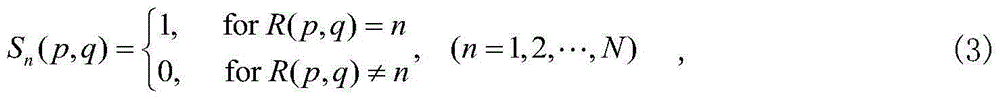Patents
Literature
46 results about "Object wave" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
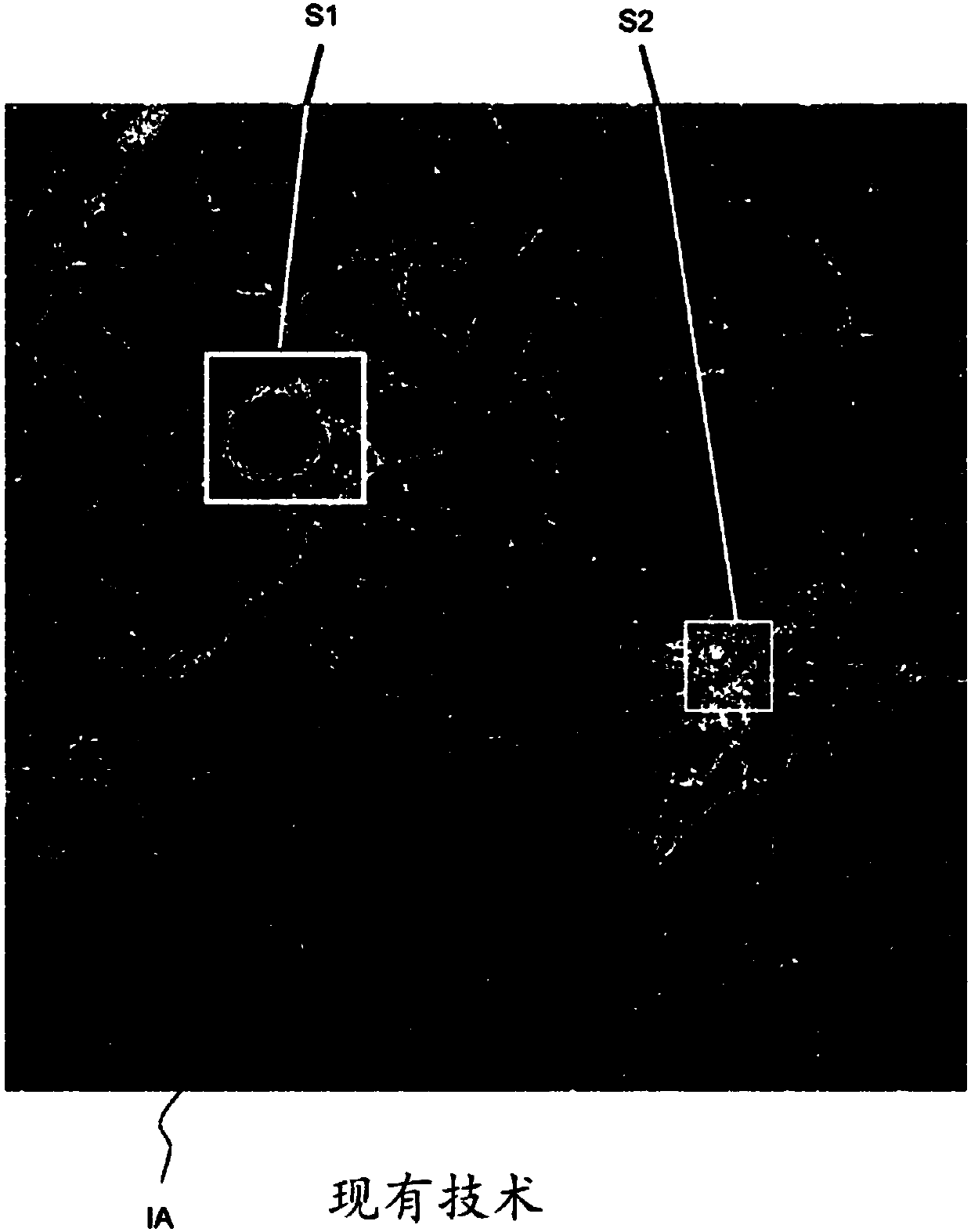
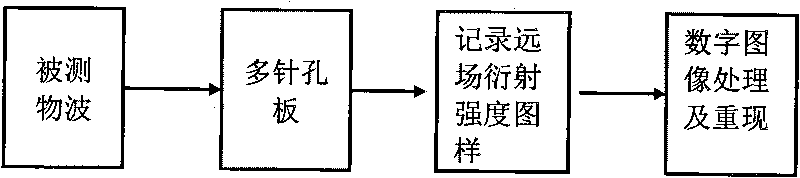
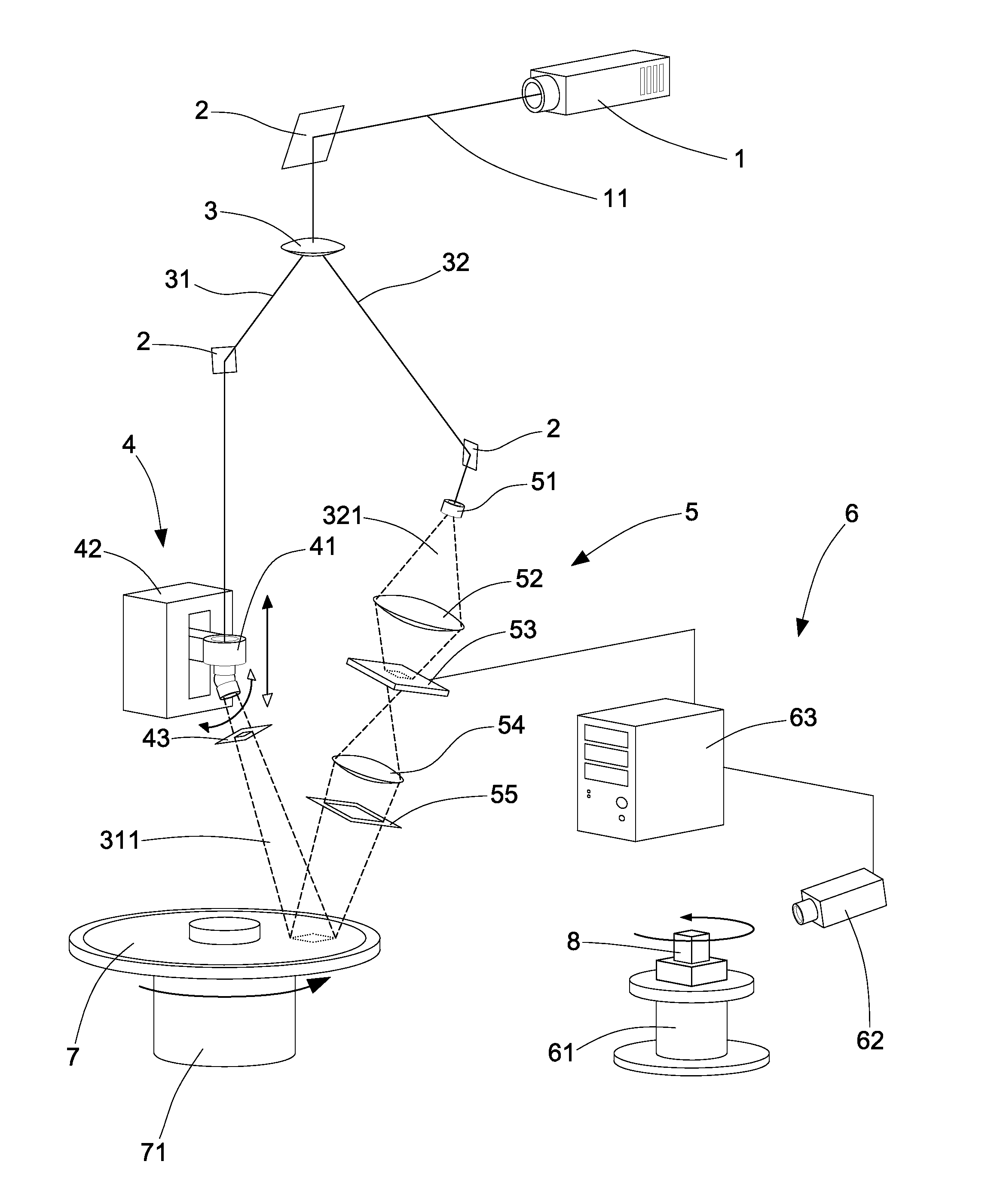
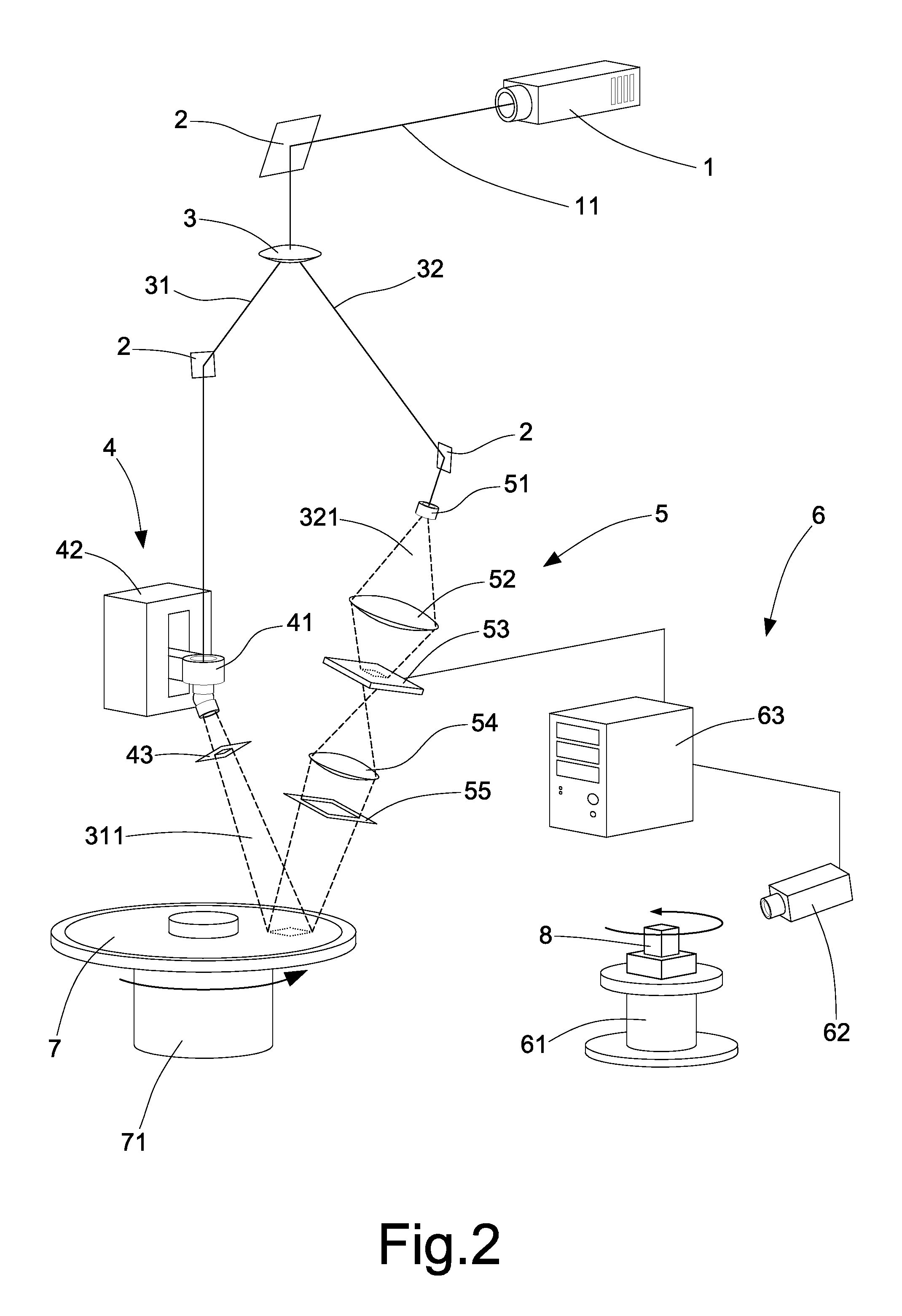
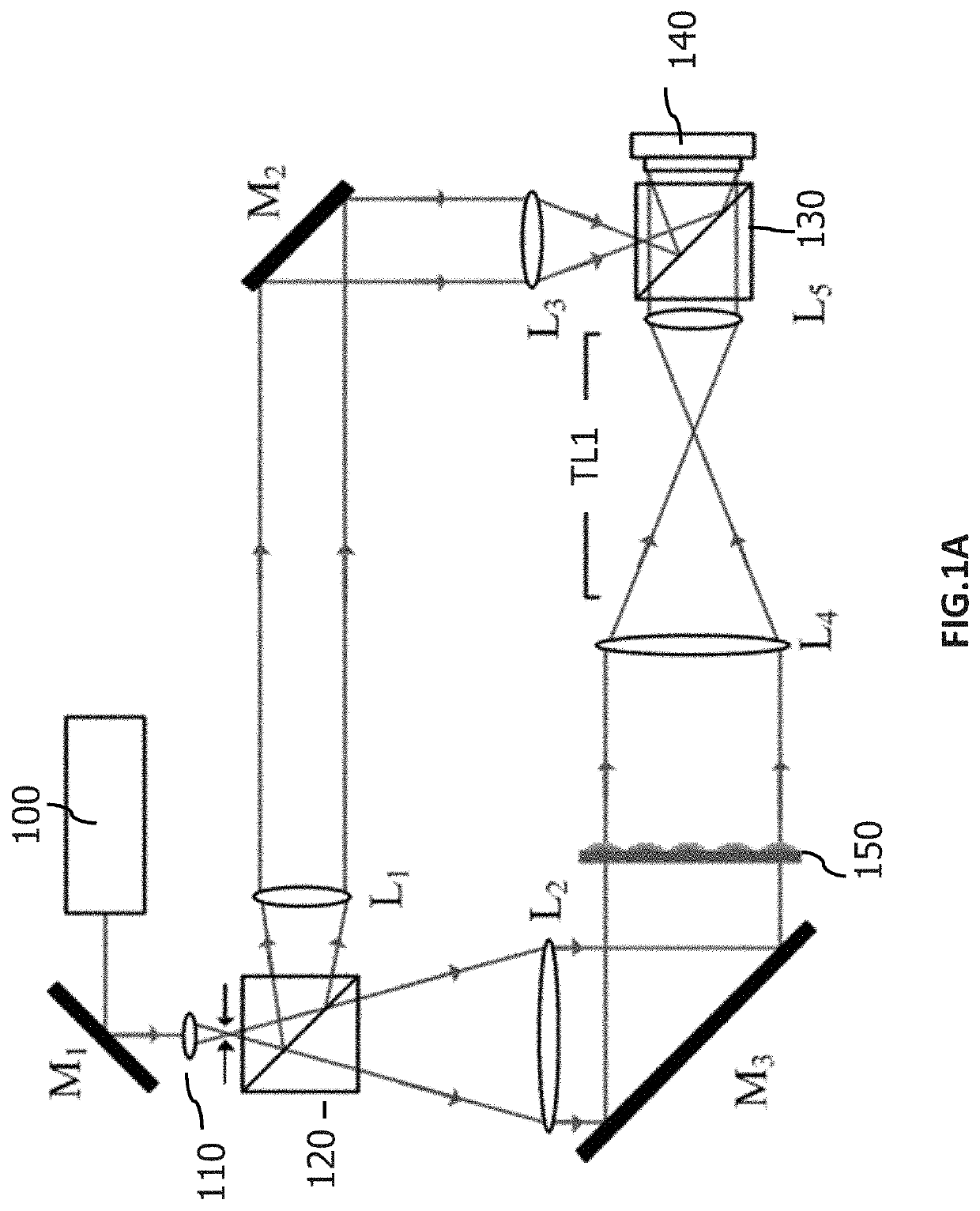
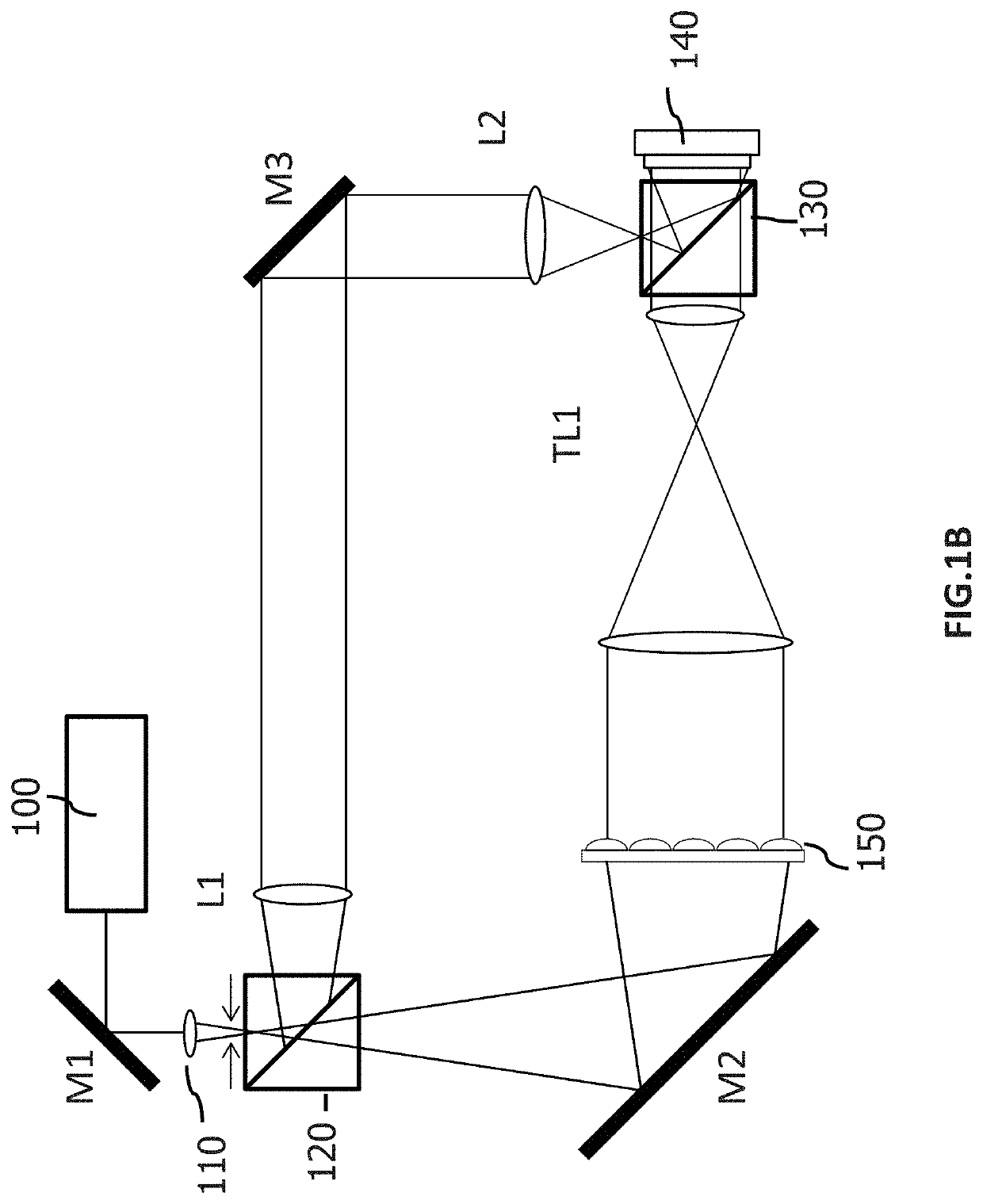
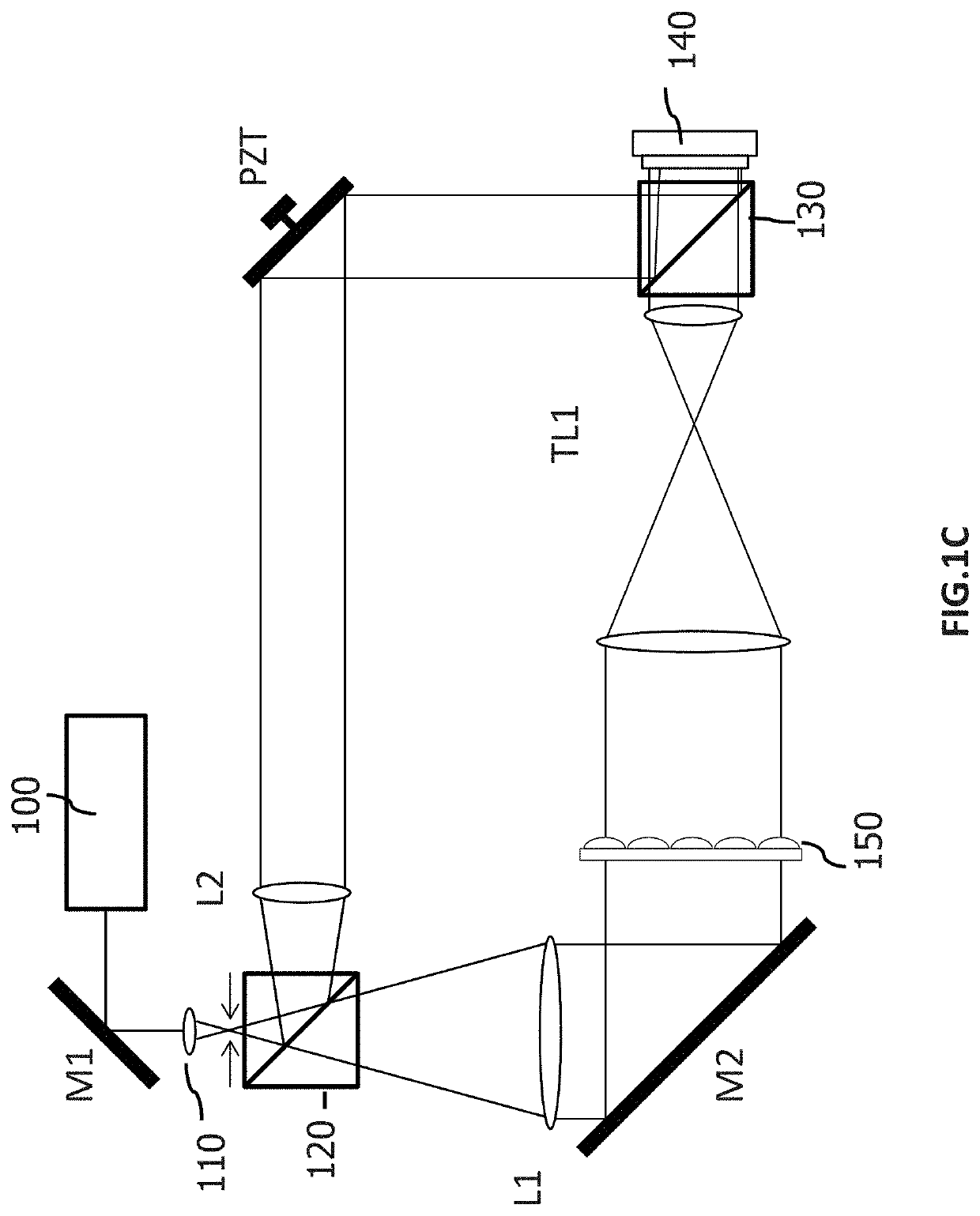
Wavefront measurement method and device based on multiple-pinhole plate
InactiveCN101726366ARealize dynamic real-time measurementEasy to manufactureOptical measurementsOptical elementsComplex amplitudeWavefront
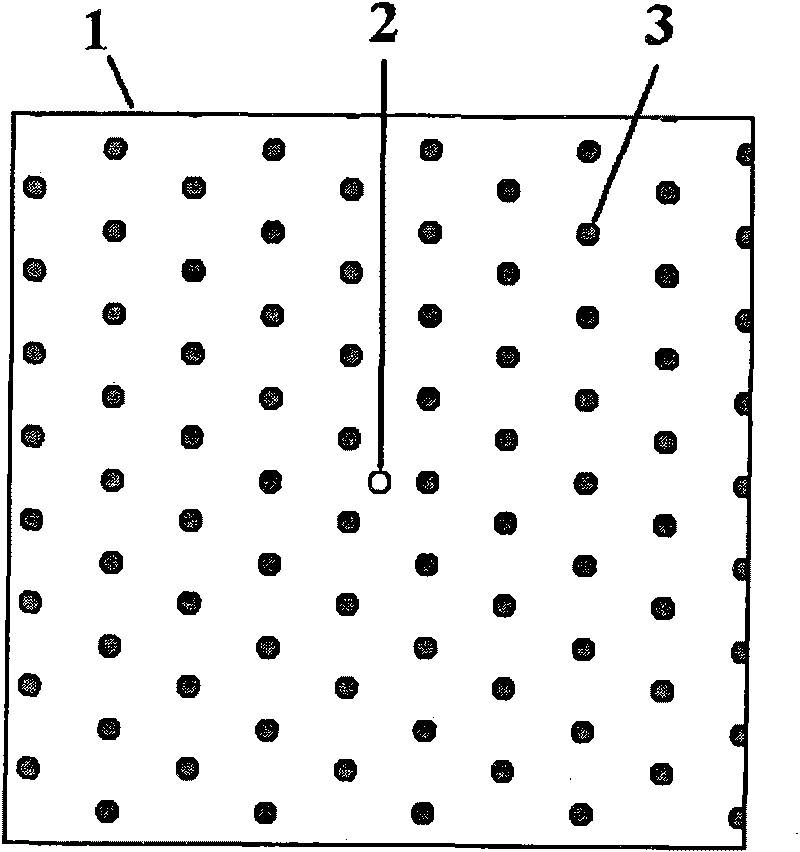
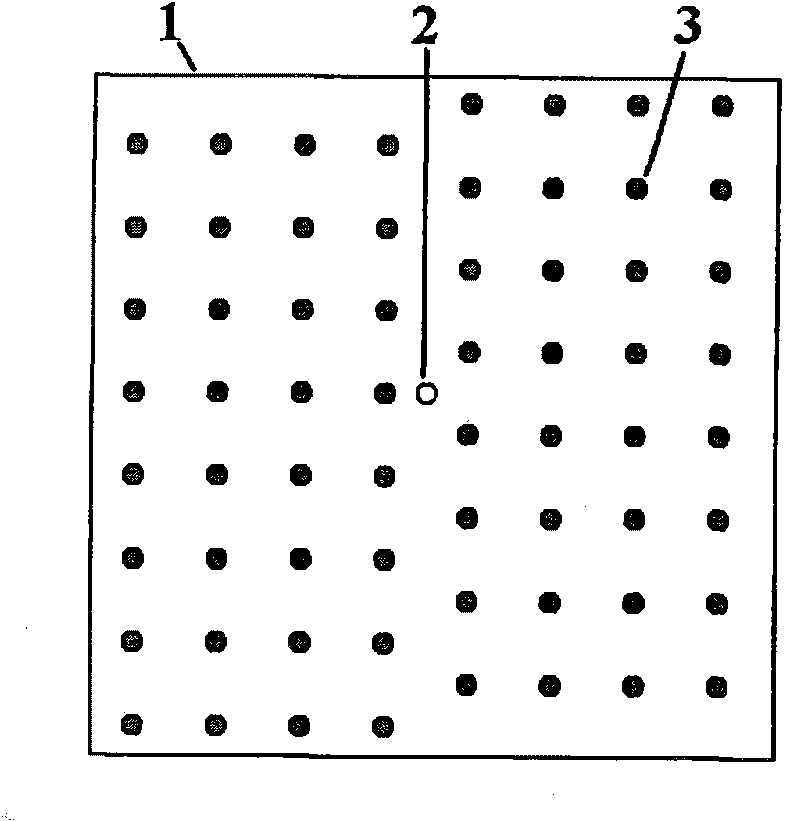
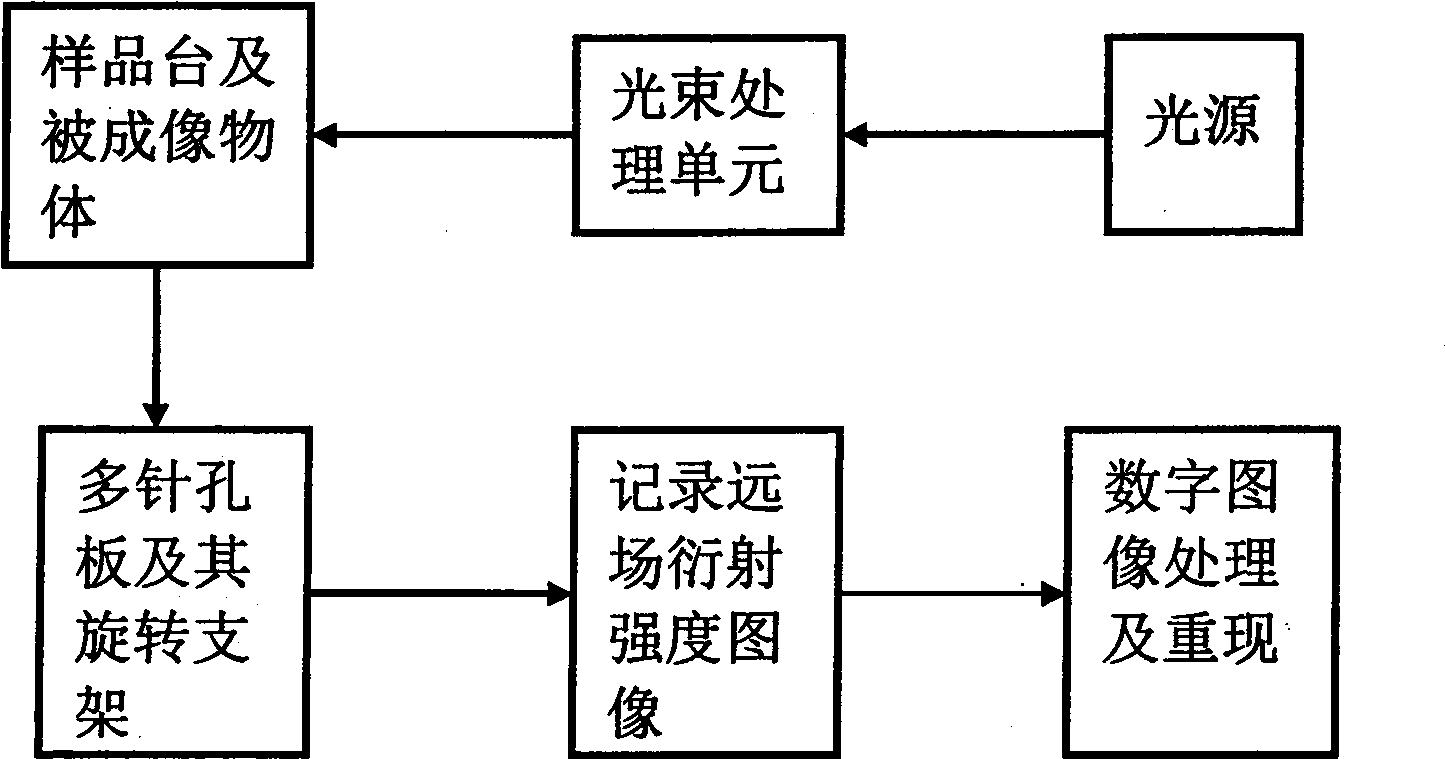
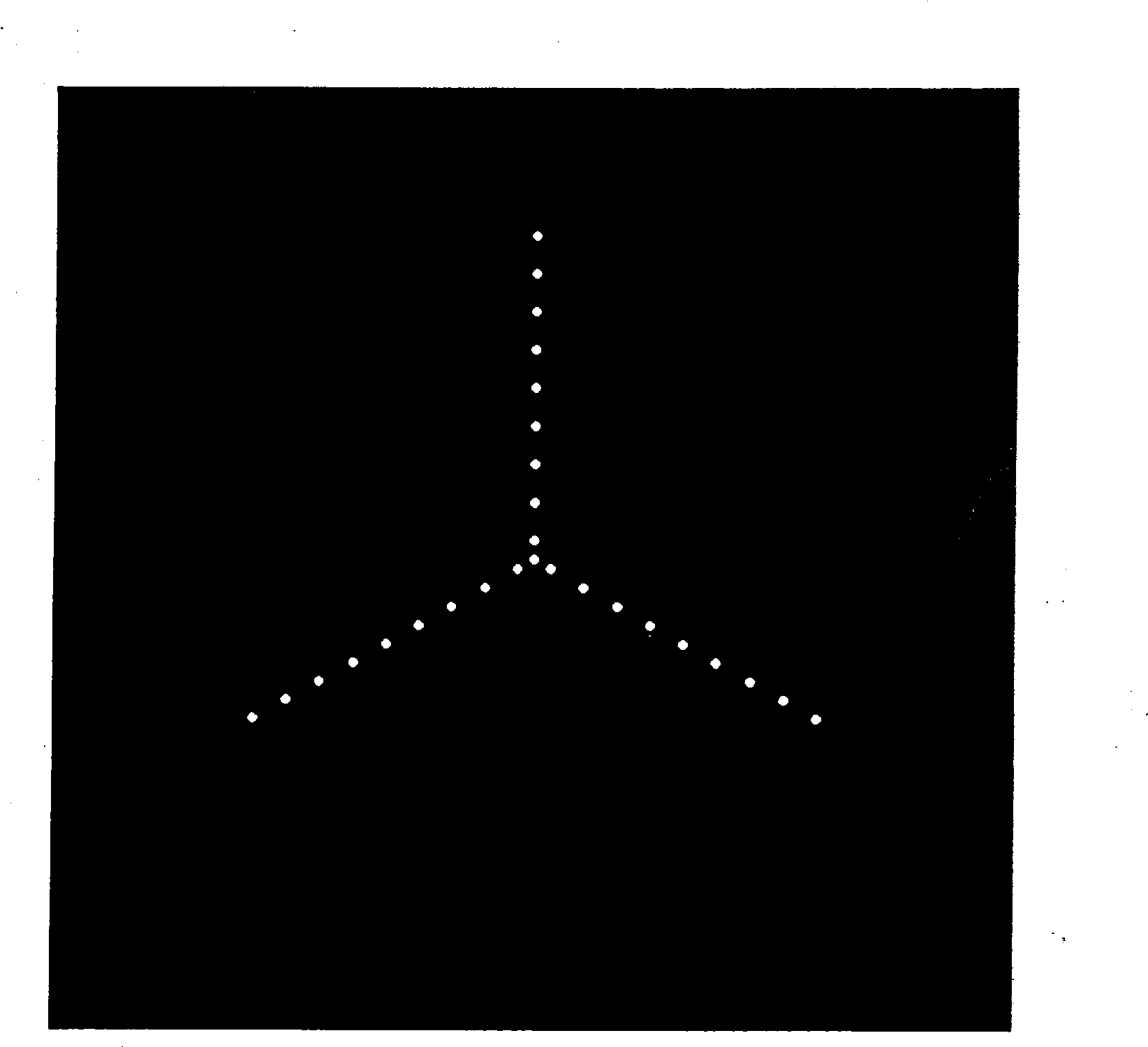
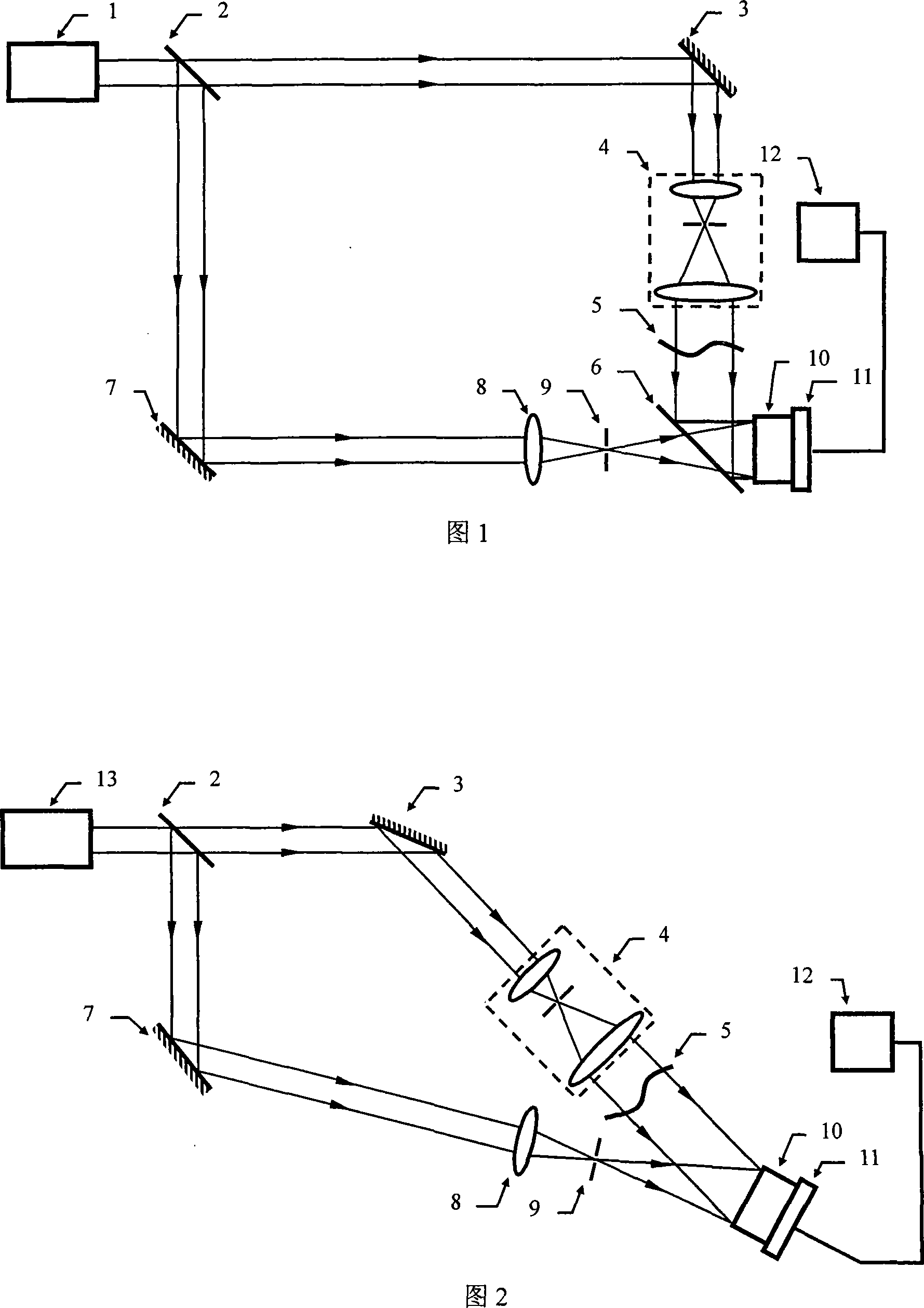
The invention discloses wavefront measurement method and device based on a multiple-pinhole plate. The wavefront measurement method comprises the following steps of: irradiating a measured object wave to the multiple-pinhole plate containing one reference pinhole and multiple measurement pinholes; recording an intensity distribution pattern of a Fraunhofer diffraction light field of the object wave transmitting the multiple-pinhole plate by an image sensor, wherein the Fraunhofer diffraction light field is in direct proportion to the Fourier transform of the object wave transmitting the multiple-pinhole plate; carrying out inverse Fourier transform on the recorded intensity distribution pattern, and extracting the function values of points which correspond to the center positions of the measurement pinholes of the multiple-pinhole plate in the inverse Fourier transform pattern, wherein the function values is in direct proportion to the complex amplitude values of the measured object wave on the measurement pinholes; and reproducing an imaged object in a computer by utilizing the complex amplitude values. The invention increases the diffraction imaging speed, has simple structure, convenient regulation and low cost, is suitable for multiple different light sources and can realize the real-time wavefront sensing and the diffraction imaging of a pure-phase object and a plural object or a three-dimensional object.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
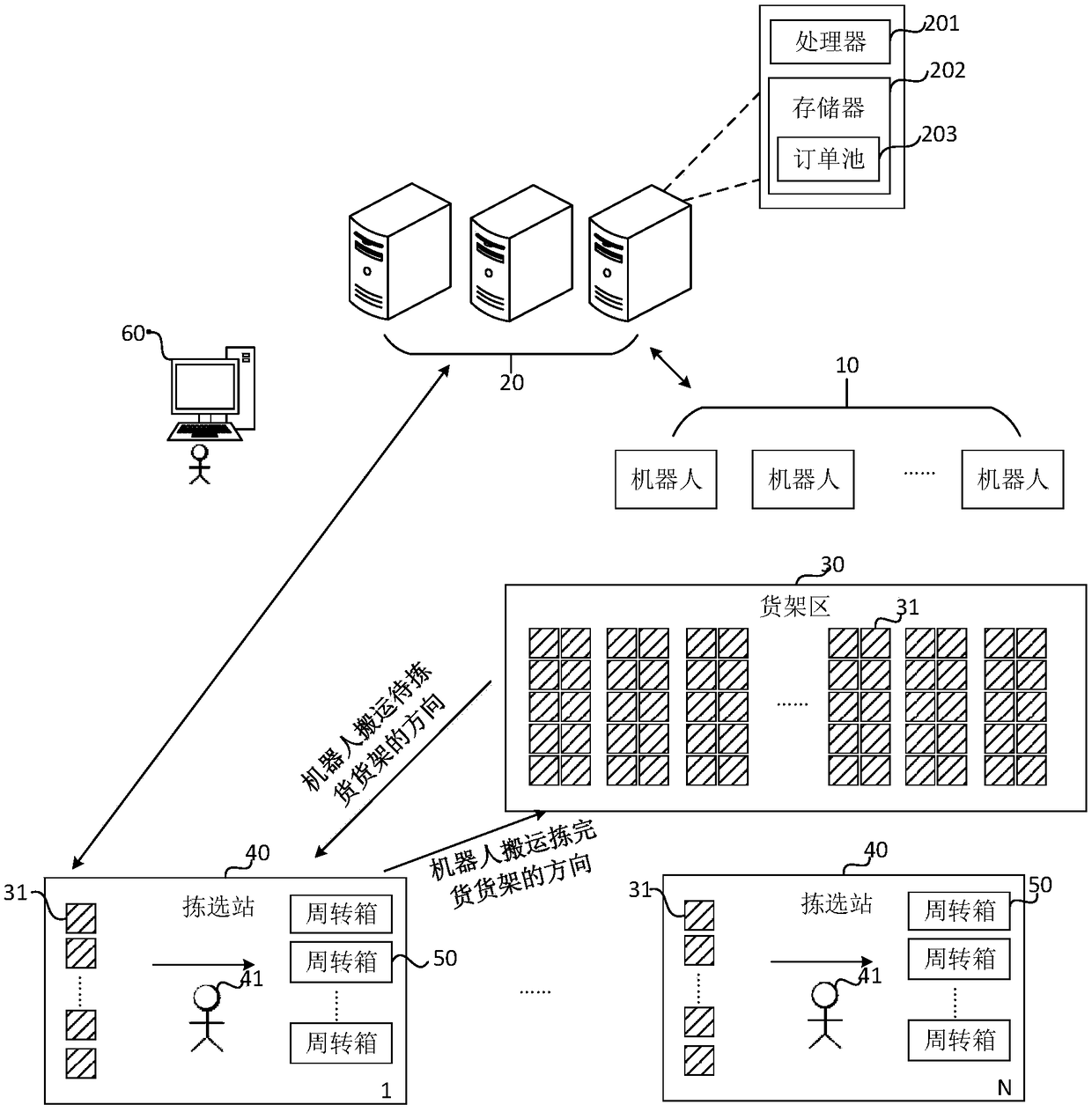
Order processing method, device thereof, server and storage medium
InactiveCN108961016AImprove the efficiency of picking and compound packagingImprove the efficiency of warehouse operation processBuying/selling/leasing transactionsOrder formOrder processing
An embodiment of the invention discloses an order processing method, a device thereof, a server and a storage medium, wherein the method comprises the steps of identifying an order form, and marking the order according to the identified order form, wherein the order form comprises a single-item single-object kind; determining single-item single-object orders according to the mark of the order form, combining the single-item single-object orders for obtaining at least one single-item single-object wave task so as to perform sorting on the single-item single-object wave task. The single-item single-object wave task comprises at least one single-item single-object order. The order processing method, the device thereof, the server and the storage medium can improve sorting and composite packaging efficiency of the single-item single-object orders and efficiency of the whole warehousing operation flow.
Owner:BEIJING JIZHIJIA TECH CO LTD
Method and device for high resolution full field interference microscopy
ActiveUS20130107275A1Easy to controlInterferometric spectrometryDiagnostic recording/measuringFull fieldPhase difference
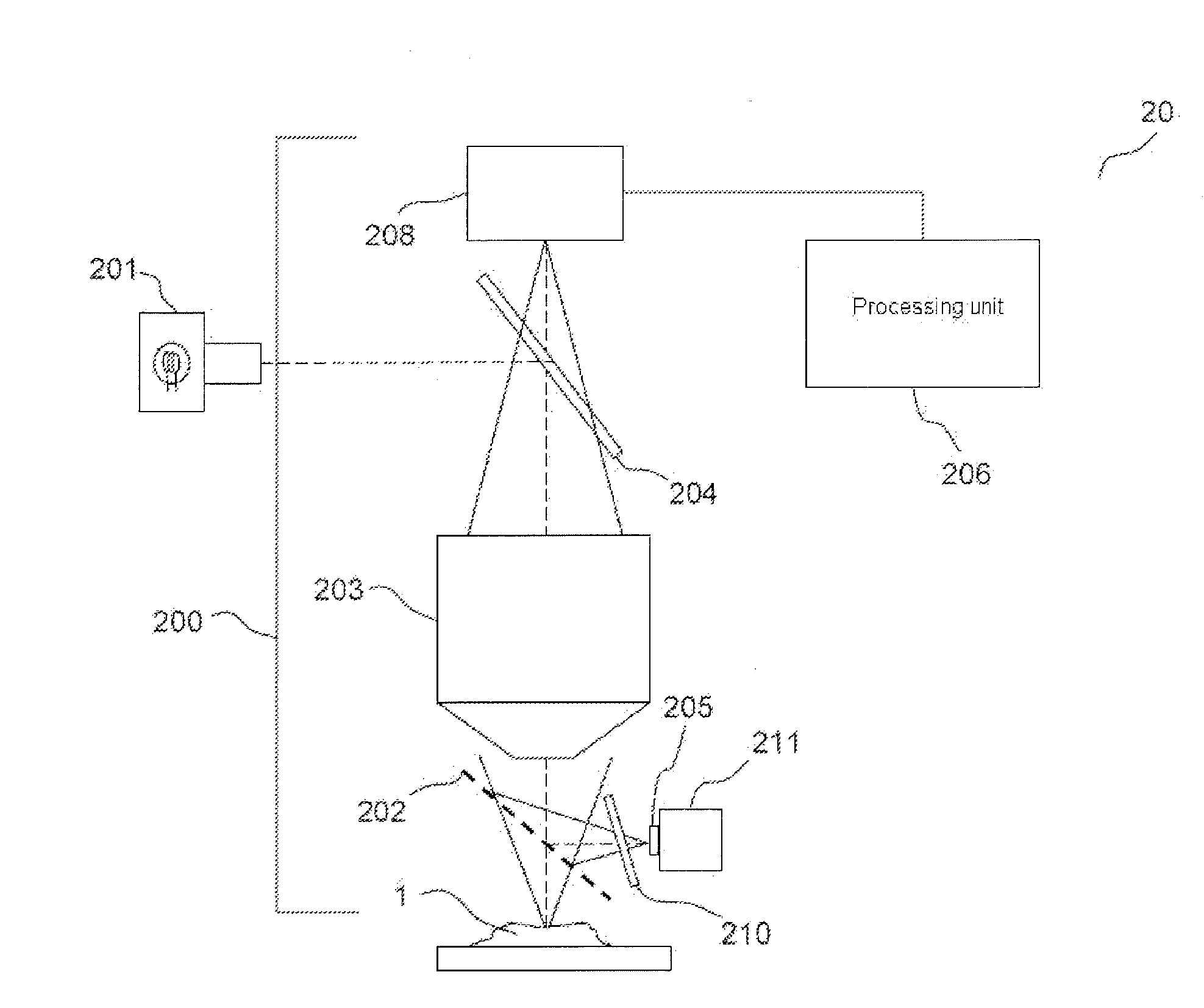
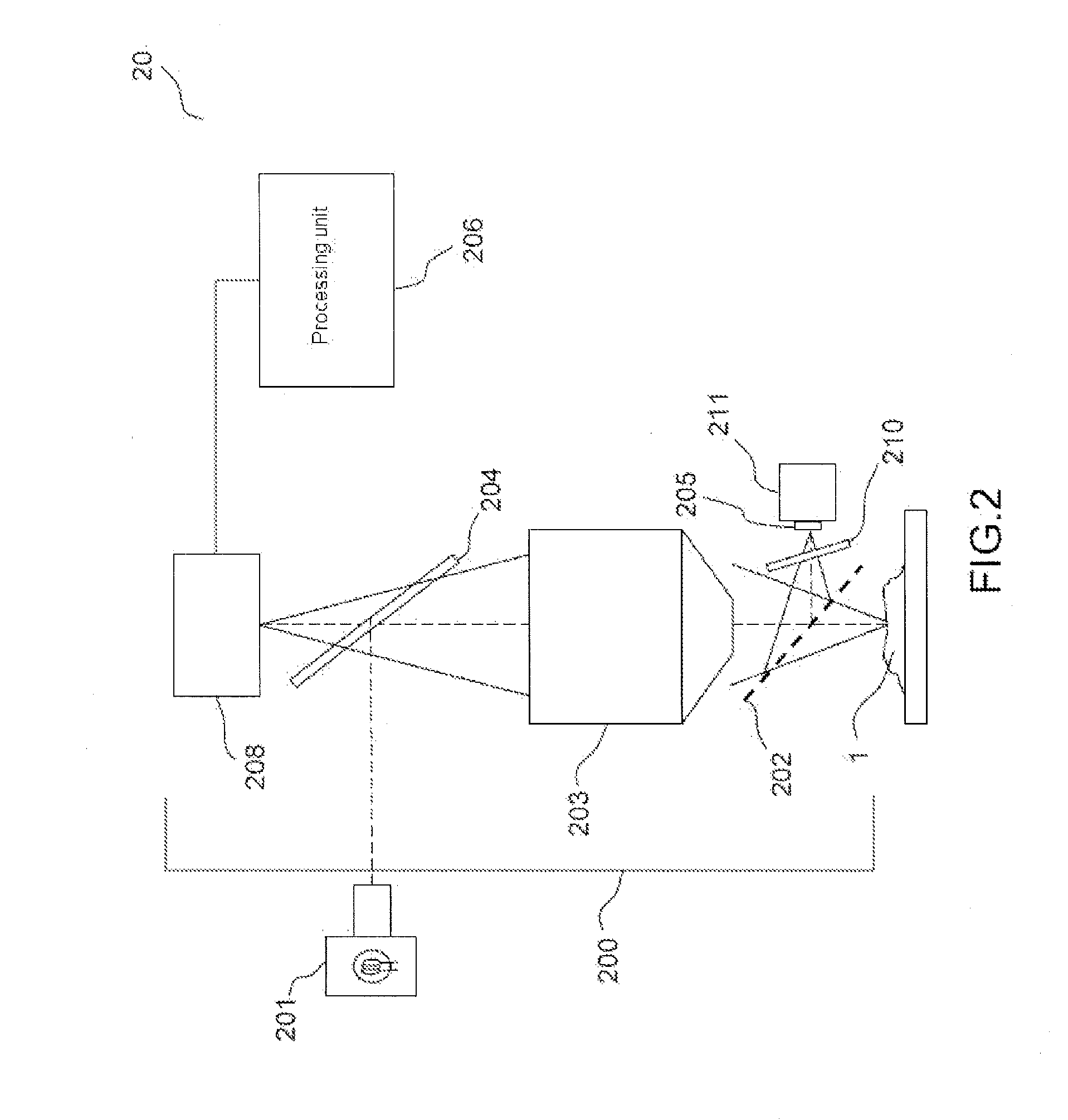
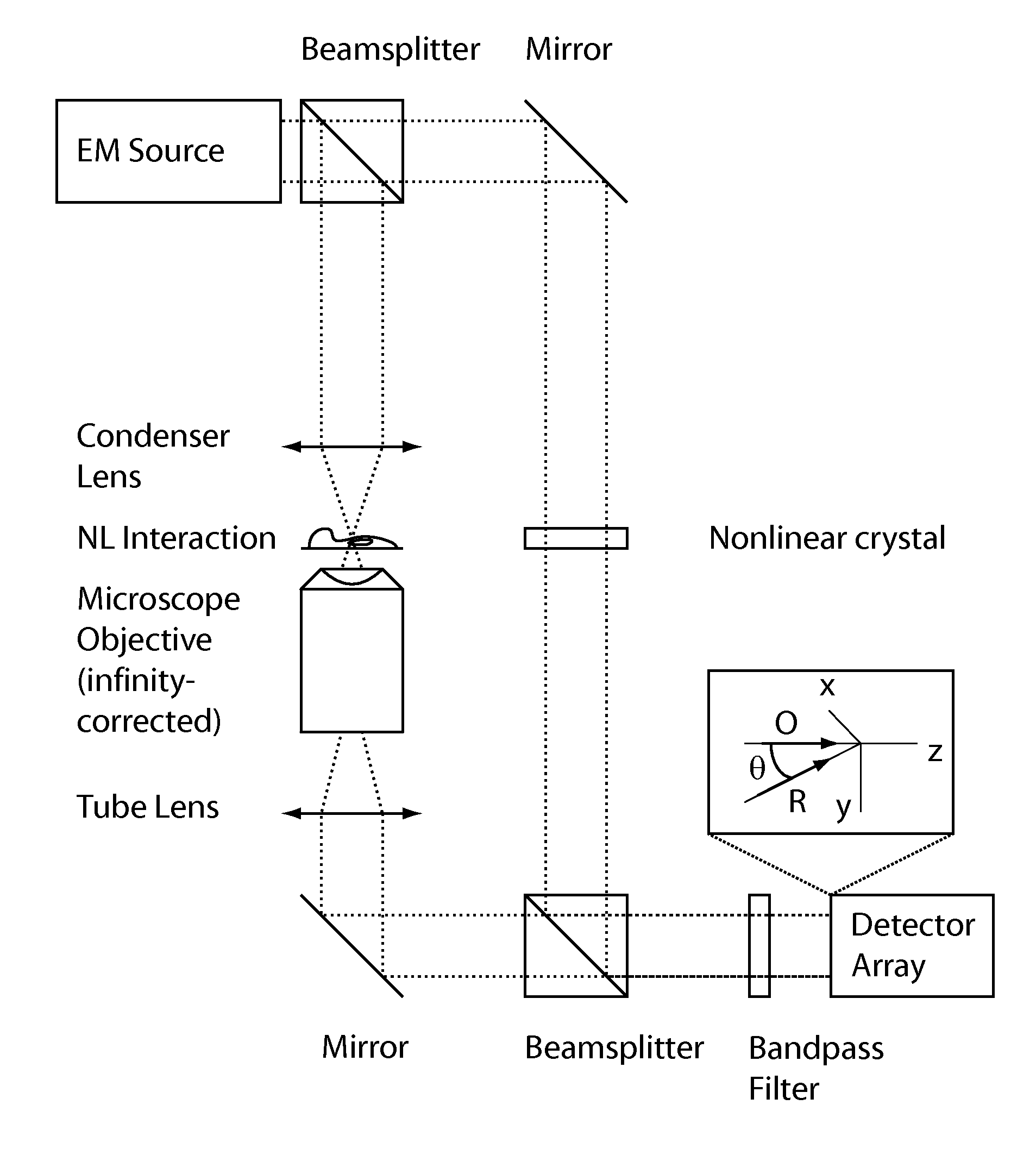
According to one aspect, the invention relates to a device (20) for three-dimensional imaging by full-field interferential microscopy of a volumic and scattering sample (1) comprising an emission source (201) for emitting an incident wave with low temporal coherence, an imaging interferometer (200) of variable magnification, allowing for the acquisition of at least one first and one second interferometric images resulting from the interference of a reference wave obtained by reflection of the incident wave on a reference mirror (205) and an object wave obtained by backscattering of the incident wave by a slice of the sample at a given depth of the sample, the at least two interferometric images having a phase difference obtained by varying the relative path difference between the object and reference arms of the interferometer, a processing unit (206) for processing said interferometric images making it possible to obtain a tomographic image of said slice of the sample, means for axially displacing the interferometer relative to the sample allowing for the acquisition of tomographic images for slices at different depths of the sample and means for varying the magnification of the imaging interferometer allowing for the acquisition of interferometric images of a slice of the sample for different magnification values.
Owner:LLTECH MANAGEMENT
Coherent diffraction imaging method and its processing equipment
InactiveCN101482503AImprove efficiencyHigh speedPhase-affecting property measurementsCorrelation functionFourier transform on finite groups
The invention discloses a coherent diffraction imaging method and processing device thereof. The object wave passes through a rotary multi-pinhole plate. The Fraunhofer diffraction intensity distribution pattern of the object wave passing through the multi-pinhole plate is recorded by an image sensor. The diffraction intensity distribution is subjected to inverse Fourier transformation to obtain the correlation function pattern of the recorded object wave, the amplitude and phase information of the object wave to be measured are directly extracted from the points corresponding with each measurement pinhole center position coordinate in the correlation function pattern and the diffraction imaging of the complex amplitude object is realized in the computer. The coherent diffraction imaging method has no need of any iterative process and greatly reduces the requirement of the scanning recording process and positioning accuracy and increases the diffraction imaging speed, with other features of simple processing device, convenient adjustment, lower cost, suitable of various different light source, and the imaging of the complex object or three-dimensional object can be realized without imaging lens, especially suitable for the situation that it is difficult to prepare high-quality X-ray using the imaging lens.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
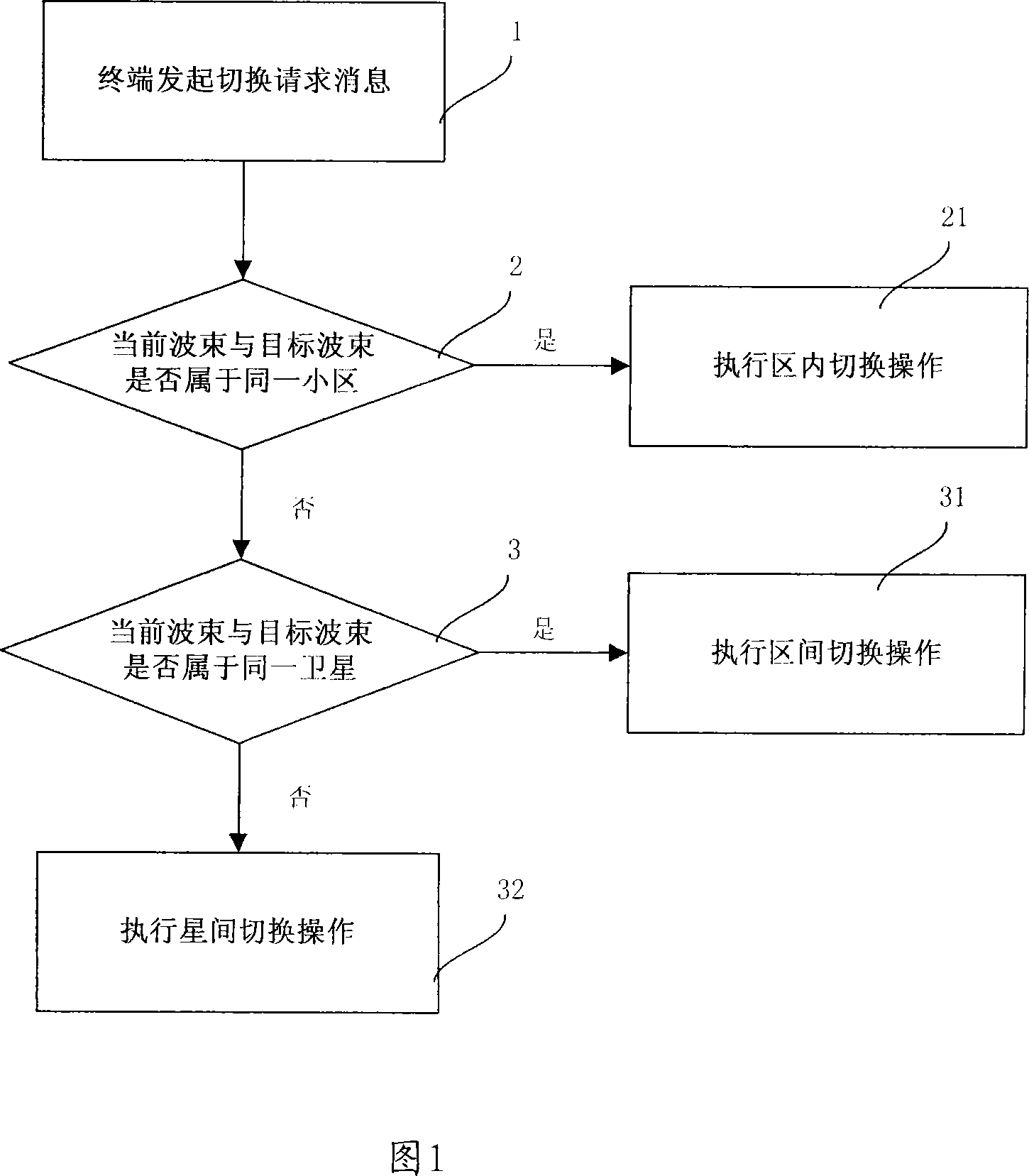
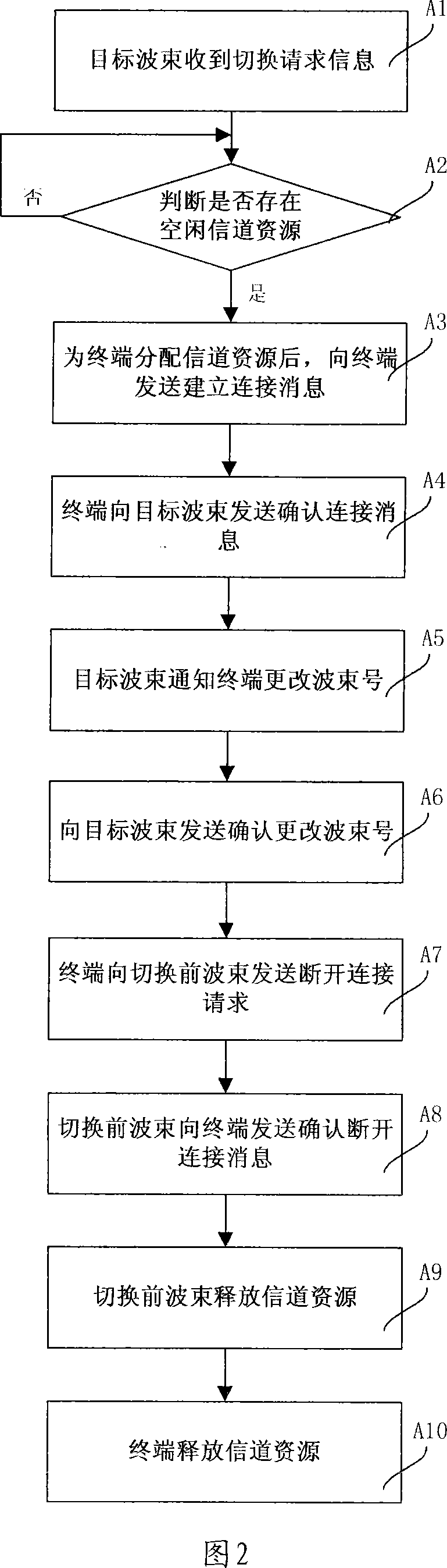
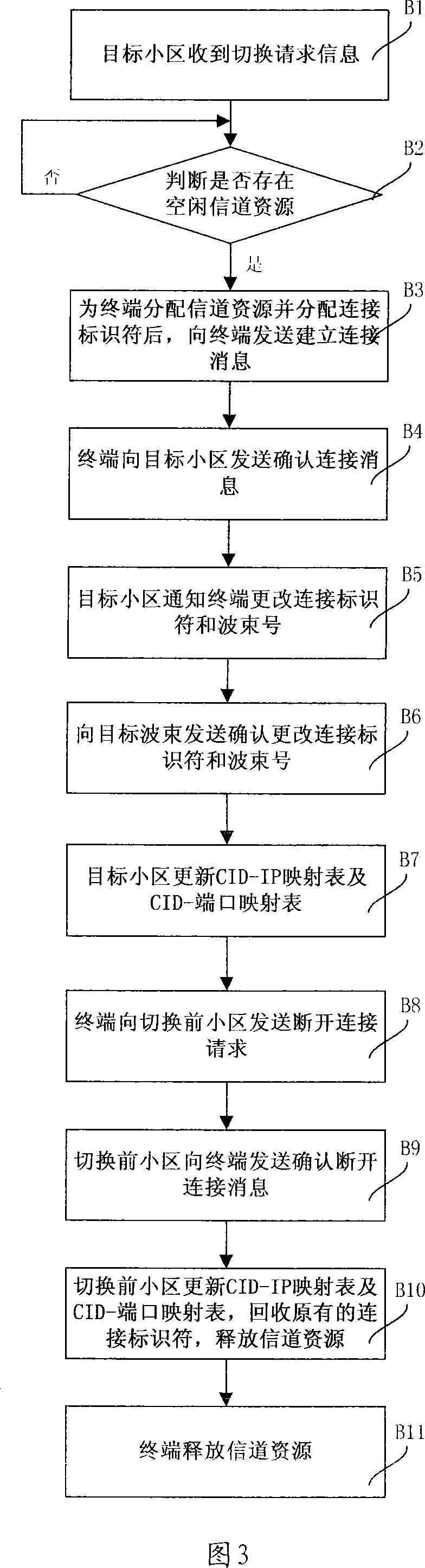
Planet-earth link switching method and planet-earth link switching mode selection processing device
InactiveCN101022668AGuaranteed Performance RequirementsReduce switching costsNetwork topologiesRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsMode selectionSatellite
A method for switching over link of satellite / ground includes selecting cell-in switching-over mode to carry out switching-over operation if current wave beam and object wave beam are in the same cell, selecting intercell switching-over mode to carry out switching-over operation if current wave beam and object wave beam are in the same satellite but not in the same cell and selecting intersatellite switching-over mode to carry out switching-over operation if current wave beam and object wave beam are not in the same satellite. The device used for realizing said method is also disclosed.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
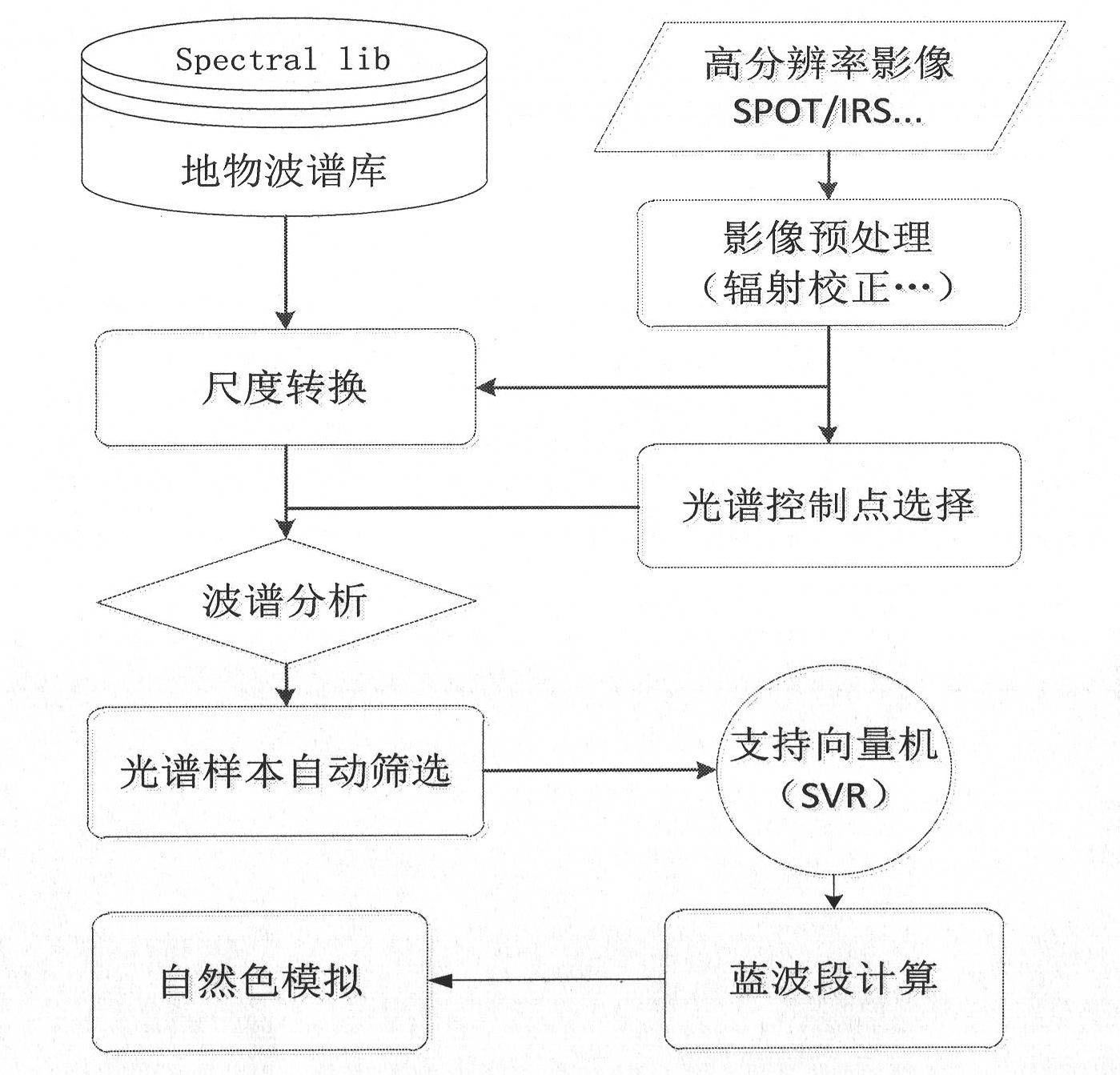
Automatic simulation method of natural-color products of high-space-resolution remote sensing images
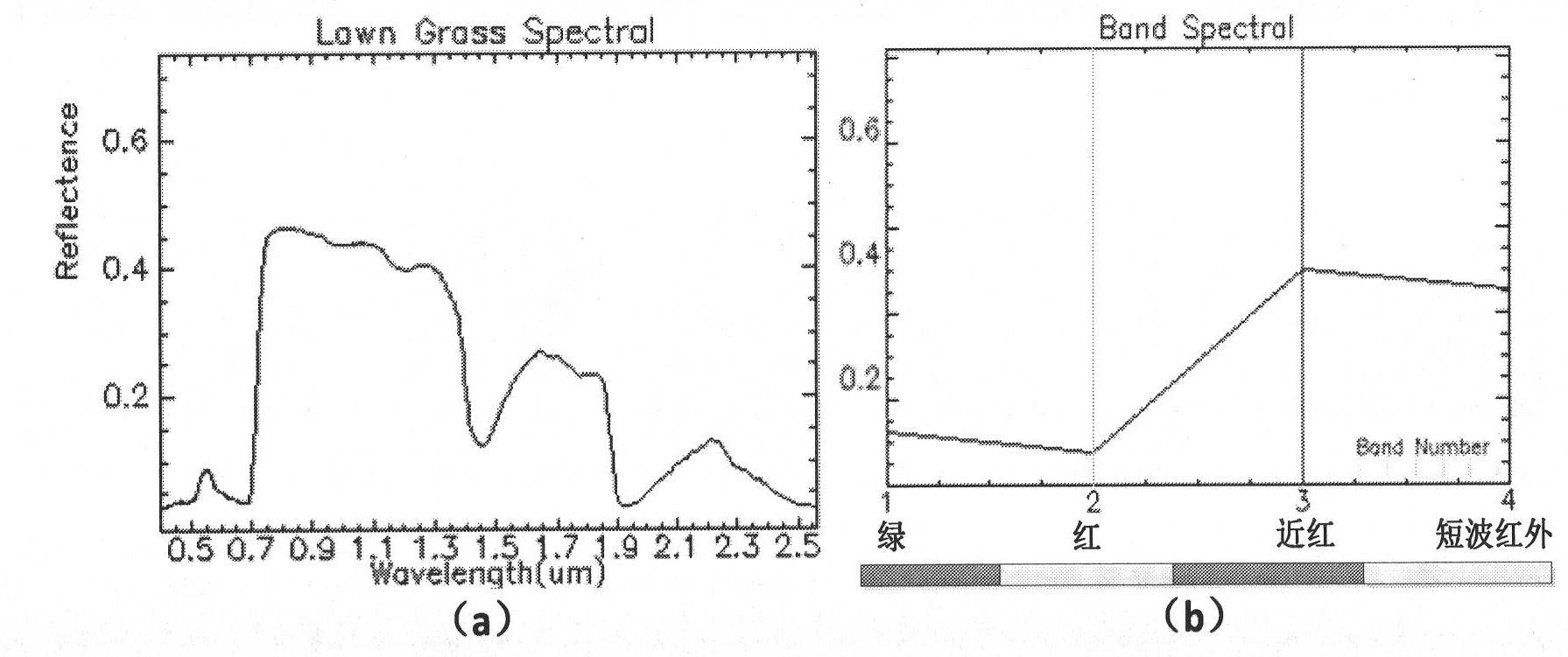
InactiveCN102222238ARich Spectral InformationTrue colorCharacter and pattern recognitionColor imageData pre-processing
The invention provides a simulation method of natural colors of high-resolution remote sensing images based on field spectroscopic data; especially for high-resolution remote sensing images without blue-light waveband (such as SPOT, IRS and the like), the difficulty of natural color synthesis of the images can be solved by simulation of the blue-light wave band. The simulation method comprises the steps of: firstly, preprocessing the field object wave spectrum data according to wavelength bandwidth setting of images to be simulated and a spectrum response function; then selecting control points of spectrum samples automatically according to the cluster result of ISODATA (iterative self-organizing data) algorithm, and selecting spectrum candidate samples by a spectral matching algorithm; next, learning and training by using a support vector machine to construct a nonlinear relation model among the blue-light wavebands to be simulated and known wavebands; and finally, realizing calculation of the blue-light wavebands according to the nonlinear relation model (SVM). The simulated natural-color image product is natural in color tone and real in color, and can be used in multiple fields, the automatic simulation of the missing blue-light wavebands of the high-space-resolution remote sensing images and the making of natural-color images are realized and the workload of manual image adjustment is greatly reduced.
Owner:REMOTE SENSING APPLIED INST CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and Apparatus of Structured Illumination Digital Holography
ActiveUS20190049896A1High resolutionHolographic optical componentsActive addressable light modulatorPhase shiftedFrequency spectrum
A method of structured illumination digital holography includes: (a) providing a structured illumination generating unit and binarization random number encoding unit to generate a coded structured illumination pattern; (b) sampling at least two patterns with phase shift which synthesized as a single structured illumination pattern to be encoded; (c) forming a single digital hologram, and wavefront reconstructing the single digital hologram; (d) performing a compressive sensing approach to recover the object wave with at least two phase shift patterns; and (e) reconstructing the separation of overlap spectrum, to obtain an image covering bandpass spectrum with different high frequency and low frequency.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
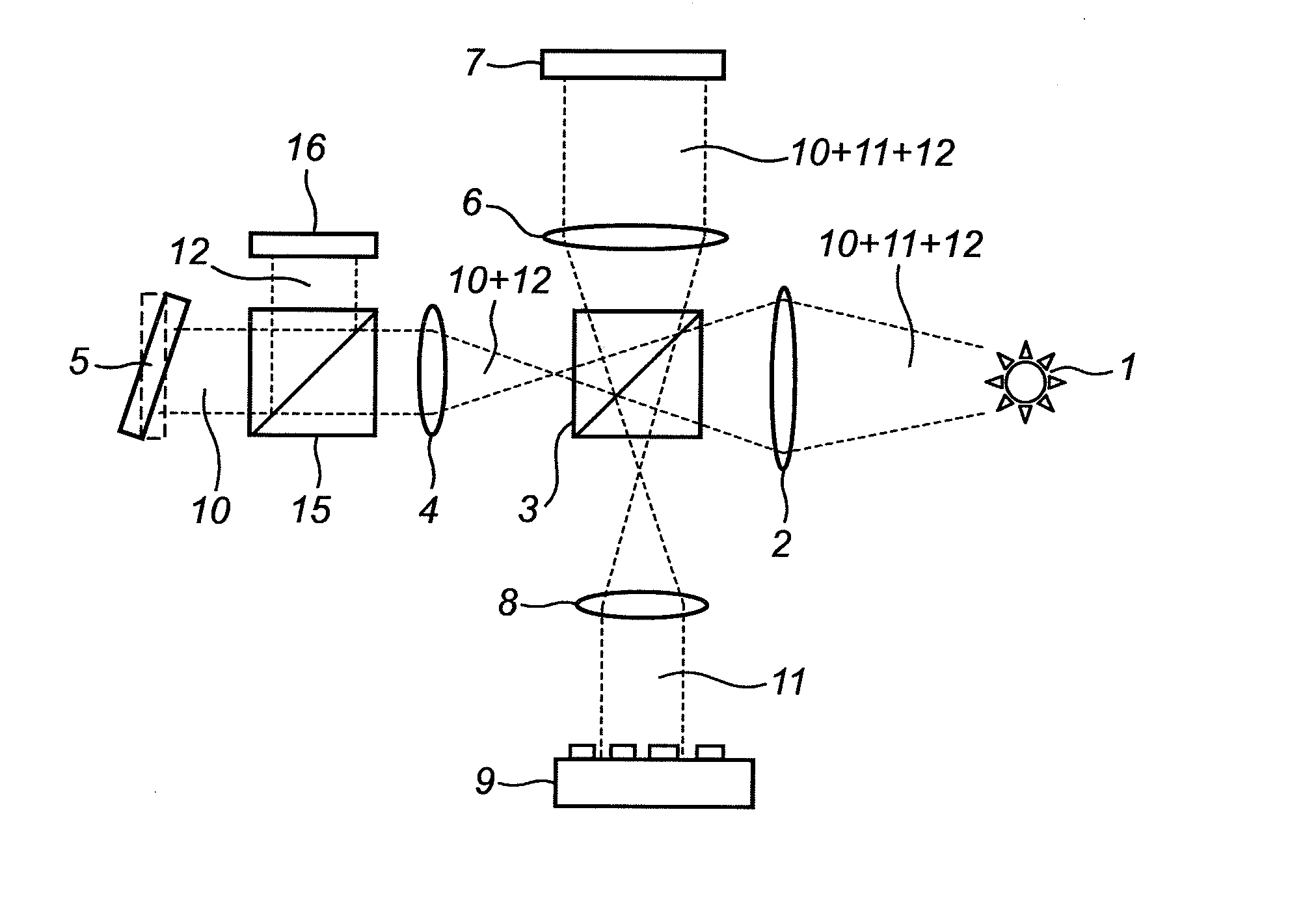
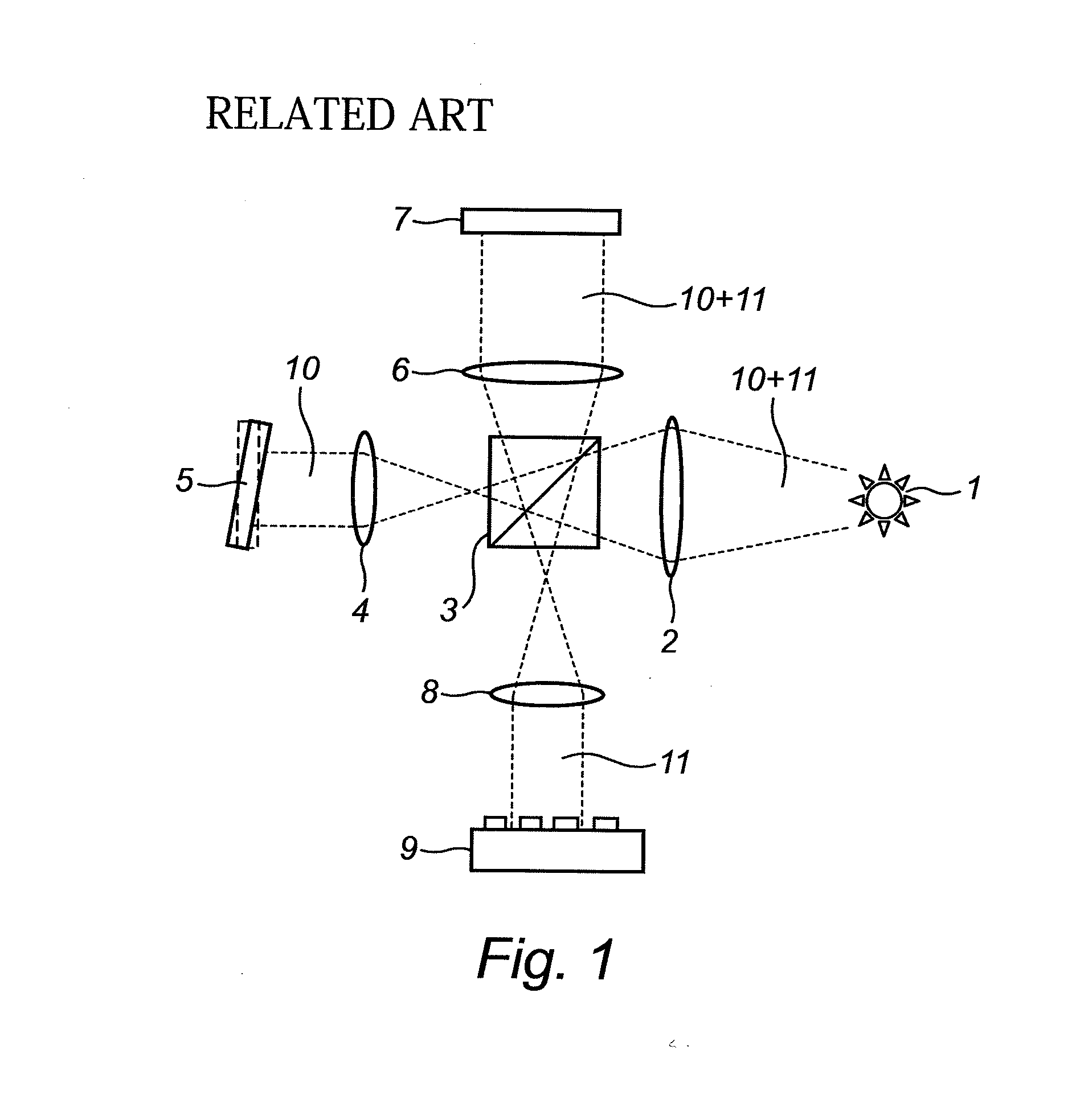
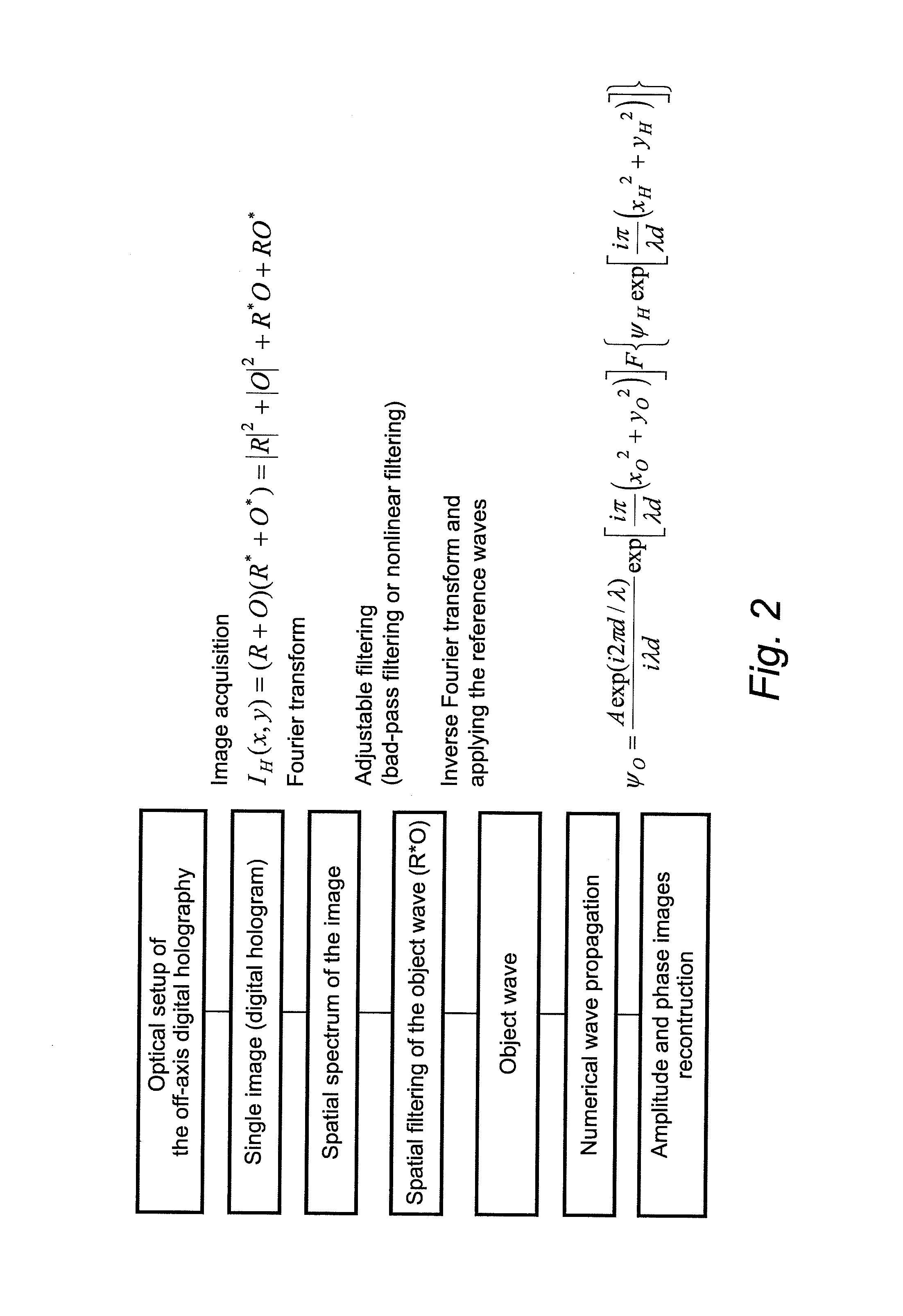
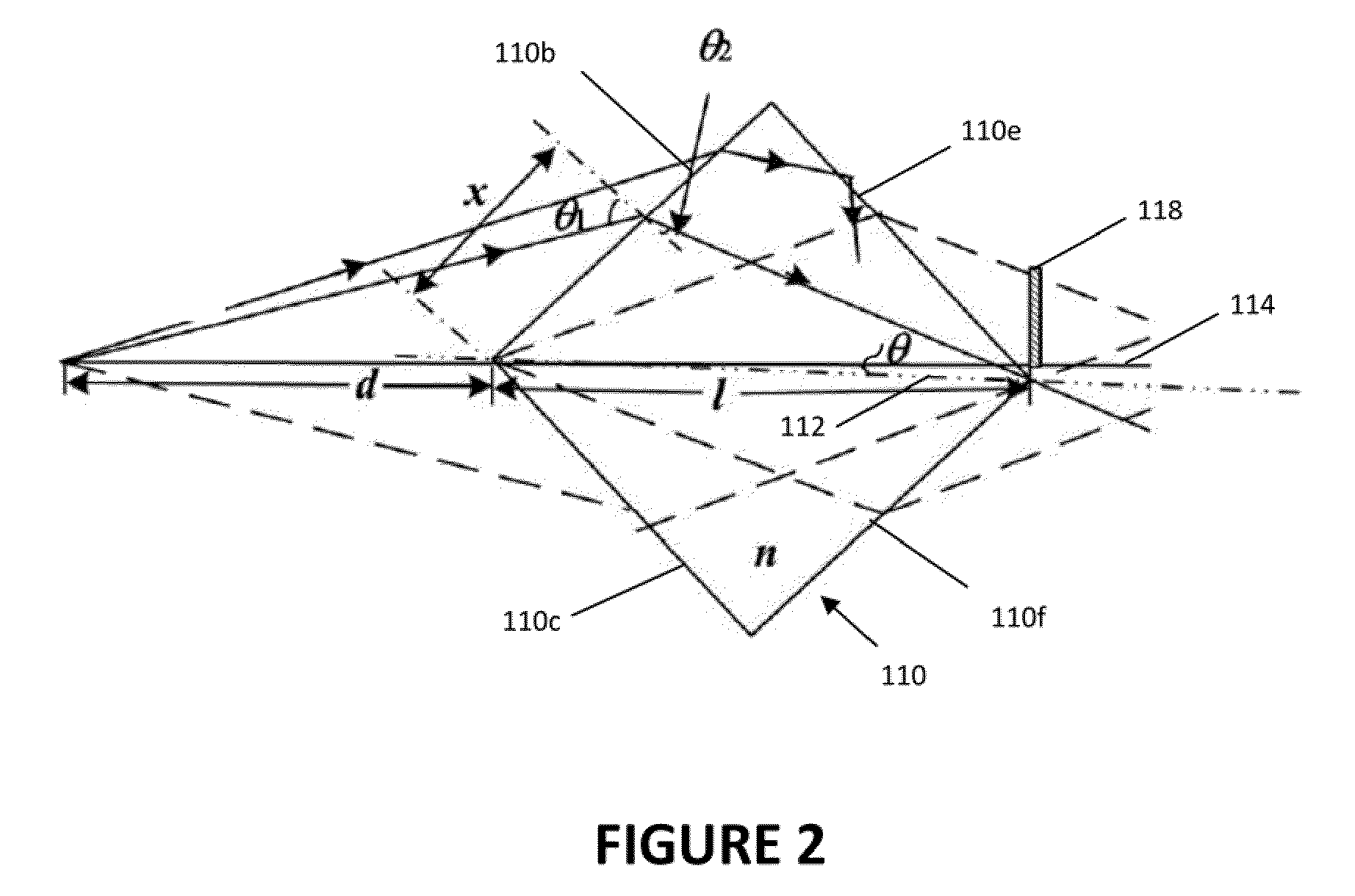
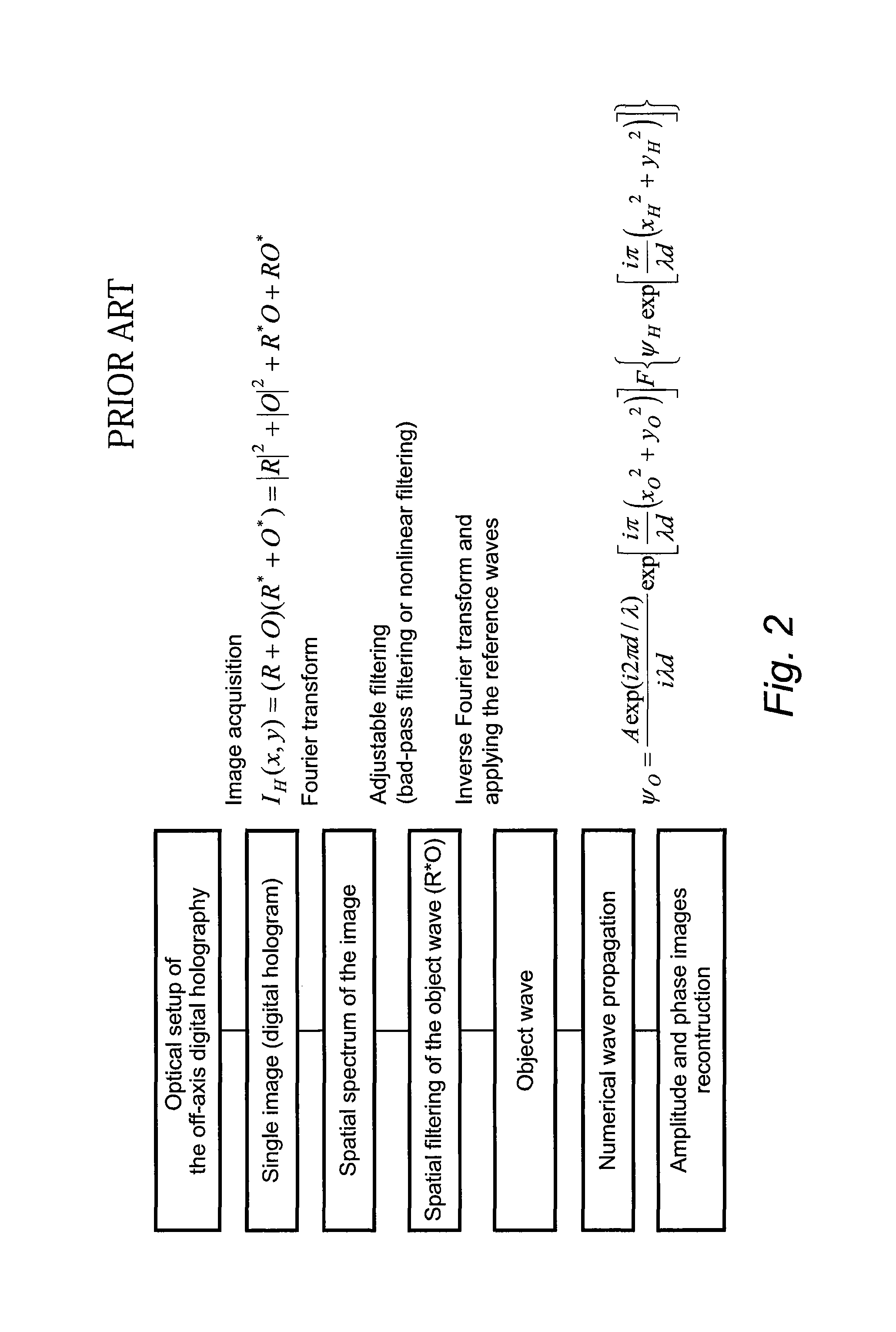
Apparatus for the exact reconstruction of the object wave in off-axis digital holography
ActiveUS20130057935A1Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsOptical axisLight beam
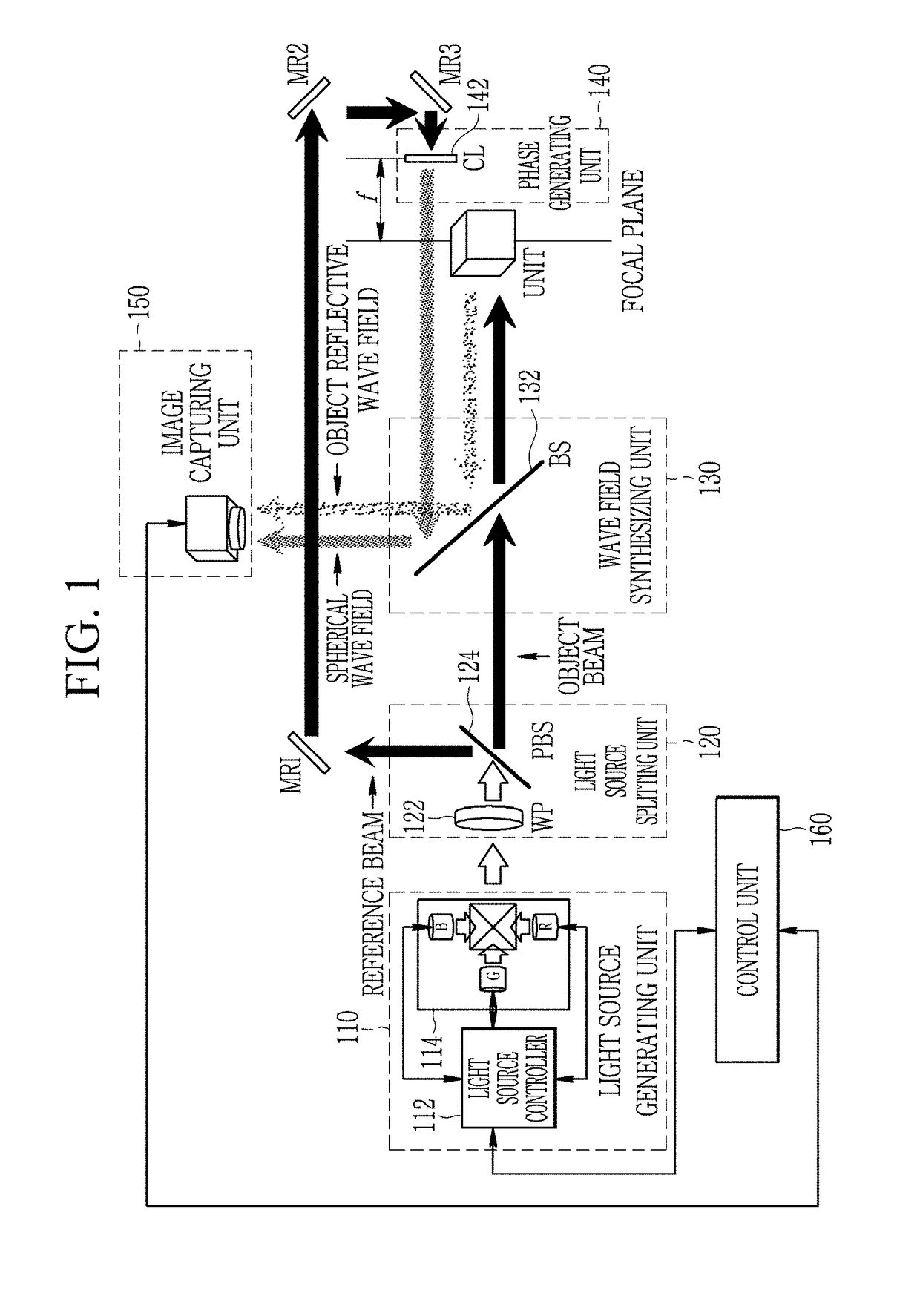
A method for preparing a digital hologram representing an image of an object, which includes generating a measurement beam and a first reference beam, irradiating the object by the measurement beam and guiding the measurement beam reflected to an optical sensor. The method also includes guiding the first reference beam to a first mirror, extending under an angle different from 90° with the optical axis of the first reference beam, and guiding the reflected beam to the optical sensor so that both beams generate an interference pattern on the sensor. The method further includes reading out the sensor and providing a digital signal representing the interference pattern on the optical sensor, and processing the signal to obtain a digital hologram.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Method and Apparatus for Defect Inspection of Transparent Substrate
ActiveUS20180188016A1Holographic optical componentsHolographic object characteristicsReference waveOptic system
A method for defect inspection of a transparent substrate comprises (a) providing an optical system for performing a diffraction process of object wave passing through a transparent substrate, (b) interfering and wavefront recording for the diffracted object wave and a reference wave to reconstruct the defect complex images (including amplitude and phase) of the transparent substrate, (c) characteristics analyzing, features classifying and sieving for the defect complex images of the transparent substrate, and (d) creating defect complex images database based-on the defect complex images for comparison and detection of the defect complex images of the transparent substrate.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
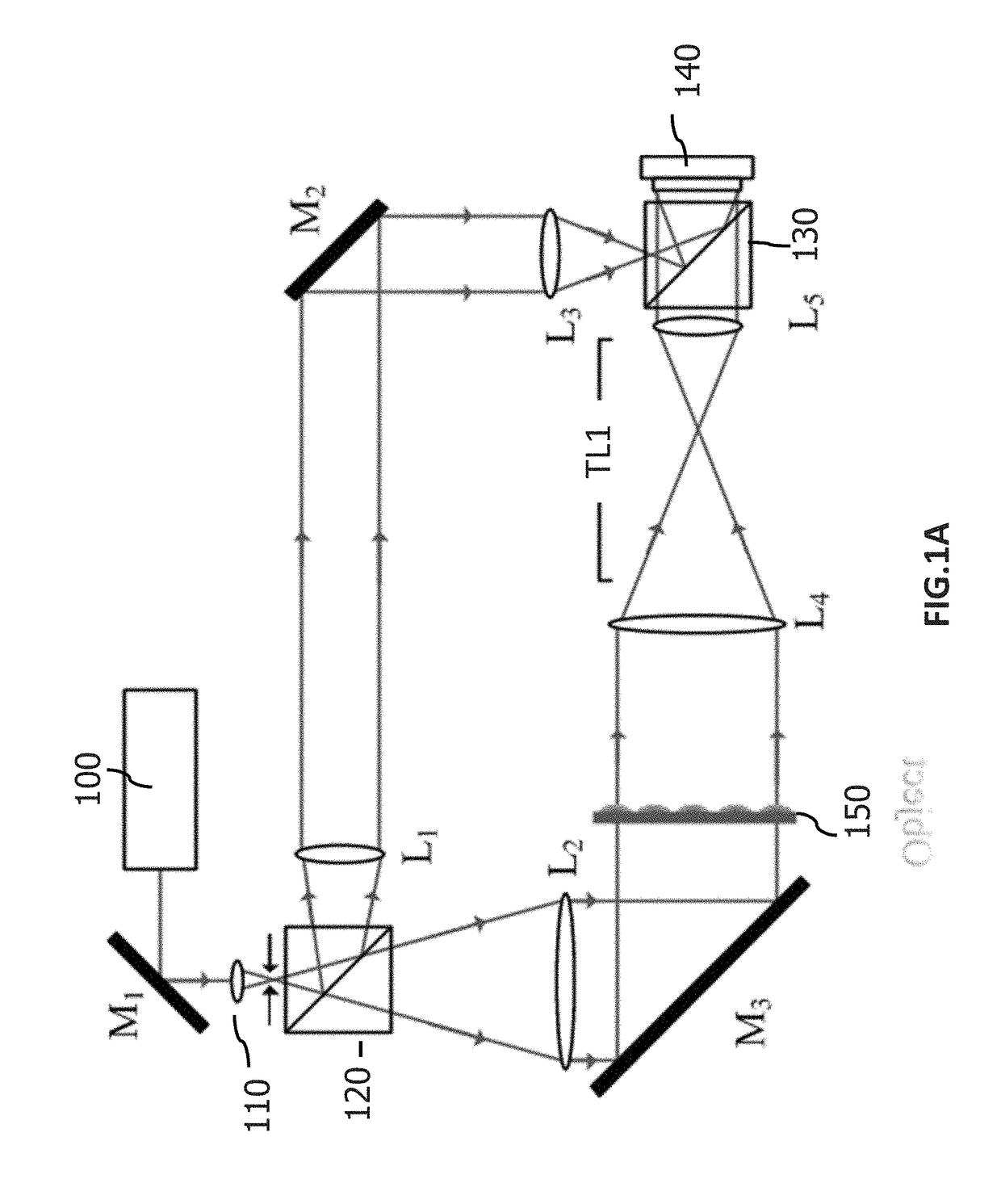
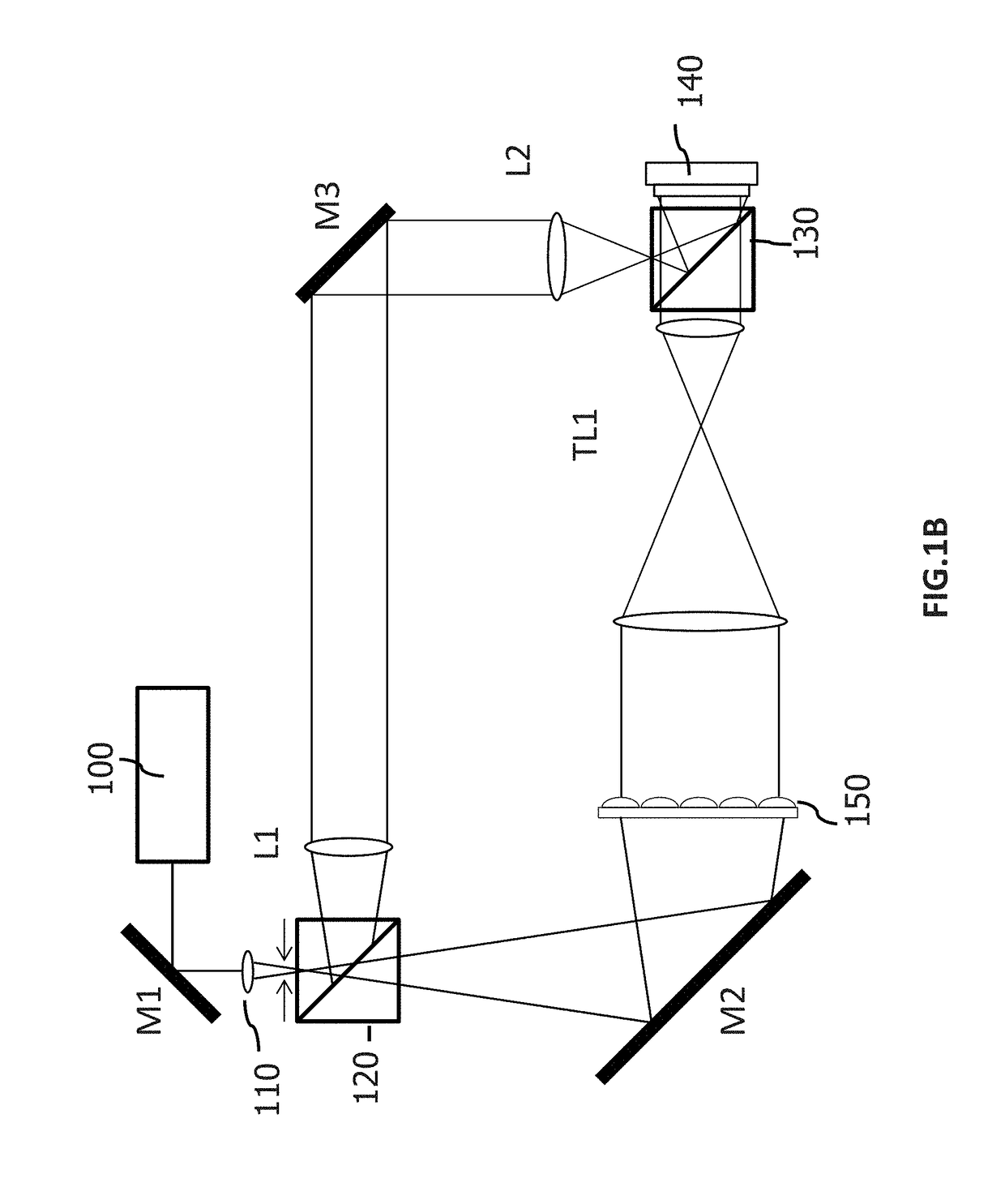
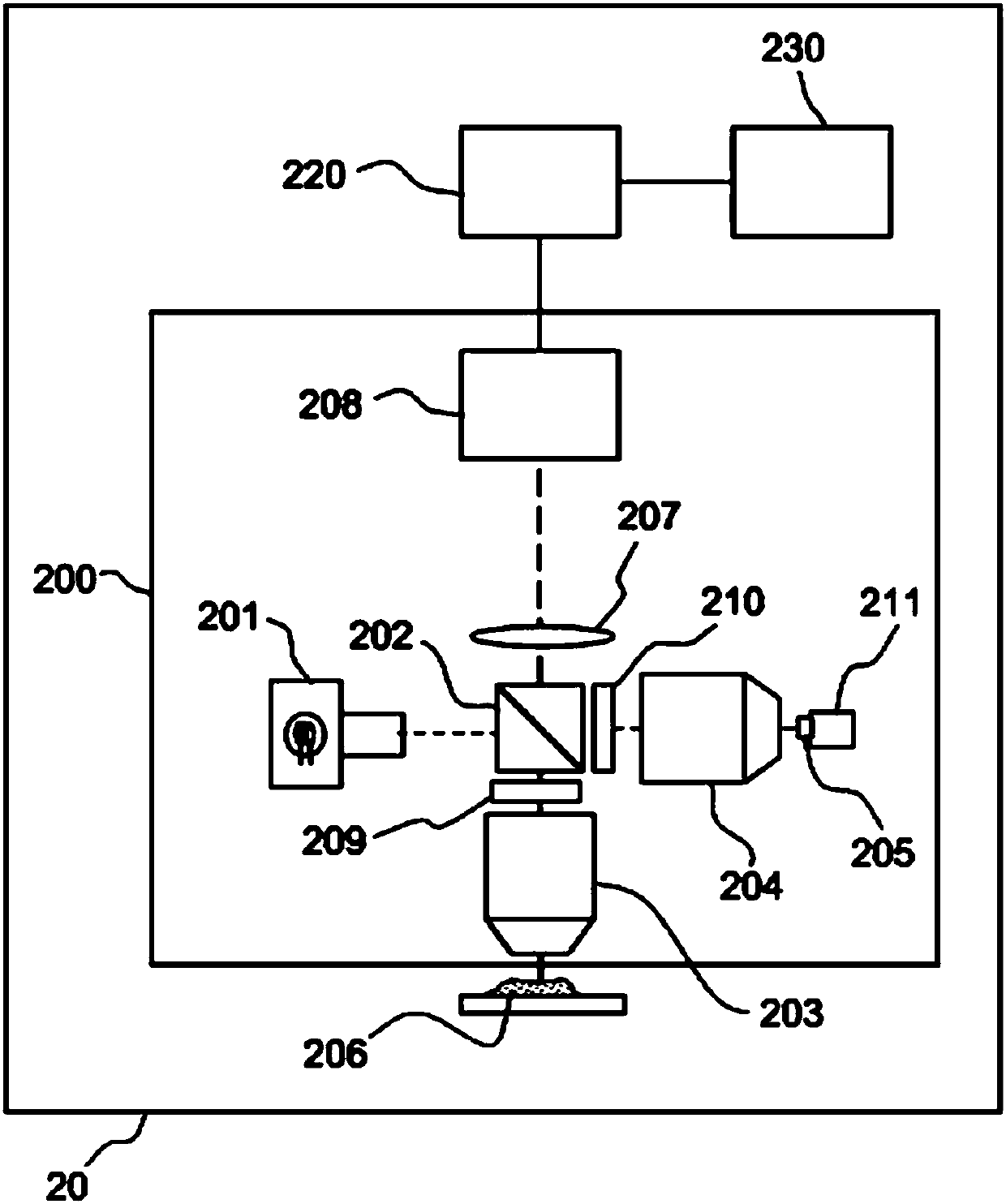
Method and system for full-field interference microscopy imaging
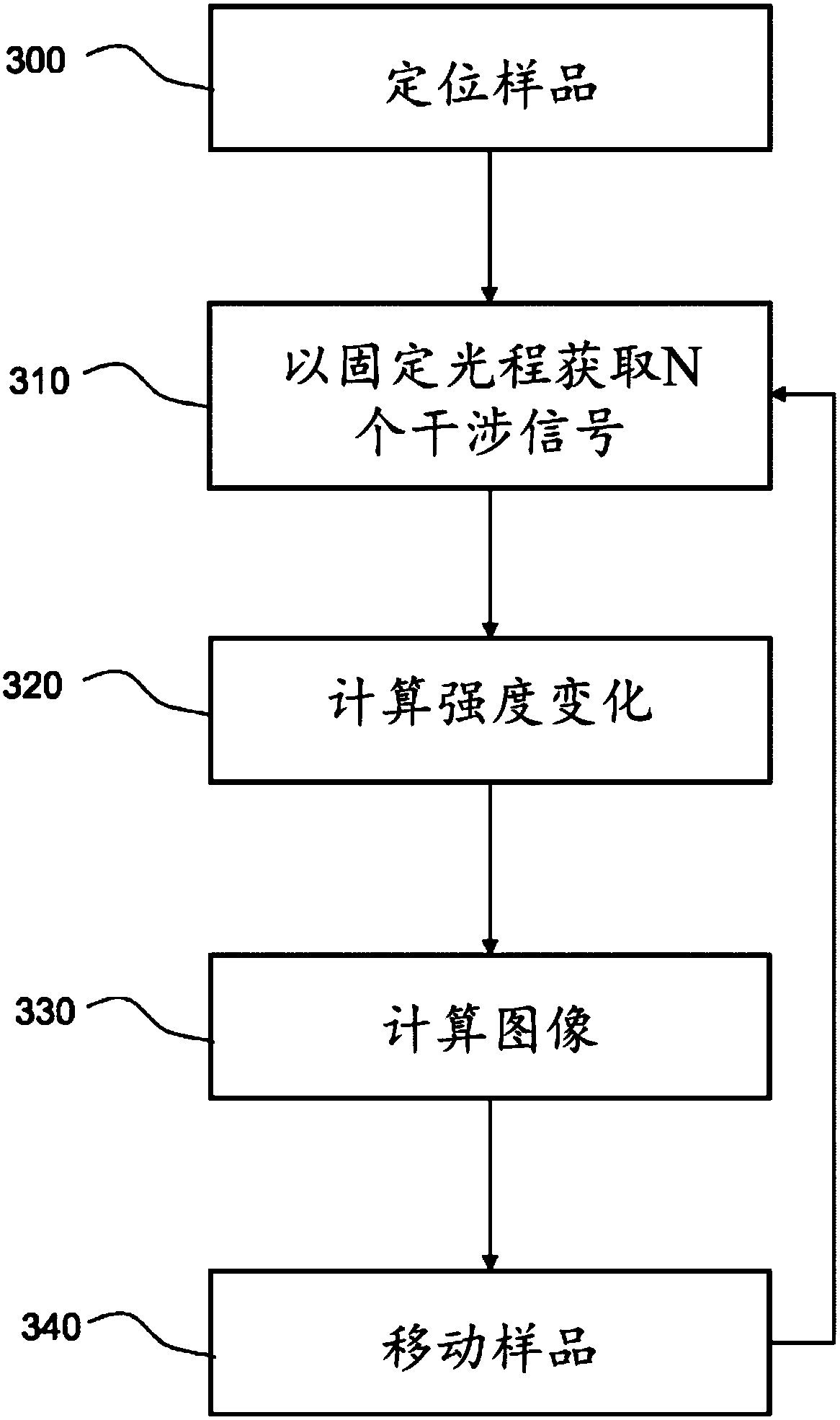
The invention relates to a system (20) for full-field interference microscopy imaging of a three-dimensional diffusing sample (206). Said system includes: an interference device (200) including a reference arm on which a reflective surface (205) is arranged, the interference device being suitable for producing, at each point of an imaging field when the sample is placed on a target arm of the interference device, interference between a reference wave, obtained by reflection of incident light waves onto a basic surface of the reflective surface (205) corresponding to said point of the imaging field, and a target wave obtained by backscattering of incident light waves by means of a voxel of a slice of the sample at a given depth, said voxel corresponding to said point of the imaging field; an acquisition device (208) suitable for acquiring, at a fixed path length difference between the target arm and the reference arm, a temporal series of N two-dimensional interferometric signals resulting from the interference produced at each point of the imaging field; and a processing unit (220) configured to calculate an image (IB, IC) representing temporal variations in intensity between saidN two-dimensional interferometric signals.
Owner:エルエルテックマネージメント
Light shift compensation device of image composition device for multicolor holography
InactiveUS20110261154A1Television system detailsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesColor imageLight Shift
A light shift compensation device of an image composition device for the multicolor holography utilizes a light source provider to emit a beam split into an object beam and a reference beam via a beamsplitting unit. The object beam, shined on a projecting unit, is transformed into an object wave for projecting two-D images of the object on a negative. The reference beam is transformed into a reference wave by a compensating unit to adjust the irradiation angle and thence project on the negative. Interference fringes formed by the object wave and the reference wave projecting on the negative record two-D images of the object on the negative. The two-D images projected by the object wave are separated into the red image, the green image, and the blue image, which are directed to the three fundamental colors. The image of one single color is adopted for being recorded on the negative each time. The images of the three fundamental colors are successively processed by three times of double-exposure on the negative to compose a true color image. The angle of projection of the reference wave is adjusted by the compensating unit, so that the angles of diffraction of the green image and the blue image recorded on the negative are changed.
Owner:CHANG JUI TSUNG
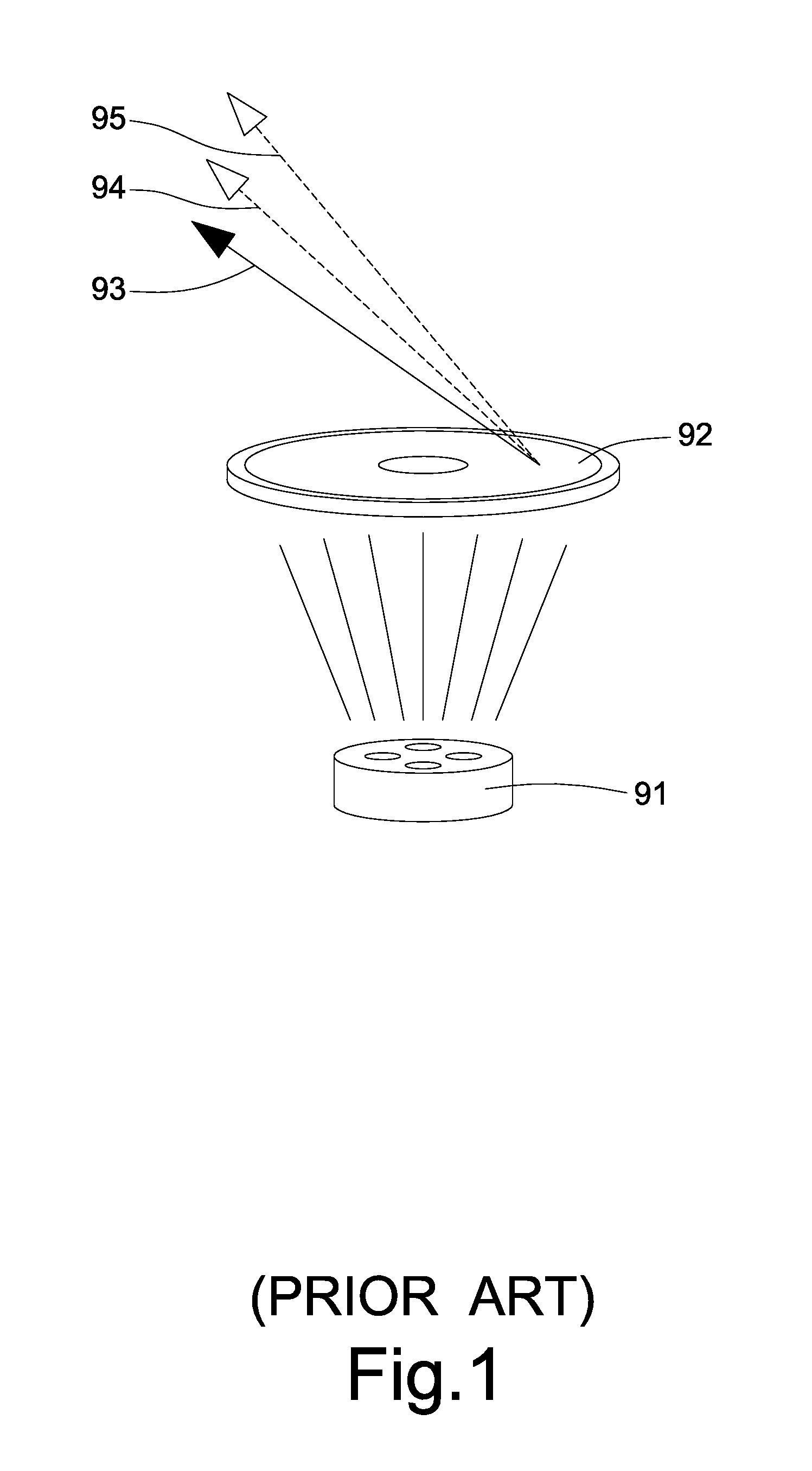
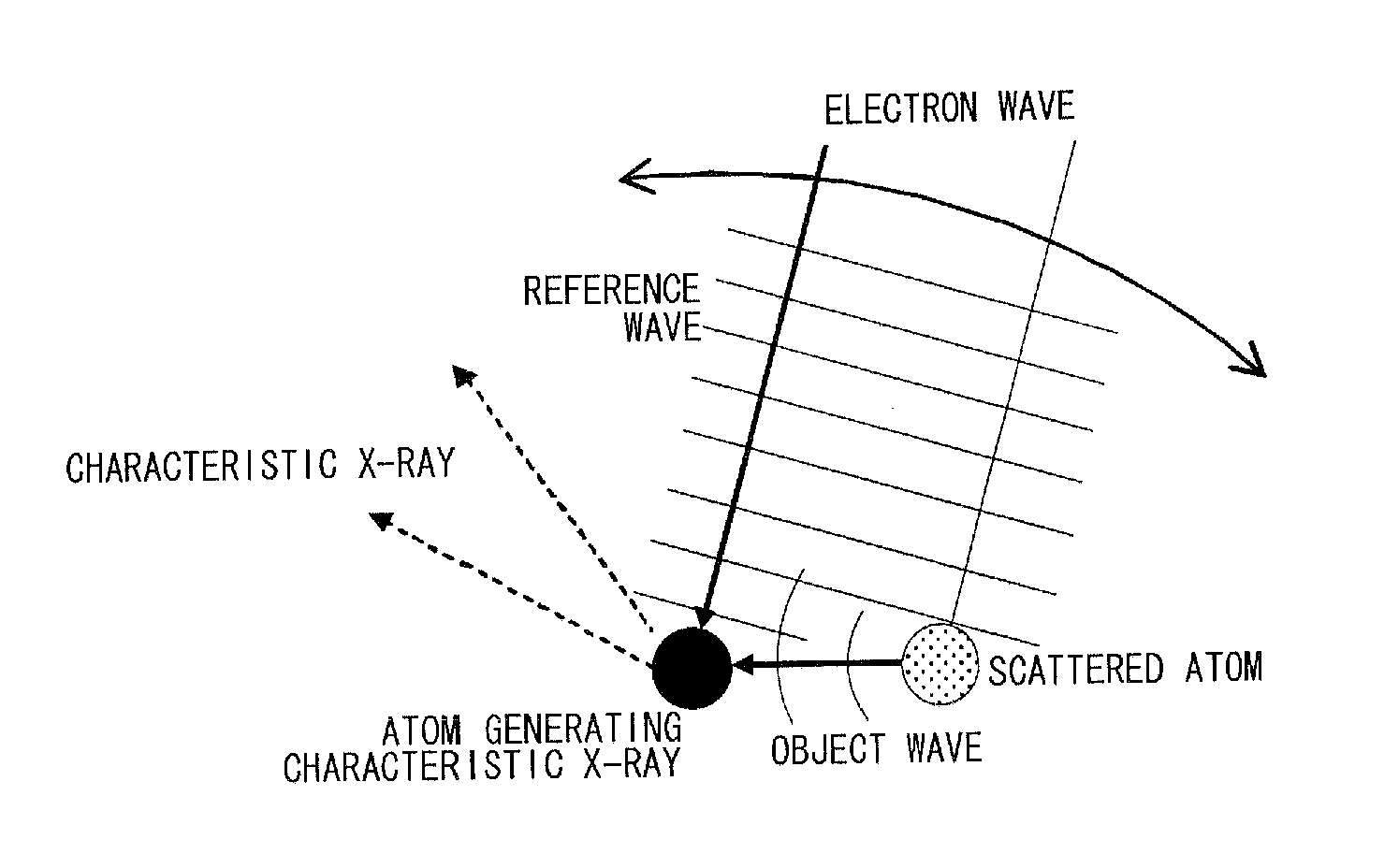
Reverse x-ray photoelectron holography device and its measuring method
InactiveUS20100074406A1Improve accuracyEasy to measureMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-ray spectral distribution measurementSoft x rayEnergy control
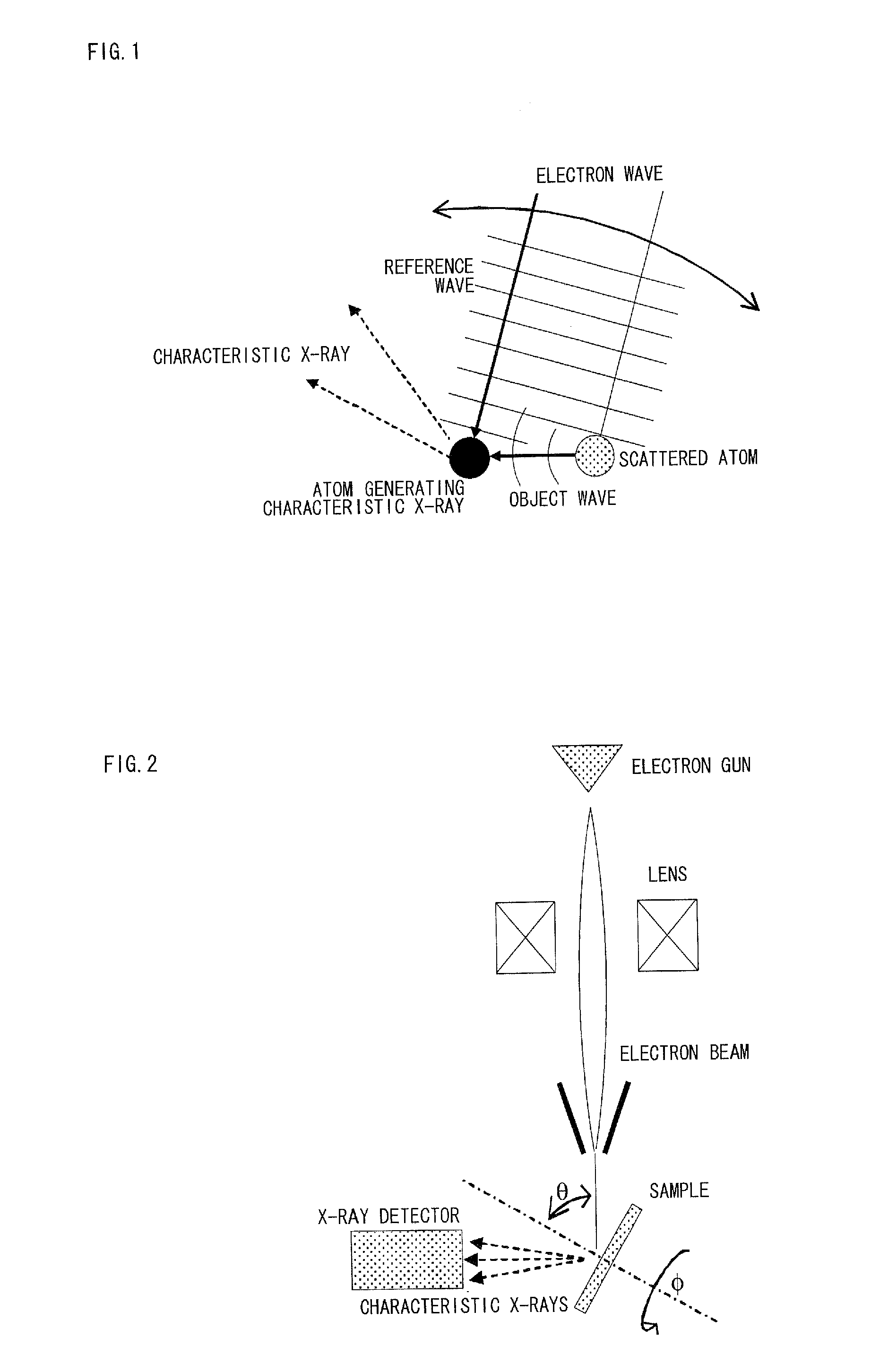
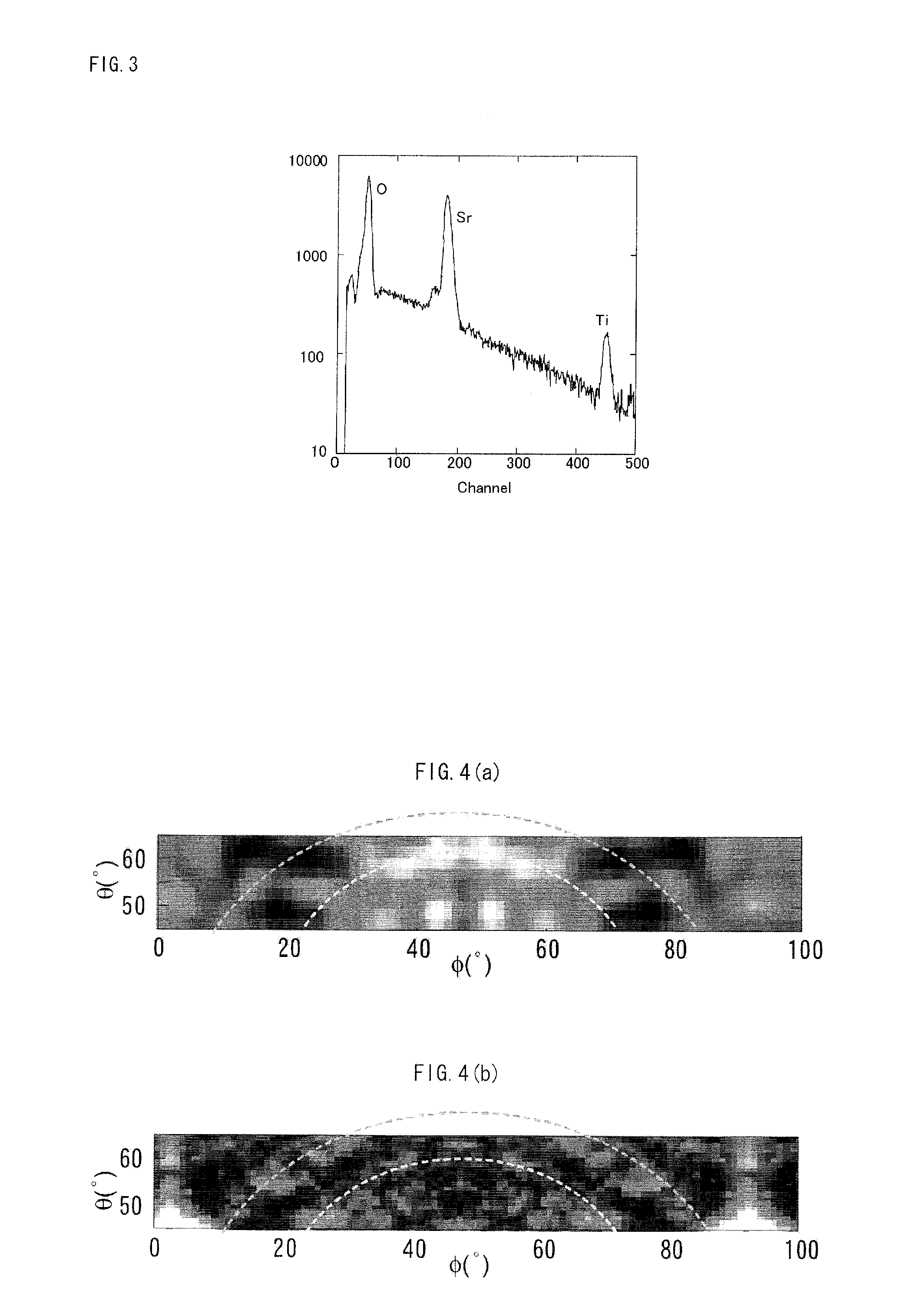
[Problems] To provide a reverse X-ray photoelectron holography device, in which energy control and convergence are facilitated and a hologram of good contrast is obtained; and to provide its measuring method.[Means for Solving Problems] A Reverse X-ray photoelectron holography measuring method where a measurement sample is irradiated with an electron beans, incident angle and rotation angle of the electron beam are varied by varying the posture of the measurement sample to the electron beam, and a variation in intensity of characteristic X-ray emitted when the measurement sample is excited is recorded as the atomic resolution hologram around the atom of a specific element, wherein, when the intensity is detected as the characteristic X-ray of the atom of the measurement sample, an object wave is generated as an electron wave scattered by the reference wave and the proximity atom in a holography where electrons incident to the measurement sample reach an atom generating specific X-ray as an electron wave, and an interference pattern is formed by compounding the reference wave with the object wave, thus monitoring the intensity of an electron beam.
Owner:JAPAN SYNCHROTRON RADIATION RES INST +1
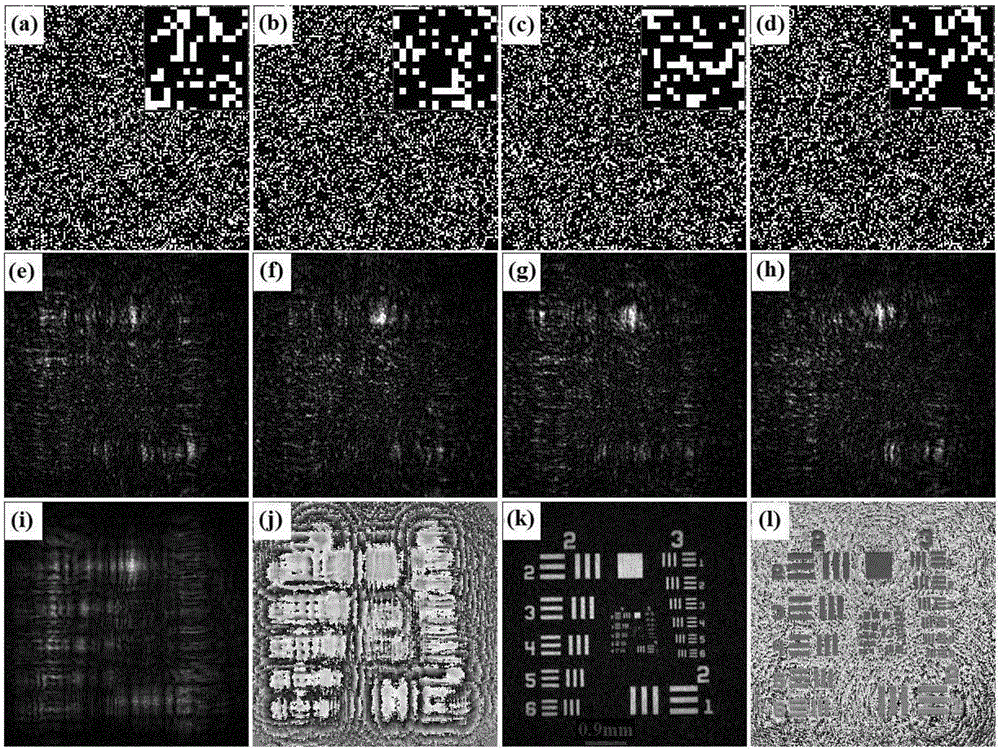
Lensless diffraction imaging method based on complementary random sampling
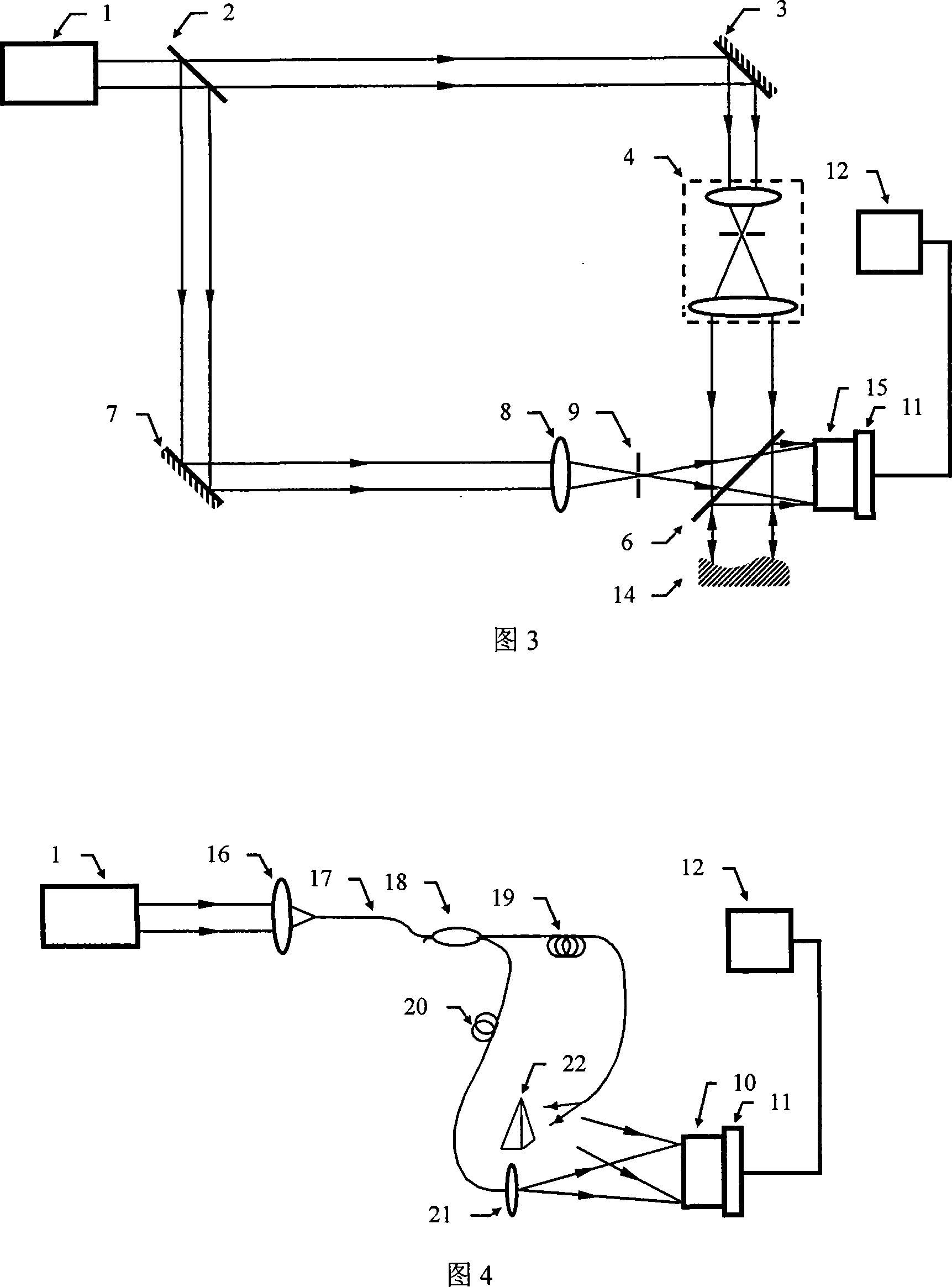
ActiveCN105158921AHigh precisionImprove efficiencyOptical measurementsPhotometryComplex amplitudeWavefront
A lensless diffraction imaging method based on complementary random sampling is characterized in that a group of binary random sampling screens with complementary characteristics is introduced; the group of binary random sampling screens is arranged between a to-be-tested object and a record plane in sequence, and intensity patterns of object waves passing through the sampling screens on the record plane are sequentially recorded; the complex amplitude distribution of to-be-tested object waves is recovered from the recorded intensity patterns, and the digital diffraction operation is conducted using the recovered complex amplitude distribution, so as to obtain the diffraction imaging of the to-be-tested object at any spatial position. According to the method, the complementary random sampling screens are inserted between the object and the record plane, so that the accuracy and the iteration efficiency of phase retrieval are greatly improved; meanwhile, wavefront sampling loss caused by the binary random sampling in the traditional method can be effectively eliminated. In addition, as the iteration operation process is only applied to the sampling plane and the record plane, the method is suitable for general complex-valued objects and does not place special limits on the object.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
High resolution ratio digital holographic image capturing device
InactiveCN101122774AUniform spatial frequencyIncrease in spatial frequencyDigital dataOptical elementsOptical path lengthDigital image processing
The invention discloses a high-resolution digital holographic image acquisition device. The first beam irradiates the sample after the beam emitted by the laser passes through the beam splitting device, and the second beam is converted into spherical light waves through the beam expander and the first beam after irradiating the sample. The light beam forms an interference area, and the linear array CCD is arranged on a two-dimensionally movable micro-displacement platform and is located in the interference area. The point source of the spherical light wave is equal to the optical path of the object light wave from the sample to the linear array CCD. The computer It is electrically connected with the linear array CCD and the micro-displacement platform. The linear array CCD push-brooms the interference fringes generated by the first and second light beams to collect and synthesize a digital hologram, and the digital hologram is numerically reconstructed by the computer through fast Fourier transform algorithm and digital image processing, etc. Finally, a high-resolution digital holographic reconstruction image is obtained. The invention effectively increases the area of the recorded hologram, improves the resolution of the digital hologram reproduced image, and increases the field of view.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
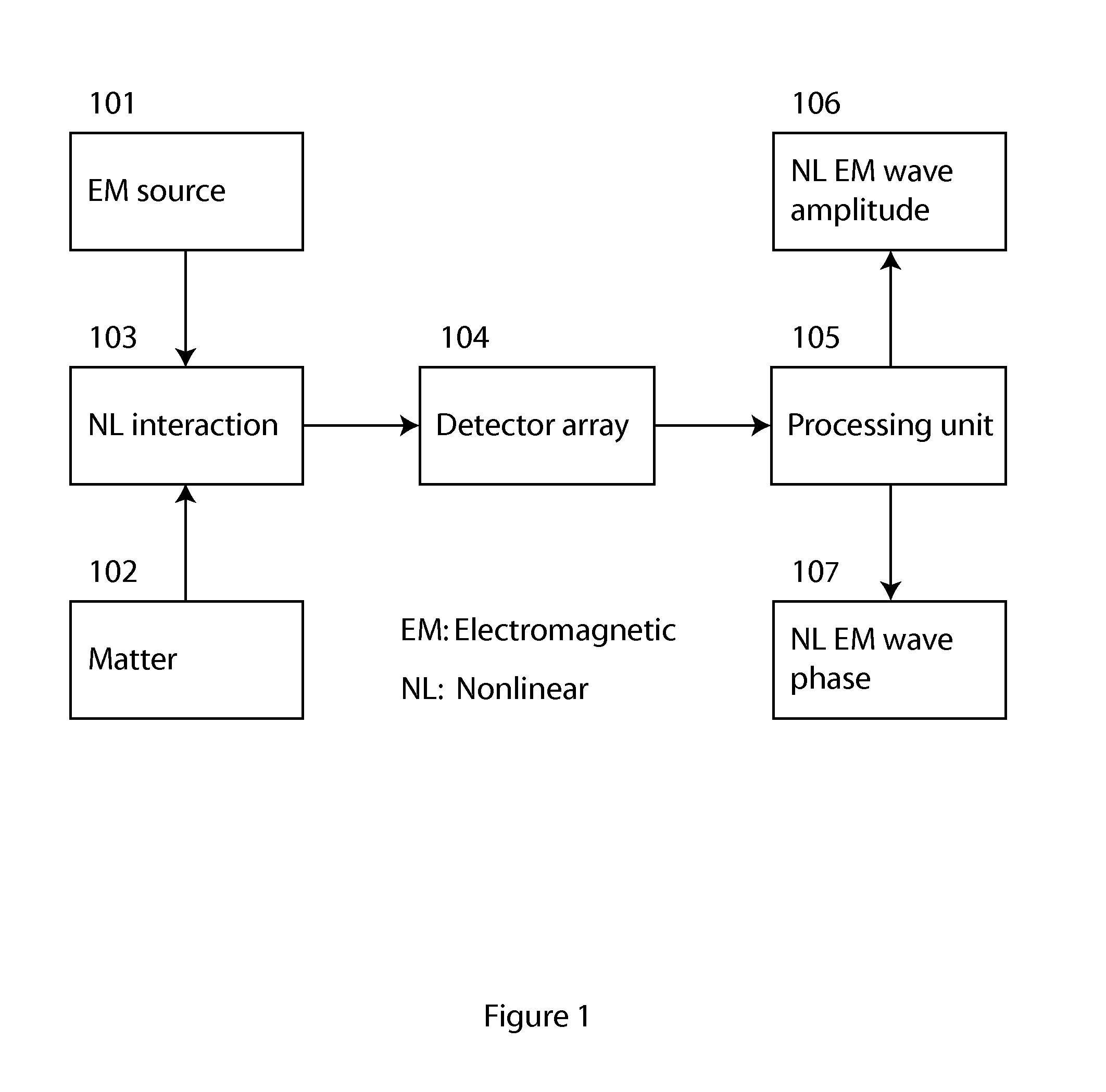
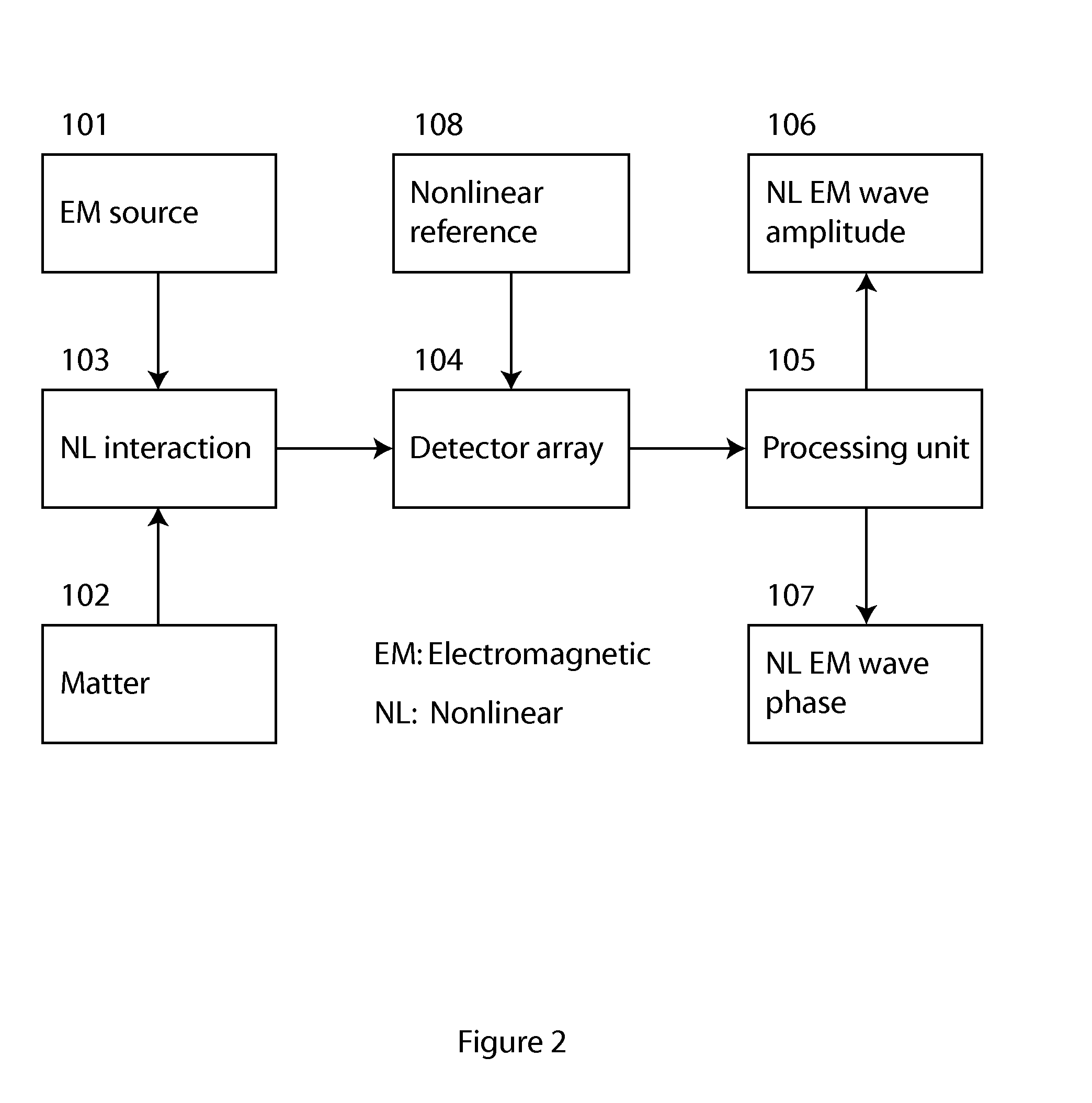
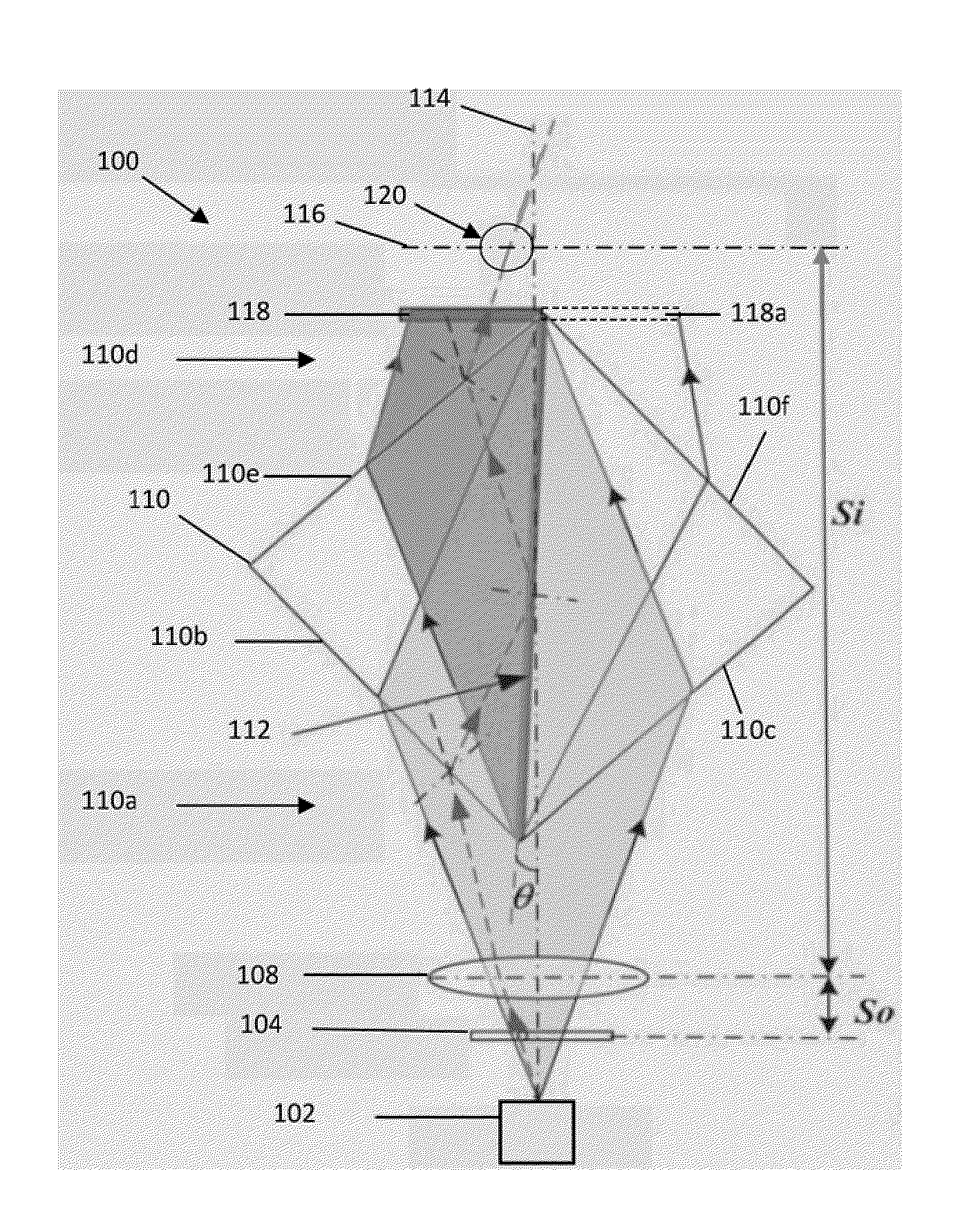
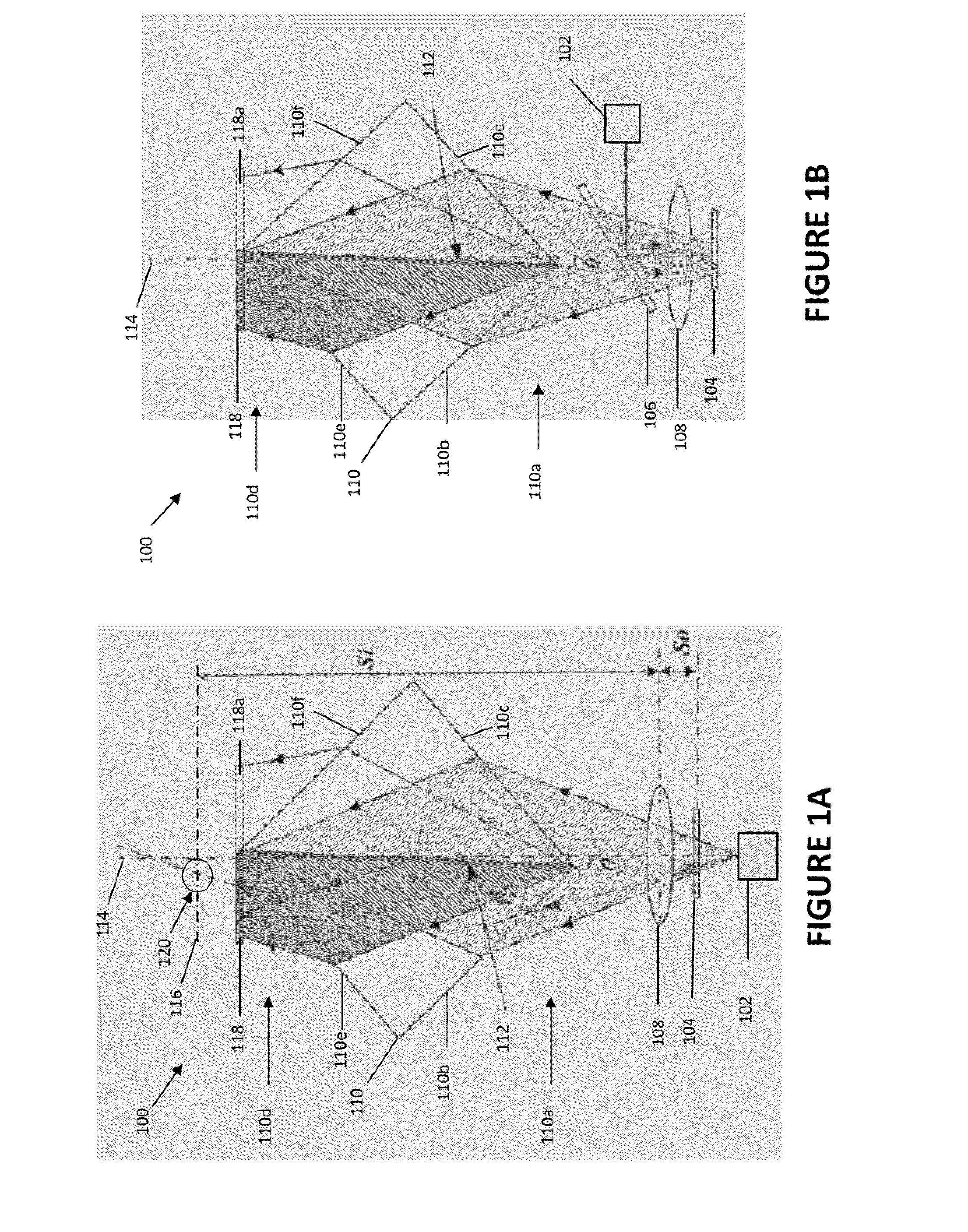
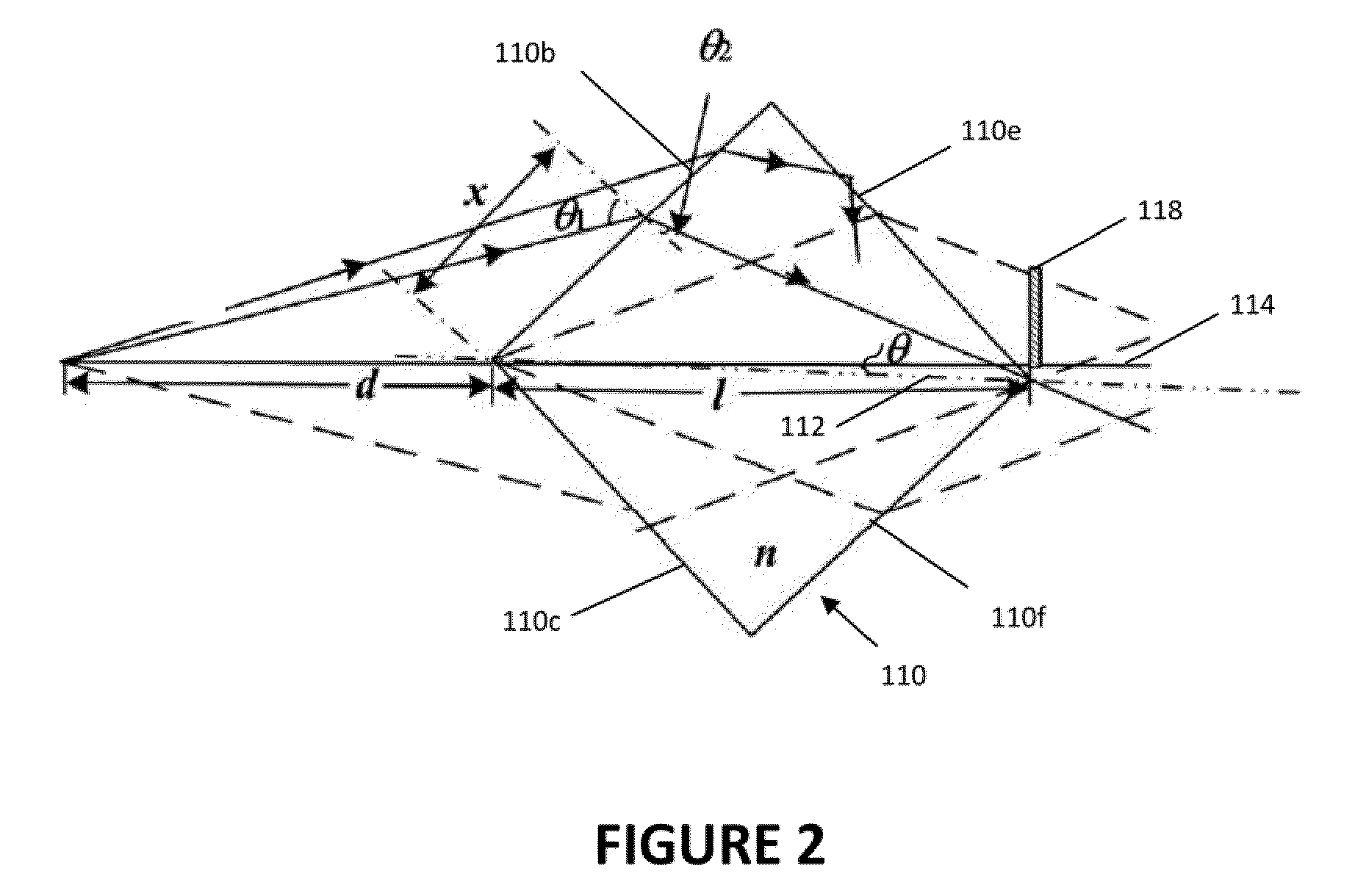
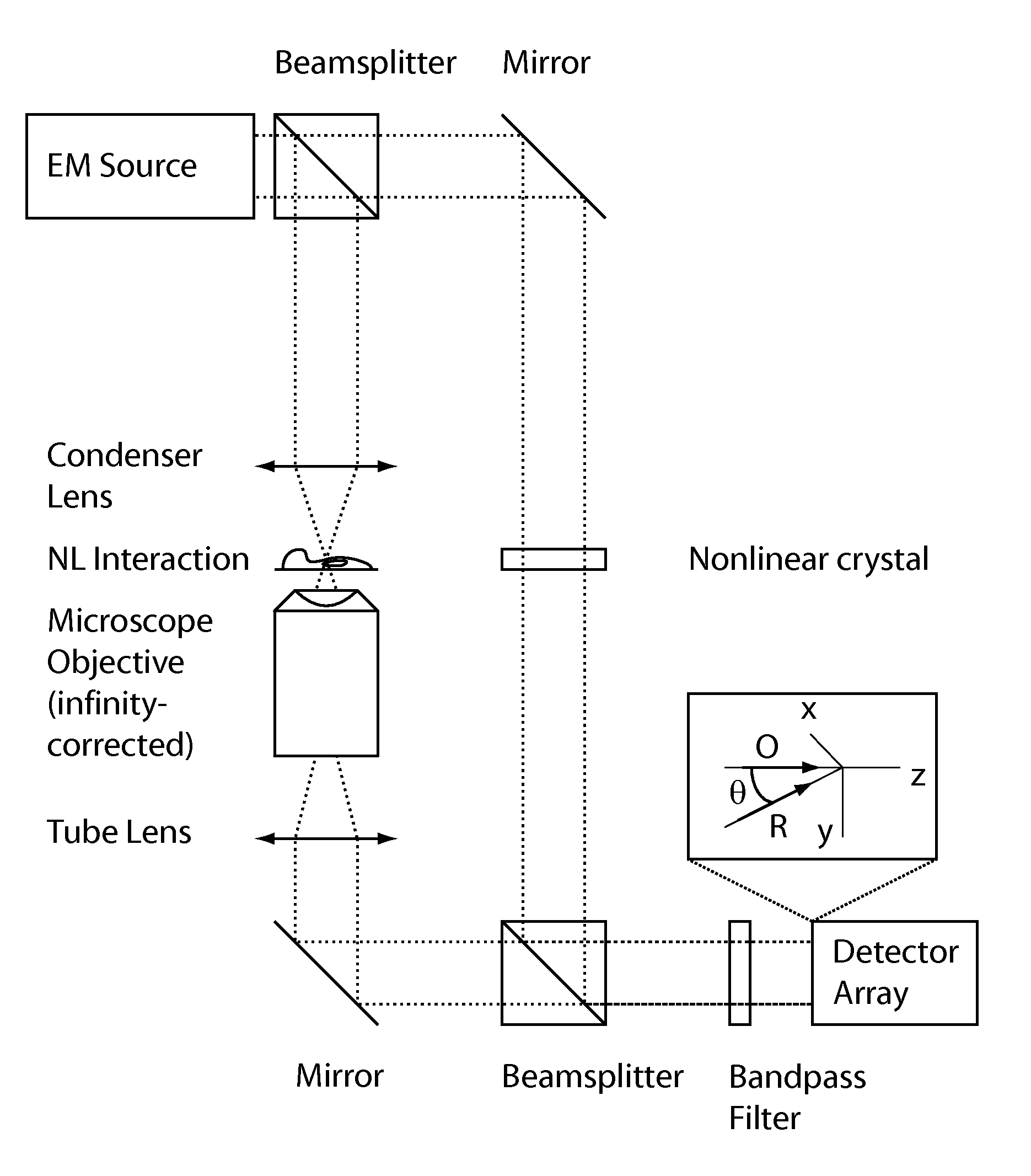
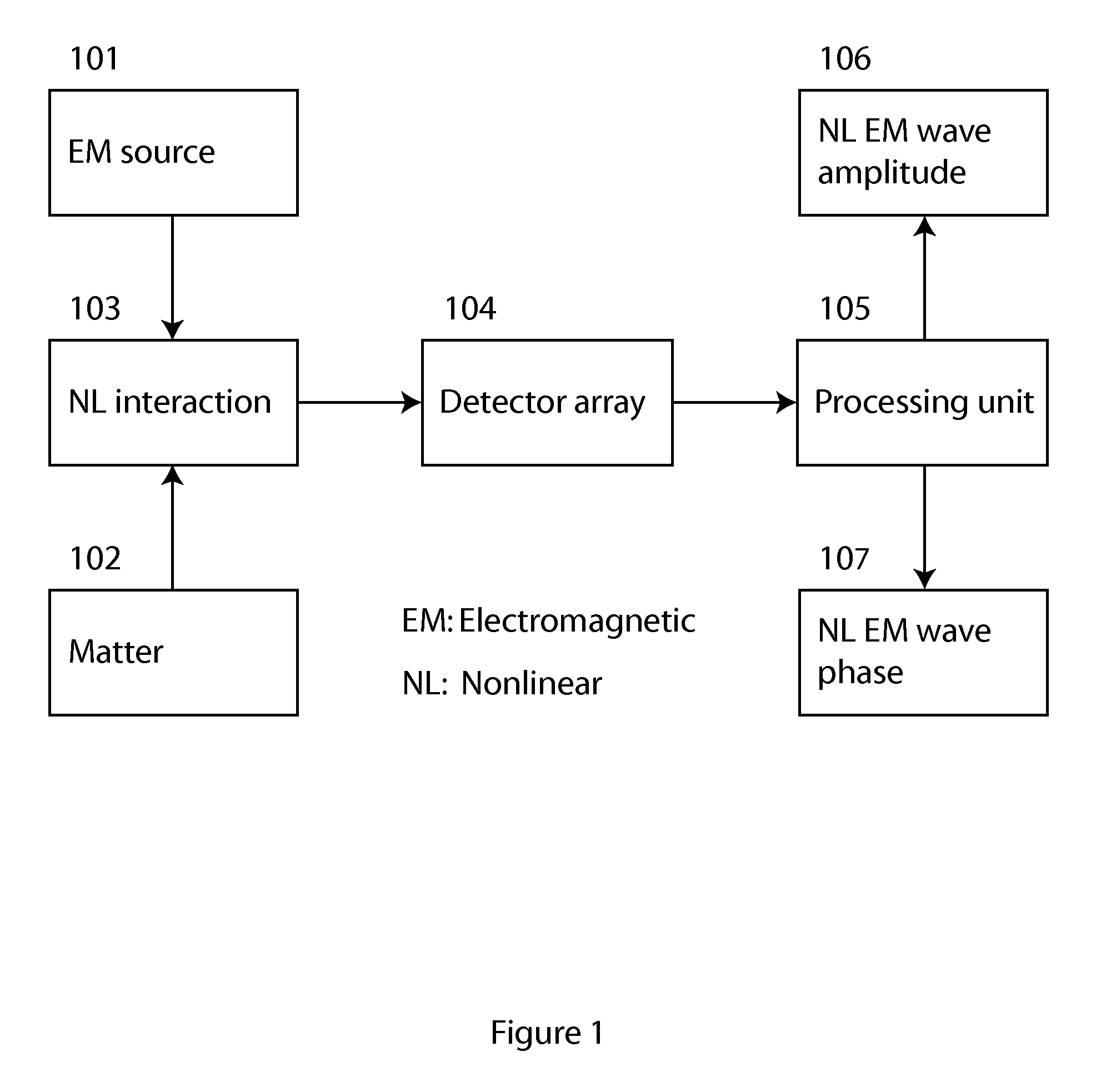
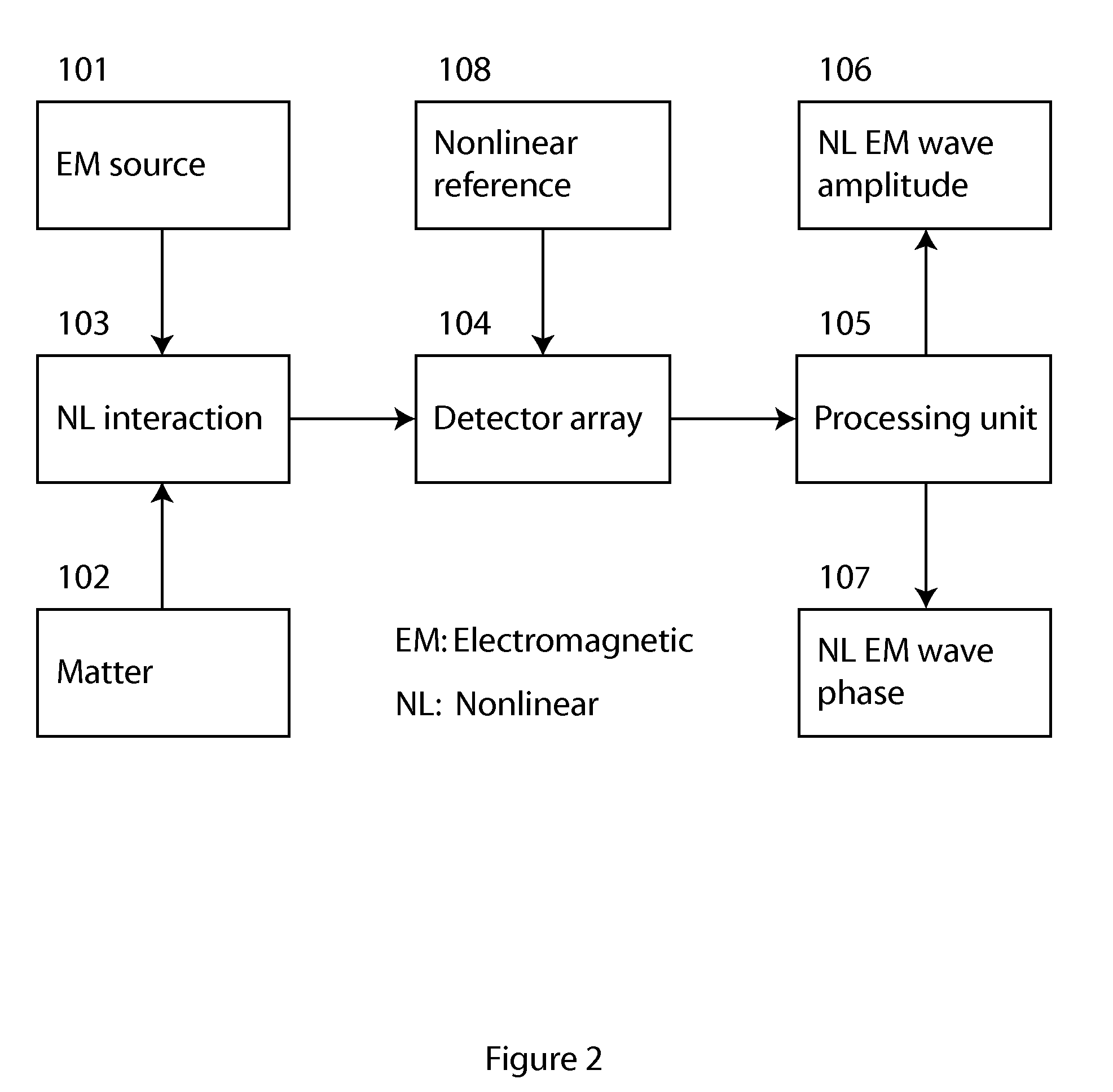
Method and apparatus for retrieval of amplitude and phase of nonlinear electromagnetic waves
The present invention discloses a method and its associated apparatus to retrieve the amplitude and, especially, the phase of nonlinear electromagnetic waves. The application field of the present invention is optical imaging. A sample is probed by coherent electromagnetic radiation, and by a nonlinear interaction such as harmonic generation a nonlinear object wave is emitted. A nonlinear reference wave is generated by interaction of the same nature with the coherent electromagnetic radiation, and an interference between the nonlinear object wave and the nonlinear reference wave is sensed by a detector array. As an example, the technique makes possible real-time nanometric localization and tracking of nonlinear field emitters, such as, but not limited to, nanoparticles.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
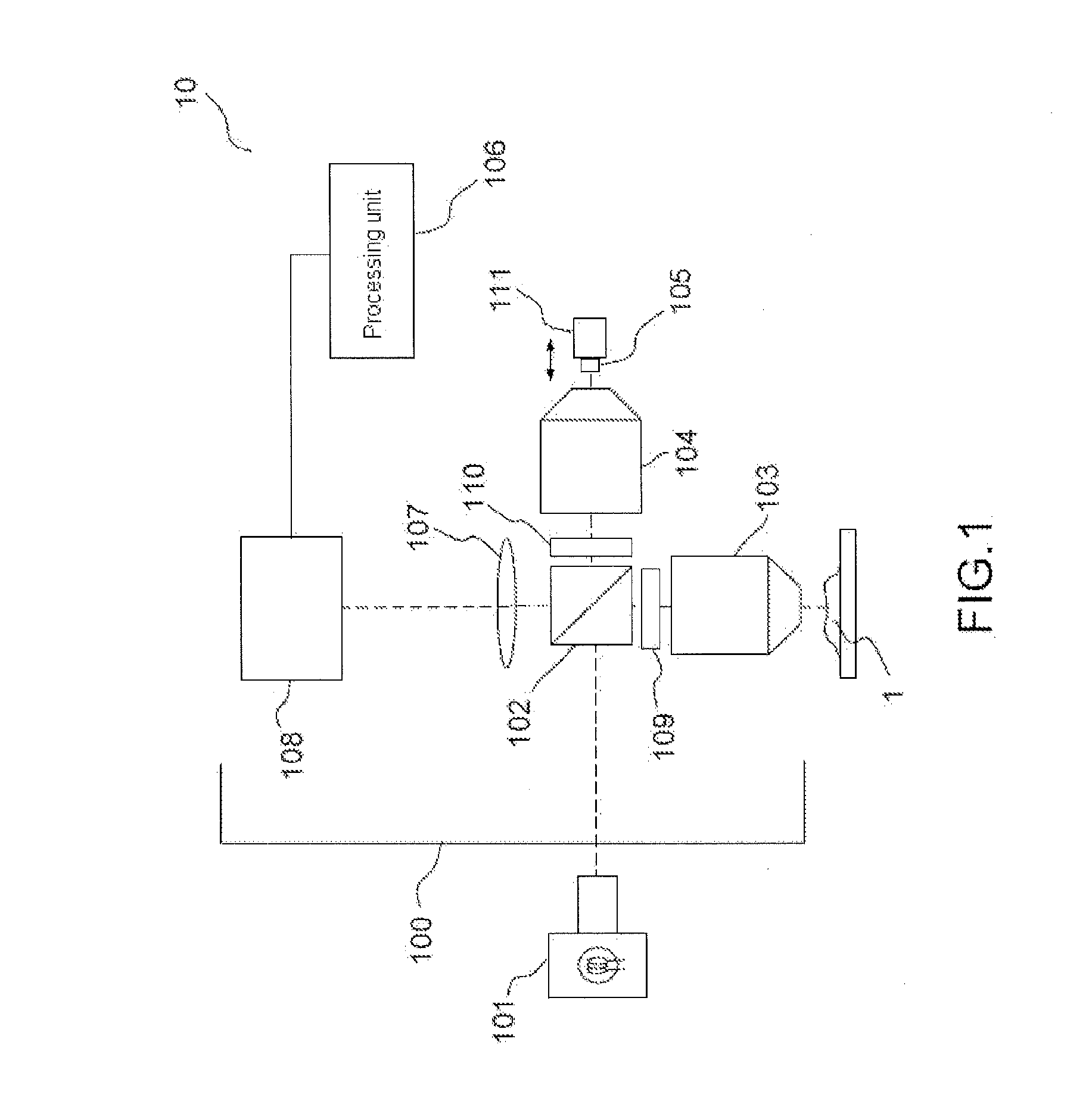
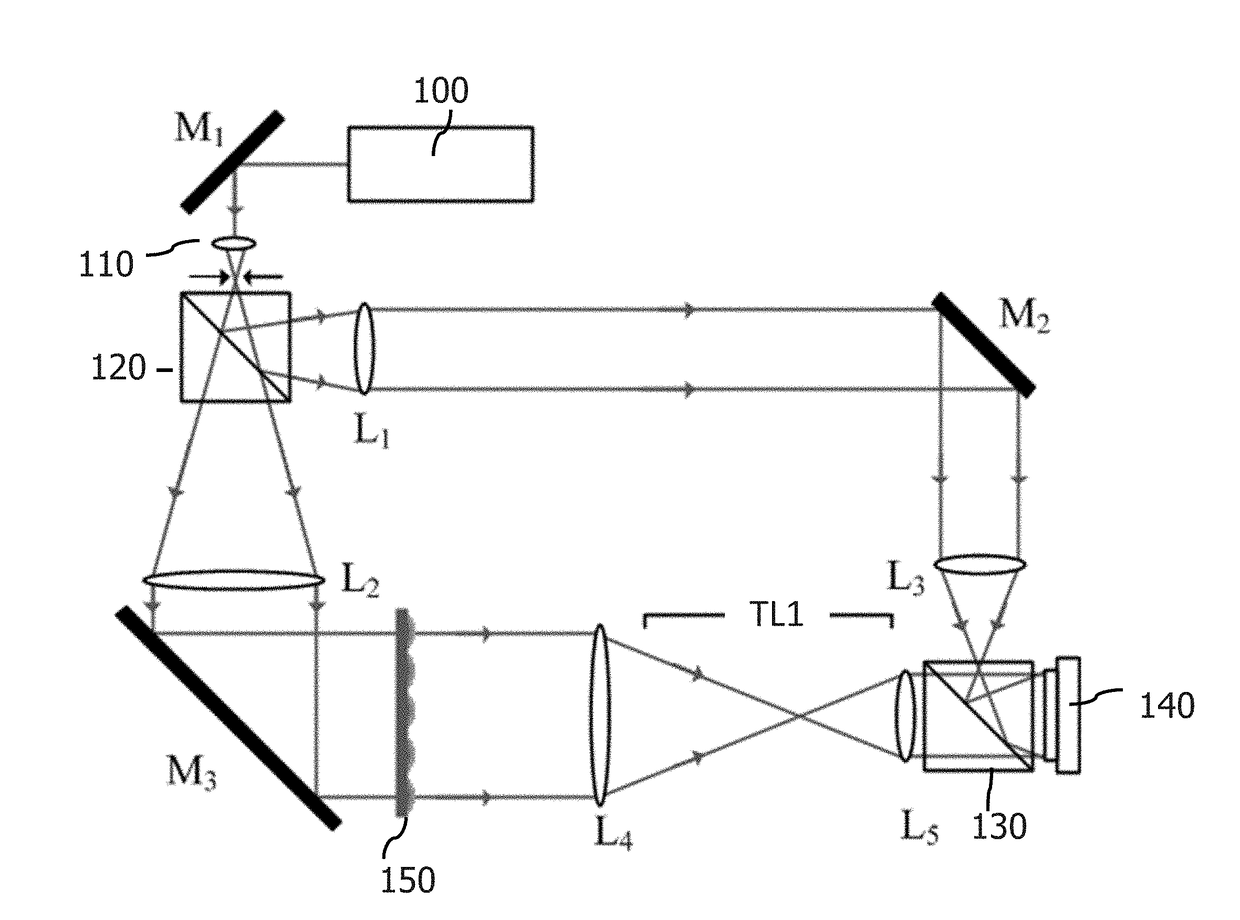
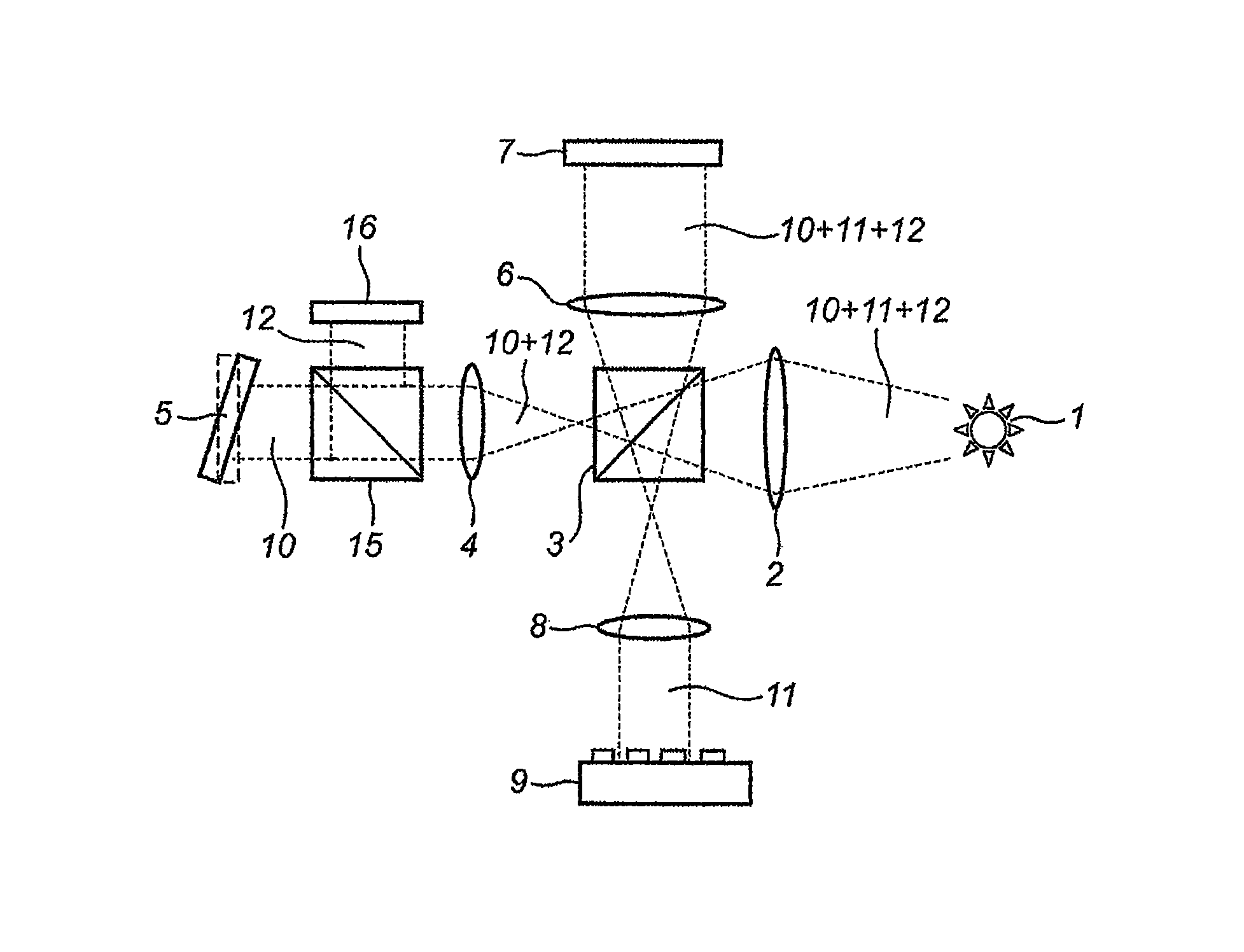
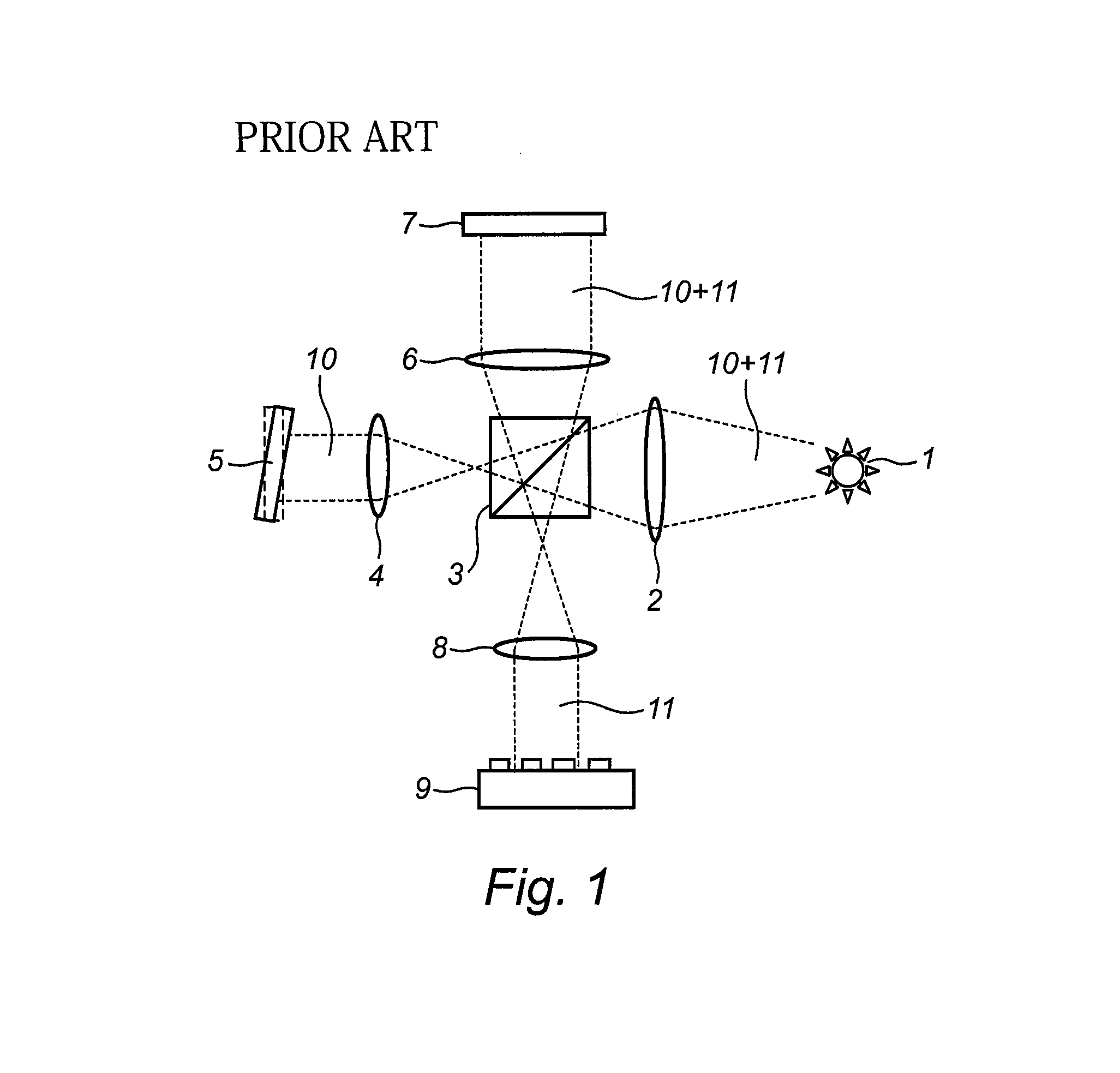
Digital holographic microscopy
ActiveUS20110043878A1Minimal numberEasy to implementHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsBeam splitterWavefront
An optical configuration for a digital holographic microscope and a method for digital holographic microscopy are presented. In one embodiment, digital off-axis holograms are obtained using a cube beam splitter (110) to both split and combine a diverging spherical wavefront emerging from a microscope objective (108). When a plane numerical reference wavefront is used for the reconstruction of the recorded digital hologram, the phase curvature introduced by the microscope objective (108) together with the illuminating wave to the object wave can be physically compensated.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
Apparatus for the exact reconstruction of the object wave in off-axis digital holography
ActiveUS8659810B2Holographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsLight beamDigital signal
A method and apparatus for preparing a digital hologram representing an image of an object includes generating a measurement beam and a first reference beam, irradiating the object by the measurement beam, and guiding the measurement beam reflected to an optical sensor. The method also includes guiding the first reference beam to a first mirror, and guiding the reflected beam to the optical sensor so that both beams generate an interference pattern on the sensor. The method includes providing a digital signal representing the interference pattern on the optical sensor, to obtain a digital hologram, and subjecting the digital hologram to a Fourier transform in the spatial frequency domain to obtain a spectrum. The method further includes replacing a section of a first image term overlapped by a DC-term by a corresponding section of a second image term.
Owner:MITUTOYO CORP
Digital holographic microscopy
ActiveUS8363316B2Minimal numberEasy to implementHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesHolographic optical componentsBeam splitterWavefront
An optical configuration for a digital holographic microscope and a method for digital holographic microscopy are presented. In one embodiment, digital off-axis holograms are obtained using a cube beam splitter (110) to both split and combine a diverging spherical wavefront emerging from a microscope objective (108). When a plane numerical reference wavefront is used for the reconstruction of the recorded digital hologram, the phase curvature introduced by the microscope objective (108) together with the illuminating wave to the object wave can be physically compensated.
Owner:NANYANG TECH UNIV +1
Method and apparatus for retrieval of amplitude and phase of nonlinear electromagnetic waves
ActiveUS9134242B2Beam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotoelectric discharge tubesHarmonicNanoparticle
The present invention discloses a method and its associated apparatus to retrieve the amplitude and, especially, the phase of nonlinear electromagnetic waves. The application field of the present invention is optical imaging. A sample is probed by coherent electromagnetic radiation, and by a nonlinear interaction such as harmonic generation a nonlinear object wave is emitted. A nonlinear reference wave is generated by interaction of the same nature with the coherent electromagnetic radiation, and an interference between the nonlinear object wave and the nonlinear reference wave is sensed by a detector array. As an example, the technique makes possible real-time nanometric localization and tracking of nonlinear field emitters, such as, but not limited to, nanoparticles.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
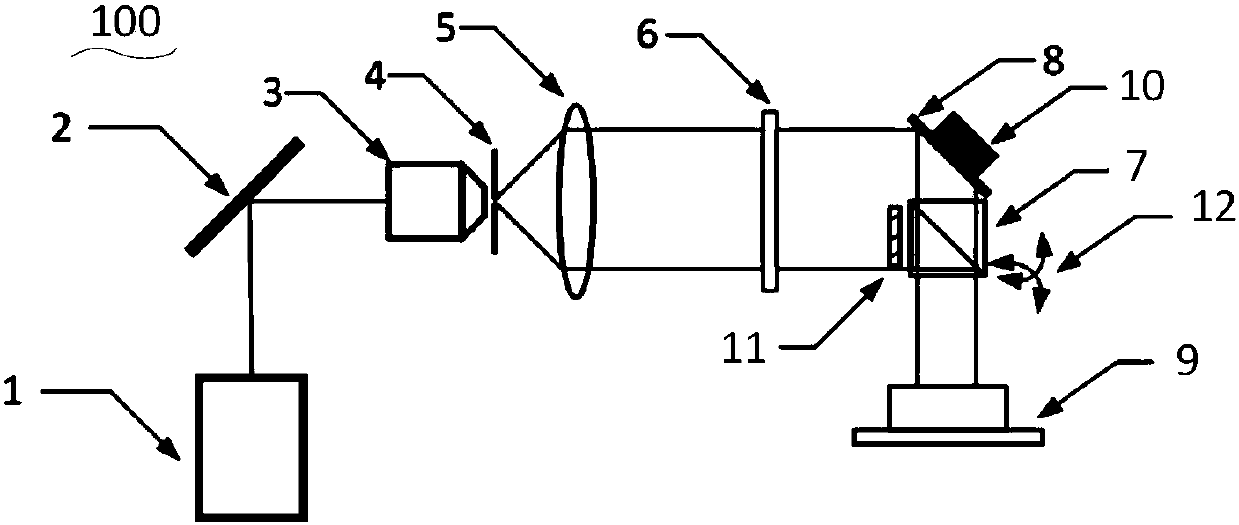
Compact type collimating common optical path phase shifting digital holography imaging system and method
The invention discloses a compact type collimating common optical path phase shifting digital holography imaging system and method. The system comprises a laser, a plane mirror, a microobjective, a pinhole, a collimating lens, a line polarizing film, an unpolarized splitting prism and a coating film reflector, and the coating film reflector is connected with piezoelectric ceramics; a picture sensor collectors a hologram, wherein the hologram is obtained by interference of object waves irradiated to objects and reference optical waves reflected by the coating film reflector, a two-dimensional rotation regulating frame with the unpolarized splitting prism is adjusted for adjusting the object light wave angle, the piezoelectric ceramic is controlled to achieve reference optical wave phase shifting, the hologram is analyzed and rebuilt through a phase shifting algorithm and a diffraction propagation method , and an imaging result is obtained. The system can adjust the two-dimensional rotation regulating frame by compactly arranging the coating film reflector driven by the piezoelectric ceramic and the unpolarized splitting prism, and the piezoelectric ceramic is controlled to obtain the holography, so that the imaging stability, practicability and reliability are effectively improved, and the system is simple and easy to obtain.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for defect inspection of transparent substrate by integrating interference and wavefront recording to reconstruct defect complex images information
ActiveUS10976152B2Holographic optical componentsHolographic object characteristicsEngineeringReference wave
A method for defect inspection of a transparent substrate comprises (a) providing an optical system for performing a diffraction process of object wave passing through a transparent substrate, (b) interfering and wavefront recording for the diffracted object wave and a reference wave to reconstruct the defect complex images (including amplitude and phase) of the transparent substrate, (c) characteristics analyzing, features classifying and sieving for the defect complex images of the transparent substrate, and (d) creating defect complex images database based-on the defect complex images for comparison and detection of the defect complex images of the transparent substrate.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Transmission method of color computer generated hologram color information
The invention relates to the technical field of manufacturing of a color computer generated hologram, in particular to a transmission method of color computer generated hologram color information, which is characterized by comprising the following steps of: 1) obtaining the tristimulus values Re, Ge and Be of colors in an electronic display color system; 2) converting the tristimulus values Re, Ge and Be of the colors in the electronic display color system into the tristimulus values Rh, Gh and Bh in a color computer generated hologram color system; and 3) converting the tristimulus values Rh, Gh and Bh in the color computer generated hologram color system into the object wave amplitude of the computer generated hologram. By adopting the method, the value of any color in the electronic display color system can be converted into the value of the color in the computer generated hologram color system, the corresponding object wave amplitude for the computer generated hologram code can be obtained, the digitalized color computer generated hologram can be obtained via the hologram code and output via a device, and thus the optically reproducible color hologram can be obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Imaging method of structured illumination digital holography
ActiveUS10613478B2High resolutionHolographic optical componentsActive addressable light modulatorPhase shiftedHolographic imaging
A method of structured illumination digital holography includes: (a) providing a structured illumination generating unit and binarization random number encoding unit to generate a coded structured illumination pattern; (b) sampling at least two patterns with phase shift which synthesized as a single structured illumination pattern to be encoded; (c) forming a single digital hologram, and wavefront reconstructing the single digital hologram; (d) performing a compressive sensing approach to recover the object wave with at least two phase shift patterns; and (e) reconstructing the separation of overlap spectrum, to obtain an image covering bandpass spectrum with different high frequency and low frequency.
Owner:NATIONAL TAIWAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
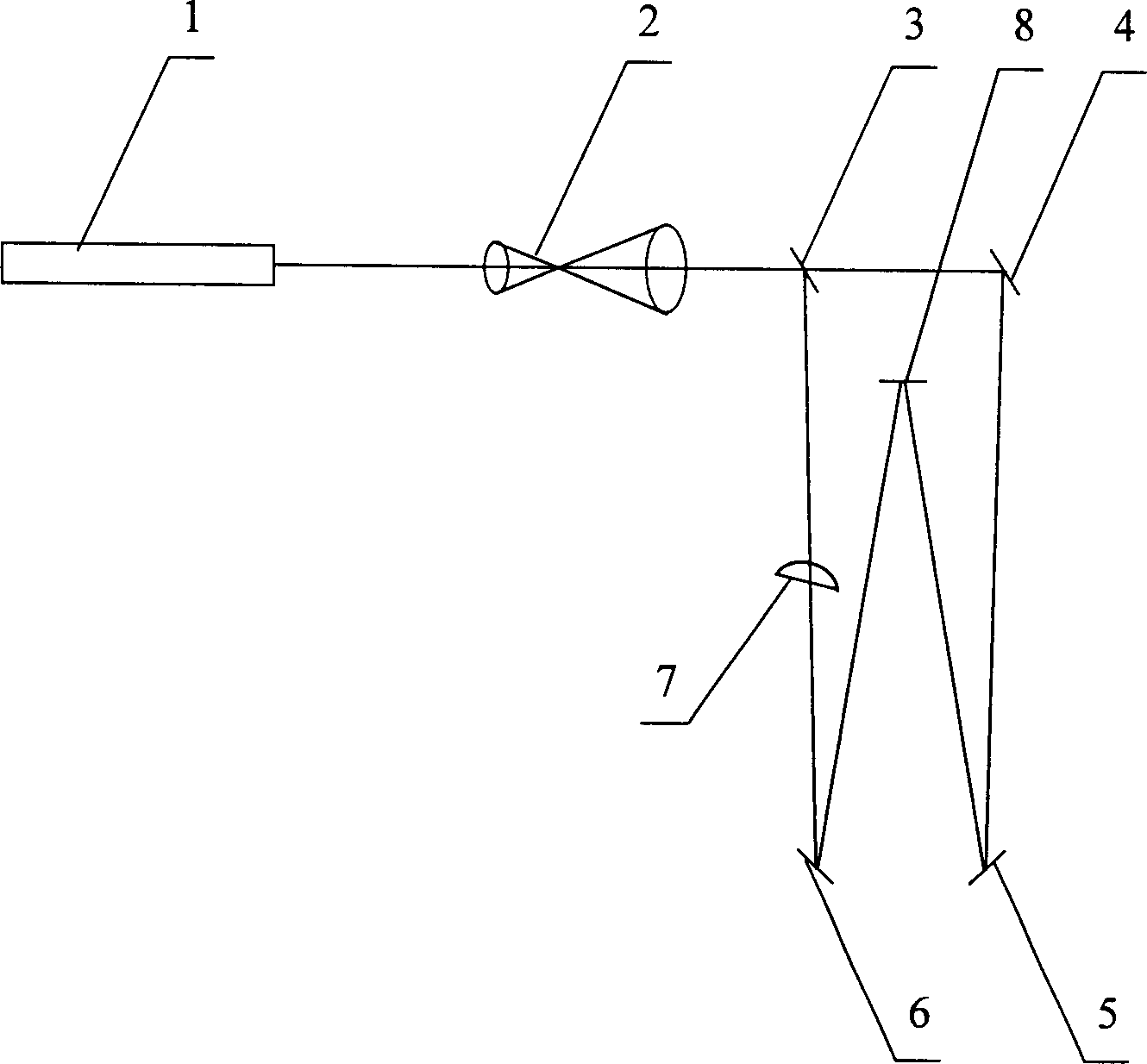
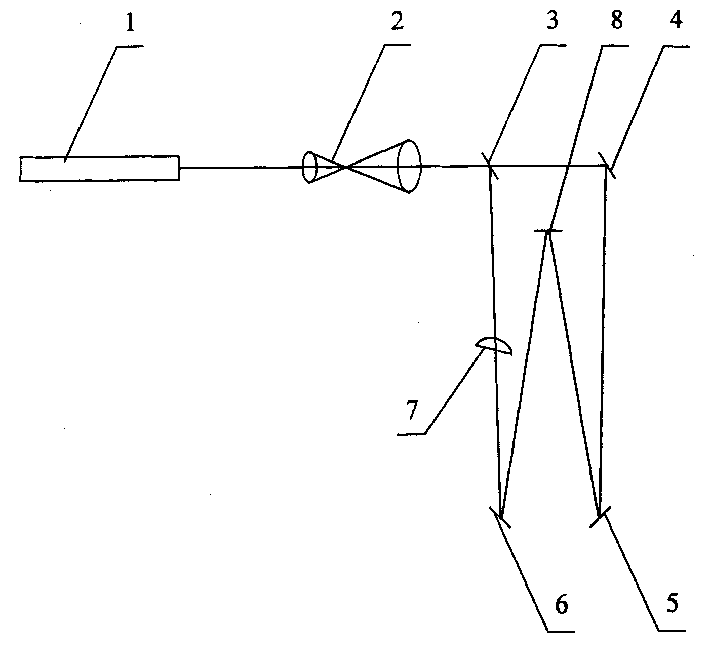
Apparatus for making frequency-variable grating using holographical method
InactiveCN1438553AHigh spatial frequencySpatial frequency varies linearlyDiffraction gratingsBeam splitterGrating
The device comprises the laser light source, the beam-expanding telescope, the beam splitter, the reflector, the cylindrical mirror and the recording media. The laser beam from the laser source being expanded by the telescope enters the beam splitter to divide the beam into two light beams: the reflected beam and the transmitted beam. The reflector reflects the reflected beam passed through the cylindrical mirror to the recording media as the object wave. The reflector reflects the transmitted light to the holographic recording media as the reference wave. The interference between the object wave and the reference wave forms hologram recorded on the media. The spatial frequency of the variable frequency grating made by the device is changed in linearity.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Apparatus and method for capturing fourier hologram
ActiveUS20180284694A1Cancel noiseHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesActive addressable light modulatorSpatial light modulatorFourier transform on finite groups
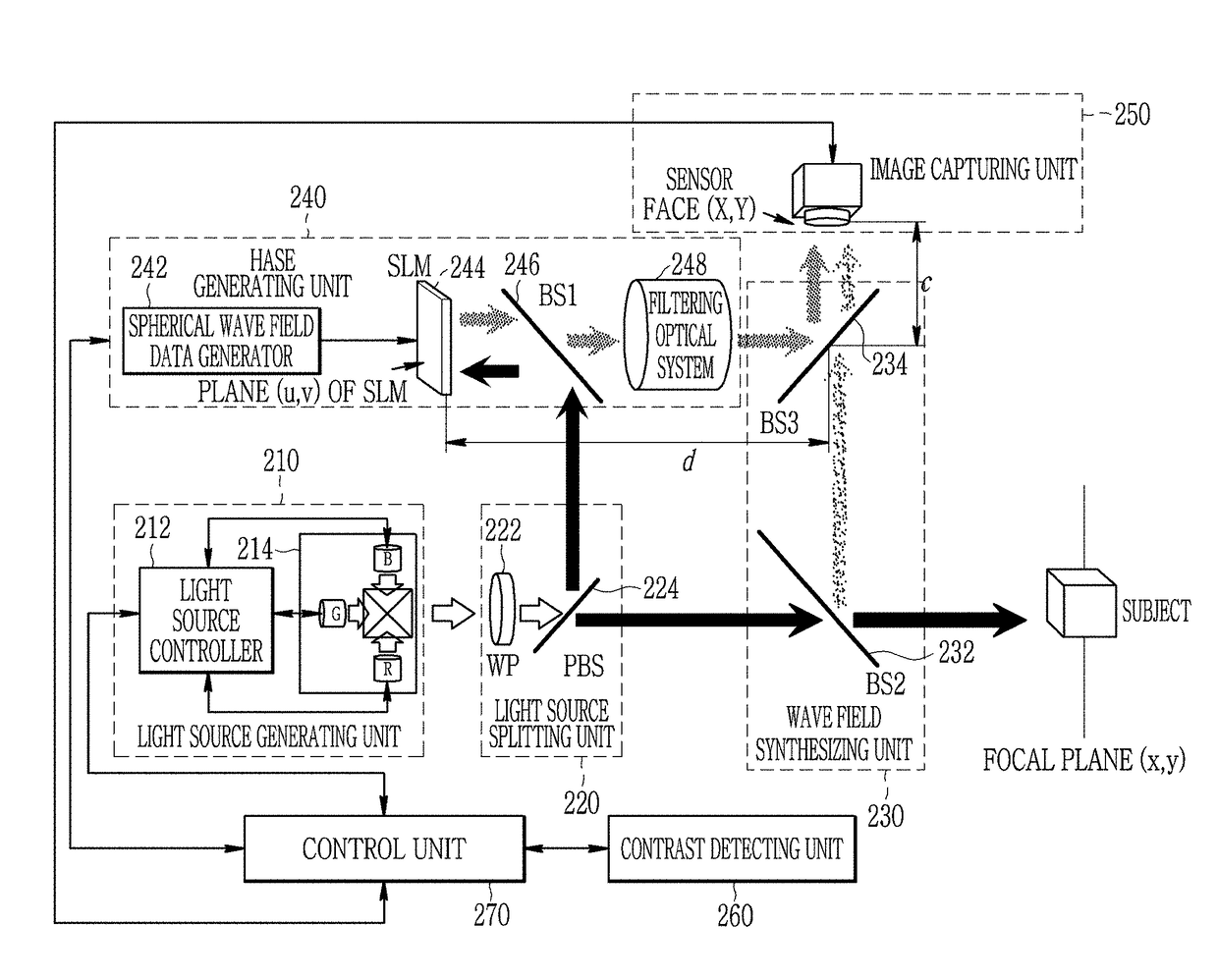
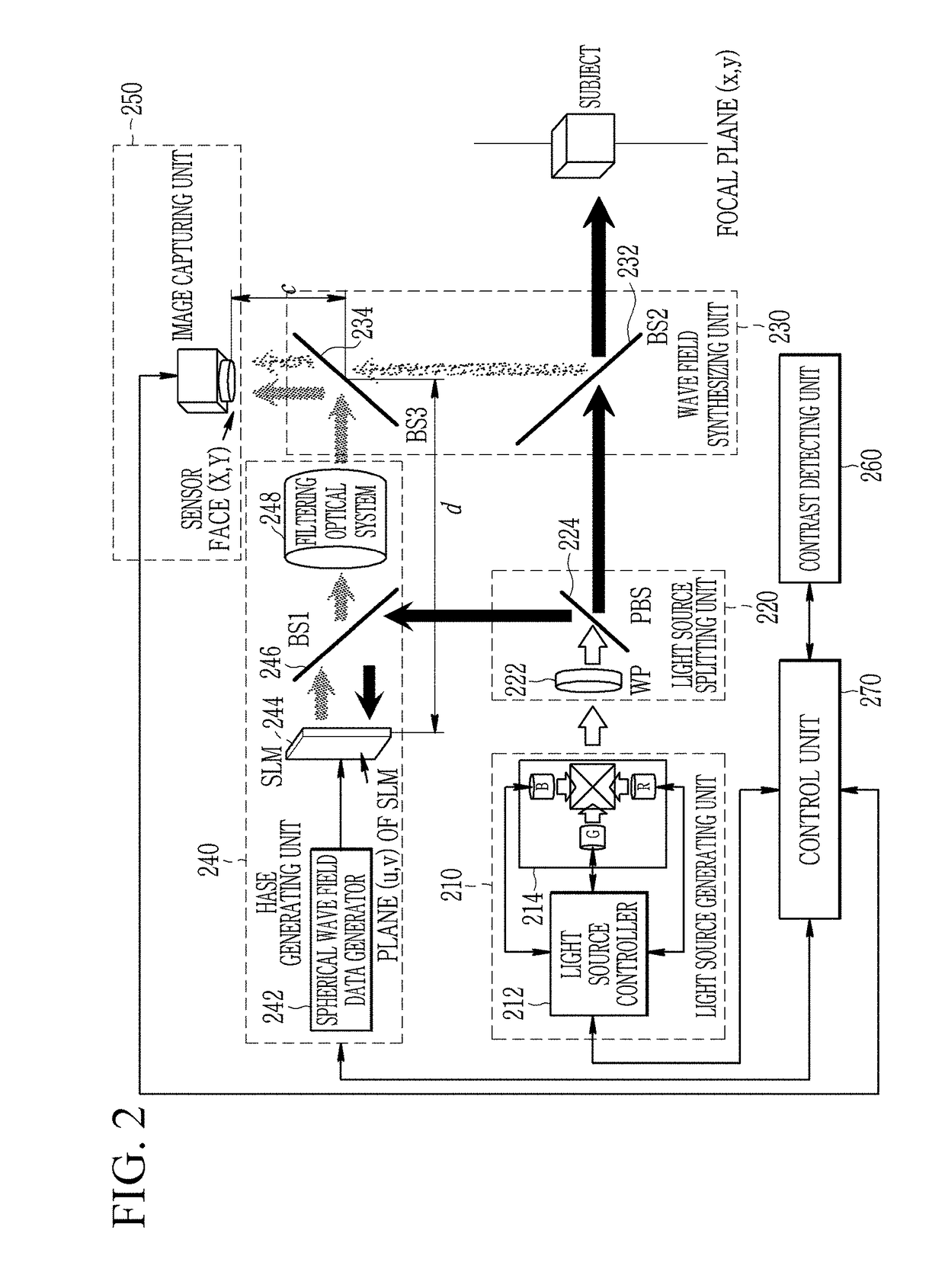
An apparatus for capturing a Fourier hologram splits a coherent light source into an object beam and a reference beam, sets a distance of a virtual focal plane of a subject, generates spherical wave field data propagated from a point source of the virtual focal plane to a central coordinate plane of a spatial light modulator, generates a spherical wave field on a space from the spherical wave field data and the reference beam by the spatial light modulator, synthesizes an object wave field generated by reflecting the object beam by the subject and the spherical wave field with each other so that an interference pattern is formed on the image sensor face, captures the interference pattern formed on the image sensor face, and then performs Fourier transformation to calculate an object wave field formed on the focal plane of the subject.
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
Digital holographic image reconstruction method based on deep learning
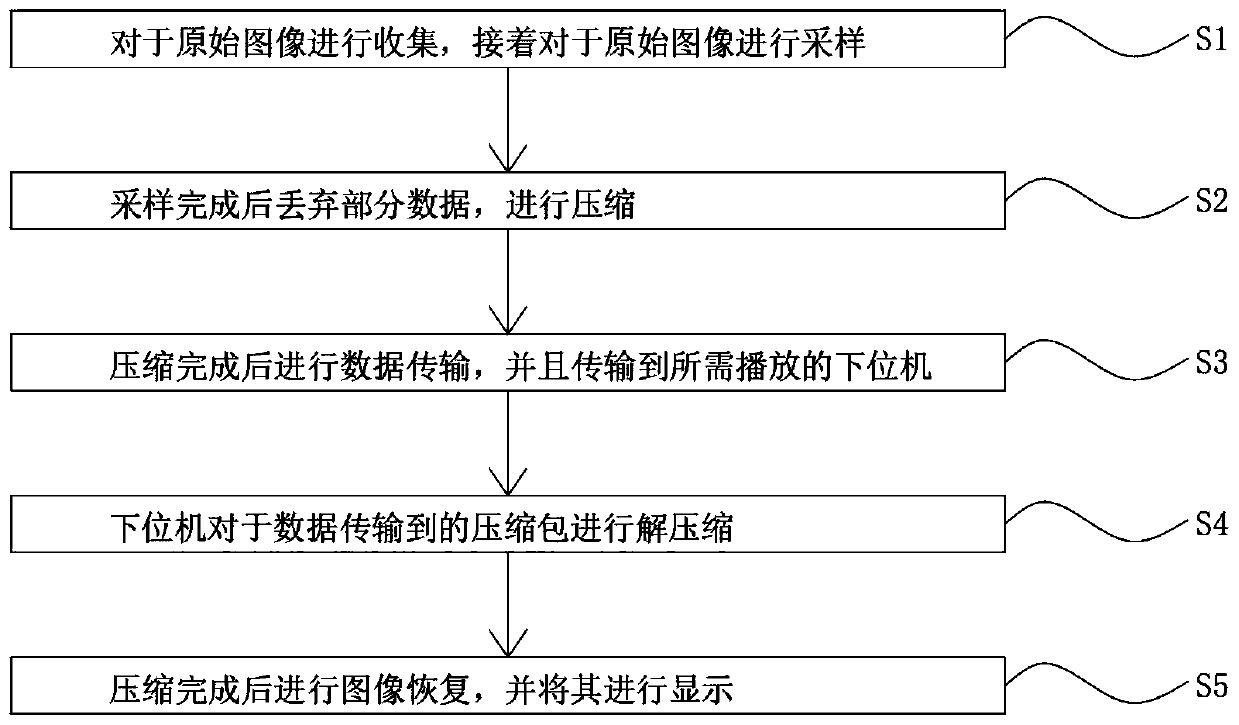
InactiveCN111311493APromote reproductionEasy transferImage enhancementImage analysisData transformationComputer graphics (images)
The invention discloses a digital holographic image reconstruction method based on deep learning, and the method comprises the following steps: S1, collecting an original image, and carrying out the sampling of the original image; s2, discarding part of data after sampling is completed, and compressing the data; s3, data transmission is performed after compression is completed, and the data is transmitted to a lower computer needing to be played; s4, the lower computer decompresses the compressed packet to which the data is transmitted; s5, after compression is completed, image restoration iscarried out, and the image is displayed; the structure is scientific and reasonable, safe and convenient use, a data acquisition card is subjected to A / D conversion and quantization post-processing, acomputer technology is introduced, and numerical calculation of a computer is utilized to simulate an object wave model function and an optical interference function, so that image data conversion isfacilitated, the conversion efficiency is improved, the transmission speed is reduced after compression, data is transmitted to a cloud end, and safety and reliability are achieved.
Owner:HEBEI UNIV OF ENG +1
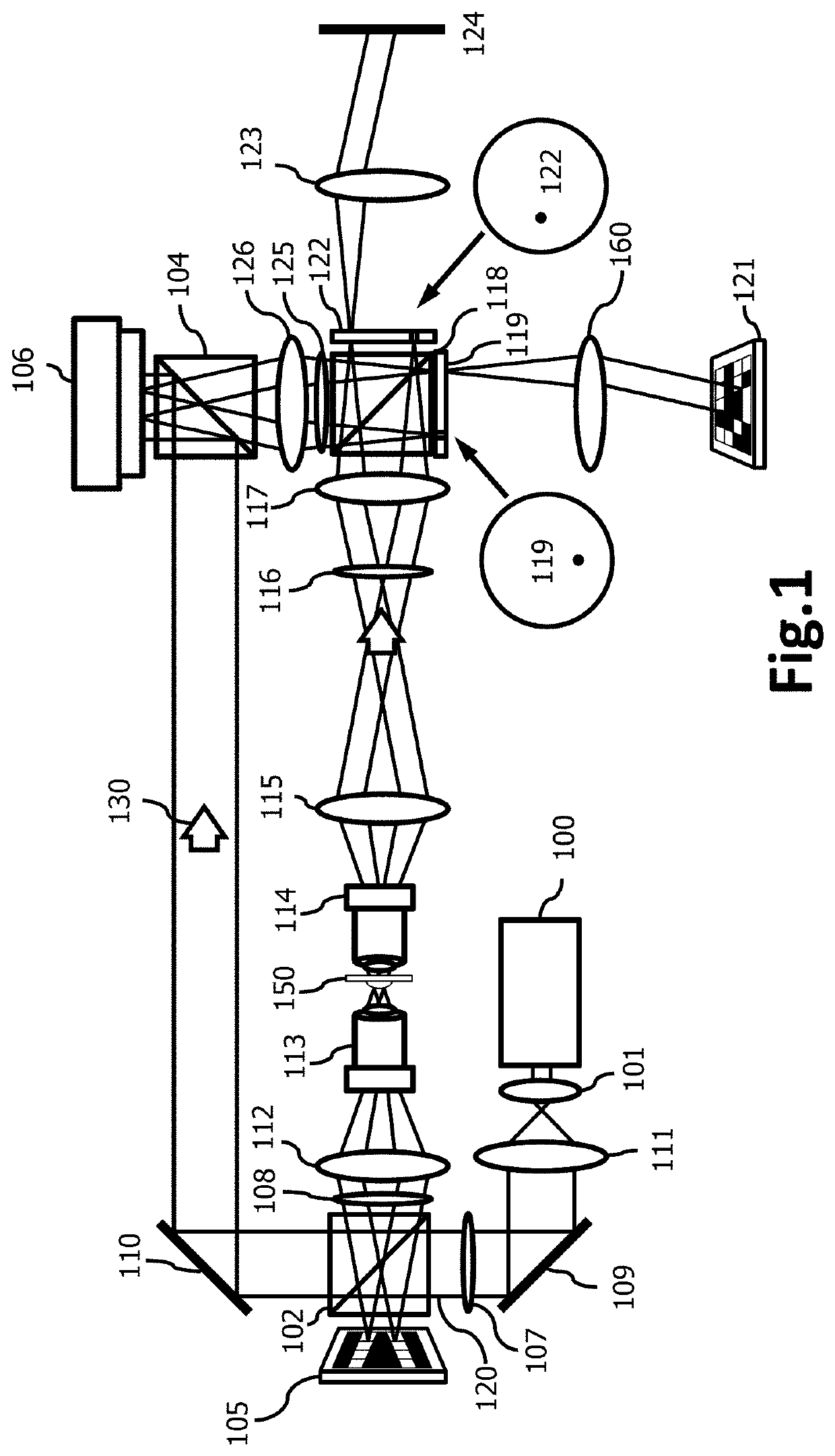
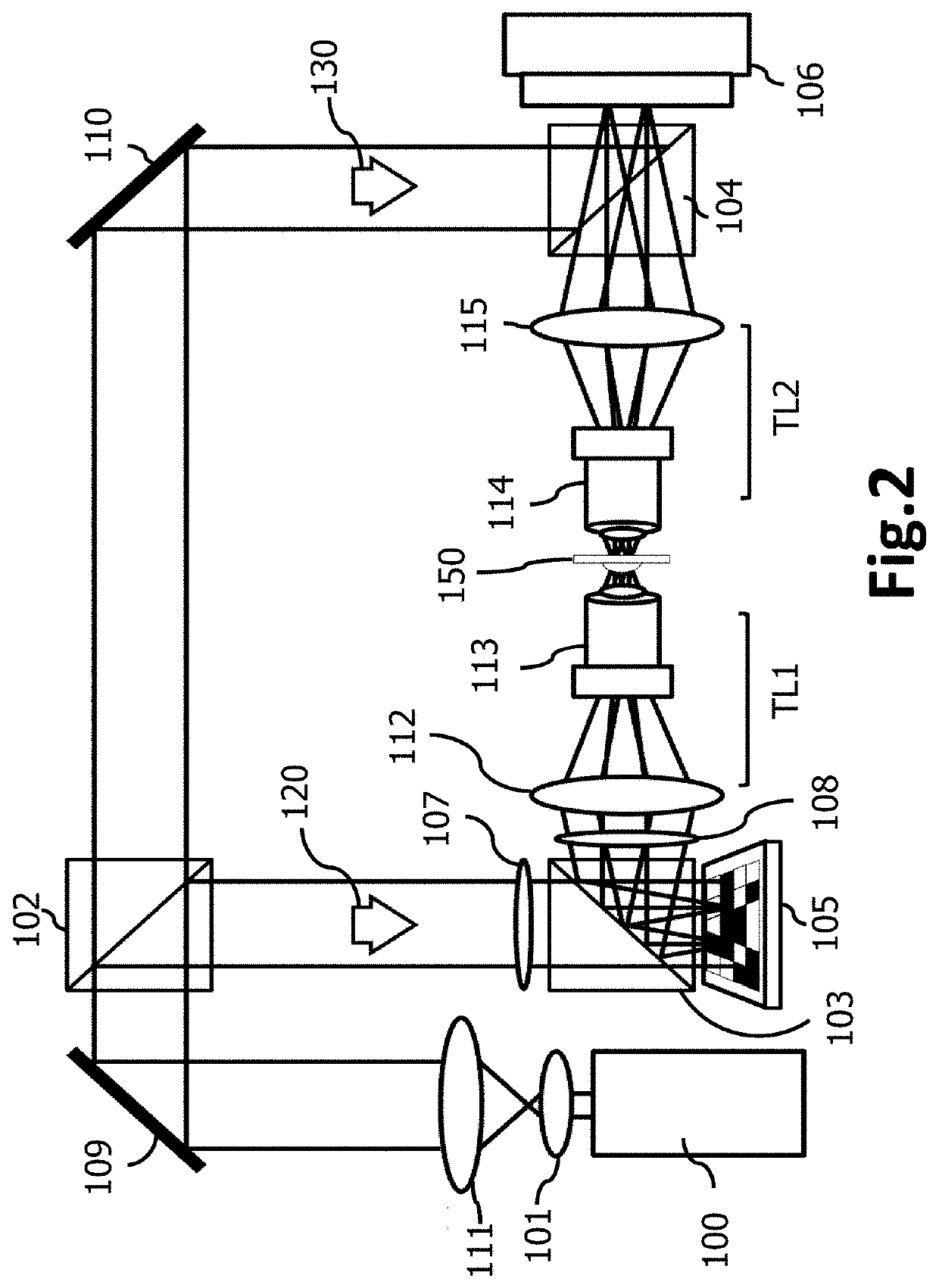
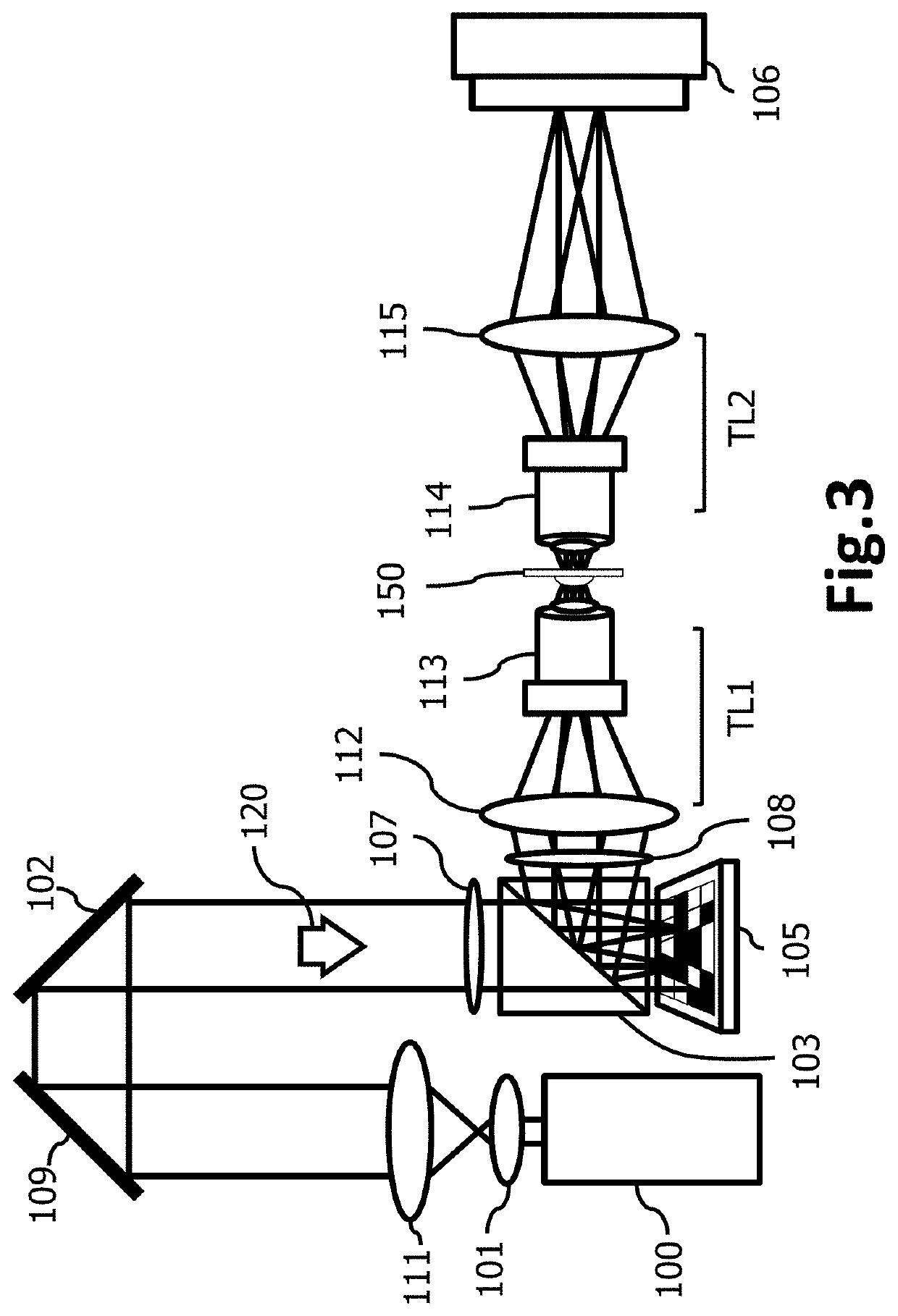
Microscope for quantitative wavefront measurements, microscope module and kit, method and computer program for computational wavefront reconstruction
PendingUS20220128412A1Improve spatial resolutionSimplify the development processOptical measurementsMicroscopesComputational physicsMicroscope objective
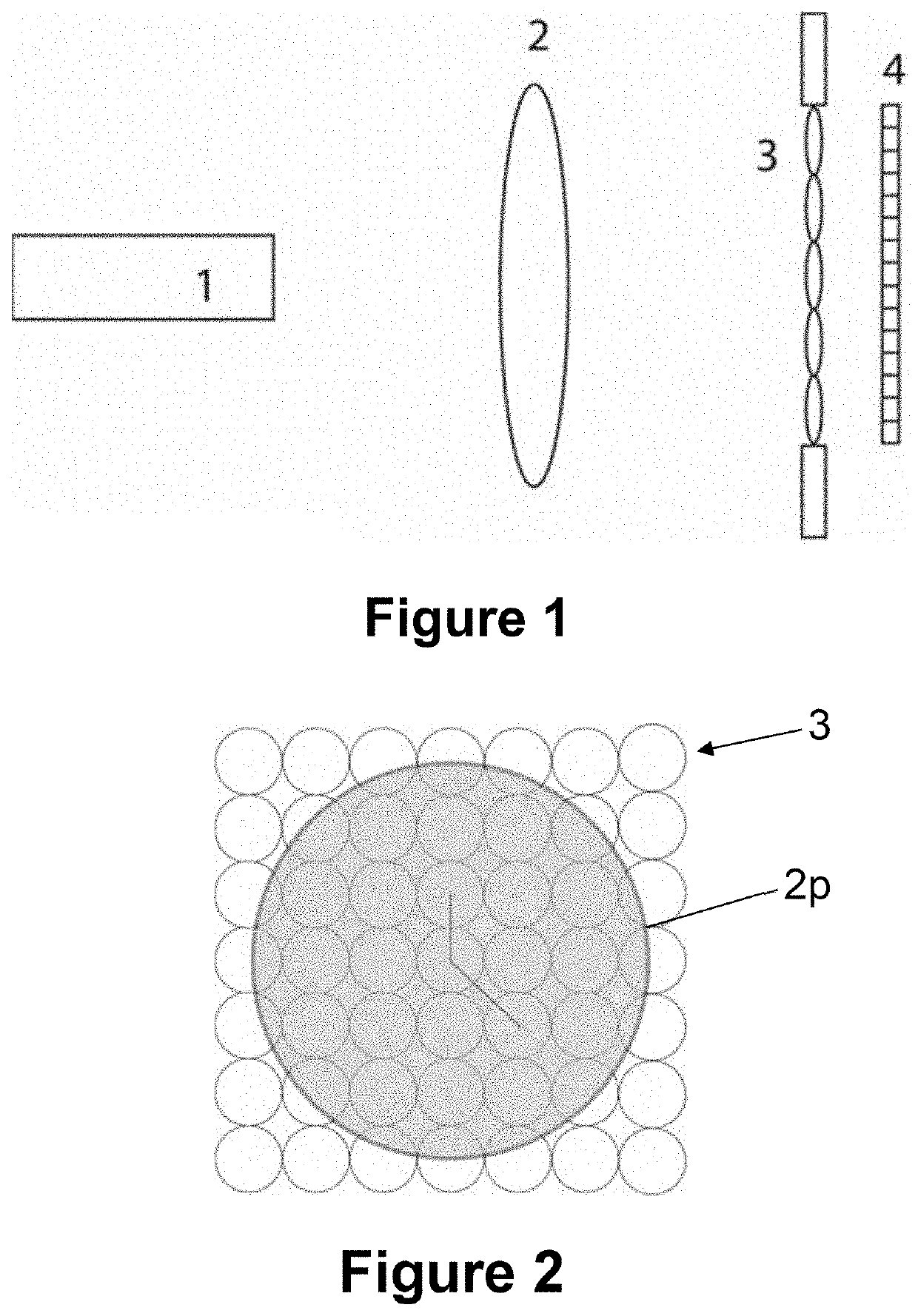
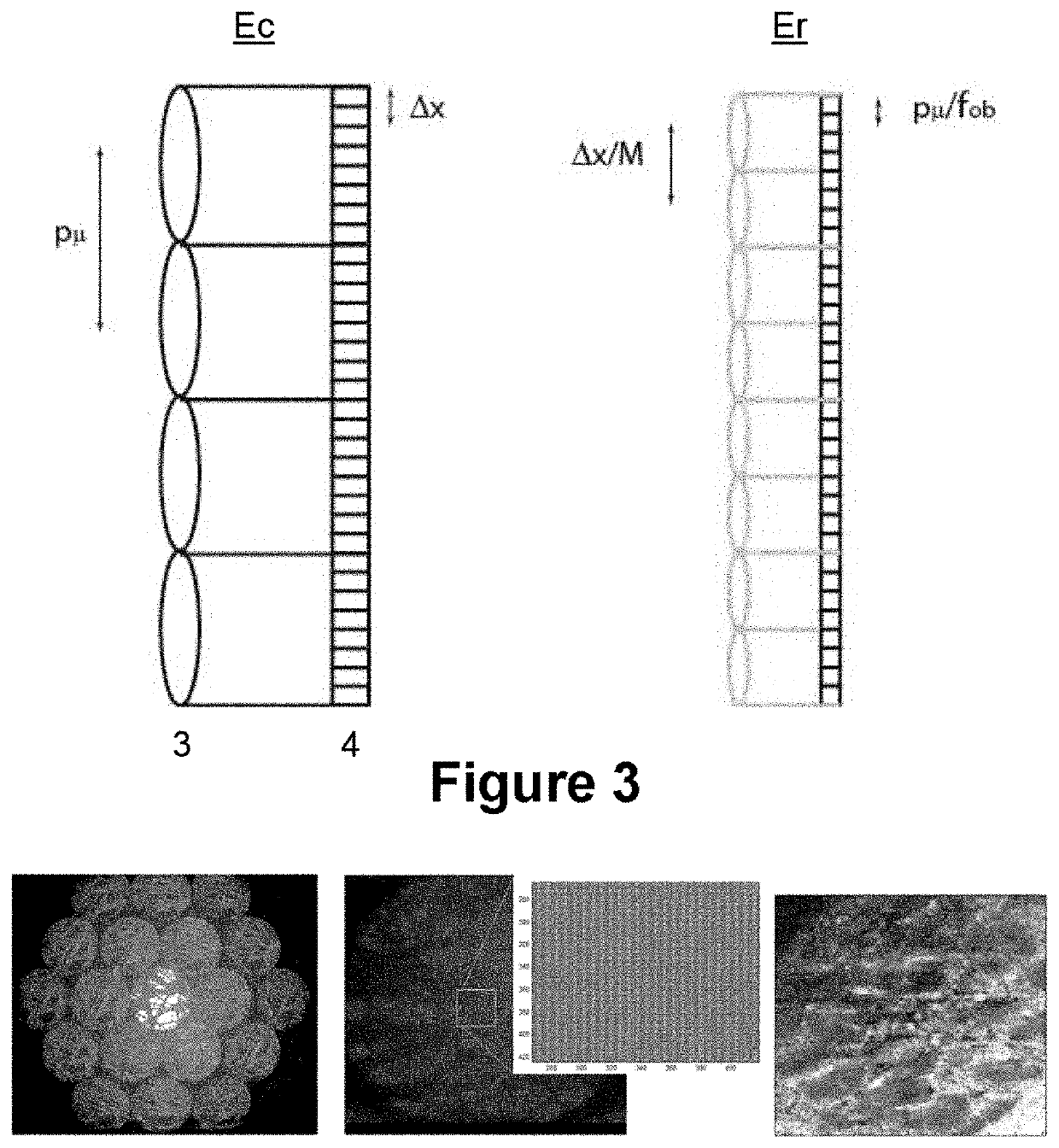
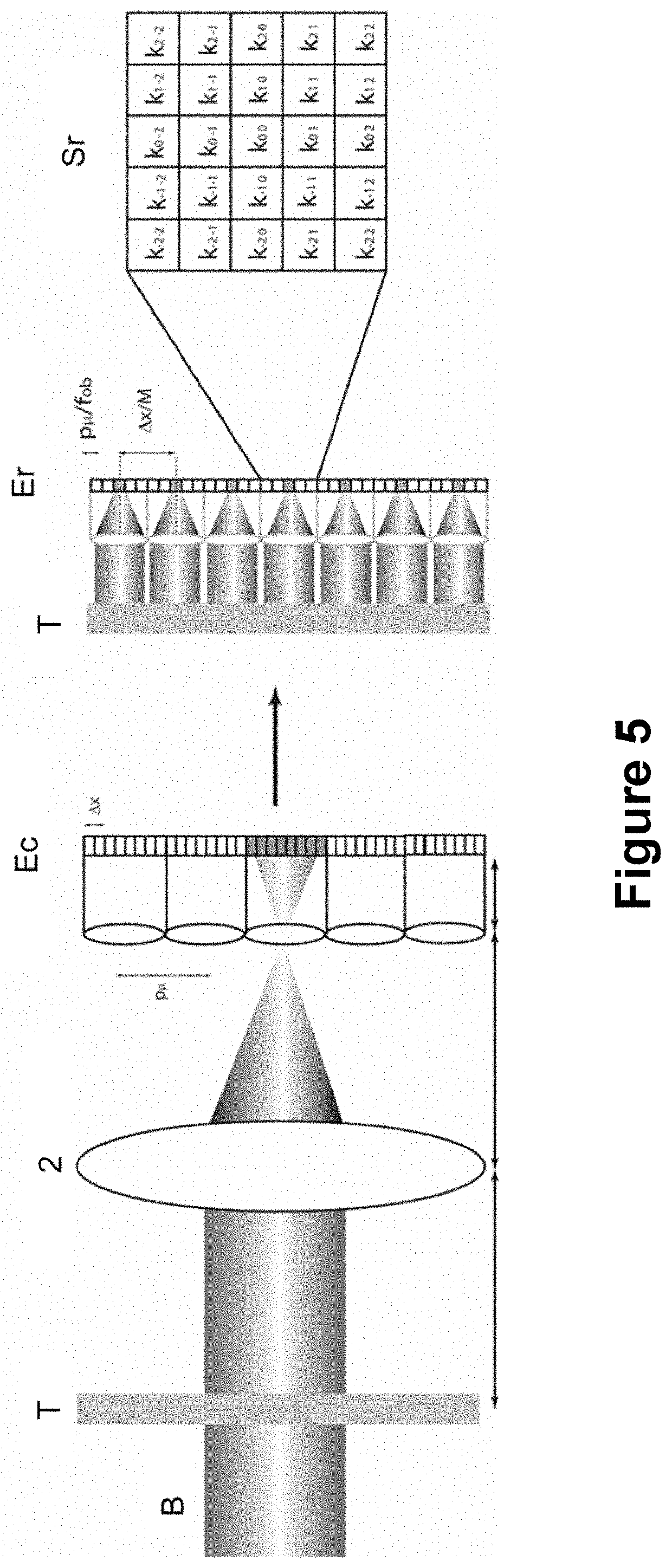
The present invention relates to a microscope for quantitative measurements of the wavefront, comprising:means for the illumination of a sample (T);an objective lens (2);an ordered two-dimensional arrangement of lenses (3), with a spacing pμ greater than 500 μm and a relative aperture of less than 10;an image sensor (4) located in a capture space (Ec) to receive the light scattered by the sample (T), and to acquire spatial and angular information on the object wavefront associated therewith; anda computational entity to perform a computational reconstruction of the object wavefront from the spatial and angular information.Other aspects of the invention relate to a method, a computer program and a product incorporating the same, adapted for the performance of the functions of the computational entity of the microscope, as well as to a module and a kit for a microscope.
Owner:UNIV DE VALENCIA
Algorithm for computational holography
The invention discloses an algorithm for computational holography and belongs to the technical field of projection. The algorithm comprises steps that S1, the object and light information is collected; S2, the object and light information is processed; S3, light field distribution on a holographic plane is expressed by computational hologram transmittance based on the encoding method; and S4, thehologram is recorded, stored and reproduced. The algorithm is advantaged in that the computational holography can be done without relying on real objects and only needs to obtain specific mathematicaldescription of object waves, so the computational hologram can be obtained through utilizing a computer and output equipment, and making and synthesizing 3D simulation book holograms can be more convenient.
Owner:JINLING INST OF TECH
A Simultaneous Dynamic Measurement Method of Refractive Index and Shape
ActiveCN106123770BAchieve integrationPhase-affecting property measurementsUsing optical meansDigital holographic microscopyFull field
The invention relates to a method for dynamically measuring two-dimensional refractive index distribution and three-dimensional shape at the same time. The method utilizes advantages of full field, high resolution and dynamic measurement of digital holographic microscopy, and introduces a dove prism with polished short edges in a measurement optical path, and thus integration of a total internal reflection digital holographic microscopy optical path and a transmission-type digital holographic microscopy optical path is achieved. By means of angle-multiplexed and polarization-multiplexed technologies, the transmission-type digital holographic microscopy optical path is used to record object wave light phase distribution information including the refractive index and thickness distribution (or shape) of an object, and the total internal reflection digital holographic microscopy optical path is used to synchronously record the two-dimensional reflective index distribution information of the object, and thus by simple mathematical operation, dynamic measurement of the two-dimensional refractive index distribution and the three-dimensional shape of the object is achieved at the same time. The involved measurement method does not require an extra filling solution, is suitable for measurement of transparent / semi-transparent liquid or solid, and overcomes defects of existing methods.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
A Lensless Diffraction Imaging Method Based on Complementary Random Sampling
ActiveCN105158921BHigh precisionImprove efficiencyOptical measurementsPhotometryComplex amplitudeWavefront
A lensless diffraction imaging method based on complementary random sampling is characterized in that a group of binary random sampling screens with complementary characteristics is introduced; the group of binary random sampling screens is arranged between a to-be-tested object and a record plane in sequence, and intensity patterns of object waves passing through the sampling screens on the record plane are sequentially recorded; the complex amplitude distribution of to-be-tested object waves is recovered from the recorded intensity patterns, and the digital diffraction operation is conducted using the recovered complex amplitude distribution, so as to obtain the diffraction imaging of the to-be-tested object at any spatial position. According to the method, the complementary random sampling screens are inserted between the object and the record plane, so that the accuracy and the iteration efficiency of phase retrieval are greatly improved; meanwhile, wavefront sampling loss caused by the binary random sampling in the traditional method can be effectively eliminated. In addition, as the iteration operation process is only applied to the sampling plane and the record plane, the method is suitable for general complex-valued objects and does not place special limits on the object.
Owner:SHANDONG NORMAL UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com