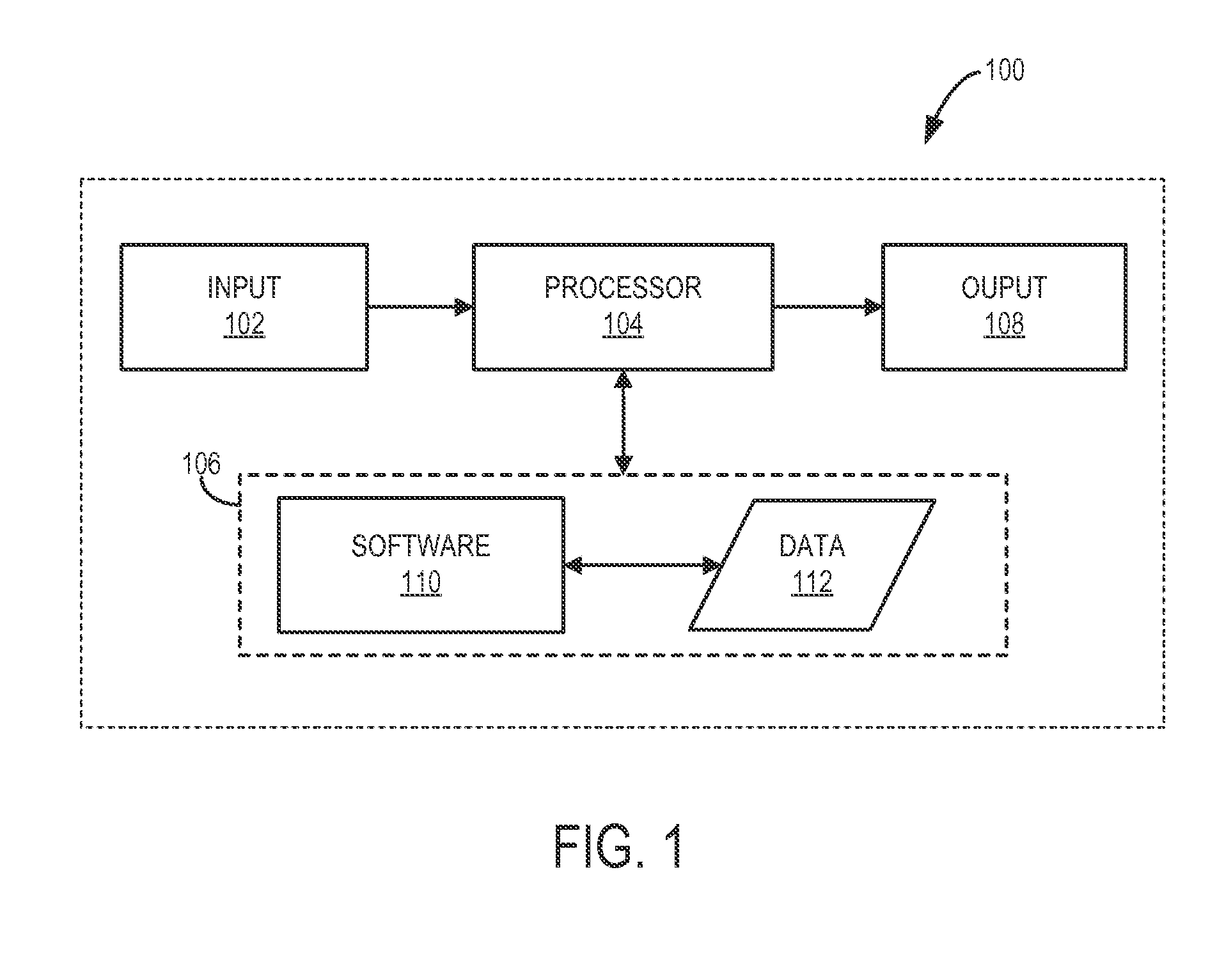
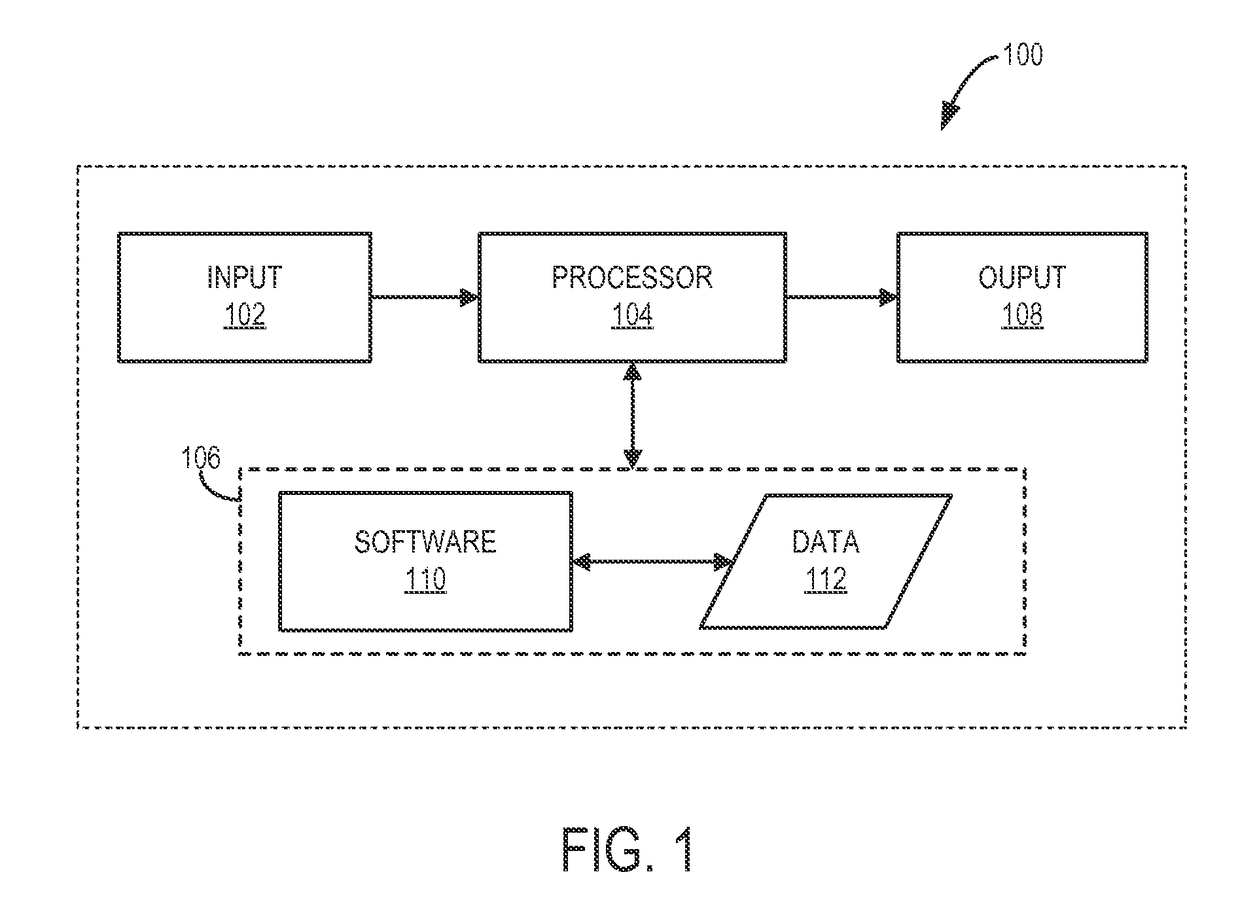
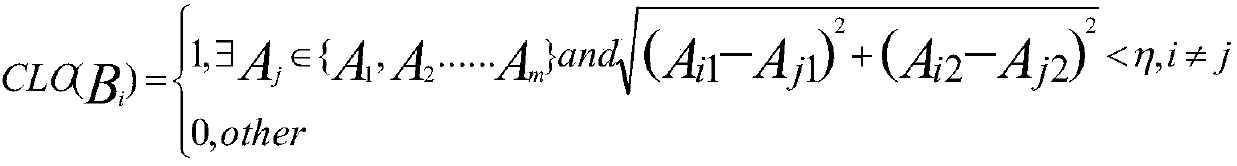Patents
Literature
71 results about "Radial coordinate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The radial coordinate is the first number in the pair of numbers used to describe polar coordinates. For example, in the polar coordinates (5, 45°), the radial coordinate is 5 (the number on the left): The radial coordinate is sometimes called the radius.
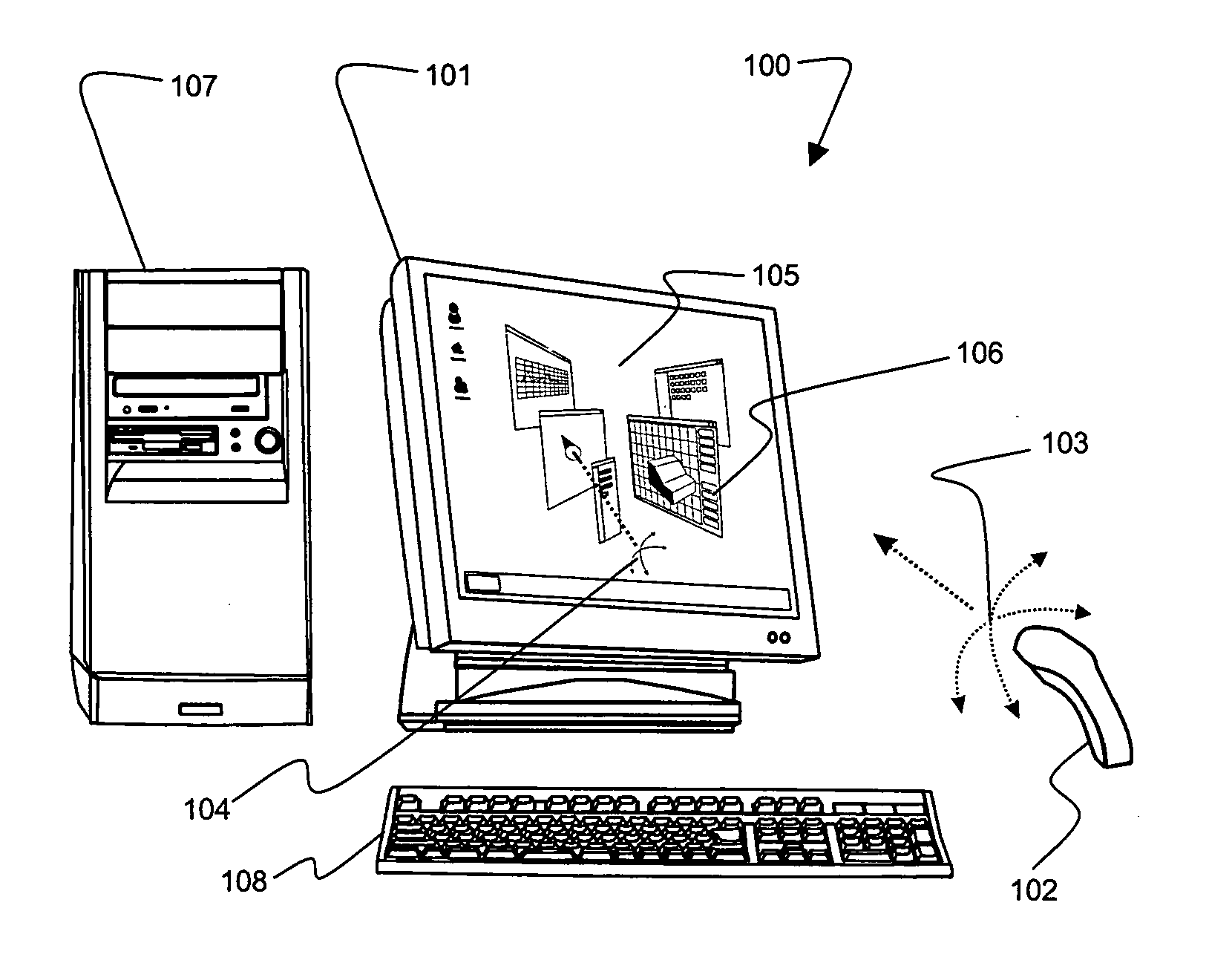
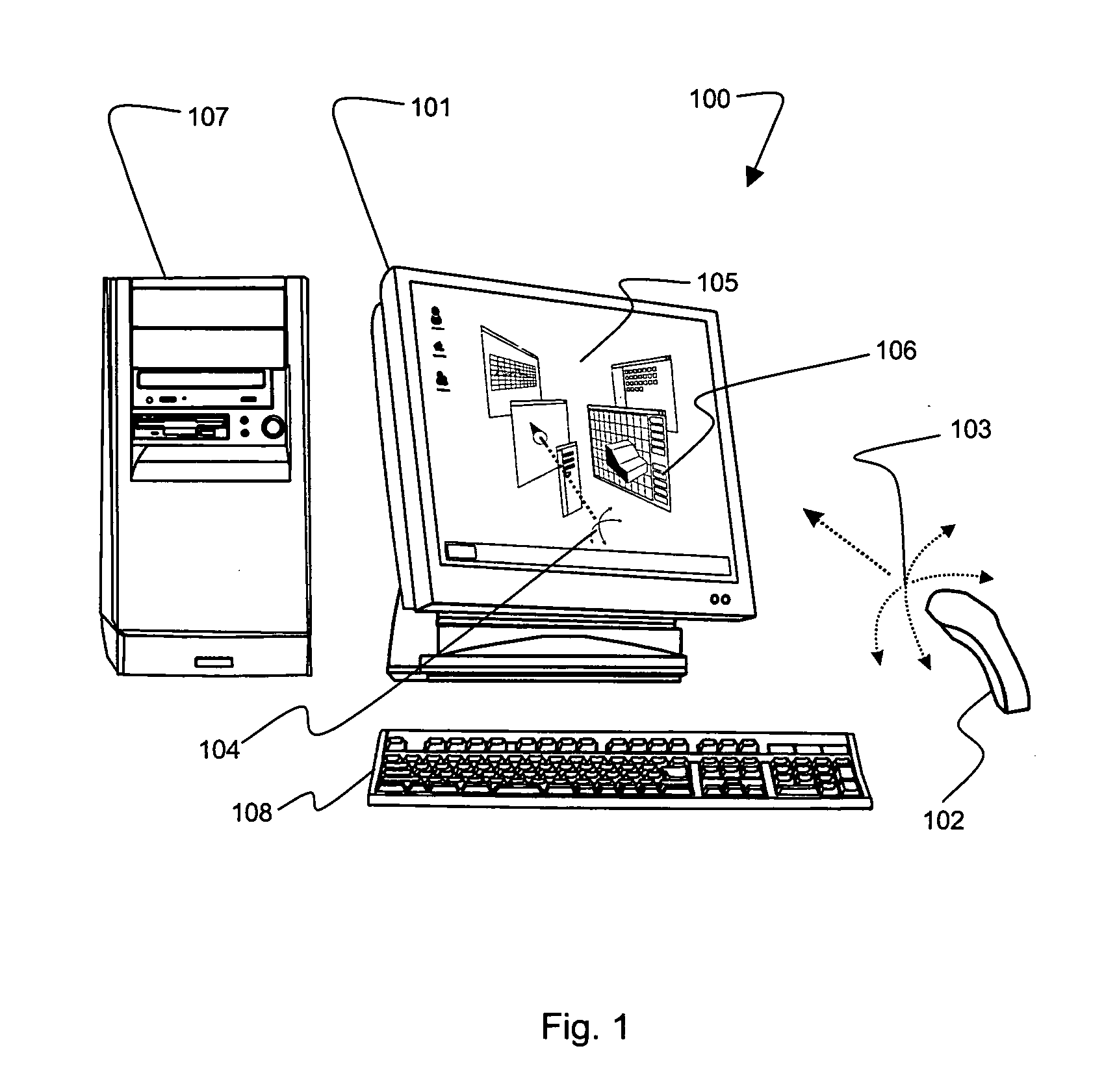
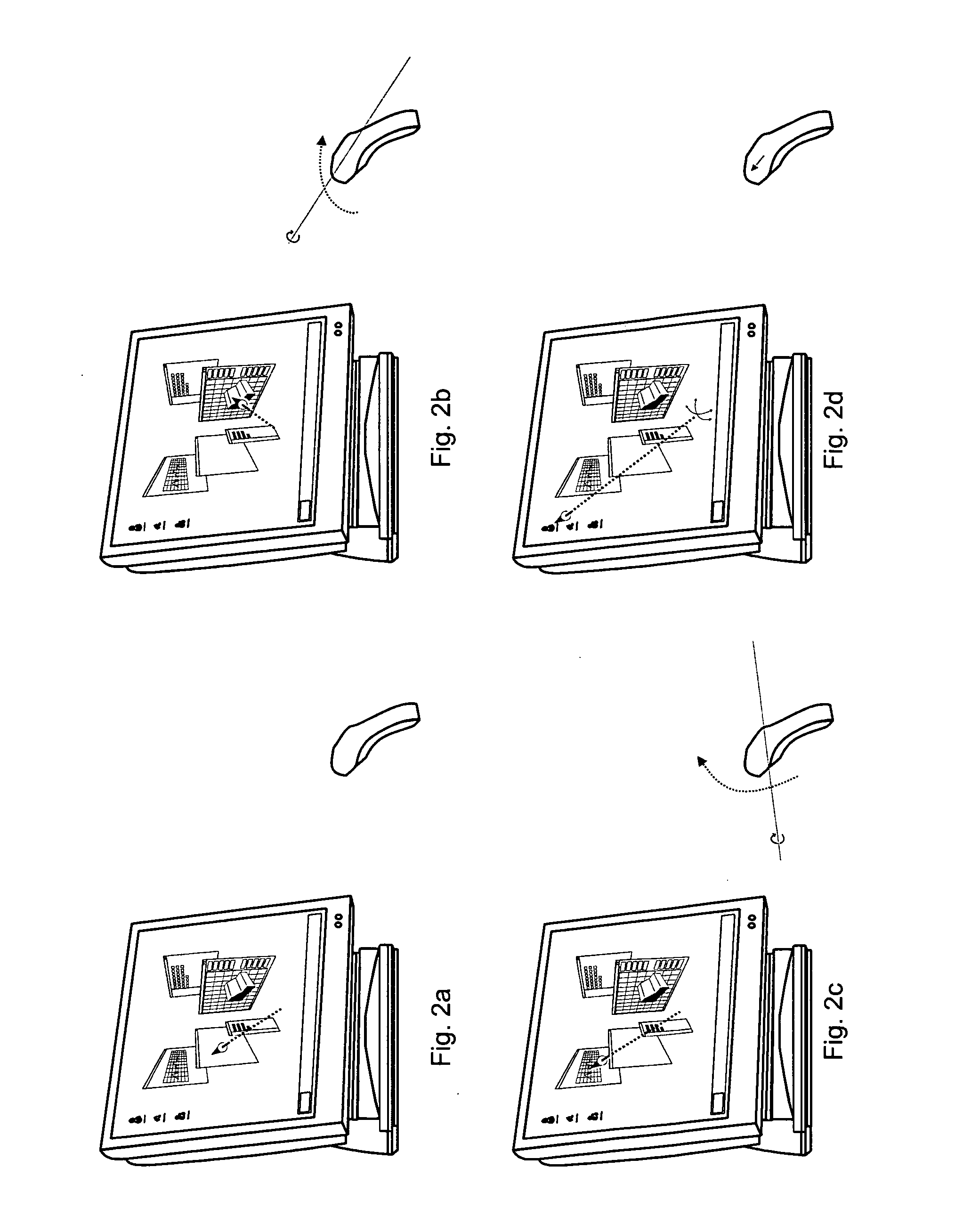
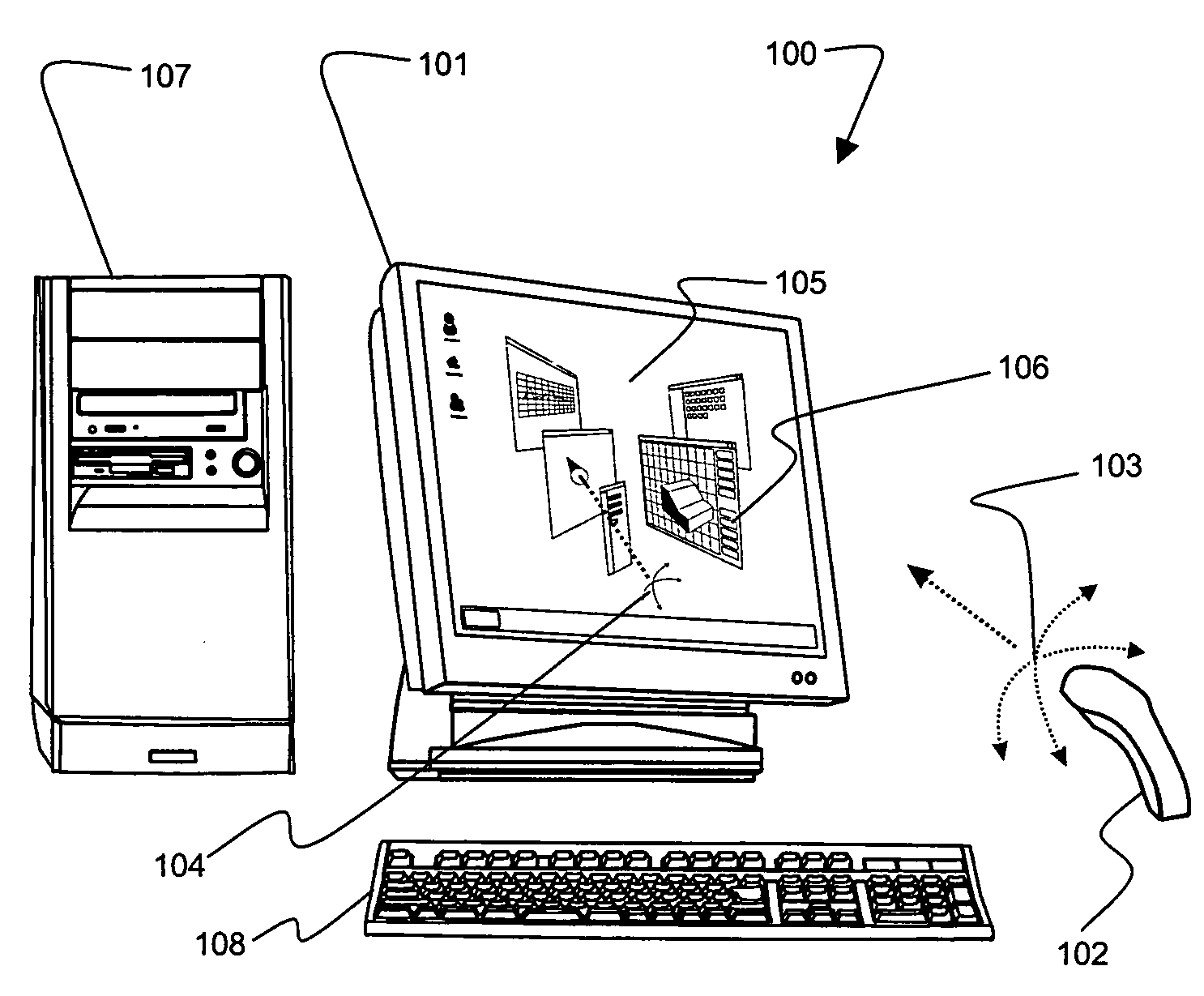
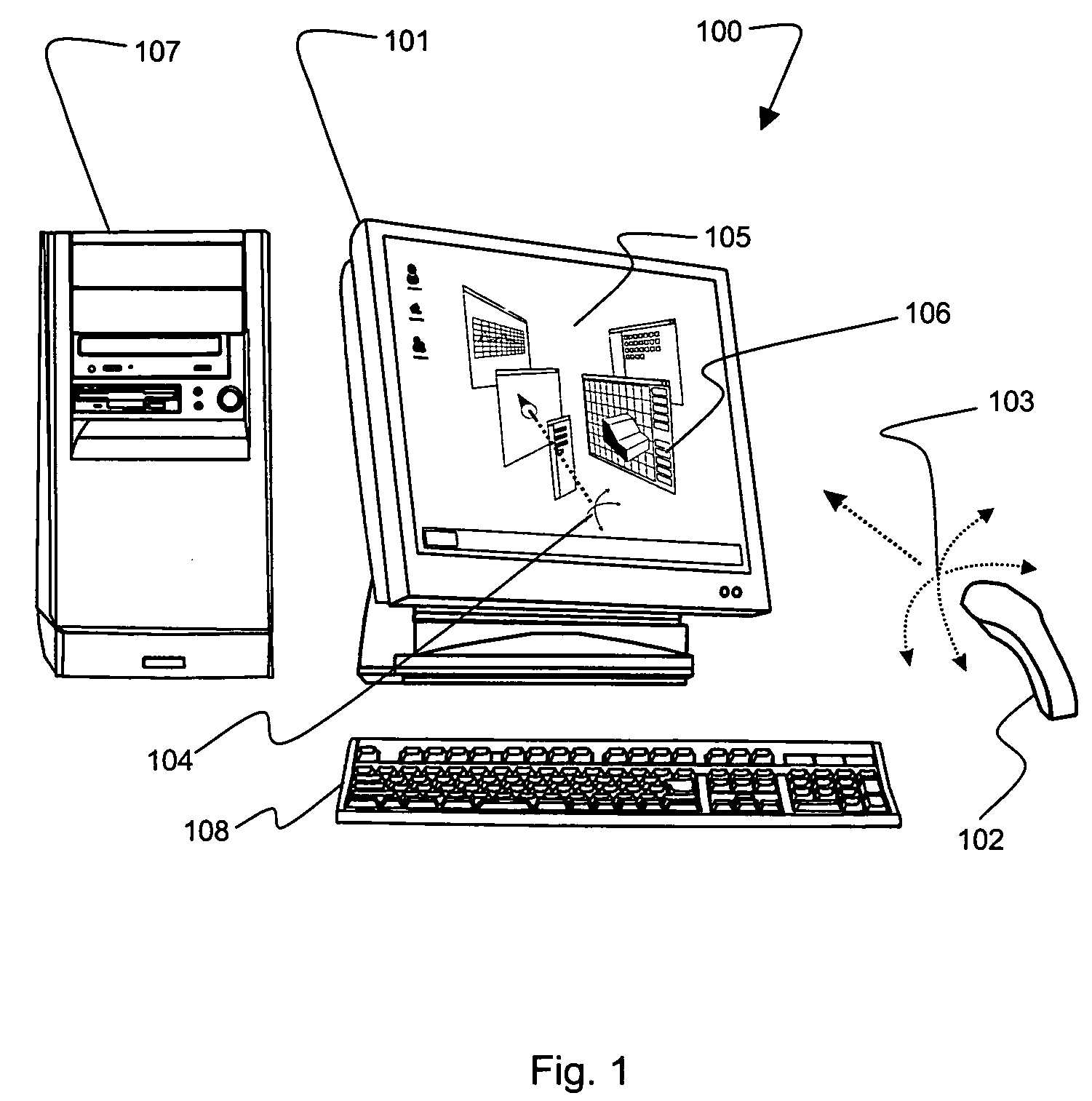
3D mouse and game controller based on spherical coordinates system and system for use
InactiveUS20060092133A1Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAccelerometerDisplay device
A computer input device constructed from at least one tilt accelerometer and at least one linear input element is disclosed. This input device can be used in a computer system to specify a position on a display using radial coordinates, cylindrical coordinates, or spherical coordinates.
Owner:TOUMA PIERRE A
3D mouse and game controller based on spherical coordinates system and system for use
InactiveUS7683883B2Cathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingAccelerometerDisplay device
A computer input device constructed from at least one tilt accelerometer and at least one linear input element is disclosed. This input device can be used in a computer system to specify a position on a display using radial coordinates, cylindrical coordinates, or spherical coordinates.
Owner:TOUMA PIERRE A
Method for forming a blood flow in surgically reconstituted segments of the blood circulatory system and devices for carrying out said method
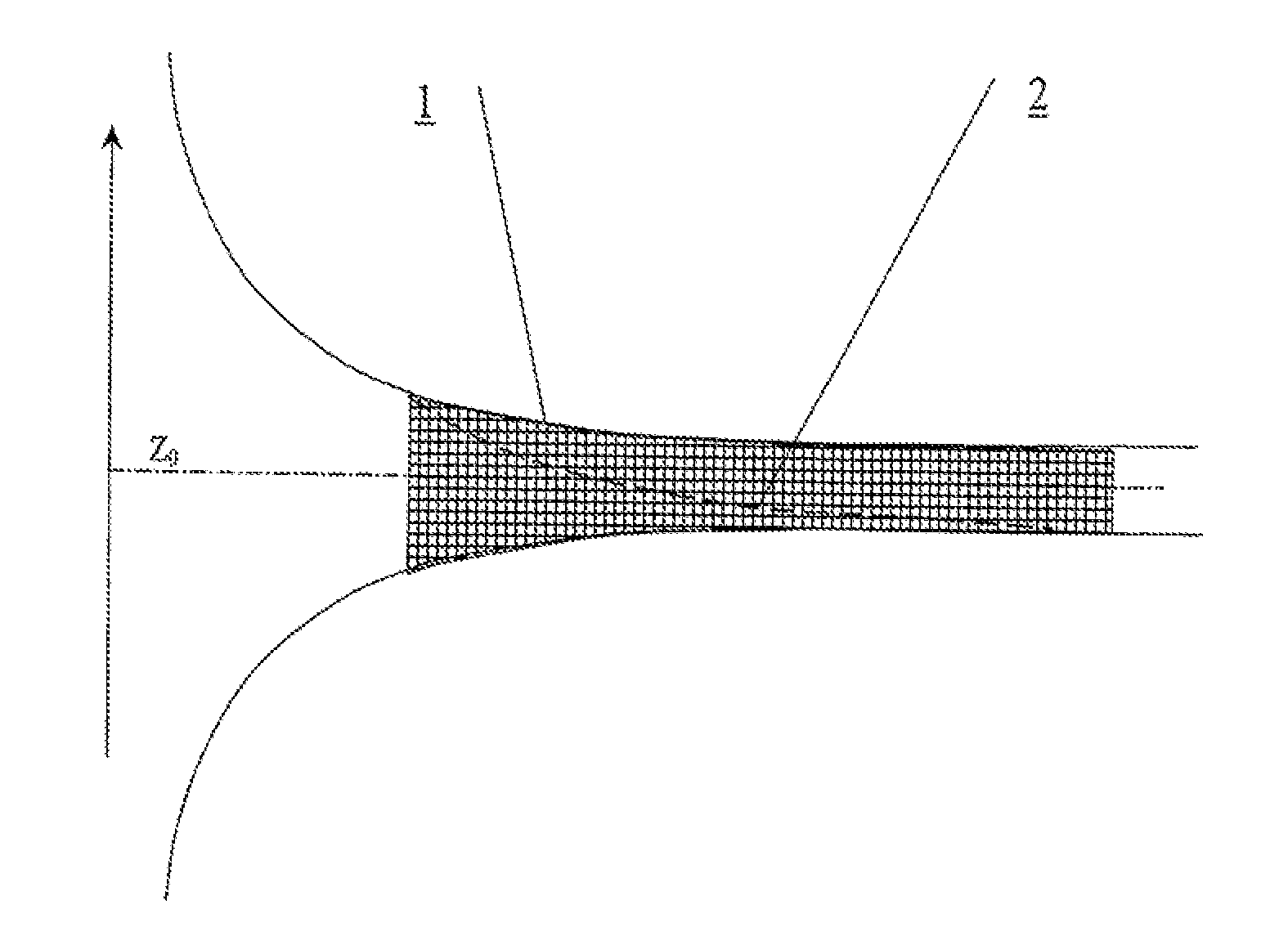
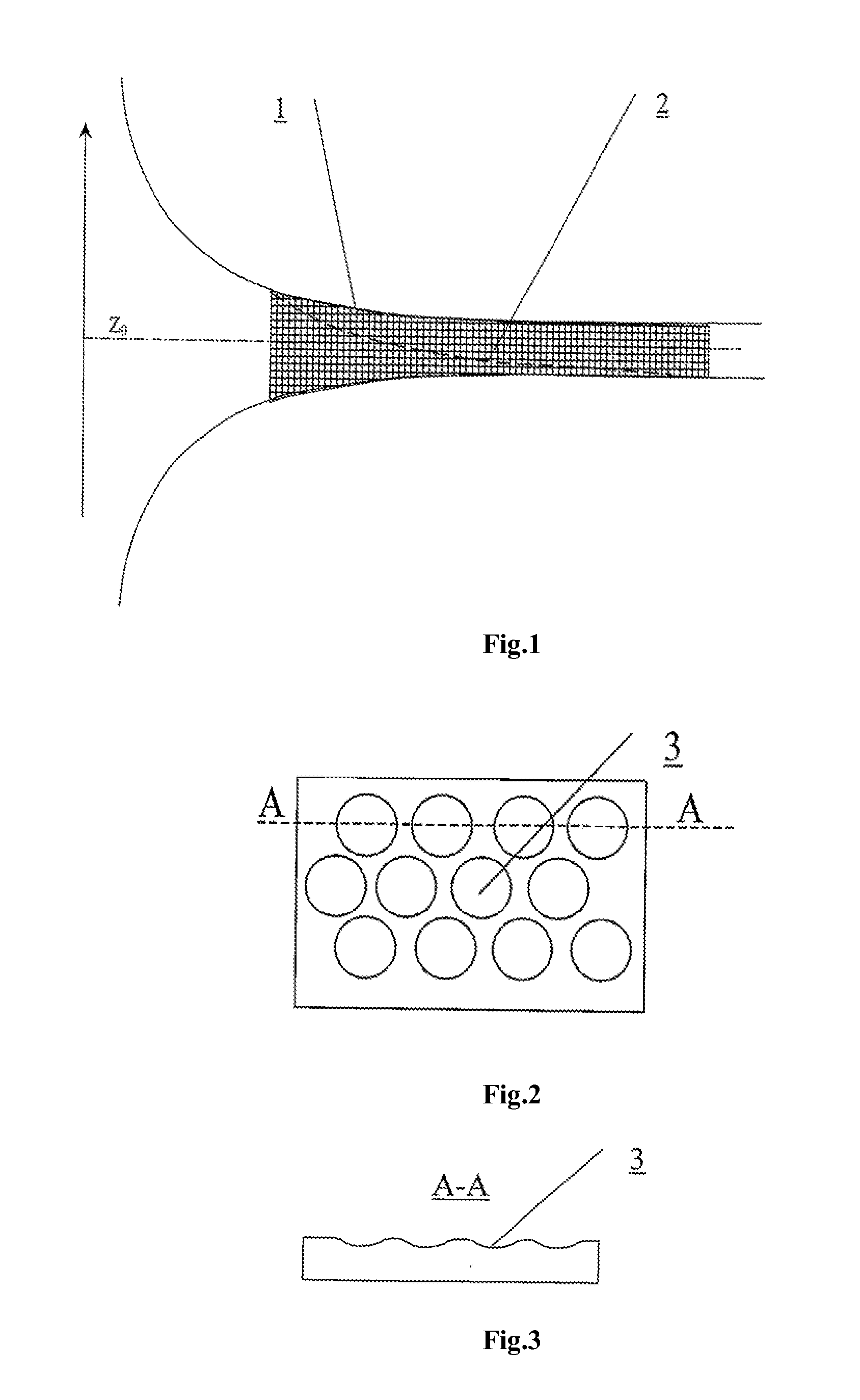
The invention relates to clinical cardiology and cardiovascular surgery. The method for forming a blood flow in research stands and in surgically reconstructed segments of the blood circulation system comprises diagnosing the individual condition of a patient's blood circulation system; measuring the blood flow velocity field in the heart chambers and great vessels; comparing the parameters measured against the physiological norm; determining parameters forming a swirled blood flow; and modeling an individual swirled blood current in the blood circulation system being diagnosed, the streamlined surfaces and guide elements of flow channels of the blood circulation system reconstructed being given shapes conforming to the flow lines of the restored normally swirled blood flow in accordance with formulas:Q(t)=[z+Z0(t)]2(1.1)ϕ=ϕ0+k(t)z(1.2)k(t)=Γ0(t) / 4πQ(t)C0(t)Vz=2C0(t)zVr=-C0(t)rVϕ=Γ0(t)2πr{1-exp[-C0(t)r22v]}(1.3)wherein: Vr, Vz, and Vφ are the radial, longitudinal, and tangential velocities of the swirled current; v is the kinematic viscosity of the medium; φ0 is the initial swirling angle in relation to the flow axis normal; φ, z and r are current values of the angular, longitudinal, and radial coordinates along the flow line; and Q(t), Z0(t), k(t), Γ0(t), and C0(t) are parameters of the swirled blood flow variable over time because of the non-stationary current and corresponding to the individual normal indicators for a physiologically swirled blood flow. The normal indicators are established by routine examination of a representative sample of patients having no changes in the cardiovascular system. A vessel prosthesis comprises a tube having an internal surface in contact with the blood flow provided with a pattern to swirl the blood flow in accordance with formulas (1.1 to 1.3) conforming to a specific localization of the segment being reconstructed. A cannula for para-corporeal perfusion devices comprises a flow channel having an internal surface that is provided with a longitudinal pattern to swirl the blood flow, the shape of the pattern being determined from formulas (1.1 to 1.3), relative to the specific localization of the point where the cannula is inserted into the vessel channel. A heart valve prosthesis comprises one or more shutoff elements arranged symmetrically in the center of a body of round and / or oval cross-section, the streamlined surfaces of the valve being provided with a pattern in accordance with formulas (1.1 to 1.3). A blood pump comprises a flow swirling unit, a flow channel, and valves at the inlet and outlet of the channel, the surface washed over by blood being provided with a relief variable over time in accordance with formulas (1.1 to 1.3). A swirling device comprises an end piece having a streamlined surface provided with guides in the form of ribs, grooves, or blades of a shape defined by formulas (1.1 to 1.3), the swirling angle of the guides relative to the flow axis being varied optionally an operator or by a special-purpose device for modeling different current conditions.
Owner:BOKERIYA LEO ANTONOVICH +2
High resolution, high pressure xenon gamma ray spectroscopy using primary and stimulated light emission
InactiveUS6486468B1Particle separator tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansPhoton detectionSpectroscopy
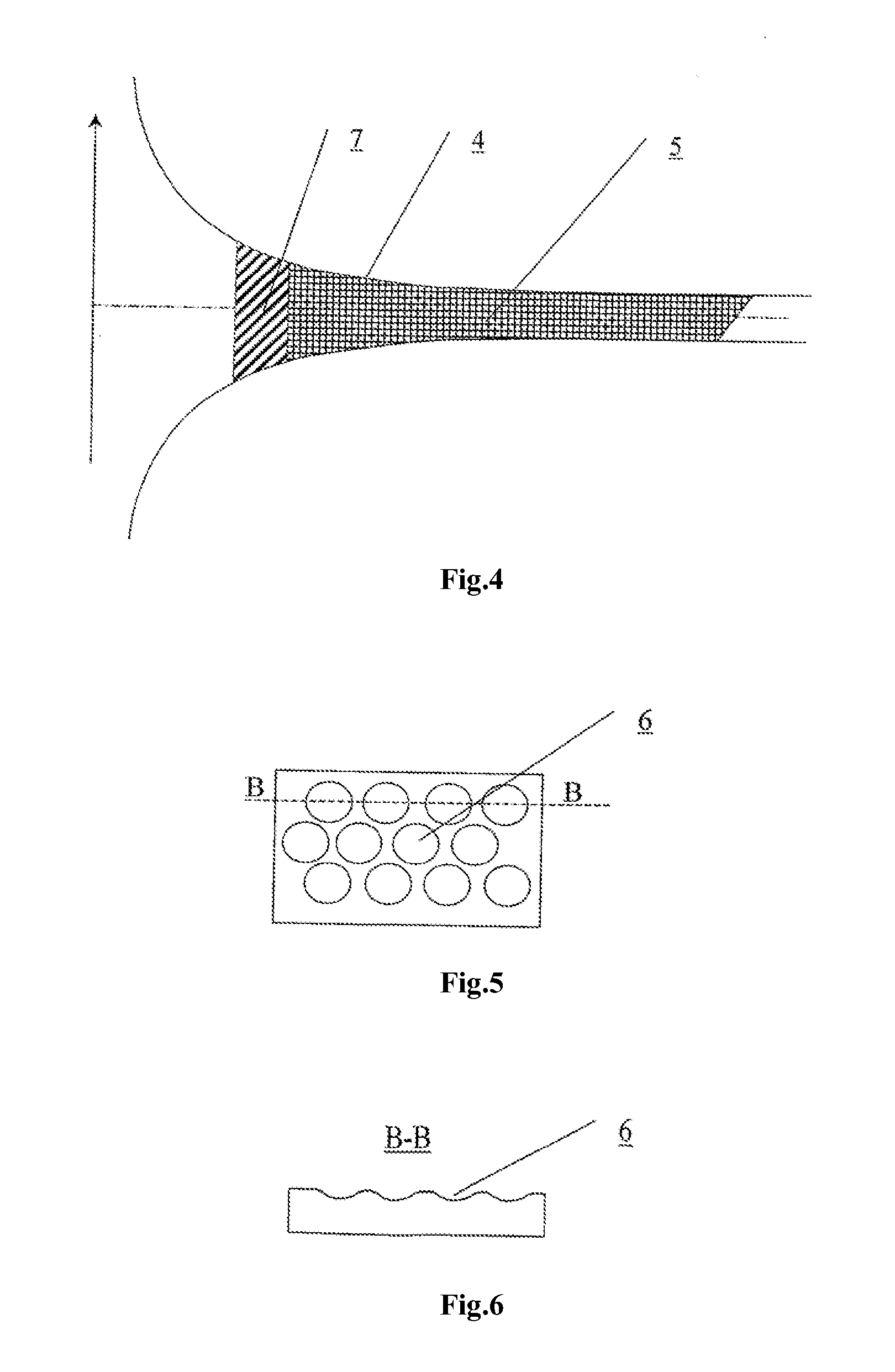
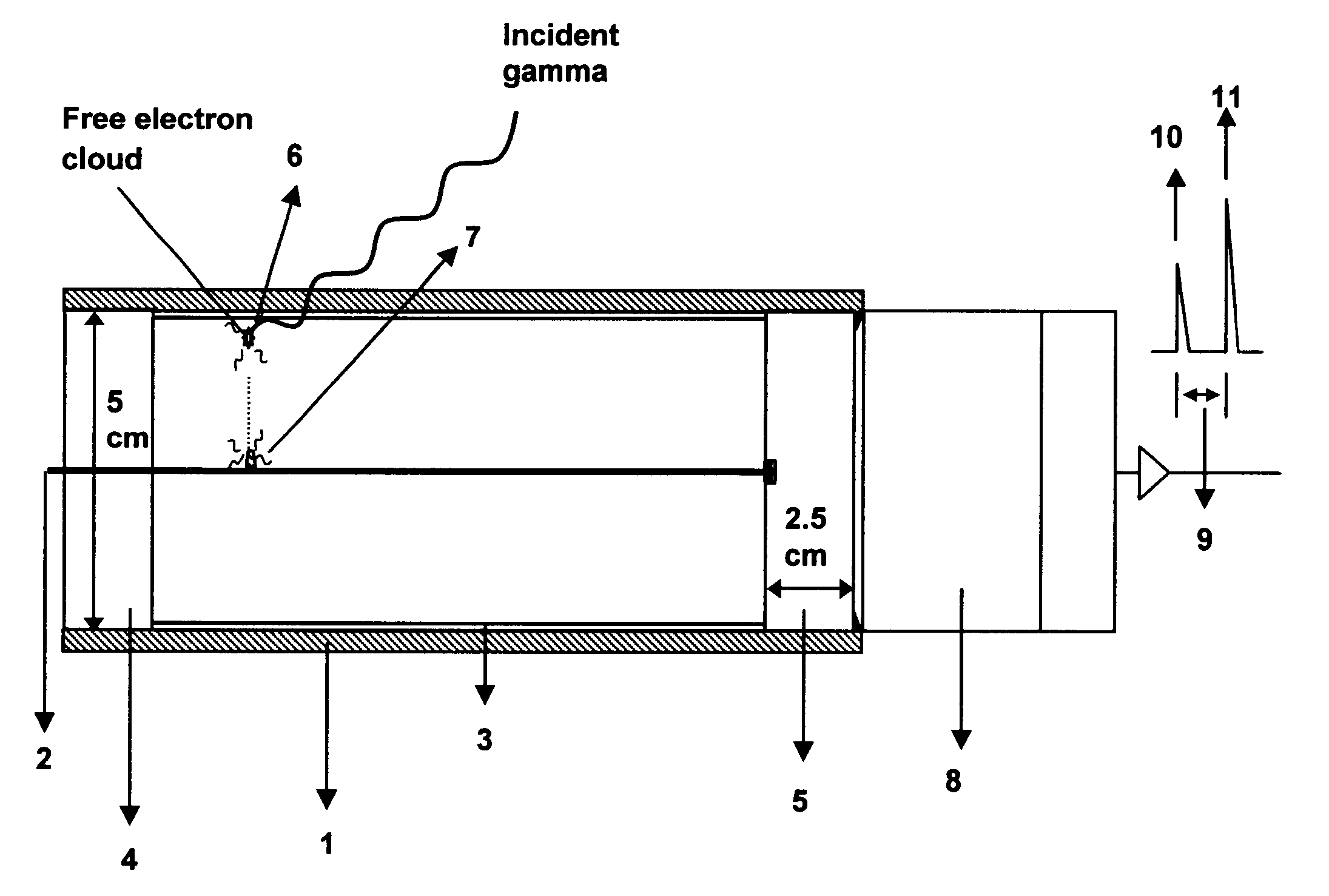
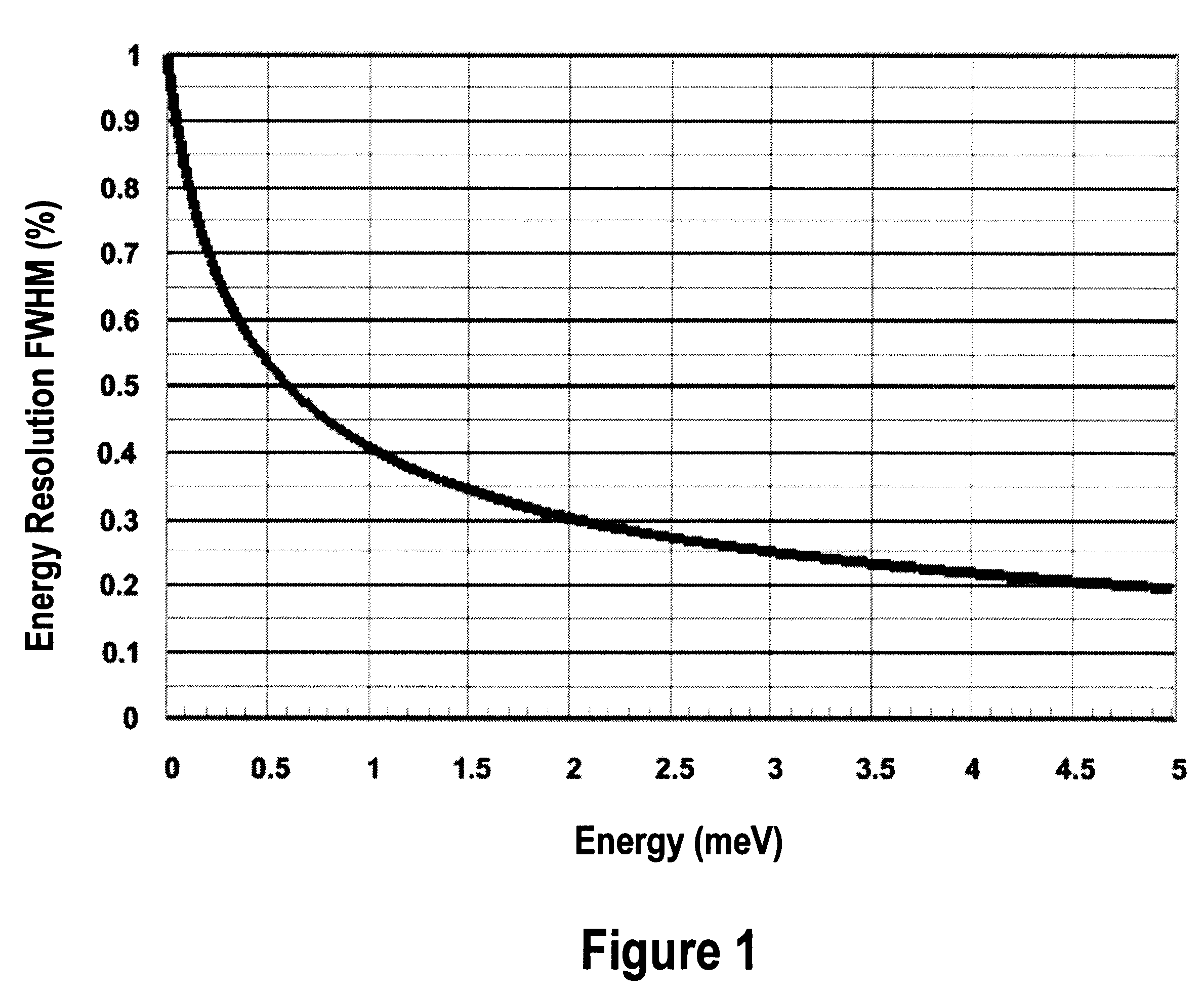
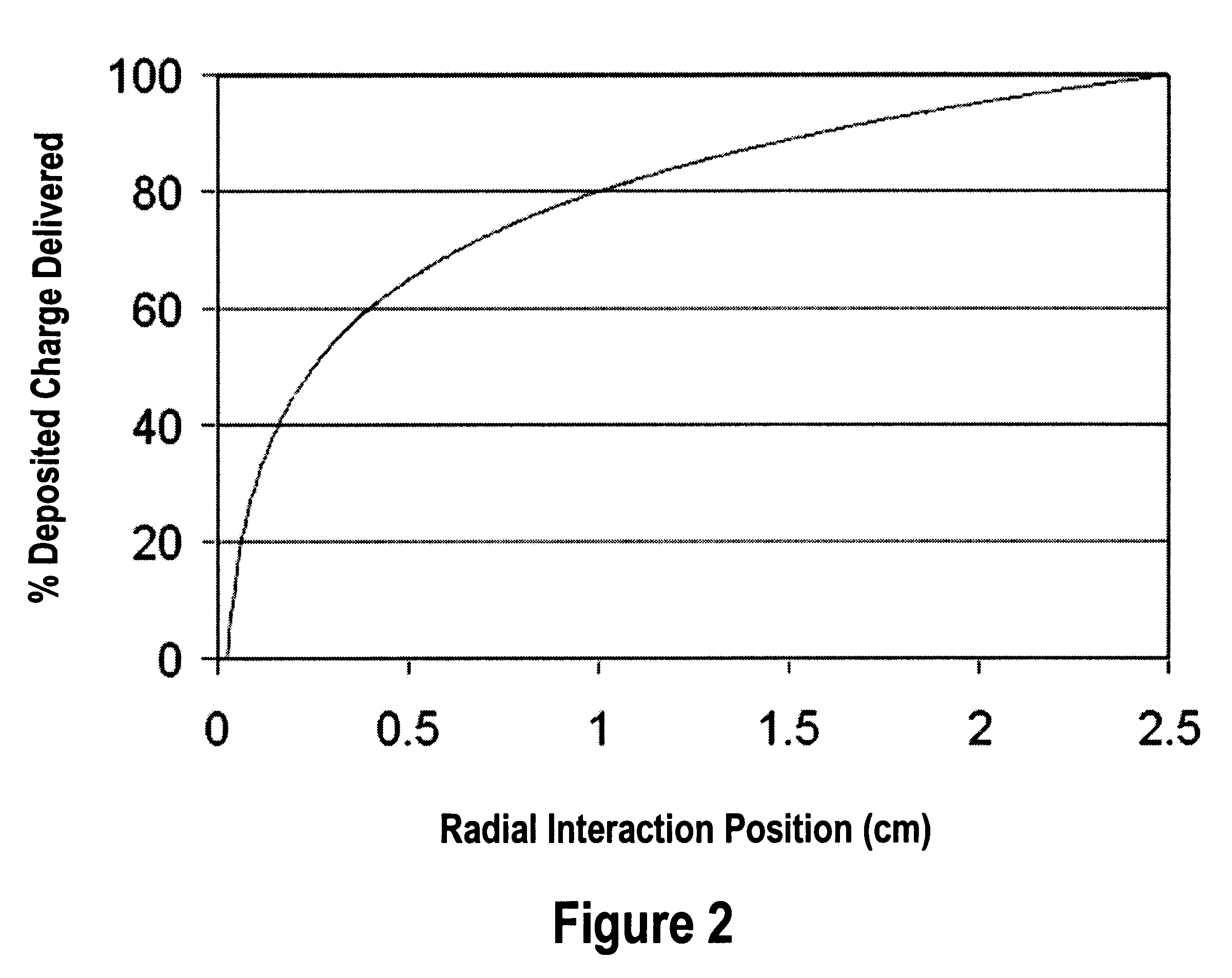
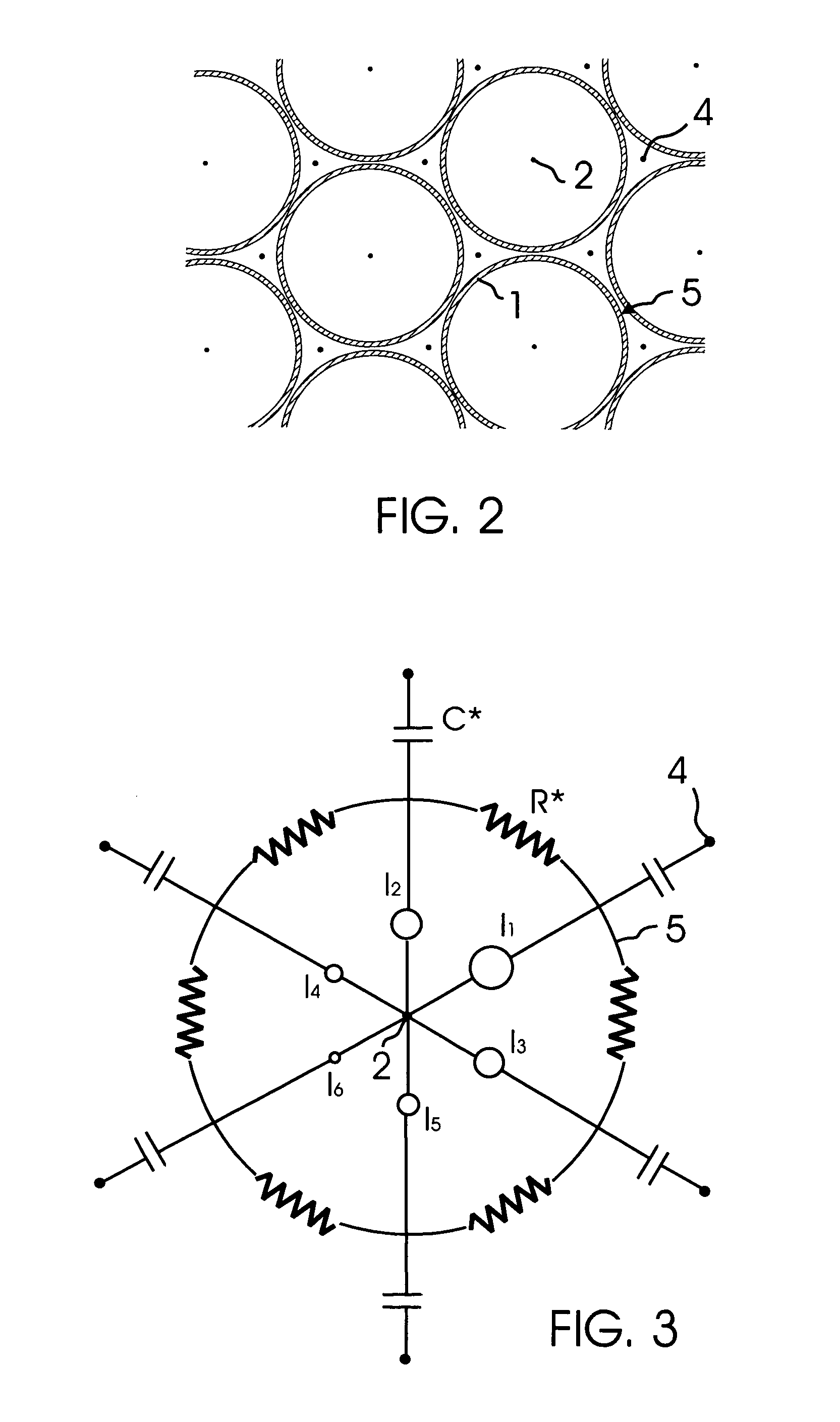
A design and readout of a xenon detection medium based device, which provides improved spectroscopic performance compared to currently commercially available devices. To achieve energy resolution improvement, a method to accurately measure radial spatial position for interacting events within a HPXe cylindrical detector is described using the plan as shown in FIG. 4. This is accomplished by utilization of light generated both at the gamma interaction site and at the collection point near the anode wire of the cylindrical detector. These light flashes are detected by a VUV photon detector. Light transmission is facilitated by incorporating a vacuum ultraviolet (VUV) light transparent window at least one end of the cylindrical ionization detector. With the known electron drift velocity in HPXe, the time between these two photopulses is sufficient to accurately determine the radial coordinate. Consequently, correction by electronic means for the electrostatic pulse dispersion using the expression graphed in FIG. 2 can be achieved in order to approach the true intrinsic energy resolution limit for HPXe.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
Illumination systems and devices for fourier ptychographic imaging
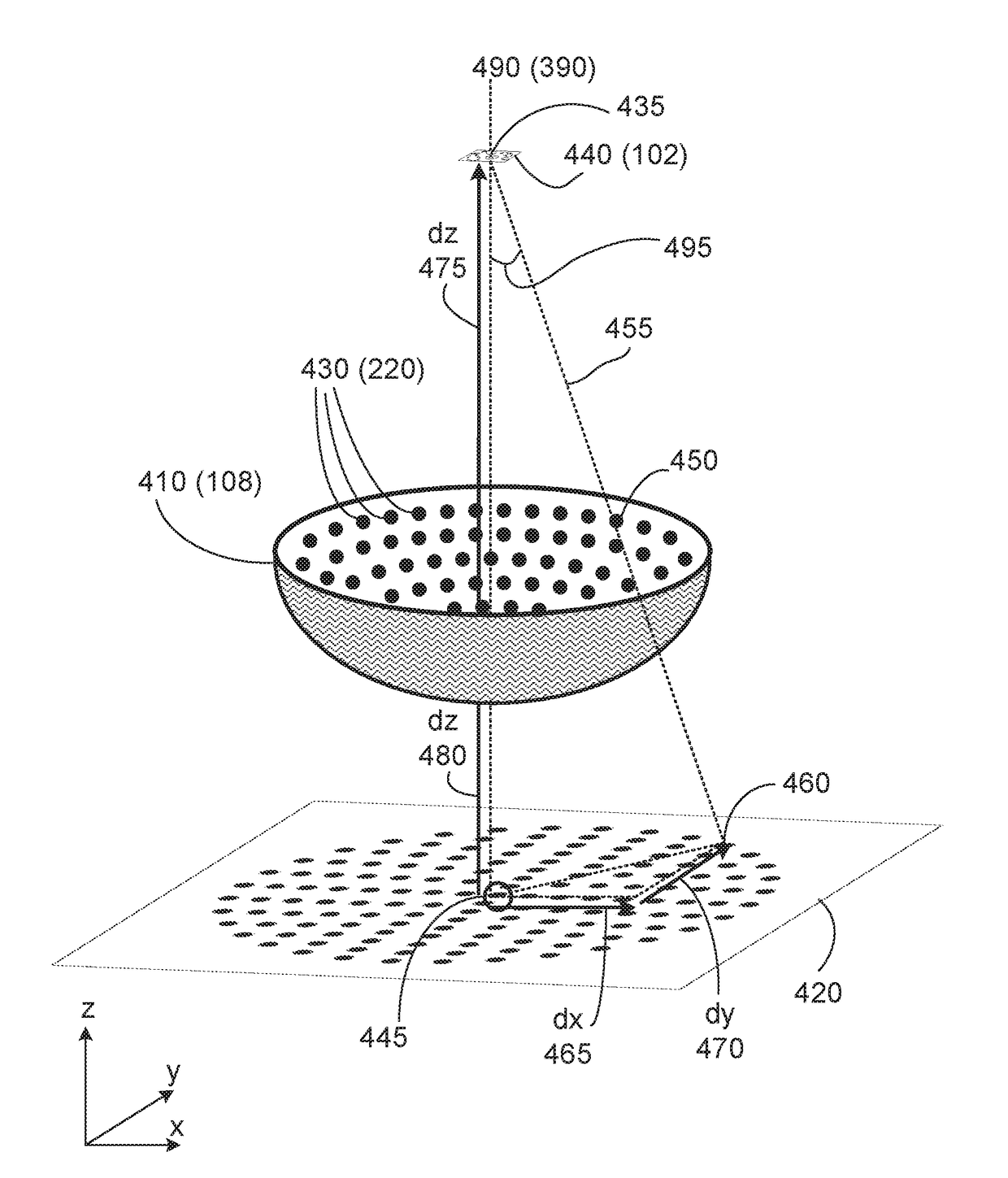
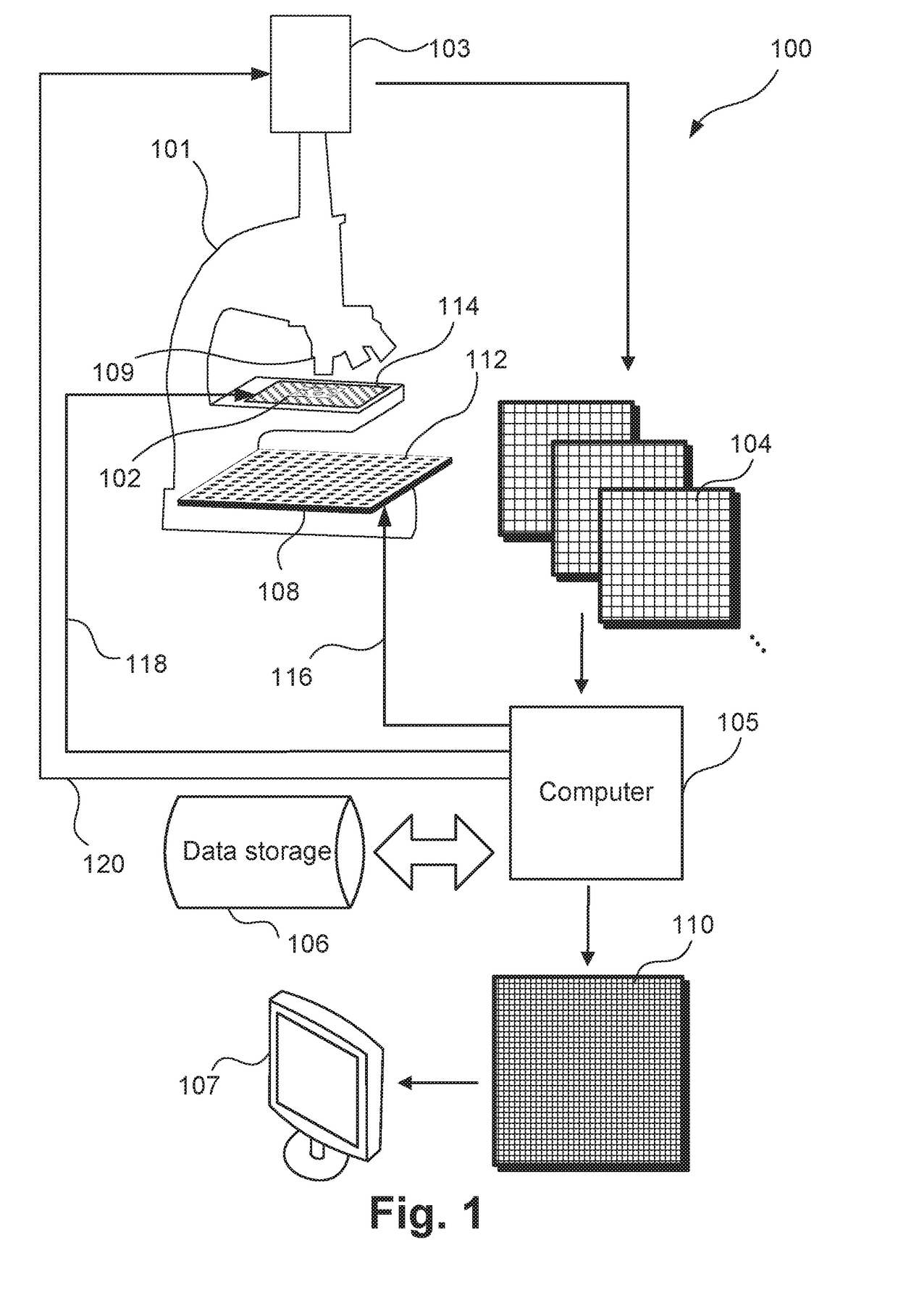
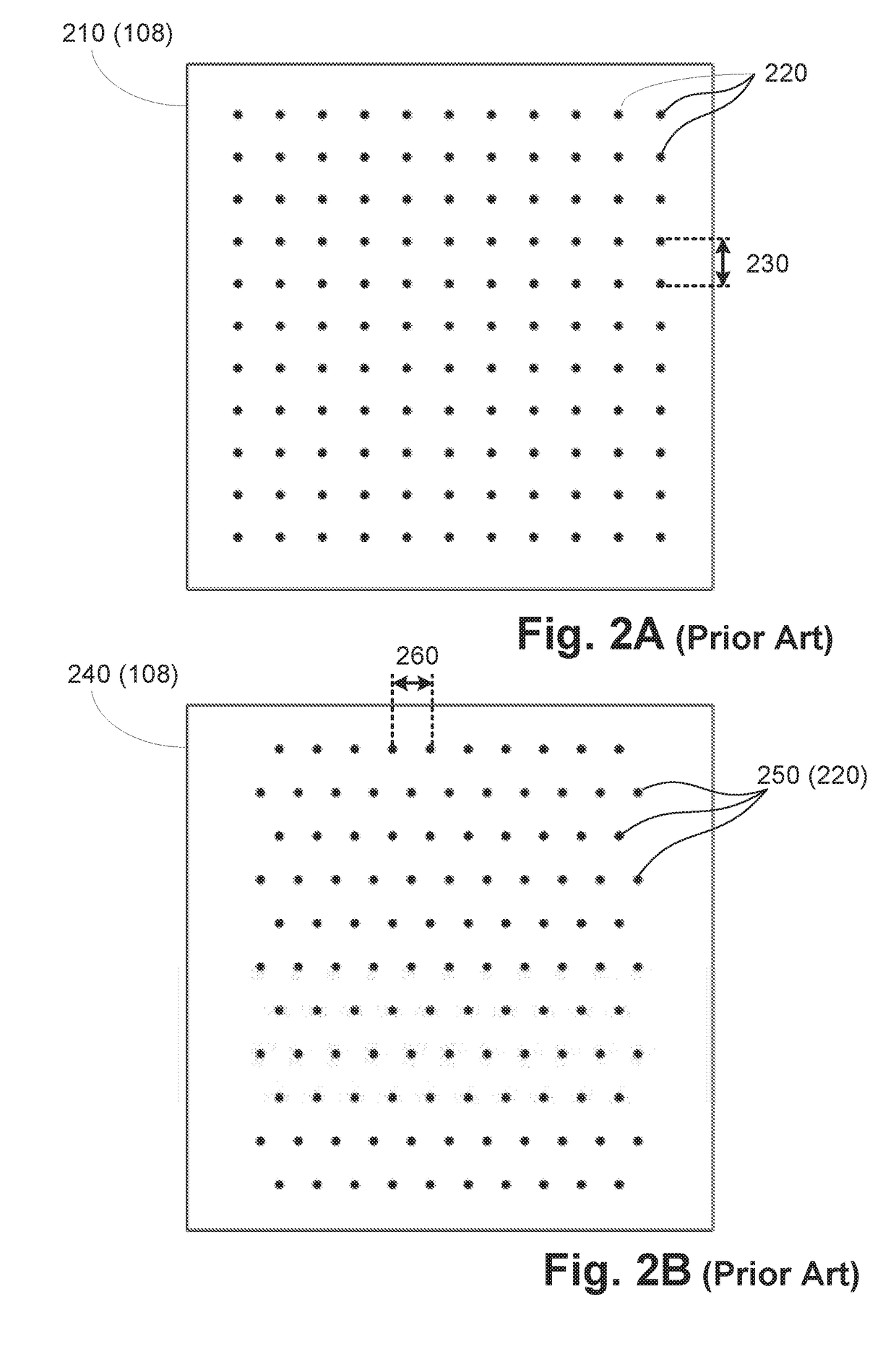
A system for forming an image (110) of a substantially translucent specimen (102) has an illuminator (108) configured to variably illuminate the specimen from a plurality of angles of illumination such that (a) when each angle (495) at a given point on the specimen is mapped to a point (445) on a plane (420) perpendicular to an optical axis (490), the points on the plane have an increasing density (e.g. FIGS. 4, 11C, 11E, 12C, 12E, 13A, 14A, 14C, 14E, 15A, 15C, 15E) towards an axial position on the plane; or (b) the illumination angles are arranged with a substantially regular pattern in a polar coordinate system (FIG. 13A,13B) defined by a radial coordinate that depends on the magnitude of the distance from an optical axis and an angular coordinate corresponding to the orientation of the angle relative to the optical axis. A detector is configured to acquire a plurality of variably illuminated, relatively lower-resolution intensity images (104) of the specimen based on light emitted from the illuminator according to variable illumination and filtered by an optical element (109). A processor is arranged to computationally reconstruct a relatively higher-resolution image of the specimen by iteratively updating overlapping regions (1005) of the relatively higher-resolution image in Fourier space (FIG. 10B) with the variably-illuminated, lower-resolution intensity images.
Owner:CANON KK
Pitch-based subresolution assist feature design
InactiveUS6964032B2Maximizes process windowFast and cost-effectivePhotomechanical apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringFeature design
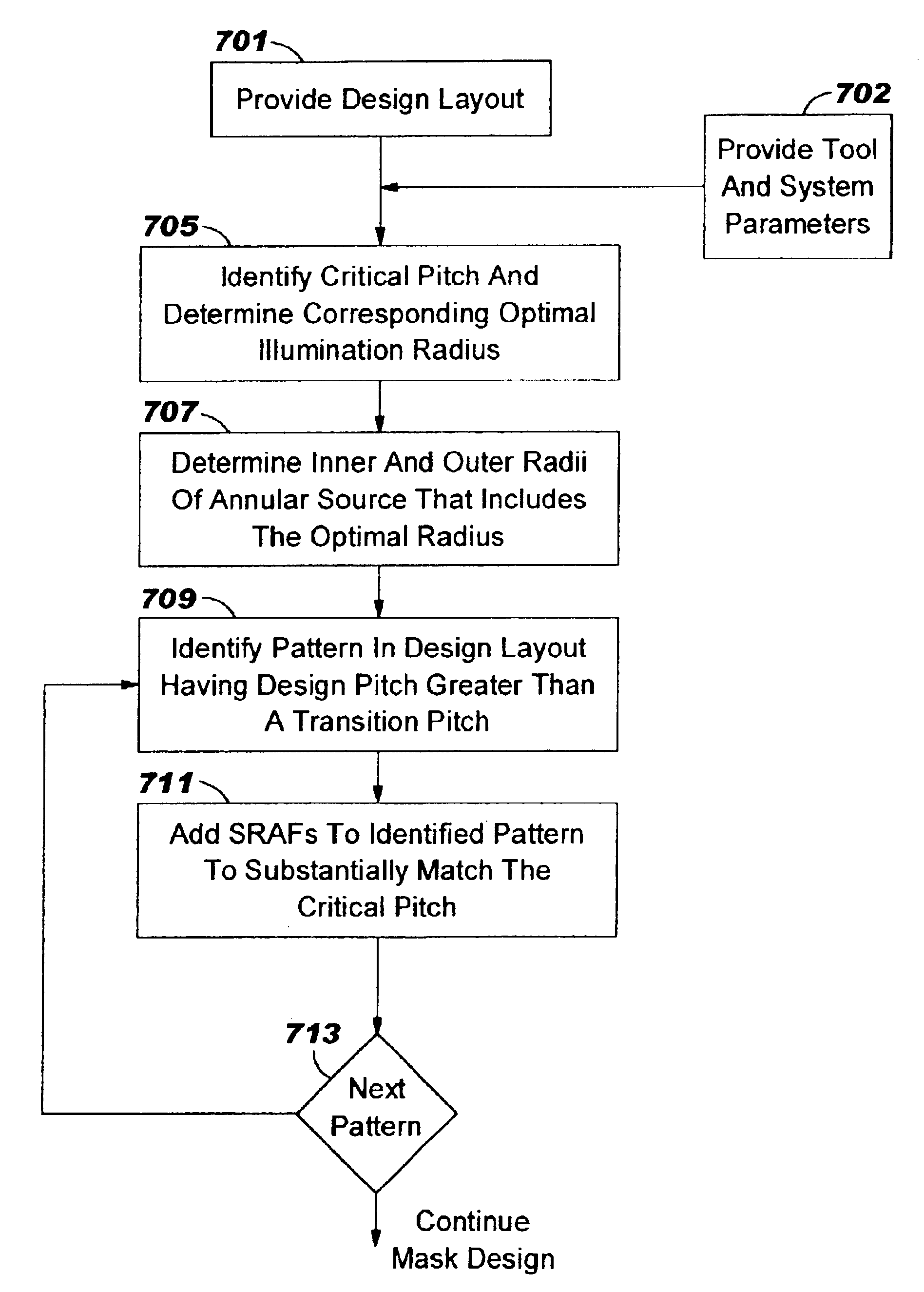
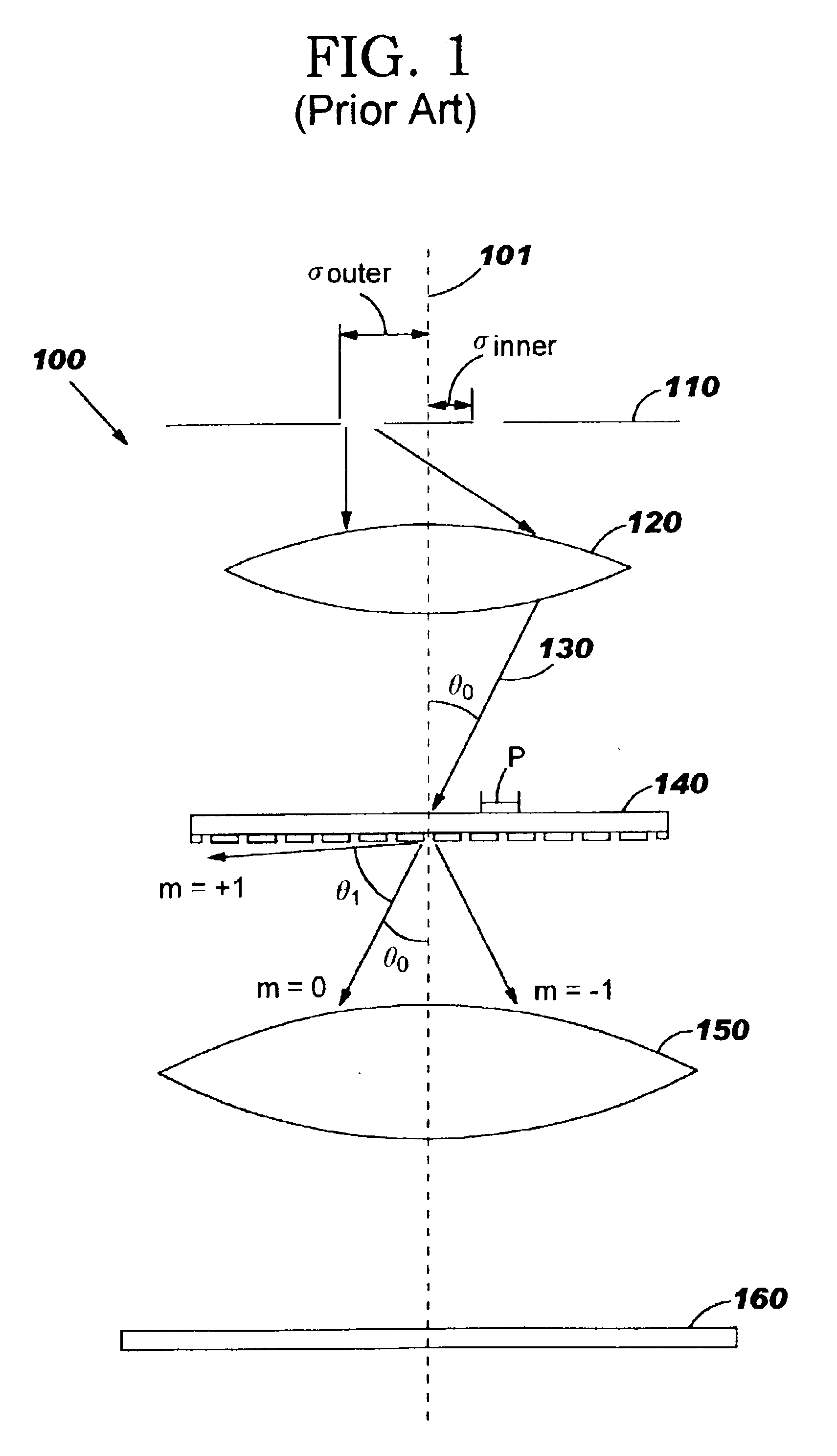
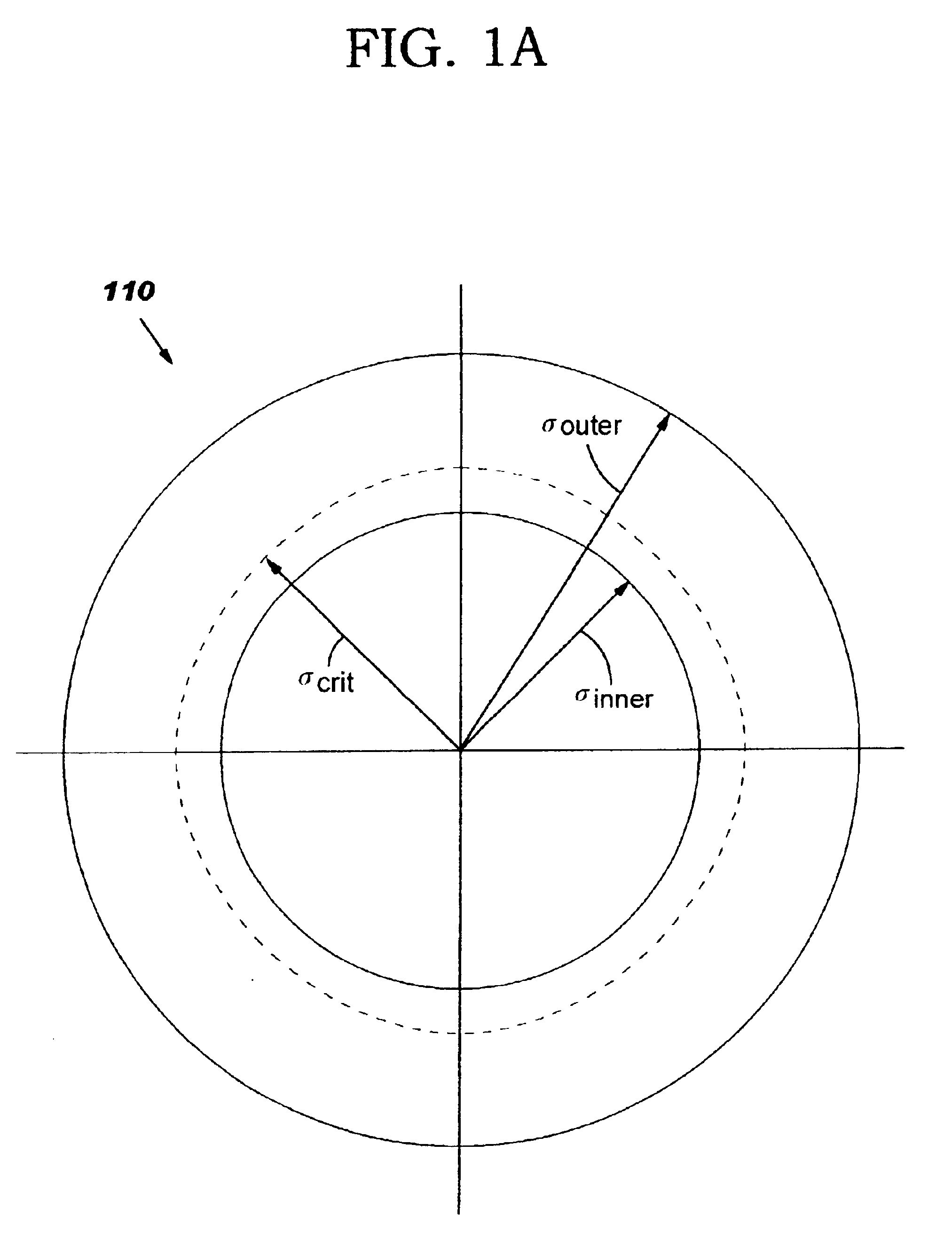
A method of designing a mask for imaging an integrated circuit (IC) design layout is provided to efficiently configure subresolution assist features (SRAFs) corresponding to an optimally configured annular illumination source of a lithographic projection system. A critical pitch is identified for the IC design, and optimal inner and outer radial coordinates of an annular illumination source are determined so that the resulting image projected through the mask will be optimized for the full range of pitches in the design layout. A relationship is provided for determining an optimal inner radius and outer radius for the annular illumination source. The number and placement of SRAFs are added to the mask design so that the resulting range of pitches substantially correspond to the critical pitch. The method of configuring SRAFs so that the image will have optimal characteristics, such as good contrast and good depth of focus, is fast.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Polar coordinates numerical control highly effective milling and gear hobbing composition machine tool
ActiveCN101011762AReduce manufacturing costImprove processing efficiencyDriving apparatusPositioning apparatusNumerical controlHobbing
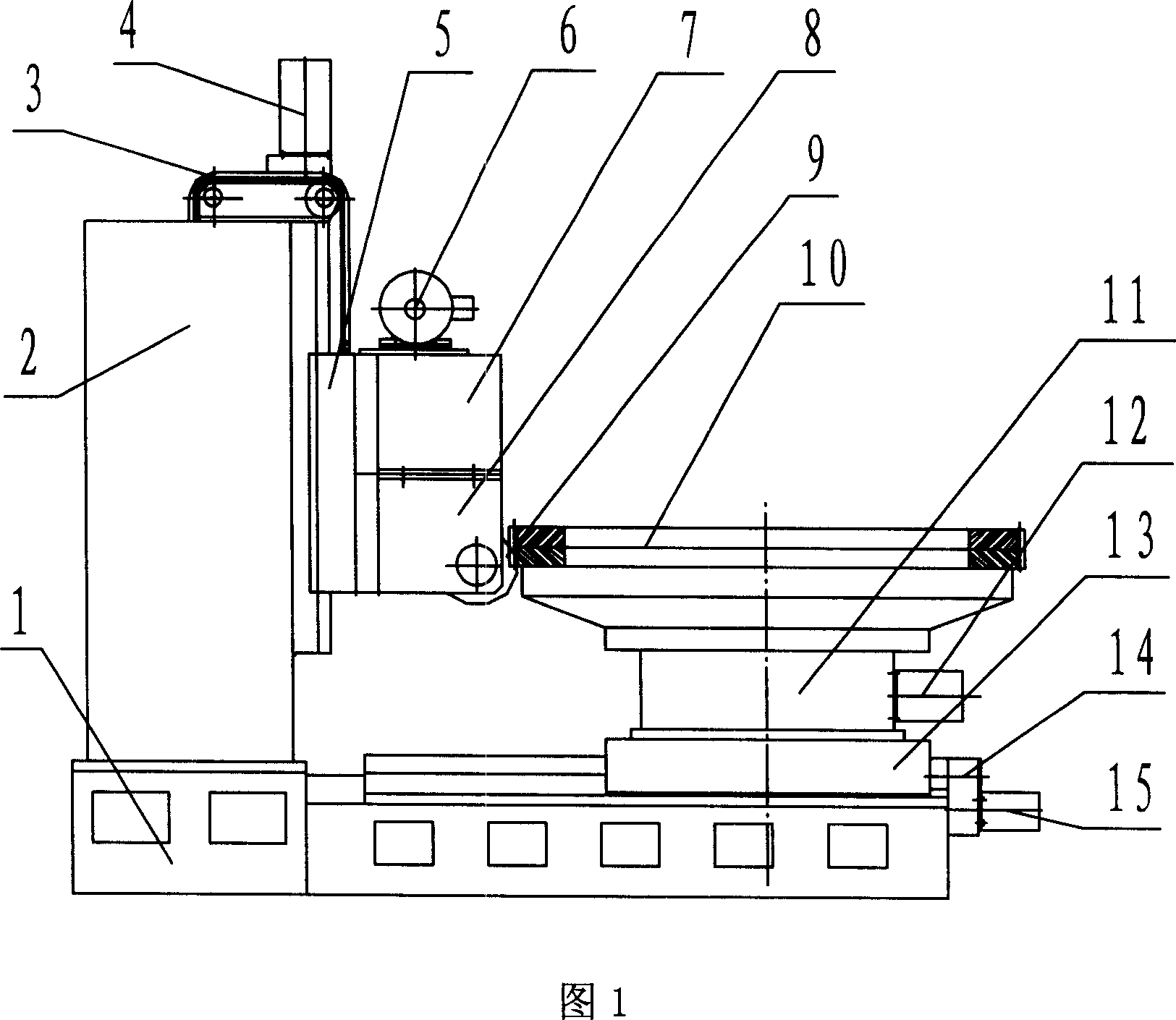
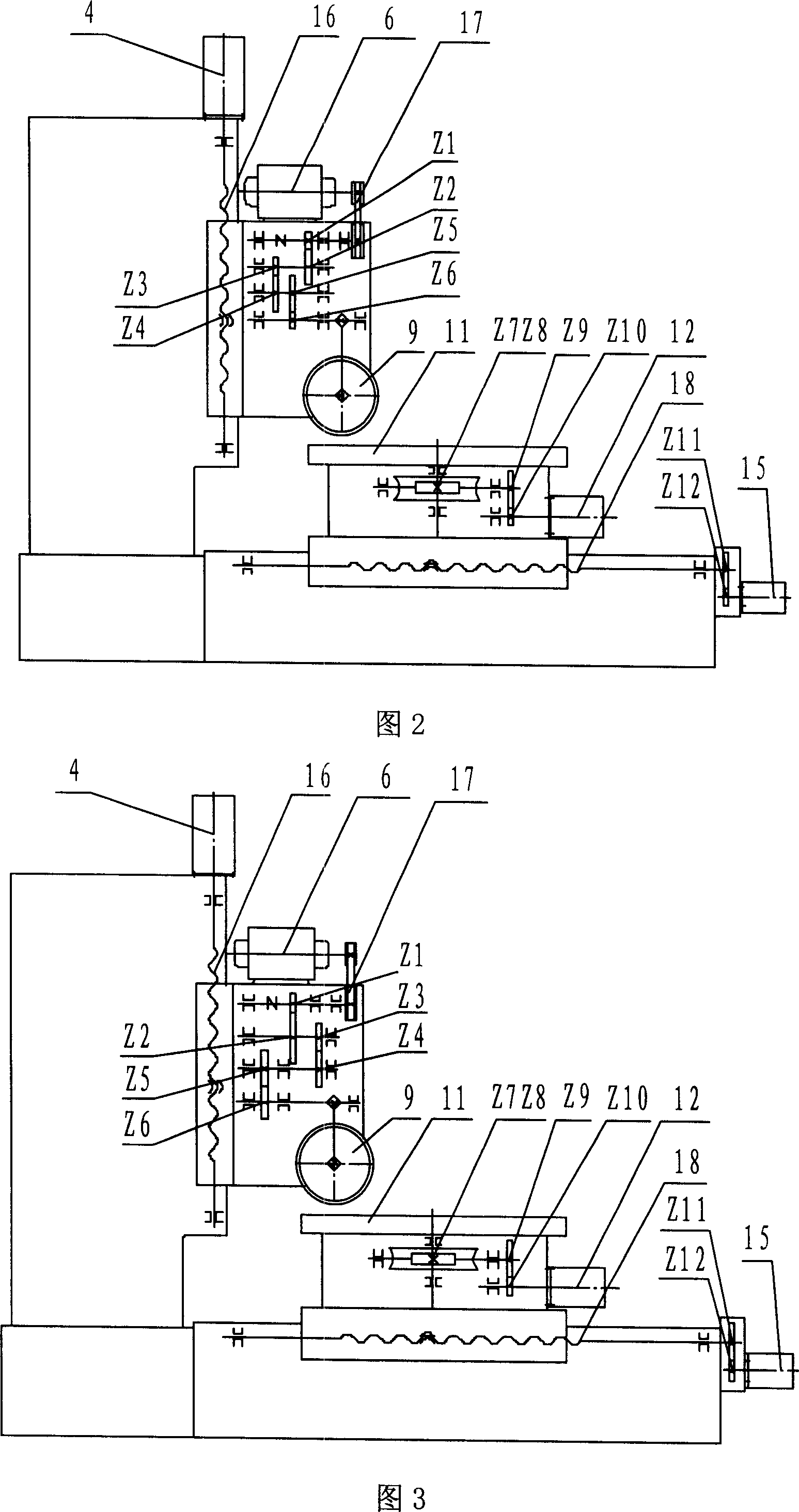
A radial coordinates digital control highly effective milling machine, hobbing composite machine, can improve machining efficiency 3-5 times, saving 50% budget, reducing land occupation 30%, with it composed of body, vertical post, horizontal feeding carriage, rotary working bench, highly effective milling and hobbing main shaft box module, with the vertical post on the body, rotary working bench fixed on the horizontal feeding carriage, highly effective milling and hobbing main shaft box module vertical to the feeding carriage. Through digital control interpolation and electronic gear box software, it realizes digital control machining.
Owner:NANJING GONGDA CNC TECH
Damman wave zone plate
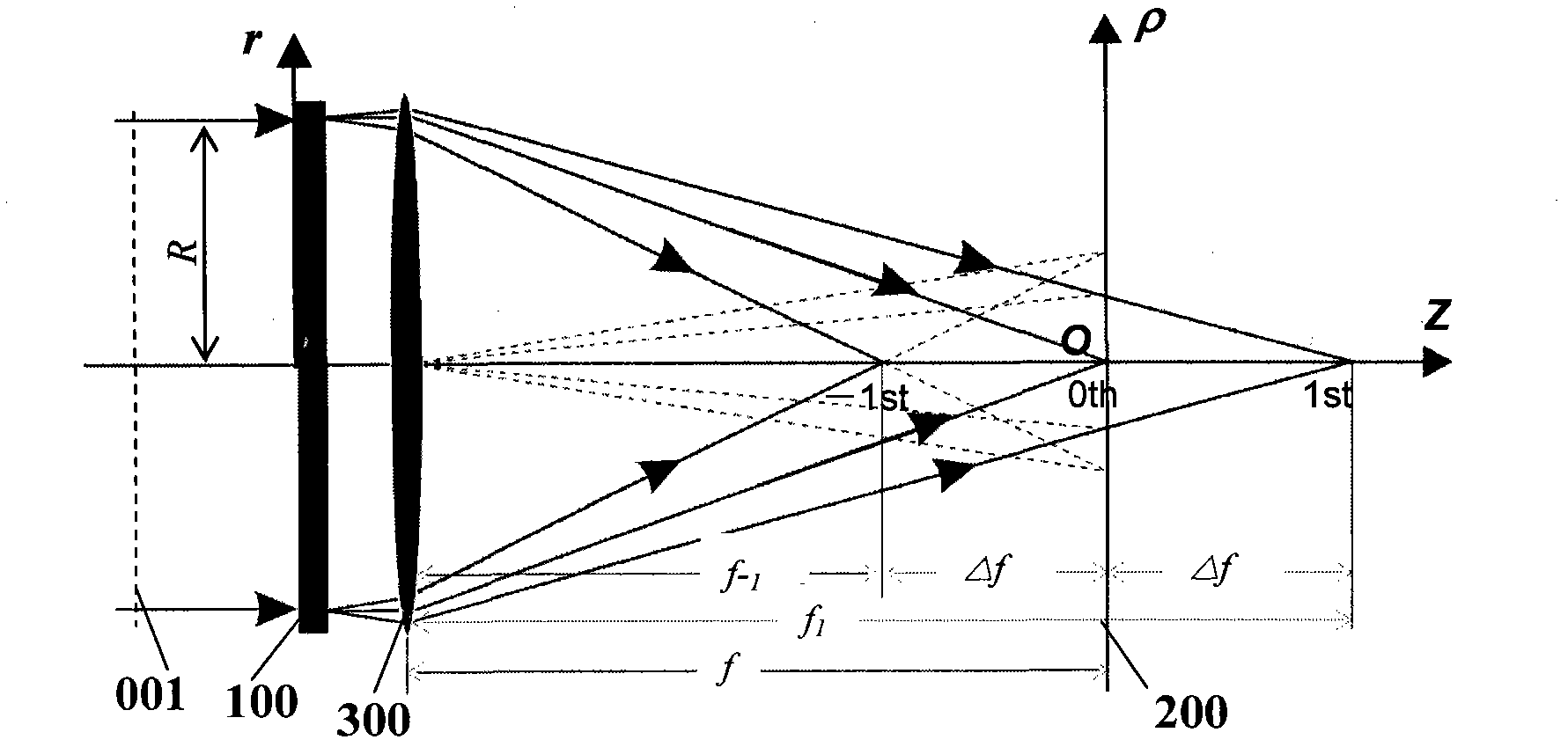
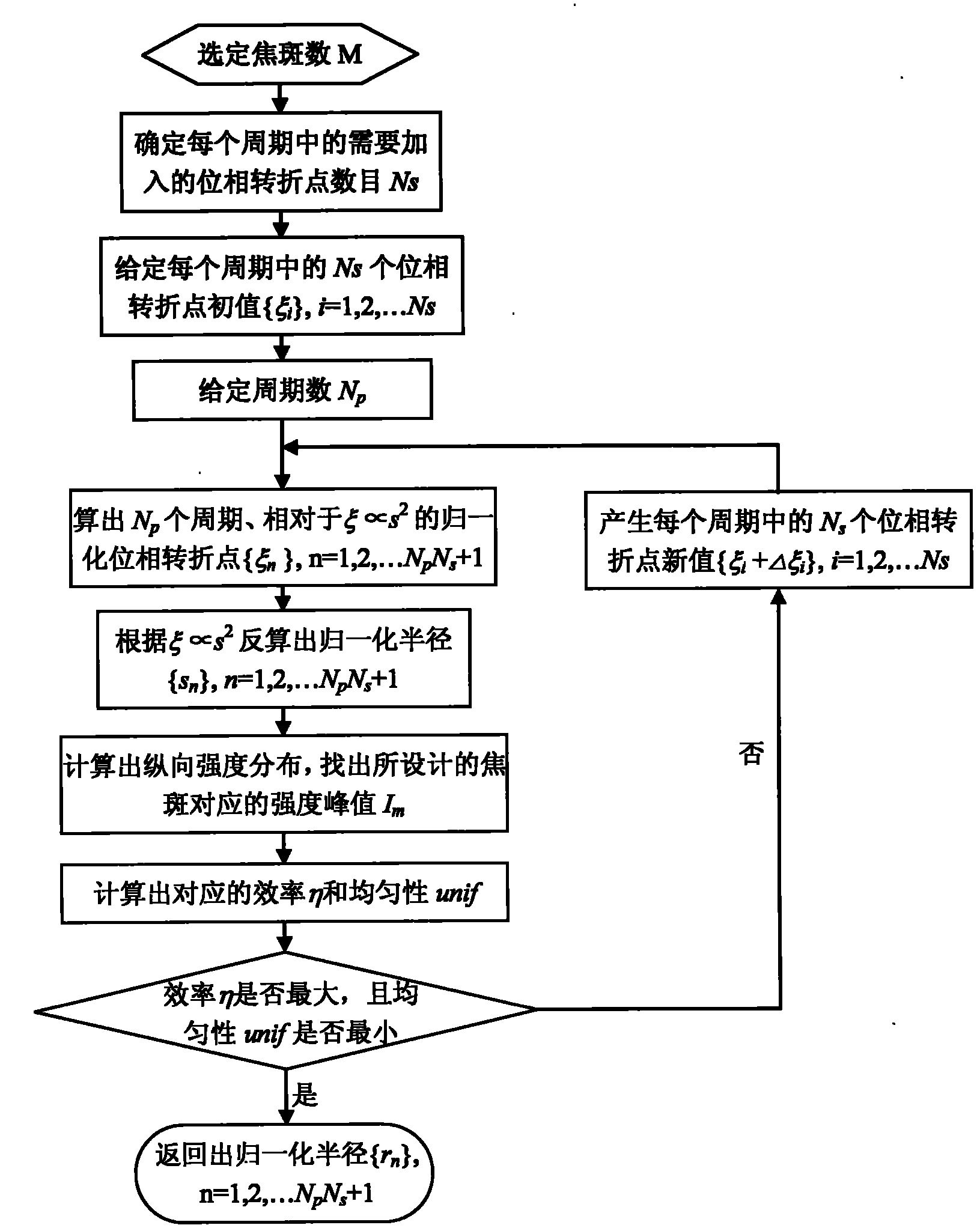
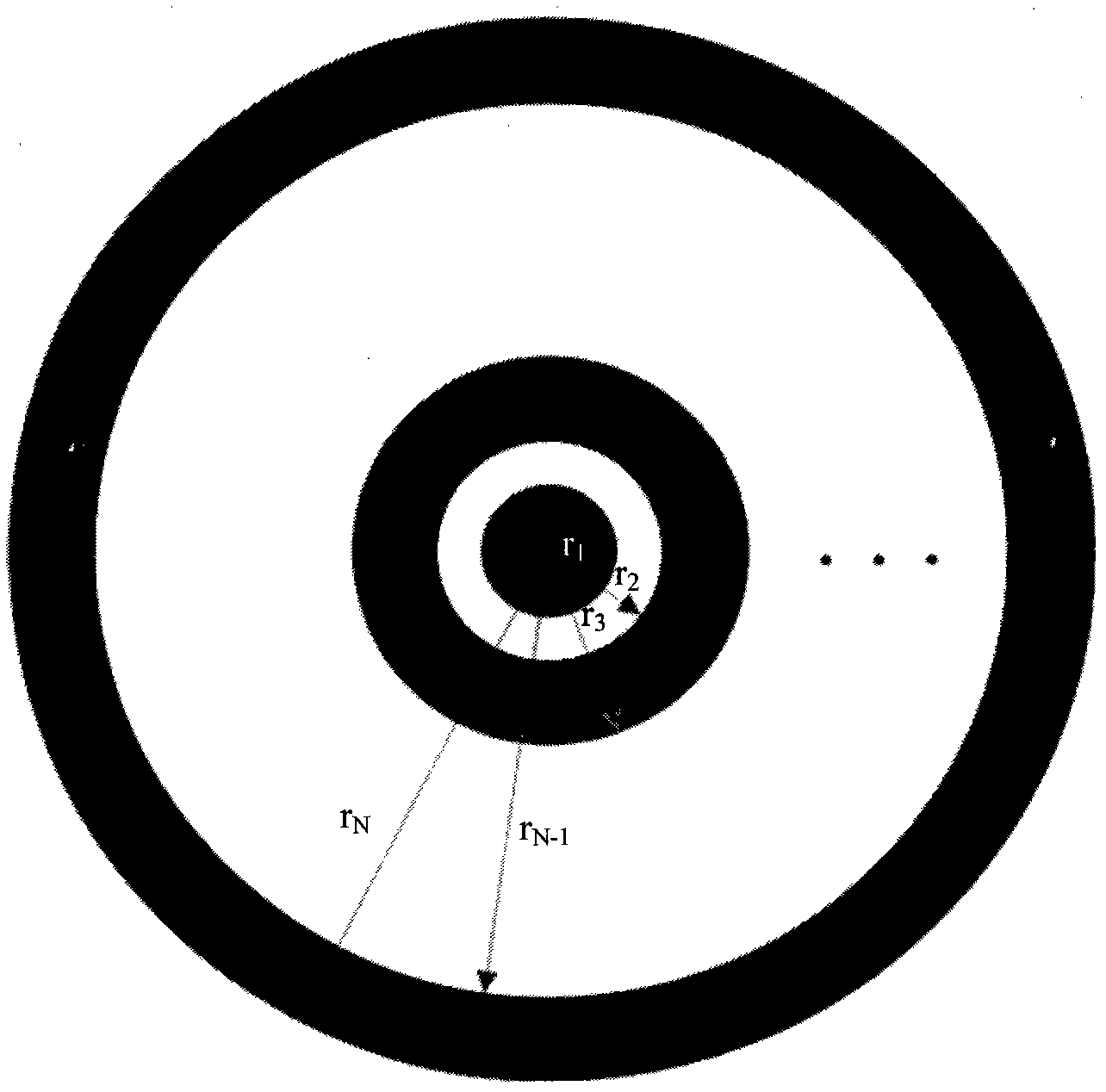
The invention relates to a damman wave zone plate which is characterized in that a phase modulation detail is added in each period of the traditional binary phase-only type (0, pi) zone wave plate structure relative to the square of the radial coordinate so as to generate axial constant-strength distribution of focal spots with any numbers within a certain range. The distribution of a plurality of constant-strength focal spots along the optical axis direction can be widely applied to imaging systems (optical microscopes), optical tweezers, implantable contact lens, and the like with large depth of field-. Besides, the damman wave zone plate in binary phase-only distribution is a series of concentric circle structures intuitively and is easy to process and duplicate. Therefore, the damman wave zone plate has important application prospect in the fields of optical imaging systems and biomedicine.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
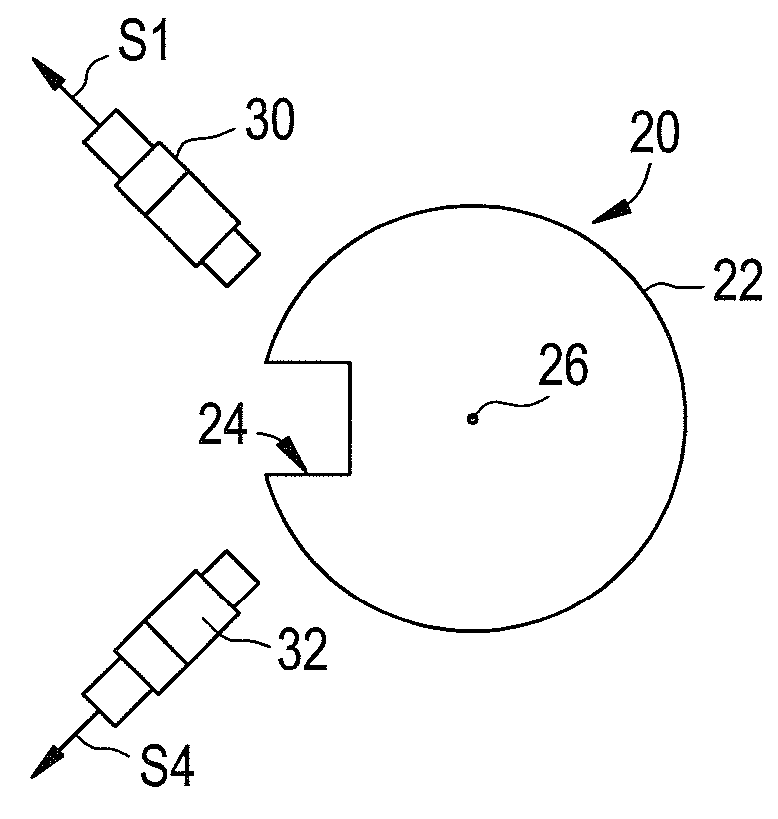
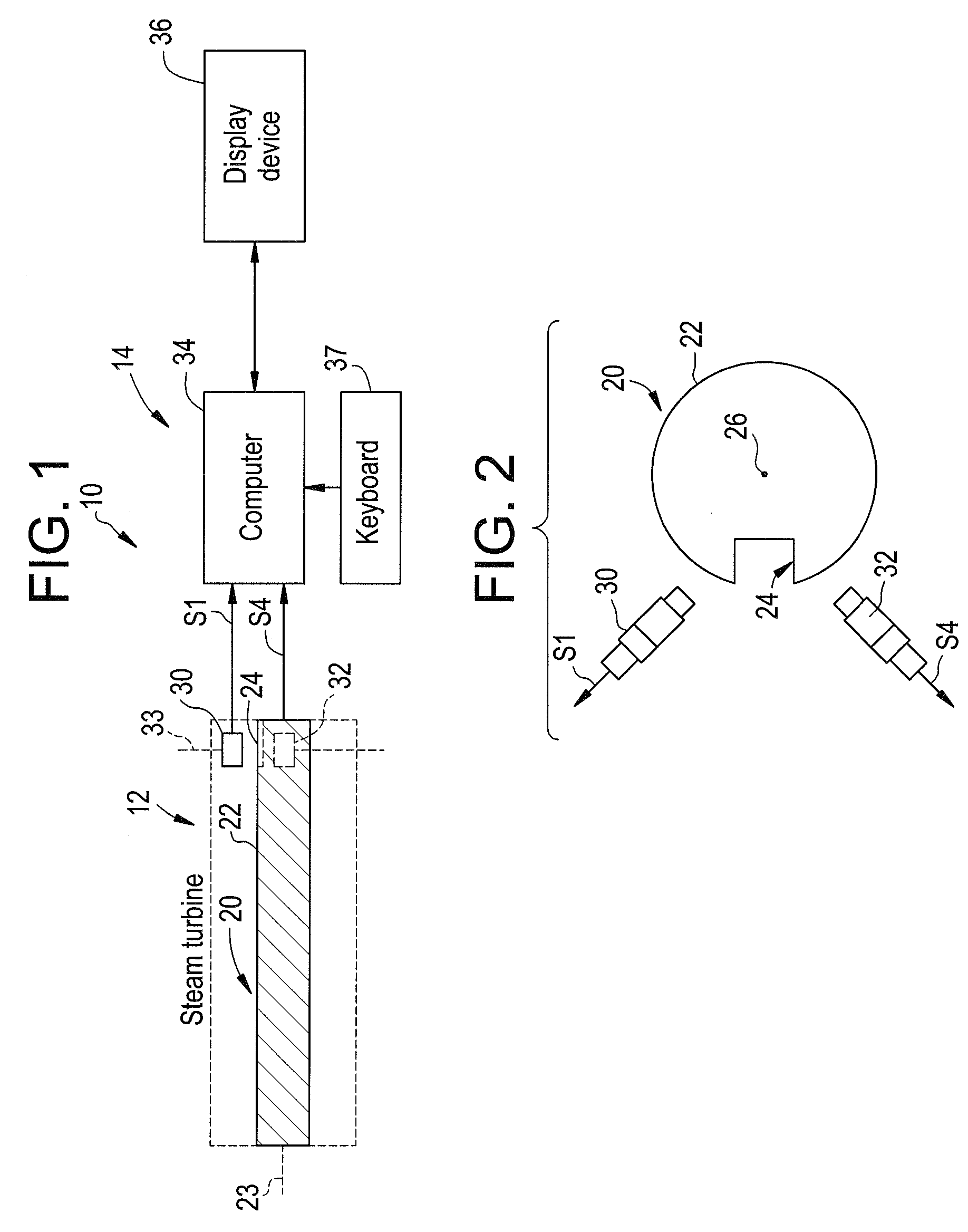
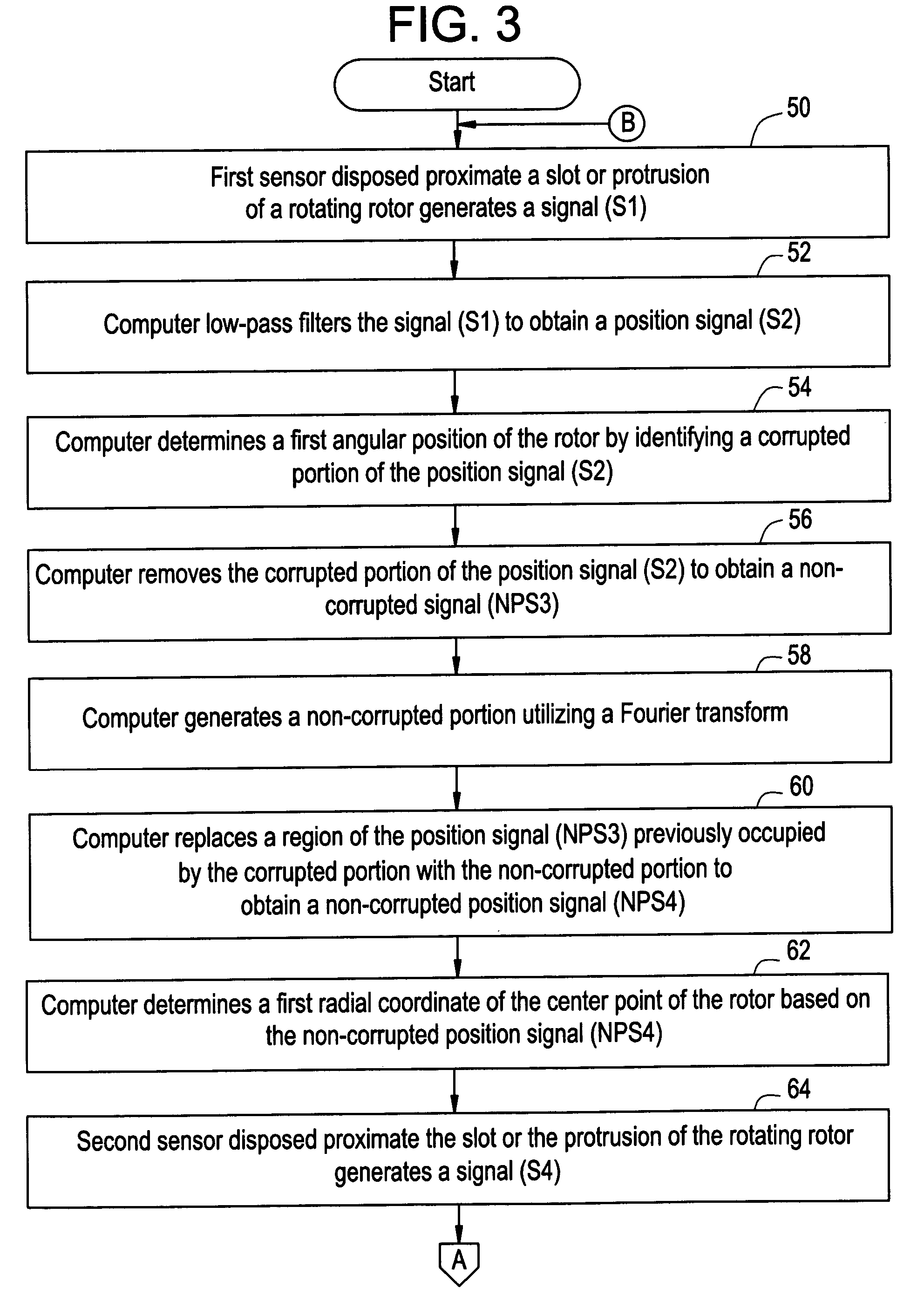
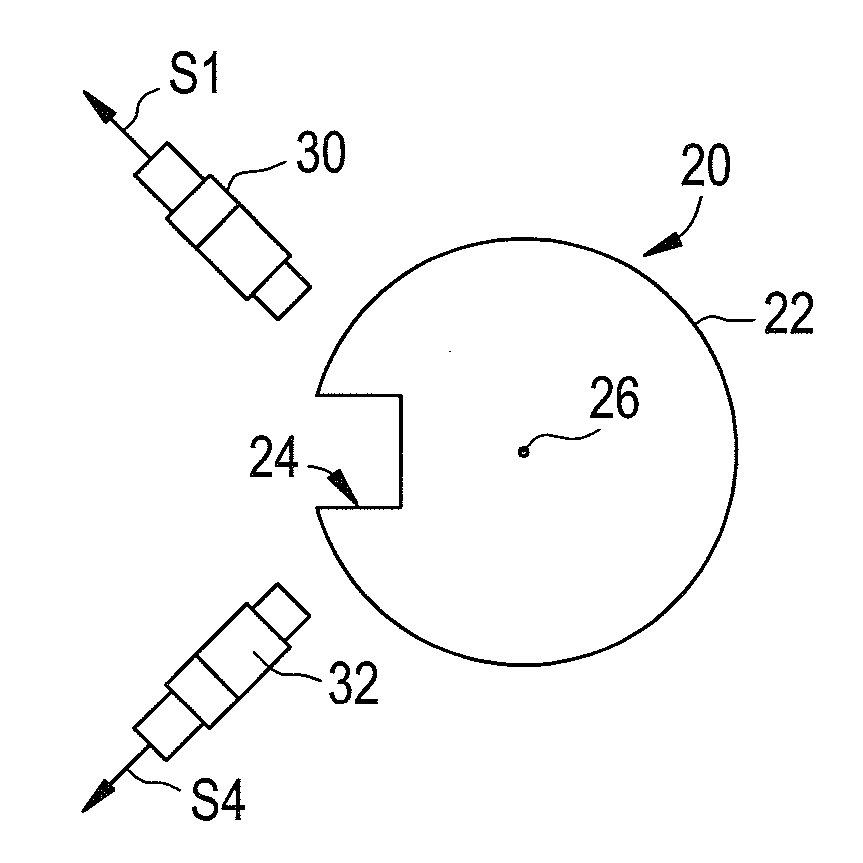
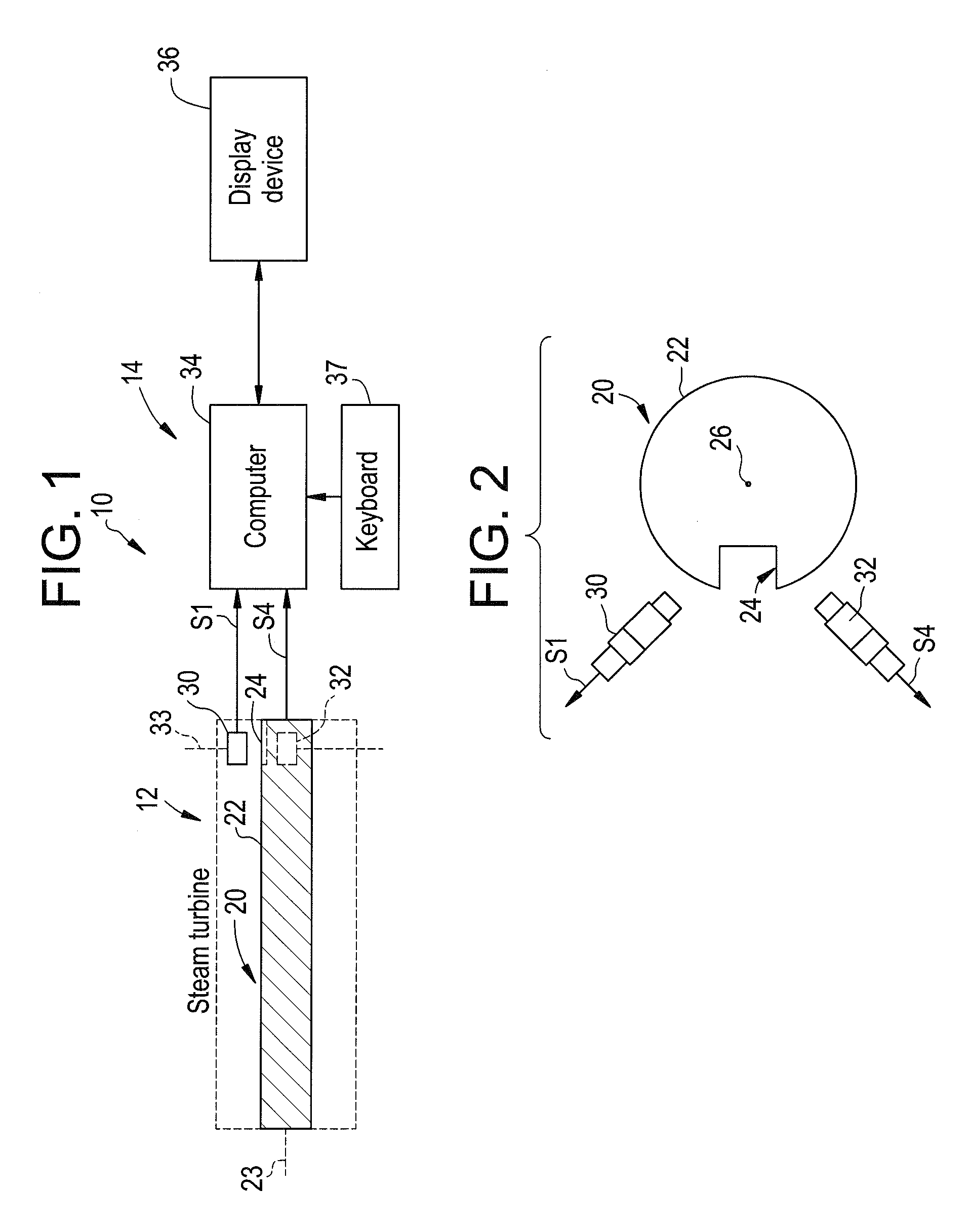
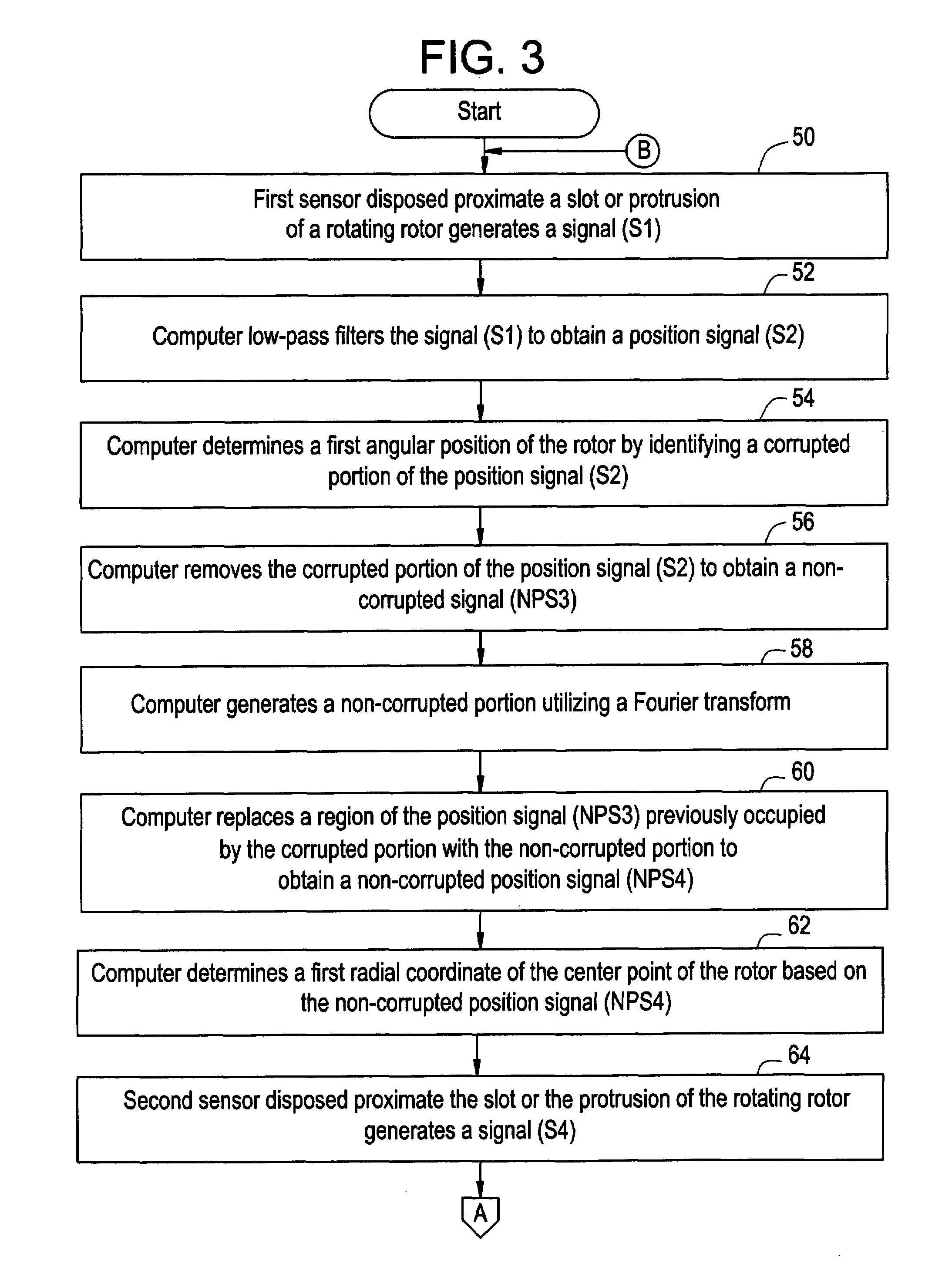
System and method for determining an angular position of a rotor and a radial position of the rotor
ActiveUS20060100819A1Digital computer detailsSpeed measurement using gyroscopic effectsRadial positionControl theory
A system and a method for determining an angular position of a rotor and a radial position of the rotor are provided. The rotor has either a slot or a protrusion on the rotor. The rotor is centered about a center point. The method includes generating a first signal utilizing a first sensor disposed proximate the slot or protrusion of the rotor. The method further includes determining a first angular position of the rotor by identifying a first corrupted portion of the first signal. The method further includes removing the first corrupted portion of the first signal to obtain a second non-corrupted position signal. The method further includes determining a first radial coordinate of the center point of the rotor based on the second non-corrupted position signal.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
Coordinate mapping system for joint treatment
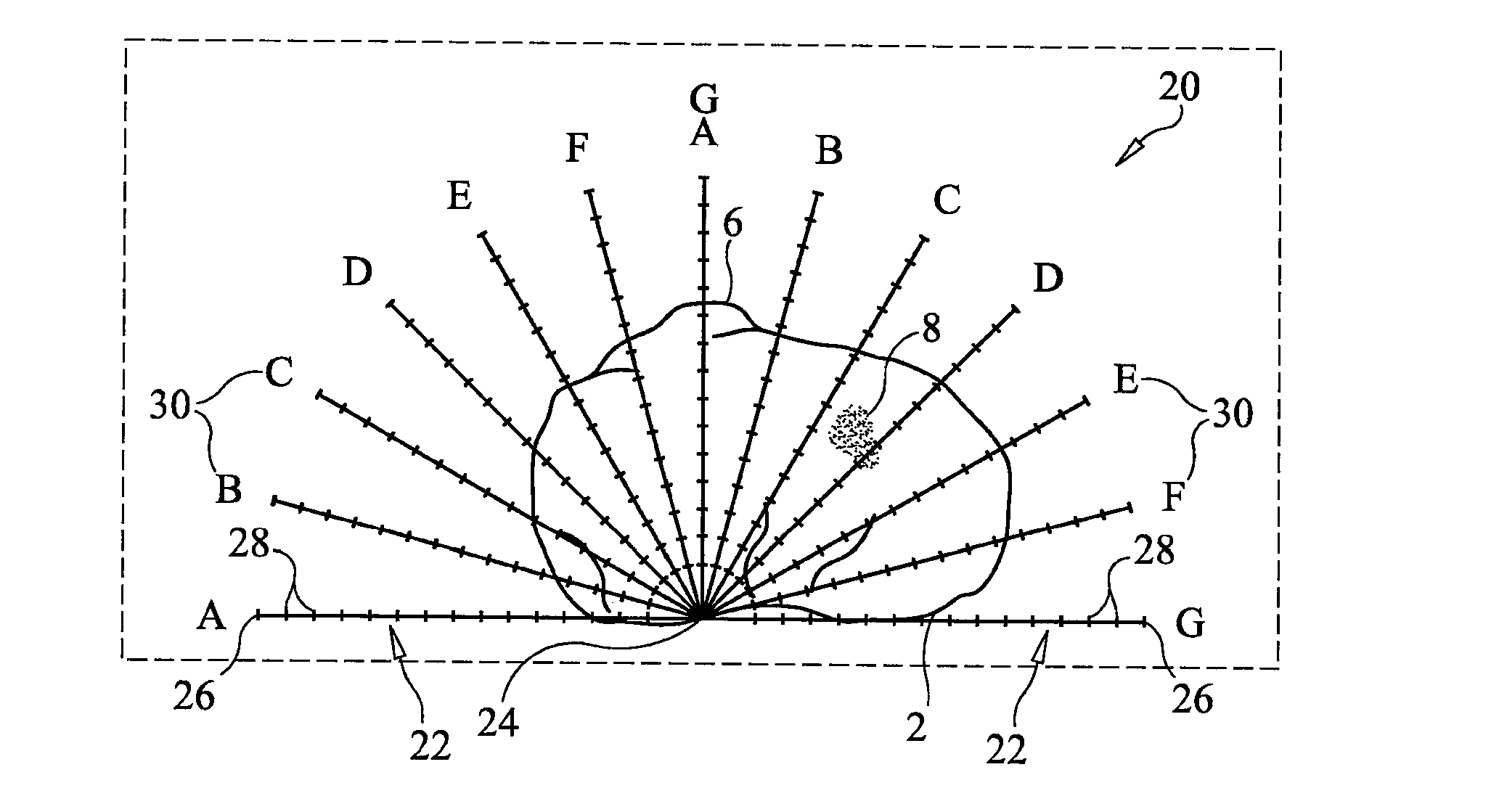
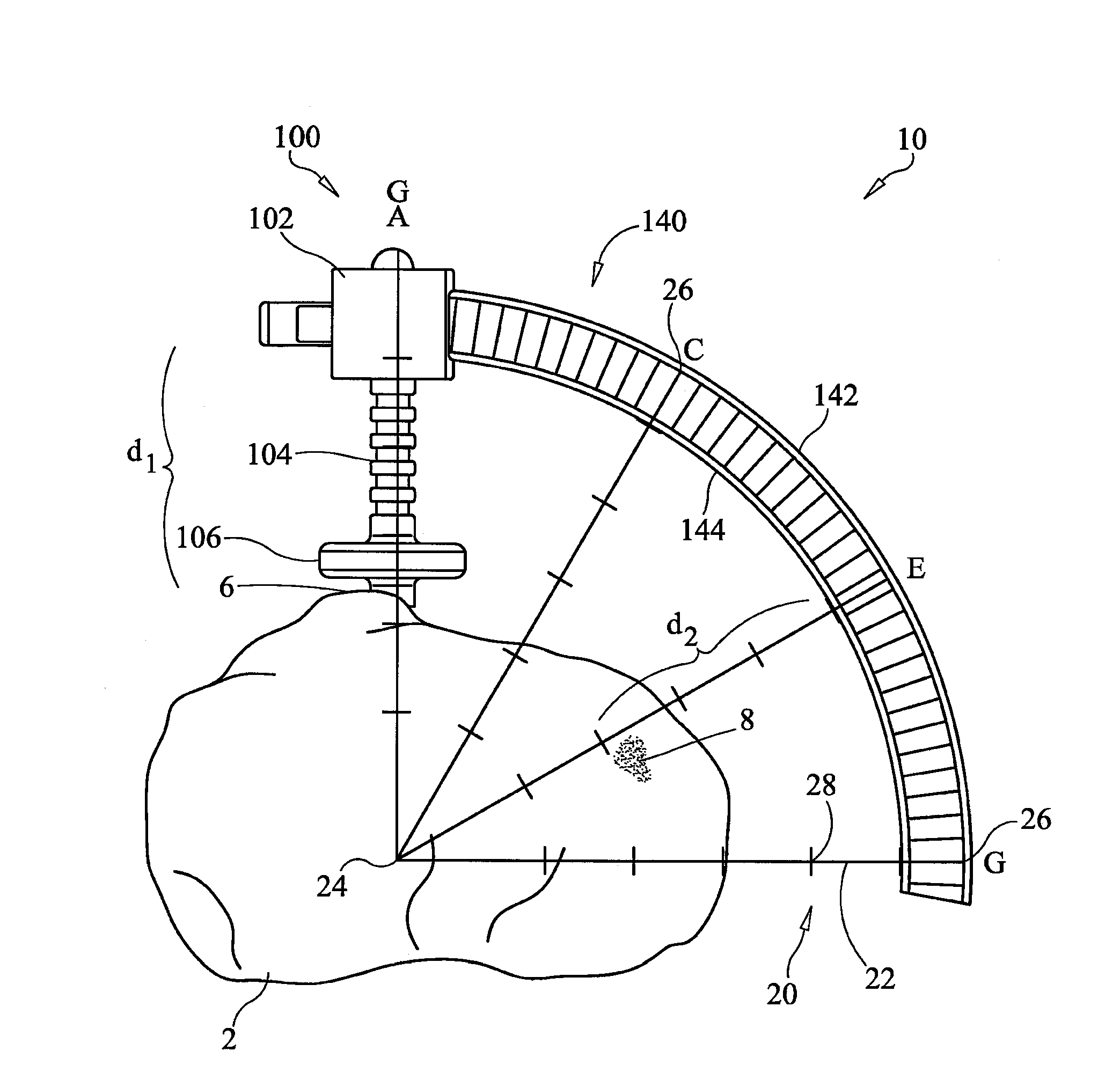
A coordinate mapping system is provided for locating a defect in a bone. The system comprises a positioning instrument for controlled delivery of a device to a target site, the instrument comprising a main body and a rail extending from the main body, the rail including a series of indicia corresponding to predefined grid lines, and a template configured to overlay an image of a bone having a defect at the target site, the template including a predefined grid for determining a set of coordinates to locate the target site using the positioning instrument. A method of accessing a target site near a defect in a bone using the radial coordinate mapping system is also provided.
Owner:KNEE CREATIONS
Cylindrical ionization detector with a resistive cathode and external readout
InactiveUS7078704B2Improve responseElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansElectrical resistance and conductanceOptoelectronics
A new design for a cylindrical ionization detector, featuring a resistive cathode, and external pickup wires that sense both the azimuthal and radial coordinates of interaction vertices. Combined with measurement of the longitudinal coordinate (using resistive anode wire charge division or other technique), the proposed design can provide an accurate 3-dimensional imaging detector and offer improved spectroscopic response.
Owner:PROPORTIONAL TECH
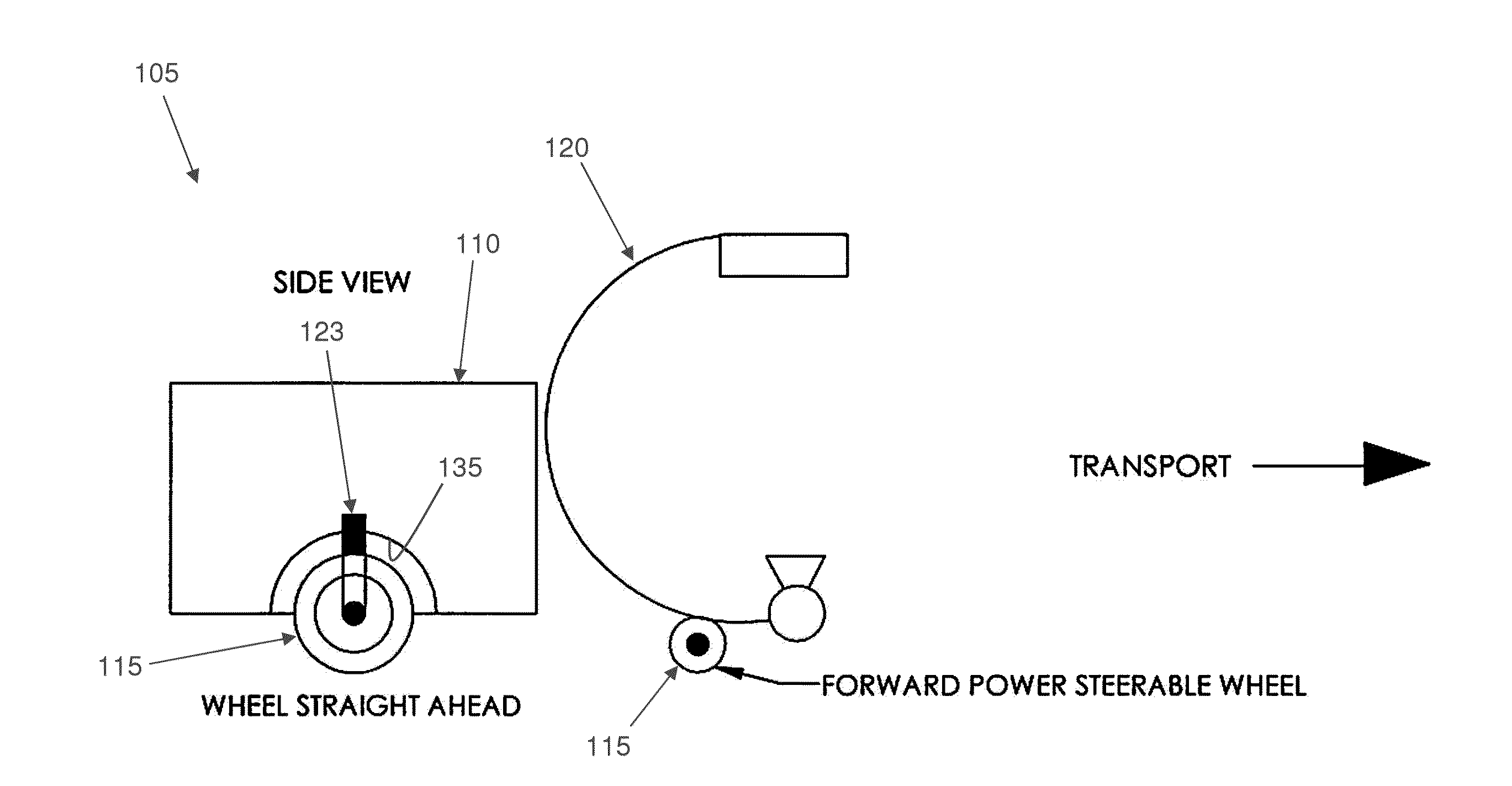
Motorized drive for mobile fluoroscopy units
A mobile C-arm fluoroscopy unit comprising a self-contained radial coordinate or vector movement mechanism utilizing at least one motor-driven wheel, wherein the at least one motor-driven wheel is individually continuously steerable around a generally vertical steering axis.
Owner:GRADY JOHN K
Optical digital mixed imaging system and method
InactiveCN101477253AOptimal phase distribution functionLarge defocus invarianceImage enhancementOptical elementsPhotovoltaic detectorsFiltration
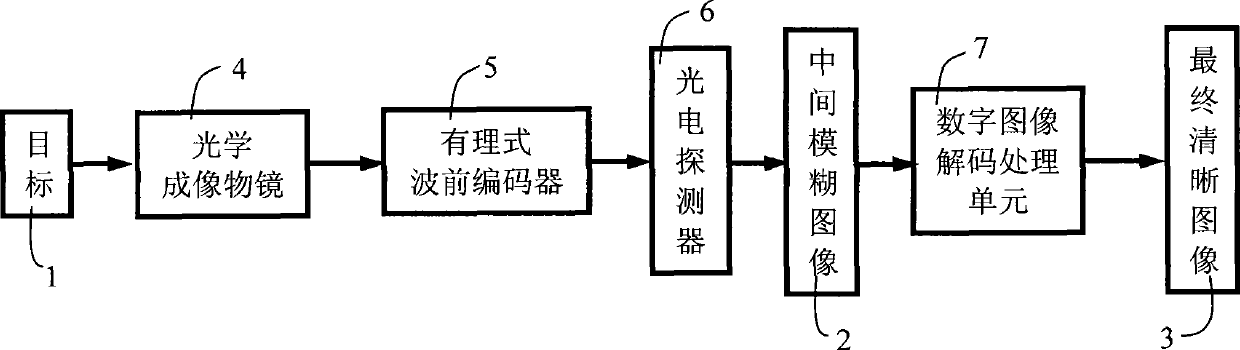
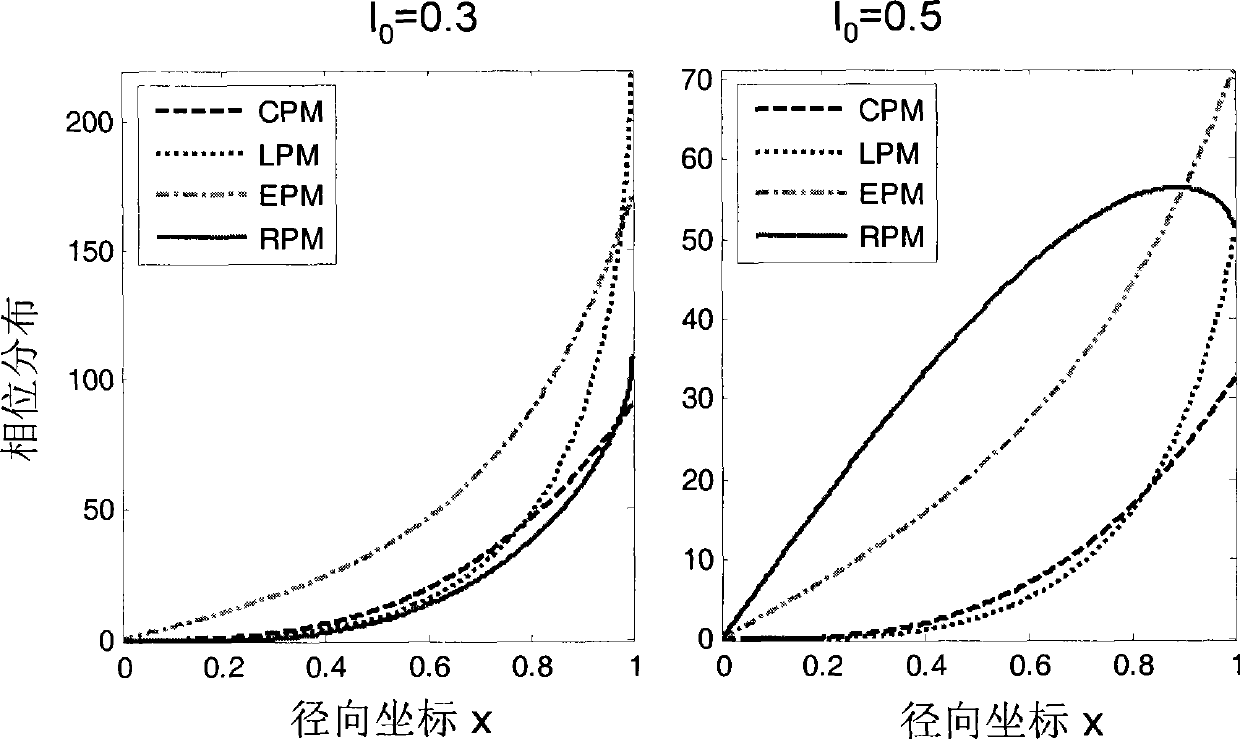
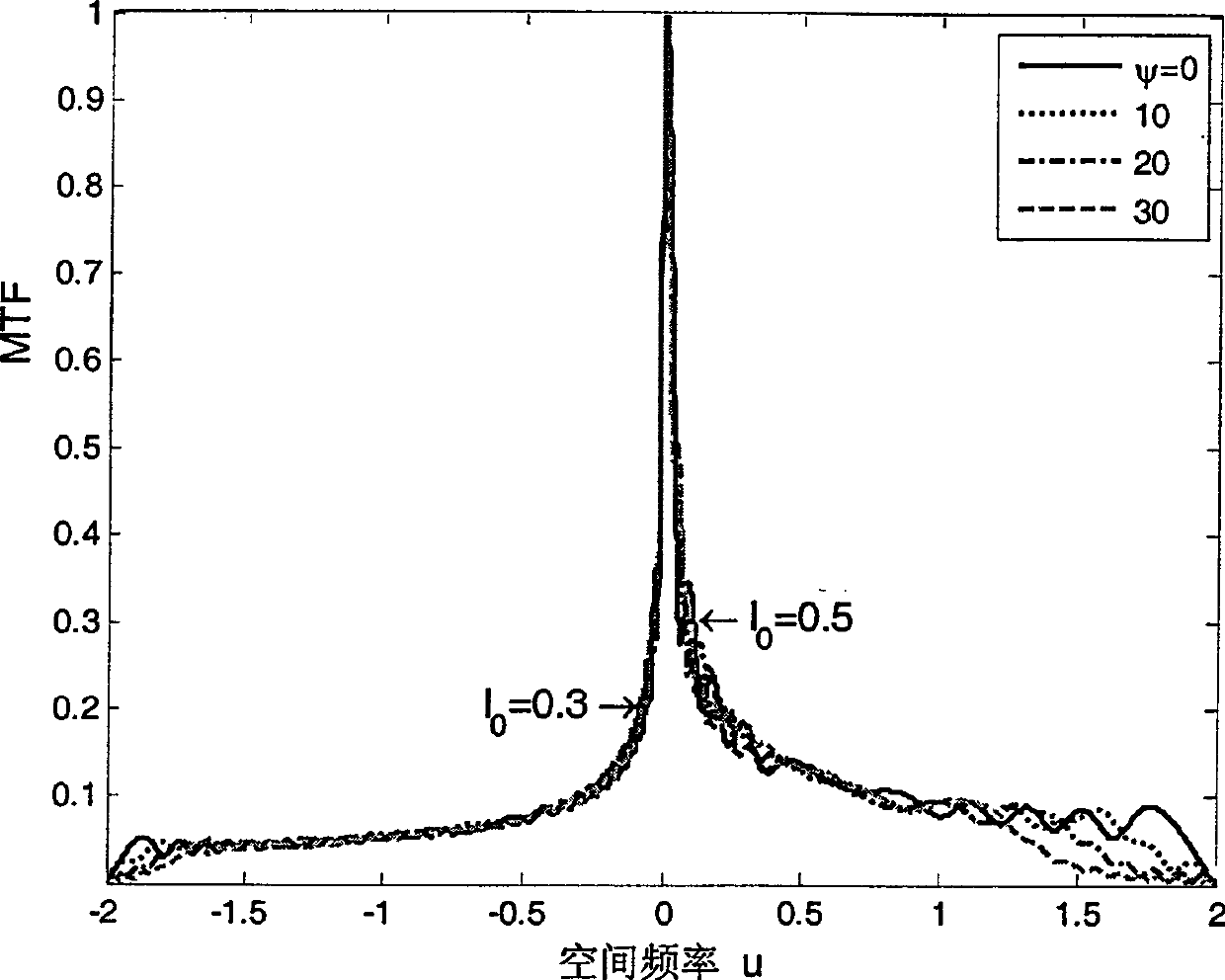
The invention relates to a system and a method for optical and digital mixed imaging. The system comprises an optical imaging object lens, a rational form wavefront coder, a photoelectrical detector and a digital image decoding and processing unit. The method adopts the rational form wavefront coder to code a wavefront phase of an incident light wave. Phi RPM(x) as an introduced phase distribution function is equal to sigma sign(x)an|x|(1+ sigma bm|x|), wherein x is a normalized radial coordinate; N and M are the highest power of a fraction and denominator polynomial respectively; {an} and {bm} are undetermined coefficients; and sign is a signum function. An intermediate blurred image which is not sensitive to defocusing is acquired on the photoelectrical detector after coding, and the digital image decoding and processing unit carries out deconvolution wave filtration on the intermediate blurred image to acquire the final clear image.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV +1
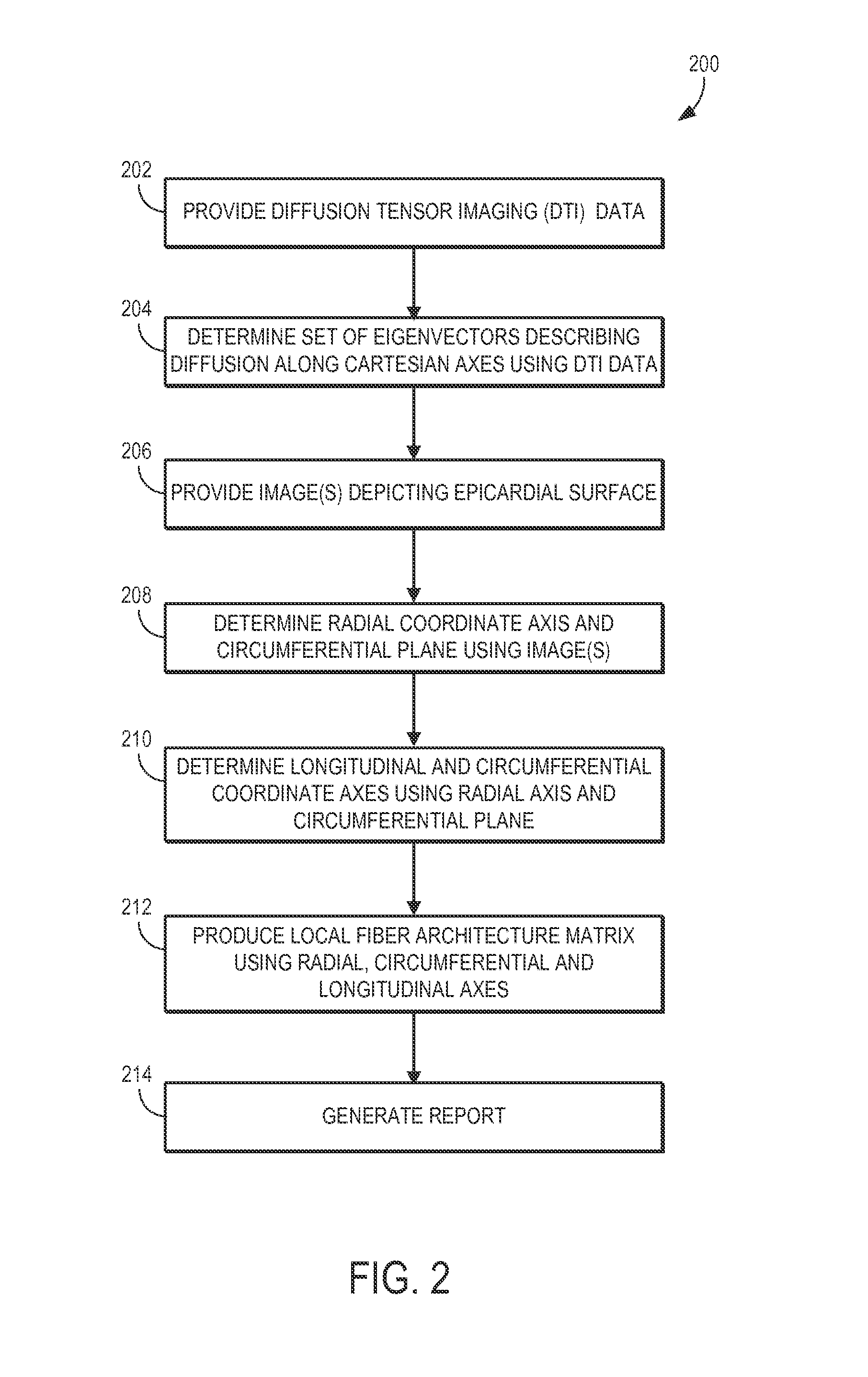
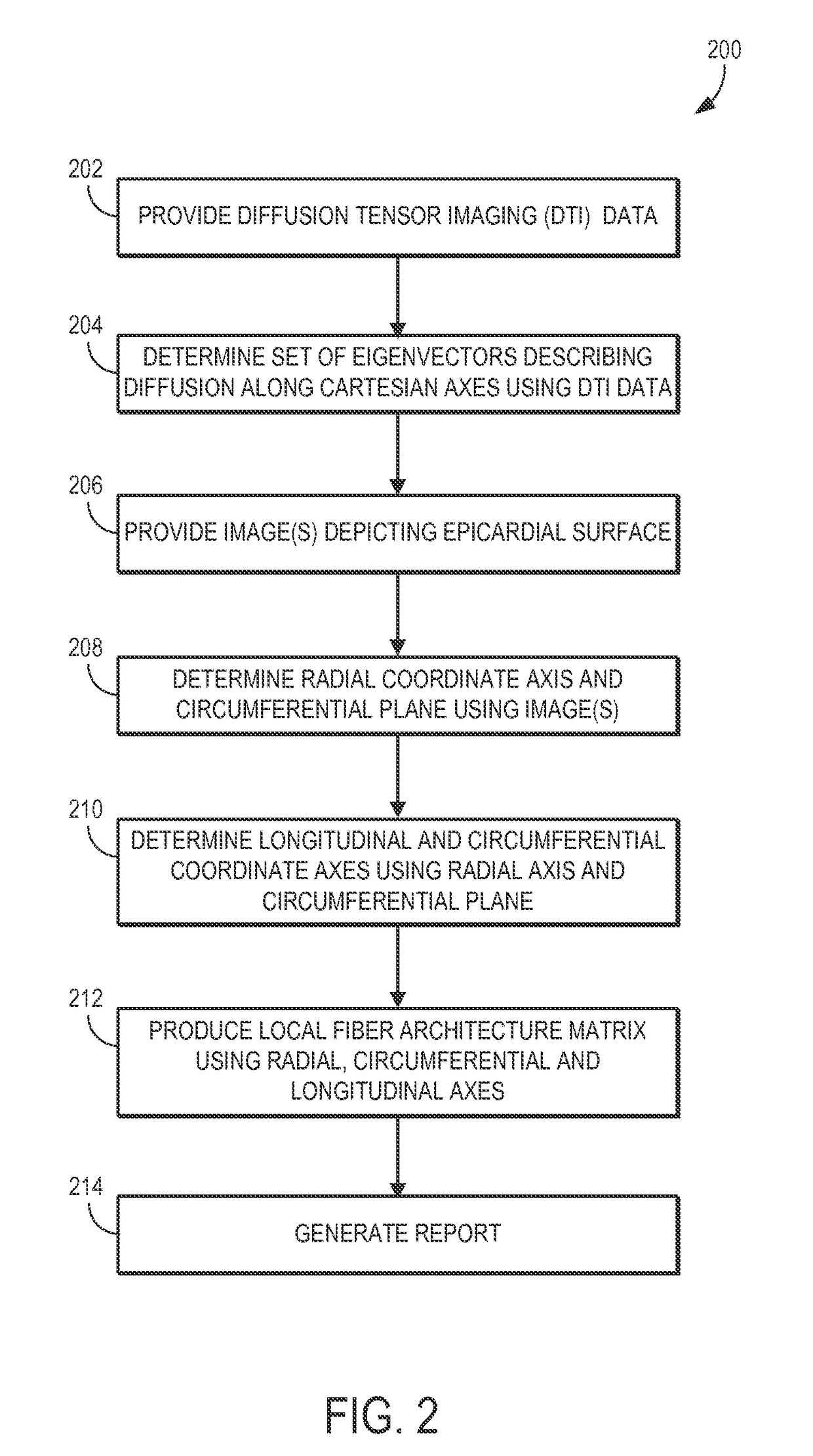
Mapping cardiac tissue architecture systems and methods
Systems and methods are provided for mapping myocardial tissue architecture based on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). A set of eigenvectors is derived from diffusion tensor data, where each eigenvector describes the diffusion of spins along one of the Cartesian directions. A radial coordinate axis and a circumferential plane are determined based on anatomical information of the subject, such as from an image depicting the epicardial surface of the subject's heart. A longitudinal coordinate axis and a circumferential coordinate axis are determined based on the radial coordinate axis and circumferential plane. A fiber architecture matrix (FAM) is then computed for locations in the subject's heart based on projecting the set of eigenvectors onto a local coordinate system defined by the circumferential, radial, and longitudinal axes, Maps that represent myocardial tissue architecture can then be generated using the FAM for locations within the subject's heart.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Visualization of stress level cardiac functional analysis results
InactiveUS20100022901A1Easy numerical comparisonImage enhancementImage analysisStress levelCardiac muscle
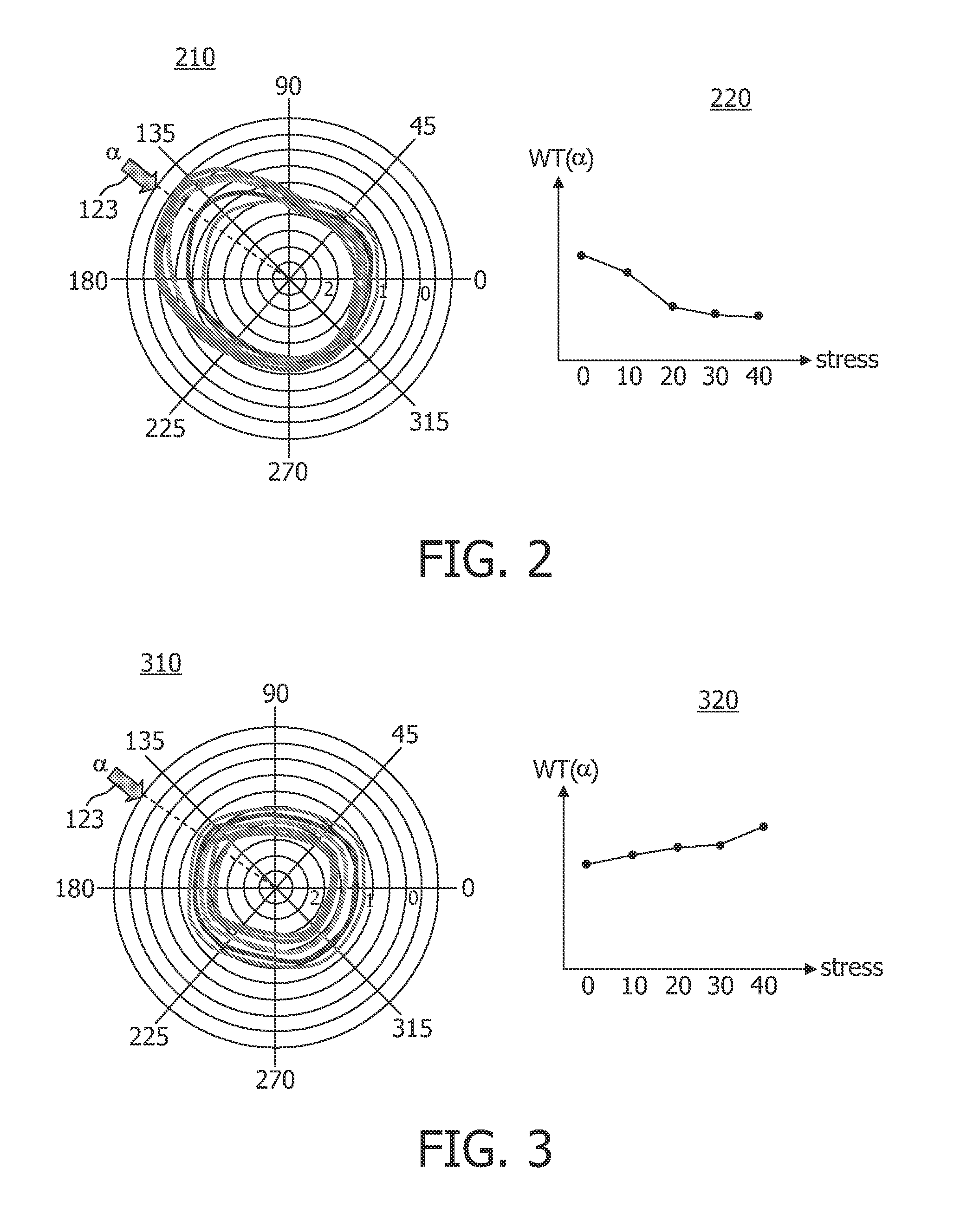
The invention relates to a system (100) for visualizing a cardiac parameter at a plurality of positions in a myocardium and at a plurality of stress levels, the system comprising a determination unit parameter at a position from the plurality of positions in the myocardium and at a stress level from the plurality of stress levels on the basis of stress level cardiac functional data, and a visualization unit (120) for visualizing the determined value of the cardiac parameter by displaying a point in a viewing plane. The visualized points are defined by their polar coordinates in a polar coordinate system in the viewing plane. A radial coordinate of the point visualizes the determined value of the cardiac parameter. An angular coordinate of the point visualizes an angular coordinate of the position in the myocardium in a cylindrical coordinate system. Thus, the system allows easy numerical comparison of local myocardial contractions at different stress level values.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Heavy-duty circuit breaker with erosion-resistant short-circuit current routing
InactiveUS20080006608A1Easy to installEasy to manufactureHigh-tension/heavy-dress switchesAir-break switchesEngineeringInternal dimension
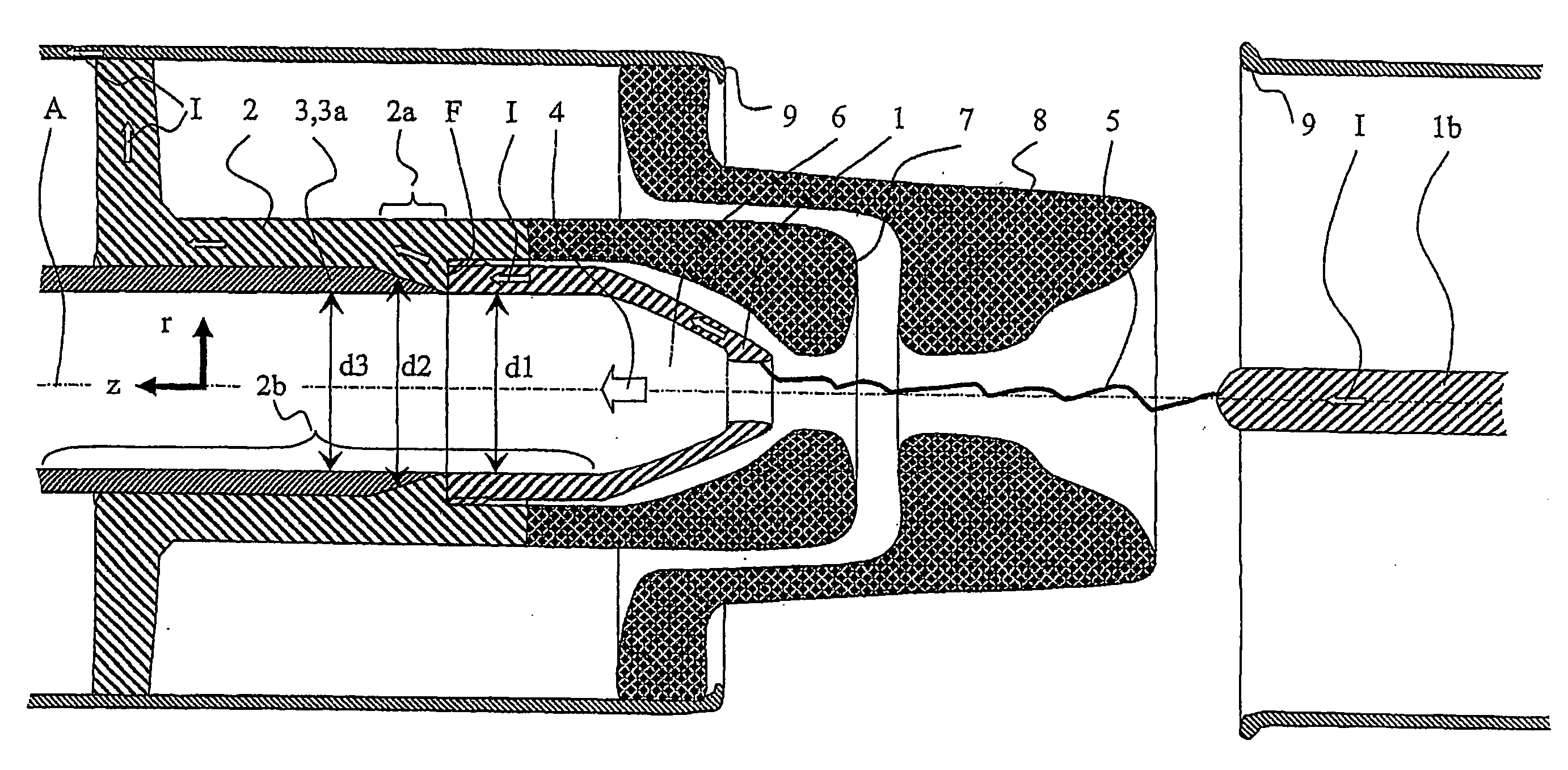
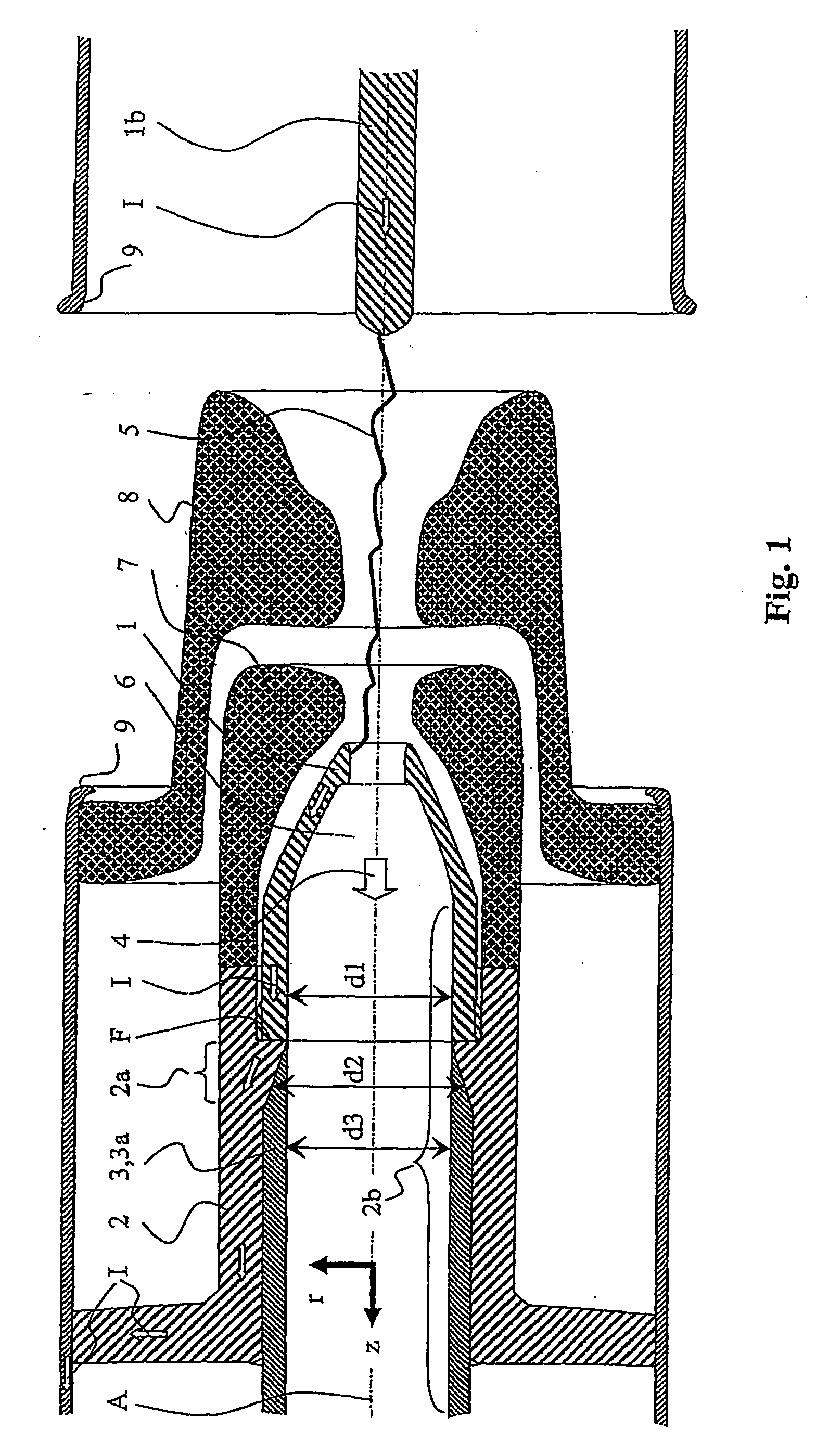
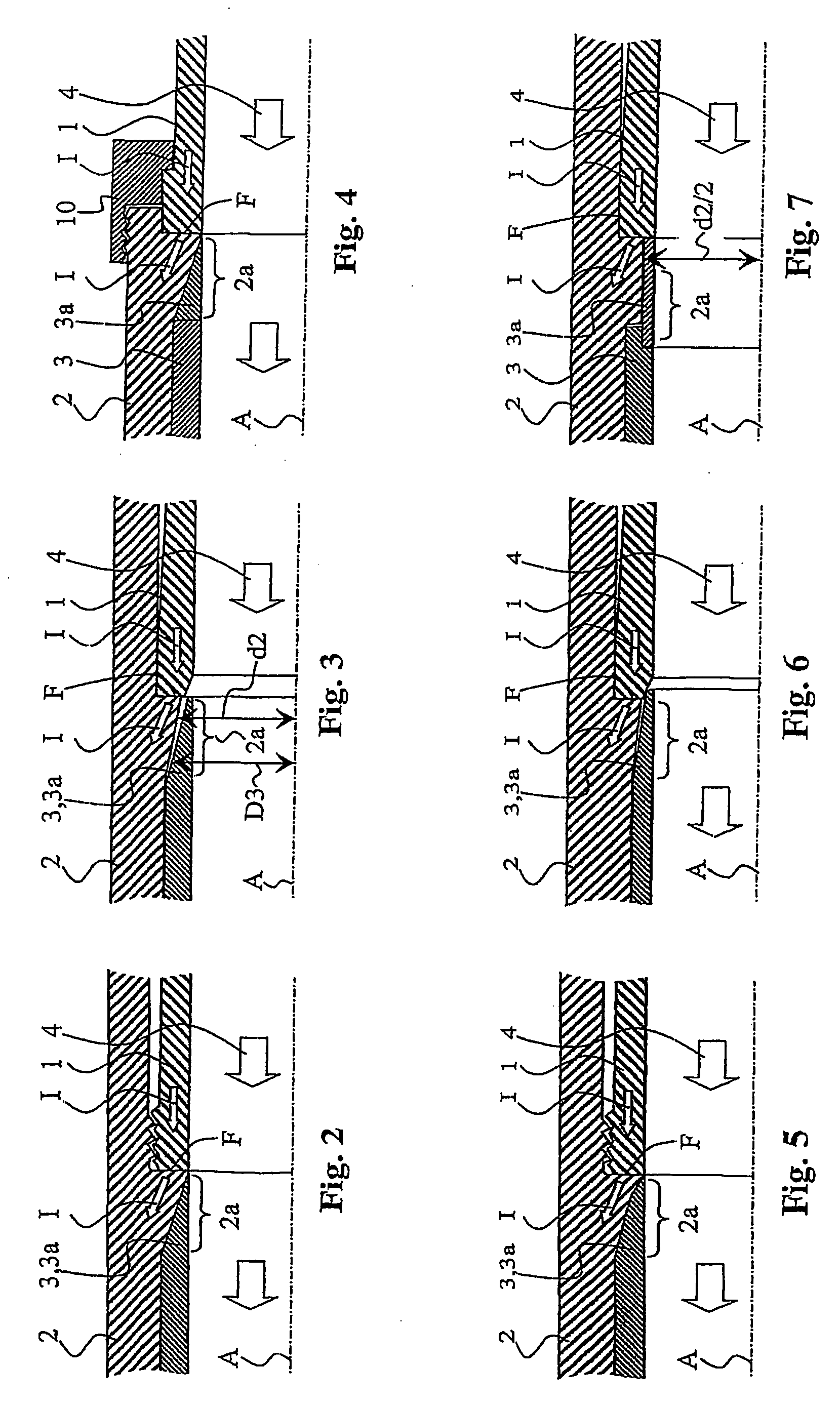
The heavy-duty circuit-breaker having an axis (A) which defines an axial coordinate (z) parallel to the axis and a radial coordinate (r) at right angles to the axis, and having an arcing contact piece, a current-carrying element and an erosion protection element, with the arcing contact piece having an opening in order to carry an essentially axial flow of a gas which has been heated by an arc which may be based on the arcing contact piece, and together with the current-carrying element forms a flat contact (F) in order to carry a short-circuit current (I) which flows through the arcing contact piece and the current-carrying element for the time during which the arc burns, and with the erosion protection element essentially shielding the current-carrying element from the flow close to the flat contact (F), is characterized in that the current-carrying element has an axial area in which a radial internal dimension (d2) of the current-carrying element increases in steps or continuously as the distance from the flat contact (F), measured parallel to the axis (A), increases. The axial area is advantageously intended, to hold the erosion protection element.
Owner:ABB TECH AG +1
Method for observing a sample
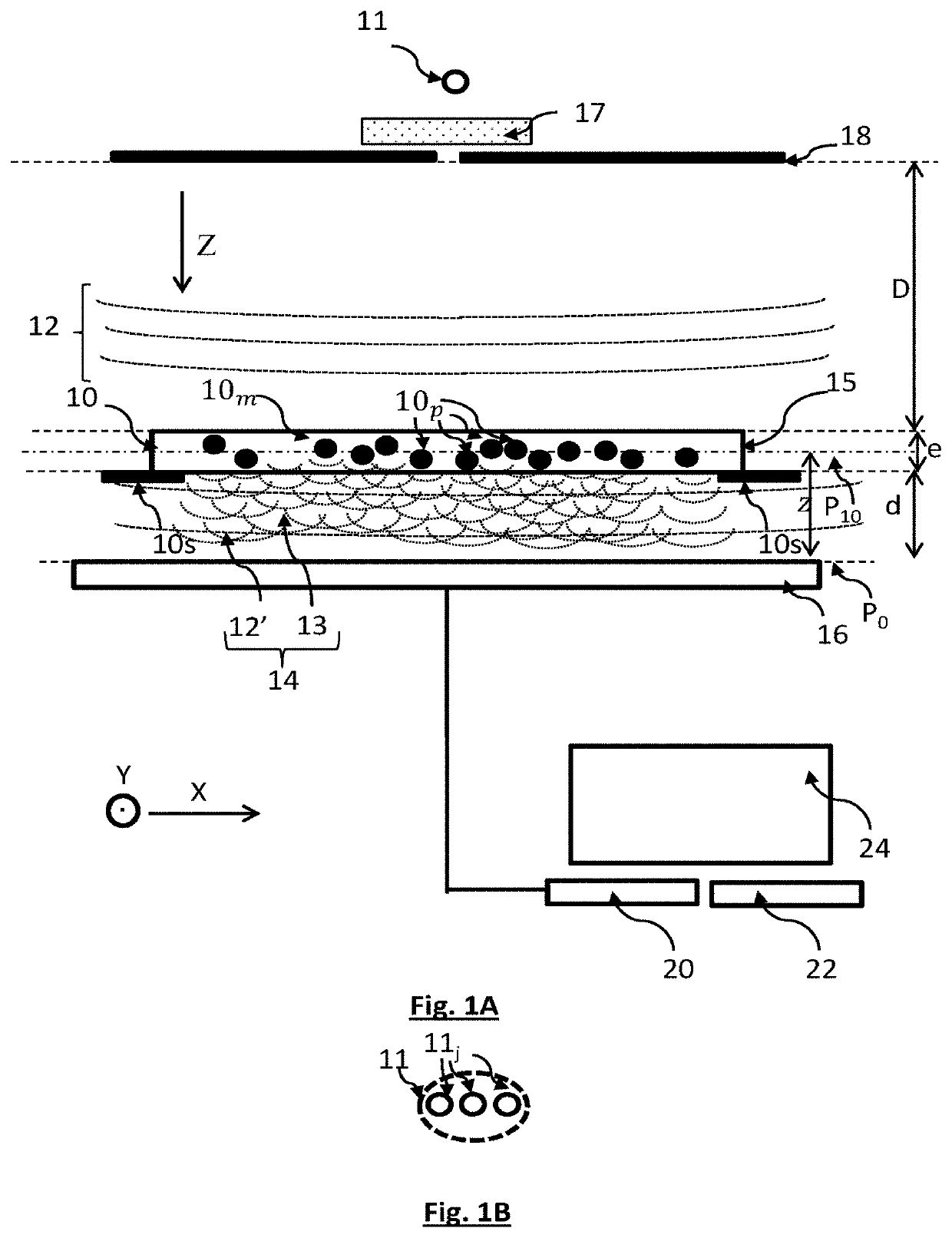
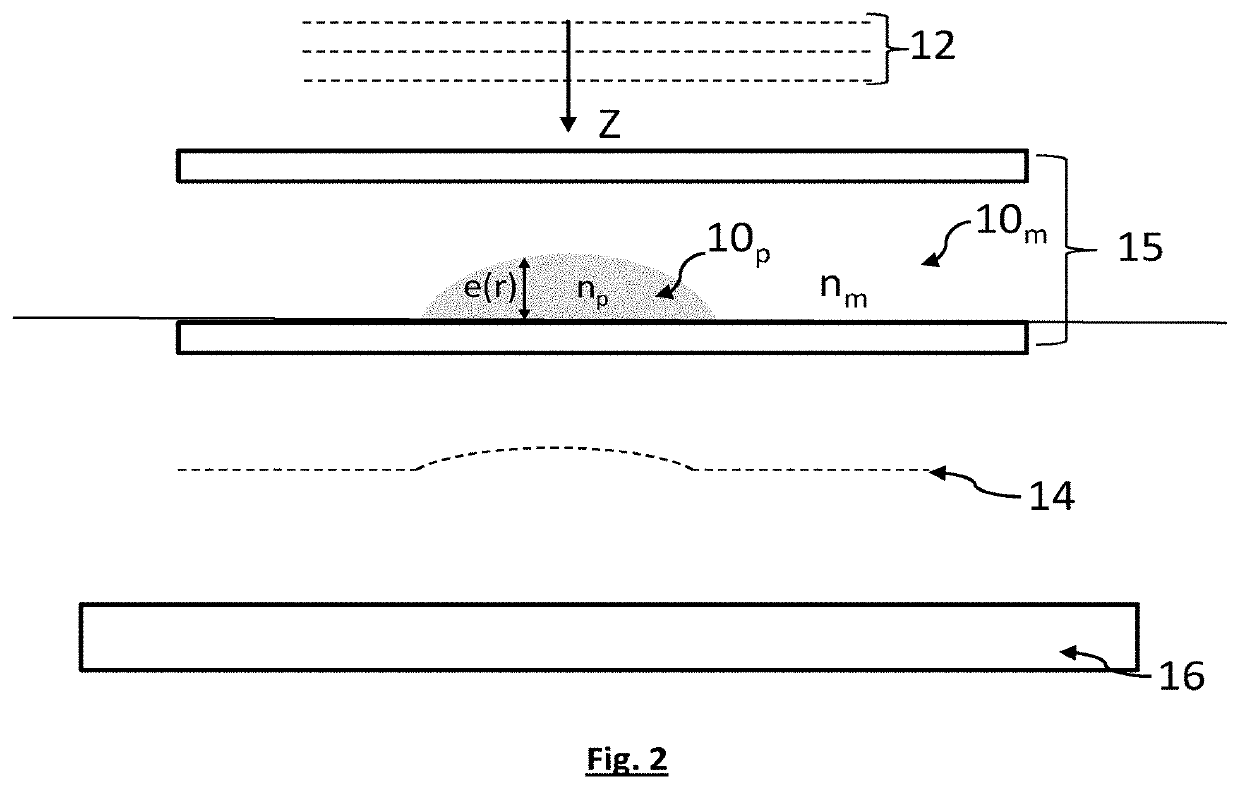
ActiveUS20200124586A1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesIndividual particle analysisImage formationComputational physics
A method for observing a sample (10), the sample lying in a plane of the sample defining radial coordinates, the method comprising the following steps:a) illuminating the sample using a light source (11), able to emit an incident light wave (12) that propagates toward the sample along a propagation axis (Z);b) acquiring, using an image sensor (16), an image (I0) of the sample (10), said image being formed in a detection plane (P0), the sample being placed between the light source (11) and the image sensor (16), such that the incident light wave sees an optical path difference, parallel to the propagation axis (Z), by passing through the sample;c) processing the image acquired by the image sensor;wherein the processing of the acquired image comprises taking into account vectors of parameters, respectively defined at a plurality of radial coordinates, in the plane of the sample, each vector of parameters being associated with one radial coordinate, and comprising a term representative of an optical parameter of the sample, at least one optical parameter being an optical path difference induced by the sample at the radial coordinate, the vectors of parameters describing the sample.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
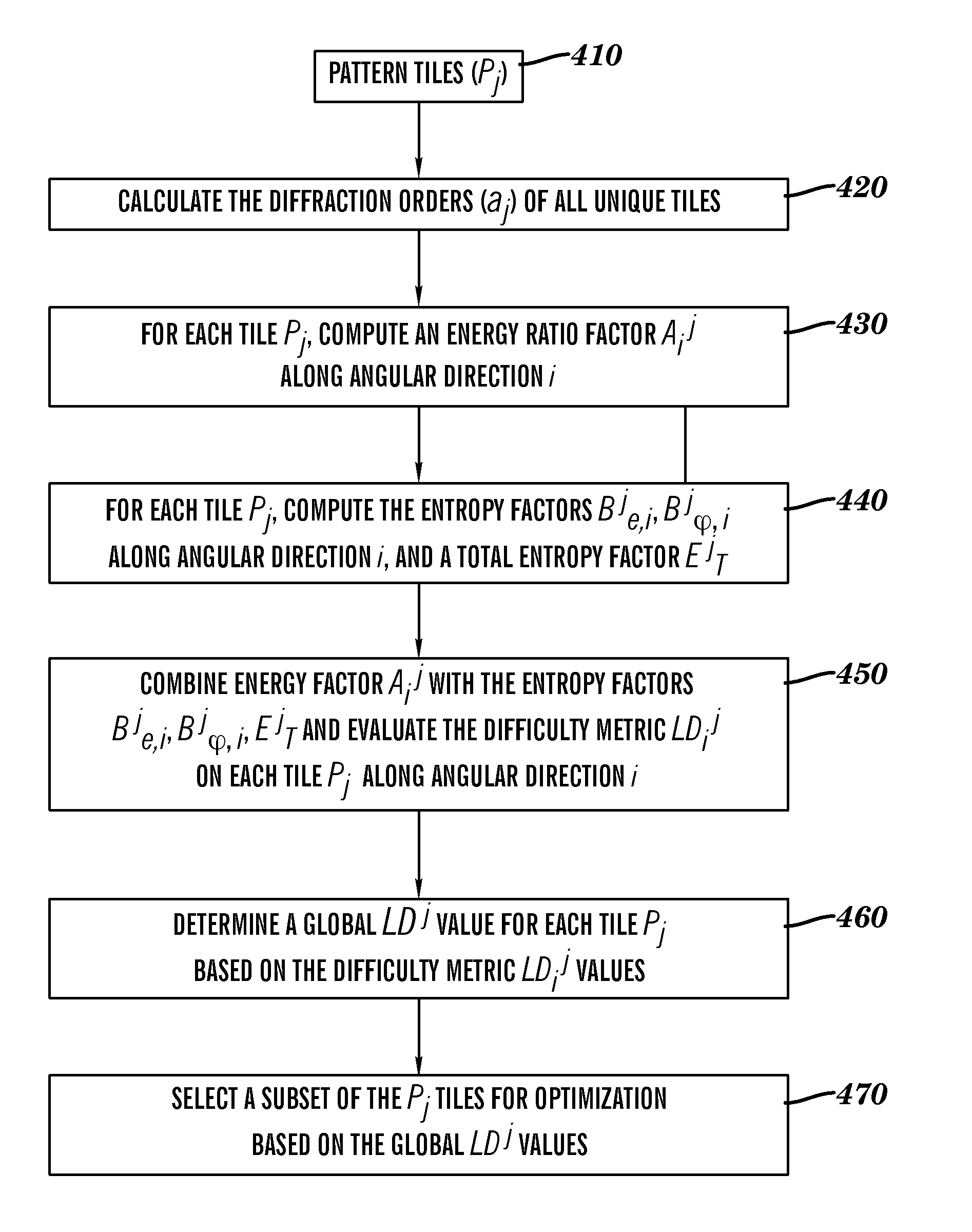
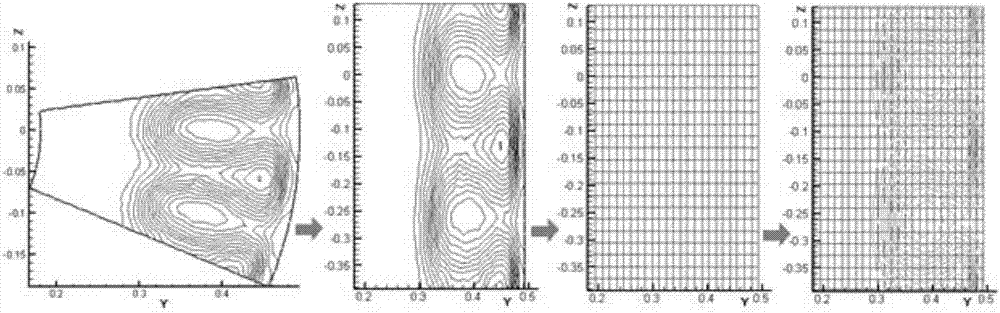
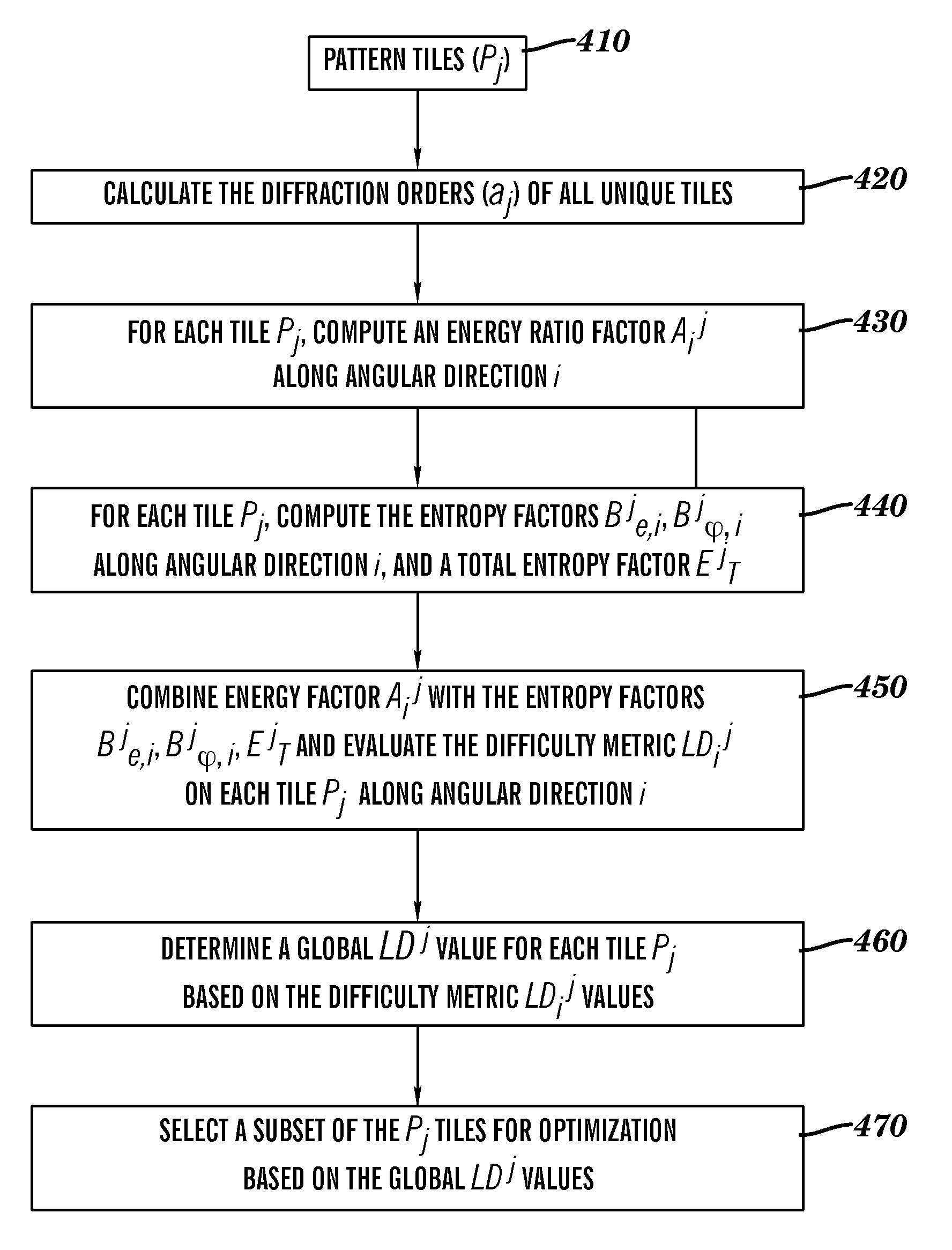
Method for fast estimation of lithographic binding patterns in an integrated circuit layout
ActiveUS20120017194A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusPrinter-friendlyBinding pattern
The present invention provides a lithographic difficulty metric that is a function of an energy ratio factor that includes a ratio of hard-to-print energy to easy-to-print energy of the diffraction orders along an angular coordinate θi spatial frequency space, an energy entropy factor comprising energy entropy of said diffraction orders along said angular coordinate θi, a phase entropy factor comprising phase entropy of said diffraction orders along said angular coordinate θi, and a total energy entropy factor comprising total energy entropy of said diffraction orders. The hard-to-print energy includes energy of the diffraction orders at values of the normalized radial coordinates r of spatial frequency space in a neighborhood of r=0 and in a neighborhood of r=1, and the easy-to-print energy includes energy of the diffraction orders located at intermediate values of normalized radial coordinates r between the neighborhood of r=0 and the neighborhood of r=1. The value of the lithographic difficulty metric may be used to identify patterns in a design layout that are binding patterns in an optimization computation. The lithographic difficulty metric may be used to design integrated circuits that have good, relatively easy-to-print characteristics.
Owner:IBM CORP
Medical image processing device and method for operating the same
RGB image signals are inputted. A B / G ratio is calculated from the B and G image signals. A G / R ratio is calculated from the G and R image signals. First, second, and third areas are located in a feature space formed by the B / G and G / R ratios. An equal angular magnification process is performed on an angle in a region R1x including a first reference line passing through the second area. An angle expansion process or an angle compression process is performed on an angle in a region R1y located outside the region R1x. An equal radial-coordinate magnification process is performed on a radial coordinate in a region R2x, which includes a second reference line passing through the second area and intersecting the first reference line. A radial-coordinate expansion process or a radial-coordinate compression process is performed on a radial coordinate in a region R2y located outside the region R2x.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
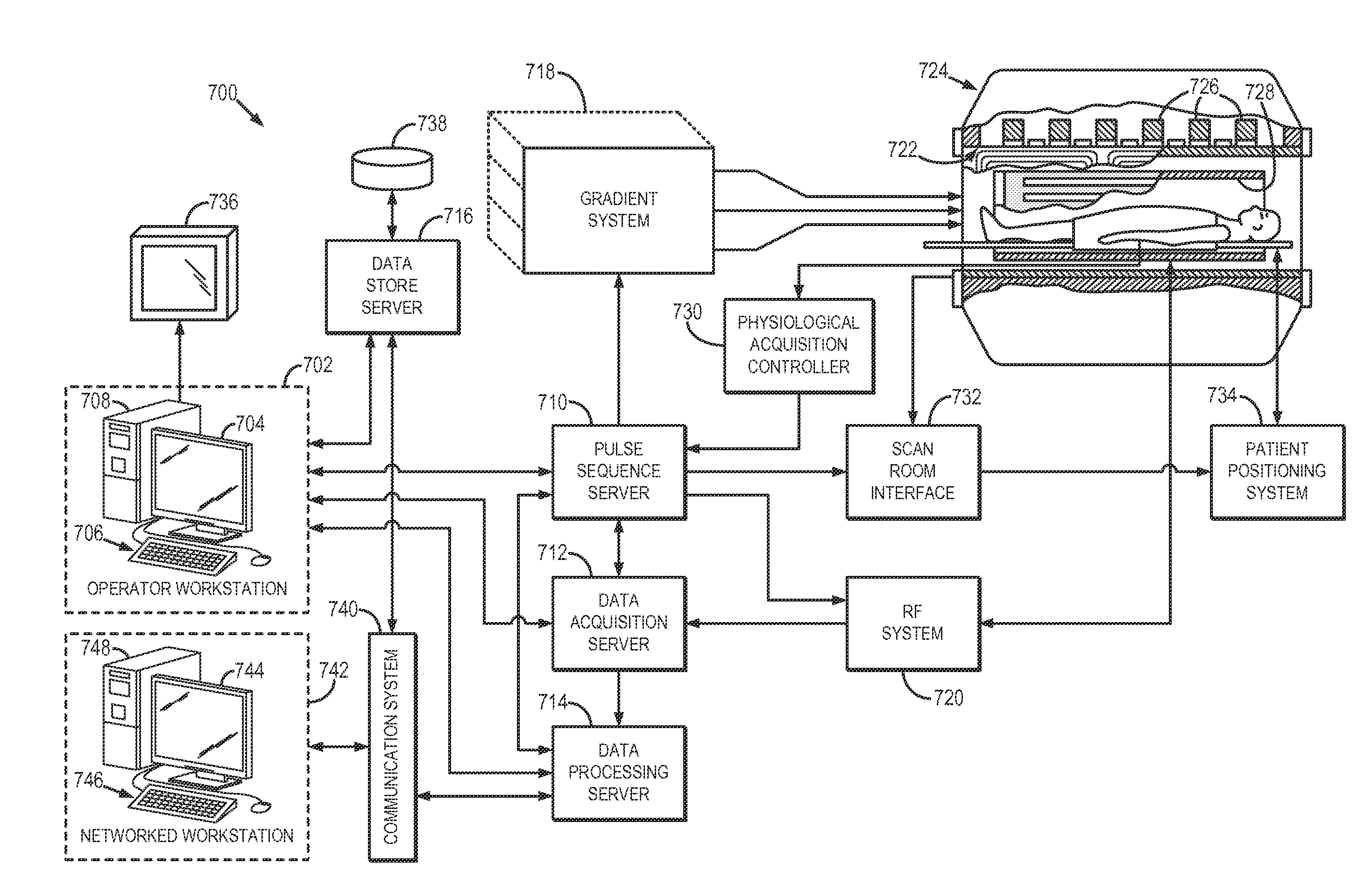
Methods for optimizing magnetic resonance imaging systems
InactiveUS6947877B2Accurately and efficiently determineMinimized volumeComputation using non-denominational number representationDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrical resistance and conductanceHomogeneous magnetic field
A computer-implemented method for optimizing the design of an electromagnetic coil arrangement that generates a uniform magnetic field in a desired region, with the electromagnetic coil arrangement having a number of coils and a shape defined by r and z, where r is the radial coordinate of a cylindrical coordinate system having (r, z, φ) coordinates, and z is the axial coordinate of the cylindrical coordinate system. The method has an important use for designing superconductive or resistive coil arrangements for MRI systems. The core of the method is to compute a solution to a master equation (25) for a set of parameters lambda_j which define the coil arrangement and the currents needed. An important advantage is that the resultant coil arrangement has a minimum volume, which saves on material, or uses a minimum power.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
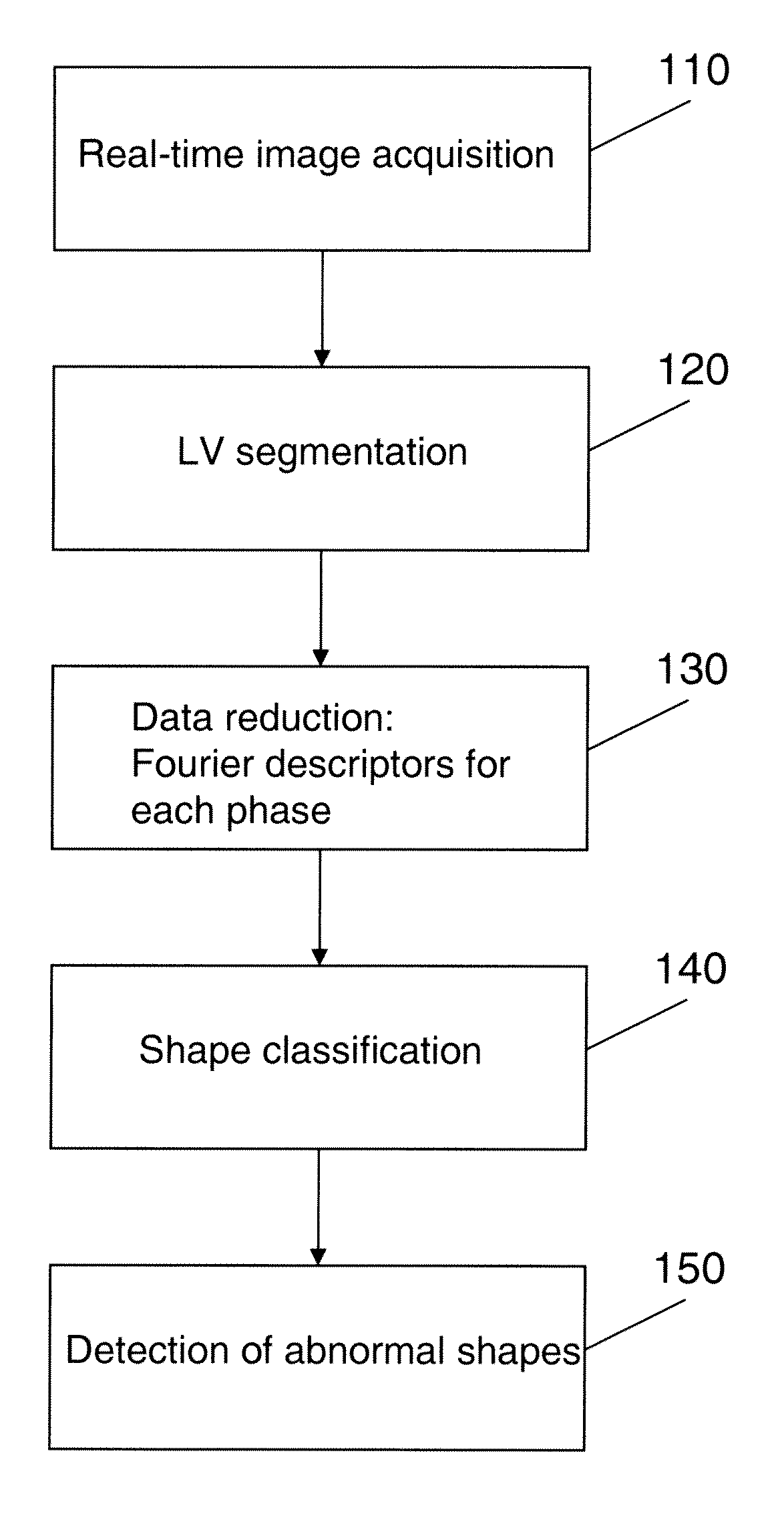
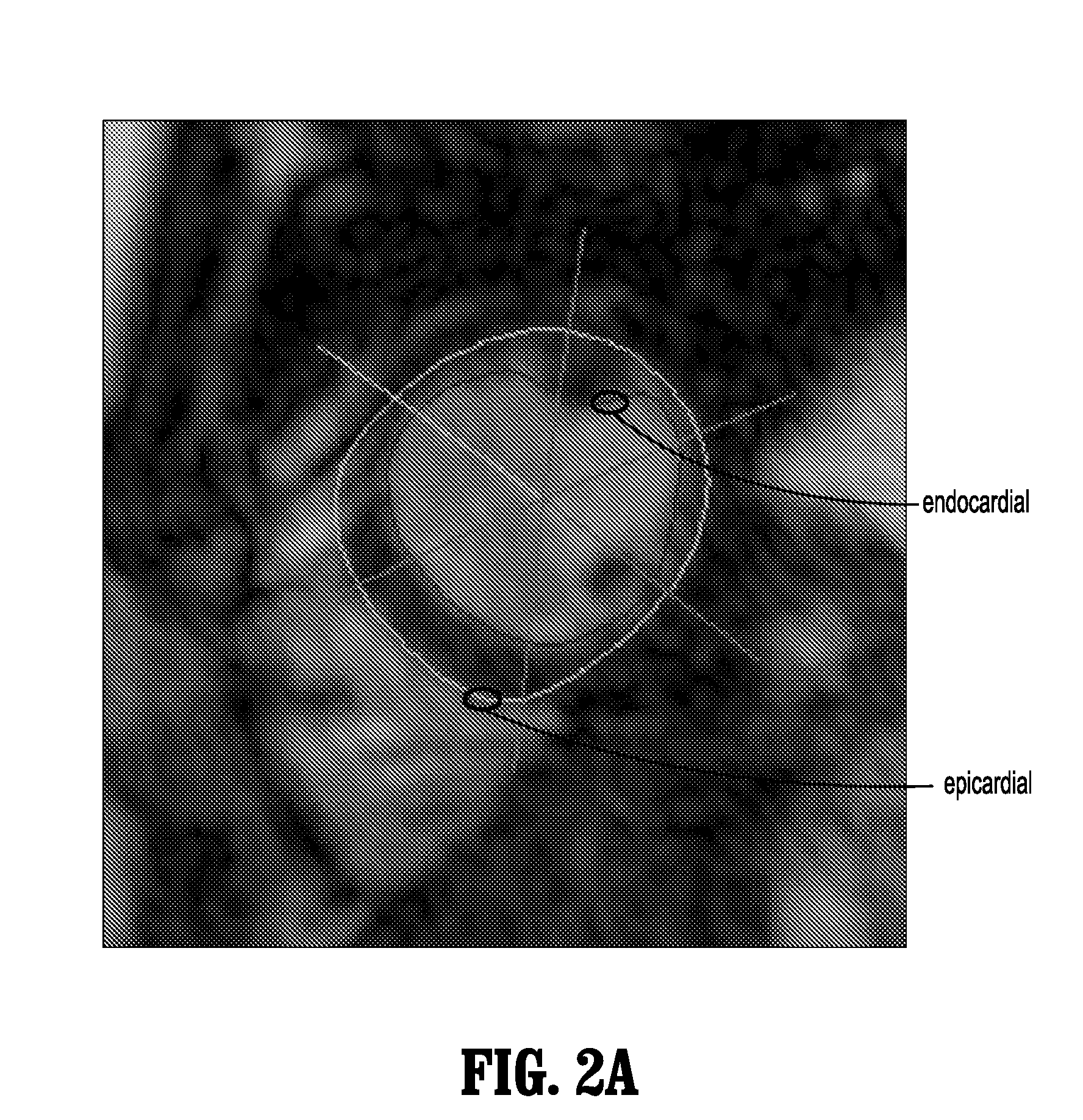
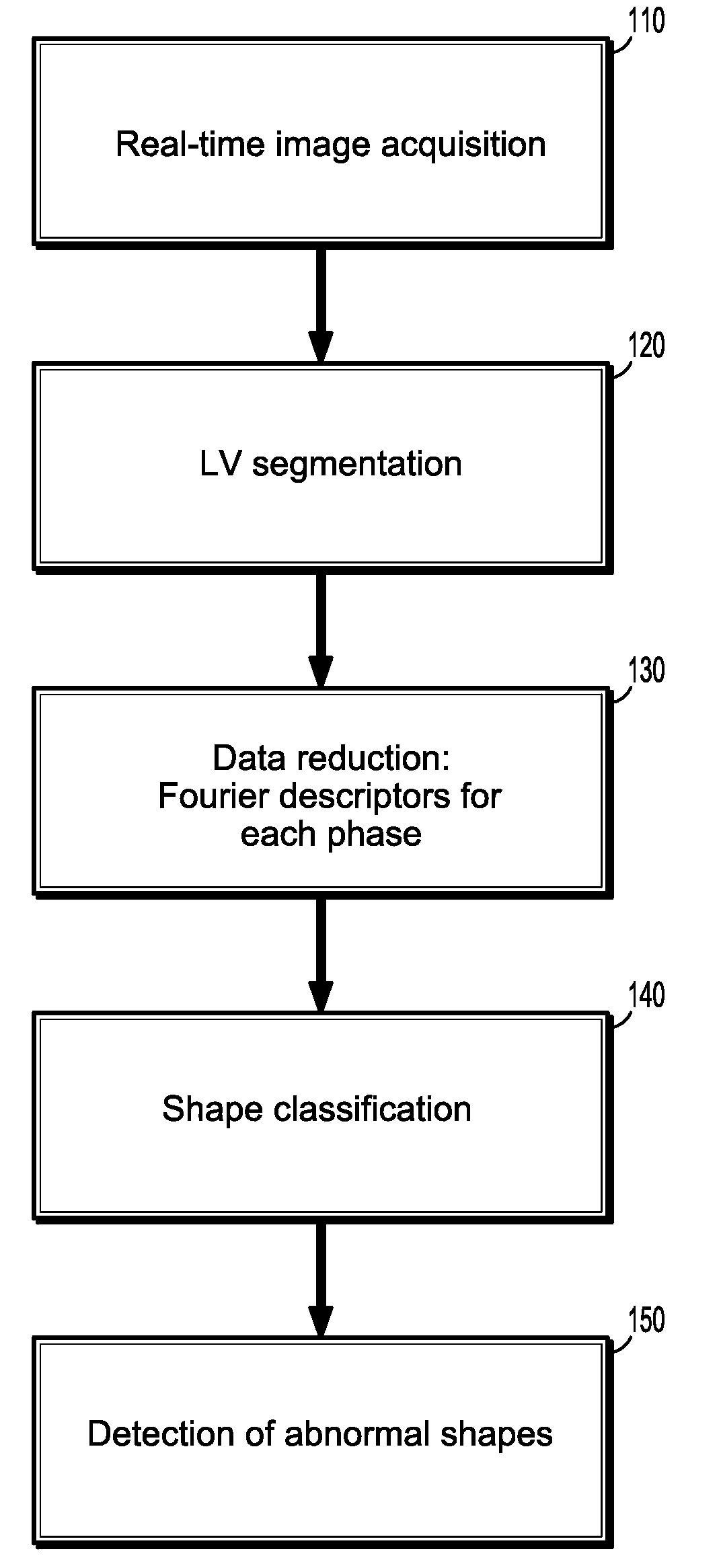
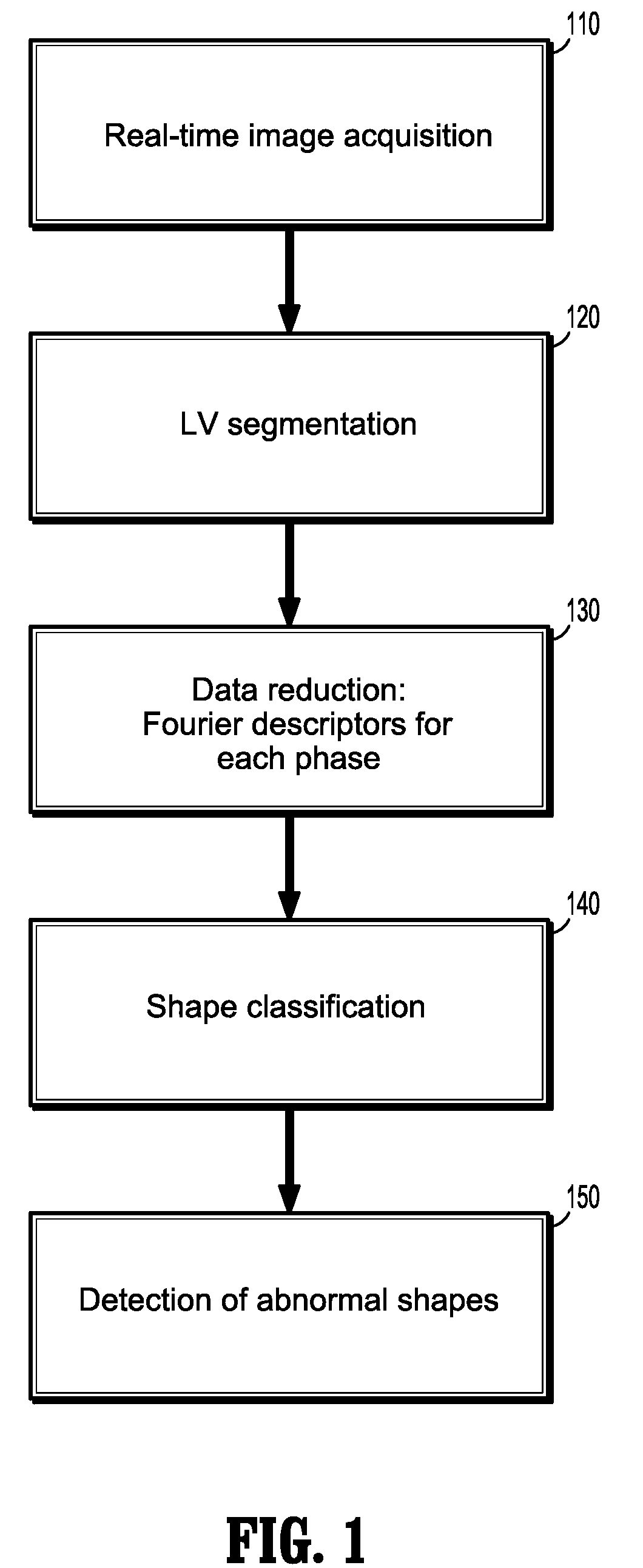
Method and System for Monitoring Cardiac Function of a Patient During a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) Procedure
InactiveUS20090093707A1Medical data miningCharacter and pattern recognitionCardiac phaseFourier transform on finite groups
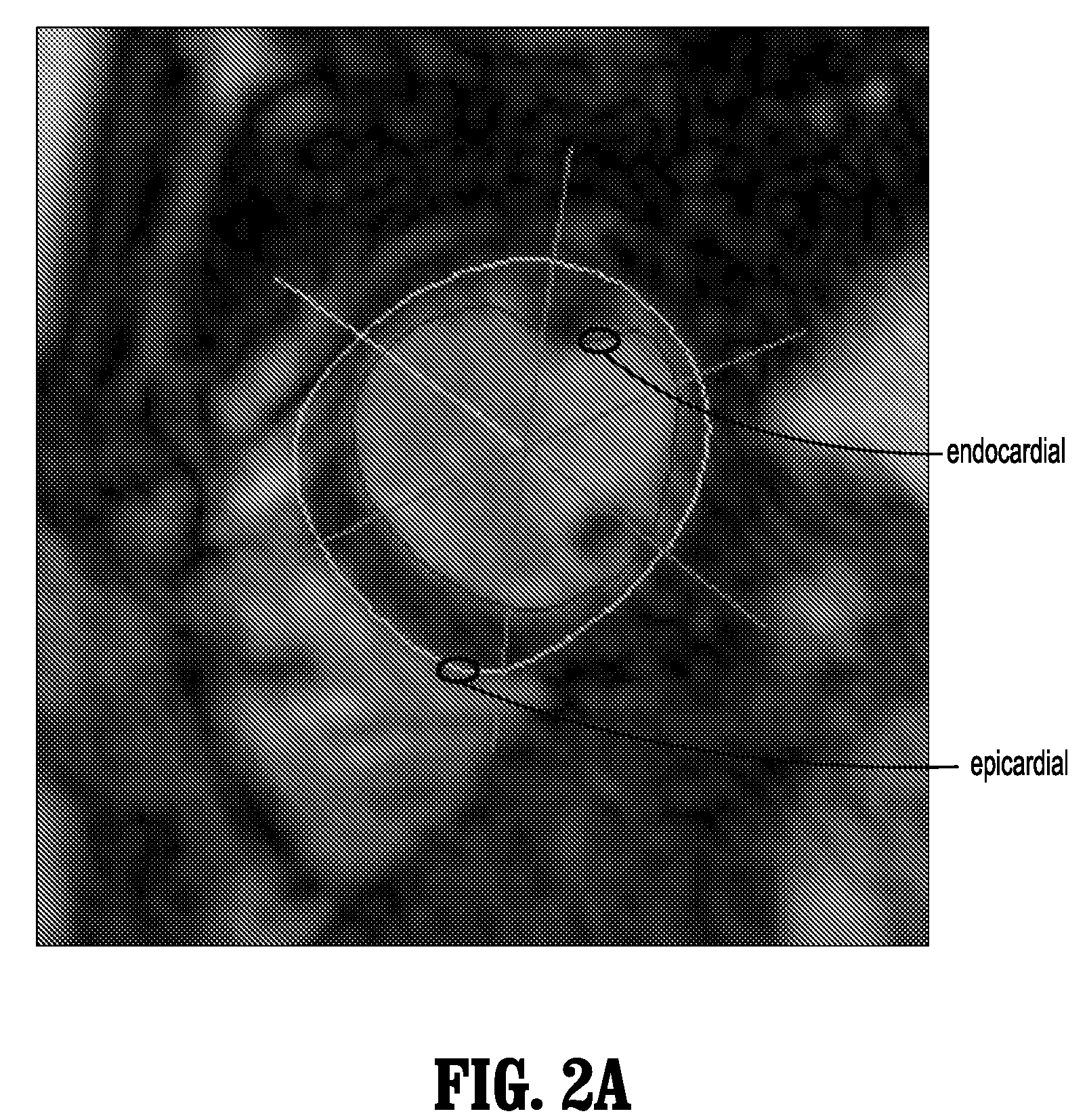
A method for monitoring cardiac function of a patient during a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedure, including: acquiring an MR image sequence of the patient's heart during a cardiac phase; segmenting a left ventricle of the patient's heart in the MR image sequence, wherein the segmentation produces endocardial and epicardial contours; representing at least one of the contours in polar or radial coordinates and computing its Fourier transform, wherein the Fourier transform produces Fourier descriptors for the contour; putting a vector of the Fourier descriptors into a classifier, wherein the classifier determines whether the contour reflects normal wall motion in the cardiac phase or whether the contour reflects abnormal wall motion in the cardiac phase; and alerting a medical practitioner when abnormal wall motion is detected.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Mapping cardiac tissue architecture systems and methods
Systems and methods are provided for mapping myocardial tissue architecture based on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI). A set of eigenvectors is derived from diffusion tensor data, where each eigenvector describes the diffusion of spins along one of the Cartesian directions. A radial coordinate axis and a circumferential plane are determined based on anatomical information of the subject, such as from an image depicting the epicardial surface of the subject's heart, A longitudinal coordinate axis and a circumferential coordinate axis are determined based on the radial coordinate axis and circumferential plane, A fiber architecture matrix (FAM) is then computed for locations in the subject's heart based on projecting the set of eigenvectors onto a local coordinate system defined by the circumferential, radial, and longitudinal axes, Maps that represent myocardial tissue architecture can then be generated using the FAM for locations within the subject's heart.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method and system for monitoring cardiac function of a patient during a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedure
A method for monitoring cardiac function of a patient during a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) procedure, including: acquiring an MR image sequence of the patient's heart during a cardiac phase; segmenting a left ventricle of the patient's heart in the MR image sequence, wherein the segmentation produces endocardial and epicardial contours; representing at least one of the contours in polar or radial coordinates and computing its Fourier transform, wherein the Fourier transform produces Fourier descriptors for the contour; putting a vector of the Fourier descriptors into a classifier, wherein the classifier determines whether the contour reflects normal wall motion in the cardiac phase or whether the contour reflects abnormal wall motion in the cardiac phase; and alerting a medical practitioner when abnormal wall motion is detected.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Processing method of axial conical pin hole for small gap of multiple stages of wheel discs of steam turbine rotor
ActiveCN104043859AImprove processing efficiencyImprove machining accuracyPortable drilling machinesBoring/drilling machinesRadial positionEngineering
The invention relates to a processing method of an axial conical pin hole for a small gap of multiple stages of wheel discs of a steam turbine rotor. The processing method comprises the following steps of 1, determining the depth and size of each stage of step bottom hole in the conical pin hole; 2, modifying drill bits according to the depth and size of each stage of step bottom hole; 3, using the drill bit I to drill in the to-be-processed position, with the depth equal to the depth of the first step bottom hole; 4, recording the coordinate of the radial position of the center of the drill bit I, and taking the drill bit I out through cutter retraction; 5, modifying the drill bit II, feeding the cutter according to the recorded radial coordinate, ensuring the coinciding of rotation centers of the two drilling bits, and thoroughly drilling according to the requirement of a drawing; 6, after the drill bit II (10) is taken out, selecting a reaming cutter with property length and the feeding tool to manually ream the taper of the conical pin hole. The method solves the problem that the conical hole in the wheel disc cannot be processed due to the too small gap between the two wheel discs when the steam turbine rotor is processed.
Owner:CHONGQING JIANGJIN SHIPBUILDING IND
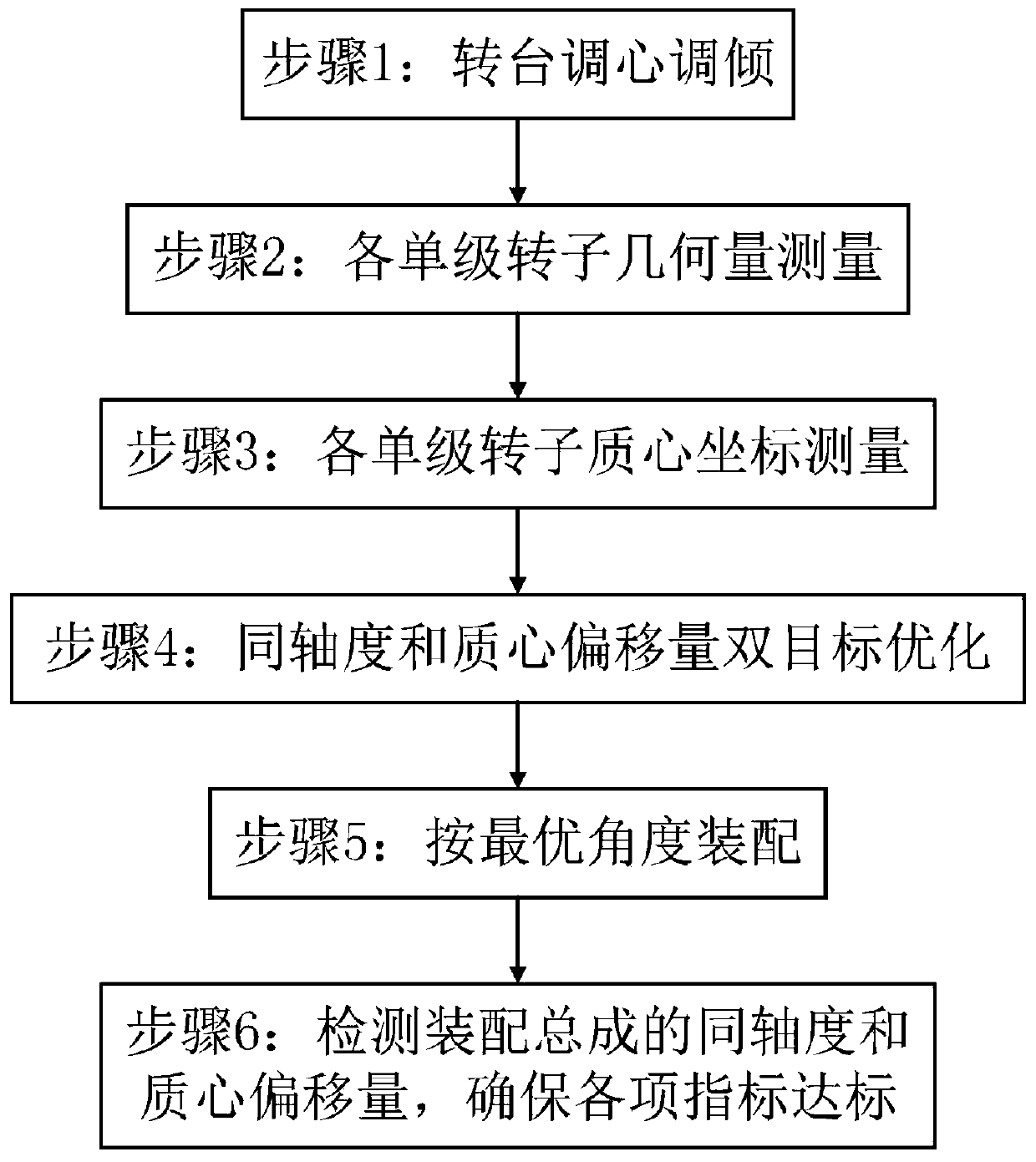
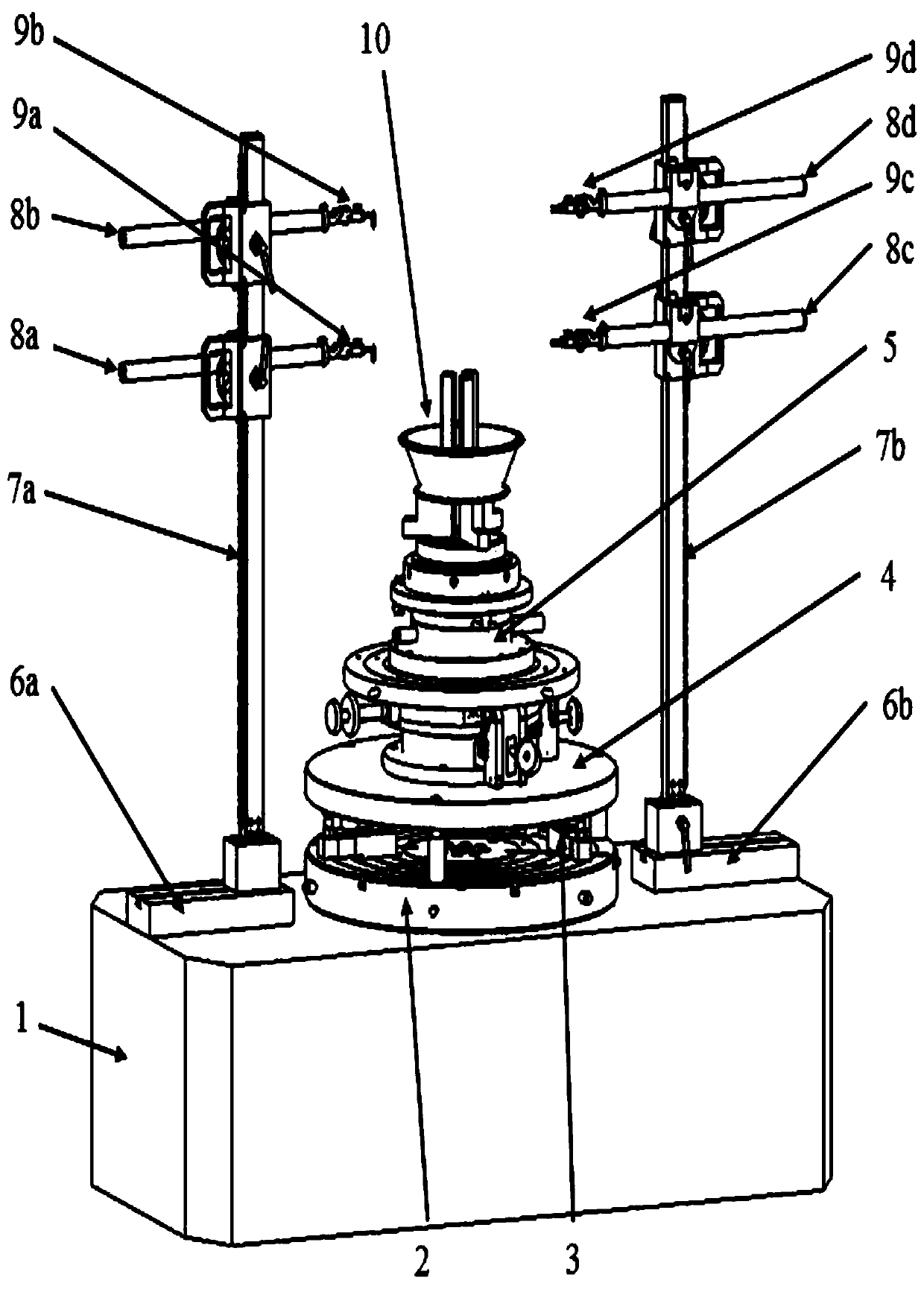
Aircraft engine rotor assembly measuring device based on three-point weighing and double-objective optimization method
InactiveCN110608668AImprove coaxialityControl unbalanceStatic/dynamic balance measurementUsing electrical meansAviationTransfer model
The invention discloses an aircraft engine rotor assembly measuring device based on three-point weighing and a double-objective optimization method. The double-objective optimization method comprisesthe following steps: determining the angle positioning of a rotary table based on a circular grating; ensuring the measurement and assembling of the concentricity, the parallelism and the center-of-mass coordinate of a measured rotor under the same reference based on an aligning and inclination adjusting device; based on a four-probe measuring device, respectively extracting concentricity errors of radial assembly surfaces and parallelism errors of axial assembly surfaces of all levels of rotors; based on a three-point weighing measuring device, respectively extracting radial coordinates of the mass centers of all levels of rotors; based on a rotor assembly pose transfer model, taking the coaxiality and center-of-mass offset of a rotor assembly as double optimization objectives, and obtaining the optimal assembly angle of each level of rotor through genetic optimization. The method can effectively solve the problem that coaxiality and an unbalance value exceed standard after the rotorof the aircraft engine is assembled, and has the characteristics of integrated measurement of the geometric and quality characteristics of the rotor, high one-time assembly qualification rate and reduction of engine vibration.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
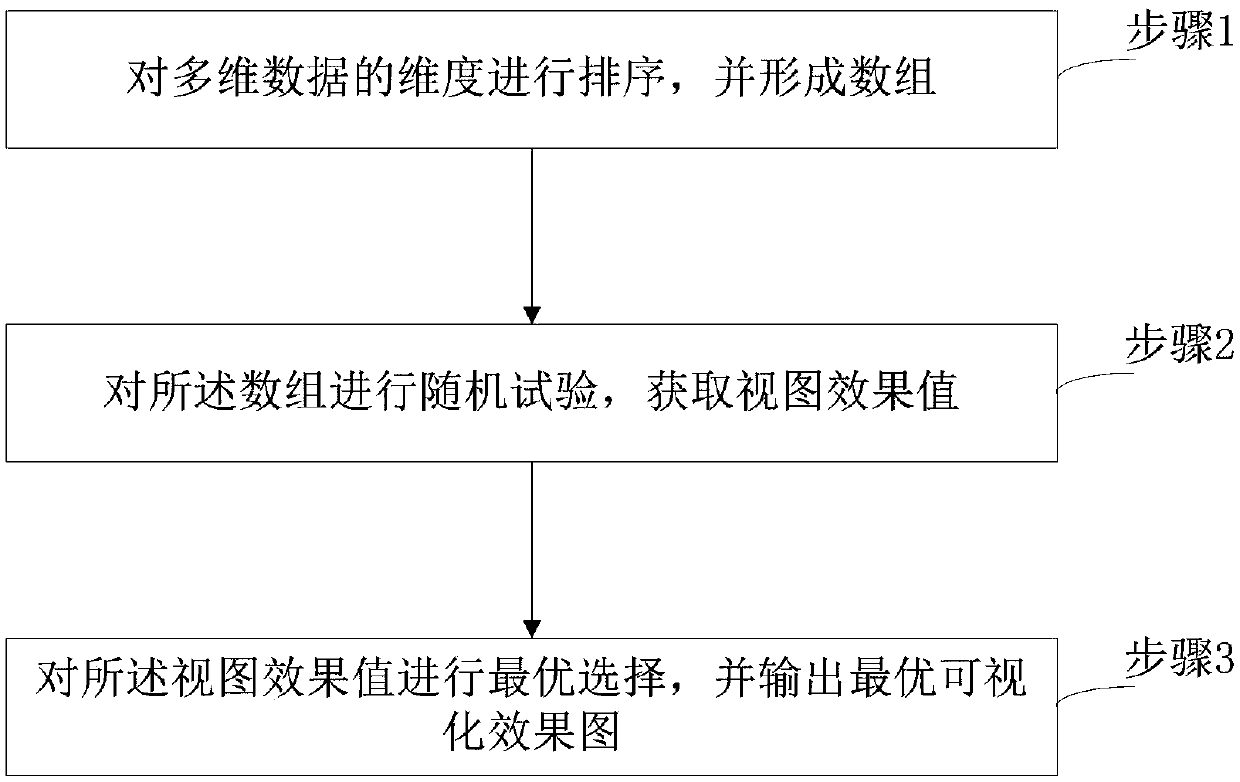
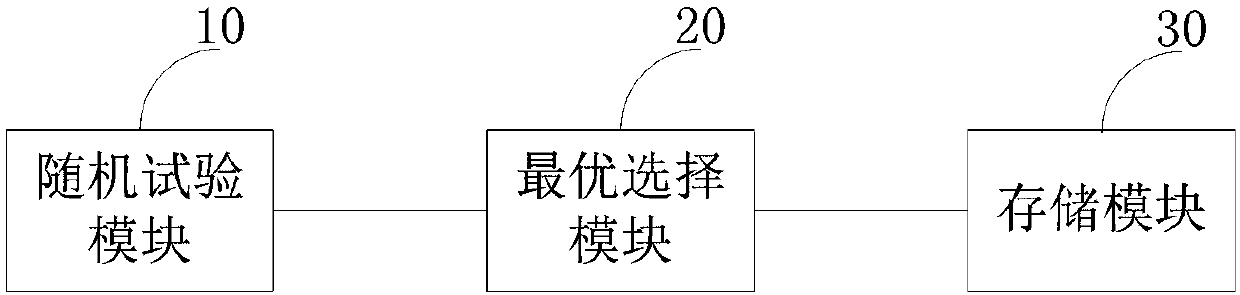
Multi-dimensional data visualization method and device based on radial coordinate optimization
ActiveCN108021716AImplement optimized processingImprove visualizationMulti-dimensional databasesSpecial data processing applicationsArray data structureMultidimensional data
The invention relates to a multi-dimensional data visualization method based on radial coordinate optimization. The method includes the steps of firstly, sequencing dimensions of multi-dimensional data to form arrays; secondly, randomly testing the arrays to obtain view effect values; thirdly, selecting the optimum view effect value, and outputting the optimum visualization effect view. By improving the three indexes including data density, data chaos and data coverage of the visualization effect and calculating and selecting the minimum view effect value, the optimum visualization effect viewis obtained and output, and the optimization treatment of an original algorithm is achieved. The embodiment of the invention further provides a multi-dimensional data visualization device based on radial coordinate optimization.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
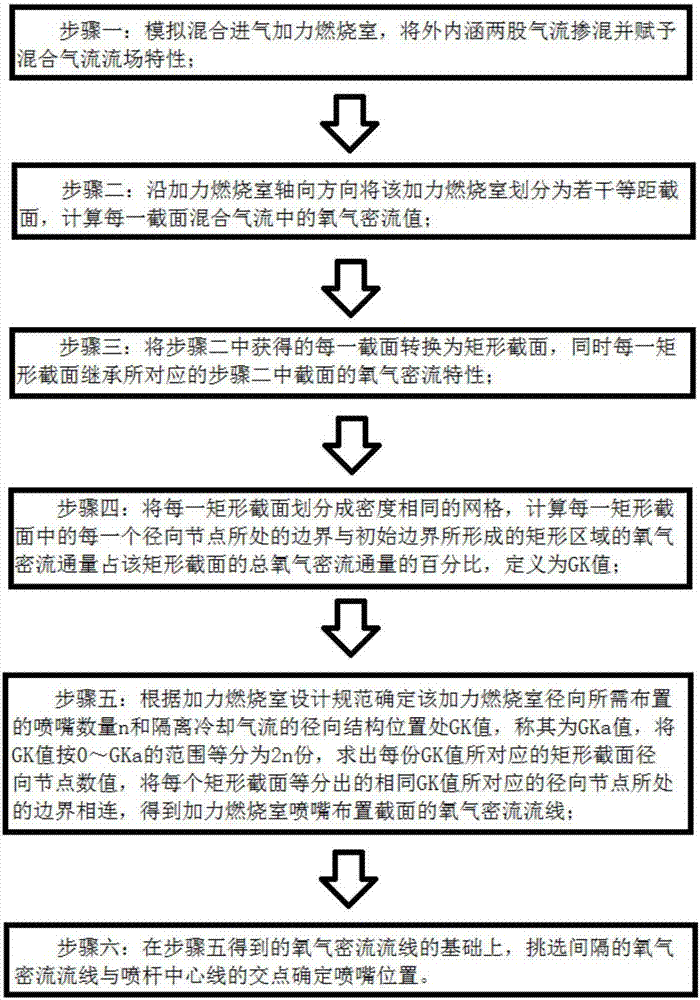
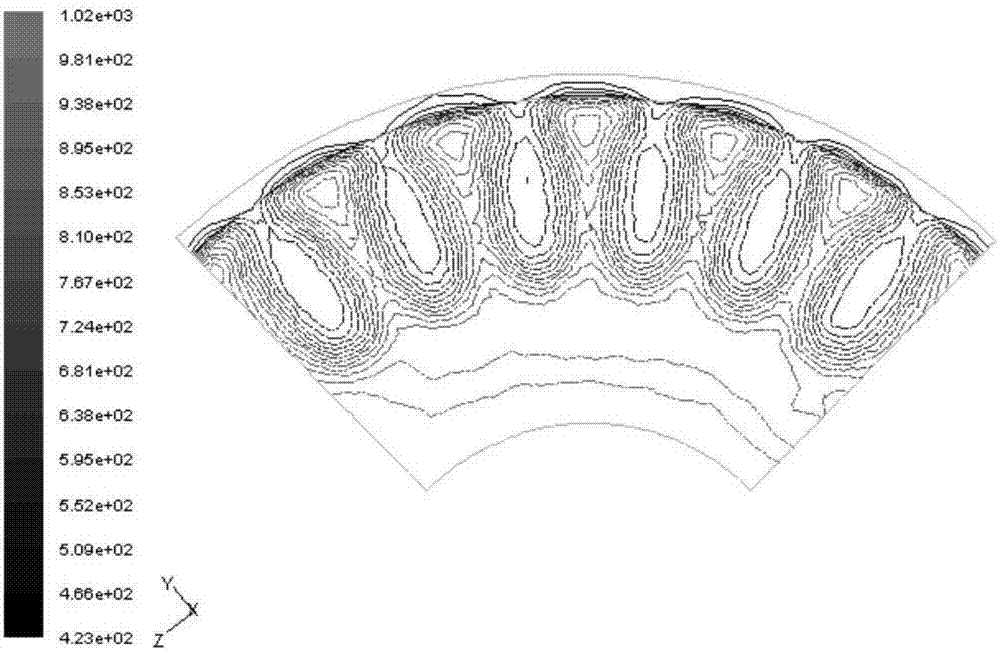
Afterburner nozzle layout method
ActiveCN107092748AHigh quality and precisionImprove design accuracyGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDemarcation pointCombustion chamber
The invention provides an afterburner nozzle layout method. According to the method, flow field simulation is performed to obtain a plurality of equidistant sections with axial coordinates being constants; an oxygen dense flow value in each section airflow is calculated; each section is converted into a rectangular section, and original dense flow characteristics are inherited; the percentage GK of dense flow flux in a rectangular region formed by each radial node of each section and an initial boundary in total dense flow flux is calculated; the number n of nozzles needed in the radial direction and a GK value GKa at a radial structure position for isolating cooling airflow are determined according to design specifications; the GK value is equally divided into 2n parts according to the range from 0 to GKa, and radial coordinates corresponding to each part of the GK value at a demarcation point are solved; the radial positions corresponding to the same equally-divided GK value of each section are connected to obtain an oxygen dense flow line; and alternate intersection points of the oxygen dense flow line and a spray rod center line are selected to determine nozzle positions. Through the method, fuel and oxygen participating in burning can be finely matched and premixed uniformly, and the method is beneficial for improving afterburning efficiency.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST
Method for fast estimation of lithographic binding patterns in an integrated circuit layout
ActiveUS8234603B2Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementPhotomechanical apparatusPrinter-friendlyDiffraction order
The present invention provides a lithographic difficulty metric that is a function of an energy ratio factor that includes a ratio of hard-to-print energy to easy-to-print energy of the diffraction orders along an angular coordinate θi of spatial frequency space, an energy entropy factor comprising energy entropy of said diffraction orders along said angular coordinate θi, a phase entropy factor comprising phase entropy of said diffraction orders along said angular coordinate θi, and a total energy entropy factor comprising total energy entropy of said diffraction orders. The hard-to-print energy includes energy of the diffraction orders at values of the normalized radial coordinates r of spatial frequency space in a neighborhood of r=0 and in a neighborhood of r=1, and the easy-to-print energy includes energy of the diffraction orders located at intermediate values of normalized radial coordinates r between the neighborhood of r=0 and the neighborhood of r=1. The value of the lithographic difficulty metric may be used to identify patterns in a design layout that are binding patterns in an optimization computation. The lithographic difficulty metric may be used to design integrated circuits that have good, relatively easy-to-print characteristics.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
System and method for determining an angular position of a rotor and a radial position of the rotor
A system and a method for determining an angular position of a rotor and a radial position of the rotor are provided. The rotor has either a slot or a protrusion on the rotor. The rotor is centered about a center point. The method includes generating a first signal utilizing a first sensor disposed proximate the slot or protrusion of the rotor. The method further includes determining a first angular position of the rotor by identifying a first corrupted portion of the first signal. The method further includes removing the first corrupted portion of the first signal to obtain a second non-corrupted position signal. The method further includes determining a first radial coordinate of the center point of the rotor based on the second non-corrupted position signal.
Owner:BAKER HUGHES INC
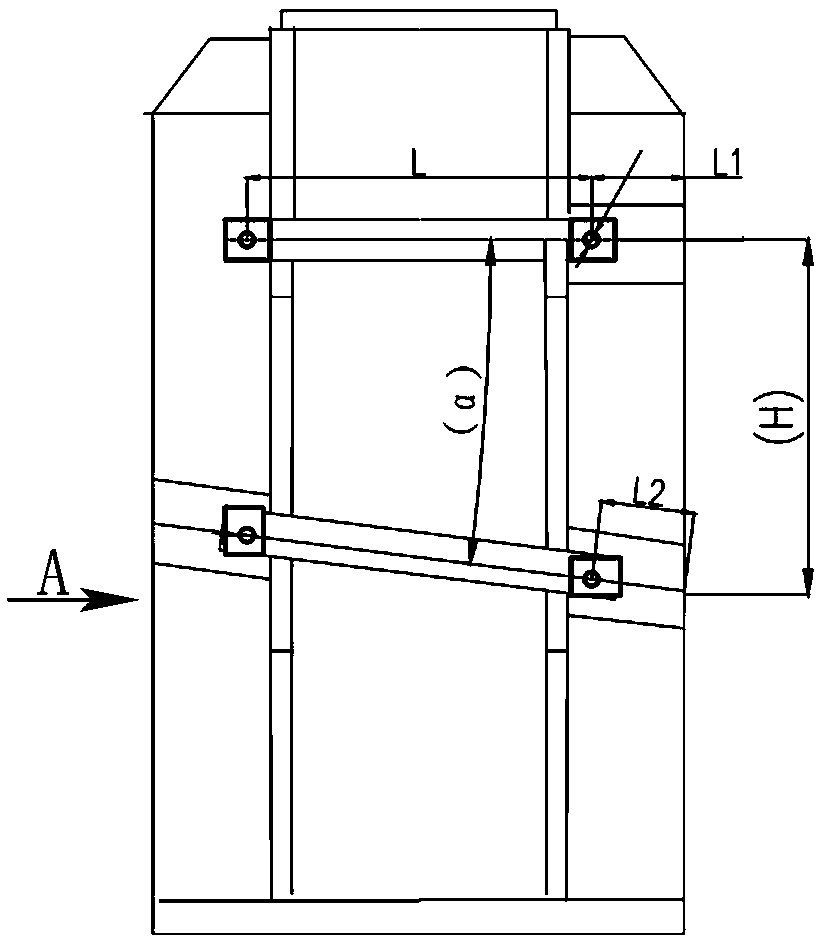
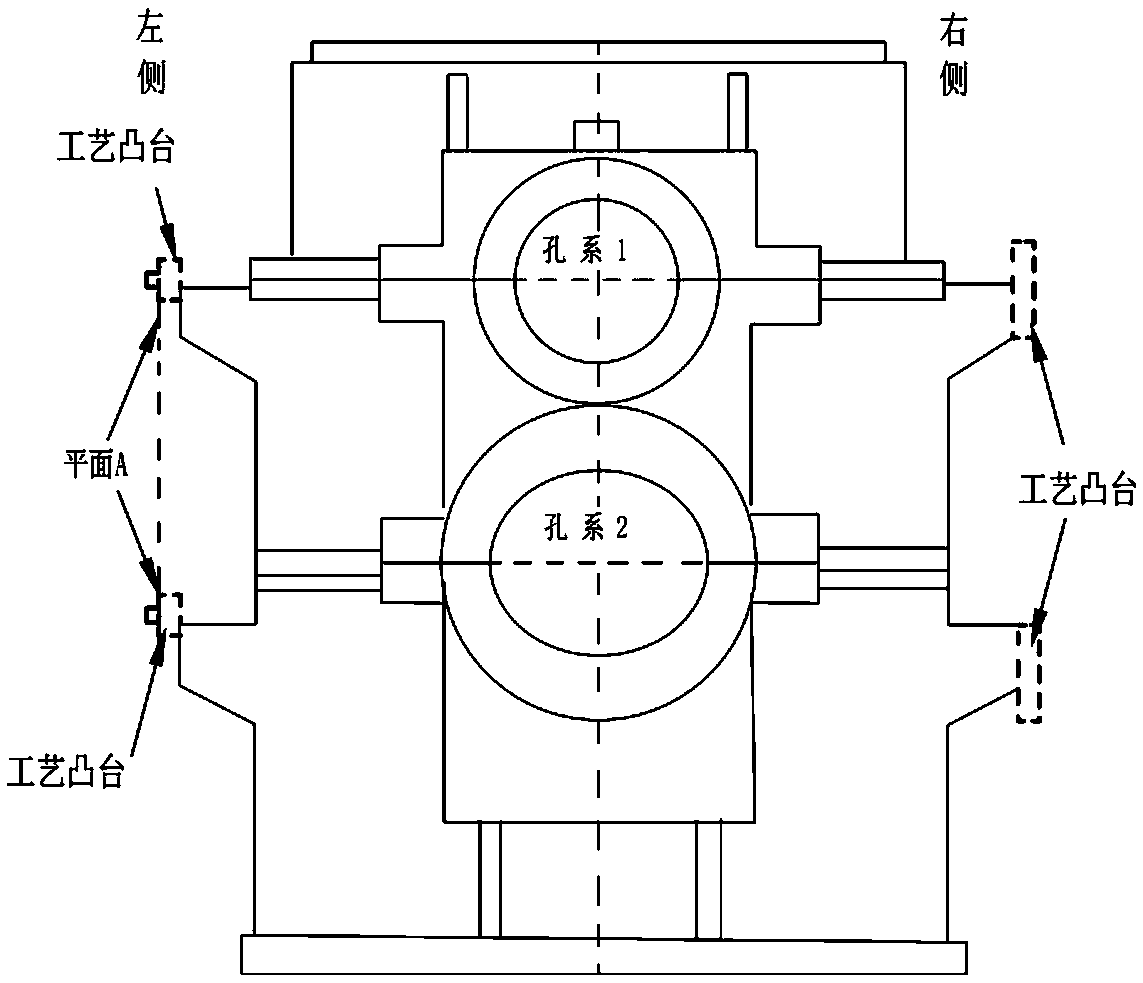
Boring method for machining hole system of crossing angle box body
ActiveCN108788208AExpand the scope of selectionLow requirement for rotation accuracyComputer-aidedComputer aid
The invention relates to a boring method for machining a hole system of a crossing angle box body. The boring method comprises the following steps: (a) a machined support surface or bottom surface ofthe angle box body is taken as a positioning reference, after four pin hole positions are drawn on the hole system by computer-aided software through conversion, two groups of positioning pin holes are machined according to coordinates, and then the plane where the pin holes are located is machined; and cylindrical pins are mounted after machining; (b) the crossing angle box body is re-clamped, and the plane where one set of hole system positioning pins and the pin holes in the set are located is corrected; the clamping mode is maintained, after a spindle is moved downwards, the coordinate ofthe vertical hole system center in the radial direction is set as "zero" position, and the axial starting point of the end face of the box body, i.e., the distance from the center of the pin holes isL1 in size, and the vertical hole system is machined; (c) the worktable angle of a machine tool is rotated to alpha, the plane where the other set of hole system positioning pins and the pin holes inthe set are located is corrected, the clamping mode is maintained, the spindle is moved downwards to the radial coordinate "zero" position of the crossing angle hole system, the axial starting point of the end face of the box body, namely, the distance from the center of the pin holes is L2 in size, and the crossing angle hole system is machined.
Owner:HANGZHOU ADVANCE GEARBOX GRP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com