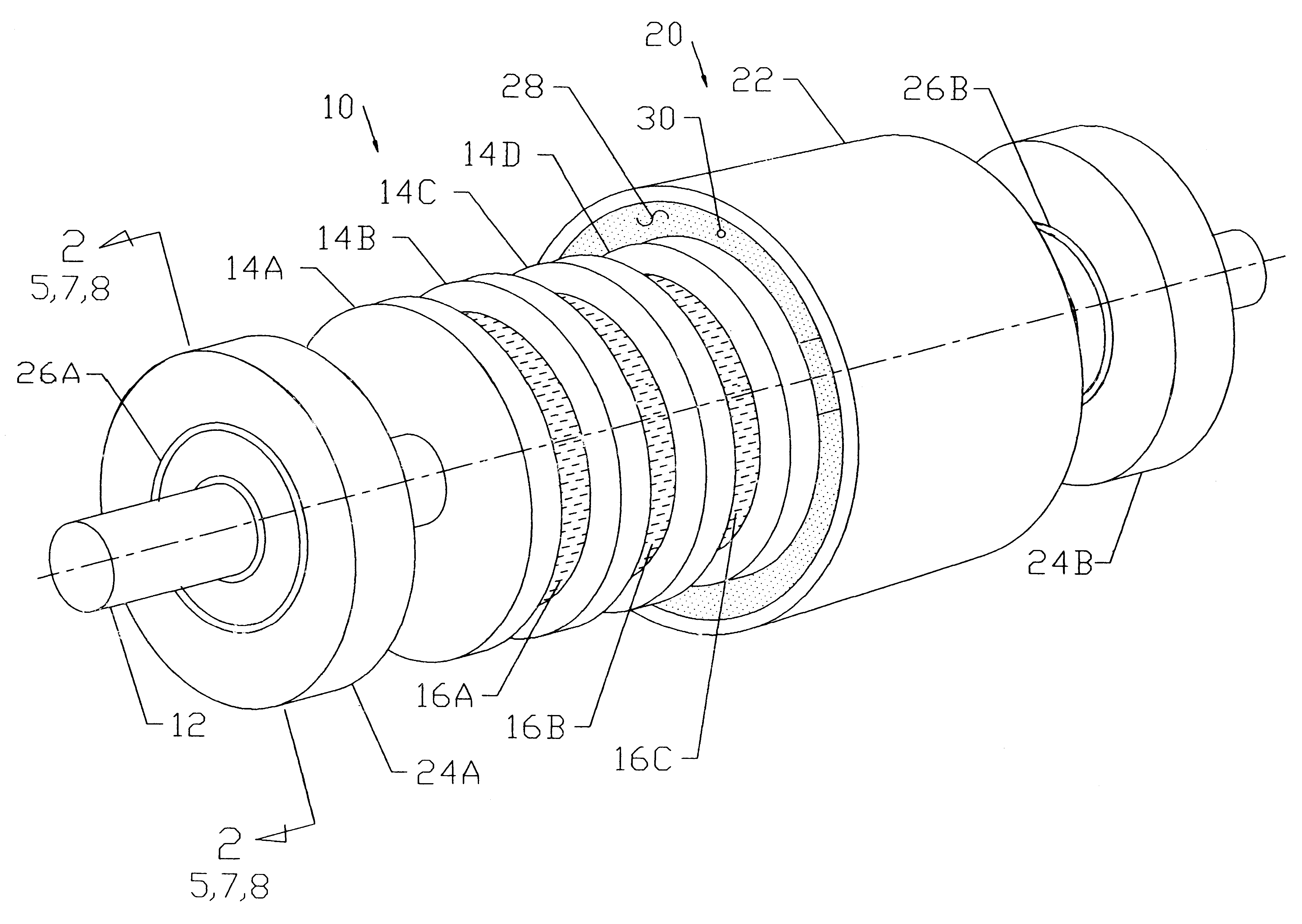
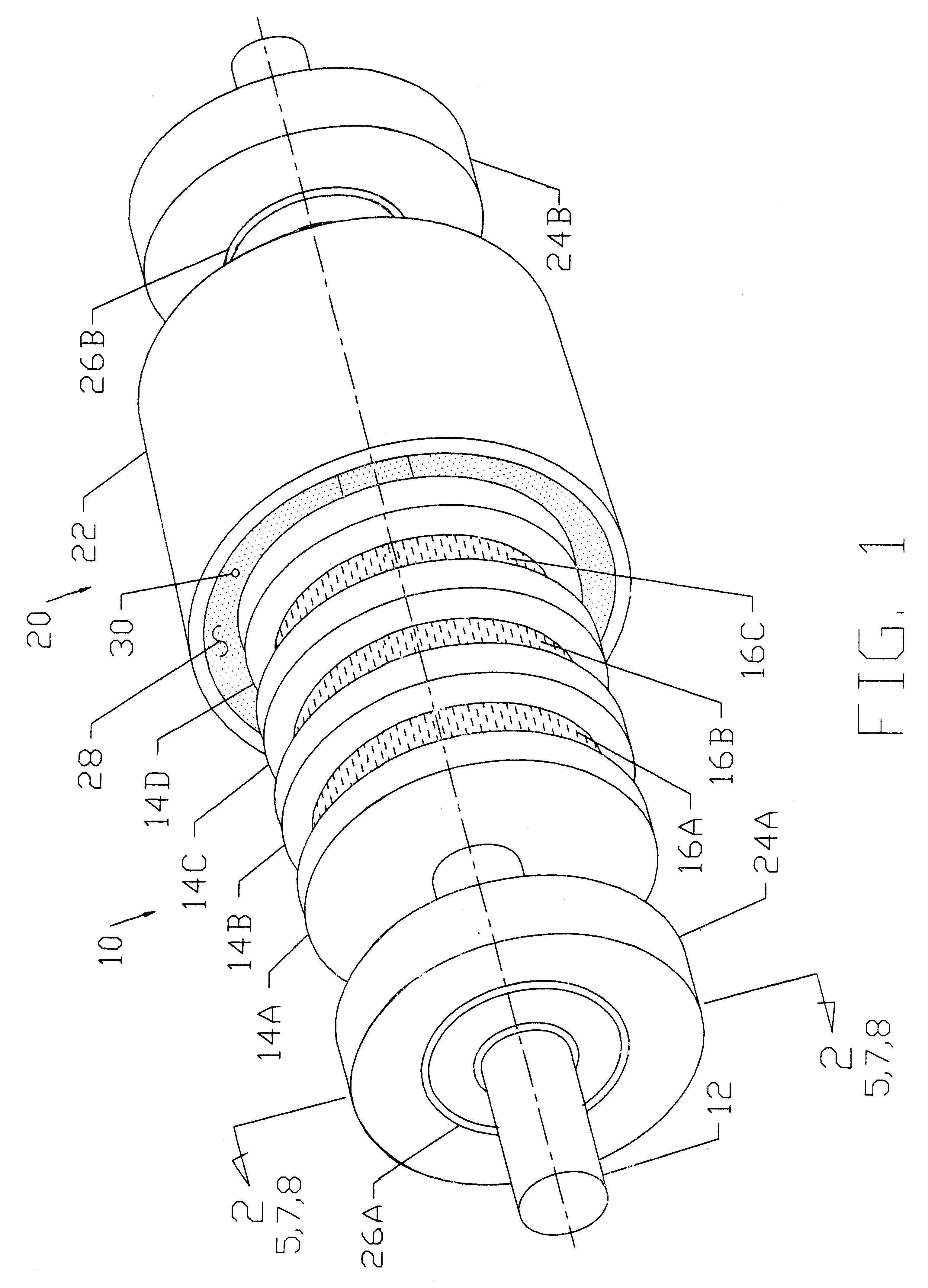
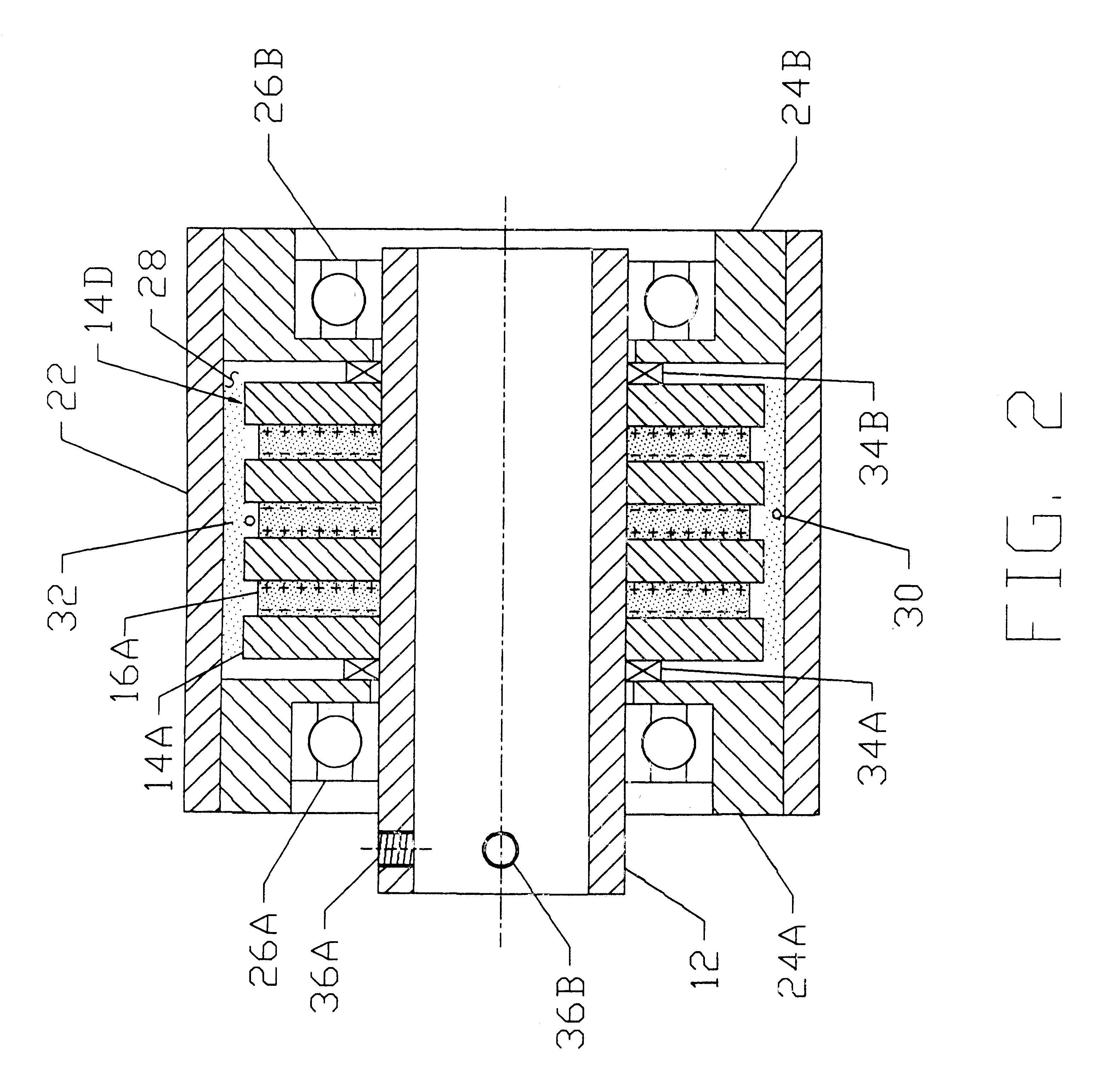
Magnetic circuit
InactiveUS6466119B1Maximize torqueMaximize heat dissipationDynamo-electric brakes/clutchesPermanent magnetsMagnetic polesMagnetism
A magnetic circuit design comprises a shaft assembly (10) consisting of a moveable shaft (12) and a series of washers (14) and magnets (16) mounted axially along the length of the shaft (12). The magnets (16) are positioned between the washers (14) with like magnetic poles facing each other. Additional washers (14) and magnets (16) may be stacked axially along the shaft (12). A cylinder assembly (20) consists of a cylinder (22) with housings (24A) and (24B) in each end. The shaft assembly (10) is positioned concentrically inside cylinder assembly (20) and is relatively rotatable to cylinder assembly (20) by means of bearings (26A) and (26B) inserted into housings (24A) and (24B). A fine magnetic powder (30) fills the air gap (28) created between the shaft (10) and the cylinder (20) assemblies.
Owner:DREW CHESTER
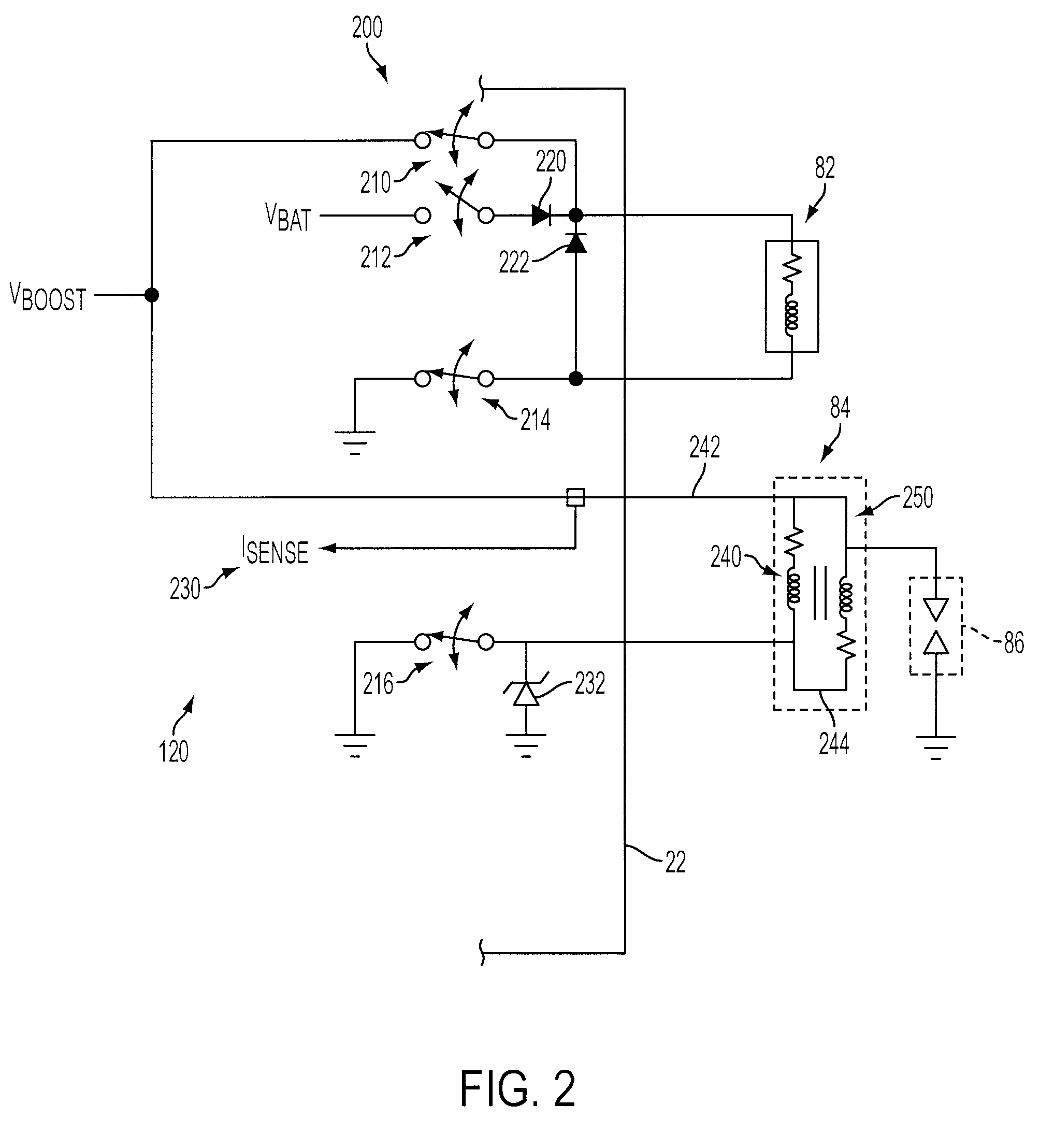
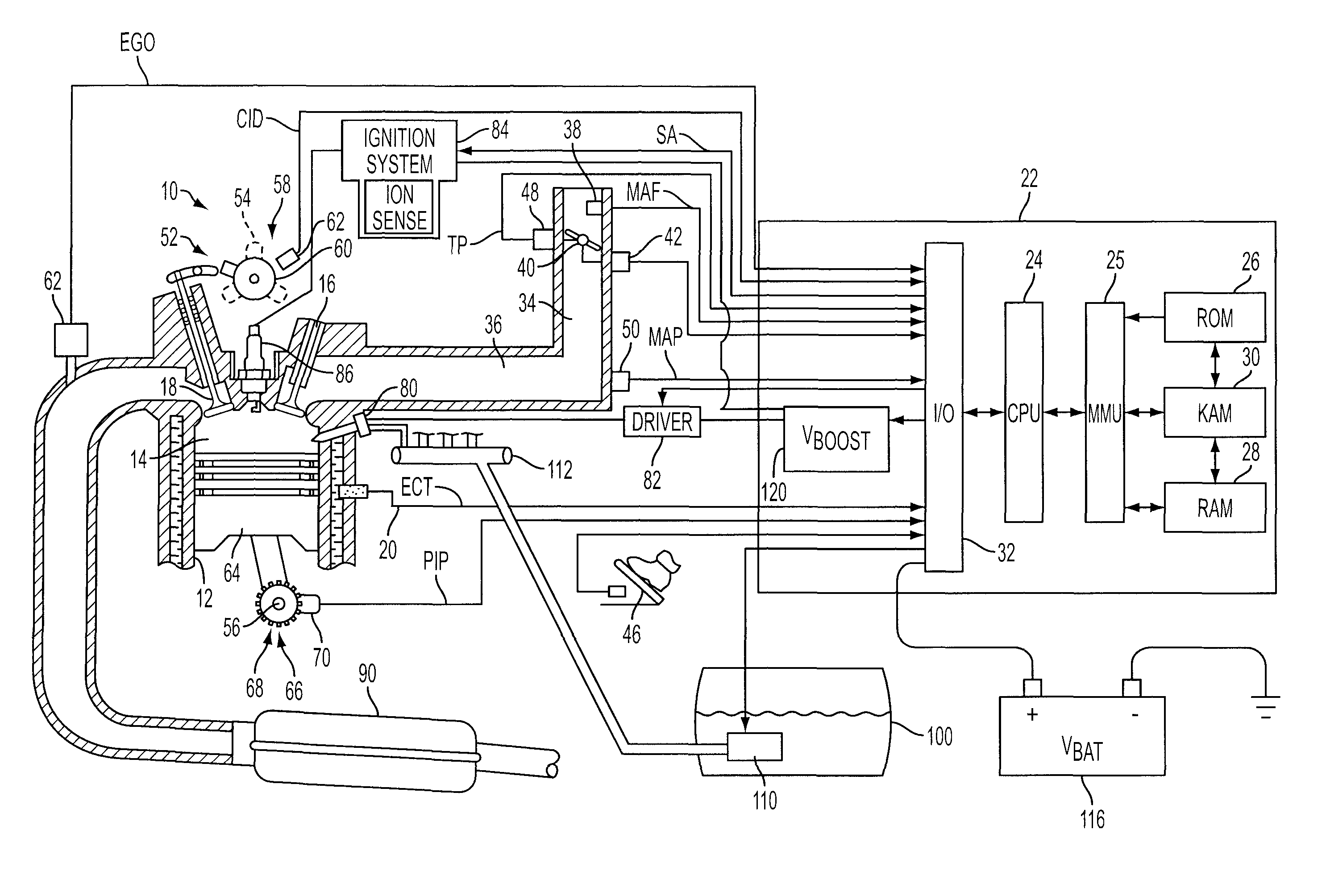
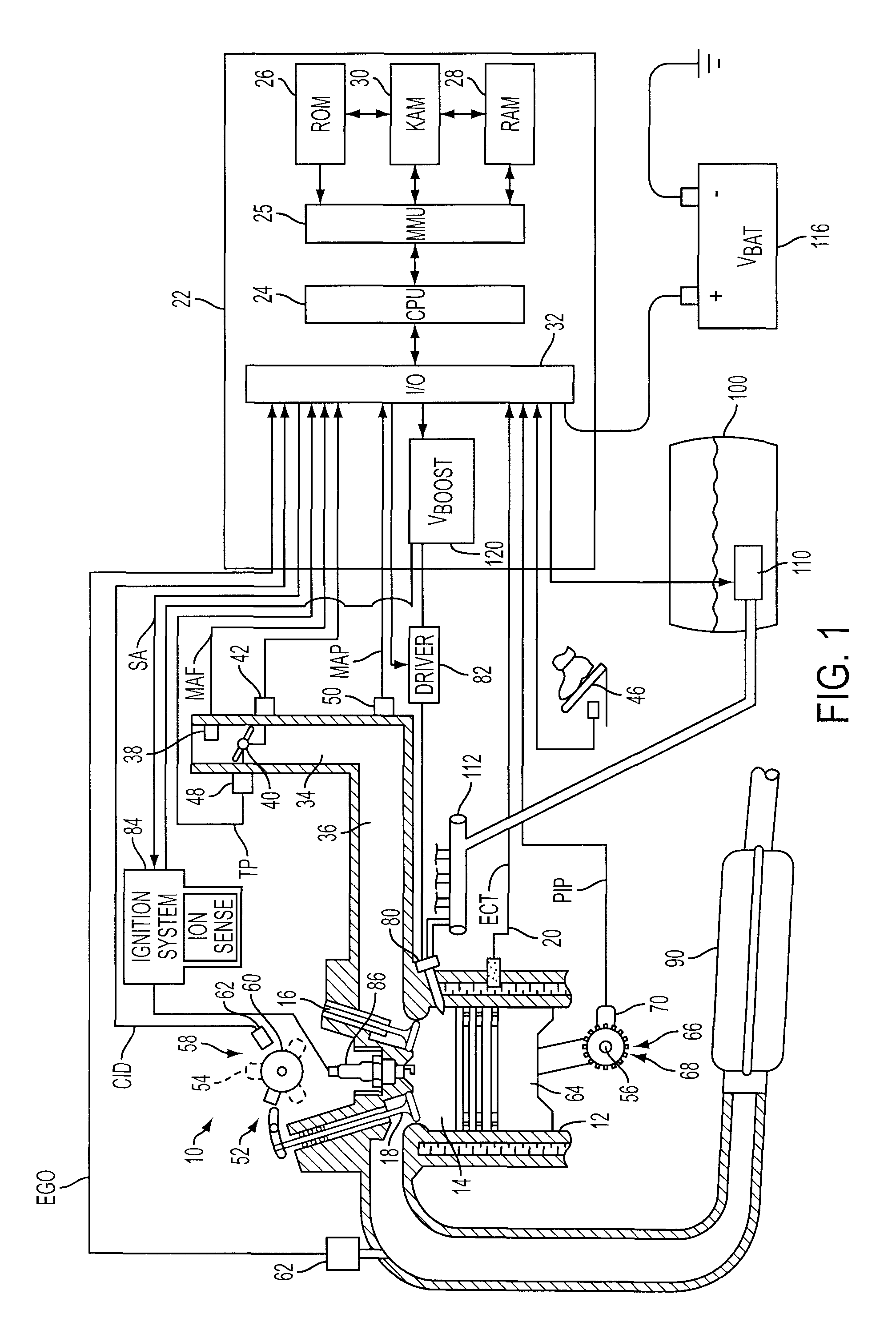
Ignition Energy Management With Ion Current Feedback To Correct Spark Plug Fouling
ActiveUS20100057324A1Reduce and eliminate plug foulingPrevent wrong actionAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlPower flowIon current
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Internal combustion engine using variable valve lift and skip fire control
An internal combustion engine capable of cylinder deactivation or skip fire control in combination with variable valve lift control. One bank of cylinders can be deactivated while the air induction of the other bank of cylinders is regulated using variable valve lift control to increase engine efficiency. An internal combustion engine with two cylinder banks, where control of one cylinder bank using skip fire control can be operating at an appropriate firing fraction in combination with variable valve lift control on the other cylinder bank. A single bank of cylinders can be controlled in a skip fire manner in conjunction with variable valve lift control.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
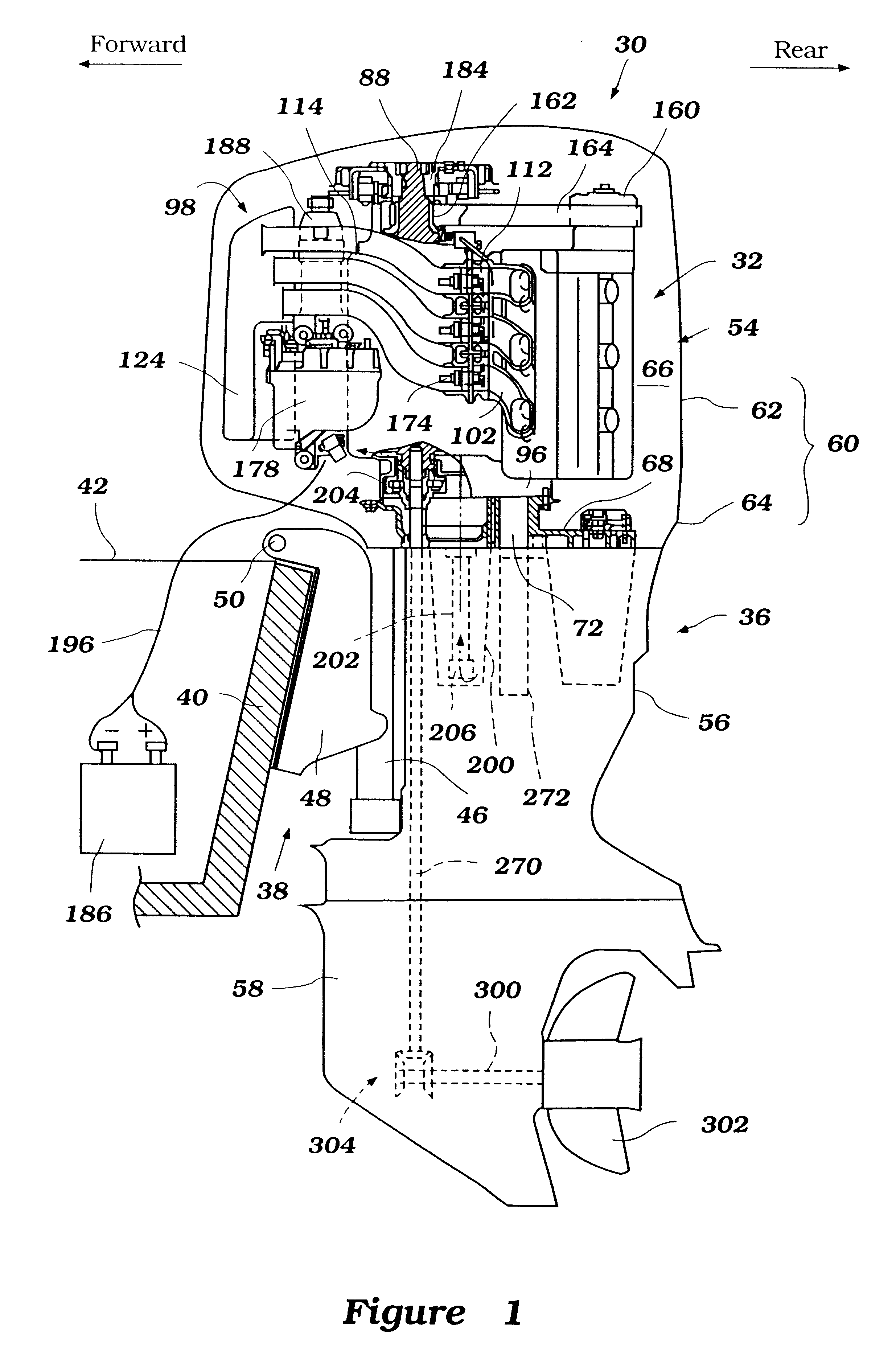
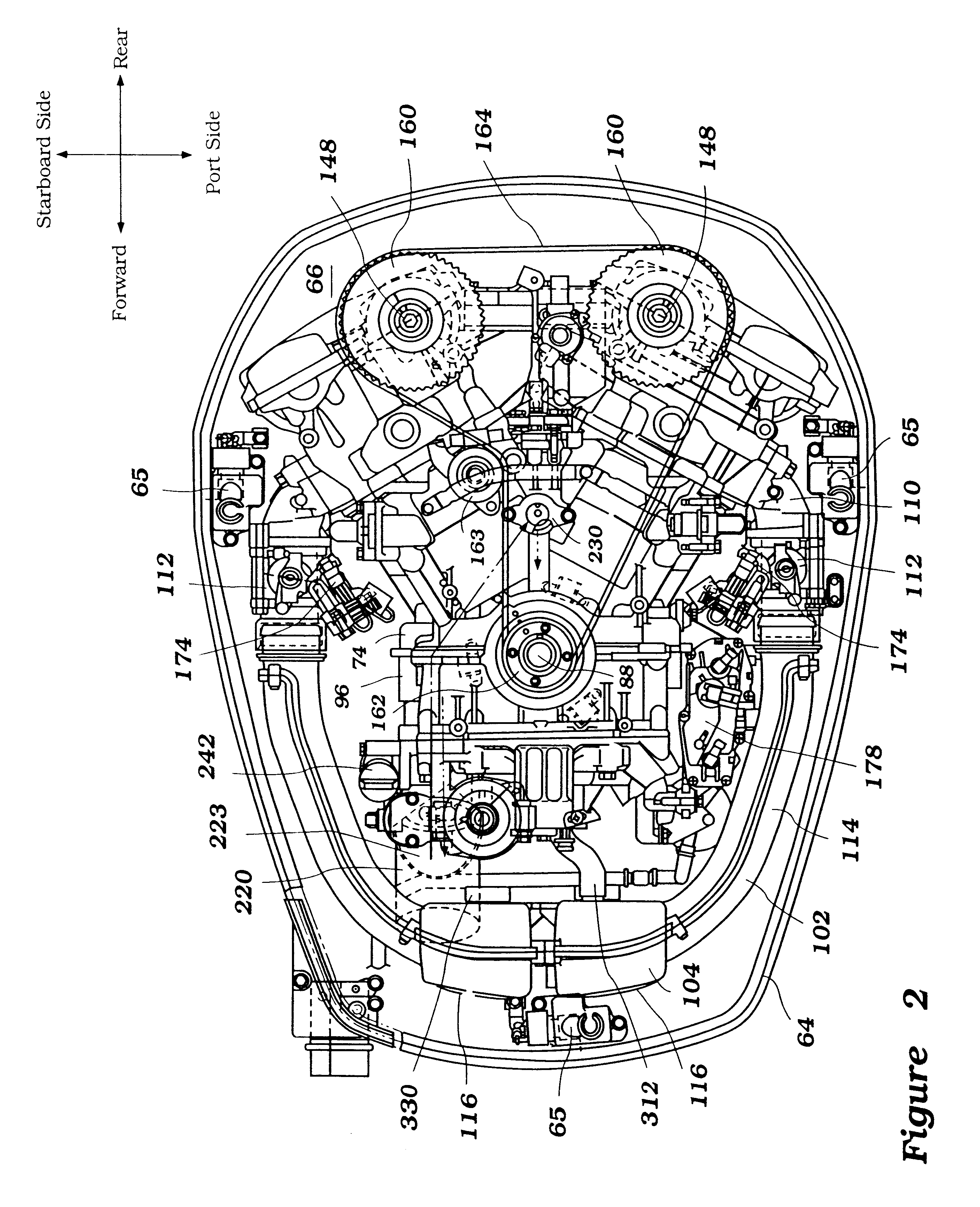
Arrangement for outboard motor
InactiveUS6346018B1Small sizeComponents is relatively effectivePower plants using condensersCasingsCombustion chamberCrankcase
An outboard motor comprises an internal combustion engine and a protective cowling that surrounds the engine. The cowling comprises at least an upper portion and a lower portion. The engine comprises a cylinder block that defines a cylinder bore. A cylinder head member is fixed at one end of the cylinder block and encloses one end of the cylinder bore. A crankcase member is fixed at the other end of the cylinder block and encloses the other end of the cylinder bore. The crankcase member forms a crankcase chamber. A piston is positioned within the cylinder bore. A crankshaft is rotably journaled in the crankcase chamber and is connected to the piston. The piston, the cylinder bore and the cylinder head together define a combustion chamber. The cylinder block, the cylinder head member and the crankcase member together defining an engine body. A first air intake conduit communicates with the engine and extends generally along a side of the engine body. The first air intake conduit communicates with an intake silencer located proximate the crankcase member. The engine further comprises a starter motor, an electronic control unit and a fuel supply system. The fuel supply system comprises a vapor separator and a fuel injector. The starter motor, the electronic control unit, the vapor separator and the fuel injectors are located in a space defined between the intake silencer, the first air intake conduit and the engine body.
Owner:SANSHIN KOGYO CO LTD
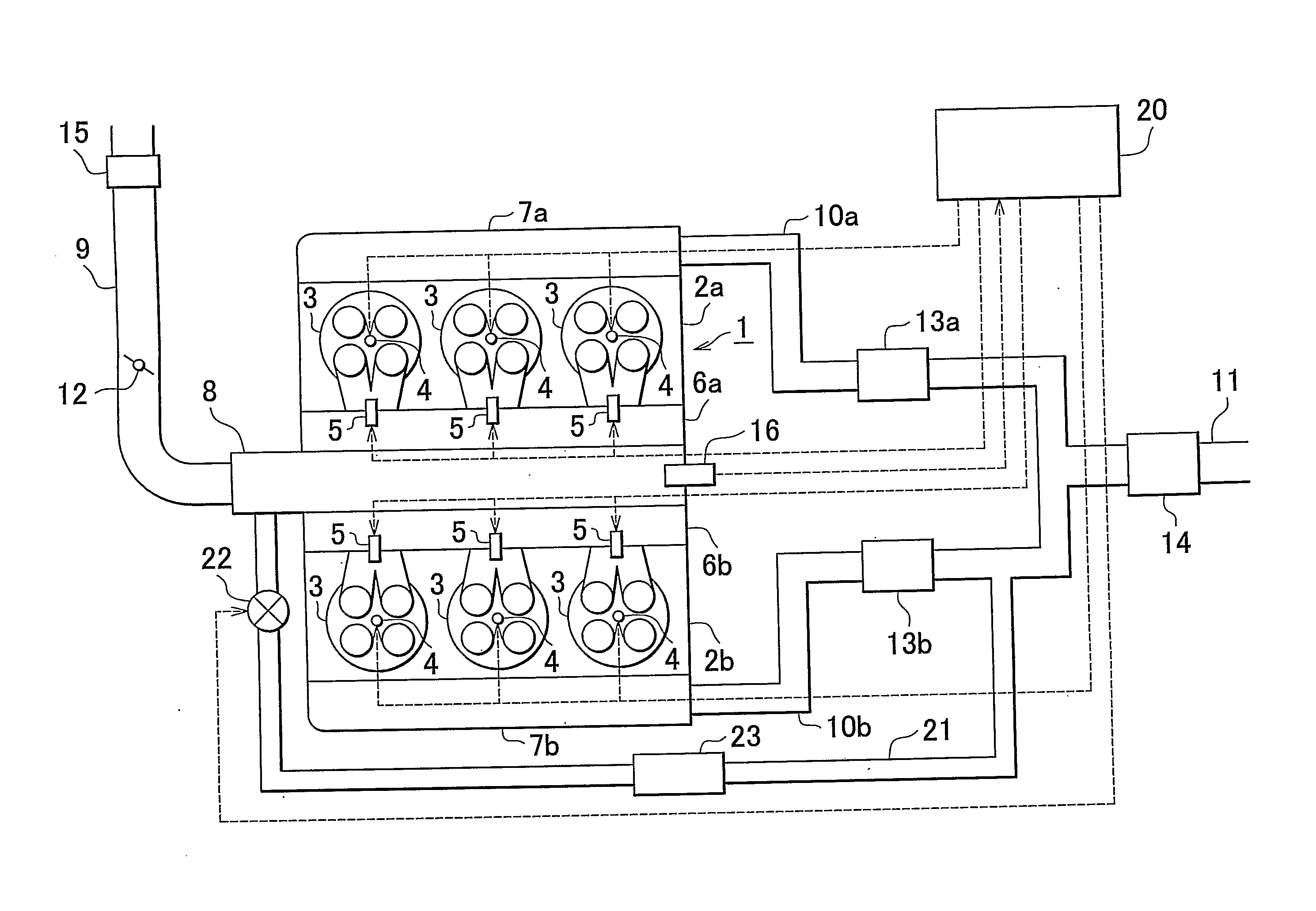
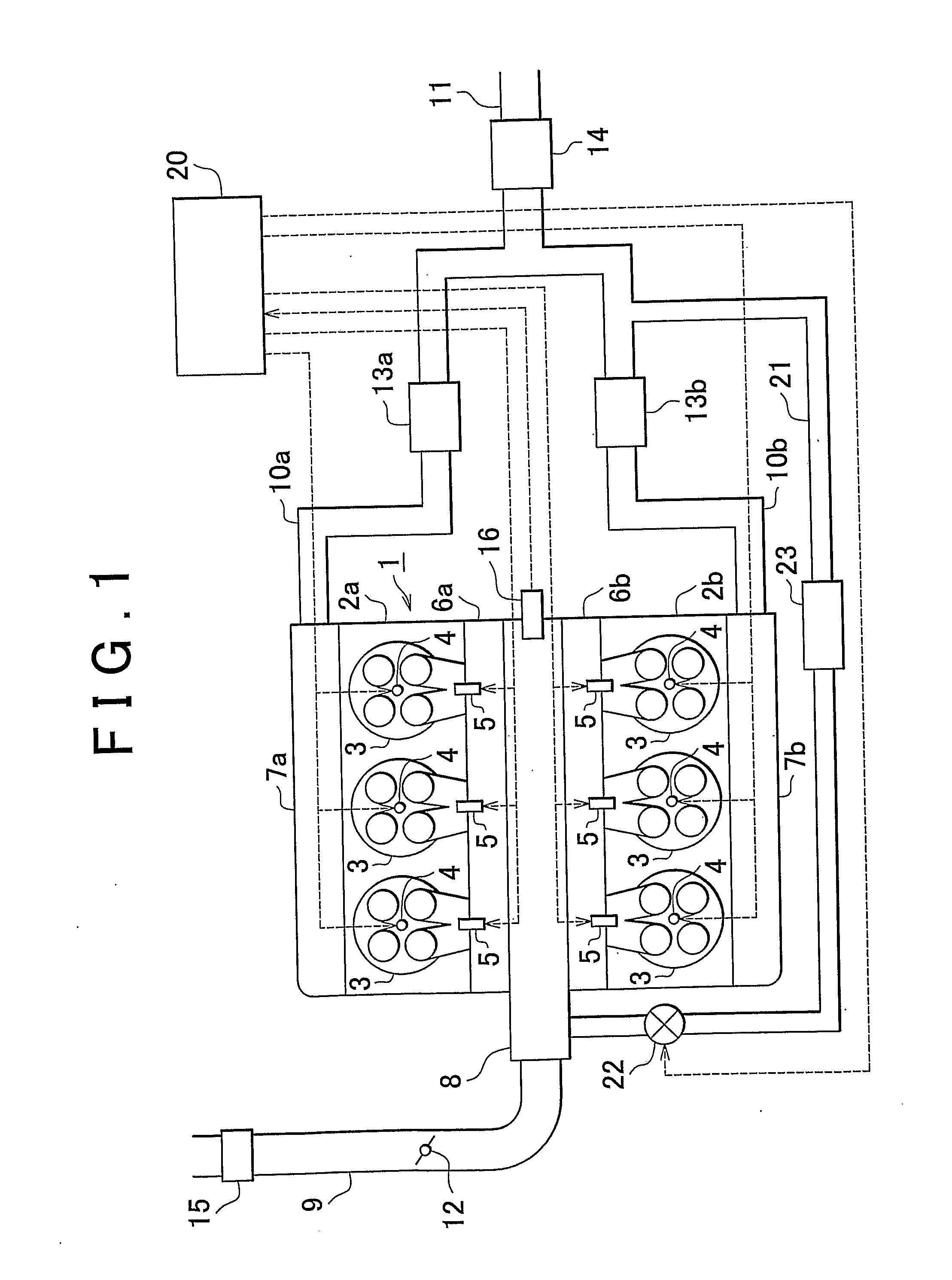
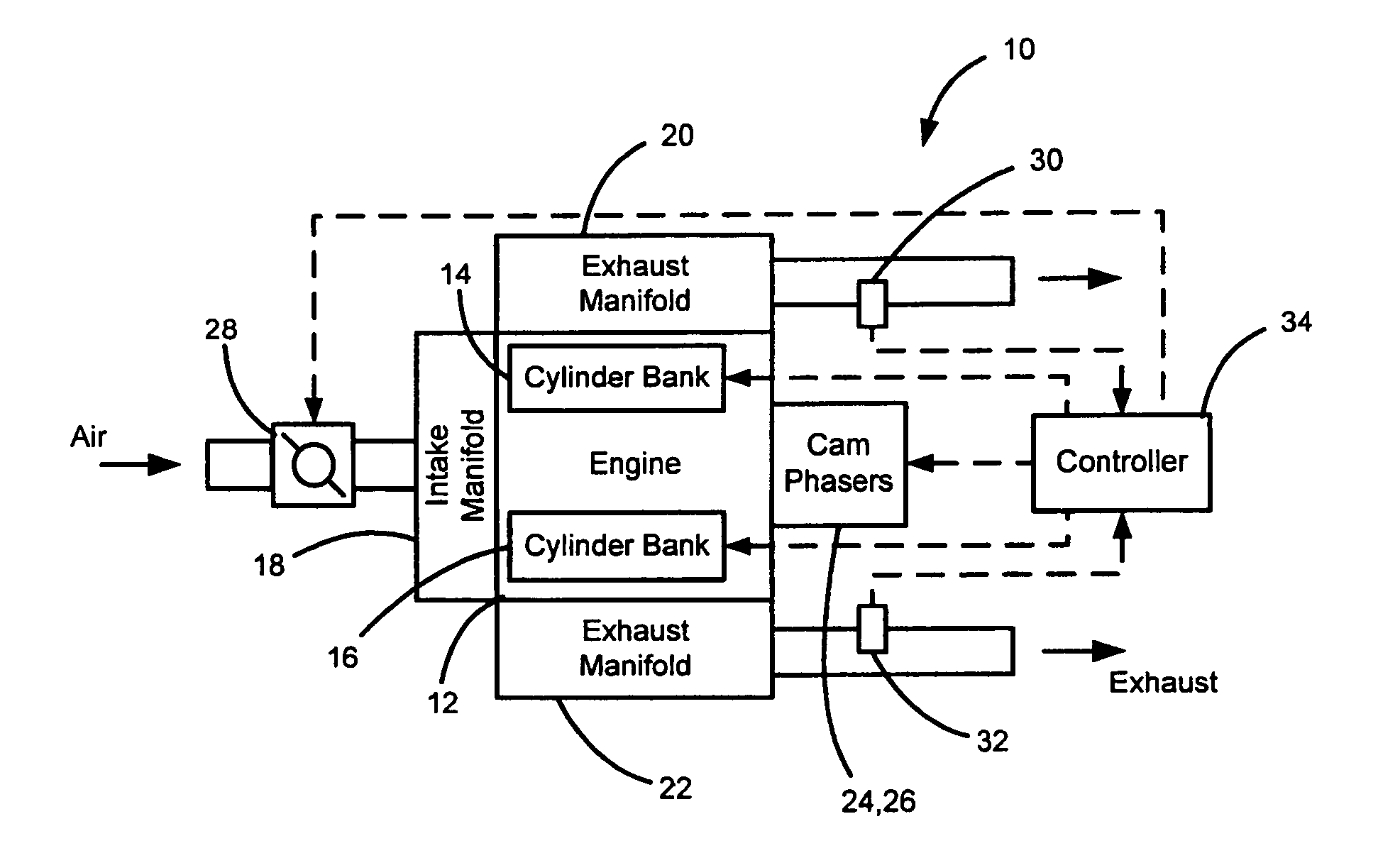
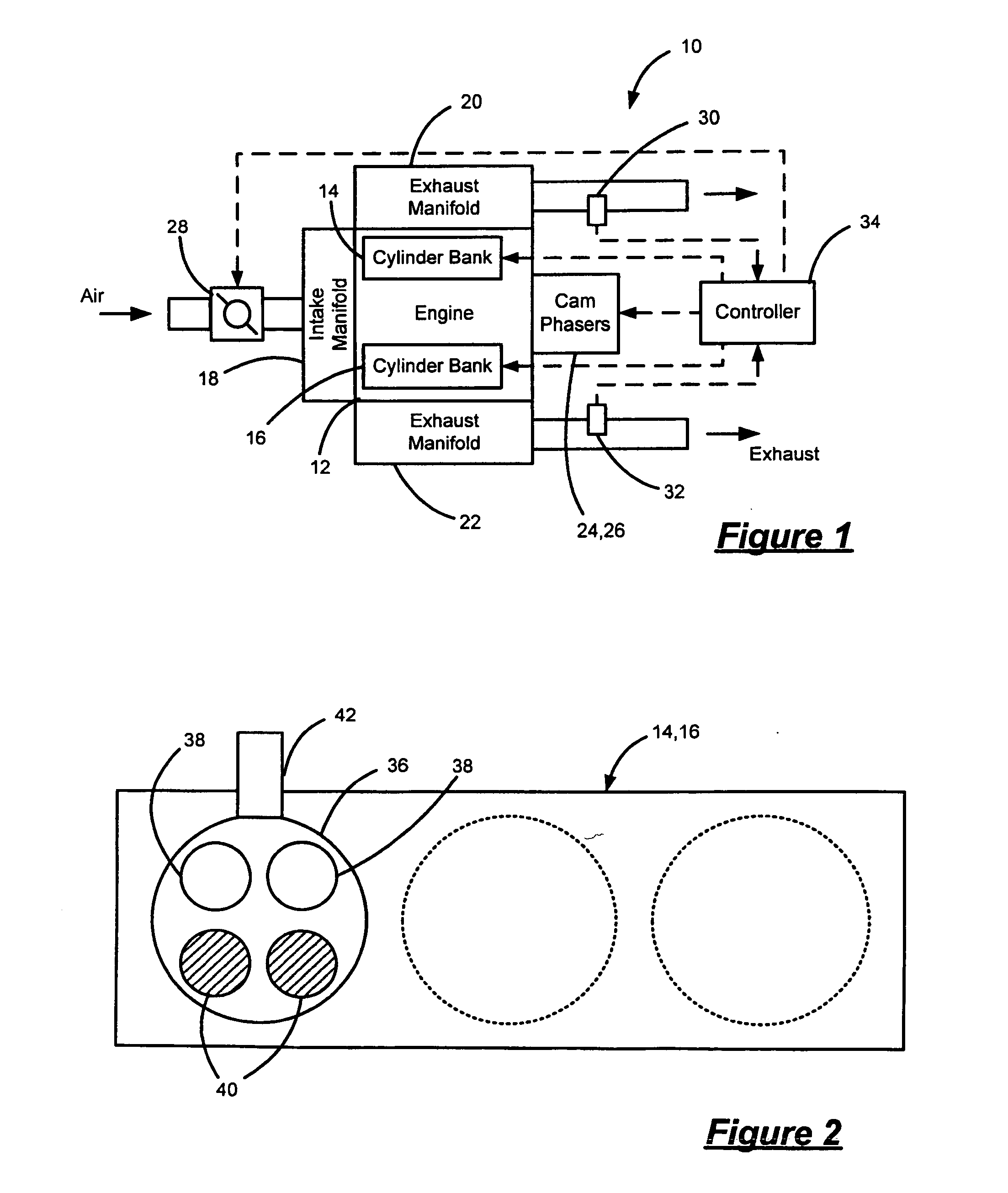
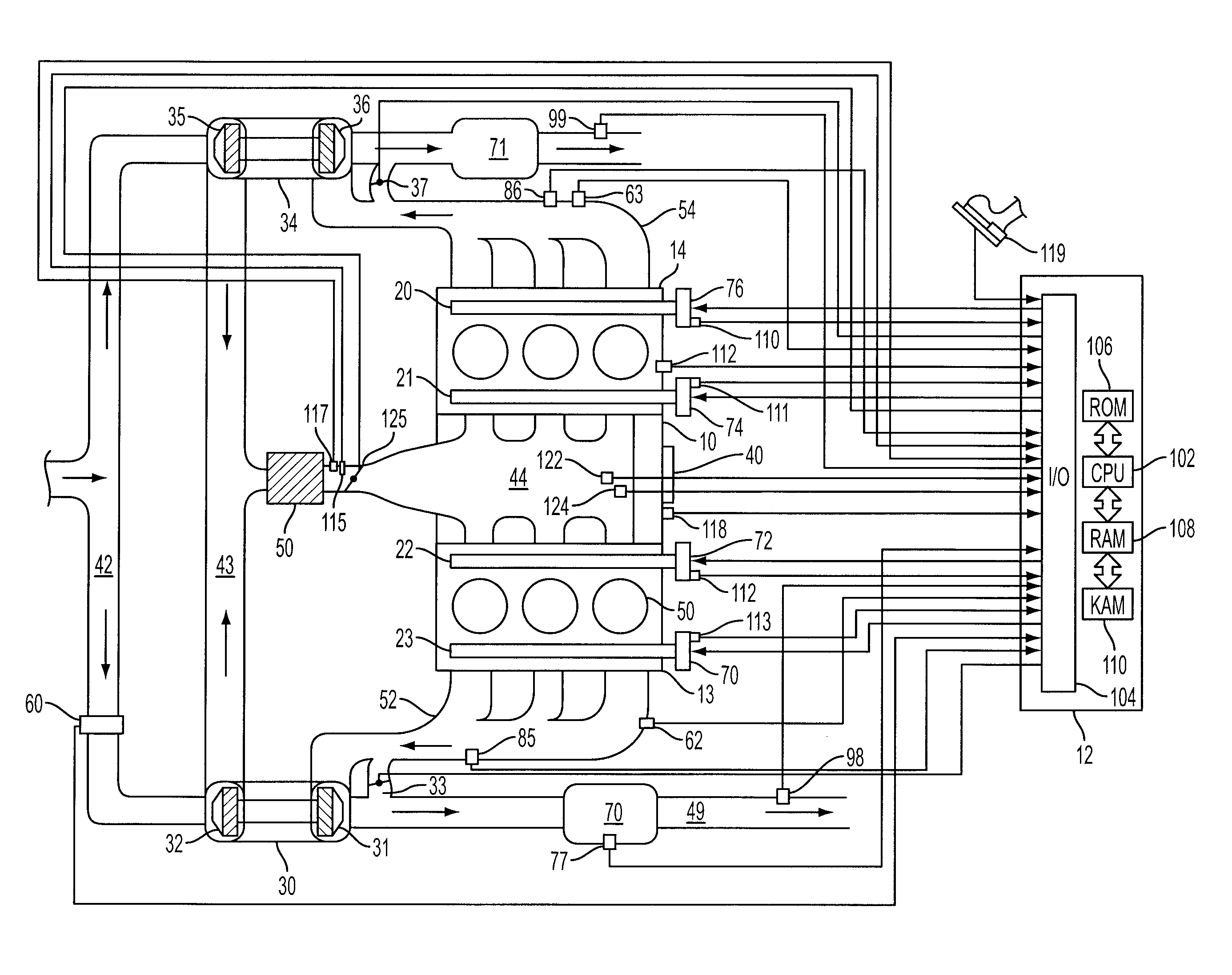
Control system and control method for internal combustion engine
InactiveUS20110023829A1Reduce stepsElectrical controlNon-fuel substance addition to fuelControl systemInternal combustion engine
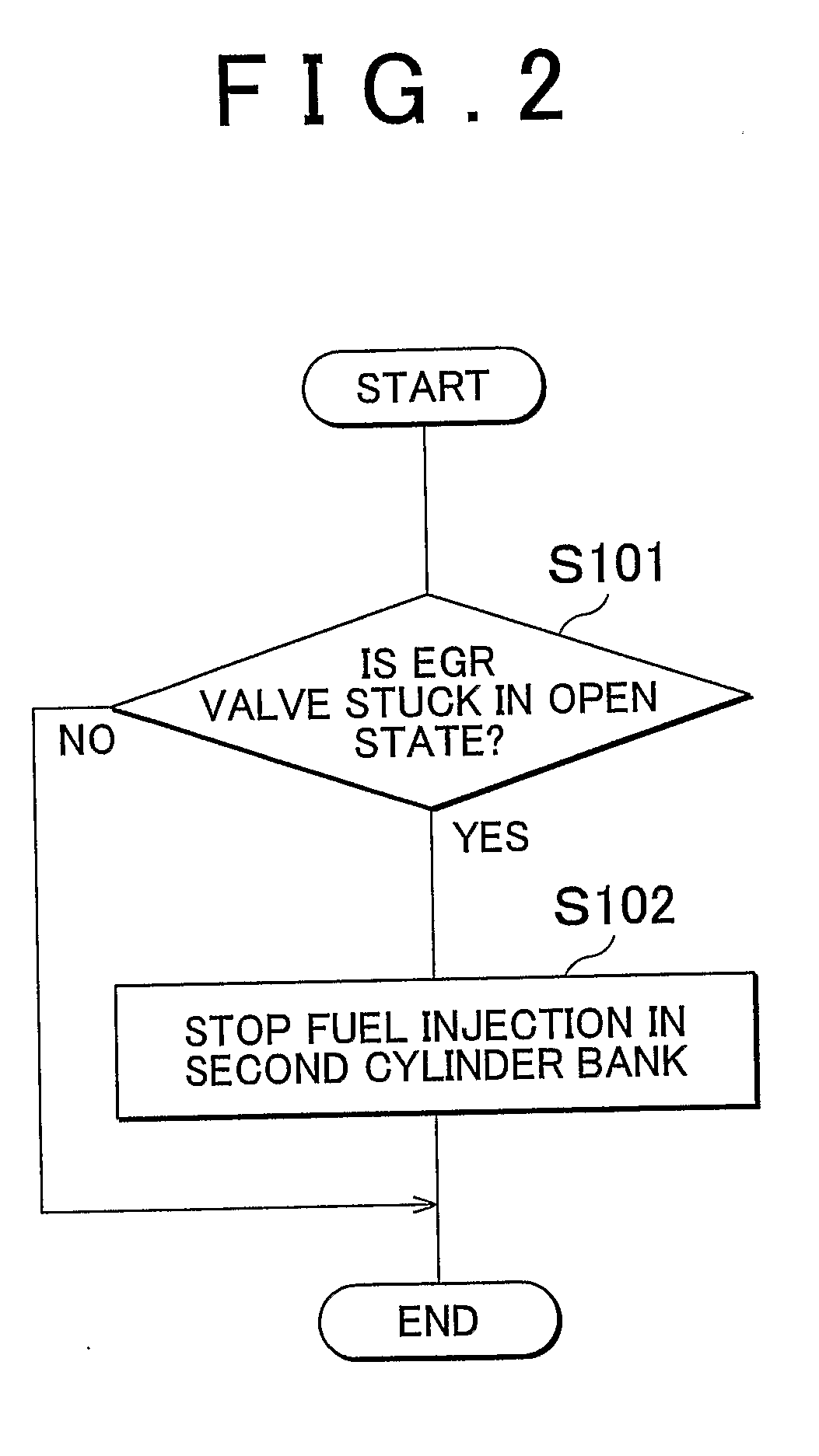
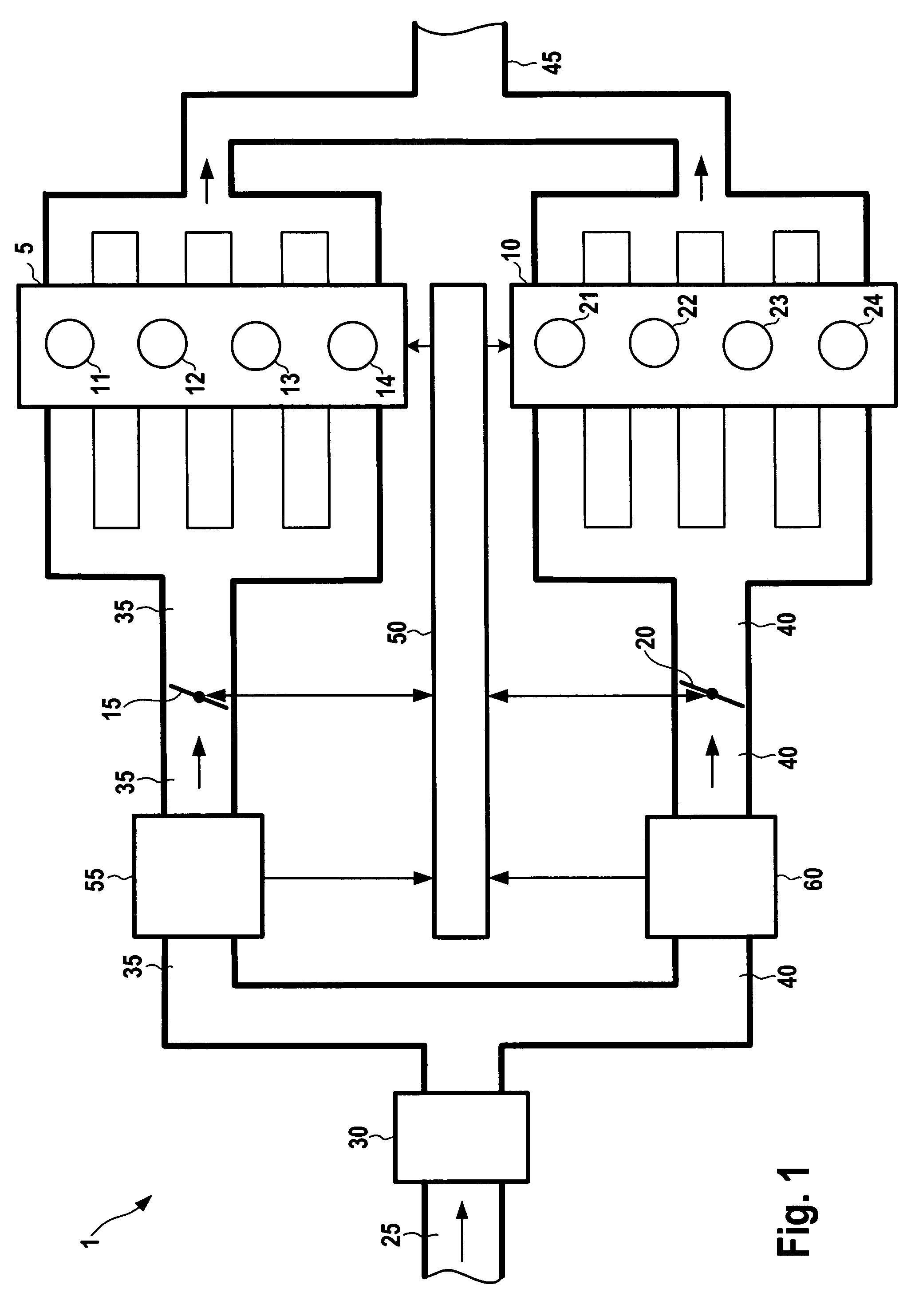
In an internal combustion engine with separate cylinder banks, separate exhaust passages are connected to each cylinder bank of an engine and a shared intake passage is connected to both cylinder banks. One end of an EGR passage is connected to the separate exhaust passage of one cylinder bank, and the other end of the EGR is connected to the shared intake passage. If it is determined that an EGR valve in the EGR passage is stuck in an open state, a fuel-cut control is executed in the cylinder bank that is connected to the separate exhaust passage to which the EGR passage is connected. Thus, even when the EGR valve is stuck in an open state, it is possible to prevent the internal combustion engine from operating unstably.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Cylinder block cooling arrangement for multi-cylinder internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7032547B2Shorten the timeImprove temperature uniformityCylinder headsCylindersCoolant flowExternal combustion engine
An insert for a siamese-type internal combustion engine that separates a water jacket surrounding the cylinders into an upper portion and a lower portion. Below a predetermined engine speed coolant flows primarily in the upper water jacket portion so as to provide enhanced cooling at the upper portions of the cylinders. Above a predetermined engine speed coolant is introduced into the lower water jacket portion from the upper water jacket portion so as to provide improved cooling of the lower cylinder portions, without compromising cooling of the upper cylinder portions or the conjoined cylinder wall portions. The water jacket insert enhances coolant flow velocity at the siamesed or conjoined portions of the cylinder walls, and directs incoming initially coolant over the exhaust-side of the cylinders. Use of the insert reduces circumferential and axial intra-cylinder temperature deviations as well as inter-cylinder temperature deviations.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
Exhaust gas recirculation and selective catalytic reduction system
InactiveUS7490466B2Internal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelThermodynamicsPtru catalyst
A power source is provided for use with an exhaust gas recirculation and selective catalytic reduction system. The power source has a main air-intake passage fluidly connected to a first air-intake passage and a second air-intake passage. A first cylinder group may be fluidly connected to the first air-intake passage and a first exhaust passage, wherein the first exhaust passage may include an ammonia-producing catalyst configured to convert at least a portion of a fluid in the first exhaust passage into ammonia. Further, a second cylinder group may be fluidly connected to the second air-intake passage and a second exhaust passage. A third cylinder group may be fluidly connected to the second air-intake passage. The power source may have a recirculation loop that includes the second air-intake passage and the third cylinder group. The power source may also have a merged exhaust passage configured to connect the first exhaust passage and the second exhaust passage to facilitate a reaction between ammonia and NOx to at least partially remove NOx from the merged exhaust passage.
Owner:CATERPILLAR INC
Fuel routing structure for a V-type engine
ActiveUS20060042601A1Compact processEasy to assembleInternal combustion piston enginesLow pressure fuel injectionCrankshaftInlet manifold
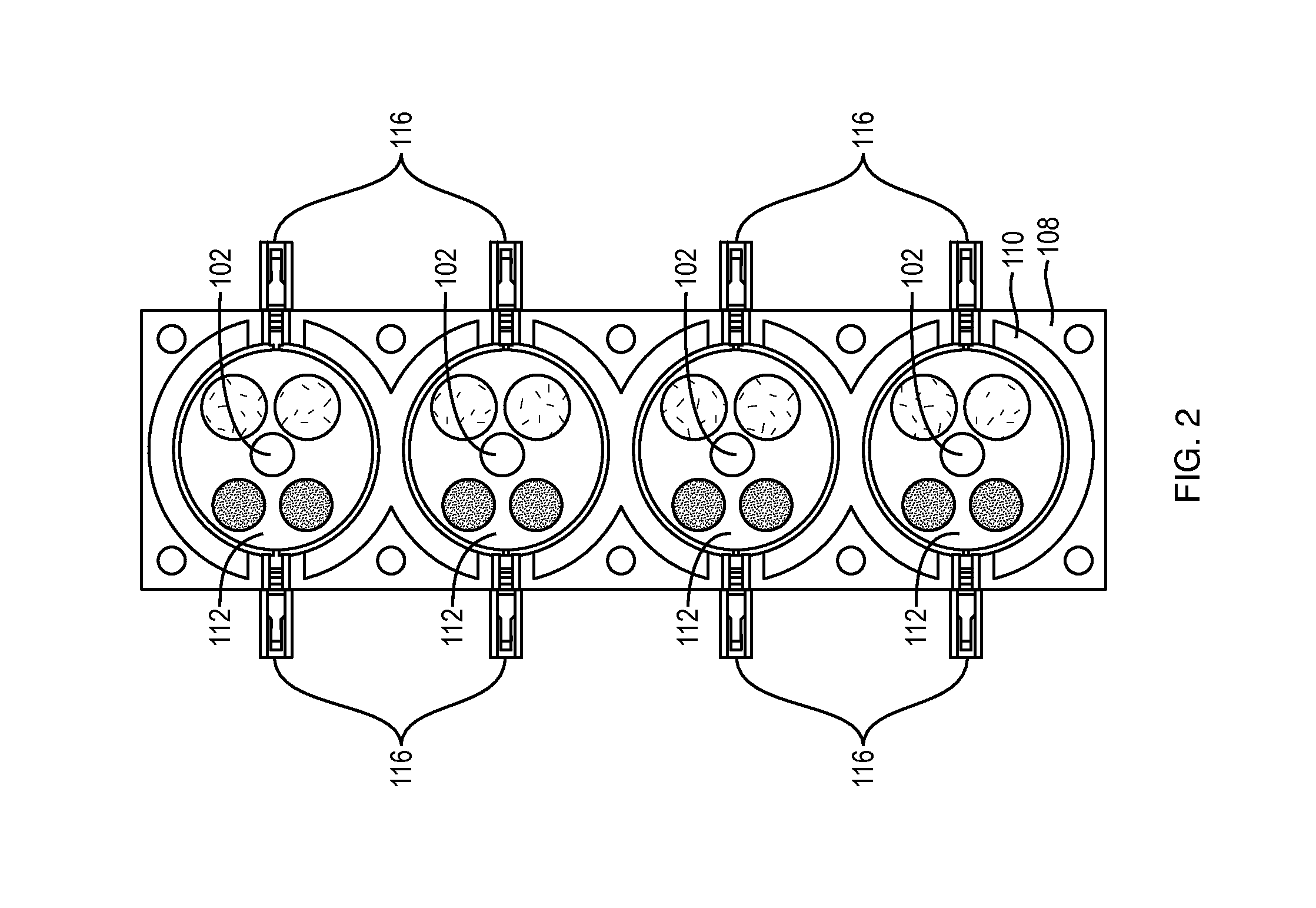
A fuel routing structure for use in a vehicle having a V-type engine is provided. The structure has fewer parts, is compact, and facilitates ease of assembly and maintenance for a vehicle where fuel injection valves are attached to an intake manifold, which contains an intake passage communicating with intake ports of a pair of cylinder banks. Each fuel injection valve is attached to an upper part of the intake manifold, so that center lines of the fuel injection valves corresponding to both banks are crossed at an intersection over the intake manifold when a vehicle is viewed from the side. A fuel rail is provided with a fuel passage pipe, the axis of which is arranged in the vicinity of the intersection of the center lines of the fuel injection valves. The axis of the fuel passage pipe may be parallel to the crankshaft and may extend linearly and connected to all the fuel injection valves.
Owner:HONDA MOTOR CO LTD
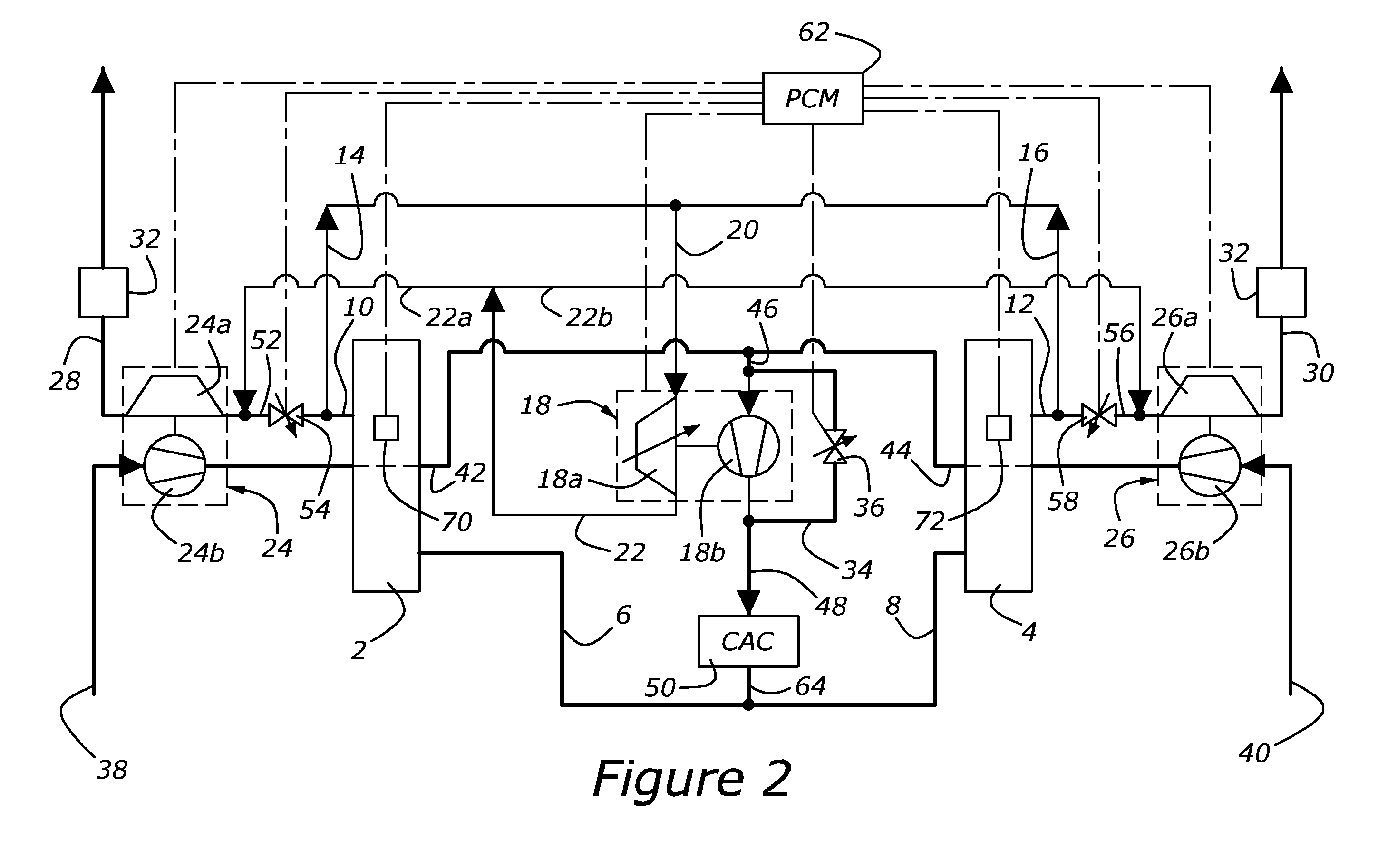
Cylinder bank work output balancing based on exhaust gas a/f ratio
A system for balancing first and second work outputs between first and second cylinder banks of an engine includes a first intake camshaft associated the first cylinder bank and a first fuel injector associated with the first cylinder bank. A controller trims a pulse-width of the first fuel injector until first and second A / F ratios of respective exhaust of the first and second cylinder banks are equivalent. The controller adjusts timing of the first intake camshaft to effect air flow into the first cylinder bank and trims the pulse-width to maintain equivalency of the first and second A / F ratios.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
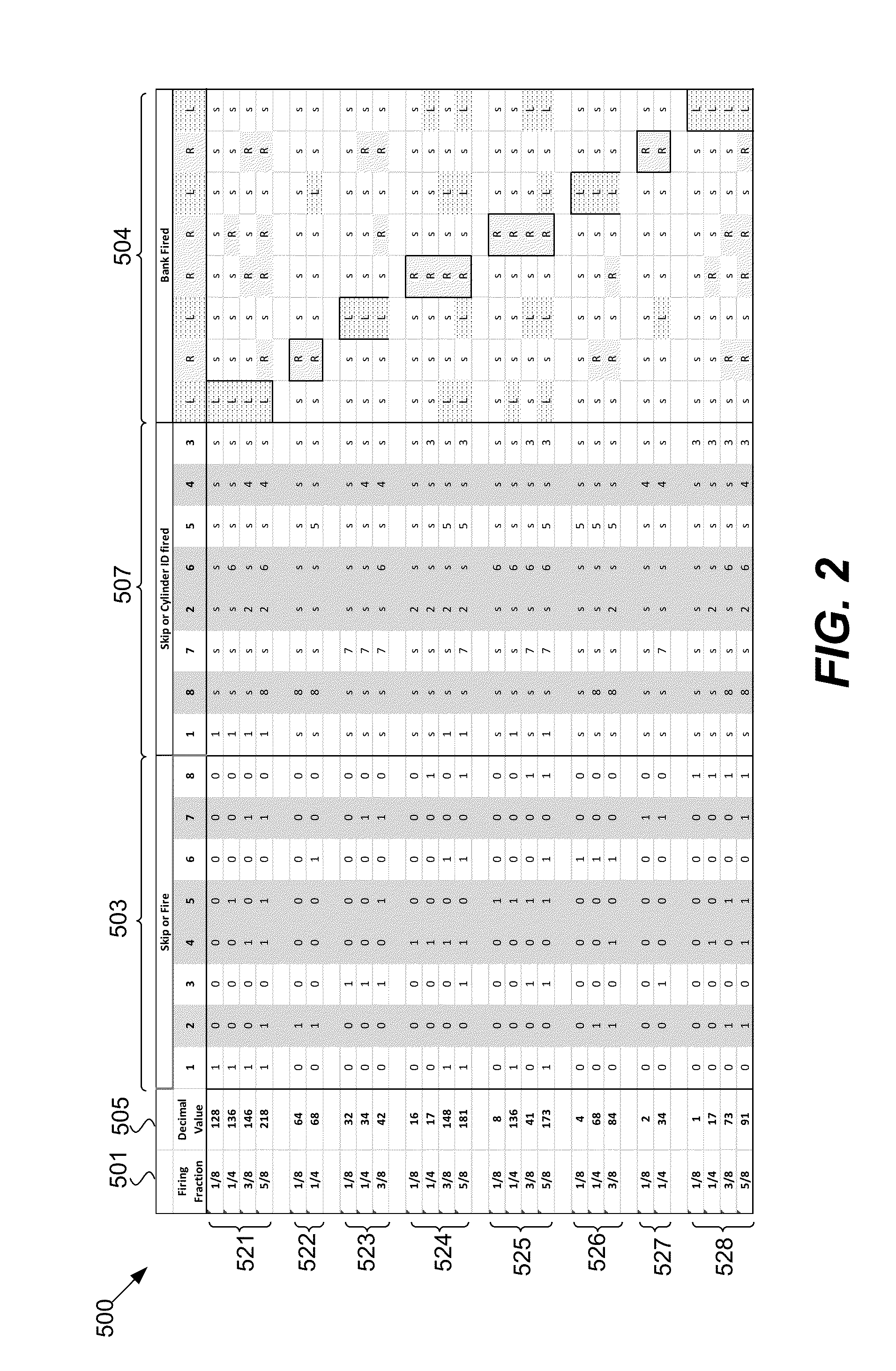
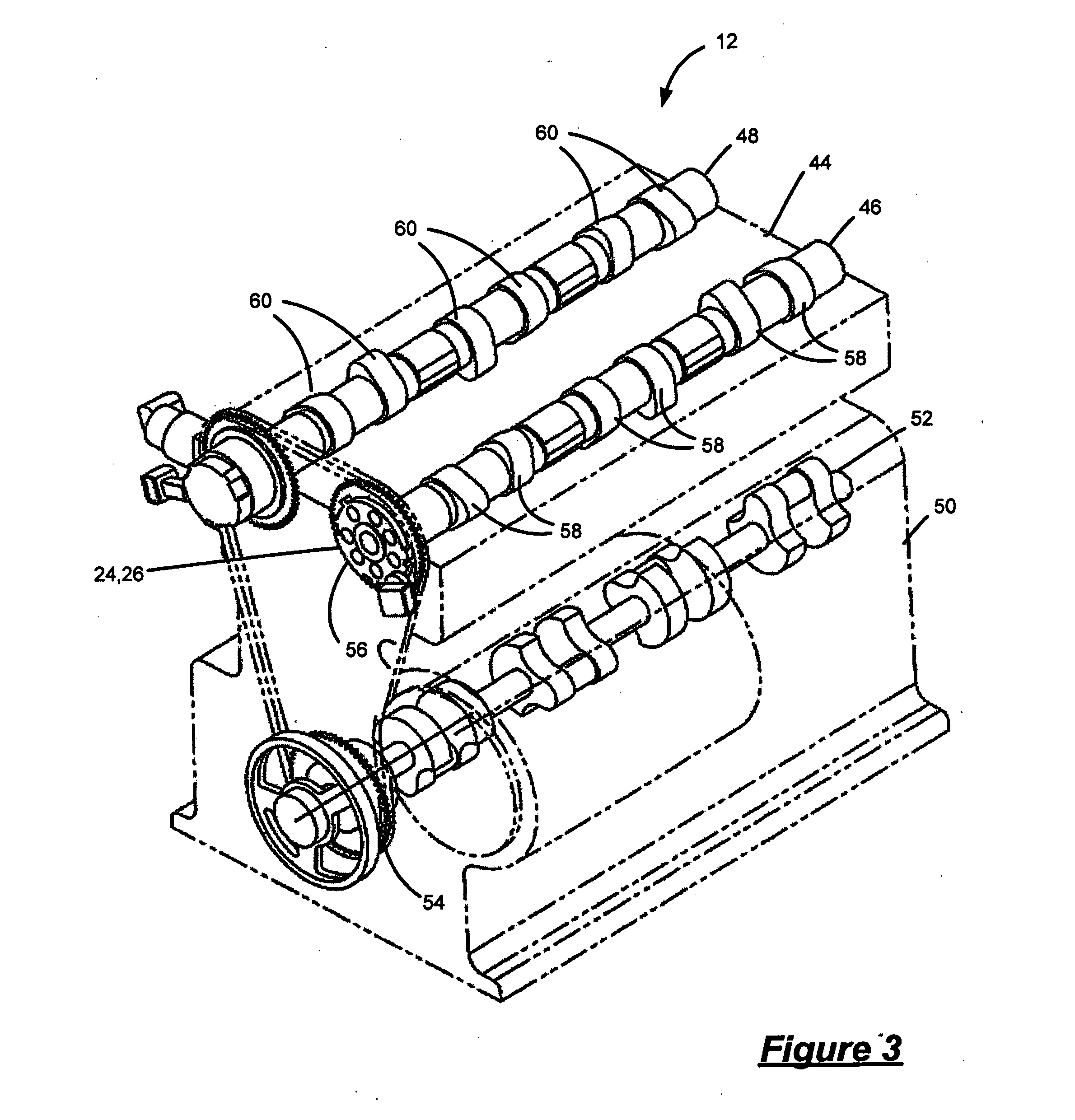
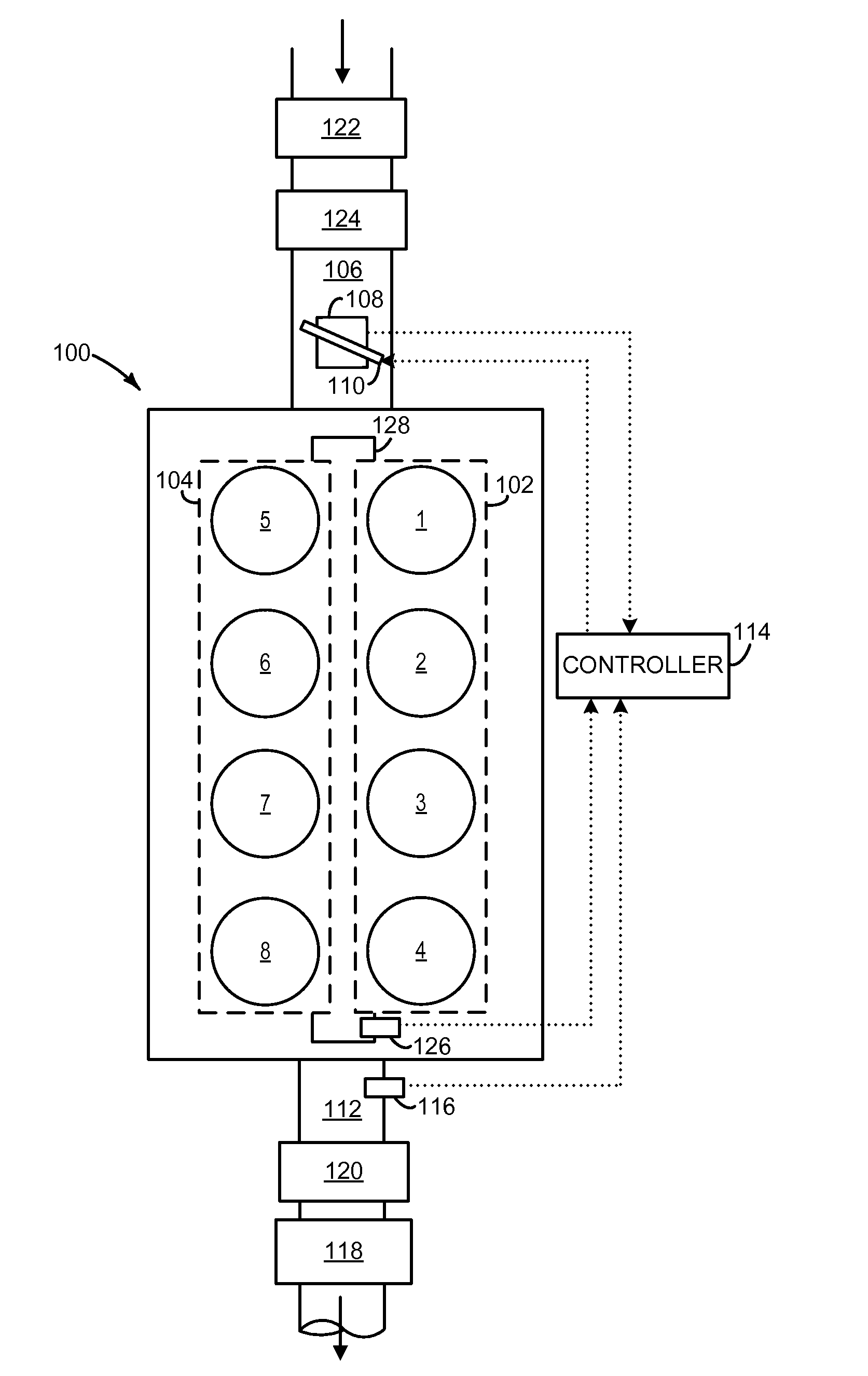
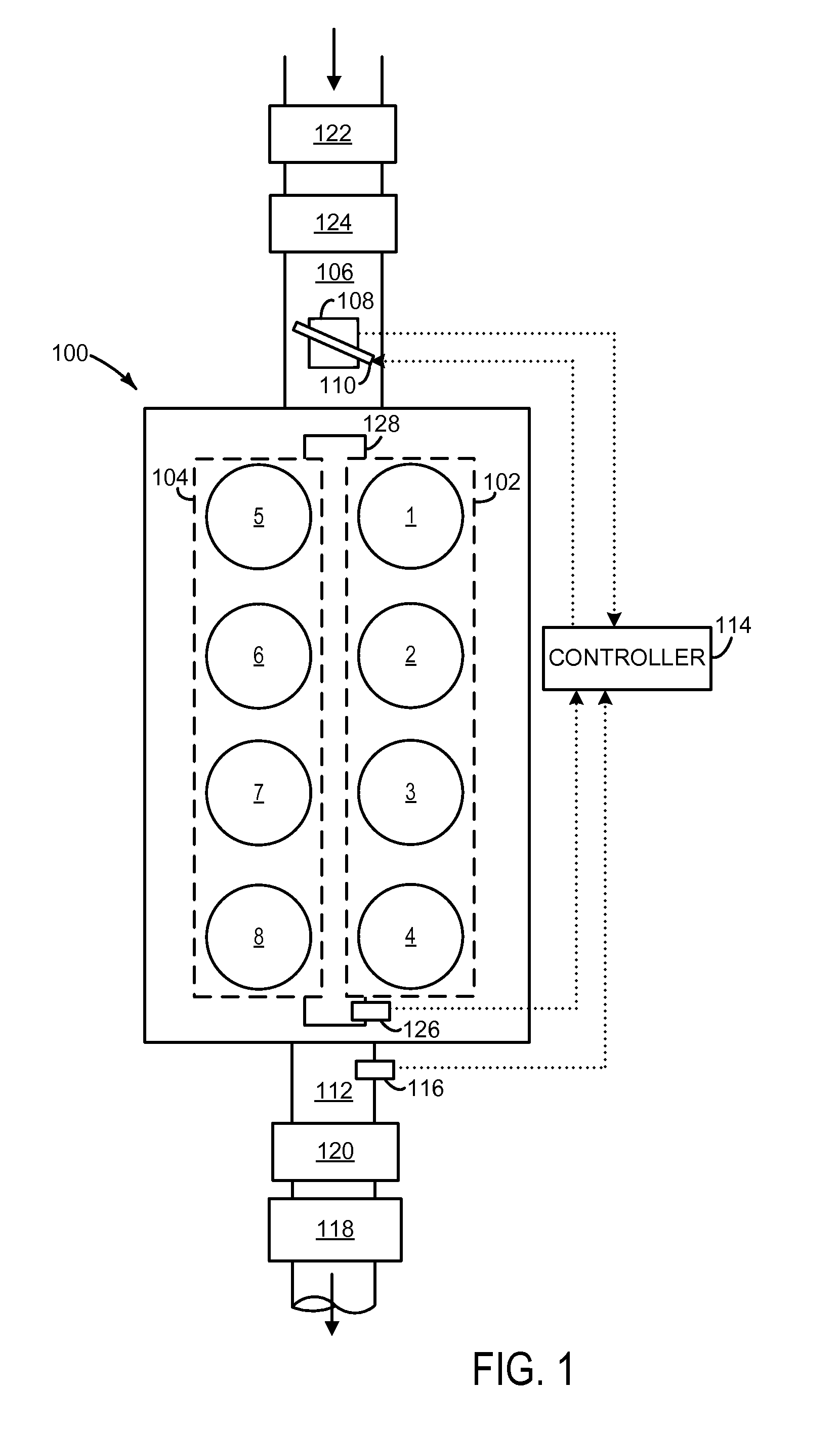
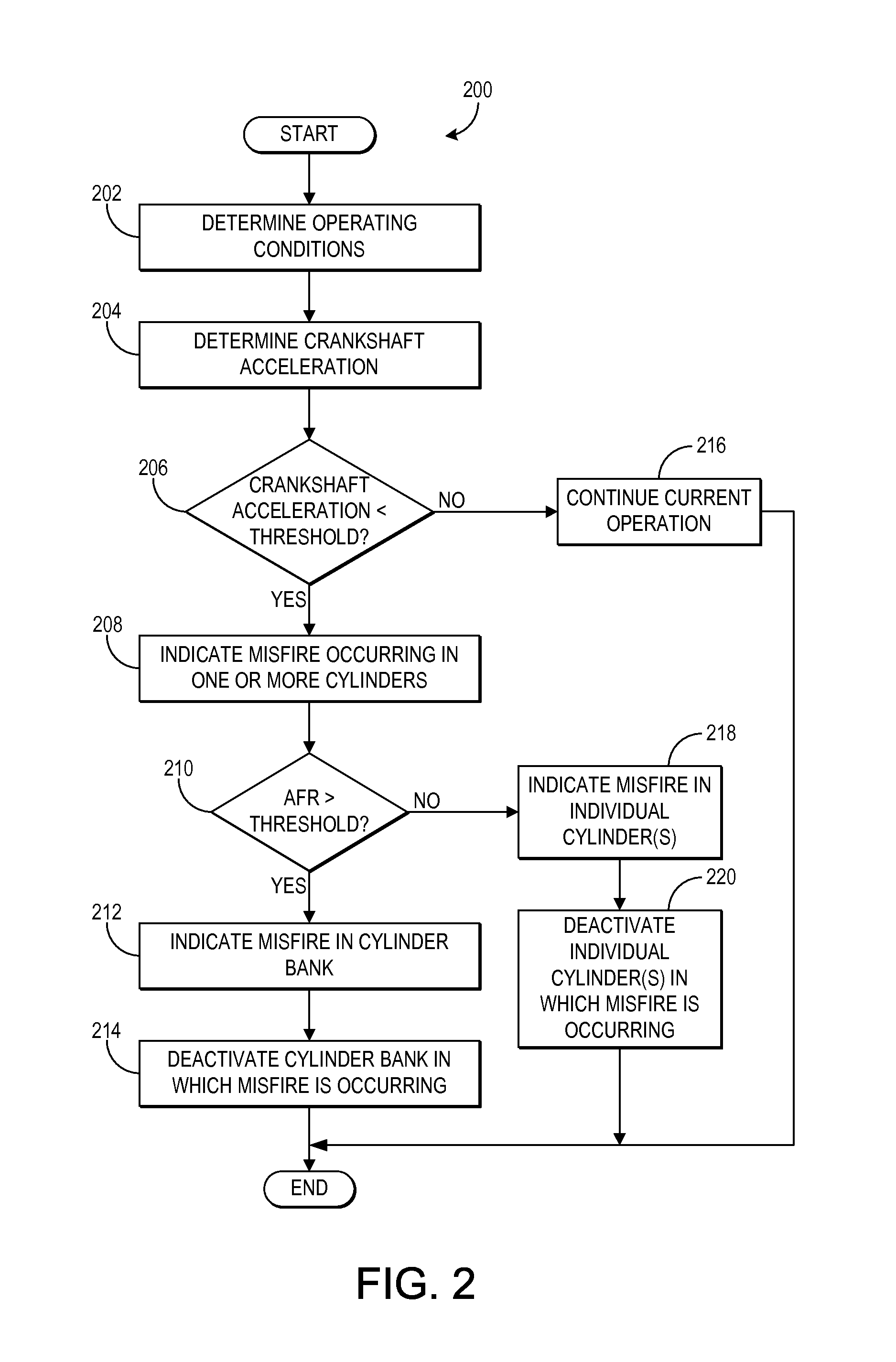
Methods and systems for cylinder bank misfire detection and reactivation
ActiveUS20140352659A1Lower performance requirementsReduce degradationElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesEngineeringAir–fuel ratio
Various systems and methods are described for deactivation and reactivation of a cylinder bank in a V-engine. In one example, the cylinder bank is deactivated responsive to an indication of misfire based on crankshaft acceleration and exhaust air fuel ratio. The cylinder bank is reactivated sequentially based on exhaust catalyst temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Engine diagnostics with skip fire control
Methods and devices are described for performing engine diagnostics during skip fire operation of an engine while a vehicle is being driven. Knowledge of the firing sequence is used to determine appropriate times to conduct selected diagnostics and / or to help better interpret sensor inputs or diagnostic results. In one aspect, selected diagnostics are executed when a single cylinder is fired a plurality of times in isolation relative to a sensor used in the diagnosis. In another aspect, selected diagnostics are conducted while the engine is operated using a firing sequence that insures that no cylinders in a first cylinder bank are fired for a plurality of engine cycles while cylinders in a second bank are at least sometimes fired. The described tests can be conducted opportunistically, when conditions are appropriate, or specific firing sequences can be commanded to achieve the desired isolation or skipping of one or more selected cylinders.
Owner:TULA TECH INC
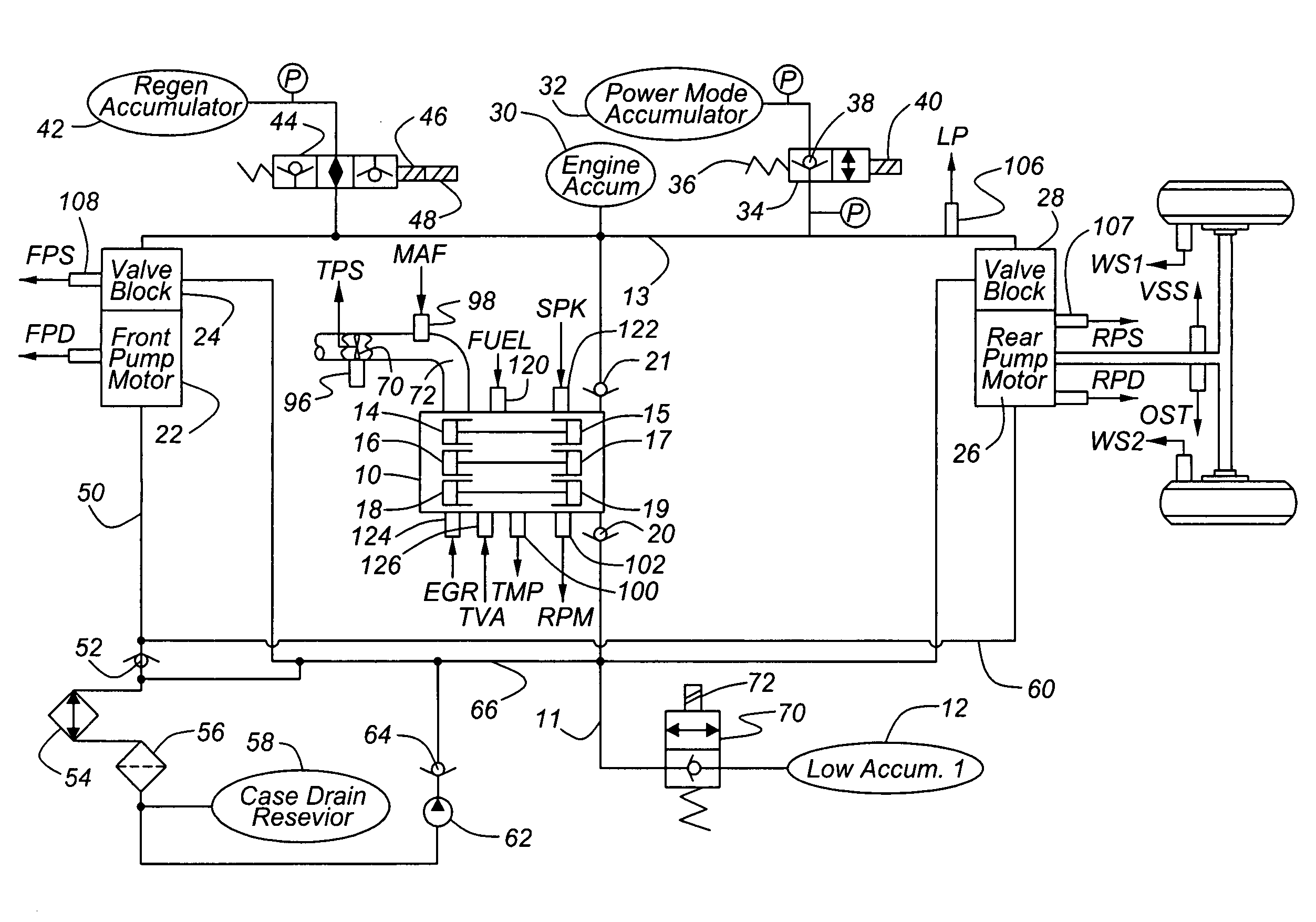
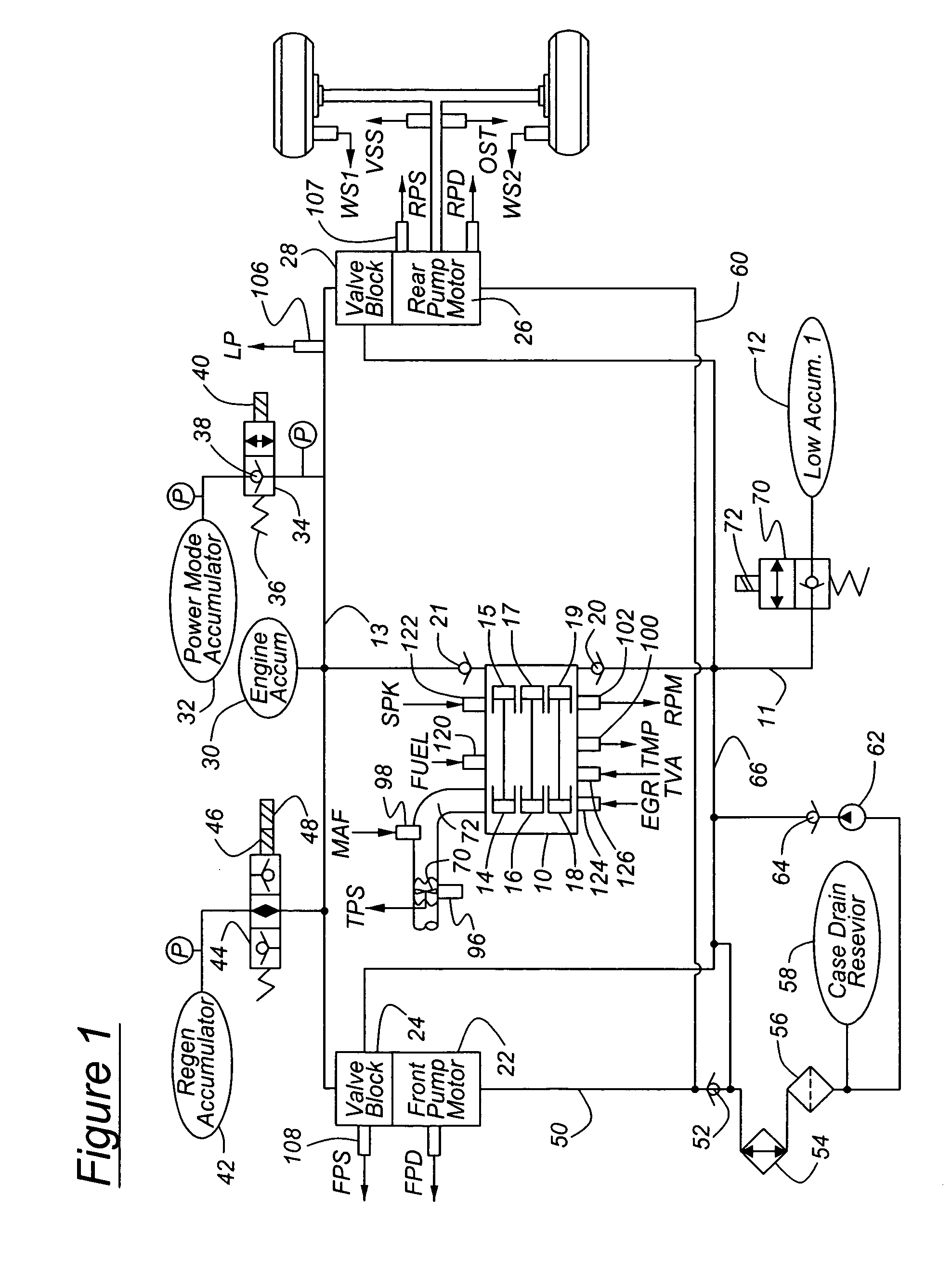
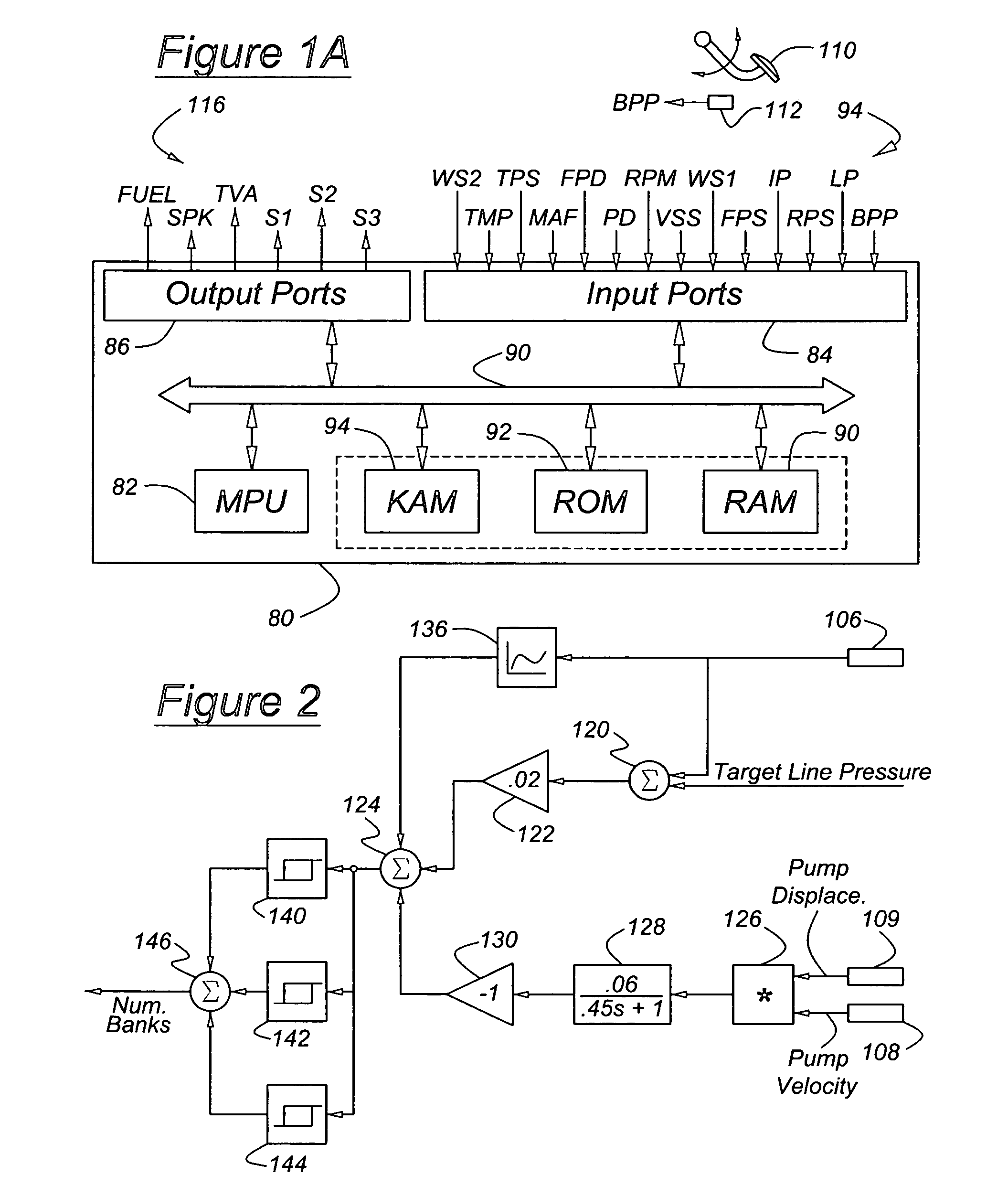
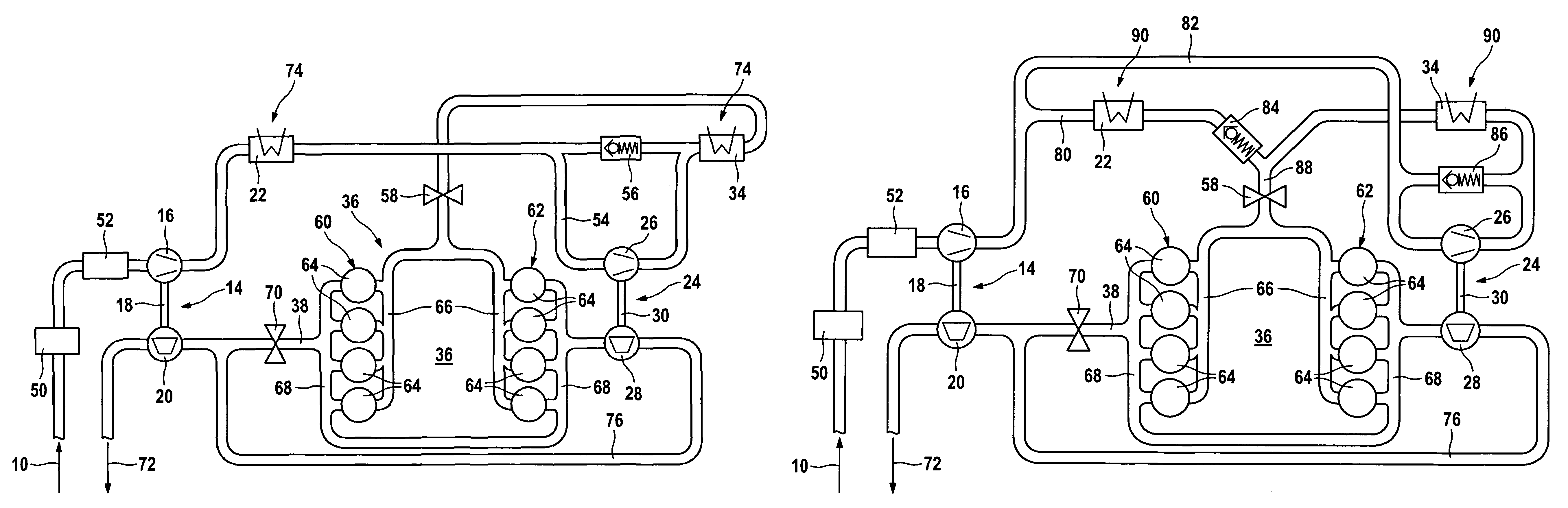
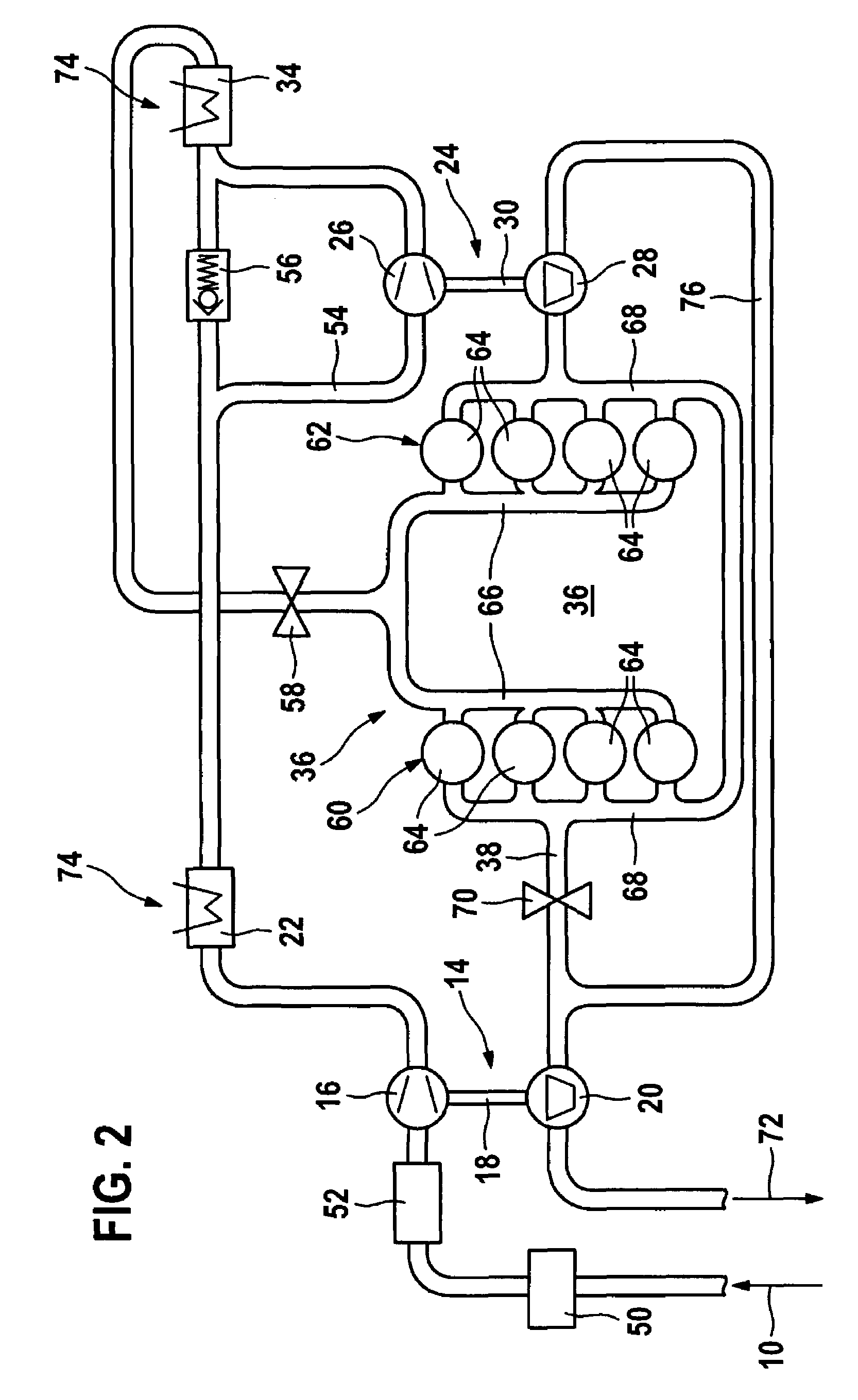
Engine control based on flow rate and pressure for hydraulic hybrid vehicle
InactiveUS6959545B2Improve fuel economyHigh activityFluid couplingsGas pressure propulsion mountingMotor speedEngineering
A system for a hydraulically driven vehicle includes an engine having multiple, selectively operating cylinder-pump banks producing fluid flow at an outlet, a pump / motor having a variable flow rate including an inlet for driving the wheels, a hydraulic line having a line pressure and connecting the outlet and the inlet, sensors producing signal representing line pressure, pump / motor speed, pump / motor displacement, and a controller for determining a target hydraulic system parameter, determining, based at least in part on the flow rate of the pump / motor and a flow rate produced by each engine cylinder bank, a number of operating cylinder-pump banks that is required to produce the target hydraulic system parameter, and in response to determining the required number of operating cylinder-pump banks, adjusting an engine operating parameter of a cylinder-pump bank such that the required number of cylinder-pump banks operate.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Ignition energy management with ion current feedback to correct spark plug fouling
ActiveUS8132556B2Prevent wrong actionEliminate spark plug depositsAnalogue computers for vehiclesEngine controllersIdle speedIonization
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Push Rod Engine With Inboard Exhaust
ActiveUS20090078240A1Shorten the lengthHeat conservationValve arrangementsInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerEngineering
A multiple cylinder internal combustion engine having an engine block with first and second cylinder banks arranged at an angle and longitudinally offset relative to one another and a camshaft disposed within the engine block for actuating valves associated with each cylinder includes first and second cylinder heads associated with the first and second cylinder banks and having an intake runner for each cylinder with an entrance disposed on an outward side, and an exhaust runner for each cylinder exiting the cylinder head on an inward side of the cylinder head generally rearward of an associated cylinder to facilitate positioning of one or more turbochargers and a fuel pump in the valley generally between the cylinder heads with the fuel pump disposed forward of the exhaust runner exits and associated exhaust manifolds while accommodating four valves per cylinder actuated by four pushrods extending through the cylinder heads forward of corresponding exhaust runner exits.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
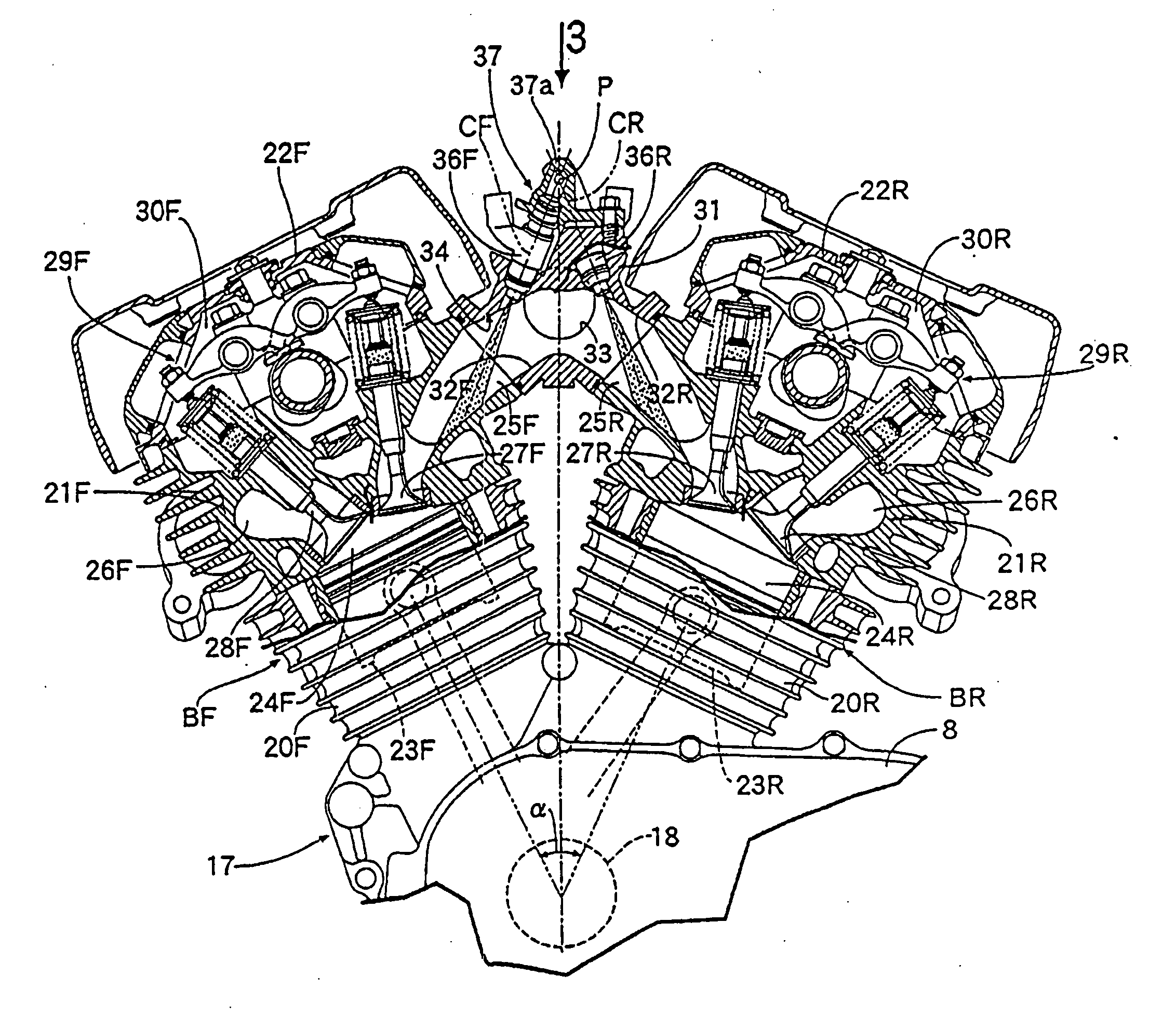
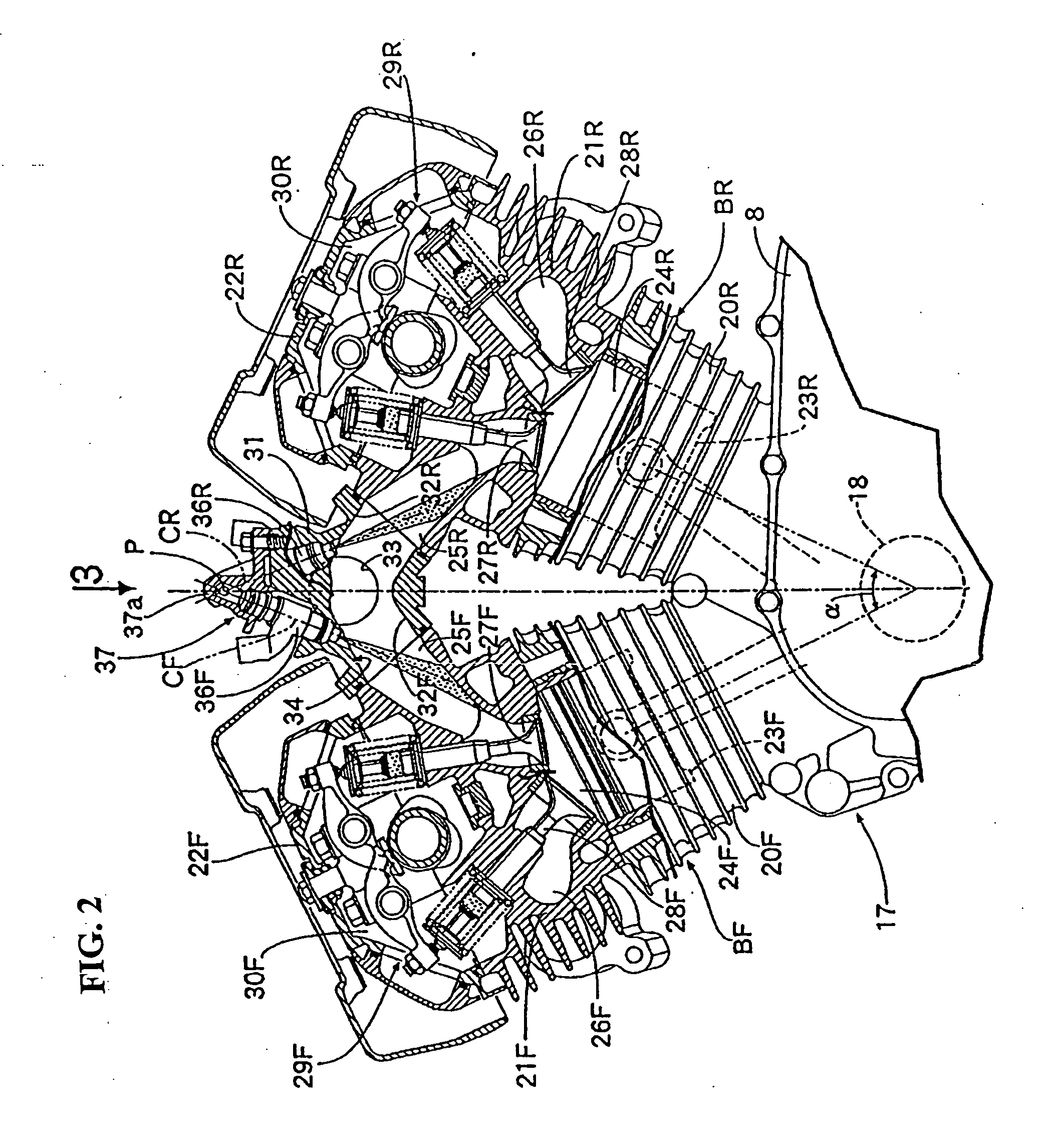
Integrated inboard exhaust manifolds for V-type engines
An internal combustion engine has a first and a second cylinder bank. The first and second cylinder banks are arranged such that they have less than a 180 degree included angle with respect to one another, thereby forming an inboard region or generally V-shaped cavity. A respective first and second cylinder head is mounted with respect to the first and second cylinder bank. Integrated within the first and second cylinder head is a first and second integrated exhaust manifold, respectively. The first and second integrated exhaust manifolds are provided on the engine in an “inboard” orientation, i.e. disposed on a side of their respective cylinder heads such that they are substantially adjacent to the generally V-shaped cavity. The first and second integrated exhaust manifold may operate to convey exhaust gases from the engine to at least one turbocharger, which is mounted substantially within the generally V-shaped cavity.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Supercharging system for two-stage supercharging of V-type internal combustion engines
InactiveUS20080034752A1Minimized pressure lossQuick buildInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustionTurbocharger
A supercharging system, in particular an at least two-stage supercharging system, including a first stage and a second stage for an internal combustion engine having two cylinder banks. The at least two-stage supercharging system includes at least two charge air coolers. An exhaust gas turbocharger representing the first stage and an exhaust gas turbocharger representing the second stage are each situated next to one of the cylinder banks of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
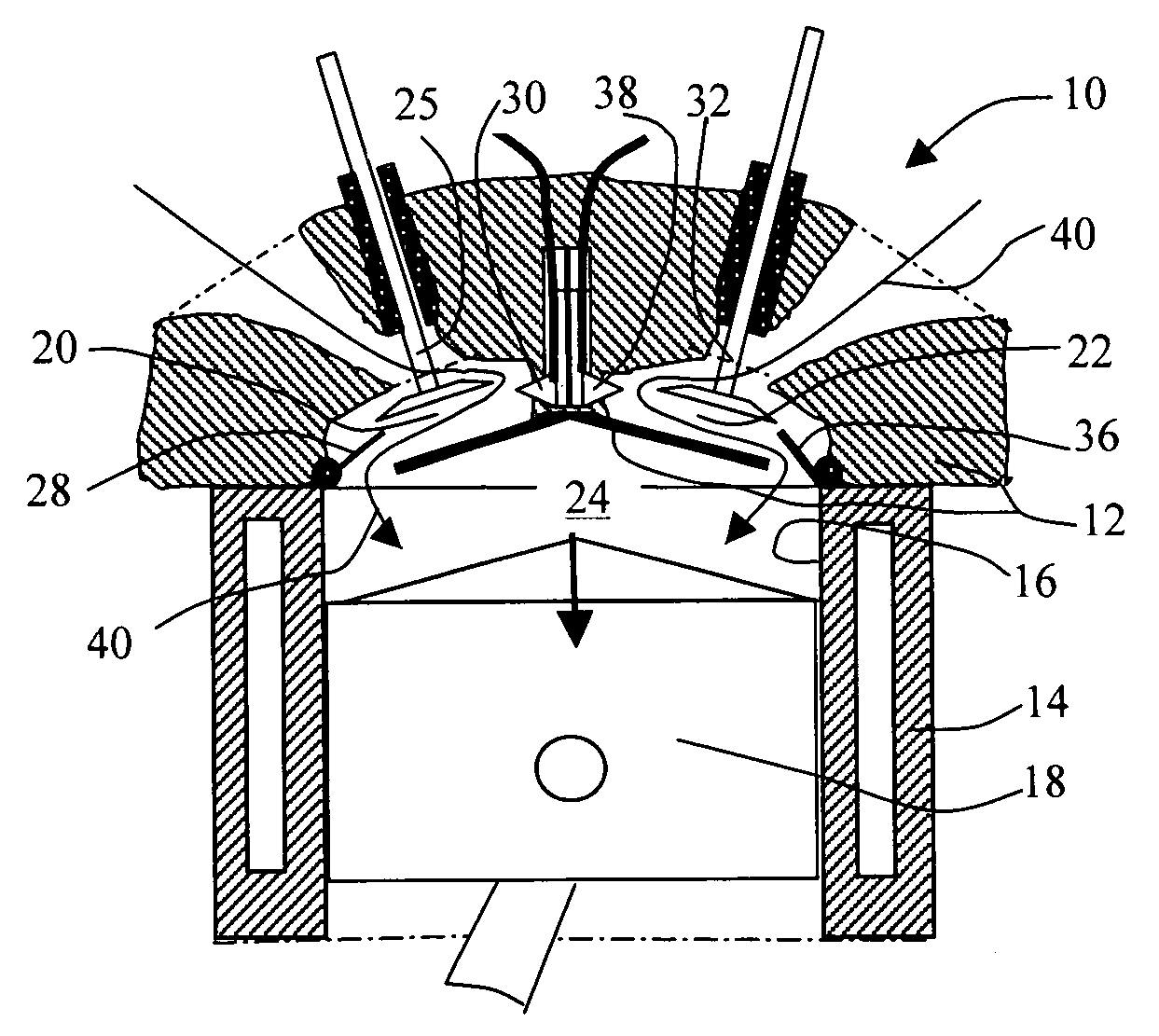
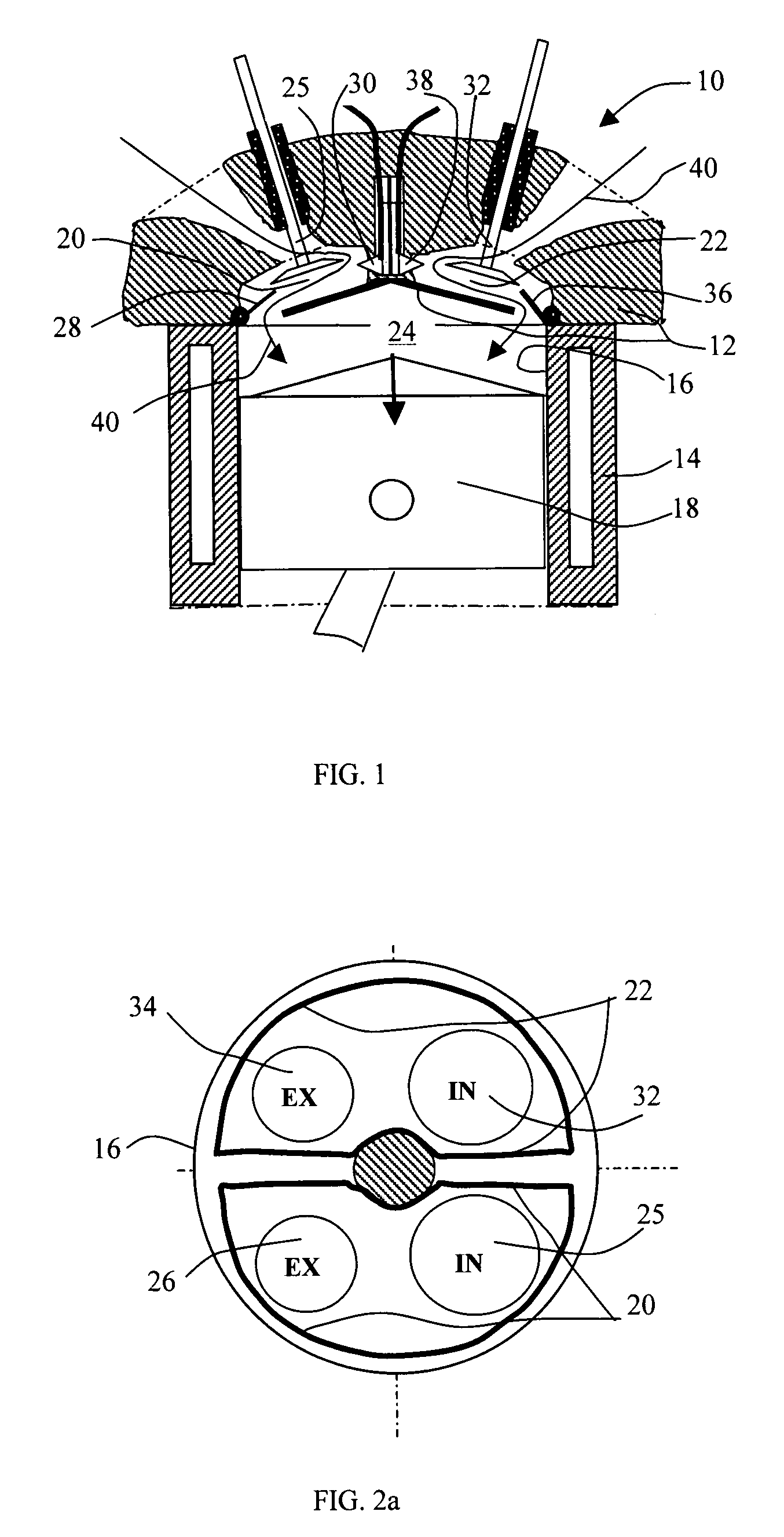
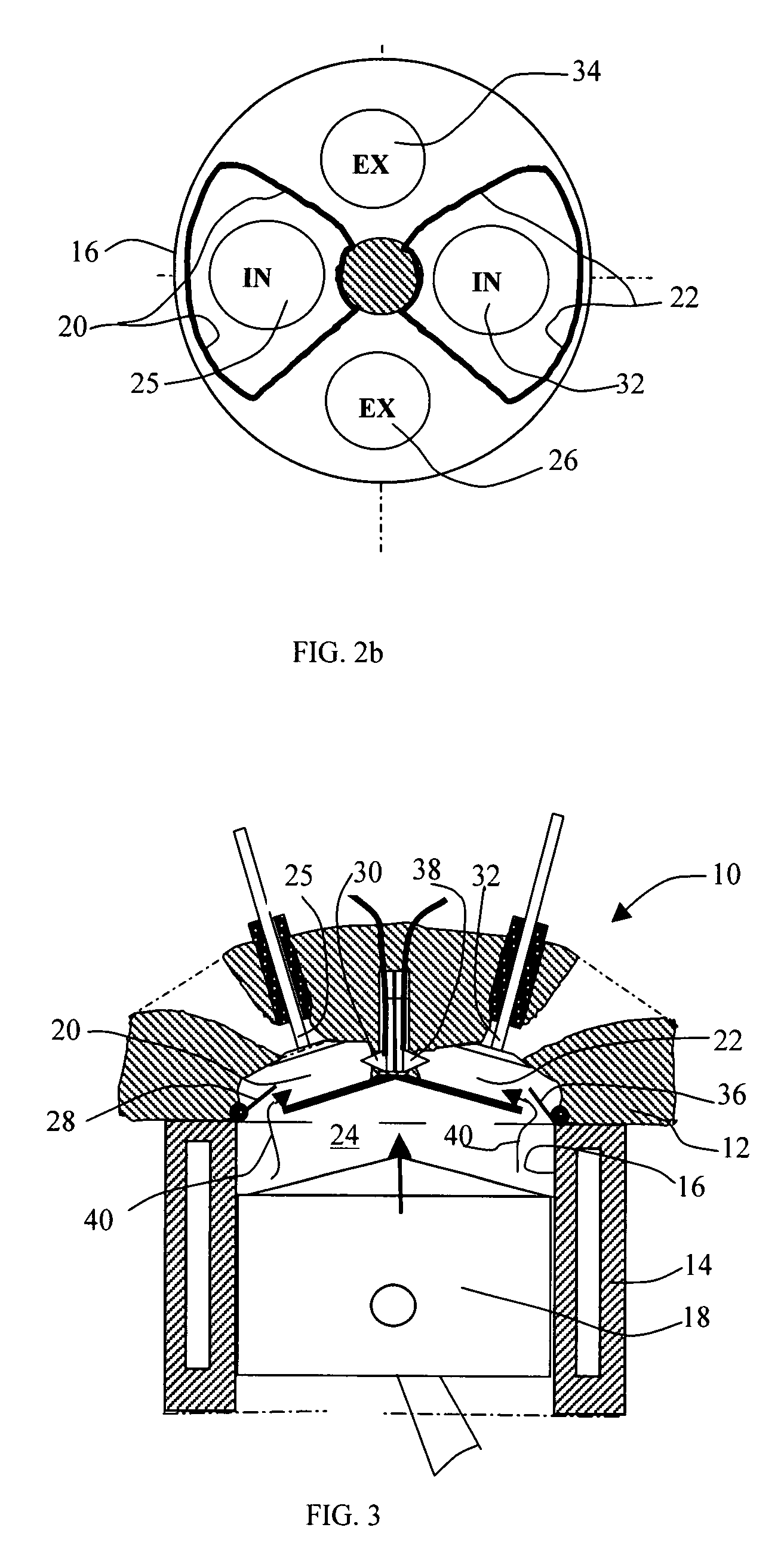
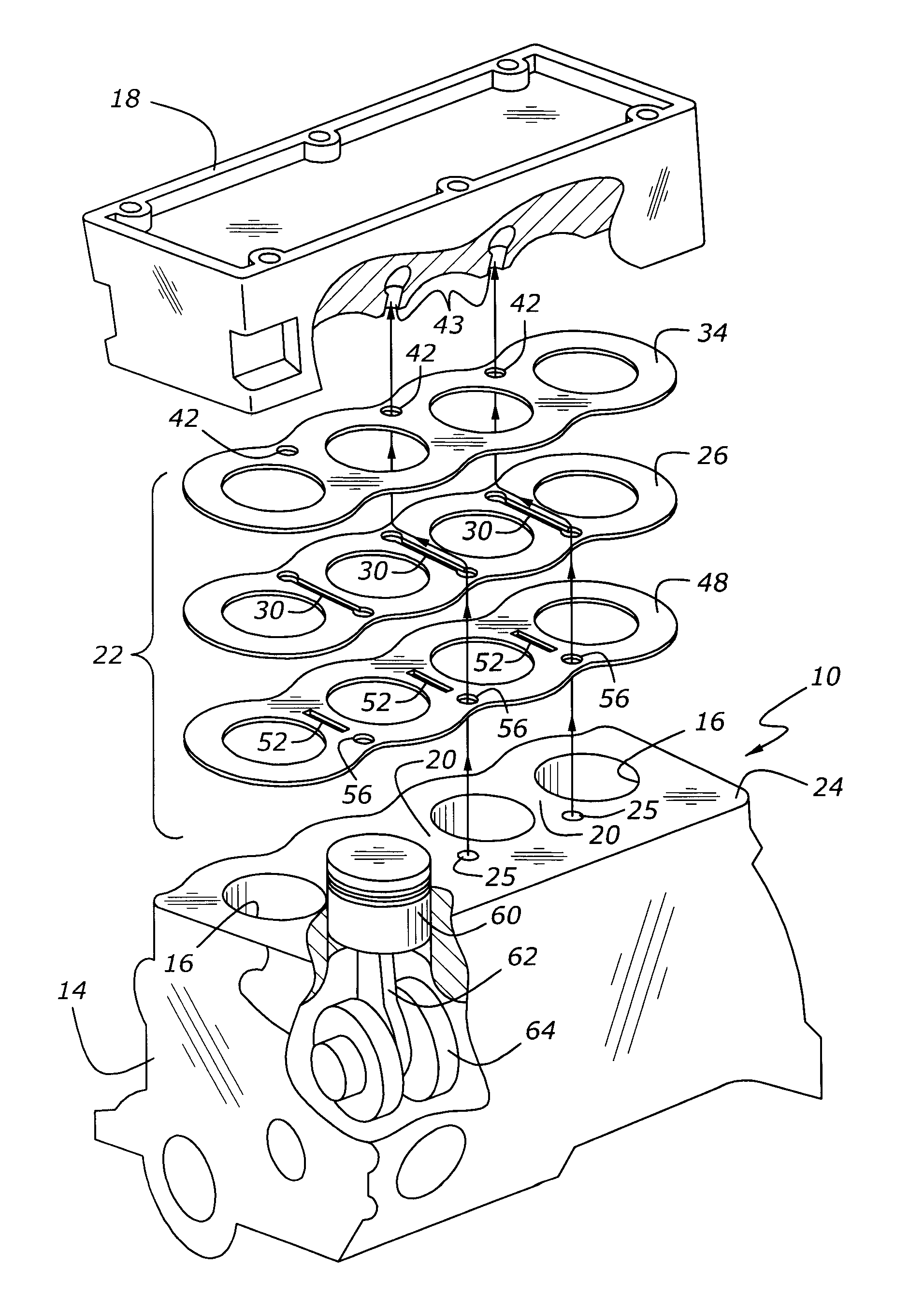
Dual pre-chamber combustion system
In one embodiment, a combustion system for an engine is disclosed. The system includes a cylinder block that defines a cylinder bore and opposing pre-chambers located along a circumference of the cylinder bore. The system also includes a fuel injector located equidistant from the circumference of the cylinder bore that injects fuel in a direction perpendicular to a diameter of the cylinder bore. The system further includes spark plugs located within the pre-chambers that ignite at least a portion of the fuel from the fuel injector to direct ignition flames into the cylinder bore.
Owner:HYUNDAI MOTOR CO LTD +2
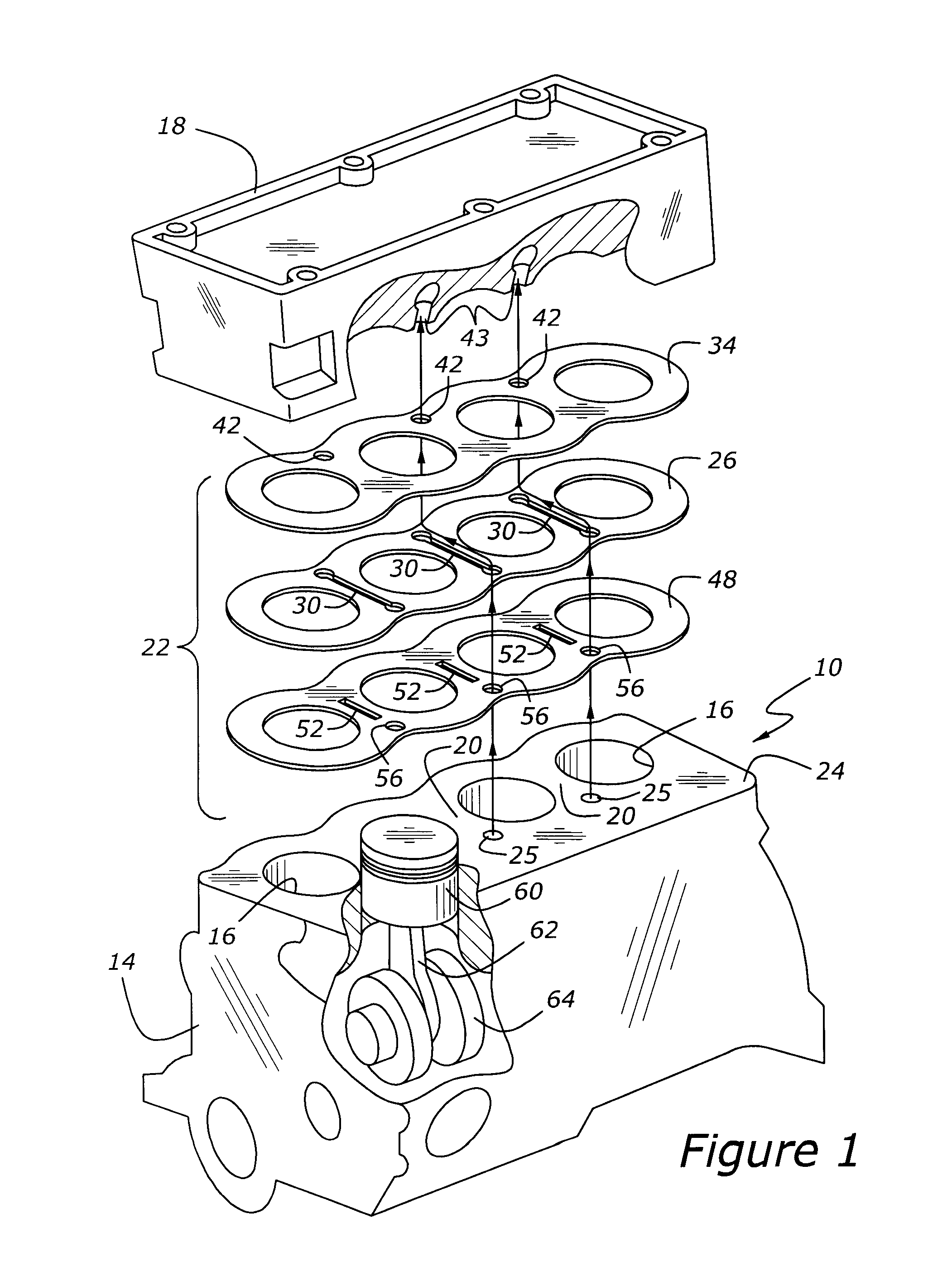
Cooling system defined in a cylinder block of an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS8555825B2Preserve integrityMinimize stress riserLiquid coolingCoolant flow controlExternal combustion engineWater jacket
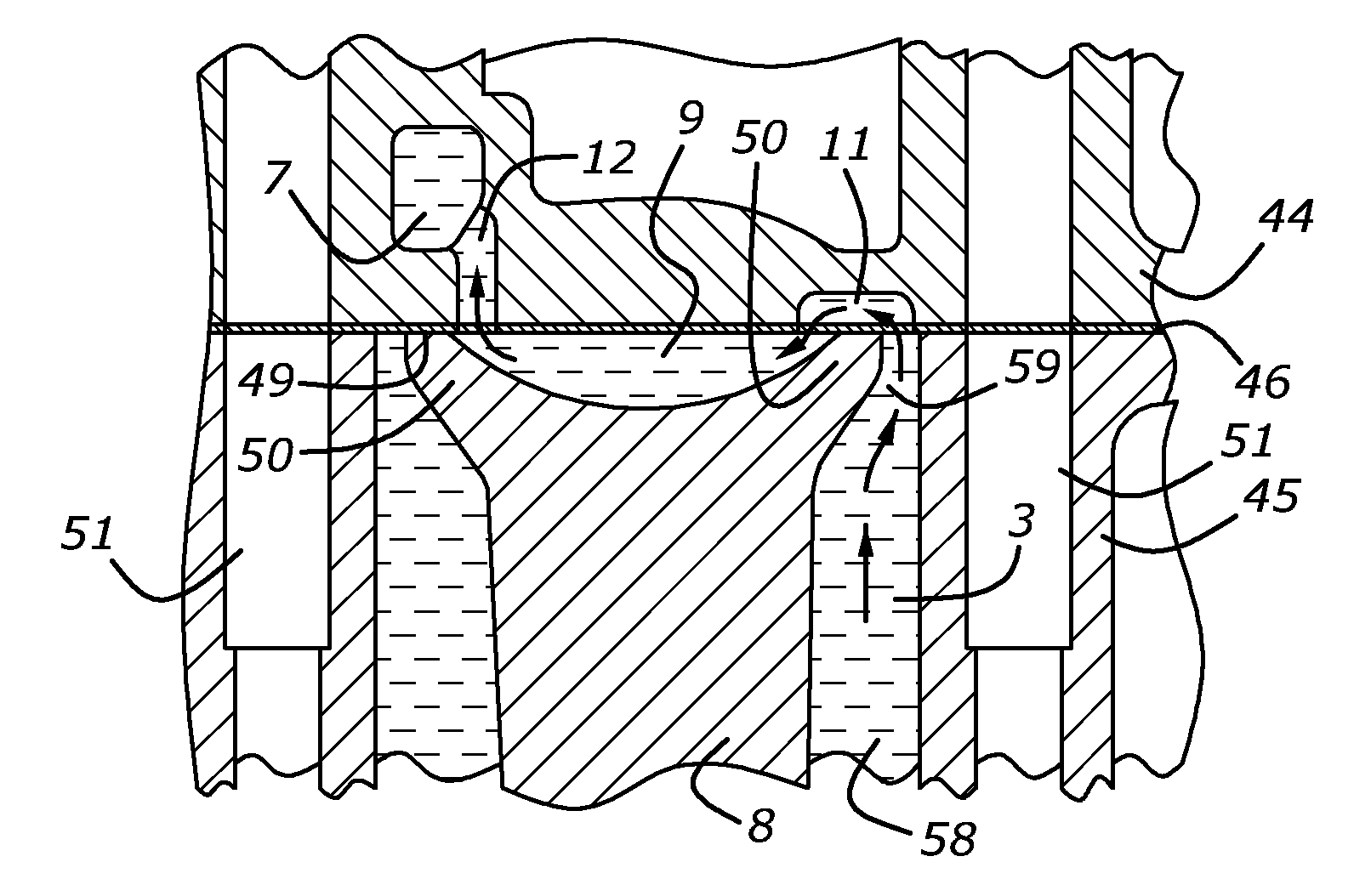
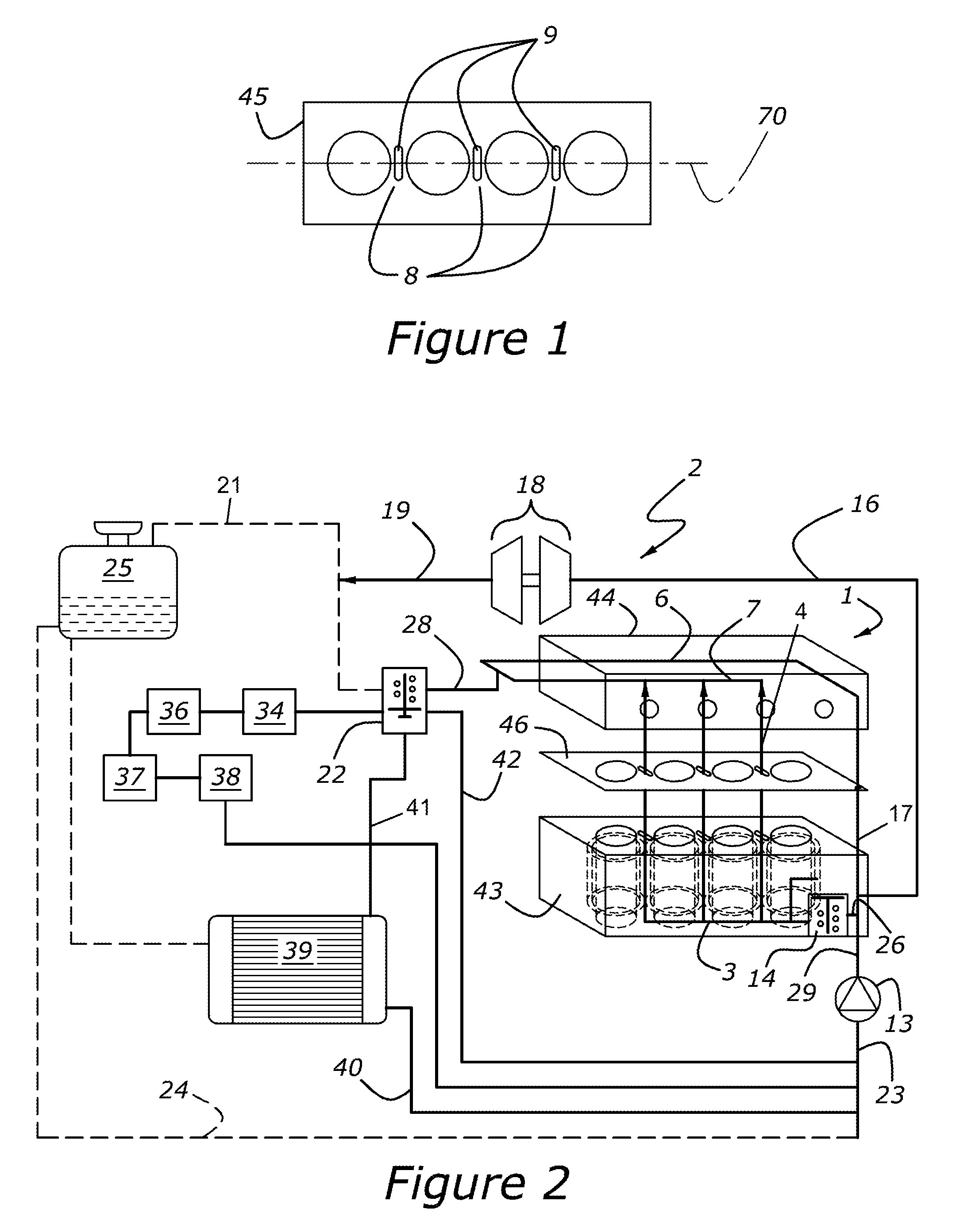
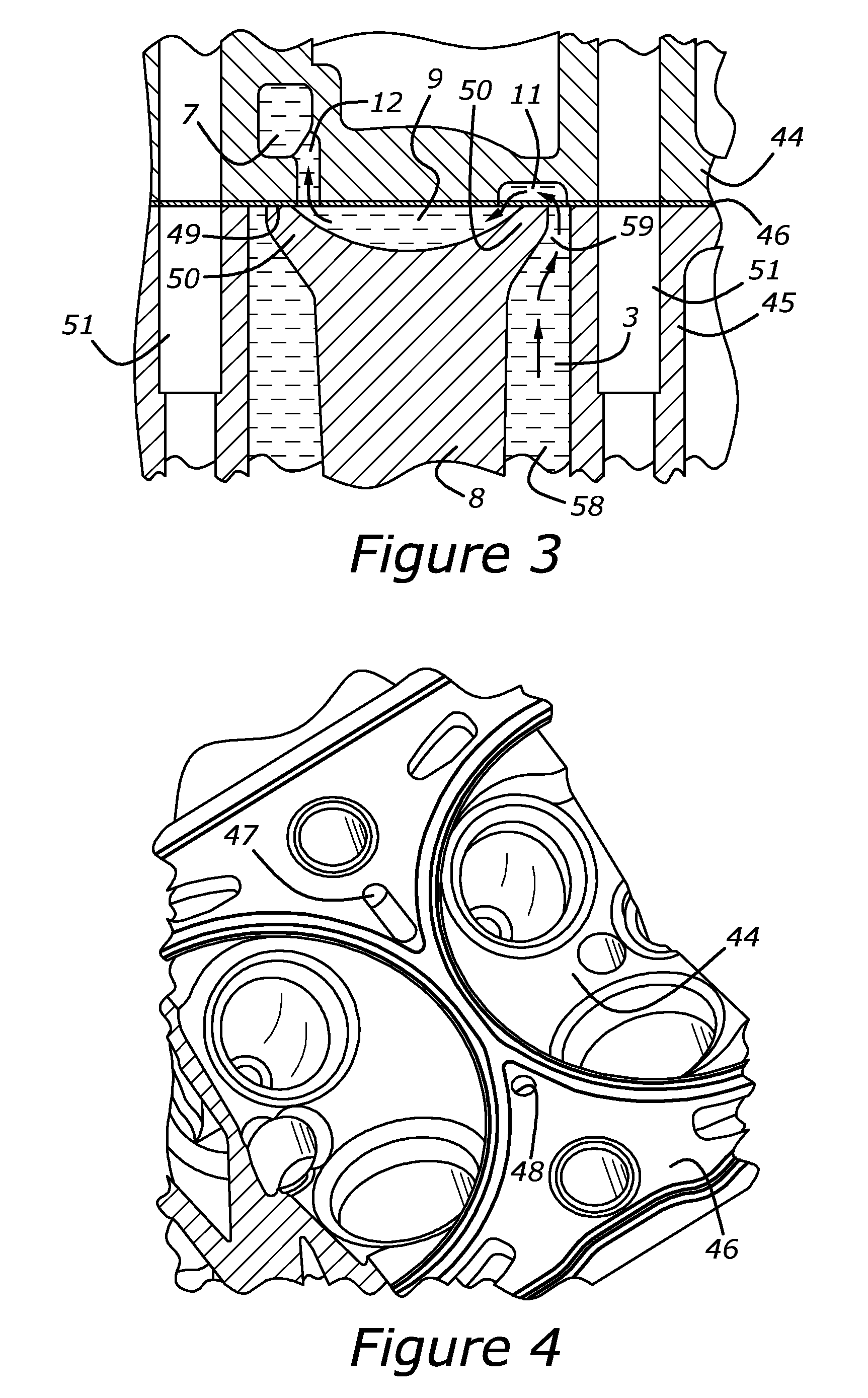
An internal combustion engine is disclosed that has a cylinder block with multiple cylinders, a bridge between adjacent cylinders, a cooling slot in the bridge, and a water jacket portion in the cylinder block. A cylinder head is coupled to the cylinder block which has a first cooling passage fluidly coupling the cooling slot and the water jacket portion in the cylinder block, a water jacket portion in the cylinder head, and a second cooling passage in the cylinder head fluidly coupling the cooling slot with the water jacket portion in the cylinder head. A cylinder head gasket is arranged between the cylinder head and the cylinder block which has a first orifice in the cylinder head gasket cooperating with the first cooling passage a second orifice in the cylinder head gasket cooperating with the second cooling passage.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Variable valve operating system for internal combustion engine
ActiveUS6877466B2Effectively suppressing or avoiding a degradation in engine performanceValve drivesOutput powerVariable valve timingExternal combustion engine
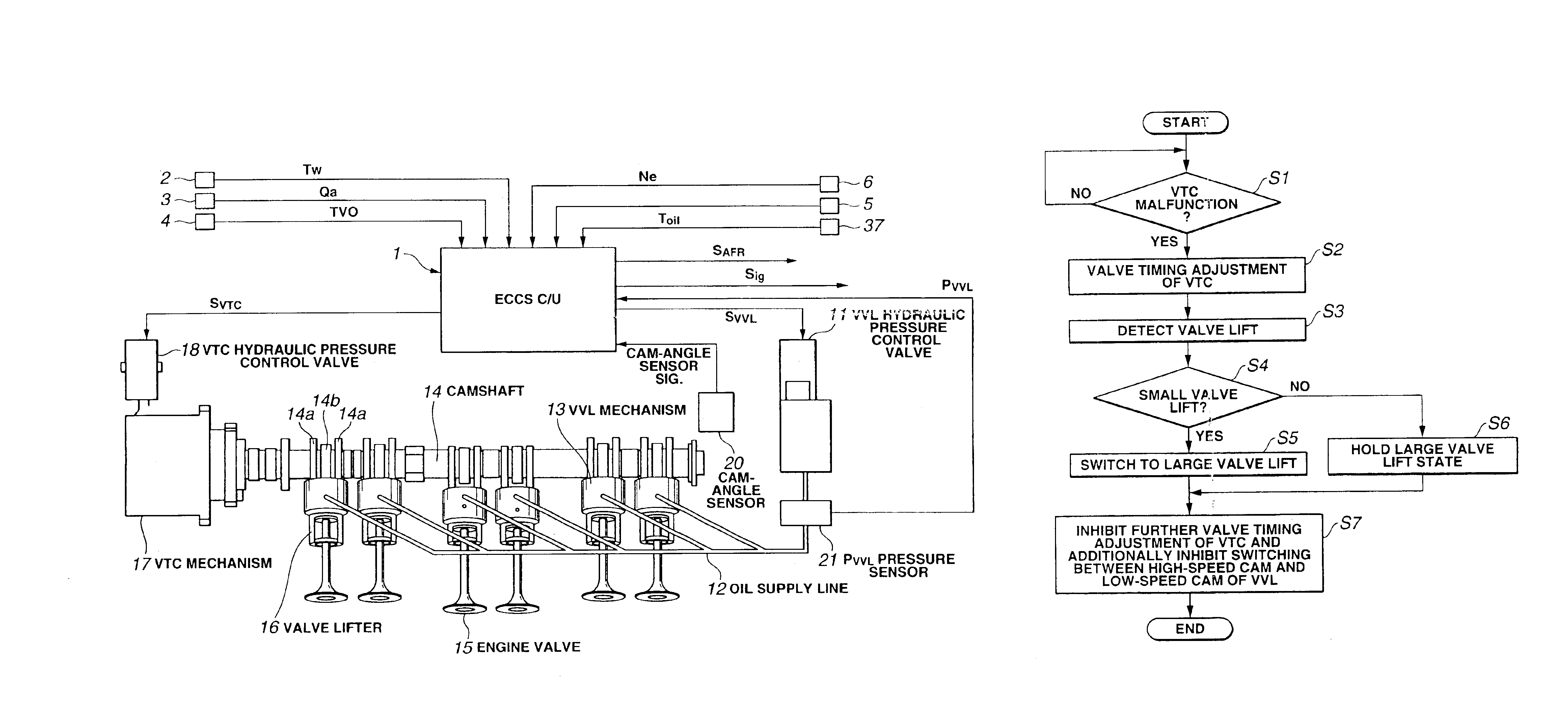
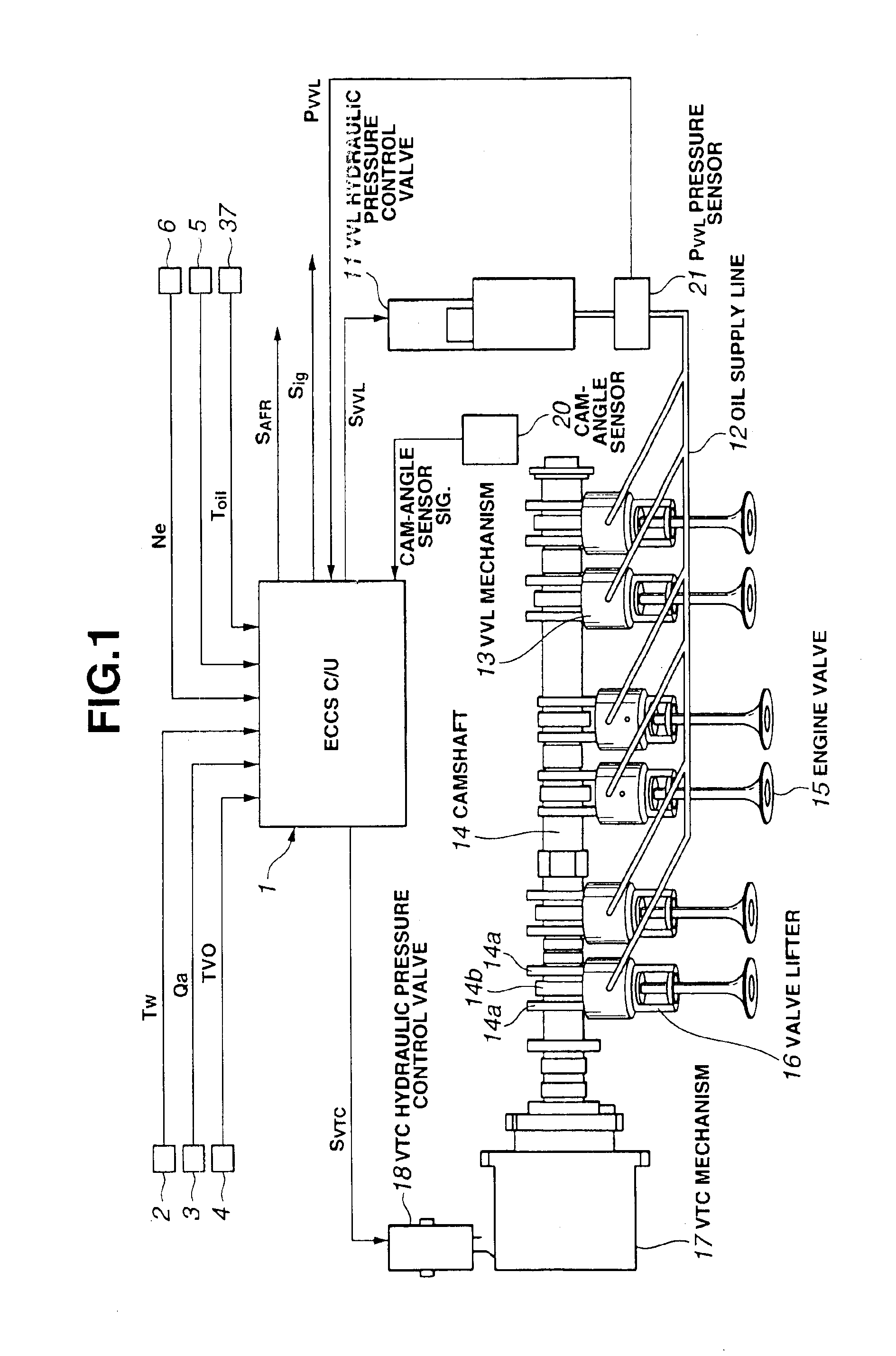
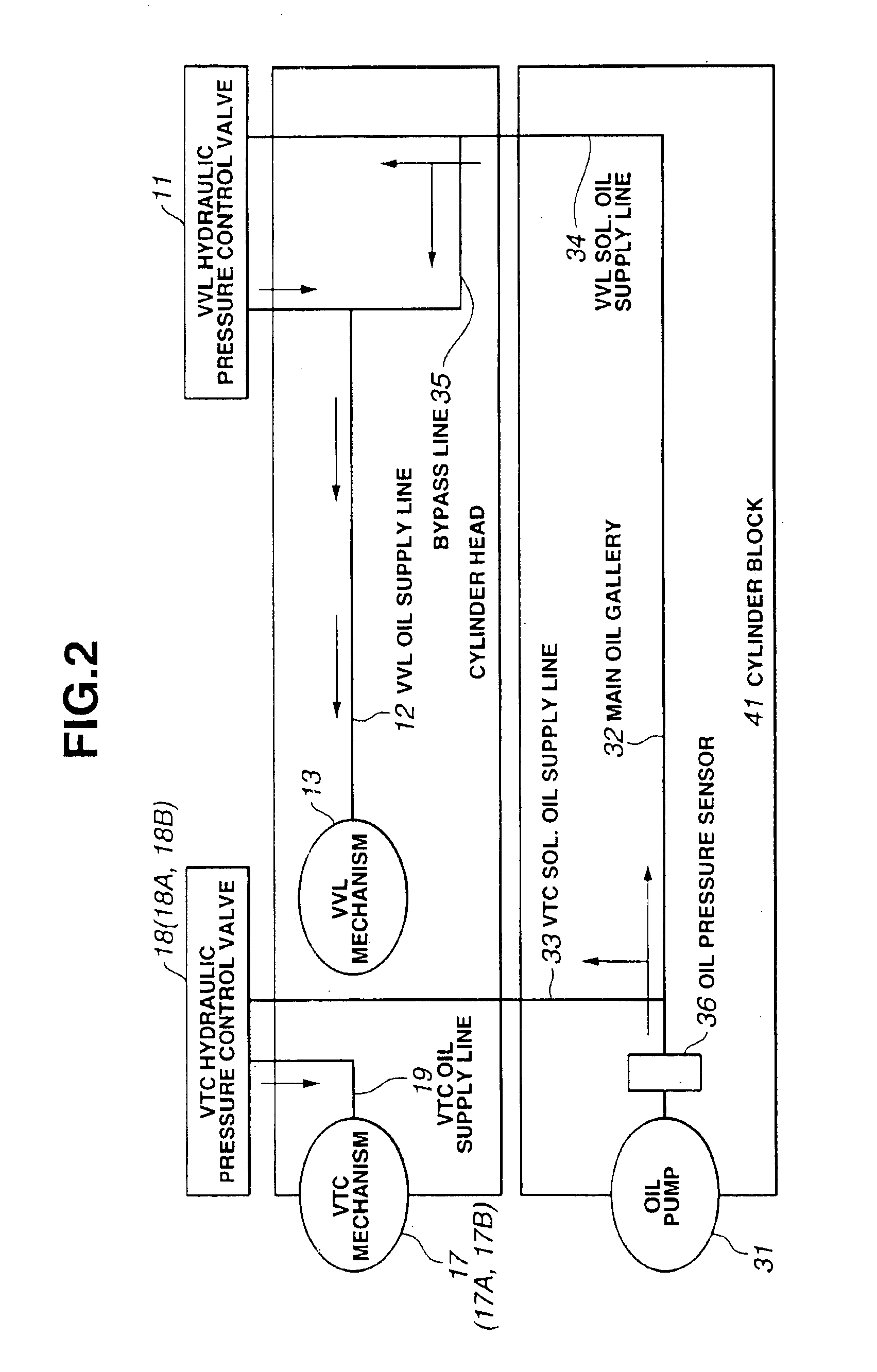
A variable valve operating system for a two-bank engine includes a variable valve-lift and working-angle control mechanism changing at least one of a valve lift and a working angle of each of engine valves arranged in each of cylinder banks, and two variable valve timing control mechanisms provided for each of the banks for changing valve timings independently of each other. A control unit responds a failure in one of the variable valve timing control mechanisms for failsafe purposes. The control unit includes a failsafe section capable of executing a failsafe operating mode in which at least one of the valve lift and the working angle of each of engine valves is increasingly compensated for by the variable valve-lift and working-angle control mechanism, when the one variable valve timing control mechanism is failed.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
Cao cycles of internal combustion engine with increased expansion ratio, constant-volume combustion, variable compression ratio, and cold start mechanism
InactiveUS7624709B2Internal combustion piston enginesOutput powerAlternative fuelsExternal combustion engine
This invention provides an internal combustion engine that has a substantially increased expansion ratio, a variable compression ratio, and subsequently a significantly improved thermal efficiency. This improvement in thermal efficiency is attained without involving a complex mechanical structure or an enlarged engine size. The engine comprises at least a piston and cylinder assembly including a piston reciprocatingly mounted within the cylinder space, and at least two combustion chambers associated with said cylinder, each said combustion chamber having a port leading to said cylinder space and a combustion-chamber valve, said valve opens and closes said port to establish or block the communication between said combustion chamber and cylinder space, wherein said internal combustion engine is adapted to operate on preferred cycles in accordance with load conditions to substantially increase the engine's expansion ratio or provide a variable compression ratio mechanism under part load conditions. For an engine having two combustion chambers associated with each cylinder, the expansion ratio or compression ratio may be nearly doubled. Additionally, a cold start mechanism particularly for an engine operating on alternative fuels, such as ethanol or methanol, and engine valves that are operationally suitable for the engine cycles in accordance with the present invention are disclosed.
Owner:CAO YIDING
Internal combustion engine with direct cooling of cylinder components
ActiveUS20100326380A1Improve impactHigh specific outputLiquid coolingEngine sealsEngineeringCylinder block
A mulitcylinder internal combustion engine includes a cylinder block, a cylinder head and a gasket mounted between the cylinder block and cylinder head. A coolant passage extends through the cylinder block and laterally along an uppermost portion of a shared cylinder wall extending between adjacent engine cylinders. The laterally extending cooling passage is defined at least in part by a passage formed in the cylinder head gasket.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
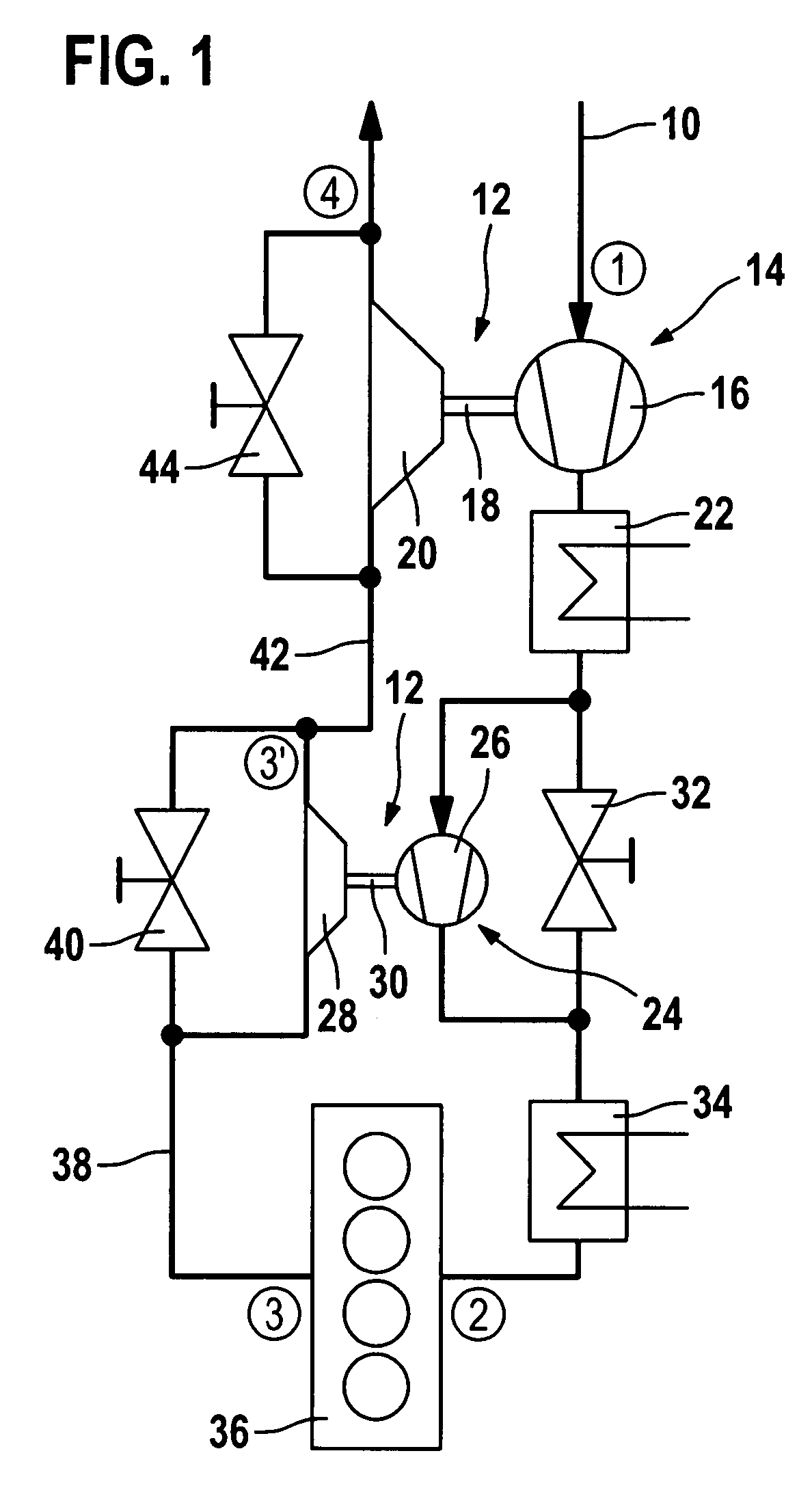
Method for balancing engine cylinder bank output using crankshaft sensing and intake cam phasing
ActiveUS6843214B1Improving equalization of power outputImprove balanceValve arrangementsElectrical controlRotation velocityCam
A method is disclosed for balancing work output from cylinder banks of an engine having a common crankshaft and separate intake camshafts with cam phasers for each bank. The method includes sensing a crankshaft rotational characteristic, such as instantaneous rotational speed or acceleration, during the power strokes of pistons of predetermined comparable cylinders (or all cylinders) of each bank, computing average crankshaft rotational characteristics for the power strokes of the comparable cylinders of each bank, and adjusting the phasing of at least one of the intake camshafts to obtain equal averages of the sensed characteristics of the crankshaft during the power strokes of the respective banks.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
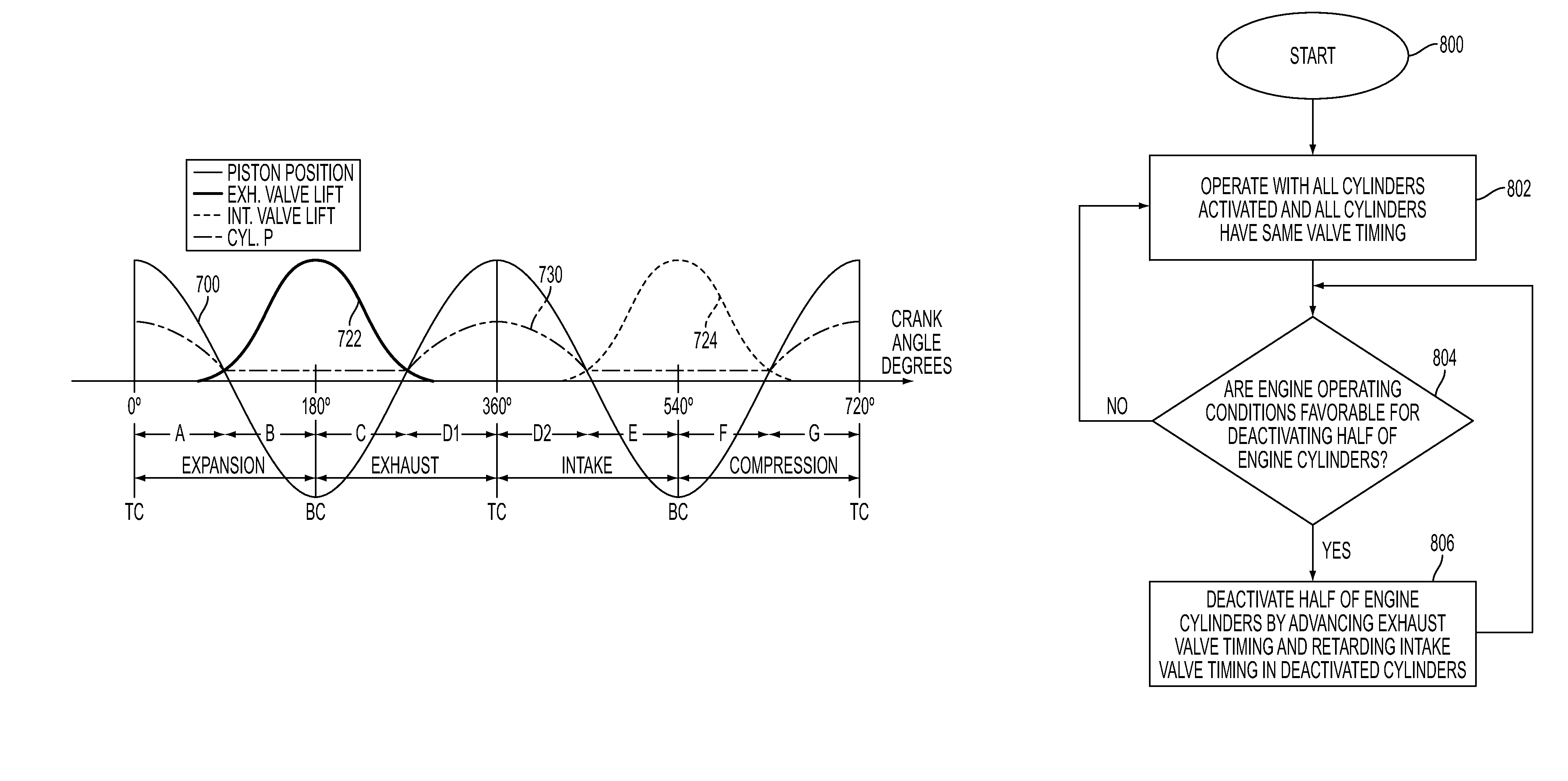
Adjusting valve timing to deactivate engine cylinders for variable displacement operation
ActiveUS8042504B2Effectively disableImprove authorityValve arrangementsYielding couplingExhaust valveExternal rotation
An internal combustion engine having two cylinder banks and adjustable camshaft timing is disclosed in which the camshafts in one cylinder bank are adjusted so that there is no net flow from the cylinders to effectively disable the cylinder bank. In particular, exhaust valve timing is advanced so that the maximum valve lift occurs approximately at bottom center between expansion and exhaust strokes and intake valve timing is advanced so that maximum valve lift occurs approximately at bottom center between intake and compression strokes. Also disclosed is an engine in which an intake and an exhaust camshaft on a single bank are coaxial with valve timings adjusted by rotating the inner of the two camshafts with respect to the outer of the two camshafts.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
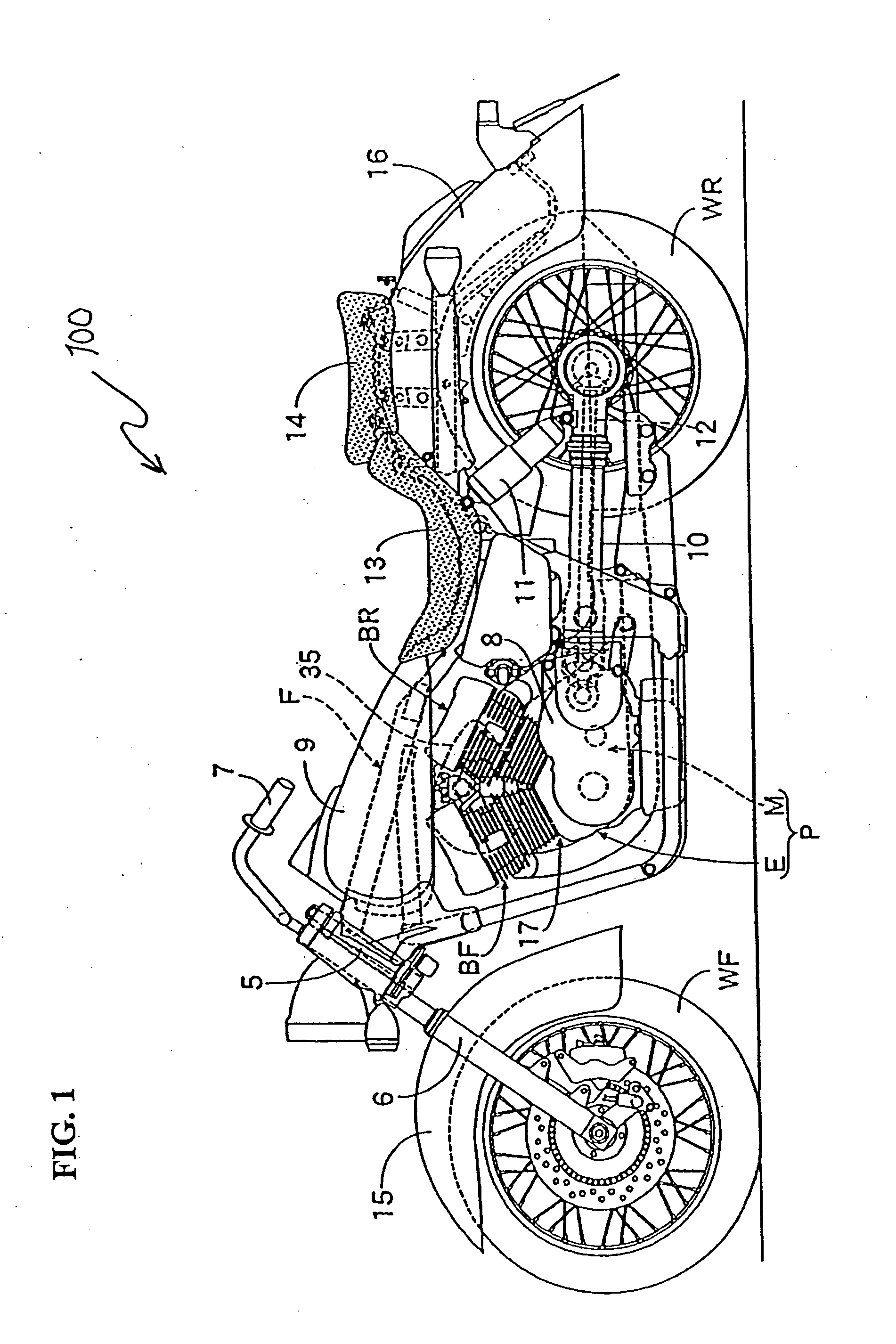
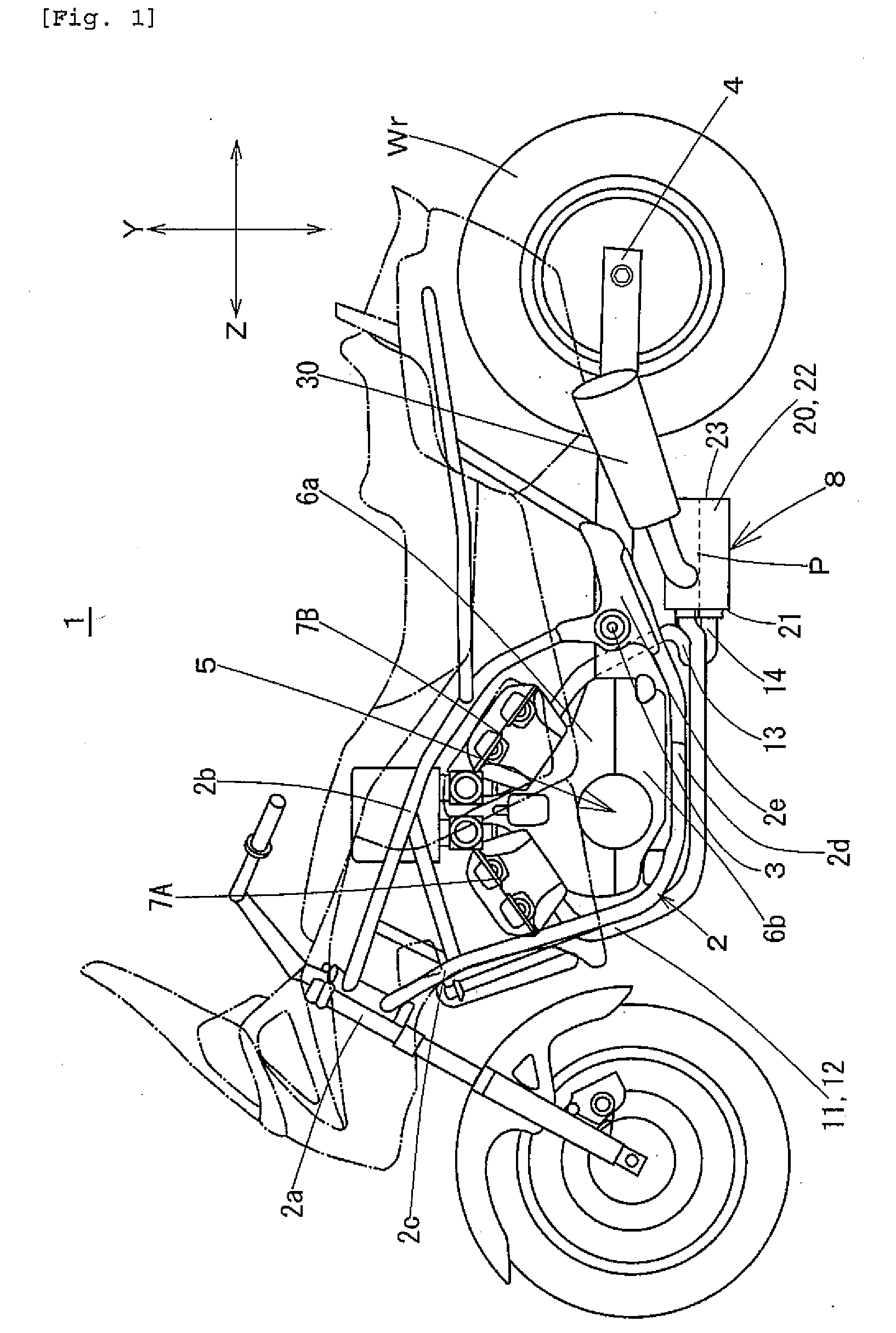
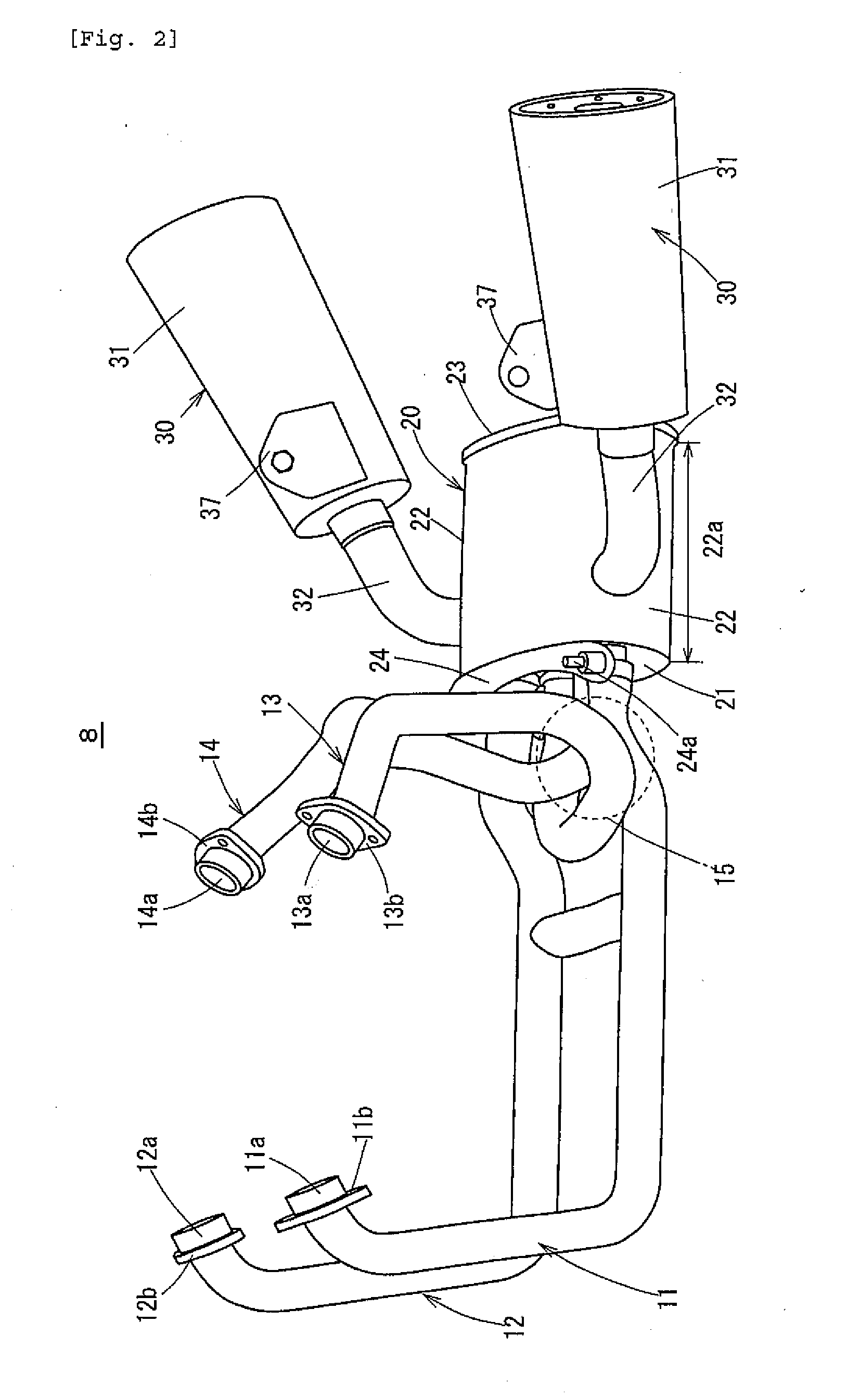
Exhaust System and Saddle-Ride Type Vehicle
InactiveUS20070181360A1Sufficient volumeConcentrating massExhaust apparatusSilencing apparatusCombustion chamberMuffler
An exhaust system for a saddle-ride type vehicle provides sufficient volume in a chamber while avoiding interference between the chamber and other parts. The vehicle center of gravity is lowered and differences in exhaust pipe length are reduced. Exhaust pipes are connected to combustion chambers of front and rear cylinder banks of a V-type engine. A chamber is connected to the exhaust pipes and mufflers are connected to the chamber. The chamber has an exhaust pipe connection wall to which the exhaust pipes are connected and opposing muffler connection walls. The mufflers are connected to positions on the muffler connection walls closer to the engine relative to a center in a longitudinal direction of the vehicle.
Owner:YAMAHA MOTOR CO LTD
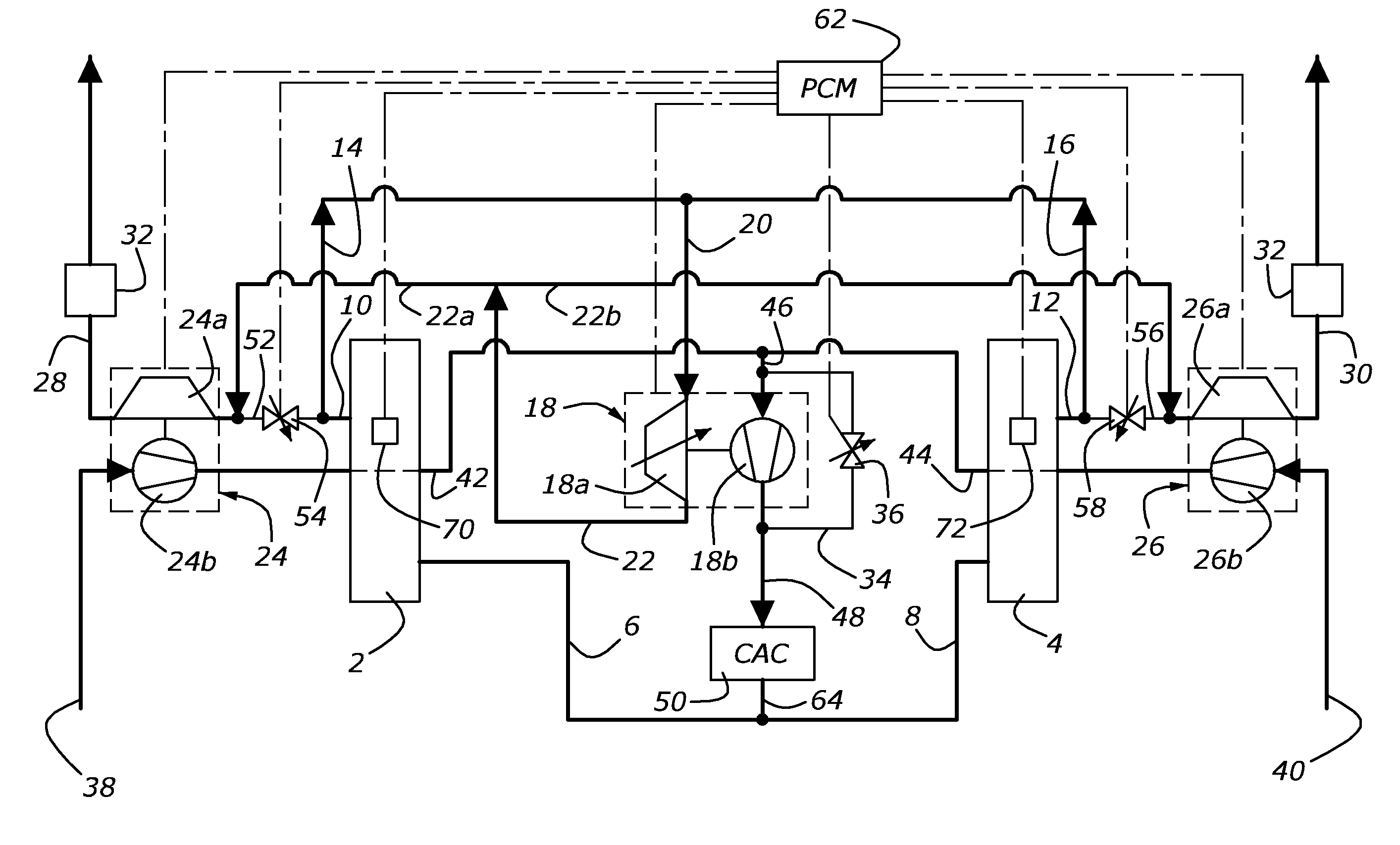
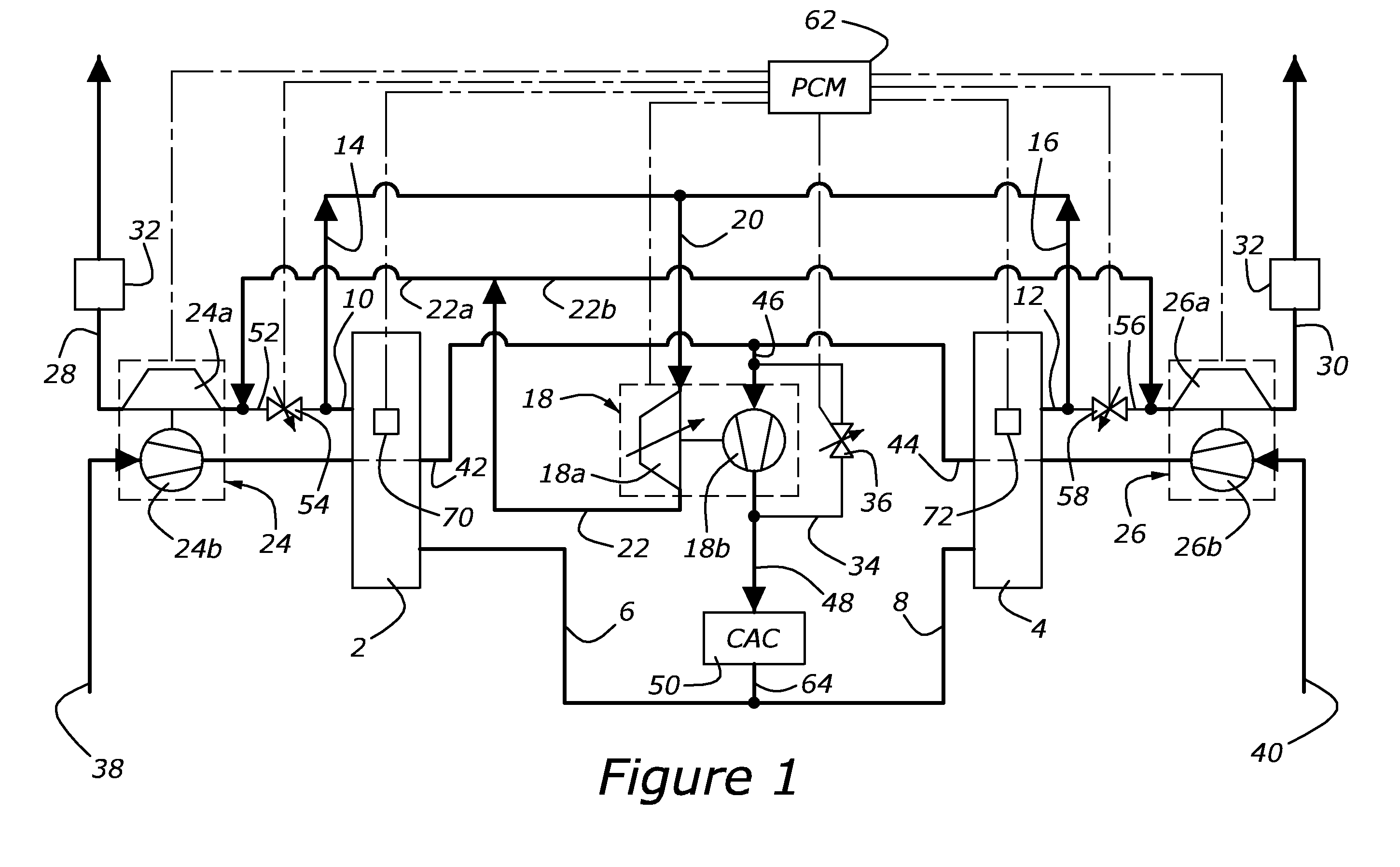
Split-Series Sequential Turbocharged Engine
InactiveUS20090183506A1Easy to operateInternal combustion piston enginesEngine controllersTurbochargerEngineering
For an internal combustion engine having two cylinder banks forming a V-shaped cylinder block, a turbocharger system including a high pressure turbocharger disposed in a valley between the cylinder banks, a first low-pressure turbocharger disposed adjacent an outer side of one of the cylinder banks, and a second low-pressure turbocharger disposed adjacent an outer side of the second cylinder bank. Intake and exhaust ducts connect the components of the engine and turbocharger system to and electronically controlled valves associated with the ducts permit the system to operate either in a split series mode or a low-pressure-only mode.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Supercharging system for two-stage supercharging of V-type internal combustion engines
InactiveUS7703284B2Minimized pressure lossQuick buildInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusCombustionTurbocharger
A supercharging system, in particular an at least two-stage supercharging system, including a first stage and a second stage for an internal combustion engine having two cylinder banks. The at least two-stage supercharging system includes at least two charge air coolers. An exhaust gas turbocharger representing the first stage and an exhaust gas turbocharger representing the second stage are each situated next to one of the cylinder banks of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
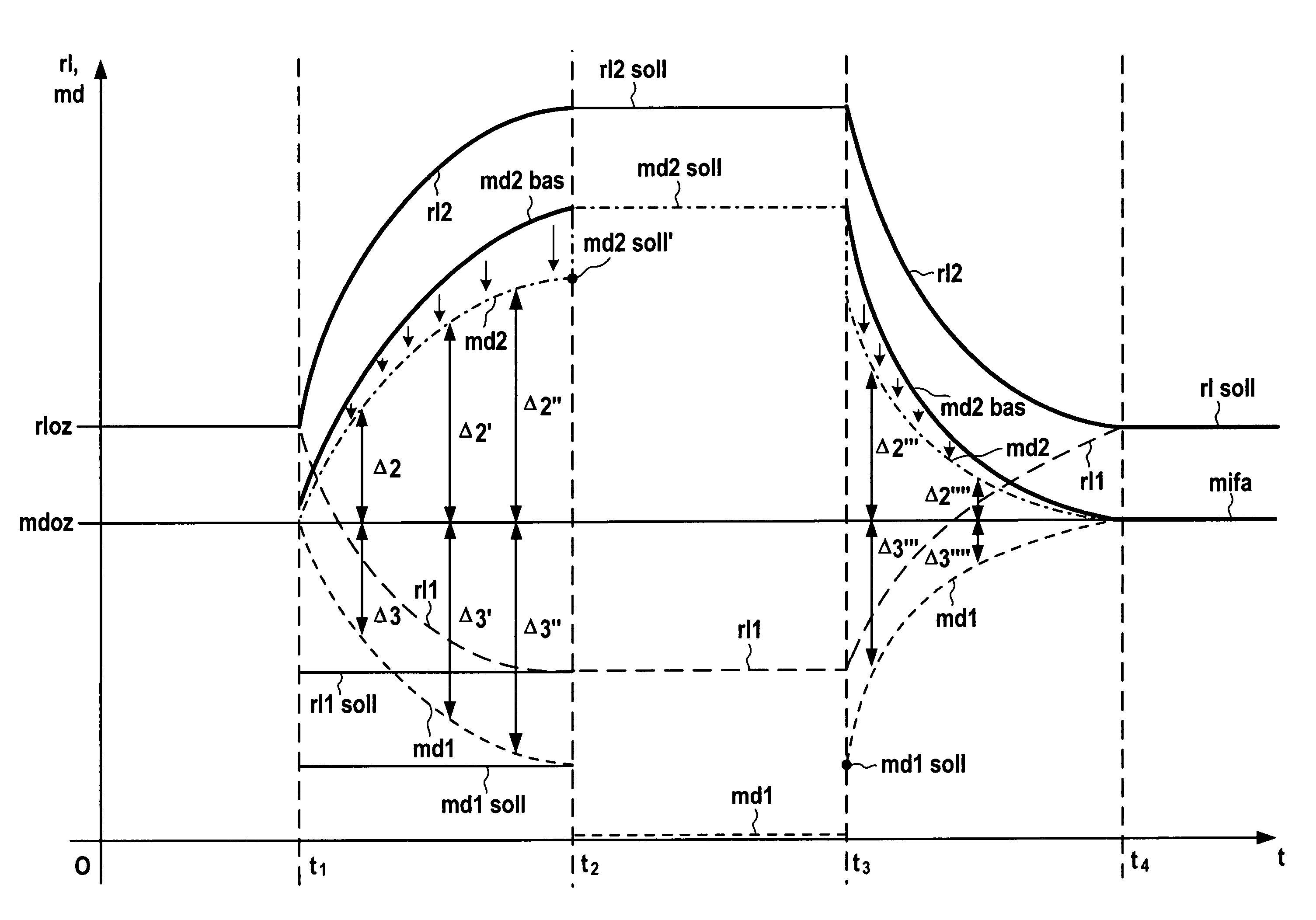
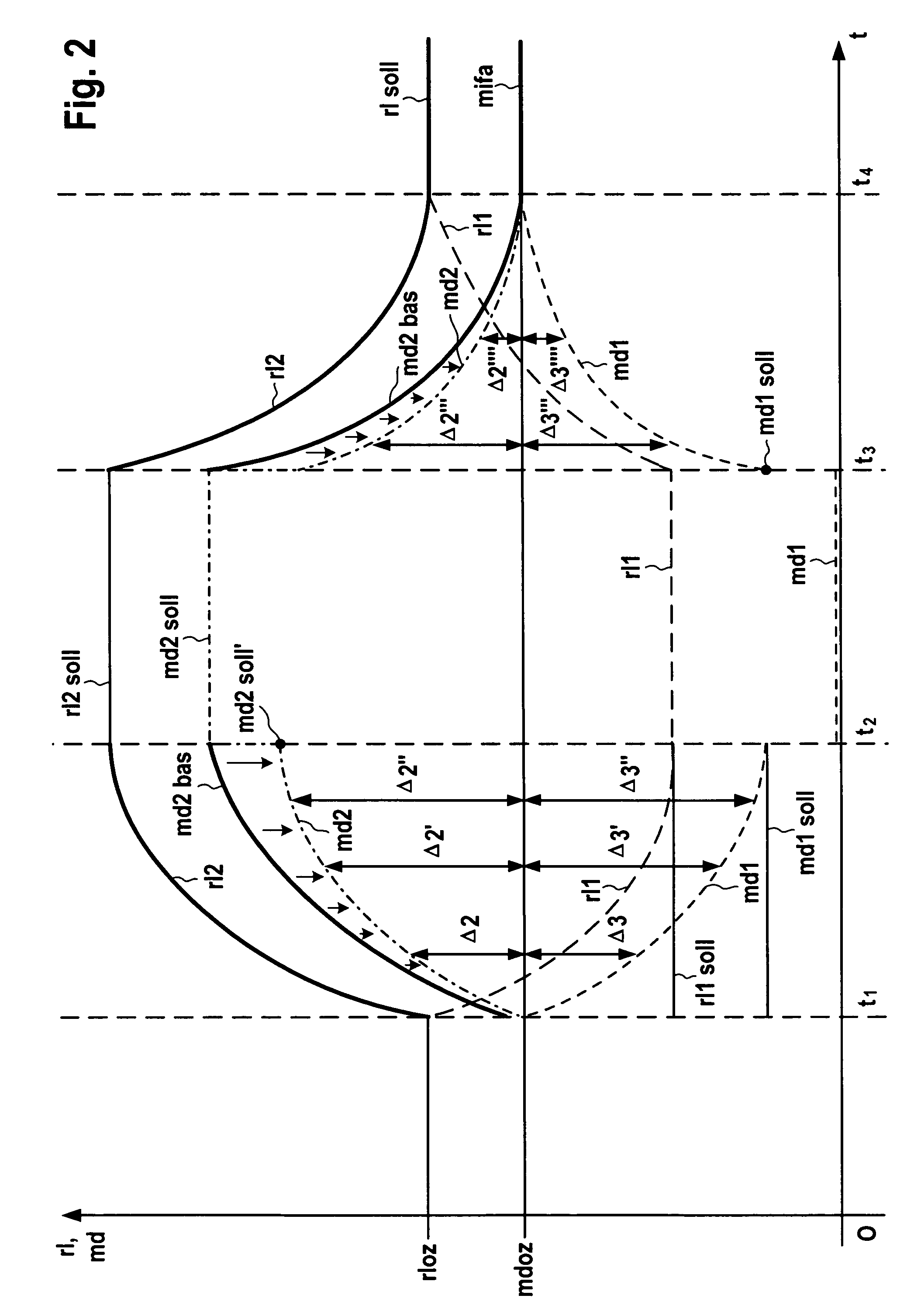
Method for operating an internal combustion engine having a plurality of cylinder banks
InactiveUS7246594B2Increase fuel consumptionIncrease exhaust temperatureElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesInternal combustion engineControl theory
A method for operating an internal combustion engine having a plurality of cylinder banks provides a cylinder cut-off using at least a reduced ignition angle retardation shift. In this context, at least one first cylinder bank is configured such that it is at least partially able to be cut off. Immediately before a cut off or immediately after a reactivation of at least one cylinder of the at least one first cylinder bank, a first output variable is set for the at least one first cylinder bank and a second output variable is set for at least one second cylinder bank. The first output variable and the second output variable are set differently from each other in such a way that an average of the first and second output variables is equivalent to a predetermined output variable of the internal combustion engine.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Controlling cylinder mixture and turbocharger operation
ActiveUS7987040B2Less variationReduce the differenceElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesTurbochargerExhaust gas
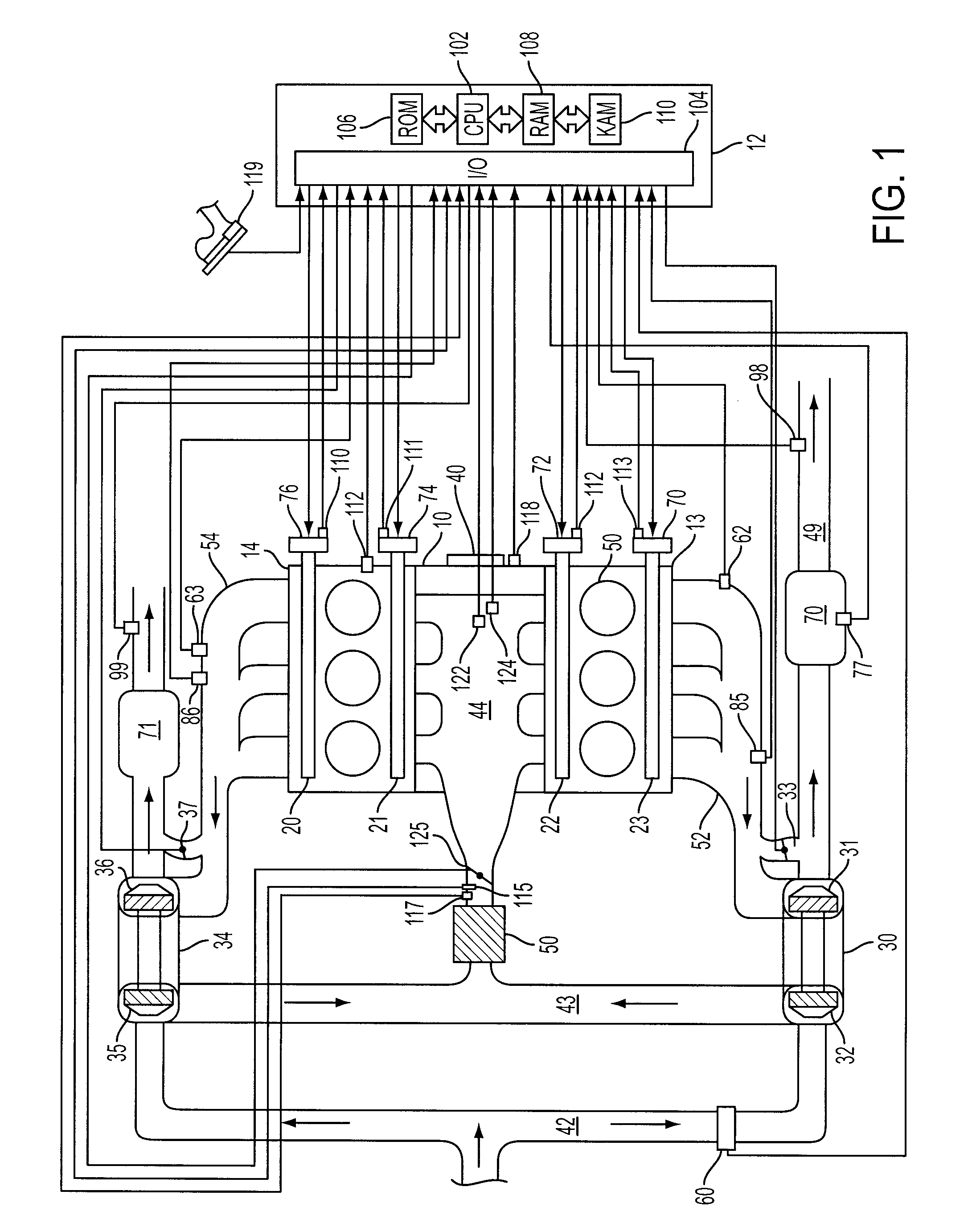
A method for controlling differences in exhaust gas residual amount for a two cylinder bank engine having at least one turbocharger is presented. In one example, the description includes a method for adjusting valve timing to reduce cylinder exhaust gas residual variation.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com