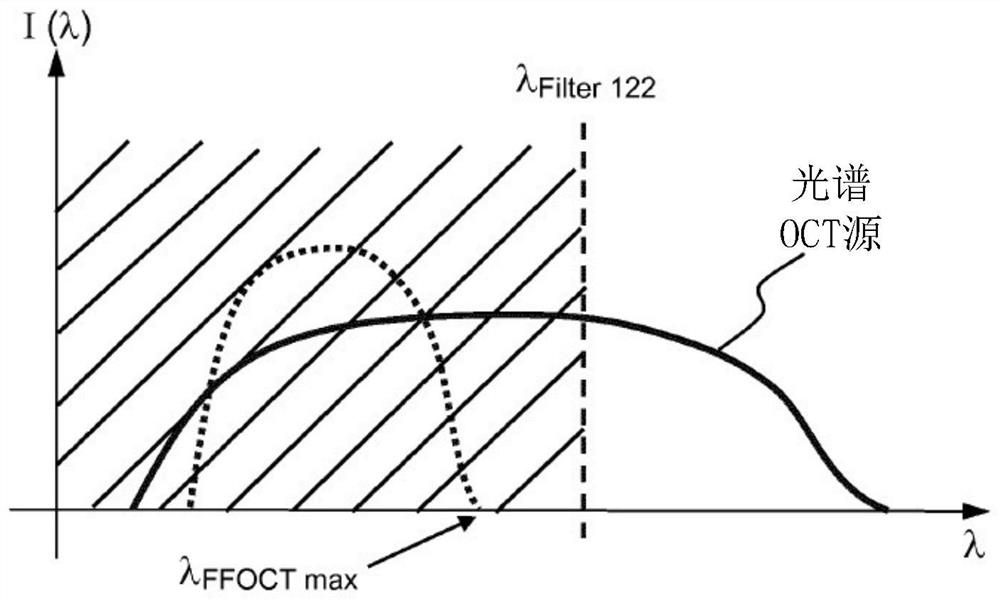
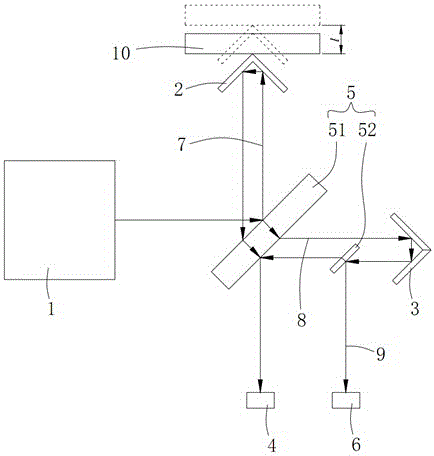
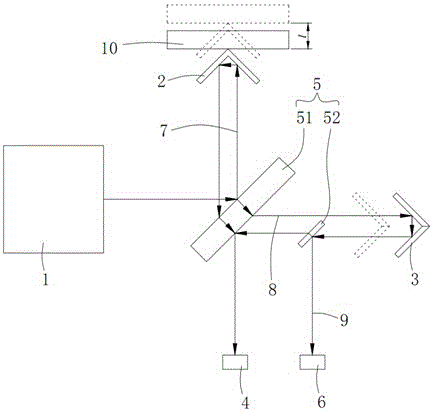
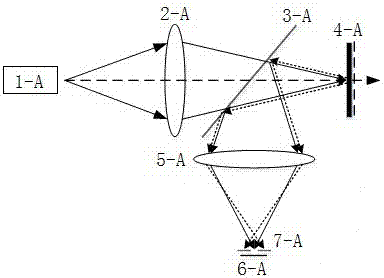
Patents
Literature
49 results about "Interference microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Interference microscopy involving measurements of differences in the path between two beams of light that have been split.
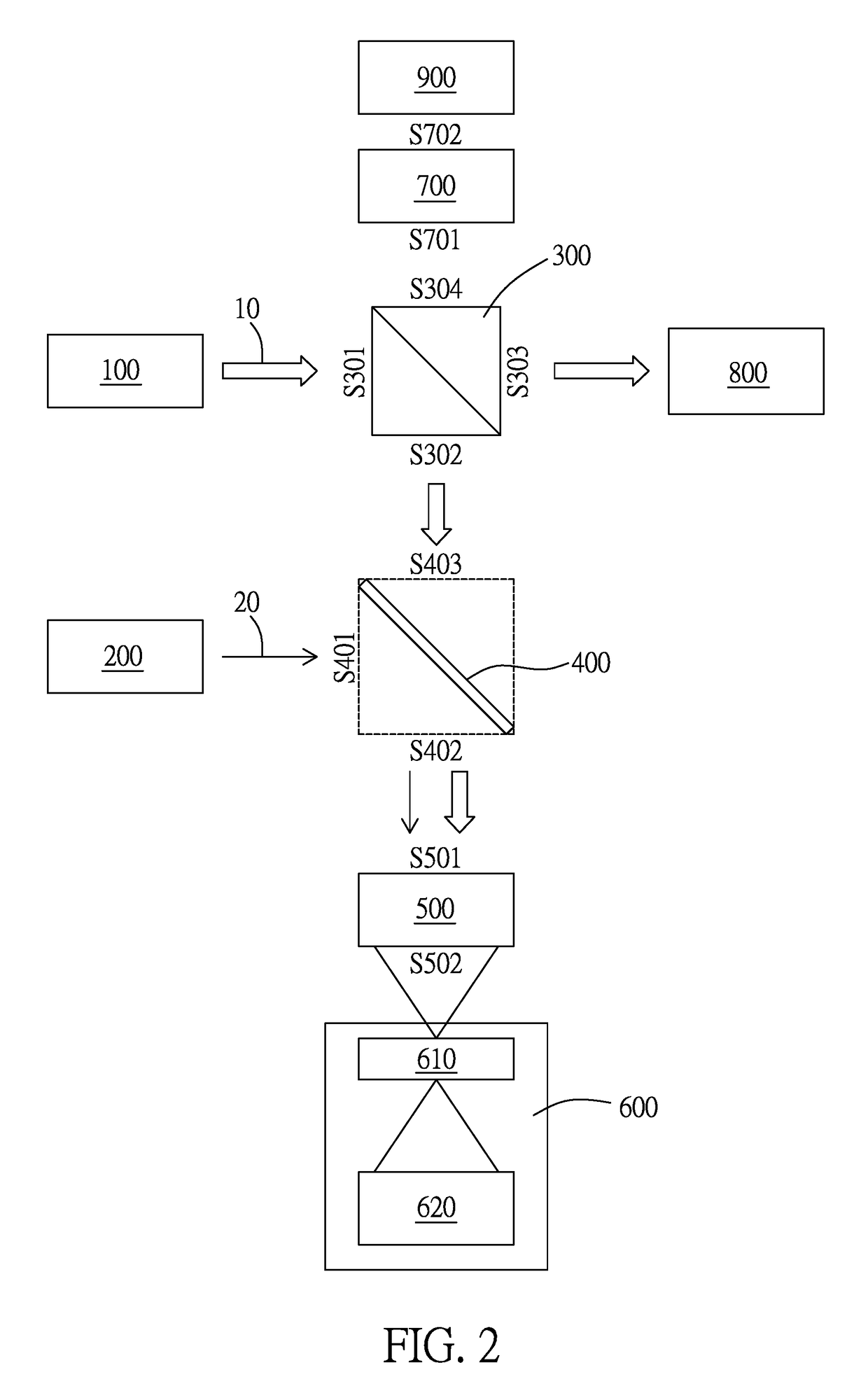
Method for fixing focus and measuring curvature radius by confocal interference
InactiveCN102175426AReduce the impactImprove focus accuracyUsing optical meansTesting optical propertiesOptical measurementsInterference microscopy
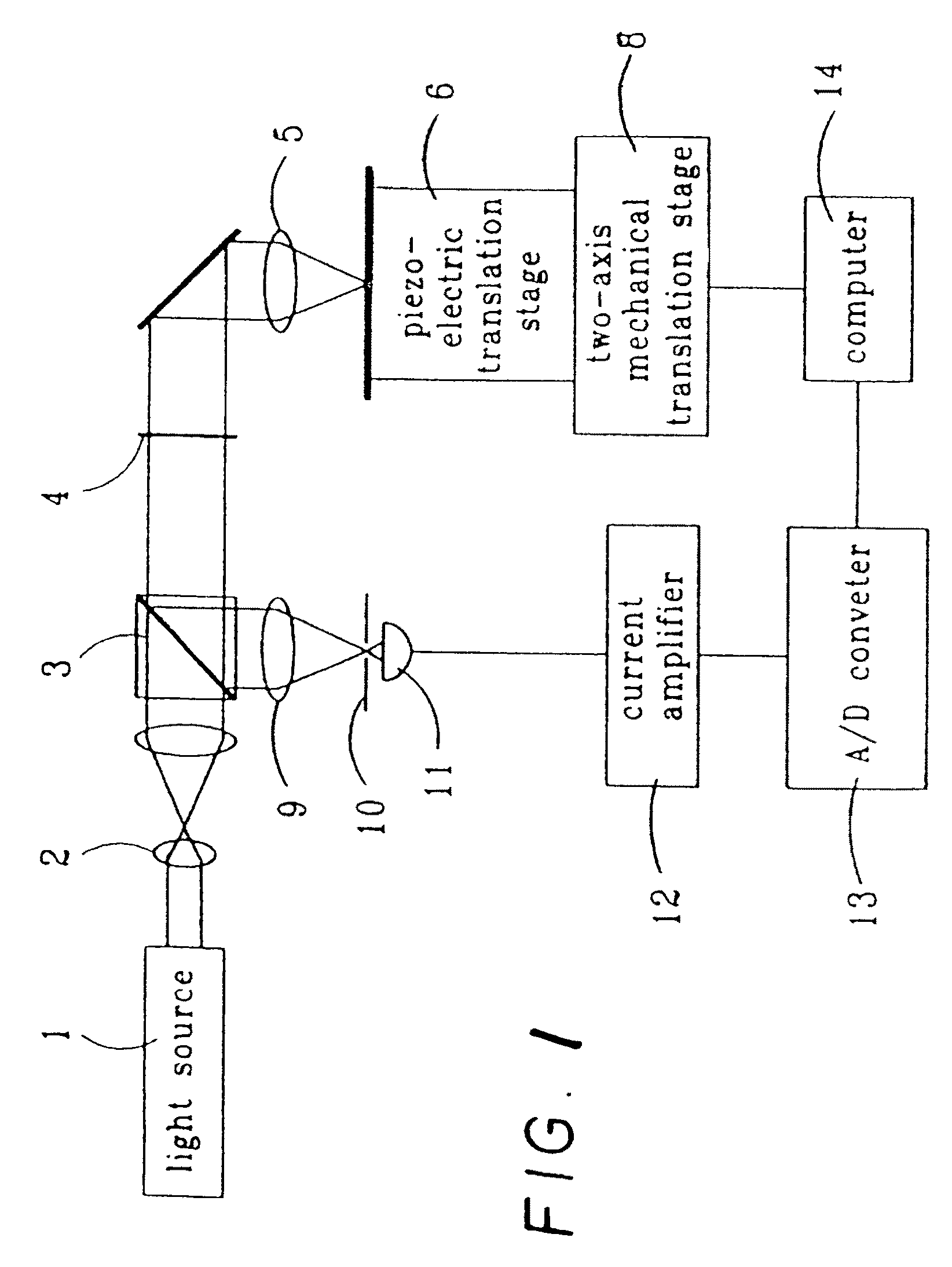
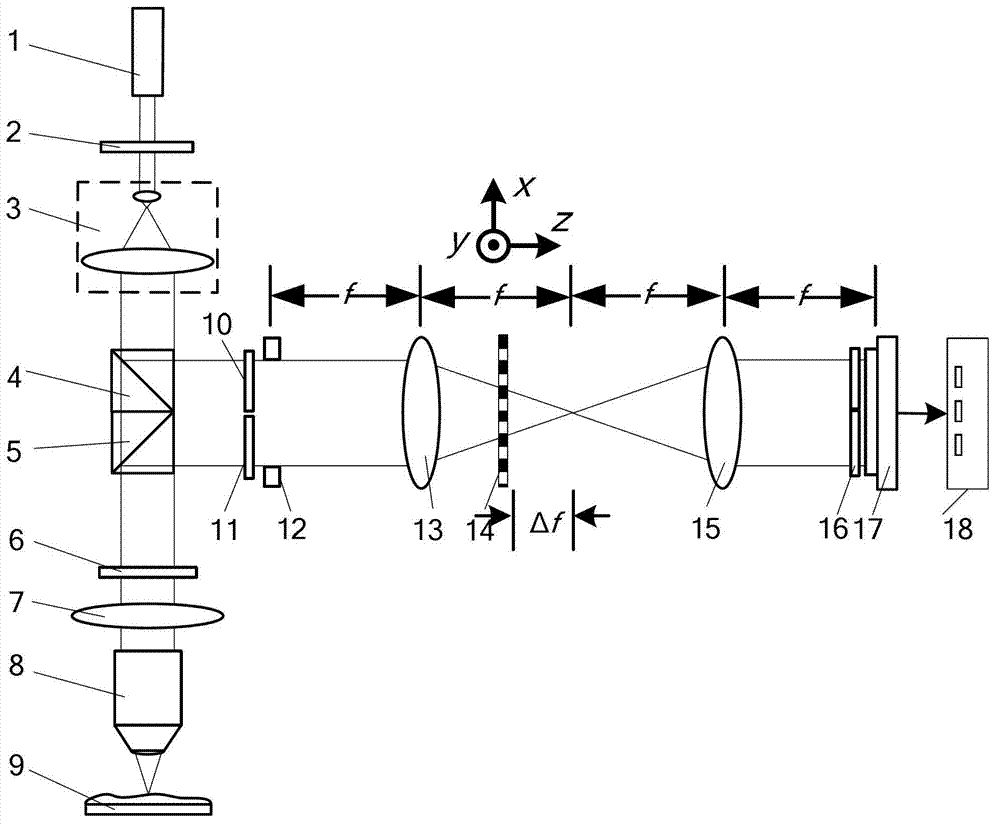
The invention relates to a method for fixing a focus and measuring a curvature radius by confocal interference, and belongs to the technical field of optical precision measurement. The method comprises the following steps of: introducing interfering reference light based on a confocal light path; precisely positioning an apex of the surface of a tested spherical element and a location of the centre of a sphere by using the maximum value of a confocal interference response curve to obtain the curvature radius of the surface of the tested spherical element; and maximumly sharpening a main lobe of the confocal response curve. By the invention, the traditional confocal interference microscopy imaging technique is first applied to improvement on the fixed-focus precision of an optical measuring system, so that the optical measuring system has a higher axial resolution and a simple structure, and the research and development costs of the system device are reduced.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Spatial Light Interference Microscopy and Fourier Transform Light Scattering for Cell and Tissue Characterization
ActiveUS20120105858A1Radiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryFourier opticsFourier transform on finite groups
Methods and apparatus for rendering quantitative phase maps across and through transparent samples. A broadband source is employed in conjunction with an objective, Fourier optics, and a programmable two-dimensional phase modulator to obtain amplitude and phase information in an image plane. Methods, referred to as Fourier transform light scattering (FTLS), measure the angular scattering spectrum of the sample. FTLS combines optical microscopy and light scattering for studying inhomogeneous and dynamic media. FTLS relies on quantifying the optical phase and amplitude associated with a coherent image field and propagating it numerically to the scattering plane. Full angular information, limited only by the microscope objective, is obtained from extremely weak scatterers, such as a single micron-sized particle. A flow cytometer may employ FTLS sorting.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
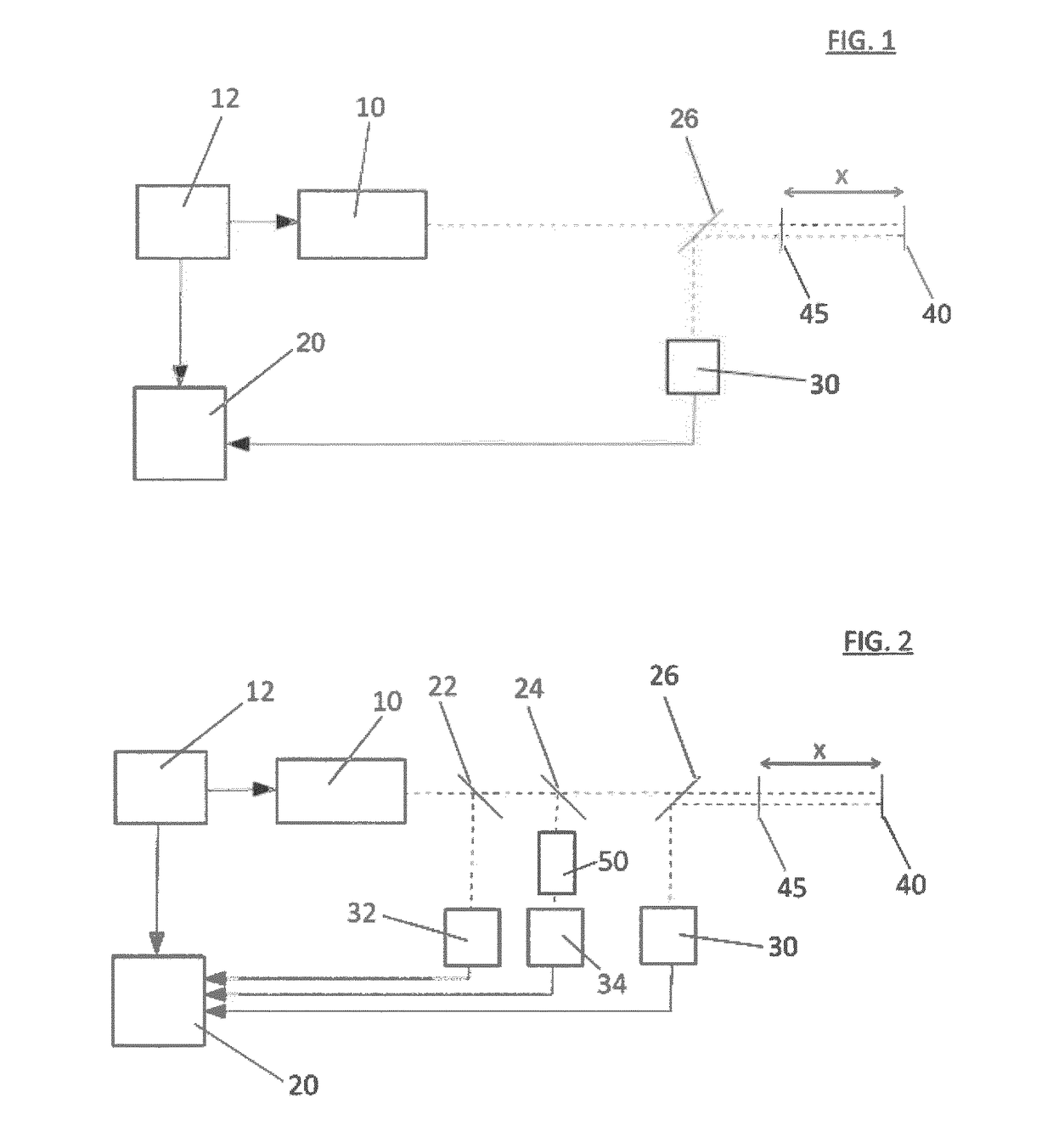
Method and device for high resolution full field interference microscopy
ActiveUS20130107275A1Easy to controlInterferometric spectrometryDiagnostic recording/measuringFull fieldPhase difference
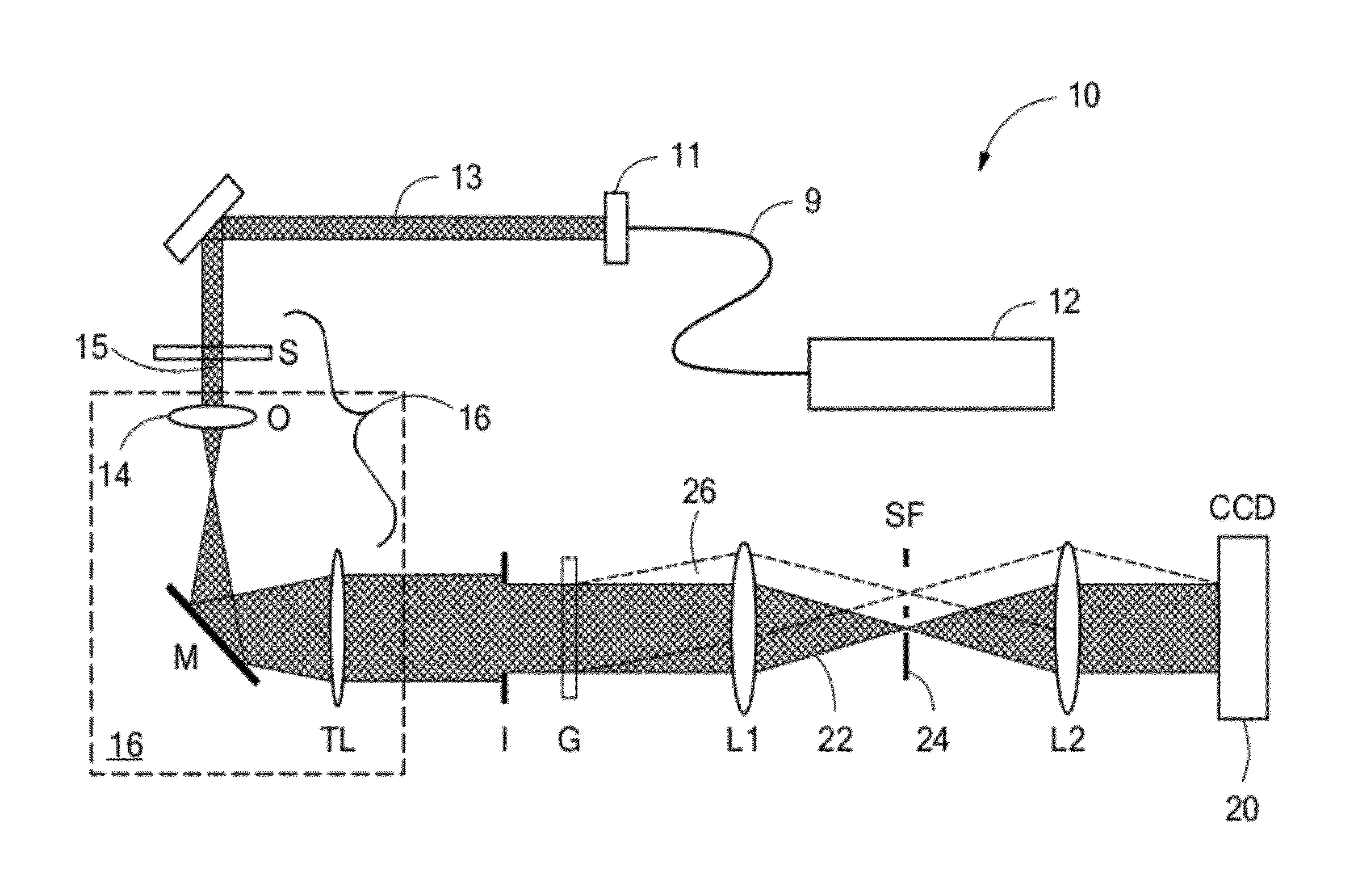
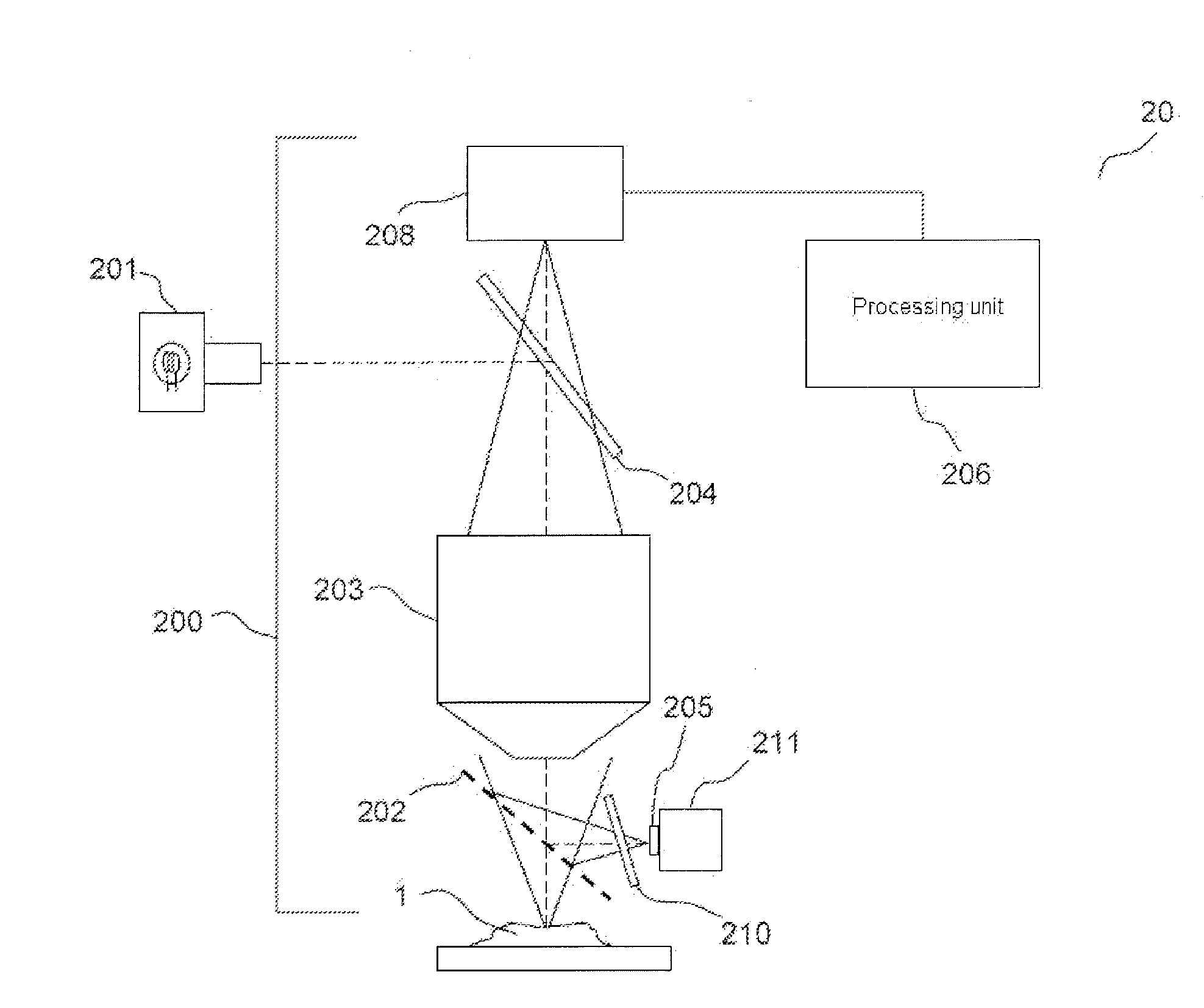
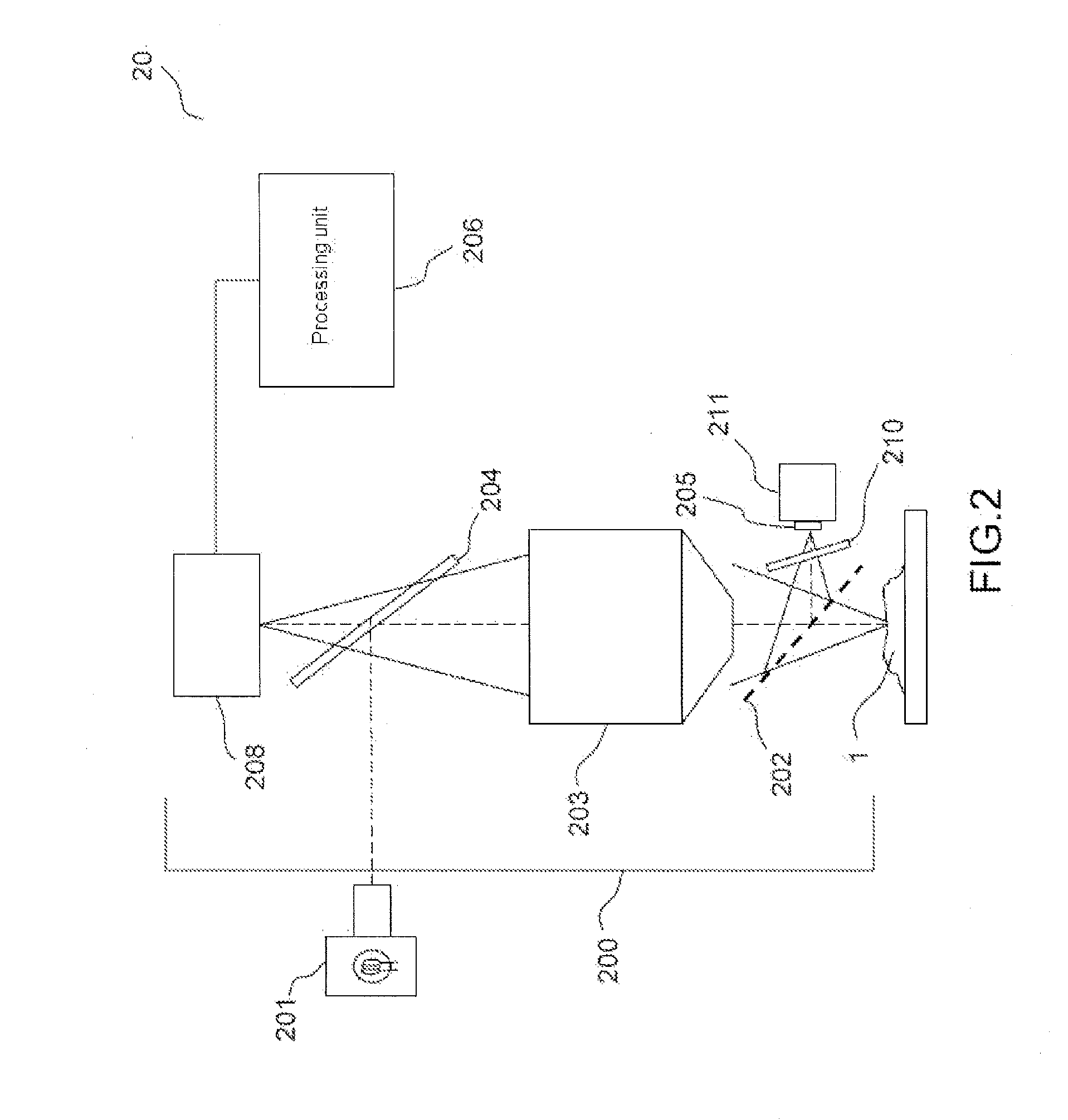
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device (20) for three-dimensional imaging by full-field interferential microscopy of a volumic and scattering sample (1) comprising an emission source (201) for emitting an incident wave with low temporal coherence, an imaging interferometer (200) of variable magnification, allowing for the acquisition of at least one first and one second interferometric images resulting from the interference of a reference wave obtained by reflection of the incident wave on a reference mirror (205) and an object wave obtained by backscattering of the incident wave by a slice of the sample at a given depth of the sample, the at least two interferometric images having a phase difference obtained by varying the relative path difference between the object and reference arms of the interferometer, a processing unit (206) for processing said interferometric images making it possible to obtain a tomographic image of said slice of the sample, means for axially displacing the interferometer relative to the sample allowing for the acquisition of tomographic images for slices at different depths of the sample and means for varying the magnification of the imaging interferometer allowing for the acquisition of interferometric images of a slice of the sample for different magnification values.
Owner:LLTECH MANAGEMENT
Multiple wavelengths real time phase shift interference microscopy
ActiveUS9880377B1Fast displacementFast vibrationPhotometryUsing optical meansUltra high speedPhase shifted
A system microscopy system and method that enable obtaining high resolution 3D images in a single shot are presented. The system is an ultra-high speed, real time multi wavelength phase shift interference microscopy system that uses three synchronized color CCD cameras. Each CCD is equipped with a precision achromatic phase mask which in turn allows obtaining π / 2 phase shifted signals in three different wavelengths simultaneously.
Owner:PHOTONICSYS
Interferometric phase microscopy one-step imaging system and method based on two-step phase shift
The invention discloses an interferometric phase microscopy one-step imaging system and method based on two-step phase shift, and adopts the technical scheme that based on a typical Mach-Zehnder interference light path, lateral displacement beam splitting mirrors are adopted to perform light splitting on sample light and reference light respectively, a wave plate is utilized as a phase shifter, and two interference figures can be acquired at the same time through single exposure, and phase imaging can be realized quickly through corresponding phase recovery operation, and a spatial form structure of a phase body is further deconstructed. The interferometric phase microscopy one-step imaging system and method are suitable for all interferometric phase microscopy imaging systems, such as traditional coaxial interference, off-axis interference and slight off-axis interference, and have high practical value and wide application prospect in the aspect of phase microscopy, particularly in the field of application and identification of biological cell morphology.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Light-splitting synchronous phase shifting interference microscopy device and detection method
The invention discloses a light-splitting synchronous phase shifting interference microscopy device and a detection method, belonging to the field of the optical interference detection. The invention aims to solve the problems of difficulty and complexity in operation and low measurement precision of the traditional optical phase shifting interference detection method. The scheme is that a light beam emitted from a light source is divided into an object light beam and a reference light beam, of which the polarization directions are mutually vertical, after passing through a polarizing film and a first polarization light splitting prism; after gathered by a second polarization light splitting prism, the object light beam and the reference light beam successively pass through a lambda / 4 wave plate, a rectangular window, a first Fourier lens, a one-dimensional period grating, a second Fourier lens, a depolarization light splitting prism and a four-quadrant polarizing film group; a polarization light beam emitted from the four-quadrant polarizing film group generates an interference pattern on the plane of an image sensor; the collected interference pattern is processed by a computer; and the phase distribution of an object to be detected is obtained.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
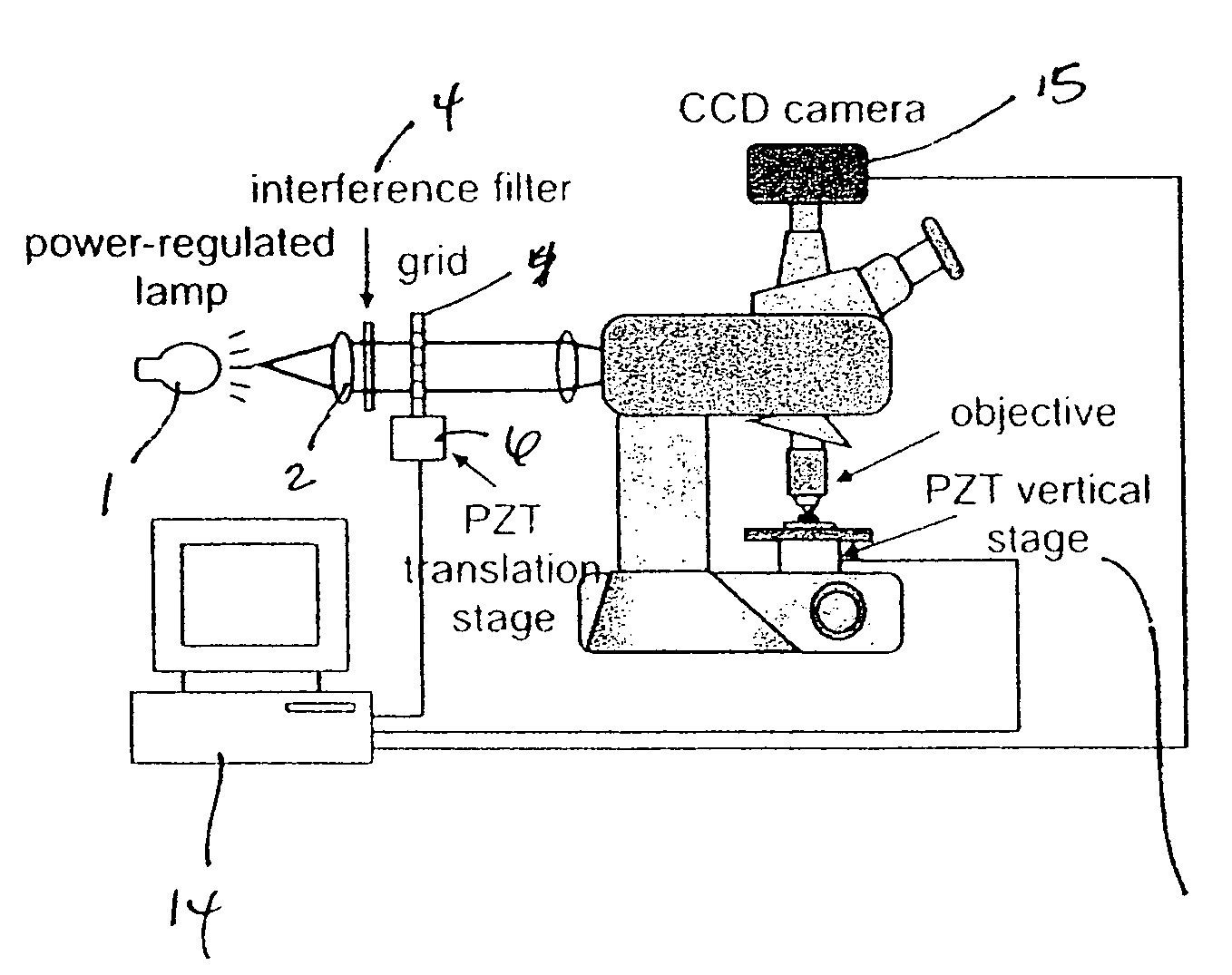
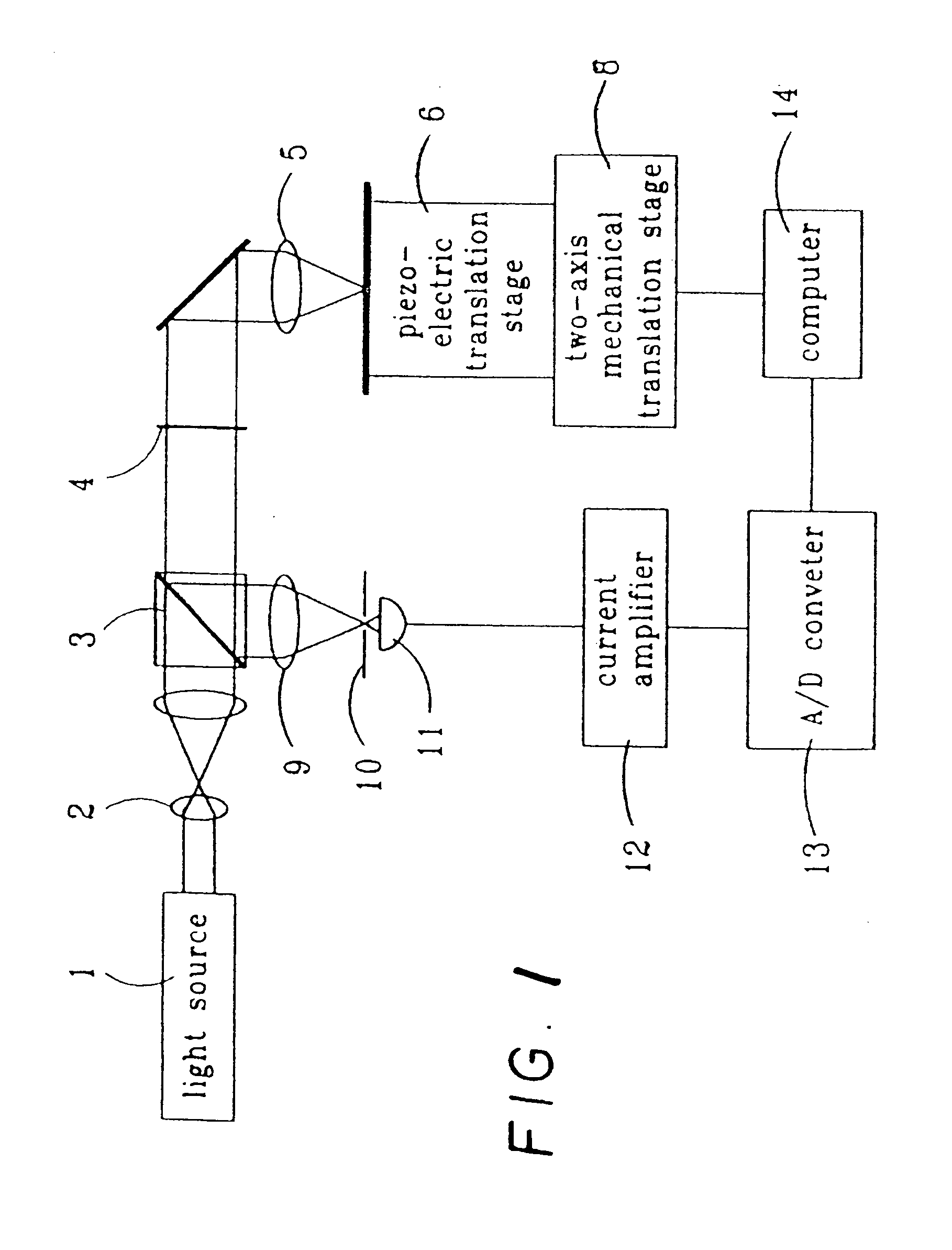
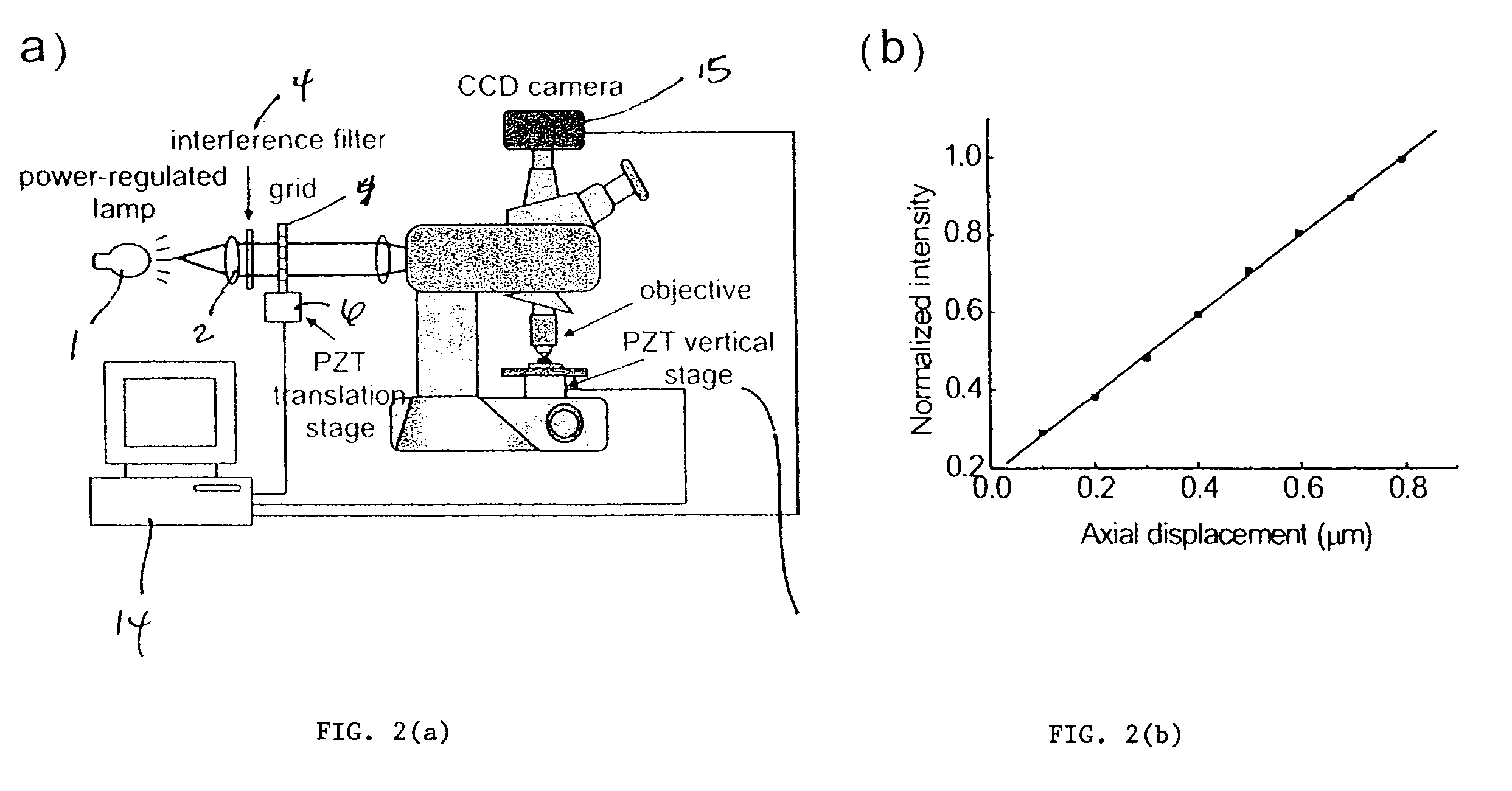
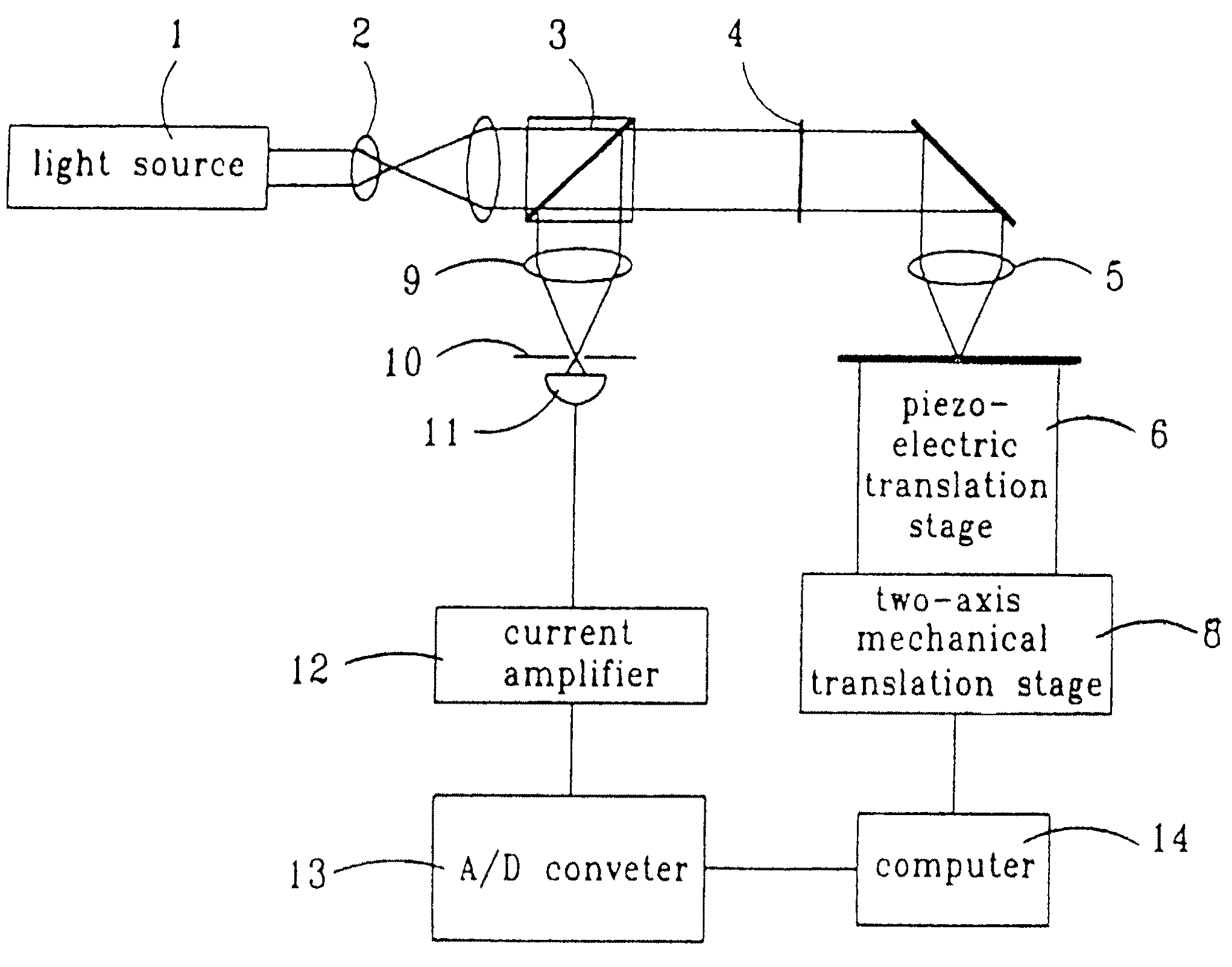
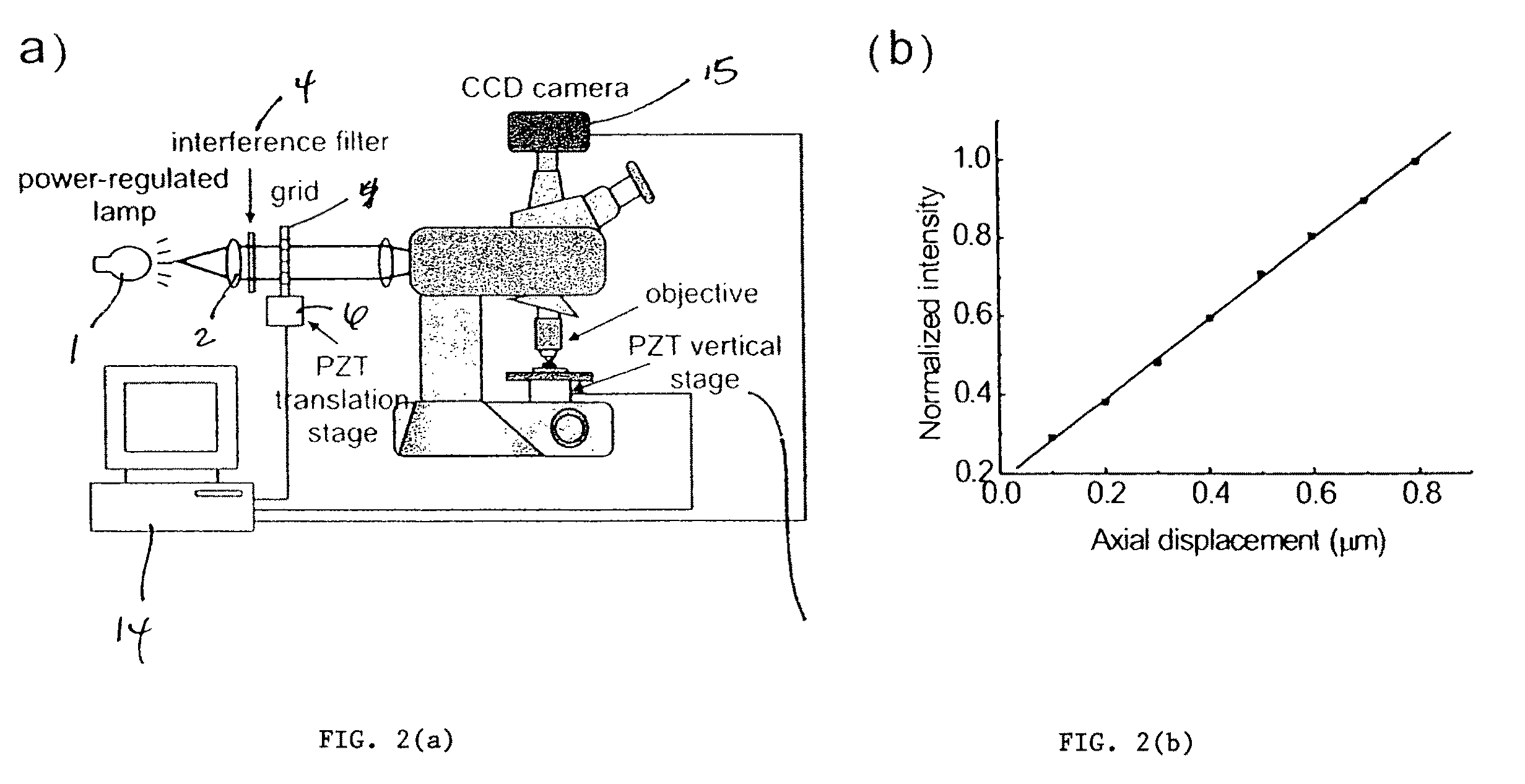
Method for characterizing transparent thin-films using differential optical sectioning interference microscopy
InactiveUS20080266548A1Easy constructionEasy CalibrationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePhase-affecting property measurementsLinear regionImage resolution
An imaging, differential optical sectioning interference microscopy (DOSIM) system and method for measuring refractive indices and thicknesses of transparent thin-films. The refractive index and thickness are calculated from two interferometric images of the sample transparent thin-film having a vertical offset that falls within the linear region of an axial response curve of optically sectioning microscopy. Here, the images are formed by a microscope objective in the normal direction, i.e., in the direction perpendicular to the latitudinal surface of the thin-film. As a result, the lateral resolution of the transparent thin-film is estimated based on the Rayleigh criterion, 0.61λ / NA.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Method of characterizing transparent thin-films using differential optical sectioning interference microscopy
InactiveUS7545510B2Easy constructionEasy CalibrationAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influencePhase-affecting property measurementsLinear regionImage resolution
An imaging, differential optical sectioning interference microscopy (DOSIM) system and method for measuring refractive indices and thicknesses of transparent thin-films. The refractive index and thickness are calculated from two interferometric images of the sample transparent thin-film having a vertical offset that falls within the linear region of an axial response curve of optically sectioning microscopy. Here, the images are formed by a microscope objective in the normal direction, i.e., in the direction perpendicular to the latitudinal surface of the thin-film. As a result, the lateral resolution of the transparent thin-film is estimated based on the Rayleigh criterion, 0.61λ / NA.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
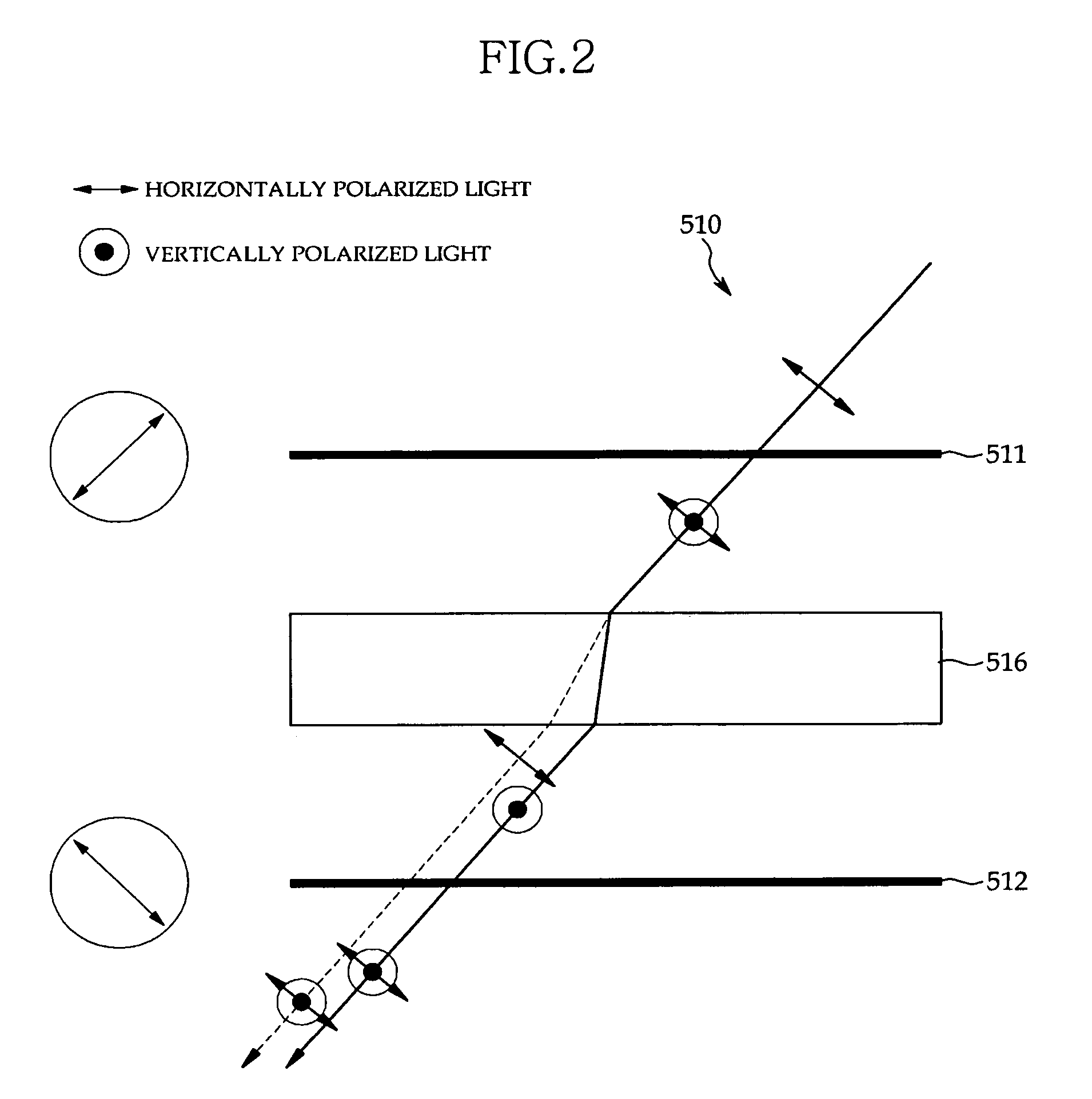
Confocal self-interference microscopy from which side lobe has been removed
The present invention relates to confocal self-interference microscopy. The confocal self-interference microscopy further includes a first polarizer for polarizing reflected or fluorescent light from a specimen, a first birefringence wave plate for separating the light from the first polarizer into two beams along a polarizing direction, a second polarizer for polarizing the two beams from the first birefringence wave plate, a second birefringence wave plate for separating the two beams from the second polarizer into four beams along the polarizing direction, and a third polarizer for polarizing the four beams from the second birefringence wave plate, in the existing confocal microscopy. Optic-axes of the first and second birefringence wave plates exist on the same plane, optic-axes of the first and second birefringence wave plates are inclined from an optical axis of the entire optical system at a predetermined angle, and self-interference spatial periods of the first and second birefringence wave plates are different from each other.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Driving system for light-emitting diode
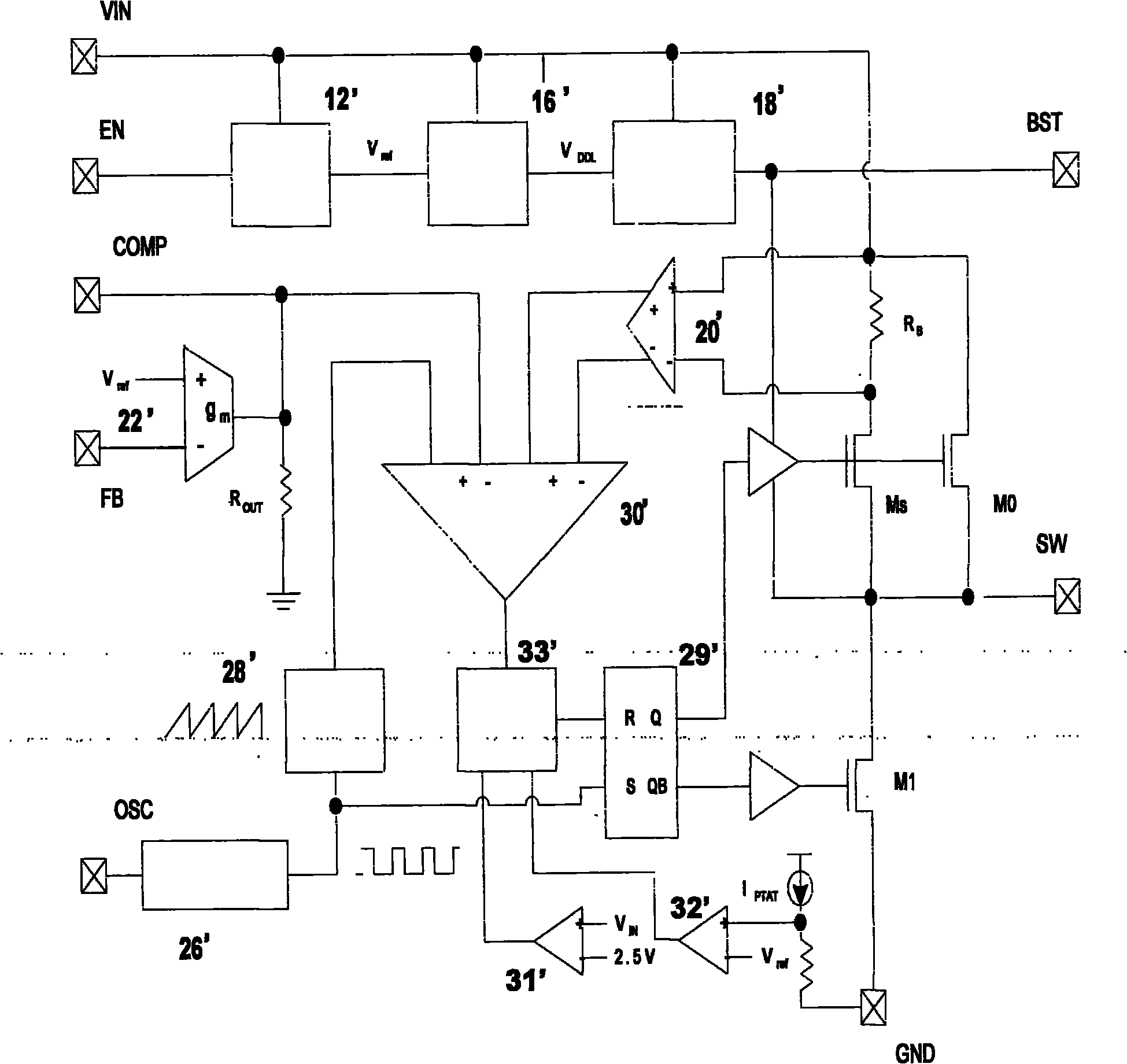
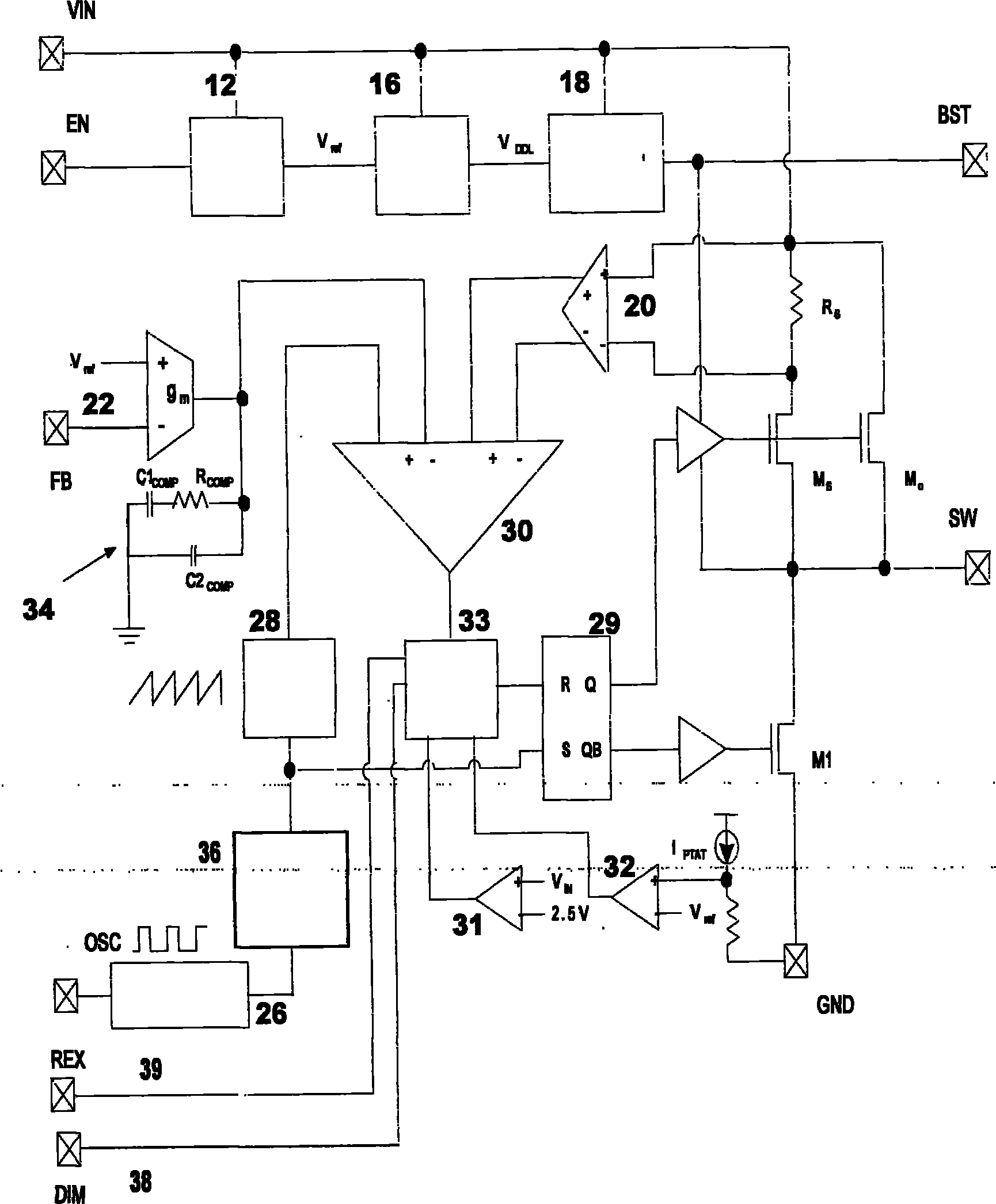
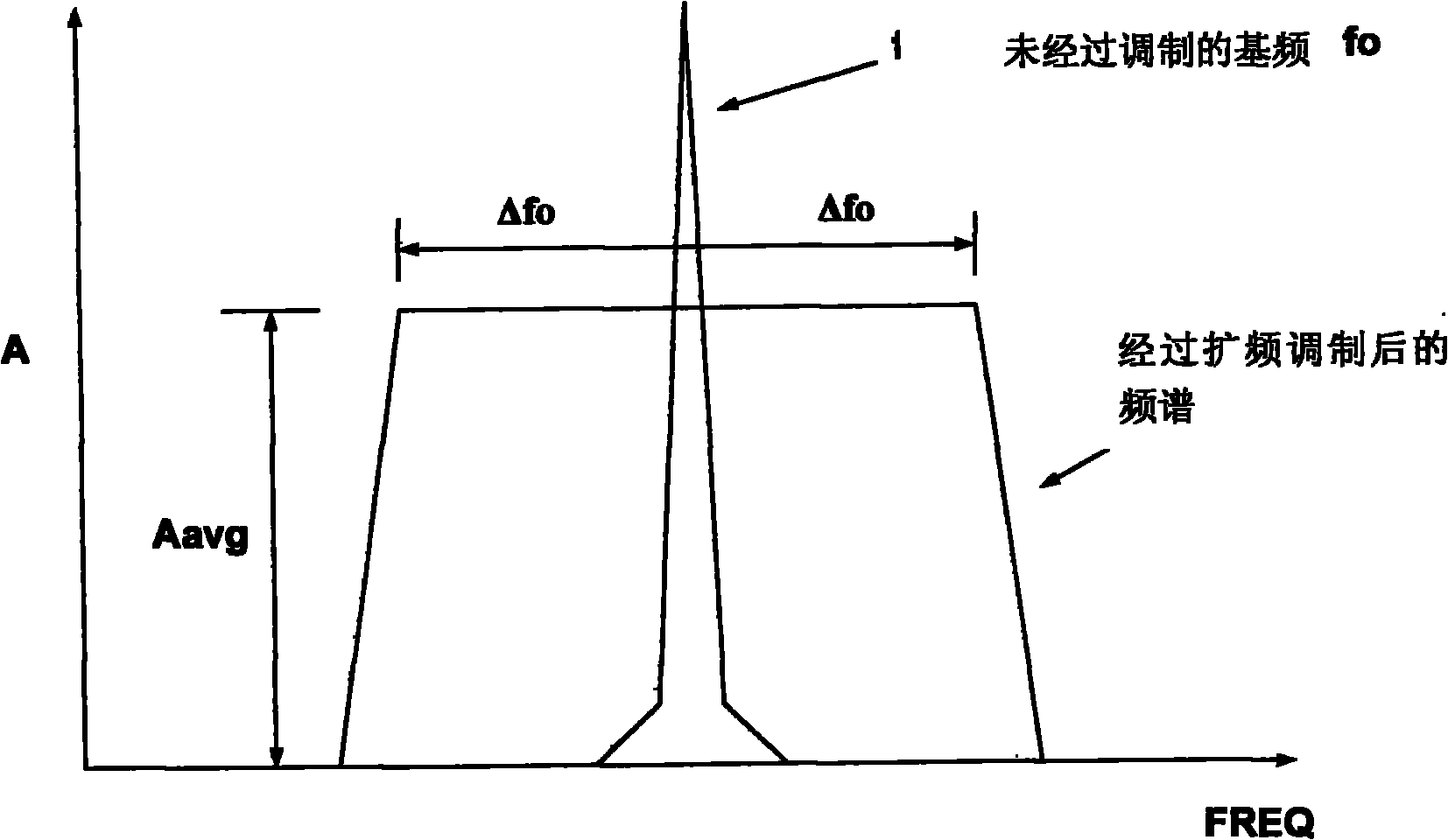
ActiveCN101917807AReduce electromagnetic noiseImprove efficiencyElectric light circuit arrangementEnergy saving control techniquesInterference microscopySystem stability
The invention relates to a driving system for a light-emitting diode. The driving system is provided with an internal compensation module, a spread spectrum modulation module, a differential interference microscopy (DIM) pin and a frequency real-time executive (REX) pin, wherein the DIM pin is driven by an external logic pulse-modulated signal; and the frequency REX pin changes an internal clock of the light-emitting diode through an external resistor. The system has the advantages of realizing system stability by an internal compensation method, saving external components, effectively reducing electromagnetic noise by spread spectrum modulation, improving the efficiency of the driving system for the light-emitting diode by adopting a dimming function, achieving a heat compensation function, enhancing the reliability of the driving system for the light-emitting diode and changing the internal oscillation efficiency of the driving system for the light-emitting diode from outside by external frequency modulation.
Owner:GIANTEC SEMICON LTD
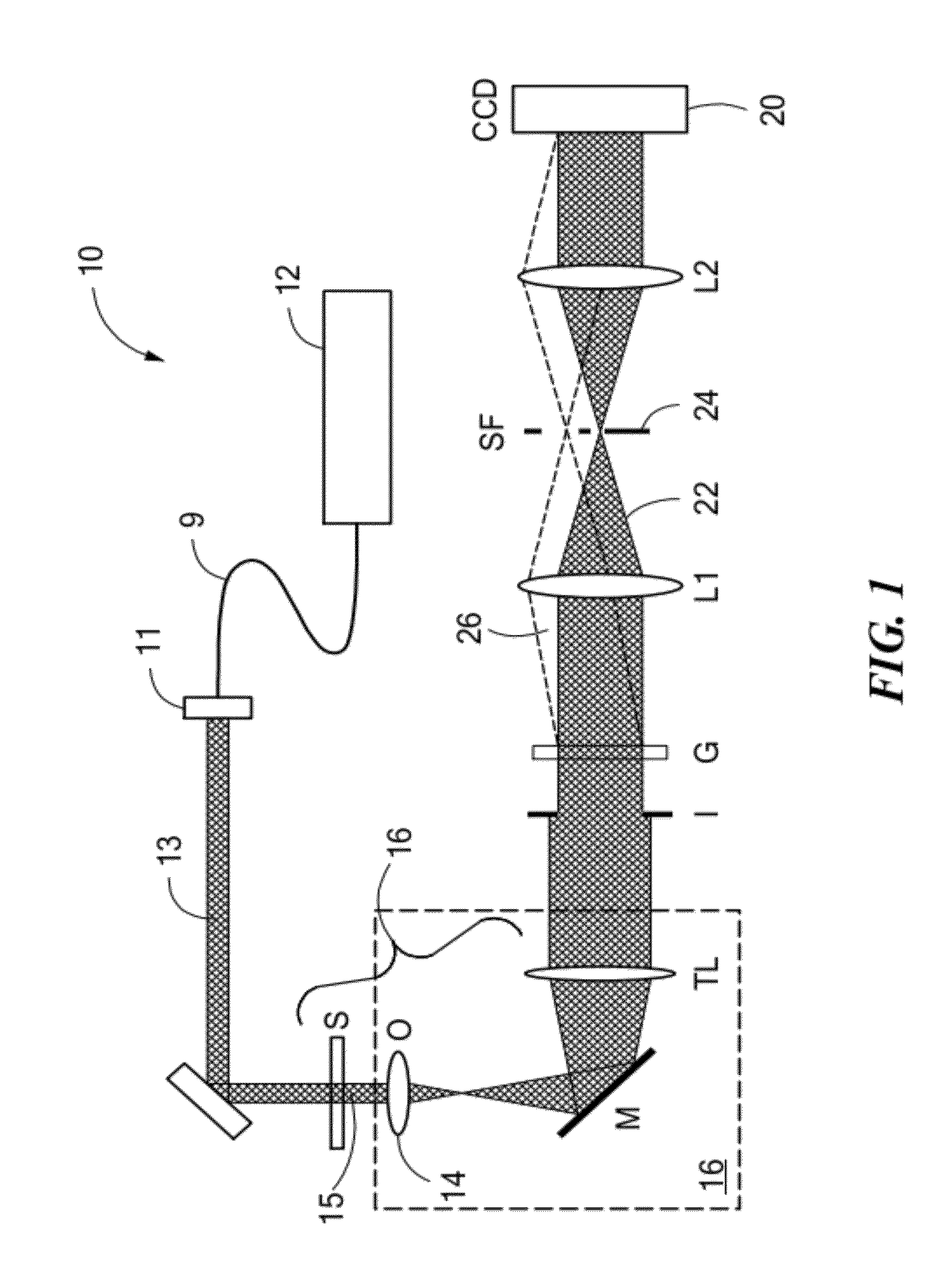
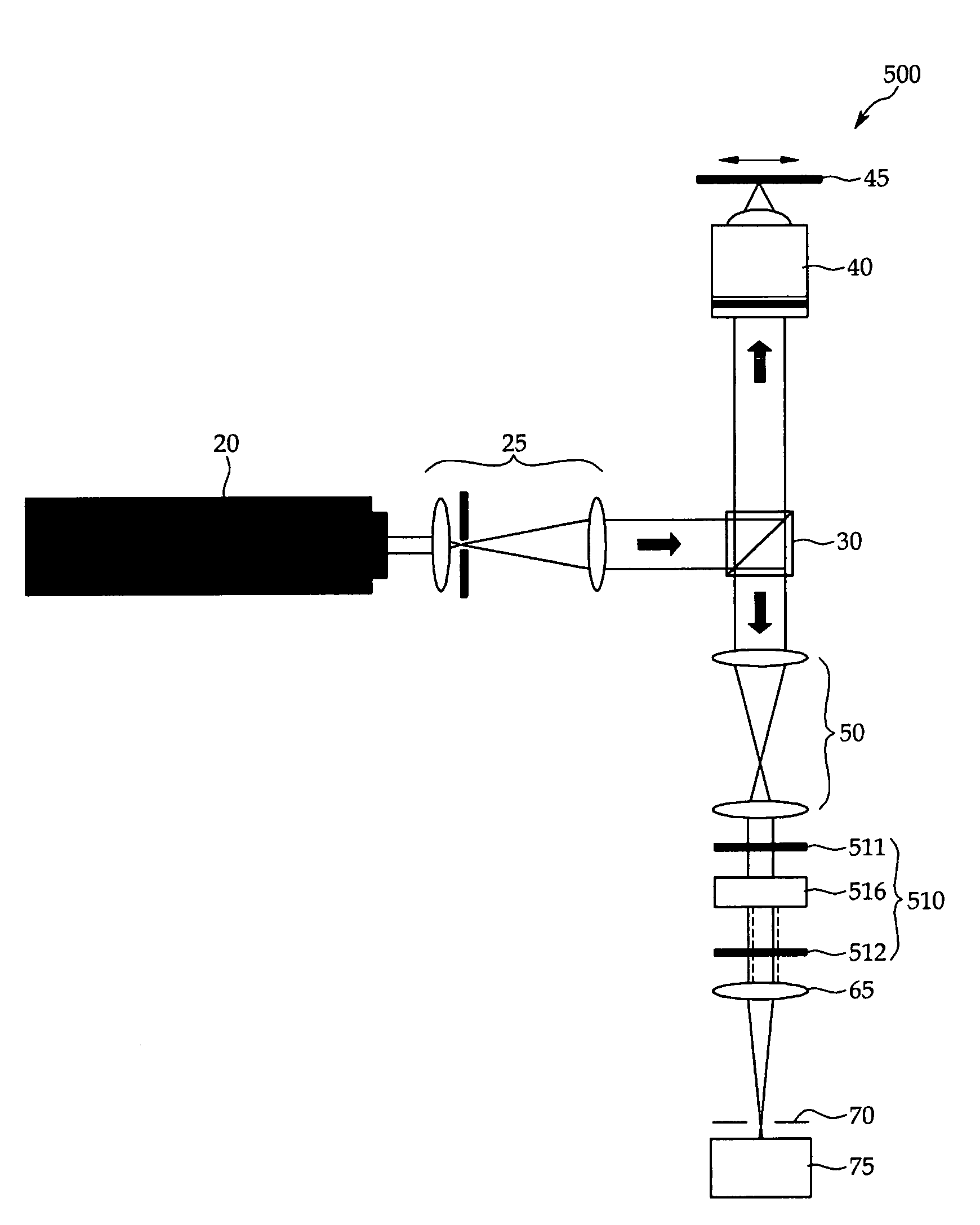
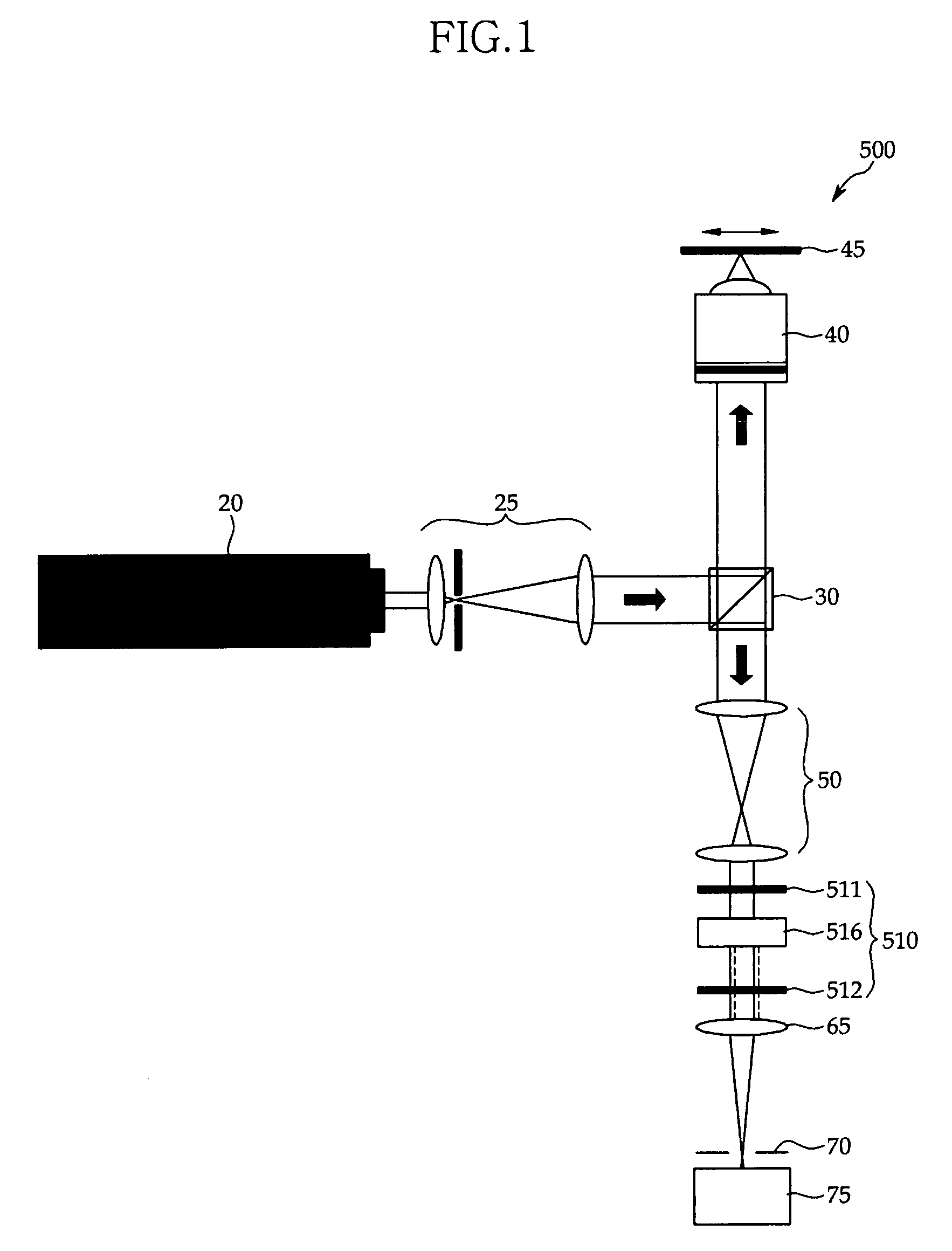
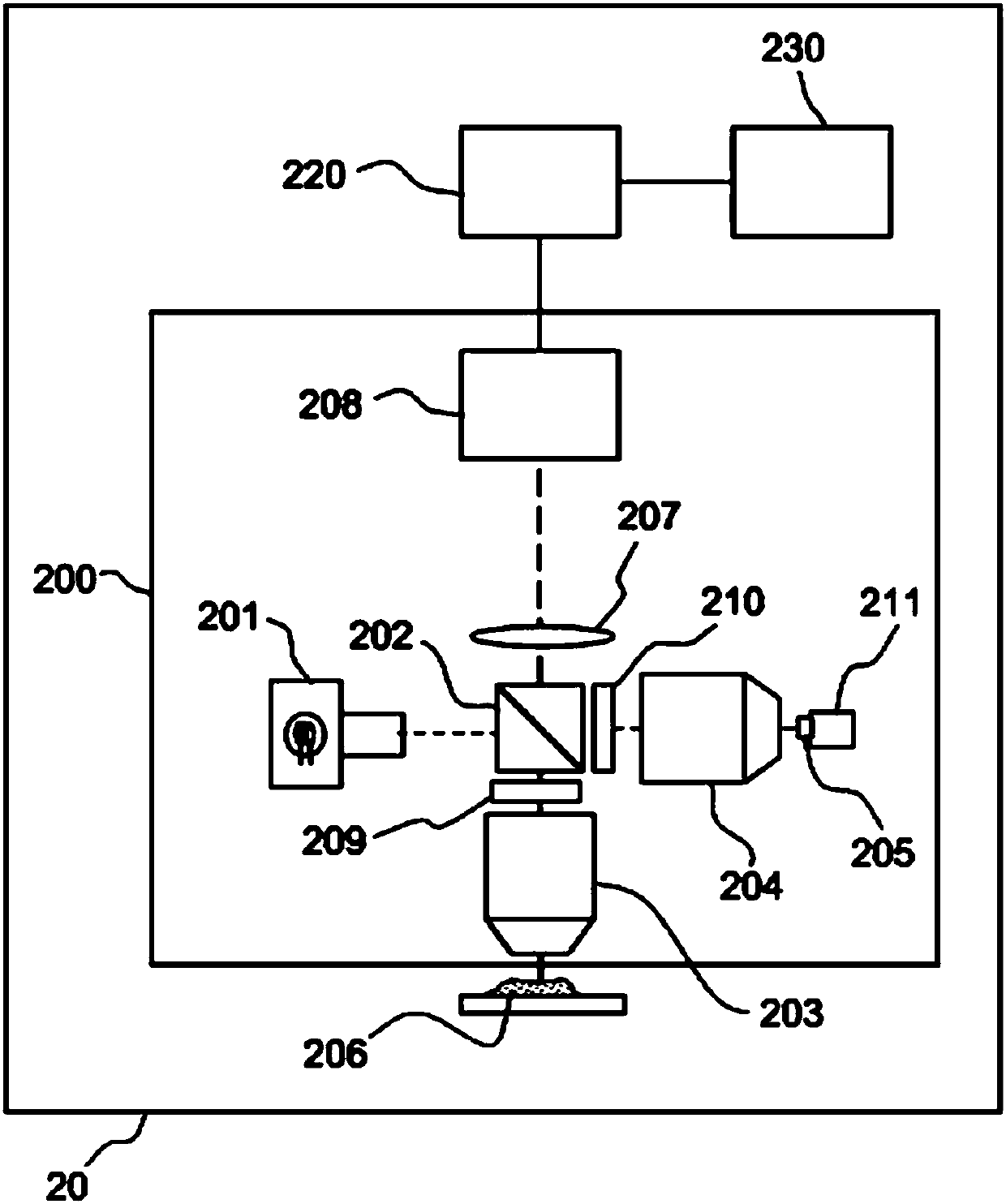
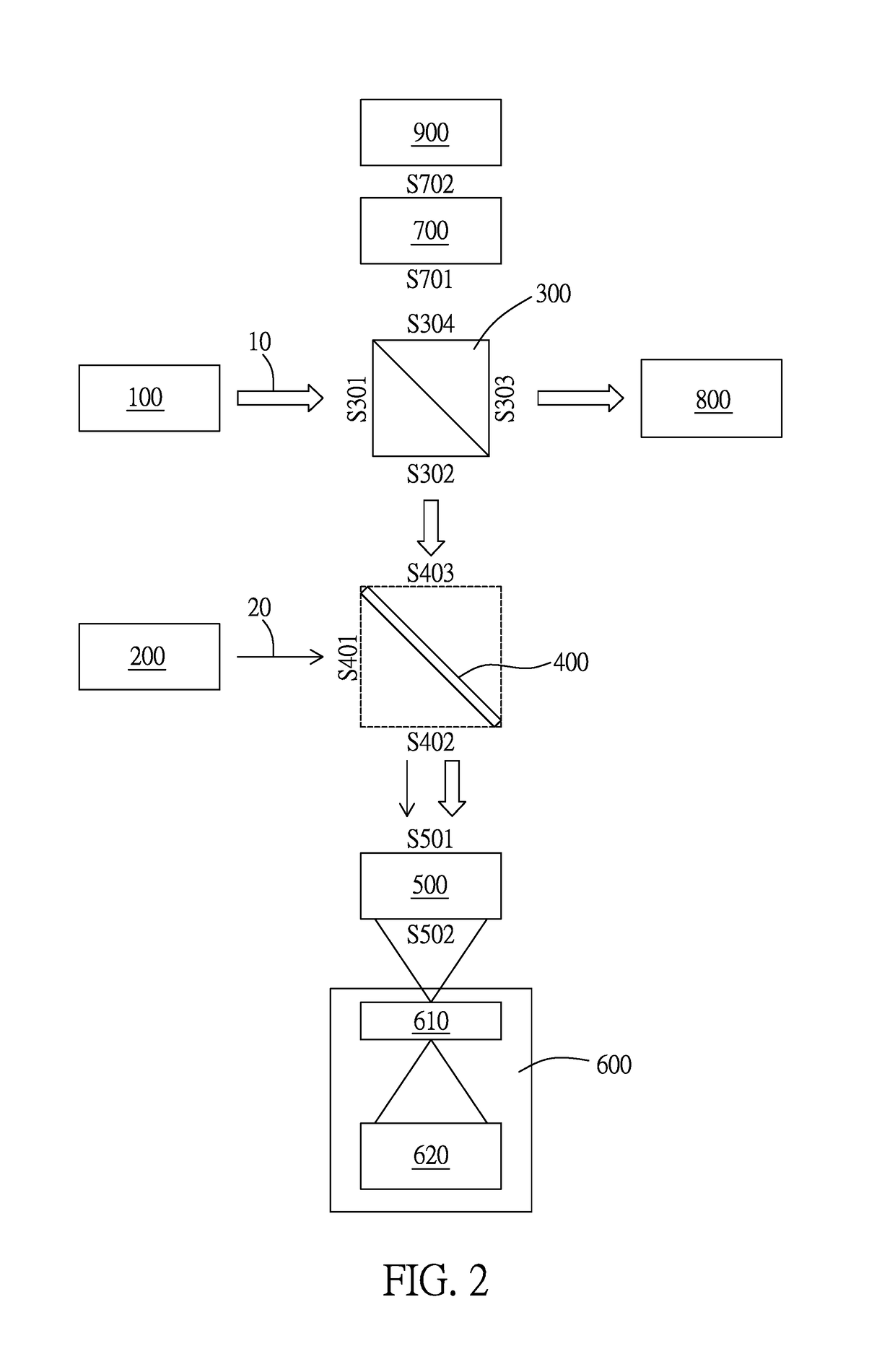
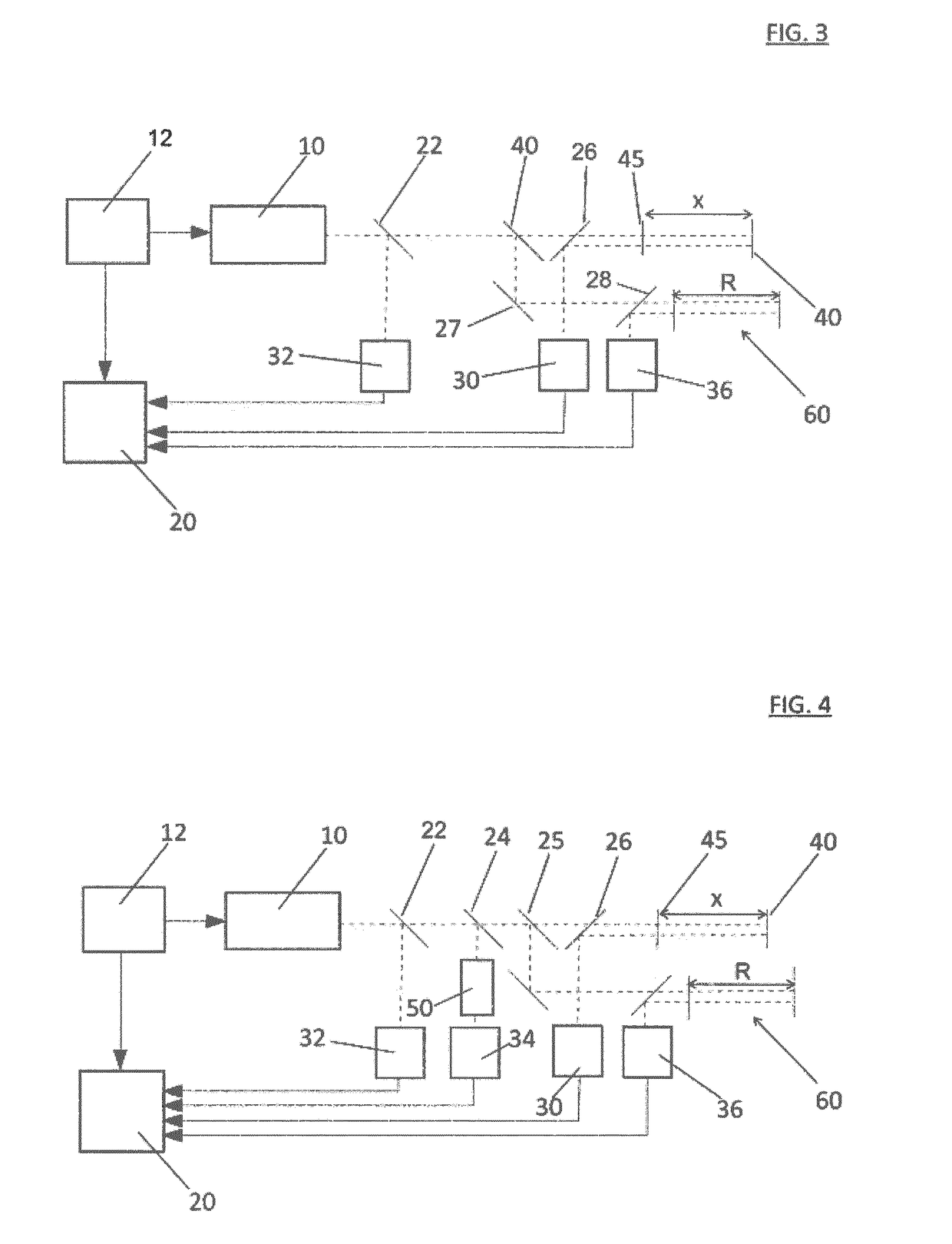
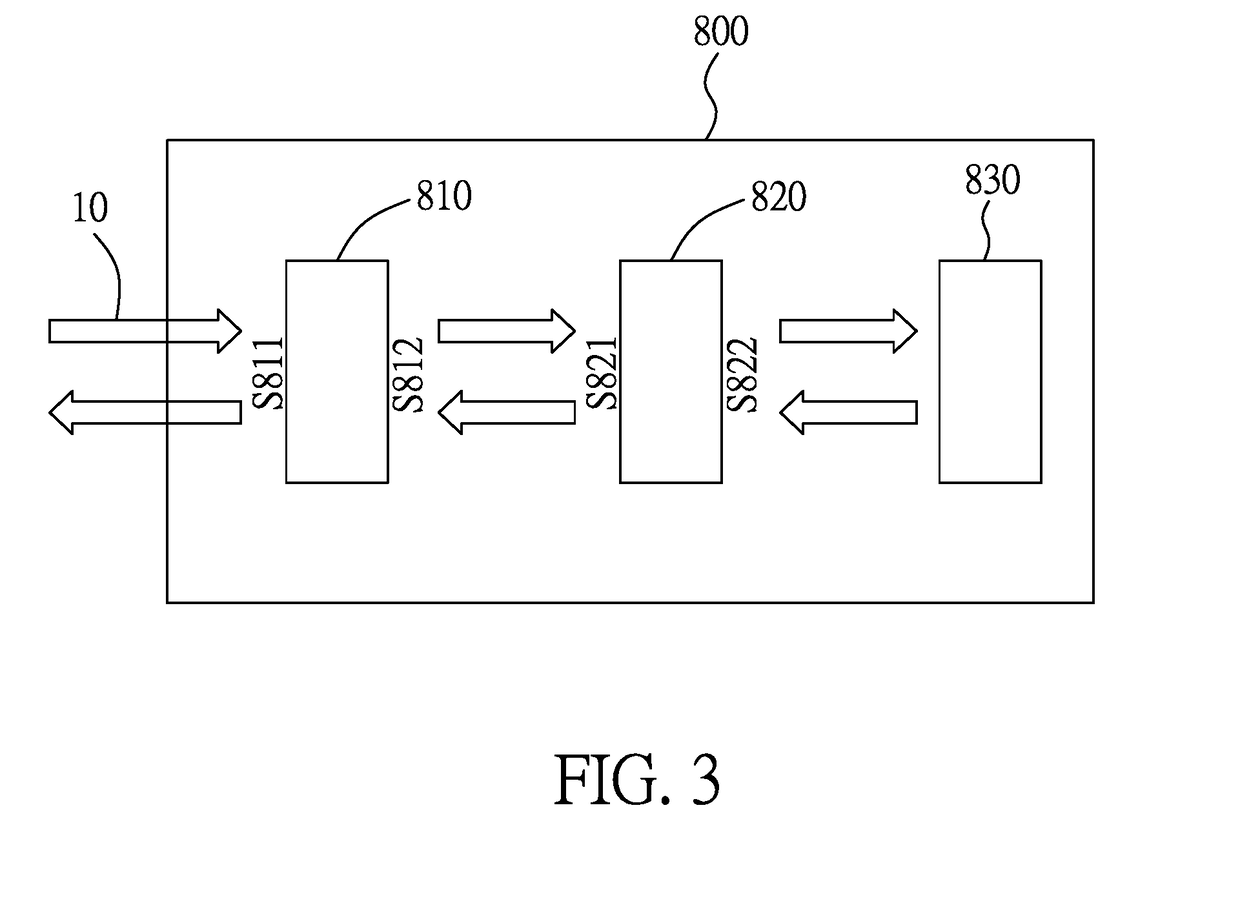
Method and system for full-field interference microscopy imaging
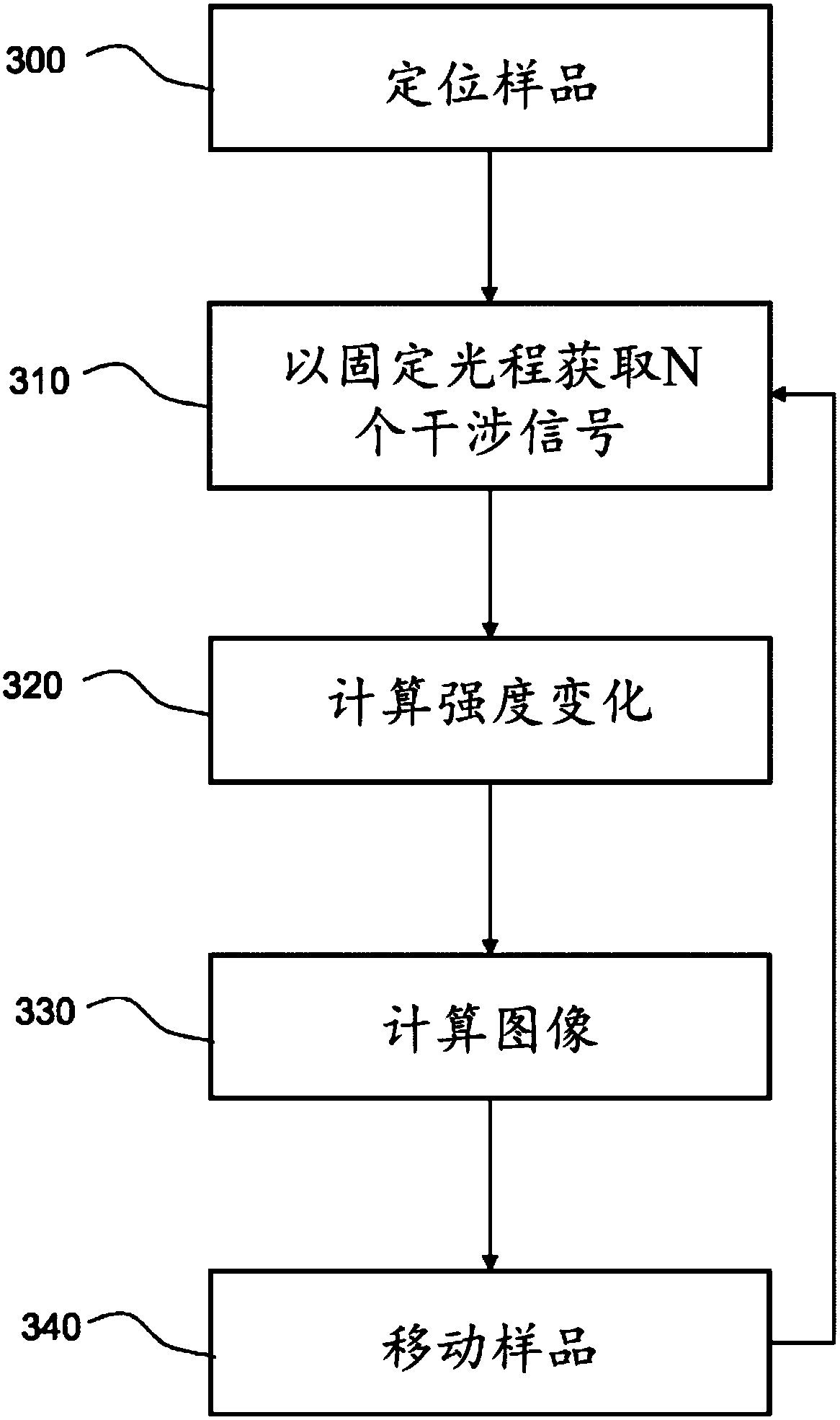
The invention relates to a system (20) for full-field interference microscopy imaging of a three-dimensional diffusing sample (206). Said system includes: an interference device (200) including a reference arm on which a reflective surface (205) is arranged, the interference device being suitable for producing, at each point of an imaging field when the sample is placed on a target arm of the interference device, interference between a reference wave, obtained by reflection of incident light waves onto a basic surface of the reflective surface (205) corresponding to said point of the imaging field, and a target wave obtained by backscattering of incident light waves by means of a voxel of a slice of the sample at a given depth, said voxel corresponding to said point of the imaging field; an acquisition device (208) suitable for acquiring, at a fixed path length difference between the target arm and the reference arm, a temporal series of N two-dimensional interferometric signals resulting from the interference produced at each point of the imaging field; and a processing unit (220) configured to calculate an image (IB, IC) representing temporal variations in intensity between saidN two-dimensional interferometric signals.
Owner:エルエルテックマネージメント
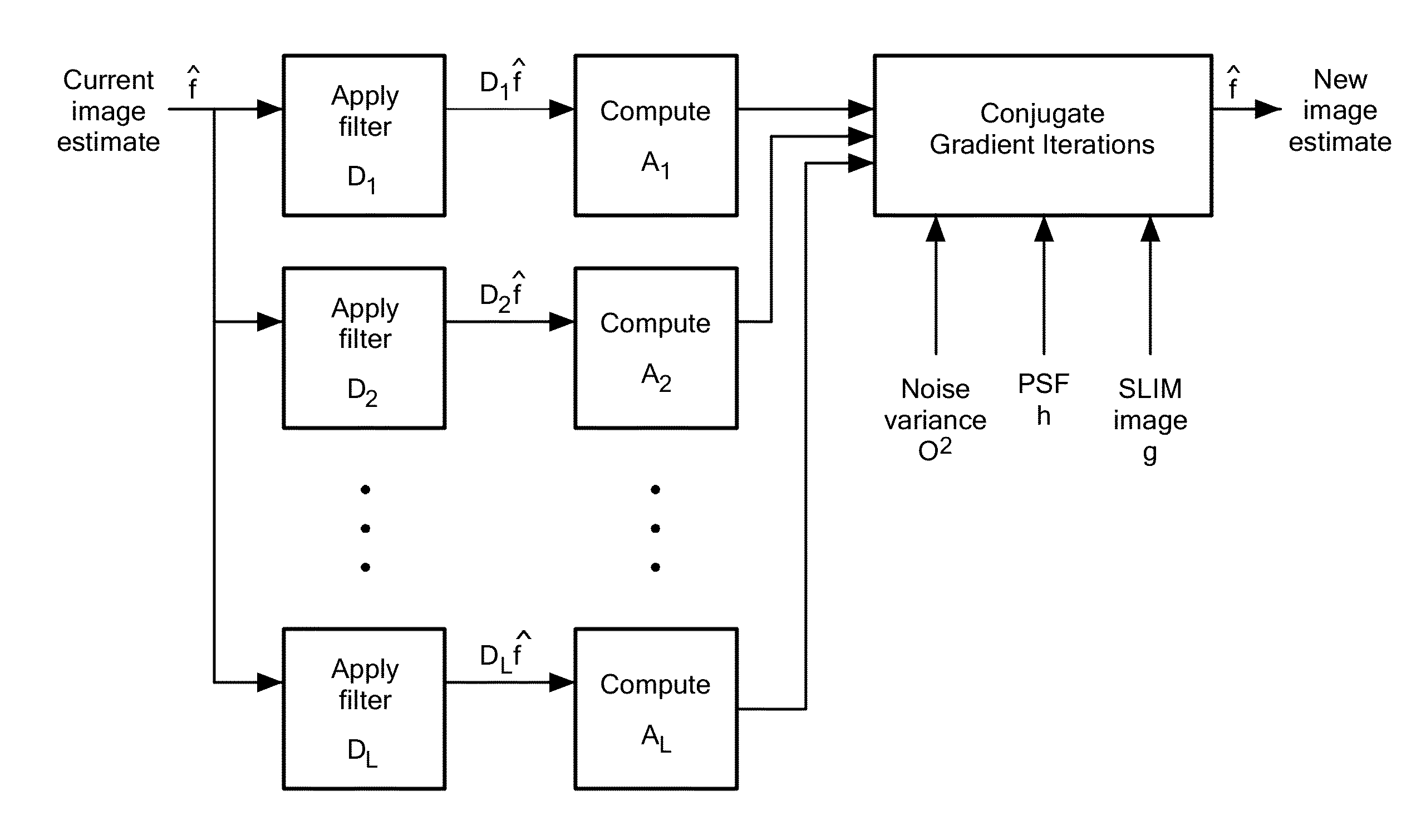
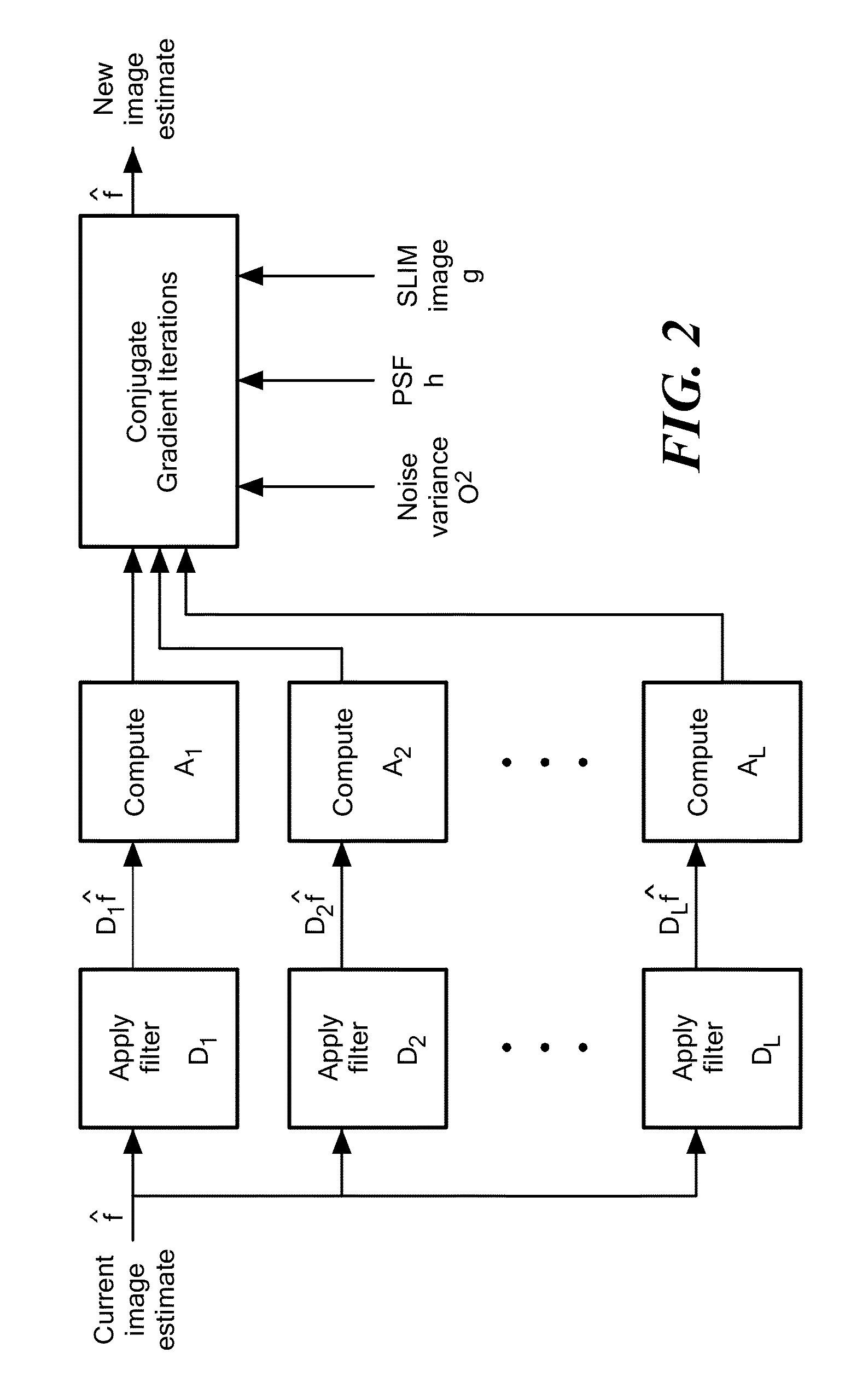
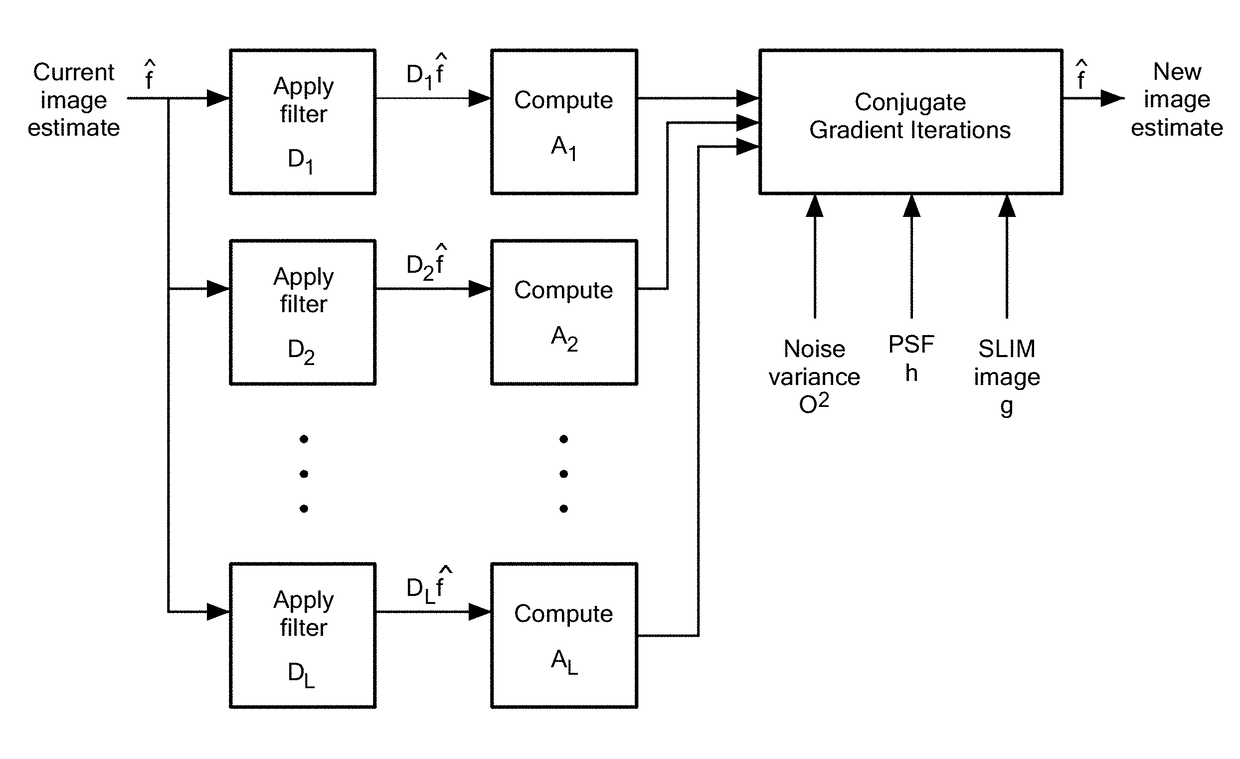
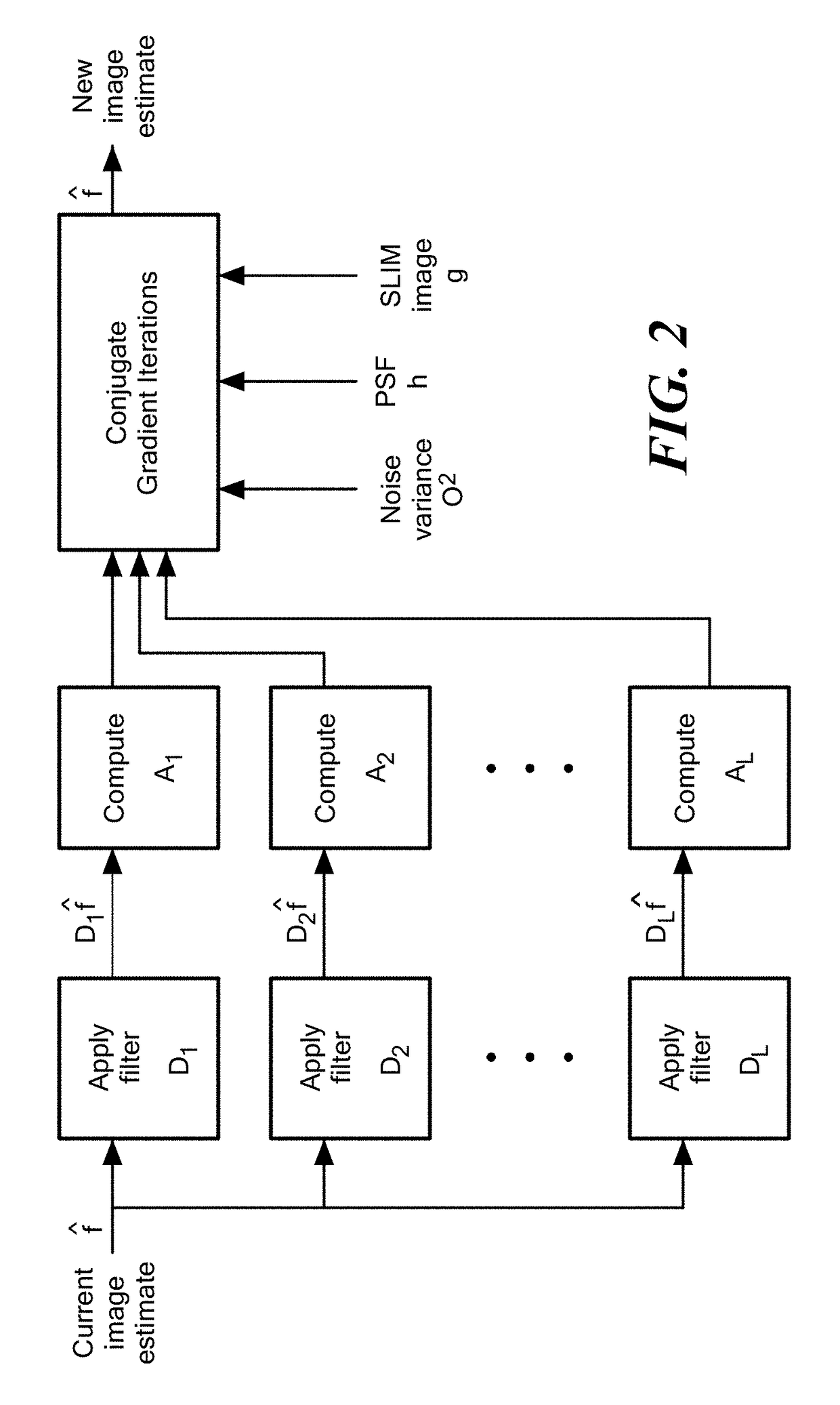
Sparse Deconvolution Spatial Light Microscopy in Two and Three Dimensions
Methods and a computer program product for applying deconvolution to spatial light interference microscopy for resolution enhancement with respect to the diffraction limit in two and three dimensions. By exploiting the sparsity properties of the phase images, which is prominent in many biological imaging applications, and modeling of the image formation via complex fields, the very fine structures can be recovered which were blurred by the optics. The resolution improvement leads to higher accuracy in monitoring dynamic activity over time. Experiments with primary brain cells, i.e. neurons and glial cells, reveal new subdiffraction structures and motions. This new information can be used for studying vesicle transport in neurons, which may shed light on dynamic cell functioning. Finally, the method may flexibly incorporate a wide range of image models for different applications and can be utilized for all imaging modalities acquiring complex field images.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Imaging interferometric microscopy
Exemplary embodiments provide an image interferometric microscope (IIM) and methods for image interferometric microscopy. The disclosed IIM can approach the linear systems limits of optical resolution by using a plurality of off-axis illuminations to access high spatial frequencies along with interferometric reintroduction of a zero-order reference beam on the low-NA side of the optical system. In some embodiments, a thin object can be placed normal to the optical axis and the frequency space limit can be extended to about [(1+NA)n / λ], where NA is the numerical-aperture of the objective lens used, n is the refraction index of the transmission medium and λ is an optical wavelength. In other embodiments, tilting the object plane can further allow collection of diffraction information up to the material transmission bandpass limited spatial frequency of about 2n / λ.
Owner:STC UNM
Synchronous phase shifting interference microscopy detection device and detection method based on orthogonal double-grating
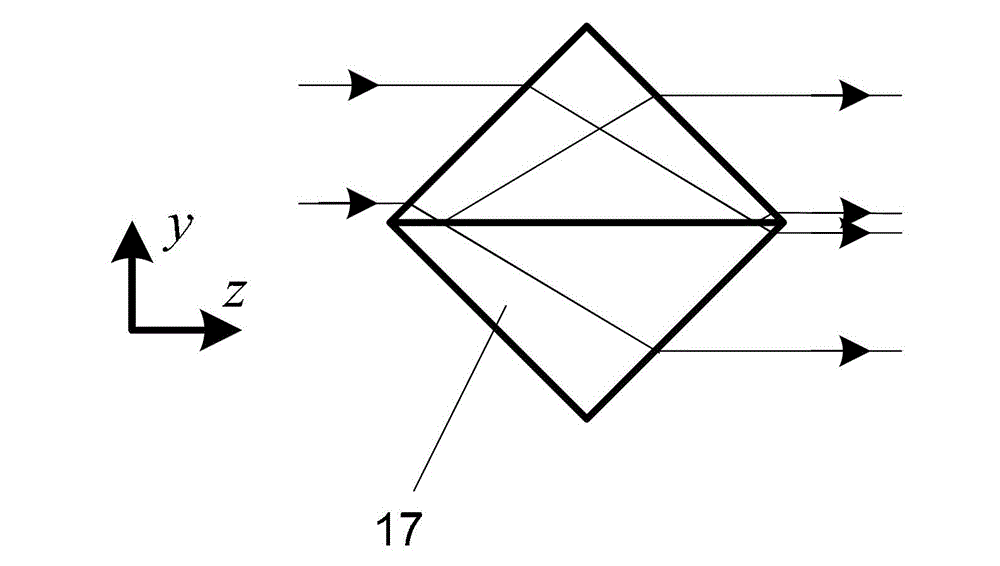
The invention discloses a synchronous phase shifting interference microscopy detection device and a detection method based on orthogonal double-grating, which belong to the technical field of optical interference microscopy detection, and solve the problem that in the existing phase shifting interference microscopy detection method, data processing for realizing phase recovery of a to-be-detected object is complex. The interference microscopy technology and the orthogonal double-grating spectral synchronous phase shifting technology are combined to realize the detection to the appearance of the to-be-detected object, linearly polarized light is divided into object beams and reference beams through a first polarized beam splitter, then the object beams and the reference beams are converged to a second polarized beam splitter side by side, finally, an interference image comprising four images is acquired by an image sensor and a computer connected with the image sensor, and the phase distribution of the to-be-detected object is calculated by use of a four-step phase shifting formula; and a optical path is free from being changed and any device component is free from being moved during the operation. The device and the method are applied to the appearance detection of the to-be-detected object.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
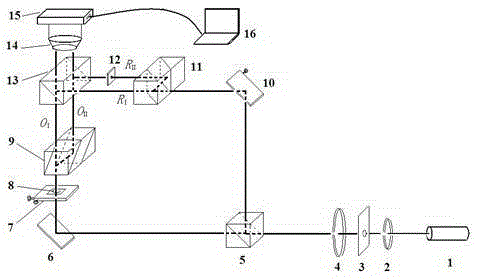
Common-path interference phase microscopy one-time imaging system and method
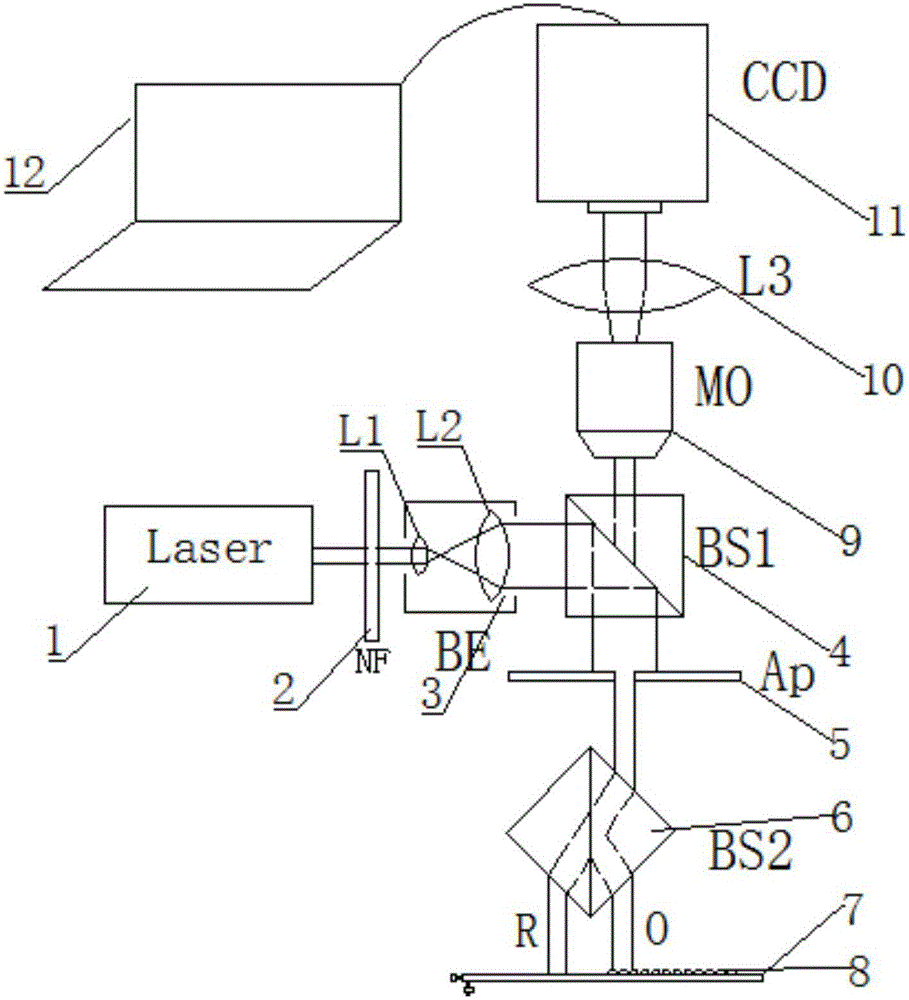
ActiveCN106770288ASimple structureEasy to operateOptical measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansBeam splitterLaser light
The invention provides a common-path interference phase microscopy one-time imaging system and method. The common-path interference phase microscopy one-time imaging system comprises a laser, a neutral adjustable damper, a beam-expanding aligner, a half transparent and half reflecting mirror, a field diaphragm, an unpolarized beam splitter prism, a reflecting objective table, a sample, a microscope objective, a third lens, a CCD (Charge Coupled Device) and a computer. The common-path interference phase microscopy one-time imaging system is based on a differential interference light path, the unpolarized beam splitter prism is used for partitioning laser light into two beams of parallel light, namely, object light and reference light, the reflecting objective table is used for reflecting the object light and the reference light totally, the object light and the reference light are combined through the unpolarized beam splitter prism and transmitted in a common-path way, and the combined light is collected by a CCD camera and transmitted to the computer to be displayed after being amplified through the microscope objective. By adopting the common-path interference phase microscopy one-time imaging system and method, the conventional path interference imaging system can be realized by adjusting the angle of the reflecting objective table, including off-axis interference, co-axial interference and slight off-axis interference. The system has a high practical value and a wide application prospect on the aspect of phase microscopy, and can be particularly applied to the field of biological cell morphological identification.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Common light path interference microscopy detection device and method based on synchronization carrier frequency phase shift
InactiveCN102967258ATake full advantage of horizontal resolutionMake the most of horizontal spaceUsing optical meansGratingBeam splitter
The invention discloses a common light path interference microscopy detection device and a method based on synchronization carrier frequency phase shift, belongs to the field of optics and overcomes the defects in prior art. The technical scheme includes that a light source is opened so that light beams emitted by the light source passes a line polaroid and are subjected to collimation beam expanding through a collimation beam expanding system to form a parallel polarized light, the light beams are emitted into a first beam splitter prism and subjected to reflection and transmission through the first beam splitter prism to finally form a reference light beam and an object light beam respectively, the reference light beam and the object light beam are gathered into a rectangular window side by side to sequentially pass through a first Fourier lens, a one-dimensional cycle optical grating, a second Fourier lens and a polariod group, polarized light beams emerged by the polariod group can generate a interference pattern on an imaging sensor plane, the interference pattern acquired by a computer is divided according to the size of a small window of the rectangular window to obtain two interference patterns, and the phase position distribution of an object to be detected can be obtained through calculation.
Owner:HARBIN ENG UNIV
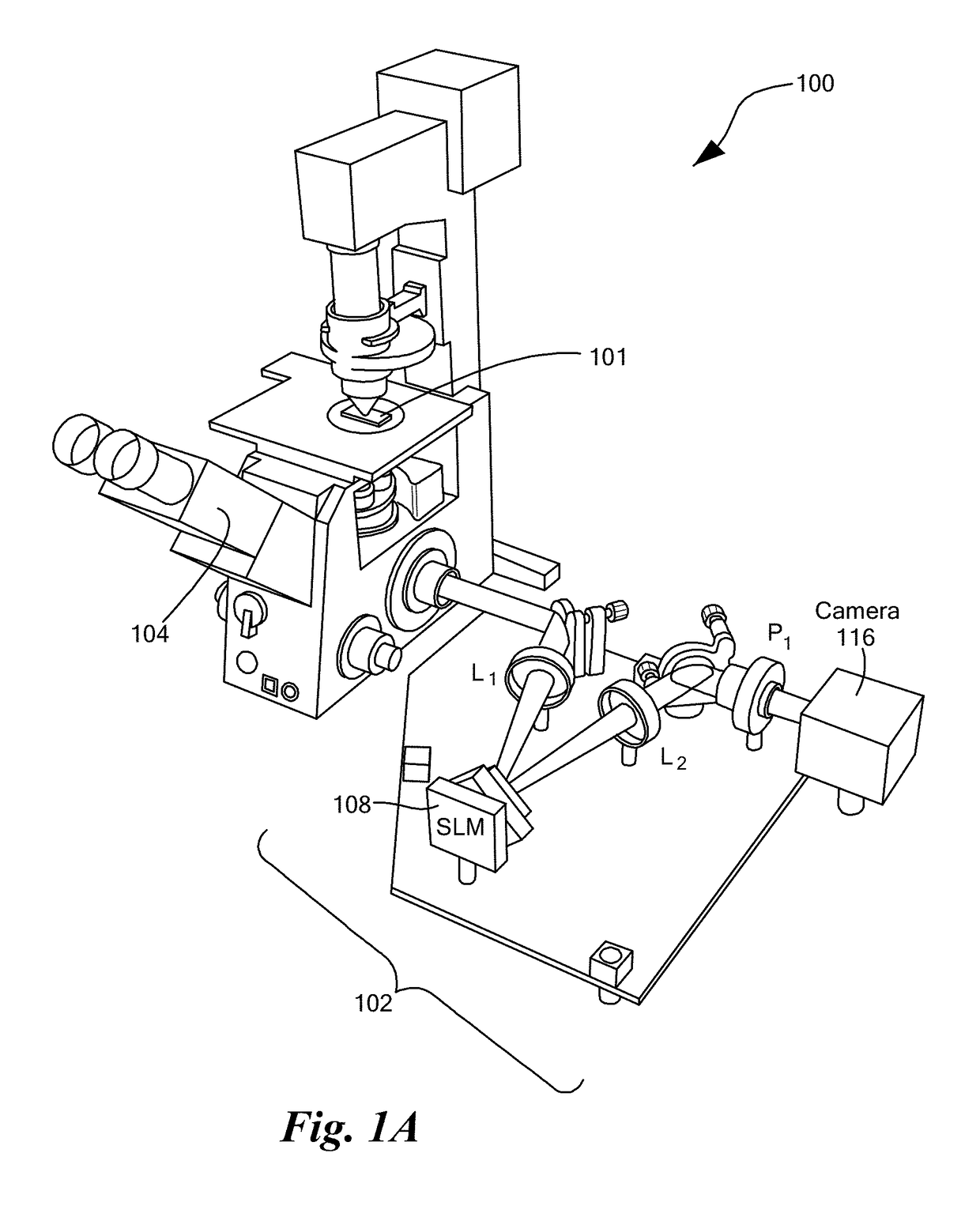
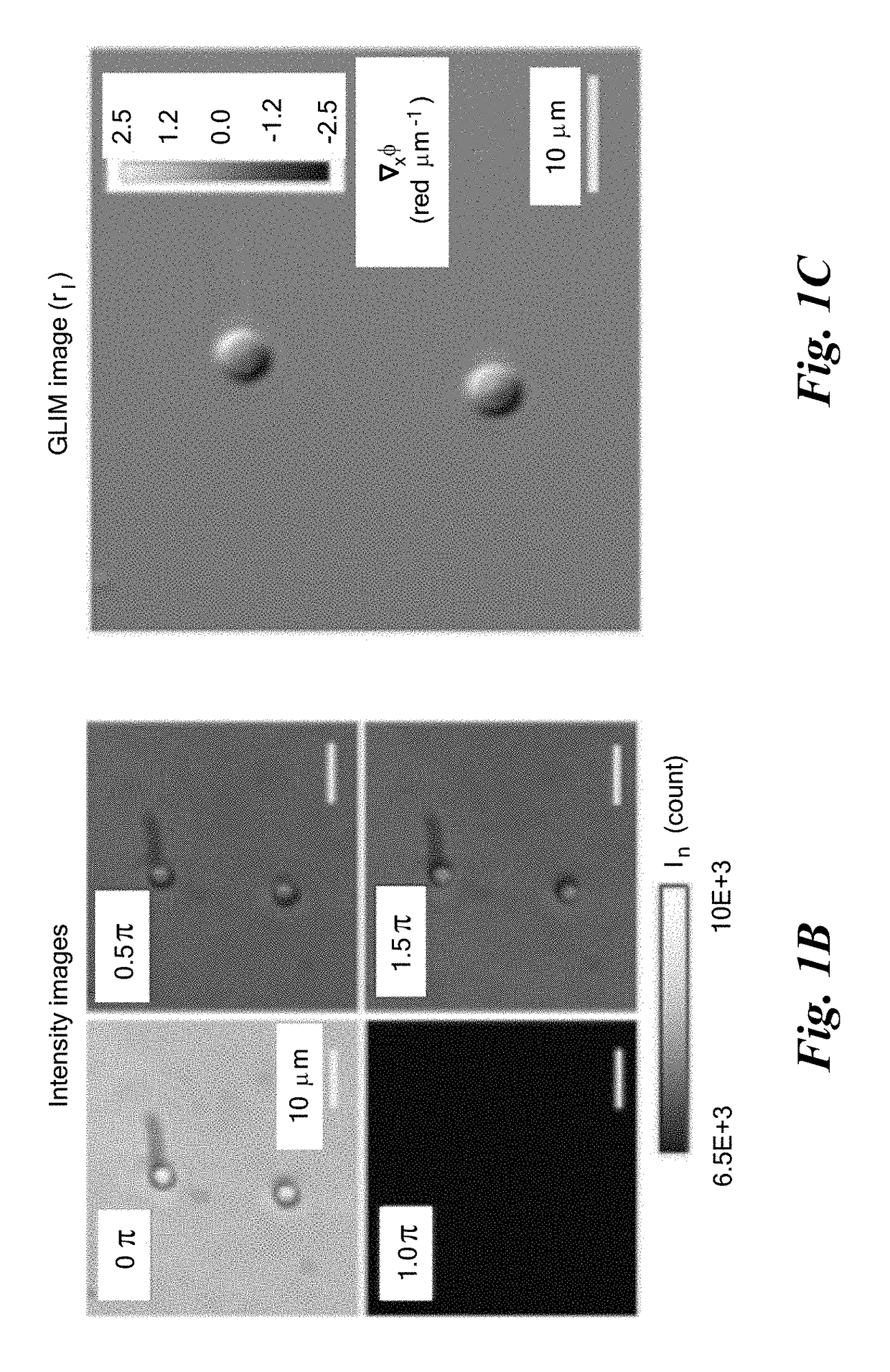
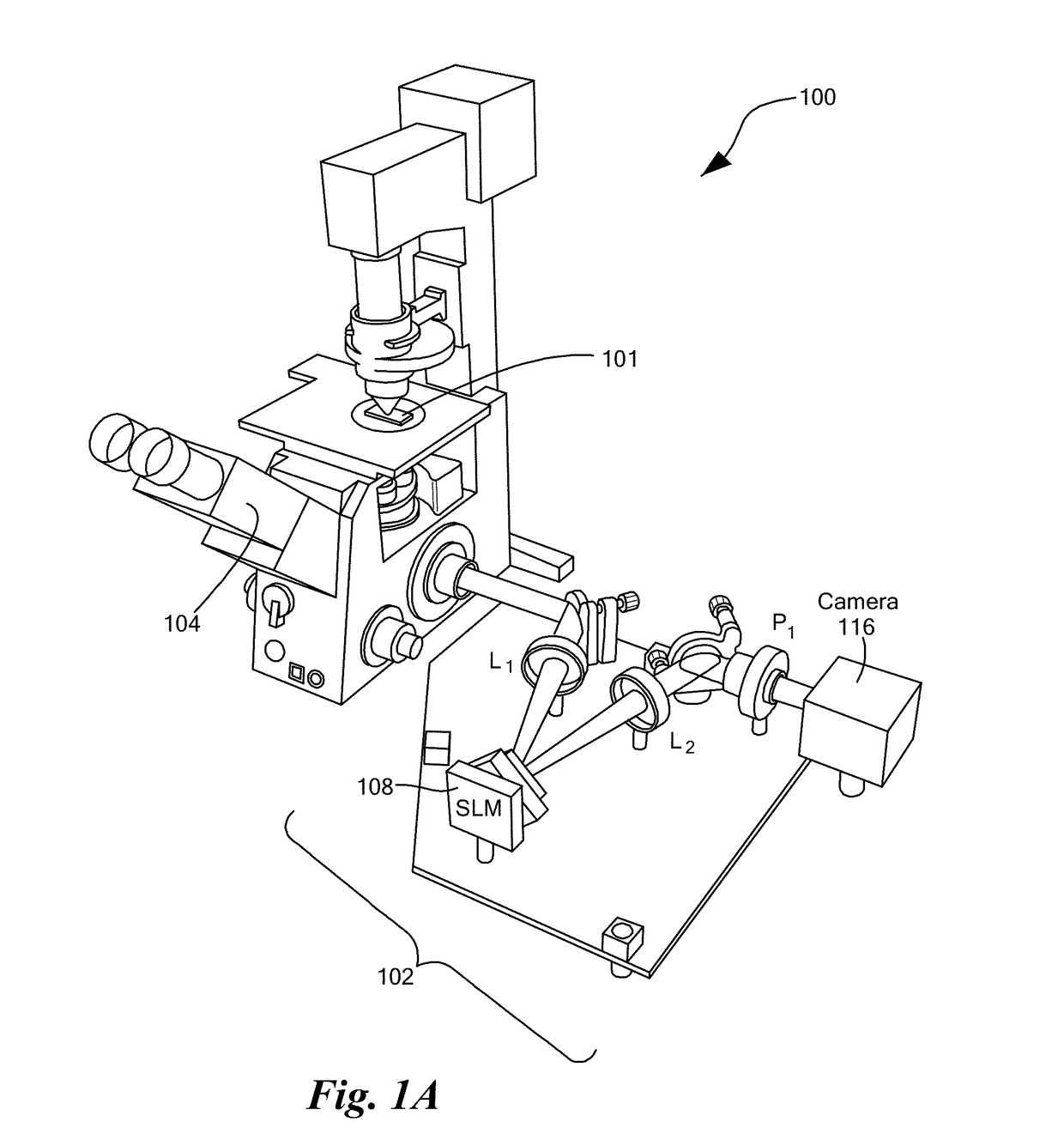
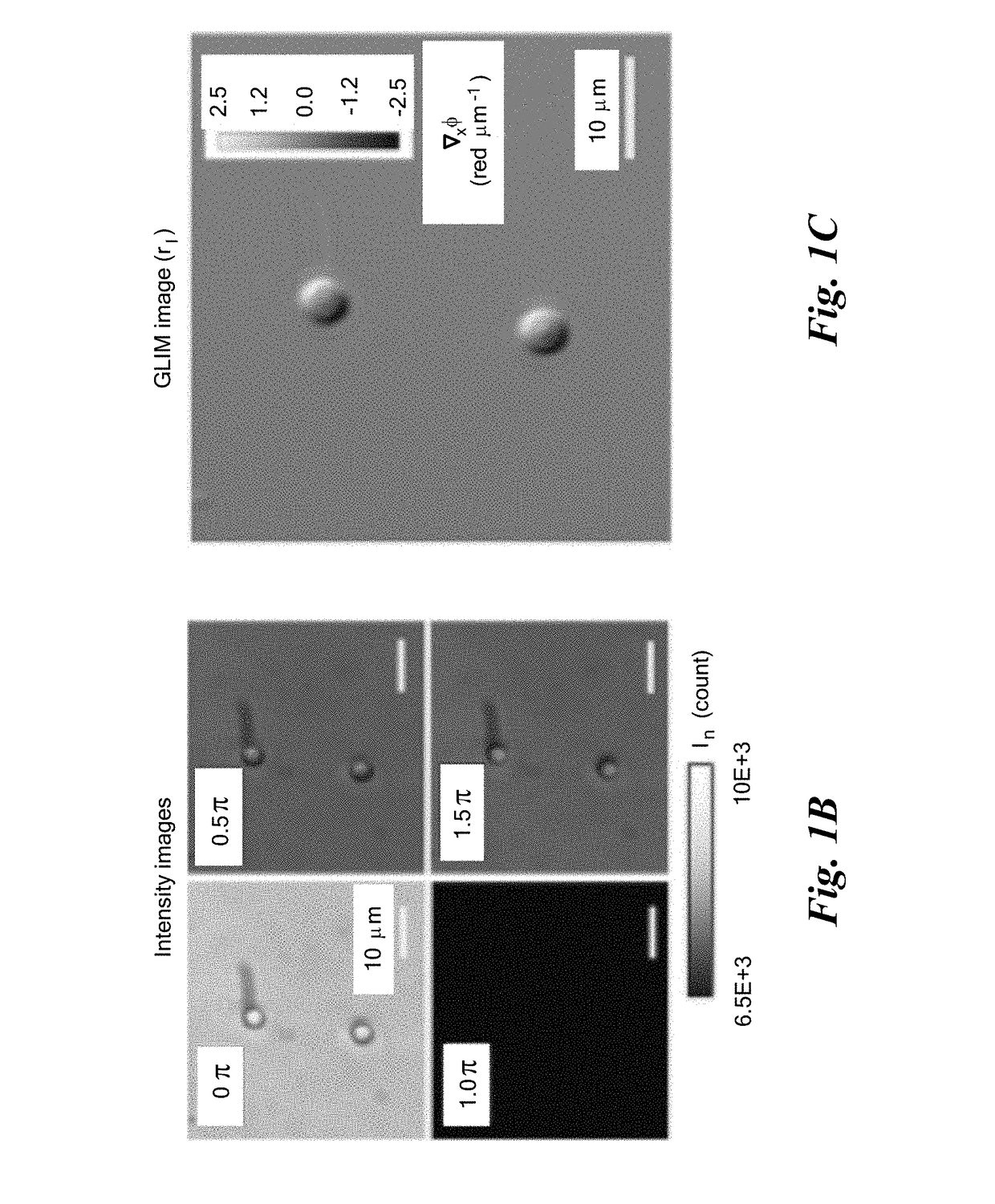
Gradient light interference microscopy for 3D imaging of unlabeled specimens
A system and methods for quantitative optical phase imaging of a sample. First second replica field of an image field are generated, characterized by a respective optical phase, cross-polarized and shifted in a shift direction transverse to a normal to the surface of the sample. The replica fields are Fourier transformed, the second replica field is retarded by four successive phase shifts, and, after inverse Fourier transforming, the first and second replica fields pass through an analyzer polarizer and superposing the first and second replica fields on a detector array to create four successive detector signals. The four successive detector signals are solved to derive a gradient of the optical phase of the image field, which may be integrated to obtain a quantitative phase image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Gradient Light Interference Microscopy for 3D Imaging of Unlabeled Specimens
ActiveUS20180143001A1Increase the sectionReduce contrastMicroscopesUsing optical meansPhase shiftedFourier transform on finite groups
A system and methods for quantitative optical phase imaging of a sample. First second replica field of an image field are generated, characterized by a respective optical phase, cross-polarized and shifted in a shift direction transverse to a normal to the surface of the sample. The replica fields are Fourier transformed, the second replica field is retarded by four successive phase shifts, and, after inverse Fourier transforming, the first and second replica fields pass through an analyzer polarizer and superposing the first and second replica fields on a detector array to create four successive detector signals. The four successive detector signals are solved to derive a gradient of the optical phase of the image field, which may be integrated to obtain a quantitative phase image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Characteristic parameters of cells and tissue from quantitative phase imaging
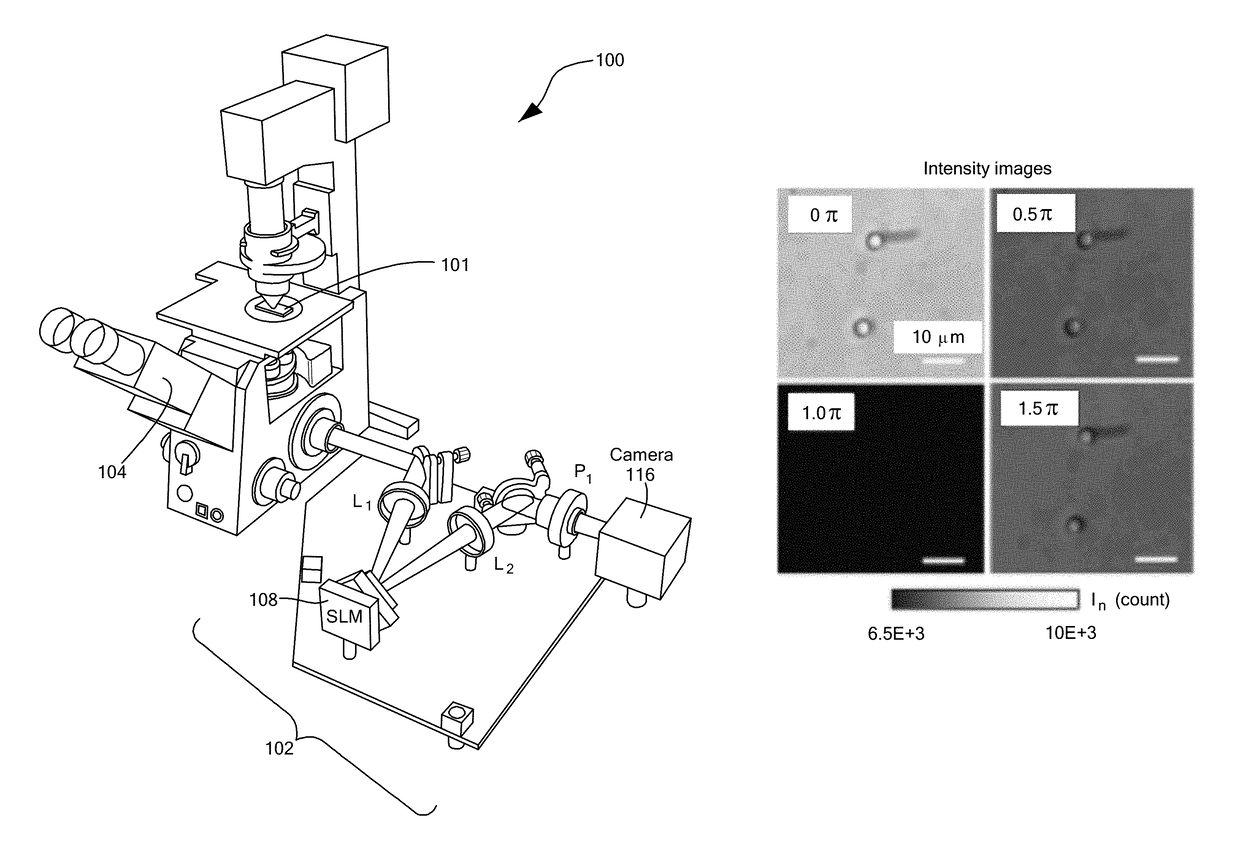
Methods mapping a characteristic parameter of a specimen, such as a scattering mean free path and a scattering anisotropy factor, based on a quantitative phase shift measurement. The methods have steps of using spatial light interference microscopy (SLIM) to determine a quantitative phase shift as a function of position in a sample, and applying a generalized scatter-phase transformation to derive at least one of a scattering mean free path (MFP), a scattering anisotropy factor, and a thickness-independent parameter as a function of position in the sample. In some cases, the sample may be a slice of tissue or a cell.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Optical sectioning apparatus using advanced optical interference microscopy
ActiveUS10151572B1High strengthReduce exposure timeInterferometersClosed circuit television systemsCamera lensBeam splitter
An optical sectioning apparatus using optical interference microscopy and fluorescence microscopy, including: a beam splitter capable of splitting an incident light beam into a reflected light beam and a transmitted light beam; a wide band light source for providing the incident light beam; a reference arm unit for making the transmitted light beam travel a round trip along an adjustable optical path; a short wavelength light source; a first dichroic splitter, with a first side facing the short wavelength light source and a third side facing the beam splitter, being capable of providing a light-blocking effect on wavelengths shorter than a preset wavelength; an objective lens, with a collimated side facing a second side of the first dichroic splitter; a sample carrier unit facing a focal side of the objective lens; and a projection lens and a sensor units for receiving an output light beam.
Owner:ACUSOLUTIONS INC
Sparse deconvolution spatial light microscopy in two and three dimensions
Methods and a computer program product for applying deconvolution to spatial light interference microscopy for resolution enhancement with respect to the diffraction limit in two and three dimensions. By exploiting the sparsity properties of the phase images, which is prominent in many biological imaging applications, and modeling of the image formation via complex fields, the very fine structures can be recovered which were blurred by the optics. The resolution improvement leads to higher accuracy in monitoring dynamic activity over time. Experiments with primary brain cells, i.e. neurons and glial cells, reveal new subdiffraction structures and motions. This new information can be used for studying vesicle transport in neurons, which may shed light on dynamic cell functioning. Finally, the method may flexibly incorporate a wide range of image models for different applications and can be utilized for all imaging modalities acquiring complex field images.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Memeasuring a cavity by means of interference spectroscopy
ActiveUS20190056213A1Improve analysis accuracyPhase-affecting property measurementsInterferometersMeasurement pointSpectroscopy
A method for interferometrically determining geometric and / or optical parameters of a cavity comprises the method steps of: tuning the frequency f of a coherent light source (10) over a frequency range Δf, deriving a target beam and a reference beam from the coherent light source (10), wherein the target beam passes through the cavity at least once, generating an interference signal I(f) which is dependent on the frequency f of the light source by superimposing the reference beam on the target beam, capturing an interference spectrum of the interference signal I(f) over the frequency range Δf of the frequency f of the coherent light source, evaluating a plurality of measurement points of the captured interference spectrum over the frequency range Δf by numerically fitting the measurement points to a mathematical function produced, and determining the geometric and / or optical parameters of the cavity (40, 45) by determining the parameters of the mathematical function produced.
Owner:HABRICH BJORN
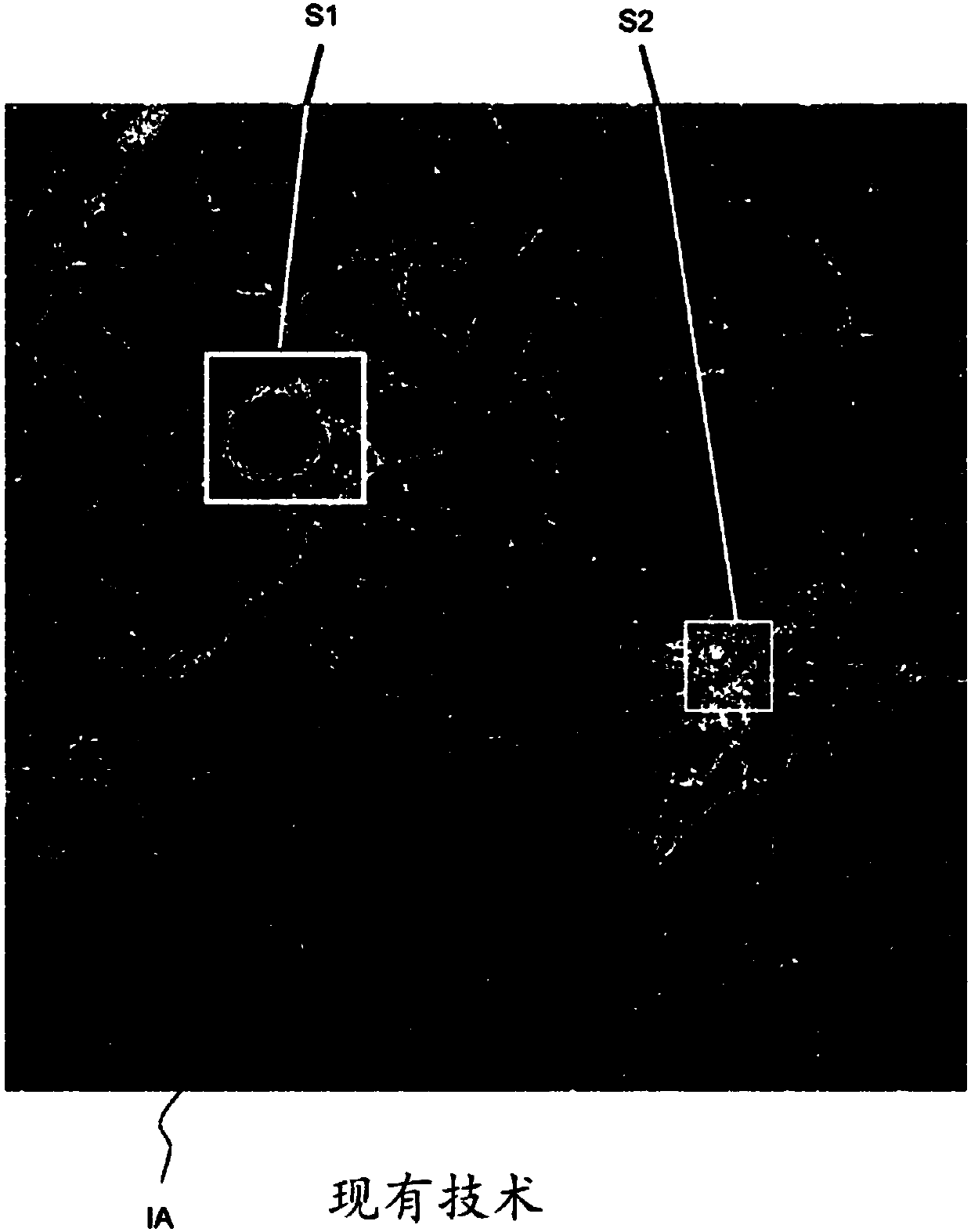
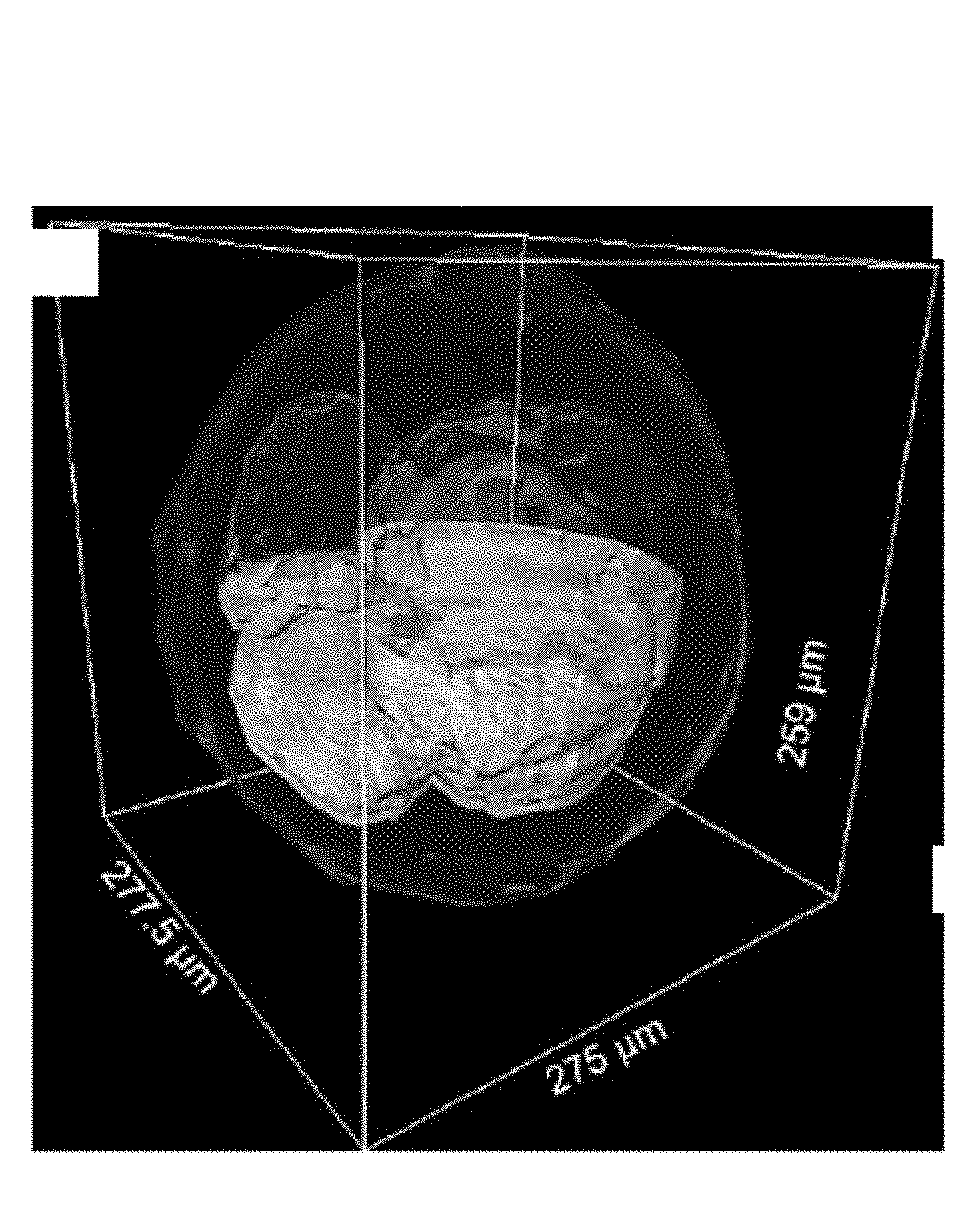
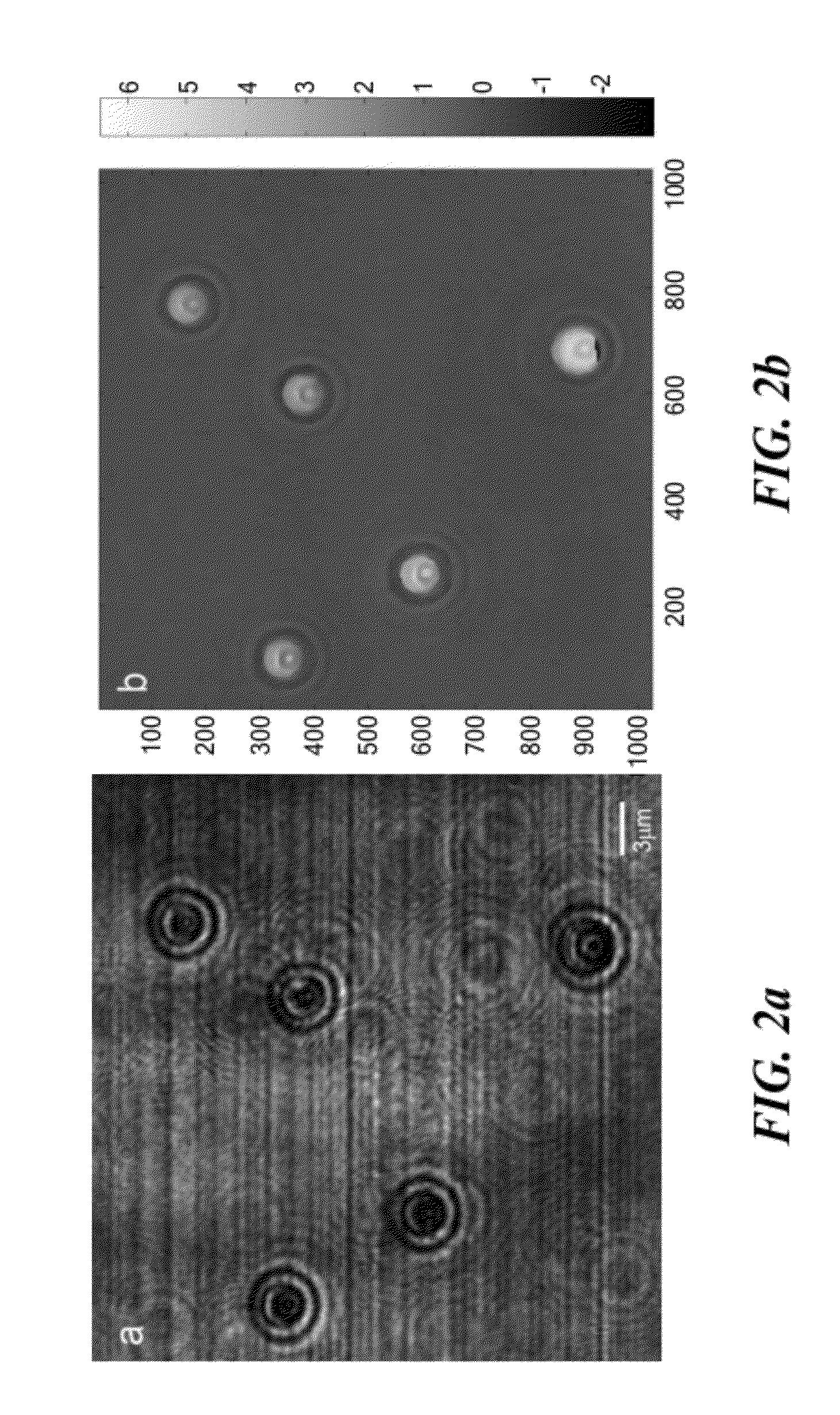
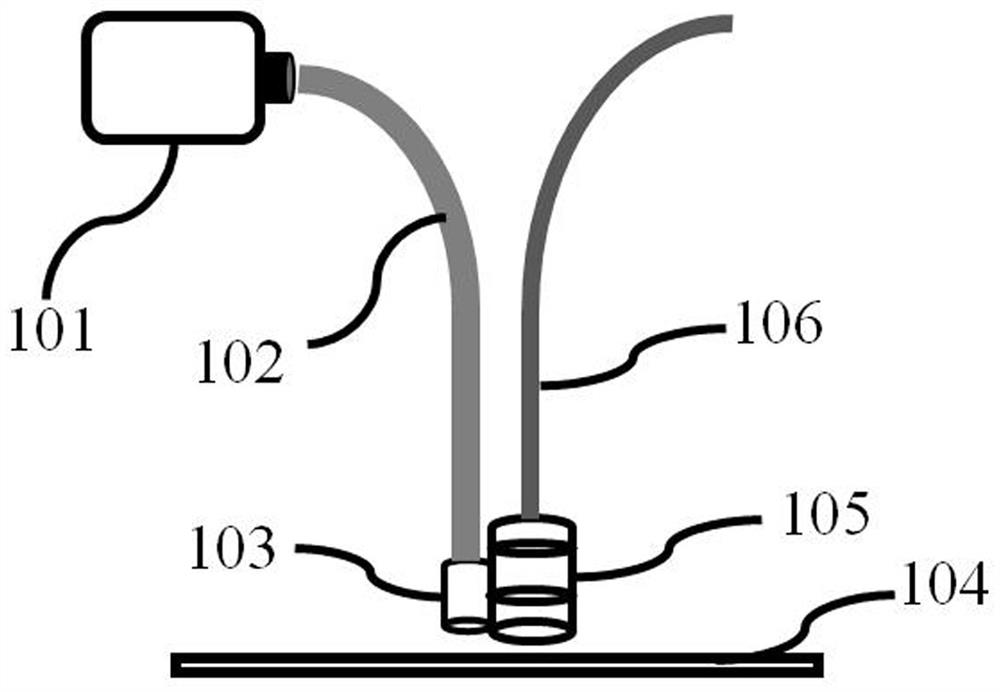
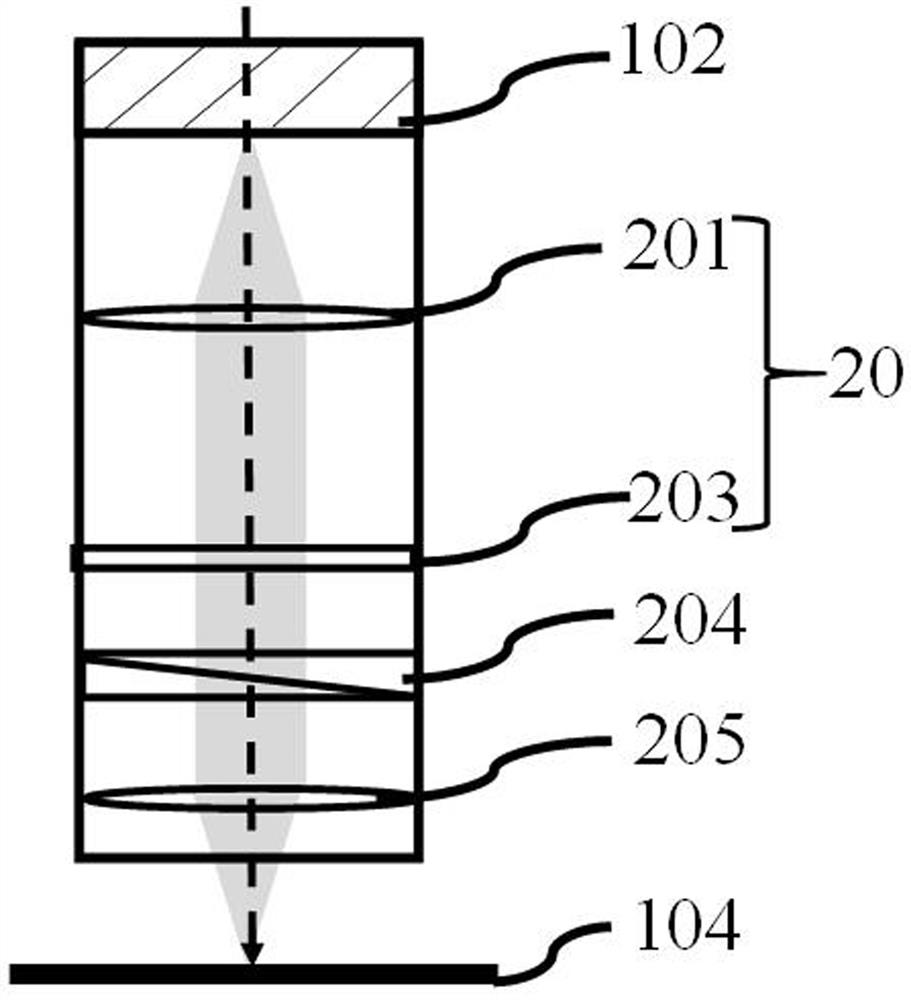
Differential confocal fixed-surface interference target outer surface defect detection method and device
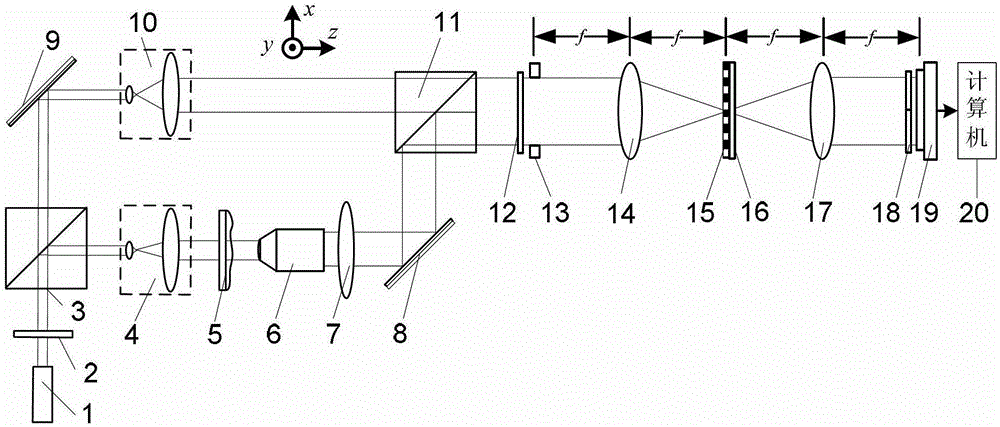
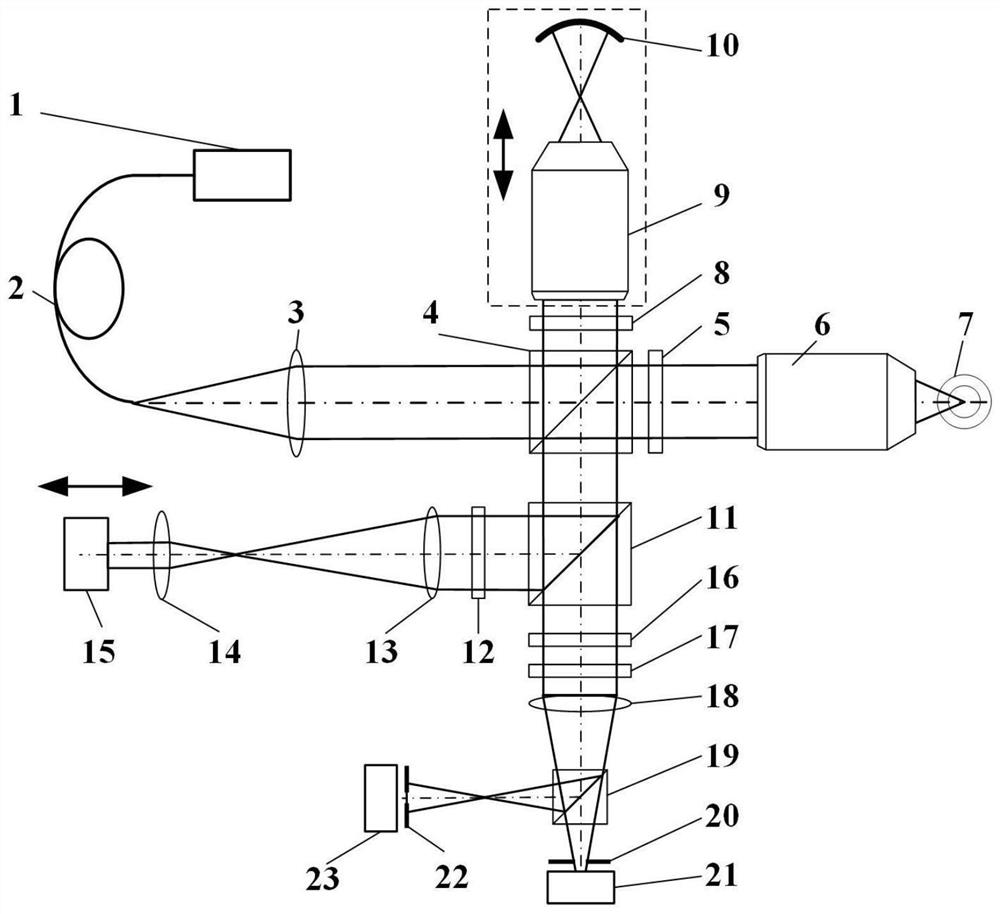
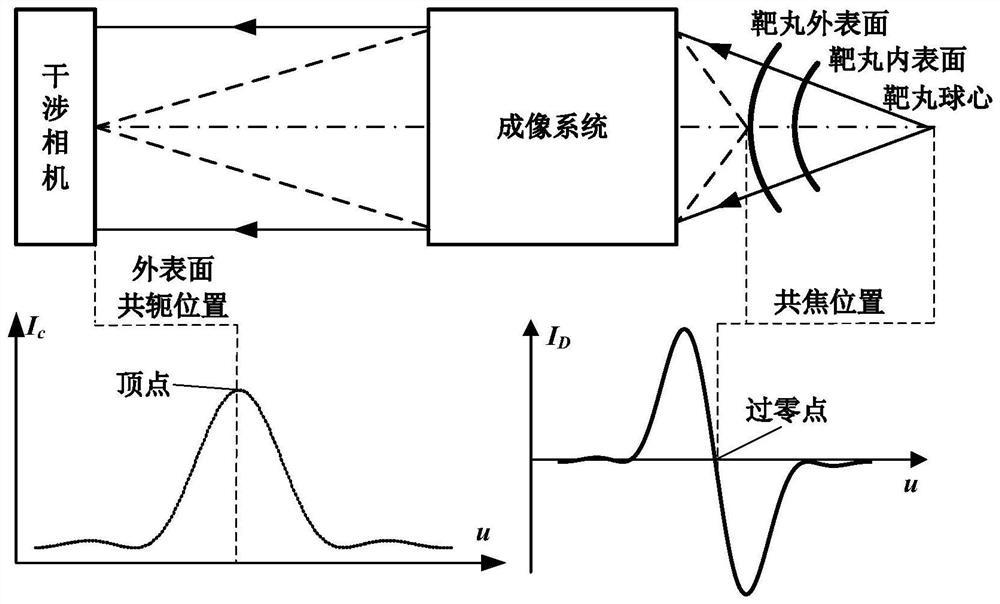
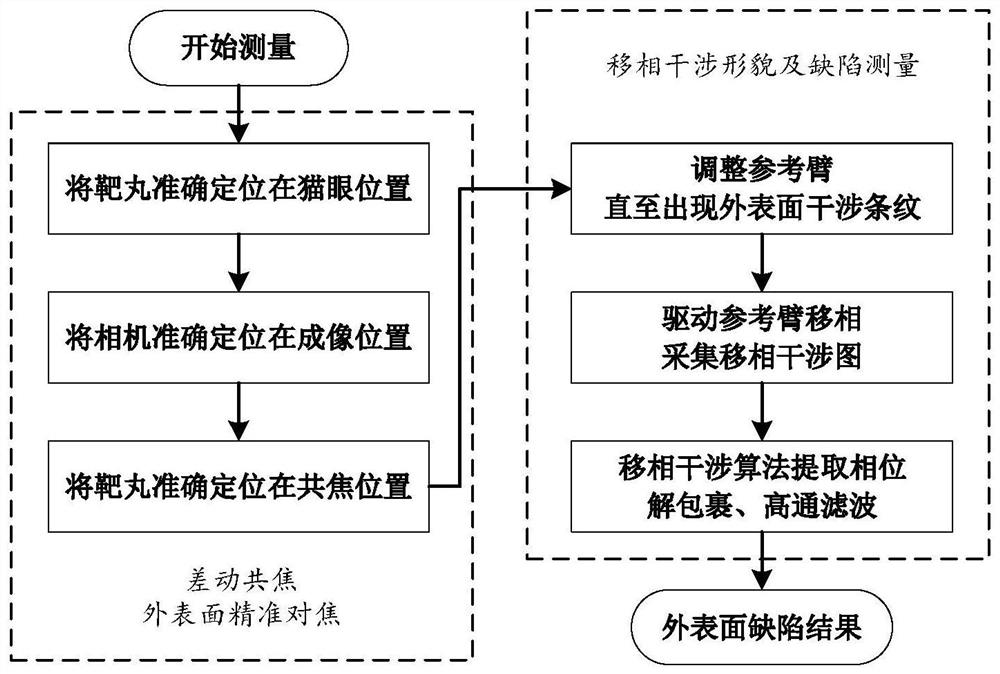
ActiveCN112666172APrecise positioningGuaranteed measurement accuracyMaterial analysis by optical meansInterference microscopyAutofocus
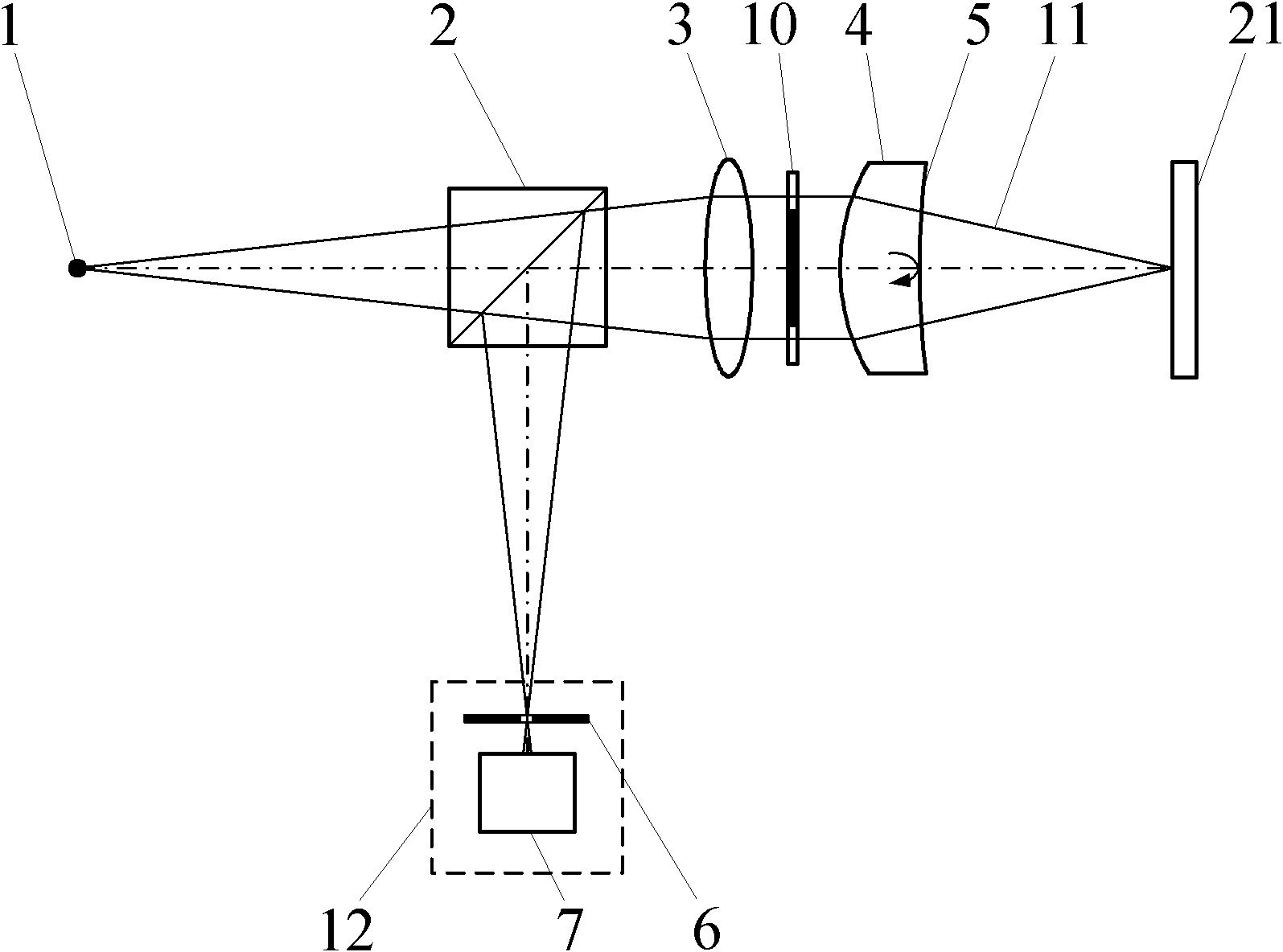
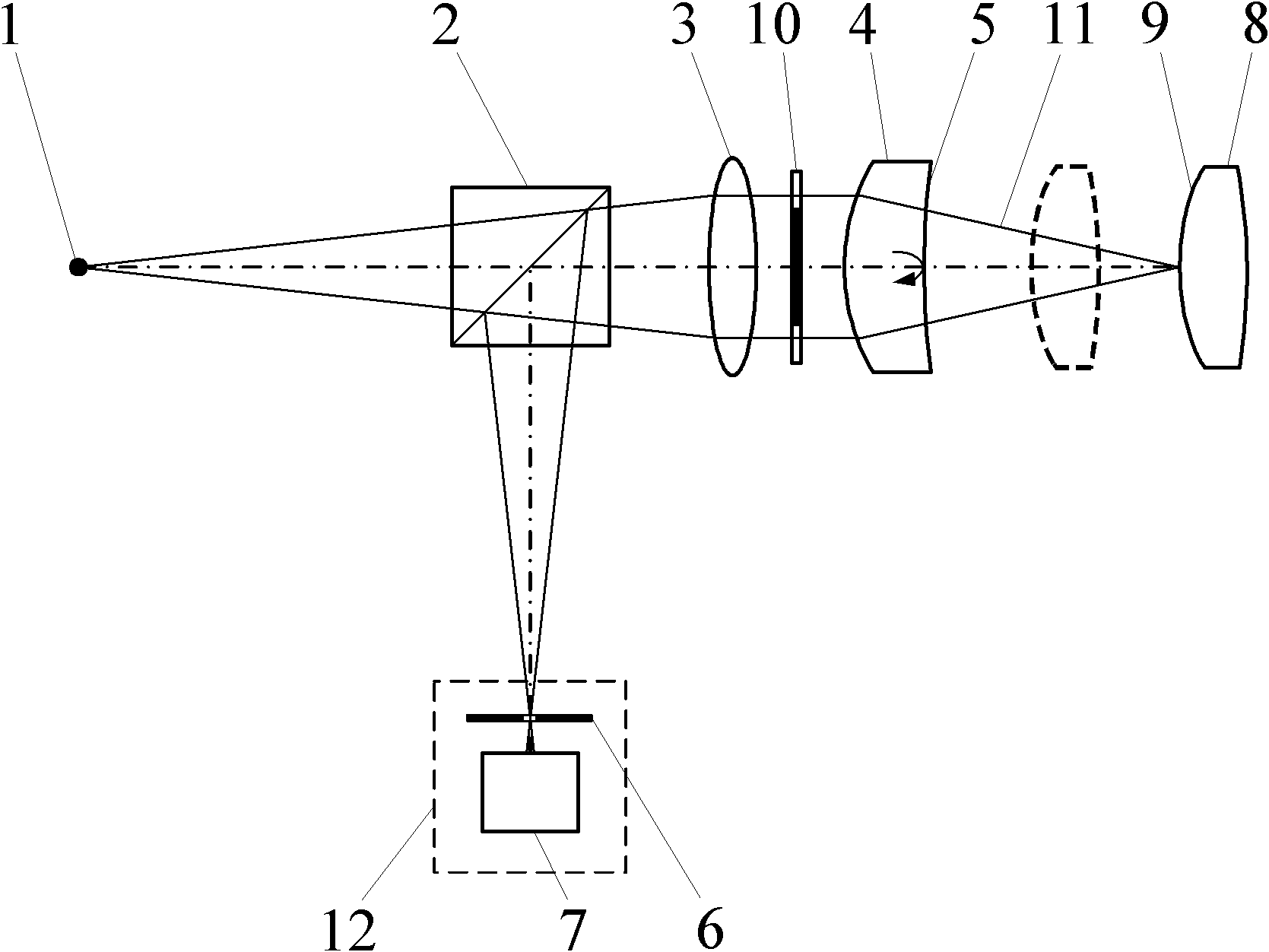
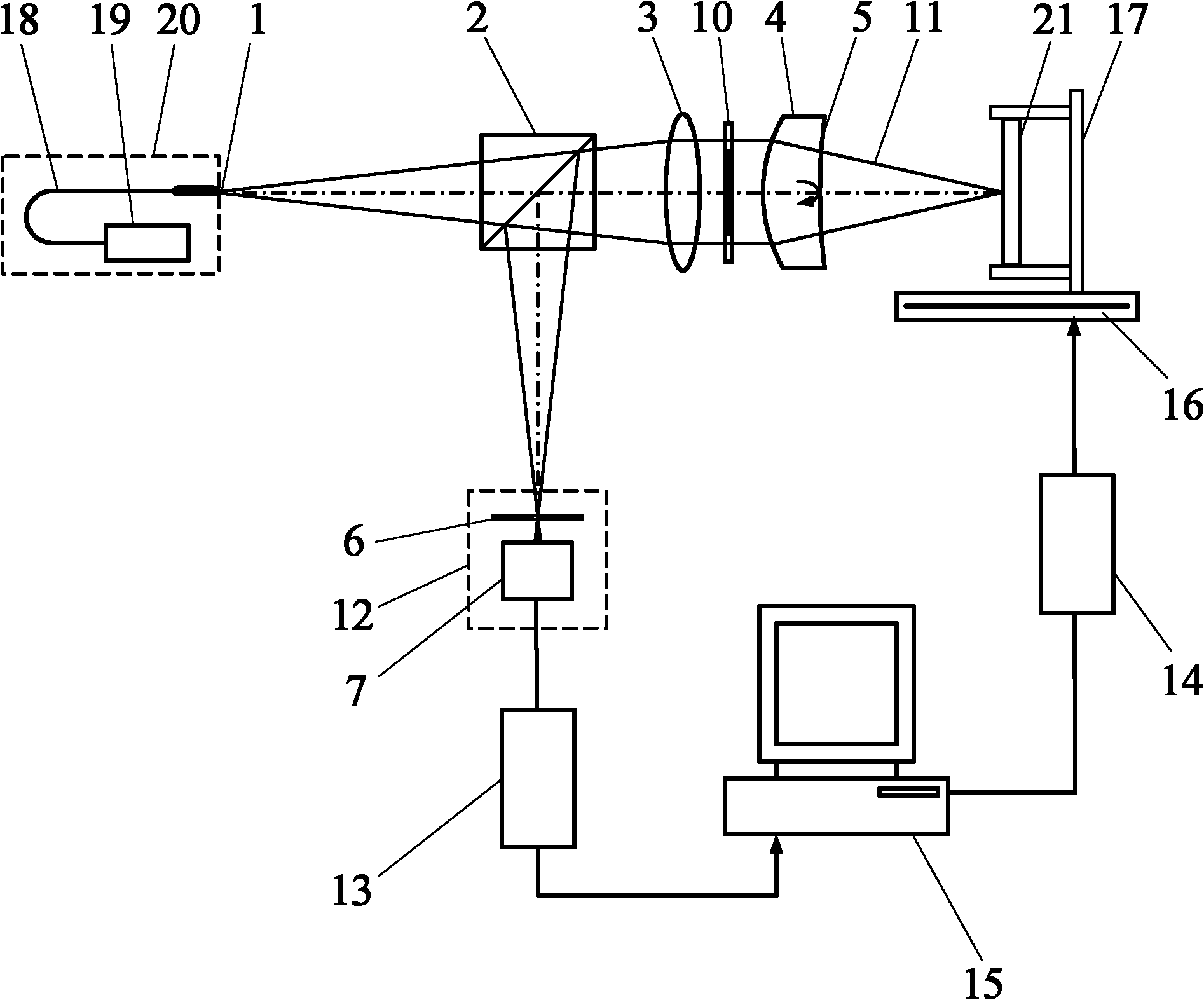
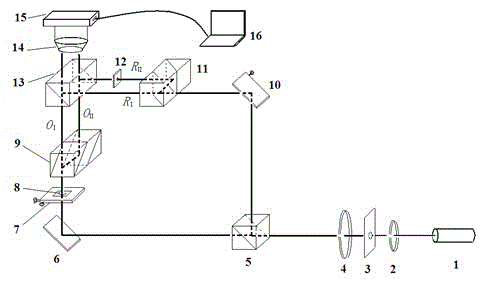
The invention relates to a differential confocal fixed-plane interference target outer surface defect detection method and device, and belongs to the technical field of optical imaging and detection. According to the method, the zero crossing point of a differential confocal light intensity response curve is used for accurately positioning the axial positions of a target (a detected surface) and a camera (a detection surface), so that accurate and automatic focusing imaging of the outer surface is realized. A short coherent light source and a spherical reference mirror are adopted in an interference microscopic light path to generate an outer surface zero interference pattern; and then measuring outer surface defect distribution from the outer surface zero interferogram by using a phase-shifting interferometry. According to the invention, a more accurate adjustment judgment basis is provided for axial position adjustment of the target and the camera by using the accurate positioning characteristic of the differential confocal technology, so that the precision and efficiency of focusing and detection of the outer surface of the traditional interference microscopy method are effectively improved, and a necessary technical guarantee is provided for automatic detection. The invention provides a new technical approach for high-precision, high-efficiency and automatic detection of the outer surface defects of a large batch of targets.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Optical sectioning apparatus using advanced optical interference microscopy
ActiveUS20180347960A1High strengthReduce exposure timeInterferometersClosed circuit television systemsBeam splitterFluorescence
An optical sectioning apparatus using optical interference microscopy and fluorescence microscopy, including: a beam splitter capable of splitting an incident light beam into a reflected light beam and a transmitted light beam; a wide band light source for providing the incident light beam; a reference arm unit for making the transmitted light beam travel a round trip along an adjustable optical path; a short wavelength light source; a first dichroic splitter, with a first side facing the short wavelength light source and a third side facing the beam splitter, being capable of providing a light-blocking effect on wavelengths shorter than a preset wavelength; an objective lens, with a collimated side facing a second side of the first dichroic splitter; a sample carrier unit facing a focal side of the objective lens; and a projection lens and a sensor units for receiving an output light beam.
Owner:ACUSOLUTIONS INC
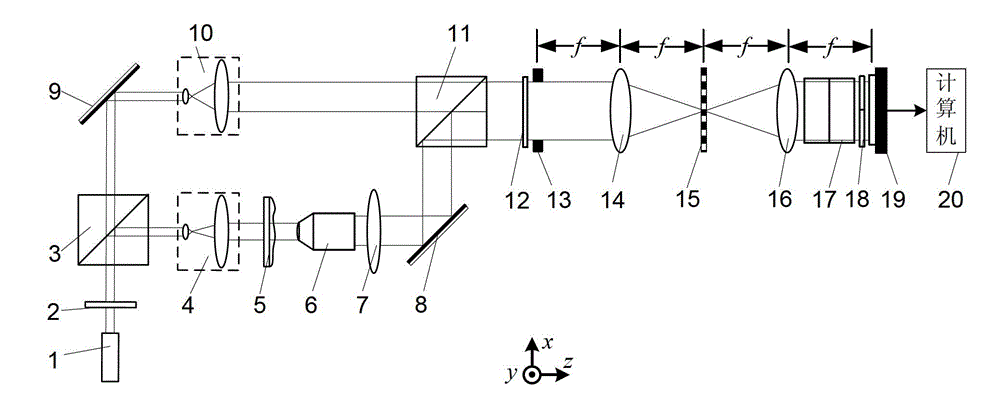
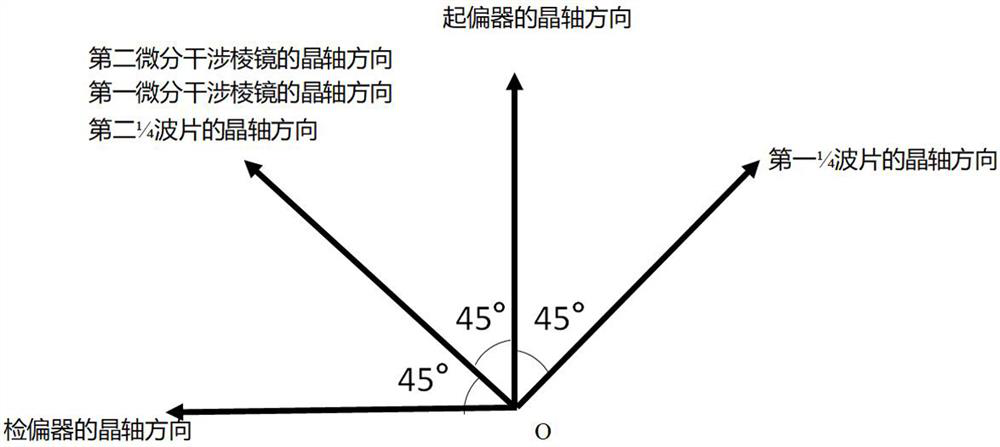
Differential interference contrast microscopic endoscopic imaging system and endoscopic imaging method
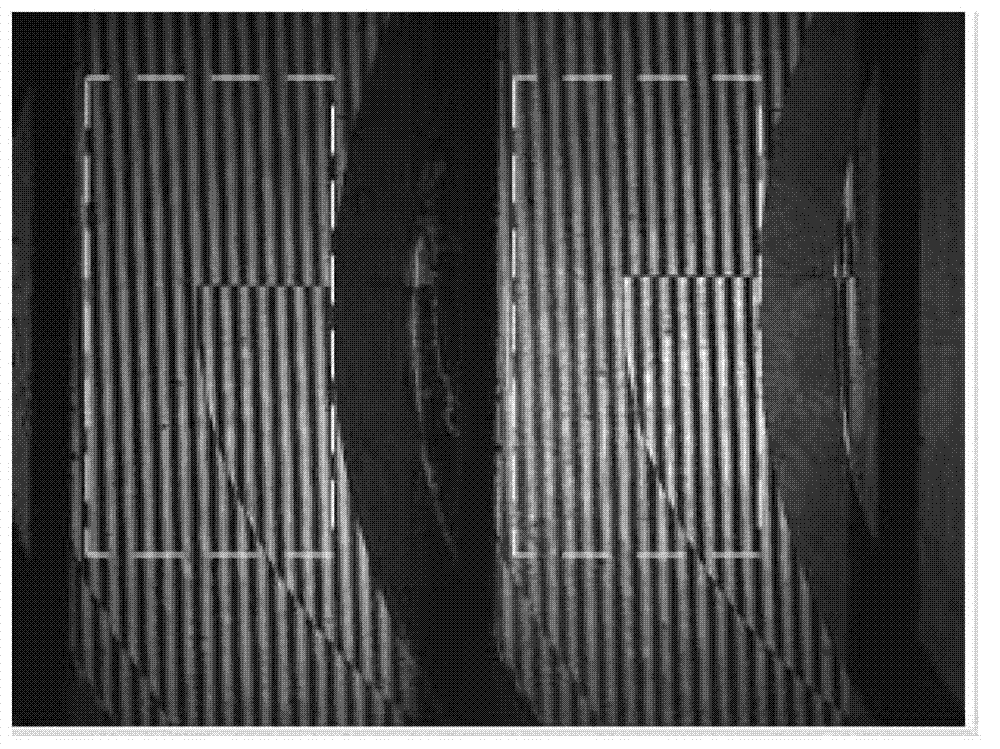
PendingCN113670854AIncrease contrastAchieving Phase ResolutionScattering properties measurementsContrast levelPrism
The invention discloses a differential interference contrast microscopic endoscopic imaging system and an endoscopic imaging method. The microscopic endoscopic imaging system comprises an illumination light source, an optical fiber, an illumination light path module, an imaging receiving module and a cable. The method has the remarkable characteristics that the contrast ratio of an observed object is enhanced, the technology utilizes a differential interference prism to generate ordinary light (o light) and extraordinary light (e light), the two beams of coherent light change the optical path difference after passing through the object and interfere with each other on an image plane, so that the tiny change of the surface height of a sample is shown in the form of strong light intensity change on an interference background, an embossment sense is formed, and the microcosmic contour of the surface of the sample can be visually reflected. The differential interference microscopy technology can realize nanoscale phase resolution of the surface of the sample, observes the fine structure of the surface of the sample, and helps doctors to judge focus characteristics according to surface fluctuation characteristics of the observed sample and make diagnosis.
Owner:ZHEJIANG LAB +1
A two-step phase-shift interferometric phase microscopy primary imaging system and method
The invention discloses an interferometric phase microscopy one-step imaging system and method based on two-step phase shift, and adopts the technical scheme that based on a typical Mach-Zehnder interference light path, lateral displacement beam splitting mirrors are adopted to perform light splitting on sample light and reference light respectively, a wave plate is utilized as a phase shifter, and two interference figures can be acquired at the same time through single exposure, and phase imaging can be realized quickly through corresponding phase recovery operation, and a spatial form structure of a phase body is further deconstructed. The interferometric phase microscopy one-step imaging system and method are suitable for all interferometric phase microscopy imaging systems, such as traditional coaxial interference, off-axis interference and slight off-axis interference, and have high practical value and wide application prospect in the aspect of phase microscopy, particularly in the field of application and identification of biological cell morphology.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
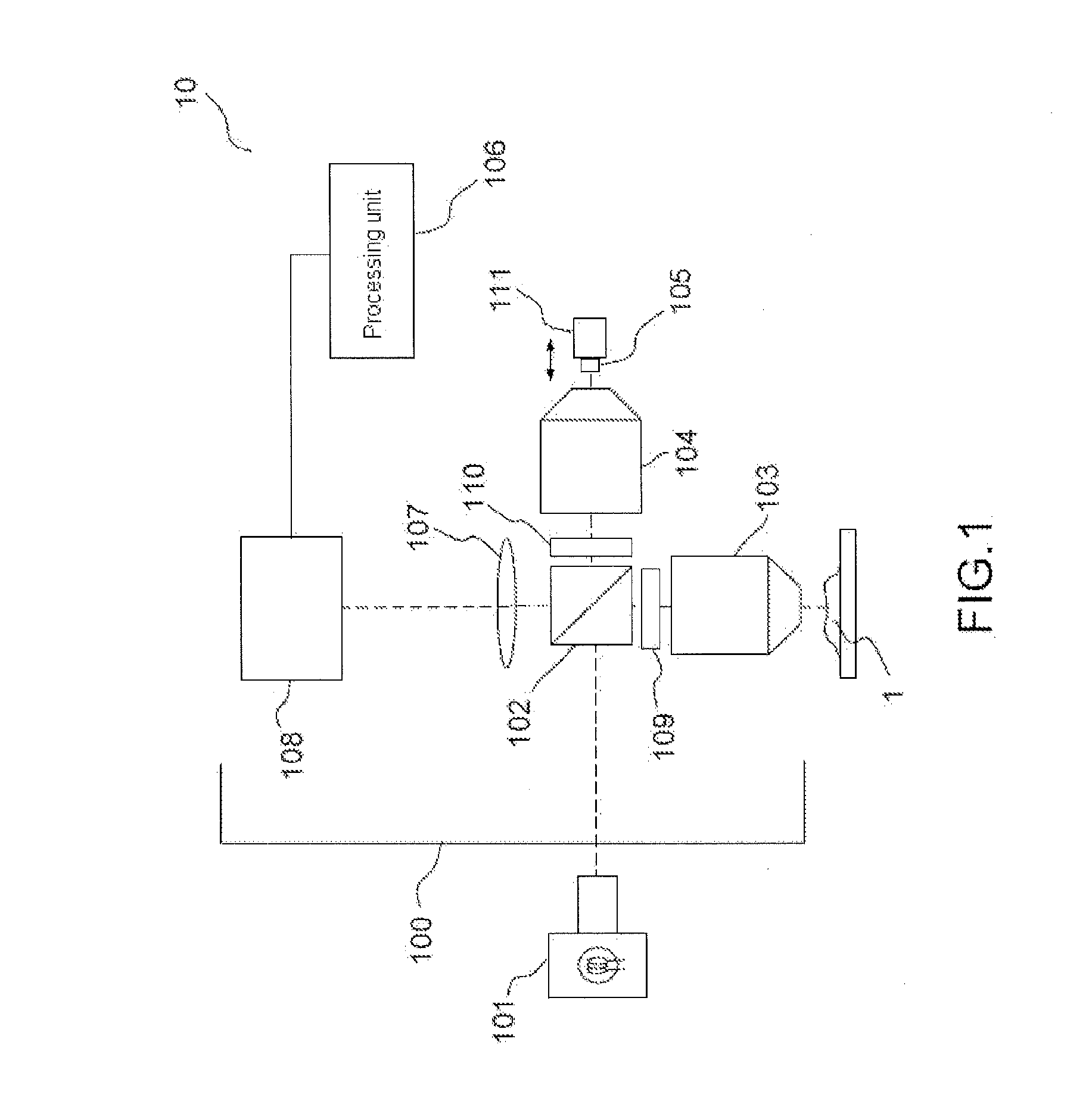
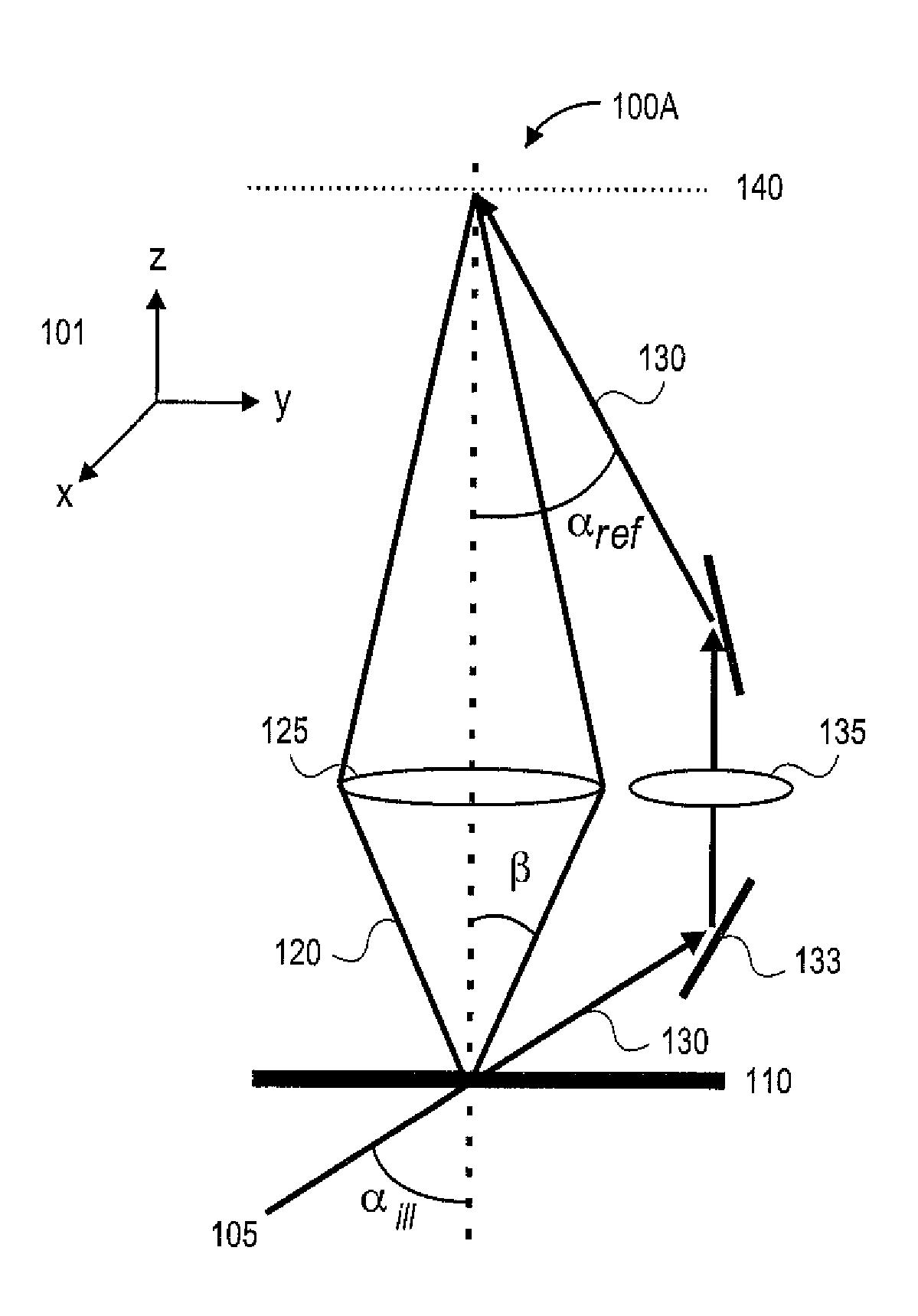
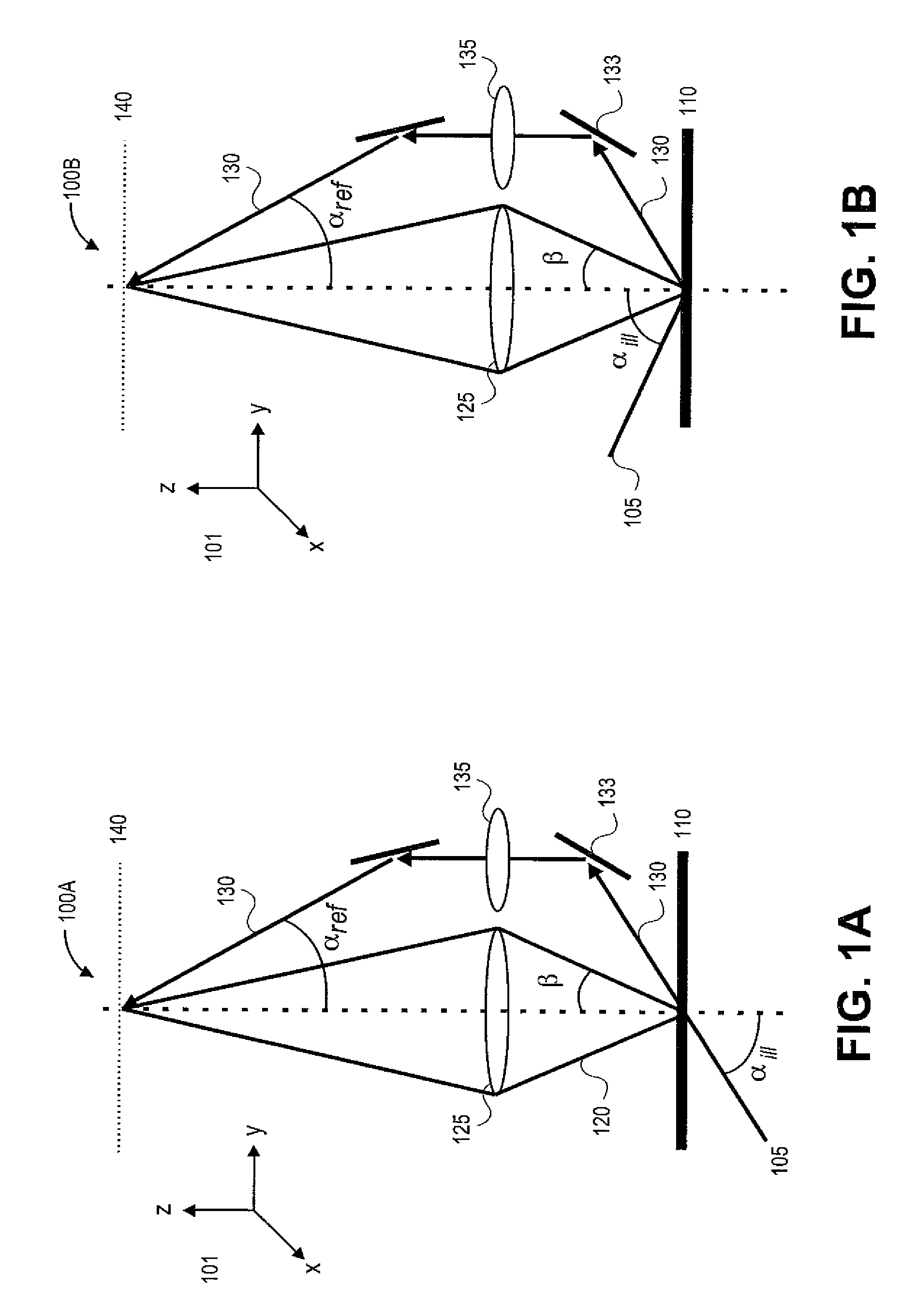
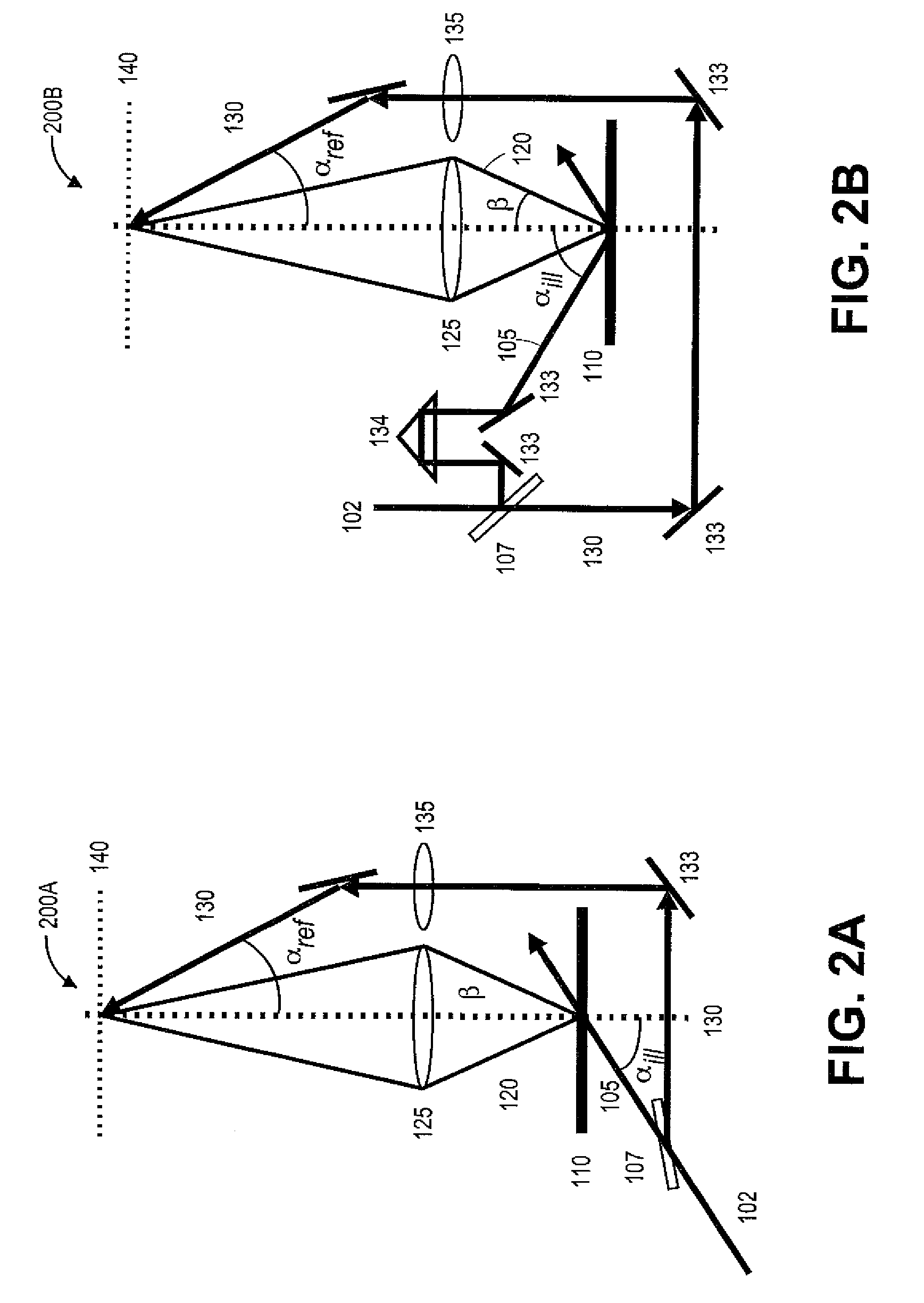
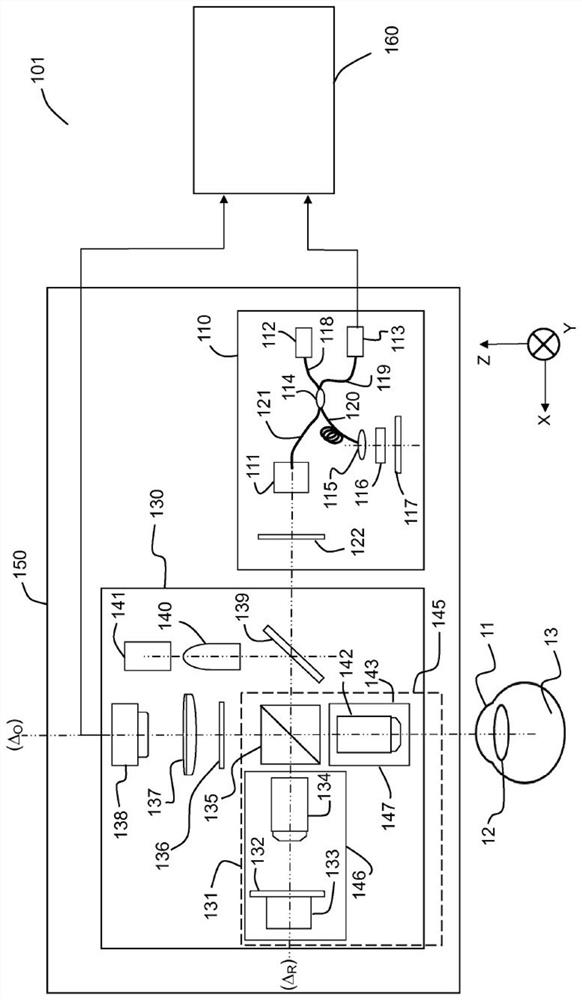
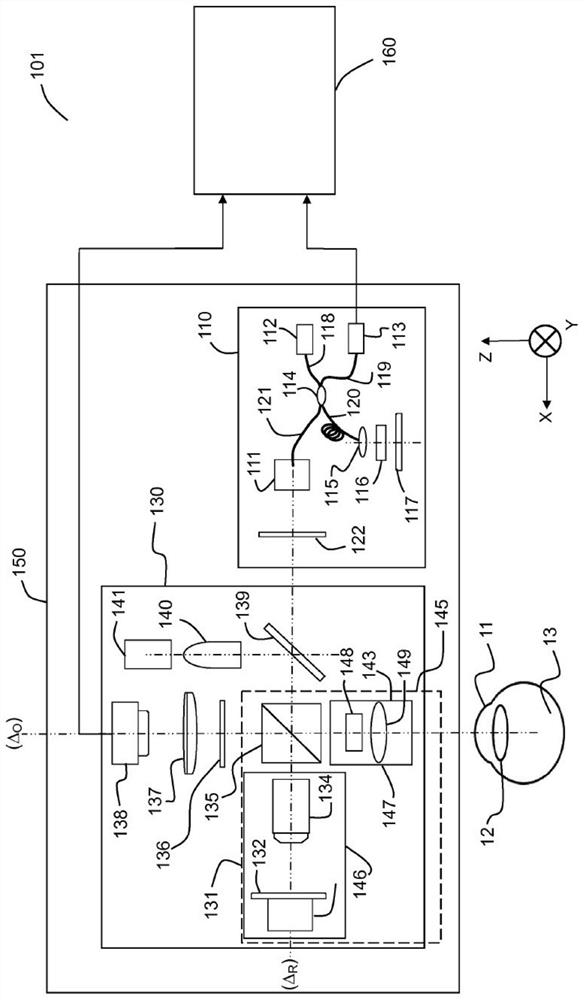
Methods and systems for in vivo full-field interference microscopy imaging
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a system (101) for in vivo, full-field interference microscopy imaging of a scattering three-dimensional sample. It comprises a full-field OCT imaging system (130) for providing en face images of the sample, wherein said full-field OCT system comprises an interference device (145) with an object arm (147) intended to receive the sample and a reference arm (146) comprising an optical lens (134) and a first reflection surface (133), and an acquisition device (138) configured to acquire a temporal succession of two-dimensional interferometric signals (I1, I2) resulting from interferences produced at each point of an imaging field; an OCT imaging system (110) for providing at the same times of acquisition of said two-dimensional interferometric signals, cross-sectional images of both the sample and a first reflection surface (133) of said full-field OCT imaging system (130); a processing unit (160) configured to determine a plurality of en face images (X - Y) of a plurality of slices of the sample, each en face image being determined from at least two two-dimensional interferometric signals (I1, I2) having a given phase shift; determine from the cross-sectional images provided by the OCT imaging system (110) at the times of acquisition of each of said two two-dimensional interferometric signals (I1, I2) a depth (z) for each en face image (X - Y) of said plurality of slices; determine a 3D image of the sample from said plurality of en face images of said plurality of slices of the sample and depths.
Owner:巴黎科学与文学基金会 +2
A comparative anti-interference micro-movement angle mirror laser interferometer, calibration method and measurement method
ActiveCN105043244BImprove anti-interference abilityHigh measurement accuracyUsing optical meansBeam splitterOptoelectronics
The invention relates to the field of precision test technologies and instruments, and particularly relates to a contrast type anti-interference micro-motion corner reflector laser interferometer, a calibration method and a measurement method. The contrast type anti-interference micro-motion corner reflector laser interferometer comprises a laser source, a micro-motion corner reflector, an interference measurement photoelectric detector, a movable corner reflector, a beam splitter group and a micro-motion platform, wherein the micro-motion corner reflector is arranged on the micro-motion platform. The contrast type anti-interference micro-motion corner reflector laser interferometer is characterized by further comprising a reflection measurement photoelectric detector. A laser beam is reflected to the beam splitter group by the movable corner reflector and then forms a reflected laser beam, and the reflected laser beam shots to the reflection measurement photoelectric detector. According to the laser interferometer provided by the invention, the reflection measurement photoelectric detector can measure the intensity of the laser beam reflected by the movable corner reflector, and the interference state of a laser interference beam is determined according to the intensity of the reflected laser beam, thereby realizing a purpose of resisting environmental interference.
Owner:润希乐生物科技(扬州)有限公司
Confocal Laser Microscope Based on Self-mixing Interference and Its Scanning Method
ActiveCN104729424BEasy to adjustSimple structureUsing optical meansConfocal laser scanning microscopePhotodetector
The invention discloses a confocal laser microscope based on self-mixing interference, which includes a helium-neon laser, a beam expander collimator lens group composed of a concave lens and a convex lens, a variable neutral density filter, an objective lens, a two-dimensional motion platform, One-dimensional motion platform, precision motion platform controller, photoelectric detector, current / voltage conversion circuit, filter, amplifier, analog / digital conversion circuit and computer unit; method of microscopic scanning using laser self-mixing interference and confocal principle Combining the advantages of simple structure and easy collimation of laser self-mixing technology and the characteristics of high axial resolution and strong anti-interference ability of confocal microscope, it solves the problem of autofocus and expanded measurement field of view of confocal laser microscope. It simplifies the structure of the traditional confocal microscope, reduces the difficulty of adjusting the reflection optical path in the confocal measurement system, and makes up for the characteristics of traditional confocal microscopes that require many optical components, high requirements for optical components, and difficult adjustment of the optical path.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
Contrast anti-interference micro-motion step planar reflector laser interferometer and calibration method and measurement method
ActiveCN105136020AAchieve anti-environmental interferenceTo achieve the purpose of anti-environmental interferenceUsing optical meansBeam splitterPhotovoltaic detectors
The invention relates to the field of precision test technologies and instruments, and particularly relates to a contrast anti-interference micro-motion step planar reflector laser interferometer and a calibration method and a measurement method. The contrast anti-interference micro-motion step planar reflector laser interferometer comprises a laser source, a micro-motion step planar reflector, an interference measurement photoelectric detector group, a mobile planar reflector, a beam splitter mirror group, and a micro-motion platform. The laser source emits z laser beams to the beam splitter mirror group. The contrast anti-interference micro-motion step planar reflector laser interferometer further comprises a reflection measurement photoelectric detector group. After a second laser beam group passes from the mobile planar reflector to the beam splitter mirror group, a reflected laser beam group is formed. Each laser beam in the reflected laser beam group shines onto one reflection measurement photoelectric detector. According to the laser interferometer of the invention, the interference state of laser interference beams is determined according to the intensity of a reflected laser beam group, and thus, the purpose of anti-environmental interference is achieved.
Owner:北信(扬州)管道技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com